Outta This World ISSUE ONE KENT ELEMENTARY SCHOOL MAGAZINE. Alisa Emedi. Bianca Knoll. Charmel Mbala Cindy Arias. Jason Medina.
|
|
|
- Caitlin Ferguson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Page1 KENT ELEMENTARY SCHOOL MAGAZINE Outta This World ISSUE ONE Alisa Emedi Bianca Knoll Charmel Mbala Cindy Arias Jason Medina Kaiden Griffin Kelasia Sayaseng Mark Carrillo Veadey Polk
2 Page2 Table of Contents The Sun....3 The Suns Physical Features No, the Sun Isn t Made Out Of Cheese-Its! Our Earth s Moon...5 The Moons Magical Powers Physical Features of the Moon The Life of a Star. 7 How a Star is made Life Cycles of a Star Black Holes of the Universe..9 How Are Black Holes Formed? What Is a Black Hole? Black Holes What Really Happened to Venus?...11 Glossary..12
3 Page3 The Sun The Suns Physical Features By: Veadey Polk Have you ever wondered how the sun even formed in the galaxy in the first place? Well, I did some research on the internet and found lots of interesting facts about the sun; I found one that explained how scientists believed that the sun formed from a big cloud of dust and gas. The enormous cloud and its gravity pulled the dust and gases together. The gas got pulled into the center first which made the center extremely hot; from all of the other gases starting to fall on top of it and the gravity holding it together; then, became the starting of a baby sun. The leftover clouds of dust started to travel to other places of the galaxy and started forming the other planets, but not exactly the same way it did with the sun because then there would just be a whole bunch of suns in space! For many years the sun has collected more clouds of dust and gas, until it is the size that it is today and now the sun can no longer collect any more clouds of dust and gas because there is no more left to collect. Its size had made an incredible change, because now the sun is 860,000 miles in circumference. You could line up 109 earths all around the suns diameter! How heavy is the sun? Fun fact If you ever asked the question of how much does the sun weigh really? That s a great question; the sun weighs about 4.4, followed by 30 zero pounds! In comparison the earth weighs about 1.3 followed by 25 zero pounds. So the suns weight would equal to 40,000 earths combined! Why did the sun do so well in School? Answer on the last Page) Would you ever believe that if earth didn t have an atmosphere to protect us humans from burning from the sun? Well it s true, without the earth s atmosphere (which is the ozone protects us) the suns heat and light could burn us very badly! These are just some facts about the sun that you now know!
4 Page4 SATURN Saturn is a very beautiful planet the only down side is that you cannot stand on Saturn. Saturn is not at all like earth. Saturn is made mostly of gases, it has a lot of helium. This is the same king of gas that they put into balloons. My theory is that if you get anywhere close to Saturn you will start talking higher than the joker. Saturn s rings Saturn s ring is a very pretty sight to me but they are not solid. They are made up of bits of ice, dust and rock. Some of these bits are as small as grains of sand. But some are much larger; they can be as tall as building. Most are up to a kilometer (more than half a mile) across. The rings are huge but thin, the rings of Saturn could go from the earth to the moon. No, the Sun Isn t Made Out Of Cheese-Its! By: Mark Carrillo Amazingly, the sun is made out of oxygen. However the oxygen isn t in the atmosphere its inside of the sun. The sun has about 850 atoms of oxygen inside of it. Have you ever wondered how the sun is burning if there is no oxygen space? Yes, things do need oxygen in order to burn but the sun isn t burning it s just really bright. The sun is also made out of carbon. According to Webster dictionary carbon is a solid that is a chemical element: it is found in all plant and animal matter and in rocks, petroleum, etc. Petroleum-an oily liquid found in earth in certain layers of rock. Carbon-is a solid that is a chemical element. Interesting Facts about Uranus It has the 4 th most mass on in the solar system that s 14.5 earths mass. It is the 3 rd largest planet in our solar system. It has rings that are hard to see and it has 27 known moons and it is named as the sky goddess People thought It was a star until 1781.
5 Page5 Our Earth s Moon The Moons Magic Powers The moon makes tides too! By: Alisa Emedi Special effects happen on the earth because of our moon. One special effect is a tide; this is when the water on the beach pulls up because of the moons gravitational pull. Then the moon lets it go back down because it is so tired of holding it for so long. Think of when your little sibling or nephew or niece wants a piggy back ride and you give it to them for so long you want to drop but they won t let you. Well that is how the moon feels about that tide. Now that you know what happens when there is a tide you can kick back and say I know what is causing this to happen. Tidal breaking is the second effects that I was talking to you about earlier. This causes the gravitational pull of the moons length to get larger by 2.3 mille second per century. Think of your height every year or so you grow by a little and in that little the moon could be growing in length by 2.3 mille second. Speaking of the gravitational pull all the energy that the earth loses gets directly picked up by the moon. This causes the moon to get farther away. Every time that you look at the moon and wonder why is the moon so far away just read this paragraph and you will soon understand why. I hope that you now understand why the moon gets farther away so all your problems revolving around the moon are solved well kind of. How far away is the moon? The average distance from the moon to the earth is miles. The metric is kilometers. The closest distance from the moon to the earth is miles. The metric is The farthest distance from the moon to the earth is miles. The metric is miles.
6 Page6 Physical Features of the Moon By Bianca Knoll The Moon s Creation Sadly the moon is not made out of cheese. But if you thought that it was then participate in reading this to find how others thought it was made. There are four theories, the Fission Theory believes that the moon was separated from the earth and most believe it to, the Capture Theory thinks that the moon was formed in a different solar system but was captured from the gravitational field of the Earth, the Condensation Theory believes that the moon and the Earth condensed individually from the nebula that formed the solar system, and last but not least the Giant Impactor Theory is certain that a planetesimal the size of Mars struck earth just after the formation of the solar system. Which do you believe? The Moon s Core The moon s core is only 420 miles long (about football fields.) The moon has a very small core in fact it is only 2% of the moons mass. The moon s rocky mantle is made up of a thick layer of hot, solid rock, iron, and magnesium. The mantle is about 825 miles thick! In the past magma in the mantle has made its way up to the surface and erupted for more than a billion years. The Moon s Mass The moon s mass is actually so big the moon is considered to be a double planet!! It is 164 sextillion pounds!!! That is HUGE!!! The equation to find the mass on your on is (Fc=mV 2 /R) but I don t get it! Outta This World JOKES! How do we know that Saturn was married more than once? Because he has a lot of rings. Which chocolate bars do you eat in space? Milky ways and Mars bars. When do astronauts have lunch? At launch time. What do you call a crazy moon? A luna-tick. Why didn t the sun go to college? Because he already had a million degrees.
7 Page7 The Life of a Star How a Star is made! By :Kelasia Sayaseng Why do we humans think of a star as a five pointed shape? Stars are actually made of gas! Molecular gas as a matter of fact. Molecular gas is made of individual atoms, and are formed together as molecules. Stars are formed by clouds of molecular gas, but are born within clouds of dust that were spread throughout the galaxy. Stars can be all different shapes and sizes, just depending on how old they are, and how they grow. The sun is a star too, And as big as it is it can live up to 10 billion years. A star is about a-fourth as big as the sun. Therefore, a star can live up to about 2 or 3 billion years. Gravity is a part of the star life too. It is what holds the stars. If there wasn t any gravity then the stars would probably be floating around in the atmosphere. You would probably think that the stars move around over night and day but sadly they don t. The only reason that you probably don t see the same constellations or stars, every night is because its depending on what star it is, is how bright it shines. Some Stars in the Sky Fun Facts About The Biggest Planet stars can be very bright and, some not so bright. In addition to that, there may be different constellations every day. It all depends on what kind of star or stars they are. Also, some stars can be very dense. But some not so big. There are billions of stars in the sky. You may not be able to see them all but just remember that they re there. Jupiter is the biggest planet in our solar system it is so big that 1300 Earths fit inside Jupiter. It has at least 63 moons! For Jupiter to be the biggest planet it can move pretty fast in fact, the planet only takes ten hours to complete a full rotation. The roman name of Jupiter is Jupiter The Greek name of Jupiter is Zeus. FUN FACTS: Jupiter is the heaviest planet in the solar system. Mercury is one of the hottest planets and it might have ice. Mercury has water even through it near the moon Venus is the hottest planet in the solar system not the sun. Jupiter is the fastest rotating planet And Uranus is the coldest place in the Solar System Side bar- Uranus is flipped over on its side
8 Page8 Life Cycles of a Star By Cindy Arias A star life cycle is very interesting. How is it interesting you may ask. It is interesting because it has three life cycles with three different endings. One life cycle is. the star is a stellar nebula, a cloud of dust and molecular gas. Then it is an average size star. An average star is 100 times larger than the earth. Next there is a red giant which is 10 to 100 times larger than the sun and has a low surface temperature. Fourth, there is a planetary nebula which is glowing shells of ionized; by the way ionized is a type of gas. And fifth, there is a white dwarf the white dwarf weights about 340,000 earths! A Second life cycle for a star steps are first, they are a massive star then a super red giant. A red giant is a bright star because of it big size their size is about 10 to 1500 times bigger than our sun. Next a super nova which is when a star explosive when it has too much energy and then a black hole.the third life cycle for a star is the same thing like the second but instead of the black hole it ends up with a neutron star if you get a teaspoon of a neutron star it weighs about one hundred million tons on earth! Neptune By Kelasia Sayaseng The origin of Neptune Neptune is a very interesting planet. It was named after the roman sea god. It is one of the stormiest planets. The winds on Neptune are stronger than any other planet. In fact, Neptune is the farthest planet from the sun. Pluto was originally the farthest. But, now, Pluto is officially not a part of our solar system. So, Neptune is now the farthest in our solar system. Now, since Pluto is the farthest, it took a voyager 12 years to reach Neptune. Originally, Neptune was discovered by three people: Urbane Le Verrier, John Coach Adams, and Johann Galle. They discovered Neptune as of 166 years ago on September 23 rd, The making of the planet Neptune is made of many things. It is made of hydrogen, helium, methane ammonia and water. Hydrogen is a flammable gas in which it has no color or odor. Helium is a very light weight gas. In fact, it is an inert gas which is the lightest gas of the gas series. Methane, also an odorless and colorless flammable gas. But, is the main part of natural gas. Ammonia is also a gas. Ammonia is a gas that dissolves in water to give a strong alkaline solution.
9 Page9 Black Holes of the Universe What Is a Black Hole? By Charmel Mbala I know that in some point of time you ve heard of a black hole, but do you really you know what it is? A black hole is a place in space where gravity is so powerful that even light can t escape its grasp. The gravity is so tough because matter has been squished into a small space. This can happen when a star is near death. people don t see black holes because no light can escape; they are invisible. Telescopes with special tools could help locate black holes and determine how stars that are near becoming a black hole act differently. Only NASA has these special tools but you could try and get them but it is almost impossible to get them unless you work for NASA or unless you buy it from the black market. How small can black holes be? A black hole can either be huge or tiny. The smallest black holes are as small as one atom, which is microscopic. One different type of black hole is called a stellar black hole. Did you know these black holes masses are 20 times more than the mass of the sun which is pretty big. There are numerous black holes in our galaxy also known as the Milky Way the galaxy where earth is. Atom: The smallest component of an element Matter: A physical substance What are the biggest black holes? Did you ever imagine what the biggest types of black holes are? Well, thanks for asking.the biggest black holes are called super massive black holes. These types of black holes have masses more than 1 million suns put together. Scientists have found evidence that every major galaxy has a super massive black hole at the center. Our super massive black hole is nick named Sagittarius. These super massive black holes have enough mass of 4 million suns, it would fill a humongous ball that could hold a few million earths. Now that you know what a black hole is and the different type of black holes you will know more about them. FACT: If another black hole comes near another black hole it would suck in the other black hole
10 Page10 Black Holes By Jason Medina Have you ever thought that a black hole could devour our earth? Well don t worry it can be possible but don t worry highly unlikely.( One scenario that a black hole could absorb us is if a black hole was rotating around like a star in the galaxy swallowing stars and planets that are not faster than the speed of light so if a black hole moved right next to our earth it would absorb us in). Then we would go to the center of the black hole and get crushed and disappear. Another scenario it s highly unlikely is because a black hole is bigger than many suns and if it was gigantic we would orbit around it because of its gravity. My last scenario on why we wouldn t get sucked in is if somehow a black hole got really close and sucked us in.so here s all the facts now you know that a black hole could suck our earth in but it s highly unlikely so don t worry it s not the end of the world but wait there s more but I m not writing it.. How Are Black Holes Formed? By Kaiden Griffin Do you think the sun is big enough to become a black hole?no it s only 860,000 miles. A star has to be 10 times as big that s 1,266,133,333 feet (that s a lot of feet. )To form a black hole a star has to fall into itself. When a black hole is formed it sucks in different objects and gases to make it a supermassive black hole. When a black hole is formed it can be a supermassive black hole or a small black hole they come in many different sizes it depends on how big the star is. This diagram is from Google A supermassive black hole has 10,000 more mass than the sun. A black hole is formed it has such an intense pull it has one way in and once you enter a black hole you can t get out. Once a star collapses into itself it causes a supernova that causes a black hole. That s how black holes are formed. Supermassive black holes- A large black hole. Supernova: A bright star that burst and ends its life. Solar system: The system where earth is.
11 Page11 What Really Happened to Venus? By Veadey Polk Climate Global Warming Venus is a very interesting planet, but sadly there is no possible way to have human life there. The reason is because Venus s orbit makes it the second planet closest to the sun, making the planet extremely hot most of the time. The surface of Venus has a very thick, toxic atmosphere that traps heat in a greenhouse effect. It has a greenhouse effect because a greenhouse soaks up hot air and prevents it from escaping into space. What happens is every 4 earth days the atmosphere is energized by a hurricane, forced with winds. Traveling roughly 224 miles per hour. This planet has temperatures hot enough to melt lead! Another reason of why Venus is so hot is because of its volcanic activity, there are more than 1,000 volcanoes or volcanic centers that are as large as 12 miles, and many of them cover Venus s surface. Mars is the fourth planet from the sun and is also the second smallest planet in the solar system. Mars is nicknamed the red planet because of its rusty like dust. Mars has been visited by several mars rovers. These robots collect samples and record important data. Did you know that the average temperature on Mars is -81 degrees. Mars seasons are twice as long as earth s seasons because it takes Mars 687 days to orbit the sun. That s twice as many days as the earth takes to orbit the sun. (365 days). Did you know that Mars is named after the Roman god of war. Mars has two moons named Deimos and Phobos. These two moons are irregular shaped and are as big as the biggest satellite Well, in the early days of Venus scientist were studying Venus and it happened to look very similar to earth. The two planets were practically almost identical, because of its size. However, after a long period of time Venus happened to actually be very different from earth. Since Venus is closer to the sun than earth that caused the planet to change its climate. Scientist thought that even though it was just a little closer to the sun, the climate was only supposed to be slightly warmer than earth. But as the years go by Venus suddenly started to get warmer by the minute, and eventually all of the water on Venus evaporated. Of course not all of the water at once, but the more water that evaporated the more the temperature started to rise further. Which caused more water to evaporate, causing the temperature just get higher. This large amount of evaporation in the atmosphere began a cycle of global warming that could not be stopped. Since the increase of the temperature, today it is most likely that all of Venus s water has evaporated into the atmosphere. Now you know lots of interesting facts about Venus! Answer: He Was Bright Student!
12 Page12 Glossary Alkaline-Having a ph greater than 7 Ammonia-A colorless gas Atmosphere-The envelope of gases surrounding the earth or another planet Atoms-The basic unit of a chemical element Circumference-The enclosing boundary of a curved geometric figure Carbon-It s a solid that s a chemical element Gravity-The force that attracts a body toward the center of the earth or any other planet Gravitational Pull-The attraction between all the masses in the universe Helium-Chemical element of atomic 2 Hydrogen-A colorless, odorless, highly flammable gas Methane- A colorless flammable gas Molecular Gas- Consisting of molecules Molecules- A group of atoms Nebula-A cloud of gas visible at night Petroleum-It s an oily liquid found in earth in certain layers of rock Solar System- The collection of planets and their moons in orbit around the sun Stellar Nebula- The nebulosity surrounding a star Super nova-a super nova is a stellar explosion that is more energetic than a nova Tidal Breaking-Tidal locking occurs when the gravitational gradient makes one side of an astronomical body always face another Ionized-To convert into ions
TABLE OF CONTENTS. click one to go to that page, or just go on. What is the Solar System? Neptune (Pluto) The Sun. Asteroids. Mercury.
 The Solar System TABLE OF CONTENTS click one to go to that page, or just go on. What is the Solar System? The Sun Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune (Pluto) Asteroids Meteors and Meteorites
The Solar System TABLE OF CONTENTS click one to go to that page, or just go on. What is the Solar System? The Sun Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune (Pluto) Asteroids Meteors and Meteorites
1. Galaxy (a) the length of a planet s day. 2. Rotational Period (b) dust and gases floating in space
 Vocabulary: Match the vocabulary terms on the left with the definitions on the right 1. Galaxy (a) the length of a planet s day 2. Rotational Period (b) dust and gases floating in space 3. Orbital Period
Vocabulary: Match the vocabulary terms on the left with the definitions on the right 1. Galaxy (a) the length of a planet s day 2. Rotational Period (b) dust and gases floating in space 3. Orbital Period
The Outer Planets. Video Script: The Outer Planets. Visual Learning Company
 11 Video Script: 1. For thousands of years people have looked up at the night sky pondering the limits of our solar system. 2. Perhaps you too, have looked up at the evening stars and planets, and wondered
11 Video Script: 1. For thousands of years people have looked up at the night sky pondering the limits of our solar system. 2. Perhaps you too, have looked up at the evening stars and planets, and wondered
known since prehistoric times almost 10 times larger than Jupiter
 Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune 40.329407-74.667345 Sun Mercury Length of rotation Temperature at surface 8 official planets large number of smaller objects including Pluto, asteroids,
Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune 40.329407-74.667345 Sun Mercury Length of rotation Temperature at surface 8 official planets large number of smaller objects including Pluto, asteroids,
Science Practice Astronomy (AstronomyJSuber)
 Name: Date: 1. The pull of gravity on Earth is a direct result of the A. mass of Earth. B. magnetic field of Earth. C. rotation of Earth on its axis. D. weight of Earth's atmosphere. This online assessment
Name: Date: 1. The pull of gravity on Earth is a direct result of the A. mass of Earth. B. magnetic field of Earth. C. rotation of Earth on its axis. D. weight of Earth's atmosphere. This online assessment
The Moon s relationship with Earth The formation of the Moon The surface of the Moon Phases of the Moon Travelling to the Moon
 The Moon The Moon s relationship with Earth The Moon orbits the Earth every 27.3 days. The tides on Earth are caused mostly by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun. The Moon's gravitational pull
The Moon The Moon s relationship with Earth The Moon orbits the Earth every 27.3 days. The tides on Earth are caused mostly by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun. The Moon's gravitational pull
CST Prep- 8 th Grade Astronomy
 CST Prep- 8 th Grade Astronomy Chapter 15 (Part 1) 1. The theory of how the universe was created is called the 2. Which equation states that matter and energy are interchangeable? 3. All matter in the
CST Prep- 8 th Grade Astronomy Chapter 15 (Part 1) 1. The theory of how the universe was created is called the 2. Which equation states that matter and energy are interchangeable? 3. All matter in the
Exploring Our Solar System
 Exploring Our Solar System Our Solar System What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
Exploring Our Solar System Our Solar System What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
UNIT 3: Chapter 8: The Solar System (pages )
 CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be turned in to your teacher
CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be turned in to your teacher
What s in Our Solar System?
 The Planets What s in Our Solar System? Our Solar System consists of a central star (the Sun), the main eight planets orbiting the sun, the dwarf planets, moons, asteroids, comets, meteors, interplanetary
The Planets What s in Our Solar System? Our Solar System consists of a central star (the Sun), the main eight planets orbiting the sun, the dwarf planets, moons, asteroids, comets, meteors, interplanetary
The Universe and Galaxies
 The Universe and Galaxies 16.1 http://dingo.care-mail.com/cards/flash/5409/galaxy.swf Universe The sum of all matter and energy that exists, that has ever existed, and that will ever exist. We will focus
The Universe and Galaxies 16.1 http://dingo.care-mail.com/cards/flash/5409/galaxy.swf Universe The sum of all matter and energy that exists, that has ever existed, and that will ever exist. We will focus
WHAT WE KNOW. Scientists observe that every object in the universe is moving away from each other. Objects furthest away are moving the fastest. So..
 ASTRONOMY THE BIG BANG THEORY WHAT WE KNOW Scientists observe that every object in the universe is moving away from each other. Objects furthest away are moving the fastest. So.. WHAT DOES THIS MEAN? If
ASTRONOMY THE BIG BANG THEORY WHAT WE KNOW Scientists observe that every object in the universe is moving away from each other. Objects furthest away are moving the fastest. So.. WHAT DOES THIS MEAN? If
Unusual Moon Information
 Saturn s Numbers Saturn is 1.35 billion km from the Sun minimum. Saturn is 1.5 billion km from the Sun maximum. One day on Saturn takes about 10.67 hours. One full rotation around the sun takes about 29.5
Saturn s Numbers Saturn is 1.35 billion km from the Sun minimum. Saturn is 1.5 billion km from the Sun maximum. One day on Saturn takes about 10.67 hours. One full rotation around the sun takes about 29.5
Introduction to Astronomy
 Introduction to Astronomy Have you ever wondered what is out there in space besides Earth? As you see the stars and moon, many questions come up with the universe, possibility of living on another planet
Introduction to Astronomy Have you ever wondered what is out there in space besides Earth? As you see the stars and moon, many questions come up with the universe, possibility of living on another planet
1UNIT. The Universe. What do you remember? Key language. Content objectives
 1UNIT The Universe What do you remember? What are the points of light in this photo? What is the difference between a star and a planet? a moon and a comet? Content objectives In this unit, you will Learn
1UNIT The Universe What do you remember? What are the points of light in this photo? What is the difference between a star and a planet? a moon and a comet? Content objectives In this unit, you will Learn
Sun Mercury Venus. Earth Mars Jupiter
 Sun Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Venus is the hottest planet in our solar system. The thick clouds on Venus hold the heat in. The sun s lights reflect off Venus s clouds making it look like the brightest
Sun Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Venus is the hottest planet in our solar system. The thick clouds on Venus hold the heat in. The sun s lights reflect off Venus s clouds making it look like the brightest
Planet Power. Of all the objects in our solar system, eight match these requirements: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, & Neptune
 Everyone knows that a planet is something that orbits the sun, right? Well, it is not that simple. In August 2006, scientists officially defined a planet as something that: 1. orbits the sun, not around
Everyone knows that a planet is something that orbits the sun, right? Well, it is not that simple. In August 2006, scientists officially defined a planet as something that: 1. orbits the sun, not around
Science Space Lessons 1-5 Notes
 Science Space Lessons 1-5 Notes The Planets in order from the Sun are: Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune To help us remember, we use the sentence: My Very Excited Mother Just Served
Science Space Lessons 1-5 Notes The Planets in order from the Sun are: Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune To help us remember, we use the sentence: My Very Excited Mother Just Served
ALL ABOUT THE PLANETS
 Venus Earth Mercury Mars ALL ABOUT THE PLANETS and a few other things By:James Cooper Elsberry Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune Mercury First I will start off with Mercury. Mercury is extremely difficult
Venus Earth Mercury Mars ALL ABOUT THE PLANETS and a few other things By:James Cooper Elsberry Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune Mercury First I will start off with Mercury. Mercury is extremely difficult
Astronomy Unit Notes Name:
 Astronomy Unit Notes Name: (DO NOT LOSE!) To help with the planets order 1 My = M 2 V = Venus 3 Eager = E 4 M = Mars 5 Just = J 6 Served = Saturn 7 Us = Uranus 8 N = N 1 Orbit: The path (usually elliptical)
Astronomy Unit Notes Name: (DO NOT LOSE!) To help with the planets order 1 My = M 2 V = Venus 3 Eager = E 4 M = Mars 5 Just = J 6 Served = Saturn 7 Us = Uranus 8 N = N 1 Orbit: The path (usually elliptical)
* Pre-Unit Assessment Solar System 5-PS2-1, MS-ESS1-2, MS-ESS1-3. Earth, Moon, Sun System K-PS3-1, 1-ESS1-1, 1-ESS1-2
 * Pre-Unit Assessment Solar System 5-PS2-1, MS-ESS1-2, MS-ESS1-3 Reading and Map Solar System Chart Solar System Size Comparison Model Earth, Moon, Sun System K-PS3-1, 1-ESS1-1, 1-ESS1-2 Reading and Diagram
* Pre-Unit Assessment Solar System 5-PS2-1, MS-ESS1-2, MS-ESS1-3 Reading and Map Solar System Chart Solar System Size Comparison Model Earth, Moon, Sun System K-PS3-1, 1-ESS1-1, 1-ESS1-2 Reading and Diagram
Which of the following planets are all made up of gas? When a planets orbit around the Sun looks like an oval, it s called a(n)
 When a planets orbit around the Sun looks like an oval, it s called a(n) - ellipse - circle - axis - rotation Which of the following planets are all made up of gas? - Venus, Mars, Saturn and Pluto - Jupiter,
When a planets orbit around the Sun looks like an oval, it s called a(n) - ellipse - circle - axis - rotation Which of the following planets are all made up of gas? - Venus, Mars, Saturn and Pluto - Jupiter,
4 HOW DID THE EARTH FORM?
 4 HOW DID THE EARTH FORM? New stars and space debris spinning like pizza dough are a couple of the things that explain the formation of solar systems like ours. In this three-part lecture, David Christian
4 HOW DID THE EARTH FORM? New stars and space debris spinning like pizza dough are a couple of the things that explain the formation of solar systems like ours. In this three-part lecture, David Christian
Solar System Test Review
 Solar System Test Review There are several planets in the solar system. What do all of these planets have in common? A.They all orbit the Sun. B. They are all close to the Moon. C.They are all called Earth.
Solar System Test Review There are several planets in the solar system. What do all of these planets have in common? A.They all orbit the Sun. B. They are all close to the Moon. C.They are all called Earth.
Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS)
![Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS) Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS)](/thumbs/77/76655554.jpg) Page1 Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS) HS-ESSI-1; HS-ESS1-2; HS-ESS1-3; HS-ESSI-4 NGSS Civic Memorial High School - Earth Science A Concept # What we will be learning Mandatory
Page1 Earth s Formation Unit [Astronomy] Student Success Sheets (SSS) HS-ESSI-1; HS-ESS1-2; HS-ESS1-3; HS-ESSI-4 NGSS Civic Memorial High School - Earth Science A Concept # What we will be learning Mandatory
Ch 23 Touring Our Solar System 23.1 The Solar System 23.2 The Terrestrial Planet 23.3 The Outer Planets 23.4 Minor Members of the Solar System
 Ch 23 Touring Our Solar System 23.1 The Solar System 23.2 The Terrestrial Planet 23.3 The Outer Planets 23.4 Minor Members of the Solar System Ch 23.1 The Solar System Terrestrial planets- Small Rocky
Ch 23 Touring Our Solar System 23.1 The Solar System 23.2 The Terrestrial Planet 23.3 The Outer Planets 23.4 Minor Members of the Solar System Ch 23.1 The Solar System Terrestrial planets- Small Rocky
Unit 2. Galaxies, Stars and the Solar System
 Strand K Astrophysics Unit 2 Galaxies, Stars and the Solar System Contents Page The Early Universe 2 The Life Cycle of Stars 4 Features of the Solar System 7 K21 The Early Universe Running the current
Strand K Astrophysics Unit 2 Galaxies, Stars and the Solar System Contents Page The Early Universe 2 The Life Cycle of Stars 4 Features of the Solar System 7 K21 The Early Universe Running the current
Unit 6 Lesson 4 What Are the Planets in Our Solar System? Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Unit 6 Lesson 4 What Are the Planets in Our Solar System? What other objects are near Earth in this part of space? Earth and millions of other objects make up our solar system. In Our Corner of Space A
Unit 6 Lesson 4 What Are the Planets in Our Solar System? What other objects are near Earth in this part of space? Earth and millions of other objects make up our solar system. In Our Corner of Space A
Name: Date: Hour: 179 degrees celsius. 5% of Earth A 70 pound person would weigh 27 pounds on Mercury.
 Planet Exploration- http://www.kidsastronomy.com/solar_.htm Mercury 1 87.9 days 58.6 days 57 million Km 465 degrees celsius Minimum -184 degrees celsius 179 degrees celsius Moons Terrestrial or Gaseous?
Planet Exploration- http://www.kidsastronomy.com/solar_.htm Mercury 1 87.9 days 58.6 days 57 million Km 465 degrees celsius Minimum -184 degrees celsius 179 degrees celsius Moons Terrestrial or Gaseous?
Inner Planets (Part II)
 Inner Planets (Part II) Sept. 18, 2002 1) Atmospheres 2) Greenhouse Effect 3) Mercury 4) Venus 5) Mars 6) Moon Announcements Due to technical difficulties, Monday s quiz doesn t count An extra credit problem
Inner Planets (Part II) Sept. 18, 2002 1) Atmospheres 2) Greenhouse Effect 3) Mercury 4) Venus 5) Mars 6) Moon Announcements Due to technical difficulties, Monday s quiz doesn t count An extra credit problem
Stars and Galaxies 1
 Stars and Galaxies 1 Characteristics of Stars 2 Star - body of gases that gives off great amounts of radiant energy as light and heat 3 Most stars look white but are actually different colors Antares -
Stars and Galaxies 1 Characteristics of Stars 2 Star - body of gases that gives off great amounts of radiant energy as light and heat 3 Most stars look white but are actually different colors Antares -
Chapter 15 & 16 Science Review (PATTERNS IN THE SKY, OUR SOLAR SYSTEM)
 Chapter 15 & 16 Science Review (PATTERNS IN THE SKY, OUR SOLAR SYSTEM) The Milky Way the galaxy that contains our solar system Our solar system is a speck in the Milky Way galaxy Pluto is now considered
Chapter 15 & 16 Science Review (PATTERNS IN THE SKY, OUR SOLAR SYSTEM) The Milky Way the galaxy that contains our solar system Our solar system is a speck in the Milky Way galaxy Pluto is now considered
ASTRONOMY SNAP GAME. with interesting facts
 ASTRONOMY SNAP GAME with interesting facts Sun Sun The Sun is the largest object in the solar system The Sun's life expectancy is approximately 5 billion more years At its core, the Sun s temperature is
ASTRONOMY SNAP GAME with interesting facts Sun Sun The Sun is the largest object in the solar system The Sun's life expectancy is approximately 5 billion more years At its core, the Sun s temperature is
The Sun s center is much hotter than the surface. The Sun looks large and bright in the sky. Other stars look much smaller.
 The Sun A star is a huge ball of hot, glowing gases. The Sun is a star. The width of the Sun is equal to the width of 100 Earths placed side by side. The Sun is extremely hot. The surface of the Sun has
The Sun A star is a huge ball of hot, glowing gases. The Sun is a star. The width of the Sun is equal to the width of 100 Earths placed side by side. The Sun is extremely hot. The surface of the Sun has
UNIT 1: THE UNIVERSE VOCABULARY
 UNIT 1: THE UNIVERSE VOCABULARY Asteroids Asteroid belt Astronomical unit (AU) Black hole Celestial body Cluster of galaxies Comets Constellation Dwarf planets Galaxy Light-year (LY) meteorites Milky Way
UNIT 1: THE UNIVERSE VOCABULARY Asteroids Asteroid belt Astronomical unit (AU) Black hole Celestial body Cluster of galaxies Comets Constellation Dwarf planets Galaxy Light-year (LY) meteorites Milky Way
Physical Science 1 Chapter 16 INTRODUCTION. Astronomy is the study of the universe, which includes all matter, energy, space and time.
 INTRODUCTION Astronomy is the study of the universe, which includes all matter, energy, space and time. Although the universe is vast and almost beyond imagination, much is known about its make-up and
INTRODUCTION Astronomy is the study of the universe, which includes all matter, energy, space and time. Although the universe is vast and almost beyond imagination, much is known about its make-up and
FCAT Review Space Science
 FCAT Review Space Science The Law of Universal Gravitation The law of universal gravitation states that ALL matter in the universe attracts each other. Gravity is greatly impacted by both mass and distance
FCAT Review Space Science The Law of Universal Gravitation The law of universal gravitation states that ALL matter in the universe attracts each other. Gravity is greatly impacted by both mass and distance
Motion of the planets
 Our Solar system Motion of the planets Our solar system is made up of the sun and the 9 planets that revolve around the sun Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune & Pluto (maybe?)
Our Solar system Motion of the planets Our solar system is made up of the sun and the 9 planets that revolve around the sun Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune & Pluto (maybe?)
TAKE A LOOK 2. Identify This star is in the last stage of its life cycle. What is that stage?
 CHAPTER 15 2 SECTION Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe The Life Cycle of Stars BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do stars change over time?
CHAPTER 15 2 SECTION Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe The Life Cycle of Stars BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do stars change over time?
Starting from closest to the Sun, name the orbiting planets in order.
 Chapter 9 Section 1: Our Solar System Solar System: The solar system includes the sun, planets and many smaller structures. A planet and its moon(s) make up smaller systems in the solar system. Scientist
Chapter 9 Section 1: Our Solar System Solar System: The solar system includes the sun, planets and many smaller structures. A planet and its moon(s) make up smaller systems in the solar system. Scientist
The Solar System. Presented By; Rahul Chaturvedi
 The Solar System Presented By; Rahul Chaturvedi What s in Our Solar System? Our Solar System consists of a central star (the Sun), the eight planets and their satellites (or moon), thousand of other smaller
The Solar System Presented By; Rahul Chaturvedi What s in Our Solar System? Our Solar System consists of a central star (the Sun), the eight planets and their satellites (or moon), thousand of other smaller
Developed in Consultation with Georgia Educators
 Developed in Consultation with Georgia Educators Table of Contents Georgia Performance Standards Correlation Chart........... 7 Performance Standards Chapter 1 Earth and Space.............................
Developed in Consultation with Georgia Educators Table of Contents Georgia Performance Standards Correlation Chart........... 7 Performance Standards Chapter 1 Earth and Space.............................
Unit 1: The Earth in the Universe
 Unit 1: The Earth in the Universe 1. The Universe 1.1. First ideas about the Universe 1.2. Components and origin 1.3. Sizes and distances 2. The Solar System 3. The planet Earth 3.1. Movements of the Earth
Unit 1: The Earth in the Universe 1. The Universe 1.1. First ideas about the Universe 1.2. Components and origin 1.3. Sizes and distances 2. The Solar System 3. The planet Earth 3.1. Movements of the Earth
SOLAR SYSTEM NOTES. Scientists believe its at least 4.6 billion years old!!! 10/26/2017 ENERGY TRANSFERS RADIATION FROM THE SUN
 SOLAR SYSTEM NOTES Our Solar System is composed of: 1. The Sun 2. The Planets 3. Asteroids 4. Comets 5. Meteors 6. Natural & Artificial satellites Remember: How old is our Solar System? Scientists believe
SOLAR SYSTEM NOTES Our Solar System is composed of: 1. The Sun 2. The Planets 3. Asteroids 4. Comets 5. Meteors 6. Natural & Artificial satellites Remember: How old is our Solar System? Scientists believe
Astronomy 1504 Section 10 Final Exam Version 1 May 6, 1999
 Astronomy 1504 Section 10 Final Exam Version 1 May 6, 1999 Reminder: When I write these questions, I believe that there is one one correct answer. The questions consist of all parts a e. Read the entire
Astronomy 1504 Section 10 Final Exam Version 1 May 6, 1999 Reminder: When I write these questions, I believe that there is one one correct answer. The questions consist of all parts a e. Read the entire
21/11/ /11/2017 Space Physics AQA Physics topic 8
 Space Physics AQA Physics topic 8 8.1 Solar System, Orbits and Satellites The eight planets of our Solar System Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune As well as the eight planets, the
Space Physics AQA Physics topic 8 8.1 Solar System, Orbits and Satellites The eight planets of our Solar System Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune As well as the eight planets, the
Formation of the Universe & What is in Space? The Big Bang Theory and components of the Universe
 Formation of the Universe & What is in Space? The Big Bang Theory and components of the Universe The Big Bang Theory The Big Bang Theory The Big Bang Theory is the most widely accepted scientific explanation
Formation of the Universe & What is in Space? The Big Bang Theory and components of the Universe The Big Bang Theory The Big Bang Theory The Big Bang Theory is the most widely accepted scientific explanation
Daily Science 03/30/2017
 Daily Science 03/30/2017 The atmospheres of different planets contain different gases. Which planet is most likely Earth? a. planet 1 b. planet 2 c. planet 3 d. planet 4 KeslerScience.com Can you name
Daily Science 03/30/2017 The atmospheres of different planets contain different gases. Which planet is most likely Earth? a. planet 1 b. planet 2 c. planet 3 d. planet 4 KeslerScience.com Can you name
Stars and Galaxies. Evolution of Stars
 Stars and Galaxies Evolution of Stars What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
Stars and Galaxies Evolution of Stars What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
Ag Earth Science Chapter 23
 Ag Earth Science Chapter 23 Chapter 23.1 Vocabulary Any of the Earth- like planets, including Mercury, Venus, and Earth terrestrial planet Jovian planet The Jupiter- like planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus,
Ag Earth Science Chapter 23 Chapter 23.1 Vocabulary Any of the Earth- like planets, including Mercury, Venus, and Earth terrestrial planet Jovian planet The Jupiter- like planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus,
SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES
 SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES Q1. The figure below shows what scientists over 1000 years ago thought the solar system was like. Give one way that the historical model of the solar
SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES Q1. The figure below shows what scientists over 1000 years ago thought the solar system was like. Give one way that the historical model of the solar
1 A Solar System Is Born
 CHAPTER 16 1 A Solar System Is Born SECTION Our Solar System California Science Standards 8.2.g, 8.4.b, 8.4.c, 8.4.d BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
CHAPTER 16 1 A Solar System Is Born SECTION Our Solar System California Science Standards 8.2.g, 8.4.b, 8.4.c, 8.4.d BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
Inner and Outer Planets
 Inner and Outer Planets Inner Planets Terrestrial planets are those that are closest to the Sun. Terrestrial planets are made mostly of rock and have similar characteristics to Earth. There are four terrestrial
Inner and Outer Planets Inner Planets Terrestrial planets are those that are closest to the Sun. Terrestrial planets are made mostly of rock and have similar characteristics to Earth. There are four terrestrial
*Generally speaking, there are two main life cycles for stars. *The factor which determines the life cycle of the star is its mass.
 Generally speaking, there are two main life cycles for stars. The factor which determines the life cycle of the star is its mass. 1 solar mass = size of our Sun Any star less than about three solar masses
Generally speaking, there are two main life cycles for stars. The factor which determines the life cycle of the star is its mass. 1 solar mass = size of our Sun Any star less than about three solar masses
The Big Bang Theory (page 854)
 Name Class Date Space Homework Packet Homework #1 Hubble s Law (pages 852 853) 1. How can astronomers use the Doppler effect? 2. The shift in the light of a galaxy toward the red wavelengths is called
Name Class Date Space Homework Packet Homework #1 Hubble s Law (pages 852 853) 1. How can astronomers use the Doppler effect? 2. The shift in the light of a galaxy toward the red wavelengths is called
Introduction to the Solar System
 Introduction to the Solar System Sep. 11, 2002 1) Introduction 2) Angular Momentum 3) Formation of the Solar System 4) Cowboy Astronomer Review Kepler s Laws empirical description of planetary motion Newton
Introduction to the Solar System Sep. 11, 2002 1) Introduction 2) Angular Momentum 3) Formation of the Solar System 4) Cowboy Astronomer Review Kepler s Laws empirical description of planetary motion Newton
A supernova is the explosion of a star. It is the largest explosion that takes place in space.
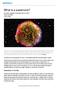 What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 974 Level 1110L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 974 Level 1110L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
Radiation - a process in which energy travels through vacuum (without a medium) Conduction a process in which energy travels through a medium
 SOLAR SYSTEM NOTES ENERGY TRANSFERS Radiation - a process in which energy travels through vacuum (without a medium) Conduction a process in which energy travels through a medium Convection - The transfer
SOLAR SYSTEM NOTES ENERGY TRANSFERS Radiation - a process in which energy travels through vacuum (without a medium) Conduction a process in which energy travels through a medium Convection - The transfer
4 HOW OUR SOLAR SYSTEM FORMED 750L
 4 HOW OUR SOLAR SYSTEM FORMED 750L HOW OUR SOLAR SYSTEM FORMED A CLOSE LOOK AT THE PLANETS ORBITING OUR SUN By Cynthia Stokes Brown, adapted by Newsela Planets come from the clouds of gas and dust that
4 HOW OUR SOLAR SYSTEM FORMED 750L HOW OUR SOLAR SYSTEM FORMED A CLOSE LOOK AT THE PLANETS ORBITING OUR SUN By Cynthia Stokes Brown, adapted by Newsela Planets come from the clouds of gas and dust that
Understanding Main Idea and Details
 C Understanding Main Idea and Details To the Student In this book, you will learn how to use the reading strategy called Understanding Main Idea and Details. With your teacher s help, you will practice
C Understanding Main Idea and Details To the Student In this book, you will learn how to use the reading strategy called Understanding Main Idea and Details. With your teacher s help, you will practice
Astronomy Teleclass Webinar!
 Welcome to the Supercharged Science Astronomy Teleclass Webinar! You can fill out this worksheet as a review exercise at the end of the class to see where your strengths are. What we re going to cover
Welcome to the Supercharged Science Astronomy Teleclass Webinar! You can fill out this worksheet as a review exercise at the end of the class to see where your strengths are. What we re going to cover
Understanding the Universe S TA R T ING WITH EARTH A ND B E YO ND
 Unit Overview: Understanding the Universe S TA R T ING WITH EARTH A ND B E YO ND Our solar system examining size and scale in space 6.11B UNDERSTAND THAT GRAVITY IS THE FORCE THAT GOVERNS MOTION IN OUR
Unit Overview: Understanding the Universe S TA R T ING WITH EARTH A ND B E YO ND Our solar system examining size and scale in space 6.11B UNDERSTAND THAT GRAVITY IS THE FORCE THAT GOVERNS MOTION IN OUR
Formation of the Universe The organization of Space
 February 21, 2014 Formation of the Universe The organization of Space Theory: A theory is An example is cell Cell Theory Cell Theory states 1. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells 2.
February 21, 2014 Formation of the Universe The organization of Space Theory: A theory is An example is cell Cell Theory Cell Theory states 1. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells 2.
Activity 12: Solar System
 ctivity 12: Solar System PRT PRT 1. The ratio of the diameter of an asteroid to the diameter of Pluto is 2 to 13. The diameter of Pluto is 1.43 x 103 miles. What is the diameter of the asteroid? 2. Sarah
ctivity 12: Solar System PRT PRT 1. The ratio of the diameter of an asteroid to the diameter of Pluto is 2 to 13. The diameter of Pluto is 1.43 x 103 miles. What is the diameter of the asteroid? 2. Sarah
Our Solar System and Its Place in the Universe
 Our Solar System and Its Place in the Universe The Formation of the Solar System Our Solar System includes: Planets Dwarf Planets Moons Small Solar System bodies Sun Outer portion created Planets and their
Our Solar System and Its Place in the Universe The Formation of the Solar System Our Solar System includes: Planets Dwarf Planets Moons Small Solar System bodies Sun Outer portion created Planets and their
Universe Celestial Object Galaxy Solar System
 ASTRONOMY Universe- Includes all known matter (everything). Celestial Object Any object outside or above Earth s atmosphere. Galaxy- A large group (billions) of stars (held together by gravity). Our galaxy
ASTRONOMY Universe- Includes all known matter (everything). Celestial Object Any object outside or above Earth s atmosphere. Galaxy- A large group (billions) of stars (held together by gravity). Our galaxy
Learning About Our Solar System
 Learning About Our Solar System By debbie Routh COPYRIGHT 2004 Mark Twain Media, Inc. ISBN 978-1-58037-876-5 Printing No. 404007-EB Mark Twain Media, Inc., Publishers Distributed by Carson-Dellosa Publishing
Learning About Our Solar System By debbie Routh COPYRIGHT 2004 Mark Twain Media, Inc. ISBN 978-1-58037-876-5 Printing No. 404007-EB Mark Twain Media, Inc., Publishers Distributed by Carson-Dellosa Publishing
Chapter 23: Touring Our Solar System
 Chapter 23: Touring Our Solar System The Sun The is the center of our solar system. The Sun makes up of all the mass of our solar system. The Sun s force holds the planets in their orbits around the Sun.
Chapter 23: Touring Our Solar System The Sun The is the center of our solar system. The Sun makes up of all the mass of our solar system. The Sun s force holds the planets in their orbits around the Sun.
Stars and Galaxies. Evolution of Stars
 chapter 13 3 Stars and Galaxies section 3 Evolution of Stars Before You Read What makes one star different from another? Do you think the Sun is the same as other stars? Write your ideas on the lines below.
chapter 13 3 Stars and Galaxies section 3 Evolution of Stars Before You Read What makes one star different from another? Do you think the Sun is the same as other stars? Write your ideas on the lines below.
Earth & Space Science ~ The Solar System
 Earth & Space Science ~ The Solar System In e r Sci Uni 11 I. Sun, Earth & Moon A. The Solar System 1. the sun & the objects orbiting it a. incl. 8 planets, other stars, asteroids, meteoroids, dwarf planets,
Earth & Space Science ~ The Solar System In e r Sci Uni 11 I. Sun, Earth & Moon A. The Solar System 1. the sun & the objects orbiting it a. incl. 8 planets, other stars, asteroids, meteoroids, dwarf planets,
Chapter 29. The Solar System. The Solar System. Section 29.1 Models of the Solar System notes Models of the Solar System
 The Solar System Chapter 29 The Solar System Section 29.1 Models of the Solar System 29.1 notes Models of the Solar System Geocentric: : Earth-centered model of the solar system. (Everything revolves around
The Solar System Chapter 29 The Solar System Section 29.1 Models of the Solar System 29.1 notes Models of the Solar System Geocentric: : Earth-centered model of the solar system. (Everything revolves around
Facts about Mercury. Mercury is a small planet which orbits closer to the sun than any other planet in our solar system.
 Planets Thank you so much for purchasing my work! I hope you enjoy it as much as I enjoyed making it! Make sure to stop by my store again for great specials! You are always a valued customer. If you have
Planets Thank you so much for purchasing my work! I hope you enjoy it as much as I enjoyed making it! Make sure to stop by my store again for great specials! You are always a valued customer. If you have
NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS
 NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 2 BASIC ASTRONOMY, AND STARS AND THEIR EVOLUTION Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics CSUSB COURSE WEBPAGE: http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen MOTIONS IN THE SOLAR SYSTEM
NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 2 BASIC ASTRONOMY, AND STARS AND THEIR EVOLUTION Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics CSUSB COURSE WEBPAGE: http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen MOTIONS IN THE SOLAR SYSTEM
STARS AND GALAXIES STARS
 STARS AND GALAXIES STARS enormous spheres of plasma formed from strong gravitational forces PLASMA the most energetic state of matter; responsible for the characteristic glow emitted by these heavenly
STARS AND GALAXIES STARS enormous spheres of plasma formed from strong gravitational forces PLASMA the most energetic state of matter; responsible for the characteristic glow emitted by these heavenly
CA Physical Science Benchmark Test 4. 1 A rocket accelerates from the launch pad. The forces on the rocket are
 Physical Science enchmark Test 4 Name: ate: 1 rocket accelerates from the launch pad. The forces on the rocket are action forces. balanced. reaction forces. unbalanced. 2 What force(s) act(s) on a rocket
Physical Science enchmark Test 4 Name: ate: 1 rocket accelerates from the launch pad. The forces on the rocket are action forces. balanced. reaction forces. unbalanced. 2 What force(s) act(s) on a rocket
The Solar System LEARNING TARGETS. Scientific Language. Name Test Date Hour
 Name Test Date Hour Astronomy#3 - Notebook The Solar System LEARNING TARGETS I can describe the objects that make up our solar system. I can identify the inner and outer planets. I can explain the difference
Name Test Date Hour Astronomy#3 - Notebook The Solar System LEARNING TARGETS I can describe the objects that make up our solar system. I can identify the inner and outer planets. I can explain the difference
JOVIAN VS. TERRESTRIAL PLANETS. To begin lets start with an outline of the solar system.
 JOVIAN VS. TERRESTRIAL PLANETS To begin lets start with an outline of the solar system. JOVIAN VS. TERRESTRIAL PLANETS What are Jovian and Terrestrial planets? Terrestrial planets are Earth like planets,
JOVIAN VS. TERRESTRIAL PLANETS To begin lets start with an outline of the solar system. JOVIAN VS. TERRESTRIAL PLANETS What are Jovian and Terrestrial planets? Terrestrial planets are Earth like planets,
Outline. Question of Scale. Planets Dance. Homework #2 was due today at 11:50am! It s too late now.
 Outline Homework #2 was due today at 11:50am! It s too late now. Planetarium observing is over. Switch Gears Solar System Introduction The Planets, the Asteroid belt, the Kupier objects, and the Oort cloud
Outline Homework #2 was due today at 11:50am! It s too late now. Planetarium observing is over. Switch Gears Solar System Introduction The Planets, the Asteroid belt, the Kupier objects, and the Oort cloud
Unit 2 Lesson 1 What Objects Are Part of the Solar System? Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Unit 2 Lesson 1 What Objects Are Part of the Solar System? Florida Benchmarks SC.5.E.5.2 Recognize the major common characteristics of all planets and compare/contrast the properties of inner and outer
Unit 2 Lesson 1 What Objects Are Part of the Solar System? Florida Benchmarks SC.5.E.5.2 Recognize the major common characteristics of all planets and compare/contrast the properties of inner and outer
Planetarium observing is over. Nighttime observing starts next week.
 Homework #2 was due today at 11:50am! It s too late now. Planetarium observing is over. Solar observing is over. Nighttime observing starts next week. Outline Switch Gears Solar System Introduction The
Homework #2 was due today at 11:50am! It s too late now. Planetarium observing is over. Solar observing is over. Nighttime observing starts next week. Outline Switch Gears Solar System Introduction The
What is the solar system?
 Notes Astronomy What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the Solar System Our solar system includes planets and dwarf planets, their moons, a star called the Sun, asteroids and comets. Planets, dwarf
Notes Astronomy What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the Solar System Our solar system includes planets and dwarf planets, their moons, a star called the Sun, asteroids and comets. Planets, dwarf
Chapter 06 Let s Make a Solar System
 like? Big picture. Chapter 06 Let s Make a Solar System How did it come to be this way? Where did it come from? Will I stop sounding like the Talking Heads? The solar system exhibits clear patterns of
like? Big picture. Chapter 06 Let s Make a Solar System How did it come to be this way? Where did it come from? Will I stop sounding like the Talking Heads? The solar system exhibits clear patterns of
Chapter 17 Solar System
 Chapter 17 Solar System Rotation Earth spinning on its axis (like a top) "TOP" imaginary rod running through the center of the Earth from North pole to South pole The Earth is tilted on its axis at an
Chapter 17 Solar System Rotation Earth spinning on its axis (like a top) "TOP" imaginary rod running through the center of the Earth from North pole to South pole The Earth is tilted on its axis at an
The Solar System. Name Test Date Hour
 Name Test Date Hour Astronomy#3 - Notebook The Solar System LEARNING TARGETS I can describe the objects that make up our solar system. I can identify the inner and outer planets. I can explain the difference
Name Test Date Hour Astronomy#3 - Notebook The Solar System LEARNING TARGETS I can describe the objects that make up our solar system. I can identify the inner and outer planets. I can explain the difference
-Melissa Greenberg, Arielle Hoffman, Zachary Feldmann, Ryan Pozin, Elizabeth Weeks, Christopher Pesota, & Sara Pilcher
 -Melissa Greenberg, Arielle Hoffman, Zachary Feldmann, Ryan Pozin, Elizabeth Weeks, Christopher Pesota, & Sara Pilcher Formation Overview All explanations as to how the solar system was formed are only
-Melissa Greenberg, Arielle Hoffman, Zachary Feldmann, Ryan Pozin, Elizabeth Weeks, Christopher Pesota, & Sara Pilcher Formation Overview All explanations as to how the solar system was formed are only
Lesson 3 THE SOLAR SYSTEM
 Lesson 3 THE SOLAR SYSTEM THE NATURE OF THE SUN At the center of our solar system is the Sun which is a typical medium sized star. Composed mainly of Hydrogen (73% by mass), 23% helium and the rest is
Lesson 3 THE SOLAR SYSTEM THE NATURE OF THE SUN At the center of our solar system is the Sun which is a typical medium sized star. Composed mainly of Hydrogen (73% by mass), 23% helium and the rest is
How did it come to be this way? Will I stop sounding like the
 Chapter 06 Let s Make a Solar System How did it come to be this way? Where did it come from? Will I stop sounding like the Talking Heads? What does the solar system look like? Big picture. The solar system
Chapter 06 Let s Make a Solar System How did it come to be this way? Where did it come from? Will I stop sounding like the Talking Heads? What does the solar system look like? Big picture. The solar system
The Solar Nebula Theory. This lecture will help you understand: Conceptual Integrated Science. Chapter 28 THE SOLAR SYSTEM
 This lecture will help you understand: Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh Conceptual Integrated Science Chapter 28 THE SOLAR SYSTEM Overview of the Solar System The Nebular Theory The Sun Asteroids, Comets, and
This lecture will help you understand: Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh Conceptual Integrated Science Chapter 28 THE SOLAR SYSTEM Overview of the Solar System The Nebular Theory The Sun Asteroids, Comets, and
Life Cycle of a Star Worksheet
 Life Cycle of a Star Worksheet A STAR IS BORN STAGES COMMON TO ALL STARS All stars start as a nebula. A nebula is a large cloud of gas and dust. Gravity can pull some of the gas and dust in a nebula together.
Life Cycle of a Star Worksheet A STAR IS BORN STAGES COMMON TO ALL STARS All stars start as a nebula. A nebula is a large cloud of gas and dust. Gravity can pull some of the gas and dust in a nebula together.
What is Earth Science?
 What is Earth Science? A.EARTH SCIENCE: the study of Earth and its history B. Earth science is divided into 4 main branches: 1. Geology: study of the lithosphere 2. Oceanography: study of oceans 3. Meteorology:
What is Earth Science? A.EARTH SCIENCE: the study of Earth and its history B. Earth science is divided into 4 main branches: 1. Geology: study of the lithosphere 2. Oceanography: study of oceans 3. Meteorology:
What If We Had No Moon?
 What If We Had No Moon? By Bob Gard Hollister Missouri church of Christ www.hollisterchurchofchrist.org Notes For Sermon, What If We Had No Moon? Slide 1 What are we talking about?... Slide 2 Moons! Let
What If We Had No Moon? By Bob Gard Hollister Missouri church of Christ www.hollisterchurchofchrist.org Notes For Sermon, What If We Had No Moon? Slide 1 What are we talking about?... Slide 2 Moons! Let
Life Cycle of a Star - Activities
 Name: Class Period: Life Cycle of a Star - Activities A STAR IS BORN STAGES COMMON TO ALL STARS All stars start as a nebula. A nebula is a large cloud of gas and dust. Gravity can pull some of the gas
Name: Class Period: Life Cycle of a Star - Activities A STAR IS BORN STAGES COMMON TO ALL STARS All stars start as a nebula. A nebula is a large cloud of gas and dust. Gravity can pull some of the gas
The Earth in the Universe
 The Earth in the Universe (OCR) Evidence for the age of the Earth Scientists once thought that the Earth was only 6000 years old. Rocks have provided lots of evidence for the world being older. 1) Erosion
The Earth in the Universe (OCR) Evidence for the age of the Earth Scientists once thought that the Earth was only 6000 years old. Rocks have provided lots of evidence for the world being older. 1) Erosion
Read each slide then use the red or some underlined words to complete the organizer.
 Read each slide then use the red or some underlined words to complete the organizer. 1B Did it start as a bang! 1B The Expanding Universe A. The Big Bang Theory: Idea that all matter began in an infinitely
Read each slide then use the red or some underlined words to complete the organizer. 1B Did it start as a bang! 1B The Expanding Universe A. The Big Bang Theory: Idea that all matter began in an infinitely
The History of the Solar System. From cloud to Sun, planets, and smaller bodies
 The History of the Solar System From cloud to Sun, planets, and smaller bodies The Birth of a Star Twenty years ago, we knew of only one star with planets the Sun and our understanding of the birth of
The History of the Solar System From cloud to Sun, planets, and smaller bodies The Birth of a Star Twenty years ago, we knew of only one star with planets the Sun and our understanding of the birth of
At this point of its orbit, any solar satellite such as a comet or a planet is farthest away from the sun. What is the aphelion?
 At this point of its orbit, any solar satellite such as a comet or a planet is farthest away from the sun. What is the aphelion? These small, rocky worlds orbit the sun generally between the orbits of
At this point of its orbit, any solar satellite such as a comet or a planet is farthest away from the sun. What is the aphelion? These small, rocky worlds orbit the sun generally between the orbits of
Your task for each planet...
 Solar System Your task for each planet... Slide 1: What type of planet is it? (either rocky terrestrial world, gas giant or ice giant) What is it made of? Does it have any moons? What is its mass relative
Solar System Your task for each planet... Slide 1: What type of planet is it? (either rocky terrestrial world, gas giant or ice giant) What is it made of? Does it have any moons? What is its mass relative
Notes: The Solar System
 Notes: The Solar System The Formation of the Solar System 1. A gas cloud collapses under the influence of gravity. 2. Solids condense at the center, forming a protostar. 3. A falttened disk of matter surrounds
Notes: The Solar System The Formation of the Solar System 1. A gas cloud collapses under the influence of gravity. 2. Solids condense at the center, forming a protostar. 3. A falttened disk of matter surrounds
Beyond Our Solar System Chapter 24
 Beyond Our Solar System Chapter 24 PROPERTIES OF STARS Distance Measuring a star's distance can be very difficult Stellar parallax Used for measuring distance to a star Apparent shift in a star's position
Beyond Our Solar System Chapter 24 PROPERTIES OF STARS Distance Measuring a star's distance can be very difficult Stellar parallax Used for measuring distance to a star Apparent shift in a star's position
Our Planetary System. Chapter 7
 Our Planetary System Chapter 7 Key Concepts for Chapter 7 and 8 Inventory of the Solar System Origin of the Solar System What does the Solar System consist of? The Sun: It has 99.85% of the mass of the
Our Planetary System Chapter 7 Key Concepts for Chapter 7 and 8 Inventory of the Solar System Origin of the Solar System What does the Solar System consist of? The Sun: It has 99.85% of the mass of the
