Extrasolar Planets. Dieter Schmitt Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research Katlenburg-Lindau
|
|
|
- Eustace Sherman
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Extrasolar Planets Dieter Schmitt Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research Katlenburg-Lindau Lecture Introduction to Solar System Physics Uni Göttingen, 8 June 2009
2 Outline Historical Overview Detection Methods Planet Statistics Formation of Planets Physical Properties Habitability
3 Historical overview 1989: planet / brown dwarf orbiting HD (Latham et al.) 1992: two planets orbiting pulsar PSR B (Wolszczan & Frail) 1995: first planet around a solar-like star 51 Peg b (Mayor & Queloz) 1999: first multiple planetary system with three planets Ups And (Edgar et al.) 2000: first planet by transit method HD b (Charbonneau et al.) 2001: atmosphere of HD b (Charbonneau et al.) 2002: astrometry applied to Gliese 876 (Benedict et al.) 2005: first planet by direct imaging GQ Lupi b (Neuhäuser et al.) 2006: Earth-like planet by gravitational microlensing (Beaulieu et al.) 2007: Gliese 581d, small exoplanet near habitability zone (Selsis et al.) 2009: Gliese 581e, smallest exoplanet with 1.9 Earth masses (Mayor et al.) As of 7 June 2009: 349 exoplanets in 296 systems (25 systems with 2 planets, 9 with 3, 2 with 4 and 1 with 5)
4 Our Solar System 1047 M J 0.39 AU M J 1 M J 0.30 M J M J M J 1 AU 5.2 AU 9.6 AU 19 AU 30 AU 1 yr 11.9 yr 29.5 yr 84 yr 165 yr
5 IAU 2006: Definition Planet in orbit around the Sun / star nearly spherical shape / sufficient mass for hydrostatic equilib. cleared neighbourhood around its orbit Pluto: dwarf planet, as Ceres Brown dwarf: masses between 14 M J and 80 M J (= 0.08 M ) fully convective, no hydrogen fusion, but deuterium fusion M < 14 M J : planet, M > 80 M J : star (red dwarf)
6 How can we detect extrasolar planets around main sequence stars? The main detection methods: Radial velocity method Astrometry Transit method Gravitational microlensing Direct imaging
7 Radial velocity method Δλ / λ = r = S v / c v sini / c a M = S S a P M P a S a P PvS = 2 π 3 P 2 = GM 4π M S 2 P sini = M << a >> v P M S P a S r 2 MSP 2πG 1/ 3
8 51 Peg b detected 1995 by Mayor & Queloz and Marcy & Butler 51 Peg: G2IV, V = 5.5, 15 pc 51 Peg b: P = 4.23 d a = 0.05 AU M sin i = 0.47 M J
9 Pegasus α And 51
10 Third parameter: eccentricity Detection limit: 51 Peg b: v r ~ 50 m/s today: λ/δλ 10 8 v r ~ 3 m/s theoretical: v r ~ 1 m/s (effect of star spots) in comparison: Jupiter around Sun: 12.5 m/s Earth 0.05 m/s
11 Astrometry Center of mass Δ = 1 mas at 10 pc Measurement of the spatial wobble of the star around the center of mass Δ = (M P /M S )(a P /d): near stars, large orbital distances current resolution: 1-2 mas (from ground), 0.1 mas (HST) example: Gliese 876 b (Benedict et al. 2002) in future: Gaia (ESA Mission)
12 Simulations: star in 50 pc, planet with 15 M J, a = 0.06 AU, e = 0.2, proper motion of 50 mas/yr motion of Sun in 10 pc distance measurement of two velocity components determination of true mass independent of sin i
13 Transit method amplitude: ΔI / I ~ R P2 / R S 2 Jupiter: ~1%, Erde: ~0.01% probability: R S / a P period: orbital period, distance from star transit duration: inclination of orbit, i ~ 90 o HD b (Charbonneau et al. 2000) Inclination Radius
14 Combination of radial velocity and transit method M sin i i, R combined: M, mean ρ
15 HD b discovered with RV by Sato et al. (2005) transit by amateur astronomer Bissinger (2005) Δm = mag! P = 2.88 d a = AU M = 0.36 M J R = 0.72 R J T eff = /- 200 K
16 Mass - Radius - Diagram red: planets detected by RV method blue: planets by transit method triangles: Jupiter Saturn (Udry & Santos 2007)
17 CoRoT mission French satellite with 27cm telescope and CCD camera with 2.8 o x2.8 o field-of-view Goal: Detection of terrestrial planets on close-in orbits CoRoT-Exo-1b (Barge et al. 2007) Launch: 27 December 2006
18 Gravitational microlensing Passing star Background star Passing star with planet Earth A foreground star acts as gravitational lens and enhances the apparent brightness of a background star. A planet around the foreground star modifies the lensing signal. Microlensing can detect small, terrestrial planets. The geometry does not repeat, however. Therefore, good for statistical studies.
19 Detection of a Jupiter/Saturn analog with microlensing OGLE L: 0.5 M, 1.5 kpc Name OGLE L b OGLE L c Mass 0.71 M J 0.27 M J Distance 2.3 AU 4.6 AU Period 1825 d 5100 d Eccentricity 0.11 Inclination 59 o (Gaudi et al. 2008) OGLE = Optical Gravitational Lens Experiment
20 Direct imaging difficulty: star several orders of magnitude brighter than planet situation improves in the infrared spectral range and for joung, hot planets
21 GQ Lupi b, first directly observed exoplanet ESO VLT-NaCo K-Band Companion: 6 mag fainter than star separation ~ 0.7 arc sec a ~ 100 AU M ~ 1-42 M J Star: T Tauri star (K7eV) V ~ 11.4, L ~ 1.6 L3 M ~ 0.7 M distance 140+/-50 pc age ~ 2 Mio years (Neuhäuser et al. 2005)
22 Detection ranges Brown Dwarf Jupiter Transits from ground Future imaging techniques, e.g. interferometry Imaging C5,C6,C8 Log M Jupiter Saturn G Uranus RV COROT/Kepler Earth Microlensing M6 G2 Astrometry Log Semi-major axis (AU)
23 Summary Radial velocity method: + most effective method so far +/- only lower mass limits Astrometry: Transit method: Microlensing: Direct imaging: + long-period planets - near stars + determines radius + in combination with RV: mass and mean density - needs follow-up confirmation + low-mass planets detectable +/- statistical information + direct observation - only for distant planets
24 Ypsilon Andromedae υ And: F8V, 1.27 M, 1.6 R, 6200 K, 3.8 Gyr, 13.5 pc υ And b: 0.06 AU, 4.62 d, 0.69 M J υ And c: 0.83 AU, 242 d, 1.97 M J υ And d: 2.54 AU, 1290 d, 3.93 M J
25 55 Cancri 55 Cnc: G8V, 0.95 M, 0.96 R, 5250 K, 4.5 Gyr, 12.5 pc 55 Cnc e: AU, 2.82 d, 0.03 M J 55 Cnc b: AU, 14.6 d, 0.82 M J 55 Cnc c: AU, 43.9 d, 0.17 M J 55 Cnc f: AU, 260 d, 0.14 M J 55 Cnc d: 5.77 AU, 5218 d, 3.84 M J
26 Planet statistics Many planets with small masses Few brown dwarfs
27 Most planets discovered are on short orbital periods selection effect
28 Most planets discovered are on short orbital periods selection effect
29
30 Hot Jupiter planets
31 Orbital eccentricity Eccentricities roughly in the same range as for binary stars. Close-in planets are on circularised orbits due to tidal interaction with their central star. (Udry & Santos 2007)
32 Planet formation in a nutshell Molecularcloudsin theism cold, dense, H 2, molecules, ~50% of ISM
33 Gravitational collaps Jeans mass, trigger, cloud fragmentation, star formation in cluster
34 Circumstellar / protoplanetary disk angular momentum conservation molecular cloud gravitational collaps star with accretion disk yr TTauri star, wind yr pre-main-seq. star evolved disk yr envelope ~8000 AU accretion disk ~100 AU main-sequence star planetary system yr Hogerheijde 2001 Kley 2008
35 Condensation, dust agglomeration, formation of planitesimals Condensation of molecules: gas to solid, 1 μm, some 1000 yr Agglomeration / coagulation of dust: 10 cm, takes longer further out, frost line at 5 AU: ice Planitesimals: 10 km, meter-size barrier
36 Formation of terrestrial planets planitesimals of ~10km gravitational focusing collisions fragmentation of smaller body accretion of fragments larger and fewer bodies runaway growth oligarchic growth ends when reservoir exhausted
37 Formation of gasplanets Core accretion model large planetary embryo of ~10M E fast accretion of gas (H 2, He, ) time scale: Jupiter: 0.5 Myr Saturn: 2 Myr Uranus: 10 Myr Neptune: 30 Myr end of growth: - stellar wind (TTauri phase) - evaporation of disk Gravitational instability model gravitational instability of knots in mass-rich disks
38 Planetary migration change of orbital radius (i.e. semimajor axis) of a planet in time still controversial, supported by Kuiper Belt Objects, Hot Jupiters, atmos. composition of Jupiter caused by interaction of planet with gas or planetary disk Type I migration: planet spiral density wave in disk imbalance inside and outside the orbit net torque inward loss of angular momentum inward migration Type II migration: large planets clear gap in disk gas from disk enters gap moves planet and gap inward
39 Physical properties relatively little known observation of hot Jupiters with HST and Spitzer during transits: determination of effective temperature chemical composition of atmosphere theoretical studies: planetary formation interior structure atmosphere magnetosphere and plasma interaction with stellar wind and magnetic field...
40 Measurement of temperature during the secondary transit at infrared wavelengths
41 Secondary transit of HD b orbital period = 3.52 days radius = 1.3 R J mass = 0.63 M J density = g cm -3 T eff = /- 150 K in comparison: Jupiter T eff = 124 K 24 micron (Deming et al. 2005) heating due to small orbital distance of the planet
42 Measurement of atmospheric composition observer observer Measure stellar light passing through the planetary atmosphere during transit configuration Measure stellar light reflected or scattered from the planetary atmosphere Measure the infrared radiation emitted by the planetary atmosphere
43 Water vapour in the atmosphere of HD b? Spectroscopy of the starlight reflected by the planet with the Spitzer IR satellite Modelled spectra (Burrows et al. 2007)
44 H, O, C and Na in the atmosphere of HD b Spectroscopy at optical and ultraviolet wavelengths during a transit (with the HST) (Charbonneau 2002, Desert 2003, Vidal-Madjar et al. 2004)
45 Habitability Potential of a planet to develop and sustain life Absolute requirements: energy source liquid water on surface environment favourable for the assembly of complex organic molecules
46 Habitable zone Orbital distance region around a star where an Earth-like planet can maintain liquid water on its surface Habitable zone depends on luminosity of star inner boundary: runaway greenhouse effect, loss of water to space outer boundary: dependent on amount of greenhouse gases (CO 2 and H 2 O)
47 Constraints on star main sequence star, spectral type F - K sufficient long stellar life UV radiation for atmospheric dynamics and chemistry habitable zone at distances outside tidal locking, no good news for M stars stability of habitable zone slow stellar evolution no gas giants close to habitable zone low stellar variability, red dwarf often very active high metallicity favours planet formation
48 Constraints on planet terrestrial sufficient mass for thick atmosphere for hot core and geological activity for iron core, dynamo, magnetic protection from stellar wind and cosmic rays small orbital eccentricity, moderate rotation, moderate tilt of rotation axis because of seasons chemistry: C, H, O, N amino acids satellites of gas giants
49 Venus Earth Mars T = 457 C p = 90 bar Atmosphere: 96 % CO 2 3,5 % N 2 runaway greenhouse T = 15 C p = 1 bar Atmosphere: 77 % N 2 21 % O 2 1 % H 2 O T = - 80 C p = bar Atmosphere: 95 % CO 2 2,7 % N 2 global fridge
50 Gliese 581 c,d,e Gliese 581: M3V, 0.31 M, 6.3 pc Gliese 581 c: AU, 12.9 d, 5 M E Gliese 581 d: 0.22 AU, 67 d, 7.1 M E Gliese 581 e: 0.03 AU, 3.15 d, 1.9 M E
51 Future missions CoRoT (CNES) Kepler (NASA) Gaia (ESA) Transits: Transits: Astrometry: Hot Earths Earth-like Statistics of of planets gas gas giants 2017 Plato? (ESA) Transits: Earth-like planets Darwin? (ESA) Direct imaging: Search for for biomarkers
52 End
Extrasolar Planets. Methods of detection Characterization Theoretical ideas Future prospects
 Extrasolar Planets Methods of detection Characterization Theoretical ideas Future prospects Methods of detection Methods of detection Methods of detection Pulsar timing Planetary motion around pulsar
Extrasolar Planets Methods of detection Characterization Theoretical ideas Future prospects Methods of detection Methods of detection Methods of detection Pulsar timing Planetary motion around pulsar
Observations of extrasolar planets
 Observations of extrasolar planets 1 Mercury 2 Venus radar image from Magellan (vertical scale exaggerated 10 X) 3 Mars 4 Jupiter 5 Saturn 6 Saturn 7 Uranus and Neptune 8 we need to look out about 10 parsecs
Observations of extrasolar planets 1 Mercury 2 Venus radar image from Magellan (vertical scale exaggerated 10 X) 3 Mars 4 Jupiter 5 Saturn 6 Saturn 7 Uranus and Neptune 8 we need to look out about 10 parsecs
Searching for Other Worlds
 Searching for Other Worlds Lecture 32 1 In-Class Question What is the Greenhouse effect? a) Optical light from the Sun is reflected into space while infrared light passes through the atmosphere and heats
Searching for Other Worlds Lecture 32 1 In-Class Question What is the Greenhouse effect? a) Optical light from the Sun is reflected into space while infrared light passes through the atmosphere and heats
Observations of Extrasolar Planets
 Observations of Extrasolar Planets Hamilton 2005 Shay Zucker Observations of Extrasolar Planets Spectroscopic detection of exoplanets Emerging properties of the sample Transiting planets Future prospects
Observations of Extrasolar Planets Hamilton 2005 Shay Zucker Observations of Extrasolar Planets Spectroscopic detection of exoplanets Emerging properties of the sample Transiting planets Future prospects
Planets and Brown Dwarfs
 Extra Solar Planets Extra Solar Planets We have estimated there may be 10 20 billion stars in Milky Way with Earth like planets, hospitable for life. But what evidence do we have that such planets even
Extra Solar Planets Extra Solar Planets We have estimated there may be 10 20 billion stars in Milky Way with Earth like planets, hospitable for life. But what evidence do we have that such planets even
Extra Solar Planetary Systems and Habitable Zones
 Lecture Overview Extra Solar Planetary Systems and Habitable Zones Our Galaxy has 200 Billion Stars, Our Sun has 8 planets. It seems like an awful waste if we are alone Exoplanets Karen J. Meech, Svetlana
Lecture Overview Extra Solar Planetary Systems and Habitable Zones Our Galaxy has 200 Billion Stars, Our Sun has 8 planets. It seems like an awful waste if we are alone Exoplanets Karen J. Meech, Svetlana
HD Transits HST/STIS First Transiting Exo-Planet. Exoplanet Discovery Methods. Paper Due Tue, Feb 23. (4) Transits. Transits.
 Paper Due Tue, Feb 23 Exoplanet Discovery Methods (1) Direct imaging (2) Astrometry position (3) Radial velocity velocity Seager & Mallen-Ornelas 2003 ApJ 585, 1038. "A Unique Solution of Planet and Star
Paper Due Tue, Feb 23 Exoplanet Discovery Methods (1) Direct imaging (2) Astrometry position (3) Radial velocity velocity Seager & Mallen-Ornelas 2003 ApJ 585, 1038. "A Unique Solution of Planet and Star
Planet formation in protoplanetary disks. Dmitry Semenov Max Planck Institute for Astronomy Heidelberg, Germany
 Planet formation in protoplanetary disks Dmitry Semenov Max Planck Institute for Astronomy Heidelberg, Germany Suggested literature "Protoplanetary Dust" (2010), eds. D. Apai & D. Lauretta, CUP "Protostars
Planet formation in protoplanetary disks Dmitry Semenov Max Planck Institute for Astronomy Heidelberg, Germany Suggested literature "Protoplanetary Dust" (2010), eds. D. Apai & D. Lauretta, CUP "Protostars
Exoplanet Search Techniques: Overview. PHY 688, Lecture 28 April 3, 2009
 Exoplanet Search Techniques: Overview PHY 688, Lecture 28 April 3, 2009 Course administration final presentations Outline see me for paper recommendations 2 3 weeks before talk see me with draft of presentation
Exoplanet Search Techniques: Overview PHY 688, Lecture 28 April 3, 2009 Course administration final presentations Outline see me for paper recommendations 2 3 weeks before talk see me with draft of presentation
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 15. Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 15 Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 15 The Formation of Planetary Systems Units of Chapter 15 15.1 Modeling Planet Formation 15.2 Terrestrial and Jovian Planets
Lecture Outlines Chapter 15 Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 15 The Formation of Planetary Systems Units of Chapter 15 15.1 Modeling Planet Formation 15.2 Terrestrial and Jovian Planets
Searching for Other Worlds: The Methods
 Searching for Other Worlds: The Methods John Bally 1 1 Center for Astrophysics and Space Astronomy Department of Astrophysical and Planetary Sciences University of Colorado, Boulder The Search Extra-Solar
Searching for Other Worlds: The Methods John Bally 1 1 Center for Astrophysics and Space Astronomy Department of Astrophysical and Planetary Sciences University of Colorado, Boulder The Search Extra-Solar
Planets & Life. Planets & Life PHYS 214. Please start all class related s with 214: 214: Dept of Physics (308A)
 Planets & Life Planets & Life PHYS 214 Dr Rob Thacker Dept of Physics (308A) thacker@astro.queensu.ca Please start all class related emails with 214: 214: Today s s lecture Assignment 1 marked will hand
Planets & Life Planets & Life PHYS 214 Dr Rob Thacker Dept of Physics (308A) thacker@astro.queensu.ca Please start all class related emails with 214: 214: Today s s lecture Assignment 1 marked will hand
II Planet Finding.
 II Planet Finding http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy229.html 1.0 Introduction There are a lot of slides in this lecture. Much of this should be familiar from PHY104 (Introduction to Astrophysics) and
II Planet Finding http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy229.html 1.0 Introduction There are a lot of slides in this lecture. Much of this should be familiar from PHY104 (Introduction to Astrophysics) and
The Transit Method: Results from the Ground
 The Transit Method: Results from the Ground Results from individual transit search programs The Mass-Radius relationships (internal structure) Global Properties The Rossiter-McClaughlin Effect There are
The Transit Method: Results from the Ground Results from individual transit search programs The Mass-Radius relationships (internal structure) Global Properties The Rossiter-McClaughlin Effect There are
EXOPLANETS. Aurélien CRIDA
 EXOPLANETS Aurélien CRIDA EXOPLANETS Giordano Bruno said that the many stars are like our Sun, with planets like our Earth, inhabited as well (in de l'infinito universo e mondi (1574) ). He was burnt alive
EXOPLANETS Aurélien CRIDA EXOPLANETS Giordano Bruno said that the many stars are like our Sun, with planets like our Earth, inhabited as well (in de l'infinito universo e mondi (1574) ). He was burnt alive
Other planetary systems
 Exoplanets are faint! Other planetary systems Planets are seen only by reflected light at optical wavelengths At the distance of another star the faint light of a planet is lost in the glare of the star
Exoplanets are faint! Other planetary systems Planets are seen only by reflected light at optical wavelengths At the distance of another star the faint light of a planet is lost in the glare of the star
Data from: The Extrasolar Planet Encyclopaedia.
 Data from: The Extrasolar Planet Encyclopaedia http://exoplanet.eu/ 2009->10 Status of Exoplanet Searches Direct Detection: 5->9 planets detected Sensitive to large planets in large orbits around faint
Data from: The Extrasolar Planet Encyclopaedia http://exoplanet.eu/ 2009->10 Status of Exoplanet Searches Direct Detection: 5->9 planets detected Sensitive to large planets in large orbits around faint
Transneptunian objects. Minor bodies in the outer Solar System. Transneptunian objects
 Transneptunian objects Minor bodies in the outer Solar System Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo Around 1980 it was proposed that the hypothetical disk of small bodies beyond Neptune (called
Transneptunian objects Minor bodies in the outer Solar System Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo Around 1980 it was proposed that the hypothetical disk of small bodies beyond Neptune (called
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 15. Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 15 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 15 Exoplanets Units of Chapter 15 15.1 Modeling Planet Formation 15.2 Solar System Regularities and Irregularities 15.3
Lecture Outlines Chapter 15 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 15 Exoplanets Units of Chapter 15 15.1 Modeling Planet Formation 15.2 Solar System Regularities and Irregularities 15.3
AST Section 2: Test 2
 AST1002 - Section 2: Test 2 Date: 11/05/2009 Name: Equations: E = m c 2 Question 1: The Sun is a stable star because 1. gravity balances forces from pressure. (!) Miniquiz 7, Q3 2. the rate of fusion equals
AST1002 - Section 2: Test 2 Date: 11/05/2009 Name: Equations: E = m c 2 Question 1: The Sun is a stable star because 1. gravity balances forces from pressure. (!) Miniquiz 7, Q3 2. the rate of fusion equals
Adam Burrows, Princeton April 7, KITP Public Lecture
 Adam Burrows, Princeton April 7, 2010 KITP Public Lecture The Ancient History of Comparative Planetology There are infinite worlds both like and unlike this world of ours...we must believe that in all
Adam Burrows, Princeton April 7, 2010 KITP Public Lecture The Ancient History of Comparative Planetology There are infinite worlds both like and unlike this world of ours...we must believe that in all
Searching for planets around other stars. Searching for planets around other stars. Searching for other planetary systems this is a hard problem!
 Reading: Chap. 21, Sect.21.4-21.6 Final Exam: Tuesday, December 12; 4:30-6:30PM Homework 10: Due in recitation Dec. 1,4 1 Brief review of last time: Formation of Planetary Systems Observational Clues:
Reading: Chap. 21, Sect.21.4-21.6 Final Exam: Tuesday, December 12; 4:30-6:30PM Homework 10: Due in recitation Dec. 1,4 1 Brief review of last time: Formation of Planetary Systems Observational Clues:
Lecture 20: Planet formation II. Clues from Exoplanets
 Lecture 20: Planet formation II. Clues from Exoplanets 1 Outline Definition of a planet Properties of exoplanets Formation models for exoplanets gravitational instability model core accretion scenario
Lecture 20: Planet formation II. Clues from Exoplanets 1 Outline Definition of a planet Properties of exoplanets Formation models for exoplanets gravitational instability model core accretion scenario
What Have We Found? 1978 planets in 1488 systems as of 11/15/15 (http://exoplanet.eu/ ) 1642 planets candidates (http://exoplanets.
 Exoplanets. II What Have We Found? 1978 planets in 1488 systems as of 11/15/15 (http://exoplanet.eu/ ) 1642 planets + 3787 candidates (http://exoplanets.org) Detected by radial velocity/astrometry: 621
Exoplanets. II What Have We Found? 1978 planets in 1488 systems as of 11/15/15 (http://exoplanet.eu/ ) 1642 planets + 3787 candidates (http://exoplanets.org) Detected by radial velocity/astrometry: 621
Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event National Exam
 Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event National Exam University of Nebraska-Lincoln May 15-16, 2015 Team Number: Team Name: Instructions: 1) Please turn in all materials at the end of the event. 2)
Science Olympiad Astronomy C Division Event National Exam University of Nebraska-Lincoln May 15-16, 2015 Team Number: Team Name: Instructions: 1) Please turn in all materials at the end of the event. 2)
Astronomy. physics.wm.edu/~hancock/171/ A. Dayle Hancock. Small 239. Office hours: MTWR 10-11am
 Astronomy A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Planetology II Key characteristics Chemical elements and planet size Radioactive dating Solar system formation Solar nebula
Astronomy A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Planetology II Key characteristics Chemical elements and planet size Radioactive dating Solar system formation Solar nebula
Chapter 15 The Formation of Planetary Systems
 Chapter 15 The Formation of Planetary Systems Units of Chapter 15 15.1 Modeling Planet Formation 15.2 Formation of the Solar System 15.3 Terrestrial and Jovian Planets 15.4 Interplanetary Debris 15.5 Solar
Chapter 15 The Formation of Planetary Systems Units of Chapter 15 15.1 Modeling Planet Formation 15.2 Formation of the Solar System 15.3 Terrestrial and Jovian Planets 15.4 Interplanetary Debris 15.5 Solar
Architecture and demographics of planetary systems
 Architecture and demographics of planetary systems Struve (1952) The demography of the planets that we detect is strongly affected by detection methods psychology of the observer Understanding planet demography
Architecture and demographics of planetary systems Struve (1952) The demography of the planets that we detect is strongly affected by detection methods psychology of the observer Understanding planet demography
Internal structure and atmospheres of planets
 Internal structure and atmospheres of planets SERGEI POPOV 1312.3323 Sizes and masses Radius vs. mass Results of modeling. Old (relaxed) planets. Colors correspond to different fractions of light elements.
Internal structure and atmospheres of planets SERGEI POPOV 1312.3323 Sizes and masses Radius vs. mass Results of modeling. Old (relaxed) planets. Colors correspond to different fractions of light elements.
Planets are plentiful
 Extra-Solar Planets Planets are plentiful The first planet orbiting another Sun-like star was discovered in 1995. We now know of 209 (Feb 07). Including several stars with more than one planet - true planetary
Extra-Solar Planets Planets are plentiful The first planet orbiting another Sun-like star was discovered in 1995. We now know of 209 (Feb 07). Including several stars with more than one planet - true planetary
Probing the Galactic Planetary Census
 Probing the Galactic Planetary Census Greg Laughlin -- UCSC Astronomy Exoplanet News from the AAS meeting (New York Times) The finding was called exciting by Dr. Kenneth Franklin of the American Museum-Hayden
Probing the Galactic Planetary Census Greg Laughlin -- UCSC Astronomy Exoplanet News from the AAS meeting (New York Times) The finding was called exciting by Dr. Kenneth Franklin of the American Museum-Hayden
III The properties of extrasolar planets
 III The properties of extrasolar planets (as of early 2016) http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy229.html 3.0 Introduction This lecture will discuss what we have found so far. It is important to remember
III The properties of extrasolar planets (as of early 2016) http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy229.html 3.0 Introduction This lecture will discuss what we have found so far. It is important to remember
Extrasolar planets Astronomy
 Extrasolar planets Astronomy 9601 1 Topics to be covered 12.11 Physics and sizes 12.2 Detecting extrasolar planets 12.3 Observations of exoplanets 12.4 Exoplanet statistics 12.5 Planets and Life 2 What
Extrasolar planets Astronomy 9601 1 Topics to be covered 12.11 Physics and sizes 12.2 Detecting extrasolar planets 12.3 Observations of exoplanets 12.4 Exoplanet statistics 12.5 Planets and Life 2 What
PLANETARY SYSTEM: FROM GALILEO TO EXOPLANETS
 PLANETARY SYSTEM: FROM GALILEO TO EXOPLANETS Rosa M. Ros Technical University of Catalonia, Barcelona (Spain) Abstract When in 1610 Galileo Galilei looked at Jupiter with the use of his telescope, he saw
PLANETARY SYSTEM: FROM GALILEO TO EXOPLANETS Rosa M. Ros Technical University of Catalonia, Barcelona (Spain) Abstract When in 1610 Galileo Galilei looked at Jupiter with the use of his telescope, he saw
EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES
 EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES Francis Nimmo Last Week - Dynamics Reynolds number, turbulent vs. laminar flow Velocity fluctuations, Kolmogorov cascade Brunt-Vaisala frequency, gravity waves Rossby waves,
EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES Francis Nimmo Last Week - Dynamics Reynolds number, turbulent vs. laminar flow Velocity fluctuations, Kolmogorov cascade Brunt-Vaisala frequency, gravity waves Rossby waves,
Searching for transiting giant extrasolar planets. Department of Physics University of Tokyo Yasushi Suto
 Searching for transiting giant extrasolar planets Department of Physics University of Tokyo Yasushi Suto Cosmology in the 20 th th century Rapid progress of cosmology since 1980 s existence of dark matter
Searching for transiting giant extrasolar planets Department of Physics University of Tokyo Yasushi Suto Cosmology in the 20 th th century Rapid progress of cosmology since 1980 s existence of dark matter
The formation & evolution of solar systems
 The formation & evolution of solar systems Content expectations Birth of the Solar System What did the material that eventually became the Sun and planets look like originally? Interstellar clouds like
The formation & evolution of solar systems Content expectations Birth of the Solar System What did the material that eventually became the Sun and planets look like originally? Interstellar clouds like
Extrasolar Planets. Today. Dwarf Planets. Extrasolar Planets. Next week. Review Tuesday. Exam Thursday. also, Homework 6 Due
 Extrasolar Planets Today Dwarf Planets Extrasolar Planets Next week Review Tuesday Exam Thursday also, Homework 6 Due will count best 5 of 6 homeworks 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson
Extrasolar Planets Today Dwarf Planets Extrasolar Planets Next week Review Tuesday Exam Thursday also, Homework 6 Due will count best 5 of 6 homeworks 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson
Extrasolar Transiting Planets: Detection and False Positive Rejection
 4 Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Extrasolar Transiting Planets: Detection and False Positive Rejection Willie Torres Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Young Planetary Systems Workshop
4 Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Extrasolar Transiting Planets: Detection and False Positive Rejection Willie Torres Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Young Planetary Systems Workshop
ASTRONOMY CURRICULUM Unit 1: Introduction to Astronomy
 Chariho Regional School District - Science Curriculum September, 2016 ASTRONOMY CURRICULUM Unit 1: Introduction to Astronomy OVERVIEW Summary Students will be introduced to the overarching concept of astronomy.
Chariho Regional School District - Science Curriculum September, 2016 ASTRONOMY CURRICULUM Unit 1: Introduction to Astronomy OVERVIEW Summary Students will be introduced to the overarching concept of astronomy.
The Main Point(s) Lecture #36: Planets Around Other Stars. Extrasolar Planets! Reading: Chapter 13. Theory Observations
 Lecture #36: Planets Around Other Stars Extrasolar Planets! Theory Observations Detection methods Results to date... Implications for "Habitable Zones" Reading: Chapter 13 Astro 102/104 1 The Main Point(s)
Lecture #36: Planets Around Other Stars Extrasolar Planets! Theory Observations Detection methods Results to date... Implications for "Habitable Zones" Reading: Chapter 13 Astro 102/104 1 The Main Point(s)
Importance of the study of extrasolar planets. Exoplanets Introduction. Importance of the study of extrasolar planets
 Importance of the study of extrasolar planets Exoplanets Introduction Planets and Astrobiology (2017-2018) G. Vladilo Technological and scientific spin-offs Exoplanet observations are driving huge technological
Importance of the study of extrasolar planets Exoplanets Introduction Planets and Astrobiology (2017-2018) G. Vladilo Technological and scientific spin-offs Exoplanet observations are driving huge technological
Exoplanetary Atmospheres: Temperature Structure of Irradiated Planets. PHY 688, Lecture 23 Mar 20, 2009
 Exoplanetary Atmospheres: Temperature Structure of Irradiated Planets PHY 688, Lecture 23 Mar 20, 2009 Outline Review of previous lecture hot Jupiters; transiting planets primary eclipses and atmospheric
Exoplanetary Atmospheres: Temperature Structure of Irradiated Planets PHY 688, Lecture 23 Mar 20, 2009 Outline Review of previous lecture hot Jupiters; transiting planets primary eclipses and atmospheric
Pluto, the Kuiper Belt, and Trans- Neptunian Objects
 Pluto, the Kuiper Belt, and Trans- Neptunian Objects 1 What about Pluto? Pluto used to be considered a planet Pluto is one of a large number of Trans-Neptunian Objects, not even the largest one! Discovery
Pluto, the Kuiper Belt, and Trans- Neptunian Objects 1 What about Pluto? Pluto used to be considered a planet Pluto is one of a large number of Trans-Neptunian Objects, not even the largest one! Discovery
Ay 1 Midterm. Due by 5pm on Wednesday, May 9 to your head TA s mailbox (249 Cahill), or hand it directly to any section TA
 Ay 1 Midterm Due by 5pm on Wednesday, May 9 to your head TA s mailbox (249 Cahill), or hand it directly to any section TA You have THREE HOURS to complete the exam, but it is about two hours long. The
Ay 1 Midterm Due by 5pm on Wednesday, May 9 to your head TA s mailbox (249 Cahill), or hand it directly to any section TA You have THREE HOURS to complete the exam, but it is about two hours long. The
Lecture notes 18: Double stars and the detection of planets
 Lecture notes 18: Double stars and the detection of planets More than half of all stars are in double star or in multiple star systems. This fact gives important clues on how stars form, but can also has
Lecture notes 18: Double stars and the detection of planets More than half of all stars are in double star or in multiple star systems. This fact gives important clues on how stars form, but can also has
Astronomy 405 Solar System and ISM
 Astronomy 405 Solar System and ISM Lecture 18 Planetary System Formation and Evolution February 25, 2013 grav collapse opposed by turbulence, B field, thermal Cartoon of Star Formation isolated, quasi-static,
Astronomy 405 Solar System and ISM Lecture 18 Planetary System Formation and Evolution February 25, 2013 grav collapse opposed by turbulence, B field, thermal Cartoon of Star Formation isolated, quasi-static,
Can We See Them?! Planet Detection! Planet is Much Fainter than Star!
 Can We See Them?! Planet Detection! Estimating f p! Not easily! Best cases were reported in late 2008! Will see these later! Problem is separating planet light from star light! Star is 10 9 times brighter
Can We See Them?! Planet Detection! Estimating f p! Not easily! Best cases were reported in late 2008! Will see these later! Problem is separating planet light from star light! Star is 10 9 times brighter
Definitions. Stars: M>0.07M s Burn H. Brown dwarfs: M<0.07M s No Burning. Planets No Burning. Dwarf planets. cosmic composition (H+He)
 Definitions Stars: M>0.07M s Burn H cosmic composition (H+He) Brown dwarfs: M
Definitions Stars: M>0.07M s Burn H cosmic composition (H+He) Brown dwarfs: M
2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Thought Question Suppose you found a star with the same mass as the Sun moving back and forth with a period of 16 months. What could you conclude? A. It has a planet orbiting at less than 1 AU. B. It has
Thought Question Suppose you found a star with the same mass as the Sun moving back and forth with a period of 16 months. What could you conclude? A. It has a planet orbiting at less than 1 AU. B. It has
Planetary system dynamics Part III Mathematics / Part III Astrophysics
 Planetary system dynamics Part III Mathematics / Part III Astrophysics Lecturer: Prof. Mark Wyatt (Dr. Amy Bonsor on 9,11 Oct) Schedule: Michaelmas 2017 Mon, Wed, Fri at 10am MR11, 24 lectures, start Fri
Planetary system dynamics Part III Mathematics / Part III Astrophysics Lecturer: Prof. Mark Wyatt (Dr. Amy Bonsor on 9,11 Oct) Schedule: Michaelmas 2017 Mon, Wed, Fri at 10am MR11, 24 lectures, start Fri
4. Direct imaging of extrasolar planets. 4.1 Expected properties of extrasolar planets. Sizes of gas giants, brown dwarfs & low-mass stars
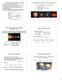 4. Direct imaging of extrasolar planets Reminder: Direct imaging is challenging: The proximity to its host star: 1 AU at 1 for alpha Cen 0.15 for the 10th most nearby solar-type star The low ratio of planet
4. Direct imaging of extrasolar planets Reminder: Direct imaging is challenging: The proximity to its host star: 1 AU at 1 for alpha Cen 0.15 for the 10th most nearby solar-type star The low ratio of planet
Atmospheric Chemistry on Substellar Objects
 Atmospheric Chemistry on Substellar Objects Channon Visscher Lunar and Planetary Institute, USRA UHCL Spring Seminar Series 2010 Image Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/R. Hurt Outline introduction to substellar
Atmospheric Chemistry on Substellar Objects Channon Visscher Lunar and Planetary Institute, USRA UHCL Spring Seminar Series 2010 Image Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/R. Hurt Outline introduction to substellar
Direct imaging of extra-solar planets
 Chapter 6 Direct imaging of extra-solar planets Direct imaging for extra-solar planets means that emission from the planet can be spatially resolved from the emission of the bright central star The two
Chapter 6 Direct imaging of extra-solar planets Direct imaging for extra-solar planets means that emission from the planet can be spatially resolved from the emission of the bright central star The two
4 1 Extrasolar Planets
 Extrasolar Planets 4 1 Introduction 4 2 So far: have looked at planets around our Sun Physics question: Is our Solar System normal? = Are there planets around other stars? can then compare solar system
Extrasolar Planets 4 1 Introduction 4 2 So far: have looked at planets around our Sun Physics question: Is our Solar System normal? = Are there planets around other stars? can then compare solar system
Actuality of Exoplanets Search. François Bouchy OHP - IAP
 Actuality of Exoplanets Search François Bouchy OHP - IAP How detect extrasolar planets? Two main difficulties : 1 A tiny angular separation 0.75 arcsec Sun Jupiter at 4 light years 4 Sun Jupiter at 100
Actuality of Exoplanets Search François Bouchy OHP - IAP How detect extrasolar planets? Two main difficulties : 1 A tiny angular separation 0.75 arcsec Sun Jupiter at 4 light years 4 Sun Jupiter at 100
ASTB01 Exoplanets Lab
 ASTB01 Exoplanets Lab Author: Anders Johansen Revision date: $Date: 2015/08/28 14:55:59 $ Planets orbiting stars other than the Sun are called exoplanets. Stellar light reflected off
ASTB01 Exoplanets Lab Author: Anders Johansen Revision date: $Date: 2015/08/28 14:55:59 $ Planets orbiting stars other than the Sun are called exoplanets. Stellar light reflected off
10/16/ Detecting Planets Around Other Stars. Chapter 10: Other Planetary Systems The New Science of Distant Worlds
 10/16/17 Lecture Outline 10.1 Detecting Planets Around Other Stars Chapter 10: Other Planetary Systems The New Science of Distant Worlds Our goals for learning: How do we detect planets around other stars?
10/16/17 Lecture Outline 10.1 Detecting Planets Around Other Stars Chapter 10: Other Planetary Systems The New Science of Distant Worlds Our goals for learning: How do we detect planets around other stars?
Searching for extrasolar planets using microlensing
 Searching for extrasolar planets using microlensing Dijana Dominis Prester 7.8.2007, Belgrade Extrasolar planets Planets outside of the Solar System (exoplanets) Various methods: mostly massive hot gaseous
Searching for extrasolar planets using microlensing Dijana Dominis Prester 7.8.2007, Belgrade Extrasolar planets Planets outside of the Solar System (exoplanets) Various methods: mostly massive hot gaseous
Synergies between E-ELT and space instrumentation for extrasolar planet science
 Synergies between E-ELT and space instrumentation for extrasolar planet science Raffaele Gratton and Mariangela Bonavita INAF Osservatorio Astronomico di Padova - ITALY Main topics in exo-planetary science
Synergies between E-ELT and space instrumentation for extrasolar planet science Raffaele Gratton and Mariangela Bonavita INAF Osservatorio Astronomico di Padova - ITALY Main topics in exo-planetary science
Astronomy 103: First Exam
 Name: Astronomy 103: First Exam Stephen Lepp October 27, 2010 Each question is worth 2 points. Write your name on this exam and on the scantron. 1 Short Answer A. What is the largest of the terrestrial
Name: Astronomy 103: First Exam Stephen Lepp October 27, 2010 Each question is worth 2 points. Write your name on this exam and on the scantron. 1 Short Answer A. What is the largest of the terrestrial
Other Planetary Systems (Chapter 13) Extrasolar Planets. Is our solar system the only collection of planets in the universe?
 Other Planetary Systems (Chapter 13) Extrasolar Planets Is our solar system the only collection of planets in the universe? Based on Chapter 13 No subsequent chapters depend on the material in this lecture
Other Planetary Systems (Chapter 13) Extrasolar Planets Is our solar system the only collection of planets in the universe? Based on Chapter 13 No subsequent chapters depend on the material in this lecture
Extrasolar Planets. to appear in Encyclopedia of Time, Sage Publishing, in preparation, H.J. Birx (Ed.)
 Extrasolar Planets to appear in Encyclopedia of Time, Sage Publishing, in preparation, H.J. Birx (Ed.) The term extrasolar planets or exoplanets stands for planets outside our Solar System, i.e. not orbiting
Extrasolar Planets to appear in Encyclopedia of Time, Sage Publishing, in preparation, H.J. Birx (Ed.) The term extrasolar planets or exoplanets stands for planets outside our Solar System, i.e. not orbiting
Astronomy 405 Solar System and ISM
 Astronomy 405 Solar System and ISM Lecture 17 Planetary System Formation and Evolution February 22, 2013 grav collapse opposed by turbulence, B field, thermal Cartoon of Star Formation isolated, quasi-static,
Astronomy 405 Solar System and ISM Lecture 17 Planetary System Formation and Evolution February 22, 2013 grav collapse opposed by turbulence, B field, thermal Cartoon of Star Formation isolated, quasi-static,
Planet Detection! Estimating f p!
 Planet Detection! Estimating f p! Can We See Them?! Not easily! Best cases were reported in late 2008! Will see these later! Problem is separating planet light from star light! Star is 10 9 times brighter
Planet Detection! Estimating f p! Can We See Them?! Not easily! Best cases were reported in late 2008! Will see these later! Problem is separating planet light from star light! Star is 10 9 times brighter
m V Formation of the Solar System and Other Planetary Systems Questions to Ponder about Solar System
 Formation of the Solar System and Other Planetary Systems Questions to Ponder about Solar System 1 1. Are all the other planets similar to Earth, or are they very different? 2. Do other planets have moons
Formation of the Solar System and Other Planetary Systems Questions to Ponder about Solar System 1 1. Are all the other planets similar to Earth, or are they very different? 2. Do other planets have moons
Practical Numerical Training UKNum
 Practical Numerical Training UKNum Conclusions PD. Dr. C. Mordasini Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, Heidelberg Programm: 1) Weiterführende Vorlesungen 2) Fragebogen 3) Eigene Forschung 4) Bachelor/Masterarbeiten
Practical Numerical Training UKNum Conclusions PD. Dr. C. Mordasini Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, Heidelberg Programm: 1) Weiterführende Vorlesungen 2) Fragebogen 3) Eigene Forschung 4) Bachelor/Masterarbeiten
You are here! The Solar System! Jo-Anne Brown
 You are here! * The Solar System! Jo-Anne Brown Outline Questions! Earth, Moon, Sun A little, teeny, tiny bit of history... Terrestrial planets Gas Giants Poor Pluto Magnetic fields Tell me what you know!
You are here! * The Solar System! Jo-Anne Brown Outline Questions! Earth, Moon, Sun A little, teeny, tiny bit of history... Terrestrial planets Gas Giants Poor Pluto Magnetic fields Tell me what you know!
Chapter 13 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Other Planetary Systems: The New Science of Distant Worlds Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 13 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Other Planetary Systems: The New Science of Distant Worlds 13.1 Detecting Planets Around Other Stars Our goals for learning: Why is it so challenging
Chapter 13 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Other Planetary Systems: The New Science of Distant Worlds 13.1 Detecting Planets Around Other Stars Our goals for learning: Why is it so challenging
Extra-solar Planets (Exoplanets)
 Extra-solar Planets (Exoplanets) The search for planets around other stars David Wood Oct 1, 2014 Outline Why do we care? Overview of our knowledge Discovery techniques Space-based observations Results
Extra-solar Planets (Exoplanets) The search for planets around other stars David Wood Oct 1, 2014 Outline Why do we care? Overview of our knowledge Discovery techniques Space-based observations Results
Observational constraints from the Solar System and from Extrasolar Planets
 Lecture 1 Part II Observational constraints from the Solar System and from Extrasolar Planets Lecture Universität Heidelberg WS 11/12 Dr. Christoph Mordasini mordasini@mpia.de Mentor Prof. T. Henning Lecture
Lecture 1 Part II Observational constraints from the Solar System and from Extrasolar Planets Lecture Universität Heidelberg WS 11/12 Dr. Christoph Mordasini mordasini@mpia.de Mentor Prof. T. Henning Lecture
Formation of the Solar System and Other Planetary Systems
 Formation of the Solar System and Other Planetary Systems 1 Questions to Ponder 1. Are all the other planets similar to Earth, or are they very different? 2. Do other planets have moons like Earth s Moon?
Formation of the Solar System and Other Planetary Systems 1 Questions to Ponder 1. Are all the other planets similar to Earth, or are they very different? 2. Do other planets have moons like Earth s Moon?
m V Density Formation of the Solar System and Other Planetary Systems Questions to Ponder
 Formation of the Solar System and Other Planetary Systems Questions to Ponder 1. Are all the other planets similar to Earth, or are they very different? 2. Do other planets have moons like Earth s Moon?
Formation of the Solar System and Other Planetary Systems Questions to Ponder 1. Are all the other planets similar to Earth, or are they very different? 2. Do other planets have moons like Earth s Moon?
Journal of Astrobiology and Outreach Dr. Jean Schneider Editorial Board member
 Journal of Astrobiology and Outreach Dr. Jean Schneider Editorial Board member Senior Researcher in Astronomy Univers et Théorie Paris Observatory Meudon France Biography Dr. Jean Schneider He is a Promoter
Journal of Astrobiology and Outreach Dr. Jean Schneider Editorial Board member Senior Researcher in Astronomy Univers et Théorie Paris Observatory Meudon France Biography Dr. Jean Schneider He is a Promoter
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Homework Ch 7, 8, 9 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Our most detailed knowledge of Uranus and Neptune comes from 1) A) the
Homework Ch 7, 8, 9 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Our most detailed knowledge of Uranus and Neptune comes from 1) A) the
Credit: NASA/Kepler Mission/Dana Berry. Exoplanets
 Credit: NASA/Kepler Mission/Dana Berry Exoplanets Outline What is an exoplanet? Why are they interesting? How can we find them? Exolife?? The future... Jon Thaler Exoplanets 2 What is an Exoplanet? Most
Credit: NASA/Kepler Mission/Dana Berry Exoplanets Outline What is an exoplanet? Why are they interesting? How can we find them? Exolife?? The future... Jon Thaler Exoplanets 2 What is an Exoplanet? Most
HW #2. Solar Nebular Theory. Predictions: Young stars have disks. Disks contain gas & dust. Solar System should contain disk remnants
 Astronomy 330: Extraterrestrial Life This class (Lecture 9): Next Class: Planet Formation Zachary Brewer Quinn Calvert Exoplanets Itamar Allali Brian Campbell-Deem HW #3 due Sunday night. Music: Another
Astronomy 330: Extraterrestrial Life This class (Lecture 9): Next Class: Planet Formation Zachary Brewer Quinn Calvert Exoplanets Itamar Allali Brian Campbell-Deem HW #3 due Sunday night. Music: Another
Planets: Name Distance from Sun Satellites Year Day Mercury 0.4AU yr 60 days Venus yr 243 days* Earth 1 1 yr 1 day Mars 1.
 The Solar System (Ch. 6 in text) We will skip from Ch. 6 to Ch. 15, only a survey of the solar system, the discovery of extrasolar planets (in more detail than the textbook), and the formation of planetary
The Solar System (Ch. 6 in text) We will skip from Ch. 6 to Ch. 15, only a survey of the solar system, the discovery of extrasolar planets (in more detail than the textbook), and the formation of planetary
Exoplanets Atmospheres. Characterization of planetary atmospheres. Photometry of planetary atmospheres from direct imaging
 Photometry of planetary atmospheres from direct imaging Exoplanets Atmospheres Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo Example: planetary system detected with direct imaging HR 8799 b, c, d (Marois
Photometry of planetary atmospheres from direct imaging Exoplanets Atmospheres Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo Example: planetary system detected with direct imaging HR 8799 b, c, d (Marois
Hunting Habitable Shadows. Elizabeth Tasker
 Hunting Habitable Shadows Elizabeth Tasker Saturn Earth Uranus Mercury Mars Jupiter Venus Neptune Saturn Earth Uranus Mercury Mars Jupiter Venus Neptune 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2004
Hunting Habitable Shadows Elizabeth Tasker Saturn Earth Uranus Mercury Mars Jupiter Venus Neptune Saturn Earth Uranus Mercury Mars Jupiter Venus Neptune 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2004
Astronomy December, 2016 Introduction to Astronomy: The Solar System. Final exam. Practice questions for Unit V. Name (written legibly):
 Astronomy 101 12 December, 2016 Introduction to Astronomy: The Solar System Final exam Practice questions for Unit V Name (written legibly): Honor Pledge: On my honor, I have neither given nor received
Astronomy 101 12 December, 2016 Introduction to Astronomy: The Solar System Final exam Practice questions for Unit V Name (written legibly): Honor Pledge: On my honor, I have neither given nor received
Universe Now. 12. Revision and highlights
 Universe Now 12. Revision and highlights Practical issues about the exam The exam is on Monday 6.5. (12.00-16.00), lecture hall B121 (Exactum). Paper will be provided. You have 4 hours to finish the exam,
Universe Now 12. Revision and highlights Practical issues about the exam The exam is on Monday 6.5. (12.00-16.00), lecture hall B121 (Exactum). Paper will be provided. You have 4 hours to finish the exam,
( ) a3 (Newton s version of Kepler s 3rd Law) Units: sec, m, kg
 Astronomy 18, UCSC Planets and Planetary Systems Generic Mid-Term Exam (A combination of exams from the past several times this class was taught) This exam consists of two parts: Part 1: Multiple Choice
Astronomy 18, UCSC Planets and Planetary Systems Generic Mid-Term Exam (A combination of exams from the past several times this class was taught) This exam consists of two parts: Part 1: Multiple Choice
Comparative Planetology I: Our Solar System
 Comparative Planetology I: Our Solar System Guiding Questions 1. Are all the other planets similar to Earth, or are they very different? 2. Do other planets have moons like Earth s Moon? 3. How do astronomers
Comparative Planetology I: Our Solar System Guiding Questions 1. Are all the other planets similar to Earth, or are they very different? 2. Do other planets have moons like Earth s Moon? 3. How do astronomers
Planet Detection. Estimating f p
 Planet Detection Estimating f p Can We See Them? Not yet, but there are plans 3 recent claims, but planets very far from star, so some doubts Problem is separating planet light from star light Star is
Planet Detection Estimating f p Can We See Them? Not yet, but there are plans 3 recent claims, but planets very far from star, so some doubts Problem is separating planet light from star light Star is
HNRS 227 Fall 2006 Chapter 13. What is Pluto? What is a Planet? There are two broad categories of planets: Terrestrial and Jovian
 Key Points of Chapter 13 HNRS 227 Fall 2006 Chapter 13 The Solar System presented by Prof. Geller 24 October 2006 Planets Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune Dwarf Planets Pluto,
Key Points of Chapter 13 HNRS 227 Fall 2006 Chapter 13 The Solar System presented by Prof. Geller 24 October 2006 Planets Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune Dwarf Planets Pluto,
[25] Exoplanet Characterization (11/30/17)
![[25] Exoplanet Characterization (11/30/17) [25] Exoplanet Characterization (11/30/17)](/thumbs/86/94788164.jpg) 1 [25] Exoplanet Characterization (11/30/17) Upcoming Items APOD 12/2/16 1. Read chapters 24.1-24.3 for Tuesday 2. We will have a final exam review in the last discussion section (Friday, Dec 8) and also
1 [25] Exoplanet Characterization (11/30/17) Upcoming Items APOD 12/2/16 1. Read chapters 24.1-24.3 for Tuesday 2. We will have a final exam review in the last discussion section (Friday, Dec 8) and also
Review III. ASTR 371, Fall Jovian Planets and Rings (Lecture Notes 9; Chap 12, 14)
 ASTR 371, Fall 2016 Review III 9. Jovian Planets and Rings (Lecture Notes 9; Chap 12, 14) 9.1-2 Introduction, Motion a. Carefully study the data for the Jovian planets. Must know the general properties
ASTR 371, Fall 2016 Review III 9. Jovian Planets and Rings (Lecture Notes 9; Chap 12, 14) 9.1-2 Introduction, Motion a. Carefully study the data for the Jovian planets. Must know the general properties
Circumstellar disks The MIDI view. Sebastian Wolf Kiel University, Germany
 Circumstellar disks The MIDI view Sebastian Wolf Kiel University, Germany MPIA MIDI SG concluding meeting May 5, 2014 Overview Circumstellar disks: Potential of IR long-baseline interferometry MIDI: Exemplary
Circumstellar disks The MIDI view Sebastian Wolf Kiel University, Germany MPIA MIDI SG concluding meeting May 5, 2014 Overview Circumstellar disks: Potential of IR long-baseline interferometry MIDI: Exemplary
LEARNING ABOUT THE OUTER PLANETS. NASA's Cassini spacecraft. Io Above Jupiter s Clouds on New Year's Day, Credit: NASA/JPL/University of Arizona
 LEARNING ABOUT THE OUTER PLANETS Can see basic features through Earth-based telescopes. Hubble Space Telescope especially useful because of sharp imaging. Distances from Kepler s 3 rd law, diameters from
LEARNING ABOUT THE OUTER PLANETS Can see basic features through Earth-based telescopes. Hubble Space Telescope especially useful because of sharp imaging. Distances from Kepler s 3 rd law, diameters from
The Physics of Exoplanets
 The Physics of Exoplanets Heike Rauer Institut für Planetenforschung, DLR, Berlin-Adlershof, Zentrum für Astronomie und Astrophysik, TU Berlin Formation in protoplanetary disk, migration Loss of primary,
The Physics of Exoplanets Heike Rauer Institut für Planetenforschung, DLR, Berlin-Adlershof, Zentrum für Astronomie und Astrophysik, TU Berlin Formation in protoplanetary disk, migration Loss of primary,
Finding habitable earths around white dwarfs with a robotic telescope transit survey
 Finding habitable earths around white dwarfs with a robotic telescope transit survey Eric Agol Associate Professor Department of Astronomy University of Washington (UW) Feb 16, 2011 1 Evolution of a Sun-Like
Finding habitable earths around white dwarfs with a robotic telescope transit survey Eric Agol Associate Professor Department of Astronomy University of Washington (UW) Feb 16, 2011 1 Evolution of a Sun-Like
Class 15 Formation of the Solar System
 Class 16 Extra-solar planets The radial-velocity technique for finding extrasolar planets Other techniques for finding extrasolar planets Class 15 Formation of the Solar System What does a successful model
Class 16 Extra-solar planets The radial-velocity technique for finding extrasolar planets Other techniques for finding extrasolar planets Class 15 Formation of the Solar System What does a successful model
Chapter 13 Other Planetary Systems. The New Science of Distant Worlds
 Chapter 13 Other Planetary Systems The New Science of Distant Worlds 13.1 Detecting Extrasolar Planets Our goals for learning Why is it so difficult to detect planets around other stars? How do we detect
Chapter 13 Other Planetary Systems The New Science of Distant Worlds 13.1 Detecting Extrasolar Planets Our goals for learning Why is it so difficult to detect planets around other stars? How do we detect
Extrasolar Planets and Chemical Abundance
 Extrasolar Planets and Chemical Abundance Intermediate Graduate Physics Seminar Waqas Bhatti May 1, 2007 Abstract Over 200 extrasolar planets have been discovered since the first confirmed observation
Extrasolar Planets and Chemical Abundance Intermediate Graduate Physics Seminar Waqas Bhatti May 1, 2007 Abstract Over 200 extrasolar planets have been discovered since the first confirmed observation
Lecture 12: Extrasolar planets. Astronomy 111 Monday October 9, 2017
 Lecture 12: Extrasolar planets Astronomy 111 Monday October 9, 2017 Reminders Star party Thursday night! Homework #6 due Monday The search for extrasolar planets The nature of life on earth and the quest
Lecture 12: Extrasolar planets Astronomy 111 Monday October 9, 2017 Reminders Star party Thursday night! Homework #6 due Monday The search for extrasolar planets The nature of life on earth and the quest
Chapter 10 Worlds of Gas and Liquid- The Giant Planets. 21st CENTURY ASTRONOMY Fifth EDITION Kay Palen Blumenthal
 Chapter 10 Worlds of Gas and Liquid- The Giant Planets 21st CENTURY ASTRONOMY Fifth EDITION Kay Palen Blumenthal What is a storm on Saturn like? The Giant Planets, Part 1 Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune
Chapter 10 Worlds of Gas and Liquid- The Giant Planets 21st CENTURY ASTRONOMY Fifth EDITION Kay Palen Blumenthal What is a storm on Saturn like? The Giant Planets, Part 1 Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune
Astronomy 241: Foundations of Astrophysics I. The Solar System
 Astronomy 241: Foundations of Astrophysics I. The Solar System Astronomy 241 is the first part of a year-long introduction to astrophysics. It uses basic classical mechanics and thermodynamics to analyze
Astronomy 241: Foundations of Astrophysics I. The Solar System Astronomy 241 is the first part of a year-long introduction to astrophysics. It uses basic classical mechanics and thermodynamics to analyze
Revision: Sun, Stars (and Planets) See web slides of Dr Clements for Planets revision. Juliet Pickering Office: Huxley 706
 Revision: Sun, Stars (and Planets) See web slides of Dr Clements for Planets revision Juliet Pickering Office: Huxley 706 Office hour (Pickering): Thursday 22nd May 12-11 pm Outline overview of first part
Revision: Sun, Stars (and Planets) See web slides of Dr Clements for Planets revision Juliet Pickering Office: Huxley 706 Office hour (Pickering): Thursday 22nd May 12-11 pm Outline overview of first part
Exoplanet Host Stars
 Exoplanet Host Stars The Hertzsprung-Russel (HR)Diagram The Hertzsprung-Russel (HR)Diagram Standard Doppler Surveys The Hertzsprung-Russel (HR)Diagram Direct Imaging detections Standard Doppler Surveys
Exoplanet Host Stars The Hertzsprung-Russel (HR)Diagram The Hertzsprung-Russel (HR)Diagram Standard Doppler Surveys The Hertzsprung-Russel (HR)Diagram Direct Imaging detections Standard Doppler Surveys
