COMPARISON OF GOES MAGNETOSPHERE MAGNETIC FIELD MEASUREMENTS WITH IMECH MAGNETOSPHERE MAGNETOSHEATH MODEL PREDICTIONS *
|
|
|
- Noreen Bell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 11 th National Congress on Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2-5 Sept. 2009, Borovets, Bulgaria COMPARISON OF GOES MAGNETOSPHERE MAGNETIC FIELD MEASUREMENTS WITH IMECH MAGNETOSPHERE MAGNETOSHEATH MODEL PREDICTIONS * P. DOBREVA, M. KARTALEV Institute of Mechanics, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, Block 4, Akad. G. Bontchev Str., Sofia 1113, Bulgaria polya@geospace4.imbm.bas.bg N. BORODKOVA, G. ZASTENKER Space Research Institute, RAN, Profsousnaya 84/32, Moscow , Russia nlbor@mail.ru ABSTRACT. We report first comparison of the measurements of GOES magnetospheric magnetic field from geosynchronous orbit with the predictions of the magnetosphere module of the new IMECH magnetosphere - magnetosheath model. The magnetosphere module of the IMECH complex model could be considered as a modification of the Tsyganenko magnetosphere magnetic field statistical model with more realistic 3D magnetopause shape and position, obtained self-consistently together with the solution of the 3D magnetosheath problem in gasdynamic approach. The pressure balance condition on the magnetopause is satisfied in this solution and the corresponding magnetopause shielding field is computed, solving the Chapmen-Ferraro problem by finite element numerical method. Thus, the resulting magnetosphere model depends on the solar wind parameters not only through the Tsyganenko's current systems, but via the shape and the position of so obtained more realistic magnetopause and shielding field. A good coincidence of the measured and predicted magnetic field values are demonstrated under real solar wind conditions. KEY WORDS: magnetosheath, magnetosphere, finite elements, gas dynamics, Chapman-Ferraro problem. * This research was partially supported under Project INTAS No
2 Dobreva, Borodkova, Kartalev, Zastenker 1. Introduction The magnetosphere models could be conventionally classified into two groups: physical models and the empirical ones. The physical models are based on the theoretical assumptions. Examples of such models are magnetosphere model of Voigt 1972, 1981 [14,15] which magnetopause consist of hemisphere and infinite cylinder, and the paraboloid model of Stern 1985 [7]. Some models are based on the numerical solution of Chapman-Ferraro problem - Toffoleto 1994 [8], Klouchek and Toffoleto [4]. The model, developed by Kartalev 1995 [2] and Koitchev 1999 [5], appeared independently of those of Toffoletto. The Chapman-Ferraro boundary value problem for the sought shielding field is solved using of non-conforming finite elements. The initial variant, concerning the two-dimensional problem - Kartalev 1995, is thereafter elaborated to the 3D variant - Koitchev 1999, but the magnetosphere boundary, consisting of a hemisphere and a cylinder, still remains fixed. Many magnetosphere model, based on statistical treatment of magnetic field data, were developed in the resent decades. Tsyganenko models are the most polular - Tsyganenko and Usmanov 1982 [9], Tsyganenko 87 [10] and Tsyganeko 1989 [11]. The more comprehensive variants - Tsyganenko 1995 [12] and Tsyganenko 2001 [13] are based on the better mathematical description of each current source and it was incorporated a real data-based megnetopause form. The experimental models have the serious shortcoming to approximate the magnetopshere boundary with an axisymmetric surface, while the theoretical models are not applicable for practical purposes, because they do not relate to the real measurements. In order to avoid the above mentioned circumstances and to match the advantages of the theoretical and the data-based models, the Imech magnetosphere-magnetosheath model was created in Geospace Hydrodynamics Laboratory. On one side, it provides a good description of the physical processes in the magnetosphere. On the other side, as a data-based model, it is adequate for practical purposes, such as comparison with experimental data. This paper presents a first attempt to compare the magnetosphere modul of the composite Imech model with real measurements of the magnetic field, obtained from GOES satellites. 2. Model description 2.1. The self-consistent model The composite IMech model incorporates two modules, working together, and calculating the numerical solution in the whole magnetosphere-magnetosheath region. For the given input data, the gas-dynamic parameters distribution and the magnetic field in the magnetosphere are received. The positions of the boundaries - bow shock and magnetopause, are also received in the process of the solution. The interaction between the two regions is attained through the boundary conditions, posed at the common boundary - the magnetopause. The construction of the
3 Comparison of GOES measurements with IMech model composite model is based on the modular approach conception, allowing separate description of each region with models of quite different types. An ideal gasdynamic model is applied in the magnetosheath region. The module could be considered as a development of the earlier axisymmetric model - Kartalev 1996 [3], approved to 3D in the present variant for a better depiction of the real flow distribution in the magnetosheath. The Euler equations are solved by an application of the grid-characteristic method, developed by Magomedov and Holodov 1988 [6]. The bow shock location is obtained as a result of the satisfaction of Renkin-Hugoniot relationships. The two regions interact through their common boundary, where the pressure balance equation is imposed - the gasdynamic pressure from magnetosheath side and the magnetic pressure from the magnetosphere side could be equalized. The magnetic pressure: 2 Bτ (2.1) p M = 8π is finding knowing the magnetic field distribution, calculated from the magnetosphere model The magnetosphere model The model is a generalization of the earlier created in Geospace Hydrodynamic Laboratory finite elements model - Koitchev 1999, developed now to an arbitrary magnetopause form, which is received as a result of pressure equilibrium. In the present variant the magnetic fields of the following sources are included: the Earth's dipole B d, the tail B t, ring B r and Birkeland B b currents, and the sought shielding field B s. The field of B r and B b are calculated, using the Tsyganenko T96 model, while B t is from Tsyganenko T01. For the sough B s field, it is supposed, that: (2.2) divu = 0, rotu = 0 and hence the field potential - a harmonic scalar function U exists: (2.3) Δ U = 0, Bs = U. The distribution of the normal magnetic field component is given at the boundary points. Standard algorithm, using 20 points serendipity finite elements, is applied - Koitchev The potential distribution in the magnetosphere region is obtained as a result of the algorithm, and the magnetic field is a gradient of the founded potential - equation 2.3. The magnetic field values, computed exactly in such a way, are used in the comparison with the experimental data. 3. The comparison algorithm GOES - Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, circles the Earth in a geosynchronous orbit (6.6 R E ) over the equator, thus observing the Earth from the exact same place all the time. They were launched to monitor the atmosphere for severe weather development such as tornadoes, flash floods, hailstorms, and
4 Dobreva, Borodkova, Kartalev, Zastenker hurricanes. The magnetic field is measured by the twin-fluxgate spinning sensor on board the satellite. Vx, km/sec Temp, ev Dens, n/sm WIND Plasma Data, 23 May, :30 16:45 17:00 17:15 UT Fig. 1. Input data for the case 23 May 2000 density, velocity and temperature, measured by WIND satellite. Table 1. Input data for the case 23 May, 2000: time moment, density ρ in sm -3, velocity V x in km/s, temperature in K, B y and B z Interplanetary magnetic field components (in nt in GSE coordinates ), Dst index and the dipole tilt angle (in radians). UT ρ V x T B y B z Dst Tilt 16: : We consider the case 23 May, 2000, and the period 16:15-17:20 UT along the orbit of GOES satellites. The input for the Imech model data - density, velocity and temperature, shown in fig. 1, are taken from WIND satellite and appropriately shifted in time. It can be seen at the figure, that at 16:55 UT all the input parameters change, as the density and temperature increase, while the velocity decreases. The standard algorithm - Dobreva 2005 [1], is applied for the choice of the input parameters and the model calculation. Namely, the interval is divided into two subintervals with relatively permanent values of the parameters. Average parameters values are chosen for each of the intervals - the data are given in table 1.
5 Comparison of GOES measurements with IMech model Table 2. Location (in GSM coordinate system) of GOES 10 for the above mentioned time moments from the trajectory of the satellite on 23 May, UT X gsm Y gsm Z gsm 16: : Model calculations are performed for each of the intervals. It is obtained the magnetic field distribution in the whole magnetosphere region. Particularly, the magnetic field at the points of the satellite location can be calculated. 60 Bx (GSM) By (GSM) GOES 10 Magnetic field, 23 May, Bz (GSM) UT 16:15 16:30 16:45 17:00 17:15 17:30 Fig. 2. Comparison between measured by GOES (solid line), numerically calculated (asterisks) and Tsyganenko 96 (circles) magnetic field for the case 23 May, The coordinates of the GOES 10, corresponding to the two time moments (16:50 and 17:10 Ut) are given in table 2. The results between measured and model received values are presented in fig. 2. The magnetic field variation between 16:50 and 17:10 UT, caused by corresponding variations in the solar wind data, could be observed also in the model results. 4. Summary Capabilities of the magnetosphere module of the IMech model are tested. It is observed a good coincidence between measured and computed magnetic field at the geostationary orbit. Magnetic field changes, caused by solar wind variation, are also registered by the model. This is a preliminary test and further investigations needed.
6 Dobreva, Borodkova, Kartalev, Zastenker R E F E R E N C E S [1] DOBREVA, P. S., M. D. KARTALEV, N. N. SHEVYREV, G. N. ZASTENKER. Compassion of a new magnetosphere-magnetosheath model with Interball-1 magnetosheath plasma measurements, Planet. Space Sci., 53, , [2] KARTALEV, M. D., M. S. KASCHIEV, D. K. KOITCHEV. Finite element numerical modeling of stationary two-dimensional magnetosphere with defined boundary, J. Comput. Phys., 119, , [3] KARTALEV, M. D., V. I. NIKOLOVA, V. F. KAMENETSKY, I. P. MASTIKOV. On the self-consistent determination of dayside magnetopause shape and position, Planet. Space Sci., 44, , [4] KLOUCEK, P., F. R. TOFFOLETTO. The three dimensional non-conforming finite element solution of the Chapman-Ferraro problem, J. Comp. Phys., 150, , [5] KOITCHEV, D. K., M. S. KASCHIEV, M. D. KARTALEV. Simplified 3D magnetospheric magnetic field, In Finite Difference Methods: Theory and Applications, , Nova Science Publishers, [6] MAGOMEDOV, K. M., A. S. HOLODOV. Grid-Characteristic Numerical Methods, Nauka, Moscow, [7] STERN, D. P. Parabolic harmonics in magnetospheric modeling: The main dipole and the ring current, J. Geophys. Res., 90, , [8] TOFFOLETTO, F. R., R. V. HILMER, T. W. HILL, G.-H. VOIGT. Solution of the Chapman-Ferraro problem with an arbitrary magnetopause, Geophys. Res. Lett., 21, , [9] TSYGANENKO, N. A., A. V. USMANOV. Determination of the magnetospheric current system parameters and development of experimental geomagnetic field models based on data from IMP and HEOS satellites, Planet. Space Sci., 30, , [10] TSYGANENKO, N. A. Global quantitative models of the geomagnetic field in the cislunar magnetosphere for different disturbance levels, Planet. Space Sci., 35, , [11] TSYGANENKO, N. A. A magnetospheric magnetic field model with a warped tail current sheet, Planet. Space Sci., 37, 5-20, [12] TSYGANENKO, N. A. A model of the near magnetosphere with a dawn-dusk asymmetry 1.Mathematical structure, J. Geophys. Res., 107, 1179, [13] TSYGANENKO, N. A. Modeling the Earth's magnetospheric magnetic field confined within a realistic magnetopause, J. Geophys. Res., 100, , [14] VOIGT, G.-H. A three dimensional analytical magnetospheric model with defined magnetopause, Z. Geophys., 38, , [15] VOIGT, G.-H. A mathematical magnetospheric field model with independent physical parameters, Planet. Space Sci., 29, 1-20, 1981.
High-latitude Bow Shock: Tilt Angle Effects
 WDS'7 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part II, 9 33, 7. ISBN 978-8-7378-1 MATFYZPRESS High-latitude Bow Shock: Tilt Angle Effects K. Jelínek, Z. Němeček, and J. Šafránková Charles University, Faculty
WDS'7 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part II, 9 33, 7. ISBN 978-8-7378-1 MATFYZPRESS High-latitude Bow Shock: Tilt Angle Effects K. Jelínek, Z. Němeček, and J. Šafránková Charles University, Faculty
The Dependence of the Magnetic Field Near the Subsolar Magnetopause on IMF in Accordance with THEMIS Data
 WDS'11 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part II, 45 50, 2011. ISBN 978-80-7378-185-9 MATFYZPRESS The Dependence of the Magnetic Field Near the Subsolar Magnetopause on IMF in Accordance with THEMIS Data
WDS'11 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part II, 45 50, 2011. ISBN 978-80-7378-185-9 MATFYZPRESS The Dependence of the Magnetic Field Near the Subsolar Magnetopause on IMF in Accordance with THEMIS Data
DAYSIDE MAGNETOPAUSE MODELS
 DAYSIDE MAGNETOPAUSE MODELS A.V. SUVOROVA, A. V. DMITRIEV and S. N. KUZNETSOV Skobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear Physics, Moscow State University, 119899, Moscow, Russia, alla@srdlan.npi.msu.su ABSTRACT -
DAYSIDE MAGNETOPAUSE MODELS A.V. SUVOROVA, A. V. DMITRIEV and S. N. KUZNETSOV Skobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear Physics, Moscow State University, 119899, Moscow, Russia, alla@srdlan.npi.msu.su ABSTRACT -
Electromagnetic Fields Inside the Magnetoshpere. Outline
 Electromagnetic Fields Inside the Magnetoshpere P. K. Toivanen Finnish Meteorological Institute, Space Research Outline Introduction to large-scale electromagnetic fields Magnetic field geometry Modelling
Electromagnetic Fields Inside the Magnetoshpere P. K. Toivanen Finnish Meteorological Institute, Space Research Outline Introduction to large-scale electromagnetic fields Magnetic field geometry Modelling
Global modeling of the magnetosphere in terms of paraboloid model of magnetospheric magnetic field
 Global modeling of the magnetosphere in terms of paraboloid model of magnetospheric magnetic field I. Alexeev, V. Kalegaev The solar wind influence on the magnetospheric state is sufficiently nonlinear
Global modeling of the magnetosphere in terms of paraboloid model of magnetospheric magnetic field I. Alexeev, V. Kalegaev The solar wind influence on the magnetospheric state is sufficiently nonlinear
Magnetospheric Currents at Quiet Times
 Magnetospheric Currents at Quiet Times Robert L. McPherron Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics University of California Los Angeles Los Angeles, CA 90095-1567 e-mail: rmcpherron@igpp.ucla.edu
Magnetospheric Currents at Quiet Times Robert L. McPherron Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics University of California Los Angeles Los Angeles, CA 90095-1567 e-mail: rmcpherron@igpp.ucla.edu
David versus Goliath 1
 David versus Goliath 1 or A Comparison of the Magnetospheres between Jupiter and Earth 1 David and Goliath is a story from the Bible that is about a normal man (David) who meets a giant (Goliath) Tomas
David versus Goliath 1 or A Comparison of the Magnetospheres between Jupiter and Earth 1 David and Goliath is a story from the Bible that is about a normal man (David) who meets a giant (Goliath) Tomas
Dependence of magnetic field just inside the magnetopause on subsolar standoff distance: Global MHD results
 Article SPECIAL ISSUE Basic Plasma Processes in Solar-Terrestrial Activities April 2012 Vol.57 No.12: 1438 1442 doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4961-6 SPECIAL TOPICS: Dependence of magnetic field just inside the
Article SPECIAL ISSUE Basic Plasma Processes in Solar-Terrestrial Activities April 2012 Vol.57 No.12: 1438 1442 doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4961-6 SPECIAL TOPICS: Dependence of magnetic field just inside the
The January 10{11, 1997 magnetic cloud: Multipoint. measurements. J. Safrankova 1,Z.Nemecek 1,L.Prech 1, G. Zastenker 2, K.I.
 1 The January 1{11, 1997 magnetic cloud: Multipoint measurements J. Safrankova 1,Z.Nemecek 1,L.Prech 1, G. Zastenker 2, K.I. Paularena 3, N. Nikolaeva 2, M. Nozdrachev 2,A.Skalsky 2, T. Mukai 4 Short title:
1 The January 1{11, 1997 magnetic cloud: Multipoint measurements J. Safrankova 1,Z.Nemecek 1,L.Prech 1, G. Zastenker 2, K.I. Paularena 3, N. Nikolaeva 2, M. Nozdrachev 2,A.Skalsky 2, T. Mukai 4 Short title:
THE ACCURACY OF PRESENT MODELS OF THE HIGH ALTITUDE POLAR MAGNETOSPHERE
 THE ACCURAC OF PRESENT MODELS OF THE HIGH ALTITUDE POLAR MAGNETOSPHERE C. T. Russell 1, J. G. Luhmann 2 and F. R. Fenrich 3 1 Department of Earth and Space Sciences, University of California Los Angeles
THE ACCURAC OF PRESENT MODELS OF THE HIGH ALTITUDE POLAR MAGNETOSPHERE C. T. Russell 1, J. G. Luhmann 2 and F. R. Fenrich 3 1 Department of Earth and Space Sciences, University of California Los Angeles
The DOK-2 Experiment to Study Energetic Particles by the Tail Probe and Auroral Probe Satellites in the INTERBALL Project
 Cosmic Research, Vol. 6, No., 998, pp. 9. Translated from Kosmicheskie Issledovaniya, Vol. 6, No., 998, pp. 98 7. Original Russian Text Copyright 998 by Lutsenko, Kudela, Sarris. The DOK- Experiment to
Cosmic Research, Vol. 6, No., 998, pp. 9. Translated from Kosmicheskie Issledovaniya, Vol. 6, No., 998, pp. 98 7. Original Russian Text Copyright 998 by Lutsenko, Kudela, Sarris. The DOK- Experiment to
Remote sensing of magnetospheric processes: Lesson 1: Configura7on of the magnetosphere
 Remote sensing of magnetospheric processes: Lesson 1: Configura7on of the magnetosphere AGF-351 Optical methods in auroral physics research UNIS, 24.-25.11.2011 Anita Aikio Dept. Physics University of
Remote sensing of magnetospheric processes: Lesson 1: Configura7on of the magnetosphere AGF-351 Optical methods in auroral physics research UNIS, 24.-25.11.2011 Anita Aikio Dept. Physics University of
Geomagnetic cutoff simulations for low-energy cosmic rays
 simulations for low-energy cosmic rays Solar Energetic Particles (SEP), Solar Modulation and Space Radiation: New Opportunities in the AMS-02 Era Honolulu, October 2015 Philip von Doetinchem philipvd@hawaii.edu
simulations for low-energy cosmic rays Solar Energetic Particles (SEP), Solar Modulation and Space Radiation: New Opportunities in the AMS-02 Era Honolulu, October 2015 Philip von Doetinchem philipvd@hawaii.edu
A Note on A-C Effects on MHD Dynamo in the Earth's Low-Latitude Magnetospheric Boundary Layer. Senkichi SHIBUYA
 Research Note J. Geomag. Geoelectr., 43, 65-70,1991 A Note on A-C Effects on MHD Dynamo in the Earth's Low-Latitude Magnetospheric Boundary Layer Senkichi SHIBUYA Faculty of Science, Yamagata University,
Research Note J. Geomag. Geoelectr., 43, 65-70,1991 A Note on A-C Effects on MHD Dynamo in the Earth's Low-Latitude Magnetospheric Boundary Layer Senkichi SHIBUYA Faculty of Science, Yamagata University,
Plasma depletion layer: its dependence on solar wind conditions and the Earth dipole tilt
 Annales Geophysicae (2) 22: 273 29 SRef-ID: 132-576/ag/2-22-273 European Geosciences Union 2 Annales Geophysicae Plasma depletion layer: its dependence on solar wind conditions and the Earth dipole tilt
Annales Geophysicae (2) 22: 273 29 SRef-ID: 132-576/ag/2-22-273 European Geosciences Union 2 Annales Geophysicae Plasma depletion layer: its dependence on solar wind conditions and the Earth dipole tilt
Cone angle control of the interaction of magnetic clouds with the Earth's bow shock
 Cone angle control of the interaction of magnetic clouds with the Earth's bow shock L. Turc1, P. Escoubet1, D. Fontaine2, E. Kilpua3 1 ESA/ESTEC, Noordwijk, The Netherlands 2 LPP-CNRS-Ecole Polytechnique-UPMC,
Cone angle control of the interaction of magnetic clouds with the Earth's bow shock L. Turc1, P. Escoubet1, D. Fontaine2, E. Kilpua3 1 ESA/ESTEC, Noordwijk, The Netherlands 2 LPP-CNRS-Ecole Polytechnique-UPMC,
Metrics of model performance for electron fluxes (<200 kev) at geostationary orbit
 Metrics of model performance for electron fluxes (
Metrics of model performance for electron fluxes (
Ion heating during geomagnetic storms measured using energetic neutral atom imaging. Amy Keesee
 Ion heating during geomagnetic storms measured using energetic neutral atom imaging Amy Keesee Outline Motivation Overview of ENA measurements Charge exchange MENA and TWINS ENA instruments Calculating
Ion heating during geomagnetic storms measured using energetic neutral atom imaging Amy Keesee Outline Motivation Overview of ENA measurements Charge exchange MENA and TWINS ENA instruments Calculating
Long-term evolution of magnetospheric current systems during storms
 Annales Geophysicae () : 1317 133 SRef-ID: 13-76/ag/--1317 European Geosciences Union Annales Geophysicae Long-term evolution of magnetospheric current systems during storms N. Yu. Ganushkina 1, T. I.
Annales Geophysicae () : 1317 133 SRef-ID: 13-76/ag/--1317 European Geosciences Union Annales Geophysicae Long-term evolution of magnetospheric current systems during storms N. Yu. Ganushkina 1, T. I.
Solar&wind+magnetosphere&coupling&via&magnetic&reconnection&likely&becomes& less&efficient&the&further&a&planetary&magnetosphere&is&from&the&sun& &
 Solar&wind+magnetosphere&coupling&via&magnetic&reconnection&likely&becomes& less&efficient&the&further&a&planetary&magnetosphere&is&from&the&sun& & Although&most&of&the&planets&in&the&Solar&System&have&an&intrinsic&magnetic&field&
Solar&wind+magnetosphere&coupling&via&magnetic&reconnection&likely&becomes& less&efficient&the&further&a&planetary&magnetosphere&is&from&the&sun& & Although&most&of&the&planets&in&the&Solar&System&have&an&intrinsic&magnetic&field&
Storm-time distortion of the inner magnetosphere: How severe can it get?
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. A5, 1209, doi:10.1029/2002ja009808, 2003 Storm-time distortion of the inner magnetosphere: How severe can it get? N. A. Tsyganenko Universities Space Research
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. A5, 1209, doi:10.1029/2002ja009808, 2003 Storm-time distortion of the inner magnetosphere: How severe can it get? N. A. Tsyganenko Universities Space Research
Response of the Earth s magnetosphere and ionosphere to the small-scale magnetic flux rope in solar wind by the MHD simulation
 Response of the Earth s magnetosphere and ionosphere to the small-scale magnetic flux rope in solar wind by the MHD simulation Kyung Sun Park 1, Dae-Young Lee 1, Myeong Joon Kim 1, Rok Soon Kim 2, Kyungsuk
Response of the Earth s magnetosphere and ionosphere to the small-scale magnetic flux rope in solar wind by the MHD simulation Kyung Sun Park 1, Dae-Young Lee 1, Myeong Joon Kim 1, Rok Soon Kim 2, Kyungsuk
The Structure of the Magnetosphere
 The Structure of the Magnetosphere The earth s magnetic field would resemble a simple magnetic dipole, much like a big bar magnet, except that the solar wind distorts its shape. As illustrated below, the
The Structure of the Magnetosphere The earth s magnetic field would resemble a simple magnetic dipole, much like a big bar magnet, except that the solar wind distorts its shape. As illustrated below, the
Simultaneous Geotail and Wind observations of reconnection at the subsolar and tail flank magnetopause
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L09104, doi:10.1029/2006gl025756, 2006 Simultaneous Geotail and Wind observations of reconnection at the subsolar and tail flank magnetopause T. D. Phan, 1 H. Hasegawa,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L09104, doi:10.1029/2006gl025756, 2006 Simultaneous Geotail and Wind observations of reconnection at the subsolar and tail flank magnetopause T. D. Phan, 1 H. Hasegawa,
PROBLEM 1 (15 points) In a Cartesian coordinate system, assume the magnetic flux density
 PROBLEM 1 (15 points) In a Cartesian coordinate system, assume the magnetic flux density varies as ( ) where is a constant, is the unit vector in x direction. a) Sketch the magnetic flux density and the
PROBLEM 1 (15 points) In a Cartesian coordinate system, assume the magnetic flux density varies as ( ) where is a constant, is the unit vector in x direction. a) Sketch the magnetic flux density and the
A Study of the LLBL Profile Using n-t Plots
 WDS'07 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part II, 42 49, 2007. ISBN 978-80-7378-024-1 MATFYZPRESS A Study of the LLBL Profile Using n-t Plots Š. Dušík, J. Šafránková, and Z. Němeček Charles University
WDS'07 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part II, 42 49, 2007. ISBN 978-80-7378-024-1 MATFYZPRESS A Study of the LLBL Profile Using n-t Plots Š. Dušík, J. Šafránková, and Z. Němeček Charles University
GE SPACE. Geomagnetic Earth Observation from SPAce
 GE SPACE Geomagnetic Earth Observation from SPAce Fit to NERC s Science Priorities Understanding the complex interactions and feedbacks within the Earth system over a range of space and time scales Fit
GE SPACE Geomagnetic Earth Observation from SPAce Fit to NERC s Science Priorities Understanding the complex interactions and feedbacks within the Earth system over a range of space and time scales Fit
Earth s Magnetosphere
 Earth s Magnetosphere General Description of the Magnetosphere Shape Pressure Balance The Earth s Magnetic Field The Geodynamo, Magnetic Reversals, Discovery Current Systems Chapman Ferraro Cross Tail
Earth s Magnetosphere General Description of the Magnetosphere Shape Pressure Balance The Earth s Magnetic Field The Geodynamo, Magnetic Reversals, Discovery Current Systems Chapman Ferraro Cross Tail
Specification of electron radiation environment at GEO and MEO for surface charging estimates
 Specification of electron radiation environment at GEO and MEO for surface charging estimates Natalia Ganushkina (University of Michigan/FMI) Collaborators: S. Dubyagin (FMI), J.-C. Matéo Vélez, A. Sicard
Specification of electron radiation environment at GEO and MEO for surface charging estimates Natalia Ganushkina (University of Michigan/FMI) Collaborators: S. Dubyagin (FMI), J.-C. Matéo Vélez, A. Sicard
Solar and Interplanetary Disturbances causing Moderate Geomagnetic Storms
 J. Astrophys. Astr. (2008) 29, 263 267 Solar and Interplanetary Disturbances causing Moderate Geomagnetic Storms Santosh Kumar, M. P. Yadav & Amita Raizada Department of P.G. Studies and Research in Physics
J. Astrophys. Astr. (2008) 29, 263 267 Solar and Interplanetary Disturbances causing Moderate Geomagnetic Storms Santosh Kumar, M. P. Yadav & Amita Raizada Department of P.G. Studies and Research in Physics
Structures in the Magnetosphere 2. Hover the curser over a point on the image. The coordinates and value at that point should appear.
 Investigating the Magnetosphere Introduction In this investigation, you will explore the properties of the regions of the magnetosphere using simulation results from the BATS-R-US model from the magnetosphere
Investigating the Magnetosphere Introduction In this investigation, you will explore the properties of the regions of the magnetosphere using simulation results from the BATS-R-US model from the magnetosphere
Why Study Magnetic Reconnection?
 Why Study Magnetic Reconnection? Fundamental Process Sun: Solar flares, Flare loops, CMEs Interplanetary Space Planetary Magnetosphere: solar wind plasma entry, causes Aurora Ultimate goal of the project
Why Study Magnetic Reconnection? Fundamental Process Sun: Solar flares, Flare loops, CMEs Interplanetary Space Planetary Magnetosphere: solar wind plasma entry, causes Aurora Ultimate goal of the project
Role of IMF B x in the solar wind magnetosphere ionosphere coupling
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2010ja015454, 2010 Role of IMF B x in the solar wind magnetosphere ionosphere coupling Z. Peng, 1 C. Wang, 1 and Y. Q. Hu 2 Received 14 March 2010;
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2010ja015454, 2010 Role of IMF B x in the solar wind magnetosphere ionosphere coupling Z. Peng, 1 C. Wang, 1 and Y. Q. Hu 2 Received 14 March 2010;
Vania K. Jordanova Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, NM 87545, USA
 Vania K. Jordanova Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, NM 87545, USA What is the contribution from different ion species to inner magnetosphere dynamics:» Simulations of ring current H +, He +,
Vania K. Jordanova Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, NM 87545, USA What is the contribution from different ion species to inner magnetosphere dynamics:» Simulations of ring current H +, He +,
Chapter 8 Geospace 1
 Chapter 8 Geospace 1 Previously Sources of the Earth's magnetic field. 2 Content Basic concepts The Sun and solar wind Near-Earth space About other planets 3 Basic concepts 4 Plasma The molecules of an
Chapter 8 Geospace 1 Previously Sources of the Earth's magnetic field. 2 Content Basic concepts The Sun and solar wind Near-Earth space About other planets 3 Basic concepts 4 Plasma The molecules of an
Natalia Ganushkina (1, 2), Stepan Dubyagin (1), Ilkka Sillanpää (1)
 From studying electron motion in the electromagnetic fields in the inner magnetosphere to the operational nowcast model for low energy (< 200 kev) electron fluxes responsible for surface charging Natalia
From studying electron motion in the electromagnetic fields in the inner magnetosphere to the operational nowcast model for low energy (< 200 kev) electron fluxes responsible for surface charging Natalia
Characterisation of Near-Earth Magnetic Field Data for Space Weather Monitoring
 Characterisation of Near-Earth Magnetic Field Data for Space Weather Monitoring Qingying Shu Space Glasgow Research Conference 28 October 2014 Acknowledgments This is an interdisciplinary PhD studentship
Characterisation of Near-Earth Magnetic Field Data for Space Weather Monitoring Qingying Shu Space Glasgow Research Conference 28 October 2014 Acknowledgments This is an interdisciplinary PhD studentship
Stormtime Dynamics of the Magnetosphere near Geosynchronous Altitudes
 Stormtime Dynamics of the Magnetosphere near Geosynchronous Altitudes William J. Burke 1, Meg A. Noah 2 and Jun Yang 2 4 November 214 1. Boston College/ISR 2. University of Massachusetts, Lowell Stormtime
Stormtime Dynamics of the Magnetosphere near Geosynchronous Altitudes William J. Burke 1, Meg A. Noah 2 and Jun Yang 2 4 November 214 1. Boston College/ISR 2. University of Massachusetts, Lowell Stormtime
CHAPTER 2 DATA. 2.1 Data Used
 CHAPTER DATA For the analysis, it is required to use geomagnetic indices, which are representatives of geomagnetic activity, and Interplanetary Magnetic Field (IMF) data in addition to f F,which is used
CHAPTER DATA For the analysis, it is required to use geomagnetic indices, which are representatives of geomagnetic activity, and Interplanetary Magnetic Field (IMF) data in addition to f F,which is used
Single particle motion and trapped particles
 Single particle motion and trapped particles Gyromotion of ions and electrons Drifts in electric fields Inhomogeneous magnetic fields Magnetic and general drift motions Trapped magnetospheric particles
Single particle motion and trapped particles Gyromotion of ions and electrons Drifts in electric fields Inhomogeneous magnetic fields Magnetic and general drift motions Trapped magnetospheric particles
Advanced modeling of low energy electrons responsible for surface charging
 Advanced modeling of low energy electrons responsible for surface charging Natalia Ganushkina (1, 2), Stepan Dubyagin (1), Ilkka Sillanpää (1), Jean-Charles Matéo Vélez (3), Dave Pitchford (4) (1) Finnish
Advanced modeling of low energy electrons responsible for surface charging Natalia Ganushkina (1, 2), Stepan Dubyagin (1), Ilkka Sillanpää (1), Jean-Charles Matéo Vélez (3), Dave Pitchford (4) (1) Finnish
Comparison of energetic ions in cusp and outer radiation belt
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 110,, doi:10.1029/2004ja010718, 2005 Comparison of energetic ions in cusp and outer radiation belt Jiasheng Chen and Theodore A. Fritz Center for Space Physics, Boston
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 110,, doi:10.1029/2004ja010718, 2005 Comparison of energetic ions in cusp and outer radiation belt Jiasheng Chen and Theodore A. Fritz Center for Space Physics, Boston
Magnetospheric currents during sawtooth events: Event-oriented magnetic field model analysis
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007ja012983, 2008 Magnetospheric currents during sawtooth events: Event-oriented magnetic field model analysis M. Kubyshkina, 1 T. I. Pulkkinen,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007ja012983, 2008 Magnetospheric currents during sawtooth events: Event-oriented magnetic field model analysis M. Kubyshkina, 1 T. I. Pulkkinen,
Low-Latitude Boundary Layer Under Different IMF Orientations
 WDS'05 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part I, 225 233, 2005. ISBN 80-86732-59-2 MATFYZPRESS Low-Latitude Boundary Layer Under Different IMF Orientations Š. Dušík, J. Šafránková, Z. Němeček, and L.
WDS'05 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part I, 225 233, 2005. ISBN 80-86732-59-2 MATFYZPRESS Low-Latitude Boundary Layer Under Different IMF Orientations Š. Dušík, J. Šafránková, Z. Němeček, and L.
Planetary Magnetospheres: Homework Problems
 Planetary Magnetospheres: Homework Problems s will be posted online at http://www.ucl.ac.uk/ ucapnac 1. In classical electromagnetic theory, the magnetic moment µ L associated with a circular current loop
Planetary Magnetospheres: Homework Problems s will be posted online at http://www.ucl.ac.uk/ ucapnac 1. In classical electromagnetic theory, the magnetic moment µ L associated with a circular current loop
Introduction to the Sun and the Sun-Earth System
 Introduction to the Sun and the Sun-Earth System Robert Fear 1,2 R.C.Fear@soton.ac.uk 1 Space Environment Physics group University of Southampton 2 Radio & Space Plasma Physics group University of Leicester
Introduction to the Sun and the Sun-Earth System Robert Fear 1,2 R.C.Fear@soton.ac.uk 1 Space Environment Physics group University of Southampton 2 Radio & Space Plasma Physics group University of Leicester
ROTATIONAL ASYMMETRY OF EARTH S BOW SHOCK
 CHINESE JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS Vol.53, No.2, 2010, pp: 198 208 ROTATIONAL ASYMMETRY OF EARTH S BOW SHOCK HU You-Qiu 1, PENG Zhong 2, WANG Chi 2 1 CAS Key Laboratory of Basic Plasma Physics, School of Earth
CHINESE JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS Vol.53, No.2, 2010, pp: 198 208 ROTATIONAL ASYMMETRY OF EARTH S BOW SHOCK HU You-Qiu 1, PENG Zhong 2, WANG Chi 2 1 CAS Key Laboratory of Basic Plasma Physics, School of Earth
Cosmic ray and solar energetic particle flux in paleomagnetospheres
 Earth Planets Space, 6, 333 345, 1 Cosmic ray and solar energetic particle flux in paleomagnetospheres Anja Stadelmann 1, Joachim Vogt, Karl-Heinz Glassmeier 1,3, May-Britt Kallenrode 4, and Gerd-Hannes
Earth Planets Space, 6, 333 345, 1 Cosmic ray and solar energetic particle flux in paleomagnetospheres Anja Stadelmann 1, Joachim Vogt, Karl-Heinz Glassmeier 1,3, May-Britt Kallenrode 4, and Gerd-Hannes
1 Introduction. Cambridge University Press Physics of Space Plasma Activity Karl Schindler Excerpt More information
 1 Introduction Space plasma phenomena have attracted particular interest since the beginning of the exploration of space about half a century ago. Already a first set of pioneering observations (e.g.,
1 Introduction Space plasma phenomena have attracted particular interest since the beginning of the exploration of space about half a century ago. Already a first set of pioneering observations (e.g.,
Morphology of the ring current derived from magnetic field observations
 Annales Geophysicae () : 67 95 SRef-ID: 3-576/ag/--67 European Geosciences Union Annales Geophysicae Morphology of the ring current derived from magnetic field observations G. Le, C. T. Russell, and K.
Annales Geophysicae () : 67 95 SRef-ID: 3-576/ag/--67 European Geosciences Union Annales Geophysicae Morphology of the ring current derived from magnetic field observations G. Le, C. T. Russell, and K.
ESS 7. October 18, 22, and 25. The Magnetosphere
 ESS 7 Lectures 10, 11 and 12 October 18, 22, and 25 The Magnetosphere Setting the Magnetosphere Scene Solar min Solar max What we have learned so far: Solar wind is a supersonic flow Has structure and
ESS 7 Lectures 10, 11 and 12 October 18, 22, and 25 The Magnetosphere Setting the Magnetosphere Scene Solar min Solar max What we have learned so far: Solar wind is a supersonic flow Has structure and
The Physics of Space Plasmas
 The Physics of Space Plasmas Magnetic Storms and Substorms William J. Burke 14 November 2012 University of Massachusetts, Lowell Lecture 9 Course term-paper topics Geomagnetic Storms: (continued ) Volland-Stern
The Physics of Space Plasmas Magnetic Storms and Substorms William J. Burke 14 November 2012 University of Massachusetts, Lowell Lecture 9 Course term-paper topics Geomagnetic Storms: (continued ) Volland-Stern
Understanding storm-time ring current development through data-model comparisons of a moderate storm
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006ja011846, 2007 Understanding storm-time ring current development through data-model comparisons of a moderate storm Jichun Zhang, 1,2 Michael
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006ja011846, 2007 Understanding storm-time ring current development through data-model comparisons of a moderate storm Jichun Zhang, 1,2 Michael
A modelling approach to infer the solar wind plasma parameters upstream of Mercury from magnetic field observations
 A modelling approach to infer the solar wind plasma parameters upstream of Mercury from magnetic field observations S. Fatemi 1, (Email: shahab@irf.se) N. Poirier 2, M. Holmström 1, J. Lindkvist 3, M.
A modelling approach to infer the solar wind plasma parameters upstream of Mercury from magnetic field observations S. Fatemi 1, (Email: shahab@irf.se) N. Poirier 2, M. Holmström 1, J. Lindkvist 3, M.
The Dynamic Magnetosphere. Ioannis A. Daglis. National Observatory of Athens, Greece
 310/1749-42 ICTP-COST-USNSWP-CAWSES-INAF-INFN International Advanced School on Space Weather 2-19 May 2006 The Dynamic Magnetosphere: Reaction to and Consequences of Solar Wind Variations Yannis DAGLIS
310/1749-42 ICTP-COST-USNSWP-CAWSES-INAF-INFN International Advanced School on Space Weather 2-19 May 2006 The Dynamic Magnetosphere: Reaction to and Consequences of Solar Wind Variations Yannis DAGLIS
Lecture 12 The Importance of Accurate Solar Wind Measurements
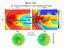 Lecture 12 The Importance of Accurate Solar Wind Measurements The Approach Magnetospheric studies usually are based on a single solar wind monitor. We propagate the solar wind from the observation point
Lecture 12 The Importance of Accurate Solar Wind Measurements The Approach Magnetospheric studies usually are based on a single solar wind monitor. We propagate the solar wind from the observation point
RELATIVISTIC ELECTRONS AND ULF-ACTIVITY DYNAMICS DURING CIR- AND CME-STORMS IN MAY 2005
 RELATIVISTIC ELECTRONS AND ULF-ACTIVITY DYNAMICS DURING CIR- AND CME-STORMS IN MAY 2005 Myagkova I.N. 1, Kozyreva O.V. 2, 3 1 Skobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear Physics, Moscow State University, Moscow; 2
RELATIVISTIC ELECTRONS AND ULF-ACTIVITY DYNAMICS DURING CIR- AND CME-STORMS IN MAY 2005 Myagkova I.N. 1, Kozyreva O.V. 2, 3 1 Skobeltsyn Institute of Nuclear Physics, Moscow State University, Moscow; 2
Low energy electron radiation environment for extreme events
 Low energy electron radiation environment for extreme events Natalia Ganushkina (1, 2) and Stepan Dubyagin (1) Special thanks to Jean-Charles Matéo-Vélez (3) (1) Finnish Meteorological Institute, Helsinki,
Low energy electron radiation environment for extreme events Natalia Ganushkina (1, 2) and Stepan Dubyagin (1) Special thanks to Jean-Charles Matéo-Vélez (3) (1) Finnish Meteorological Institute, Helsinki,
Features of energetic particle radial profiles inferred from geosynchronous responses to solar wind dynamic pressure enhancements
 Author(s) 2009. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Annales Geophysicae Features of energetic particle radial profiles inferred from geosynchronous responses to
Author(s) 2009. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Annales Geophysicae Features of energetic particle radial profiles inferred from geosynchronous responses to
Cluster and DEMETER Satellite Data. Fabien Darrouzet (Belgian Institute for Space Aeronomy (IASB-BIRA))
 Cluster and DEMETER Satellite Data Fabien Darrouzet (Belgian Institute for Space Aeronomy (IASB-BIRA)) 1 Outline Magnetosphere Plasmasphere Cluster Mission WHISPER Instrument and Data DEMETER Mission ISL
Cluster and DEMETER Satellite Data Fabien Darrouzet (Belgian Institute for Space Aeronomy (IASB-BIRA)) 1 Outline Magnetosphere Plasmasphere Cluster Mission WHISPER Instrument and Data DEMETER Mission ISL
cos 6 λ m sin 2 λ m Mirror Point latitude Equatorial Pitch Angle Figure 5.1: Mirror point latitude as function of equatorial pitch angle.
 Chapter 5 The Inner Magnetosphere 5.1 Trapped Particles The motion of trapped particles in the inner magnetosphere is a combination of gyro motion, bounce motion, and gradient and curvature drifts. In
Chapter 5 The Inner Magnetosphere 5.1 Trapped Particles The motion of trapped particles in the inner magnetosphere is a combination of gyro motion, bounce motion, and gradient and curvature drifts. In
Space Physics. An Introduction to Plasmas and Particles in the Heliosphere and Magnetospheres. May-Britt Kallenrode. Springer
 May-Britt Kallenrode Space Physics An Introduction to Plasmas and Particles in the Heliosphere and Magnetospheres With 170 Figures, 9 Tables, Numerous Exercises and Problems Springer Contents 1. Introduction
May-Britt Kallenrode Space Physics An Introduction to Plasmas and Particles in the Heliosphere and Magnetospheres With 170 Figures, 9 Tables, Numerous Exercises and Problems Springer Contents 1. Introduction
Effect of CME Events of Geomagnetic Field at Indian Station Alibag and Pondicherry
 Effect of CME Events of Geomagnetic Field at Indian Station Alibag and Pondicherry Babita Chandel Sri Sai University Palampur, Himachal Pradesh, India Abstract: Space weather activity CMEs, and solar energetic
Effect of CME Events of Geomagnetic Field at Indian Station Alibag and Pondicherry Babita Chandel Sri Sai University Palampur, Himachal Pradesh, India Abstract: Space weather activity CMEs, and solar energetic
On the climate of the solar-terrestrial space
 On the climate of the solar-terrestrial space Crisan Demetrescu, Venera Dobrica, Georgeta Maris Muntean, Institute of Geodynamics, Romanian Academy, Bucharest, Romania, crisan@geodin.ro Katya Georgieva,
On the climate of the solar-terrestrial space Crisan Demetrescu, Venera Dobrica, Georgeta Maris Muntean, Institute of Geodynamics, Romanian Academy, Bucharest, Romania, crisan@geodin.ro Katya Georgieva,
Modular model for Mercury s magnetospheric magnetic field confined within the average observed magnetopause
 PUBLICATIONS Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics RESEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: First Mercury magnetic field model confined to observed magnetopause Model includes internal dipole and field from
PUBLICATIONS Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics RESEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: First Mercury magnetic field model confined to observed magnetopause Model includes internal dipole and field from
РС INDEX AS INDICATOR OF THE SOLAR WIND ENERGY ENTERED INTO THE MAGNETOSPHERE: RELATION TO INTERPLANETARY ELECTRIC FIELD AND MAGNETIC DISTURBANCES
 РС INDEX AS INDICATOR OF THE SOLAR WIND ENERGY ENTERED INTO THE MAGNETOSPHERE: RELATION TO INTERPLANETARY ELECTRIC FIELD AND MAGNETIC DISTURBANCES О. A.Troshichev Arctic and Antarcrtic Research Institute,
РС INDEX AS INDICATOR OF THE SOLAR WIND ENERGY ENTERED INTO THE MAGNETOSPHERE: RELATION TO INTERPLANETARY ELECTRIC FIELD AND MAGNETIC DISTURBANCES О. A.Troshichev Arctic and Antarcrtic Research Institute,
INNER MAGNETOSPHERE PLASMA DENSITIES. Bodo W. Reinisch and Xueqin Huang
 XA0303034 INNER MAGNETOSPHERE PLASMA DENSITIES Bodo W. Reinisch and Xueqin Huang Environmental, Earth, and Atmospheric Sciences Department, Centerfor Atmospheric Research, University of Massachusetts Lowell,
XA0303034 INNER MAGNETOSPHERE PLASMA DENSITIES Bodo W. Reinisch and Xueqin Huang Environmental, Earth, and Atmospheric Sciences Department, Centerfor Atmospheric Research, University of Massachusetts Lowell,
STUDY ON RELATIONSHIP OF MAGNETOSPHERIC SUBSTORM AND MAGNETIC STORM
 Prosiding Seminar Nasional Penelitian, Pendidikan dan Penerapan MIPA Fakultas MIPA, Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta, 16 Mei 2009 STUDY ON RELATIONSHIP OF MAGNETOSPHERIC SUBSTORM AND MAGNETIC STORM L. Muhammad
Prosiding Seminar Nasional Penelitian, Pendidikan dan Penerapan MIPA Fakultas MIPA, Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta, 16 Mei 2009 STUDY ON RELATIONSHIP OF MAGNETOSPHERIC SUBSTORM AND MAGNETIC STORM L. Muhammad
VITREOUS CARBON TECHNOLOGY. Assoc. Prof. Dimitar Teodosiev, PhD, SRTI-BAS
 VITREOUS CARBON TECHNOLOGY Assoc. Prof. Dimitar Teodosiev, PhD, SRTI-BAS email: dteod@space.bas.bg Spherical probes for measurements of electric fields aboard satellites Use of a double probe - measuring
VITREOUS CARBON TECHNOLOGY Assoc. Prof. Dimitar Teodosiev, PhD, SRTI-BAS email: dteod@space.bas.bg Spherical probes for measurements of electric fields aboard satellites Use of a double probe - measuring
Magnetic Reconnection
 Magnetic Reconnection? On small scale-lengths (i.e. at sharp gradients), a diffusion region (physics unknown) can form where the magnetic field can diffuse through the plasma (i.e. a breakdown of the frozenin
Magnetic Reconnection? On small scale-lengths (i.e. at sharp gradients), a diffusion region (physics unknown) can form where the magnetic field can diffuse through the plasma (i.e. a breakdown of the frozenin
Cluster observations of sudden impulses in the magnetotail caused by interplanetary shocks and pressure increases
 Annales Geophysicae (25) 23: 69 624 SRef-ID: 1432-576/ag/25-23-69 European Geosciences Union 25 Annales Geophysicae Cluster observations of sudden impulses in the magnetotail caused by interplanetary shocks
Annales Geophysicae (25) 23: 69 624 SRef-ID: 1432-576/ag/25-23-69 European Geosciences Union 25 Annales Geophysicae Cluster observations of sudden impulses in the magnetotail caused by interplanetary shocks
The Solar wind - magnetosphere - ionosphere interaction
 The Solar wind - magnetosphere - ionosphere interaction Research seminar on Sun-Earth connections Eija Tanskanen Friday January 27, 2006 12-14 a.m., D115 Outline 1. Basics of the Earth s magnetosphere
The Solar wind - magnetosphere - ionosphere interaction Research seminar on Sun-Earth connections Eija Tanskanen Friday January 27, 2006 12-14 a.m., D115 Outline 1. Basics of the Earth s magnetosphere
Comparison of energetic electron flux and phase space density in the magnetosheath and in the magnetosphere
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2012ja017520, 2012 Comparison of energetic electron flux and phase space density in the magnetosheath and in the magnetosphere Bingxian Luo, 1 Xinlin
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2012ja017520, 2012 Comparison of energetic electron flux and phase space density in the magnetosheath and in the magnetosphere Bingxian Luo, 1 Xinlin
Cluster observations of a magnetic field cavity in the plasma sheet
 Cluster observations of a magnetic field cavity in the plasma sheet N.C. Draper a, M. Lester a, S.W.H. Cowley a, J.-M. Bosqued b, A. Grocott a, J.A. Wild a, Y. Bogdanova c, A.N. Fazakerley c, J.A. Davies
Cluster observations of a magnetic field cavity in the plasma sheet N.C. Draper a, M. Lester a, S.W.H. Cowley a, J.-M. Bosqued b, A. Grocott a, J.A. Wild a, Y. Bogdanova c, A.N. Fazakerley c, J.A. Davies
Sharp boundaries of small- and middle-scale solar wind structures
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 110,, doi:10.1029/2005ja011307, 2005 Sharp boundaries of small- and middle-scale solar wind structures M. O. Riazantseva 1 and G. N. Zastenker Space Research Institute,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 110,, doi:10.1029/2005ja011307, 2005 Sharp boundaries of small- and middle-scale solar wind structures M. O. Riazantseva 1 and G. N. Zastenker Space Research Institute,
Physics of Solar Wind and Terrestrial Magnetospheric Plasma Interactions With the Moon
 Physics of Solar Wind and Terrestrial Magnetospheric Plasma Interactions With the Moon R.P. Lin Physics Dept & Space Sciences Laboratory University of California, Berkeley with help from J. Halekas, M.
Physics of Solar Wind and Terrestrial Magnetospheric Plasma Interactions With the Moon R.P. Lin Physics Dept & Space Sciences Laboratory University of California, Berkeley with help from J. Halekas, M.
Earth s bow shock and magnetopause in the case of a field-aligned upstream flow: Observation and model comparison
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. A7, 1269, doi:10.1029/2002ja009697, 2003 Earth s bow shock and magnetopause in the case of a field-aligned upstream flow: Observation and model comparison
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. A7, 1269, doi:10.1029/2002ja009697, 2003 Earth s bow shock and magnetopause in the case of a field-aligned upstream flow: Observation and model comparison
MAGNETIC STORM EFFECTS IN THE ATMOSPHERIC ELECTRIC FIELD VARIATIONS
 MAGNETIC STORM EFFECTS IN THE ATMOSPHERIC ELECTRIC FIELD VARIATIONS N.G. Kleimenova 1, O.V. Kozyreva 1, S. Michnowski 2, M. Kubicki 2, N.N. Nikiforova 1 1 Institute of the Earth Physics RAS, Moscow, Russia,
MAGNETIC STORM EFFECTS IN THE ATMOSPHERIC ELECTRIC FIELD VARIATIONS N.G. Kleimenova 1, O.V. Kozyreva 1, S. Michnowski 2, M. Kubicki 2, N.N. Nikiforova 1 1 Institute of the Earth Physics RAS, Moscow, Russia,
Dynamics of ring current and electric fields in the inner magnetosphere during disturbed periods: CRCM BATS R US coupled model
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009ja014621, 2010 Dynamics of ring current and electric fields in the inner magnetosphere during disturbed periods:
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009ja014621, 2010 Dynamics of ring current and electric fields in the inner magnetosphere during disturbed periods:
ON THE PERIODIC MODULATION OF ENERG TitleELECTRONS IN THE MAGNETOSPHERIC SKI REGION.
 ON THE PERIODIC MODULATION OF ENERG TitleELECTRONS IN THE MAGNETOSPHERIC SKI REGION Author(s) SAKURAI, Kunitomo Citation Special Contributions of the Geophy University (1967), 7: 15-21 Issue Date 1967-12
ON THE PERIODIC MODULATION OF ENERG TitleELECTRONS IN THE MAGNETOSPHERIC SKI REGION Author(s) SAKURAI, Kunitomo Citation Special Contributions of the Geophy University (1967), 7: 15-21 Issue Date 1967-12
From the Chapman-Ferraro Magnetosphere To the Dungey-Alfvén Magnetosphere
 From the Chapman-Ferraro Magnetosphere To the Dungey-Alfvén Magnetosphere Two Magnetosphere Types Chapman-Ferraro Dungey-Alfvén Chapman-Ferraro Type Hands-off, no-touch vacuum coupling Dungey-Alfvén Type
From the Chapman-Ferraro Magnetosphere To the Dungey-Alfvén Magnetosphere Two Magnetosphere Types Chapman-Ferraro Dungey-Alfvén Chapman-Ferraro Type Hands-off, no-touch vacuum coupling Dungey-Alfvén Type
COMPARISON OF PC5 GEOMAGNETIC PULSATIONS ASSOCIATED WITH CIR-DRIVEN AND CME-DRIVEN STORMS. O. V. Kozyreva and N.G. Kleimenova
 COMPARISON OF PC5 GEOMAGNETIC PULSATIONS ASSOCIATED WITH CIR-DRIVEN AND CME-DRIVEN STORMS O. V. Kozyreva and N.G. Kleimenova Institute of Physics of the Earth RAS, B. Gruzinskaya 10, Moscow 123995, Russia,
COMPARISON OF PC5 GEOMAGNETIC PULSATIONS ASSOCIATED WITH CIR-DRIVEN AND CME-DRIVEN STORMS O. V. Kozyreva and N.G. Kleimenova Institute of Physics of the Earth RAS, B. Gruzinskaya 10, Moscow 123995, Russia,
Relation between the ring current and the tail current during magnetic storms
 Annales Geophysicae (25) 23: 523 533 SRef-ID: 1432-576/ag/25-23-523 European Geosciences Union 25 Annales Geophysicae Relation between the ring current and the tail current during magnetic storms V. V.
Annales Geophysicae (25) 23: 523 533 SRef-ID: 1432-576/ag/25-23-523 European Geosciences Union 25 Annales Geophysicae Relation between the ring current and the tail current during magnetic storms V. V.
The Structure and Properties of Martian Magnetosphere at ~ 70 Solar-Zenith Angle in MSE Coordinates as Observed on MAVEN
 The Structure and Properties of Martian Magnetosphere at ~ 70 Solar-Zenith Angle in MSE Coordinates as Observed on MAVEN O. L. Vaisberg 1, V. N. Ermakov 1,2, S. D. Shuvalov 1, L. M. Zelenyi 1, J. Halekas
The Structure and Properties of Martian Magnetosphere at ~ 70 Solar-Zenith Angle in MSE Coordinates as Observed on MAVEN O. L. Vaisberg 1, V. N. Ermakov 1,2, S. D. Shuvalov 1, L. M. Zelenyi 1, J. Halekas
DYNAMICS OF THE EARTH S MAGNETOSPHERE
 DYNAMICS OF THE EARTH S MAGNETOSPHERE PROF JIM WILD j.wild@lancaster.ac.uk @jim_wild With thanks to: Stan Cowley, Rob Fear & Steve Milan OUTLINE So far: Dungey cycle - the stirring of the magnetosphere
DYNAMICS OF THE EARTH S MAGNETOSPHERE PROF JIM WILD j.wild@lancaster.ac.uk @jim_wild With thanks to: Stan Cowley, Rob Fear & Steve Milan OUTLINE So far: Dungey cycle - the stirring of the magnetosphere
Storm-time convection electric field in the near-earth plasma sheet
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 11, A4213, doi:1.129/24ja1449, 25 Storm-time convection electric field in the near-earth plasma sheet T. Hori, 1 A. T. Y. Lui, S. Ohtani, P. C:son Brandt, B. H. Mauk,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 11, A4213, doi:1.129/24ja1449, 25 Storm-time convection electric field in the near-earth plasma sheet T. Hori, 1 A. T. Y. Lui, S. Ohtani, P. C:son Brandt, B. H. Mauk,
EFFECT OF SOLAR AND INTERPLANETARY DISTURBANCES ON SPACE WEATHER
 Indian J.Sci.Res.3(2) : 121-125, 2012 EFFECT OF SOLAR AND INTERPLANETARY DISTURBANCES ON SPACE WEATHER a1 b c SHAM SINGH, DIVYA SHRIVASTAVA AND A.P. MISHRA Department of Physics, A.P.S.University, Rewa,M.P.,
Indian J.Sci.Res.3(2) : 121-125, 2012 EFFECT OF SOLAR AND INTERPLANETARY DISTURBANCES ON SPACE WEATHER a1 b c SHAM SINGH, DIVYA SHRIVASTAVA AND A.P. MISHRA Department of Physics, A.P.S.University, Rewa,M.P.,
Zach Meeks. Office: Ford ES&T Phone: (918) Please let me know if you have any questions!
 Zach Meeks Office: Ford ES&T 2114 Email: zachary.meeks@gatech.edu Phone: (918) 515-0052 Please let me know if you have any questions! The scope of space physics Solar-Terrestrial Relations Solar-Terrestrial
Zach Meeks Office: Ford ES&T 2114 Email: zachary.meeks@gatech.edu Phone: (918) 515-0052 Please let me know if you have any questions! The scope of space physics Solar-Terrestrial Relations Solar-Terrestrial
A comparison of IMP 8 observed bow shock positions with model predictions
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. A2, 1077, doi:10.1029/2002ja009384, 2003 A comparison of IMP 8 observed bow shock positions with model predictions J. Merka, 1,2 A. Szabo, 1 T. W. Narock,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. A2, 1077, doi:10.1029/2002ja009384, 2003 A comparison of IMP 8 observed bow shock positions with model predictions J. Merka, 1,2 A. Szabo, 1 T. W. Narock,
FEATURES OF HIGH LATITUDE MAGNETOSPHERIC TOPOLOGY AND MAGNETOSPHERIC SUBSTORM
 Physics of Auroral Phenomena, Proc. XXXII Annual Seminar, Apatity, pp. 9-16, 2009 Kola Science Centre, Russian Academy of Science, 2009 Polar Geophysical Institute FEATURES OF HIGH LATITUDE MAGNETOSPHERIC
Physics of Auroral Phenomena, Proc. XXXII Annual Seminar, Apatity, pp. 9-16, 2009 Kola Science Centre, Russian Academy of Science, 2009 Polar Geophysical Institute FEATURES OF HIGH LATITUDE MAGNETOSPHERIC
Energetic particle fluxes in the exterior cusp and the high-latitude dayside magnetosphere: statistical results from the Cluster/RAPID instrument
 Annales Geophysicae, 23, 2217 2230, 2005 SRef-ID: 1432-0576/ag/2005-23-2217 European Geosciences Union 2005 Annales Geophysicae Energetic particle fluxes in the exterior cusp and the high-latitude dayside
Annales Geophysicae, 23, 2217 2230, 2005 SRef-ID: 1432-0576/ag/2005-23-2217 European Geosciences Union 2005 Annales Geophysicae Energetic particle fluxes in the exterior cusp and the high-latitude dayside
Uppsala universitet Institutionen för astronomi och rymdfysik Anders Eriksson
 Tentamen för Rymdfysik I 2006-08-15 Uppsala universitet Institutionen för astronomi och rymdfysik Anders Eriksson Please write your name on all papers, and on the first page your address, e-mail and phone
Tentamen för Rymdfysik I 2006-08-15 Uppsala universitet Institutionen för astronomi och rymdfysik Anders Eriksson Please write your name on all papers, and on the first page your address, e-mail and phone
Low energy electrons in the inner Earth s magnetosphere
 Low energy electrons in the inner Earth s magnetosphere Natalia Ganushkina (1, 2) (1) University of Michigan, Ann Arbor MI, USA (2) Finnish Meteorological Institute, Helsinki, Finland The research leading
Low energy electrons in the inner Earth s magnetosphere Natalia Ganushkina (1, 2) (1) University of Michigan, Ann Arbor MI, USA (2) Finnish Meteorological Institute, Helsinki, Finland The research leading
Uneven compression levels of Earth s magnetic fields by shocked solar wind
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2010ja016149, 2011 Uneven compression levels of Earth s magnetic fields by shocked solar wind J. H. Shue, 1 Y. S. Chen, 1 W. C. Hsieh, 1 M. Nowada,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2010ja016149, 2011 Uneven compression levels of Earth s magnetic fields by shocked solar wind J. H. Shue, 1 Y. S. Chen, 1 W. C. Hsieh, 1 M. Nowada,
Time Series of Images of the Auroral Substorm
 ESS 7 Lecture 13 October 27, 2010 Substorms Time Series of Images of the Auroral Substorm This set of images in the ultra-violet from the Polar satellite shows changes that occur during an auroral substorm.
ESS 7 Lecture 13 October 27, 2010 Substorms Time Series of Images of the Auroral Substorm This set of images in the ultra-violet from the Polar satellite shows changes that occur during an auroral substorm.
High latitude magnetospheric topology and magnetospheric substorm
 Ann. Geophys., 27, 4069 4073, 2009 Author(s) 2009. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Annales Geophysicae High latitude magnetospheric topology and magnetospheric
Ann. Geophys., 27, 4069 4073, 2009 Author(s) 2009. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Annales Geophysicae High latitude magnetospheric topology and magnetospheric
Statistical study of O + transport from the cusp to the lobes with Cluster CODIF data
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2010ja015613, 2010 Statistical study of O + transport from the cusp to the lobes with Cluster CODIF data J. Liao, 1 L. M. Kistler, 1 C. G. Mouikis,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2010ja015613, 2010 Statistical study of O + transport from the cusp to the lobes with Cluster CODIF data J. Liao, 1 L. M. Kistler, 1 C. G. Mouikis,
Geomagnetic Disturbance Report Reeve Observatory
 Event type: Geomagnetic disturbances due to recurrent coronal hole high-speed stream Background: This background section defines the events covered. A coronal hole is a large dark region of less dense
Event type: Geomagnetic disturbances due to recurrent coronal hole high-speed stream Background: This background section defines the events covered. A coronal hole is a large dark region of less dense
Large-scale jets in the magnetosheath and plasma penetration across the
 Large-scale jets in the magnetosheath and plasma penetration across the magnetopause: THEMIS observations A. V. Dmitriev 1,2 and A. V. Suvorova 1,2 1 Institute of Space Sciences, National Central University,
Large-scale jets in the magnetosheath and plasma penetration across the magnetopause: THEMIS observations A. V. Dmitriev 1,2 and A. V. Suvorova 1,2 1 Institute of Space Sciences, National Central University,
CRCM + BATS-R-US two-way coupling
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: SPACE PHYSICS, VOL. 118, 135 15, doi:1.1/jgra.51, 13 CRCM + BATS-R-US two-way coupling A. Glocer, 1 M. Fok, 1 X. Meng, G. Toth, N. Buzulukova, 3, S. Chen, 5 and K. Lin
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH: SPACE PHYSICS, VOL. 118, 135 15, doi:1.1/jgra.51, 13 CRCM + BATS-R-US two-way coupling A. Glocer, 1 M. Fok, 1 X. Meng, G. Toth, N. Buzulukova, 3, S. Chen, 5 and K. Lin
