particle acceleration in reconnection regions and cosmic ray excess from the heliotail
|
|
|
- Archibald Thompson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 particle acceleration in reconnection regions and cosmic ray excess from the heliotail Paolo Desiati 1,2 & Alexander Lazarian 2 1 IceCube Research Center 2 Department of Astronomy University of Wisconsin - Madison Midwest Magnetic Fields Workshop, Madison, WI May 6 th,
2 cosmic rays ΦCR(E) CR below the knee (~ ev) believed to be galactic CR above ~ ev believed to be extra-galactic galactic CR believed to be accelerated in expanding shock waves initiated by supernova explosions anisotropy anisotropy in arrival direction expected from discrete sources distribution & propagation in heterogenous IM and turbulent LIMF 2 GeV TeV PeV EeV
3 low energy cosmic ray anisotropy in arrival direction Nagashima et al., J. Geophys. Res., Vol 103, No. A8, Pag. 17,429 (1998) heliospheric-tail! loss-cone region! Mt Norikura Nagoya Relative Intensity! E ~ 10 4 GeV! E ~ 66 GeV! E ~ 60 GeV! heliospheric-tail! E ~ 331 GeV! Sakashita E ~ 387 GeV! Hobart E ~ 180 GeV! Sidereal local time! tail-in excess region! 3
4 medium / small scale anisotropy ARGO YBJ J.L. Zhang et al., ICRC Łódź - Poland (2009) loss-cone region! tail-in excess region! 0.7 TeV global amplitude of large scale anisotropy increases with energy up to ~ 1-10 TeV and decreases above it 1.5 TeV 3.9 TeV origin of anisotropy is unknown large scale anisotropy shows smaller angular features, some of which highly significant 4 TeV 6.2 TeV small angular features might reveal properties of the boundary region between solar wind and interstellar wind 12 TeV 50 TeV isolate small scale features 4 Tibet-III Amenomori et al., Science Vol. 314, pp. 439 (2006)
5 angular scale in cosmic ray arrival direction loss-cone region! tail-in excess region! 5
6 angular scale in cosmic ray arrival direction loss-cone region! tail-in excess region! 5
7 angular scale in cosmic ray arrival direction loss-cone region! tail-in excess region! 5
8 medium / small scale anisotropy Abdo A.A. et al., 2008, Phys. Rev. Lett., 101, hr = 30 2 hr = 30 Milagro events median CR energy ~ 1 TeV = ev average angular resolution < 1 o 2hr time window 10 smoothing filter all angular features > 30 technique used in gamma ray searches 6
9 medium / small scale anisotropy Abdo A.A. et al., 2008, Phys. Rev. Lett., 101, hr = 30 2 hr = 30 Milagro events median CR energy ~ 1 TeV = ev average angular resolution < 1 o 2hr time window 10 smoothing filter all angular features > 30 technique used in gamma ray searches harder spectrum in region A 6
10 origin of small scale anisotropy : astrophysics? localized excess of cosmic rays from nearby (~150 pc ~ AU) recent (~ 350 kyr) supernova that gave birth to Geminga Pulsar fine tuning of propagation through interstellar medium incidentally requires magnetic connection to the faraway source loss-cone region! tail-in excess region! small scale features likely from local processes Abdo et al., Phys. Rev. Lett., 101, ,
11 origin of tail-in anisotropy heliospheric-tail! loss-cone region! broad tail-in excess of sub-tev cosmic rays attributed to heliotail Relative Intensity! E ~ 10 4 GeV! E ~ 66 GeV! heliospheric-tail! E ~ 60 GeV! localized excess of multi-tev cosmic rays from the direction of the heliotail E ~ 331 GeV! E ~ 387 GeV! medium/small scale modulation to be connected to nearby perturbations first-order Fermi acceleration in magnetic reconnection regions in the heliotail E ~ 180 GeV! Sidereal local time! tail-in excess region! Nagashima et al., J. Geophys. Res., Vol 103, No. A8,17429, 1998 loss-cone region! tail-in excess region! Abdo et al., Phys. Rev. Lett., 101, ,
12 magnetic heliotail Lazarian & Desiati, ApJ, 722, 188, 2010 magnetic polarity reversals due to the 11- year solar cycles compressed by the solar wind in the magneto-tail! 3D simulation of heliosphere/heliotail Pogorelov et al., ApJ, 696, 1478,
13 magnetic heliotail Lazarian & Desiati, ApJ, 722, 188, 2010 magnetic polarity reversals due to the 11- year solar cycles compressed by the solar wind in the magneto-tail! 3D simulation of heliosphere/heliotail Pogorelov et al., ApJ, 696, 1478, 2009 ubiquitous turbulence makes reconnection fast and not affected by ohmic dissipation Sweet, IAU Symposium 6, Electromagnetic Phenomena in Cosmical Physics, 123, Parker, J. Geophys. Rev., 62, 509, 1957 Lazarian & Vishniac, ApJ, 517, 700,
14 stochastic magnetic reconnection verification of Lazarian & V i s h n i a c w i t h numerical calculations Kowal et al., ApJ, 700, 63, 2009 reconnection speed does not depend on resistivity reconnection speed increases with turbulence injection power reconnection speed ~ local turbulent velocity 11
15 acceleration in weakly stochastic reconnection regions first order Fermi acceleration from volumefilling magnetic reconnection de Gouveia Dal Pino & Lazarian, 2005 magnetic reconnection as site of acceleration N(E)dE E 5 2 de magnetic tubes contraction leads to increase of particle energy as long as they are within the contracting magnetic loop application to pulsars, microquasars, solar flares acceleration de Gouveia Dal Pino & Lazarian, 2000, 2003, 2005 Lazarian,
16 acceleration in weakly stochastic reconnection regions test particle verification of Lazarian & Vishniac 1999 with numerical calculations magnetic energy transferred into energy of contracting loops Lazarian et al., Pl. and Sp. Sci & Kowal et al., ApJ, 700, 63, 2009 Turbulence with reconnection fast reconnection induces efficient acceleration of cosmic rays complexity of acceleration: contracting loops & current sheets; 1 st order Fermi & drift acceleration Turbulence without reconnection more studies : Kowal et al., arxiv:
17 acceleration in reconnection regions N(E)dE E 5 2 de first-order Fermi acceleration of test particle in magnetic mirrors N(E)dE E 3 2 de particle back-reaction Drake et al., Nature, 443, 553, 2006 E max ev B Lzone 1µB 134 AU solar wind down-stream TS 100 km/sec E max 20 TeV B 1µB unlikely to expect energies > 10 TeV Milagro harder spectrum in region A 14 14
18 application on anomalous cosmic rays magnetic field reversals from Sun s rotation compress heliospheric current sheets regions at heliopause Lazarian & Opher, ApJ 703, 8, 2009 reconnection and acceleration induced in the heliosheath closer to the heliopause Voyager 1/2 did not observe ACR termination shock, but still increasing other models available as well also Drake et al., ApJ, 709, 963,
19 magnetic reconnection in the heliosphere 3D simulations of heliosphere Opher et al., arxiv: D simulation of heliosphere/heliotail Pogorelov et al., ApJ, 696, 1478, 2009 ~150 AU ~150 AU 16 ~1,000 AU
20 conclusions broad tail-in excess of sub-tev cosmic rays and localized excess of multi-tev cosmic rays from the direction of the heliotail could have a common origin 1 st order Fermi acceleration in magnetic reconnection regions in the heliotail on-going numerical calculations to verify whether magnetic reconnection regions in the heliotail may be site of efficient acceleration acceleration mechanisms in stochastic reconnection regions might explain the puzzling excess region of cosmic rays potential testbed of large-scale acceleration mechanism in stochastic reconnection regions (ACR, heliotail,...) multi-tev cosmic rays to probe outer heliospheric boundary 17
21 back up slides 18
22 origin of small scale anisotropy : heliospheric tail heliospheric-tail! loss-cone region! neutron monitor Tsumeb, Namibia Relative Intensity! E ~ 10 4 GeV! E ~ 66 GeV! heliospheric-tail! E ~ 60 GeV! E ~ 331 GeV! E ~ 387 GeV! E ~ 180 GeV! Sidereal local time! tail-in excess region! negative polarity positive polarity Nagashima et al., J. Geophys. Res., Vol 103, No. A8, Pag. 17,429 (1998) Karapetyan, Astrop. Phys., 33, 146, 2010 sub-tev cosmic ray tail-in excess by some unknown asymmetry caused by the heliotail solar magnetic field reversal should affect galactic anisotropy origin of excess is heliospheric 19
23 anisotropy vs energy Tibet ASγ Amenomori et al., ApJ. 626, L29, 2005 IceCube-22 Abbasi et al., ApJ, 718, L194, 2010 [%] 2 Abreu et al., Astrop. Phys., 34, 627, 2011 IceCube-59 EAS-TOP Aglietta et al., ApJ, 692, L130, Energy [GeV] ,000 pc (3 µg) gyro-radius (pc) ,000 70,000 gyro-radius (AU) 20 heliospheric influence galactic influence
magnetic reconnection as the cause of cosmic ray excess from the heliospheric tail
 magnetic reconnection as the cause of cosmic ray excess from the heliospheric tail Paolo Desiati 1,2 & Alexander Lazarian 2 1 IceCube Research Center 2 Department of Astronomy University of Wisconsin -
magnetic reconnection as the cause of cosmic ray excess from the heliospheric tail Paolo Desiati 1,2 & Alexander Lazarian 2 1 IceCube Research Center 2 Department of Astronomy University of Wisconsin -
3D Reconnection of Weakly Stochastic Magnetic Field and its Implications
 3D Reconnection of Weakly Stochastic Magnetic Field and its Implications Alex Lazarian Astronomy Department and Center for Magnetic Self- Organization in Astrophysical and Laboratory Plasmas Collaboration:
3D Reconnection of Weakly Stochastic Magnetic Field and its Implications Alex Lazarian Astronomy Department and Center for Magnetic Self- Organization in Astrophysical and Laboratory Plasmas Collaboration:
Cosmic Ray Anisotropy with Milagro
 Cosmic Ray Anisotropy with Milagro John Pretz For the Milagro Collabora;on TeV Par;cle Astrophysics Conference May 15, 2009 Milagro Collabora+on A. Abdo, B. Allen, D. Berley, G. Christopher, T. DeYoung,
Cosmic Ray Anisotropy with Milagro John Pretz For the Milagro Collabora;on TeV Par;cle Astrophysics Conference May 15, 2009 Milagro Collabora+on A. Abdo, B. Allen, D. Berley, G. Christopher, T. DeYoung,
Searching for the Origin of Cosmic Rays with IceCube
 Searching for the Origin of Cosmic Rays with IceCube Stefan Westerhoff University of Wisconsin-Madison Fall 2010 Physics Seminar Wichita State University September 29, 2010 1 2 3 Outline Cosmic Rays and
Searching for the Origin of Cosmic Rays with IceCube Stefan Westerhoff University of Wisconsin-Madison Fall 2010 Physics Seminar Wichita State University September 29, 2010 1 2 3 Outline Cosmic Rays and
Lessons 19 and 20. Detection of C.R. with energy > TeV Study of the C.R. isotropy/anisotropy Ground based detectors:
 Lessons 19 and 20 Detection of C.R. with energy > TeV Study of the C.R. isotropy/anisotropy Ground based detectors: Detection at ground of extensive Air Showers: nature, direction and energy of the primary
Lessons 19 and 20 Detection of C.R. with energy > TeV Study of the C.R. isotropy/anisotropy Ground based detectors: Detection at ground of extensive Air Showers: nature, direction and energy of the primary
High-Energy Plasma Astrophysics and Next Generation Gamma-Ray Observatory Cherenkov Telescope Array
 High-Energy Plasma Astrophysics and Next Generation Gamma-Ray Observatory Cherenkov Telescope Array FAPESP CUNY Week, New York, November 2018 M82 Star Formation- Clouds-SNRturbulence connection Sun & Stars
High-Energy Plasma Astrophysics and Next Generation Gamma-Ray Observatory Cherenkov Telescope Array FAPESP CUNY Week, New York, November 2018 M82 Star Formation- Clouds-SNRturbulence connection Sun & Stars
Science Questions from inside 150AU Heliosheath/Heliopause. Merav Opher Boston University
 Science Questions from inside 150AU Heliosheath/Heliopause Merav Opher Boston University The heliosphere as test-bed for other astrospheres WISE bow shock image, PIA13455 Closeup of IRS8, resolving the
Science Questions from inside 150AU Heliosheath/Heliopause Merav Opher Boston University The heliosphere as test-bed for other astrospheres WISE bow shock image, PIA13455 Closeup of IRS8, resolving the
TeV Cosmic Ray Anisotropies at Various Angular Scales
 TeV Cosmic Ray Anisotropies at Various Angular Scales Gwenael Giacinti University of Oxford, Clarendon Laboratory Based on : GG & G.Sigl GG, M.Kachelriess, D.Semikoz Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 071101(2012)
TeV Cosmic Ray Anisotropies at Various Angular Scales Gwenael Giacinti University of Oxford, Clarendon Laboratory Based on : GG & G.Sigl GG, M.Kachelriess, D.Semikoz Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 071101(2012)
Seeing the moon shadow in CRs
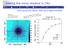 Seeing the moon shadow in CRs and using the Earth field as a spectrometer Tibet III Amenomori et al. arxiv:0810.3757 see also ARGO-YBJ results Bartoli et. al, arxiv:1107.4887 Milargo: 100% coverage r owe
Seeing the moon shadow in CRs and using the Earth field as a spectrometer Tibet III Amenomori et al. arxiv:0810.3757 see also ARGO-YBJ results Bartoli et. al, arxiv:1107.4887 Milargo: 100% coverage r owe
1939 Baade&Zwicky 1949 Fermi 1977 (Krymski; Axford; Bell; Blandford & Ostriker
 46 1939 Baade&Zwicky 1949 Fermi 1977 (Krymski; Axford; Bell; Blandford & Ostriker From Aharonian et al. 2011 From Letessier-Sevon & Stanev 2011 Fermi 2-year sky map Outline 1. 2. 3. 4. knee ankle (b)
46 1939 Baade&Zwicky 1949 Fermi 1977 (Krymski; Axford; Bell; Blandford & Ostriker From Aharonian et al. 2011 From Letessier-Sevon & Stanev 2011 Fermi 2-year sky map Outline 1. 2. 3. 4. knee ankle (b)
Particle Acceleration by Reconnection and VHE emission Around Black Holes and Relativistic Jets
 Particle Acceleration by Reconnection and VHE emission Around Black Holes and Relativistic Jets Deciphering the Violent Universe, Playa del Carmen, December 11-15, 2017 Accretion disk coronae Star Formation
Particle Acceleration by Reconnection and VHE emission Around Black Holes and Relativistic Jets Deciphering the Violent Universe, Playa del Carmen, December 11-15, 2017 Accretion disk coronae Star Formation
Galactic Sources with Milagro and HAWC. Jordan Goodman for the HAWC and Milagro Collaborations
 Galactic Sources with Milagro and HAWC Jordan Goodman for the HAWC and Milagro Collaborations Snowpack 2010 Milagro and HAWC Milagro was a first generation wide-field gamma-ray telescope: Proposed in 1990
Galactic Sources with Milagro and HAWC Jordan Goodman for the HAWC and Milagro Collaborations Snowpack 2010 Milagro and HAWC Milagro was a first generation wide-field gamma-ray telescope: Proposed in 1990
Cosmic Ray Astronomy. Qingling Ni
 Cosmic Ray Astronomy Qingling Ni What is Cosmic Ray? Mainly charged particles: protons (hydrogen nuclei)+helium nuclei+heavier nuclei What s the origin of them? What happened during their propagation?
Cosmic Ray Astronomy Qingling Ni What is Cosmic Ray? Mainly charged particles: protons (hydrogen nuclei)+helium nuclei+heavier nuclei What s the origin of them? What happened during their propagation?
Astroparticle Physics with IceCube
 Astroparticle Physics with IceCube Nick van Eijndhoven nickve.nl@gmail.com http://w3.iihe.ac.be f or the IceCube collaboration Vrije Universiteit Brussel - IIHE(ULB-VUB) Pleinlaan 2, B-1050 Brussel, Belgium
Astroparticle Physics with IceCube Nick van Eijndhoven nickve.nl@gmail.com http://w3.iihe.ac.be f or the IceCube collaboration Vrije Universiteit Brussel - IIHE(ULB-VUB) Pleinlaan 2, B-1050 Brussel, Belgium
A Large High Altitude Air Shower Observatory : the LHAASO Project
 A Large High Altitude Air Shower Observatory : the LHAASO Project Olivier Deligny CNRS/IN2P3 - IPN Orsay on behalf the LHAASO Collaboration Contact Person: Zhen CAO, IHEP Rencontres de Moriond, 9/16 March
A Large High Altitude Air Shower Observatory : the LHAASO Project Olivier Deligny CNRS/IN2P3 - IPN Orsay on behalf the LHAASO Collaboration Contact Person: Zhen CAO, IHEP Rencontres de Moriond, 9/16 March
Modeling Heliophysics Phenomena with Multi-Scale Fluid-Kinetic Simulation Suite
 Blue Waters Symposium Sunriver, OR, 16 19 May, 2017 Modeling Heliophysics Phenomena with Multi-Scale Fluid-Kinetic Simulation Suite N.V. Pogorelov and J. Heerikhuisen University of Alabama in Huntsville
Blue Waters Symposium Sunriver, OR, 16 19 May, 2017 Modeling Heliophysics Phenomena with Multi-Scale Fluid-Kinetic Simulation Suite N.V. Pogorelov and J. Heerikhuisen University of Alabama in Huntsville
What is New in the Outer Heliosphere?: Voyager and IBEX
 What is New in the Outer Heliosphere?: Voyager and IBEX Marty Lee Durham, New Hampshire USA 1 Our Local Interstellar Environment From E. Möbius Pogorelov et al., 2008 Plasma & Neutral Parameters R = 1
What is New in the Outer Heliosphere?: Voyager and IBEX Marty Lee Durham, New Hampshire USA 1 Our Local Interstellar Environment From E. Möbius Pogorelov et al., 2008 Plasma & Neutral Parameters R = 1
8.2.2 Rudiments of the acceleration of particles
 430 The solar wind in the Universe intergalactic magnetic fields that these fields should not perturb them. Their arrival directions should thus point back to their sources in the sky, which does not appear
430 The solar wind in the Universe intergalactic magnetic fields that these fields should not perturb them. Their arrival directions should thus point back to their sources in the sky, which does not appear
Cosmic Rays in CMSO. Ellen Zweibel University of Wisconsin-Madison Santa Fe, 2014
 Cosmic Rays in CMSO Ellen Zweibel University of Wisconsin-Madison Santa Fe, 2014 Galaxies are Pervaded by Magnetic Fields & Relativistic Particles Synchrotron radiation from M51 (MPIfR/NRAO) Galactic molecular
Cosmic Rays in CMSO Ellen Zweibel University of Wisconsin-Madison Santa Fe, 2014 Galaxies are Pervaded by Magnetic Fields & Relativistic Particles Synchrotron radiation from M51 (MPIfR/NRAO) Galactic molecular
How are the present solar minimum conditions transmitted to the outer heliosphere and heliosheath? John Richardson M.I.T.
 How are the present solar minimum conditions transmitted to the outer heliosphere and heliosheath? John Richardson M.I.T. Heliosphere Overview Heliopause: boundary of LIC and SW plasma He H Termination
How are the present solar minimum conditions transmitted to the outer heliosphere and heliosheath? John Richardson M.I.T. Heliosphere Overview Heliopause: boundary of LIC and SW plasma He H Termination
Measurement of the CR e+/e- ratio with ground-based instruments
 Measurement of the CR e+/e- ratio with ground-based instruments Pierre Colin Max-Planck-Institut für Physik CR Moon shadow MPP retreat - 21 January 2014 Cosmic ray electrons Observation: Above the atmosphere:
Measurement of the CR e+/e- ratio with ground-based instruments Pierre Colin Max-Planck-Institut für Physik CR Moon shadow MPP retreat - 21 January 2014 Cosmic ray electrons Observation: Above the atmosphere:
PLASMA ASTROPHYSICS. ElisaBete M. de Gouveia Dal Pino IAG-USP. NOTES: (references therein)
 PLASMA ASTROPHYSICS ElisaBete M. de Gouveia Dal Pino IAG-USP NOTES:http://www.astro.iag.usp.br/~dalpino (references therein) ICTP-SAIFR, October 7-18, 2013 Contents What is plasma? Why plasmas in astrophysics?
PLASMA ASTROPHYSICS ElisaBete M. de Gouveia Dal Pino IAG-USP NOTES:http://www.astro.iag.usp.br/~dalpino (references therein) ICTP-SAIFR, October 7-18, 2013 Contents What is plasma? Why plasmas in astrophysics?
Interstellar Neutral Atoms and Their Journey Through the Heliosphere Elena Moise
 Interstellar Neutral Atoms and Their Journey Through the Heliosphere Elena Moise Institute for Astronomy, University of Hawai i Solar and Heliospheric Influences on the Geospace Bucharest, 1-5 Oct 2012
Interstellar Neutral Atoms and Their Journey Through the Heliosphere Elena Moise Institute for Astronomy, University of Hawai i Solar and Heliospheric Influences on the Geospace Bucharest, 1-5 Oct 2012
First Light with the HAWC Gamma-Ray Observatory
 , for the HAWC Collaboration Wisconsin IceCube Particle Astrophysics Center (WIPAC) and Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin Madison, Madison, WI 53706, USA E-mail: westerhoff@wisc.edu The High-Altitude
, for the HAWC Collaboration Wisconsin IceCube Particle Astrophysics Center (WIPAC) and Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin Madison, Madison, WI 53706, USA E-mail: westerhoff@wisc.edu The High-Altitude
HAWC and the cosmic ray quest
 HAWC and the cosmic ray quest J.C. Arteaga-Velázquez for the HAWC Collaboration Instituto de Física y Matemáticas, Universidad Michoacana, Mexico Structure of the talk: 1) The HAWC gamma-ray observatory
HAWC and the cosmic ray quest J.C. Arteaga-Velázquez for the HAWC Collaboration Instituto de Física y Matemáticas, Universidad Michoacana, Mexico Structure of the talk: 1) The HAWC gamma-ray observatory
Cosmic Rays in the Heliosphere. J. R. Jokipii University of Arizona
 Cosmic Rays in the Heliosphere J. R. Jokipii University of Arizona Presentation at the 2011 Heliophysics Summer School, Boulder, July 29, 2011 Outline of Lecture Brief introduction to the heliosphere.
Cosmic Rays in the Heliosphere J. R. Jokipii University of Arizona Presentation at the 2011 Heliophysics Summer School, Boulder, July 29, 2011 Outline of Lecture Brief introduction to the heliosphere.
Propagation of TeV PeV Cosmic Rays in the Galactic Magnetic Field
 Propagation of TeV PeV Cosmic Rays in the Galactic Magnetic Field Gwenael Giacinti Clarendon Laboratory, University of Oxford In collaboration with : GG & G.Sigl / Based on : Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 071101(2012)
Propagation of TeV PeV Cosmic Rays in the Galactic Magnetic Field Gwenael Giacinti Clarendon Laboratory, University of Oxford In collaboration with : GG & G.Sigl / Based on : Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 071101(2012)
Interstellar Medium V1
 Interstellar Medium V1 Heliosheath Termina/on Shock V2 which can be used to distinguish spatial and temporal effects. The V2 flows derived from the energetic particles using the Compton-Getting effect
Interstellar Medium V1 Heliosheath Termina/on Shock V2 which can be used to distinguish spatial and temporal effects. The V2 flows derived from the energetic particles using the Compton-Getting effect
W.R. Webber 1 and D.S. Intriligator 2
 A Forecast for a South Heliopause Crossing by Voyager 2 in Late 2014 Using Intensity-time Features of Energetic Particles Observed by V1 and V2 in the North and South Heliosheaths W.R. Webber 1 and D.S.
A Forecast for a South Heliopause Crossing by Voyager 2 in Late 2014 Using Intensity-time Features of Energetic Particles Observed by V1 and V2 in the North and South Heliosheaths W.R. Webber 1 and D.S.
Air Shower Measurements from PeV to EeV
 Air Shower Measurements from PeV to EeV Andreas Haungs haungs@ik.fzk.de James L. Pinfold August 2006 TeV workshop Madison, US Andreas Haungs 1 Cosmic Rays around the knee(s) EeV PeV Knee 2 nd Knee? Ralph
Air Shower Measurements from PeV to EeV Andreas Haungs haungs@ik.fzk.de James L. Pinfold August 2006 TeV workshop Madison, US Andreas Haungs 1 Cosmic Rays around the knee(s) EeV PeV Knee 2 nd Knee? Ralph
The Galactic diffuse gamma ray emission in the energy range 30 TeV 3 PeV
 The Galactic diffuse gamma ray emission in the energy range 30 TeV 3 PeV Mount Rainier by Will Christiansen Silvia Vernetto & Paolo Lipari 35th ICRC 12-20 July 2017 - Busan - South Korea Gamma ray astronomy
The Galactic diffuse gamma ray emission in the energy range 30 TeV 3 PeV Mount Rainier by Will Christiansen Silvia Vernetto & Paolo Lipari 35th ICRC 12-20 July 2017 - Busan - South Korea Gamma ray astronomy
Astro2020 Science White Paper Prospects for the detection of synchrotron halos around middle-age pulsars
 Astro2020 Science White Paper Prospects for the detection of synchrotron halos around middle-age pulsars Thematic Areas: Planetary Systems Star and Planet Formation Formation and Evolution of Compact Objects
Astro2020 Science White Paper Prospects for the detection of synchrotron halos around middle-age pulsars Thematic Areas: Planetary Systems Star and Planet Formation Formation and Evolution of Compact Objects
An Auger Observatory View of Centaurus A
 An Auger Observatory View of Centaurus A Roger Clay, University of Adelaide based on work particularly done with: Bruce Dawson, Adelaide Jose Bellido, Adelaide Ben Whelan, Adelaide and the Auger Collaboration
An Auger Observatory View of Centaurus A Roger Clay, University of Adelaide based on work particularly done with: Bruce Dawson, Adelaide Jose Bellido, Adelaide Ben Whelan, Adelaide and the Auger Collaboration
HELIOSPHERIC RADIO EMISSIONS
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 TWO RECENT khz OUTER HELIOSPHERIC RADIO EMISSIONS SEEN AT VOYAGER 1 - WHAT ARE THE INTERPLANETARY EVENTS THAT TRIGGER THEM AND WHERE ARE THESE EVENTS WHEN THE RADIO EMISSIONS START?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 TWO RECENT khz OUTER HELIOSPHERIC RADIO EMISSIONS SEEN AT VOYAGER 1 - WHAT ARE THE INTERPLANETARY EVENTS THAT TRIGGER THEM AND WHERE ARE THESE EVENTS WHEN THE RADIO EMISSIONS START?
Properties of Elementary Particle Fluxes in Cosmic Rays. TeVPA Aug. 7, Yuan-Hann Chang National Central University, Taiwan
 Properties of Elementary Particle Fluxes in Cosmic Rays TeVPA Aug. 7, 2017 Yuan-Hann Chang National Central University, Taiwan Elementary Particles in Space There are hundreds of different kinds of charged
Properties of Elementary Particle Fluxes in Cosmic Rays TeVPA Aug. 7, 2017 Yuan-Hann Chang National Central University, Taiwan Elementary Particles in Space There are hundreds of different kinds of charged
The Physics of Cosmic Rays! Ellen Zweibel! University of Wisconsin-Madison! &! Center for Magnetic Self-Organization!
 The Physics of Cosmic Rays! Ellen Zweibel! University of Wisconsin-Madison! &! Center for Magnetic Self-Organization! Galaxies(are(Pervaded(by(Magne2c( Fields(&(Rela2vis2c(Par2cles( Synchrotron radiation
The Physics of Cosmic Rays! Ellen Zweibel! University of Wisconsin-Madison! &! Center for Magnetic Self-Organization! Galaxies(are(Pervaded(by(Magne2c( Fields(&(Rela2vis2c(Par2cles( Synchrotron radiation
Cosmic Ray Transport (in the Galaxy) Luke Drury. Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies Institiúid Ard-Léinn Bhaile Átha Cliath
 Cosmic Ray Transport (in the Galaxy) Luke Drury Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies Institiúid Ard-Léinn Bhaile Átha Cliath 1 A few disclaimers and preliminary remarks! Not my main field of research
Cosmic Ray Transport (in the Galaxy) Luke Drury Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies Institiúid Ard-Léinn Bhaile Átha Cliath 1 A few disclaimers and preliminary remarks! Not my main field of research
PERSPECTIVES of HIGH ENERGY NEUTRINO ASTRONOMY. Paolo Lipari Vulcano 27 may 2006
 PERSPECTIVES of HIGH ENERGY NEUTRINO ASTRONOMY Paolo Lipari Vulcano 27 may 2006 High Energy Neutrino Astrophysics will CERTAINLY become an essential field in a New Multi-Messenger Astrophysics What is
PERSPECTIVES of HIGH ENERGY NEUTRINO ASTRONOMY Paolo Lipari Vulcano 27 may 2006 High Energy Neutrino Astrophysics will CERTAINLY become an essential field in a New Multi-Messenger Astrophysics What is
Galactic diffuse gamma-rays
 Galactic diffuse gamma-rays Masaki Mori Department of Physics, College of Science & Engineering, Ritsumeikan University 1 July 31, 2009, Dept. Astronomy, Kyoto University GeV gamma-ray sky by EGRET Compton
Galactic diffuse gamma-rays Masaki Mori Department of Physics, College of Science & Engineering, Ritsumeikan University 1 July 31, 2009, Dept. Astronomy, Kyoto University GeV gamma-ray sky by EGRET Compton
Plasma Physics for Astrophysics
 - ' ' * ' Plasma Physics for Astrophysics RUSSELL M. KULSRUD PRINCETON UNIVERSITY E;RESS '. ' PRINCETON AND OXFORD,, ', V. List of Figures Foreword by John N. Bahcall Preface Chapter 1. Introduction 1
- ' ' * ' Plasma Physics for Astrophysics RUSSELL M. KULSRUD PRINCETON UNIVERSITY E;RESS '. ' PRINCETON AND OXFORD,, ', V. List of Figures Foreword by John N. Bahcall Preface Chapter 1. Introduction 1
The Voyager Journey to the Giant Planets and Interstellar Space
 The Voyager Journey to the Giant Planets and Interstellar Space E. C. STONE HST- Orion 8/11/11 Gary Flandro 1965 Plasma Science (Voyager 2) J.D. Richardson, J. W. Belcher, L. F. Burlaga, A.J. Lazarus,
The Voyager Journey to the Giant Planets and Interstellar Space E. C. STONE HST- Orion 8/11/11 Gary Flandro 1965 Plasma Science (Voyager 2) J.D. Richardson, J. W. Belcher, L. F. Burlaga, A.J. Lazarus,
Mesoscale Variations in the Heliospheric Magnetic Field and their Consequences in the Outer Heliosphere
 Mesoscale Variations in the Heliospheric Magnetic Field and their Consequences in the Outer Heliosphere L. A. Fisk Department of Atmospheric, Oceanic, and Space Sciences, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor,
Mesoscale Variations in the Heliospheric Magnetic Field and their Consequences in the Outer Heliosphere L. A. Fisk Department of Atmospheric, Oceanic, and Space Sciences, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor,
ON PROBABLE CONTRIBUTION OF NEARBY SOURCES TO ANISOTROPY AND SPECTRUM OF COSMIC RAYS AT TEV-PEV-ENERGIES
 ON PROBABLE CONTRIBUTION OF NEARBY SOURCES TO ANISOTROPY AND SPECTRUM OF COSMIC RAYS AT TEV-PEV-ENERGIES SVESHNIKOVA L.G. 1, STRELNIKOVA O.N. 1, PTUSKIN V.S. 3 1 Lomonosov Moscow State University, SINP,
ON PROBABLE CONTRIBUTION OF NEARBY SOURCES TO ANISOTROPY AND SPECTRUM OF COSMIC RAYS AT TEV-PEV-ENERGIES SVESHNIKOVA L.G. 1, STRELNIKOVA O.N. 1, PTUSKIN V.S. 3 1 Lomonosov Moscow State University, SINP,
A-Exam: e + e Cosmic Rays and the Fermi Large Array Telescope
 A-Exam: e + e Cosmic Rays and the Fermi Large Array Telescope Walter Hopkins Physics Department, Cornell University. The Fermi Large Area Telescope is a particle detector in space with an effective collecting
A-Exam: e + e Cosmic Rays and the Fermi Large Array Telescope Walter Hopkins Physics Department, Cornell University. The Fermi Large Area Telescope is a particle detector in space with an effective collecting
Solar energetic particles and cosmic rays
 Solar energetic particles and cosmic rays Energetic particles in the heliosphere Solar energetic particles and cosmic rays Energy spectra and acceleration Particle propagation and transport Pick-up ions,
Solar energetic particles and cosmic rays Energetic particles in the heliosphere Solar energetic particles and cosmic rays Energy spectra and acceleration Particle propagation and transport Pick-up ions,
Cosmic rays, astrophysical turbulence and magnetic reconnection
 Workshop, -, 09:15 am - 09:30 am 10:00 am - 10:10 am 10:10 am - 10:50 am 10:50 am - 11:30 am 11:30 am - 12:10 pm 01:10 pm - 01:50 pm 01:50 pm - 02:30 pm 02:30 pm - 03:00 pm 03:00 pm - 03:40 pm 03:40 pm
Workshop, -, 09:15 am - 09:30 am 10:00 am - 10:10 am 10:10 am - 10:50 am 10:50 am - 11:30 am 11:30 am - 12:10 pm 01:10 pm - 01:50 pm 01:50 pm - 02:30 pm 02:30 pm - 03:00 pm 03:00 pm - 03:40 pm 03:40 pm
High energy neutrino production in the core region of radio galaxies due to particle acceleration by magnetic reconnection
 High energy neutrino production in the core region of radio galaxies due to particle acceleration by magnetic reconnection University of Sao Paulo) E-mail: bkhiali@usp Elisabete de Gouveia Dal Pino University
High energy neutrino production in the core region of radio galaxies due to particle acceleration by magnetic reconnection University of Sao Paulo) E-mail: bkhiali@usp Elisabete de Gouveia Dal Pino University
From the Knee to the toes: The challenge of cosmic-ray composition
 New Views of the Universe December 8 th 13 th, 2005, Chicago From the Knee to the toes: The challenge of cosmic-ray composition Jörg R. Hörandel University of Karlsruhe www-ik.fzk.de/~joerg New Views of
New Views of the Universe December 8 th 13 th, 2005, Chicago From the Knee to the toes: The challenge of cosmic-ray composition Jörg R. Hörandel University of Karlsruhe www-ik.fzk.de/~joerg New Views of
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 30 May 2014
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 30 May 2014 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 30 May 2014](/thumbs/95/124608543.jpg) PeV neutrinos from interactions of cosmic rays with the interstellar medium in the Galaxy A. Neronov 1, D.Semikoz 2, C.Tchernin 1 1 ISDC, Department of Astronomy, University of Geneva, Ch. d Ecogia 16,
PeV neutrinos from interactions of cosmic rays with the interstellar medium in the Galaxy A. Neronov 1, D.Semikoz 2, C.Tchernin 1 1 ISDC, Department of Astronomy, University of Geneva, Ch. d Ecogia 16,
Measurement of the cosmic ray spectrum and chemical composition in the ev energy range
 Measurement of the cosmic ray spectrum and chemical composition in the - 18 ev energy range Andrea Chiavassa 1, 1 Dipartimento di Fisica dell Universitá degli Studi di Torino & INFN Via Pietro Giuria 1,
Measurement of the cosmic ray spectrum and chemical composition in the - 18 ev energy range Andrea Chiavassa 1, 1 Dipartimento di Fisica dell Universitá degli Studi di Torino & INFN Via Pietro Giuria 1,
COSMIC-RAY ENERGY CHANGES IN THE HELIOSPHERE. II. THE EFFECT ON K-CAPTURE ELECTRON SECONDARIES
 The Astrophysical Journal, 663:1335Y1339, 2007 July 10 # 2007. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. COSMIC-RAY ENERGY CHANGES IN THE HELIOSPHERE. II. THE EFFECT ON
The Astrophysical Journal, 663:1335Y1339, 2007 July 10 # 2007. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. COSMIC-RAY ENERGY CHANGES IN THE HELIOSPHERE. II. THE EFFECT ON
The LHAASO-KM2A detector array and physical expectations. Reporter:Sha Wu Mentor: Huihai He and Songzhan Chen
 The LHAASO-KM2A detector array and physical expectations Reporter:Sha Wu Mentor: Huihai He and Songzhan Chen Outline 1. Introduction 2. The KM2A Detector Array 3. Physical Expectations 3.1 Sensitivity
The LHAASO-KM2A detector array and physical expectations Reporter:Sha Wu Mentor: Huihai He and Songzhan Chen Outline 1. Introduction 2. The KM2A Detector Array 3. Physical Expectations 3.1 Sensitivity
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 630 (20) 22 27 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/nima
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 630 (20) 22 27 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/nima
Superdiffusive and subdiffusive transport of energetic particles in astrophysical plasmas: numerical simulations and experimental evidence
 Superdiffusive and subdiffusive transport of energetic particles in astrophysical plasmas: numerical simulations and experimental evidence Gaetano Zimbardo S. Perri, P. Pommois, and P. Veltri Universita
Superdiffusive and subdiffusive transport of energetic particles in astrophysical plasmas: numerical simulations and experimental evidence Gaetano Zimbardo S. Perri, P. Pommois, and P. Veltri Universita
Cosmic Ray Acceleration by Magnetic Reconnection
 Cosmic Ray Acceleration by Magnetic Reconnection Black Hole sources are Cosmic Ray (CR) accelerators and Very High Energy (VHE) emitters AGNs (blazars, radio-galaxies, seyferts) Black Hole Binaries (Microquasars)
Cosmic Ray Acceleration by Magnetic Reconnection Black Hole sources are Cosmic Ray (CR) accelerators and Very High Energy (VHE) emitters AGNs (blazars, radio-galaxies, seyferts) Black Hole Binaries (Microquasars)
Searches for cosmic ray anisotropies at ultra-high energies
 Searches for cosmic ray anisotropies at ultra-high energies Haris Lyberis*, on behalf the Pierre Auger Collaboration * U n i v e r s i t é P a r i s V I I D e n i s d i d e r o t, P a r i s, F r a n c
Searches for cosmic ray anisotropies at ultra-high energies Haris Lyberis*, on behalf the Pierre Auger Collaboration * U n i v e r s i t é P a r i s V I I D e n i s d i d e r o t, P a r i s, F r a n c
Correlation between energetic ion enhancements and heliospheric current sheet crossings in the outer heliosphere
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L21112, doi:10.1029/2006gl027578, 2006 Correlation between energetic ion enhancements and heliospheric current sheet crossings in the
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L21112, doi:10.1029/2006gl027578, 2006 Correlation between energetic ion enhancements and heliospheric current sheet crossings in the
Topics. 1. Towards a unified picture of CRs production and propagation: 2. AMS-02 good candidates for Dark Matter space search
 Nicolò Masi Bologna University and INFN - 31 May 2016 Topics 1. Towards a unified picture of CRs production and propagation: Astrophysical uncertainties with GALPROP Local Interstellar Spectra: AMS-02
Nicolò Masi Bologna University and INFN - 31 May 2016 Topics 1. Towards a unified picture of CRs production and propagation: Astrophysical uncertainties with GALPROP Local Interstellar Spectra: AMS-02
Cosmic Accelerators. 2. Pulsars, Black Holes and Shock Waves. Roger Blandford KIPAC Stanford
 Cosmic Accelerators 2. Pulsars, Black Holes and Shock Waves Roger Blandford KIPAC Stanford Particle Acceleration Unipolar Induction Stochastic Acceleration V ~ Ω Φ I ~ V / Z 0 Z 0 ~100Ω P ~ V I ~ V 2 /Z
Cosmic Accelerators 2. Pulsars, Black Holes and Shock Waves Roger Blandford KIPAC Stanford Particle Acceleration Unipolar Induction Stochastic Acceleration V ~ Ω Φ I ~ V / Z 0 Z 0 ~100Ω P ~ V I ~ V 2 /Z
Cosmic Rays, Photons and Neutrinos
 Cosmic Rays, Photons and Neutrinos Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Introduction Outline Plan of the lectures: Cosmic rays Galactic cosmic rays Basic observations Acceleration Supernova remnants Problems
Cosmic Rays, Photons and Neutrinos Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Introduction Outline Plan of the lectures: Cosmic rays Galactic cosmic rays Basic observations Acceleration Supernova remnants Problems
Multifractal Structures Detected by Voyager 1 at the Heliospheric Boundaries
 Multifractal Structures Detected by Voyager 1 at the Heliospheric Boundaries W. M. Macek 1,2, A. Wawrzaszek 2, and L. F. Burlaga 3 Received ; accepted Submitted to Ap. J. Lett., 15 July 2014, accepted
Multifractal Structures Detected by Voyager 1 at the Heliospheric Boundaries W. M. Macek 1,2, A. Wawrzaszek 2, and L. F. Burlaga 3 Received ; accepted Submitted to Ap. J. Lett., 15 July 2014, accepted
Cosmic Rays. Discovered in 1912 by Viktor Hess using electroscopes to measure ionization at altitudes via balloon
 Cosmic Rays Discovered in 1912 by Viktor Hess using electroscopes to measure ionization at altitudes via balloon Nobel Prize in 1936 Origin of high energy cosmic rays is still not completely understood
Cosmic Rays Discovered in 1912 by Viktor Hess using electroscopes to measure ionization at altitudes via balloon Nobel Prize in 1936 Origin of high energy cosmic rays is still not completely understood
Cosmic Pevatrons in the Galaxy
 Cosmic Pevatrons in the Galaxy Jonathan Arons UC Berkeley Cosmic Rays Acceleration in Supernova Remnants Pulsar Wind Nebulae Cosmic rays Cronin, 1999, RMP, 71, S165 J(E) = AE! p, p " 2.7,1GeV < E
Cosmic Pevatrons in the Galaxy Jonathan Arons UC Berkeley Cosmic Rays Acceleration in Supernova Remnants Pulsar Wind Nebulae Cosmic rays Cronin, 1999, RMP, 71, S165 J(E) = AE! p, p " 2.7,1GeV < E
Dept. of Physics and Astronomy, Michigan State University, 567 Wilson Rd., East Lansing, MI 48824, USA
 EPJ Web of Conferences 116, 11004 (2016) DOI: 10.1051/epjconf/201611611004 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2016 Results from IceCube Tyce DeYoung a for the IceCube Collaboration Dept.
EPJ Web of Conferences 116, 11004 (2016) DOI: 10.1051/epjconf/201611611004 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2016 Results from IceCube Tyce DeYoung a for the IceCube Collaboration Dept.
HAWC Observation of Supernova Remnants and Pulsar Wind Nebulae
 HAWC Observation of Supernova Remnants and Pulsar Wind Nebulae a, and H. Zhou a for the HAWC Collaboration b a Department of Physics, Michigan Technological University 1400 Townsend Drive, Houghton, MI,
HAWC Observation of Supernova Remnants and Pulsar Wind Nebulae a, and H. Zhou a for the HAWC Collaboration b a Department of Physics, Michigan Technological University 1400 Townsend Drive, Houghton, MI,
A Multi-ion Model of the Heliosphere with Secondary Charge Exchange
 A Multi-ion Model of the Heliosphere with Secondary Charge Exchange Matthew Bedford, University of Alabama in Huntsville, Department of Space Science Nikolai Pogorelov, faculty advisor The heliosphere
A Multi-ion Model of the Heliosphere with Secondary Charge Exchange Matthew Bedford, University of Alabama in Huntsville, Department of Space Science Nikolai Pogorelov, faculty advisor The heliosphere
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 7 Nov 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 7 Nov 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 7 Nov 2018](/thumbs/89/100768182.jpg) IAUS 342: Perseus in Sicily: from black hole to cluster outskirts Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 342, 2018 Keiichi Asada, Elisabete de Gouveia Dal Pino, c 2018 International Astronomical Union Hiroshi Nagai,
IAUS 342: Perseus in Sicily: from black hole to cluster outskirts Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 342, 2018 Keiichi Asada, Elisabete de Gouveia Dal Pino, c 2018 International Astronomical Union Hiroshi Nagai,
The Escape Model. Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim. with G.Giacinti, O.Kalashev, A.Nernov, V.Savchenko, D.Semikoz
 The Escape Model Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] with G.Giacinti, O.Kalashev, A.Nernov, V.Savchenko, D.Semikoz Introduction Outline Outline of the talk 1 Introduction Results on Composition 2 Escape
The Escape Model Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] with G.Giacinti, O.Kalashev, A.Nernov, V.Savchenko, D.Semikoz Introduction Outline Outline of the talk 1 Introduction Results on Composition 2 Escape
Low-Energy Cosmic Rays
 Low-Energy Cosmic Rays Cosmic rays, broadly defined, are charged particles from outside the solar system. These can be electrons, protons, or ions; the latter two dominate the number observed. They are
Low-Energy Cosmic Rays Cosmic rays, broadly defined, are charged particles from outside the solar system. These can be electrons, protons, or ions; the latter two dominate the number observed. They are
Balloon-borne observations of the galactic positron fraction during solar minimum negative polarity
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2009ja014225, 2009 Balloon-borne observations of the galactic positron fraction during solar minimum negative polarity John Clem 1 and Paul Evenson
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2009ja014225, 2009 Balloon-borne observations of the galactic positron fraction during solar minimum negative polarity John Clem 1 and Paul Evenson
Gamma-Ray Astronomy with a Wide Field of View detector operated at Extreme Altitude in the Southern Hemisphere.
 Gamma-Ray Astronomy with a Wide Field of View detector operated at Extreme Altitude in the Southern Hemisphere., S. Miozzi, R. Santonico INFN - Rome Tor Vergata, Italy E-mail: disciascio@roma.infn.it P.
Gamma-Ray Astronomy with a Wide Field of View detector operated at Extreme Altitude in the Southern Hemisphere., S. Miozzi, R. Santonico INFN - Rome Tor Vergata, Italy E-mail: disciascio@roma.infn.it P.
Revue sur le rayonnement cosmique
 Revue sur le rayonnement cosmique Vladimir Ptuskin IZMIRAN Galactic wind termination shock GRB N cr ~ 10-10 cm -3 - total number density w cr ~ 1.5 ev/cm 3 - energy density E max ~ 3x10 20 ev - max. detected
Revue sur le rayonnement cosmique Vladimir Ptuskin IZMIRAN Galactic wind termination shock GRB N cr ~ 10-10 cm -3 - total number density w cr ~ 1.5 ev/cm 3 - energy density E max ~ 3x10 20 ev - max. detected
On the scientific motivation for a wide field-of-view TeV gamma-ray observatory in the Southern Hemisphere
 On the scientific motivation for a wide field-of-view TeV gamma-ray observatory in the Southern Hemisphere for the HAWC collaboration E-mail: miguel@psu.edu Observations of high energy gamma rays are an
On the scientific motivation for a wide field-of-view TeV gamma-ray observatory in the Southern Hemisphere for the HAWC collaboration E-mail: miguel@psu.edu Observations of high energy gamma rays are an
Recent Observations of Supernova Remnants
 1 Recent Observations of Supernova Remnants with VERITAS Tülün Ergin (U. of Massachusetts Amherst, MA) on behalf of the VERITAS Collaboration (http://veritas.sao.arizona.edu) 2 Contents Supernova Remnants
1 Recent Observations of Supernova Remnants with VERITAS Tülün Ergin (U. of Massachusetts Amherst, MA) on behalf of the VERITAS Collaboration (http://veritas.sao.arizona.edu) 2 Contents Supernova Remnants
The Physics of Fluids and Plasmas
 The Physics of Fluids and Plasmas An Introduction for Astrophysicists ARNAB RAI CHOUDHURI CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface Acknowledgements xiii xvii Introduction 1 1. 3 1.1 Fluids and plasmas in the
The Physics of Fluids and Plasmas An Introduction for Astrophysicists ARNAB RAI CHOUDHURI CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface Acknowledgements xiii xvii Introduction 1 1. 3 1.1 Fluids and plasmas in the
STATUS OF ULTRA HIGH ENERGY COSMIC RAYS
 STATUS OF ULTRA HIGH ENERGY COSMIC RAYS Esteban Roulet (Bariloche) COSMO / CosPA 2010, Tokyo Power law flux stochastic (Fermi) acceleration in shocks cosmic ray flux Small fractional energy gain after
STATUS OF ULTRA HIGH ENERGY COSMIC RAYS Esteban Roulet (Bariloche) COSMO / CosPA 2010, Tokyo Power law flux stochastic (Fermi) acceleration in shocks cosmic ray flux Small fractional energy gain after
Windows on the Cosmos
 Windows on the Cosmos Three types of information carriers about what s out there arrive on Earth: Electromagnetic Radiation Visible light, UV, IR => telescopes (Earth/Space) Radio waves => Antennae ( Dishes
Windows on the Cosmos Three types of information carriers about what s out there arrive on Earth: Electromagnetic Radiation Visible light, UV, IR => telescopes (Earth/Space) Radio waves => Antennae ( Dishes
Cosmic Rays: A Way to Introduce Modern Physics Concepts. Steve Schnetzer
 Cosmic Rays: A Way to Introduce Modern Physics Concepts Steve Schnetzer Rutgers CR Workshop May 19, 2007 Concepts Astrophysics Particle Physics Radiation Relativity (time dilation) Solar Physics Particle
Cosmic Rays: A Way to Introduce Modern Physics Concepts Steve Schnetzer Rutgers CR Workshop May 19, 2007 Concepts Astrophysics Particle Physics Radiation Relativity (time dilation) Solar Physics Particle
Space Physics: Recent Advances and Near-term Challenge. Chi Wang. National Space Science Center, CAS
 Space Physics: Recent Advances and Near-term Challenge Chi Wang National Space Science Center, CAS Feb.25, 2014 Contents Significant advances from the past decade Key scientific challenges Future missions
Space Physics: Recent Advances and Near-term Challenge Chi Wang National Space Science Center, CAS Feb.25, 2014 Contents Significant advances from the past decade Key scientific challenges Future missions
The Energetic Particle Populations of the Distant Heliosphere
 The Energetic Particle Populations of the Distant Heliosphere F. B. McDonald *, A. C. Cummings, E. C. Stone, B. C. Heikkila, N. Lal, and W. R. Webber * Institute for Physical Science and Technology, University
The Energetic Particle Populations of the Distant Heliosphere F. B. McDonald *, A. C. Cummings, E. C. Stone, B. C. Heikkila, N. Lal, and W. R. Webber * Institute for Physical Science and Technology, University
Magnetic Effects Change Our View of the Heliosheath
 Magnetic Effects Change Our View of the Heliosheath M. Opher Λ, P. C. Liewer Λ, M. Velli, T. I. Gombosi ΛΛ, W.Manchester ΛΛ,D. L. DeZeeuw ΛΛ,G.Toth ΛΛ and I. Sokolov ΛΛ Λ Jet Propulsion Laboratory, MS
Magnetic Effects Change Our View of the Heliosheath M. Opher Λ, P. C. Liewer Λ, M. Velli, T. I. Gombosi ΛΛ, W.Manchester ΛΛ,D. L. DeZeeuw ΛΛ,G.Toth ΛΛ and I. Sokolov ΛΛ Λ Jet Propulsion Laboratory, MS
Cosmic Ray Physics with ARGO-YBJ
 Cosmic Ray Physics with ARGO-YBJ Ivan De Mitri University of Salento and Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare Lecce, Italy On behalf of the ARGO-YBJ Collaboration RICAP-13 Roma International Conference
Cosmic Ray Physics with ARGO-YBJ Ivan De Mitri University of Salento and Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare Lecce, Italy On behalf of the ARGO-YBJ Collaboration RICAP-13 Roma International Conference
Highlights from ARGO-YBJ
 Highlights from ARGO-YBJ G. Di Sciascio INFN Sez. Roma Tor Vergata On behalf of the ARGO-YBJ Collaboration Vulcano Workshop 2010 May 25, 2010 The ARGO-YBJ experiment An unconventional EAS-array exploiting
Highlights from ARGO-YBJ G. Di Sciascio INFN Sez. Roma Tor Vergata On behalf of the ARGO-YBJ Collaboration Vulcano Workshop 2010 May 25, 2010 The ARGO-YBJ experiment An unconventional EAS-array exploiting
SKY-MAPS OF THE SIDEREAL ANISOTROPY OF GALACTIC COSMIC RAY INTENSITY AND ITS ENERGY DEPENDENCE
 SKY-MAPS OF THE SIDEREAL ANISOTROPY OF GALACTIC COSMIC RAY INTENSITY AND ITS ENERGY DEPENDENCE K. MUNAKATA 1, N. MATSUMOTO 1, S. YASUE 1, C. KATO 1, S. MORI 1, M. TAKITA 2, M. L. DULDIG 3, J. E. HUMBLE
SKY-MAPS OF THE SIDEREAL ANISOTROPY OF GALACTIC COSMIC RAY INTENSITY AND ITS ENERGY DEPENDENCE K. MUNAKATA 1, N. MATSUMOTO 1, S. YASUE 1, C. KATO 1, S. MORI 1, M. TAKITA 2, M. L. DULDIG 3, J. E. HUMBLE
Justin Vandenbroucke (KIPAC, Stanford / SLAC) for the Fermi LAT collaboration
 Measurement of the cosmic ray positron spectrum with the Fermi LAT using the Earth s magnetic field Justin Vandenbroucke (KIPAC, Stanford / SLAC) for the Fermi LAT collaboration International Cosmic Ray
Measurement of the cosmic ray positron spectrum with the Fermi LAT using the Earth s magnetic field Justin Vandenbroucke (KIPAC, Stanford / SLAC) for the Fermi LAT collaboration International Cosmic Ray
The Origin of the Galactic Cosmic Radiation
 The Origin of the Galactic Cosmic Radiation A White Paper submitted to the Stars and Stellar Evolution Science Panel of Astro2010 - The Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey Corresponding Author: G.
The Origin of the Galactic Cosmic Radiation A White Paper submitted to the Stars and Stellar Evolution Science Panel of Astro2010 - The Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey Corresponding Author: G.
1. New Mexico State University, Department of Astronomy, Las Cruces, NM 88003, USA
 A Comparison of the Galactic Cosmic Ray H, He and C/O Nuclei Spectra Measured Between ~5 and 500 MeV/nuc Beyond 122 AU at Voyager 1 with the Predictions of a Diffusion Model for Propagation in the Galaxy
A Comparison of the Galactic Cosmic Ray H, He and C/O Nuclei Spectra Measured Between ~5 and 500 MeV/nuc Beyond 122 AU at Voyager 1 with the Predictions of a Diffusion Model for Propagation in the Galaxy
A Search for Cosmic-ray Proton Anisotropy with the Fermi Large Area Telescope
 A Search for Cosmic-ray Proton Anisotropy with the Fermi Large Area Telescope, Justin Vandenbroucke on behalf of the Fermi-LAT Collaboration Department of Physics and Wisconsin IceCube Particle Astrophysics
A Search for Cosmic-ray Proton Anisotropy with the Fermi Large Area Telescope, Justin Vandenbroucke on behalf of the Fermi-LAT Collaboration Department of Physics and Wisconsin IceCube Particle Astrophysics
EXCESS OF VHE COSMIC RAYS IN THE CENTRAL 100 PC OF THE MILKY WAY. Léa Jouvin, A. Lemière and R. Terrier
 1 EXCESS OF VHE COSMIC RAYS IN THE CENTRAL 100 PC OF THE MILKY WAY Léa Jouvin, A. Lemière and R. Terrier 2 Excess of VHE cosmic rays (CRs) γ-ray count map Matter traced by CS 150 pc After subtracting the
1 EXCESS OF VHE COSMIC RAYS IN THE CENTRAL 100 PC OF THE MILKY WAY Léa Jouvin, A. Lemière and R. Terrier 2 Excess of VHE cosmic rays (CRs) γ-ray count map Matter traced by CS 150 pc After subtracting the
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114, A02103, doi: /2008ja013689, 2009
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008ja013689, 2009 Galactic propagation of cosmic ray nuclei in a model with an increasing diffusion coefficient at low
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008ja013689, 2009 Galactic propagation of cosmic ray nuclei in a model with an increasing diffusion coefficient at low
Measurement of the Solar Magnetic Field effect on cosmic rays using the Sun shadow observed by the ARGO-YBJ experiment
 Measurement of the Solar Magnetic Field effect on cosmic rays using the Sun shadow observed by the ARGO-YBJ experiment Key Laboratory of Particle Astrophysics, Institute of High Energy Physics, CAS, Beijing
Measurement of the Solar Magnetic Field effect on cosmic rays using the Sun shadow observed by the ARGO-YBJ experiment Key Laboratory of Particle Astrophysics, Institute of High Energy Physics, CAS, Beijing
UC Irvine UC Irvine Previously Published Works
 UC Irvine UC Irvine Previously Published Works Title Study of the Shadows of the Moon and the Sun with VHE Cosmic Rays Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/7xp0j97v Authors Atkins, R Benbow, W Berley,
UC Irvine UC Irvine Previously Published Works Title Study of the Shadows of the Moon and the Sun with VHE Cosmic Rays Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/7xp0j97v Authors Atkins, R Benbow, W Berley,
Anomalous cosmic rays in the distant heliosphere and the reversal of the Sun s magnetic polarity in Cycle 23
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L05105, doi:10.1029/2006gl028932, 2007 Anomalous cosmic rays in the distant heliosphere and the reversal of the Sun s magnetic polarity
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L05105, doi:10.1029/2006gl028932, 2007 Anomalous cosmic rays in the distant heliosphere and the reversal of the Sun s magnetic polarity
Cosmic Rays in the Dynamic Heliosphere
 J. Plasma Fusion Res. SERIES, Vol. 8 (2009) Cosmic Rays in the Dynamic Heliosphere Marius S. POTGIETER Unit for Space Physics, North-West University, 2520 Potchefstroom, South Africa (Received: 27 August
J. Plasma Fusion Res. SERIES, Vol. 8 (2009) Cosmic Rays in the Dynamic Heliosphere Marius S. POTGIETER Unit for Space Physics, North-West University, 2520 Potchefstroom, South Africa (Received: 27 August
GALACTIC COSMIC-RAY MODULATION USING A SOLAR MINIMUM MHD HELIOSPHERE: A STOCHASTIC PARTICLE APPROACH
 The Astrophysical Journal, 634:1116 1125, 2005 December 1 # 2005. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. GALACTIC COSMIC-RAY MODULATION USING A SOLAR MINIMUM MHD HELIOSPHERE:
The Astrophysical Journal, 634:1116 1125, 2005 December 1 # 2005. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. GALACTIC COSMIC-RAY MODULATION USING A SOLAR MINIMUM MHD HELIOSPHERE:
99 Years from Discovery : What is our current picture on Cosmic Rays? #6 How cosmic rays travel to Earth? Presented by Nahee Park
 99 Years from Discovery : What is our current picture on Cosmic Rays? #6 How cosmic rays travel to Earth? Presented by Nahee Park #5 How do Cosmic Rays gain their energy? I. Acceleration mechanism of CR
99 Years from Discovery : What is our current picture on Cosmic Rays? #6 How cosmic rays travel to Earth? Presented by Nahee Park #5 How do Cosmic Rays gain their energy? I. Acceleration mechanism of CR
Understanding High Energy Neutrinos
 Understanding High Energy Neutrinos Paolo Lipari: INFN Roma Sapienza NOW-2014 Conca Specchiulla 12th september 2014 An old dream is becoming a reality : Observing the Universe with Neutrinos ( A new way
Understanding High Energy Neutrinos Paolo Lipari: INFN Roma Sapienza NOW-2014 Conca Specchiulla 12th september 2014 An old dream is becoming a reality : Observing the Universe with Neutrinos ( A new way
IBEX discoveries over a half decade of observing the outer heliosphere
 IBEX discoveries over a half decade of observing the outer heliosphere David J. McComas 1,2,3 1 Southwest Research Institute, San Antonio, TX 78228, USA 2 University of Texas at San Antonio, San Antonio,
IBEX discoveries over a half decade of observing the outer heliosphere David J. McComas 1,2,3 1 Southwest Research Institute, San Antonio, TX 78228, USA 2 University of Texas at San Antonio, San Antonio,
Publications of Francesco Arneodo: journal articles
 Publications of Francesco Arneodo: journal articles Figure 1: Citation report from ISI Web of Science (IF=31.0) [1] E. Aprile et al., First Axion Results from the XENON100 Experiment, arxiv.org (submitted
Publications of Francesco Arneodo: journal articles Figure 1: Citation report from ISI Web of Science (IF=31.0) [1] E. Aprile et al., First Axion Results from the XENON100 Experiment, arxiv.org (submitted
Highlights from the ARGO-YBJ Experiment
 Highlights from the ARGO-YBJ Experiment Ivan De Mitri University of Salento and Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare Lecce, Italy On behalf of the ARGO-YBJ Collaboration 12th International Conference
Highlights from the ARGO-YBJ Experiment Ivan De Mitri University of Salento and Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare Lecce, Italy On behalf of the ARGO-YBJ Collaboration 12th International Conference
