Comet Prospects for 2010
|
|
|
- Byron Kennedy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Comet Prospects for sees a very favourable return of 103P/Hartley, which should reach naked eye visibility during a close pass to the earth in the autumn. Newly discovered comet 2009 R1 (McNaught) could reach 5 th magnitude in June, but will be low in the summer twilight. Comet 2P/Encke will be a bright object at perihelion, but is then too close to the Sun for observation from the ground. 81P/Wild should be a binocular object in the spring. Theories on the structure of comets suggest that any comet could fragment at any time, so it is worth keeping an eye on some of the fainter periodic comets, which are often ignored. This would make a useful project for CCD observers. Perhaps the most spectacular example of such fragmentation is 73P/Schwassmann-Wachmann, which exhibited a debris string of over 60 components as it passed close to the Earth in May Ephemerides for new and currently observable comets are published in the Circulars, Comet Section Newsletters and on the Section, CBAT and Seiichi Yoshida's web pages. Complete ephemerides and magnitude parameters for all comets predicted to be brighter than about 21 m are given in the International Comet Quarterly Handbook; details of subscription to the ICQ are available on the Internet. A section booklet on comet observing is available from the BAA Office. This is comet 2P/Encke's 61 st observed return to perihelion since its discovery by Mechain in The orbit is quite stable, and with a period of 3.3 years apparitions repeat on a 10-year cycle. This year it has a poor elongation prior to perihelion, but it will be visible passing through the SOHO LASCO field and that of its successors, the twin STEREO satellites in late July and early August. After perihelion the comet becomes visible from the Southern Hemisphere in mid August as a fading binocular object, and can be followed throughout September. BAA Members have been observing the comet for over 50 years and there is little evidence for a secular fading, although the comet is often brighter post perihelion than it is before. The comet is the progenitor of the Taurid meteor complex and may be associated with several Apollo asteroids. 10P/Tempel makes its 23 rd observed return since its discovery by William Tempel (Milan, Italy) as a 9 th magnitude object in Several unfavourable returns were missed in the earlier years. The orbit is very stable, which is one reason why it is a favoured target for planned spacecraft missions. In 1983 the IRAS satellite detected an extensive dust trail behind the comet. Normally the light curve is highly asymmetric with a late turn on. There is a rapid rise in brightness as perihelion approaches, which continues more slowly for a couple more weeks after perihelion, followed by a slow decline until activity switches off. With a 5.5 year period alternate returns are favourable and this is one of them, although not the best. A combination of summer twilight and a southerly declination will make viewing from the UK difficult until mid July, when it will be near its brightest at 10 th magnitude. It remains a morning object in Cetus throughout the UK apparition, slowly fading and moving south. Circumstances are better in the Southern Hemisphere and it will be visible throughout the apparition, although best in the morning sky.
2 29P/Schwassmann-Wachmann is an annual comet that has outbursts, which in recent years seem to have become more frequent. The outbursts were more or less continuous in 2008/9 and at some the comet became as bright as 10 m. The comet is an ideal target for those equipped with CCDs and it should be observed at every opportunity. The comet begins the year retrograding in Leo and reaches opposition on February 11, when it may show some additional brightening because of the small phase angle. It returns to Cancer in mid March and resumes direct motion in mid April. It is still in Cancer when UK observers will loose it in mid May. The comet passes through solar conjunction in late August and will emerge into the morning sky in Leo in late October. It crosses the celestial equator in early December, and remains a morning object at the end of the year. 81P/Wild is a new comet that made a very close (0.006 AU) approach to Jupiter in Prior to this it was in a 40 year orbit that had perihelion at 5 AU and aphelion at 25 AU. The comet was discovered by Paul Wild with the 40/60-cm Schmidt at Zimmerwald on 1978 January 6. The Stardust spacecraft visited it in 2004 and the recovered material was returned to earth in 2006, throwing more light on the origin of comets. The 2010 return is a good one and the comet should be visible in binoculars at around 9 th magnitude when at its brightest in March. It is a good apparition for UK observers, starting the year as a 10 th magnitude morning object in Virgo and will remain in that constellation until lost in the mid-summer twilight. In 1982 comet 103P/Hartley made a close approach to Jupiter, and it was discovered by Hartley four years later, around nine months after perihelion. It was accidentally recovered by T V Kryachko of Majdanak, USSR, on 1991 July 9.85, returning 5.6 days earlier than predicted. It was well observed by the section at this return and observations showed that the brightness peaked around 13 days after perihelion. The 1997 return was also good, with the comet peaking at 8 th magnitude, but the 2004 return was poor. This return is exceptionally good and the comet will pass only AU from the Earth on October If it behaves similarly to previous returns it should be recovered visually in July or August and will be a well placed binocular object in Cygnus in September. Remaining in Cygnus for most of October, it should be visible to the naked eye throughout October and into November as it fades and still be visible in telescopes as a 10 th magnitude object at the end of the year. The orbit comes close to that of the Earth and it could produce a meteor shower at the descending node in November. Calculations by Harold Ridley gave a radiant of 19h56m +14, some 5 Nf Altair, with a likely maximum around November 17, however Robert McNaught gave 19h50m +29 around November 2. No meteors were seen at the favourable return in 1997 and later calculations suggest that there are no favourable encounters with likely dust trails until Donald Machholz discovered 141P/Machholz with his 0.25-m reflector at 10 m in August It proved to have multiple components, first reported by Michael Jager (Vienna, Austria). The four secondary components could all be described by the same orbit, but with perihelion delayed by up to half a day from the primary. At times there seemed to be a faint trail of material linking the components. The comet has a short period of 5.2 years with a perihelion distance of 0.75 AU and aphelion just inside the orbit of Jupiter. The orbit has been slowly evolving, with progressive changes occurring about every 50 years, thanks to approaches to Jupiter. The most recent close
3 approach was in With a relatively stable perihelion distance, which is slowly increasing, it is perhaps surprising that the comet was not discovered earlier. There was a favourable return in winter of 1978/79 when it might have reached 8 th magnitude and very favourable returns in the autumns of 1920, 1936 and 1957 when it might have reached 6 th magnitude. The fact that it was not discovered at any of these returns suggests that the absolute magnitude at the 1994 return was not typical, and was the result of the fragmentation. At present the earth passes about 0.25 AU outside the descending node and the orbital evolution will slowly decrease this distance, raising the possibility of meteor shower from the comet in a few hundred years time. The main component of the comet (A) again reached 10 th magnitude in 1999, with the secondary (D) at least a magnitude fainter, but the last return was unfavourable and only component A was recovered. This is a very poor return and visual observations are very unlikely. 157P/Tritton was discovered by Keith Tritton in 1978 when working on the Southern UK Schmidt Sky Survey. The comet was only observed over a very short arc and it was very faint at discovery. The first return was very unfavourable, so it couldn't be seen, and the orbital inaccuracy was so large that the predictions for the second return had huge uncertainties and it was lost. In October 2003 Paulo Holvorcem reported that Charles Juels had found a fast moving cometary object at around 12 th magnitude and this was confirmed by other observers. Following suggestions from Sebastian Hoenig, based on computations by Maik Meyer, Brian Marsden was able to confirm the identity with comet D/1978 (Tritton). The linkage showed that the period estimated from the 1978 apparition was incorrect and so the early searches were perhaps doomed to failure. The brightness in 2003 suggested that the object was in outburst and its future brightness is uncertain. Comet 2009 K5 (McNaught) is another of the many comets discovered by Rob McNaught during the course of the Siding Spring Survey. The comet could reach 10 th magnitude in late April. It moves out from conjunction into the morning sky in late February as an 11 th magnitude object and becomes circumpolar by mid April. It fades slowly, but remains relatively well placed in the northern sky until July. Comet 2009 O2 (Catalina) was discovered during the Catalina Sky Survey, but not immediately recognised as a comet until verified by other observers. It emerges from solar conjunction in late February at 12 th magnitude and could reach 9 th magnitude by the equinox, when it passes north of M31. Thereafter it heads south and UK observers will loose it by late April, by which time it will have faded to 11 th magnitude. Comet 2009 R1 (McNaught) was Rob s 51 st discovery and promises to be an easily observable comet, though it will be low in the summer twilight when at its brightest. It emerges from solar conjunction relatively slowly and it will already be 9 th magnitude before UK observers pick it up in late May. It brightens rapidly and moves into the evening sky, however it is never high in the sky. The best viewing will probably be around mid June, when it is highest in a moonless sky, though it will brighten another magnitude by the time we loose it at the end of the month. A couple of SOHO comets are predicted to return, and although both objects have been seen at two returns, the exact linkages of these members of the Marsden family of
4 comets remain a little uncertain. Here I use a provisional numbering scheme for the periodic SOHO objects, as none has yet been introduced by the IAU. This follows the scheme for periodic comets that are known to return, and I number them in order of discovery of the second member of any pairings. A more permanent numbering scheme is also needed, although with incomplete SOHO coverage and cascading fragmentation this is difficult. M01 is 1999 J6 and 2004 V9, which split to give a minor component 2004 V10. M02 is 1999 N5, which split to give 2005 E4 (M02A), which returns in 2010 and 2005 G2 (M02B), which returns in Both M01 and M02 themselves probably split from a progenitor that was at perihelion in 1993 November. The other periodic and parabolic comets that are at perihelion during 2010 are unlikely to become brighter than 12 th magnitude or are poorly placed. Ephemerides for these can be found on the CBAT WWW pages. D/van Houten was observed for just over a month in 1960, but was not recovered at the two subsequent returns. D/Haneda- Campos was observed for four months at its discovery apparition, but was not recovered at the four subsequent returns. Searches at favourable returns in the intervening period have failed to reveal the comets and it is possible that they are no longer active. Looking ahead to 2011 rather fewer comets make good returns, however comet 2009 P1 (Garradd) might reach 7 th magnitude at the end of the year. 45P/Honda-Mrkos- Pajdusakova makes a close pass to the earth and will be well placed in the Southern Hemisphere prior to perihelion in September and in the north post perihelion. 73P/Schwassmann-Wachmann also returns, but it is not clear how many of the multiple fragments will be visible and even the brightest is likely to be fainter than 12 th magnitude. P/Levy (2006 T1) may reach 9 th magnitude at the end of the year. Comets reaching perihelion in 2010 Comet T q P N H 1 K 1 Peak mag Hill (2009 O4) Jan P/Shoemaker-Levy Jan LINEAR (2009 T3) Jan P/Gehrels Jan P/La Sagra (2009 T2) Jan P/LINEAR-NEAT (2009 Q2) Jan Catalina (2009 K2) Feb P/Korlevic Feb Boattini (2009 P2) Feb P/Mueller Feb P/Tritton Feb P/Wild Feb P/IRAS Feb P/McNaught (2004 R1) Feb P/Gunn Mar P/LINEAR Mar P/Siding Spring Mar Hill (2009 U3) Mar Catalina (2009 O2) Mar P/LINEAR-Skiff (2001 R6) Mar P/Russell Mar P/Reinmuth Apr Spacewatch (2007 VO 5 ) Apr
5 McNaught (2009 K5) Apr M01P/SOHO May P/Kowal May P-Machholz-A May P-Machholz-D May ? 142P/Ge-Wang May D/Haneda-Campos (1978 R1) Jun ? 215P/NEAT Jun P/Wolf-Harrington Jul McNaught (2009 R1) Jul P/Tempel Jul Garradd (2009 U1) Jul P/LINEAR (1999 U3) Jul P/Encke Aug P/Skiff (2009 L18) Aug P/Catalina-LINEAR (2009 S4) Sep P/LINEAR (2002 UY 215 ) Sep P/Schwassmann-Wachmann Sep Lemmon-Siding Spring (2008 FK 7 ) Sep P/NEAT (2002 X2) Oct D/van Houten (1960 S1) Oct ? 103P/Hartley Oct M02AP/SOHO Oct P/LINEAR (2000 G1) Nov P/LINEAR (2004 HC 18 ) Dec Grauer (2009 U5) Aug The date of perihelion (T), perihelion distance (q), period (P), the number of previously observed returns (N), the magnitude parameters H 1 and K 1 and the brightest magnitude (which must be regarded as uncertain) are given for each comet. D/Haneda-Campos and D/van Houten have not been seen for several returns. The orbit of D/ van Houten is based on only 8 observations and other predictions suggest a possible return in Note: m 1 = H * log(d) + K 1 * log(r) References and sources Belyaev, N. A., Kresak, L., Pittich, E. M. and Pushkarev, A. N., Catalogue of short Period Comets, Bratislava (1986). Kozlov, E. A., Medvedev, Y. D., Pittichova, J., and Pittich, E. M. Catalogue of short Period Comets, 2 nd edition, ( (2003). Kronk, G. W., Cometographia, Cambridge University Press, (1999, 2004, 2007) and Marsden, B. G. and Williams, G. V. Catalogue of Cometary Orbits, 17th edition, IAU MPC/CBAT, (2008). Minor Planet Circulars Nakano Notes at Nakano, S. and Green D. W. E., Eds, International Comet Quarterly 2009 Comet Handbook, (2009). Shanklin, J. D., Observing Guide to Comets, 2 nd edition (2002) Jonathan Shanklin
Comet Prospects for 2013
 Comet Prospects for 2013 2013 has the prospect of two naked eye comets, but shows little promise for the return of periodic comets. Only two periodic comets are likely to be readily visible, but one is
Comet Prospects for 2013 2013 has the prospect of two naked eye comets, but shows little promise for the return of periodic comets. Only two periodic comets are likely to be readily visible, but one is
Comet Prospects for 2018
 Comet Prospects for 2018 Of the three periodic comets that should come into binocular range, two may be visible to the naked eye. The other is a Halley type comet last seen at its 1980 return, which is
Comet Prospects for 2018 Of the three periodic comets that should come into binocular range, two may be visible to the naked eye. The other is a Halley type comet last seen at its 1980 return, which is
Comets, quasi-comets and the Comet Section. Jonathan Shanklin Director, BAA Comet Section
 Comets, quasi-comets and the Comet Section Jonathan Shanklin Director, BAA Comet Section BAA founded 1890 Comet Section formed 1891 Around 40,000 observations Virtually all extant observations are post
Comets, quasi-comets and the Comet Section Jonathan Shanklin Director, BAA Comet Section BAA founded 1890 Comet Section formed 1891 Around 40,000 observations Virtually all extant observations are post
Professor Comet Report. March The Bright Comets for 2010!
 Professor Comet Report March 2010 The Bright Comets for 2010! C/2009 K5 (McNaught) This comet is currently bright at a visual magnitude of 9.1 and expected to reach visual Mag 8.8 by 27 March 2010. Then
Professor Comet Report March 2010 The Bright Comets for 2010! C/2009 K5 (McNaught) This comet is currently bright at a visual magnitude of 9.1 and expected to reach visual Mag 8.8 by 27 March 2010. Then
So it is possibly a new visitor from the Oort cloud way out on the outer fringes of the solar system.
 Comet CATALINA C/2013 US10 Dave Eagle FRAS. This December starts what could be a very nice apparition of a reasonably bright comet in our northerly skies. Maps of the comets path at the end of this article.
Comet CATALINA C/2013 US10 Dave Eagle FRAS. This December starts what could be a very nice apparition of a reasonably bright comet in our northerly skies. Maps of the comets path at the end of this article.
Astronomical events in 2018
 La Société Guernesiaise Astronomy Section Astronomical events in 2018 as seen from Guernsey compiled by David Le Conte This year sees a very favourable opposition of Mars on 27 July and, on the same day,
La Société Guernesiaise Astronomy Section Astronomical events in 2018 as seen from Guernsey compiled by David Le Conte This year sees a very favourable opposition of Mars on 27 July and, on the same day,
A Tail of Two Comets. by Paul Robinson. PanSTARRS and ISON
 A Tail of Two Comets by Paul Robinson PanSTARRS and ISON Comet PanSTARRS 2011-L4 Panoramic Survey Telescope And Rapid Response System Perihelion March 10, 2013: 0.30 AU from sun. Only about 3 weeks away!!
A Tail of Two Comets by Paul Robinson PanSTARRS and ISON Comet PanSTARRS 2011-L4 Panoramic Survey Telescope And Rapid Response System Perihelion March 10, 2013: 0.30 AU from sun. Only about 3 weeks away!!
Earth & Beyond Teacher Newsletter
 Paul Floyd s Astronomy & Space Website Earth & Beyond Teacher Newsletter www.nightskyonline.info Earth & Beyond Teaching opportunities for 2012 This special edition has been prepared to assist you with
Paul Floyd s Astronomy & Space Website Earth & Beyond Teacher Newsletter www.nightskyonline.info Earth & Beyond Teaching opportunities for 2012 This special edition has been prepared to assist you with
Special Report 2016! A Tale of Two Comets
 Special Report 2016! A Tale of Two Comets On the third and final full week of March 2016 (the dates of 20 th 26 th ) there are two comets on a perihelion approach to the Earth on the nights of 21 23 March
Special Report 2016! A Tale of Two Comets On the third and final full week of March 2016 (the dates of 20 th 26 th ) there are two comets on a perihelion approach to the Earth on the nights of 21 23 March
The Professor Comet s Report. Early Autumn October 2011
 1 Mr. Justin J McCollum (BS, MS Physics) Lab Physics Coordinator Dept. of Physics Lamar University Chris Cook (www.abmedia.com/astro/comets), 2011. Welcome to the comet report which is a monthly article
1 Mr. Justin J McCollum (BS, MS Physics) Lab Physics Coordinator Dept. of Physics Lamar University Chris Cook (www.abmedia.com/astro/comets), 2011. Welcome to the comet report which is a monthly article
Friday April 21, :30 MDT (7:30 pm) All TAAS and other new and not so new astronomers are invited. Ursa Major. Photo Courtesy of Naoyuki Kurita
 TAAS Fabulous Fifty Friday April 21, 2017 19:30 MDT (7:30 pm) Ursa Major Photo Courtesy of Naoyuki Kurita All TAAS and other new and not so new astronomers are invited Evening Events 7:30 pm Meet inside
TAAS Fabulous Fifty Friday April 21, 2017 19:30 MDT (7:30 pm) Ursa Major Photo Courtesy of Naoyuki Kurita All TAAS and other new and not so new astronomers are invited Evening Events 7:30 pm Meet inside
Astronomy Club of Asheville January 2016 Sky Events
 January 2016 Sky Events The Planets this Month - page 2 Planet Highlights - page 7 All 5 Naked-Eye Planets in the Dawn Sky - page 10 Moon Phases - page 11 Earth Reaches Perihelion on Jan. 4 - page 12 Quadrantid
January 2016 Sky Events The Planets this Month - page 2 Planet Highlights - page 7 All 5 Naked-Eye Planets in the Dawn Sky - page 10 Moon Phases - page 11 Earth Reaches Perihelion on Jan. 4 - page 12 Quadrantid
Physics Lab #4: Learning Starry Night, Part 3
 Physics 10293 Lab #4: Learning Starry Night, Part 3 Introduction In this lab, we will continue using Starry Night to explore some of the most important concepts we will cover in lecture. Continue with
Physics 10293 Lab #4: Learning Starry Night, Part 3 Introduction In this lab, we will continue using Starry Night to explore some of the most important concepts we will cover in lecture. Continue with
Astronomy Club of Asheville April 2017 Sky Events
 April 2017 Sky Events The Planets this Month page 2 April 6 th - Regulus and the Gibbous Moon page 5 April 10 th -The Full Moon Joins Jupiter and Spica page 6 Planet Highlights page 7 Moon Phases page
April 2017 Sky Events The Planets this Month page 2 April 6 th - Regulus and the Gibbous Moon page 5 April 10 th -The Full Moon Joins Jupiter and Spica page 6 Planet Highlights page 7 Moon Phases page
Abstract. 2.1 Random Meteors. Chapter 2. Sporadic Meteors
 Chapter 2 Abstract It turns out that some sporadic meteors are not so random after all. There are groups of nonshower meteors that encounter Earth on a daily basis, adding a few meteors per hour to the
Chapter 2 Abstract It turns out that some sporadic meteors are not so random after all. There are groups of nonshower meteors that encounter Earth on a daily basis, adding a few meteors per hour to the
Introduction to the sky
 Introduction to the sky On a clear, moonless night, far from city lights, the night sky is magnificent. Roughly 2000 stars are visible to the unaided eye. If you know where to look, you can see Mercury,
Introduction to the sky On a clear, moonless night, far from city lights, the night sky is magnificent. Roughly 2000 stars are visible to the unaided eye. If you know where to look, you can see Mercury,
The Night Sky in May, 2017
 The Night Sky in May, 2017 The dominating object in the sky this month is the planet Jupiter. It was at opposition on April 7 th when it was on the opposite side of the Earth from the Sun and was at its
The Night Sky in May, 2017 The dominating object in the sky this month is the planet Jupiter. It was at opposition on April 7 th when it was on the opposite side of the Earth from the Sun and was at its
Deep Impact Continued Investigations (DI3) Tony Farnham
 Deep Impact Continued Investigations (DI3) Tony Farnham Deep Impact Spacecraft Medium Resolution Imager (MRI) 8 broad and narrowband filters OH, CN, C2 and continuum 10 µrad/pix High Resolution Imager
Deep Impact Continued Investigations (DI3) Tony Farnham Deep Impact Spacecraft Medium Resolution Imager (MRI) 8 broad and narrowband filters OH, CN, C2 and continuum 10 µrad/pix High Resolution Imager
Astronomy Club of Asheville March 2018 Sky Events
 March 2018 Sky Events The Planets this Month - page 2 Close Conjunction of Venus and Mercury page 5 The Crescent Moon Joins Venus and Mercury page 6 A Crescent Moon Pairs with Aldebaran page 7 Planet Highlights
March 2018 Sky Events The Planets this Month - page 2 Close Conjunction of Venus and Mercury page 5 The Crescent Moon Joins Venus and Mercury page 6 A Crescent Moon Pairs with Aldebaran page 7 Planet Highlights
Astrochart Links: Pennsic 43: coming July 25
 Astrochart Links: Pennsic 43: coming July 25 Here are the views of the sky each night of Pennsic XLIII, July & August 2014. Stars begin to come out half an hour after sunset, around 9 o'clock to half past,
Astrochart Links: Pennsic 43: coming July 25 Here are the views of the sky each night of Pennsic XLIII, July & August 2014. Stars begin to come out half an hour after sunset, around 9 o'clock to half past,
Astronomical Events for 2018 (compiled from Astropixels.com and RASC Observer s Handbook)
 Astronomical Events for 2018 (compiled from Astropixels.com and RASC Observer s Handbook) Date EST Event (h:m) JANUARY Jan 01 Mon 15:00 Mercury at Greatest Elongation 22.7 W 01 Mon 16:54 Moon at Perigee:
Astronomical Events for 2018 (compiled from Astropixels.com and RASC Observer s Handbook) Date EST Event (h:m) JANUARY Jan 01 Mon 15:00 Mercury at Greatest Elongation 22.7 W 01 Mon 16:54 Moon at Perigee:
Astronomical Events 2019 (edited somewhat) from:
 Astronomical Events 2019 (edited somewhat) from: http://astropixels.com/ephemeris/astrocal/astrocal2019gmt.html January Note: Time column is UT, subtract 5 hours for local EST, 4 hours for DST Jan 1 to
Astronomical Events 2019 (edited somewhat) from: http://astropixels.com/ephemeris/astrocal/astrocal2019gmt.html January Note: Time column is UT, subtract 5 hours for local EST, 4 hours for DST Jan 1 to
Astronomy Club of Asheville November 2017 Sky Events
 November 2017 Sky Events The Planets this Month page 2 Close Conjunction of Venus and Jupiter page 7 Conjunction of Crescent Moon, Saturn & Mercury page 8 Planet Highlights page 9 Moon Phases page 12 November
November 2017 Sky Events The Planets this Month page 2 Close Conjunction of Venus and Jupiter page 7 Conjunction of Crescent Moon, Saturn & Mercury page 8 Planet Highlights page 9 Moon Phases page 12 November
Sky views October 2007 revised 10/8/07 (excerpted from Astronomy magazine, 10/2007 issue) by Barbara Wiese
 Sky views October 2007 revised 10/8/07 (excerpted from Astronomy magazine, 10/2007 issue) by Barbara Wiese Monthly Overview - Views by Date Definitions Overview Viewing Notes Jupiter in Ophiuchus Neptune
Sky views October 2007 revised 10/8/07 (excerpted from Astronomy magazine, 10/2007 issue) by Barbara Wiese Monthly Overview - Views by Date Definitions Overview Viewing Notes Jupiter in Ophiuchus Neptune
Lecture 2 Motions in the Sky September 10, 2018
 1 Lecture 2 Motions in the Sky September 10, 2018 2 What is your year in school? A. New freshman B. Returning freshman C. Sophomore D. Junior E. Senior F. I ve been here, like, forever 3 What is your major?
1 Lecture 2 Motions in the Sky September 10, 2018 2 What is your year in school? A. New freshman B. Returning freshman C. Sophomore D. Junior E. Senior F. I ve been here, like, forever 3 What is your major?
Deep Impact hit by 9P/Tempel
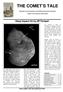 THE COMET S TALE Newsletter of the Comet Section of the British Astronomical Association Volume 12, No 2 (Issue 24), 2005 October The Deep Impact (DI) mission has returned spectacular images of 9P/Tempel,
THE COMET S TALE Newsletter of the Comet Section of the British Astronomical Association Volume 12, No 2 (Issue 24), 2005 October The Deep Impact (DI) mission has returned spectacular images of 9P/Tempel,
Name: Class: Date: ID: A
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ Astro Quiz 2 (ch2) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Star A has an apparent visual magnitude of 13.4 and star B has
Name: Class: _ Date: _ Astro Quiz 2 (ch2) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Star A has an apparent visual magnitude of 13.4 and star B has
Comets in the sky in 2014
 Comets in the sky in 2014 As of July 2013 there were 4,894 known comets, and this number is steadily increasing. However, this represents only a tiny fraction of the total potential comet population, as
Comets in the sky in 2014 As of July 2013 there were 4,894 known comets, and this number is steadily increasing. However, this represents only a tiny fraction of the total potential comet population, as
Observing Meteor Showers
 Observing Meteor Showers The Solar System is a dynamic arrangement of planets, dwarf planets and small solar-system bodies in orbit around the Sun. However, solid bodies much smaller than asteroids and
Observing Meteor Showers The Solar System is a dynamic arrangement of planets, dwarf planets and small solar-system bodies in orbit around the Sun. However, solid bodies much smaller than asteroids and
5 - Seasons. Figure 1 shows two pictures of the Sun taken six months apart with the same camera, at the same time of the day, from the same location.
 ASTR 110L 5 - Seasons Purpose: To plot the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. What do you think? Write answers to questions
ASTR 110L 5 - Seasons Purpose: To plot the distance of the Earth from the Sun over one year and to use the celestial sphere to understand the cause of the seasons. What do you think? Write answers to questions
JEWELS of the COSMIC DEEP Messier's first guide to the night sky
 JEWELS of the COSMIC DEEP Messier's first guide to the night sky Shane L. Larson USU Physics & Cache Valley Stargazers s.larson@usu.edu Cache Valley Stargazers 12 March 2010 M78 IN ORION 1 Storyline What
JEWELS of the COSMIC DEEP Messier's first guide to the night sky Shane L. Larson USU Physics & Cache Valley Stargazers s.larson@usu.edu Cache Valley Stargazers 12 March 2010 M78 IN ORION 1 Storyline What
TAAS Fabulous Fifty. Friday July 14, MDT (8:00 pm) All TAAS and other new and not so new astronomers are invited.
 TAAS Fabulous Fifty Scorpius Friday July 14, 2017 2000 MDT (8:00 pm) All TAAS and other new and not so new astronomers are invited Photo Courtesy of Naoyuki Kurita Evening Events 8:00 pm Meet inside the
TAAS Fabulous Fifty Scorpius Friday July 14, 2017 2000 MDT (8:00 pm) All TAAS and other new and not so new astronomers are invited Photo Courtesy of Naoyuki Kurita Evening Events 8:00 pm Meet inside the
DiggingIntoComets. Student Workbook. A lesson on the role of comets in our Solar System
 A lesson on the role of comets in our Solar System Student Workbook appropriate for ages 12 and up keywords: comets, Kuiper Belt, minor planets, Oort Cloud, orbit, Solar System, water A product of Inspiring
A lesson on the role of comets in our Solar System Student Workbook appropriate for ages 12 and up keywords: comets, Kuiper Belt, minor planets, Oort Cloud, orbit, Solar System, water A product of Inspiring
Mars Opposition Friday 27 th July 2018
 Mars Opposition Friday 27 th July 2018 Mars is about 6,780 kilometres in diameter or roughly half the size of the Earth whose diameter is 12,742km. As they orbit the Sun, the minimum distance between the
Mars Opposition Friday 27 th July 2018 Mars is about 6,780 kilometres in diameter or roughly half the size of the Earth whose diameter is 12,742km. As they orbit the Sun, the minimum distance between the
Explore the Universe Observing Certificate and Pin #3
 Explore the Universe Observing Certificate and Pin #3 Lunar Phases (4 of 8) Waxing Crescent Day 3 seen within 3h of sunset First Quarter within +- 18 hours Waxing Gibbous 3-4 days after First Quarter Full
Explore the Universe Observing Certificate and Pin #3 Lunar Phases (4 of 8) Waxing Crescent Day 3 seen within 3h of sunset First Quarter within +- 18 hours Waxing Gibbous 3-4 days after First Quarter Full
Astronomy Club of Asheville December 2017 Sky Events
 December 2017 Sky Events The Planets this Month - page 2 December 13-16 Crescent Moon with Jupiter and Mars page 8 Planet Highlights - page 9 Moon Phases - page 12 December 13 th Geminid Meteor Shower
December 2017 Sky Events The Planets this Month - page 2 December 13-16 Crescent Moon with Jupiter and Mars page 8 Planet Highlights - page 9 Moon Phases - page 12 December 13 th Geminid Meteor Shower
The Professor Comet s Report. Early Spring April 2012
 1 Mr. Justin J McCollum (BS, MS Physics) Lab Physics Coordinator Dept. of Physics Lamar University Welcome to the comet report which is a monthly article on the observations of comets by the amateur astronomy
1 Mr. Justin J McCollum (BS, MS Physics) Lab Physics Coordinator Dept. of Physics Lamar University Welcome to the comet report which is a monthly article on the observations of comets by the amateur astronomy
C:/comets/Comets Page/ Letter. The Impending Demise of Comet C/2012 S1 ISON
 1 C:/comets/Comets Page/131002 Letter The Impending Demise of Comet C/2012 S1 ISON Ignacio Ferrín, Institute of Physics, Faculty of Exact and Natural Sciences, University of Antioquia, Medellin, Colombia,
1 C:/comets/Comets Page/131002 Letter The Impending Demise of Comet C/2012 S1 ISON Ignacio Ferrín, Institute of Physics, Faculty of Exact and Natural Sciences, University of Antioquia, Medellin, Colombia,
John Hopkins, Editor. Index
 John Hopkins, Editor Index Abraham Lincoln and the Almanac Defense Volume 13, Issue 4 October December, 2013 Amateur Astronomer Makes a Discovery, an Impact Spot on Jupiter Volume 9, Issue 4 October December,
John Hopkins, Editor Index Abraham Lincoln and the Almanac Defense Volume 13, Issue 4 October December, 2013 Amateur Astronomer Makes a Discovery, an Impact Spot on Jupiter Volume 9, Issue 4 October December,
A search for main-belt comets in the Palomar Transient Factory survey
 A search for main-belt comets in the Palomar Transient Factory survey ADAM WASZCZAK 1, ERAN O. OFEK 2, ODED AHARONSON 1,3, SHRINIVAS R. KULKARNI 4, DAVID POLISHOOK 5,JAMES M. BAUER 6, DAVID B. LEVITAN
A search for main-belt comets in the Palomar Transient Factory survey ADAM WASZCZAK 1, ERAN O. OFEK 2, ODED AHARONSON 1,3, SHRINIVAS R. KULKARNI 4, DAVID POLISHOOK 5,JAMES M. BAUER 6, DAVID B. LEVITAN
TILT, DAYLIGHT AND SEASONS WORKSHEET
 TILT, DAYLIGHT AND SEASONS WORKSHEET Activity Description: Students will use a data table to make a graph for the length of day and average high temperature in Utah. They will then answer questions based
TILT, DAYLIGHT AND SEASONS WORKSHEET Activity Description: Students will use a data table to make a graph for the length of day and average high temperature in Utah. They will then answer questions based
Seasons ASTR 101 2/12/2018
 Seasons ASTR 101 2/12/2018 1 What causes the seasons? Perihelion: closest to Sun around January 4 th Northern Summer Southern Winter 147 million km 152 million km Aphelion (farthest to Sun) around July
Seasons ASTR 101 2/12/2018 1 What causes the seasons? Perihelion: closest to Sun around January 4 th Northern Summer Southern Winter 147 million km 152 million km Aphelion (farthest to Sun) around July
Think about. Aug. 13, What is science?
 Think about Aug. 13, 2018 What is science? Science Science is both a body of knowledge and a process for building that body of knowledge. This involves inquiry, that is, developing explanations for why
Think about Aug. 13, 2018 What is science? Science Science is both a body of knowledge and a process for building that body of knowledge. This involves inquiry, that is, developing explanations for why
Calculations Equation of Time. EQUATION OF TIME = apparent solar time - mean solar time
 Calculations Equation of Time APPARENT SOLAR TIME is the time that is shown on sundials. A MEAN SOLAR DAY is a constant 24 hours every day of the year. Apparent solar days are measured from noon one day
Calculations Equation of Time APPARENT SOLAR TIME is the time that is shown on sundials. A MEAN SOLAR DAY is a constant 24 hours every day of the year. Apparent solar days are measured from noon one day
The Night Sky in September, 2018
 The Night Sky in September, 2018 Hello all! Welcome to the September Newsletter! September is usually recognised by astronomers as the beginning of the observing year. Here s hoping for some warm nights
The Night Sky in September, 2018 Hello all! Welcome to the September Newsletter! September is usually recognised by astronomers as the beginning of the observing year. Here s hoping for some warm nights
Exploring the Night Sky
 Lincoln Hills Astronomy Group Exploring the Night Sky October 14, 2009 1 Lincoln Hills Astronomy Group Exploring the Night Sky Objectives Learn how to locate and identify objects in the night sky using
Lincoln Hills Astronomy Group Exploring the Night Sky October 14, 2009 1 Lincoln Hills Astronomy Group Exploring the Night Sky Objectives Learn how to locate and identify objects in the night sky using
Astronomy Club of Asheville June 2018 Sky Events
 June 2018 Sky Events The Planets this Month - page 2 June 14 th Dusk s Venus, Mercury and a Sliver of Moon page 5 June 27 th Conjunction of the Full Moon with Saturn page 6 Planet Highlights - page 7 Moon
June 2018 Sky Events The Planets this Month - page 2 June 14 th Dusk s Venus, Mercury and a Sliver of Moon page 5 June 27 th Conjunction of the Full Moon with Saturn page 6 Planet Highlights - page 7 Moon
C:/comets/Comets Page/ Letter. The Impending Demise of Comet C/2012 S1 ISON
 1 C:/comets/Comets Page/131001 Letter The Impending Demise of Comet C/2012 S1 ISON Ignacio Ferrín, Institute of Physics, Faculty of Exact and Natural Sciences, University of Antioquia, Medellín, Colombia,
1 C:/comets/Comets Page/131001 Letter The Impending Demise of Comet C/2012 S1 ISON Ignacio Ferrín, Institute of Physics, Faculty of Exact and Natural Sciences, University of Antioquia, Medellín, Colombia,
WHAT'S UP THIS MONTH MAY 2018
 WHAT'S UP THIS MONTH MAY 2018 THESE PAGES ARE INTENDED TO HELP YOU FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE SKY The chart on the last page is included for printing off and use outside The chart above shows the whole night
WHAT'S UP THIS MONTH MAY 2018 THESE PAGES ARE INTENDED TO HELP YOU FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE SKY The chart on the last page is included for printing off and use outside The chart above shows the whole night
Aside from my last lecture: my solar cooker!
 Aside from my last lecture: my solar cooker! Don t forget to turn in homework. Bring star wheel on Wed! Remember, no class next Monday, Nov 11, Veteran s day Wed Nov 13: second Kitt Peak trip: many more
Aside from my last lecture: my solar cooker! Don t forget to turn in homework. Bring star wheel on Wed! Remember, no class next Monday, Nov 11, Veteran s day Wed Nov 13: second Kitt Peak trip: many more
The Night Sky in August, 2018
 The Night Sky in August, 2018 An interesting bit of news this month is that 12 new moons have been found in orbit around Jupiter! This brings the total number to 79 instead of a mere 67! The new moons
The Night Sky in August, 2018 An interesting bit of news this month is that 12 new moons have been found in orbit around Jupiter! This brings the total number to 79 instead of a mere 67! The new moons
Earth Motions Packet 14
 Earth Motions Packet 14 Your Name Group Members Score Minutes Standard 4 Key Idea 1 Performance Indicator 1.1 Explain complex phenomena, such as tides, variations in day length, solar insolation, apparent
Earth Motions Packet 14 Your Name Group Members Score Minutes Standard 4 Key Idea 1 Performance Indicator 1.1 Explain complex phenomena, such as tides, variations in day length, solar insolation, apparent
Comet Lovejoy (C/2011 W3)
 1 Comet Lovejoy (C/2011 W3) Mr. Justin J McCollum (BS, MS Physics) Lab Physics Coordinator Dept. of Physics Lamar University Lovejoy emerging from the Corona Dec 16 2011 Courtesy of SDO/NASA Welcome to
1 Comet Lovejoy (C/2011 W3) Mr. Justin J McCollum (BS, MS Physics) Lab Physics Coordinator Dept. of Physics Lamar University Lovejoy emerging from the Corona Dec 16 2011 Courtesy of SDO/NASA Welcome to
6 The Orbit of Mercury
 6 The Orbit of Mercury Name: Date: Of the five planets known since ancient times (Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn), Mercury is the most difficult to see. In fact, of the 6 billion people on the
6 The Orbit of Mercury Name: Date: Of the five planets known since ancient times (Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn), Mercury is the most difficult to see. In fact, of the 6 billion people on the
Top 8 Must-See Sky Events for 2018
 Top 8 Must-See Sky Events for 2018 Get ready to see amazing eclipses, a comet encounter, planetary pairings, and more celestial wonders. A shadow falls across the face of the moon during a lunar eclipse.
Top 8 Must-See Sky Events for 2018 Get ready to see amazing eclipses, a comet encounter, planetary pairings, and more celestial wonders. A shadow falls across the face of the moon during a lunar eclipse.
Planetary Science Update. David Schurr Deputy Director Planetary Science July 23, 2014
 Planetary Science Update David Schurr Deputy Director Planetary Science July 23, 2014 Outline Planetary upcoming mission events Recent accomplishments Use of Astrophysics Telescopes R&A status Planetary
Planetary Science Update David Schurr Deputy Director Planetary Science July 23, 2014 Outline Planetary upcoming mission events Recent accomplishments Use of Astrophysics Telescopes R&A status Planetary
The Inferior Planets. Culpeper Astronomy Club Meeting October 23, 2017
 The Inferior Planets Culpeper Astronomy Club Meeting October 23, 2017 Overview Introductions Dark Matter (Ben Abbott) Mercury and Venus Stellarium Constellations: Aquila, Cygnus Observing Session (?) Image
The Inferior Planets Culpeper Astronomy Club Meeting October 23, 2017 Overview Introductions Dark Matter (Ben Abbott) Mercury and Venus Stellarium Constellations: Aquila, Cygnus Observing Session (?) Image
Astronomy 100 Section 2 MWF Greg Hall
 Astronomy 100 Section 2 MWF 1200-1300 100 Greg Hall Leslie Looney Phone: 217-244-3615 Email: lwl @ uiuc. edu Office: Astro Building #218 Office Hours: MTF 10:30-11:30 a.m. or by appointment Class Web Page
Astronomy 100 Section 2 MWF 1200-1300 100 Greg Hall Leslie Looney Phone: 217-244-3615 Email: lwl @ uiuc. edu Office: Astro Building #218 Office Hours: MTF 10:30-11:30 a.m. or by appointment Class Web Page
WHAT S UP? JULY The Night Sky for Mid-Month at 10PM (Credit: Cartes du Ceil)
 WHAT S UP? JULY 2013 The monsoon season begins in earnest in July (we hope!), which could definitely affect evening viewing, at least shortly after sunset, until the storm clouds die down. Constellations
WHAT S UP? JULY 2013 The monsoon season begins in earnest in July (we hope!), which could definitely affect evening viewing, at least shortly after sunset, until the storm clouds die down. Constellations
METEORS. Astronomical Calendar 2018
 1 These descriptions of the annual meteor showers are fuller than in the TIMETABLE OF EVENTS but still bare; I expect to amplify them later. Shower can be an optimistic term. You may see a few shooting
1 These descriptions of the annual meteor showers are fuller than in the TIMETABLE OF EVENTS but still bare; I expect to amplify them later. Shower can be an optimistic term. You may see a few shooting
Directed Reading. Section: Viewing the Universe THE VALUE OF ASTRONOMY. Skills Worksheet. 1. How did observations of the sky help farmers in the past?
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Viewing the Universe 1. How did observations of the sky help farmers in the past? 2. How did observations of the sky help sailors in the past? 3. What is the
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Viewing the Universe 1. How did observations of the sky help farmers in the past? 2. How did observations of the sky help sailors in the past? 3. What is the
Astronomy 291. Professor Bradley M. Peterson
 Astronomy 291 Professor Bradley M. Peterson The Sky As a first step, we need to understand the appearance of the sky. Important points (to be explained): The relative positions of stars remain the same
Astronomy 291 Professor Bradley M. Peterson The Sky As a first step, we need to understand the appearance of the sky. Important points (to be explained): The relative positions of stars remain the same
DOZENALS. A project promoting base 12 counting and measuring. Ideas and designs by DSA member (#342) and board member, Timothy F. Travis.
 R AENBO DOZENALS A project promoting base 12 counting and measuring. Ideas and designs by DSA member (#342) and board member Timothy F. Travis. I became aware as a teenager of base twelve numbering from
R AENBO DOZENALS A project promoting base 12 counting and measuring. Ideas and designs by DSA member (#342) and board member Timothy F. Travis. I became aware as a teenager of base twelve numbering from
WHAT'S UP THIS MONTH FEBRUARY 2016
 WHAT'S UP THIS MONTH FEBRUARY 2016 THESE PAGES ARE INTENDED TO HELP YOU FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE SKY The chart above shows the night sky as it appears on 15 th February at 21:00 (9 o clock) in the evening
WHAT'S UP THIS MONTH FEBRUARY 2016 THESE PAGES ARE INTENDED TO HELP YOU FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE SKY The chart above shows the night sky as it appears on 15 th February at 21:00 (9 o clock) in the evening
The Population and Mass of the Oort Cloud
 The Population and Mass of the Oort Cloud Luke Dones Southwest Research Institute Boulder, Colorado Megan E. Schwamb Yale Center for Astronomy and Astrophysics and Department of Physics Yale University
The Population and Mass of the Oort Cloud Luke Dones Southwest Research Institute Boulder, Colorado Megan E. Schwamb Yale Center for Astronomy and Astrophysics and Department of Physics Yale University
Celestial Events for 2018 Hōkūlani Imaginarium Windward Community College Joseph Ciotti
 Celestial Events for 2018 Hōkūlani Imaginarium Windward Community College Joseph Ciotti all times HST Month Day Time Celestial Event 2018 Jan 1 11:54 am Moon at (closest to earth) 1 4:24 pm Full Moon Super
Celestial Events for 2018 Hōkūlani Imaginarium Windward Community College Joseph Ciotti all times HST Month Day Time Celestial Event 2018 Jan 1 11:54 am Moon at (closest to earth) 1 4:24 pm Full Moon Super
Astronomy wall calendar
 to Free oad nl w o for d t n i! pr and nal use o pers The Centre for Astronomical Heritage (CfAH) is a non-profit company working to protect South Africa s astronomical heritage. Donations are always welcome,
to Free oad nl w o for d t n i! pr and nal use o pers The Centre for Astronomical Heritage (CfAH) is a non-profit company working to protect South Africa s astronomical heritage. Donations are always welcome,
Biblical Astronomy February 2009
 Biblical Astronomy February 2009 Editor Robert Scott Wadsworth P.O. Box 2272, Oregon City, OR 97045 Phone (503) 655-7430 e-mail starguy1@comcast.net Website www.biblicalastronomy.com NEW MOON
Biblical Astronomy February 2009 Editor Robert Scott Wadsworth P.O. Box 2272, Oregon City, OR 97045 Phone (503) 655-7430 e-mail starguy1@comcast.net Website www.biblicalastronomy.com NEW MOON
Saudi Arabia. July present. Desert Locust Information Service FAO, Rome Red Sea coast outbreak
 Saudi Arabia July 2016 - present coast outbreak Desert Locust Information Service FAO, Rome www.fao.org/ag/locusts Keith Cressman (Senior Locust Forecasting Officer) updated: 24 January 2017 undetected
Saudi Arabia July 2016 - present coast outbreak Desert Locust Information Service FAO, Rome www.fao.org/ag/locusts Keith Cressman (Senior Locust Forecasting Officer) updated: 24 January 2017 undetected
The Night Sky in October, 2016
 The Night Sky in October, 2016 At the beginning of October, the Sun will rise at 07:12 BST and set at 18:45 BST. By the end of the month it will rise at 07:07 GMT and set at 16:38 GMT. So let s hope for
The Night Sky in October, 2016 At the beginning of October, the Sun will rise at 07:12 BST and set at 18:45 BST. By the end of the month it will rise at 07:07 GMT and set at 16:38 GMT. So let s hope for
4 Solar System and Time
 4 olar ystem and Time 4.1 The Universe 4.1.1 Introduction The Universe consists of countless galaxies distributed throughout space. The bodies used in astro navigation belong to the Galaxy known as the
4 olar ystem and Time 4.1 The Universe 4.1.1 Introduction The Universe consists of countless galaxies distributed throughout space. The bodies used in astro navigation belong to the Galaxy known as the
ENGINE SERIAL NUMBERS
 ENGINE SERIAL NUMBERS The engine number was also the serial number of the car. Engines were numbered when they were completed, and for the most part went into a chassis within a day or so. However, some
ENGINE SERIAL NUMBERS The engine number was also the serial number of the car. Engines were numbered when they were completed, and for the most part went into a chassis within a day or so. However, some
Physics Lab #2:! Starry Night Introduction!
 Physics 10293 Lab #2: Starry Night Introduction Introduction In this lab, we'll learn how to use the Starry Night software to learn about the sky. Starry Night has a large number of features and options,
Physics 10293 Lab #2: Starry Night Introduction Introduction In this lab, we'll learn how to use the Starry Night software to learn about the sky. Starry Night has a large number of features and options,
Main Event: Comets by Paul Jenkins
 Main Event: Comets by Paul Jenkins Most people realise that comets come from the Oort Cloud, a huge ball of objects surrounding the solar system but which has a bias of objects towards the plane of the
Main Event: Comets by Paul Jenkins Most people realise that comets come from the Oort Cloud, a huge ball of objects surrounding the solar system but which has a bias of objects towards the plane of the
PTYS/ASTR 206 Section 2 Spring 2007 Homework #1 (Page 1/4)
 PTYS/ASTR 206 Section 2 Spring 2007 Homework #1 (Page 1/4) NAME: KEY Due Date: start of class 1/25/2007 5 pts extra credit if turned in before 9:00AM (early!) (To get the extra credit, the assignment must
PTYS/ASTR 206 Section 2 Spring 2007 Homework #1 (Page 1/4) NAME: KEY Due Date: start of class 1/25/2007 5 pts extra credit if turned in before 9:00AM (early!) (To get the extra credit, the assignment must
Lecture 2: Motions of the Earth and Moon. Astronomy 111 Wednesday August 30, 2017
 Lecture 2: Motions of the Earth and Moon Astronomy 111 Wednesday August 30, 2017 Reminders Online homework #1 due Monday at 3pm Labs start next week Motions of the Earth ASTR111 Lecture 2 Observation:
Lecture 2: Motions of the Earth and Moon Astronomy 111 Wednesday August 30, 2017 Reminders Online homework #1 due Monday at 3pm Labs start next week Motions of the Earth ASTR111 Lecture 2 Observation:
Astronomy Club of Asheville February 2018 Sky Events
 February 2018 Sky Events The Planets this Month page 2 The Gibbous Moon Joins Jupiter, Mars and Antares page 7 A Crescent Moon Pairs with Venus page 8 Conjunction of Near Full Moon with Regulus page 9
February 2018 Sky Events The Planets this Month page 2 The Gibbous Moon Joins Jupiter, Mars and Antares page 7 A Crescent Moon Pairs with Venus page 8 Conjunction of Near Full Moon with Regulus page 9
Drought in Southeast Colorado
 Drought in Southeast Colorado Nolan Doesken and Roger Pielke, Sr. Colorado Climate Center Prepared by Tara Green and Odie Bliss http://climate.atmos.colostate.edu 1 Historical Perspective on Drought Tourism
Drought in Southeast Colorado Nolan Doesken and Roger Pielke, Sr. Colorado Climate Center Prepared by Tara Green and Odie Bliss http://climate.atmos.colostate.edu 1 Historical Perspective on Drought Tourism
WHEN IS IT EVER GOING TO RAIN? Table of Average Annual Rainfall and Rainfall For Selected Arizona Cities
 WHEN IS IT EVER GOING TO RAIN? Table of Average Annual Rainfall and 2001-2002 Rainfall For Selected Arizona Cities Phoenix Tucson Flagstaff Avg. 2001-2002 Avg. 2001-2002 Avg. 2001-2002 October 0.7 0.0
WHEN IS IT EVER GOING TO RAIN? Table of Average Annual Rainfall and 2001-2002 Rainfall For Selected Arizona Cities Phoenix Tucson Flagstaff Avg. 2001-2002 Avg. 2001-2002 Avg. 2001-2002 October 0.7 0.0
3) During retrograde motion a planet appears to be A) dimmer than usual. B) the same brightness as usual C) brighter than usual.
 Descriptive Astronomy (ASTR 108) Exam 1 B February 17, 2010 Name: In each of the following multiple choice questions, select the best possible answer. In the line on the scan sheet corresponding to the
Descriptive Astronomy (ASTR 108) Exam 1 B February 17, 2010 Name: In each of the following multiple choice questions, select the best possible answer. In the line on the scan sheet corresponding to the
1) Kepler's third law allows us to find the average distance to a planet from observing its period of rotation on its axis.
 Descriptive Astronomy (ASTR 108) Exam 1 A February 17, 2010 Name: In each of the following multiple choice questions, select the best possible answer. In the line on the scan sheet corresponding to the
Descriptive Astronomy (ASTR 108) Exam 1 A February 17, 2010 Name: In each of the following multiple choice questions, select the best possible answer. In the line on the scan sheet corresponding to the
Agricultural Science Climatology Semester 2, Anne Green / Richard Thompson
 Agricultural Science Climatology Semester 2, 2006 Anne Green / Richard Thompson http://www.physics.usyd.edu.au/ag/agschome.htm Course Coordinator: Mike Wheatland Course Goals Evaluate & interpret information,
Agricultural Science Climatology Semester 2, 2006 Anne Green / Richard Thompson http://www.physics.usyd.edu.au/ag/agschome.htm Course Coordinator: Mike Wheatland Course Goals Evaluate & interpret information,
Feasible Mission Designs for Solar Probe Plus to Launch in 2015, 2016, 2017, or November 19, 2008
 Feasible Mission Designs for Solar Probe Plus to Launch in 2015, 2016, 2017, or 2018 2007 Solar Probe Study & Mission Requirements Trajectory study and mission design trades were conducted in the fall
Feasible Mission Designs for Solar Probe Plus to Launch in 2015, 2016, 2017, or 2018 2007 Solar Probe Study & Mission Requirements Trajectory study and mission design trades were conducted in the fall
The Perennial Ecliptic Calendar
 The Perennial Ecliptic Calendar INTRODUCTION The Perennial Ecliptic Calendar is a system for marking time in which weeks vary between seven and eight days in length, but everything else is completely regular:
The Perennial Ecliptic Calendar INTRODUCTION The Perennial Ecliptic Calendar is a system for marking time in which weeks vary between seven and eight days in length, but everything else is completely regular:
Science : Introduction to Astronomy. Lecture 2 : Visual Astronomy -- Stars and Planets. Robert Fisher
 Science 3210 001 : Introduction to Astronomy Lecture 2 : Visual Astronomy -- Stars and Planets Robert Fisher Items Add/Drop Day Office Hours Vote 5 PM Tuesday 5 PM Thursday 12 Noon Friday Course Webpage
Science 3210 001 : Introduction to Astronomy Lecture 2 : Visual Astronomy -- Stars and Planets Robert Fisher Items Add/Drop Day Office Hours Vote 5 PM Tuesday 5 PM Thursday 12 Noon Friday Course Webpage
Morrison Pl anetarium. Meteor Showers Planet Watching Seasons and the Sun Eclipses Phases of the Moon
 Morrison Pl anetarium Meteor Showers Planet Watching Seasons and the Sun Eclipses Phases of the Moon P o c k e t A l m a n ac SEASONS AND THE SUN The terms below apply to the Northern Hemisphere. South
Morrison Pl anetarium Meteor Showers Planet Watching Seasons and the Sun Eclipses Phases of the Moon P o c k e t A l m a n ac SEASONS AND THE SUN The terms below apply to the Northern Hemisphere. South
Fundamentals of meteor science
 WGN, the Journal of the IMO 34:3 (2006) 71 Fundamentals of meteor science Visual Sporadic Meteor Rates Jürgen Rendtel 1 Activity from the antihelion region can be regarded as a series of ecliptical showers
WGN, the Journal of the IMO 34:3 (2006) 71 Fundamentals of meteor science Visual Sporadic Meteor Rates Jürgen Rendtel 1 Activity from the antihelion region can be regarded as a series of ecliptical showers
SKYCAL - Sky Events Calendar
 SKYCAL - Sky Events Calendar Your web browser must have Javascript turned on. The following browsers have been successfully tested: Macintosh - Firefox 3.0 (Safari NOT supported) Windows - Firefox 3.0,
SKYCAL - Sky Events Calendar Your web browser must have Javascript turned on. The following browsers have been successfully tested: Macintosh - Firefox 3.0 (Safari NOT supported) Windows - Firefox 3.0,
Chapter 1: Discovering the Night Sky. The sky is divided into 88 unequal areas that we call constellations.
 Chapter 1: Discovering the Night Sky Constellations: Recognizable patterns of the brighter stars that have been derived from ancient legends. Different cultures have associated the patterns with their
Chapter 1: Discovering the Night Sky Constellations: Recognizable patterns of the brighter stars that have been derived from ancient legends. Different cultures have associated the patterns with their
Planetary Motion from an Earthly Perspective
 1 Planetary Motion from an Earthly Perspective Stars appear fixed from night-to-night providing the familiar background of the constellations and asterisms. We see the same star patterns that were visible
1 Planetary Motion from an Earthly Perspective Stars appear fixed from night-to-night providing the familiar background of the constellations and asterisms. We see the same star patterns that were visible
Exercise 6. Solar Panel Orientation EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION OUTLINE. Introduction to the importance of solar panel orientation DISCUSSION
 Exercise 6 Solar Panel Orientation EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will understand how the solar illumination at any location on Earth varies over the course of a year. You
Exercise 6 Solar Panel Orientation EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will understand how the solar illumination at any location on Earth varies over the course of a year. You
Lecture 4: DM: time and Diurnal Motion
 Dr. W. Pezzaglia Astronomy 10, Fall 2006 Page 8 Lecture 4: DM: time and Diurnal Motion Schedules: Aug 30, Wed (today) o Homework #2 due (see solutions below) o Web Site changed to: http://lpc1.clpccd.cc.ca.us/lpc/astronomy/course_websites/pezzaglia/index.html
Dr. W. Pezzaglia Astronomy 10, Fall 2006 Page 8 Lecture 4: DM: time and Diurnal Motion Schedules: Aug 30, Wed (today) o Homework #2 due (see solutions below) o Web Site changed to: http://lpc1.clpccd.cc.ca.us/lpc/astronomy/course_websites/pezzaglia/index.html
- SPACE/TIME GUIDE ARIES. Matariki rises late evening & is visible until early morning. Matariki rises. at dusk & is visible until late LEO
 TEACHER RESOURCE STARDOME OBSERVATORY & PLANETARIUM FACTS, RESOURCES AND ACTIVITIES ON... MATARIKI SCIENCE CONTENT/ CURRICULUM LINK ASTRONOMICAL SYSTEMS - SPACE/TIME GUIDE The star cluster Matariki plays
TEACHER RESOURCE STARDOME OBSERVATORY & PLANETARIUM FACTS, RESOURCES AND ACTIVITIES ON... MATARIKI SCIENCE CONTENT/ CURRICULUM LINK ASTRONOMICAL SYSTEMS - SPACE/TIME GUIDE The star cluster Matariki plays
Life Cycle of Convective Systems over Western Colombia
 Life Cycle of Convective Systems over Western Colombia Meiry Sakamoto Uiversidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil Colombia Life Cycle of Convective Systems over Western Colombia Convective System (CS)
Life Cycle of Convective Systems over Western Colombia Meiry Sakamoto Uiversidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil Colombia Life Cycle of Convective Systems over Western Colombia Convective System (CS)
Constellations. For each hour earlier, add 15 days to the date For each hour later, subtract 15 days to the date
 General CCD Imaging Programs E-Mail and Other Constellations Below is a table of the 88 constellations and the approximate date when constellation is highest in the sky for the times below. Clicking the
General CCD Imaging Programs E-Mail and Other Constellations Below is a table of the 88 constellations and the approximate date when constellation is highest in the sky for the times below. Clicking the
observer s page How to observe Meteors Tim Cooper (Director, Comet and Meteor Section)
 observer s page How to observe Meteors Tim Cooper (Director, Comet and Meteor Section) Observing meteors is an ideal way to start observing. You don t need any fancy instrumentation; just your eyes, some
observer s page How to observe Meteors Tim Cooper (Director, Comet and Meteor Section) Observing meteors is an ideal way to start observing. You don t need any fancy instrumentation; just your eyes, some
(All times listed are UT); Singapore Standard (Local) Time = UT + 8 h
 SKYTRACK Diary of Astronomical Events 2011 (All times listed are UT); Singapore Standard (Local) Time = UT + 8 h January 02 15 Mercury 4º N of Moon 04 09 NEW MOOM (Partial Solar Eclipse not visible from
SKYTRACK Diary of Astronomical Events 2011 (All times listed are UT); Singapore Standard (Local) Time = UT + 8 h January 02 15 Mercury 4º N of Moon 04 09 NEW MOOM (Partial Solar Eclipse not visible from
Planets in the Sky ASTR 101 2/16/2018
 Planets in the Sky ASTR 101 2/16/2018 1 Planets in the Sky 2018 paths of Jupiter among stars (2017/2018) Unlike stars which have fixed positions in the sky (celestial sphere), planets seem to move with
Planets in the Sky ASTR 101 2/16/2018 1 Planets in the Sky 2018 paths of Jupiter among stars (2017/2018) Unlike stars which have fixed positions in the sky (celestial sphere), planets seem to move with
Paper Reference. Paper Reference(s) 1627/01 Edexcel GCSE Astronomy Paper 01. Friday 15 May 2009 Morning Time: 2 hours
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 1627/01 Edexcel GCSE Astronomy Paper 01 Friday 15 May 2009 Morning Time: 2 hours Materials required for examination Calculator Items included with question papers
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 1627/01 Edexcel GCSE Astronomy Paper 01 Friday 15 May 2009 Morning Time: 2 hours Materials required for examination Calculator Items included with question papers
Chapter 2 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Discovering the Universe for Yourself Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 2 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Discovering the Universe for Yourself Discovering the Universe for Yourself 2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What does the
Chapter 2 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Discovering the Universe for Yourself Discovering the Universe for Yourself 2.1 Patterns in the Night Sky Our goals for learning: What does the
