Globular Clusters. This list contains 135 of the brightest and largest globular clusters from the Astroleague's observing program/list.
|
|
|
- Kenneth Sanders
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Globular Clusters A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbit a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, giving them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. A globular cluster is sometimes known more simply as a globular. Globular clusters, which are found in the halo of a galaxy, contain considerably more stars and are much older than the less dense open clusters, which are found in the disk. Globular clusters are fairly common; there are about 150 to 158 currently known globular clusters in the Milky Way, with perhaps 10 to 20 more still undiscovered. These globular clusters orbit the Galaxy at radii of 40 kiloparsecs (130,000 lightyears) or more. Larger galaxies can have more: The Andromeda galaxy may have as many as 500 while giant elliptical galaxies, such as M87, may have as many as 13,000 globular clusters. Every galaxy of sufficient mass in the Local Group has an associated group of globular clusters, and almost every large galaxy surveyed has been found to possess a system of globular clusters. The Sagittarius Dwarf galaxy and the disputed Canis Major Dwarf galaxy appear to be in the process of donating their associated globular clusters (such as Palomar 12) to the Milky Way, demonstrating how many of this galaxy's globular clusters might have been acquired in the past. Although it appears that globular clusters contain some of the first stars to be produced in the galaxy, their origins and their role in galactic evolution are still unclear. It does appear clear that globular clusters are significantly different from dwarf elliptical galaxies and were formed as part of the star formation of the parent galaxy rather than as a separate galaxy. However, recent conjectures by astronomers suggest that globular clusters and dwarf spheroidals may not be clearly separate and distinct types of objects. This list contains 135 of the brightest and largest globular clusters from the Astroleague's observing program/list. Globular Clusters 1
2 Globular Cluster Types b Hub Globulars o Halo Globulars r Far Halo Globulars m Magellanic Globulars x External Globulars (none) Unknown/No Classification Catalogs Arp Djorg ESO HP IC M N Pal Rup Ter Ton Arp & Van den Bergh Djorgoski European Southern Observatory Haute-Provence Index Catalog Messier Catalog New General Catalog (NGC) Palomar Globulars Ruprecht Terzan Clusters Tonantzintla Globular Clusters 2
3 Globular Clusters Object Const RA Dec Mag Size Type N104 Tuc 00h 24m 05s -72º 04.9' ' o N121 In SMC 00h 26m 47s -71º 32.2' ' m N288 Scl 00h 52m 45s -26º 35.0' ' o N362 Tuc 01h 03m 14s -70º 50.9' ' o N1049 For 02h 39m 48s -34º 15.5' ' x N1261 Hor 03h 12m 16s -55º 13.0' ' Pal 1 Cep 03h 33m 21s +79º 34.9' ' Pal 2 Aur 04h 46m 06s +31º 22.9' ' N1851 Col 05h 14m 07s -40º 02.8' ' M79 Lep 05h 24m 11s -24º 31.5' ' N2298 Pup 06h 48m 59s -36º 00.3' ' N2419 Lyn 07h 38m 08s +38º 55.9' ' N2808 Car 09h 12m 03s -64º 51.8' ' o ESO 37-1 Cha 09h 20m 56s -77º 16.7' 11.4 o Pal 3 Sex 10h 05m 31s +00º 04.3' ' r N3201 Vel 10h 17m 37s -46º 24.7' ' o Pal 4 Uma 11h 29m 16s +28º 58.4' ' r N4147 Com 12h 10m 06s +18º 32.5' ' r N4372 Mus 12h 25m 47s -72º 39.2' ' o Rup 106 Cen 12h 38m 39s -51º 09.1' ' r M68 Hya 12h 39m 28s -26º 44.6' ' o N4833 Mus 12h 59m 34s -70º 52.5' ' o M53 Com 13h 12m 55s +18º 10.1' ' r N5053 Com 13h 16m 27s +17º 41.9' ' r N5139 Cen 13h 26m 46s -47º 28.6' ' o M3 Cvn 13h 42m 11s +28º 22.7' ' o N5286 Cen 13h 46m 27s -51º 22.6' ' o N5466 Boo 14h 05m 27s +28º 32.1' ' r N5634 Vir 14h 29m 37s -05º 58.6' ' r N5694 Hya 14h 39m 36s -26º 32.3' ' r IC 4499 Aps 15h 00m 19s -82º 12.8' ' r N5824 Lup 15h 03m 59s -33º 04.1' ' r Pal 5 Ser 15h 16m 05s -00º 06.7' ' r N5897 Lib 15h 17m 24s -21º 00.6' ' o M5 Ser 15h 18m 33s -02º 05.0' ' o N5927 Lup 15h 28m 01s -50º 40.4' ' b Globular Clusters 3
4 Object Const RA Dec Mag Size Type N5946 Nor 15h 35m 29s -50º 39.6' ' o N5986 Lup 15h 46m 03s -37º 47.1' ' b Pal 14 Her 16h 10m 59s +14º 57.5' ' r M80 Sco 16h 17m 02s -22º 58.5' ' b M4 Sco 16h 23m 35s -26º 31.5' ' o N6101 Aps 16h 25m 49s -72º 12.0' ' r N6144 Sco 16h 27m 14s -26º 01.3' ' b N6139 Sco 16h 27m 40s -38º 50.9' ' b Ter 3 Sco 16h 28m 40s -35º 20.6' ' b M107 Oph 16h 32m 32s -13º 03.2' ' b M13 Her 16h 41m 41s +36º 27.6' ' o N6229 Her 16h 46m 59s +47º 31.7' ' r M12 Oph 16h 47m 14s -01º 56.8' ' b N6235 Oph 16h 53m 25s -22º 10.6' ' b M10 Oph 16h 57m 09s -04º 06.0' ' b N6256 Sco 16h 59m 33s -37º 07.3' ' b Pal 15 Oph 16h 59m 51s -00º 32.5' ' r M62 Oph 17h 01m 13s -30º 06.8' ' b M19 Oph 17h 02m 38s -26º 16.1' ' b N6284 Oph 17h 04m 29s -24º 45.9' ' o N6287 Oph 17h 05m 09s -22º 42.5' ' b N6293 Oph 17h 10m 10s -26º 34.9' ' b N6304 Oph 17h 14m 32s -29º 27.7' ' b N6316 Oph 17h 16m 37s -28º 08.4' ' b M92 Her 17h 17m 07s +43º 08.8' ' o N6325 Oph 17h 17m 59s -23º 46.0' ' b M9 Oph 17h 19m 12s -18º 31.0' ' b N6342 Oph 17h 21m 10s -19º 35.2' ' b N6355 Oph 17h 23m 58s -26º 21.2' b N6356 Oph 17h 23m 35s -17º 48.8' ' o IC 1257 Oph 17h 21m 08s -07º 05.6' ' r N6352 Ara 17h 25m 29s -48º 25.4' ' b N6366 Oph 17h 27m 44s -05º 04.6' ' o Ter 2 Sco 17h 27m 33s -30º 48.2' ' b HP 1 Oph 17h 31m 05s -29º 59.0' ' b N6362 Ara 17h 31m 55s -67º 02.9' ' o N6380 Sco 17h 34m 28s -39º 04.2' ' b Ter 1 Sco 17h 35m 47s -30º 28.9' ' b Globular Clusters 4
5 Object Const RA Dec Mag Size Type Ton 2 Sco 17h 36m 11s -38º 33.2' ' b N6388 Sco 17h 36m 17s -44º 44.1' ' b N6401 Oph 17h 38m 37s -23º 54.6' ' b M14 Oph 17h 37m 36s -03º 14.8' ' b N6397 Ara 17h 40m 42s -53º 40.4' ' o Pal 6 Oph 17h 43m 42s -26º 13.4' ' b N6426 Oph 17h 44m 54s +03º 10.2' ' o Ter 5 Sgr 17h 48m 05s -24º 46.8' ' b N6440 Sgr 17h 48m 53s -20º 21.6' ' b N6441 Sco 17h 50m 13s -37º 03.1' ' b Ter 6 Sco 17h 50m 47s -31º 16.5' ' b N6453 Sco 17h 50m 52s -34º 35.9' ' b N6496 Sco 17h 59m 03s -44º 15.9' ' b N6517 Oph 18h 01m 51s -08º 57.5' ' b Djorg 2 Sco 18h 01m 49s -27º 49.5' ' b Ter 10 Sgr 18h 02m 58s -26º 04.0' ' b N6522 Sgr 18h 03m 35s -30º 02.1' ' b N6535 Ser 18h 03m 51s -00º 17.8' ' b N6539 Ser 18h 04m 50s -07º 35.2' ' b N6528 Sgr 18h 04m 49s -30º 03.4' ' b N6540 Sgr 18h 06m 09s -27º 45.9' ' b N6544 Sgr 18h 07m 20s -24º 59.9' ' o N6541 Cra 18h 08m 02s -43º 42.9' ' b N6553 Sgr 18h 09m 17s -25º 54.5' ' b N6558 Sgr 18h 10m 18s -31º 45.8' ' b IC 1276 Ser 18h 10m 45s -07º 12.8' ' b N6569 Sgr 18h 13m 38s -31º 49.6' ' b N6584 Tel 18h 18m 38s -52º 12.9' ' o N6624 Sgr 18h 23m 40s -30º 21.5' ' b M28 Sgr 18h 24m 33s -24º 52.2' ' b M69 Sgr 18h 31m 23s -32º 20.9' ' b N6638 Sgr 18h 30m 56s -25º 29.8' ' b N6642 Sgr 18h 31m 54s -23º 28.5' ' b N6652 Sgr 18h 35m 46s -32º 59.4' ' b M22 Sgr 18h 36m 24s -23º 54.2' ' b Pal 8 Sgr 18h 41m 30s -19º 49.6' ' o M70 Sgr 18h 43m 13s -32º 17.5' ' b N6712 Set 18h 53m 04s -08º 42.3' ' b Globular Clusters 5
6 Object Const RA Dec Mag Size Type M54 Sgr 18h 55m 03s -30º 28.7' ' x N6717 Sgr 18h 55m 06s -22º 42.1' ' b N6723 Sgr 18h 59m 33s -36º 37.9' ' b N6749 Aql 19h 05m 15s +01º 54.1' ' o N6752 Pav 19h 10m 52s -59º 58.9' ' o N6760 Aql 19h 11m 12s +01º 01.9' ' b M56 Lyr 19h 16m 36s +30º 11.1' ' o Ter 7 Sgr 19h 17m 44s -34º 39.5' ' x Pal 10 Sge 19h 18m 02s +18º 34.3' ' o Arp 2 Sgr 19h 28m 44s -30º 21.2' ' x M55 Sgr 19h 40m 00s -30º 57.7' ' b Ter 8 Sgr 19h 41m 44s -34º 00.0' ' x Pal 11 Aql 19h 45m 14s -08º 00.4' ' o M71 Sge 19h 53m 46s +18º 46.7' ' o M75 Sgr 20h 06m 05s -21º 55.3' ' o N6934 Del 20h 34m 11s +07º 24.3' ' o M72 Aqr 20h 53m 28s -12º 32.2' ' o N7006 Del 21h 01m 29s +16º 11.2' ' r M15 Peg 21h 29m 58s +12º 10.0' ' o M2 Aqr 21h 33m 27s -00º 49.4' ' o M30 Cap 21h 40m 22s -23º 10.7' ' o Pal 12 Cap 21h 46m 39s -21º 15.1' ' r N7492 Aqr 23h 08m 27s -15º 36.6' ' r Globular Clusters 6
7 Globular Cluster Observing Log (1) Object Date Object Date N104 M5 N121 N5927 N288 N5946 N362 N5986 N1049 Pal 14 N1261 M80 Pal 1 M4 Pal 2 N6101 N1851 N6144 M79 N6139 N2298 Ter 3 N2419 M107 N2808 M13 ESO 37-1 N6229 Pal 3 M12 N3201 N6235 Pal 4 M10 N4147 N6256 N4372 Pal 15 Rup 106 M62 M68 M19 N4833 N6284 M53 N6287 N5053 N6293 N5139 N6304 M3 N6316 N5286 M92 N5466 N6325 N5634 M9 N5694 N6342 IC 4499 N6355 N5824 N6356 Pal 5 IC 1257 N5897 N6352 Globular Clusters 7
8 Globular Cluster Observing Log (2) Object Date Object Date N6366 N6624 Ter 2 M28 HP 1 M69 N6362 N6638 N6380 N6642 Ter 1 N6652 Ton 2 M22 N6388 Pal 8 N6401 M70 M14 N6712 N6397 M54 Pal 6 N6717 N6426 N6723 Ter 5 N6749 N6440 N6752 N6441 N6760 Ter 6 M56 N6453 Ter 7 N6496 Pal 10 N6517 Arp 2 Djorg 2 M55 Ter 10 Ter 8 N6522 Pal 11 N6535 M71 N6539 M75 N6528 N6934 N6540 M72 N6544 N7006 N6541 M15 N6553 M2 N6558 M30 IC 1276 Pal 12 N6569 N7492 N6584 Globular Clusters 8
Palomar Globular Clusters
 Tacande Observatory, La Palma www.astropalma.com Palomar Globular Clusters Like Abell's planetary nebulae, Palomar globular clusters were discovered in the 1950 s on the recognition plates of the Palomar
Tacande Observatory, La Palma www.astropalma.com Palomar Globular Clusters Like Abell's planetary nebulae, Palomar globular clusters were discovered in the 1950 s on the recognition plates of the Palomar
Sheet1. Page 1. Object R.A. DEC Mag Type NGC SMC NGC NGC
 Object R.A. DEC Mag Type Const NGC 104 0 24.1-72 5 4.5 GbCl Tuc SMC 0 52.8-72 50 2.7 Glxy Tuc NGC 362 1 3.2-70 51 6.6 GbCl Tuc NGC 1261 3 12.3-55 13 8.4 GbCl Hor NGC 1851 5 14.1-40 3 7.2 GbCl Col LMC 5
Object R.A. DEC Mag Type Const NGC 104 0 24.1-72 5 4.5 GbCl Tuc SMC 0 52.8-72 50 2.7 Glxy Tuc NGC 362 1 3.2-70 51 6.6 GbCl Tuc NGC 1261 3 12.3-55 13 8.4 GbCl Hor NGC 1851 5 14.1-40 3 7.2 GbCl Col LMC 5
Messier Marathon Checkoff List 1
 Messier Marathon Checkoff List 1 by Ken Graun DATE 8 p.m. 2 74 3, 77, 52, 31/32/110, 33, 103, 111/112, 76, 34 M74 1h 36.7m +15 47' Psc Spiral Galaxy 9.2 10' x 9' The Phantom M77 2h 42.7m 0 01' Cet Spiral
Messier Marathon Checkoff List 1 by Ken Graun DATE 8 p.m. 2 74 3, 77, 52, 31/32/110, 33, 103, 111/112, 76, 34 M74 1h 36.7m +15 47' Psc Spiral Galaxy 9.2 10' x 9' The Phantom M77 2h 42.7m 0 01' Cet Spiral
Globular Clusters 1
 Globular Clusters 1 www.faintfuzzies.com Globular Clusters 2 www.faintfuzzies.com Globular Clusters (Includes all known globulars in the Milky Way above declination of -50º plus some extras) by Alvin Huey
Globular Clusters 1 www.faintfuzzies.com Globular Clusters 2 www.faintfuzzies.com Globular Clusters (Includes all known globulars in the Milky Way above declination of -50º plus some extras) by Alvin Huey
Observing Stellar Evolution Observing List
 Observing Stellar Evolution Observing List Bill Pellerin, Houston Astronomical Society This list is organized by category of object. Within each category, the list is sorted by RA to help you plan your
Observing Stellar Evolution Observing List Bill Pellerin, Houston Astronomical Society This list is organized by category of object. Within each category, the list is sorted by RA to help you plan your
Ch. 25 In-Class Notes: Beyond Our Solar System
 Ch. 25 In-Class Notes: Beyond Our Solar System ES2a. The solar system is located in an outer edge of the disc-shaped Milky Way galaxy, which spans 100,000 light years. ES2b. Galaxies are made of billions
Ch. 25 In-Class Notes: Beyond Our Solar System ES2a. The solar system is located in an outer edge of the disc-shaped Milky Way galaxy, which spans 100,000 light years. ES2b. Galaxies are made of billions
FINEST SIGHTS for LX200
 FINEST SIGHTS for LX200 1. M81 UMa M81 (8) Spiral galaxy 09:56 +69.1 2. M82 UMa M82 (9) Irregular galaxy 09:56 +69.7 3. Gamma Leo *296 (3, 4)[4.5"] Double star 10:20 +19.9 4. NGC3242 Hya NGC3242 (9) Planetary
FINEST SIGHTS for LX200 1. M81 UMa M81 (8) Spiral galaxy 09:56 +69.1 2. M82 UMa M82 (9) Irregular galaxy 09:56 +69.7 3. Gamma Leo *296 (3, 4)[4.5"] Double star 10:20 +19.9 4. NGC3242 Hya NGC3242 (9) Planetary
Testing Cosmology with Phase-Space Correlations in Systems of Satellite Galaxies. Current Studies and Future Prospects
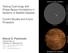 Observed MW satellites Testing Cosmology with Phase-Space Correlations in Systems of Satellite Galaxies Current Studies and Future Prospects http://marcelpawlowski.com/research/movies-astronomy/ Marcel
Observed MW satellites Testing Cosmology with Phase-Space Correlations in Systems of Satellite Galaxies Current Studies and Future Prospects http://marcelpawlowski.com/research/movies-astronomy/ Marcel
BYU Astronomical Society Observation Log Book
 BYU Astronomical Society Observation Log Book Introduction The NightLog is a combination of two elements designed for the amateur astronomer: an observation program, and a log book. Brigham Young University
BYU Astronomical Society Observation Log Book Introduction The NightLog is a combination of two elements designed for the amateur astronomer: an observation program, and a log book. Brigham Young University
Normal Galaxies ASTR 2120 Sarazin
 Normal Galaxies ASTR 2120 Sarazin Test #2 Monday, April 8, 11-11:50 am ASTR 265 (classroom) Bring pencils, paper, calculator You may not consult the text, your notes, or any other materials or any person
Normal Galaxies ASTR 2120 Sarazin Test #2 Monday, April 8, 11-11:50 am ASTR 265 (classroom) Bring pencils, paper, calculator You may not consult the text, your notes, or any other materials or any person
ASTRO 1050 LAB #10: The Structure of the Milky Way Galaxy
 ASTRO 1050 LAB #10: The Structure of the Milky Way Galaxy ABSTRACT In this lab, you will learn that we live in the Milky Way galaxy. Our Solar System and all the stars you can see with your own eyes are
ASTRO 1050 LAB #10: The Structure of the Milky Way Galaxy ABSTRACT In this lab, you will learn that we live in the Milky Way galaxy. Our Solar System and all the stars you can see with your own eyes are
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics. Fall 2014
 ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
Galaxies: The Nature of Galaxies
 Galaxies: The Nature of Galaxies The Milky Way The Milky Way is visible to the unaided eye at most place on Earth Galileo in 1610 used his telescope to resolve the faint band into numerous stars In the
Galaxies: The Nature of Galaxies The Milky Way The Milky Way is visible to the unaided eye at most place on Earth Galileo in 1610 used his telescope to resolve the faint band into numerous stars In the
Three Major Components
 The Milky Way Three Major Components Bulge young and old stars Disk young stars located in spiral arms Halo oldest stars and globular clusters Components are chemically, kinematically, and spatially distinct
The Milky Way Three Major Components Bulge young and old stars Disk young stars located in spiral arms Halo oldest stars and globular clusters Components are chemically, kinematically, and spatially distinct
Chapter 23 The Milky Way Galaxy Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 23 The Milky Way Galaxy The Milky Way is our own galaxy viewed from the inside. It is a vast collection of more than 200 billion stars, planets, nebulae, clusters, dust and gas. Our own sun and
Chapter 23 The Milky Way Galaxy The Milky Way is our own galaxy viewed from the inside. It is a vast collection of more than 200 billion stars, planets, nebulae, clusters, dust and gas. Our own sun and
Binocular Universe: Messier Madness
 Binocular Universe: Messier Madness March 2014 Phil Harrington B aseball can have the World's Series, football can have the Super Bowl, and hockey can have its Stanley Cup. We observers have a full-blown
Binocular Universe: Messier Madness March 2014 Phil Harrington B aseball can have the World's Series, football can have the Super Bowl, and hockey can have its Stanley Cup. We observers have a full-blown
Selected Small Galaxy Groups 1
 Selected Small Galaxy Groups 1 www.faintfuzzies.com Selected Small Galaxy Groups 2 www.faintfuzzies.com Observing Selected Small Galaxy Groups Alvin H. Huey www.faintfuzzies.com Last updated: February
Selected Small Galaxy Groups 1 www.faintfuzzies.com Selected Small Galaxy Groups 2 www.faintfuzzies.com Observing Selected Small Galaxy Groups Alvin H. Huey www.faintfuzzies.com Last updated: February
Planetary Nebula Observations
 ABELL 31 Mar 15 2005 Cnc Pl Neb 3a VF,PATCHY,LARGE,R=F PK 219+31.1 ABELL 36 Jul 13 2013 Vir 1 Pl Neb PK 318+41.1 VF,VS,R=F. NO CENTRAL STAR NOTED. USED OIII FILTER. ABELL 56 Aql 19mmW DIFF,MF,VL,PATCHY,R=G
ABELL 31 Mar 15 2005 Cnc Pl Neb 3a VF,PATCHY,LARGE,R=F PK 219+31.1 ABELL 36 Jul 13 2013 Vir 1 Pl Neb PK 318+41.1 VF,VS,R=F. NO CENTRAL STAR NOTED. USED OIII FILTER. ABELL 56 Aql 19mmW DIFF,MF,VL,PATCHY,R=G
View of the Galaxy from within. Lecture 12: Galaxies. Comparison to an external disk galaxy. Where do we lie in our Galaxy?
 Lecture 12: Galaxies View of the Galaxy from within The Milky Way galaxy Rotation curves and dark matter External galaxies and the Hubble classification scheme Plotting the sky brightness in galactic coordinates,
Lecture 12: Galaxies View of the Galaxy from within The Milky Way galaxy Rotation curves and dark matter External galaxies and the Hubble classification scheme Plotting the sky brightness in galactic coordinates,
The Light Curves Of RR Lyrae Field Stars
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Norman R. Simon Papers Research Papers in Physics and Astronomy 10-15-1982 The Light Curves Of RR Lyrae Field Stars Norman
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Norman R. Simon Papers Research Papers in Physics and Astronomy 10-15-1982 The Light Curves Of RR Lyrae Field Stars Norman
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 23. Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 23 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 23 The Milky Way Galaxy Units of Chapter 23 23.1 Our Parent Galaxy 23.2 Measuring the Milky Way Discovery 23-1 Early Computers
Lecture Outlines Chapter 23 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 23 The Milky Way Galaxy Units of Chapter 23 23.1 Our Parent Galaxy 23.2 Measuring the Milky Way Discovery 23-1 Early Computers
Lecture 30. The Galactic Center
 Lecture 30 History of the Galaxy Populations and Enrichment Galactic Evolution Spiral Arms Galactic Types Apr 5, 2006 Astro 100 Lecture 30 1 The Galactic Center The nature of the center of the Galaxy is
Lecture 30 History of the Galaxy Populations and Enrichment Galactic Evolution Spiral Arms Galactic Types Apr 5, 2006 Astro 100 Lecture 30 1 The Galactic Center The nature of the center of the Galaxy is
BYU Astronomical Society Observation Log Book
 BYU Astronomical Society Observation Log Book The earth rolls upon her wings, and the sun giveth his light by day, and the moon giveth her light by night, and the stars also give their light, as they roll
BYU Astronomical Society Observation Log Book The earth rolls upon her wings, and the sun giveth his light by day, and the moon giveth her light by night, and the stars also give their light, as they roll
Galaxy classification
 Galaxy classification Questions of the Day What are elliptical, spiral, lenticular and dwarf galaxies? What is the Hubble sequence? What determines the colors of galaxies? Top View of the Milky Way The
Galaxy classification Questions of the Day What are elliptical, spiral, lenticular and dwarf galaxies? What is the Hubble sequence? What determines the colors of galaxies? Top View of the Milky Way The
The Milky Way. Finding the Center. Milky Way Composite Photo. Finding the Center. Milky Way : A band of and a. Milky Way
 The Milky Way Milky Way : A band of and a The band of light we see is really 100 billion stars Milky Way probably looks like Andromeda. Milky Way Composite Photo Milky Way Before the 1920 s, astronomers
The Milky Way Milky Way : A band of and a The band of light we see is really 100 billion stars Milky Way probably looks like Andromeda. Milky Way Composite Photo Milky Way Before the 1920 s, astronomers
The Meaning Of Life. ****Birth ****************************************************************************** NGC 6618, M 17, Cr 377, Swan Nebula
 This observing list tells a story of birth, life and death within the Universe. Each entry has the essential facts about the object in tabular form and then a paragraph or two explaining why the object
This observing list tells a story of birth, life and death within the Universe. Each entry has the essential facts about the object in tabular form and then a paragraph or two explaining why the object
An Atlas of Stellar Spectra
 An Atlas of Stellar Spectra with an Outline of Spectral Classification W. W. Morgan Philip C. Keenan Edith Kellman Astrophysical Monographs Sponsored by The Astrophysical Journal Paul W. Merrill Mount
An Atlas of Stellar Spectra with an Outline of Spectral Classification W. W. Morgan Philip C. Keenan Edith Kellman Astrophysical Monographs Sponsored by The Astrophysical Journal Paul W. Merrill Mount
Visual observations ASTB01 Lab 1
 Visual observations ASTB01 Lab 1 Lab instructors: Giorgi Kokaia Matthäus Schulik giorgi@astro.lu.se 046 222 1622 schulik@astro.lu.se 046 222 1622 Lund Observatory Lund University 1 Introduction The laboratory
Visual observations ASTB01 Lab 1 Lab instructors: Giorgi Kokaia Matthäus Schulik giorgi@astro.lu.se 046 222 1622 schulik@astro.lu.se 046 222 1622 Lund Observatory Lund University 1 Introduction The laboratory
Intrinsic variable types on the Hertzsprung Russell diagram. Image credit: Wikipedia
 Studying intrinsically pulsating variable stars plays a very important role in stellar evolution understanding. The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is a powerful tool to track which stage of stellar life is
Studying intrinsically pulsating variable stars plays a very important role in stellar evolution understanding. The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is a powerful tool to track which stage of stellar life is
Laboratory: Milky Way
 Department of Physics and Geology Laboratory: Milky Way Astronomy 1402 Equipment Needed Quantity Equipment Needed Quantity Milky Way galaxy Model 1 Ruler 1 1.1 Our Milky Way Part 1: Background Milky Way
Department of Physics and Geology Laboratory: Milky Way Astronomy 1402 Equipment Needed Quantity Equipment Needed Quantity Milky Way galaxy Model 1 Ruler 1 1.1 Our Milky Way Part 1: Background Milky Way
The Neighbors Looking outward from the Sun s location in the Milky Way, we can see a variety of other galaxies:
 Galaxies The Neighbors Looking outward from the Sun s location in the Milky Way, we can see a variety of other galaxies: Small Magellanic Cloud (Digital Sky Survey) Large Magellanic Cloud (credit: Eckhard
Galaxies The Neighbors Looking outward from the Sun s location in the Milky Way, we can see a variety of other galaxies: Small Magellanic Cloud (Digital Sky Survey) Large Magellanic Cloud (credit: Eckhard
STATISTICALLY EVOLUTION CONSIDERED THE PROBLEM OF STELLAR. conspicuous progression, indicating an increase in the motions of the stars with
 THE PROBLEM OF STELLAR EVOLUTION CONSIDERED STATISTICALLY OTTO STRUVE UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA The specific problem which I should like to bring to the attention of the statisticians is the following:
THE PROBLEM OF STELLAR EVOLUTION CONSIDERED STATISTICALLY OTTO STRUVE UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA The specific problem which I should like to bring to the attention of the statisticians is the following:
SPACE MOTIONS OF GALACTIC GLOBULAR CLUSTERS: NEW RESULTS AND HALO-FORMATION IMPLICATIONS
 SPACE MOTIONS OF GALACTIC GLOBULAR CLUSTERS: NEW RESULTS AND HALO-FORMATION IMPLICATIONS Dana I. Casetti-Dinescu, Terrence M. Girard, David Herrera, William F. van Altena, Young-Wook Lee, Carlos Lopez
SPACE MOTIONS OF GALACTIC GLOBULAR CLUSTERS: NEW RESULTS AND HALO-FORMATION IMPLICATIONS Dana I. Casetti-Dinescu, Terrence M. Girard, David Herrera, William F. van Altena, Young-Wook Lee, Carlos Lopez
National Aeronautics and Space Administration. Glos. Glossary. of Astronomy. Terms. Related to Galaxies
 National Aeronautics and Space Administration Glos of Astronomy Glossary Terms Related to Galaxies Asterism: A pattern formed by stars not recognized as one of the official 88 constellations. Examples
National Aeronautics and Space Administration Glos of Astronomy Glossary Terms Related to Galaxies Asterism: A pattern formed by stars not recognized as one of the official 88 constellations. Examples
Culmination of a Constellation
 Culmination of a Constellation Over any night, stars and constellations in the sky will appear to move from east to west due to the Earth s rotation on its axis. A constellation will culminate (reach its
Culmination of a Constellation Over any night, stars and constellations in the sky will appear to move from east to west due to the Earth s rotation on its axis. A constellation will culminate (reach its
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 5 Jul 2006
 THE DWARF SATELLITES OF M31 AND THE GALAXY Sidney van den Bergh Dominion Astrophysical Observatory, Herzberg Institute of Astrophysics, National Research Council of Canada, 5071 West Saanich Road, Victoria,
THE DWARF SATELLITES OF M31 AND THE GALAXY Sidney van den Bergh Dominion Astrophysical Observatory, Herzberg Institute of Astrophysics, National Research Council of Canada, 5071 West Saanich Road, Victoria,
UMa II and the Orphan Stream
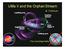 UMa II and the Orphan Stream M. Fellhauer The Cambridge Mafia Field of Streams Belokurov et al. 2006 A short The Bifurcation of the Sagittarius stream: (a typical Sagittarius like simulation) Fellhauer
UMa II and the Orphan Stream M. Fellhauer The Cambridge Mafia Field of Streams Belokurov et al. 2006 A short The Bifurcation of the Sagittarius stream: (a typical Sagittarius like simulation) Fellhauer
Galaxies Guiding Questions
 Galaxies Guiding Questions How did astronomers first discover other galaxies? How did astronomers first determine the distances to galaxies? Do all galaxies have spiral arms, like the Milky Way? How do
Galaxies Guiding Questions How did astronomers first discover other galaxies? How did astronomers first determine the distances to galaxies? Do all galaxies have spiral arms, like the Milky Way? How do
Chapter 14 The Milky Way Galaxy
 Chapter 14 The Milky Way Galaxy Spiral Galaxy M81 - similar to our Milky Way Galaxy Our Parent Galaxy A galaxy is a giant collection of stellar and interstellar matter held together by gravity Billions
Chapter 14 The Milky Way Galaxy Spiral Galaxy M81 - similar to our Milky Way Galaxy Our Parent Galaxy A galaxy is a giant collection of stellar and interstellar matter held together by gravity Billions
MERGERS OF GLOBULAR CLUSTERS
 MERGERS OF GLOBULAR CLUSTERS SIDNEY VAN DEN BERGH Dominion Astrophysical Observatory 5071 West Saanich Road Victoria, British Columbia V8X 4M6, Canada vandenbergh@dao.nrc.ca Received: 1996 July 1 ; accepted:
MERGERS OF GLOBULAR CLUSTERS SIDNEY VAN DEN BERGH Dominion Astrophysical Observatory 5071 West Saanich Road Victoria, British Columbia V8X 4M6, Canada vandenbergh@dao.nrc.ca Received: 1996 July 1 ; accepted:
2 Galaxy morphology and classification
 2 Galaxy morphology and classification Galaxy classification is an important first step towards a physical understanding of the nature of these objects. For a detailed description of classification systems
2 Galaxy morphology and classification Galaxy classification is an important first step towards a physical understanding of the nature of these objects. For a detailed description of classification systems
Our Solar System: A Speck in the Milky Way
 GALAXIES Lesson 2 Our Solar System: A Speck in the Milky Way The Milky Way appears to be curved when we view it but in reality it is a straight line. It is curved due to the combination of pictures taken
GALAXIES Lesson 2 Our Solar System: A Speck in the Milky Way The Milky Way appears to be curved when we view it but in reality it is a straight line. It is curved due to the combination of pictures taken
Milky Way Globular Clusters (Rob Horvat) 47 Tucanae (47 Tuc). Credit: Gerry Aarts (WSAAG). This globular cluster has more than one million stars.
 Milky Way Globular Clusters (Rob Horvat) 47 Tucanae (47 Tuc). Credit: Gerry Aarts (WSAAG). This globular cluster has more than one million stars. MulCple Star Systems A small Cght group of stars (usually
Milky Way Globular Clusters (Rob Horvat) 47 Tucanae (47 Tuc). Credit: Gerry Aarts (WSAAG). This globular cluster has more than one million stars. MulCple Star Systems A small Cght group of stars (usually
Variable star light curve activity
 Variable star light curve activity 2013. All rights reserved. SPIRIT is based at The University of Western Australia. 2016. All rights reserved. SPIRIT is based at The University of Western Australia 2
Variable star light curve activity 2013. All rights reserved. SPIRIT is based at The University of Western Australia. 2016. All rights reserved. SPIRIT is based at The University of Western Australia 2
Chapter 30. Galaxies and the Universe. Chapter 30:
 Chapter 30 Galaxies and the Universe Chapter 30: Galaxies and the Universe Chapter 30.1: Stars with varying light output allowed astronomers to map the Milky Way, which has a halo, spiral arm, and a massive
Chapter 30 Galaxies and the Universe Chapter 30: Galaxies and the Universe Chapter 30.1: Stars with varying light output allowed astronomers to map the Milky Way, which has a halo, spiral arm, and a massive
Astronomy 114. Lecture 29: Internal Properties of Galaxies. Martin D. Weinberg. UMass/Astronomy Department
 Astronomy 114 Lecture 29: Internal Properties of Galaxies Martin D. Weinberg weinberg@astro.umass.edu UMass/Astronomy Department A114: Lecture 29 20 Apr 2007 Read: Ch. 26 Astronomy 114 1/16 Announcements
Astronomy 114 Lecture 29: Internal Properties of Galaxies Martin D. Weinberg weinberg@astro.umass.edu UMass/Astronomy Department A114: Lecture 29 20 Apr 2007 Read: Ch. 26 Astronomy 114 1/16 Announcements
Our Galaxy. Milky Way Galaxy = Sun + ~100 billion other stars + gas and dust. Held together by gravity! The Milky Way with the Naked Eye
 Our Galaxy Milky Way Galaxy = Sun + ~100 billion other stars + gas and dust Held together by gravity! The Milky Way with the Naked Eye We get a special view of our own galaxy because we are part of it!
Our Galaxy Milky Way Galaxy = Sun + ~100 billion other stars + gas and dust Held together by gravity! The Milky Way with the Naked Eye We get a special view of our own galaxy because we are part of it!
Distance Measuring Techniques and The Milky Way Galaxy
 Distance Measuring Techniques and The Milky Way Galaxy Measuring distances to stars is one of the biggest challenges in Astronomy. If we had some standard candle, some star with a known luminosity, then
Distance Measuring Techniques and The Milky Way Galaxy Measuring distances to stars is one of the biggest challenges in Astronomy. If we had some standard candle, some star with a known luminosity, then
Galaxies and Star Systems
 Chapter 5 Section 5.1 Galaxies and Star Systems Galaxies Terms: Galaxy Spiral Galaxy Elliptical Galaxy Irregular Galaxy Milky Way Galaxy Quasar Black Hole Types of Galaxies A galaxy is a huge group of
Chapter 5 Section 5.1 Galaxies and Star Systems Galaxies Terms: Galaxy Spiral Galaxy Elliptical Galaxy Irregular Galaxy Milky Way Galaxy Quasar Black Hole Types of Galaxies A galaxy is a huge group of
Lecture 7: the Local Group and nearby clusters
 Lecture 7: the Local Group and nearby clusters in this lecture we move up in scale, to explore typical clusters of galaxies the Local Group is an example of a not very rich cluster interesting topics include:
Lecture 7: the Local Group and nearby clusters in this lecture we move up in scale, to explore typical clusters of galaxies the Local Group is an example of a not very rich cluster interesting topics include:
Morphology The Study of the Basic Pattern of Things
 Morphology The Study of the Basic Pattern of Things Fundamental Considerations Different libraries of galaxies are liable to lead to the ID of different classes Images in library must be homogeneous (filter,
Morphology The Study of the Basic Pattern of Things Fundamental Considerations Different libraries of galaxies are liable to lead to the ID of different classes Images in library must be homogeneous (filter,
Galaxies. What is a Galaxy? A bit of History. A bit of History. Three major components: 1. A thin disk consisting of young and intermediate age stars
 What is a Galaxy? Galaxies A galaxy is a collection of billions of stars, dust, and gas all held together by gravity. Galaxies are scattered throughout the universe. They vary greatly in size and shape.
What is a Galaxy? Galaxies A galaxy is a collection of billions of stars, dust, and gas all held together by gravity. Galaxies are scattered throughout the universe. They vary greatly in size and shape.
Chapter 19 Reading Quiz Clickers. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Our Galaxy Pearson Education, Inc.
 Reading Quiz Clickers The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Our Galaxy 19.1 The Milky Way Revealed What does our galaxy look like? How do stars orbit in our galaxy? Where are globular clusters located
Reading Quiz Clickers The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Our Galaxy 19.1 The Milky Way Revealed What does our galaxy look like? How do stars orbit in our galaxy? Where are globular clusters located
The TESS RR Lyrae and Cepheid Survey
 The TESS RR Lyrae and Cepheid Survey Róbert Szabó 1, Katrien Kolenberg 2,3 (chairs) László Molnár 1, Emese Plachy 1, and TASC WG#6 1 Konkoly Observatory, MTA CSFK, Budapest, Hungary email: szabo.robert@csfk.mta.hu
The TESS RR Lyrae and Cepheid Survey Róbert Szabó 1, Katrien Kolenberg 2,3 (chairs) László Molnár 1, Emese Plachy 1, and TASC WG#6 1 Konkoly Observatory, MTA CSFK, Budapest, Hungary email: szabo.robert@csfk.mta.hu
midterm exam thurs june 14 morning? evening? fri june 15 morning? evening? sat june 16 morning? afternoon? sun june 17 morning? afternoon?
 Prof. Jeff Kenney Class 11 June 11, 2018 midterm exam thurs june 14 morning? evening? fri june 15 morning? evening? sat june 16 morning? afternoon? sun june 17 morning? afternoon? observing session tomorrow
Prof. Jeff Kenney Class 11 June 11, 2018 midterm exam thurs june 14 morning? evening? fri june 15 morning? evening? sat june 16 morning? afternoon? sun june 17 morning? afternoon? observing session tomorrow
IDENTIFICATION CHARTS FOR 42 VARIABLE STARS DISCOVERED AT HARVARD. Arville D. Walker and Margaret Olmsted Harvard College Observatory
 IDENTIFICATION CHARTS FOR 42 VARIABLE STARS DISCOVERED AT HARVARD Arville D. Walker and Margaret Olmsted Harvard College Observatory Some time ago Dr. G. H. Herbig, acting for Commissions 27 and 29 of
IDENTIFICATION CHARTS FOR 42 VARIABLE STARS DISCOVERED AT HARVARD Arville D. Walker and Margaret Olmsted Harvard College Observatory Some time ago Dr. G. H. Herbig, acting for Commissions 27 and 29 of
The Local Group of Galaxies
 The Local Group of Galaxies Two large spiral galaxies Milky Way & Andromeda (Messier 31 or M31) Distance between them: D = 700 kpc = 2.3 x 10 6 light yrs Each large spiral galaxy has several smaller satellite
The Local Group of Galaxies Two large spiral galaxies Milky Way & Andromeda (Messier 31 or M31) Distance between them: D = 700 kpc = 2.3 x 10 6 light yrs Each large spiral galaxy has several smaller satellite
Dark Matter: Observational Constraints
 Dark Matter: Observational Constraints Properties of Dark Matter: What is it? And what isn t it? Leo Blitz UC Berkeley Stanford July 31, 2007 How much is there? WMAP results Rotation curves of Galaxies
Dark Matter: Observational Constraints Properties of Dark Matter: What is it? And what isn t it? Leo Blitz UC Berkeley Stanford July 31, 2007 How much is there? WMAP results Rotation curves of Galaxies
Milky Way Companions. Dave Nero. February 3, UT Astronomy Bag Lunch
 UT Astronomy Bag Lunch February 3, 2008 Outline 1 Background 2 Cats and Dogs, Hair and a Hero 3 Theoretical Evolution of the Galactic Halo Outline Background 1 Background 2 Cats and Dogs, Hair and a Hero
UT Astronomy Bag Lunch February 3, 2008 Outline 1 Background 2 Cats and Dogs, Hair and a Hero 3 Theoretical Evolution of the Galactic Halo Outline Background 1 Background 2 Cats and Dogs, Hair and a Hero
DISCOVERY OF VERY RED GIANTS IN THE FORNAX GALAXY
 Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific 91:761-765, December 1979 DISCOVERY OF VERY RED GIANTS IN THE FORNAX GALAXY SERGE DEMERS 0 Université de Montréal, Observatoire Astronomique du mont
Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific 91:761-765, December 1979 DISCOVERY OF VERY RED GIANTS IN THE FORNAX GALAXY SERGE DEMERS 0 Université de Montréal, Observatoire Astronomique du mont
Milky Way star clusters
 Using Γα ια for studying Milky Way star clusters Eugene Vasiliev Institute of Astronomy, Cambridge MODEST-, 26 June Overview of Gaia mission Scanning the entire sky every couple of weeks Astrometry for
Using Γα ια for studying Milky Way star clusters Eugene Vasiliev Institute of Astronomy, Cambridge MODEST-, 26 June Overview of Gaia mission Scanning the entire sky every couple of weeks Astrometry for
Ay162, Spring 2006 Week 8 p. 1 of 15
 Astronomy 162, Week 8 Milky Way Galaxy, continued Patrick S. Osmer Spring, 2006 Rotation of Galaxy How do we know the galaxy is rotating, and how do we measure its rotation? Measure radial velocities of
Astronomy 162, Week 8 Milky Way Galaxy, continued Patrick S. Osmer Spring, 2006 Rotation of Galaxy How do we know the galaxy is rotating, and how do we measure its rotation? Measure radial velocities of
It is about 100,000 ly across, 2,000 ly thick, and our solar system is located 26,000 ly away from the center of the galaxy.
 The Galaxies The Milky Way Galaxy Is a spiral galaxy in which our solar system is located. The center of the galaxy lies in the Sagittarius Constellation. It is about 100,000 ly across, 2,000 ly thick,
The Galaxies The Milky Way Galaxy Is a spiral galaxy in which our solar system is located. The center of the galaxy lies in the Sagittarius Constellation. It is about 100,000 ly across, 2,000 ly thick,
Analytical Solution for Stellar Density in Globular Clusters
 J. Astrophys. Astr. 2011) 32, 371 376 c Indian Academy of Sciences Analytical Solution for Stellar Density in Globular Clusters M. A. Sharaf &A.M.Sendi Department of Astronomy, Faculty of Science, King
J. Astrophys. Astr. 2011) 32, 371 376 c Indian Academy of Sciences Analytical Solution for Stellar Density in Globular Clusters M. A. Sharaf &A.M.Sendi Department of Astronomy, Faculty of Science, King
24.1 Hubble s Galaxy Classification
 Chapter 24 Galaxies Units of Chapter 24 24.1 Hubble s Galaxy Classification 24.2 The Distribution of Galaxies in Space 24.3 Hubble s Law 24.4 XXActive Galactic Nuclei XXRelativistic Redshifts and Look-Back
Chapter 24 Galaxies Units of Chapter 24 24.1 Hubble s Galaxy Classification 24.2 The Distribution of Galaxies in Space 24.3 Hubble s Law 24.4 XXActive Galactic Nuclei XXRelativistic Redshifts and Look-Back
Galaxies. The majority of known galaxies fall into one of three major classes: spirals (78 %), ellipticals (18 %) and irregulars (4 %).
 Galaxies Collection of stars, gas and dust bound together by their common gravitational pull. Galaxies range from 10,000 to 200,000 light-years in size. 1781 Charles Messier 1923 Edwin Hubble The distribution
Galaxies Collection of stars, gas and dust bound together by their common gravitational pull. Galaxies range from 10,000 to 200,000 light-years in size. 1781 Charles Messier 1923 Edwin Hubble The distribution
BHS Astronomy: Galaxy Classification and Evolution
 Name Pd Date BHS Astronomy: Galaxy Classification and Evolution This lab comes from http://cosmos.phy.tufts.edu/~zirbel/ast21/homework/hw-8.pdf (Tufts University) The word galaxy, having been used in English
Name Pd Date BHS Astronomy: Galaxy Classification and Evolution This lab comes from http://cosmos.phy.tufts.edu/~zirbel/ast21/homework/hw-8.pdf (Tufts University) The word galaxy, having been used in English
My Favorite Deep Sky Go-To Tour (aka: The List)
 The following list is a result of too many nights racing through Messier marathons, wandering through the Herschel 400, scanning the southern horizon for unexpected treasures, star-hopping for invisible
The following list is a result of too many nights racing through Messier marathons, wandering through the Herschel 400, scanning the southern horizon for unexpected treasures, star-hopping for invisible
Chapter 17. Galaxies. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 17 Galaxies Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Galaxies Beyond the Milky Way are billions of other galaxies Some galaxies are spiral like
Chapter 17 Galaxies Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Galaxies Beyond the Milky Way are billions of other galaxies Some galaxies are spiral like
Lecture 14: Other Galaxies A2020 Prof. Tom Megeath. The Milky Way in the Infrared 3/17/10. NGC 7331: the Milky Way s Twins. Spiral Galaxy bulge halo
 Lecture 14: Other Galaxies A2020 Prof. Tom Megeath Our Galaxy: Side View We see our galaxy edge-on Primary features: Disk: young and old stars where we live. Bulge: older stars Halo: oldest stars, globular
Lecture 14: Other Galaxies A2020 Prof. Tom Megeath Our Galaxy: Side View We see our galaxy edge-on Primary features: Disk: young and old stars where we live. Bulge: older stars Halo: oldest stars, globular
GALAXIES: BRIGHTEST AND NEAREST
 330 Brightest and Nearest Galaxies GALAXIES: BRIGHTEST AND NEAREST BY BARRY F. MADORE AND IAN STEER External galaxies are generally of such low surface brightness that they often prove disappointing objects
330 Brightest and Nearest Galaxies GALAXIES: BRIGHTEST AND NEAREST BY BARRY F. MADORE AND IAN STEER External galaxies are generally of such low surface brightness that they often prove disappointing objects
M31 - Andromeda Galaxy M110 M32
 UNIT 4 - Galaxies XIV. The Milky Way galaxy - a huge collection of millions or billions of stars, gas, and dust, isolated in space and held together by its own gravity M110 M31 - Andromeda Galaxy A. Structure
UNIT 4 - Galaxies XIV. The Milky Way galaxy - a huge collection of millions or billions of stars, gas, and dust, isolated in space and held together by its own gravity M110 M31 - Andromeda Galaxy A. Structure
Our Milky Way Galaxy
 Our Milky Way Galaxy What is our Milky Way Galaxy made of? Stars and gas orbit the galaxy. Dark, unseen, matter makes up most of the mass. Test 3 (New date) Thurs, 9 April One cheat sheet Study guide &
Our Milky Way Galaxy What is our Milky Way Galaxy made of? Stars and gas orbit the galaxy. Dark, unseen, matter makes up most of the mass. Test 3 (New date) Thurs, 9 April One cheat sheet Study guide &
The Milky Way & Galaxies
 The Milky Way & Galaxies The Milky Way Appears as a milky band of light across the sky A small telescope reveals that it is composed of many stars (Galileo again!) Our knowledge of the Milky Way comes
The Milky Way & Galaxies The Milky Way Appears as a milky band of light across the sky A small telescope reveals that it is composed of many stars (Galileo again!) Our knowledge of the Milky Way comes
Introduction to Galaxies
 Introduction to Galaxies History Famous Galaxies Catalogs and Atlases Classification Schemes What is a galaxy? - A gravitationally bound collection of stars - A galaxy has 10 6 to 10 12 stars - Participates
Introduction to Galaxies History Famous Galaxies Catalogs and Atlases Classification Schemes What is a galaxy? - A gravitationally bound collection of stars - A galaxy has 10 6 to 10 12 stars - Participates
The Universe o. Galaxies. The Universe of. Galaxies. Ajit Kembhavi IUCAA
 Hello! The Universe of Galaxies The Universe o Galaxies Ajit Kembhavi IUCAA Galaxies: Stars: ~10 11 Mass: ~10 11 M Sun Contain stars, gas and dust, possibly a supermassive black hole at the centre. Much
Hello! The Universe of Galaxies The Universe o Galaxies Ajit Kembhavi IUCAA Galaxies: Stars: ~10 11 Mass: ~10 11 M Sun Contain stars, gas and dust, possibly a supermassive black hole at the centre. Much
Applications and Remote Sensing, Penteli, Athens, Hellas; noa.gr. Astronomy and Mechanics, Zografos, Athens, Hellas; phys.uoa.
 Binaries with aδscuti component: Results from a long term observational survey, updated catalogue and future prospects arxiv:1506.07409v1 [astro-ph.sr] 24 Jun 2015 Alexios Liakos 1 and Panagiotis Niarchos
Binaries with aδscuti component: Results from a long term observational survey, updated catalogue and future prospects arxiv:1506.07409v1 [astro-ph.sr] 24 Jun 2015 Alexios Liakos 1 and Panagiotis Niarchos
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 24. Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 24 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 24 Galaxies Units of Chapter 24 24.1 Hubble s Galaxy Classification 24.2 The Distribution of Galaxies in Space 24.3 Hubble
Lecture Outlines Chapter 24 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 24 Galaxies Units of Chapter 24 24.1 Hubble s Galaxy Classification 24.2 The Distribution of Galaxies in Space 24.3 Hubble
The Milky Way Galaxy
 The Milky Way Galaxy A. Expert - I have done a lot of reading in this area already. B. Above Average - I have learned some information about this topic. C. Moderate - I know a little about this topic.
The Milky Way Galaxy A. Expert - I have done a lot of reading in this area already. B. Above Average - I have learned some information about this topic. C. Moderate - I know a little about this topic.
Galaxies. CESAR s Booklet
 What is a galaxy? Figure 1: A typical galaxy: our Milky Way (artist s impression). (Credit: NASA) A galaxy is a huge collection of stars and interstellar matter isolated in space and bound together by
What is a galaxy? Figure 1: A typical galaxy: our Milky Way (artist s impression). (Credit: NASA) A galaxy is a huge collection of stars and interstellar matter isolated in space and bound together by
Outline. The Rotation of the Galaxy. Astronomy: The Big Picture
 I decided to cancel class next week! No homework until you get back. Honor credit need to have those papers soon! Exam 2 Grades are posted. Nighttime observing should be posted today. Interest in grade
I decided to cancel class next week! No homework until you get back. Honor credit need to have those papers soon! Exam 2 Grades are posted. Nighttime observing should be posted today. Interest in grade
03:00 Dec h. Men. 06 h. 07 h. 08h. 09h. Cha. Ara Tel. 12 h. Nor. CrA. Lup. Sco. Sgr Cap Lib. Ser. Sct Aql Oph. Ser. Finder Chart 3. Boo.
 ConCards (Field edition) Version 4.5 ConCards (Field edition) Version 4.5 mid-february to September Jan Feb Mar Apr ConCards May Jun (Field Jul edition) Aug Version 4.5 Sep Oct Nov Dec April to mid-october
ConCards (Field edition) Version 4.5 ConCards (Field edition) Version 4.5 mid-february to September Jan Feb Mar Apr ConCards May Jun (Field Jul edition) Aug Version 4.5 Sep Oct Nov Dec April to mid-october
Astronomy A BEGINNER S GUIDE TO THE UNIVERSE EIGHTH EDITION
 Astronomy A BEGINNER S GUIDE TO THE UNIVERSE EIGHTH EDITION CHAPTER 14 The Milky Way Galaxy Lecture Presentation 14.0 the Milky Way galaxy How do we know the Milky Way exists? We can see it even though
Astronomy A BEGINNER S GUIDE TO THE UNIVERSE EIGHTH EDITION CHAPTER 14 The Milky Way Galaxy Lecture Presentation 14.0 the Milky Way galaxy How do we know the Milky Way exists? We can see it even though
Atlantis Challenger Columbia. Discovery Endeavour Enterprise
 T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 SCORE: 150 / 150 + Bonus 2 KEY: Alternative, acceptable answers are given in brackets Bonus: Name NASA s 6 space shuttles 1 bonus point per 3 correct answers. (2 pts total) Atlantis Challenger
T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 SCORE: 150 / 150 + Bonus 2 KEY: Alternative, acceptable answers are given in brackets Bonus: Name NASA s 6 space shuttles 1 bonus point per 3 correct answers. (2 pts total) Atlantis Challenger
The Milky Way Galaxy
 1/5/011 The Milky Way Galaxy Distribution of Globular Clusters around a Point in Sagittarius About 00 globular clusters are distributed in random directions around the center of our galaxy. 1 1/5/011 Structure
1/5/011 The Milky Way Galaxy Distribution of Globular Clusters around a Point in Sagittarius About 00 globular clusters are distributed in random directions around the center of our galaxy. 1 1/5/011 Structure
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 17 Aug 2001
 HOW DID GLOBULAR CLUSTERS FORM? Sidney van den Bergh Dominion Astrophysical Observatory, Herzberg Institute of Astrophysics, National arxiv:astro-ph/0108298v1 17 Aug 2001 Research Council of Canada, 5071
HOW DID GLOBULAR CLUSTERS FORM? Sidney van den Bergh Dominion Astrophysical Observatory, Herzberg Institute of Astrophysics, National arxiv:astro-ph/0108298v1 17 Aug 2001 Research Council of Canada, 5071
Introduction to SDSS -instruments, survey strategy, etc
 Introduction to SDSS -instruments, survey strategy, etc (materials from http://www.sdss.org/) Shan Huang 17 February 2010 Survey type Status Imaging and Spectroscopy Basic Facts SDSS-II completed, SDSS-III
Introduction to SDSS -instruments, survey strategy, etc (materials from http://www.sdss.org/) Shan Huang 17 February 2010 Survey type Status Imaging and Spectroscopy Basic Facts SDSS-II completed, SDSS-III
The role of SW Sex stars in the evolution of CVs
 European Southern Observatory Chile Wild Stars in the West II, Tucson 2009 The orbital period distribution SW Sextantis stars in a nutshell Original definition (Thorstensen et al. 1991, AJ 102, 272): novalike
European Southern Observatory Chile Wild Stars in the West II, Tucson 2009 The orbital period distribution SW Sextantis stars in a nutshell Original definition (Thorstensen et al. 1991, AJ 102, 272): novalike
Galaxies. Lecture Topics. Lecture 23. Discovering Galaxies. Galaxy properties. Local Group. History Cepheid variable stars. Classifying galaxies
 Galaxies Lecture 23 APOD: NGC 3628 (The Hamburger Galaxy) 1 Lecture Topics Discovering Galaxies History Cepheid variable stars Galaxy properties Classifying galaxies Local Group 2 23-1 Discovering Galaxies
Galaxies Lecture 23 APOD: NGC 3628 (The Hamburger Galaxy) 1 Lecture Topics Discovering Galaxies History Cepheid variable stars Galaxy properties Classifying galaxies Local Group 2 23-1 Discovering Galaxies
The Milky Way: Home to Star Clusters
 Chapter 2 The Milky Way: Home to The Milky Our Galaxy, the Milky Way, is something of a paradox. It is just one of the many billions of galaxies scattered throughout the Universe, a large, but quite normal
Chapter 2 The Milky Way: Home to The Milky Our Galaxy, the Milky Way, is something of a paradox. It is just one of the many billions of galaxies scattered throughout the Universe, a large, but quite normal
Chapter 15 The Milky Way Galaxy. The Milky Way
 Chapter 15 The Milky Way Galaxy The Milky Way Almost everything we see in the night sky belongs to the Milky Way We see most of the Milky Way as a faint band of light across the sky From the outside, our
Chapter 15 The Milky Way Galaxy The Milky Way Almost everything we see in the night sky belongs to the Milky Way We see most of the Milky Way as a faint band of light across the sky From the outside, our
A galaxy is a self-gravitating system composed of an interstellar medium, stars, and dark matter.
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 What is a Galaxy? It s surprisingly difficult to answer the question what is a galaxy? Many astronomers seem content to say I know one when I see one. But one possible definition
Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 What is a Galaxy? It s surprisingly difficult to answer the question what is a galaxy? Many astronomers seem content to say I know one when I see one. But one possible definition
11.1 Galaxies: Morphology and the Hubble Sequence
 11.1 Galaxies: Morphology and the Hubble Sequence Galaxies The basic constituents of the universe at large scales Distinct from the LSS as being too dense by a factor of ~10 3, indicative of an extra collapse,
11.1 Galaxies: Morphology and the Hubble Sequence Galaxies The basic constituents of the universe at large scales Distinct from the LSS as being too dense by a factor of ~10 3, indicative of an extra collapse,
Halo Tidal Star Streams with DECAM. Brian Yanny Fermilab. DECam Community Workshop NOAO Tucson Aug
 Halo Tidal Star Streams with DECAM Brian Yanny Fermilab DECam Community Workshop NOAO Tucson Aug 19 2011 M31 (Andromeda) Our Local Group neighbors: Spiral galaxies similar to The Milky Way 150 kpc M33
Halo Tidal Star Streams with DECAM Brian Yanny Fermilab DECam Community Workshop NOAO Tucson Aug 19 2011 M31 (Andromeda) Our Local Group neighbors: Spiral galaxies similar to The Milky Way 150 kpc M33
Evolution of second generation stars in stellar disks of globular and nuclear clusters: ω Centauri as a test case
 Evolution of second generation stars in stellar disks of globular and nuclear clusters: ω Centauri as a test case Alessandra Mastrobuono-Battisti & Hagai Perets Outline Dense stellar clusters: Nuclear
Evolution of second generation stars in stellar disks of globular and nuclear clusters: ω Centauri as a test case Alessandra Mastrobuono-Battisti & Hagai Perets Outline Dense stellar clusters: Nuclear
Stellar Systems with HST
 Stellar Systems with HST (With European Impact) Topics: Surprizing Globular Clusters in the Milky Way The MW Bulge and its Globulars The Bulge, Halo, Stream and Disk of Andromeda Bulges at high redshifts
Stellar Systems with HST (With European Impact) Topics: Surprizing Globular Clusters in the Milky Way The MW Bulge and its Globulars The Bulge, Halo, Stream and Disk of Andromeda Bulges at high redshifts
The Classification of Galaxies
 Admin. 11/9/17 1. Class website http://www.astro.ufl.edu/~jt/teaching/ast1002/ 2. Optional Discussion sections: Tue. ~11.30am (period 5), Bryant 3; Thur. ~12.30pm (end of period 5 and period 6), start
Admin. 11/9/17 1. Class website http://www.astro.ufl.edu/~jt/teaching/ast1002/ 2. Optional Discussion sections: Tue. ~11.30am (period 5), Bryant 3; Thur. ~12.30pm (end of period 5 and period 6), start
Stellar Populations in the Local Group
 Stellar Populations in the Local Group Recall what we ve learned from the Milky Way: Age and metallicity tend to be correlated: older -> lower heavy element content younger -> greater heavy element content
Stellar Populations in the Local Group Recall what we ve learned from the Milky Way: Age and metallicity tend to be correlated: older -> lower heavy element content younger -> greater heavy element content
Troubleshooting Checklist
 Appendix A Troubleshooting Checklist Troubleshooting Steps for the SkyPortal Alignment If you are having difficulty with your SkyPortal system, please review these steps before calling for technical support:
Appendix A Troubleshooting Checklist Troubleshooting Steps for the SkyPortal Alignment If you are having difficulty with your SkyPortal system, please review these steps before calling for technical support:
Our Galaxy. We are located in the disk of our galaxy and this is why the disk appears as a band of stars across the sky.
 Our Galaxy Our Galaxy We are located in the disk of our galaxy and this is why the disk appears as a band of stars across the sky. Early attempts to locate our solar system produced erroneous results.
Our Galaxy Our Galaxy We are located in the disk of our galaxy and this is why the disk appears as a band of stars across the sky. Early attempts to locate our solar system produced erroneous results.
