The Higgs field as the Origin of the Big Bang The first second of the Universe (and the following years!)
|
|
|
- Melvin Booker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Higgs field as the Origin of the Big Bang The first second of the Universe (and the following years!) Daniel G. Figueroa CERN, Theory Division
2 Cosmology = Study of the Universe as a WHOLE (Evolution, Content, "Birth", "Death", )
3 UNiVERSE space' CONTAINER of MATTER (atoms, galaxies, + more exotic objects')
4 UNiVERSE = Space Containing all Matter 'Geometry'??? 'Energy'
5 UNiVERSE = Space Containing all Matter 'Geometry'??? 'Energy' Space-Time' Geometry dictates Movement of Matter Presence of Matter (Energy) dictates Space-Time' Geometry
6 UNiVERSE = Space Containing all Matter 'Geometry'??? 'Energy' Space-Time' Geometry dictates Movement of Matter Presence of Matter (Energy) dictates Space-Time' Geometry
7 UNiVERSE = Space Containing all Matter 'Geometry'??? 'Energy' Space-Time' Geometry dictates Movement of Matter Presence of Matter (Energy) dictates Space-Time' Geometry
8 Space-Time Matter Theory of GENERAL RELATIVITY (Einstein,1915) GENERAL RELATIVITY = THEORY of GRAVITY
9 UNiVERSE = Space Containing all Matter
10 UNiVERSE = Space Containing all Matter
11 UNiVERSE at LARGE SCALES?
12 UNiVERSE at LARGE SCALES? Cosmological Principle: HOMOGENEOUS and ISOTROPIC
13 UNiVERSE at LARGE SCALES? Cosmological Principle: HOMOGENEOUS and ISOTROPIC SAME EVERYWHERE! SAME IN EVERY DIRECTION!
14 HOMOGENEOUS and ISOTROPIC (Millenium Simulation)
15 UNiVERSE: HOMOGENEOUS and isotropic ENERGY-MATTER GENERAL RELATIVITY SPACE-TIME GEOMETRY
16 UNiVERSE: HOMOGENEOUS and isotropic ENERGY-MATTER GENERAL RELATIVITY SPACE-TIME GEOMETRY Cosmological Principle HOMOGENEOUS & ISOTROPIC
17 UNiVERSE: HOMOGENEOUS and isotropic ENERGY-MATTER GENERAL RELATIVITY SPACE-TIME GEOMETRY Cosmological Principle HOMOGENEOUS & ISOTROPIC 1) Geometry: Flat/Close/Open 2) Dynamics: EXPANDING UNIVERSE!
18 UNiVERSE: HOMOGENEOUS and isotropic ENERGY-MATTER GENERAL RELATIVITY SPACE-TIME GEOMETRY Cosmological Principle HOMOGENEOUS & ISOTROPIC 1) Geometry: Flat/Close/Open 2) Dynamics: EXPANDING UNIVERSE! Theoretical Basis for BIG BANG theory!
19 UNiVERSE: HOMOGENEOUS and isotropic BIG BANG THEORY: { Geometry: Close/Open/Flat Dynamics: EXPANDING Universe
20 UNiVERSE: HOMOGENEOUS and isotropic BIG BANG THEORY: { Geometry: Close/Open/Flat Dynamics: EXPANDING Universe
21 UNiVERSE: HOMOGENEOUS and isotropic BIG BANG THEORY: { Geometry: Close/Open/Flat Dynamics: EXPANDING Universe
22 UNiVERSE: HOMOGENEOUS and isotropic BIG BANG THEORY: { Geometry: Close/Open/Flat Dynamics: EXPANDING Universe BIG BANG? t = 0?
23 COSMIC HISTORY of the UNiVERSE
24 COSMIC HISTORY of the UNiVERSE TODAY [Galaxies, Clusters, ] ( Million years) FIRST GALAXIES (500 Millions years) ATOMS CREATION ( years) ATOMIC NUCLEI CREATION (3 minutes!!!) FIRST SECOND of the UNIVERSE!!
25 Universe SUMMARY Homogeneous & Isotropic Universe is Expanding (Geom: Flat, Close, Open) Cosmic Epochs: Galaxy Formation, Creation of Atoms, Creation of atomic nuclei, Creation of all elementary particles
26 Cosmic Epochs: Galaxy Formation (500 Million years) GAS of PARTiCLES (homogeneous & isotropic) Gravitational Attraction 'Lumps
27 Cosmic Epochs: Galaxy Formation (500 Million years) GAS of PARTiCLES (homogeneous & isotropic) Gravitational Attraction 'Lumps GALAXIES!
28 Cosmic Epochs: Galaxy Formation (500 Million years) GAS of PARTiCLES (homogeneous & isotropic) [not completely!] = (1 ± ) O(10 5 ) Gravitational Attraction 'Lumps GALAXIES!
29 Etapas Cósmicas: Formación Galaxias (500 Millones años) GAS of PARTiCLES Gravitational (homogeneous & isotropic) Attraction [not completely!] = (1 ± ) O(10 5 ) Gravitational Attraction 'Lumps GALAXIES! ( 1)
30 LARGE SCALE STRUCTURE of the UNIVERSE MILLENNIUM Simulations AREPO Simulations
31 COSMIC HISTORY of the UNiVERSE BiGGER size, SMALLER Temp TODAY [Galaxies, Clusters, ] ( Million years) FIRST GALAXIES (500 Millions years) ATOMS CREATION ( years) ATOMIC NUCLEI CREATION (3 minutes!!!) SMALLER SIZE, LARGER Temperature FIRST SECOND of the UNIVERSE!!
32 Cosmic Epochs: Formation of atoms ( yrs) Past, hotter Protons, Electrons, Photons Interact electromagnetically Universe cools down Photons do not have enough energy to break apart atoms, Then electrons join to the atomic nuclei: Atoms formed!!! Atoms formed! Light (electromagnetic radiation) set free! Later, colder
33 Cosmic Epochs: Formation of atoms ( yrs) Photons red-shifted and dispersed by gravity wells! Atom Formation: Free propagation of light!! (Recombination)
34 Cosmic Epochs: Formation of atoms ( yrs) Where is that light? Everywhere! BiGGER size, SMALLER Temp TODAY [Galaxies, Clusters, ] ( Million years) FIRST GALAXIES (500 Millions years) ATOMS FORMATION ( years) Emission of Cosmic Microwave Radiation! ATOMIC NUCLEI FORMATION (3 minutes!!!) SMALLER SIZE, LARGER Temperature FIRST SECOND of the UNIVERSE!!
35 Cosmic Epochs: Formation of atoms ( yrs) Where is that light? Everywhere! T (2) Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) T (1) c t
36 Cosmic Epochs: Formation of atoms ( yrs) Where is that light? Everywhere! PLANCK Satellite Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) Definitive proof of the Big Bang Theory! (almost-)isotropic But. There are small Inhomogeneities'!!! (variations of 1/ )
37 Cosmic Epochs: Formation of atoms ( yrs) Properties of the Cosmic Microwave Background Properties of the Anisotropies then. Geometry of the Universe! The UNIVERSE has FLAT GEOMETRY!
38 COSMIC HISTORY of the UNiVERSE BiGGER size, SMALLER Temp TODAY [Galaxies, Clusters, ] ( Million years) FIRST GALAXIES (500 Millions years) ATOMS FORMATION ( years) (+ CMB emisión!) ATOMIC NUCLEI FORMATION (3 minutes!) SMALLER SIZE, LARGER Temperature FIRST SECOND of the UNIVERSE!!
39 Cosmic Epochs: Formation of atomic nuclei (3 mins) Past, hotter (1 second) Afterwards, colder (3 minutes) Protons, Neutrons Interact strongly Universe cools down protons and neutrons don't have sufficient energy anymore Then they join together forming atomic nuclei: Nuclear Physics! Atomic Nuclei created!
40 Cosmic Epochs: Formation of atomic nuclei (3 mins) NUCLEAR PHYSICS (measured in the lab) Lets to predict abundances of H, 4 He, D, 3 He, 7 Li,... Another definitive proof of the Big Bang theory!
41 COSMIC HISTORY of the UNiVERSE BiGGER size, SMALLER Temp TODAY [Galaxies, Clusters, ] ( Million years) FIRST GALAXIES (500 Millions years) ATOMS CREATION ( years) (+ CMB emisión!) ATOMIC NUCLEI FORMATION (3 minutes!) SMALLER SIZE, LARGER Temperature FIRST SECOND of the UNIVERSE!!
42 $ 000$yr >$400. CMB$ $Photons$(light)$decouple$ ($$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$)$ and$propagate$freely$$ Cosmic 00$yr$ ~$400.0 Epochs: Notation : The first Second of the Universe! 10 n RECOMBINATION$ Protons$and$electrons$ seg = seg $($$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$)$ combine$to$form$atoms$ $ 000$yr ~$300. NUCLEOSYNTHESIS$ Light$Nucleii$form,$aLer$ electron^positron$annihila6on$ and$neutrino$decoupling$$ $ $3$min $ c e s $ 1 $($$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$)$ QUARK$CONFINEMENT$ Quarks$bind$into$Hadrons$ ($$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$)$ (protons$&$neutrons)$ EW$UNIFICATION$ ElectroMagne6sm$&$ ($$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$)$ weak$interac6ons$unify$ c$ 10^4 $se c ^ 1 0 $se 10 BARYOGENESIS$?$ $ MaVer$remains,$$$ ($$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$)$ An6^MaVer$disappears$ GRAND$UNIFICATION$?$ ^ 3 5 $sec$? >$10 All$forces$unified$ ($$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$)$ into$a$single$one$?$ c$?$ REHEATING$ ^ 3 5 $se 10 All$maVer$in$the$$ ($$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$)$ Universe$is$created$ ^ 3 6 $sec$ >$10 INFLATION$ ($$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$)$ Exponen6al$Expansion$$ of$the$universe$ c ^ 3 6 $se 0 ^43$ $1 10 $ $??$ Particle Accelerators (LHC): Reach up to 10 CopyleL:$Daniel$G.$Figueroa,$June$2014$ 10 sec
43 SUMMARY Universe has expanded for million years! Several Epochs have been crucial in the evolution of the Universe The first second is crucial to understand the evolution afterwards But yet we DON'T UNDERSTAND that First Second!
44 WHAT DID I NOT TELL YOU? MANY THINGS!!!
45 WHAT DID I NOT TELL YOU? COSMIC INFLATION! Needed for Consistency of the Big Bang theory! 1 cm cm
46 WHAT DID I NOT TELL YOU? Reheating: Production of all the particles in the Universe (after Inflation) SM SM * Higgs is the only Spin = 0 particle in the Standard Model! -X 10 s Reheating ~ 1 s Thermal Plasma SM BBN (p, n, ) SM SM * How to connect Inflation with the Standard Model: Possibly through the Higgs! (but we don t know)
47 WHAT DID I NOT TELL YOU? DARK ENERGY! (Accelerated Expansion) DARK MATTER!
48 WHAT DID I NOT TELL YOU? Matter content within the Universe
49 WHAT DID I NOT TELL YOU?
50 WHAT DID I NOT TELL YOU? THANKS FOR YOUR ATTENTION!!
51 To know more (books) The first three minutes (S. Weinberg) Big Bang Theory Black holes and warped spacetime (K. Thorne) Gravity The Charm of Physics (S. L. Glashow) Particle Physics The Elegant Universe (B. Green) El Inflationary Universe (A. Guth) String Theory Inflationary Paradigm
52 Open Questions What is Dark Matter made of? What is Dark Energy? Is there a "before" the Big Bang? Is the Universe Infinite? How did the anti-matter disappear? How did the Universe appeared? Did Inflation really occurred?...
Lab Monday optional: review for Quiz 3. Lab Tuesday optional: review for Quiz 3.
 Announcements SEIs! Quiz 3 Friday. Lab Monday optional: review for Quiz 3. Lab Tuesday optional: review for Quiz 3. Lecture today, Wednesday, next Monday. Final Labs Monday & Tuesday next week. Quiz 3
Announcements SEIs! Quiz 3 Friday. Lab Monday optional: review for Quiz 3. Lab Tuesday optional: review for Quiz 3. Lecture today, Wednesday, next Monday. Final Labs Monday & Tuesday next week. Quiz 3
Astr 2320 Thurs. May 7, 2015 Today s Topics Chapter 24: New Cosmology Problems with the Standard Model Cosmic Nucleosynthesis Particle Physics Cosmic
 Astr 2320 Thurs. May 7, 2015 Today s Topics Chapter 24: New Cosmology Problems with the Standard Model Cosmic Nucleosynthesis Particle Physics Cosmic Inflation Galaxy Formation 1 Chapter 24: #3 Chapter
Astr 2320 Thurs. May 7, 2015 Today s Topics Chapter 24: New Cosmology Problems with the Standard Model Cosmic Nucleosynthesis Particle Physics Cosmic Inflation Galaxy Formation 1 Chapter 24: #3 Chapter
Implications of the Hubble Law: - it is not static, unchanging - Universe had a beginning!! - could not have been expanding forever HUBBLE LAW:
 Cosmology and the Evolution of the Universe Edwin Hubble, 1929: -almost all galaxies have a redshift -moving away from us -greater distance greater redshift Implications of the Hubble Law: - Universe is
Cosmology and the Evolution of the Universe Edwin Hubble, 1929: -almost all galaxies have a redshift -moving away from us -greater distance greater redshift Implications of the Hubble Law: - Universe is
Cosmology and the Evolution of the Universe. Implications of the Hubble Law: - Universe is changing (getting bigger!) - it is not static, unchanging
 Cosmology and the Evolution of the Edwin Hubble, 1929: -almost all galaxies have a redshift -moving away from us -exceptions in Local Group -with distance measurements - found a relationship greater distance
Cosmology and the Evolution of the Edwin Hubble, 1929: -almost all galaxies have a redshift -moving away from us -exceptions in Local Group -with distance measurements - found a relationship greater distance
Astronomy 113. Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D.
 Astronomy 113 Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. The Big Bang & Matter 17-2 Cosmology ³ The study of the origins, structure, and evolution of the universe ³ Key moments: ² Einstein General Theory of Relativity
Astronomy 113 Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. The Big Bang & Matter 17-2 Cosmology ³ The study of the origins, structure, and evolution of the universe ³ Key moments: ² Einstein General Theory of Relativity
Astronomy 113. Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. The Big Bang & Matter. Olber s Paradox. Cosmology. Olber s Paradox. Assumptions 4/20/18
 Astronomy 113 Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. The Big Bang & Matter Cosmology ³The study of the origins, structure, and evolution of the universe ³Key moments: ²Einstein General Theory of Relativity ²Hubble
Astronomy 113 Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. The Big Bang & Matter Cosmology ³The study of the origins, structure, and evolution of the universe ³Key moments: ²Einstein General Theory of Relativity ²Hubble
Particles in the Early Universe
 Particles in the Early Universe David Morrissey Saturday Morning Physics, October 16, 2010 Using Little Stuff to Explain Big Stuff David Morrissey Saturday Morning Physics, October 16, 2010 Can we explain
Particles in the Early Universe David Morrissey Saturday Morning Physics, October 16, 2010 Using Little Stuff to Explain Big Stuff David Morrissey Saturday Morning Physics, October 16, 2010 Can we explain
ASTR 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies
 ASTR 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies ANNOUNCEMENTS FINAL EXAM: THURSDAY, May 14 th, 11:15am Last Astronomy public talk, May 8 th (up to 3% Extra class credit (see Blackboard announcement for details)
ASTR 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies ANNOUNCEMENTS FINAL EXAM: THURSDAY, May 14 th, 11:15am Last Astronomy public talk, May 8 th (up to 3% Extra class credit (see Blackboard announcement for details)
Astronomy 182: Origin and Evolution of the Universe
 Astronomy 182: Origin and Evolution of the Universe Prof. Josh Frieman Lecture 12 Nov. 18, 2015 Today Big Bang Nucleosynthesis and Neutrinos Particle Physics & the Early Universe Standard Model of Particle
Astronomy 182: Origin and Evolution of the Universe Prof. Josh Frieman Lecture 12 Nov. 18, 2015 Today Big Bang Nucleosynthesis and Neutrinos Particle Physics & the Early Universe Standard Model of Particle
ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies. OUR Universe: Accelerating Universe
 ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies FINAL: Saturday, Dec 12th, 7:30pm, HERE ALTERNATE FINAL: Monday, Dec 7th, 5:30pm in Muenzinger E131 Last OBSERVING session, Tue, Dec.8th, 7pm Please check
ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies FINAL: Saturday, Dec 12th, 7:30pm, HERE ALTERNATE FINAL: Monday, Dec 7th, 5:30pm in Muenzinger E131 Last OBSERVING session, Tue, Dec.8th, 7pm Please check
Chapter 22 Reading Quiz Clickers. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. The Birth of the Universe Pearson Education, Inc.
 Reading Quiz Clickers The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition The Birth of the Universe 22.1 The Big Bang Theory What were conditions like in the early universe? How did the early universe change with time?
Reading Quiz Clickers The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition The Birth of the Universe 22.1 The Big Bang Theory What were conditions like in the early universe? How did the early universe change with time?
Chapter 22 Back to the Beginning of Time
 Chapter 22 Back to the Beginning of Time Expansion of Universe implies dense, hot start: Big Bang Back to the Big Bang The early Universe was both dense and hot. Equivalent mass density of radiation (E=mc
Chapter 22 Back to the Beginning of Time Expansion of Universe implies dense, hot start: Big Bang Back to the Big Bang The early Universe was both dense and hot. Equivalent mass density of radiation (E=mc
i>clicker Quiz #14 Which of the following statements is TRUE?
 i>clicker Quiz #14 Which of the following statements is TRUE? A. Hubble s discovery that most distant galaxies are receding from us tells us that we are at the center of the Universe B. The Universe started
i>clicker Quiz #14 Which of the following statements is TRUE? A. Hubble s discovery that most distant galaxies are receding from us tells us that we are at the center of the Universe B. The Universe started
What forms AGN Jets? Magnetic fields are ferociously twisted in the disk.
 What forms AGN Jets? Magnetic fields are ferociously twisted in the disk. Charged particles are pulled out of the disk and accelerated like a sling-shot. Particles are bound to the magnetic fields, focussed
What forms AGN Jets? Magnetic fields are ferociously twisted in the disk. Charged particles are pulled out of the disk and accelerated like a sling-shot. Particles are bound to the magnetic fields, focussed
Lecture 24: Cosmology: The First Three Minutes. Astronomy 111 Monday November 27, 2017
 Lecture 24: Cosmology: The First Three Minutes Astronomy 111 Monday November 27, 2017 Reminders Last star party of the semester tomorrow night! Online homework #11 due Monday at 3pm The first three minutes
Lecture 24: Cosmology: The First Three Minutes Astronomy 111 Monday November 27, 2017 Reminders Last star party of the semester tomorrow night! Online homework #11 due Monday at 3pm The first three minutes
THE PHYSICS/COSMOLOGY CONNECTION. 1. Summary of Particle Physics: The Standard Model limitations of the standard model
 THE PHYSICS/COSMOLOGY CONNECTION 1. Summary of Particle Physics: The Standard Model limitations of the standard model 2. Summary of Cosmology: The Big Bang Model limitations of the Big Bang model 3. Unifying
THE PHYSICS/COSMOLOGY CONNECTION 1. Summary of Particle Physics: The Standard Model limitations of the standard model 2. Summary of Cosmology: The Big Bang Model limitations of the Big Bang model 3. Unifying
Chapter 22 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective. Seventh Edition. The Birth of the Universe Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 22 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition The Birth of the Universe The Birth of the Universe 22.1 The Big Bang Theory Our goals for learning: What were conditions like in the early universe?
Chapter 22 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition The Birth of the Universe The Birth of the Universe 22.1 The Big Bang Theory Our goals for learning: What were conditions like in the early universe?
Chapter 22: Cosmology - Back to the Beginning of Time
 Chapter 22: Cosmology - Back to the Beginning of Time Expansion of Universe implies dense, hot start: Big Bang Future of universe depends on the total amount of dark and normal matter Amount of matter
Chapter 22: Cosmology - Back to the Beginning of Time Expansion of Universe implies dense, hot start: Big Bang Future of universe depends on the total amount of dark and normal matter Amount of matter
MIT Exploring Black Holes
 THE UNIVERSE and Three Examples Alan Guth, MIT MIT 8.224 Exploring Black Holes EINSTEIN'S CONTRIBUTIONS March, 1916: The Foundation of the General Theory of Relativity Feb, 1917: Cosmological Considerations
THE UNIVERSE and Three Examples Alan Guth, MIT MIT 8.224 Exploring Black Holes EINSTEIN'S CONTRIBUTIONS March, 1916: The Foundation of the General Theory of Relativity Feb, 1917: Cosmological Considerations
I V E R S U N. The Hot Big Bang I T Y T H E O F E. Andrew Liddle R G. Image: NASA/WMAP Science Team
 The Hot Big Bang Andrew Liddle T H E O F E U N D I I V E R S N U B R G I T Y H Image: NASA/WMAP Science Team The Standard Model The discovery of the Higgs particle completes the Standard Model of Particle
The Hot Big Bang Andrew Liddle T H E O F E U N D I I V E R S N U B R G I T Y H Image: NASA/WMAP Science Team The Standard Model The discovery of the Higgs particle completes the Standard Model of Particle
Cosmology: Building the Universe.
 Cosmology: Building the Universe. The term has several different meanings. We are interested in physical cosmology - the study of the origin and development of the physical universe, and all the structure
Cosmology: Building the Universe. The term has several different meanings. We are interested in physical cosmology - the study of the origin and development of the physical universe, and all the structure
Today. Last homework Due next time FINAL EXAM: 8:00 AM TUE Dec. 14 Course Evaluations Open. Modern Cosmology. Big Bang Nucleosynthesis.
 Today Modern Cosmology Big Bang Nucleosynthesis Dark Matter Dark Energy Last homework Due next time FINAL EXAM: 8:00 AM TUE Dec. 14 Course Evaluations Open Elements of Modern Cosmology 1.Expanding Universe
Today Modern Cosmology Big Bang Nucleosynthesis Dark Matter Dark Energy Last homework Due next time FINAL EXAM: 8:00 AM TUE Dec. 14 Course Evaluations Open Elements of Modern Cosmology 1.Expanding Universe
Chapter 27 The Early Universe Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 27 The Early Universe Units of Chapter 27 27.1 Back to the Big Bang 27.2 The Evolution of the Universe More on Fundamental Forces 27.3 The Formation of Nuclei and Atoms 27.4 The Inflationary Universe
Chapter 27 The Early Universe Units of Chapter 27 27.1 Back to the Big Bang 27.2 The Evolution of the Universe More on Fundamental Forces 27.3 The Formation of Nuclei and Atoms 27.4 The Inflationary Universe
Lecture 36: The First Three Minutes Readings: Sections 29-1, 29-2, and 29-4 (29-3)
 Lecture 36: The First Three Minutes Readings: Sections 29-1, 29-2, and 29-4 (29-3) Key Ideas Physics of the Early Universe Informed by experimental & theoretical physics Later stages confirmed by observations
Lecture 36: The First Three Minutes Readings: Sections 29-1, 29-2, and 29-4 (29-3) Key Ideas Physics of the Early Universe Informed by experimental & theoretical physics Later stages confirmed by observations
Chapter 21 Evidence of the Big Bang. Expansion of the Universe. Big Bang Theory. Age of the Universe. Hubble s Law. Hubble s Law
 Chapter 21 Evidence of the Big Bang Hubble s Law Universal recession: Slipher (1912) and Hubble found that all galaxies seem to be moving away from us: the greater the distance, the higher the redshift
Chapter 21 Evidence of the Big Bang Hubble s Law Universal recession: Slipher (1912) and Hubble found that all galaxies seem to be moving away from us: the greater the distance, the higher the redshift
Early (Expanding) Universe. Average temperature decreases with expansion.
 Early (Expanding) Universe Average temperature decreases with expansion. Particles & Anti-Particles Very short wavelength photons collide and form electron-positron pairs. E=mc 2 electron=matter positron=antimatter
Early (Expanding) Universe Average temperature decreases with expansion. Particles & Anti-Particles Very short wavelength photons collide and form electron-positron pairs. E=mc 2 electron=matter positron=antimatter
Hubble's Law. H o = 71 km/s / Mpc. The further a galaxy is away, the faster it s moving away from us. V = H 0 D. Modern Data.
 Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the origin and evolution of the Universe, addressing the grandest issues: How "big" is the Universe? Does it have an "edge"? What is its large-scale structure? How did
Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the origin and evolution of the Universe, addressing the grandest issues: How "big" is the Universe? Does it have an "edge"? What is its large-scale structure? How did
Brief Introduction to Cosmology
 Brief Introduction to Cosmology Matias Zaldarriaga Harvard University August 2006 Basic Questions in Cosmology: How does the Universe evolve? What is the universe made off? How is matter distributed? How
Brief Introduction to Cosmology Matias Zaldarriaga Harvard University August 2006 Basic Questions in Cosmology: How does the Universe evolve? What is the universe made off? How is matter distributed? How
The first 400,000 years
 The first 400,000 years All about the Big Bang Temperature Chronology of the Big Bang The Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) The VERY early universe Our Evolving Universe 1 Temperature and the Big Bang
The first 400,000 years All about the Big Bang Temperature Chronology of the Big Bang The Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) The VERY early universe Our Evolving Universe 1 Temperature and the Big Bang
Lecture 19 Big Bang Nucleosynthesis
 Lecture 19 Big Bang Nucleosynthesis As with all course material (including homework, exams), these lecture notes are not be reproduced, redistributed, or sold in any form. The CMB as seen by the WMAP satellite.!2
Lecture 19 Big Bang Nucleosynthesis As with all course material (including homework, exams), these lecture notes are not be reproduced, redistributed, or sold in any form. The CMB as seen by the WMAP satellite.!2
Chapter 17 Cosmology
 Chapter 17 Cosmology Over one thousand galaxies visible The Universe on the Largest Scales No evidence of structure on a scale larger than 200 Mpc On very large scales, the universe appears to be: Homogenous
Chapter 17 Cosmology Over one thousand galaxies visible The Universe on the Largest Scales No evidence of structure on a scale larger than 200 Mpc On very large scales, the universe appears to be: Homogenous
Island Universes. Up to 1920 s, many thought that Milky Way encompassed entire universe.
 Island Universes Up to 1920 s, many thought that Milky Way encompassed entire universe. Observed three types of nebulas (clouds): - diffuse, spiral, elliptical - many were faint, indistinct - originally
Island Universes Up to 1920 s, many thought that Milky Way encompassed entire universe. Observed three types of nebulas (clouds): - diffuse, spiral, elliptical - many were faint, indistinct - originally
The Beginning of the Universe 8/11/09. Astronomy 101
 The Beginning of the Universe 8/11/09 Astronomy 101 Astronomy Picture of the Day Astronomy 101 Outline for Today Astronomy Picture of the Day Return Lab 11 Astro News Q&A Session Dark Energy Cosmic Microwave
The Beginning of the Universe 8/11/09 Astronomy 101 Astronomy Picture of the Day Astronomy 101 Outline for Today Astronomy Picture of the Day Return Lab 11 Astro News Q&A Session Dark Energy Cosmic Microwave
The Big Bang Theory, General Timeline. The Planck Era. (Big Bang To 10^-35 Seconds) Inflationary Model Added. (10^-35 to 10^-33 Of A Second)
 The Big Bang Theory, General Timeline The Planck Era. (Big Bang To 10^-35 Seconds) The time from the exact moment of the Big Bang until 10^-35 of a second later is referred to as the Planck Era. While
The Big Bang Theory, General Timeline The Planck Era. (Big Bang To 10^-35 Seconds) The time from the exact moment of the Big Bang until 10^-35 of a second later is referred to as the Planck Era. While
Assignments. Read all (secs ) of DocOnotes-cosmology. HW7 due today; accepted till Thurs. w/ 5% penalty
 Assignments Read all (secs. 25-29) of DocOnotes-cosmology. HW7 due today; accepted till Thurs. w/ 5% penalty Term project due last day of class, Tues. May 17 Final Exam Thurs. May 19, 3:30 p.m. here Olber
Assignments Read all (secs. 25-29) of DocOnotes-cosmology. HW7 due today; accepted till Thurs. w/ 5% penalty Term project due last day of class, Tues. May 17 Final Exam Thurs. May 19, 3:30 p.m. here Olber
The Expanding Universe
 Cosmology Expanding Universe History of the Universe Cosmic Background Radiation The Cosmological Principle Cosmology and General Relativity Dark Matter and Dark Energy Primitive Cosmology If the universe
Cosmology Expanding Universe History of the Universe Cosmic Background Radiation The Cosmological Principle Cosmology and General Relativity Dark Matter and Dark Energy Primitive Cosmology If the universe
VU lecture Introduction to Particle Physics. Thomas Gajdosik, FI & VU. Big Bang (model)
 Big Bang (model) What can be seen / measured? basically only light _ (and a few particles: e ±, p, p, ν x ) in different wave lengths: microwave to γ-rays in different intensities (measured in magnitudes)
Big Bang (model) What can be seen / measured? basically only light _ (and a few particles: e ±, p, p, ν x ) in different wave lengths: microwave to γ-rays in different intensities (measured in magnitudes)
The Cosmic Microwave Background
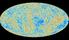 The Cosmic Microwave Background Our probe of the birth of the universe Will Handley wh260@cam.ac.uk Astrophysics Department Cavendish Laboratory University of Cambridge 20 th March 2013 Overview Light
The Cosmic Microwave Background Our probe of the birth of the universe Will Handley wh260@cam.ac.uk Astrophysics Department Cavendish Laboratory University of Cambridge 20 th March 2013 Overview Light
The Early Universe: A Journey into the Past
 Gravity: Einstein s General Theory of Relativity The Early Universe A Journey into the Past Texas A&M University March 16, 2006 Outline Gravity: Einstein s General Theory of Relativity Galileo and falling
Gravity: Einstein s General Theory of Relativity The Early Universe A Journey into the Past Texas A&M University March 16, 2006 Outline Gravity: Einstein s General Theory of Relativity Galileo and falling
The Universe: What We Know and What we Don t. Fundamental Physics Cosmology Elementary Particle Physics
 The Universe: What We Know and What we Don t Fundamental Physics Cosmology Elementary Particle Physics 1 Cosmology Study of the universe at the largest scale How big is the universe? Where What Are did
The Universe: What We Know and What we Don t Fundamental Physics Cosmology Elementary Particle Physics 1 Cosmology Study of the universe at the largest scale How big is the universe? Where What Are did
Lecture 17: the CMB and BBN
 Lecture 17: the CMB and BBN As with all course material (including homework, exams), these lecture notes are not be reproduced, redistributed, or sold in any form. Peering out/back into the Universe As
Lecture 17: the CMB and BBN As with all course material (including homework, exams), these lecture notes are not be reproduced, redistributed, or sold in any form. Peering out/back into the Universe As
Cosmology. Big Bang and Inflation
 Cosmology Big Bang and Inflation What is the Universe? Everything we can know about is part of the universe. Everything we do know about is part of the universe. Everything! The Universe is expanding If
Cosmology Big Bang and Inflation What is the Universe? Everything we can know about is part of the universe. Everything we do know about is part of the universe. Everything! The Universe is expanding If
Chapter 27: The Early Universe
 Chapter 27: The Early Universe The plan: 1. A brief survey of the entire history of the big bang universe. 2. A more detailed discussion of each phase, or epoch, from the Planck era through particle production,
Chapter 27: The Early Universe The plan: 1. A brief survey of the entire history of the big bang universe. 2. A more detailed discussion of each phase, or epoch, from the Planck era through particle production,
The Early Universe: A Journey into the Past
 The Early Universe A Journey into the Past Texas A&M University March 16, 2006 Outline Galileo and falling bodies Galileo Galilei: all bodies fall at the same speed force needed to accelerate a body is
The Early Universe A Journey into the Past Texas A&M University March 16, 2006 Outline Galileo and falling bodies Galileo Galilei: all bodies fall at the same speed force needed to accelerate a body is
The Big Bang The Beginning of Time
 The Big Bang The Beginning of Time What were conditions like in the early universe? The early universe must have been extremely hot and dense Photons converted into particle-antiparticle pairs and vice-versa
The Big Bang The Beginning of Time What were conditions like in the early universe? The early universe must have been extremely hot and dense Photons converted into particle-antiparticle pairs and vice-versa
Cosmology. An Analogy 11/28/2010. Cosmology Study of the origin, evolution and future of the Universe
 Cosmology Cosmology Study of the origin, evolution and future of the Universe Obler s Paradox If the Universe is infinite why is the sky dark at night? Newtonian Universe The Universe is infinite and unchanging
Cosmology Cosmology Study of the origin, evolution and future of the Universe Obler s Paradox If the Universe is infinite why is the sky dark at night? Newtonian Universe The Universe is infinite and unchanging
The Early Universe and the Big Bang
 The Early Universe and the Big Bang Class 24 Prof J. Kenney June 28, 2018 Final Exam: Friday June 29 at 2-5pm in Watson A48 What the Final Exam will emphasize: Classroom lectures 10-24 (starting FRI June
The Early Universe and the Big Bang Class 24 Prof J. Kenney June 28, 2018 Final Exam: Friday June 29 at 2-5pm in Watson A48 What the Final Exam will emphasize: Classroom lectures 10-24 (starting FRI June
Dark Energy and the Accelerating Universe
 Dark Energy and the Accelerating Universe Dragan Huterer Department of Physics University of Michigan The universe today presents us with a grand puzzle: What is 95% of it made of? Shockingly, we still
Dark Energy and the Accelerating Universe Dragan Huterer Department of Physics University of Michigan The universe today presents us with a grand puzzle: What is 95% of it made of? Shockingly, we still
What is the 'cosmological principle'?
 What is the 'cosmological principle'? Modern cosmology always starts from this basic assumption the Universe is homogeneous and isotropic. This idea seems strange there's empty space between me and the
What is the 'cosmological principle'? Modern cosmology always starts from this basic assumption the Universe is homogeneous and isotropic. This idea seems strange there's empty space between me and the
Lecture 19 Nuclear Astrophysics. Baryons, Dark Matter, Dark Energy. Experimental Nuclear Physics PHYS 741
 Lecture 19 Nuclear Astrophysics Baryons, Dark Matter, Dark Energy Experimental Nuclear Physics PHYS 741 heeger@wisc.edu References and Figures from: - Haxton, Nuclear Astrophysics - Basdevant, Fundamentals
Lecture 19 Nuclear Astrophysics Baryons, Dark Matter, Dark Energy Experimental Nuclear Physics PHYS 741 heeger@wisc.edu References and Figures from: - Haxton, Nuclear Astrophysics - Basdevant, Fundamentals
The Contents of the Universe (or/ what do we mean by dark matter and dark energy?)
 The Contents of the Universe (or/ what do we mean by dark matter and dark energy?) Unseen Influences Dark Matter: An undetected form of mass that emits little or no light but whose existence we infer from
The Contents of the Universe (or/ what do we mean by dark matter and dark energy?) Unseen Influences Dark Matter: An undetected form of mass that emits little or no light but whose existence we infer from
ASTR 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies
 ASTR 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies ANNOUNCEMENTS MIDTERM III: Tuesday, Nov 24 th Midterm alternate day: Fri, Nov 20th, 11am, ESS 450 At LAST: In the very Beginning BIG BANG: beginning of Time
ASTR 101 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies ANNOUNCEMENTS MIDTERM III: Tuesday, Nov 24 th Midterm alternate day: Fri, Nov 20th, 11am, ESS 450 At LAST: In the very Beginning BIG BANG: beginning of Time
Unity in the Whole Structure
 Cosmology II Unity in the Whole Structure How is it possible by any methods of observation yet known to the astronomer to learn anything about the universe as a whole? It is possible only because the universe,
Cosmology II Unity in the Whole Structure How is it possible by any methods of observation yet known to the astronomer to learn anything about the universe as a whole? It is possible only because the universe,
The Early Universe. 1. Inflation Theory: The early universe expanded enormously in a brief instance in time.
 The Early Universe The Early Universe 1. Inflation Theory: The early universe expanded enormously in a brief instance in time. 2. The fundamental forces change during the first second after the big bang.
The Early Universe The Early Universe 1. Inflation Theory: The early universe expanded enormously in a brief instance in time. 2. The fundamental forces change during the first second after the big bang.
4 The Big Bang, the genesis of the Universe, the origin of the microwave background
 4 The Big Bang, the genesis of the Universe, the origin of the microwave background a(t) = 0 The origin of the universe: a(t) = 0 Big Bang coined by Fred Hoyle he calculated the ratio of elements created
4 The Big Bang, the genesis of the Universe, the origin of the microwave background a(t) = 0 The origin of the universe: a(t) = 0 Big Bang coined by Fred Hoyle he calculated the ratio of elements created
v = H o d Hubble s Law: Distant galaxies move away fastest Velocity (v) is proportional to Distance (d):
 Hubble s Law: Distant galaxies move away fastest Velocity (v) is proportional to Distance (d): v = H o d The Hubble Constant was measured after decades of observation: H 0 = 70 km/s/mpc Velocity (km/s)
Hubble s Law: Distant galaxies move away fastest Velocity (v) is proportional to Distance (d): v = H o d The Hubble Constant was measured after decades of observation: H 0 = 70 km/s/mpc Velocity (km/s)
The Mystery of Dark Matter
 The Mystery of Dark Matter Maxim Perelstein, LEPP/Cornell U. CIPT Fall Workshop, Ithaca NY, September 28 2013 Introduction Last Fall workshop focused on physics of the very small - elementary particles
The Mystery of Dark Matter Maxim Perelstein, LEPP/Cornell U. CIPT Fall Workshop, Ithaca NY, September 28 2013 Introduction Last Fall workshop focused on physics of the very small - elementary particles
Ta-Pei Cheng PCNY 9/16/2011
 PCNY 9/16/2011 Ta-Pei Cheng For a more quantitative discussion, see Relativity, Gravitation & Cosmology: A Basic Introduction (Oxford Univ Press) 2 nd ed. (2010) dark matter & dark energy Astronomical
PCNY 9/16/2011 Ta-Pei Cheng For a more quantitative discussion, see Relativity, Gravitation & Cosmology: A Basic Introduction (Oxford Univ Press) 2 nd ed. (2010) dark matter & dark energy Astronomical
Astronomy 182: Origin and Evolution of the Universe
 Astronomy 182: Origin and Evolution of the Universe Prof. Josh Frieman Lecture 13 Nov. 20, 2015 Today Particle Physics & the Early Universe Baryogenesis The Inflationary Scenario Assignments Today: Essay
Astronomy 182: Origin and Evolution of the Universe Prof. Josh Frieman Lecture 13 Nov. 20, 2015 Today Particle Physics & the Early Universe Baryogenesis The Inflationary Scenario Assignments Today: Essay
FURTHER COSMOLOGY Book page T H E M A K E U P O F T H E U N I V E R S E
 FURTHER COSMOLOGY Book page 675-683 T H E M A K E U P O F T H E U N I V E R S E COSMOLOGICAL PRINCIPLE Is the Universe isotropic or homogeneous? There is no place in the Universe that would be considered
FURTHER COSMOLOGY Book page 675-683 T H E M A K E U P O F T H E U N I V E R S E COSMOLOGICAL PRINCIPLE Is the Universe isotropic or homogeneous? There is no place in the Universe that would be considered
Astronomy 182: Origin and Evolution of the Universe
 Astronomy 182: Origin and Evolution of the Universe Prof. Josh Frieman Lecture 14 Dec. 2, 2015 Today The Inflationary Universe Origin of Density Perturbations Gravitational Waves Origin and Evolution of
Astronomy 182: Origin and Evolution of the Universe Prof. Josh Frieman Lecture 14 Dec. 2, 2015 Today The Inflationary Universe Origin of Density Perturbations Gravitational Waves Origin and Evolution of
Cosmology and particle physics
 Fedora GNU/Linux; LATEX 2ɛ; xfig Cosmology and particle physics Mark Alford Washington University Saint Louis, USA Outline I Particle physics: What the universe is made of. quarks, leptons, and the forces
Fedora GNU/Linux; LATEX 2ɛ; xfig Cosmology and particle physics Mark Alford Washington University Saint Louis, USA Outline I Particle physics: What the universe is made of. quarks, leptons, and the forces
Cosmic Background Radiation
 Cosmic Background Radiation The Big Bang generated photons, which scattered frequently in the very early Universe, which was opaque. Once recombination happened the photons are scattered one final time
Cosmic Background Radiation The Big Bang generated photons, which scattered frequently in the very early Universe, which was opaque. Once recombination happened the photons are scattered one final time
Astro-2: History of the Universe. Lecture 12; May
 Astro-2: History of the Universe Lecture 12; May 23 2013 Previously on astro-2 The four fundamental interactions are? Strong, weak, electromagnetic and gravity. We think they are unified at high energies,
Astro-2: History of the Universe Lecture 12; May 23 2013 Previously on astro-2 The four fundamental interactions are? Strong, weak, electromagnetic and gravity. We think they are unified at high energies,
COSMOLOGY AND GRAVITATIONAL WAVES. Chiara Caprini (APC)
 COSMOLOGY AND GRAVITATIONAL WAVES Chiara Caprini (APC) the direct detection of GW by the LIGO interferometers has opened a new era in Astronomy - we now have a new messenger bringing complementary informations
COSMOLOGY AND GRAVITATIONAL WAVES Chiara Caprini (APC) the direct detection of GW by the LIGO interferometers has opened a new era in Astronomy - we now have a new messenger bringing complementary informations
Exam #3. Final Exam. Exam 3 review. How do we measure properties of a star? A detailed outline of study topics is here:
 Exam #3 Exam #3 is Thursday 4/9 in this room You can bring page of notes (front and back) Bring your calculator and a # pencil Exam 3 covers material from 4/1 onward (only 8 lectures) Consequently, no
Exam #3 Exam #3 is Thursday 4/9 in this room You can bring page of notes (front and back) Bring your calculator and a # pencil Exam 3 covers material from 4/1 onward (only 8 lectures) Consequently, no
Lecture #25: Plan. Cosmology. The early Universe (cont d) The fate of our Universe The Great Unanswered Questions
 Lecture #25: Plan Cosmology The early Universe (cont d) The fate of our Universe The Great Unanswered Questions Announcements Course evaluations: CourseEvalUM.umd.edu Review sheet #3 was emailed to you
Lecture #25: Plan Cosmology The early Universe (cont d) The fate of our Universe The Great Unanswered Questions Announcements Course evaluations: CourseEvalUM.umd.edu Review sheet #3 was emailed to you
Hot Big Bang model: early Universe and history of matter
 Hot Big Bang model: early Universe and history of matter nitial soup with elementary particles and radiation in thermal equilibrium. adiation dominated era (recall energy density grows faster than matter
Hot Big Bang model: early Universe and history of matter nitial soup with elementary particles and radiation in thermal equilibrium. adiation dominated era (recall energy density grows faster than matter
Plasma Universe. The origin of CMB
 Plasma Universe As we go back in time, temperature goes up. T=2.73(1+z) K At z~1100, T~3000 K About the same temperature as M-dwarfs Ionization of hydrogen atoms H + photon! p + e - Inverse process: recombination
Plasma Universe As we go back in time, temperature goes up. T=2.73(1+z) K At z~1100, T~3000 K About the same temperature as M-dwarfs Ionization of hydrogen atoms H + photon! p + e - Inverse process: recombination
Physics 133: Extragalactic Astronomy and Cosmology. Week 8
 Physics 133: Extragalactic Astronomy and Cosmology Week 8 Outline for Week 8 Primordial Nucleosynthesis Successes of the standard Big Bang model Olbers paradox/age of the Universe Hubble s law CMB Chemical/Physical
Physics 133: Extragalactic Astronomy and Cosmology Week 8 Outline for Week 8 Primordial Nucleosynthesis Successes of the standard Big Bang model Olbers paradox/age of the Universe Hubble s law CMB Chemical/Physical
MASAHIDE YAMAGUCHI. Quantum generation of density perturbations in the early Universe. (Tokyo Institute of Technology)
 Quantum generation of density perturbations in the early Universe MASAHIDE YAMAGUCHI (Tokyo Institute of Technology) 03/07/16@Symposium: New Generation Quantum Theory -Particle Physics, Cosmology, and
Quantum generation of density perturbations in the early Universe MASAHIDE YAMAGUCHI (Tokyo Institute of Technology) 03/07/16@Symposium: New Generation Quantum Theory -Particle Physics, Cosmology, and
Modern Physics notes Spring 2005 Paul Fendley Lecture 38
 Modern Physics notes Spring 2005 Paul Fendley fendley@virginia.edu Lecture 38 Dark matter and energy Cosmic Microwave Background Weinberg, chapters II and III cosmological parameters: Tegmark et al, http://arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0310723
Modern Physics notes Spring 2005 Paul Fendley fendley@virginia.edu Lecture 38 Dark matter and energy Cosmic Microwave Background Weinberg, chapters II and III cosmological parameters: Tegmark et al, http://arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0310723
A100 Exploring the Universe Big Bang Theory and the Early Universe. Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy
 A100 Exploring the Universe and the Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy astron100-mdw@courses.umass.edu December 02, 2014 Read: Chap 23 12/04/14 slide 1 Assignment on Chaps 22 23, at the end of next week,
A100 Exploring the Universe and the Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy astron100-mdw@courses.umass.edu December 02, 2014 Read: Chap 23 12/04/14 slide 1 Assignment on Chaps 22 23, at the end of next week,
Mass (Energy) in the Universe:
 Mass (Energy) in the Universe: smooth (vacuum) clumping Parameters of our Universe present values H = (71±4)km/s/Mpc = 1.0±0.0 m = 0.7±0.0 incl. b = 0.044±0.004 and < 0.014 photons r = 4.9-5 dark energy
Mass (Energy) in the Universe: smooth (vacuum) clumping Parameters of our Universe present values H = (71±4)km/s/Mpc = 1.0±0.0 m = 0.7±0.0 incl. b = 0.044±0.004 and < 0.014 photons r = 4.9-5 dark energy
The Cosmic Microwave Background
 The Cosmic Microwave Background Class 22 Prof J. Kenney June 26, 2018 The Cosmic Microwave Background Class 22 Prof J. Kenney November 28, 2016 Cosmic star formation history inf 10 4 3 2 1 0 z Peak of
The Cosmic Microwave Background Class 22 Prof J. Kenney June 26, 2018 The Cosmic Microwave Background Class 22 Prof J. Kenney November 28, 2016 Cosmic star formation history inf 10 4 3 2 1 0 z Peak of
Astronomy 182: Origin and Evolution of the Universe
 Astronomy 182: Origin and Evolution of the Universe Prof. Josh Frieman Lecture 11 Nov. 13, 2015 Today Cosmic Microwave Background Big Bang Nucleosynthesis Assignments This week: read Hawley and Holcomb,
Astronomy 182: Origin and Evolution of the Universe Prof. Josh Frieman Lecture 11 Nov. 13, 2015 Today Cosmic Microwave Background Big Bang Nucleosynthesis Assignments This week: read Hawley and Holcomb,
Formation of the Universe. What evidence supports current scientific theory?
 Formation of the Universe What evidence supports current scientific theory? Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the Nature, Structure, Origin, And fate of the universe. How did it all begin? Astronomers
Formation of the Universe What evidence supports current scientific theory? Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the Nature, Structure, Origin, And fate of the universe. How did it all begin? Astronomers
A100H Exploring the Universe: Big Bang Theory. Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy
 A100H Exploring the : Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy astron100h-mdw@courses.umass.edu April 21, 2016 Read: Chap 23 04/26/16 slide 1 Early Final Exam: Friday 29 Apr at 10:30 am 12:30 pm, here! Emphasizes
A100H Exploring the : Martin D. Weinberg UMass Astronomy astron100h-mdw@courses.umass.edu April 21, 2016 Read: Chap 23 04/26/16 slide 1 Early Final Exam: Friday 29 Apr at 10:30 am 12:30 pm, here! Emphasizes
Inflationary Universe and. Quick survey about iclickers Review of Big Bang model of universe Review of Evidence for Big Bang Examining Inflation
 Inflationary Universe and Quick survey about iclickers Review of Big Bang model of universe Review of Evidence for Big Bang Examining Inflation Survey questions 1. The iclickers used in class encouraged
Inflationary Universe and Quick survey about iclickers Review of Big Bang model of universe Review of Evidence for Big Bang Examining Inflation Survey questions 1. The iclickers used in class encouraged
Survey questions. Inflationary Universe and. Survey Questions. Survey questions. Survey questions
 Inflationary Universe and Quick survey about iclickers Review of Big Bang model of universe Review of Evidence for Big Bang Examining Inflation Survey questions 1. The iclickers used in class encouraged
Inflationary Universe and Quick survey about iclickers Review of Big Bang model of universe Review of Evidence for Big Bang Examining Inflation Survey questions 1. The iclickers used in class encouraged
Origin, early history, and fate of the Universe Does the Universe have a beginning? An end? What physics processes caused the Universe to be what it
 Cosmology Origin, early history, and fate of the Universe Does the Universe have a beginning? An end? What physics processes caused the Universe to be what it is? Are other universes possible? Would they
Cosmology Origin, early history, and fate of the Universe Does the Universe have a beginning? An end? What physics processes caused the Universe to be what it is? Are other universes possible? Would they
Large Scale Structure in the Universe
 Large Scale Structure in the Universe We seem to be located at the edge of a Local Supercluster, which contains dozens of clusters and groups over a 40 Mpc region. Galaxies and clusters seem to congregate
Large Scale Structure in the Universe We seem to be located at the edge of a Local Supercluster, which contains dozens of clusters and groups over a 40 Mpc region. Galaxies and clusters seem to congregate
Lecture 20 Cosmology, Inflation, dark matter
 The Nature of the Physical World November 19th, 2008 Lecture 20 Cosmology, Inflation, dark matter Arán García-Bellido 1 News Exam 2: good job! Ready for pick up after class or in my office Average: 74/100
The Nature of the Physical World November 19th, 2008 Lecture 20 Cosmology, Inflation, dark matter Arán García-Bellido 1 News Exam 2: good job! Ready for pick up after class or in my office Average: 74/100
Hubble s Law. Our goals for learning. What is Hubble s Law? How do distance measurements tell us the age of the universe?
 Hubble s Law Our goals for learning What is Hubble s Law? How do distance measurements tell us the age of the universe? How does the universe s expansion affect our distance measurements? We measure speeds
Hubble s Law Our goals for learning What is Hubble s Law? How do distance measurements tell us the age of the universe? How does the universe s expansion affect our distance measurements? We measure speeds
The expansion of the Universe, and the big bang
 The expansion of the Universe, and the big bang Q: What is Hubble s law? A. The larger the galaxy, the faster it is moving way from us. B. The farther away the galaxy, the faster it is moving away from
The expansion of the Universe, and the big bang Q: What is Hubble s law? A. The larger the galaxy, the faster it is moving way from us. B. The farther away the galaxy, the faster it is moving away from
Announcements. Homework. Set 8now open. due late at night Friday, Dec 10 (3AM Saturday Nov. 11) Set 7 answers on course web site.
 Homework. Set 8now. due late at night Friday, Dec 10 (3AM Saturday Nov. 11) Set 7 answers on course web site. Review for Final. In class on Thursday. Course Evaluation. https://rateyourclass.msu.edu /
Homework. Set 8now. due late at night Friday, Dec 10 (3AM Saturday Nov. 11) Set 7 answers on course web site. Review for Final. In class on Thursday. Course Evaluation. https://rateyourclass.msu.edu /
Astronomy 122 Outline
 Astronomy 122 Outline This Class (Lecture 26): The Primeval Fireball Next Class: Dark Matter & Dark Energy ICES Form!!! HW10 due Friday Hubble s Law implications An expanding Universe! Run in movie in
Astronomy 122 Outline This Class (Lecture 26): The Primeval Fireball Next Class: Dark Matter & Dark Energy ICES Form!!! HW10 due Friday Hubble s Law implications An expanding Universe! Run in movie in
Homework 6 Name: Due Date: June 9, 2008
 Homework 6 Name: Due Date: June 9, 2008 1. Where in the universe does the general expansion occur? A) everywhere in the universe, including our local space upon Earth, the solar system, our galaxy and
Homework 6 Name: Due Date: June 9, 2008 1. Where in the universe does the general expansion occur? A) everywhere in the universe, including our local space upon Earth, the solar system, our galaxy and
An Introduction to Particle Physics
 An Introduction to Particle Physics The Universe started with a Big Bang The Universe started with a Big Bang What is our Universe made of? Particle physics aims to understand Elementary (fundamental)
An Introduction to Particle Physics The Universe started with a Big Bang The Universe started with a Big Bang What is our Universe made of? Particle physics aims to understand Elementary (fundamental)
OUSSEP Final Week. If we run out of time you can look at uploaded slides Pearson Education, Inc.
 OUSSEP Final Week Last week hopefully read Holiday-Week 23rd November Lecture notes Hand in your Hubble Deep Field Reports today! (If not today then in my mail box @ International College.) Today we will
OUSSEP Final Week Last week hopefully read Holiday-Week 23rd November Lecture notes Hand in your Hubble Deep Field Reports today! (If not today then in my mail box @ International College.) Today we will
The Cosmological Principle
 Cosmological Models John O Byrne School of Physics University of Sydney Using diagrams and pp slides from Seeds Foundations of Astronomy and the Supernova Cosmology Project http://www-supernova.lbl.gov
Cosmological Models John O Byrne School of Physics University of Sydney Using diagrams and pp slides from Seeds Foundations of Astronomy and the Supernova Cosmology Project http://www-supernova.lbl.gov
Origin of the Universe - 2 ASTR 2120 Sarazin. What does it all mean?
 Origin of the Universe - 2 ASTR 2120 Sarazin What does it all mean? Fundamental Questions in Cosmology 1. Why did the Big Bang occur? 2. Why is the Universe old? 3. Why is the Universe made of matter?
Origin of the Universe - 2 ASTR 2120 Sarazin What does it all mean? Fundamental Questions in Cosmology 1. Why did the Big Bang occur? 2. Why is the Universe old? 3. Why is the Universe made of matter?
Katsushi Arisaka University of California, Los Angeles Department of Physics and Astronomy
 11/14/12 Katsushi Arisaka 1 Katsushi Arisaka University of California, Los Angeles Department of Physics and Astronomy arisaka@physics.ucla.edu Seven Phases of Cosmic Evolution 11/14/12 Katsushi Arisaka
11/14/12 Katsushi Arisaka 1 Katsushi Arisaka University of California, Los Angeles Department of Physics and Astronomy arisaka@physics.ucla.edu Seven Phases of Cosmic Evolution 11/14/12 Katsushi Arisaka
Planetarium/Observing: the clock is ticking! Don t forget to fill out your Planetarium/ Observing impression online.
 Announcements HW #5 Due Wed, Dec. 10th. Planetarium/Observing: the clock is ticking! Don t forget to fill out your Planetarium/ Observing impression online. NOTE: Planetarium: Large dome you sit inside.
Announcements HW #5 Due Wed, Dec. 10th. Planetarium/Observing: the clock is ticking! Don t forget to fill out your Planetarium/ Observing impression online. NOTE: Planetarium: Large dome you sit inside.
Cosmology: The Origin and Evolution of the Universe Chapter Twenty-Eight. Guiding Questions
 Cosmology: The Origin and Evolution of the Universe Chapter Twenty-Eight Guiding Questions 1. What does the darkness of the night sky tell us about the nature of the universe? 2. As the universe expands,
Cosmology: The Origin and Evolution of the Universe Chapter Twenty-Eight Guiding Questions 1. What does the darkness of the night sky tell us about the nature of the universe? 2. As the universe expands,
Monday, November 25, 2013 Reading: Chapter 12 all; Chapter 13 all. There will be class on Wednesday. Astronomy in the news?
 Monday, November 25, 2013 Reading: Chapter 12 all; Chapter 13 all There will be class on Wednesday Astronomy in the news? Goal: To understand what the Dark Energy implies for the shape and fate of the
Monday, November 25, 2013 Reading: Chapter 12 all; Chapter 13 all There will be class on Wednesday Astronomy in the news? Goal: To understand what the Dark Energy implies for the shape and fate of the
Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014
![Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014 Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014](/thumbs/75/72758061.jpg) 1 Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014 2 Structure of the Universe Does clustering of galaxies go on forever? Looked at very narrow regions of space to far distances. On large scales the
1 Lecture 37 Cosmology [not on exam] January 16b, 2014 2 Structure of the Universe Does clustering of galaxies go on forever? Looked at very narrow regions of space to far distances. On large scales the
Unity in the Whole Structure Evolution of the Universe from 13 to 4 Billion Years Ago
 Unity in the Whole Structure Evolution of the Universe from 13 to 4 Billion Years Ago Prof. Dr. Harold Geller hgeller@gmu.edu http://physics.gmu.edu/~hgeller/ Department of Physics and Astronomy George
Unity in the Whole Structure Evolution of the Universe from 13 to 4 Billion Years Ago Prof. Dr. Harold Geller hgeller@gmu.edu http://physics.gmu.edu/~hgeller/ Department of Physics and Astronomy George
Inflation of the Observed Universe as a Function of Time
 Inflation of the Observed Universe as a Function of Time Asit Baran Bhattacharya 1 and Bipasa Raha 2 1,2 Department of Physics, University of Kalyani, Kalyani 741235, West Bengal, India ABSTRACT The present
Inflation of the Observed Universe as a Function of Time Asit Baran Bhattacharya 1 and Bipasa Raha 2 1,2 Department of Physics, University of Kalyani, Kalyani 741235, West Bengal, India ABSTRACT The present
Modeling the Universe A Summary
 Modeling the Universe A Summary Questions to Consider 1. What does the darkness of the night sky tell us about the nature of the universe? 2. As the universe expands, what, if anything, is it expanding
Modeling the Universe A Summary Questions to Consider 1. What does the darkness of the night sky tell us about the nature of the universe? 2. As the universe expands, what, if anything, is it expanding
