Where are they (E.T.I.) anyway?
|
|
|
- Garey Atkinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Welcome to Class 1: Drake EquaCon, SETI & Fermi Paradox Is it crazy to search for intelligent life? Where are they (E.T.I.) anyway? What would you like to spend most of our last class on? 1. Early SETI, Modern search methods, listen vs transmisng Methods used by SETI and two problems. How these problems are being addressed.. 2 statements of Fermi s Paradox, and the three categories of solucons. Remember to set your channel to 80! 1 2 Opinion QuesCon: Has this class changed your view on life elsewhere? 1. I am a stronger believer in extraterrestrial life. 2. I am scll a strong believer in extraterrestrial life.. I did believe, but now I am not so certain there is life elsewhere. 4. I never believed and scll don t believe in ET life.. I didn t believe, but I think I do believe in ET life now. Remember to set your channel to 80! He designed an equacon to escmate: Who is this man? Number of Civilizations in the Milky Way capable of interstellar communication NOW. Your book has simplified the Drake EquaCon to: # = N hp x f life x f civ x f now N hp = Number of habitable planets in the Milky Way. F life = FracCon of those planets which will develop life. F civ = FracCon of those which develop Civilized life. F now = FracCon of those planets with Civilized life NOW. Let s consider some possible values for the Drake EquaCon.. Frank Drake Frank Drake also designed the first contact message sent to nearby stars. He was director of Arecibo Radio Telescope, and sent the message from there in (7 yrs ago) 4 N hp : How many habitable planets are in the Milky Way presently? (recall, there are a few 100 billion stars in the M.W.) F life : What fraccon of those planets develop life (of any kind)? billion 2. 1 billion. 1 million. 1/100th 4. 1,000. None 6
2 F civ : What fraccon of life- bearing planets developed civilizacons capable of communicacon at SOME Cme?. 1/100th. None F civ : What fraccon of those life- bearing planets capable of communicacon exist NOW?. 1/100th. None 7 8 What does this lead to? Early claims to communicate with E.T.I. MulCply together the classes four most popular input values: N hp x f life x f civ x f now = Total number of intelligent civilizacons from whom we could potencally get a signal now. 9 Marconi Early pioneers of electricity, Marconi and Tesla, also introduced radio (electro magnecc radiacon) communicacon. They both thought they where hearing E.T.I. Tesla Unfortunately, the radio wavelengths they were working at (AM radio, khz) cannot pass through (from outside or inside) Earth s ionosphere. 10 PRS : Why do we listen rather than send out a signal? Are we missing signals from E.T.I.? 1. Stay hidden from E.T. 2. Faster. Easier 4. Cheaper. All of the above 1. We don t know which direccon in the sky they are. 2. We assume they d use `light, but we don t know what kind of electromagnecc radiacon they are using.. We don t know how strong those signals are, or how far away they are coming from. 4. Is the signal concnuous, or does it stop and start every year, every minute?. Do we need to go back and re- observe all direccons? 11 12
3 INCREASING NOISE What FREQUENCY should we be listening? QUIET Where the universe is most quiet! But WHERE.. There is an infinite number of stacons : A civilized life would have astronomers who have built radio telescopes to observe H (hydrogen) and OH (hydroxyl) in the Galaxy. Even in this range, there exists an infinite number of FREQUENCIES to listen, depending on how broad a band (the `bandwidth ) you will consider to listen. There is also the amount of TIME you listen, and which DIRECTION you listen. 1 What DIRECTION should we be listening? How about starcng with nearby sun- like stars with exo- planets? All the stars listed here have exoplanets and are within 60 light years of Earth. This would be a TARGETED search A SURVEY search would sweep the sky randomly. 14 Challenges facing SETI sciencsts SETI sciencsts design unique radio receivers to work with radio telescope from ,000 MHz. Problem 1: SETI gets limle Cme to do targeted searches. Most of their Cme is looking where the telescopes happen to be looking (piggy backing other astronomy programs for free ). Arecibo SETI InsCtutes new SETI@Home Problem 2: NOISE H, OH lines fall HERE! Man- made, terrestrial noise is gesng louder and covering a greater amount of the frequency range. The Allen Telescope Array Mobile Phones have wiped out the special H, OH quiet zone! The FIRST, high- powered, DEDICATED, SETI- search radio telescopes. (Funded in part by Paul Allen, Microson co- founder). This allows for deeper, significant, TARGETED searches listening for E.T.I. MHz Frequency Limle can be done. SETI may need to move to the far side of the Moon. 1 This is what a signal would look like above. However, this one is due to terrestrial transmimers 16 F civ : fraccon of life- bearing planets developing commuicacng civilizacons = INTELLIGENCE.. 1/100th. None A philosophical argument about E.T.I. We are NOT special Intelligence has occurred elsewhere in our Galaxy We should be surrounded by evidence of this intelligence (civilizacons) Intelligence is an observed phenomenon which came about through natural causes. Given the vast age and number of planets in the Galaxy, intelligent civilizacon, more sophisccated than us, exists and would have colonized the encre Galaxy by now. We have no credible evidence that such a civilizacon exists in the Galaxy. 17 Where is everybody? THERE IS NO E.T.I. This is known as Fermi s Paradox 18
4 What is a paradox? Def. An argument that apparently derives self- contradictory conclusions by valid deduccon (through reasoning) from accepted premises. CriCcal premises leading to Fermi s Paradox 1) Intelligent civilizacons exist through out the Galaxy and have colonized the Galaxy by now. 2) Those intelligent civilizacons would communicate to us in such a way that we would know of their existence. Opinion: Premise 1. How sure are we that intelligent civilizacons would have colonized the en@re Galaxy? 1. Given the size and age of the Galaxy, absolutely yes. 2. Given the age of the Galaxy, its very likely.. Even with the age of the Galaxy, it is unlikely given its size. 4. I vote no. I don t believe any civilizacon has ever existed that can colonize the Galaxy Opinion: Premise 2: Provided such a colonizing civilizacon does exist, how sure are we it would communicate itself to us? 1. Absolutely 2. Probably. Maybe 4. No, probably not. Fermi s Paradox depend on BOTH premises to be absolutely true. 21 Possible solucons to Fermi s Paradox 1) We are alone. Humans are unique (or at least the first). 2) We aren t alone, but nobody has colonized the Galaxy Why? ColonizaCon of the Galaxy isn t so easy: a) Technological reasons (space is simply too big) b) Sociological reasons (they don t want to, waste of resources) c) CivilizaCons self destruct or die out before they get that far. ) They have colonized the Galaxy, but they are hiding it from us. (this is the Zoo Hypothesis) 22 What do YOU think is the solucon to Fermi s Paradox? 1. No E.T.I. exist. 2. CivilizaCons exist, but none have colonized the encre Galaxy yet.. The Galaxy HAS been colonized, but we ve not been asked to join the `club yet.. Final in class quiz!! 2
5 1. The Drake equacon tells us how many civilizacons in the Milky Way 2. We know Marconi & Tesla were not hearing E.T.I. because 1. are trying to communicate with us. 2. are capable of communicacng with us. 1. Their receivers were not sensicve enough. 2. They where hearing lightning.. The atmosphere blocks the radio waves where they were listening. 4. The noise in their system was too high SETI sciencsts selected radio frequencies to listen because 4. SETI sciencsts piggy bag on telescopes used by astronomers. What does this mean? 1. The receivers are most sensicve there 2. They can build big radio telescopes. We know E.T.I. would be sending signals there. 4. It is the quietest part of the electromagnecc spectrum. 1. They obtain the same data as the astronomers. 2. They are looking in the same direccon as the astronomers.. They use the same detectors as the astronomers. 4. All of the above The Fermi Paradox can be resolved by amacking/falsifying the 1. conclusions 2. contradiccon. deduccon 4. premises 29
The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence
 The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence Methods for searching for life! Direct searches for microbial life in the solar system! rovers, sample return missions to Mars, Europa, etc.! Indirect searches
The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence Methods for searching for life! Direct searches for microbial life in the solar system! rovers, sample return missions to Mars, Europa, etc.! Indirect searches
The Jamie Drake Equation
 The Science of The Jamie Drake Equation From wafer- sized spaceships to the extraterrestrial Wow! signal, here s more about the real- life science in The Jamie Drake Equation. Aliens don t really exist,
The Science of The Jamie Drake Equation From wafer- sized spaceships to the extraterrestrial Wow! signal, here s more about the real- life science in The Jamie Drake Equation. Aliens don t really exist,
The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence
 The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence Methods for searching for life Direct searches for microbial life in the solar system rovers, sample return missions to Mars, Europa, etc. Indirect searches
The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence Methods for searching for life Direct searches for microbial life in the solar system rovers, sample return missions to Mars, Europa, etc. Indirect searches
Lecture #26: Searching for Other Civilizations. SETI = Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence Searching for signals from other beings
 Lecture #26: Searching for Other Civilizations SETI = Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence Searching for signals from other beings Searching for Other Civilizations Searching for signals from other
Lecture #26: Searching for Other Civilizations SETI = Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence Searching for signals from other beings Searching for Other Civilizations Searching for signals from other
Primary KS1 1 VotesForSchools2018
 Primary KS1 1 Do aliens exist? This photo of Earth was taken by an astronaut on the moon! Would you like to stand on the moon? What is an alien? You probably drew some kind of big eyed, blue-skinned,
Primary KS1 1 Do aliens exist? This photo of Earth was taken by an astronaut on the moon! Would you like to stand on the moon? What is an alien? You probably drew some kind of big eyed, blue-skinned,
The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI)
 The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI) Our goals for learning What is the Drake equation? How many habitable planets have life? How many civilizations are out there? How does SETI work? Can
The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI) Our goals for learning What is the Drake equation? How many habitable planets have life? How many civilizations are out there? How does SETI work? Can
AST 205. Lecture 23. December 8, 2003 SETI, Interstellar Travel and the Fermi Paradox. Assignments for week of Dec 8
 AST 205. Lecture 23. December 8, 2003 SETI, Interstellar Travel and the Fermi Paradox Evaluation of the Drake Equation SETI: Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence Good news Bad news Interstellar travel
AST 205. Lecture 23. December 8, 2003 SETI, Interstellar Travel and the Fermi Paradox Evaluation of the Drake Equation SETI: Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence Good news Bad news Interstellar travel
Lecture 40: SETI. Astronomy Winter This lecture is about SETI, the Search for Extra- Terrestrial Intelligence.
 Lecture 40 SETI: The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence Astronomy 141 Winter 2012 This lecture is about SETI, the Search for Extra- Terrestrial Intelligence. Searching for artificial radio signals
Lecture 40 SETI: The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence Astronomy 141 Winter 2012 This lecture is about SETI, the Search for Extra- Terrestrial Intelligence. Searching for artificial radio signals
Extraterrestrial Life Group Discussion
 Extraterrestrial Life Group Discussion Group Assignment Meet with the other members of your group. Assign group roles. Print names below. Your name must appear below in order to receive credit. Recorder
Extraterrestrial Life Group Discussion Group Assignment Meet with the other members of your group. Assign group roles. Print names below. Your name must appear below in order to receive credit. Recorder
Searching for Life: Chapter 20: Life on Other Worlds. Life in the Universe. Earliest Fossils. Laboratory Experiments.
 Chapter 20: Life on Other Worlds Searching for Life: What does life look like here? How did Earth get life? Is Earth ordinary or extraordinary? If Earth is ordinary, where is everyone else? Life in the
Chapter 20: Life on Other Worlds Searching for Life: What does life look like here? How did Earth get life? Is Earth ordinary or extraordinary? If Earth is ordinary, where is everyone else? Life in the
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Life in the Universe
 Life in the Universe Life in the Universe The only place we know life exists is here on Earth One of humanity s Big Questions is whether it exists elsewhere We can get some clues by considering life s
Life in the Universe Life in the Universe The only place we know life exists is here on Earth One of humanity s Big Questions is whether it exists elsewhere We can get some clues by considering life s
What is Astrobiology?
 What is Astrobiology? Astrobiology is the study of life in the universe. It investigates the origin, evolution, distribution, & future of life on Earth, & the search for life beyond Earth. Astrobiology
What is Astrobiology? Astrobiology is the study of life in the universe. It investigates the origin, evolution, distribution, & future of life on Earth, & the search for life beyond Earth. Astrobiology
Lecture #26: Plan. Cosmology: Search for Intelligent Life in the Universe. The Great Unanswered Questions (cont d)
 Lecture #26: Plan Cosmology: The Great Unanswered Questions (cont d) Search for Intelligent Life in the Universe Reminders Course evaluations: CourseEvalUM.umd.edu Review session: Monday, December 11,
Lecture #26: Plan Cosmology: The Great Unanswered Questions (cont d) Search for Intelligent Life in the Universe Reminders Course evaluations: CourseEvalUM.umd.edu Review session: Monday, December 11,
The Quest for Extraterrestrial Signals. Ron Maddalena National Radio Astronomy Observatory Green Bank, WV
 The Quest for Extraterrestrial Signals Ron Maddalena National Radio Astronomy Observatory Green Bank, WV Associated Universities, Inc; April/2016 2 Preliminary thoughts a. How certain are you that other
The Quest for Extraterrestrial Signals Ron Maddalena National Radio Astronomy Observatory Green Bank, WV Associated Universities, Inc; April/2016 2 Preliminary thoughts a. How certain are you that other
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 28. Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 28 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 28 Life in the Universe Units of Chapter 28 28.1 Cosmic Evolution Discovery 28-1 The Virus 28.2 Life in the Solar System
Lecture Outlines Chapter 28 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 28 Life in the Universe Units of Chapter 28 28.1 Cosmic Evolution Discovery 28-1 The Virus 28.2 Life in the Solar System
Are We Alone? Dreams of Life Elsewhere
 Are We Alone? Dreams of Life Elsewhere Where is everybody? Fermi s paradox (1950 lunch conversation) Assume 3 levels of extraterrestrial civilizations ETC1, like ours (energy resources of a planet) ETC2,
Are We Alone? Dreams of Life Elsewhere Where is everybody? Fermi s paradox (1950 lunch conversation) Assume 3 levels of extraterrestrial civilizations ETC1, like ours (energy resources of a planet) ETC2,
Search Strategies. Basic Problem: where to look? Possible Scenarios Powerful, omnidirectional beacons
 Communication, 2. Search Strategies Basic Problem: where to look? Possible Scenarios Powerful, omnidirectional beacons Implies very advanced civilization Seeking to attract attention of new civilizations
Communication, 2. Search Strategies Basic Problem: where to look? Possible Scenarios Powerful, omnidirectional beacons Implies very advanced civilization Seeking to attract attention of new civilizations
Chapter 24 Life in the Universe. Earliest Life Forms. When did life arise on Earth? Fossils in Sedimentary Rock. Fossils in Sedimentary Rock
 Chapter 24 Life in the Universe 24.1 Life on Earth Our goals for learning When did life arise on Earth? How did life arise on Earth? What are the necessities of life? When did life arise on Earth? Earliest
Chapter 24 Life in the Universe 24.1 Life on Earth Our goals for learning When did life arise on Earth? How did life arise on Earth? What are the necessities of life? When did life arise on Earth? Earliest
Measuring Distances to Galaxies. Galaxies in Motion. Hubble s Law. Galaxy Redshifts. Type Ia Supernovae. Supernovae are Good Standard Candles
 Measuring Distances to Galaxies Too far for parallax! Standard Candles: Cepheid Variables (for Local Group) Type Ia Supernovae Redshifts Type Ia Supernovae These are another standard candle used to measure
Measuring Distances to Galaxies Too far for parallax! Standard Candles: Cepheid Variables (for Local Group) Type Ia Supernovae Redshifts Type Ia Supernovae These are another standard candle used to measure
! Communication, 2.!
 Communication, 2. Search Strategies Basic Problem: where to look? Possible Scenarios Powerful, omnidirectional beacons Implies very advanced civilization Seeking to attract attention of new civilizations
Communication, 2. Search Strategies Basic Problem: where to look? Possible Scenarios Powerful, omnidirectional beacons Implies very advanced civilization Seeking to attract attention of new civilizations
Sociological Factors. Putting it all Together: How far away? How many stars to search?
 f c = /2? Sociological Factors at least, maybe 3 intelligent species on Earth with technology for remote communication L > 75 years Longevity - how long are they detectable? leakage of VHF/UHF signals
f c = /2? Sociological Factors at least, maybe 3 intelligent species on Earth with technology for remote communication L > 75 years Longevity - how long are they detectable? leakage of VHF/UHF signals
Search Strategies. Basic Problem: where to look? Possible Scenarios Powerful, omnidirectional beacons
 Communication, 2. Search Strategies Basic Problem: where to look? Possible Scenarios Powerful, omnidirectional beacons Implies very advanced civilization Seeking to attract attention of new civilizations
Communication, 2. Search Strategies Basic Problem: where to look? Possible Scenarios Powerful, omnidirectional beacons Implies very advanced civilization Seeking to attract attention of new civilizations
Young Solar-like Systems
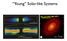 Young Solar-like Systems FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show 2.9,1.3,and 0.87 mm ALMA continuum images of other panels, as well as an inset with an enlarged view of the inner 300 mas centered on the (f) show
Young Solar-like Systems FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show 2.9,1.3,and 0.87 mm ALMA continuum images of other panels, as well as an inset with an enlarged view of the inner 300 mas centered on the (f) show
Chapter 24: Life in the Universe
 Chapter 24 Lecture Chapter 24: Life in the Universe Life in the Universe 24.1 Life on Earth Our goals for learning: When did life arise on Earth? How did life arise on Earth? What are the necessities of
Chapter 24 Lecture Chapter 24: Life in the Universe Life in the Universe 24.1 Life on Earth Our goals for learning: When did life arise on Earth? How did life arise on Earth? What are the necessities of
PH104 Lab 2 Measuring Distances Pre-Lab
 Name: Lab Time: PH04 Lab 2 Measuring Distances Pre-Lab 2. Goals This is the second lab. Like the first lab this lab does not seem to be part of a complete sequence of the study of astronomy, but it will
Name: Lab Time: PH04 Lab 2 Measuring Distances Pre-Lab 2. Goals This is the second lab. Like the first lab this lab does not seem to be part of a complete sequence of the study of astronomy, but it will
Nov 17, 2003 Astronomy 100 Fall _tips_ html
 Next week is Thanksgiving break Leonid meteor shower can be seen the night of the 18 th (really the early morning of the 19 th ). Should see dozens of meteors per hour at the peak 1:30 am CST. The shower
Next week is Thanksgiving break Leonid meteor shower can be seen the night of the 18 th (really the early morning of the 19 th ). Should see dozens of meteors per hour at the peak 1:30 am CST. The shower
The evolution of a Solar-like system. Young Solar-like Systems. Searching for Extrasolar Planets: Motivation
 Young Solar-like Systems The evolution of a Solar-like system FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show2.9,1.3,and0.87mmALMAcontinuum images of HL Tau. Panel (d) shows the 1.3 mm psf for the same FOV as the other
Young Solar-like Systems The evolution of a Solar-like system FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show2.9,1.3,and0.87mmALMAcontinuum images of HL Tau. Panel (d) shows the 1.3 mm psf for the same FOV as the other
Part I---Introduction: planets, and habitable planets
 Part I---Introduction: planets, and habitable planets star--about 10 11 in our galaxy. Average separation is a few light years. (Compare with size of Galaxy: about 100,000 light years) planet--indirect
Part I---Introduction: planets, and habitable planets star--about 10 11 in our galaxy. Average separation is a few light years. (Compare with size of Galaxy: about 100,000 light years) planet--indirect
The Physical Basis of Life
 Origins of Life Physics 113 Goderya Chapter(s): 19 Learning Outcomes: The Physical Basis of Life All life forms on Earth, from viruses to complex mammals (including humans) are based on carbon chemistry.
Origins of Life Physics 113 Goderya Chapter(s): 19 Learning Outcomes: The Physical Basis of Life All life forms on Earth, from viruses to complex mammals (including humans) are based on carbon chemistry.
Simon P. Balm Astro 5 Test #3 Sample Questions
 Simon P. Balm Astro 5 Test #3 Sample Questions 1. What do we mean by the general habitability of a planet? A. the suitability for Life on it surface B. the suitability for Life beneath its surface C. its
Simon P. Balm Astro 5 Test #3 Sample Questions 1. What do we mean by the general habitability of a planet? A. the suitability for Life on it surface B. the suitability for Life beneath its surface C. its
Final Exam. 12:30 2:30 pm, Friday, May 6th, in this room. Written Questions covering all the material from this semester.
 Final Exam 12:30 2:30 pm, Friday, May 6th, in this room. Written Questions covering all the material from this semester. Dark Matter Black Holes Dark matter is noninteracting, so it has no way of losing
Final Exam 12:30 2:30 pm, Friday, May 6th, in this room. Written Questions covering all the material from this semester. Dark Matter Black Holes Dark matter is noninteracting, so it has no way of losing
Lab 4. Habitable Worlds: Where Should NASA Send a Probe to Look for Life?
 Lab Handout Lab 4. Habitable Worlds: Where Should NASA Send a Probe to Look for Life? Introduction Our solar system consists of the star we call the Sun, the planets and dwarf plants that orbit it, and
Lab Handout Lab 4. Habitable Worlds: Where Should NASA Send a Probe to Look for Life? Introduction Our solar system consists of the star we call the Sun, the planets and dwarf plants that orbit it, and
ASTR 380 The Drake Equation
 ASTR 380 The Drake Equation Aside: Rosetta Mission - Landing on a Comet! Aside: Rosetta Mission - Landing on a Comet! ASTR 380 The Drake Equation Drake Equation Methodology Reviewing Drake Equation factors
ASTR 380 The Drake Equation Aside: Rosetta Mission - Landing on a Comet! Aside: Rosetta Mission - Landing on a Comet! ASTR 380 The Drake Equation Drake Equation Methodology Reviewing Drake Equation factors
NSCI EXTRASOLAR PLANETS (CONTINUED) AND THE DRAKE EQUATION. Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics, CSUSB
 NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 14 - EXTRASOLAR PLANETS (CONTINUED) AND THE DRAKE EQUATION Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics, CSUSB http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen/ METHODS FOR DETECTING EXTRASOLAR
NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 14 - EXTRASOLAR PLANETS (CONTINUED) AND THE DRAKE EQUATION Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics, CSUSB http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen/ METHODS FOR DETECTING EXTRASOLAR
Extrasolar Planets What are the odds?
 Honors 228: Astrobiology using Bennett and Shostak Chapter 12 overview Spring 2007 Dr. H. Geller What s talked about The Drake Equation (12.1) The Question of Intelligence (12.2) Searching for Intelligence
Honors 228: Astrobiology using Bennett and Shostak Chapter 12 overview Spring 2007 Dr. H. Geller What s talked about The Drake Equation (12.1) The Question of Intelligence (12.2) Searching for Intelligence
THE SIZE AND SCALE OF THE UNIVERSE
 1 THE SIZE AND SCALE OF THE UNIVERSE 1. Scientific notation review Write the following in proper scientific notation, giving the proper number of significant figures. 1.a Thirty-one million, seven hundred
1 THE SIZE AND SCALE OF THE UNIVERSE 1. Scientific notation review Write the following in proper scientific notation, giving the proper number of significant figures. 1.a Thirty-one million, seven hundred
Ultimate Events. Galaxy clustering in ever deeper surveys. Models of universe and its fates
 ASTR 1040 Accel Astro: Stars & Galaxies Ultimate Events Prof. Juri Toomre TA: Nicholas Nelson Lecture 30 Thur 28 Apr 2011 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre toomre Allen Telescope Array Review current big
ASTR 1040 Accel Astro: Stars & Galaxies Ultimate Events Prof. Juri Toomre TA: Nicholas Nelson Lecture 30 Thur 28 Apr 2011 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre toomre Allen Telescope Array Review current big
WHERE ARE THEY? The Fermi Paradox
 WHERE ARE THEY? The Fermi Paradox Milan S. Dimitrijević Astronomical Observatory, Volgina 7, 11160 Belgrade, Serbia ENRICO FERMI FERMI PARADOX Or GREAT SILENCE (Brin 1983) Or ASTROSOCIOLOGICAL PARADOX
WHERE ARE THEY? The Fermi Paradox Milan S. Dimitrijević Astronomical Observatory, Volgina 7, 11160 Belgrade, Serbia ENRICO FERMI FERMI PARADOX Or GREAT SILENCE (Brin 1983) Or ASTROSOCIOLOGICAL PARADOX
Physics can only take us so far!
 Physics can only take us so far! The usual approach of science of constructing a mathematical model cannot answer the questions of why there should be a universe for the model to describe. Why does the
Physics can only take us so far! The usual approach of science of constructing a mathematical model cannot answer the questions of why there should be a universe for the model to describe. Why does the
Star. Planet. Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe. 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe?
 Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in the
Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in the
Decoding an Extraterrestrial Message
 CLASSROOM ACTIVITY Decoding an Extraterrestrial Message General information Level: elementary cycle three and secondary I to V. Students per group: individual activity or in pairs. How long: 30 minutes.
CLASSROOM ACTIVITY Decoding an Extraterrestrial Message General information Level: elementary cycle three and secondary I to V. Students per group: individual activity or in pairs. How long: 30 minutes.
ASTR 380 The Drake Equation
 ASTR 380 The Drake Equation 1 ASTR 380 The Drake Equation Drake Equation Methodology Reviewing Drake Equation factors that we know The star formation rate Estimating the number of Earth-like planets or
ASTR 380 The Drake Equation 1 ASTR 380 The Drake Equation Drake Equation Methodology Reviewing Drake Equation factors that we know The star formation rate Estimating the number of Earth-like planets or
CONNECTIONS to the COSMOS: the search for life beyond Earth
 CONNECTIONS to the COSMOS: the search for life beyond Earth Shane L. Larson shane@science.weber.edu Open House 18 April 2008 Weber State University Storyline What are we talking about? What might life
CONNECTIONS to the COSMOS: the search for life beyond Earth Shane L. Larson shane@science.weber.edu Open House 18 April 2008 Weber State University Storyline What are we talking about? What might life
Homework 13 (not graded; only some example ques!ons for the material from the last week or so of class)
 Homework 13 (not graded; only some example ques!ons for the material from the last week or so of class)! This is a preview of the draft version of the quiz Started: Apr 28 at 9:27am Quiz Instruc!ons Question
Homework 13 (not graded; only some example ques!ons for the material from the last week or so of class)! This is a preview of the draft version of the quiz Started: Apr 28 at 9:27am Quiz Instruc!ons Question
(Astro)Physics 343 Lecture # 14: the Search for Extra Terrestrial Intelligence
 (Astro)Physics 343 Lecture # 14: the Search for Extra Terrestrial Intelligence Astrobiology: a useful starting point astrobiology (Lafleur 1941) cosmobiology (Bernal 1952) exobiology (Lederberg 1960) bioastronomy
(Astro)Physics 343 Lecture # 14: the Search for Extra Terrestrial Intelligence Astrobiology: a useful starting point astrobiology (Lafleur 1941) cosmobiology (Bernal 1952) exobiology (Lederberg 1960) bioastronomy
 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lhtsfozun Lo Explanation: Comet Lovejoy was captured last week passing well in front of spiral galaxy M63. Discovered only three months ago and currently near its maximum
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lhtsfozun Lo Explanation: Comet Lovejoy was captured last week passing well in front of spiral galaxy M63. Discovered only three months ago and currently near its maximum
Galaxies and The Milky Way
 Galaxies and The Milky Way Attendance Quiz Are you here today? Here! (a) yes (b) no (c) To infinity and beyond! Next Tuesday, 5/30, I will be away at a meeting. There will be a guest lecture by Dr. Jorge
Galaxies and The Milky Way Attendance Quiz Are you here today? Here! (a) yes (b) no (c) To infinity and beyond! Next Tuesday, 5/30, I will be away at a meeting. There will be a guest lecture by Dr. Jorge
It is a very human trait to wonder where we are in this universe. Usually, the only hint of the vastness of the universe comes at night.
 Chapter 01 Part 1 Our Place in Space We all wonder It is a very human trait to wonder where we are in this universe. Usually, the only hint of the vastness of the universe comes at night. There seems to
Chapter 01 Part 1 Our Place in Space We all wonder It is a very human trait to wonder where we are in this universe. Usually, the only hint of the vastness of the universe comes at night. There seems to
Astrobiology: The Semester in Review
 A Universe of Life Astrobiology: The Semester in Review Honors 228 with Dr. Harold Geller Searching for life everywhere Planets, stars, galaxies, Big Bang Conception of size and distance Stars and the
A Universe of Life Astrobiology: The Semester in Review Honors 228 with Dr. Harold Geller Searching for life everywhere Planets, stars, galaxies, Big Bang Conception of size and distance Stars and the
Life on Other Worlds: The Drake Equation Author: Meagan Morscher GK-12 Reach for the Stars Fellow, Northwestern University
 Life on Other Worlds: The Drake Equation Author: Meagan Morscher GK-12 Reach for the Stars Fellow, Northwestern University Time 2-3 class periods (will vary depending on grade level and experience with
Life on Other Worlds: The Drake Equation Author: Meagan Morscher GK-12 Reach for the Stars Fellow, Northwestern University Time 2-3 class periods (will vary depending on grade level and experience with
The Search for Extra-terrestrial. Is there anybody out there?
 The Search for Extra-terrestrial Intelligence! Is there anybody out there? Summary: we will investigate (a) the Drake Equation and (b) the factors that determine how many, if any, other civilizations
The Search for Extra-terrestrial Intelligence! Is there anybody out there? Summary: we will investigate (a) the Drake Equation and (b) the factors that determine how many, if any, other civilizations
Intelligent Life in the Universe
 Intelligent Life in the Universe Lecture 33 APoD: Easter Island Eclipse In-Class Question 1) Do you think life exists elsewhere in the Universe? a) Yes b) No c) Don t know d) Don t care 2 33-1 Lecture
Intelligent Life in the Universe Lecture 33 APoD: Easter Island Eclipse In-Class Question 1) Do you think life exists elsewhere in the Universe? a) Yes b) No c) Don t know d) Don t care 2 33-1 Lecture
Astronomy 330 HW 2. Outline. Presentations. ! Kira Bonk ascension.html
 Astronomy 330 This class (Lecture 11): What is f p? Eric Gobst Suharsh Sivakumar Next Class: Life in the Solar System HW 2 Kira Bonk http://www.ufodigest.com/news/0308/ ascension.html Matthew Tenpas http://morphman.hubpages.com/hub/alien-
Astronomy 330 This class (Lecture 11): What is f p? Eric Gobst Suharsh Sivakumar Next Class: Life in the Solar System HW 2 Kira Bonk http://www.ufodigest.com/news/0308/ ascension.html Matthew Tenpas http://morphman.hubpages.com/hub/alien-
Cosmology Overview (so far): Cosmology Overview (so far): The Age of the Universe. The Big Bang. The Age of the Universe
 Cosmology Overview (so far): The Universe: Everything Observable Universe: Everything we can The Universe has no special locations No If no, then no Cosmology Overview (so far): Oblers s Paradox: The sky
Cosmology Overview (so far): The Universe: Everything Observable Universe: Everything we can The Universe has no special locations No If no, then no Cosmology Overview (so far): Oblers s Paradox: The sky
-- Lewis Carroll, Alice in Wonderland
 Where Are They? There s no use trying, she said: one can t believe impossible things. I daresay you haven t had much practice, said the Queen. When I was your age, I always did it for half-anhour a day.
Where Are They? There s no use trying, she said: one can t believe impossible things. I daresay you haven t had much practice, said the Queen. When I was your age, I always did it for half-anhour a day.
January December. Journey Back in Time. Review: The ScienCfic Search for Origins How did our world come to be? 4/27/10
 Lecture 23 The Cosmic Calendar & The Search for Life A1010 Prof. Tom Megeath Review: The ScienCfic Search for Origins How did our world come to be? The formacon of stars The formacon of planets The origin
Lecture 23 The Cosmic Calendar & The Search for Life A1010 Prof. Tom Megeath Review: The ScienCfic Search for Origins How did our world come to be? The formacon of stars The formacon of planets The origin
ABCs of Space By: John Kraus
 North American AstroPhysical Observatory (NAAPO) Cosmic Search: Issue 3 (Volume 1 Number 3; Summer 1979) [Article in magazine started on page 36] ABCs of Space By: John Kraus A. Stars and Their Spectra;
North American AstroPhysical Observatory (NAAPO) Cosmic Search: Issue 3 (Volume 1 Number 3; Summer 1979) [Article in magazine started on page 36] ABCs of Space By: John Kraus A. Stars and Their Spectra;
ASTR : Stars & Galaxies (Spring 2019)... Study Guide for Midterm 1
 ASTR-1200-01: Stars & Galaxies (Spring 2019)........................ Study Guide for Midterm 1 The first midterm exam for ASTR-1200 takes place in class on Wednesday, February 13, 2019. The exam covers
ASTR-1200-01: Stars & Galaxies (Spring 2019)........................ Study Guide for Midterm 1 The first midterm exam for ASTR-1200 takes place in class on Wednesday, February 13, 2019. The exam covers
4 Decoding the Arecibo Message
 4 Decoding the Arecibo Message In 1974, the Arecebo radio telescope was used to send a message into space. The message was directed at the globular cluster M13, which is an assembly of hundreds of thousands
4 Decoding the Arecibo Message In 1974, the Arecebo radio telescope was used to send a message into space. The message was directed at the globular cluster M13, which is an assembly of hundreds of thousands
ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration. Instructor: Dr. David Alexander Web-site:
 ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration Instructor: Dr. David Alexander Web-site: www.ruf.rice.edu/~dalex/astr202_s07 Class 37: Life in the Universe [4/18/07] Announcements Habitability of
ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration Instructor: Dr. David Alexander Web-site: www.ruf.rice.edu/~dalex/astr202_s07 Class 37: Life in the Universe [4/18/07] Announcements Habitability of
Start with known facts and reasonable guesses. More on order of magnitude Astronomy How many piano tuners are there in Boulder County?
 ASTR 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies Prof. Rosalba Perna TA: Cameron Clarke http://amalfi.astrosunysb.edu/rosalba/ast101/ast101.html MAKE SURE TO GO OVER THE SYLLABUS (if you haven t already
ASTR 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies Prof. Rosalba Perna TA: Cameron Clarke http://amalfi.astrosunysb.edu/rosalba/ast101/ast101.html MAKE SURE TO GO OVER THE SYLLABUS (if you haven t already
Our Place in the Universe (Chapter 1) The Structure and Size of the Universe
 Our Place in the Universe (Chapter 1) The Structure and Size of the Universe Based on Chapter 1 This material will be useful for understanding Chapters 2, 3, and 13 on Years, Seasons, and Months, The Orbits
Our Place in the Universe (Chapter 1) The Structure and Size of the Universe Based on Chapter 1 This material will be useful for understanding Chapters 2, 3, and 13 on Years, Seasons, and Months, The Orbits
Astronomy 1504 Section 10 Final Exam Version 1 May 6, 1999
 Astronomy 1504 Section 10 Final Exam Version 1 May 6, 1999 Reminder: When I write these questions, I believe that there is one one correct answer. The questions consist of all parts a e. Read the entire
Astronomy 1504 Section 10 Final Exam Version 1 May 6, 1999 Reminder: When I write these questions, I believe that there is one one correct answer. The questions consist of all parts a e. Read the entire
What s the longest single-shot exposure ever recorded of any object or area of space by Hubble?
 Hubblecast Episode 50: Q&A with Dr J 00:00 Have you ever wondered why Hubble can make detailed images of of galaxies, but stars appear as featureless blobs? What the most distant object ever observed is?
Hubblecast Episode 50: Q&A with Dr J 00:00 Have you ever wondered why Hubble can make detailed images of of galaxies, but stars appear as featureless blobs? What the most distant object ever observed is?
ASTR 380: Life in the Universe - Astrobiology Professor Sylvain Veilleux
 ASTR 380: Life in the Universe - Astrobiology Professor Sylvain Veilleux Some of Life s Fundamental Questions Are we alone? How did life develop on Earth? What are the conditions for life? Could life happen
ASTR 380: Life in the Universe - Astrobiology Professor Sylvain Veilleux Some of Life s Fundamental Questions Are we alone? How did life develop on Earth? What are the conditions for life? Could life happen
Detection of Earth-like planets
 Planets and life Successful detections of extrasolar giant planets suggests that planetary systems may be fairly common could we detect Earthlike planets? is it likely that such planets would have life?
Planets and life Successful detections of extrasolar giant planets suggests that planetary systems may be fairly common could we detect Earthlike planets? is it likely that such planets would have life?
The Physical Basis of Life. The Origin of Life on Earth. Information Storage and Duplication
 The Physical Basis of Life All life forms on Earth, from viruses to complex mammals (including humans) are based on carbon chemistry. Carbon-based DNA and RNA molecule strands are the basic carriers of
The Physical Basis of Life All life forms on Earth, from viruses to complex mammals (including humans) are based on carbon chemistry. Carbon-based DNA and RNA molecule strands are the basic carriers of
Sex in Space: Astronomy 330 TR Noyes Laboratory 217. Outline. Discussion Class
 Sex in Space: Astronomy 330 TR 1000-1050 Noyes Laboratory 217 This class (Lecture 3): Expanding Universe Next Class: Cosmology Music: Galaxies Laura Veirs HW1 due tonight! (grace period until Feb 3 rd
Sex in Space: Astronomy 330 TR 1000-1050 Noyes Laboratory 217 This class (Lecture 3): Expanding Universe Next Class: Cosmology Music: Galaxies Laura Veirs HW1 due tonight! (grace period until Feb 3 rd
Other migration processes. New transiting hot Jupiters from last week. First success from CoRoT. Kozai mechanism
 Other migration processes Previous lecture: Migration through planet-disk interactions Type I: low-mass planet (does not clear a gap in disk) Type II: high-mass panet (has cleared gap) Type III: runaway
Other migration processes Previous lecture: Migration through planet-disk interactions Type I: low-mass planet (does not clear a gap in disk) Type II: high-mass panet (has cleared gap) Type III: runaway
Planets, Stars and Galaxies Section 1 Mon. & Weds. 3:35-4:50. Prof. Todd Adams. Welcome! Department of Physics Florida State University
 Planets, Stars and Galaxies Section 1 Mon. & Weds. 3:35-4:50 Prof. Todd Adams Welcome! Department of Physics Florida State University Astronomy is the study of objects beyond the Earth s atmosphere and
Planets, Stars and Galaxies Section 1 Mon. & Weds. 3:35-4:50 Prof. Todd Adams Welcome! Department of Physics Florida State University Astronomy is the study of objects beyond the Earth s atmosphere and
Ari Schjelderup David Schaffer PHYS /30/11 The Big Bang Theory
 Schjelderup 1 Ari Schjelderup David Schaffer PHYS-1040-009 10/30/11 The Big Bang Theory When I was a little girl I asked my mom how long God had been around. She told me he had been around forever. When
Schjelderup 1 Ari Schjelderup David Schaffer PHYS-1040-009 10/30/11 The Big Bang Theory When I was a little girl I asked my mom how long God had been around. She told me he had been around forever. When
HOW COMMON IS LIFE IN THE UNIVERSE?
 HOW COMMON IS LIFE IN THE UNIVERSE? Joseph Silk Gresham College 2 March 2016 It is often said that all the conditions for the first production of a living organism are now present, which could ever have
HOW COMMON IS LIFE IN THE UNIVERSE? Joseph Silk Gresham College 2 March 2016 It is often said that all the conditions for the first production of a living organism are now present, which could ever have
SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES
 SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES Q1. The figure below shows what scientists over 1000 years ago thought the solar system was like. Give one way that the historical model of the solar
SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES Q1. The figure below shows what scientists over 1000 years ago thought the solar system was like. Give one way that the historical model of the solar
MITOCW watch?v=gfbgoivnyuw
 MITOCW watch?v=gfbgoivnyuw The phone content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free. To make
MITOCW watch?v=gfbgoivnyuw The phone content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free. To make
Bell s spaceship paradox
 Bell s spaceship paradox If the two ships start accelerating at the same time, I always see them travelling at the same velocity, and keeping a constant distance... But I said the objects get shorter when
Bell s spaceship paradox If the two ships start accelerating at the same time, I always see them travelling at the same velocity, and keeping a constant distance... But I said the objects get shorter when
Planet discovery accounced Feb. 3
 Announcements The third homework is due Monday, Feb. 9. The first exam is Wednesday, Feb. 11. Monday, Feb. 9, will be a review, please e-mail questions. If you need help to go an Astronomy tutorial; the
Announcements The third homework is due Monday, Feb. 9. The first exam is Wednesday, Feb. 11. Monday, Feb. 9, will be a review, please e-mail questions. If you need help to go an Astronomy tutorial; the
N = R *! f p! n e! f l! f i! f c! L
 Leslie Looney Phone: 244-3615 Email: lwl1@1uiuc1.1edu Office: Astro Building #218 Office Hours: W: 11- noon or by appointment Sex in Space: 134 Astronomy Building This class (Lecture 3): Cosmology Next
Leslie Looney Phone: 244-3615 Email: lwl1@1uiuc1.1edu Office: Astro Building #218 Office Hours: W: 11- noon or by appointment Sex in Space: 134 Astronomy Building This class (Lecture 3): Cosmology Next
Section 3- The history and future of space exploration
 Unit 1: Space Section 3- The history and future of space exploration Ancient Astronomer Speed Dating Remember: Speak to your partner, don t copy notes Keep points brief, don t write paragraphs Stick to
Unit 1: Space Section 3- The history and future of space exploration Ancient Astronomer Speed Dating Remember: Speak to your partner, don t copy notes Keep points brief, don t write paragraphs Stick to
TAKEN FROM HORIZONS 7TH EDITION CHAPTER 1 TUTORIAL QUIZ
 TAKEN FROM HORIZONS 7TH EDITION CHAPTER 1 TUTORIAL QUIZ 1. If the solar system is scaled down so that the Sun is represented by a basketball, a. a ping-pong ball located 500 feet away would properly represent
TAKEN FROM HORIZONS 7TH EDITION CHAPTER 1 TUTORIAL QUIZ 1. If the solar system is scaled down so that the Sun is represented by a basketball, a. a ping-pong ball located 500 feet away would properly represent
12/5/ Life on Earth. Chapter 19: Life in the Universe. When did life arise on Earth? Earliest Life Forms. Important Stuff (Section 001)
 Important Stuff (Section 001) The Final Exam is Thursday, December 22, 8:00 10:00 am The Final Exam will be given in: Willey 175 Don t come to Anderson 210. No one will be there. No one. Bring 2 pencils
Important Stuff (Section 001) The Final Exam is Thursday, December 22, 8:00 10:00 am The Final Exam will be given in: Willey 175 Don t come to Anderson 210. No one will be there. No one. Bring 2 pencils
Notes 9: Extrasolar Planets and Exo-biology
 Notes 9: Extrasolar Planets and Exo-biology This is an interesting section. We have all sorts of observations and data concerning extrasolar planets (planets outside the solar system), but no evidence
Notes 9: Extrasolar Planets and Exo-biology This is an interesting section. We have all sorts of observations and data concerning extrasolar planets (planets outside the solar system), but no evidence
AST 309 part 2: Extraterrestrial Life. The Search For Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI)
 AST 309 part 2: Extraterrestrial Life The Search For Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI) The Drake Equation: N = N * f pl n hab f L f C f T L/T Stars? Planets? Habitable Origin Complex Intelligence, Life;me
AST 309 part 2: Extraterrestrial Life The Search For Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI) The Drake Equation: N = N * f pl n hab f L f C f T L/T Stars? Planets? Habitable Origin Complex Intelligence, Life;me
Life on a New Planet
 Life on a New Planet Your Assignment: A national magazine is sponsoring a short story contest. Your teacher has assigned your class the task of entering this contest. The first, second, and third place
Life on a New Planet Your Assignment: A national magazine is sponsoring a short story contest. Your teacher has assigned your class the task of entering this contest. The first, second, and third place
[02] Quantitative Reasoning in Astronomy (8/31/17)
![[02] Quantitative Reasoning in Astronomy (8/31/17) [02] Quantitative Reasoning in Astronomy (8/31/17)](/thumbs/79/79198497.jpg) 1 [02] Quantitative Reasoning in Astronomy (8/31/17) Upcoming Items 1. Read Chapter 2.1 by next lecture. As always, I recommend that you do the self-study quizzes in MasteringAstronomy 2. Homework #1 due
1 [02] Quantitative Reasoning in Astronomy (8/31/17) Upcoming Items 1. Read Chapter 2.1 by next lecture. As always, I recommend that you do the self-study quizzes in MasteringAstronomy 2. Homework #1 due
what scientist believe happened to form the universe, and it is called the Big Bang Theory.
 Schjelderup 1 Ari Schjelderup David Schaffer PHYS-1040-009 10/30/11 The Big Bang Theory When I was a little girl I asked my mom how long god had been around. She told me he had been around forever. When
Schjelderup 1 Ari Schjelderup David Schaffer PHYS-1040-009 10/30/11 The Big Bang Theory When I was a little girl I asked my mom how long god had been around. She told me he had been around forever. When
Phys 214. Planets and Life
 Phys 214. Planets and Life Dr. Cristina Buzea Department of Physics Room 259 E-mail: cristi@physics.queensu.ca (Please use PHYS214 in e-mail subject) Lecture 6. The Structure and Scale of the Universe
Phys 214. Planets and Life Dr. Cristina Buzea Department of Physics Room 259 E-mail: cristi@physics.queensu.ca (Please use PHYS214 in e-mail subject) Lecture 6. The Structure and Scale of the Universe
Alternative Standard Frequencies for Interstellar Communication. C Sivaram. Indian Institute of Astrophysics. Bangalore , India
 Running title: Alternate standard frequency Alternative Standard requencies for Interstellar Communication C Sivaram Indian Institute of Astrophysics angalore - 560 0, India Kenath Arun * Christ Junior
Running title: Alternate standard frequency Alternative Standard requencies for Interstellar Communication C Sivaram Indian Institute of Astrophysics angalore - 560 0, India Kenath Arun * Christ Junior
Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence
 Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence Life in the Universe? What is life? (as we know it) Auto-regulation (ex. : sweating) Organization (A cell is more organized than a bunch of atoms) Metabolism :
Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence Life in the Universe? What is life? (as we know it) Auto-regulation (ex. : sweating) Organization (A cell is more organized than a bunch of atoms) Metabolism :
Introduction to Astronomy
 Introduction to Astronomy Have you ever wondered what is out there in space besides Earth? As you see the stars and moon, many questions come up with the universe, possibility of living on another planet
Introduction to Astronomy Have you ever wondered what is out there in space besides Earth? As you see the stars and moon, many questions come up with the universe, possibility of living on another planet
ASTRO 114 Lecture Okay. What we re going to discuss today are what we call radiation laws. We ve
 ASTRO 114 Lecture 15 1 Okay. What we re going to discuss today are what we call radiation laws. We ve been spending a lot of time talking about laws. We ve talked about gravitational laws, we ve talked
ASTRO 114 Lecture 15 1 Okay. What we re going to discuss today are what we call radiation laws. We ve been spending a lot of time talking about laws. We ve talked about gravitational laws, we ve talked
Monday, January 30, 2012 First exam Friday. First Sky Watch due. Review sheet posted. Reading posted under announcements on web page, Chapter 6 -
 Monday, January 30, 2012 First exam Friday. First Sky Watch due. Review sheet posted. Reading posted under announcements on web page, Chapter 6 - Sections 6.1, 6.2, 6.3 (also sections 1.2.4, 2.1-2.5, and
Monday, January 30, 2012 First exam Friday. First Sky Watch due. Review sheet posted. Reading posted under announcements on web page, Chapter 6 - Sections 6.1, 6.2, 6.3 (also sections 1.2.4, 2.1-2.5, and
How Did the Universe Begin?
 How Did the Universe Begin? As we will discuss in this lecture, it looks like the Universe started about 14 billion years ago and has been expanding (space stretching) ever since. The model of what happened
How Did the Universe Begin? As we will discuss in this lecture, it looks like the Universe started about 14 billion years ago and has been expanding (space stretching) ever since. The model of what happened
News English.com Ready-to-use ESL / EFL Lessons
 www.breaking News English.com Ready-to-use ESL / EFL Lessons 1,000 IDEAS & ACTIVITIES FOR LANGUAGE TEACHERS The Breaking News English.com Resource Book http://www.breakingnewsenglish.com/book.html NASA
www.breaking News English.com Ready-to-use ESL / EFL Lessons 1,000 IDEAS & ACTIVITIES FOR LANGUAGE TEACHERS The Breaking News English.com Resource Book http://www.breakingnewsenglish.com/book.html NASA
HOW TO GET LIGHT FROM THE DARK AGES
 HOW TO GET LIGHT FROM THE DARK AGES Anthony Smith Lunar Seminar Presentation 2/2/2010 OUTLINE Basics of Radio Astronomy Why go to the moon? What should we find there? BASICS OF RADIO ASTRONOMY Blackbody
HOW TO GET LIGHT FROM THE DARK AGES Anthony Smith Lunar Seminar Presentation 2/2/2010 OUTLINE Basics of Radio Astronomy Why go to the moon? What should we find there? BASICS OF RADIO ASTRONOMY Blackbody
Wallace Hall Academy Physics Department. Space. Pupil Notes Name:
 Wallace Hall Academy Physics Department Space Pupil Notes Name: Learning intentions for this unit? Be able to state what the value is for acceleration due to gravity during freefall Be able to explain
Wallace Hall Academy Physics Department Space Pupil Notes Name: Learning intentions for this unit? Be able to state what the value is for acceleration due to gravity during freefall Be able to explain
Sex in Space: Astronomy 330 TR English Building. Outline. Astro 330: Sex in Space? Be Careful of Science. ! The Drake equation
 Sex in Space: Astronomy 330 TR 1000-1050 160 English Building Leslie Looney Phone: 244-3615 Email: lwl1@1uiuc1.1edu Office: Astro Building #218 Office Hours: W: 11:00 a.m. noon or by appointment This class
Sex in Space: Astronomy 330 TR 1000-1050 160 English Building Leslie Looney Phone: 244-3615 Email: lwl1@1uiuc1.1edu Office: Astro Building #218 Office Hours: W: 11:00 a.m. noon or by appointment This class
Hubble s Law: Finding the Age of the Universe
 Lab 16 Name: Hubble s Law: Finding the Age of the Universe 16.1 Introduction In your lecture sessions (or the lab on spectroscopy), you will find out that an object s spectrum can be used to determine
Lab 16 Name: Hubble s Law: Finding the Age of the Universe 16.1 Introduction In your lecture sessions (or the lab on spectroscopy), you will find out that an object s spectrum can be used to determine
Phys 100 Astronomy (Dr. Ilias Fernini) Review Questions for Chapter 1
 Phys 100 Astronomy (Dr. Ilias Fernini) Review Questions for Chapter 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE (Right answers are reported in red) 1.. A solar system contains a. primarily planets. b. large amounts of gas and dust
Phys 100 Astronomy (Dr. Ilias Fernini) Review Questions for Chapter 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE (Right answers are reported in red) 1.. A solar system contains a. primarily planets. b. large amounts of gas and dust
Mike Garrett. Sir Bernard Lovell Chair, Prof. of Astrophysics. Director Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics
 The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI) All-sky Radio Mike Garrett SETI Sir Bernard Lovell Chair, Prof. of Astrophysics. Director Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics Mike Garrett Sir Bernard
The Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI) All-sky Radio Mike Garrett SETI Sir Bernard Lovell Chair, Prof. of Astrophysics. Director Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics Mike Garrett Sir Bernard
Astronomy 330 HW 2. Outline. Presentations. ! Alex Bara
 Astronomy 330 This class (Lecture 10): Origin of the Moon Ilana Strauss Next Class: Our Planet Scott Huber Thomas Hymel HW 2! Alex Bara http://userpages.bright.net/~phobia/main.htm! Margaret Sharp http://hubpages.com/hub/proof-that-ufos-exist---
Astronomy 330 This class (Lecture 10): Origin of the Moon Ilana Strauss Next Class: Our Planet Scott Huber Thomas Hymel HW 2! Alex Bara http://userpages.bright.net/~phobia/main.htm! Margaret Sharp http://hubpages.com/hub/proof-that-ufos-exist---
