A NON-HAMILTONIAN GRAPH. W.T. Tutte. (received June 30, 1959)
|
|
|
- Quentin Little
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A NON-HAMILTONIAN GRAPH W.T. Tutte (received June 30, 1959) There is a remarkable cubic graph of 28 vertices, discovered by Prof. H.S.M. Coxeter, which has no circuit of fewer than 7 edges and in which all oriented arcs made up of three edges are equivalent under the automorphism group. The structure of the graph is as follows. There are three disjoint heptagons Ai^i^^S^^S^b^J^l) > B(bjb5b2b > b3b-7b^b^) and C(c^c/ c^^cyc^cocj). We denote the seven remaining vertices by d^, d,... > dy. For each suffix i the three edges incident with dj_ join it to a^, b^ and ci. In drawing a diagram of the graph it seems best to show only the heptagons A, B and C, leaving the rest of the figure to the imagination. The purpose of this note is to establish another property of the graph, that it has no Hamiltonian circuit. A Hamiltonian circuit of a graph is a simple closed curve made up of edges and passing through all the vertices. Now if the given graph G has a Hamiltonian circuit H passing through aj^ and a 2 a 3> then the circuit passes also through b2d2 and C2d (since it does not contain the edge a2d2). We abbreviate this proposition as (a 1 a 2, a2a 3 ) > (^2^2* c 2 d 2)> and we shall make extensive use of implications of this kind. We note the existence of an automorphism U of G which maps X onto x^]_, where xisa, b, cord, 1 ^ i 4 7, and x 8 = x 1# Assume G has a Hamiltonian circuit H. Clearly H does not include all the edges of A. Let s denote the maximum number of consecutive edges of A in H. Then s ^ 6. Moreover Can. Math. Bull, vol.3, no.l, Jan. I960. 1
2 s ^ 2 since each vertex of A is incident with two edges of H. We split up the proof into 5 cases corresponding to the values of s from 2 to 6» Case I: s = 6. Because of the automorphism U we can suppose H contains the edges a x a 2, a 2 a 3, a 3 a 4, a 4 a5, &$&(} and a^ay of A. Since it does not contain a^a7 it must include also a^d^ and ayd^. We note the following implications. (a 1 a 2, a z a 3 ) ^ ( b 2 d 2> c 2 d 2 ) (a 2 a 3, a 3 a 4 ) * ( b 3 d 3> c 3 d 3) (a 3 a 4, a 4 a 5 ) > ( b 4d 4, c 4 d 4 ) (a 4 a 5, a 5 a 6 ) $> ( b 5 d 5> c 5 d 5) (a 5 a 6? a 6 a? ) > ( b ^, c 6 d 6 ) The part of H so far determined is shown by thick lines in Figure 1. We note that it is invariant under an automorphism V of G mapping x^ onto xg_. But H must include one of the two edges b}b 4 and b 4 b7. As these are equivalent under V we may suppose H includes b}b 4. We can now extend our knowledge of H with the following implications. (b x b 4, b 4 d 4 ) ^ (b 3 b 7) h 3 d 3 ) > (b 2 b 6? b d 2 ) > (b 1 b 4, bjb 5 ) > (a^dy, hydj) < ^ (c 5 c 7, c 5 d 5 ) > ( Cl c 3, cjdi) > (b 3 b 7, (b 2 b 6, (bibg, (ajdj, (c 2 c 7, (c 1 c 3, (c 4 c 6, b 7 d 7 ) b ô d 6) b 5 d 5 ) c l d l) c 5 c? ) c 3 d 3 ) c 6 d 6) H is now completely determined. separate circuits It consists of two Hi - (a 1 a 2 a3a 4 a 5 a 6 a 7 d 7 b 7 b i Q3C3C 1 d 1 a 1 ) and H 2 = ( b l b 5 d 5 c 5 c 7 c 2 d 2 b 2 b 6 d 6 c 6 c 4 d 4 b 4 b l)» So H is not Hamiltonian, contrary to assumption, 2
3 > p CFQ* H" OQ O^ O 3
4 Case II: s = 5. Because of the automorphism U we can assume H includes all the edges of A except a 7 a^ and a^a2«but H must include one of these two edges since it has two edges incident with a^. The case s = 5 is thus impossible. Case III: s = 4. We may suppose H contains aja2, a2a 3, a 3 a 4, a 4 a5> a^dj and a^d^. We have the following implications. ( a l a 2> a 2 a 3 ) ~^ < b 2 d 2' c 2 d 2> ( a 2 a 3> a 3 a 4) > ( b 3 d 3> c 3 d 3) (a 3 a 4, a 4 a 5 ) > (h^, c 4 d 4 ) (a 1 a 2, &i d \) > (a^a 7, a 7 d? ) (a 4 a 5, a 5 d 5 ) -> (a 6 a?, a 6 d 6 ) The part of H so far determined is shown thickly in Figure 2. It is invariant under an automorphism W of G mapping x^ into x 6-i' w'here XQ = x 7 and x _ ^ = x^. But H must include one of the two edges b 3 bk and b 3 b 7, which are equivalent under W, We may therefore suppose H contains boby. We continue with the following implications. (b 3 b 7, b 3 d 3 ) > ( b 2 b 6> b 6 d 6^ (b 2 b 6, b 2 d 2 ) -> (b^, b 5 d 5 ) ' ( b 6 d 6> a 6 d 6) ^ ( c l c 6» C 4 C 6) (b^d 5, a 5^5) > ( C 3 C 5> C 5 C 7^ (c 3 c 5, c 3 d 3 ) > ( c l c 6' c l d l) {dl l d l, c 1 d 1 ) => (b x b 4, b 1 b 5 ) (b x b 4, b 4 d 4 ) > (b 3 b 7, b? d? ) (c 4 c è, c 4 d 4 ) > (c 2 c 7, c 2 d 2 ) H is now completely determined as the pair of circuits and (a 1 a z a 3 a 4 a 5 d 5 b 5 b 1 b 4 d 4 c 4 c 6 c 1 d 1 a 1 ) < b 2 d 2 c 2 c 7 c 5 c 3 d 3 b 3 b 7 d 7 a 7 a 6 d 6 b 6 b 2)» contrary to its definition as Hamiltonian. Before going on to the remaining cases we note the existence of an automorphism X defined by the following table. 4
5 X maps each element of the first row into the corresponding element of the second row. a l a 2 a 3 a 4 a 5 a 6 a 7 b l b 5 b 2 b 6 b 3 b 7 b 4 c l c 6 c 4 c 2 c 7 c 5 c 3 d l d 2 d 3 d 4 d 5 d 6 d 7 a 1 a 2 a 3 d 3 c 3 c 1 d 1 d 7 c 7 c 2 c 4 d 4 b 4 b 7 a 6 d 6 b 6 b 2 b 5 d 5 a 5 a 7 d 2 a 4 b 3 c 5 c 6 b 1 Case IV: s = 2. We can suppose H contains the edges a^a 2, a 2 a 3, a^d^ and a3d 3/ But then H contains 4 consecutive edges of the heptagon a i a 2 a 3^3 c 3 c i^i a p which is equivalent to A under X» So this case can be reduced to the preceding cases. Case V: s = 3. We can suppose H contains the edges a 4 a5, z^a^, a 4 d 4 and a 7 d 7. We have the implications a^a-^, (a 4 a 5, a 4 d 4 ) > ( a 2 a 3> a 3 d 3^ ' (a^a 7, a 7 d 7 ) - > (a^a 2, a l d l^9 So H contains a^2, a a3, a^d^ and a3d 3. Accordingly Case V reduces to earlier cases in the same way as Case IV. University of Toronto 5
Graph homomorphisms. Peter J. Cameron. Combinatorics Study Group Notes, September 2006
 Graph homomorphisms Peter J. Cameron Combinatorics Study Group Notes, September 2006 Abstract This is a brief introduction to graph homomorphisms, hopefully a prelude to a study of the paper [1]. 1 Homomorphisms
Graph homomorphisms Peter J. Cameron Combinatorics Study Group Notes, September 2006 Abstract This is a brief introduction to graph homomorphisms, hopefully a prelude to a study of the paper [1]. 1 Homomorphisms
SELF-DUAL GRAPHS BRIGITTE SERVATIUS AND HERMAN SERVATIUS
 SELF-DUAL GRAPHS BRIGITTE SERVATIUS AND HERMAN SERVATIUS Abstract. We consider the three forms of self-duality that can be exhibited by a planar graph G, map self-duality, graph self-duality and matroid
SELF-DUAL GRAPHS BRIGITTE SERVATIUS AND HERMAN SERVATIUS Abstract. We consider the three forms of self-duality that can be exhibited by a planar graph G, map self-duality, graph self-duality and matroid
Eulerian Subgraphs in Graphs with Short Cycles
 Eulerian Subgraphs in Graphs with Short Cycles Paul A. Catlin Hong-Jian Lai Abstract P. Paulraja recently showed that if every edge of a graph G lies in a cycle of length at most 5 and if G has no induced
Eulerian Subgraphs in Graphs with Short Cycles Paul A. Catlin Hong-Jian Lai Abstract P. Paulraja recently showed that if every edge of a graph G lies in a cycle of length at most 5 and if G has no induced
arxiv: v3 [cs.dm] 18 Oct 2017
![arxiv: v3 [cs.dm] 18 Oct 2017 arxiv: v3 [cs.dm] 18 Oct 2017](/thumbs/76/73498857.jpg) Decycling a Graph by the Removal of a Matching: Characterizations for Special Classes arxiv:1707.02473v3 [cs.dm] 18 Oct 2017 Fábio Protti and Uéverton dos Santos Souza Institute of Computing - Universidade
Decycling a Graph by the Removal of a Matching: Characterizations for Special Classes arxiv:1707.02473v3 [cs.dm] 18 Oct 2017 Fábio Protti and Uéverton dos Santos Souza Institute of Computing - Universidade
On certain Regular Maps with Automorphism group PSL(2, p) Martin Downs
 BULLETIN OF THE GREEK MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 53, 2007 (59 67) On certain Regular Maps with Automorphism group PSL(2, p) Martin Downs Received 18/04/2007 Accepted 03/10/2007 Abstract Let p be any prime
BULLETIN OF THE GREEK MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 53, 2007 (59 67) On certain Regular Maps with Automorphism group PSL(2, p) Martin Downs Received 18/04/2007 Accepted 03/10/2007 Abstract Let p be any prime
Imprimitive symmetric graphs with cyclic blocks
 Imprimitive symmetric graphs with cyclic blocks Sanming Zhou Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Melbourne Joint work with Cai Heng Li and Cheryl E. Praeger December 17, 2008 Outline
Imprimitive symmetric graphs with cyclic blocks Sanming Zhou Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Melbourne Joint work with Cai Heng Li and Cheryl E. Praeger December 17, 2008 Outline
UNIQUENESS OF HIGHLY REPRESENTATIVE SURFACE EMBEDDINGS
 UNIQUENESS OF HIGHLY REPRESENTATIVE SURFACE EMBEDDINGS P. D. Seymour Bellcore 445 South St. Morristown, New Jersey 07960, USA and Robin Thomas 1 School of Mathematics Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta,
UNIQUENESS OF HIGHLY REPRESENTATIVE SURFACE EMBEDDINGS P. D. Seymour Bellcore 445 South St. Morristown, New Jersey 07960, USA and Robin Thomas 1 School of Mathematics Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta,
M INIM UM DEGREE AND F-FACTORS IN GRAPHS
 NEW ZEALAND JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 29 (2000), 33-40 M INIM UM DEGREE AND F-FACTORS IN GRAPHS P. K a t e r in is a n d N. T s ik o p o u l o s (Received June 1998) Abstract. Let G be a graph, a,
NEW ZEALAND JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 29 (2000), 33-40 M INIM UM DEGREE AND F-FACTORS IN GRAPHS P. K a t e r in is a n d N. T s ik o p o u l o s (Received June 1998) Abstract. Let G be a graph, a,
A MATROID EXTENSION RESULT
 A MATROID EXTENSION RESULT JAMES OXLEY Abstract. Adding elements to matroids can be fraught with difficulty. In the Vámos matroid V 8, there are four independent sets X 1, X 2, X 3, and X 4 such that (X
A MATROID EXTENSION RESULT JAMES OXLEY Abstract. Adding elements to matroids can be fraught with difficulty. In the Vámos matroid V 8, there are four independent sets X 1, X 2, X 3, and X 4 such that (X
A counterexample to the pseudo 2-factor isomorphic graph conjecture
 A counterexample to the pseudo 2-factor isomorphic graph conjecture Jan Goedgebeur a,1 arxiv:1412.3350v2 [math.co] 27 May 2015 Abstract a Department of Applied Mathematics, Computer Science & Statistics
A counterexample to the pseudo 2-factor isomorphic graph conjecture Jan Goedgebeur a,1 arxiv:1412.3350v2 [math.co] 27 May 2015 Abstract a Department of Applied Mathematics, Computer Science & Statistics
GIRTH SIX CUBIC GRAPHS HAVE PETERSEN MINORS
 GIRTH SIX CUBIC GRAPHS HAVE PETERSEN MINORS Neil Robertson 1 Department of Mathematics Ohio State University 231 W. 18th Ave. Columbus, Ohio 43210, USA P. D. Seymour Bellcore 445 South St. Morristown,
GIRTH SIX CUBIC GRAPHS HAVE PETERSEN MINORS Neil Robertson 1 Department of Mathematics Ohio State University 231 W. 18th Ave. Columbus, Ohio 43210, USA P. D. Seymour Bellcore 445 South St. Morristown,
Nowhere-zero 3-flows in triangularly connected graphs
 Nowhere-zero 3-flows in triangularly connected graphs Genghua Fan 1, Hongjian Lai 2, Rui Xu 3, Cun-Quan Zhang 2, Chuixiang Zhou 4 1 Center for Discrete Mathematics Fuzhou University Fuzhou, Fujian 350002,
Nowhere-zero 3-flows in triangularly connected graphs Genghua Fan 1, Hongjian Lai 2, Rui Xu 3, Cun-Quan Zhang 2, Chuixiang Zhou 4 1 Center for Discrete Mathematics Fuzhou University Fuzhou, Fujian 350002,
Fullerenes with distant pentagons
 Fullerenes with distant pentagons Jan Goedgebeur a, Brendan D. McKay b arxiv:1508.02878v1 [math.co] 12 Aug 2015 a Department of Applied Mathematics, Computer Science & Statistics Ghent University Krijgslaan
Fullerenes with distant pentagons Jan Goedgebeur a, Brendan D. McKay b arxiv:1508.02878v1 [math.co] 12 Aug 2015 a Department of Applied Mathematics, Computer Science & Statistics Ghent University Krijgslaan
arxiv: v1 [math.co] 27 Aug 2015
![arxiv: v1 [math.co] 27 Aug 2015 arxiv: v1 [math.co] 27 Aug 2015](/thumbs/96/128712557.jpg) arxiv:1508.06934v1 [math.co] 27 Aug 2015 TRIANGLE-FREE UNIQUELY 3-EDGE COLORABLE CUBIC GRAPHS SARAH-MARIE BELCASTRO AND RUTH HAAS Abstract. This paper presents infinitely many new examples of triangle-free
arxiv:1508.06934v1 [math.co] 27 Aug 2015 TRIANGLE-FREE UNIQUELY 3-EDGE COLORABLE CUBIC GRAPHS SARAH-MARIE BELCASTRO AND RUTH HAAS Abstract. This paper presents infinitely many new examples of triangle-free
Combining the cycle index and the Tutte polynomial?
 Combining the cycle index and the Tutte polynomial? Peter J. Cameron University of St Andrews Combinatorics Seminar University of Vienna 23 March 2017 Selections Students often meet the following table
Combining the cycle index and the Tutte polynomial? Peter J. Cameron University of St Andrews Combinatorics Seminar University of Vienna 23 March 2017 Selections Students often meet the following table
Characteristic flows on signed graphs and short circuit covers
 Characteristic flows on signed graphs and short circuit covers Edita Máčajová Martin Škoviera Department of Computer Science Faculty of Mathematics, Physics and Informatics Comenius University 842 48 Bratislava,
Characteristic flows on signed graphs and short circuit covers Edita Máčajová Martin Škoviera Department of Computer Science Faculty of Mathematics, Physics and Informatics Comenius University 842 48 Bratislava,
STRAND J: TRANSFORMATIONS, VECTORS and MATRICES
 Mathematics SKE, Strand J STRAND J: TRANSFORMATIONS, VECTORS and MATRICES J4 Matrices Text Contents * * * * Section J4. Matrices: Addition and Subtraction J4.2 Matrices: Multiplication J4.3 Inverse Matrices:
Mathematics SKE, Strand J STRAND J: TRANSFORMATIONS, VECTORS and MATRICES J4 Matrices Text Contents * * * * Section J4. Matrices: Addition and Subtraction J4.2 Matrices: Multiplication J4.3 Inverse Matrices:
Locke and Witte in [9] presented a class of circulant nonhamiltonian oriented graphs of type Cay(Z 2k ; a; b; b + k) Theorem 1 (Locke,Witte [9, Thm 41
![Locke and Witte in [9] presented a class of circulant nonhamiltonian oriented graphs of type Cay(Z 2k ; a; b; b + k) Theorem 1 (Locke,Witte [9, Thm 41 Locke and Witte in [9] presented a class of circulant nonhamiltonian oriented graphs of type Cay(Z 2k ; a; b; b + k) Theorem 1 (Locke,Witte [9, Thm 41](/thumbs/80/82224654.jpg) Arc Reversal in Nonhamiltonian Circulant Oriented Graphs Jozef Jirasek Department of Computer Science P J Safarik University Kosice, Slovakia jirasek@kosiceupjssk 8 March 2001 Abstract Locke and Witte
Arc Reversal in Nonhamiltonian Circulant Oriented Graphs Jozef Jirasek Department of Computer Science P J Safarik University Kosice, Slovakia jirasek@kosiceupjssk 8 March 2001 Abstract Locke and Witte
Group connectivity of certain graphs
 Group connectivity of certain graphs Jingjing Chen, Elaine Eschen, Hong-Jian Lai May 16, 2005 Abstract Let G be an undirected graph, A be an (additive) Abelian group and A = A {0}. A graph G is A-connected
Group connectivity of certain graphs Jingjing Chen, Elaine Eschen, Hong-Jian Lai May 16, 2005 Abstract Let G be an undirected graph, A be an (additive) Abelian group and A = A {0}. A graph G is A-connected
CONDITIONS FOR THE EXISTENCE OF HAMILTONIAN CIRCUITS IN GRAPHS BASED ON VERTEX DEGREES
 CONDITIONS FOR THE EXISTENCE OF HAMILTONIAN CIRCUITS IN GRAPHS BASED ON VERTEX DEGREES AHMED AINOUCHE AND NICOS CHRISTOFIDES 1. Introduction The terminology used in this paper is that of [7]. The term
CONDITIONS FOR THE EXISTENCE OF HAMILTONIAN CIRCUITS IN GRAPHS BASED ON VERTEX DEGREES AHMED AINOUCHE AND NICOS CHRISTOFIDES 1. Introduction The terminology used in this paper is that of [7]. The term
Tough graphs and hamiltonian circuits
 Discrete Mathematics 306 (2006) 910 917 www.elsevier.com/locate/disc Tough graphs and hamiltonian circuits V. Chvátal Centre de Recherches Mathématiques, Université de Montréal, Montréal, Canada Abstract
Discrete Mathematics 306 (2006) 910 917 www.elsevier.com/locate/disc Tough graphs and hamiltonian circuits V. Chvátal Centre de Recherches Mathématiques, Université de Montréal, Montréal, Canada Abstract
Compatible Circuit Decompositions of 4-Regular Graphs
 Compatible Circuit Decompositions of 4-Regular Graphs Herbert Fleischner, François Genest and Bill Jackson Abstract A transition system T of an Eulerian graph G is a family of partitions of the edges incident
Compatible Circuit Decompositions of 4-Regular Graphs Herbert Fleischner, François Genest and Bill Jackson Abstract A transition system T of an Eulerian graph G is a family of partitions of the edges incident
Eulerian Subgraphs and Hamilton-Connected Line Graphs
 Eulerian Subgraphs and Hamilton-Connected Line Graphs Hong-Jian Lai Department of Mathematics West Virginia University Morgantown, WV 2606, USA Dengxin Li Department of Mathematics Chongqing Technology
Eulerian Subgraphs and Hamilton-Connected Line Graphs Hong-Jian Lai Department of Mathematics West Virginia University Morgantown, WV 2606, USA Dengxin Li Department of Mathematics Chongqing Technology
Generalized Cayley Digraphs
 Pure Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 1, 2012, no. 1, 1-12 Generalized Cayley Digraphs Anil Kumar V. Department of Mathematics, University of Calicut Malappuram, Kerala, India 673 635 anilashwin2003@yahoo.com
Pure Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 1, 2012, no. 1, 1-12 Generalized Cayley Digraphs Anil Kumar V. Department of Mathematics, University of Calicut Malappuram, Kerala, India 673 635 anilashwin2003@yahoo.com
4 CONNECTED PROJECTIVE-PLANAR GRAPHS ARE HAMILTONIAN. Robin Thomas* Xingxing Yu**
 4 CONNECTED PROJECTIVE-PLANAR GRAPHS ARE HAMILTONIAN Robin Thomas* Xingxing Yu** School of Mathematics Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, Georgia 30332, USA May 1991, revised 23 October 1993. Published
4 CONNECTED PROJECTIVE-PLANAR GRAPHS ARE HAMILTONIAN Robin Thomas* Xingxing Yu** School of Mathematics Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, Georgia 30332, USA May 1991, revised 23 October 1993. Published
Nowhere-zero flows in signed series-parallel graphs arxiv: v1 [math.co] 6 Nov 2014
![Nowhere-zero flows in signed series-parallel graphs arxiv: v1 [math.co] 6 Nov 2014 Nowhere-zero flows in signed series-parallel graphs arxiv: v1 [math.co] 6 Nov 2014](/thumbs/94/119170375.jpg) Nowhere-zero flows in signed series-parallel graphs arxiv:1411.1788v1 [math.co] 6 Nov 2014 Tomáš Kaiser 1,2 Edita Rollová 1,3 Abstract Bouchet conjectured in 1983 that each signed graph that admits a nowhere-zero
Nowhere-zero flows in signed series-parallel graphs arxiv:1411.1788v1 [math.co] 6 Nov 2014 Tomáš Kaiser 1,2 Edita Rollová 1,3 Abstract Bouchet conjectured in 1983 that each signed graph that admits a nowhere-zero
Vectors 1C. 6 k) = =0 = =17
 Vectors C For each problem, calculate the vector product in the bracet first and then perform the scalar product on the answer. a b c= 3 0 4 =4i j 3 a.(b c=(5i+j.(4i j 3 =0 +3= b c a = 3 0 4 5 = 8i+3j+6
Vectors C For each problem, calculate the vector product in the bracet first and then perform the scalar product on the answer. a b c= 3 0 4 =4i j 3 a.(b c=(5i+j.(4i j 3 =0 +3= b c a = 3 0 4 5 = 8i+3j+6
Chordal Coxeter Groups
 arxiv:math/0607301v1 [math.gr] 12 Jul 2006 Chordal Coxeter Groups John Ratcliffe and Steven Tschantz Mathematics Department, Vanderbilt University, Nashville TN 37240, USA Abstract: A solution of the isomorphism
arxiv:math/0607301v1 [math.gr] 12 Jul 2006 Chordal Coxeter Groups John Ratcliffe and Steven Tschantz Mathematics Department, Vanderbilt University, Nashville TN 37240, USA Abstract: A solution of the isomorphism
4 = [A, : at(a0)l Finally an amalgam A is finite if A (i = 0, ±1) are finite groups.
 PROCEEDINGS of the AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 80, Number 1, September 1980 A CLASS OF FINITE GROUP-AMALGAMS DRAGOMIR Z. DJOKOVIC1 Abstract. Let A_\ and A, be finite groups such that A_ n Ax =
PROCEEDINGS of the AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 80, Number 1, September 1980 A CLASS OF FINITE GROUP-AMALGAMS DRAGOMIR Z. DJOKOVIC1 Abstract. Let A_\ and A, be finite groups such that A_ n Ax =
The L 3 (4) near octagon
 The L 3 (4) near octagon A. Bishnoi and B. De Bruyn October 8, 206 Abstract In recent work we constructed two new near octagons, one related to the finite simple group G 2 (4) and another one as a sub-near-octagon
The L 3 (4) near octagon A. Bishnoi and B. De Bruyn October 8, 206 Abstract In recent work we constructed two new near octagons, one related to the finite simple group G 2 (4) and another one as a sub-near-octagon
 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Math 6023 Topics: Design and Graph Theory ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Math 6023 Topics: Design and Graph Theory ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
A Variation of the nil-temperley-lieb algebras of type A
 A Variation of the nil-temperley-lieb algebras of type A Niket Gowravaram Abstract We investigate a variation on the nil-temperley-lieb algebras of type A. This variation is formed by removing one of the
A Variation of the nil-temperley-lieb algebras of type A Niket Gowravaram Abstract We investigate a variation on the nil-temperley-lieb algebras of type A. This variation is formed by removing one of the
MORE EXERCISES FOR SECTIONS II.1 AND II.2. There are drawings on the next two pages to accompany the starred ( ) exercises.
 Math 133 Winter 2013 MORE EXERCISES FOR SECTIONS II.1 AND II.2 There are drawings on the next two pages to accompany the starred ( ) exercises. B1. Let L be a line in R 3, and let x be a point which does
Math 133 Winter 2013 MORE EXERCISES FOR SECTIONS II.1 AND II.2 There are drawings on the next two pages to accompany the starred ( ) exercises. B1. Let L be a line in R 3, and let x be a point which does
T i t l e o f t h e w o r k : L a M a r e a Y o k o h a m a. A r t i s t : M a r i a n o P e n s o t t i ( P l a y w r i g h t, D i r e c t o r )
 v e r. E N G O u t l i n e T i t l e o f t h e w o r k : L a M a r e a Y o k o h a m a A r t i s t : M a r i a n o P e n s o t t i ( P l a y w r i g h t, D i r e c t o r ) C o n t e n t s : T h i s w o
v e r. E N G O u t l i n e T i t l e o f t h e w o r k : L a M a r e a Y o k o h a m a A r t i s t : M a r i a n o P e n s o t t i ( P l a y w r i g h t, D i r e c t o r ) C o n t e n t s : T h i s w o
HOMEWORK #2 - MATH 3260
 HOMEWORK # - MATH 36 ASSIGNED: JANUARAY 3, 3 DUE: FEBRUARY 1, AT :3PM 1) a) Give by listing the sequence of vertices 4 Hamiltonian cycles in K 9 no two of which have an edge in common. Solution: Here is
HOMEWORK # - MATH 36 ASSIGNED: JANUARAY 3, 3 DUE: FEBRUARY 1, AT :3PM 1) a) Give by listing the sequence of vertices 4 Hamiltonian cycles in K 9 no two of which have an edge in common. Solution: Here is
Aunu Integer Sequence as Non-Associative Structure and Their Graph Theoretic Properties
 Advances in Pure Mathematics, 2016, 6, 409-419 Published Online May 2016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/apm http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/apm.2016.66028 Aunu Integer Sequence as Non-Associative Structure
Advances in Pure Mathematics, 2016, 6, 409-419 Published Online May 2016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/apm http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/apm.2016.66028 Aunu Integer Sequence as Non-Associative Structure
(This is a sample cover image for this issue. The actual cover is not yet available at this time.)
 (This is a sample cover image for this issue. The actual cover is not yet available at this time.) This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author
(This is a sample cover image for this issue. The actual cover is not yet available at this time.) This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author
Bulletin of the. Iranian Mathematical Society
 ISSN: 1017-060X (Print) ISSN: 1735-8515 (Online) Bulletin of the Iranian Mathematical Society Vol. 43 (2017), No. 3, pp. 951 974. Title: Normal edge-transitive Cayley graphs on the nonabelian groups of
ISSN: 1017-060X (Print) ISSN: 1735-8515 (Online) Bulletin of the Iranian Mathematical Society Vol. 43 (2017), No. 3, pp. 951 974. Title: Normal edge-transitive Cayley graphs on the nonabelian groups of
Exercises for Unit V (Introduction to non Euclidean geometry)
 Exercises for Unit V (Introduction to non Euclidean geometry) V.1 : Facts from spherical geometry Ryan : pp. 84 123 [ Note : Hints for the first two exercises are given in math133f07update08.pdf. ] 1.
Exercises for Unit V (Introduction to non Euclidean geometry) V.1 : Facts from spherical geometry Ryan : pp. 84 123 [ Note : Hints for the first two exercises are given in math133f07update08.pdf. ] 1.
Compatible Circuit Decompositions of Eulerian Graphs
 Compatible Circuit Decompositions of Eulerian Graphs Herbert Fleischner, François Genest and Bill Jackson Septemeber 5, 2006 1 Introduction Let G = (V, E) be an Eulerian graph. Given a bipartition (X,
Compatible Circuit Decompositions of Eulerian Graphs Herbert Fleischner, François Genest and Bill Jackson Septemeber 5, 2006 1 Introduction Let G = (V, E) be an Eulerian graph. Given a bipartition (X,
CHAPTER 6 : LITERATURE REVIEW
 CHAPTER 6 : LITERATURE REVIEW Chapter : LITERATURE REVIEW 77 M E A S U R I N G T H E E F F I C I E N C Y O F D E C I S I O N M A K I N G U N I T S A B S T R A C T A n o n l i n e a r ( n o n c o n v e
CHAPTER 6 : LITERATURE REVIEW Chapter : LITERATURE REVIEW 77 M E A S U R I N G T H E E F F I C I E N C Y O F D E C I S I O N M A K I N G U N I T S A B S T R A C T A n o n l i n e a r ( n o n c o n v e
P E R E N C O - C H R I S T M A S P A R T Y
 L E T T I C E L E T T I C E I S A F A M I L Y R U N C O M P A N Y S P A N N I N G T W O G E N E R A T I O N S A N D T H R E E D E C A D E S. B A S E D I N L O N D O N, W E H A V E T H E P E R F E C T R
L E T T I C E L E T T I C E I S A F A M I L Y R U N C O M P A N Y S P A N N I N G T W O G E N E R A T I O N S A N D T H R E E D E C A D E S. B A S E D I N L O N D O N, W E H A V E T H E P E R F E C T R
CLASSIFICATION OF CUBIC EDGE-TRANSITIVE GRAPHS OF ORDER 14p 2
 Hacettepe Journal of Mathematics and Statistics Volume 41(2) (2012), 277 282 CLASSIFICATION OF CUBIC EDGE-TRANSITIVE GRAPHS OF ORDER 14p 2 Mehdi Alaeiyan and Mohsen Lashani Received 11:12:2010 : Accepted
Hacettepe Journal of Mathematics and Statistics Volume 41(2) (2012), 277 282 CLASSIFICATION OF CUBIC EDGE-TRANSITIVE GRAPHS OF ORDER 14p 2 Mehdi Alaeiyan and Mohsen Lashani Received 11:12:2010 : Accepted
Odd Components of Co-Trees and Graph Embeddings 1
 Odd Components of Co-Trees and Graph Embeddings 1 Han Ren, Dengju Ma and Junjie Lu Department of Mathematics, East China Normal University, Shanghai 0006, P.C.China Abstract: In this paper we investigate
Odd Components of Co-Trees and Graph Embeddings 1 Han Ren, Dengju Ma and Junjie Lu Department of Mathematics, East China Normal University, Shanghai 0006, P.C.China Abstract: In this paper we investigate
Independent Dominating Sets and a Second Hamiltonian Cycle in Regular Graphs
 Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series B 72, 104109 (1998) Article No. TB971794 Independent Dominating Sets and a Second Hamiltonian Cycle in Regular Graphs Carsten Thomassen Department of Mathematics,
Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series B 72, 104109 (1998) Article No. TB971794 Independent Dominating Sets and a Second Hamiltonian Cycle in Regular Graphs Carsten Thomassen Department of Mathematics,
FINITE IRREFLEXIVE HOMOMORPHISM-HOMOGENEOUS BINARY RELATIONAL SYSTEMS 1
 Novi Sad J. Math. Vol. 40, No. 3, 2010, 83 87 Proc. 3rd Novi Sad Algebraic Conf. (eds. I. Dolinka, P. Marković) FINITE IRREFLEXIVE HOMOMORPHISM-HOMOGENEOUS BINARY RELATIONAL SYSTEMS 1 Dragan Mašulović
Novi Sad J. Math. Vol. 40, No. 3, 2010, 83 87 Proc. 3rd Novi Sad Algebraic Conf. (eds. I. Dolinka, P. Marković) FINITE IRREFLEXIVE HOMOMORPHISM-HOMOGENEOUS BINARY RELATIONAL SYSTEMS 1 Dragan Mašulović
LINEAR SPACES. Define a linear space to be a near linear space in which any two points are on a line.
 LINEAR SPACES Define a linear space to be a near linear space in which any two points are on a line. A linear space is an incidence structure I = (P, L) such that Axiom LS1: any line is incident with at
LINEAR SPACES Define a linear space to be a near linear space in which any two points are on a line. A linear space is an incidence structure I = (P, L) such that Axiom LS1: any line is incident with at
arxiv: v1 [cs.dm] 24 Jan 2008
![arxiv: v1 [cs.dm] 24 Jan 2008 arxiv: v1 [cs.dm] 24 Jan 2008](/thumbs/73/69543041.jpg) 5-cycles and the Petersen graph arxiv:0801.3714v1 [cs.dm] 24 Jan 2008 M. DeVos, V. V. Mkrtchyan, S. S. Petrosyan, Department of Mathematics, Simon Fraser University, Canada Department of Informatics and
5-cycles and the Petersen graph arxiv:0801.3714v1 [cs.dm] 24 Jan 2008 M. DeVos, V. V. Mkrtchyan, S. S. Petrosyan, Department of Mathematics, Simon Fraser University, Canada Department of Informatics and
x y x y 15 y is directly proportional to x. a Draw the graph of y against x.
 3 8.1 Direct proportion 1 x 2 3 5 10 12 y 6 9 15 30 36 B a Draw the graph of y against x. y 40 30 20 10 0 0 5 10 15 20 x b Write down a rule for y in terms of x.... c Explain why y is directly proportional
3 8.1 Direct proportion 1 x 2 3 5 10 12 y 6 9 15 30 36 B a Draw the graph of y against x. y 40 30 20 10 0 0 5 10 15 20 x b Write down a rule for y in terms of x.... c Explain why y is directly proportional
THE STRUCTURE AND EXISTENCE OF 2-FACTORS IN ITERATED LINE GRAPHS
 Discussiones Mathematicae Graph Theory 27 (2007) 507 526 THE STRUCTURE AND EXISTENCE OF 2-FACTORS IN ITERATED LINE GRAPHS Michael Ferrara Department of Theoretical and Applied Mathematics The University
Discussiones Mathematicae Graph Theory 27 (2007) 507 526 THE STRUCTURE AND EXISTENCE OF 2-FACTORS IN ITERATED LINE GRAPHS Michael Ferrara Department of Theoretical and Applied Mathematics The University
Standard Diraphs the (unique) digraph with no vertices or edges. (modulo n) for every 1 i n A digraph whose underlying graph is a complete graph.
 5 Directed Graphs What is a directed graph? Directed Graph: A directed graph, or digraph, D, consists of a set of vertices V (D), a set of edges E(D), and a function which assigns each edge e an ordered
5 Directed Graphs What is a directed graph? Directed Graph: A directed graph, or digraph, D, consists of a set of vertices V (D), a set of edges E(D), and a function which assigns each edge e an ordered
Perfect matchings in highly cyclically connected regular graphs
 Perfect matchings in highly cyclically connected regular graphs arxiv:1709.08891v1 [math.co] 6 Sep 017 Robert Lukot ka Comenius University, Bratislava lukotka@dcs.fmph.uniba.sk Edita Rollová University
Perfect matchings in highly cyclically connected regular graphs arxiv:1709.08891v1 [math.co] 6 Sep 017 Robert Lukot ka Comenius University, Bratislava lukotka@dcs.fmph.uniba.sk Edita Rollová University
arxiv: v1 [math.co] 21 Jan 2016
![arxiv: v1 [math.co] 21 Jan 2016 arxiv: v1 [math.co] 21 Jan 2016](/thumbs/95/124148803.jpg) Cores, joins and the Fano-flow conjectures Ligang Jin, Giuseppe Mazzuoccolo, Eckhard Steffen August 13, 2018 arxiv:1601.05762v1 [math.co] 21 Jan 2016 Abstract The Fan-Raspaud Conjecture states that every
Cores, joins and the Fano-flow conjectures Ligang Jin, Giuseppe Mazzuoccolo, Eckhard Steffen August 13, 2018 arxiv:1601.05762v1 [math.co] 21 Jan 2016 Abstract The Fan-Raspaud Conjecture states that every
CORES, JOINS AND THE FANO-FLOW CONJECTURES
 Discussiones Mathematicae Graph Theory 38 (2018) 165 175 doi:10.7151/dmgt.1999 CORES, JOINS AND THE FANO-FLOW CONJECTURES Ligang Jin, Eckhard Steffen Paderborn University Institute of Mathematics and Paderborn
Discussiones Mathematicae Graph Theory 38 (2018) 165 175 doi:10.7151/dmgt.1999 CORES, JOINS AND THE FANO-FLOW CONJECTURES Ligang Jin, Eckhard Steffen Paderborn University Institute of Mathematics and Paderborn
Long Cycles in 3-Connected Graphs
 Long Cycles in 3-Connected Graphs Guantao Chen Department of Mathematics & Statistics Georgia State University Atlanta, GA 30303 Xingxing Yu School of Mathematics Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta,
Long Cycles in 3-Connected Graphs Guantao Chen Department of Mathematics & Statistics Georgia State University Atlanta, GA 30303 Xingxing Yu School of Mathematics Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta,
Multiple Petersen subdivisions in permutation graphs
 Multiple Petersen subdivisions in permutation graphs arxiv:1204.1989v1 [math.co] 9 Apr 2012 Tomáš Kaiser 1 Jean-Sébastien Sereni 2 Zelealem Yilma 3 Abstract A permutation graph is a cubic graph admitting
Multiple Petersen subdivisions in permutation graphs arxiv:1204.1989v1 [math.co] 9 Apr 2012 Tomáš Kaiser 1 Jean-Sébastien Sereni 2 Zelealem Yilma 3 Abstract A permutation graph is a cubic graph admitting
Hamilton cycles and closed trails in iterated line graphs
 Hamilton cycles and closed trails in iterated line graphs Paul A. Catlin, Department of Mathematics Wayne State University, Detroit MI 48202 USA Iqbalunnisa, Ramanujan Institute University of Madras, Madras
Hamilton cycles and closed trails in iterated line graphs Paul A. Catlin, Department of Mathematics Wayne State University, Detroit MI 48202 USA Iqbalunnisa, Ramanujan Institute University of Madras, Madras
TOWARDS A SPLITTER THEOREM FOR INTERNALLY 4-CONNECTED BINARY MATROIDS IV
 TOWARDS A SPLITTER THEOREM FOR INTERNALLY 4-CONNECTED BINARY MATROIDS IV CAROLYN CHUN, DILLON MAYHEW, AND JAMES OXLEY Abstract. In our quest to find a splitter theorem for internally 4-connected binary
TOWARDS A SPLITTER THEOREM FOR INTERNALLY 4-CONNECTED BINARY MATROIDS IV CAROLYN CHUN, DILLON MAYHEW, AND JAMES OXLEY Abstract. In our quest to find a splitter theorem for internally 4-connected binary
Cycles in 4-Connected Planar Graphs
 Cycles in 4-Connected Planar Graphs Guantao Chen Department of Mathematics & Statistics Georgia State University Atlanta, GA 30303 matgcc@panther.gsu.edu Genghua Fan Institute of Systems Science Chinese
Cycles in 4-Connected Planar Graphs Guantao Chen Department of Mathematics & Statistics Georgia State University Atlanta, GA 30303 matgcc@panther.gsu.edu Genghua Fan Institute of Systems Science Chinese
Pentavalent symmetric graphs of order twice a prime power
 Pentavalent symmetric graphs of order twice a prime power Yan-Quan Feng Mathematics, Beijing Jiaotong University Beijing 100044, P.R. China yqfeng@bjtu.edu.cn A joint work with Yan-Tao Li, Da-Wei Yang,
Pentavalent symmetric graphs of order twice a prime power Yan-Quan Feng Mathematics, Beijing Jiaotong University Beijing 100044, P.R. China yqfeng@bjtu.edu.cn A joint work with Yan-Tao Li, Da-Wei Yang,
Isomorphisms and Normality of Cayley Digraphs of A5
 Isomorphisms and Normality of Cayley Digraphs of A5 Dachang Guo* Department of Mathematics and Physics Guangdong University of Technology Guangzhou 510643, People's Republic of China Abstract It is proved
Isomorphisms and Normality of Cayley Digraphs of A5 Dachang Guo* Department of Mathematics and Physics Guangdong University of Technology Guangzhou 510643, People's Republic of China Abstract It is proved
Every line graph of a 4-edge-connected graph is Z 3 -connected
 European Journal of Combinatorics 0 (2009) 595 601 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect European Journal of Combinatorics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ejc Every line graph of a 4-edge-connected
European Journal of Combinatorics 0 (2009) 595 601 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect European Journal of Combinatorics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ejc Every line graph of a 4-edge-connected
Introduction to Graph Theory
 Introduction to Graph Theory George Voutsadakis 1 1 Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 351 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) Introduction to Graph Theory August 2018 1 /
Introduction to Graph Theory George Voutsadakis 1 1 Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 351 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) Introduction to Graph Theory August 2018 1 /
and critical partial Latin squares.
 Nowhere-zero 4-flows, simultaneous edge-colorings, and critical partial Latin squares Rong Luo Department of Mathematical Sciences Middle Tennessee State University Murfreesboro, TN 37132, U.S.A luor@math.wvu.edu
Nowhere-zero 4-flows, simultaneous edge-colorings, and critical partial Latin squares Rong Luo Department of Mathematical Sciences Middle Tennessee State University Murfreesboro, TN 37132, U.S.A luor@math.wvu.edu
Generalized knight s tours on rectangular chessboards
 Discrete Applied Mathematics 150 (2005) 80 98 www.elsevier.com/locate/dam Generalized knight s tours on rectangular chessboards G.L. Chia, Siew-Hui Ong Institute of Mathematical Sciences, University of
Discrete Applied Mathematics 150 (2005) 80 98 www.elsevier.com/locate/dam Generalized knight s tours on rectangular chessboards G.L. Chia, Siew-Hui Ong Institute of Mathematical Sciences, University of
COMPOSITIO MATHEMATICA
 COMPOSITIO MATHEMATICA OSWALD WYLER Order in projective and in descriptive geometry Compositio Mathematica, tome 11 (1953), p. 60-70 Foundation Compositio
COMPOSITIO MATHEMATICA OSWALD WYLER Order in projective and in descriptive geometry Compositio Mathematica, tome 11 (1953), p. 60-70 Foundation Compositio
HAMILTONICITY AND FORBIDDEN SUBGRAPHS IN 4-CONNECTED GRAPHS
 HAMILTONICITY AND FORBIDDEN SUBGRAPHS IN 4-CONNECTED GRAPHS FLORIAN PFENDER Abstract. Let T be the line graph of the unique tree F on 8 vertices with degree sequence (3, 3, 3,,,,, ), i.e. T is a chain
HAMILTONICITY AND FORBIDDEN SUBGRAPHS IN 4-CONNECTED GRAPHS FLORIAN PFENDER Abstract. Let T be the line graph of the unique tree F on 8 vertices with degree sequence (3, 3, 3,,,,, ), i.e. T is a chain
On the connectivity of extremal Ramsey graphs
 On the connectivity of extremal Ramsey graphs Andrew Beveridge and Oleg Pikhurko Department of Mathematical Sciences Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213 Abstract An (r, b)-graph is a graph
On the connectivity of extremal Ramsey graphs Andrew Beveridge and Oleg Pikhurko Department of Mathematical Sciences Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213 Abstract An (r, b)-graph is a graph
Properties of θ-super positive graphs
 Properties of θ-super positive graphs Cheng Yeaw Ku Department of Mathematics, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117543 matkcy@nus.edu.sg Kok Bin Wong Institute of Mathematical Sciences, University
Properties of θ-super positive graphs Cheng Yeaw Ku Department of Mathematics, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117543 matkcy@nus.edu.sg Kok Bin Wong Institute of Mathematical Sciences, University
TOWARDS A SPLITTER THEOREM FOR INTERNALLY 4-CONNECTED BINARY MATROIDS II
 TOWARDS A SPLITTER THEOREM FOR INTERNALLY 4-CONNECTED BINARY MATROIDS II CAROLYN CHUN, DILLON MAYHEW, AND JAMES OXLEY Abstract. Let M and N be internally 4-connected binary matroids such that M has a proper
TOWARDS A SPLITTER THEOREM FOR INTERNALLY 4-CONNECTED BINARY MATROIDS II CAROLYN CHUN, DILLON MAYHEW, AND JAMES OXLEY Abstract. Let M and N be internally 4-connected binary matroids such that M has a proper
Supereulerian planar graphs
 Supereulerian planar graphs Hong-Jian Lai and Mingquan Zhan Department of Mathematics West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV 26506, USA Deying Li and Jingzhong Mao Department of Mathematics Central China
Supereulerian planar graphs Hong-Jian Lai and Mingquan Zhan Department of Mathematics West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV 26506, USA Deying Li and Jingzhong Mao Department of Mathematics Central China
Factors in Graphs With Multiple Degree Constraints
 Factors in Graphs With Multiple Degree Constraints Richard C. Brewster, Morten Hegner Nielsen, and Sean McGuinness Thompson Rivers University Kamloops, BC V2C0C8 Canada October 4, 2011 Abstract For a graph
Factors in Graphs With Multiple Degree Constraints Richard C. Brewster, Morten Hegner Nielsen, and Sean McGuinness Thompson Rivers University Kamloops, BC V2C0C8 Canada October 4, 2011 Abstract For a graph
Compact hyperbolic Coxeter n-polytopes with n + 3 facets
 Compact hyperbolic Coxeter n-polytopes with n + 3 facets Pavel Tumarkin Independent University of Moscow B. Vlassievskii 11, 11900 Moscow, Russia pasha@mccme.ru Submitted: Apr 3, 007; Accepted: Sep 30,
Compact hyperbolic Coxeter n-polytopes with n + 3 facets Pavel Tumarkin Independent University of Moscow B. Vlassievskii 11, 11900 Moscow, Russia pasha@mccme.ru Submitted: Apr 3, 007; Accepted: Sep 30,
Homomorphism Bounded Classes of Graphs
 Homomorphism Bounded Classes of Graphs Timothy Marshall a Reza Nasraser b Jaroslav Nešetřil a Email: nesetril@kam.ms.mff.cuni.cz a: Department of Applied Mathematics and Institute for Theoretical Computer
Homomorphism Bounded Classes of Graphs Timothy Marshall a Reza Nasraser b Jaroslav Nešetřil a Email: nesetril@kam.ms.mff.cuni.cz a: Department of Applied Mathematics and Institute for Theoretical Computer
Decompositions of graphs into cycles with chords
 Decompositions of graphs into cycles with chords Paul Balister Hao Li Richard Schelp May 22, 2017 In memory of Dick Schelp, who passed away shortly after the submission of this paper Abstract We show that
Decompositions of graphs into cycles with chords Paul Balister Hao Li Richard Schelp May 22, 2017 In memory of Dick Schelp, who passed away shortly after the submission of this paper Abstract We show that
A Family of Perfect Factorisations of Complete Bipartite Graphs
 Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series A 98, 328 342 (2002) doi:10.1006/jcta.2001.3240, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on A Family of Perfect Factorisations of Complete Bipartite Graphs
Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series A 98, 328 342 (2002) doi:10.1006/jcta.2001.3240, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on A Family of Perfect Factorisations of Complete Bipartite Graphs
M-saturated M={ } M-unsaturated. Perfect Matching. Matchings
 Matchings A matching M of a graph G = (V, E) is a set of edges, no two of which are incident to a common vertex. M-saturated M={ } M-unsaturated Perfect Matching 1 M-alternating path M not M M not M M
Matchings A matching M of a graph G = (V, E) is a set of edges, no two of which are incident to a common vertex. M-saturated M={ } M-unsaturated Perfect Matching 1 M-alternating path M not M M not M M
A shorter proof of Thomassen s theorem on Tutte paths in plane graphs
 A shorter proof of Thomassen s theorem on Tutte paths in plane graphs Kenta Ozeki National Institute of Informatics, 2-1-2 Hitotsubashi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 101-8430, Japan and JST, ERATO, Kawarabayashi
A shorter proof of Thomassen s theorem on Tutte paths in plane graphs Kenta Ozeki National Institute of Informatics, 2-1-2 Hitotsubashi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 101-8430, Japan and JST, ERATO, Kawarabayashi
Connectivity and tree structure in finite graphs arxiv: v5 [math.co] 1 Sep 2014
![Connectivity and tree structure in finite graphs arxiv: v5 [math.co] 1 Sep 2014 Connectivity and tree structure in finite graphs arxiv: v5 [math.co] 1 Sep 2014](/thumbs/74/71106298.jpg) Connectivity and tree structure in finite graphs arxiv:1105.1611v5 [math.co] 1 Sep 2014 J. Carmesin R. Diestel F. Hundertmark M. Stein 20 March, 2013 Abstract Considering systems of separations in a graph
Connectivity and tree structure in finite graphs arxiv:1105.1611v5 [math.co] 1 Sep 2014 J. Carmesin R. Diestel F. Hundertmark M. Stein 20 March, 2013 Abstract Considering systems of separations in a graph
Ring Sums, Bridges and Fundamental Sets
 1 Ring Sums Definition 1 Given two graphs G 1 = (V 1, E 1 ) and G 2 = (V 2, E 2 ) we define the ring sum G 1 G 2 = (V 1 V 2, (E 1 E 2 ) (E 1 E 2 )) with isolated points dropped. So an edge is in G 1 G
1 Ring Sums Definition 1 Given two graphs G 1 = (V 1, E 1 ) and G 2 = (V 2, E 2 ) we define the ring sum G 1 G 2 = (V 1 V 2, (E 1 E 2 ) (E 1 E 2 )) with isolated points dropped. So an edge is in G 1 G
Sergey Norin Department of Mathematics and Statistics McGill University Montreal, Quebec H3A 2K6, Canada. and
 NON-PLANAR EXTENSIONS OF SUBDIVISIONS OF PLANAR GRAPHS Sergey Norin Department of Mathematics and Statistics McGill University Montreal, Quebec H3A 2K6, Canada and Robin Thomas 1 School of Mathematics
NON-PLANAR EXTENSIONS OF SUBDIVISIONS OF PLANAR GRAPHS Sergey Norin Department of Mathematics and Statistics McGill University Montreal, Quebec H3A 2K6, Canada and Robin Thomas 1 School of Mathematics
Lengths of Snakes in Boxes
 JOURNAL OF COMBINATORIAL THEORY 2, 258-265 (1967) Lengths of Snakes in Boxes LUDWIG DANZER AND VICTOR KLEE* University of Gdttingen, Gi~ttingen, Germany, and University of Washington, Seattle, Washington
JOURNAL OF COMBINATORIAL THEORY 2, 258-265 (1967) Lengths of Snakes in Boxes LUDWIG DANZER AND VICTOR KLEE* University of Gdttingen, Gi~ttingen, Germany, and University of Washington, Seattle, Washington
0-Sum and 1-Sum Flows in Regular Graphs
 0-Sum and 1-Sum Flows in Regular Graphs S. Akbari Department of Mathematical Sciences Sharif University of Technology Tehran, Iran School of Mathematics, Institute for Research in Fundamental Sciences
0-Sum and 1-Sum Flows in Regular Graphs S. Akbari Department of Mathematical Sciences Sharif University of Technology Tehran, Iran School of Mathematics, Institute for Research in Fundamental Sciences
Hamilton weight and Petersen minor
 Hamilton weight and Petersen minor Hong-Jian Lai and Cun-Quan Zhang Department of Mathematics West Virginia University Morgantown, WV 26506-6310, USA Email: hjlai@math.wvu.edu, cqzhang@math.wvu.edu Abstract
Hamilton weight and Petersen minor Hong-Jian Lai and Cun-Quan Zhang Department of Mathematics West Virginia University Morgantown, WV 26506-6310, USA Email: hjlai@math.wvu.edu, cqzhang@math.wvu.edu Abstract
A more detailed classification of symmetric cubic graphs
 A more detailed classification of symmetric cubic graphs Marston Conder 1 Roman Nedela 2 Department of Mathematics University of Auckland Private Bag 92019 Auckland New Zealand Email: m.conder@auckland.ac.nz
A more detailed classification of symmetric cubic graphs Marston Conder 1 Roman Nedela 2 Department of Mathematics University of Auckland Private Bag 92019 Auckland New Zealand Email: m.conder@auckland.ac.nz
Parity Versions of 2-Connectedness
 Parity Versions of 2-Connectedness C. Little Institute of Fundamental Sciences Massey University Palmerston North, New Zealand c.little@massey.ac.nz A. Vince Department of Mathematics University of Florida
Parity Versions of 2-Connectedness C. Little Institute of Fundamental Sciences Massey University Palmerston North, New Zealand c.little@massey.ac.nz A. Vince Department of Mathematics University of Florida
Notes for Science and Engineering Foundation Discrete Mathematics
 Notes for Science and Engineering Foundation Discrete Mathematics by Robin Whitty BSc PhD CMath FIMA 2009/2010 Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 The Laws of Arithmetic....................... 2 2 Polynomial
Notes for Science and Engineering Foundation Discrete Mathematics by Robin Whitty BSc PhD CMath FIMA 2009/2010 Contents 1 Introduction 1 1.1 The Laws of Arithmetic....................... 2 2 Polynomial
Antoni Marczyk A NOTE ON ARBITRARILY VERTEX DECOMPOSABLE GRAPHS
 Opuscula Mathematica Vol. 6 No. 1 006 Antoni Marczyk A NOTE ON ARBITRARILY VERTEX DECOMPOSABLE GRAPHS Abstract. A graph G of order n is said to be arbitrarily vertex decomposable if for each sequence (n
Opuscula Mathematica Vol. 6 No. 1 006 Antoni Marczyk A NOTE ON ARBITRARILY VERTEX DECOMPOSABLE GRAPHS Abstract. A graph G of order n is said to be arbitrarily vertex decomposable if for each sequence (n
Longest paths in circular arc graphs. Paul N. Balister Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Memphis
 Longest paths in circular arc graphs (Final version: February, 2003) Paul N Balister Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Memphis (balistep@mscimemphisedu) Ervin Győri Rényi Institute of
Longest paths in circular arc graphs (Final version: February, 2003) Paul N Balister Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Memphis (balistep@mscimemphisedu) Ervin Győri Rényi Institute of
CLASS-IX MATHEMATICS. For. Pre-Foundation Course CAREER POINT
 CLASS-IX MATHEMATICS For Pre-Foundation Course CAREER POINT CONTENTS S. No. CHAPTERS PAGE NO. 0. Number System... 0 3 0. Polynomials... 39 53 03. Co-ordinate Geometry... 54 04. Introduction to Euclid's
CLASS-IX MATHEMATICS For Pre-Foundation Course CAREER POINT CONTENTS S. No. CHAPTERS PAGE NO. 0. Number System... 0 3 0. Polynomials... 39 53 03. Co-ordinate Geometry... 54 04. Introduction to Euclid's
CSCE 750 Final Exam Answer Key Wednesday December 7, 2005
 CSCE 750 Final Exam Answer Key Wednesday December 7, 2005 Do all problems. Put your answers on blank paper or in a test booklet. There are 00 points total in the exam. You have 80 minutes. Please note
CSCE 750 Final Exam Answer Key Wednesday December 7, 2005 Do all problems. Put your answers on blank paper or in a test booklet. There are 00 points total in the exam. You have 80 minutes. Please note
The Interlace Polynomial of Graphs at 1
 The Interlace Polynomial of Graphs at 1 PN Balister B Bollobás J Cutler L Pebody July 3, 2002 Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Memphis, Memphis, TN 38152 USA Abstract In this paper we
The Interlace Polynomial of Graphs at 1 PN Balister B Bollobás J Cutler L Pebody July 3, 2002 Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Memphis, Memphis, TN 38152 USA Abstract In this paper we
Part III: Traveling salesman problems
 Transportation Logistics Part III: Traveling salesman problems c R.F. Hartl, S.N. Parragh 1/282 Motivation Motivation Why do we study the TSP? c R.F. Hartl, S.N. Parragh 2/282 Motivation Motivation Why
Transportation Logistics Part III: Traveling salesman problems c R.F. Hartl, S.N. Parragh 1/282 Motivation Motivation Why do we study the TSP? c R.F. Hartl, S.N. Parragh 2/282 Motivation Motivation Why
Representing graphs in Steiner triple systems - II
 AUSTRALASIAN JOURNAL OF COMBINATORICS Volume 67(2) (2017), Pages 243 258 Representing graphs in Steiner triple systems - II Dan Archdeacon Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Vermont
AUSTRALASIAN JOURNAL OF COMBINATORICS Volume 67(2) (2017), Pages 243 258 Representing graphs in Steiner triple systems - II Dan Archdeacon Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Vermont
SOLUTIONS TO ADDITIONAL EXERCISES FOR II.1 AND II.2
 SOLUTIONS TO ADDITIONAL EXERCISES FOR II.1 AND II.2 Here are the solutions to the additional exercises in betsepexercises.pdf. B1. Let y and z be distinct points of L; we claim that x, y and z are not
SOLUTIONS TO ADDITIONAL EXERCISES FOR II.1 AND II.2 Here are the solutions to the additional exercises in betsepexercises.pdf. B1. Let y and z be distinct points of L; we claim that x, y and z are not
MAXIMAL INDEPENDENT COLLECTIONS OF CLOSED SETS
 proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume 32, Number 2, April 1972 MAXIMAL INDEPENDENT COLLECTIONS OF CLOSED SETS HARVY LEE BAKER, JR. Abstract. A theorem is proved which implies that if
proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume 32, Number 2, April 1972 MAXIMAL INDEPENDENT COLLECTIONS OF CLOSED SETS HARVY LEE BAKER, JR. Abstract. A theorem is proved which implies that if
HAMILTON CYCLES IN CAYLEY GRAPHS
 Hamiltonicity of (2, s, 3)- University of Primorska July, 2011 Hamiltonicity of (2, s, 3)- Lovász, 1969 Does every connected vertex-transitive graph have a Hamilton path? Hamiltonicity of (2, s, 3)- Hamiltonicity
Hamiltonicity of (2, s, 3)- University of Primorska July, 2011 Hamiltonicity of (2, s, 3)- Lovász, 1969 Does every connected vertex-transitive graph have a Hamilton path? Hamiltonicity of (2, s, 3)- Hamiltonicity
Regular Hamiltonian embeddings of the complete bipartite graph K n,n in an orientable surface
 Regular Hamiltonian embeddings of the complete bipartite graph K n,n in an orientable surface M. J. Grannell, T. S. Griggs Department of Pure Mathematics The Open University Walton Hall Milton Keynes MK7
Regular Hamiltonian embeddings of the complete bipartite graph K n,n in an orientable surface M. J. Grannell, T. S. Griggs Department of Pure Mathematics The Open University Walton Hall Milton Keynes MK7
Section 5.8. (i) ( 3 + i)(14 2i) = ( 3)(14 2i) + i(14 2i) = {( 3)14 ( 3)(2i)} + i(14) i(2i) = ( i) + (14i + 2) = i.
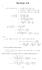 1. Section 5.8 (i) ( 3 + i)(14 i) ( 3)(14 i) + i(14 i) {( 3)14 ( 3)(i)} + i(14) i(i) ( 4 + 6i) + (14i + ) 40 + 0i. (ii) + 3i 1 4i ( + 3i)(1 + 4i) (1 4i)(1 + 4i) (( + 3i) + ( + 3i)(4i) 1 + 4 10 + 11i 10
1. Section 5.8 (i) ( 3 + i)(14 i) ( 3)(14 i) + i(14 i) {( 3)14 ( 3)(i)} + i(14) i(i) ( 4 + 6i) + (14i + ) 40 + 0i. (ii) + 3i 1 4i ( + 3i)(1 + 4i) (1 4i)(1 + 4i) (( + 3i) + ( + 3i)(4i) 1 + 4 10 + 11i 10
Eves Equihoop, The Card Game SET, and Abstract SET
 Eves Equihoop, The Card Game SET, and Abstract SET Arthur Holshouser 3600 Bullard St Charlotte, NC, USA Harold Reiter Department of Mathematics, University of North Carolina Charlotte, Charlotte, NC 83,
Eves Equihoop, The Card Game SET, and Abstract SET Arthur Holshouser 3600 Bullard St Charlotte, NC, USA Harold Reiter Department of Mathematics, University of North Carolina Charlotte, Charlotte, NC 83,
