1.72, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. Charles Harvey Lecture Packet #4: Continuity and Flow Nets
|
|
|
- Corey McDaniel
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1.7, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. Charles Harvey Lecture Packet #4: Continuity and Flow Nets Equation of Continuity Our equations of hydrogeology are a combination of o Conservation of mass o Some empirical law (Darcy s Law, Fick s Law) Develop a control volume, rectangular parallelepiped, REV (Representative Elementary Volume) z dz dy, y, z d y mass inflow rate mass outflow rate = change in mass storage q = specific discharge in -direction (volume flu per area) at a point,y,z L 3 /L -T Consider mass flow through plane y-z at (,y,z) q ρ dy dz L/T M/L 3 L L = M/T Rate of change of mass flu in the -direction per unit time per cross-section is [ρ q ] dydz, y, z dz d dy - d/ + d/ Prof. Charles Harvey Page 1 of 13
2 mass flow into the entry plane y-z is d [ρ q ] dydz [ρ q ] dydz And mass flow out of the eit plane y-z is d [ρ q ] dydz + [ρ q ] dydz In the -direction, the flow in minus the flow out is [ρ q ] ddydz Similarly, the flow in the y-direction through the plane ddz (figure on left), y, z, y, z dz dz d dy d dy [ρ q ] ddz [ρ q y ] dy ddz [ρ q ] ddz + [ρ q y ] dy ddz = [ρ q ] y y y ddydz y y y for the net y-mass flu. Similarly, we get for the net mass flu in the z-direction: [ρ q z ] ddydz z The total mass flu (flow out of the bo) is [ρ q ] [ρ q y ] [ρ q ] z ddydz y z Prof. Charles Harvey Page of 13
3 Let s consider time derivative = 0 (Steady State System) [ρ q ] [ρ q ] y [ρ q ] z M + + ddydz = = 0 y z t How does Darcy s Law fit into this? = q = h y q = q z zz y yy h z For anisotropy (with alignment of coordinate aes and tensor principal r directions), or q = h Assuming constant density for groundwater [ q + [q ] y ] [ q ] 0 = ρ z + y z substituting for q, h + 0 = ( )( )ρ + y y y z z z Steady-state flow equation for heterogeneous, anisotropic conditions: h h 0= + y + z y y z z For isotropic, homogeneous conditions ( is not directional) h h h 0 = + + y z This is the diffusion equation or heat-flow equation For Steady State ( cancels) This is called the Laplace equation. is the Laplacian operator. = + + giving = = h y z h h h 0 = + + y z Prof. Charles Harvey Page 3 of 13
4 Note that the full equation at this point can be written in summation notation as: 0 = ( i ij ) h i y z 1 3 = y yy yz z zy zz The first Equation (flow in the direction) is: + y + y z z or h h What is the head distribution in a SS homogeneous system? Consider solution to steady-state problem (1-Dimensional) 1D Confined Aquifer Head Distribution (=0) = H 0 and h(=l) = 0 H 0 1) 0 = 0 =? 0 =0 =L Steady h distribution not f() h is independent of. Prof. Charles Harvey Page 4 of 13
5 Flow Nets As we have seen, to work with the groundwater flow equation in any meaningful way, we have to find some kind of a solution to the equation. This solution is based on boundary conditions, and in the transient case, on initial conditions. Let us look at the two-dimensional, steady-state case. In other words, let the following equation apply: h 0 = + y y (Map View) A solution to this equation requires us to specify boundary condition. For our purposes with flow nets, let us consider No-flow boundaries ( = 0, where n is the direction perpendicular to the n boundary). Constant-head boundaries (h = constant) Water-table boundary (free surface, h is not a constant) A relatively straightforward graphical technique can be used to find the solution to the GW flow equation for many such situations. This technique involves the construction of a flow net. A flow net is the set of equipotential lines (constant head) and the associated flow lines (lines along which groundwater moves) for a particular set of boundary conditions. For a given GW flow equation and a given value of, the boundary conditions completely determine the solution, and therefore a flow net. In addition, let us first consider only homogeneous, isotropic conditions: h h 0 = + (Cross-Section) z Prof. Charles Harvey Page 5 of 13
6 C D h 1 E h F O 1 Dam 8 h G Sand and gravel 3 7 A Impermeable Layer B y h 1 C y D M G E h F A 60 B h 16 A h=h B H q=0 q 1 C h=0 D h=h 50 G q q 3 h q 4 q 5 E q=q F Prof. Charles Harvey Page 6 of 13
7 Let s look at flow in the vicinity of each of these boundaries. (Isotropic, homogeneous conditions). No-Flow Boundaries: = 0 or = 0 y or = 0 n Flow is parallel to the boundary. Equipotentials are perpendicular to the boundary Constant-Head Boundaries: h = constant Flow is perpendicular to the boundary. Equipotentials are parallel to the boundary. Water Table Boundaries: h=z Anywhere in an aquifer, total head is pressure head plus elevation head: h = ψ + z However, at the water table, ψ = 0. Therefore, h = z Neither flow nor equipotentials are necessarily perpendicular to the boundary. Prof. Charles Harvey Page 7 of 13
8 Rules for Flow Nets (Isotropic, Homogeneous System): In addition to the boundary conditions the following rules must apply in a flow net: 1) Flow is perpendicular to equipotentials everywhere. ) Flow lines never intersect. 3) The areas between flow lines and equipotentials are curvilinear squares. In other words, the central dimensions of the squares are the same (but the flow lines or equipotentials can curve). If you draw a circle inside the curvilinear square, it is tangential to all four sides at some point. h=h 1 Reservoir Dam h=h Why are these circles? It preserves dq along any stream tube. dq = dm; dh/ds = dh ds dq dm dq dq If dm = ds (i.e. ellipse, not circle), then a constant factor is used. Other points: It is not necessary that flow nets have finite boundaries on all sides; regions of flow that etend to infinity in one or more directions are possible (e.g., see the figure above). A flow net can have partial stream tubes along the edge. A flow net can have partial squares at the edges or ends of the flow system. Calculations from Flow Nets: It is possible to make many good, quantitative predictions from flow nets. In fact, at one time flow nest were the major tool used for solving the GW flow equation. Prof. Charles Harvey Page 8 of 13
9 Probably the most important calculation is discharge from the system. For a system with one recharge area and one discharge area, we can calculate the discharge with the following epression: Q = n f dh H = n d dh Gives: Q = n f /n d H Where Q is the volume discharge rate per unit thickness of section perpendicular to the flow net; n f is the number of stream tubes (or flow channels); n d is the number of head drops; is the uniform hydraulic conductivity; and H is the total head drop over the region of flow. Note that neither n f nor n d is necessarily an integer, but it is often helpful if you construct the flow net such that one of them is an integer. If you choose n f as an integer, it is unlikely that n d will be an integer. Note that to do this calculation, you do not need to know any lengths. Flow Nets in Anisotropic, Homogeneous Systems: Before construction of a flow net in an anisotropic system ( we have to transform the system. = y or = z etc.), For homogeneous, h h + z = 0 z z Introduce the transformed variable h z h + =0 z Z= z z Applying this variable gives: h + = 0 Z With this equation we can apply flownets eactly as we did before. We just have to remember how Z relates to the actual dimension z. In an anisotropic medium, perform the following steps in constructing a flow net: 1. Transform the system (the area where a flow net is desired) by the following ratio: z Z =Z' where z is the original vertical dimension of the system (on your page, in cm, inches, etc.) and Z is the transformed vertical dimension. Prof. Charles Harvey Page 9 of 13
10 is the hydraulic conductivity horizontally on your page, and z is the hydraulic conductivity vertically on your page. This transformation is not specific to the - dimension or the y-dimension.. On the transformed system, follow the eact same principles for flow nets as outlined for a homogeneous, isotropic system. 3. Perform the inverse transform on the system, i.e. Z = Z ' z 4. If any flow calculations are needed, do these calculations on the homogeneous (step ) section. Use the following for hydraulic conductivity: ' = Where is the homogeneous hydraulic conductivity of the transformed section. (NOTE: This transformed is not real! It is only used for calculations on the transformed section.) Eamples: z h = 100 h = 0 T I Prof. Charles Harvey Page 10 of 13
11 Flow Nets in Heterogeneous Systems: We will only deal with construction of flow nets in the simplest types of heterogeneous systems. We will restrict ourselves to layered heterogeneity. In a layered system, the same rules apply as in a homogeneous system, with the following important eceptions: 1. Curvilinear squares can only be drawn in ONE layer. In other words, in a twolayer system, you will only have curvilinear squares in one of the layers. Which layer to draw squares in is your choice: in general you should choose the thicker/larger layer.. At boundaries between layers, flow lines are refracted (in a similar way to the way light is refracted between two different media). The relationship between the angles in two layers is given by the tangent law : U 1 θ 1 n m θ U h 1 = h 1 m = m (1) No sudden head changes 1 1 = n n () Conservation of Mass Layer 1 Layer u : 1 U sinθ 1 1 = 1 U m = m u y : U 1 1 cosθ 1 = 1 U cosθ = n n U1 sin θ 1 U sinθ By (1): = 1 By (): U1 cosθ 1 = U cosθ 1 tanθ = 1 tanθ Prof. Charles Harvey Page 11 of 13
12 You can rearrange the tangent law in any way to determine one unknown quantity. For eample, to determine the angle θ : θ =tan 1 tan θ 1 1 One important consequence for a medium with large contrasts in : high- layers will often have almost horizontal flow (in general), while low- layers will often have almost vertical flow (in general). Eample: In a three-layer system, 1 = m/s and = m/s. 3 = 1. Flow in the system is 14 o below horizontal. What do flow in layers and 3 look like? 76 o θ = tan o tan 76 = o What is the angle in layer 3? If you do the calculation, you will find it is 76 o again. Prof. Charles Harvey Page 1 of 13
13 When drawing flow nets with different layers, a very helpful question to ask is What layer allows water to go from the entrance point to the eit point the easiest? Or, in other words, What is the easiest (frictionally speaking) way for water to go from here to there? = 10 Prof. Charles Harvey Page 13 of 13
GG655/CEE623 Groundwater Modeling. Aly I. El-Kadi
 GG655/CEE63 Groundwater Modeling Model Theory Water Flow Aly I. El-Kadi Hydrogeology 1 Saline water in oceans = 97.% Ice caps and glaciers =.14% Groundwater = 0.61% Surface water = 0.009% Soil moisture
GG655/CEE63 Groundwater Modeling Model Theory Water Flow Aly I. El-Kadi Hydrogeology 1 Saline water in oceans = 97.% Ice caps and glaciers =.14% Groundwater = 0.61% Surface water = 0.009% Soil moisture
Hydraulic properties of porous media
 PART 5 Hydraulic properties of porous media Porosity Definition: Void space: n V void /V total total porosity e V void /V solid Primary porosity - between grains Secondary porosity - fracture or solution
PART 5 Hydraulic properties of porous media Porosity Definition: Void space: n V void /V total total porosity e V void /V solid Primary porosity - between grains Secondary porosity - fracture or solution
(Refer Slide Time: 02:10)
 Soil Mechanics Prof. B.V.S. Viswanathan Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture 24 Flow of water through soils-v Welcome to lecture five of flow of water through
Soil Mechanics Prof. B.V.S. Viswanathan Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture 24 Flow of water through soils-v Welcome to lecture five of flow of water through
Darcy s law in 3-D. K * xx K * yy K * zz
 PART 7 Equations of flow Darcy s law in 3-D Specific discarge (vector) is calculated by multiplying te ydraulic conductivity (second-order tensor) by te ydraulic gradient (vector). We obtain a general
PART 7 Equations of flow Darcy s law in 3-D Specific discarge (vector) is calculated by multiplying te ydraulic conductivity (second-order tensor) by te ydraulic gradient (vector). We obtain a general
LECTURE NOTES - III. Prof. Dr. Atıl BULU
 LECTURE NOTES - III «FLUID MECHANICS» Istanbul Technical University College of Civil Engineering Civil Engineering Department Hydraulics Division CHAPTER KINEMATICS OF FLUIDS.. FLUID IN MOTION Fluid motion
LECTURE NOTES - III «FLUID MECHANICS» Istanbul Technical University College of Civil Engineering Civil Engineering Department Hydraulics Division CHAPTER KINEMATICS OF FLUIDS.. FLUID IN MOTION Fluid motion
1.72, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. Charles Harvey Lecture Packet #5: Groundwater Flow Patterns. Local Flow System. Intermediate Flow System
 1.72, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. Charles Harvey Lecture Packet #5: Groundwater Flow Patterns c Local Flow System 10,000 feet Intermediate Flow System Regional Flow System 20,000 feet Hydrologic section
1.72, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. Charles Harvey Lecture Packet #5: Groundwater Flow Patterns c Local Flow System 10,000 feet Intermediate Flow System Regional Flow System 20,000 feet Hydrologic section
" = ˆ i # #x + ˆ j # #y + ˆ k # #z. "t = D #2 h
 del operator " = ˆ i # #x + ˆ j # #y + ˆ k # #z Hydrology Gradient: "h = ˆ i #h #x + ˆ j #h #y + k ˆ #h #z q = - K"h Darcy s Law Divergence: " q = #q 1 #x + #q 2 #y + #q 3 #z Laplacian: " 2 h = #2 h #x
del operator " = ˆ i # #x + ˆ j # #y + ˆ k # #z Hydrology Gradient: "h = ˆ i #h #x + ˆ j #h #y + k ˆ #h #z q = - K"h Darcy s Law Divergence: " q = #q 1 #x + #q 2 #y + #q 3 #z Laplacian: " 2 h = #2 h #x
5. TWO-DIMENSIONAL FLOW OF WATER THROUGH SOILS 5.1 INTRODUCTION
 5. TWO-DIMENSIONAL FLOW OF WATER TROUG SOILS 5.1 INTRODUCTION In many instances the flo of ater through soils is neither one-dimensional nor uniform over the area perpendicular to flo. It is often necessary
5. TWO-DIMENSIONAL FLOW OF WATER TROUG SOILS 5.1 INTRODUCTION In many instances the flo of ater through soils is neither one-dimensional nor uniform over the area perpendicular to flo. It is often necessary
Geo-E2010 Advanced Soil Mechanics L Wojciech Sołowski. 26 February 2017
 Geo-E2010 Advanced Soil Mechanics L Wojciech Sołowski 26 February 2017 Permeability, consolidation and seepage Department of Civil Engineering Advanced Soil Mechanics W. Sołowski 2 To learn 1. What is
Geo-E2010 Advanced Soil Mechanics L Wojciech Sołowski 26 February 2017 Permeability, consolidation and seepage Department of Civil Engineering Advanced Soil Mechanics W. Sołowski 2 To learn 1. What is
3.3.1 Linear functions yet again and dot product In 2D, a homogenous linear scalar function takes the general form:
 3.3 Gradient Vector and Jacobian Matri 3 3.3 Gradient Vector and Jacobian Matri Overview: Differentiable functions have a local linear approimation. Near a given point, local changes are determined by
3.3 Gradient Vector and Jacobian Matri 3 3.3 Gradient Vector and Jacobian Matri Overview: Differentiable functions have a local linear approimation. Near a given point, local changes are determined by
Mechanical Energy. Kinetic Energy. Gravitational Potential Energy
 Mechanical Energy Kinetic Energy E k = 1 2 mv2 where E k is energy (kg-m 2 /s 2 ) v is velocity (m/s) Gravitational Potential Energy E g = W = mgz where w is work (kg-m 2 /s 2 ) m is mass (kg) z is elevation
Mechanical Energy Kinetic Energy E k = 1 2 mv2 where E k is energy (kg-m 2 /s 2 ) v is velocity (m/s) Gravitational Potential Energy E g = W = mgz where w is work (kg-m 2 /s 2 ) m is mass (kg) z is elevation
Mathematics Trigonometry: Unit Circle
 a place of mind F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Department of Curriculum and Pedagog Mathematics Trigonometr: Unit Circle Science and Mathematics Education Research Group Supported b UBC Teaching and
a place of mind F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Department of Curriculum and Pedagog Mathematics Trigonometr: Unit Circle Science and Mathematics Education Research Group Supported b UBC Teaching and
In all of the following equations, is the coefficient of permeability in the x direction, and is the hydraulic head.
 Groundwater Seepage 1 Groundwater Seepage Simplified Steady State Fluid Flow The finite element method can be used to model both steady state and transient groundwater flow, and it has been used to incorporate
Groundwater Seepage 1 Groundwater Seepage Simplified Steady State Fluid Flow The finite element method can be used to model both steady state and transient groundwater flow, and it has been used to incorporate
Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad. Chapter (7)
 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad Chapter (7) 2017-2016 Soil Properties Physical Properties Mechanical Properties Gradation and Structure Compressibility Soil-Water Relationships Shear Strength Bearing Capacity
Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad Chapter (7) 2017-2016 Soil Properties Physical Properties Mechanical Properties Gradation and Structure Compressibility Soil-Water Relationships Shear Strength Bearing Capacity
6. The Momentum Equation
 6. The Momentum Equation [This material relates predominantly to modules ELP034, ELP035] 6. Definition of the momentum equation Applications of the momentum equation: 6. The force due to the flow around
6. The Momentum Equation [This material relates predominantly to modules ELP034, ELP035] 6. Definition of the momentum equation Applications of the momentum equation: 6. The force due to the flow around
ADVANCED SOIL MECHANICS
 BERNOULLI S EQUATION h Where: u w g Z h = Total Head u = Pressure = Velocity g = Acceleration due to Graity w = Unit Weight of Water h 14.531 ADVANCED SOIL MECHANICS BERNOULLI S EQUATION IN SOIL u w g
BERNOULLI S EQUATION h Where: u w g Z h = Total Head u = Pressure = Velocity g = Acceleration due to Graity w = Unit Weight of Water h 14.531 ADVANCED SOIL MECHANICS BERNOULLI S EQUATION IN SOIL u w g
Water in Soil Sections in Craig
 Water in Soil Sections 2.1-2.6 in Craig Outlines Introduction Darcy s Law Volume of water flowing per unit time Measuring K in laboratory Seepage Theory Flow Net Introduction All soils are permeable materials,
Water in Soil Sections 2.1-2.6 in Craig Outlines Introduction Darcy s Law Volume of water flowing per unit time Measuring K in laboratory Seepage Theory Flow Net Introduction All soils are permeable materials,
Reg. No. : Question Paper Code : B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, JANUARY First Semester. Marine Engineering
 WK Reg No : Question Paper Code : 78 BE/BTech DEGREE EXAMINATION, JANUARY 4 First Semester Marine Engineering MA 65 MATHEMATICS FOR MARINE ENGINEERING I (Regulation ) Time : Three hours Maimum : marks
WK Reg No : Question Paper Code : 78 BE/BTech DEGREE EXAMINATION, JANUARY 4 First Semester Marine Engineering MA 65 MATHEMATICS FOR MARINE ENGINEERING I (Regulation ) Time : Three hours Maimum : marks
Summer Review Packet for Students Entering AP Calculus BC. Complex Fractions
 Summer Review Packet for Students Entering AP Calculus BC Comple Fractions When simplifying comple fractions, multiply by a fraction equal to 1 which has a numerator and denominator composed of the common
Summer Review Packet for Students Entering AP Calculus BC Comple Fractions When simplifying comple fractions, multiply by a fraction equal to 1 which has a numerator and denominator composed of the common
ACS MATHEMATICS GRADE 10 WARM UP EXERCISES FOR IB HIGHER LEVEL MATHEMATICS
 ACS MATHEMATICS GRADE 0 WARM UP EXERCISES FOR IB HIGHER LEVEL MATHEMATICS DO AS MANY OF THESE AS POSSIBLE BEFORE THE START OF YOUR FIRST YEAR IB HIGHER LEVEL MATH CLASS NEXT SEPTEMBER Write as a single
ACS MATHEMATICS GRADE 0 WARM UP EXERCISES FOR IB HIGHER LEVEL MATHEMATICS DO AS MANY OF THESE AS POSSIBLE BEFORE THE START OF YOUR FIRST YEAR IB HIGHER LEVEL MATH CLASS NEXT SEPTEMBER Write as a single
12 th Class Mathematics Paper
 th Class Mathematics Paper Maimum Time: hours Maimum Marks: 00 General Instructions: (i) All questions are compulsory. (ii) The question paper consists of 9 questions divided into four sections A, B, C
th Class Mathematics Paper Maimum Time: hours Maimum Marks: 00 General Instructions: (i) All questions are compulsory. (ii) The question paper consists of 9 questions divided into four sections A, B, C
7.4 The Elementary Beam Theory
 7.4 The Elementary Beam Theory In this section, problems involving long and slender beams are addressed. s with pressure vessels, the geometry of the beam, and the specific type of loading which will be
7.4 The Elementary Beam Theory In this section, problems involving long and slender beams are addressed. s with pressure vessels, the geometry of the beam, and the specific type of loading which will be
the Cartesian coordinate system (which we normally use), in which we characterize points by two coordinates (x, y) and
 2.5.2 Standard coordinate systems in R 2 and R Similarly as for functions of one variable, integrals of functions of two or three variables may become simpler when changing coordinates in an appropriate
2.5.2 Standard coordinate systems in R 2 and R Similarly as for functions of one variable, integrals of functions of two or three variables may become simpler when changing coordinates in an appropriate
az - ah= 0 or Homogeneous, Isotropic Systems
 5.1 Flow Nets by Graphical Construction We have seen in Chapter 2 that a groundwater flow system can be represented by a three-dimensional set of equipotential surfaces and a corresponding set of orthogonal
5.1 Flow Nets by Graphical Construction We have seen in Chapter 2 that a groundwater flow system can be represented by a three-dimensional set of equipotential surfaces and a corresponding set of orthogonal
SECTION 6.3: VECTORS IN THE PLANE
 (Section 6.3: Vectors in the Plane) 6.18 SECTION 6.3: VECTORS IN THE PLANE Assume a, b, c, and d are real numbers. PART A: INTRO A scalar has magnitude but not direction. We think of real numbers as scalars,
(Section 6.3: Vectors in the Plane) 6.18 SECTION 6.3: VECTORS IN THE PLANE Assume a, b, c, and d are real numbers. PART A: INTRO A scalar has magnitude but not direction. We think of real numbers as scalars,
Lines and points. Lines and points
 omogeneous coordinates in the plane Homogeneous coordinates in the plane A line in the plane a + by + c is represented as (a, b, c). A line is a subset of points in the plane. All vectors (ka, kb, kc)
omogeneous coordinates in the plane Homogeneous coordinates in the plane A line in the plane a + by + c is represented as (a, b, c). A line is a subset of points in the plane. All vectors (ka, kb, kc)
Chapter 5. The Differential Forms of the Fundamental Laws
 Chapter 5 The Differential Forms of the Fundamental Laws 1 5.1 Introduction Two primary methods in deriving the differential forms of fundamental laws: Gauss s Theorem: Allows area integrals of the equations
Chapter 5 The Differential Forms of the Fundamental Laws 1 5.1 Introduction Two primary methods in deriving the differential forms of fundamental laws: Gauss s Theorem: Allows area integrals of the equations
GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING II (Subject Code: 06CV64) UNIT 4: FLOW NETS 4.1 Introduction
 GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING II (Subject Code: 06CV64) UNIT 4: FLOW NETS 4.1 Introduction In this chapter the topics that are covered include principles of seepage analysis, graphical solutions for seepage
GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING II (Subject Code: 06CV64) UNIT 4: FLOW NETS 4.1 Introduction In this chapter the topics that are covered include principles of seepage analysis, graphical solutions for seepage
*** ***! " " ) * % )!( & ' % # $. 0 1 %./ +, - 7 : %8% 9 ) 7 / ( * 7 : %8% 9 < ;14. " > /' ;-,=. / ١
 ١ ******!" #$ % & '!( ) % * ") +,-./ % 01. 3 ( 4 56 7/4 ) 8%9 % : 7 ;14 < 8%9 % : *7./ = ;-, >/'." Soil Permeability & Seepage ٢ Soil Permeability- Definition ٣ What is Permeability? Permeability is the
١ ******!" #$ % & '!( ) % * ") +,-./ % 01. 3 ( 4 56 7/4 ) 8%9 % : 7 ;14 < 8%9 % : *7./ = ;-, >/'." Soil Permeability & Seepage ٢ Soil Permeability- Definition ٣ What is Permeability? Permeability is the
LEARN ABOUT the Math
 1.5 Inverse Relations YOU WILL NEED graph paper graphing calculator GOAL Determine the equation of an inverse relation and the conditions for an inverse relation to be a function. LEARN ABOUT the Math
1.5 Inverse Relations YOU WILL NEED graph paper graphing calculator GOAL Determine the equation of an inverse relation and the conditions for an inverse relation to be a function. LEARN ABOUT the Math
Module 2 Lecture 9 Permeability and Seepage -5 Topics
 Module 2 Lecture 9 Permeability and Seepage -5 Topics 1.2.7 Numerical Analysis of Seepage 1.2.8 Seepage Force per Unit Volume of Soil Mass 1.2.9 Safety of Hydraulic Structures against Piping 1.2.10 Calculation
Module 2 Lecture 9 Permeability and Seepage -5 Topics 1.2.7 Numerical Analysis of Seepage 1.2.8 Seepage Force per Unit Volume of Soil Mass 1.2.9 Safety of Hydraulic Structures against Piping 1.2.10 Calculation
Flow in Open Channel Flow Conditions
 Civil Engineering Hydraulics Flow The graduate with a Science degree asks, "Why does it work?" The graduate with an Engineering degree asks, "How does it work?" The graduate with an Accounting degree asks,
Civil Engineering Hydraulics Flow The graduate with a Science degree asks, "Why does it work?" The graduate with an Engineering degree asks, "How does it work?" The graduate with an Accounting degree asks,
Classical Mechanics. Luis Anchordoqui
 1 Rigid Body Motion Inertia Tensor Rotational Kinetic Energy Principal Axes of Rotation Steiner s Theorem Euler s Equations for a Rigid Body Eulerian Angles Review of Fundamental Equations 2 Rigid body
1 Rigid Body Motion Inertia Tensor Rotational Kinetic Energy Principal Axes of Rotation Steiner s Theorem Euler s Equations for a Rigid Body Eulerian Angles Review of Fundamental Equations 2 Rigid body
6.5 Trigonometric Equations
 6. Trigonometric Equations In this section, we discuss conditional trigonometric equations, that is, equations involving trigonometric functions that are satisfied only by some values of the variable (or
6. Trigonometric Equations In this section, we discuss conditional trigonometric equations, that is, equations involving trigonometric functions that are satisfied only by some values of the variable (or
Fluid Mechanics II. Newton s second law applied to a control volume
 Fluid Mechanics II Stead flow momentum equation Newton s second law applied to a control volume Fluids, either in a static or dnamic motion state, impose forces on immersed bodies and confining boundaries.
Fluid Mechanics II Stead flow momentum equation Newton s second law applied to a control volume Fluids, either in a static or dnamic motion state, impose forces on immersed bodies and confining boundaries.
Fundamentals of Algebra, Geometry, and Trigonometry. (Self-Study Course)
 Fundamentals of Algebra, Geometry, and Trigonometry (Self-Study Course) This training is offered eclusively through the Pennsylvania Department of Transportation, Business Leadership Office, Technical
Fundamentals of Algebra, Geometry, and Trigonometry (Self-Study Course) This training is offered eclusively through the Pennsylvania Department of Transportation, Business Leadership Office, Technical
11.4 Polar Coordinates
 11. Polar Coordinates 917 11. Polar Coordinates In Section 1.1, we introduced the Cartesian coordinates of a point in the plane as a means of assigning ordered pairs of numbers to points in the plane.
11. Polar Coordinates 917 11. Polar Coordinates In Section 1.1, we introduced the Cartesian coordinates of a point in the plane as a means of assigning ordered pairs of numbers to points in the plane.
Transformations. Chapter D Transformations Translation
 Chapter 4 Transformations Transformations between arbitrary vector spaces, especially linear transformations, are usually studied in a linear algebra class. Here, we focus our attention to transformation
Chapter 4 Transformations Transformations between arbitrary vector spaces, especially linear transformations, are usually studied in a linear algebra class. Here, we focus our attention to transformation
Chapter 7 Permeability and Seepage
 Permeability and Seepage - N. Sivakugan (2005) 1 7.1 INTRODUCTION Chapter 7 Permeability and Seepage Permeability, as the name implies (ability to permeate), is a measure of how easily a fluid can flow
Permeability and Seepage - N. Sivakugan (2005) 1 7.1 INTRODUCTION Chapter 7 Permeability and Seepage Permeability, as the name implies (ability to permeate), is a measure of how easily a fluid can flow
Modeling Seepage Control in Hydraulic Structures
 Number 3 Volume 13 September2006 Journal of Engineering Dr. Rafa H. El-Suhaili Professor Environmental Engineering Department College of Engineering Fawaz M. Aziz Al-Joubori M.Sc Student Irrigation and
Number 3 Volume 13 September2006 Journal of Engineering Dr. Rafa H. El-Suhaili Professor Environmental Engineering Department College of Engineering Fawaz M. Aziz Al-Joubori M.Sc Student Irrigation and
A.P. Calculus Summer Assignment
 A.P. Calculus Summer Assignment This assignment is due the first day of class at the beginning of the class. It will be graded and counts as your first test grade. This packet contains eight sections and
A.P. Calculus Summer Assignment This assignment is due the first day of class at the beginning of the class. It will be graded and counts as your first test grade. This packet contains eight sections and
Matrices and Vectors
 Matrices and Vectors James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University November 11, 2013 Outline 1 Matrices and Vectors 2 Vector Details 3 Matrix
Matrices and Vectors James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University November 11, 2013 Outline 1 Matrices and Vectors 2 Vector Details 3 Matrix
Uniformity of the Universe
 Outline Universe is homogenous and isotropic Spacetime metrics Friedmann-Walker-Robertson metric Number of numbers needed to specify a physical quantity. Energy-momentum tensor Energy-momentum tensor of
Outline Universe is homogenous and isotropic Spacetime metrics Friedmann-Walker-Robertson metric Number of numbers needed to specify a physical quantity. Energy-momentum tensor Energy-momentum tensor of
Edexcel past paper questions. Core Mathematics 4. Parametric Equations
 Edexcel past paper questions Core Mathematics 4 Parametric Equations Edited by: K V Kumaran Email: kvkumaran@gmail.com C4 Maths Parametric equations Page 1 Co-ordinate Geometry A parametric equation of
Edexcel past paper questions Core Mathematics 4 Parametric Equations Edited by: K V Kumaran Email: kvkumaran@gmail.com C4 Maths Parametric equations Page 1 Co-ordinate Geometry A parametric equation of
Flow toward Pumping Well, next to river = line source = constant head boundary
 Flow toward Pumping Well, next to river = line source = constant head boundary Plan view River Channel after Domenico & Schwartz (1990) Line Source Leonhard Euler 1707-1783 e i" +1 = 0 wikimedia.org Charles
Flow toward Pumping Well, next to river = line source = constant head boundary Plan view River Channel after Domenico & Schwartz (1990) Line Source Leonhard Euler 1707-1783 e i" +1 = 0 wikimedia.org Charles
All soils in natural are permeable materials, water being free to flow through the interconnected pores between the solid particles.
 8.1 Introduction Among construction materials, soil is very unique. Because of a relatively large space of void in its constituent, water can flow through soil. The water flow (seepage) characteristics
8.1 Introduction Among construction materials, soil is very unique. Because of a relatively large space of void in its constituent, water can flow through soil. The water flow (seepage) characteristics
6.1 Momentum Equation for Frictionless Flow: Euler s Equation The equations of motion for frictionless flow, called Euler s
 Chapter 6 INCOMPRESSIBLE INVISCID FLOW All real fluids possess viscosity. However in many flow cases it is reasonable to neglect the effects of viscosity. It is useful to investigate the dynamics of an
Chapter 6 INCOMPRESSIBLE INVISCID FLOW All real fluids possess viscosity. However in many flow cases it is reasonable to neglect the effects of viscosity. It is useful to investigate the dynamics of an
Review of the Fundamentals of Groundwater Flow
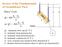 Review of te Fundamentals of Groundwater Flow Darc s Law 1 A 1 L A or L 1 datum L : volumetric flow rate [L 3 T -1 ] 1 : draulic ead upstream [L] A : draulic ead downstream [L] : draulic conductivit [L
Review of te Fundamentals of Groundwater Flow Darc s Law 1 A 1 L A or L 1 datum L : volumetric flow rate [L 3 T -1 ] 1 : draulic ead upstream [L] A : draulic ead downstream [L] : draulic conductivit [L
Hydraulics for Urban Storm Drainage
 Urban Hydraulics Hydraulics for Urban Storm Drainage Learning objectives: understanding of basic concepts of fluid flow and how to analyze conduit flows, free surface flows. to analyze, hydrostatic pressure
Urban Hydraulics Hydraulics for Urban Storm Drainage Learning objectives: understanding of basic concepts of fluid flow and how to analyze conduit flows, free surface flows. to analyze, hydrostatic pressure
Numerical Heat and Mass Transfer
 Master degree in Mechanical Engineering Numerical Heat and Mass Transfer 02-Transient Conduction Fausto Arpino f.arpino@unicas.it Outline Introduction Conduction ü Heat conduction equation ü Boundary conditions
Master degree in Mechanical Engineering Numerical Heat and Mass Transfer 02-Transient Conduction Fausto Arpino f.arpino@unicas.it Outline Introduction Conduction ü Heat conduction equation ü Boundary conditions
(C) Global Journal Of Engineering Science And Researches
 GLOBAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND RESEARCHES MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF GROUNDWATER FLOW Luma Naji Mohammed Tawfiq *1 and Alaa K. Jabber 2 *1 College of Education for Pure Science I bn Al-Haitham,
GLOBAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND RESEARCHES MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF GROUNDWATER FLOW Luma Naji Mohammed Tawfiq *1 and Alaa K. Jabber 2 *1 College of Education for Pure Science I bn Al-Haitham,
Exact Solutions of the Einstein Equations
 Notes from phz 6607, Special and General Relativity University of Florida, Fall 2004, Detweiler Exact Solutions of the Einstein Equations These notes are not a substitute in any manner for class lectures.
Notes from phz 6607, Special and General Relativity University of Florida, Fall 2004, Detweiler Exact Solutions of the Einstein Equations These notes are not a substitute in any manner for class lectures.
vand v 3. Find the area of a parallelogram that has the given vectors as adjacent sides.
 Name: Date: 1. Given the vectors u and v, find u vand v v. u= 8,6,2, v = 6, 3, 4 u v v v 2. Given the vectors u nd v, find the cross product and determine whether it is orthogonal to both u and v. u= 1,8,
Name: Date: 1. Given the vectors u and v, find u vand v v. u= 8,6,2, v = 6, 3, 4 u v v v 2. Given the vectors u nd v, find the cross product and determine whether it is orthogonal to both u and v. u= 1,8,
MATHEMATICS 200 April 2010 Final Exam Solutions
 MATHEMATICS April Final Eam Solutions. (a) A surface z(, y) is defined by zy y + ln(yz). (i) Compute z, z y (ii) Evaluate z and z y in terms of, y, z. at (, y, z) (,, /). (b) A surface z f(, y) has derivatives
MATHEMATICS April Final Eam Solutions. (a) A surface z(, y) is defined by zy y + ln(yz). (i) Compute z, z y (ii) Evaluate z and z y in terms of, y, z. at (, y, z) (,, /). (b) A surface z f(, y) has derivatives
Advanced Hydrology Prof. Dr. Ashu Jain Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur. Lecture 6
 Advanced Hydrology Prof. Dr. Ashu Jain Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture 6 Good morning and welcome to the next lecture of this video course on Advanced Hydrology.
Advanced Hydrology Prof. Dr. Ashu Jain Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture 6 Good morning and welcome to the next lecture of this video course on Advanced Hydrology.
Maths A Level Summer Assignment & Transition Work
 Maths A Level Summer Assignment & Transition Work The summer assignment element should take no longer than hours to complete. Your summer assignment for each course must be submitted in the relevant first
Maths A Level Summer Assignment & Transition Work The summer assignment element should take no longer than hours to complete. Your summer assignment for each course must be submitted in the relevant first
1. Introduction - Tutorials
 1. Introduction - Tutorials 1.1 Physical properties of fluids Give the following fluid and physical properties(at 20 Celsius and standard pressure) with a 4-digit accuracy. Air density : Water density
1. Introduction - Tutorials 1.1 Physical properties of fluids Give the following fluid and physical properties(at 20 Celsius and standard pressure) with a 4-digit accuracy. Air density : Water density
Lecture 6, September 1, 2017
 Engineering Mathematics Fall 07 Lecture 6, September, 07 Escape Velocity Suppose we have a planet (or any large near to spherical heavenly body) of radius R and acceleration of gravity at the surface of
Engineering Mathematics Fall 07 Lecture 6, September, 07 Escape Velocity Suppose we have a planet (or any large near to spherical heavenly body) of radius R and acceleration of gravity at the surface of
HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION MATHEMATICS 4 UNIT (ADDITIONAL) Time allowed Three hours (Plus 5 minutes reading time)
 N E W S O U T H W A L E S HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION 996 MATHEMATICS 4 UNIT (ADDITIONAL) Time allowed Three hours (Plus 5 minutes reading time) DIRECTIONS TO CANDIDATES Attempt ALL questions.
N E W S O U T H W A L E S HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION 996 MATHEMATICS 4 UNIT (ADDITIONAL) Time allowed Three hours (Plus 5 minutes reading time) DIRECTIONS TO CANDIDATES Attempt ALL questions.
Monroe Township High School Mathematics Department
 To: AP Calculus AB Re: Summer Project 017 Date: June 017 Monroe Township High School Mathematics Department To help begin your study of Calculus, you will be required to complete a review project this
To: AP Calculus AB Re: Summer Project 017 Date: June 017 Monroe Township High School Mathematics Department To help begin your study of Calculus, you will be required to complete a review project this
Example 2.1. Draw the points with polar coordinates: (i) (3, π) (ii) (2, π/4) (iii) (6, 2π/4) We illustrate all on the following graph:
 Section 10.3: Polar Coordinates The polar coordinate system is another way to coordinatize the Cartesian plane. It is particularly useful when examining regions which are circular. 1. Cartesian Coordinates
Section 10.3: Polar Coordinates The polar coordinate system is another way to coordinatize the Cartesian plane. It is particularly useful when examining regions which are circular. 1. Cartesian Coordinates
ENGI 3424 First Order ODEs Page 1-01
 ENGI 344 First Order ODEs Page 1-01 1. Ordinary Differential Equations Equations involving only one independent variable and one or more dependent variables, together with their derivatives with respect
ENGI 344 First Order ODEs Page 1-01 1. Ordinary Differential Equations Equations involving only one independent variable and one or more dependent variables, together with their derivatives with respect
Review of Engineering Dynamics
 Review of Engineering Dynamics Part 1: Kinematics of Particles and Rigid Bodies by James Doane, PhD, PE Contents 1.0 Course Overview... 4.0 Basic Introductory Concepts... 4.1 Introduction... 4.1.1 Vectors
Review of Engineering Dynamics Part 1: Kinematics of Particles and Rigid Bodies by James Doane, PhD, PE Contents 1.0 Course Overview... 4.0 Basic Introductory Concepts... 4.1 Introduction... 4.1.1 Vectors
3.5 Continuity of a Function One Sided Continuity Intermediate Value Theorem... 23
 Chapter 3 Limit and Continuity Contents 3. Definition of Limit 3 3.2 Basic Limit Theorems 8 3.3 One sided Limit 4 3.4 Infinite Limit, Limit at infinity and Asymptotes 5 3.4. Infinite Limit and Vertical
Chapter 3 Limit and Continuity Contents 3. Definition of Limit 3 3.2 Basic Limit Theorems 8 3.3 One sided Limit 4 3.4 Infinite Limit, Limit at infinity and Asymptotes 5 3.4. Infinite Limit and Vertical
Fundamentals of Transport Processes Prof. Kumaran Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Chemical Engineering
 Fundamentals of Transport Processes Prof. Kumaran Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Chemical Engineering Module No # 05 Lecture No # 25 Mass and Energy Conservation Cartesian Co-ordinates Welcome
Fundamentals of Transport Processes Prof. Kumaran Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Chemical Engineering Module No # 05 Lecture No # 25 Mass and Energy Conservation Cartesian Co-ordinates Welcome
Darcy's Law. Laboratory 2 HWR 531/431
 Darcy's Law Laboratory HWR 531/431-1 Introduction In 1856, Henry Darcy, a French hydraulic engineer, published a report in which he described a series of experiments he had performed in an attempt to quantify
Darcy's Law Laboratory HWR 531/431-1 Introduction In 1856, Henry Darcy, a French hydraulic engineer, published a report in which he described a series of experiments he had performed in an attempt to quantify
MAT389 Fall 2016, Problem Set 4
 MAT389 Fall 2016, Problem Set 4 Harmonic conjugates 4.1 Check that each of the functions u(x, y) below is harmonic at every (x, y) R 2, and find the unique harmonic conjugate, v(x, y), satisfying v(0,
MAT389 Fall 2016, Problem Set 4 Harmonic conjugates 4.1 Check that each of the functions u(x, y) below is harmonic at every (x, y) R 2, and find the unique harmonic conjugate, v(x, y), satisfying v(0,
Introduction to Well Hydraulics Fritz R. Fiedler
 Introduction to Well Hydraulics Fritz R. Fiedler A well is a pipe placed in a drilled hole that has slots (screen) cut into it that allow water to enter the well, but keep the aquifer material out. A well
Introduction to Well Hydraulics Fritz R. Fiedler A well is a pipe placed in a drilled hole that has slots (screen) cut into it that allow water to enter the well, but keep the aquifer material out. A well
Omm Al-Qura University Dr. Abdulsalam Ai LECTURE OUTLINE CHAPTER 3. Vectors in Physics
 LECTURE OUTLINE CHAPTER 3 Vectors in Physics 3-1 Scalars Versus Vectors Scalar a numerical value (number with units). May be positive or negative. Examples: temperature, speed, height, and mass. Vector
LECTURE OUTLINE CHAPTER 3 Vectors in Physics 3-1 Scalars Versus Vectors Scalar a numerical value (number with units). May be positive or negative. Examples: temperature, speed, height, and mass. Vector
NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS
 Mathematics Higher Prelim Eamination 04/05 Paper Assessing Units & + Vectors NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS Time allowed - hour 0 minutes Read carefully Calculators may NOT be used in this paper. Section A -
Mathematics Higher Prelim Eamination 04/05 Paper Assessing Units & + Vectors NATIONAL QUALIFICATIONS Time allowed - hour 0 minutes Read carefully Calculators may NOT be used in this paper. Section A -
Determination of Locally Varying Directions through Mass Moment of Inertia Tensor
 Determination of Locally Varying Directions through Mass Moment of Inertia Tensor R. M. Hassanpour and C.V. Deutsch Centre for Computational Geostatistics Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering
Determination of Locally Varying Directions through Mass Moment of Inertia Tensor R. M. Hassanpour and C.V. Deutsch Centre for Computational Geostatistics Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering
Brief Revision Notes and Strategies
 Brief Revision Notes and Strategies Straight Line Distance Formula d = ( ) + ( y y ) d is distance between A(, y ) and B(, y ) Mid-point formula +, y + M y M is midpoint of A(, y ) and B(, y ) y y Equation
Brief Revision Notes and Strategies Straight Line Distance Formula d = ( ) + ( y y ) d is distance between A(, y ) and B(, y ) Mid-point formula +, y + M y M is midpoint of A(, y ) and B(, y ) y y Equation
Building ground level
 TMA4195 MATHEMATICAL MODELLING PROJECT 212: AQUIFER THERMAL ENERGY STORAGE 1. Introduction In the project we will study a so-called Aquifer Thermal Energy Storage (ATES) system with the aim of climitizing
TMA4195 MATHEMATICAL MODELLING PROJECT 212: AQUIFER THERMAL ENERGY STORAGE 1. Introduction In the project we will study a so-called Aquifer Thermal Energy Storage (ATES) system with the aim of climitizing
(a) Show that there is a root α of f (x) = 0 in the interval [1.2, 1.3]. (2)
![(a) Show that there is a root α of f (x) = 0 in the interval [1.2, 1.3]. (2) (a) Show that there is a root α of f (x) = 0 in the interval [1.2, 1.3]. (2)](/thumbs/85/92620692.jpg) . f() = 4 cosec 4 +, where is in radians. (a) Show that there is a root α of f () = 0 in the interval [.,.3]. Show that the equation f() = 0 can be written in the form = + sin 4 Use the iterative formula
. f() = 4 cosec 4 +, where is in radians. (a) Show that there is a root α of f () = 0 in the interval [.,.3]. Show that the equation f() = 0 can be written in the form = + sin 4 Use the iterative formula
Further factorising, simplifying, completing the square and algebraic proof
 Further factorising, simplifying, completing the square and algebraic proof 8 CHAPTER 8. Further factorising Quadratic epressions of the form b c were factorised in Section 8. by finding two numbers whose
Further factorising, simplifying, completing the square and algebraic proof 8 CHAPTER 8. Further factorising Quadratic epressions of the form b c were factorised in Section 8. by finding two numbers whose
CALC1 SUMMER REVIEW WORK
 CALC SUMMER REVIEW WORK The following problems are all ALGEBRA concepts you must know cold in order to be able to handle Calculus. Most of them are from Algebra, some are from Pre-Calc. This packet is
CALC SUMMER REVIEW WORK The following problems are all ALGEBRA concepts you must know cold in order to be able to handle Calculus. Most of them are from Algebra, some are from Pre-Calc. This packet is
Particulate transport through heterogeneous porous media; numerical studies using finite element method
 Int. Jnl. of Multiphysics Volume 7 umber 3 3 45 Particulate transport through heterogeneous porous media; numerical studies using finite element method Marcel Ilie* Sat Tomsani, Com. Costestii din Vale,
Int. Jnl. of Multiphysics Volume 7 umber 3 3 45 Particulate transport through heterogeneous porous media; numerical studies using finite element method Marcel Ilie* Sat Tomsani, Com. Costestii din Vale,
And similarly in the other directions, so the overall result is expressed compactly as,
 SQEP Tutorial Session 5: T7S0 Relates to Knowledge & Skills.5,.8 Last Update: //3 Force on an element of area; Definition of principal stresses and strains; Definition of Tresca and Mises equivalent stresses;
SQEP Tutorial Session 5: T7S0 Relates to Knowledge & Skills.5,.8 Last Update: //3 Force on an element of area; Definition of principal stresses and strains; Definition of Tresca and Mises equivalent stresses;
i.e. the conservation of mass, the conservation of linear momentum, the conservation of energy.
 04/04/2017 LECTURE 33 Geometric Interpretation of Stream Function: In the last class, you came to know about the different types of boundary conditions that needs to be applied to solve the governing equations
04/04/2017 LECTURE 33 Geometric Interpretation of Stream Function: In the last class, you came to know about the different types of boundary conditions that needs to be applied to solve the governing equations
PreCalculus First Semester Exam Review
 PreCalculus First Semester Eam Review Name You may turn in this eam review for % bonus on your eam if all work is shown (correctly) and answers are correct. Please show work NEATLY and bo in or circle
PreCalculus First Semester Eam Review Name You may turn in this eam review for % bonus on your eam if all work is shown (correctly) and answers are correct. Please show work NEATLY and bo in or circle
ψ ae is equal to the height of the capillary rise in the soil. Ranges from about 10mm for gravel to 1.5m for silt to several meters for clay.
 Contents 1 Infiltration 1 1a Hydrologic soil horizons...................... 1 1b Infiltration Process......................... 2 1c Measurement............................ 2 1d Richard s Equation.........................
Contents 1 Infiltration 1 1a Hydrologic soil horizons...................... 1 1b Infiltration Process......................... 2 1c Measurement............................ 2 1d Richard s Equation.........................
NUMERICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF SEEPAGE BENEATH A MODEL OF A GRAVITY DAM
 Engineering Review Vol. 33, Issue 2, 75-84, 2013. 75 NUMERICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF SEEPAGE BENEATH A MODEL OF A GRAVITY DAM T. Jelenkovi V. Travaš * Chair of Hydraulic Engineering, Faculty of
Engineering Review Vol. 33, Issue 2, 75-84, 2013. 75 NUMERICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF SEEPAGE BENEATH A MODEL OF A GRAVITY DAM T. Jelenkovi V. Travaš * Chair of Hydraulic Engineering, Faculty of
3.3 Limits and Infinity
 Calculus Maimus. Limits Infinity Infinity is not a concrete number, but an abstract idea. It s not a destination, but a really long, never-ending journey. It s one of those mind-warping ideas that is difficult
Calculus Maimus. Limits Infinity Infinity is not a concrete number, but an abstract idea. It s not a destination, but a really long, never-ending journey. It s one of those mind-warping ideas that is difficult
Groundwater Flow and Solute Transport Modeling
 Groundwater Flow and Solute Transport Modeling Ye Zhang Dept. of Geology & Geophysics University of Wyoming c Draft date February 13, 2016 Contents Contents i 0.1 Introduction..............................
Groundwater Flow and Solute Transport Modeling Ye Zhang Dept. of Geology & Geophysics University of Wyoming c Draft date February 13, 2016 Contents Contents i 0.1 Introduction..............................
CHAPTER 4 Stress Transformation
 CHAPTER 4 Stress Transformation ANALYSIS OF STRESS For this topic, the stresses to be considered are not on the perpendicular and parallel planes only but also on other inclined planes. A P a a b b P z
CHAPTER 4 Stress Transformation ANALYSIS OF STRESS For this topic, the stresses to be considered are not on the perpendicular and parallel planes only but also on other inclined planes. A P a a b b P z
C.B.S.E Class XII Delhi & Outside Delhi Sets
 SOLVED PAPER With CBSE Marking Scheme C.B.S.E. 8 Class XII Delhi & Outside Delhi Sets Mathematics Time : Hours Ma. Marks : General Instructions : (i) All questions are compulsory. (ii) The question paper
SOLVED PAPER With CBSE Marking Scheme C.B.S.E. 8 Class XII Delhi & Outside Delhi Sets Mathematics Time : Hours Ma. Marks : General Instructions : (i) All questions are compulsory. (ii) The question paper
1.72, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. Charles Harvey Lecture Packet #9: Numerical Modeling of Groundwater Flow
 1.7, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. Carles Harvey Lecture Packet #9: Numerical Modeling of Groundwater Flow Simulation: Te prediction of quantities of interest (dependent variables) based upon an equation
1.7, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. Carles Harvey Lecture Packet #9: Numerical Modeling of Groundwater Flow Simulation: Te prediction of quantities of interest (dependent variables) based upon an equation
National Quali cations
 National Quali cations AH08 X747/77/ Mathematics THURSDAY, MAY 9:00 AM :00 NOON Total marks 00 Attempt ALL questions. You may use a calculator. Full credit will be given only to solutions which contain
National Quali cations AH08 X747/77/ Mathematics THURSDAY, MAY 9:00 AM :00 NOON Total marks 00 Attempt ALL questions. You may use a calculator. Full credit will be given only to solutions which contain
Warmup for AP Calculus BC
 Nichols School Mathematics Department Summer Work Packet Warmup for AP Calculus BC Who should complete this packet? Students who have completed Advanced Functions or and will be taking AP Calculus BC in
Nichols School Mathematics Department Summer Work Packet Warmup for AP Calculus BC Who should complete this packet? Students who have completed Advanced Functions or and will be taking AP Calculus BC in
Math 234 Review Problems for the Final Exam
 Math 234 eview Problems for the Final Eam Marc Conrad ecember 13, 2007 irections: Answer each of the following questions. Pages 1 and 2 contain the problems. The solutions are on pages 3 through 7. Problem
Math 234 eview Problems for the Final Eam Marc Conrad ecember 13, 2007 irections: Answer each of the following questions. Pages 1 and 2 contain the problems. The solutions are on pages 3 through 7. Problem
Summer AP Assignment Coversheet Falls Church High School
 Summer AP Assignment Coversheet Falls Church High School Course: AP Calculus AB Teacher Name/s: Veronica Moldoveanu, Ethan Batterman Assignment Title: AP Calculus AB Summer Packet Assignment Summary/Purpose:
Summer AP Assignment Coversheet Falls Church High School Course: AP Calculus AB Teacher Name/s: Veronica Moldoveanu, Ethan Batterman Assignment Title: AP Calculus AB Summer Packet Assignment Summary/Purpose:
8.1 Solutions to Exercises
 Last edited 9/6/17 8.1 Solutions to Exercises 1. Since the sum of all angles in a triangle is 180, 180 = 70 + 50 + α. Thus α = 60. 10 α B The easiest way to find A and B is to use Law of Sines. sin( )
Last edited 9/6/17 8.1 Solutions to Exercises 1. Since the sum of all angles in a triangle is 180, 180 = 70 + 50 + α. Thus α = 60. 10 α B The easiest way to find A and B is to use Law of Sines. sin( )
Nonlinear Oscillations and Chaos
 CHAPTER 4 Nonlinear Oscillations and Chaos 4-. l l = l + d s d d l l = l + d m θ m (a) (b) (c) The unetended length of each spring is, as shown in (a). In order to attach the mass m, each spring must be
CHAPTER 4 Nonlinear Oscillations and Chaos 4-. l l = l + d s d d l l = l + d m θ m (a) (b) (c) The unetended length of each spring is, as shown in (a). In order to attach the mass m, each spring must be
Condensed. Mathematics. General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Examination January Unit Pure Core 2.
 General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Eamination January 0 Mathematics MPC Unit Pure Core Monday 0 January 0 9.00 am to 0.0 am For this paper you must have: the blue AQA booklet of formulae
General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Eamination January 0 Mathematics MPC Unit Pure Core Monday 0 January 0 9.00 am to 0.0 am For this paper you must have: the blue AQA booklet of formulae
In this section, mathematical description of the motion of fluid elements moving in a flow field is
 Jun. 05, 015 Chapter 6. Differential Analysis of Fluid Flow 6.1 Fluid Element Kinematics In this section, mathematical description of the motion of fluid elements moving in a flow field is given. A small
Jun. 05, 015 Chapter 6. Differential Analysis of Fluid Flow 6.1 Fluid Element Kinematics In this section, mathematical description of the motion of fluid elements moving in a flow field is given. A small
7.3 Inverse Trigonometric Functions
 58 transcendental functions 73 Inverse Trigonometric Functions We now turn our attention to the inverse trigonometric functions, their properties and their graphs, focusing on properties and techniques
58 transcendental functions 73 Inverse Trigonometric Functions We now turn our attention to the inverse trigonometric functions, their properties and their graphs, focusing on properties and techniques
Edexcel Core Mathematics 4 Parametric equations.
 Edexcel Core Mathematics 4 Parametric equations. Edited by: K V Kumaran kumarmaths.weebly.com 1 Co-ordinate Geometry A parametric equation of a curve is one which does not give the relationship between
Edexcel Core Mathematics 4 Parametric equations. Edited by: K V Kumaran kumarmaths.weebly.com 1 Co-ordinate Geometry A parametric equation of a curve is one which does not give the relationship between
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD SCHEME OF VALUATION. Subject : MATHEMATICS Subject Code : 35
 GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH APRIL 0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject : MATHEMATICS Subject Code : 5 PART A Write the prime
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH APRIL 0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject : MATHEMATICS Subject Code : 5 PART A Write the prime
a b = a a a and that has been used here. ( )
 Review Eercise ( i j+ k) ( i+ j k) i j k = = i j+ k (( ) ( ) ) (( ) ( ) ) (( ) ( ) ) = i j+ k = ( ) i ( ( )) j+ ( ) k = j k Hence ( ) ( i j+ k) ( i+ j k) = ( ) + ( ) = 8 = Formulae for finding the vector
Review Eercise ( i j+ k) ( i+ j k) i j k = = i j+ k (( ) ( ) ) (( ) ( ) ) (( ) ( ) ) = i j+ k = ( ) i ( ( )) j+ ( ) k = j k Hence ( ) ( i j+ k) ( i+ j k) = ( ) + ( ) = 8 = Formulae for finding the vector
4: birefringence and phase matching
 /3/7 4: birefringence and phase matching Polarization states in EM Linear anisotropic response χ () tensor and its symmetry properties Working with the index ellipsoid: angle tuning Phase matching in crystals
/3/7 4: birefringence and phase matching Polarization states in EM Linear anisotropic response χ () tensor and its symmetry properties Working with the index ellipsoid: angle tuning Phase matching in crystals
