Macroeconomics II Dynamic macroeconomics Class 1: Introduction and rst models
|
|
|
- Blanche Stevens
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Macroeconomics II Dynamic macroeconomics Class 1: Introduction and rst models Prof. George McCandless UCEMA Spring Class 1: introduction and rst models What we will do today 1. Organization of course (a) Parallel course on Matlab (Francisco) (b) Structure of classes (c) Exercises each week (to be turned in) (d) Final exam (take home) 2. Today s class (a) De nition of our topic (b) Correction of data (Hordrick-Prescott lter) (c) First model (Solow) i. build model ii. study stationary states iii. make log-linear version to study stochastic properties Dynamic Macroeconomics Why dynamic models Much of what we are interested in in economics occurs over time in ation growth asset pricing 1
2 dynamic e ects of government policies models with stochastic elements Various models for handling this Older "Keynesian" reduced form models Models that can be resolved as a single recursive problem via Bellman equations or variational methods Models that need to be approximated (why?) linear approximations quadratic or higher approximations Need modeling techniques and solution techniques Dynamic Macroeconomics RBC models 1. Based on growth models (Solow) 2. Kydland and Prescott (won Nobel prize for this) (a) Their model is quite complicated (b) Ours will be based on model by Hansen 3. We use lots of other models Overlapping generations Models of money Credit markets Restrictions in prices and wages Open economy models. 1.1 What are RBC models What are RBC models? 1. Micro-foundations based models 2. Full speci cation of (a) preferences (b) production technologies (c) budget constraints 3. Dynamic 2
3 (a) In nite horizon (b) Rational expectations 4. Solve linear or quadratic approximation of model (a) Dynamic programing (Bellmans equation) (b) Log-linearization of model (c) Linear quadratic techniques 5. Get time path of economy 1.2 What is a successful RBC model A successful RBC model 1. Captures the second moments of the economy 2. Captures correlation with output 3. Mimics the impulse-response functions of the economy 4. Rules of Prescott (a) One needs to know the question one wants to ask (b) Model should be designed for that question (c) Model should use o -the-shelf technology (d) Model should be explicitly dynamic What data do we use 1. Model is compared to the data (a) How well do second moments match those of data (b) Compare impulse response of model to those of data 2. Data is normally ltered (a) Models are solved around stationary state (b) Mimic stationary state using lter i. Remove trends ii. Remove long run growth 3. Hodrick-Prescott Filter is frequently used 3
4 1.3 Hodrick-Prescott lter Hodrick-Prescott Filter I 1. Want to nd economic cycles 2. Times series data can be seen as of the form Y t+1 = Y t + t + " t 3. is the auto-regressive coe cient 4. is the linear trend (one could add quadratic trends, etc.) 5. What is the value of? (a) If jj 1 time path is explosive (called unit root when jj = 1) (b) if jaj < 1 time path stable i. n! 0 as n! 1 Hodrick-Prescott Filter II 1. One wants to remove trends 2. Formula for H-P lter 1 min fu tg T TX (y t u t ) 2 + T t=1 TX 1 h(u t+1 u t ) (u t u t 1 ) 2i t=2 3. The sequence fu t g is the trend P 1 T 4. T t=1 (y t u t ) 2 is sum of squared errors 5. T P T 1 t=2 derivative h (u t+1 u t ) (u t u t 1 ) 2i is a discrete version of the second (a) is parameter that controls smoothing (b) H-P recommend = The detrended data (used for models) is y t u t Example of HP lter on Argentina GDP data Filtered data with lambda = 1600 Problems with H-P lter 1. Not sure what it means (a) Can change characteristics of time series process 4
5 3.2 x λ= λ= λ= Figure 1: Three Hodrick-Prescott lters 3.5 x filtered data data cycles that remain (data thatwe use) Figure 2: GDP data, HP trend, and detrended GDP data 5
6 (b) Removes certain (low) frequences from the process (c) What does the data explain after the ltering? 2. Endpoint problems (a) Because it is a weighed average of points (b) At endpoints, only have one side of average 3. However, has become common practice to use H-P lter 1.4 Solow s growth model Solow s growth model 1. First model we will study 2. Basis for RBC and New Keynesian models 3. Touch some of the basics of course (a) Micro foundations (b) Generates time path (c) Can nd linear version (d) See how much of the cycle the model explains Reference: Robert Solow: A Contribution to the Theory of Economic Growth (1956) Solow s growth model Production function Y t = A t F (K t ; N t ) Y t = output, K t = stock of capital, N t = labor, A t = (1 + ) t A 0 = the level of technology Properties of F () twice continuously di erentiable homogenous of degree 1 increasing in both arguments F (K t ; N t ) = F (K t ; N t ) Strictly concave: F i > 0, F ii < 0, F ij > 0 6
7 Inada conditions: F (K t ; 0) = 0, F (0; N t ) = 0, F N (K t ; 0) = 1, F K (0; N t ) = 1; F N (K t ; 1) = 0, F K (1; N t ) = 0 Solow model: population growth Constant net growth rate of population (and labor) = The labor supply follows the rule: N t+1 = (1 + ) N t Solow model: Capital accumulation process Capital follows the accumulation rule K t+1 = (1 ) K t + I t I t is the investment at time t Savings rule Savings is a xed fraction of output (major simpli cation of Solow) S t = sy t No household optimization for savings decision the parameter s is given exogenously Equilibrium conditions for investment-savings S t = I t The full model Y t = A t F (K t ; N t ) K t+1 = (1 ) K t + I t S t = sy t S t = I t N t+1 = (1 + ) N t The rst four can be combined to give the equation K t+1 = (1 ) K t + sa t F (K t ; N t ) Put everything into per unit of labor terms Divide both sides of K t+1 = (1 ) K t + sa t F (K t ; N t ) by N t+1 = (1 + ) N t to get K t+1 = (1 ) K t + sa tf (K t ; N t ) N t+1 (1 + ) N t (1 + ) N t 7
8 De ning per-worker terms: k t = K t =N t, y t = Y t =N t, this can be written as k t+1 = (1 ) (1 + ) k t + sa t F (K t ; N t ) (1 + ) N t Because the production function is homogenous of degree 1, F (K t ; N t ) Kt = F ; N t = F (k t ; 1) f (k t ) ; N t N t N t The Solow di erence equation can be written as k t+1 = G (k t ) = (1 ) (1 + ) k t + sa t (1 + ) f (k t) We will (in class) let A t = A 0, a constant technology Model with constant technological growth where = 0 A t = (1 + ) t A 0 Using the Cobb-Douglas production function and zero technological growth f (k t ) = A 0 k t The Solow rst di erence equation is k t+1 = b G (k t ) = (1 ) (1 + ) k t + sa 0 (1 + ) k t Given some initial k 0, the time path for the economy can be found Where the solution k to the equation k = b G (k) = (1 ) (1 + ) k + sa 0 (1 + ) k is a stationary state capital stock for the economy 1.5 Stability conditions for Solow Model Solow Graph [5cm]7cm 5cm Stability conditions for Solow model 8
9 kt kt Figure 3: Stability conditions There are two stationary states zero at 1 sa0 1 k = + this last is an attractor A result of Solow Model Poor countries (those with less capital) grow faster than rich Gross growth rate of capital can be written as t = k t+1 k t = (1 )k t + sa 0 f(k t ) (1 + )k t : And taking the derivative with respect to capital: when k t > 0. d t dk t = sa 0 (1 + )k 2 t [f 0 (k t )k t f(k t )] < 0 Countries with higher k t have smaller growth rates of capital Stochastic variables A probability space: (; F; P ) is a set that contains all possible states of nature that might occur What is a state of nature F is a collection of subsets of Why do we need this? P is a probability measure over F Some draw from is observed each period 9
10 2 A stochastic Solow Model A stochastic Solow Model Suppose that technology is stochastic, A is positive A t = Ae "t random term " t has a normal distribution with mean zero So in stationary state (with " t = 0), e "t = 1 : e "t is never negative The stochastic version of the Solow rst order di erence equation is k t+1 = (1 )k t + sae "t f(k t ) (1 + ) Version in Logs (model is simpler this way) 1. Divide both sides by k t 2. replace k t+1 =k t by growth rate t 3. There is a problem with ln (1 )k t + sae "t f(k t ) 4. Take logs of both sides 1 sa ln t = ln 1 + (1 + n) + ln f(k t) + " t : k t 5. Use Cobb-Douglas production function, f(k t ) = kt, to get 1 ln t = ' 1 + (1 ) ln k t + " t ; where ' ln sa=(1 + ) Simulation of stochastic Solow model [5cm] 8cm 5cm Parameters used A = 1 s = :2 = :02 = :1 = :36 2 " =:2 Log-linear version of (no growth trend) Solow model 10
11 Figure 4: Three simulations of the exact Solow model 1. We have a second way to handle dynamics 2. Make an (log) linear approximation of the model 3. Study the dynamics of this linear model 4. Exists technology for solving dynamic linear models Log-linear version of (no growth trend) Solow model 1. Begin with the Solow di erence equation (1 + ) k t+1 = (1 )k t + sae "t kt ; 2. De ne e k t = ln(k t k), where k is the stationary state value of capital 3. Then k t = ke e k t 4. The Solow di erence equation is now (1 + ) ke e k t+1 = (1 )ke e k t + sae "t k e e k t ; 5. Use the approximation that for small e k t, e ae k t = 1 + a e k t 6. This approximation comes from a rst order Taylor expansion of e ae k t Log-linear Solow model 11
12 1. The approximation of (1 + ) ke e k t+1 = (1 )ke e k t + sak e e k t+e " t ; (note that e "t e e k t = e e k t+e " t ) is (1 + ) k 1 + e k t+1 = (1 )k 1 + e k t + sak 1 + e k t + e "t : 2. The 1 s in parenthisis drop out because (1 + ) k = (1 )k + sak : 3. The log-linear version of the model is (1 + ) k e h k t+1 = (1 )k + sak i ekt + sak e "t : Log-linear Solow model (continued) 1. This further simpli es (since + = sak 1 ) to e kt+1 = 1 + ( + ) e kt + + : e"t 2. Notice that (1 ) + ( + ) 1 + = 1 + (1 ) 1 + < 1 3. Let B = 1+ (1 ) 1+ and C = + 1+ < 1 and time t + 1 capital is equal to 1X e kt+1 = C B i " t i=0 i This is a convergent sequence Variance of capital The variance of time t + 1 capital is equal to var ekt+1 2 = E ekt+1 = E = C 2 E! 1X B i " t i i=0 1! X C B i " t i i=0! 1X B i " t i i=0 C! 1X B i " t i i=0 12
13 Figure 5: Simulations of the exact and log-linear Solow model Since the shocks are independent, E (" i " j ) = 0 if i 6= j, and = 2 if i = j. cross terms drop out and the sums become var ekt+1 = C 2 2 E 1X B 2i = i=0 C2 1 B 2 2 Using the parameters given before, B = 0: and C = : so that All var ekt+1 (: )2 = 1 (0:971 76) 2 2 = : The variance of capital is very small compared to the technology shock variance Time path of capital (comparing approximate to exact models) Variance of output 1. Output comes from the equation 2. A log-linear approximation of this is y t = A t k t = Ae "t k t y (1 + ey t ) ye eyt = Ak e e k t+" t Ak 1 + e k t + " t which simpli es to ey t e k t + " t 13
14 The variance of output is almost entirely made up of variance in technology. The e ect of changes in the capital stock are very small Solow model does not explain the persistence of shocks (cycles) in an economy Homework Usando un modelo de Solow con crecimiento en tecnologia de A t = (1 + ) t A 0 con A 0 = 5 y = :01, encuentre los caminos de capital y de producto per capita por 25 periodo cuando k(0) = :1 y cuando k(0) = 40. Gra ce los.caminos de capital Usa s = :15, = :57, y = :018. (Nota: debe usar Matlab para esta problema). 2. Muestre los gra cos de los las tasas de crecimiento de capitalen problema Describe the time path for a Solow model where there is an externality for each rm and each rm has the production function y j t = A t k t h 1 t Kt 1 : Lower case letters are for the rm and upper case letters are for the economy as a whole. The total capital in the economy functions as an externality for each rm. 14
Solow Growth Model. Michael Bar. February 28, Introduction Some facts about modern growth Questions... 4
 Solow Growth Model Michael Bar February 28, 208 Contents Introduction 2. Some facts about modern growth........................ 3.2 Questions..................................... 4 2 The Solow Model 5
Solow Growth Model Michael Bar February 28, 208 Contents Introduction 2. Some facts about modern growth........................ 3.2 Questions..................................... 4 2 The Solow Model 5
4- Current Method of Explaining Business Cycles: DSGE Models. Basic Economic Models
 4- Current Method of Explaining Business Cycles: DSGE Models Basic Economic Models In Economics, we use theoretical models to explain the economic processes in the real world. These models de ne a relation
4- Current Method of Explaining Business Cycles: DSGE Models Basic Economic Models In Economics, we use theoretical models to explain the economic processes in the real world. These models de ne a relation
ECON607 Fall 2010 University of Hawaii Professor Hui He TA: Xiaodong Sun Assignment 2
 ECON607 Fall 200 University of Hawaii Professor Hui He TA: Xiaodong Sun Assignment 2 The due date for this assignment is Tuesday, October 2. ( Total points = 50). (Two-sector growth model) Consider the
ECON607 Fall 200 University of Hawaii Professor Hui He TA: Xiaodong Sun Assignment 2 The due date for this assignment is Tuesday, October 2. ( Total points = 50). (Two-sector growth model) Consider the
Economic Growth
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 14.452 Economic Growth Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 14.452 Economic Growth: Lecture
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 14.452 Economic Growth Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 14.452 Economic Growth: Lecture
RBC Model with Indivisible Labor. Advanced Macroeconomic Theory
 RBC Model with Indivisible Labor Advanced Macroeconomic Theory 1 Last Class What are business cycles? Using HP- lter to decompose data into trend and cyclical components Business cycle facts Standard RBC
RBC Model with Indivisible Labor Advanced Macroeconomic Theory 1 Last Class What are business cycles? Using HP- lter to decompose data into trend and cyclical components Business cycle facts Standard RBC
New Notes on the Solow Growth Model
 New Notes on the Solow Growth Model Roberto Chang September 2009 1 The Model The firstingredientofadynamicmodelisthedescriptionofthetimehorizon. In the original Solow model, time is continuous and the
New Notes on the Solow Growth Model Roberto Chang September 2009 1 The Model The firstingredientofadynamicmodelisthedescriptionofthetimehorizon. In the original Solow model, time is continuous and the
The Solow Model in Discrete Time Allan Drazen October 2017
 The Solow Model in Discrete Time Allan Drazen October 2017 1 Technology There is a single good Y t produced by means of two factors of production capital K t in place at the beginning of the period and
The Solow Model in Discrete Time Allan Drazen October 2017 1 Technology There is a single good Y t produced by means of two factors of production capital K t in place at the beginning of the period and
Macroeconomics IV Problem Set I
 14.454 - Macroeconomics IV Problem Set I 04/02/2011 Due: Monday 4/11/2011 1 Question 1 - Kocherlakota (2000) Take an economy with a representative, in nitely-lived consumer. The consumer owns a technology
14.454 - Macroeconomics IV Problem Set I 04/02/2011 Due: Monday 4/11/2011 1 Question 1 - Kocherlakota (2000) Take an economy with a representative, in nitely-lived consumer. The consumer owns a technology
14.05: Section Handout #1 Solow Model
 14.05: Section Handout #1 Solow Model TA: Jose Tessada September 16, 2005 Today we will review the basic elements of the Solow model. Be prepared to ask any questions you may have about the derivation
14.05: Section Handout #1 Solow Model TA: Jose Tessada September 16, 2005 Today we will review the basic elements of the Solow model. Be prepared to ask any questions you may have about the derivation
The Basic New Keynesian Model. Jordi Galí. June 2008
 The Basic New Keynesian Model by Jordi Galí June 28 Motivation and Outline Evidence on Money, Output, and Prices: Short Run E ects of Monetary Policy Shocks (i) persistent e ects on real variables (ii)
The Basic New Keynesian Model by Jordi Galí June 28 Motivation and Outline Evidence on Money, Output, and Prices: Short Run E ects of Monetary Policy Shocks (i) persistent e ects on real variables (ii)
Hansen s basic RBC model
 ansen s basic RBC model George McCandless UCEMA Spring ansen s RBC model ansen s RBC model First RBC model was Kydland and Prescott (98) "Time to build and aggregate uctuations," Econometrica Complicated
ansen s basic RBC model George McCandless UCEMA Spring ansen s RBC model ansen s RBC model First RBC model was Kydland and Prescott (98) "Time to build and aggregate uctuations," Econometrica Complicated
1 The Basic RBC Model
 IHS 2016, Macroeconomics III Michael Reiter Ch. 1: Notes on RBC Model 1 1 The Basic RBC Model 1.1 Description of Model Variables y z k L c I w r output level of technology (exogenous) capital at end of
IHS 2016, Macroeconomics III Michael Reiter Ch. 1: Notes on RBC Model 1 1 The Basic RBC Model 1.1 Description of Model Variables y z k L c I w r output level of technology (exogenous) capital at end of
Business Cycles: The Classical Approach
 San Francisco State University ECON 302 Business Cycles: The Classical Approach Introduction Michael Bar Recall from the introduction that the output per capita in the U.S. is groing steady, but there
San Francisco State University ECON 302 Business Cycles: The Classical Approach Introduction Michael Bar Recall from the introduction that the output per capita in the U.S. is groing steady, but there
The Basic New Keynesian Model. Jordi Galí. November 2010
 The Basic New Keynesian Model by Jordi Galí November 2 Motivation and Outline Evidence on Money, Output, and Prices: Short Run E ects of Monetary Policy Shocks (i) persistent e ects on real variables (ii)
The Basic New Keynesian Model by Jordi Galí November 2 Motivation and Outline Evidence on Money, Output, and Prices: Short Run E ects of Monetary Policy Shocks (i) persistent e ects on real variables (ii)
Real Business Cycle Model (RBC)
 Real Business Cycle Model (RBC) Seyed Ali Madanizadeh November 2013 RBC Model Lucas 1980: One of the functions of theoretical economics is to provide fully articulated, artificial economic systems that
Real Business Cycle Model (RBC) Seyed Ali Madanizadeh November 2013 RBC Model Lucas 1980: One of the functions of theoretical economics is to provide fully articulated, artificial economic systems that
ECON 5118 Macroeconomic Theory
 ECON 5118 Macroeconomic Theory Winter 013 Test 1 February 1, 013 Answer ALL Questions Time Allowed: 1 hour 0 min Attention: Please write your answers on the answer book provided Use the right-side pages
ECON 5118 Macroeconomic Theory Winter 013 Test 1 February 1, 013 Answer ALL Questions Time Allowed: 1 hour 0 min Attention: Please write your answers on the answer book provided Use the right-side pages
Macroeconomics II Money in the Utility function
 McCless]Prof. McCless UCEMA Prof. McCless UCEMA Macroeconomics II Money in the Utility function [ October, 00 Money in the Utility function Money in the Utility function Alternative way to add money to
McCless]Prof. McCless UCEMA Prof. McCless UCEMA Macroeconomics II Money in the Utility function [ October, 00 Money in the Utility function Money in the Utility function Alternative way to add money to
Lecture 3, November 30: The Basic New Keynesian Model (Galí, Chapter 3)
 MakØk3, Fall 2 (blok 2) Business cycles and monetary stabilization policies Henrik Jensen Department of Economics University of Copenhagen Lecture 3, November 3: The Basic New Keynesian Model (Galí, Chapter
MakØk3, Fall 2 (blok 2) Business cycles and monetary stabilization policies Henrik Jensen Department of Economics University of Copenhagen Lecture 3, November 3: The Basic New Keynesian Model (Galí, Chapter
Advanced Economic Growth: Lecture 8, Technology Di usion, Trade and Interdependencies: Di usion of Technology
 Advanced Economic Growth: Lecture 8, Technology Di usion, Trade and Interdependencies: Di usion of Technology Daron Acemoglu MIT October 3, 2007 Daron Acemoglu (MIT) Advanced Growth Lecture 8 October 3,
Advanced Economic Growth: Lecture 8, Technology Di usion, Trade and Interdependencies: Di usion of Technology Daron Acemoglu MIT October 3, 2007 Daron Acemoglu (MIT) Advanced Growth Lecture 8 October 3,
Public Economics The Macroeconomic Perspective Chapter 2: The Ramsey Model. Burkhard Heer University of Augsburg, Germany
 Public Economics The Macroeconomic Perspective Chapter 2: The Ramsey Model Burkhard Heer University of Augsburg, Germany October 3, 2018 Contents I 1 Central Planner 2 3 B. Heer c Public Economics: Chapter
Public Economics The Macroeconomic Perspective Chapter 2: The Ramsey Model Burkhard Heer University of Augsburg, Germany October 3, 2018 Contents I 1 Central Planner 2 3 B. Heer c Public Economics: Chapter
Econ 7110 slides Growth models: Solow, Diamond, Malthus. January 8, 2017
 Econ 7110 slides Growth models: Solow, Diamond, Malthus January 8, 2017 Production functions Standard setting: Y =output, K (capital) and L (labor) K, L referred to as inputs Usually assumed to satisfy:
Econ 7110 slides Growth models: Solow, Diamond, Malthus January 8, 2017 Production functions Standard setting: Y =output, K (capital) and L (labor) K, L referred to as inputs Usually assumed to satisfy:
Dynamic Macroeconomics: Problem Set 4
 Dynamic Macroeconomics: Problem Set 4 Universität Siegen Dynamic Macroeconomics 1 / 28 1 Computing growth rates 2 Golden rule saving rate 3 Simulation of the Solow Model 4 Growth accounting Dynamic Macroeconomics
Dynamic Macroeconomics: Problem Set 4 Universität Siegen Dynamic Macroeconomics 1 / 28 1 Computing growth rates 2 Golden rule saving rate 3 Simulation of the Solow Model 4 Growth accounting Dynamic Macroeconomics
Chapter 9 Solow. O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos. Computational Economics: a concise introduction
 Chapter 9 Solow O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics: a concise introduction O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 1 / 27 Overview 1 Introduction 2 Economic model 3 Computational
Chapter 9 Solow O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics: a concise introduction O. Afonso, P. B. Vasconcelos Computational Economics 1 / 27 Overview 1 Introduction 2 Economic model 3 Computational
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK AT ALBANY Department of Economics
 STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK AT ALBANY Department of Economics Ph. D. Comprehensive Examination: Macroeconomics Fall, 202 Answer Key to Section 2 Questions Section. (Suggested Time: 45 Minutes) For 3 of
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK AT ALBANY Department of Economics Ph. D. Comprehensive Examination: Macroeconomics Fall, 202 Answer Key to Section 2 Questions Section. (Suggested Time: 45 Minutes) For 3 of
Growth. Growth Theory. Mark Huggett 1. 1 Georgetown. January 26, 2018
 Growth Theory Mark Huggett 1 1 Georgetown January 26, 2018 Growth Theory: The Agenda 1. Facts motivating theory 2. Basic Solow model 3. Model properties 4. How to use the model 5. Full Solow model 6. Use
Growth Theory Mark Huggett 1 1 Georgetown January 26, 2018 Growth Theory: The Agenda 1. Facts motivating theory 2. Basic Solow model 3. Model properties 4. How to use the model 5. Full Solow model 6. Use
EC744 Lecture Notes: Economic Dynamics. Prof. Jianjun Miao
 EC744 Lecture Notes: Economic Dynamics Prof. Jianjun Miao 1 Deterministic Dynamic System State vector x t 2 R n State transition function x t = g x 0 ; t; ; x 0 = x 0 ; parameter 2 R p A parametrized dynamic
EC744 Lecture Notes: Economic Dynamics Prof. Jianjun Miao 1 Deterministic Dynamic System State vector x t 2 R n State transition function x t = g x 0 ; t; ; x 0 = x 0 ; parameter 2 R p A parametrized dynamic
Assumption 5. The technology is represented by a production function, F : R 3 + R +, F (K t, N t, A t )
 6. Economic growth Let us recall the main facts on growth examined in the first chapter and add some additional ones. (1) Real output (per-worker) roughly grows at a constant rate (i.e. labor productivity
6. Economic growth Let us recall the main facts on growth examined in the first chapter and add some additional ones. (1) Real output (per-worker) roughly grows at a constant rate (i.e. labor productivity
ECON2285: Mathematical Economics
 ECON2285: Mathematical Economics Yulei Luo Economics, HKU September 17, 2018 Luo, Y. (Economics, HKU) ME September 17, 2018 1 / 46 Static Optimization and Extreme Values In this topic, we will study goal
ECON2285: Mathematical Economics Yulei Luo Economics, HKU September 17, 2018 Luo, Y. (Economics, HKU) ME September 17, 2018 1 / 46 Static Optimization and Extreme Values In this topic, we will study goal
Solving a Dynamic (Stochastic) General Equilibrium Model under the Discrete Time Framework
 Solving a Dynamic (Stochastic) General Equilibrium Model under the Discrete Time Framework Dongpeng Liu Nanjing University Sept 2016 D. Liu (NJU) Solving D(S)GE 09/16 1 / 63 Introduction Targets of the
Solving a Dynamic (Stochastic) General Equilibrium Model under the Discrete Time Framework Dongpeng Liu Nanjing University Sept 2016 D. Liu (NJU) Solving D(S)GE 09/16 1 / 63 Introduction Targets of the
Small Open Economy RBC Model Uribe, Chapter 4
 Small Open Economy RBC Model Uribe, Chapter 4 1 Basic Model 1.1 Uzawa Utility E 0 t=0 θ t U (c t, h t ) θ 0 = 1 θ t+1 = β (c t, h t ) θ t ; β c < 0; β h > 0. Time-varying discount factor With a constant
Small Open Economy RBC Model Uribe, Chapter 4 1 Basic Model 1.1 Uzawa Utility E 0 t=0 θ t U (c t, h t ) θ 0 = 1 θ t+1 = β (c t, h t ) θ t ; β c < 0; β h > 0. Time-varying discount factor With a constant
1 Regression with Time Series Variables
 1 Regression with Time Series Variables With time series regression, Y might not only depend on X, but also lags of Y and lags of X Autoregressive Distributed lag (or ADL(p; q)) model has these features:
1 Regression with Time Series Variables With time series regression, Y might not only depend on X, but also lags of Y and lags of X Autoregressive Distributed lag (or ADL(p; q)) model has these features:
1 Bewley Economies with Aggregate Uncertainty
 1 Bewley Economies with Aggregate Uncertainty Sofarwehaveassumedawayaggregatefluctuations (i.e., business cycles) in our description of the incomplete-markets economies with uninsurable idiosyncratic risk
1 Bewley Economies with Aggregate Uncertainty Sofarwehaveassumedawayaggregatefluctuations (i.e., business cycles) in our description of the incomplete-markets economies with uninsurable idiosyncratic risk
Economics Computation Winter Prof. Garey Ramey. Exercises : 5 ; B = AX = B: 5 ; h 3 1 6
 Economics 80 - Computation Winter 01-18 Prof. Garey Ramey Exercises Exercise 1. Consider the following maices: 9 A = 1 8 ; B = 1 1 1 : a. Enter A and B as Matlab variables. b. Calculate the following maices:
Economics 80 - Computation Winter 01-18 Prof. Garey Ramey Exercises Exercise 1. Consider the following maices: 9 A = 1 8 ; B = 1 1 1 : a. Enter A and B as Matlab variables. b. Calculate the following maices:
Analysis of the speed of convergence
 Analysis of the speed of convergence Lionel Artige HEC Université de Liège 30 january 2010 Neoclassical Production Function We will assume a production function of the Cobb-Douglas form: F[K(t), L(t),
Analysis of the speed of convergence Lionel Artige HEC Université de Liège 30 january 2010 Neoclassical Production Function We will assume a production function of the Cobb-Douglas form: F[K(t), L(t),
Neoclassical Growth Model / Cake Eating Problem
 Dynamic Optimization Institute for Advanced Studies Vienna, Austria by Gabriel S. Lee February 1-4, 2008 An Overview and Introduction to Dynamic Programming using the Neoclassical Growth Model and Cake
Dynamic Optimization Institute for Advanced Studies Vienna, Austria by Gabriel S. Lee February 1-4, 2008 An Overview and Introduction to Dynamic Programming using the Neoclassical Growth Model and Cake
Advanced Macroeconomics II. Monetary Models with Nominal Rigidities. Jordi Galí Universitat Pompeu Fabra April 2018
 Advanced Macroeconomics II Monetary Models with Nominal Rigidities Jordi Galí Universitat Pompeu Fabra April 208 Motivation Empirical Evidence Macro evidence on the e ects of monetary policy shocks (i)
Advanced Macroeconomics II Monetary Models with Nominal Rigidities Jordi Galí Universitat Pompeu Fabra April 208 Motivation Empirical Evidence Macro evidence on the e ects of monetary policy shocks (i)
Solutions to Problem Set 4 Macro II (14.452)
 Solutions to Problem Set 4 Macro II (14.452) Francisco A. Gallego 05/11 1 Money as a Factor of Production (Dornbusch and Frenkel, 1973) The shortcut used by Dornbusch and Frenkel to introduce money in
Solutions to Problem Set 4 Macro II (14.452) Francisco A. Gallego 05/11 1 Money as a Factor of Production (Dornbusch and Frenkel, 1973) The shortcut used by Dornbusch and Frenkel to introduce money in
The Ramsey Model. Alessandra Pelloni. October TEI Lecture. Alessandra Pelloni (TEI Lecture) Economic Growth October / 61
 The Ramsey Model Alessandra Pelloni TEI Lecture October 2015 Alessandra Pelloni (TEI Lecture) Economic Growth October 2015 1 / 61 Introduction Introduction Introduction Ramsey-Cass-Koopmans model: di ers
The Ramsey Model Alessandra Pelloni TEI Lecture October 2015 Alessandra Pelloni (TEI Lecture) Economic Growth October 2015 1 / 61 Introduction Introduction Introduction Ramsey-Cass-Koopmans model: di ers
Advanced Macroeconomics II. Real Business Cycle Models. Jordi Galí. Universitat Pompeu Fabra Spring 2018
 Advanced Macroeconomics II Real Business Cycle Models Jordi Galí Universitat Pompeu Fabra Spring 2018 Assumptions Optimization by consumers and rms Perfect competition General equilibrium Absence of a
Advanced Macroeconomics II Real Business Cycle Models Jordi Galí Universitat Pompeu Fabra Spring 2018 Assumptions Optimization by consumers and rms Perfect competition General equilibrium Absence of a
Foundation of (virtually) all DSGE models (e.g., RBC model) is Solow growth model
 THE BASELINE RBC MODEL: THEORY AND COMPUTATION FEBRUARY, 202 STYLIZED MACRO FACTS Foundation of (virtually all DSGE models (e.g., RBC model is Solow growth model So want/need/desire business-cycle models
THE BASELINE RBC MODEL: THEORY AND COMPUTATION FEBRUARY, 202 STYLIZED MACRO FACTS Foundation of (virtually all DSGE models (e.g., RBC model is Solow growth model So want/need/desire business-cycle models
Economics 202A Lecture Outline #3 (version 1.0)
 Economics 202A Lecture Outline #3 (version.0) Maurice Obstfeld Steady State of the Ramsey-Cass-Koopmans Model In the last few lectures we have seen how to set up the Ramsey-Cass- Koopmans Model in discrete
Economics 202A Lecture Outline #3 (version.0) Maurice Obstfeld Steady State of the Ramsey-Cass-Koopmans Model In the last few lectures we have seen how to set up the Ramsey-Cass- Koopmans Model in discrete
Econ 5110 Solutions to the Practice Questions for the Midterm Exam
 Econ 50 Solutions to the Practice Questions for the Midterm Exam Spring 202 Real Business Cycle Theory. Consider a simple neoclassical growth model (notation similar to class) where all agents are identical
Econ 50 Solutions to the Practice Questions for the Midterm Exam Spring 202 Real Business Cycle Theory. Consider a simple neoclassical growth model (notation similar to class) where all agents are identical
Ramsey Cass Koopmans Model (1): Setup of the Model and Competitive Equilibrium Path
 Ramsey Cass Koopmans Model (1): Setup of the Model and Competitive Equilibrium Path Ryoji Ohdoi Dept. of Industrial Engineering and Economics, Tokyo Tech This lecture note is mainly based on Ch. 8 of Acemoglu
Ramsey Cass Koopmans Model (1): Setup of the Model and Competitive Equilibrium Path Ryoji Ohdoi Dept. of Industrial Engineering and Economics, Tokyo Tech This lecture note is mainly based on Ch. 8 of Acemoglu
Neoclassical Business Cycle Model
 Neoclassical Business Cycle Model Prof. Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Fall 2015 1 / 36 Production Economy Last time: studied equilibrium in an endowment economy Now: study equilibrium in an economy
Neoclassical Business Cycle Model Prof. Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Fall 2015 1 / 36 Production Economy Last time: studied equilibrium in an endowment economy Now: study equilibrium in an economy
problem. max Both k (0) and h (0) are given at time 0. (a) Write down the Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman (HJB) Equation in the dynamic programming
 1. Endogenous Growth with Human Capital Consider the following endogenous growth model with both physical capital (k (t)) and human capital (h (t)) in continuous time. The representative household solves
1. Endogenous Growth with Human Capital Consider the following endogenous growth model with both physical capital (k (t)) and human capital (h (t)) in continuous time. The representative household solves
A simple macro dynamic model with endogenous saving rate: the representative agent model
 A simple macro dynamic model with endogenous saving rate: the representative agent model Virginia Sánchez-Marcos Macroeconomics, MIE-UNICAN Macroeconomics (MIE-UNICAN) A simple macro dynamic model with
A simple macro dynamic model with endogenous saving rate: the representative agent model Virginia Sánchez-Marcos Macroeconomics, MIE-UNICAN Macroeconomics (MIE-UNICAN) A simple macro dynamic model with
Dynamic Optimization: An Introduction
 Dynamic Optimization An Introduction M. C. Sunny Wong University of San Francisco University of Houston, June 20, 2014 Outline 1 Background What is Optimization? EITM: The Importance of Optimization 2
Dynamic Optimization An Introduction M. C. Sunny Wong University of San Francisco University of Houston, June 20, 2014 Outline 1 Background What is Optimization? EITM: The Importance of Optimization 2
Chapter 6. Maximum Likelihood Analysis of Dynamic Stochastic General Equilibrium (DSGE) Models
 Chapter 6. Maximum Likelihood Analysis of Dynamic Stochastic General Equilibrium (DSGE) Models Fall 22 Contents Introduction 2. An illustrative example........................... 2.2 Discussion...................................
Chapter 6. Maximum Likelihood Analysis of Dynamic Stochastic General Equilibrium (DSGE) Models Fall 22 Contents Introduction 2. An illustrative example........................... 2.2 Discussion...................................
TOBB-ETU - Econ 532 Practice Problems II (Solutions)
 TOBB-ETU - Econ 532 Practice Problems II (Solutions) Q: Ramsey Model: Exponential Utility Assume that in nite-horizon households maximize a utility function of the exponential form 1R max U = e (n )t (1=)e
TOBB-ETU - Econ 532 Practice Problems II (Solutions) Q: Ramsey Model: Exponential Utility Assume that in nite-horizon households maximize a utility function of the exponential form 1R max U = e (n )t (1=)e
Evaluating Structural Vector Autoregression Models in Monetary Economies
 Evaluating Structural Vector Autoregression Models in Monetary Economies Bin Li Research Department International Monetary Fund March 9 Abstract This paper uses Monte Carlo simulations to evaluate alternative
Evaluating Structural Vector Autoregression Models in Monetary Economies Bin Li Research Department International Monetary Fund March 9 Abstract This paper uses Monte Carlo simulations to evaluate alternative
(a) Write down the Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman (HJB) Equation in the dynamic programming
 1. Government Purchases and Endogenous Growth Consider the following endogenous growth model with government purchases (G) in continuous time. Government purchases enhance production, and the production
1. Government Purchases and Endogenous Growth Consider the following endogenous growth model with government purchases (G) in continuous time. Government purchases enhance production, and the production
The Solow Model. Prof. Lutz Hendricks. January 26, Econ520
 The Solow Model Prof. Lutz Hendricks Econ520 January 26, 2017 1 / 28 Issues The production model measures the proximate causes of income gaps. Now we start to look at deep causes. The Solow model answers
The Solow Model Prof. Lutz Hendricks Econ520 January 26, 2017 1 / 28 Issues The production model measures the proximate causes of income gaps. Now we start to look at deep causes. The Solow model answers
Part A: Answer question A1 (required), plus either question A2 or A3.
 Ph.D. Core Exam -- Macroeconomics 5 January 2015 -- 8:00 am to 3:00 pm Part A: Answer question A1 (required), plus either question A2 or A3. A1 (required): Ending Quantitative Easing Now that the U.S.
Ph.D. Core Exam -- Macroeconomics 5 January 2015 -- 8:00 am to 3:00 pm Part A: Answer question A1 (required), plus either question A2 or A3. A1 (required): Ending Quantitative Easing Now that the U.S.
Endogenous Growth Theory
 Endogenous Growth Theory Lecture Notes for the winter term 2010/2011 Ingrid Ott Tim Deeken October 21st, 2010 CHAIR IN ECONOMIC POLICY KIT University of the State of Baden-Wuerttemberg and National Laboratory
Endogenous Growth Theory Lecture Notes for the winter term 2010/2011 Ingrid Ott Tim Deeken October 21st, 2010 CHAIR IN ECONOMIC POLICY KIT University of the State of Baden-Wuerttemberg and National Laboratory
From Difference to Differential Equations I
 From Difference to Differential Equations I Start with a simple difference equation x (t + 1) x (t) = g(x (t)). (30) Now consider the following approximation for any t [0, 1], x (t + t) x (t) t g(x (t)),
From Difference to Differential Equations I Start with a simple difference equation x (t + 1) x (t) = g(x (t)). (30) Now consider the following approximation for any t [0, 1], x (t + t) x (t) t g(x (t)),
1 The social planner problem
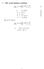 The social planner problem max C t;k t+ U t = E t X t C t () that can be written as: s.t.: Y t = A t K t (2) Y t = C t + I t (3) I t = K t+ (4) A t = A A t (5) et t i:i:d: 0; 2 max C t;k t+ U t = E t "
The social planner problem max C t;k t+ U t = E t X t C t () that can be written as: s.t.: Y t = A t K t (2) Y t = C t + I t (3) I t = K t+ (4) A t = A A t (5) et t i:i:d: 0; 2 max C t;k t+ U t = E t "
Fluctuations. Shocks, Uncertainty, and the Consumption/Saving Choice
 Fluctuations. Shocks, Uncertainty, and the Consumption/Saving Choice Olivier Blanchard April 2002 14.452. Spring 2002. Topic 2. 14.452. Spring, 2002 2 Want to start with a model with two ingredients: ²
Fluctuations. Shocks, Uncertainty, and the Consumption/Saving Choice Olivier Blanchard April 2002 14.452. Spring 2002. Topic 2. 14.452. Spring, 2002 2 Want to start with a model with two ingredients: ²
Modeling Economic Growth Using Differential Equations
 Modeling Economic Growth Using Differential Equations Chad Tanioka Occidental College February 25, 2016 Chad Tanioka (Occidental College) Modeling Economic Growth using DE February 25, 2016 1 / 28 Overview
Modeling Economic Growth Using Differential Equations Chad Tanioka Occidental College February 25, 2016 Chad Tanioka (Occidental College) Modeling Economic Growth using DE February 25, 2016 1 / 28 Overview
Intermediate Macroeconomics, EC2201. L2: Economic growth II
 Intermediate Macroeconomics, EC2201 L2: Economic growth II Anna Seim Department of Economics, Stockholm University Spring 2017 1 / 64 Contents and literature The Solow model. Human capital. The Romer model.
Intermediate Macroeconomics, EC2201 L2: Economic growth II Anna Seim Department of Economics, Stockholm University Spring 2017 1 / 64 Contents and literature The Solow model. Human capital. The Romer model.
Housing and the Business Cycle
 Housing and the Business Cycle Morris Davis and Jonathan Heathcote Winter 2009 Huw Lloyd-Ellis () ECON917 Winter 2009 1 / 21 Motivation Need to distinguish between housing and non housing investment,!
Housing and the Business Cycle Morris Davis and Jonathan Heathcote Winter 2009 Huw Lloyd-Ellis () ECON917 Winter 2009 1 / 21 Motivation Need to distinguish between housing and non housing investment,!
Growth: Facts and Theories
 Notes on Growth: Facts and Theories Intermediate Macroeconomics Spring 2006 Guido Menzio University of Pennsylvania Growth In the last part of the course we are going to study economic growth, i.e. the
Notes on Growth: Facts and Theories Intermediate Macroeconomics Spring 2006 Guido Menzio University of Pennsylvania Growth In the last part of the course we are going to study economic growth, i.e. the
Problem 1 (30 points)
 Problem (30 points) Prof. Robert King Consider an economy in which there is one period and there are many, identical households. Each household derives utility from consumption (c), leisure (l) and a public
Problem (30 points) Prof. Robert King Consider an economy in which there is one period and there are many, identical households. Each household derives utility from consumption (c), leisure (l) and a public
Lecture 3: Dynamics of small open economies
 Lecture 3: Dynamics of small open economies Open economy macroeconomics, Fall 2006 Ida Wolden Bache September 5, 2006 Dynamics of small open economies Required readings: OR chapter 2. 2.3 Supplementary
Lecture 3: Dynamics of small open economies Open economy macroeconomics, Fall 2006 Ida Wolden Bache September 5, 2006 Dynamics of small open economies Required readings: OR chapter 2. 2.3 Supplementary
FEDERAL RESERVE BANK of ATLANTA
 FEDERAL RESERVE BANK of ATLANTA On the Solution of the Growth Model with Investment-Specific Technological Change Jesús Fernández-Villaverde and Juan Francisco Rubio-Ramírez Working Paper 2004-39 December
FEDERAL RESERVE BANK of ATLANTA On the Solution of the Growth Model with Investment-Specific Technological Change Jesús Fernández-Villaverde and Juan Francisco Rubio-Ramírez Working Paper 2004-39 December
Lecture 5: The neoclassical growth model
 THE UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON Paul Klein Office: Murray Building, 3005 Email: p.klein@soton.ac.uk URL: http://paulklein.se Economics 3010 Topics in Macroeconomics 3 Autumn 2010 Lecture 5: The neoclassical
THE UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON Paul Klein Office: Murray Building, 3005 Email: p.klein@soton.ac.uk URL: http://paulklein.se Economics 3010 Topics in Macroeconomics 3 Autumn 2010 Lecture 5: The neoclassical
1. Using the model and notations covered in class, the expected returns are:
 Econ 510a second half Yale University Fall 2006 Prof. Tony Smith HOMEWORK #5 This homework assignment is due at 5PM on Friday, December 8 in Marnix Amand s mailbox. Solution 1. a In the Mehra-Prescott
Econ 510a second half Yale University Fall 2006 Prof. Tony Smith HOMEWORK #5 This homework assignment is due at 5PM on Friday, December 8 in Marnix Amand s mailbox. Solution 1. a In the Mehra-Prescott
The Ramsey Model. (Lecture Note, Advanced Macroeconomics, Thomas Steger, SS 2013)
 The Ramsey Model (Lecture Note, Advanced Macroeconomics, Thomas Steger, SS 213) 1 Introduction The Ramsey model (or neoclassical growth model) is one of the prototype models in dynamic macroeconomics.
The Ramsey Model (Lecture Note, Advanced Macroeconomics, Thomas Steger, SS 213) 1 Introduction The Ramsey model (or neoclassical growth model) is one of the prototype models in dynamic macroeconomics.
Macroeconomics Field Exam. August 2007
 Macroeconomics Field Exam August 2007 Answer all questions in the exam. Suggested times correspond to the questions weights in the exam grade. Make your answers as precise as possible, using graphs, equations,
Macroeconomics Field Exam August 2007 Answer all questions in the exam. Suggested times correspond to the questions weights in the exam grade. Make your answers as precise as possible, using graphs, equations,
Modern Macroeconomics II
 Modern Macroeconomics II Katsuya Takii OSIPP Katsuya Takii (Institute) Modern Macroeconomics II 1 / 461 Introduction Purpose: This lecture is aimed at providing students with standard methods in modern
Modern Macroeconomics II Katsuya Takii OSIPP Katsuya Takii (Institute) Modern Macroeconomics II 1 / 461 Introduction Purpose: This lecture is aimed at providing students with standard methods in modern
Economic Growth: Lecture 8, Overlapping Generations
 14.452 Economic Growth: Lecture 8, Overlapping Generations Daron Acemoglu MIT November 20, 2018 Daron Acemoglu (MIT) Economic Growth Lecture 8 November 20, 2018 1 / 46 Growth with Overlapping Generations
14.452 Economic Growth: Lecture 8, Overlapping Generations Daron Acemoglu MIT November 20, 2018 Daron Acemoglu (MIT) Economic Growth Lecture 8 November 20, 2018 1 / 46 Growth with Overlapping Generations
Session 4: Money. Jean Imbs. November 2010
 Session 4: Jean November 2010 I So far, focused on real economy. Real quantities consumed, produced, invested. No money, no nominal in uences. I Now, introduce nominal dimension in the economy. First and
Session 4: Jean November 2010 I So far, focused on real economy. Real quantities consumed, produced, invested. No money, no nominal in uences. I Now, introduce nominal dimension in the economy. First and
Graduate Macro Theory II: Notes on Quantitative Analysis in DSGE Models
 Graduate Macro Theory II: Notes on Quantitative Analysis in DSGE Models Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Spring 2011 This note describes very briefly how to conduct quantitative analysis on a linearized
Graduate Macro Theory II: Notes on Quantitative Analysis in DSGE Models Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Spring 2011 This note describes very briefly how to conduct quantitative analysis on a linearized
Economics 2: Growth (Growth in the Solow Model)
 Economics 2: Growth (Growth in the Solow Model) Lecture 3, Week 7 Solow Model - I Definition (Solow Model I) The most basic Solow model with no population growth or technological progress. Solow Model
Economics 2: Growth (Growth in the Solow Model) Lecture 3, Week 7 Solow Model - I Definition (Solow Model I) The most basic Solow model with no population growth or technological progress. Solow Model
PANEL DISCUSSION: THE ROLE OF POTENTIAL OUTPUT IN POLICYMAKING
 PANEL DISCUSSION: THE ROLE OF POTENTIAL OUTPUT IN POLICYMAKING James Bullard* Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis 33rd Annual Economic Policy Conference St. Louis, MO October 17, 2008 Views expressed are
PANEL DISCUSSION: THE ROLE OF POTENTIAL OUTPUT IN POLICYMAKING James Bullard* Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis 33rd Annual Economic Policy Conference St. Louis, MO October 17, 2008 Views expressed are
Lecture 7: Linear-Quadratic Dynamic Programming Real Business Cycle Models
 Lecture 7: Linear-Quadratic Dynamic Programming Real Business Cycle Models Shinichi Nishiyama Graduate School of Economics Kyoto University January 10, 2019 Abstract In this lecture, we solve and simulate
Lecture 7: Linear-Quadratic Dynamic Programming Real Business Cycle Models Shinichi Nishiyama Graduate School of Economics Kyoto University January 10, 2019 Abstract In this lecture, we solve and simulate
A Summary of Economic Methodology
 A Summary of Economic Methodology I. The Methodology of Theoretical Economics All economic analysis begins with theory, based in part on intuitive insights that naturally spring from certain stylized facts,
A Summary of Economic Methodology I. The Methodology of Theoretical Economics All economic analysis begins with theory, based in part on intuitive insights that naturally spring from certain stylized facts,
Lecture 1: The Classical Optimal Growth Model
 Lecture 1: The Classical Optimal Growth Model This lecture introduces the classical optimal economic growth problem. Solving the problem will require a dynamic optimisation technique: a simple calculus
Lecture 1: The Classical Optimal Growth Model This lecture introduces the classical optimal economic growth problem. Solving the problem will require a dynamic optimisation technique: a simple calculus
z = f (x; y) f (x ; y ) f (x; y) f (x; y )
 BEEM0 Optimization Techiniques for Economists Lecture Week 4 Dieter Balkenborg Departments of Economics University of Exeter Since the fabric of the universe is most perfect, and is the work of a most
BEEM0 Optimization Techiniques for Economists Lecture Week 4 Dieter Balkenborg Departments of Economics University of Exeter Since the fabric of the universe is most perfect, and is the work of a most
Advanced Economic Growth: Lecture 21: Stochastic Dynamic Programming and Applications
 Advanced Economic Growth: Lecture 21: Stochastic Dynamic Programming and Applications Daron Acemoglu MIT November 19, 2007 Daron Acemoglu (MIT) Advanced Growth Lecture 21 November 19, 2007 1 / 79 Stochastic
Advanced Economic Growth: Lecture 21: Stochastic Dynamic Programming and Applications Daron Acemoglu MIT November 19, 2007 Daron Acemoglu (MIT) Advanced Growth Lecture 21 November 19, 2007 1 / 79 Stochastic
The Solow Growth Model
 The Solow Growth Model 1. Set-Up 2. Dynamics, Simulations and Steady-States 3. Comparative Dynamics 4. Golden Rule 5. Convergence 1 Set-Up Closed economy, single good produced each period, Yt. Discrete
The Solow Growth Model 1. Set-Up 2. Dynamics, Simulations and Steady-States 3. Comparative Dynamics 4. Golden Rule 5. Convergence 1 Set-Up Closed economy, single good produced each period, Yt. Discrete
Volume 29, Issue 4. Stability under learning: the neo-classical growth problem
 Volume 29, Issue 4 Stability under learning: the neo-classical growth problem Orlando Gomes ISCAL - IPL; Economics Research Center [UNIDE/ISCTE - ERC] Abstract A local stability condition for the standard
Volume 29, Issue 4 Stability under learning: the neo-classical growth problem Orlando Gomes ISCAL - IPL; Economics Research Center [UNIDE/ISCTE - ERC] Abstract A local stability condition for the standard
Chapter 9. Natural Resources and Economic Growth. Instructor: Dmytro Hryshko
 Chapter 9. Natural Resources and Economic Growth Instructor: Dmytro Hryshko Motivation We want to understand growth in the presence of the earth's nite supply of arable land and nonrenewable natural resources
Chapter 9. Natural Resources and Economic Growth Instructor: Dmytro Hryshko Motivation We want to understand growth in the presence of the earth's nite supply of arable land and nonrenewable natural resources
Topic 5: The Difference Equation
 Topic 5: The Difference Equation Yulei Luo Economics, HKU October 30, 2017 Luo, Y. (Economics, HKU) ME October 30, 2017 1 / 42 Discrete-time, Differences, and Difference Equations When time is taken to
Topic 5: The Difference Equation Yulei Luo Economics, HKU October 30, 2017 Luo, Y. (Economics, HKU) ME October 30, 2017 1 / 42 Discrete-time, Differences, and Difference Equations When time is taken to
Chapter 11 The Stochastic Growth Model and Aggregate Fluctuations
 George Alogoskoufis, Dynamic Macroeconomics, 2016 Chapter 11 The Stochastic Growth Model and Aggregate Fluctuations In previous chapters we studied the long run evolution of output and consumption, real
George Alogoskoufis, Dynamic Macroeconomics, 2016 Chapter 11 The Stochastic Growth Model and Aggregate Fluctuations In previous chapters we studied the long run evolution of output and consumption, real
Learning to Optimize: Theory and Applications
 Learning to Optimize: Theory and Applications George W. Evans University of Oregon and University of St Andrews Bruce McGough University of Oregon WAMS, December 12, 2015 Outline Introduction Shadow-price
Learning to Optimize: Theory and Applications George W. Evans University of Oregon and University of St Andrews Bruce McGough University of Oregon WAMS, December 12, 2015 Outline Introduction Shadow-price
Problem Set 2: Sketch of Answers
 Problem Set 2: Sketch of Answers HEC Lausanne, Département d économie politique Business Cycles 2003 Prof. Aude Pommeret Ivan Jaccard April 30, 2004 Part I: Open questions 1. Explain why the consensus
Problem Set 2: Sketch of Answers HEC Lausanne, Département d économie politique Business Cycles 2003 Prof. Aude Pommeret Ivan Jaccard April 30, 2004 Part I: Open questions 1. Explain why the consensus
Macroeconomics Theory II
 Macroeconomics Theory II Francesco Franco FEUNL February 2016 Francesco Franco Macroeconomics Theory II 1/23 Housekeeping. Class organization. Website with notes and papers as no "Mas-Collel" in macro
Macroeconomics Theory II Francesco Franco FEUNL February 2016 Francesco Franco Macroeconomics Theory II 1/23 Housekeeping. Class organization. Website with notes and papers as no "Mas-Collel" in macro
Lecture 2: Firms, Jobs and Policy
 Lecture 2: Firms, Jobs and Policy Economics 522 Esteban Rossi-Hansberg Princeton University Spring 2014 ERH (Princeton University ) Lecture 2: Firms, Jobs and Policy Spring 2014 1 / 34 Restuccia and Rogerson
Lecture 2: Firms, Jobs and Policy Economics 522 Esteban Rossi-Hansberg Princeton University Spring 2014 ERH (Princeton University ) Lecture 2: Firms, Jobs and Policy Spring 2014 1 / 34 Restuccia and Rogerson
Practice Questions for Mid-Term I. Question 1: Consider the Cobb-Douglas production function in intensive form:
 Practice Questions for Mid-Term I Question 1: Consider the Cobb-Douglas production function in intensive form: y f(k) = k α ; α (0, 1) (1) where y and k are output per worker and capital per worker respectively.
Practice Questions for Mid-Term I Question 1: Consider the Cobb-Douglas production function in intensive form: y f(k) = k α ; α (0, 1) (1) where y and k are output per worker and capital per worker respectively.
Solution for Problem Set 3
 Solution for Problem Set 3 Q. Heterogeneous Expectations. Consider following dynamic IS-LM economy in Lecture Notes 8: IS curve: y t = ar t + u t (.) where y t is output, r t is the real interest rate,
Solution for Problem Set 3 Q. Heterogeneous Expectations. Consider following dynamic IS-LM economy in Lecture Notes 8: IS curve: y t = ar t + u t (.) where y t is output, r t is the real interest rate,
The Solow Growth Model
 The Solow Growth Model Lectures 5, 6 & 7 Topics in Macroeconomics Topic 2 October 20, 21 & 27, 2008 Lectures 5, 6 & 7 1/37 Topics in Macroeconomics From Growth Accounting to the Solow Model Goal 1: Stylized
The Solow Growth Model Lectures 5, 6 & 7 Topics in Macroeconomics Topic 2 October 20, 21 & 27, 2008 Lectures 5, 6 & 7 1/37 Topics in Macroeconomics From Growth Accounting to the Solow Model Goal 1: Stylized
Competitive Equilibrium and the Welfare Theorems
 Competitive Equilibrium and the Welfare Theorems Craig Burnside Duke University September 2010 Craig Burnside (Duke University) Competitive Equilibrium September 2010 1 / 32 Competitive Equilibrium and
Competitive Equilibrium and the Welfare Theorems Craig Burnside Duke University September 2010 Craig Burnside (Duke University) Competitive Equilibrium September 2010 1 / 32 Competitive Equilibrium and
Non-convex Aggregate Technology and Optimal Economic Growth
 Non-convex Aggregate Technology and Optimal Economic Growth N. M. Hung y, C. Le Van z, P. Michel x September 26, 2007 Abstract This paper examines a model of optimal growth where the aggregation of two
Non-convex Aggregate Technology and Optimal Economic Growth N. M. Hung y, C. Le Van z, P. Michel x September 26, 2007 Abstract This paper examines a model of optimal growth where the aggregation of two
Macroeconomics Theory II
 Macroeconomics Theory II Francesco Franco FEUNL February 2016 Francesco Franco (FEUNL) Macroeconomics Theory II February 2016 1 / 18 Road Map Research question: we want to understand businesses cycles.
Macroeconomics Theory II Francesco Franco FEUNL February 2016 Francesco Franco (FEUNL) Macroeconomics Theory II February 2016 1 / 18 Road Map Research question: we want to understand businesses cycles.
Equilibrium in a Model with Overlapping Generations
 Equilibrium in a Model with Overlapping Generations Dynamic Macroeconomic Analysis Universidad Autonóma de Madrid Fall 2012 Dynamic Macroeconomic Analysis (UAM) OLG Fall 2012 1 / 69 1 OLG with physical
Equilibrium in a Model with Overlapping Generations Dynamic Macroeconomic Analysis Universidad Autonóma de Madrid Fall 2012 Dynamic Macroeconomic Analysis (UAM) OLG Fall 2012 1 / 69 1 OLG with physical
1 Objective. 2 Constrained optimization. 2.1 Utility maximization. Dieter Balkenborg Department of Economics
 BEE020 { Basic Mathematical Economics Week 2, Lecture Thursday 2.0.0 Constrained optimization Dieter Balkenborg Department of Economics University of Exeter Objective We give the \ rst order conditions"
BEE020 { Basic Mathematical Economics Week 2, Lecture Thursday 2.0.0 Constrained optimization Dieter Balkenborg Department of Economics University of Exeter Objective We give the \ rst order conditions"
Comprehensive Exam. Macro Spring 2014 Retake. August 22, 2014
 Comprehensive Exam Macro Spring 2014 Retake August 22, 2014 You have a total of 180 minutes to complete the exam. If a question seems ambiguous, state why, sharpen it up and answer the sharpened-up question.
Comprehensive Exam Macro Spring 2014 Retake August 22, 2014 You have a total of 180 minutes to complete the exam. If a question seems ambiguous, state why, sharpen it up and answer the sharpened-up question.
The Real Business Cycle Model
 The Real Business Cycle Model Macroeconomics II 2 The real business cycle model. Introduction This model explains the comovements in the fluctuations of aggregate economic variables around their trend.
The Real Business Cycle Model Macroeconomics II 2 The real business cycle model. Introduction This model explains the comovements in the fluctuations of aggregate economic variables around their trend.
Lecture 9: The monetary theory of the exchange rate
 Lecture 9: The monetary theory of the exchange rate Open Economy Macroeconomics, Fall 2006 Ida Wolden Bache October 24, 2006 Macroeconomic models of exchange rate determination Useful reference: Chapter
Lecture 9: The monetary theory of the exchange rate Open Economy Macroeconomics, Fall 2006 Ida Wolden Bache October 24, 2006 Macroeconomic models of exchange rate determination Useful reference: Chapter
Macroeconomics - Data & Theory
 Macroeconomics - Data & Theory Wouter J. Den Haan University of Amsterdam October 24, 2009 How to isolate the business cycle component? Easy way is to use the Hodrick-Prescott (HP) lter min fx τ,t g T
Macroeconomics - Data & Theory Wouter J. Den Haan University of Amsterdam October 24, 2009 How to isolate the business cycle component? Easy way is to use the Hodrick-Prescott (HP) lter min fx τ,t g T
