Constrained motion and generalized coordinates
|
|
|
- Jocelyn Terry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Constrained motion and generalized coordinates based on FW-13 Often, the motion of particles is restricted by constraints, and we want to: work only with independent degrees of freedom (coordinates) k = 1 k = 2 k = 2 (4) constraints correspond to forces eliminate forces of constraint Motion of N particles, n = 3N degrees of freedom, subject to k equations relating coordinates: can be time dependent the system has n - k = 3N - k degrees of freedom! holonomic constraints 66 Generalized coordinates: cartesian coordinates subject to k constraints any set of n - k = 3N - k independent coordinates that completely specify the system change of a cartesian coordinate induced from changes in generalized coordinates in dt: or, in a compact way: partial derivatives! (all other variables are kept constant) 67
2 Virtual displacements: i = 1,..., n are defined as infinitesimal, instantaneous displacements of the coordinates consistent with the constraints. 68 D Alembert s Principle based on FW-14 The forces of constraint do no work under a virtual displacement: forces of constraint are perpendicular to the direction of motion and thus they do no work We can rewrite Newton s 2nd law as: applied force D Alembert s principle: or reaction force (constraint) rotation about point 1 (perpendicular to tension) forces of constraint have disappeared! 69
3 Lagrange s equations based on FW-15 We want to rewrite D Alembert s principle in terms of the generalized coordinates. The applied force piece: The virtual work done by applied forces under virtual displacement generalized forces can be calculated directly from this definition, or from computing the virtual work done by applied forces for virtual displacement along a given generalized coordinate 70 Juggling with time derivatives: i i useful formulas: only functions of q and t function of generalized coordinates, generalized velocities and time - all physically independent variables! (if specified at a given time, subsequent motion of the system is determined) other variables are kept constant when taking partial derivatives the order of partial derivatives can be interchanged 71
4 The momentum piece: kinetic energy: 72 Now we can rewrite D Alembert s principle in terms of the generalized coordinates: generalized forces kinetic energy Lagrange s equations: all q are independent and arbitrary n-k equations for n-k independent generalized coordinates (equivalent to Newton s 2nd law) 73
5 For conservative forces (potential energy depends only on the position): generalized forces are given by negative gradients with respect to corresponding generalized coordinate: Lagrange s equations for conservative forces: Lagrangian 74 Using Lagrange s equations Pendulum: θ is the generalized coordinate based on FW-16. θ pendulum equation, small small-amplitude approximation - oscillations with 75
6 Bead on a Rotating Wire Hoop: θ is the generalized coordinate hoop rotates with constant angular velocity about an axis perpendicular to the plane of the hoop and passing through the edge of the hoop. No friction, no gravity. pendulum equation 76 Moving inside a cone: A particle of mass m is constrained to move on the inside surface of a smooth cone of half-angle α. The particle is subject to a gravitational force. Determine a set of generalized coordinates and find Lagrange's equations of motion. 77
7 Rotating pendulum: The point of support of a simple pendulum of length b moves on a massless rim of radius a rotating with constant angular velocity ω. Find the equation of motion for the angle θ. 78 Pendulum with horizontally moving support: A simple pendulum of mass m2 with a mass m1 at the point of support which can move on a horizontal line in the plane in which m2 moves. Find the equation of motion for x and the angle ϕ. 79
LAGRANGIAN AND HAMILTONIAN
 LAGRANGIAN AND HAMILTONIAN A. Constraints and Degrees of Freedom. A constraint is a restriction on the freedom of motion of a system of particles in the form of a condition. The number of independent ways
LAGRANGIAN AND HAMILTONIAN A. Constraints and Degrees of Freedom. A constraint is a restriction on the freedom of motion of a system of particles in the form of a condition. The number of independent ways
Generalized Coordinates, Lagrangians
 Generalized Coordinates, Lagrangians Sourendu Gupta TIFR, Mumbai, India Classical Mechanics 2012 August 10, 2012 Generalized coordinates Consider again the motion of a simple pendulum. Since it is one
Generalized Coordinates, Lagrangians Sourendu Gupta TIFR, Mumbai, India Classical Mechanics 2012 August 10, 2012 Generalized coordinates Consider again the motion of a simple pendulum. Since it is one
D Alembert s principle of virtual work
 PH101 Lecture 9 Review of Lagrange s equations from D Alembert s Principle, Examples of Generalized Forces a way to deal with friction, and other non-conservative forces D Alembert s principle of virtual
PH101 Lecture 9 Review of Lagrange s equations from D Alembert s Principle, Examples of Generalized Forces a way to deal with friction, and other non-conservative forces D Alembert s principle of virtual
06. Lagrangian Mechanics II
 University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Classical Dynamics Physics Course Materials 2015 06. Lagrangian Mechanics II Gerhard Müller University of Rhode Island, gmuller@uri.edu Creative Commons License
University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Classical Dynamics Physics Course Materials 2015 06. Lagrangian Mechanics II Gerhard Müller University of Rhode Island, gmuller@uri.edu Creative Commons License
Rigid bodies - general theory
 Rigid bodies - general theory Kinetic Energy: based on FW-26 Consider a system on N particles with all their relative separations fixed: it has 3 translational and 3 rotational degrees of freedom. Motion
Rigid bodies - general theory Kinetic Energy: based on FW-26 Consider a system on N particles with all their relative separations fixed: it has 3 translational and 3 rotational degrees of freedom. Motion
Assignments VIII and IX, PHYS 301 (Classical Mechanics) Spring 2014 Due 3/21/14 at start of class
 Assignments VIII and IX, PHYS 301 (Classical Mechanics) Spring 2014 Due 3/21/14 at start of class Homeworks VIII and IX both center on Lagrangian mechanics and involve many of the same skills. Therefore,
Assignments VIII and IX, PHYS 301 (Classical Mechanics) Spring 2014 Due 3/21/14 at start of class Homeworks VIII and IX both center on Lagrangian mechanics and involve many of the same skills. Therefore,
PHY321 Homework Set 10
 PHY321 Homework Set 10 1. [5 pts] A small block of mass m slides without friction down a wedge-shaped block of mass M and of opening angle α. Thetriangular block itself slides along a horizontal floor,
PHY321 Homework Set 10 1. [5 pts] A small block of mass m slides without friction down a wedge-shaped block of mass M and of opening angle α. Thetriangular block itself slides along a horizontal floor,
Physics 106a, Caltech 16 October, Lecture 5: Hamilton s Principle with Constraints. Examples
 Physics 106a, Caltech 16 October, 2018 Lecture 5: Hamilton s Principle with Constraints We have been avoiding forces of constraint, because in many cases they are uninteresting, and the constraints can
Physics 106a, Caltech 16 October, 2018 Lecture 5: Hamilton s Principle with Constraints We have been avoiding forces of constraint, because in many cases they are uninteresting, and the constraints can
Physics 351, Spring 2015, Homework #5. Due at start of class, Friday, February 20, 2015 Course info is at positron.hep.upenn.
 Physics 351, Spring 2015, Homework #5. Due at start of class, Friday, February 20, 2015 Course info is at positron.hep.upenn.edu/p351 When you finish this homework, remember to visit the feedback page
Physics 351, Spring 2015, Homework #5. Due at start of class, Friday, February 20, 2015 Course info is at positron.hep.upenn.edu/p351 When you finish this homework, remember to visit the feedback page
Lecture 19: Calculus of Variations II - Lagrangian
 Lecture 19: Calculus of Variations II - Lagrangian 1. Key points Lagrangian Euler-Lagrange equation Canonical momentum Variable transformation Maple VariationalCalculus package EulerLagrange 2. Newton's
Lecture 19: Calculus of Variations II - Lagrangian 1. Key points Lagrangian Euler-Lagrange equation Canonical momentum Variable transformation Maple VariationalCalculus package EulerLagrange 2. Newton's
Lecture 4. Alexey Boyarsky. October 6, 2015
 Lecture 4 Alexey Boyarsky October 6, 2015 1 Conservation laws and symmetries 1.1 Ignorable Coordinates During the motion of a mechanical system, the 2s quantities q i and q i, (i = 1, 2,..., s) which specify
Lecture 4 Alexey Boyarsky October 6, 2015 1 Conservation laws and symmetries 1.1 Ignorable Coordinates During the motion of a mechanical system, the 2s quantities q i and q i, (i = 1, 2,..., s) which specify
Applied Mathematics B Study Guide
 Science, Engineering and Technology Portfolio School of Life and Physical Sciences Foundation Studies (Applied Science/Engineering) Applied Mathematics B Study Guide Topics Kinematics Dynamics Work, Energy
Science, Engineering and Technology Portfolio School of Life and Physical Sciences Foundation Studies (Applied Science/Engineering) Applied Mathematics B Study Guide Topics Kinematics Dynamics Work, Energy
Physical Dynamics (PHY-304)
 Physical Dynamics (PHY-304) Gabriele Travaglini March 31, 2012 1 Review of Newtonian Mechanics 1.1 One particle Lectures 1-2. Frame, velocity, acceleration, number of degrees of freedom, generalised coordinates.
Physical Dynamics (PHY-304) Gabriele Travaglini March 31, 2012 1 Review of Newtonian Mechanics 1.1 One particle Lectures 1-2. Frame, velocity, acceleration, number of degrees of freedom, generalised coordinates.
28. Pendulum phase portrait Draw the phase portrait for the pendulum (supported by an inextensible rod)
 28. Pendulum phase portrait Draw the phase portrait for the pendulum (supported by an inextensible rod) θ + ω 2 sin θ = 0. Indicate the stable equilibrium points as well as the unstable equilibrium points.
28. Pendulum phase portrait Draw the phase portrait for the pendulum (supported by an inextensible rod) θ + ω 2 sin θ = 0. Indicate the stable equilibrium points as well as the unstable equilibrium points.
Non-Linear Response of Test Mass to External Forces and Arbitrary Motion of Suspension Point
 LASER INTERFEROMETER GRAVITATIONAL WAVE OBSERVATORY -LIGO- CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Technical Note LIGO-T980005-01- D 10/28/97 Non-Linear Response of Test
LASER INTERFEROMETER GRAVITATIONAL WAVE OBSERVATORY -LIGO- CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Technical Note LIGO-T980005-01- D 10/28/97 Non-Linear Response of Test
Phys 270 Final Exam. Figure 1: Question 1
 Phys 270 Final Exam Time limit: 120 minutes Each question worths 10 points. Constants: g = 9.8m/s 2, G = 6.67 10 11 Nm 2 kg 2. 1. (a) Figure 1 shows an object with moment of inertia I and mass m oscillating
Phys 270 Final Exam Time limit: 120 minutes Each question worths 10 points. Constants: g = 9.8m/s 2, G = 6.67 10 11 Nm 2 kg 2. 1. (a) Figure 1 shows an object with moment of inertia I and mass m oscillating
Video 2.1a Vijay Kumar and Ani Hsieh
 Video 2.1a Vijay Kumar and Ani Hsieh Robo3x-1.3 1 Introduction to Lagrangian Mechanics Vijay Kumar and Ani Hsieh University of Pennsylvania Robo3x-1.3 2 Analytical Mechanics Aristotle Galileo Bernoulli
Video 2.1a Vijay Kumar and Ani Hsieh Robo3x-1.3 1 Introduction to Lagrangian Mechanics Vijay Kumar and Ani Hsieh University of Pennsylvania Robo3x-1.3 2 Analytical Mechanics Aristotle Galileo Bernoulli
Problem 1. Mathematics of rotations
 Problem 1. Mathematics of rotations (a) Show by algebraic means (i.e. no pictures) that the relationship between ω and is: φ, ψ, θ Feel free to use computer algebra. ω X = φ sin θ sin ψ + θ cos ψ (1) ω
Problem 1. Mathematics of rotations (a) Show by algebraic means (i.e. no pictures) that the relationship between ω and is: φ, ψ, θ Feel free to use computer algebra. ω X = φ sin θ sin ψ + θ cos ψ (1) ω
Lecture 13: Forces in the Lagrangian Approach
 Lecture 3: Forces in the Lagrangian Approach In regular Cartesian coordinates, the Lagrangian for a single particle is: 3 L = T U = m x ( ) l U xi l= Given this, we can readily interpret the physical significance
Lecture 3: Forces in the Lagrangian Approach In regular Cartesian coordinates, the Lagrangian for a single particle is: 3 L = T U = m x ( ) l U xi l= Given this, we can readily interpret the physical significance
4.1 Important Notes on Notation
 Chapter 4. Lagrangian Dynamics (Most of the material presented in this chapter is taken from Thornton and Marion, Chap. 7) 4.1 Important Notes on Notation In this chapter, unless otherwise stated, the
Chapter 4. Lagrangian Dynamics (Most of the material presented in this chapter is taken from Thornton and Marion, Chap. 7) 4.1 Important Notes on Notation In this chapter, unless otherwise stated, the
Chapter 5 Oscillatory Motion
 Chapter 5 Oscillatory Motion Simple Harmonic Motion An object moves with simple harmonic motion whenever its acceleration is proportional to its displacement from some equilibrium position and is oppositely
Chapter 5 Oscillatory Motion Simple Harmonic Motion An object moves with simple harmonic motion whenever its acceleration is proportional to its displacement from some equilibrium position and is oppositely
S13 PHY321: Final May 1, NOTE: Show all your work. No credit for unsupported answers. Turn the front page only when advised by the instructor!
 Name: Student ID: S13 PHY321: Final May 1, 2013 NOTE: Show all your work. No credit for unsupported answers. Turn the front page only when advised by the instructor! The exam consists of 6 problems (60
Name: Student ID: S13 PHY321: Final May 1, 2013 NOTE: Show all your work. No credit for unsupported answers. Turn the front page only when advised by the instructor! The exam consists of 6 problems (60
Chapter 14 Oscillations. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 14 Oscillations Oscillations of a Spring Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator Simple Harmonic Motion Related to Uniform Circular Motion The Simple Pendulum The Physical
Chapter 14 Oscillations Oscillations of a Spring Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator Simple Harmonic Motion Related to Uniform Circular Motion The Simple Pendulum The Physical
Chapter 14 Oscillations. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 14 Oscillations 14-1 Oscillations of a Spring If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic. The
Chapter 14 Oscillations 14-1 Oscillations of a Spring If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic. The
Lagrange s Equations of Motion and the Generalized Inertia
 Lagrange s Equations of Motion and the Generalized Inertia The Generalized Inertia Consider the kinetic energy for a n degree of freedom mechanical system with coordinates q, q 2,... q n. If the system
Lagrange s Equations of Motion and the Generalized Inertia The Generalized Inertia Consider the kinetic energy for a n degree of freedom mechanical system with coordinates q, q 2,... q n. If the system
Classical Mechanics and Electrodynamics
 Classical Mechanics and Electrodynamics Lecture notes FYS 3120 Jon Magne Leinaas Department of Physics, University of Oslo December 2009 2 Preface These notes are prepared for the physics course FYS 3120,
Classical Mechanics and Electrodynamics Lecture notes FYS 3120 Jon Magne Leinaas Department of Physics, University of Oslo December 2009 2 Preface These notes are prepared for the physics course FYS 3120,
Question 1: A particle starts at rest and moves along a cycloid whose equation is. 2ay y a
 Stephen Martin PHYS 10 Homework #1 Question 1: A particle starts at rest and moves along a cycloid whose equation is [ ( ) a y x = ± a cos 1 + ] ay y a There is a gravitational field of strength g in the
Stephen Martin PHYS 10 Homework #1 Question 1: A particle starts at rest and moves along a cycloid whose equation is [ ( ) a y x = ± a cos 1 + ] ay y a There is a gravitational field of strength g in the
Physics 235 Chapter 7. Chapter 7 Hamilton's Principle - Lagrangian and Hamiltonian Dynamics
 Chapter 7 Hamilton's Principle - Lagrangian and Hamiltonian Dynamics Many interesting physics systems describe systems of particles on which many forces are acting. Some of these forces are immediately
Chapter 7 Hamilton's Principle - Lagrangian and Hamiltonian Dynamics Many interesting physics systems describe systems of particles on which many forces are acting. Some of these forces are immediately
REVIEW. Hamilton s principle. based on FW-18. Variational statement of mechanics: (for conservative forces) action Equivalent to Newton s laws!
 Hamilton s principle Variational statement of mechanics: (for conservative forces) action Equivalent to Newton s laws! based on FW-18 REVIEW the particle takes the path that minimizes the integrated difference
Hamilton s principle Variational statement of mechanics: (for conservative forces) action Equivalent to Newton s laws! based on FW-18 REVIEW the particle takes the path that minimizes the integrated difference
ANALYTISK MEKANIK I HT 2016
 Karlstads Universitet Fysik ANALYTISK MEKANIK I HT 2016 Kursens kod: FYGB08 Kursansvarig lärare: Jürgen Fuchs rum 21F 316 tel. 054-700 1817 el.mail: juerfuch@kau.se FYGB08 HT 2016 Exercises 1 2016-12-14
Karlstads Universitet Fysik ANALYTISK MEKANIK I HT 2016 Kursens kod: FYGB08 Kursansvarig lärare: Jürgen Fuchs rum 21F 316 tel. 054-700 1817 el.mail: juerfuch@kau.se FYGB08 HT 2016 Exercises 1 2016-12-14
Chapter 14 Oscillations
 Chapter 14 Oscillations If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic. The mass and spring system is a
Chapter 14 Oscillations If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic. The mass and spring system is a
Classical Mechanics and Electrodynamics
 Classical Mechanics and Electrodynamics Lecture notes FYS 3120 Jon Magne Leinaas Department of Physics, University of Oslo 2 Preface FYS 3120 is a course in classical theoretical physics, which covers
Classical Mechanics and Electrodynamics Lecture notes FYS 3120 Jon Magne Leinaas Department of Physics, University of Oslo 2 Preface FYS 3120 is a course in classical theoretical physics, which covers
!T = 2# T = 2! " The velocity and acceleration of the object are found by taking the first and second derivative of the position:
 A pendulum swinging back and forth or a mass oscillating on a spring are two examples of (SHM.) SHM occurs any time the position of an object as a function of time can be represented by a sine wave. We
A pendulum swinging back and forth or a mass oscillating on a spring are two examples of (SHM.) SHM occurs any time the position of an object as a function of time can be represented by a sine wave. We
Goldstein Problem 2.17 (3 rd ed. # 2.18)
 Goldstein Problem.7 (3 rd ed. #.8) The geometry of the problem: A particle of mass m is constrained to move on a circular hoop of radius a that is vertically oriented and forced to rotate about the vertical
Goldstein Problem.7 (3 rd ed. #.8) The geometry of the problem: A particle of mass m is constrained to move on a circular hoop of radius a that is vertically oriented and forced to rotate about the vertical
Physics 351, Spring 2017, Homework #3. Due at start of class, Friday, February 3, 2017
 Physics 351, Spring 2017, Homework #3. Due at start of class, Friday, February 3, 2017 Course info is at positron.hep.upenn.edu/p351 When you finish this homework, remember to visit the feedback page at
Physics 351, Spring 2017, Homework #3. Due at start of class, Friday, February 3, 2017 Course info is at positron.hep.upenn.edu/p351 When you finish this homework, remember to visit the feedback page at
Physics 351, Spring 2015, Homework #6. Due at start of class, Friday, February 27, 2015
 Physics 351, Spring 2015, Homework #6. Due at start of class, Friday, February 27, 2015 Course info is at positron.hep.upenn.edu/p351 When you finish this homework, remember to visit the feedback page
Physics 351, Spring 2015, Homework #6. Due at start of class, Friday, February 27, 2015 Course info is at positron.hep.upenn.edu/p351 When you finish this homework, remember to visit the feedback page
For a rigid body that is constrained to rotate about a fixed axis, the gravitational torque about the axis is
 Experiment 14 The Physical Pendulum The period of oscillation of a physical pendulum is found to a high degree of accuracy by two methods: theory and experiment. The values are then compared. Theory For
Experiment 14 The Physical Pendulum The period of oscillation of a physical pendulum is found to a high degree of accuracy by two methods: theory and experiment. The values are then compared. Theory For
ANALYTISK MEKANIK I HT 2014
 Karlstads Universitet Fysik ANALYTISK MEKANIK I HT 2014 Kursens kod: FYGB08 Undervisande lärare: Jürgen Fuchs rum 21F 316 tel. 054-700 1817 el.mail: jfuchs@fuchs.tekn.kau.se FYGB08 HT 2014 Exercises 1
Karlstads Universitet Fysik ANALYTISK MEKANIK I HT 2014 Kursens kod: FYGB08 Undervisande lärare: Jürgen Fuchs rum 21F 316 tel. 054-700 1817 el.mail: jfuchs@fuchs.tekn.kau.se FYGB08 HT 2014 Exercises 1
NIU Physics PhD Candidacy Exam Fall 2017 Classical Mechanics
 NIU Physics PhD Candidacy Exam Fall 2017 Classical Mechanics You may solve ALL FOUR problems, if you choose. Only the THREE BEST PROBLEM GRADES count towards your score. Total points on each problem =
NIU Physics PhD Candidacy Exam Fall 2017 Classical Mechanics You may solve ALL FOUR problems, if you choose. Only the THREE BEST PROBLEM GRADES count towards your score. Total points on each problem =
Force, Energy & Periodic Motion. Preparation for unit test
 Force, Energy & Periodic Motion Preparation for unit test Summary of assessment standards (Unit assessment standard only) In the unit test you can expect to be asked at least one question on each sub-skill.
Force, Energy & Periodic Motion Preparation for unit test Summary of assessment standards (Unit assessment standard only) In the unit test you can expect to be asked at least one question on each sub-skill.
UPDATED: NOVEMBER A particle of mass m and energy E moving in one dimension comes in from - and encounters the repulsive potential:
 UVA PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHD QUALIFYING EXAM PROBLEM FILE CLASSICAL MECHANICS UPDATED: NOVEMBER 007 1. A particle of mass m and energy E moving in one dimension comes in from - and encounters the repulsive
UVA PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHD QUALIFYING EXAM PROBLEM FILE CLASSICAL MECHANICS UPDATED: NOVEMBER 007 1. A particle of mass m and energy E moving in one dimension comes in from - and encounters the repulsive
B.Sc. (Semester - 5) Subject: Physics Course: US05CPHY01 Classical Mechanics
 1 B.Sc. (Semester - 5) Subject: Physics Course: US05CPHY01 Classical Mechanics Question Bank UNIT: I Multiple choice questions: (1) The gravitational force between two masses is (a) Repulsive (b) Attractive
1 B.Sc. (Semester - 5) Subject: Physics Course: US05CPHY01 Classical Mechanics Question Bank UNIT: I Multiple choice questions: (1) The gravitational force between two masses is (a) Repulsive (b) Attractive
Homework 1. Due Thursday, January 21
 Homework 1. Due Thursday, January 21 Problem 1. Rising Snake A snake of length L and linear mass density ρ rises from the table. It s head is moving straight up with the constant velocity v. What force
Homework 1. Due Thursday, January 21 Problem 1. Rising Snake A snake of length L and linear mass density ρ rises from the table. It s head is moving straight up with the constant velocity v. What force
2007 Problem Topic Comment 1 Kinematics Position-time equation Kinematics 7 2 Kinematics Velocity-time graph Dynamics 6 3 Kinematics Average velocity
 2007 Problem Topic Comment 1 Kinematics Position-time equation Kinematics 7 2 Kinematics Velocity-time graph Dynamics 6 3 Kinematics Average velocity Energy 7 4 Kinematics Free fall Collisions 3 5 Dynamics
2007 Problem Topic Comment 1 Kinematics Position-time equation Kinematics 7 2 Kinematics Velocity-time graph Dynamics 6 3 Kinematics Average velocity Energy 7 4 Kinematics Free fall Collisions 3 5 Dynamics
Lecture 13 REVIEW. Physics 106 Spring What should we know? What should we know? Newton s Laws
 Lecture 13 REVIEW Physics 106 Spring 2006 http://web.njit.edu/~sirenko/ What should we know? Vectors addition, subtraction, scalar and vector multiplication Trigonometric functions sinθ, cos θ, tan θ,
Lecture 13 REVIEW Physics 106 Spring 2006 http://web.njit.edu/~sirenko/ What should we know? Vectors addition, subtraction, scalar and vector multiplication Trigonometric functions sinθ, cos θ, tan θ,
7. The gyroscope. 7.1 Introduction. 7.2 Theory. a) The gyroscope
 K 7. The gyroscope 7.1 Introduction This experiment concerns a special type of motion of a gyroscope, called precession. From the angular frequency of the precession, the moment of inertia of the spinning
K 7. The gyroscope 7.1 Introduction This experiment concerns a special type of motion of a gyroscope, called precession. From the angular frequency of the precession, the moment of inertia of the spinning
Lecture 9: Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors in Classical Mechanics (See Section 3.12 in Boas)
 Lecture 9: Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors in Classical Mechanics (See Section 3 in Boas) As suggested in Lecture 8 the formalism of eigenvalues/eigenvectors has many applications in physics, especially in
Lecture 9: Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors in Classical Mechanics (See Section 3 in Boas) As suggested in Lecture 8 the formalism of eigenvalues/eigenvectors has many applications in physics, especially in
AN INTRODUCTION TO LAGRANGE EQUATIONS. Professor J. Kim Vandiver October 28, 2016
 AN INTRODUCTION TO LAGRANGE EQUATIONS Professor J. Kim Vandiver October 28, 2016 kimv@mit.edu 1.0 INTRODUCTION This paper is intended as a minimal introduction to the application of Lagrange equations
AN INTRODUCTION TO LAGRANGE EQUATIONS Professor J. Kim Vandiver October 28, 2016 kimv@mit.edu 1.0 INTRODUCTION This paper is intended as a minimal introduction to the application of Lagrange equations
Simple and Physical Pendulums Challenge Problem Solutions
 Simple and Physical Pendulums Challenge Problem Solutions Problem 1 Solutions: For this problem, the answers to parts a) through d) will rely on an analysis of the pendulum motion. There are two conventional
Simple and Physical Pendulums Challenge Problem Solutions Problem 1 Solutions: For this problem, the answers to parts a) through d) will rely on an analysis of the pendulum motion. There are two conventional
Mechanics Departmental Exam Last updated November 2013
 Mechanics Departmental Eam Last updated November 213 1. Two satellites are moving about each other in circular orbits under the influence of their mutual gravitational attractions. The satellites have
Mechanics Departmental Eam Last updated November 213 1. Two satellites are moving about each other in circular orbits under the influence of their mutual gravitational attractions. The satellites have
P321(b), Assignement 1
 P31(b), Assignement 1 1 Exercise 3.1 (Fetter and Walecka) a) The problem is that of a point mass rotating along a circle of radius a, rotating with a constant angular velocity Ω. Generally, 3 coordinates
P31(b), Assignement 1 1 Exercise 3.1 (Fetter and Walecka) a) The problem is that of a point mass rotating along a circle of radius a, rotating with a constant angular velocity Ω. Generally, 3 coordinates
M2A2 Problem Sheet 3 - Hamiltonian Mechanics
 MA Problem Sheet 3 - Hamiltonian Mechanics. The particle in a cone. A particle slides under gravity, inside a smooth circular cone with a vertical axis, z = k x + y. Write down its Lagrangian in a) Cartesian,
MA Problem Sheet 3 - Hamiltonian Mechanics. The particle in a cone. A particle slides under gravity, inside a smooth circular cone with a vertical axis, z = k x + y. Write down its Lagrangian in a) Cartesian,
Classical Mechanics Comprehensive Exam Solution
 Classical Mechanics Comprehensive Exam Solution January 31, 011, 1:00 pm 5:pm Solve the following six problems. In the following problems, e x, e y, and e z are unit vectors in the x, y, and z directions,
Classical Mechanics Comprehensive Exam Solution January 31, 011, 1:00 pm 5:pm Solve the following six problems. In the following problems, e x, e y, and e z are unit vectors in the x, y, and z directions,
HW 6 Mathematics 503, Mathematical Modeling, CSUF, June 24, 2007
 HW 6 Mathematics 503, Mathematical Modeling, CSUF, June 24, 2007 Nasser M. Abbasi June 15, 2014 Contents 1 Problem 1 (section 3.5,#9, page 197 1 2 Problem 1 (section 3.5,#9, page 197 7 1 Problem 1 (section
HW 6 Mathematics 503, Mathematical Modeling, CSUF, June 24, 2007 Nasser M. Abbasi June 15, 2014 Contents 1 Problem 1 (section 3.5,#9, page 197 1 2 Problem 1 (section 3.5,#9, page 197 7 1 Problem 1 (section
TOPIC E: OSCILLATIONS EXAMPLES SPRING Q1. Find general solutions for the following differential equations:
 TOPIC E: OSCILLATIONS EXAMPLES SPRING 2019 Mathematics of Oscillating Systems Q1. Find general solutions for the following differential equations: Undamped Free Vibration Q2. A 4 g mass is suspended by
TOPIC E: OSCILLATIONS EXAMPLES SPRING 2019 Mathematics of Oscillating Systems Q1. Find general solutions for the following differential equations: Undamped Free Vibration Q2. A 4 g mass is suspended by
Solution Set Two. 1 Problem #1: Projectile Motion Cartesian Coordinates Polar Coordinates... 3
 : Solution Set Two Northwestern University, Classical Mechanics Classical Mechanics, Third Ed.- Goldstein October 7, 2015 Contents 1 Problem #1: Projectile Motion. 2 1.1 Cartesian Coordinates....................................
: Solution Set Two Northwestern University, Classical Mechanics Classical Mechanics, Third Ed.- Goldstein October 7, 2015 Contents 1 Problem #1: Projectile Motion. 2 1.1 Cartesian Coordinates....................................
Problem Goldstein 2-12
 Problem Goldstein -1 The Rolling Constraint: A small circular hoop of radius r and mass m hoop rolls without slipping on a stationary cylinder of radius R. The only external force is that of gravity. Let
Problem Goldstein -1 The Rolling Constraint: A small circular hoop of radius r and mass m hoop rolls without slipping on a stationary cylinder of radius R. The only external force is that of gravity. Let
Advanced Dynamics. - Lecture 4 Lagrange Equations. Paolo Tiso Spring Semester 2017 ETH Zürich
 Advanced Dynamics - Lecture 4 Lagrange Equations Paolo Tiso Spring Semester 2017 ETH Zürich LECTURE OBJECTIVES 1. Derive the Lagrange equations of a system of particles; 2. Show that the equation of motion
Advanced Dynamics - Lecture 4 Lagrange Equations Paolo Tiso Spring Semester 2017 ETH Zürich LECTURE OBJECTIVES 1. Derive the Lagrange equations of a system of particles; 2. Show that the equation of motion
Structural Dynamics Lecture 4. Outline of Lecture 4. Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems. Formulation of Equations of Motions. Undamped Eigenvibrations.
 Outline of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems Formulation of Equations of Motions. Newton s 2 nd Law Applied to Free Masses. D Alembert s Principle. Basic Equations of Motion for Forced Vibrations of Linear
Outline of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems Formulation of Equations of Motions. Newton s 2 nd Law Applied to Free Masses. D Alembert s Principle. Basic Equations of Motion for Forced Vibrations of Linear
Rigid Body Kinetics :: Force/Mass/Acc
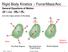 Rigid Body Kinetics :: Force/Mass/Acc General Equations of Motion G is the mass center of the body Action Dynamic Response 1 Rigid Body Kinetics :: Force/Mass/Acc Fixed Axis Rotation All points in body
Rigid Body Kinetics :: Force/Mass/Acc General Equations of Motion G is the mass center of the body Action Dynamic Response 1 Rigid Body Kinetics :: Force/Mass/Acc Fixed Axis Rotation All points in body
Physics 106a, Caltech 4 December, Lecture 18: Examples on Rigid Body Dynamics. Rotating rectangle. Heavy symmetric top
 Physics 106a, Caltech 4 December, 2018 Lecture 18: Examples on Rigid Body Dynamics I go through a number of examples illustrating the methods of solving rigid body dynamics. In most cases, the problem
Physics 106a, Caltech 4 December, 2018 Lecture 18: Examples on Rigid Body Dynamics I go through a number of examples illustrating the methods of solving rigid body dynamics. In most cases, the problem
Chapter 14 Periodic Motion
 Chapter 14 Periodic Motion 1 Describing Oscillation First, we want to describe the kinematical and dynamical quantities associated with Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM), for example, x, v x, a x, and F x.
Chapter 14 Periodic Motion 1 Describing Oscillation First, we want to describe the kinematical and dynamical quantities associated with Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM), for example, x, v x, a x, and F x.
the EL equation for the x coordinate is easily seen to be (exercise)
 Physics 6010, Fall 2016 Relevant Sections in Text: 1.3 1.6 Examples After all this formalism it is a good idea to spend some time developing a number of illustrative examples. These examples represent
Physics 6010, Fall 2016 Relevant Sections in Text: 1.3 1.6 Examples After all this formalism it is a good idea to spend some time developing a number of illustrative examples. These examples represent
Chapter 8: Momentum, Impulse, & Collisions. Newton s second law in terms of momentum:
 linear momentum: Chapter 8: Momentum, Impulse, & Collisions Newton s second law in terms of momentum: impulse: Under what SPECIFIC condition is linear momentum conserved? (The answer does not involve collisions.)
linear momentum: Chapter 8: Momentum, Impulse, & Collisions Newton s second law in terms of momentum: impulse: Under what SPECIFIC condition is linear momentum conserved? (The answer does not involve collisions.)
Lagrangian Dynamics: Generalized Coordinates and Forces
 Lecture Outline 1 2.003J/1.053J Dynamics and Control I, Spring 2007 Professor Sanjay Sarma 4/2/2007 Lecture 13 Lagrangian Dynamics: Generalized Coordinates and Forces Lecture Outline Solve one problem
Lecture Outline 1 2.003J/1.053J Dynamics and Control I, Spring 2007 Professor Sanjay Sarma 4/2/2007 Lecture 13 Lagrangian Dynamics: Generalized Coordinates and Forces Lecture Outline Solve one problem
Homework 1. Due Tuesday, January 29.
 Homework 1. Due Tuesday, January 29. Problem 1. An ideal rope (no friction) lying on a table slides from its edge down to a scales lying on the floor. The table s height is h. Find a stationary velocity
Homework 1. Due Tuesday, January 29. Problem 1. An ideal rope (no friction) lying on a table slides from its edge down to a scales lying on the floor. The table s height is h. Find a stationary velocity
UPDATED: OCTOBER Problem #1
 UVA PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHD QUALIFYING EXAM PROBLEM FILE CLASSICAL MECHANICS UPDATED: OCTOBER 008 1. Consider the system shown below of two masses, a fixed wall, and three massless, ideal springs. Motion
UVA PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHD QUALIFYING EXAM PROBLEM FILE CLASSICAL MECHANICS UPDATED: OCTOBER 008 1. Consider the system shown below of two masses, a fixed wall, and three massless, ideal springs. Motion
Euler-Lagrange's equations in several variables
 Euler-Lagrange's equations in several variables So far we have studied one variable and its derivative Let us now consider L2:1 More:1 Taylor: 226-227 (This proof is slightly more general than Taylor's.)
Euler-Lagrange's equations in several variables So far we have studied one variable and its derivative Let us now consider L2:1 More:1 Taylor: 226-227 (This proof is slightly more general than Taylor's.)
Dynamics. Dynamics of mechanical particle and particle systems (many body systems)
 Dynamics Dynamics of mechanical particle and particle systems (many body systems) Newton`s first law: If no net force acts on a body, it will move on a straight line at constant velocity or will stay at
Dynamics Dynamics of mechanical particle and particle systems (many body systems) Newton`s first law: If no net force acts on a body, it will move on a straight line at constant velocity or will stay at
Physics 2211 A & B Quiz #4 Solutions Fall 2016
 Physics 22 A & B Quiz #4 Solutions Fall 206 I. (6 points) A pendulum bob of mass M is hanging at rest from an ideal string of length L. A bullet of mass m traveling horizontally at speed v 0 strikes it
Physics 22 A & B Quiz #4 Solutions Fall 206 I. (6 points) A pendulum bob of mass M is hanging at rest from an ideal string of length L. A bullet of mass m traveling horizontally at speed v 0 strikes it
CHAPTER 6 WORK AND ENERGY
 CHAPTER 6 WORK AND ENERGY ANSWERS TO FOCUS ON CONCEPTS QUESTIONS (e) When the force is perpendicular to the displacement, as in C, there is no work When the force points in the same direction as the displacement,
CHAPTER 6 WORK AND ENERGY ANSWERS TO FOCUS ON CONCEPTS QUESTIONS (e) When the force is perpendicular to the displacement, as in C, there is no work When the force points in the same direction as the displacement,
Lecture D10 - Angular Impulse and Momentum
 J. Peraire 6.07 Dynamics Fall 2004 Version.2 Lecture D0 - Angular Impulse and Momentum In addition to the equations of linear impulse and momentum considered in the previous lecture, there is a parallel
J. Peraire 6.07 Dynamics Fall 2004 Version.2 Lecture D0 - Angular Impulse and Momentum In addition to the equations of linear impulse and momentum considered in the previous lecture, there is a parallel
Homework 1. Due whatever day you decide to have the homework session.
 Homework 1. Due whatever day you decide to have the homework session. Problem 1. Rising Snake A snake of length L and linear mass density ρ rises from the table. It s head is moving straight up with the
Homework 1. Due whatever day you decide to have the homework session. Problem 1. Rising Snake A snake of length L and linear mass density ρ rises from the table. It s head is moving straight up with the
16. Rotational Dynamics
 6. Rotational Dynamics A Overview In this unit we will address examples that combine both translational and rotational motion. We will find that we will need both Newton s second law and the rotational
6. Rotational Dynamics A Overview In this unit we will address examples that combine both translational and rotational motion. We will find that we will need both Newton s second law and the rotational
Physics 6010, Fall 2016 Constraints and Lagrange Multipliers. Relevant Sections in Text:
 Physics 6010, Fall 2016 Constraints and Lagrange Multipliers. Relevant Sections in Text: 1.3 1.6 Constraints Often times we consider dynamical systems which are defined using some kind of restrictions
Physics 6010, Fall 2016 Constraints and Lagrange Multipliers. Relevant Sections in Text: 1.3 1.6 Constraints Often times we consider dynamical systems which are defined using some kind of restrictions
Oscillations. Phys101 Lectures 28, 29. Key points: Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) SHM Related to Uniform Circular Motion The Simple Pendulum
 Phys101 Lectures 8, 9 Oscillations Key points: Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) SHM Related to Uniform Circular Motion The Simple Pendulum Ref: 11-1,,3,4. Page 1 Oscillations of a Spring If an object oscillates
Phys101 Lectures 8, 9 Oscillations Key points: Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) SHM Related to Uniform Circular Motion The Simple Pendulum Ref: 11-1,,3,4. Page 1 Oscillations of a Spring If an object oscillates
Physics 351 Wednesday, February 14, 2018
 Physics 351 Wednesday, February 14, 2018 HW4 due Friday. For HW help, Bill is in DRL 3N6 Wed 4 7pm. Grace is in DRL 2C2 Thu 5:30 8:30pm. Respond at pollev.com/phys351 or text PHYS351 to 37607 once to join,
Physics 351 Wednesday, February 14, 2018 HW4 due Friday. For HW help, Bill is in DRL 3N6 Wed 4 7pm. Grace is in DRL 2C2 Thu 5:30 8:30pm. Respond at pollev.com/phys351 or text PHYS351 to 37607 once to join,
PHY 5246: Theoretical Dynamics, Fall September 28 th, 2015 Midterm Exam # 1
 Name: SOLUTIONS PHY 5246: Theoretical Dynamics, Fall 2015 September 28 th, 2015 Mierm Exam # 1 Always remember to write full work for what you do. This will help your grade in case of incomplete or wrong
Name: SOLUTIONS PHY 5246: Theoretical Dynamics, Fall 2015 September 28 th, 2015 Mierm Exam # 1 Always remember to write full work for what you do. This will help your grade in case of incomplete or wrong
Lagrangian Dynamics: Derivations of Lagrange s Equations
 Constraints and Degrees of Freedom 1.003J/1.053J Dynamics and Control I, Spring 007 Professor Thomas Peacock 4/9/007 Lecture 15 Lagrangian Dynamics: Derivations of Lagrange s Equations Constraints and
Constraints and Degrees of Freedom 1.003J/1.053J Dynamics and Control I, Spring 007 Professor Thomas Peacock 4/9/007 Lecture 15 Lagrangian Dynamics: Derivations of Lagrange s Equations Constraints and
Physical Dynamics (SPA5304) Lecture Plan 2018
 Physical Dynamics (SPA5304) Lecture Plan 2018 The numbers on the left margin are approximate lecture numbers. Items in gray are not covered this year 1 Advanced Review of Newtonian Mechanics 1.1 One Particle
Physical Dynamics (SPA5304) Lecture Plan 2018 The numbers on the left margin are approximate lecture numbers. Items in gray are not covered this year 1 Advanced Review of Newtonian Mechanics 1.1 One Particle
Mechanics IV: Oscillations
 Mechanics IV: Oscillations Chapter 4 of Morin covers oscillations, including damped and driven oscillators in detail. Also see chapter 10 of Kleppner and Kolenkow. For more on normal modes, see any book
Mechanics IV: Oscillations Chapter 4 of Morin covers oscillations, including damped and driven oscillators in detail. Also see chapter 10 of Kleppner and Kolenkow. For more on normal modes, see any book
W13D1-1 Reading Quiz and Concept Questions
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.01 Fall Term 2009 W13D1-1 Reading Quiz and Concept Questions A person spins a tennis ball on a string in a horizontal circle (so that
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.01 Fall Term 2009 W13D1-1 Reading Quiz and Concept Questions A person spins a tennis ball on a string in a horizontal circle (so that
Classical Mechanics III (8.09) Fall 2014 Assignment 3
 Classical Mechanics III (8.09) Fall 2014 Assignment 3 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Physics Department Due September 29, 2014 September 22, 2014 6:00pm Announcements This week we continue our discussion
Classical Mechanics III (8.09) Fall 2014 Assignment 3 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Physics Department Due September 29, 2014 September 22, 2014 6:00pm Announcements This week we continue our discussion
is conserved, calculating E both at θ = 0 and θ = π/2 we find that this happens for a value ω = ω given by: 2g
 UNIVERSITETET I STAVANGER Institutt for matematikk og naturvitenskap Suggested solutions, FYS 500 Classical Mechanics Theory 2016 fall Set 5 for 23. September 2016 Problem 27: A string can only support
UNIVERSITETET I STAVANGER Institutt for matematikk og naturvitenskap Suggested solutions, FYS 500 Classical Mechanics Theory 2016 fall Set 5 for 23. September 2016 Problem 27: A string can only support
Oscillations. Oscillations and Simple Harmonic Motion
 Oscillations AP Physics C Oscillations and Simple Harmonic Motion 1 Equilibrium and Oscillations A marble that is free to roll inside a spherical bowl has an equilibrium position at the bottom of the bowl
Oscillations AP Physics C Oscillations and Simple Harmonic Motion 1 Equilibrium and Oscillations A marble that is free to roll inside a spherical bowl has an equilibrium position at the bottom of the bowl
ANALYTICAL MECHANICS. LOUIS N. HAND and JANET D. FINCH CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS
 ANALYTICAL MECHANICS LOUIS N. HAND and JANET D. FINCH CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface xi 1 LAGRANGIAN MECHANICS l 1.1 Example and Review of Newton's Mechanics: A Block Sliding on an Inclined Plane 1
ANALYTICAL MECHANICS LOUIS N. HAND and JANET D. FINCH CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface xi 1 LAGRANGIAN MECHANICS l 1.1 Example and Review of Newton's Mechanics: A Block Sliding on an Inclined Plane 1
Lagrangian Mechanics I
 Lagrangian Mechanics I Wednesday, 11 September 2013 How Lagrange revolutionized Newtonian mechanics Physics 111 Newton based his dynamical theory on the notion of force, for which he gave a somewhat incomplete
Lagrangian Mechanics I Wednesday, 11 September 2013 How Lagrange revolutionized Newtonian mechanics Physics 111 Newton based his dynamical theory on the notion of force, for which he gave a somewhat incomplete
Axis Balanced Forces Centripetal force. Change in velocity Circular Motion Circular orbit Collision. Conservation of Energy
 When something changes its velocity The rate of change of velocity of a moving object. Can result from a change in speed and/or a change in direction On surface of earth, value is 9.8 ms-²; increases nearer
When something changes its velocity The rate of change of velocity of a moving object. Can result from a change in speed and/or a change in direction On surface of earth, value is 9.8 ms-²; increases nearer
Physics for Scientists and Engineers 4th Edition, 2017
 A Correlation of Physics for Scientists and Engineers 4th Edition, 2017 To the AP Physics C: Mechanics Course Descriptions AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which was not
A Correlation of Physics for Scientists and Engineers 4th Edition, 2017 To the AP Physics C: Mechanics Course Descriptions AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which was not
Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics. UCVTS AIT Physics
 Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics UCVTS AIT Physics Angular Position Axis of rotation is the center of the disc Choose a fixed reference line Point P is at a fixed distance r from the origin Angular Position,
Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics UCVTS AIT Physics Angular Position Axis of rotation is the center of the disc Choose a fixed reference line Point P is at a fixed distance r from the origin Angular Position,
Classical Mechanics. FIG. 1. Figure for (a), (b) and (c). FIG. 2. Figure for (d) and (e).
 Classical Mechanics 1. Consider a cylindrically symmetric object with a total mass M and a finite radius R from the axis of symmetry as in the FIG. 1. FIG. 1. Figure for (a), (b) and (c). (a) Show that
Classical Mechanics 1. Consider a cylindrically symmetric object with a total mass M and a finite radius R from the axis of symmetry as in the FIG. 1. FIG. 1. Figure for (a), (b) and (c). (a) Show that
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Physics. Final Examination December 17, 2004
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Physics Course: 8.09 Classical Mechanics Term: Fall 004 Final Examination December 17, 004 Instructions Do not start until you are told to do so. Solve
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Physics Course: 8.09 Classical Mechanics Term: Fall 004 Final Examination December 17, 004 Instructions Do not start until you are told to do so. Solve
15. Hamiltonian Mechanics
 University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Classical Dynamics Physics Course Materials 2015 15. Hamiltonian Mechanics Gerhard Müller University of Rhode Island, gmuller@uri.edu Creative Commons License
University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Classical Dynamics Physics Course Materials 2015 15. Hamiltonian Mechanics Gerhard Müller University of Rhode Island, gmuller@uri.edu Creative Commons License
Mechanics Lecture Notes
 Mechanics Lecture Notes Lectures 0 and : Motion in a circle. Introduction The important result in this lecture concerns the force required to keep a particle moving on a circular path: if the radius of
Mechanics Lecture Notes Lectures 0 and : Motion in a circle. Introduction The important result in this lecture concerns the force required to keep a particle moving on a circular path: if the radius of
Dynamics 12e. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd. Chapter 20 3D Kinematics of a Rigid Body
 Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics 12e Chapter 20 3D Kinematics of a Rigid Body Chapter Objectives Kinematics of a body subjected to rotation about a fixed axis and general plane motion. Relative-motion analysis
Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics 12e Chapter 20 3D Kinematics of a Rigid Body Chapter Objectives Kinematics of a body subjected to rotation about a fixed axis and general plane motion. Relative-motion analysis
Chapter 12. Recall that when a spring is stretched a distance x, it will pull back with a force given by: F = -kx
 Chapter 1 Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Oscillatory Motion Recall that when a spring is stretched a distance x, it will pull back with a force given by: F = -kx When the mass is released, the spring will pull
Chapter 1 Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Oscillatory Motion Recall that when a spring is stretched a distance x, it will pull back with a force given by: F = -kx When the mass is released, the spring will pull
The Principle of Least Action
 The Principle of Least Action In their never-ending search for general principles, from which various laws of Physics could be derived, physicists, and most notably theoretical physicists, have often made
The Principle of Least Action In their never-ending search for general principles, from which various laws of Physics could be derived, physicists, and most notably theoretical physicists, have often made
DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS. University at Albany State University of New York. Comprehensive Field Examination. Classical. Monday, May 21, 2018
 DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS University at Albany State University of New York Comprehensive Field Examination Classical Monday, May 21, 218 1: AM - 1: PM Instruction: Answer any four out of five questions Please
DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS University at Albany State University of New York Comprehensive Field Examination Classical Monday, May 21, 218 1: AM - 1: PM Instruction: Answer any four out of five questions Please
FIRST YEAR MATHS FOR PHYSICS STUDENTS NORMAL MODES AND WAVES. Hilary Term Prof. G.G.Ross. Question Sheet 1: Normal Modes
 FIRST YEAR MATHS FOR PHYSICS STUDENTS NORMAL MODES AND WAVES Hilary Term 008. Prof. G.G.Ross Question Sheet : Normal Modes [Questions marked with an asterisk (*) cover topics also covered by the unstarred
FIRST YEAR MATHS FOR PHYSICS STUDENTS NORMAL MODES AND WAVES Hilary Term 008. Prof. G.G.Ross Question Sheet : Normal Modes [Questions marked with an asterisk (*) cover topics also covered by the unstarred
Physics 218 Comprehensive Exam
 Physics 218 Comprehensive Exam Spring 2018 (all UP sections) April 27 th, 2018 Rules of the exam: Please fill out the information and read the instructions below, but do not open the exam until told to
Physics 218 Comprehensive Exam Spring 2018 (all UP sections) April 27 th, 2018 Rules of the exam: Please fill out the information and read the instructions below, but do not open the exam until told to
