Science homework booklet Energy
|
|
|
- Agnes Gibbs
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Merrylands High School Science homework booklet Energy Due date: Thursday November 14 Name:
2 How to complete this homework booklet This homework booklet is divided into lessons. There are 5 lessons altogether. Each lesson has a video for you to watch and them some worksheets for you to complete. If you don t understand the concepts that are explained video, you can rewind the video and re-watch it. If you still don t understand, you can ask Miss Leung on Edmodo or at school. Posting a question onto Edmodo will also allow other students in your class to help you. The video lessons are online at If you don t have internet at home, ask Miss Leung to give you a USB with the videos so you can watch the videos with no internet connection. After you watch each video, the worksheets require you to hand write answers and contribute to discussions on Edmodo if you have internet at home. When to hand in this homework booklet This homework booklet needs to be shown to Miss Leung every Tuesday. She will mark the work that you have done each week. You need to complete at least one lesson every week, but you can do more if you want to and finish the booklet early. The whole booklet needs to be finished and handed in by Thursday November 14.
3 Energy Lesson 1 - Types of Energy Watch the Energy Lesson 1 video before doing any of the activities in this booklet for lesson 1. Go to or use the videos Miss Leung gave you. Learning intention To understand there are different types of energy Success criteria I can describe different kinds of energy I can define kinetic and potential energy I know the difference between renewable and non-renewable energy Activity 1 Types of energy Read the information in the box below. energy come from greek words meaning containing work, Energy was what you needed to do work or to change something. energy may be difficult to describe but you can see the changes caused by it. Energy can be divide into different types. you are already familiar with heat enrgy, light energy and sound energy as they are detected by your senses. Heat energy is detected by your skin light energy by your eyes and sound energy bye your ears Another form of energy is electrical energy. this is the type of energy that is most easily changed into other forms of energy. A electrical heater, electric light and sound system are designed to change electrical energy into heat light or sound energy at the flick of a switch. The text above has mistakes: punctuation, incorrect verbs, tense and spelling. The text is also written as one long text with no paragraphs. Write out the text below, correcting all the errors and beginning new paragraphs where they are needed.
4 Activity 2 Kinetic and potential energy Read the information in the box below. Moving objects have energy called kinetic energy. You feel the effects of kinetic energy if a moving object hits you. Energy stored in an object is called potential energy. Potential means having the ability to do something. When an object has potential energy, it means it has the ability to do work. An object has potential energy when it is placed up high and can fall down. Potential energy can be stored in any object that can be stretched, bent, compressed (squashed) or twisted out of shape. If the object is allowed to return to its original shape the potential energy changes to kinetic energy. Kinetic and potential energy can be explained in a rollercoaster ride. When the rollercoaster is moving up and down the ride, it has kinetic energy because the rollercoaster is moving. When the rollercoaster is at a peak, it is not moving but it has the ability to move downwards. Therefore the rollercoaster has potential energy. Label whether the rollercoaster has potential energy or kinetic energy in the diagram above.
5 Activity 3 - Describing energy situations Complete the table by using one of the terms below to describe each situation. a person running a radiator giving out heat a glowing light globe a squashed spring listening to the radio batteries for a torch Name the energy in each situation using the list of energy words: electrical, heat, kinetic, light, potential, sound. Situation involving energy Describe the situation Name given to the energy Eg. A radiator giving out Eg. Heat heat
6 Activity 4 - Edmodo Discussion Go and reply to the post What do you think is the most important type of energy? Why? Do you think people need to use more renewable sources of energy? Why or Why not? Also reply to at least one student s post on this thread.
7 Energy Lesson 2 Energy Changes Watch the Energy Lesson 2 video before doing any of the activities in this booklet for lesson 1. Go to or use the videos Miss Leung gave you. Learning intention To understand that energy changes from one type to another Success criteria I can identify energy changes I can say that energy cannot be created or destroyed I can describe the law of conservation of energy I can use arrows to show energy changes Activity 1 - Describing energy transformations Transform means change. One type of energy can be changed into another type of energy. For example, when you turn on a light, electrical energy is transformed into light energy. When you roll a ball down a ruler, potential energy is transformed into kinetic energy. You can demonstrate that energy undergoes transformations by completing the sentences below. In an electric heater electrical energy is changed into h energy. When lightning strikes electrical energy is changed to l energy that you can see and s energy that you can hear. When you lift an object upwards the object gains p energy. If you let the object fall this potential energy is changed into k energy of the moving object. An electric fan changes e energy to kinetic energy.
8 Activity 2 Using arrows to show energy transformations For each of the following situations, use arrows to show the kinds of energy transformations taking place. Situation A heater is changing electrical energy into heat energy. Energy transformation with arrows Electrical Heat Lightning is changing electrical energy into light and sound energy. Electrical Light + Sound A spoon being dropped is changing potential energy into kinetic energy. An electric fan is changing electrical energy into kinetic energy. A candle is changing chemical energy into light energy. A vacuum cleaner is changing electrical energy into kinetic energy and sound energy. + Clapping your hands is changing kinetic energy into sound and heat energy. +
9 Activity 4 Edmodo discussion Go to here and reply to the post When you clap your hands, you change kinetic energy into sound and heat energy. How much of the energy you put into clapping are changed into the sound and heat energy? All of it or some of it? Also reply to at least one student s post on this thread.
10 Energy Lesson 5 Light and sound energy Watch the Energy Lesson 3 video before doing any of the activities in this booklet for lesson 1. Go to or use the videos Miss Leung gave you. Learning intention To understand how sound and light energy travels from one place to another Success criteria I can identify that sound energy travels through vibrations I can identify that light travels in straight lines I can explain why sound cannot travel through a vacuum I can recall that light can travel through a vacuum Activity 1 Sound energy Read the information and fill in the missing words. What is sound energy? All sounds are caused by vibrations. When you speak or sing, the vocal cords in your throat vibrates. You can feel the vibrations if you put your hand over the front of your throat. These vibrations cause the air in your throat and mouth to vibrate. The air around you vibrates. The sound is heard by you or someone else when air surrounding you vibrates. The travelling vibration is called a sound wave. Sound energy needs to travel through a medium. A medium is any substance or matter such as air or water. There is no matter in space so sound cannot travel through space. How does sound energy travel The way sound energy travels is explained by the particle model. The particle model states that all substances are made of particles and these particles vibrate. Sound makes particles in a substance vibrate forwards and backwards. These moving particles hit the particles beside them, passing on the energy so the next particles start to vibrate. And so on it goes, until the energy has passed right through the substance.
11 Example: sound travelling through a solid All substances are made of particles. The sound energy makes the particles in the solid closest to it vibrate. The particles vibrating pass on their energy to the next particles by bumping them, carrying the sound energy. The vibrations carrying the sound energy is passed on to all of the particles in the solid. Fill in the missing words Sound can only move through because sound energy needs to travel by making particles in matter vibrate forwards and backwards in a pattern called a sound wave. Sound cannot be heard in space because space has no. The substance that sound energy travels through is called. The way sound energy travels is explained by the model. Word Bank medium particle particles sound matter matter The particle model states that all matte are made of. When vibrating particles hit other particles, they pass on energy. Energy can be passed from one particle to another particle without changing the that is heard.
12 Activity 2 Light energy Fill in the missing words in the passage below. Light is a form of e that does not require a m to travel. This means light can travel through a vacuum (an area with no matter). The sun s rays travel through the vacuum of s before finally reaching Earth. But we don t hear the massive explosions on the sun since sound cannot travel through ha vacuum. Light travels in s lines. We can see this when we examine the light shining from a torch. The l have edges that are s. If you hold up your hand in front of a light projector you will notice the shadow has a sharp edge. Like any other kind of energy, light can be t into other types of energy. Other types of energy can also be transformed into light energy. For example, light energy can t into e energy into solar powered calculators. Chemical energy can transform into light energy in glow sticks. Activity 3 Edmodo discussion Go to here and reply to the post Explain the phrase In space no one can hear your scream by explaining why no one can hear you if you scream in space.
13 Energy Lesson 4 Electrical energy Watch the Energy Lesson 4 video before doing any of the activities in this booklet for lesson 1. Go to or use the videos Miss Leung gave you. Lesson intention To understand what is and how electricity moves Success criteria I can describe electrical energy as energy of moving charges I can identify that electrical energy moves though a circuit I can name the main parts of a circuit I can use symbols to interpret electrical circuits Activity 1 What is electricity? Fill in the missing words in the passage below. E is the most u form of energy as it is most easily transformed to another form of energy. Energy is transferred in electric circuits. When you t on a light or torch, turn on a computer or press play on a DVD player, you are c an electric circuit. This allows electric charges to travel around the circuit. These charges carry e energy, which is t to useful forms of energy by electrical components in the circuit. An electric circuit usually has an energy source such as a transformer or battery, a conducting path such as wires, a switch and a load, which changes electrical energy into another type of energy. To save time describing circuits, s are used to form a circuit diagram. A circuit diagram shows the parts or components of a circuit, what each is connected to and the order in which they are connected. Below are common symbols used to draw electric circuits.
14 Activity 2 Drawing electric circuits For each circuit below, use circuit symbols to draw a diagram for each circuit. The first circuit has been done for you.
15 Activity 3 Edmodo discussion Go to here and reply to the post Why do we as scientists use symbols to draw circuits?
16 Energy lesson 5 Heat transfer Watch the Energy Lesson 5 video before doing any of the activities in this booklet for lesson 1. Go to or use the videos Miss Leung gave you. Learning intention To understand how heat is transferred or moved from one place to another Success criteria I can describe conduction, convection and radiation Activity 1 Conduction, convection and radiation Read the information and answer the questions. Heat energy conduction, convection and radiation Heat energy can increase the temperature of a substance. Heat can move from one place to another in three ways conduction, convection or radiation. Conduction Heat is transferred in solids by conduction. Conduction occurs when the particles in the part of an object near the heat source vibrate more, and these vibrations are passed on from particle to particle through the object. The particles do not move along the length of the object; they only pass on the increased vibrations. Different substances conduct at heat different rates. Substances that can allow heat to travel through it quickly are called conductors. Substances that do not allow heat to travel through it quickly are called insulators. Metals are generally good conductors of heat while non-metals like paper and plastic are insulators of heat.
17 Convection In liquids and gases (fluids), heat is transferred by convection. When a liquid or gas is heated, the particles in the heated region gain more energy. As a result, they spread out and rise. The cooler particles then come in and take their place. These particles are heated and gain more energy. As they reach the stop, they cool down and have less energy and fall back down to be heated again. Radiation Radiation is the transfer of heat energy by invisible waves and does not need a material to travel through. All objects give out heat radiation the hotter an object is, the more heat it radiates. Dark objects give out more radiation than light-coloured objects. Questions 1. Identify the three ways that heat can move from one place to another. 2. Explain how conduction occurs in terms of particles. 3. Contrast conductors and insulators of heat. 4. True or false: convection is heat transfer in a liquid. 5. Explain how convection occurs in terms of particles. 6. Define radiation.
18 7. Many people wear light-coloured clothes in summer to keep cool and darkcoloured clothes in winter to keep warm. Propose a reason for this. 8. Alex wanted to know which type of saucepan will be the quickest at heating water. She performed an experiment to find this out. Her results are shown in the table below. (a) Which saucepan material was the quickest at heating water? (b) Which saucepan material is the best conductor for heat? (c) Which saucepan material is the poorest conductor for heat? Activity 2 Edmodo discussion Go to and reply to the post Why is the second floor of the school hotter than the first floor of the school? Explain this using conduction, convection or radiation. Also reply to at least one student s post on this thread.
Year 7 Recall Booklet. Name: Class:
 Year 7 Recall Booklet Name: Class: Energy Kinetic energy Moving things have kinetic energy. The heavier a thing is and the faster it moves the more kinetic energy it has. All moving things have kinetic
Year 7 Recall Booklet Name: Class: Energy Kinetic energy Moving things have kinetic energy. The heavier a thing is and the faster it moves the more kinetic energy it has. All moving things have kinetic
KS3 Science. Heat and Energy
 KS3 Science Heat and Energy Heat and Energy Key Words Write a definition for each of the key words listed below Key words States of matter Melt Freeze Evaporate Condense Heat Conduction Convention Radiation
KS3 Science Heat and Energy Heat and Energy Key Words Write a definition for each of the key words listed below Key words States of matter Melt Freeze Evaporate Condense Heat Conduction Convention Radiation
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Forms of Energy Lesson 2 Energy Transformations Lesson 3 Thermal Energy on the Move Chapter Wrap-Up
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Forms of Energy Lesson 2 Energy Transformations Lesson 3 Thermal Energy on the Move Chapter Wrap-Up What is energy, and what are energy transformations? What do you think?
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Forms of Energy Lesson 2 Energy Transformations Lesson 3 Thermal Energy on the Move Chapter Wrap-Up What is energy, and what are energy transformations? What do you think?
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Forms of Energy Lesson 2 Energy Transformations Lesson 3 Thermal Energy on the Move Chapter Wrap-Up
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Forms of Energy Lesson 2 Energy Transformations Lesson 3 Thermal Energy on the Move Chapter Wrap-Up What is energy, and what are energy transformations? What do you think?
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Forms of Energy Lesson 2 Energy Transformations Lesson 3 Thermal Energy on the Move Chapter Wrap-Up What is energy, and what are energy transformations? What do you think?
Electric energy Radiant energy Nuclear energy
 CHAPTER 7 LESSON 1: FORMS OF ENERGY Potential Energy Stored Energy Energy Kinetic Potential Work What is Energy? Mechanical Sound Thermal Electric Radiant Nuclear Potential is stored due to the interactions
CHAPTER 7 LESSON 1: FORMS OF ENERGY Potential Energy Stored Energy Energy Kinetic Potential Work What is Energy? Mechanical Sound Thermal Electric Radiant Nuclear Potential is stored due to the interactions
What Is Air Temperature?
 2.2 Read What Is Air Temperature? In Learning Set 1, you used a thermometer to measure air temperature. But what exactly was the thermometer measuring? What is different about cold air and warm air that
2.2 Read What Is Air Temperature? In Learning Set 1, you used a thermometer to measure air temperature. But what exactly was the thermometer measuring? What is different about cold air and warm air that
Energy - Heat, Light, and Sound
 Energy - Heat, Light, and Sound Source: Utah State Office of Education A two-year-old has plenty of it, and the sun has a bunch of it. Do you know what it is? If not, let me give you a definition: A source
Energy - Heat, Light, and Sound Source: Utah State Office of Education A two-year-old has plenty of it, and the sun has a bunch of it. Do you know what it is? If not, let me give you a definition: A source
Chapter 1 Heating Processes
 Chapter 1 Heating Processes Section 1.1 Heat and temperature Worked example: Try yourself 1.1.1 CALCULATING THE CHANGE IN INTERNAL ENERGY A student places a heating element and a paddle wheel apparatus
Chapter 1 Heating Processes Section 1.1 Heat and temperature Worked example: Try yourself 1.1.1 CALCULATING THE CHANGE IN INTERNAL ENERGY A student places a heating element and a paddle wheel apparatus
Question 1: For the positions labeled on the image, list in order from highest to lowest potential energy of the roller coaster. How is the kinetic
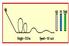 Question 1: For the positions labeled on the image, list in order from highest to lowest potential energy of the roller coaster. How is the kinetic energy of the roller coaster related to these values?
Question 1: For the positions labeled on the image, list in order from highest to lowest potential energy of the roller coaster. How is the kinetic energy of the roller coaster related to these values?
Topic 6: Transferring Energy
 Topic 6: Transferring Energy Transferring Energy Thermal energy can be transferred 3 ways: 1) Radiation 2) Conduction 3) Convection 1) RADIATIONTRANSFERS ENERGY Use p. 226 to answer the following questions
Topic 6: Transferring Energy Transferring Energy Thermal energy can be transferred 3 ways: 1) Radiation 2) Conduction 3) Convection 1) RADIATIONTRANSFERS ENERGY Use p. 226 to answer the following questions
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *1691942825* PHYSICS 0625/33 Paper 3 Theory (Core) October/November 2016 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *1691942825* PHYSICS 0625/33 Paper 3 Theory (Core) October/November 2016 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates
Created by Ken Mattingly Combined Curriculum Document Science Seventh Grade
 Combined Curriculum Document Science Seventh Grade Big Idea: Energy Transformations (Unifying Concepts) Grade 7 Energy transformations are inherent in almost every system in the universe from tangible
Combined Curriculum Document Science Seventh Grade Big Idea: Energy Transformations (Unifying Concepts) Grade 7 Energy transformations are inherent in almost every system in the universe from tangible
Energy is the ability to do work. Q: What is energy? Work is done when a force causes an object to move. Q: What is work? Q: Potential Energy
 Q: What is energy? Energy is the ability to do work. Q: What is work? Work is done when a force causes an object to move. Q: Potential Energy The energy of an object due to its position, shape, or condition
Q: What is energy? Energy is the ability to do work. Q: What is work? Work is done when a force causes an object to move. Q: Potential Energy The energy of an object due to its position, shape, or condition
Topic 2: Heat Affects Matter in Different Ways
 Topic 2: Heat Affects Matter in Different Ways 1 2.1 States of Matter and the Particle Model of Matter A. States of 1. Matter is made up of tiny particles and exist in 3 states:, and. 2. Matter can change
Topic 2: Heat Affects Matter in Different Ways 1 2.1 States of Matter and the Particle Model of Matter A. States of 1. Matter is made up of tiny particles and exist in 3 states:, and. 2. Matter can change
Section 1: The Science of Energy¹
 SECTION1: THE SCIENCE OF ENERGY Section 1: The Science of Energy¹ What Is Energy? Energy is the ability to do work or the ability to make a change. Everything that happens in the world involves the exchange
SECTION1: THE SCIENCE OF ENERGY Section 1: The Science of Energy¹ What Is Energy? Energy is the ability to do work or the ability to make a change. Everything that happens in the world involves the exchange
heat By cillian bryan and scott doyle
 heat By cillian bryan and scott doyle What is heat Heat energy is the result of the movement of tiny particles called atoms molecules or ions in solids, liquids and gases. Heat energy can be transferred
heat By cillian bryan and scott doyle What is heat Heat energy is the result of the movement of tiny particles called atoms molecules or ions in solids, liquids and gases. Heat energy can be transferred
Energy and Energy Transformations
 CHAPTER 2 Energy and Energy Transformations Forms of Energy What do you think? Read the three statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you
CHAPTER 2 Energy and Energy Transformations Forms of Energy What do you think? Read the three statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you
Energy and Energy Resources
 chapter 32 Energy and Energy Resources section 1 What is energy? PS 4.1d: Different forms of energy include heat, light, electrical, mechanical, sound, nuclear, and chemical. Energy is transformed in many
chapter 32 Energy and Energy Resources section 1 What is energy? PS 4.1d: Different forms of energy include heat, light, electrical, mechanical, sound, nuclear, and chemical. Energy is transformed in many
Edexcel GCSE. Paper Reference(s) 5PH2F/01
 Paper Reference(s) 5PH2F/01 Edexcel GCSE Physics/Additional Science Unit P2: Physics for Your Future Foundation Tier Tuesday 18 June 2013 Morning Time: 1 hour plus your additional time allowance INSTRUCTIONS
Paper Reference(s) 5PH2F/01 Edexcel GCSE Physics/Additional Science Unit P2: Physics for Your Future Foundation Tier Tuesday 18 June 2013 Morning Time: 1 hour plus your additional time allowance INSTRUCTIONS
Heat: the transfer of thermal energy from one substance to another. Electrons: the small particles inside an atom that have negative charge.
 GRADE 5 0 Energy: the ability to cause change OR to do work Kinetic energy: energy of motion Potential energy: energy of position (stored energy) Thermal energy: the energy that moves particles of matter
GRADE 5 0 Energy: the ability to cause change OR to do work Kinetic energy: energy of motion Potential energy: energy of position (stored energy) Thermal energy: the energy that moves particles of matter
Energy - the ability to do work or cause change. 1 point
 Energy and Waves Energy - the ability to do work or cause change Work - the transfer of energy Work = Force X Distance Power - the rate at which work is done Power = Work Time Kinetic Energy - the energy
Energy and Waves Energy - the ability to do work or cause change Work - the transfer of energy Work = Force X Distance Power - the rate at which work is done Power = Work Time Kinetic Energy - the energy
Heat and Temperature
 Chapter 4 Heat Heat and Temperature Heat is a form of energy Heat is the energy of random motion of molecules constituting the body. It flows from a hot body to a cold body. Unit of heat is joule (J) and
Chapter 4 Heat Heat and Temperature Heat is a form of energy Heat is the energy of random motion of molecules constituting the body. It flows from a hot body to a cold body. Unit of heat is joule (J) and
Temperature and Heat. Chapter 10. Table of Contents. Chapter 10. Chapter 10. Bellringer. Objectives. Chapter 10. Chapter 10
 Heat and Heat Technology Table of Contents Temperature and Heat Section 3 Matter and Heat Bellringer Objectives The temperature of boiling water is 100 on the Celsius scale and 212 on the Fahrenheit scale.
Heat and Heat Technology Table of Contents Temperature and Heat Section 3 Matter and Heat Bellringer Objectives The temperature of boiling water is 100 on the Celsius scale and 212 on the Fahrenheit scale.
Heat Transfer Lesson Plan
 Heat Transfer Lesson Plan I. Benchmarks: P.EN.M.4 Energy Transfer- Energy is transferred from a source to a receiver by radiation, conduction, and convection. When energy is transferred from one system
Heat Transfer Lesson Plan I. Benchmarks: P.EN.M.4 Energy Transfer- Energy is transferred from a source to a receiver by radiation, conduction, and convection. When energy is transferred from one system
L 18 Thermodynamics [3] Heat flow. Conduction. Convection. Thermal Conductivity. heat conduction. Heat transfer
![L 18 Thermodynamics [3] Heat flow. Conduction. Convection. Thermal Conductivity. heat conduction. Heat transfer L 18 Thermodynamics [3] Heat flow. Conduction. Convection. Thermal Conductivity. heat conduction. Heat transfer](/thumbs/78/76842080.jpg) L 18 Thermodynamics [3] Heat transfer convection conduction emitters of seeing behind closed doors Greenhouse effect Heat Capacity How to boil water Heat flow HEAT the energy that flows from one system
L 18 Thermodynamics [3] Heat transfer convection conduction emitters of seeing behind closed doors Greenhouse effect Heat Capacity How to boil water Heat flow HEAT the energy that flows from one system
Year 9 Science Exam. Multiple Choice Answer Sheet
 Name: Year 9 Science Exam Multiple Choice Answer Sheet Circle the letter indicating the best answer. 1 A B C D 2 A B C D 3 A B C D 4 A B C D 5 A B C D 6 A B C D 7 A B C D 8 A B C D 9 A B C D 10 A B C D
Name: Year 9 Science Exam Multiple Choice Answer Sheet Circle the letter indicating the best answer. 1 A B C D 2 A B C D 3 A B C D 4 A B C D 5 A B C D 6 A B C D 7 A B C D 8 A B C D 9 A B C D 10 A B C D
Where is the shadow?
 Where is the shadow? Light H 29 time 70 minutes learning outcomes To: discover that light travels in a straight line; obstacles placed in the way of the light cause it to change direction know how a shadow
Where is the shadow? Light H 29 time 70 minutes learning outcomes To: discover that light travels in a straight line; obstacles placed in the way of the light cause it to change direction know how a shadow
Gr 10 Physics Worksheet paper 1. Sound and hearing
 Gr 10 Physics Worksheet paper 1 Sound and hearing 1 (a)which row of the table is correct for both infrasound radiation and infrared radiation? Put a cross ( ) in the box next to your answer. [1] (b) Describe
Gr 10 Physics Worksheet paper 1 Sound and hearing 1 (a)which row of the table is correct for both infrasound radiation and infrared radiation? Put a cross ( ) in the box next to your answer. [1] (b) Describe
What is mechanical energy? How do we use it? Energy Energy
 You probably already have some idea what energy is. is easy to recognize. Yet it can be hard to describe. Where do you think you ve seen energy today? How do you think you will use energy tomorrow? Let
You probably already have some idea what energy is. is easy to recognize. Yet it can be hard to describe. Where do you think you ve seen energy today? How do you think you will use energy tomorrow? Let
2,000-gram mass of water compared to a 1,000-gram mass.
 11.2 Heat To change the temperature, you usually need to add or subtract energy. For example, when it s cold outside, you turn up the heat in your house or apartment and the temperature goes up. You know
11.2 Heat To change the temperature, you usually need to add or subtract energy. For example, when it s cold outside, you turn up the heat in your house or apartment and the temperature goes up. You know
NIT 6 MATTER AND HEAT
 NIT 6 MATTER AND HEAT Radiation Convection Thermostat Spread as Spread as Conduction Used in technology as Spread as Bi-Metal Strips HEAT Solid state In Solids Liquid Gas state state State Changes causes
NIT 6 MATTER AND HEAT Radiation Convection Thermostat Spread as Spread as Conduction Used in technology as Spread as Bi-Metal Strips HEAT Solid state In Solids Liquid Gas state state State Changes causes
Stage 7J Current electricity 7K Forces 7L Sound 7I Energy
 Year 7 Physics Stage 7J Current electricity 7K Forces 7L Sound 7I Energy Pink I can Problem solve using the skills I have acquired. AND Describe how voltage is divided between the components in a series
Year 7 Physics Stage 7J Current electricity 7K Forces 7L Sound 7I Energy Pink I can Problem solve using the skills I have acquired. AND Describe how voltage is divided between the components in a series
Science 7 Unit C: Heat and Temperature. Topic 6. Transferring Energy. pp WORKBOOK. Name:
 Science 7 Unit C: Heat and Temperature Topic 6 Transferring Energy pp. 226-236 WORKBOOK Name: 0 Read pp. 226-227 object or material that can transfer energy to other objects Example: light bulb, the Sun
Science 7 Unit C: Heat and Temperature Topic 6 Transferring Energy pp. 226-236 WORKBOOK Name: 0 Read pp. 226-227 object or material that can transfer energy to other objects Example: light bulb, the Sun
Pre-Leaving Certificate Examination, 2014 Triailscrúdú na hardteistiméireachta, 2014
 *B16* Pre-Leaving Certificate Examination, 2014 Triailscrúdú na hardteistiméireachta, 2014 PHYSICS ORDINARY LEVEL TIME: 3 HOURS Answer three questions from Section A and five questions from Section B.
*B16* Pre-Leaving Certificate Examination, 2014 Triailscrúdú na hardteistiméireachta, 2014 PHYSICS ORDINARY LEVEL TIME: 3 HOURS Answer three questions from Section A and five questions from Section B.
FCAT REVIEW Physical Science: Force and Energy
 FCAT REVIEW Physical Science: Force and Energy Force and Motion A force is a push or pull that starts, stops, or changes the direction of an object. Some examples of contact forces are gravity and friction.
FCAT REVIEW Physical Science: Force and Energy Force and Motion A force is a push or pull that starts, stops, or changes the direction of an object. Some examples of contact forces are gravity and friction.
is energy in particles of matter. Chemical energy can be released, for example in or, when these particles react to form new substances.
 TYPES OF ENERGY Energy can be in many different. Students should know sources and properties of the following forms of energy: is the transfer of energy (energy that is associated with the of the particles
TYPES OF ENERGY Energy can be in many different. Students should know sources and properties of the following forms of energy: is the transfer of energy (energy that is associated with the of the particles
The Sun and the Stars
 Objective Concepts (gravity, climate, solar system, hydrogen, helium, elements, ultraviolet rays, cluster, galaxy, Milky Way Galaxy); Sight words (surface, core, dangerous, causes, amount, glowing, tiny,
Objective Concepts (gravity, climate, solar system, hydrogen, helium, elements, ultraviolet rays, cluster, galaxy, Milky Way Galaxy); Sight words (surface, core, dangerous, causes, amount, glowing, tiny,
Heat and Temperature
 Heat and Temperature Temperature What does temperature have to do with energy? What three temperature scales are commonly used? What makes things feel hot or cold? Intro: Discussion A person from Seattle
Heat and Temperature Temperature What does temperature have to do with energy? What three temperature scales are commonly used? What makes things feel hot or cold? Intro: Discussion A person from Seattle
Conducting Energy and Heat. Energy Likes to Move. Radiating Energy
 Energy Likes to Move If there is a temperature difference in a system, heat will naturally move from high to low temperatures. The place you find the higher temperature is the heat source. The area where
Energy Likes to Move If there is a temperature difference in a system, heat will naturally move from high to low temperatures. The place you find the higher temperature is the heat source. The area where
Compound Words. Eye of the Storm. Spelling Words. Name
 Compound Words Generalization A compound word is made of two or more words. Keep all the letters when spelling compounds: shoelace. Word Sort Sort the list words by words you know how to spell and words
Compound Words Generalization A compound word is made of two or more words. Keep all the letters when spelling compounds: shoelace. Word Sort Sort the list words by words you know how to spell and words
Being a Chemist. Summary Sheets. Gleniffer High School
 Being a Chemist Summary Sheets Gleniffer High School 0 State that the light year is a measure of astronomical distance State the speed at which light travels Give examples of the relative distance between
Being a Chemist Summary Sheets Gleniffer High School 0 State that the light year is a measure of astronomical distance State the speed at which light travels Give examples of the relative distance between
Name Date Hour Table Lesson One
 Lesson One Lesson Two Directions: Circle the term in parentheses that correctly completes each sentence. 1. The law of conservation of energy says that energy can be (reduced, transformed) from one
Lesson One Lesson Two Directions: Circle the term in parentheses that correctly completes each sentence. 1. The law of conservation of energy says that energy can be (reduced, transformed) from one
Transfer of Energy in Collision
 Energy can be moved from place to place by moving objects through sound, light, or electric currents. Most energy must have a medium through which to travel. The transfer of this energy changes the way
Energy can be moved from place to place by moving objects through sound, light, or electric currents. Most energy must have a medium through which to travel. The transfer of this energy changes the way
Unit Two Worksheet Matter and Energy WS PS U2
 Unit Two Worksheet Matter and Energy WS PS U2 Name Period Section 4.1 Matching. Match the definition with the term that best correlates to it. 1. Chemical potential energy 2. Elastic potential energy 3.
Unit Two Worksheet Matter and Energy WS PS U2 Name Period Section 4.1 Matching. Match the definition with the term that best correlates to it. 1. Chemical potential energy 2. Elastic potential energy 3.
Name: Packet Due Date: Tuesday, 9/18. Science
 Name: Packet Due Date: Tuesday, 9/18 Science Module 2 Chapter 1 Phase Change Describing Phase Change at Two Scales What happened to the liquid in Titan s Lake? (NGSS Performance Expectations: MS-PS1-1;
Name: Packet Due Date: Tuesday, 9/18 Science Module 2 Chapter 1 Phase Change Describing Phase Change at Two Scales What happened to the liquid in Titan s Lake? (NGSS Performance Expectations: MS-PS1-1;
Q2: What is meant by energy transfer? Energy is converted from one form into others. The total amount will be the same.
 Q1: What is a Sankey diagram used to show? A diagram that represents energy transfers by arrows. The width of each arrow depends upon the amount of energy it represents. Q2: What is meant by energy transfer?
Q1: What is a Sankey diagram used to show? A diagram that represents energy transfers by arrows. The width of each arrow depends upon the amount of energy it represents. Q2: What is meant by energy transfer?
the ability to do work or cause change (work is force exerted on an object causing it to move a distance)
 Vocabulary Terms - Energy energy the ability to do work or cause change (work is force exerted on an object causing it to move a distance) heat Heat is a form of energy that flows between two substances
Vocabulary Terms - Energy energy the ability to do work or cause change (work is force exerted on an object causing it to move a distance) heat Heat is a form of energy that flows between two substances
Heat Transfer. Conduction, Convection, and Radiation. Review: Temperature
 Heat Transfer Conduction, Convection, and Radiation Review: Temperature! Temperature is:! The quantity that tells how hot or cold something is compared with a standard! A measure of the average kinetic
Heat Transfer Conduction, Convection, and Radiation Review: Temperature! Temperature is:! The quantity that tells how hot or cold something is compared with a standard! A measure of the average kinetic
Packet # 4 Where does energy come from and where does it go?
 Packet # 4 Where does energy come from and where does it go? 4-1 What is Energy? o To recognize and describe kinetic and potential energy events. energy: the ability to make something happen potential
Packet # 4 Where does energy come from and where does it go? 4-1 What is Energy? o To recognize and describe kinetic and potential energy events. energy: the ability to make something happen potential
5.1, Building a thermometer
 5.1, Building a thermometer 1) Draw Room Temperature Line (See R on diagram) 2) Draw water line and record temperature after thermometer has been in cold bath for 5 minutes. Record cold temp. = ºC 3) Draw
5.1, Building a thermometer 1) Draw Room Temperature Line (See R on diagram) 2) Draw water line and record temperature after thermometer has been in cold bath for 5 minutes. Record cold temp. = ºC 3) Draw
Useful Information. W = F x. U g = mgh P=I V. v = fλ. Conceptual Physics Final Exam Review Work and Energy. DC Circuits
 Useful Information Work and Energy W = F x W = work [J] F = force [N] x = displacement [m] U g = mgh U g = gravitational potential energy [J] m = mass [kg] h = height [m] DC Circuits I =!! I = current
Useful Information Work and Energy W = F x W = work [J] F = force [N] x = displacement [m] U g = mgh U g = gravitational potential energy [J] m = mass [kg] h = height [m] DC Circuits I =!! I = current
What does temperature have to do with energy? What three temperature scales are commonly used? What makes things feel hot or cold?
 Heat and Temperature Section 1: Temperature What does temperature have to do with energy? What three temperature scales are commonly used? What makes things feel hot or cold? 1 Intro: Discussion A person
Heat and Temperature Section 1: Temperature What does temperature have to do with energy? What three temperature scales are commonly used? What makes things feel hot or cold? 1 Intro: Discussion A person
London Examinations IGCSE
 Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Initial(s) Paper Reference(s) 4420/1F London Examinations IGCSE Physics Paper 1F Foundation Tier Wednesday 4 May 2005 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials
Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Initial(s) Paper Reference(s) 4420/1F London Examinations IGCSE Physics Paper 1F Foundation Tier Wednesday 4 May 2005 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials
PHY2F (JAN08PHY2F01) General Certifi cate of Secondary Education January ADDITIONAL SCIENCE Unit Physics P2. PHYSICS Unit Physics P2
 Surname Other Names For Examiner s Use Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certifi cate of Secondary Education January 2008 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE Unit Physics P2 PHYSICS Unit Physics
Surname Other Names For Examiner s Use Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certifi cate of Secondary Education January 2008 ADDITIONAL SCIENCE Unit Physics P2 PHYSICS Unit Physics
Name: Number: Class: Date: What is light? 1. What is the name for all these types of light? 2. What type of light can humans see?
 Name: Number: Class: Date: What is light? Worksheet 1 1. What is the name for all these types of light? 2. What type of light can humans see? 3. What type of light has the longest wavelength? 4. What types
Name: Number: Class: Date: What is light? Worksheet 1 1. What is the name for all these types of light? 2. What type of light can humans see? 3. What type of light has the longest wavelength? 4. What types
Preparing for your mock exams - AQA P1
 Name Topic title 1.1 Infrared radiation and surfaces Preparing for your mock exams - AQA P1 Know that all materials emit and absorb infrared radiation. Understand that the hotter an object is, the higher
Name Topic title 1.1 Infrared radiation and surfaces Preparing for your mock exams - AQA P1 Know that all materials emit and absorb infrared radiation. Understand that the hotter an object is, the higher
An Introduction to Electricity and Circuits
 An Introduction to Electricity and Circuits Materials prepared by Daniel Duke 4 th Sept 2013. This document may be copied and edited freely with attribution. This course has been designed to introduce
An Introduction to Electricity and Circuits Materials prepared by Daniel Duke 4 th Sept 2013. This document may be copied and edited freely with attribution. This course has been designed to introduce
1. The type of energy described by Energy C is which type of energy?
 Energy A Energy B Energy C Energy D Energy E Energy stores within a particle (measured by the particle s temperature). Energy generated by the sun. Energy released when particles react to form a new substance.
Energy A Energy B Energy C Energy D Energy E Energy stores within a particle (measured by the particle s temperature). Energy generated by the sun. Energy released when particles react to form a new substance.
Lesson 1: Force as an Interaction
 1.1 Observe and Represent Lesson 1: Force as an Interaction a) Pick up a tennis ball and hold it in your hand. Now pick up a medicine ball and hold it. Do you feel the difference? How can you describe
1.1 Observe and Represent Lesson 1: Force as an Interaction a) Pick up a tennis ball and hold it in your hand. Now pick up a medicine ball and hold it. Do you feel the difference? How can you describe
WAVES AND RADIATION. 1 Measuring the focal length of a lens. Topic 7 Physics. The diagram shows how to measure the focal length of a lens.
 1 Measuring the focal length of a lens The diagram shows how to measure the focal length of a lens. Which of these is the correct distance for the focal length? A from the window to the lens B from the
1 Measuring the focal length of a lens The diagram shows how to measure the focal length of a lens. Which of these is the correct distance for the focal length? A from the window to the lens B from the
You are about to start an exciting series of lessons on physical science. God s Design for the Physical World
 Table of of Contents Unit 1 - Forms of Energy Lesson 1 Forms of Energy 8 Lesson 2 Mechanical Energy 12 Lesson 3 Chemical Energy 16 Lesson 4 Nuclear Energy 18 Lesson 5 Nuclear Weapons 21 Special Feature
Table of of Contents Unit 1 - Forms of Energy Lesson 1 Forms of Energy 8 Lesson 2 Mechanical Energy 12 Lesson 3 Chemical Energy 16 Lesson 4 Nuclear Energy 18 Lesson 5 Nuclear Weapons 21 Special Feature
Being a Physicist Unit 5. Summary Sheets. Gleniffer High School
 Being a Physicist Unit 5 Summary Sheets Gleniffer High School 0 Experiences & Outcomes I can explain how sound vibrations are carried by waves through air, water and other materials SCN 2-11a By exploring
Being a Physicist Unit 5 Summary Sheets Gleniffer High School 0 Experiences & Outcomes I can explain how sound vibrations are carried by waves through air, water and other materials SCN 2-11a By exploring
INTRODUCTION TO LESSON CLUSTER 8 Explaining Evaporation and Boiling
 INTRODUCTION TO LESSON CLUSTER 8 Explaining Evaporation and Boiling A. Lesson Cluster Goals and Lesson Objectives Goals: Students should be able to explain evaporation and boiling, both in macroscopic
INTRODUCTION TO LESSON CLUSTER 8 Explaining Evaporation and Boiling A. Lesson Cluster Goals and Lesson Objectives Goals: Students should be able to explain evaporation and boiling, both in macroscopic
Energy can be transformed in to: Mechanical Electrical Thermal Light Sound
 Energy and Force Study Guide CBA 2 STANDARD 5.6A Explore the uses of energy, including mechanical, light, thermal, electrical, and sound energy 5.6B demonstrate that the flow of electricity in circuits
Energy and Force Study Guide CBA 2 STANDARD 5.6A Explore the uses of energy, including mechanical, light, thermal, electrical, and sound energy 5.6B demonstrate that the flow of electricity in circuits
Identify all the forms of energy you see in the picture below.
 Identify all the forms of energy you see in the picture below. Essential Question: How are forms of energy alike and different? Standards: S8P2c. Compare and contrast the different forms of energy (heat,
Identify all the forms of energy you see in the picture below. Essential Question: How are forms of energy alike and different? Standards: S8P2c. Compare and contrast the different forms of energy (heat,
Course Guide. Introduction... 2
 Introduction... 2 Unit 1: Matter, States, & Interactions Lesson 1: Properties of Matter... 2 Lesson 2: States of Matter... 2 Lesson 3: Matter Particles... 3 Lesson 4: Organization of Matter... 3 Lesson
Introduction... 2 Unit 1: Matter, States, & Interactions Lesson 1: Properties of Matter... 2 Lesson 2: States of Matter... 2 Lesson 3: Matter Particles... 3 Lesson 4: Organization of Matter... 3 Lesson
Sixth Grade Science BLOCK 3 ASSESSMENT Heat, Light, and Sound
 Sixth Grade Science BLOCK 3 ASSESSMENT Heat, Light, and Sound 2008-09 Directions: Choose the best answer for each question. Then mark your choice on your answer sheet. 1. Which is the best activity to
Sixth Grade Science BLOCK 3 ASSESSMENT Heat, Light, and Sound 2008-09 Directions: Choose the best answer for each question. Then mark your choice on your answer sheet. 1. Which is the best activity to
Full Moon. Phases of the Moon
 Phases of the Moon The Moon takes 29.5 days to orbit Earth. This is a lunar month. The gravity of the Earth keeps the Moon in orbit. The Moon does not produce light. We see the Moon because it reflects
Phases of the Moon The Moon takes 29.5 days to orbit Earth. This is a lunar month. The gravity of the Earth keeps the Moon in orbit. The Moon does not produce light. We see the Moon because it reflects
YEAR 11 PHYSICS TIME: 2 hours
 DIRECTORATE FOR QUALITY AND STANDARDS IN EDUCATION Department of Curriculum Management Educational Assessment Unit Annual Examinations for Secondary Schools 2017 Track 2 YEAR 11 PHYSICS TIME: 2 hours Name:
DIRECTORATE FOR QUALITY AND STANDARDS IN EDUCATION Department of Curriculum Management Educational Assessment Unit Annual Examinations for Secondary Schools 2017 Track 2 YEAR 11 PHYSICS TIME: 2 hours Name:
Yr. 9 Electricity WorkBook
 Yr. 9 Electricity WorkBook On completion of this booklet students should be able to: Recall the structure of a neutral atom: three particles, their charges, their location; Nucleus (Proton positive, Neutron-
Yr. 9 Electricity WorkBook On completion of this booklet students should be able to: Recall the structure of a neutral atom: three particles, their charges, their location; Nucleus (Proton positive, Neutron-
produce sugar, which contains stored chemical energy. Most of the energy that we use on Earth originally came from the Sun.
 Conservation of Energy Energy can be in many different forms. Students should know sources and properties of the following forms of energy: Heat energy is the transfer of thermal energy (energy that is
Conservation of Energy Energy can be in many different forms. Students should know sources and properties of the following forms of energy: Heat energy is the transfer of thermal energy (energy that is
Experimenting with Forces
 A mother hears a loud crash in the living room. She walks into the room to see her seven-year-old son looking at a broken vase on the floor. How did that happen? she asks. I don t know. The vase just fell
A mother hears a loud crash in the living room. She walks into the room to see her seven-year-old son looking at a broken vase on the floor. How did that happen? she asks. I don t know. The vase just fell
Southern Nevada Regional Professional Development Program. What happens when water changes to a solid?
 3-5 Physical Science What happens when water changes to a solid? Two large soft vials with caps One plastic 50 ml syringe Plastic ice tray Water Freezer compartment 1. Completely fill the ice tray and
3-5 Physical Science What happens when water changes to a solid? Two large soft vials with caps One plastic 50 ml syringe Plastic ice tray Water Freezer compartment 1. Completely fill the ice tray and
Name Class Date. What are three kinds of energy transfer? What are conductors and insulators? What makes something a good conductor of heat?
 CHAPTER 14 SECTION Heat and Temperature 2 Energy Transfer KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What are three kinds of energy transfer? What are conductors and insulators?
CHAPTER 14 SECTION Heat and Temperature 2 Energy Transfer KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What are three kinds of energy transfer? What are conductors and insulators?
Fourth Grade News Flash
 S Fourth Grade News Flash November 8, 2013 Dates to Remember 11/4 - No School 11/8 - End of 1 st Trimester 11/13 and 11/14 - Family Breakfast 11/15 - Report Cards sent home Language Arts This week s selection
S Fourth Grade News Flash November 8, 2013 Dates to Remember 11/4 - No School 11/8 - End of 1 st Trimester 11/13 and 11/14 - Family Breakfast 11/15 - Report Cards sent home Language Arts This week s selection
Thermal Energy. Chapter 6 2 Transferring Thermal Energy
 Thermal Energy Chapter 6 2 Transferring Thermal Energy Objectives Compare and contrast conduction, convection, and radiation. Compare and contrast conductors and insulators. CLE 3202.2.3 Examine the applications
Thermal Energy Chapter 6 2 Transferring Thermal Energy Objectives Compare and contrast conduction, convection, and radiation. Compare and contrast conductors and insulators. CLE 3202.2.3 Examine the applications
Embedded Assessment Notes
 Embedded Assessment Notes Investigation, Part Energy and Electromagnetism Date Got it! Concept Concept Reflections/Next Steps Investigation, Part Date Got it! Concept Concept Reflections/Next Steps Embedded
Embedded Assessment Notes Investigation, Part Energy and Electromagnetism Date Got it! Concept Concept Reflections/Next Steps Investigation, Part Date Got it! Concept Concept Reflections/Next Steps Embedded
Conceptual Physics Final Exam Review
 Useful Information Work and Energy W = F x W = work [J] F = force [N] x = displacement [m] U g = mgh U g = gravitational potential energy [J] m = mass [kg] h = height [m] g = 10 m/s 2 DC Circuits I =!!
Useful Information Work and Energy W = F x W = work [J] F = force [N] x = displacement [m] U g = mgh U g = gravitational potential energy [J] m = mass [kg] h = height [m] g = 10 m/s 2 DC Circuits I =!!
International General Certificate of Secondary Education UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE LOCAL EXAMINATIONS SYNDICATE
 Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Name International General Certificate of Secondary Education UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE LOCAL EXAMINATIONS SYNDICATE PHYSICS 0625/3 PAPER 3 MAY/JUNE SESSION 2000
Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Name International General Certificate of Secondary Education UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE LOCAL EXAMINATIONS SYNDICATE PHYSICS 0625/3 PAPER 3 MAY/JUNE SESSION 2000
Physical Science Across The Grades K-7
 S C I E N C E G R A D E L E V E L CO N T E N T E X P E C TAT I O N S Physical Science Across The Grades K-7 PHYSICAL LIFE The Office of School Improvement has developed the Science Across the Grades companion
S C I E N C E G R A D E L E V E L CO N T E N T E X P E C TAT I O N S Physical Science Across The Grades K-7 PHYSICAL LIFE The Office of School Improvement has developed the Science Across the Grades companion
4. What verb is used to describe Earth s
 Name: Date: 1 Read the text and then answer the questions. No matter where on Earth you live, you have day and night. That happens because of a movement of Earth called rotation. Earth rotates, or turns,
Name: Date: 1 Read the text and then answer the questions. No matter where on Earth you live, you have day and night. That happens because of a movement of Earth called rotation. Earth rotates, or turns,
3.P 10.1 and 10.2 Forms of Energy
 3.P 10.1 and 10.2 Forms of Energy STEMscopedia Forms of Energy Addressed Benchmarks: SC.3.P.10.1: Identify some basic forms of energy, such as light, heat, thermal, sound, electrical, and mechanical. SC.3.P.10.2:
3.P 10.1 and 10.2 Forms of Energy STEMscopedia Forms of Energy Addressed Benchmarks: SC.3.P.10.1: Identify some basic forms of energy, such as light, heat, thermal, sound, electrical, and mechanical. SC.3.P.10.2:
Forces. Unit 2. Why are forces important? In this Unit, you will learn: Key words. Previously PHYSICS 219
 Previously Remember From Page 218 Forces are pushes and pulls that can move or squash objects. An object s speed is the distance it travels every second; if its speed increases, it is accelerating. Unit
Previously Remember From Page 218 Forces are pushes and pulls that can move or squash objects. An object s speed is the distance it travels every second; if its speed increases, it is accelerating. Unit
Chapter: Motion, Acceleration, and Forces
 Chapter 3 Table of Contents Chapter: Motion, Acceleration, and Forces Section 1: Describing Motion Section 2: Acceleration Section 3: Motion and Forces 1 Motion Describing Motion Distance and time are
Chapter 3 Table of Contents Chapter: Motion, Acceleration, and Forces Section 1: Describing Motion Section 2: Acceleration Section 3: Motion and Forces 1 Motion Describing Motion Distance and time are
The sun s energy is transferred to the Earth with a wide range of wave lengths consisting of visible light, infrared, and ultraviolet.
 TEACHING LEARNING COLLABORATIVE (TLC) EARTH SCIENCE Heat Moves Grade 6 Created by: Sandra Cornell (Terrace Middle School); Sue Cascio (Coyote Valley Elementary School); and Stacy Holland (Terrace Middle
TEACHING LEARNING COLLABORATIVE (TLC) EARTH SCIENCE Heat Moves Grade 6 Created by: Sandra Cornell (Terrace Middle School); Sue Cascio (Coyote Valley Elementary School); and Stacy Holland (Terrace Middle
9/27/12. Chapter: Motion, Acceleration, and Forces. Motion and Position. Motion. Distance. Relative Motion
 9/7/ Table of Contents Chapter: Motion,, and Forces Section : Chapter Section : Section : Motion Distance and time are important. In order to win a race, you must cover the distance in the shortest amount
9/7/ Table of Contents Chapter: Motion,, and Forces Section : Chapter Section : Section : Motion Distance and time are important. In order to win a race, you must cover the distance in the shortest amount
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education PHYSICS 0625/02
 Centre Number Candidate Number Name UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education PHYSICS 0625/02 Paper 2 Candidates answer on the Question
Centre Number Candidate Number Name UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education PHYSICS 0625/02 Paper 2 Candidates answer on the Question
Grade 7 Physical Pretest
 Grade 7 Physical Pretest Select the best answer to each question. 1. Energy from the sun arrives as electromagnetic radiation with a wide range of wavelengths and frequencies. Of the four wave types listed,
Grade 7 Physical Pretest Select the best answer to each question. 1. Energy from the sun arrives as electromagnetic radiation with a wide range of wavelengths and frequencies. Of the four wave types listed,
radio, riding This curriculum
 NERGY RADE ASSESSMENT PACKET Energy is the mover and shaker of the universe. Heat from the sun, sounds from your radio, riding a bike and watching a movie are all expressionss of different forms of energy.
NERGY RADE ASSESSMENT PACKET Energy is the mover and shaker of the universe. Heat from the sun, sounds from your radio, riding a bike and watching a movie are all expressionss of different forms of energy.
London Examinations IGCSE
 Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Initial(s) Paper Reference(s) 4420/1F London Examinations IGCSE Physics Paper 1F Foundation Tier Monday 31 October 2005 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Examiner
Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Initial(s) Paper Reference(s) 4420/1F London Examinations IGCSE Physics Paper 1F Foundation Tier Monday 31 October 2005 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Examiner
STUDY GUIDE - 6TH GRADE WEEK 12 CCA
 1. Which of the following statements about energy is true? STUDY GUIDE - 6TH GRADE WEEK 12 CCA A. Potential energy and kinetic energy are different names for the same kind of energy. B. Gravity has nothing
1. Which of the following statements about energy is true? STUDY GUIDE - 6TH GRADE WEEK 12 CCA A. Potential energy and kinetic energy are different names for the same kind of energy. B. Gravity has nothing
Unit C REVIEW Heat and Temperature
 Science 7 Name: Date: Unit C REVIEW Heat and Temperature 1. Read each sentence and circle the correct bold word. Scientists explain changes in state using the particle model of substances / matter. This
Science 7 Name: Date: Unit C REVIEW Heat and Temperature 1. Read each sentence and circle the correct bold word. Scientists explain changes in state using the particle model of substances / matter. This
Stars and Galaxies. The Sun and Other Stars
 CHAPTER 22 Stars and Galaxies LESSON 2 The Sun and Other Stars What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you
CHAPTER 22 Stars and Galaxies LESSON 2 The Sun and Other Stars What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you
P1 REVISION CHAPTER 1a Energy Tfr by Heating
 P1 REVISION CHAPTER 1a Energy Tfr by Heating Infrared Radiation What gives off infrared radiation? What is a vacuum? Surfaces & Radiation What surfaces are good absorbers of infrared radiation? What surfaces
P1 REVISION CHAPTER 1a Energy Tfr by Heating Infrared Radiation What gives off infrared radiation? What is a vacuum? Surfaces & Radiation What surfaces are good absorbers of infrared radiation? What surfaces
Problem Solver Skill 5. Defines multiple or complex problems and brainstorms a variety of solutions
 Motion and Forces Broad Concept: Newton s laws of motion and gravitation describe and predict the motion of most objects. LS 1.1 Compare and contrast vector quantities (such as, displacement, velocity,
Motion and Forces Broad Concept: Newton s laws of motion and gravitation describe and predict the motion of most objects. LS 1.1 Compare and contrast vector quantities (such as, displacement, velocity,
How Does the Sun s Energy Cause Rain?
 1.2 Investigate 3.3 Read How Does the Sun s Energy Cause Rain? In the water-cycle simulation, you observed water change from a liquid to a gas, and then back to a liquid falling to the bottom of the container.
1.2 Investigate 3.3 Read How Does the Sun s Energy Cause Rain? In the water-cycle simulation, you observed water change from a liquid to a gas, and then back to a liquid falling to the bottom of the container.
Unit 4 Review. Vocabulary. Key Concepts. Unit 4 Review. Fill in the blank with the term that best completes the sentence.
 Name Vocabulary Fill in the blank with the term that best completes the sentence. 1 The of an object describes the speed and the direction in which it is going. 2 is the energy transferred from an object
Name Vocabulary Fill in the blank with the term that best completes the sentence. 1 The of an object describes the speed and the direction in which it is going. 2 is the energy transferred from an object
XX. Introductory Physics, High School
 XX. Introductory Physics, High School High School Introductory Physics Test The spring 015 high school Introductory Physics test was based on learning standards in the Introductory Physics content strand
XX. Introductory Physics, High School High School Introductory Physics Test The spring 015 high school Introductory Physics test was based on learning standards in the Introductory Physics content strand
Introduction of Heat Transfer. Prepared by: Nimesh Gajjar GIT-MED
 Introduction of Heat Transfer Prepared by: Nimesh Gajjar GIT-MED Difference between heat and temperature Temperature is a measure of the amount of energy possessed by the molecules of a substance. It manifests
Introduction of Heat Transfer Prepared by: Nimesh Gajjar GIT-MED Difference between heat and temperature Temperature is a measure of the amount of energy possessed by the molecules of a substance. It manifests
McGraw-Hill Science 2000, Texas Edition TAKS Practice Test. Grade 3, Chapter 6 Energy. Name. Date
 McGraw-Hill Science 2000, Texas Edition TAKS Practice Test Grade 3, Chapter 6 Energy Name Date Use the text, illustration and your knowledge of science to answer Questions 1 to 4. The illustration shows
McGraw-Hill Science 2000, Texas Edition TAKS Practice Test Grade 3, Chapter 6 Energy Name Date Use the text, illustration and your knowledge of science to answer Questions 1 to 4. The illustration shows
