3-manifolds and their groups
|
|
|
- Ophelia McGee
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 3-manifolds and their groups Dale Rolfsen University of British Columbia Marseille, September 2010 Dale Rolfsen (2010) 3-manifolds and their groups Marseille, September / 31
2 3-manifolds and their groups A 3-manifold M is a space which is locally modelled on R 3, or R 3 + for boundary points. M is closed if it is compact and has no boundary points. What does π 1 (M) tell us about M itself? That question is the theme of these talks. Dale Rolfsen (2010) 3-manifolds and their groups Marseille, September / 31
3 How is a 3-manifold given? One can describe a 3-manifold by: triangulation Heegaard splitting surgery on a link in S 3 orbit space of group of isometries of a geometry special constructions such as Seifert fibre spaces and fibre bundles over S 1 In each case, calculation of a presentation for π 1 (M) is straightforward. Dale Rolfsen (2010) 3-manifolds and their groups Marseille, September / 31
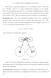
4 A Heegaard diagram of Poincaré s dodecahedral space. Dale Rolfsen (2010) 3-manifolds and their groups Marseille, September / 31
5 The Poincaré conjecture Recently proved by Perelman a century after conjecture by Poincaré If M is a closed 3-manifold, then π 1 (M) = 1 iff M = S 3 An equivalent form of this theorem is If M is a compact contractible 3-manifold with boundary, then M is a 3-dimensional ball. Dale Rolfsen (2010) 3-manifolds and their groups Marseille, September / 31
6 History: Kneser s conjecture If π 1 (M) = G 1 G 2 is a free product of nontrivial groups, then M is a connected sum M = M 1 M 2 with π 1 (M i ) = G i. In other words, there is a 2-sphere in M separating it into two submanifolds which realizes the splitting of the group. By a theorem of Milnor, a closed 3-manifold has a unique splitting M = M 1 M 2 M n into prime factors (up to order of the factors). Dale Rolfsen (2010) 3-manifolds and their groups Marseille, September / 31
7 Now that the PC is proved we have π 1 (M) is a free product if and only if M is a connected sum. Or, put another way... M is prime if and only if π 1 (M) does not split as a free product. Dale Rolfsen (2010) 3-manifolds and their groups Marseille, September / 31
8 History: Sphere theorem Speaking of 2-spheres, there is a nice algebraic criterion for the existence of an essential S 2 in a 3-manifold. If M is an orientable 3-manifold, then M contains an embedded homotopically nontrivial 2-sphere if and only if π 2 (M) = 0 From the same era (about 50 years ago) came Dehn s lemma and the loop theorem useful technical tools for detecting essential surfaces, doing surgery, etc. We won t discuss them today, though they are part of the story of algebra reflecting topology. Dale Rolfsen (2010) 3-manifolds and their groups Marseille, September / 31
9 Does π 1 (M) determine M? Certainly not! For example certain lens spaces have isomorphic (cyclic) fundamental groups, but may not be homeomorphic, or even homotopy equivalent. As another example, the complements of the reef knot and granny knot in S 3 have isomorphic groups, but they are not topologically equivalent. Dale Rolfsen (2010) 3-manifolds and their groups Marseille, September / 31
10 Does π 1 (M) determine M? An important class of 3-manifolds is the Haken manifold. M is Haken if it is compact, orientable and irreducible and sufficiently large in the sense that it contains an incompressible surface. Irreducible means that every (tame) 2-sphere bounds a 3-ball in M. A prime manifold is irreducible, or else homeomorphic to S 1 S 2. The surface S in M is incompressible if it is not a sphere and the inclusion-induced homomorphism π 1 (S) π 1 (M) is injective. Being Haken enables one to prove properties of M by induction, using a heirarchy obtained by cutting M open along S, showing the result contains another impressible surface, then cut along that surface, etc. After a finite number of steps M is decomposed into a disjoint union of 3-balls. Dale Rolfsen (2010) 3-manifolds and their groups Marseille, September / 31
11 Does π 1 (M) determine M? Positive results in this direction are due to Waldhausen (1968). Suppose M 1 and M 2 are compact orientable manifolds with nonempty boundary, and φ : π 1 (M 1 ) π 1 (M 2 ) an isomorphism. Then φ is induced by a homeomorphism M 1 M 2 provided the M i are irreducible and the boundary components are incompressible and φ preserves the peripheral structure. This has been generalized in several directions since then. Dale Rolfsen (2010) 3-manifolds and their groups Marseille, September / 31
12 Geometric structures Thurston showed that their are eight possible 3-dimensional geometric structures on 3-manifolds: Hyperbolic (H 3 ), spherical (S 3 ) and euclidean (E 3 ) and S 2 E 1, H 2 E 1, Nil, Sol and PSL(2, R) A 3-manifold is geometric if it can be expressed as the orbit space of a discrete group of isometries acting freely on the model geometry. Dale Rolfsen (2010) 3-manifolds and their groups Marseille, September / 31
13 Geometric structures Thurston also showed: If the compact 3-manifold M is geometric, then π 1 (M) determines its geometry. Dale Rolfsen (2010) 3-manifolds and their groups Marseille, September / 31
14 JSJ decomposition Jaco and Shalen, and (independently) Johannson proved Irreducible orientable closed 3-manifolds have a unique (up to isotopy) minimal collection of disjointly embedded incompressible tori such that each component of the 3-manifold obtained by cutting along the tori is either atoroidal or Seifert-fibered. The tori correspond to Z Z subgroups of the fundamental group. Atoroidal means there is no essential torus, or in algebraic terms, the fundamental group contains no subgroup isomorphic with Z Z. Dale Rolfsen (2010) 3-manifolds and their groups Marseille, September / 31
15 Thurston s geometrization conjecture A Seifert-fibred 3-manifold (roughly speaking) is one which is the disjoint union of topological circles. Such manifolds, with the exception of RP 3 RP 3, are irreducible. It is known that irreducible Seifert-fibred 3-manifolds are geometric. Thurston s geometrization conjecture asserts that each component of the JSJ decomposition is geometric. Dale Rolfsen (2010) 3-manifolds and their groups Marseille, September / 31
16 Thurston s geometrization conjecture TGC was proved for Haken manifolds by Thurston and others. It was recently proved in general by Perelman. Each component of the JSJ decomposition is geometric. It has many consequences. Dale Rolfsen (2010) 3-manifolds and their groups Marseille, September / 31
17 Consequences of TGC The spherical space form conjecture... If π 1 (M) is finite, then M has a metric of constant positive curvature. Dale Rolfsen (2010) 3-manifolds and their groups Marseille, September / 31
18 Consequences of TGC If the prime 3-manifold M is non-haken and has infinite fundamental group, then M is Seifert fibred or hyperbolic. Dale Rolfsen (2010) 3-manifolds and their groups Marseille, September / 31
19 Consequences of TGC Combining with other recent results, it solves the homeomorphism problem. There is an algorithm to decide if two given compact 3-manifolds are homeomorphic. This is in contrast with dimensions greater than 3, in which the homeomorphism problem cannot be solved algorithmically. Dale Rolfsen (2010) 3-manifolds and their groups Marseille, September / 31
20 Further consequences of PC Collapsing and simple-homotopy: Suppose the finite polyhedron K has a simplex σ n which has a free face τ n 1 (meaning int(τ) does not intersect any other part of K). Then the transition: K K \ {int(σ) int(τ)} is called an elementary collapse. The inverse of this operation is an elementary expansion. Dale Rolfsen (2010) 3-manifolds and their groups Marseille, September / 31
21 Further consequences of PC J. H. C. Whitehead defined simple homotopy to be the equivalence relation among polyhedra which is generated by elementary collapse and expansion. Subdivision is also allowed. If two polyhedra have the same simple homotopy type, then they are homotopy equivalent, but the converse is not true. Whitehead torsion is an obstruction to going in the other direction. A sequence of expansions and collapses involving simplices of dimension at most n is called an n-deformation. Dale Rolfsen (2010) 3-manifolds and their groups Marseille, September / 31
22 Further consequences of PC (Whitehead-Wall): If n 2, and the polyhedra K n and L n are simple-homotopy equivalent, then there exists an n + 1-deformation from K to L. The case n = 2 is still open. It is related to a problem which is equivalent to a group-theoretic conjecture made by Andrews and Curtis that a balanced presentation of the trivial group can be reduced to the trivial presentation by certain specific moves. Dale Rolfsen (2010) 3-manifolds and their groups Marseille, September / 31
23 Further consequences of PC The A-C conjecture concerns presentations of the trivial group which are balanced in the sense of having the same number of generators and relations. Examples x, y x, y x, y x p y q, x r y s, ps rq = ±1 x, y x 1 y 2 x = y 3, y 1 x 2 y = x 3 x, y x 4 y 3 = y 2 x 2, x 6 y 4 = y 3 x 3 x, y, z y 1 xy = x 2, z 1 yz = y 2, x 1 zx = z 2, all present the trivial group. Dale Rolfsen (2010) 3-manifolds and their groups Marseille, September / 31
24 Further consequences of PC Given a presentation x 1,..., x n ; r 1,... r m of a group, consider the operations, which do not change the group presented: (1) replace r i by its inverse r 1 i, (2) replace r i by r i r j, i j, (3) replace r i by gr i g 1, where g F (x 1,..., x n ). (4) introduce a generator x n+1 and relator r n+1 which is just x n+1. Andrews-Curtis Conjecture: A balanced presentation of the trivial group can be reduced to the empty presentation by (1)-(3) above, and operation (4) and its inverse. Dale Rolfsen (2010) 3-manifolds and their groups Marseille, September / 31
25 Further consequences of PC The A-C conjecture is equivalent to Geometric Andrews-Curtis conjecture: If K 2 is contractible then K 3-deforms to a point. The A-C conjectures remains open in general, but the PC implies some progress in this... If a 2-complex happens to embed in a 3-manifold, we will call it a spine. One sees easily that a regular neighbourhood of a spine collapses to the spine. There is an algorithm, due to Neuwirth, to decide if a given 2-complex is a spine. Dale Rolfsen (2010) 3-manifolds and their groups Marseille, September / 31
26 Further consequences of PC The (geometric) A-C conjecture is true for spines. proof: Let N 3 be a regular neighbourhood in a manifold containing the contractible K 2, so that N collapses to K. The PC implies N 3 is homeomorphic with the standard 3-ball, and hence collapsible to a point. This gives the 3-deformation asserted by the ACC: K 2 N 3 pt Dale Rolfsen (2010) 3-manifolds and their groups Marseille, September / 31
27 Further consequences of PC Zeeman conjecture: If K 2 is a contractible complex, then K I collapses to a point. Clearly the ZC implies the ACC, because the transition K K I pt gives a 3-deformation. The ZC also implies the PC, by the following argument: Suppose that Q 3 is a compact, contractible manifold. Q collapses to a spine K 2, also contractible. By ZC, K I collapses to a point. Then Q I collapses to K I, which then collapses to a point. Being a collapsible 4-manifold, Q I must be a 4-ball. Now Q clearly embeds in (Q I ), which is a 3-sphere. Therefore Q is a 3-ball. Dale Rolfsen (2010) 3-manifolds and their groups Marseille, September / 31
28 Further consequences of PC A converse... A 2-complex is standard if it is modeled on the cone upon 3 1, the 1-skeleton of a 3-simplex. Every 3-manifold with nonempty boundary collapses to a standard spine and is determined by such a spine. Local structure of a standard complex Dale Rolfsen (2010) 3-manifolds and their groups Marseille, September / 31
29 Further consequences of PC Bing s house with two rooms A standard spine of the cube It is contractible, but not collapsible Dale Rolfsen (2010) 3-manifolds and their groups Marseille, September / 31
30 Further consequences of PC The igloo Another contractible, non-collapsible 2-polyhedron Dale Rolfsen (2010) 3-manifolds and their groups Marseille, September / 31
31 Further consequences of PC (Gillman - R.) The ZC, restricted to standard spines, is equivalent to the PC. Key idea of the proof: We ve already seen that the ZC implies the PC. Since every 3-manifold with boundary collapses to a special spine, the same proof works for ZC, restricted to standard spines. For the converse, if K 2 is a standard spine of M 3 and has trivial homology groups, then (by an explicit construction) K I collapses to a subset homeomorphic to M. If K is contractible, so is M, and assuming PC, M is a 3-ball, and so K I M verifies the ZC for K. Corollary The ZC and ACC are true for standard spines. Dale Rolfsen (2010) 3-manifolds and their groups Marseille, September / 31
Invariants of knots and 3-manifolds: Survey on 3-manifolds
 Invariants of knots and 3-manifolds: Survey on 3-manifolds Wolfgang Lück Bonn Germany email wolfgang.lueck@him.uni-bonn.de http://131.220.77.52/lueck/ Bonn, 10. & 12. April 2018 Wolfgang Lück (MI, Bonn)
Invariants of knots and 3-manifolds: Survey on 3-manifolds Wolfgang Lück Bonn Germany email wolfgang.lueck@him.uni-bonn.de http://131.220.77.52/lueck/ Bonn, 10. & 12. April 2018 Wolfgang Lück (MI, Bonn)
PRELIMINARY LECTURES ON KLEINIAN GROUPS
 PRELIMINARY LECTURES ON KLEINIAN GROUPS KEN ICHI OHSHIKA In this two lectures, I shall present some backgrounds on Kleinian group theory, which, I hope, would be useful for understanding more advanced
PRELIMINARY LECTURES ON KLEINIAN GROUPS KEN ICHI OHSHIKA In this two lectures, I shall present some backgrounds on Kleinian group theory, which, I hope, would be useful for understanding more advanced
HYPERBOLIC GEOMETRY AND HEEGAARD SPLITTINGS
 HYPERBOLIC GEOMETRY AND HEEGAARD SPLITTINGS TALK GIVEN BY HOSSEIN NAMAZI 1. Preliminary Remarks The lecture is based on joint work with J. Brock, Y. Minsky and J. Souto. Example. Suppose H + and H are
HYPERBOLIC GEOMETRY AND HEEGAARD SPLITTINGS TALK GIVEN BY HOSSEIN NAMAZI 1. Preliminary Remarks The lecture is based on joint work with J. Brock, Y. Minsky and J. Souto. Example. Suppose H + and H are
ALGEBRAICALLY TRIVIAL, BUT TOPOLOGICALLY NON-TRIVIAL MAP. Contents 1. Introduction 1
 ALGEBRAICALLY TRIVIAL, BUT TOPOLOGICALLY NON-TRIVIAL MAP HONG GYUN KIM Abstract. I studied the construction of an algebraically trivial, but topologically non-trivial map by Hopf map p : S 3 S 2 and a
ALGEBRAICALLY TRIVIAL, BUT TOPOLOGICALLY NON-TRIVIAL MAP HONG GYUN KIM Abstract. I studied the construction of an algebraically trivial, but topologically non-trivial map by Hopf map p : S 3 S 2 and a
MA4J2 Three Manifolds
 MA4J2 Three Manifolds Lectured by Dr Saul Schleimer Typeset by Matthew Pressland Assisted by Anna Lena Winstel and David Kitson Lecture 13 Proof. We complete the proof of the existence of connect sum decomposition.
MA4J2 Three Manifolds Lectured by Dr Saul Schleimer Typeset by Matthew Pressland Assisted by Anna Lena Winstel and David Kitson Lecture 13 Proof. We complete the proof of the existence of connect sum decomposition.
The Classification of 3-Manifolds A Brief Overview
 The Classification of 3-Manifolds A Brief Overview Allen Hatcher Our aim here is to sketch the very nice conjectural picture of the classification of closed orientable 3 manifolds that emerged around 1980
The Classification of 3-Manifolds A Brief Overview Allen Hatcher Our aim here is to sketch the very nice conjectural picture of the classification of closed orientable 3 manifolds that emerged around 1980
arxiv: v1 [math.gr] 13 Aug 2013
![arxiv: v1 [math.gr] 13 Aug 2013 arxiv: v1 [math.gr] 13 Aug 2013](/thumbs/88/116024469.jpg) CONJUGACY PROBLEM IN GROUPS OF ORIENTED GEOMETRIZABLE 3-MANIFOLDS Jean-Philippe PRÉAUX1 arxiv:1308.2888v1 [math.gr] 13 Aug 2013 Abstract. The aim of this paper is to show that the fundamental group of
CONJUGACY PROBLEM IN GROUPS OF ORIENTED GEOMETRIZABLE 3-MANIFOLDS Jean-Philippe PRÉAUX1 arxiv:1308.2888v1 [math.gr] 13 Aug 2013 Abstract. The aim of this paper is to show that the fundamental group of
Geometric structures of 3-manifolds and quantum invariants
 Geometric structures of 3-manifolds and quantum invariants Effie Kalfagianni Michigan State University ETH/Zurich, EKPA/Athens, APTH/Thessalonikh, June 2017 Effie Kalfagianni (MSU) J 1 / 21 Settings and
Geometric structures of 3-manifolds and quantum invariants Effie Kalfagianni Michigan State University ETH/Zurich, EKPA/Athens, APTH/Thessalonikh, June 2017 Effie Kalfagianni (MSU) J 1 / 21 Settings and
Notes on Geometry and 3-Manifolds. Walter D. Neumann Appendices by Paul Norbury
 Notes on Geometry and 3-Manifolds Walter D. Neumann Appendices by Paul Norbury Preface These are a slightly revised version of the course notes that were distributed during the course on Geometry of 3-Manifolds
Notes on Geometry and 3-Manifolds Walter D. Neumann Appendices by Paul Norbury Preface These are a slightly revised version of the course notes that were distributed during the course on Geometry of 3-Manifolds
PSEUDO-ANOSOV MAPS AND SIMPLE CLOSED CURVES ON SURFACES
 MATH. PROC. CAMB. PHIL. SOC. Volume 128 (2000), pages 321 326 PSEUDO-ANOSOV MAPS AND SIMPLE CLOSED CURVES ON SURFACES Shicheng Wang 1, Ying-Qing Wu 2 and Qing Zhou 1 Abstract. Suppose C and C are two sets
MATH. PROC. CAMB. PHIL. SOC. Volume 128 (2000), pages 321 326 PSEUDO-ANOSOV MAPS AND SIMPLE CLOSED CURVES ON SURFACES Shicheng Wang 1, Ying-Qing Wu 2 and Qing Zhou 1 Abstract. Suppose C and C are two sets
Chapter 1. Canonical Decomposition. Notes on Basic 3-Manifold Topology. 1. Prime Decomposition
 1.1 Prime Decomposition 1 Chapter 1. Canonical Decomposition Notes on Basic 3-Manifold Topology Allen Hatcher Chapter 1. Canonical Decomposition 1. Prime Decomposition. 2. Torus Decomposition. Chapter
1.1 Prime Decomposition 1 Chapter 1. Canonical Decomposition Notes on Basic 3-Manifold Topology Allen Hatcher Chapter 1. Canonical Decomposition 1. Prime Decomposition. 2. Torus Decomposition. Chapter
L-spaces and left-orderability
 1 L-spaces and left-orderability Cameron McA. Gordon (joint with Steve Boyer and Liam Watson) Special Session on Low-Dimensional Topology Tampa, March 2012 2 Left Orderability A group G 1 is left orderable
1 L-spaces and left-orderability Cameron McA. Gordon (joint with Steve Boyer and Liam Watson) Special Session on Low-Dimensional Topology Tampa, March 2012 2 Left Orderability A group G 1 is left orderable
Bundles, handcuffs, and local freedom
 Bundles, handcuffs, and local freedom RICHARD P. KENT IV Abstract We answer a question of J. Anderson s by producing infinitely many commensurability classes of fibered hyperbolic 3 manifolds whose fundamental
Bundles, handcuffs, and local freedom RICHARD P. KENT IV Abstract We answer a question of J. Anderson s by producing infinitely many commensurability classes of fibered hyperbolic 3 manifolds whose fundamental
The 3-Dimensional Geometrisation Conjecture Of W. P. Thurston
 The 3-Dimensional Geometrisation Conjecture Of W. P. Thurston May 14, 2002 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 G-manifolds 3 2.1 Definitions and basic examples................... 3 2.2 Foliations...............................
The 3-Dimensional Geometrisation Conjecture Of W. P. Thurston May 14, 2002 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 G-manifolds 3 2.1 Definitions and basic examples................... 3 2.2 Foliations...............................
Ordered Groups and Topology
 Ordered Groups and Topology Dale Rolfsen University of British Columbia Luminy, June 2001 Outline: Lecture 1: Basics of ordered groups Lecture 2: Topology and orderings π 1, applications braid groups mapping
Ordered Groups and Topology Dale Rolfsen University of British Columbia Luminy, June 2001 Outline: Lecture 1: Basics of ordered groups Lecture 2: Topology and orderings π 1, applications braid groups mapping
Introduction to Poincare Conjecture and the Hamilton-Perelman program
 Introduction to Poincare Conjecture and the Hamilton-Perelman program David Glickenstein Math 538, Spring 2009 January 20, 2009 1 Introduction This lecture is mostly taken from Tao s lecture 2. In this
Introduction to Poincare Conjecture and the Hamilton-Perelman program David Glickenstein Math 538, Spring 2009 January 20, 2009 1 Introduction This lecture is mostly taken from Tao s lecture 2. In this
Linearization in 3-Dimensional Topology
 Proceedings of the International Congress of Mathematicians Helsinki, 1978 Linearization in 3-Dimensional Topology A. E. Hatcher The message from Thurston is clear: geometry dominates topology in dimension
Proceedings of the International Congress of Mathematicians Helsinki, 1978 Linearization in 3-Dimensional Topology A. E. Hatcher The message from Thurston is clear: geometry dominates topology in dimension
Geometric structures on the Figure Eight Knot Complement. ICERM Workshop
 Figure Eight Knot Institut Fourier - Grenoble Sep 16, 2013 Various pictures of 4 1 : K = figure eight The complete (real) hyperbolic structure M = S 3 \ K carries a complete hyperbolic metric M can be
Figure Eight Knot Institut Fourier - Grenoble Sep 16, 2013 Various pictures of 4 1 : K = figure eight The complete (real) hyperbolic structure M = S 3 \ K carries a complete hyperbolic metric M can be
SURGERY ON A KNOT IN SURFACE I
 SURGERY ON A KNOT IN SURFACE I MARTIN SCHARLEMANN AND ABIGAIL THOMPSON Abstract. Suppose F is a compact orientable surface, K is a knot in F I, and (F I) surg is the 3-manifold obtained by some non-trivial
SURGERY ON A KNOT IN SURFACE I MARTIN SCHARLEMANN AND ABIGAIL THOMPSON Abstract. Suppose F is a compact orientable surface, K is a knot in F I, and (F I) surg is the 3-manifold obtained by some non-trivial
The Skinning Map. 1 Motivation
 The Skinning Map The skinning map σ is a particular self-map of the Teichmüller space T (Σ). It arises in the theory of geometrization of 3-manifolds. Let us start by understanding the geometrization of
The Skinning Map The skinning map σ is a particular self-map of the Teichmüller space T (Σ). It arises in the theory of geometrization of 3-manifolds. Let us start by understanding the geometrization of
ORDERING THURSTON S GEOMETRIES BY MAPS OF NON-ZERO DEGREE
 ORDERING THURSTON S GEOMETRIES BY MAPS OF NON-ZERO DEGREE CHRISTOFOROS NEOFYTIDIS ABSTRACT. We obtain an ordering of closed aspherical 4-manifolds that carry a non-hyperbolic Thurston geometry. As application,
ORDERING THURSTON S GEOMETRIES BY MAPS OF NON-ZERO DEGREE CHRISTOFOROS NEOFYTIDIS ABSTRACT. We obtain an ordering of closed aspherical 4-manifolds that carry a non-hyperbolic Thurston geometry. As application,
GEOMETRIC STRUCTURES ON BRANCHED COVERS OVER UNIVERSAL LINKS. Kerry N. Jones
 GEOMETRIC STRUCTURES ON BRANCHED COVERS OVER UNIVERSAL LINKS Kerry N. Jones Abstract. A number of recent results are presented which bear on the question of what geometric information can be gleaned from
GEOMETRIC STRUCTURES ON BRANCHED COVERS OVER UNIVERSAL LINKS Kerry N. Jones Abstract. A number of recent results are presented which bear on the question of what geometric information can be gleaned from
PLANES IN 3-MANIFOLDS OF FINITE GENUS AT INFINITY. Bobby Neal Winters. 1. Introduction and Definitions
 PLANES IN 3-MANIFOLDS OF FINITE GENUS AT INFINITY Bobby Neal Winters 1. Introduction and Definitions In the study of 3-manifolds, there is a long tradition of cutting up a 3-manifold along embedded 2-manifolds
PLANES IN 3-MANIFOLDS OF FINITE GENUS AT INFINITY Bobby Neal Winters 1. Introduction and Definitions In the study of 3-manifolds, there is a long tradition of cutting up a 3-manifold along embedded 2-manifolds
On the stable complexity and the stable presentation length for 3-manifolds. Ken ichi Yoshida
 1960 2015 59-68 59 On the stable complexity and the stable presentation length for 3-manifolds Ken ichi Yoshida Graduate School of Mathematical Sciences, The University of Tokyo 1 Introduction This article
1960 2015 59-68 59 On the stable complexity and the stable presentation length for 3-manifolds Ken ichi Yoshida Graduate School of Mathematical Sciences, The University of Tokyo 1 Introduction This article
Part II. Algebraic Topology. Year
 Part II Year 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2017 Paper 3, Section II 18I The n-torus is the product of n circles: 5 T n = } S 1. {{.. S } 1. n times For all n 1 and 0
Part II Year 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2017 Paper 3, Section II 18I The n-torus is the product of n circles: 5 T n = } S 1. {{.. S } 1. n times For all n 1 and 0
The Classification of Nonsimple Algebraic Tangles
 The Classification of Nonsimple Algebraic Tangles Ying-Qing Wu 1 A tangle is a pair (B, T ), where B is a 3-ball, T is a pair of properly embedded arcs. When there is no ambiguity we will simply say that
The Classification of Nonsimple Algebraic Tangles Ying-Qing Wu 1 A tangle is a pair (B, T ), where B is a 3-ball, T is a pair of properly embedded arcs. When there is no ambiguity we will simply say that
LERF, tameness and Simon s conjecture.
 LERF, tameness and Simon s conjecture. D. D. Long & A. W. Reid November 18, 2003 Abstract This paper discusses applications of LERF to tame covers of certain hyperbolic 3-manifolds. For example, if M =
LERF, tameness and Simon s conjecture. D. D. Long & A. W. Reid November 18, 2003 Abstract This paper discusses applications of LERF to tame covers of certain hyperbolic 3-manifolds. For example, if M =
Kazuhiro Ichihara. Dehn Surgery. Nara University of Education
 , 2009. 7. 9 Cyclic and finite surgeries on Montesinos knots Kazuhiro Ichihara Nara University of Education This talk is based on K. Ichihara and I.D. Jong Cyclic and finite surgeries on Montesinos knots
, 2009. 7. 9 Cyclic and finite surgeries on Montesinos knots Kazuhiro Ichihara Nara University of Education This talk is based on K. Ichihara and I.D. Jong Cyclic and finite surgeries on Montesinos knots
The Geometrization Theorem
 The Geometrization Theorem Matthew D. Brown Wednesday, December 19, 2012 In this paper, we discuss the Geometrization Theorem, formerly Thurston s Geometrization Conjecture, which is essentially the statement
The Geometrization Theorem Matthew D. Brown Wednesday, December 19, 2012 In this paper, we discuss the Geometrization Theorem, formerly Thurston s Geometrization Conjecture, which is essentially the statement
Three-manifolds and Baumslag Solitar groups
 Topology and its Applications 110 (2001) 113 118 Three-manifolds and Baumslag Solitar groups Peter B. Shalen Department of Mathematics, Statistics and Computer Science, University of Illinois at Chicago,
Topology and its Applications 110 (2001) 113 118 Three-manifolds and Baumslag Solitar groups Peter B. Shalen Department of Mathematics, Statistics and Computer Science, University of Illinois at Chicago,
Covering Invariants and Cohopficity of 3-manifold Groups
 Covering Invariants and Cohopficity of 3-manifold Groups Shicheng Wang 1 and Ying-Qing Wu 2 Abstract A 3-manifold M is called to have property C if the degrees of finite coverings over M are determined
Covering Invariants and Cohopficity of 3-manifold Groups Shicheng Wang 1 and Ying-Qing Wu 2 Abstract A 3-manifold M is called to have property C if the degrees of finite coverings over M are determined
arxiv: v2 [math.gt] 28 Feb 2017
![arxiv: v2 [math.gt] 28 Feb 2017 arxiv: v2 [math.gt] 28 Feb 2017](/thumbs/76/73323229.jpg) ON THE THE BERGE CONJECTURE FOR TUNNEL NUMBER ONE KNOTS YOAV MORIAH AND TALI PINSKY arxiv:1701.01421v2 [math.gt] 28 Feb 2017 Abstract. In this paper we use an approach based on dynamics to prove that if
ON THE THE BERGE CONJECTURE FOR TUNNEL NUMBER ONE KNOTS YOAV MORIAH AND TALI PINSKY arxiv:1701.01421v2 [math.gt] 28 Feb 2017 Abstract. In this paper we use an approach based on dynamics to prove that if
Topological rigidity for non-aspherical manifolds by M. Kreck and W. Lück
 Topological rigidity for non-aspherical manifolds by M. Kreck and W. Lück July 11, 2006 Abstract The Borel Conjecture predicts that closed aspherical manifolds are topological rigid. We want to investigate
Topological rigidity for non-aspherical manifolds by M. Kreck and W. Lück July 11, 2006 Abstract The Borel Conjecture predicts that closed aspherical manifolds are topological rigid. We want to investigate
Some non-trivial PL knots whose complements are homotopy circles
 Some non-trivial PL knots whose complements are homotopy circles Greg Friedman Vanderbilt University May 16, 2006 Dedicated to the memory of Jerry Levine (May 4, 1937 - April 8, 2006) 2000 Mathematics
Some non-trivial PL knots whose complements are homotopy circles Greg Friedman Vanderbilt University May 16, 2006 Dedicated to the memory of Jerry Levine (May 4, 1937 - April 8, 2006) 2000 Mathematics
CW-complexes. Stephen A. Mitchell. November 1997
 CW-complexes Stephen A. Mitchell November 1997 A CW-complex is first of all a Hausdorff space X equipped with a collection of characteristic maps φ n α : D n X. Here n ranges over the nonnegative integers,
CW-complexes Stephen A. Mitchell November 1997 A CW-complex is first of all a Hausdorff space X equipped with a collection of characteristic maps φ n α : D n X. Here n ranges over the nonnegative integers,
arxiv:math/ v5 [math.gt] 29 Oct 2007
![arxiv:math/ v5 [math.gt] 29 Oct 2007 arxiv:math/ v5 [math.gt] 29 Oct 2007](/thumbs/84/89698984.jpg) ISSN numbers are printed here 1 JSJ-decompositions of knot and link complements in S 3 arxiv:math/0506523v5 [math.gt] 29 Oct 2007 Abstract Ryan Budney Mathematics and Statistics, University of Victoria
ISSN numbers are printed here 1 JSJ-decompositions of knot and link complements in S 3 arxiv:math/0506523v5 [math.gt] 29 Oct 2007 Abstract Ryan Budney Mathematics and Statistics, University of Victoria
OPEN 3-MANIFOLDS WHOSE FUNDAMENTAL GROUPS HAVE INFINITE CENTER, AND A TORUS THEOREM FOR 3-ORBIFOLDS
 TRANSACTIONS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 355, Number 11, Pages 4595 4638 S 0002-9947(03)03319-1 Article electronically published on July 8, 2003 OPEN 3-MANIFOLDS WHOSE FUNDAMENTAL GROUPS
TRANSACTIONS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 355, Number 11, Pages 4595 4638 S 0002-9947(03)03319-1 Article electronically published on July 8, 2003 OPEN 3-MANIFOLDS WHOSE FUNDAMENTAL GROUPS
676 JAMES W. ANDERSON
 676 JAMES W. ANDERSON Such a limit set intersection theorem has been shown to hold under various hypotheses. Maskit [17] shows that it holds for pairs of analytically finite component subgroups of a Kleinian
676 JAMES W. ANDERSON Such a limit set intersection theorem has been shown to hold under various hypotheses. Maskit [17] shows that it holds for pairs of analytically finite component subgroups of a Kleinian
RANK GRADIENT AND THE JSJ DECOMPOSITION
 RANK GRADIENT AND THE JSJ DECOMPOSITION JASON DEBLOIS By the rank of a manifold M, rk M, we will refer to the rank of its fundamental group; that is, the minimal cardinality of a generating set. Given
RANK GRADIENT AND THE JSJ DECOMPOSITION JASON DEBLOIS By the rank of a manifold M, rk M, we will refer to the rank of its fundamental group; that is, the minimal cardinality of a generating set. Given
MIXED 3 MANIFOLDS ARE VIRTUALLY SPECIAL
 MIXED 3 MANIFOLDS ARE VIRTUALLY SPECIAL PIOTR PRZYTYCKI AND DANIEL T. WISE arxiv:1205.6742v2 [math.gr] 24 Jul 2013 Abstract. Let M be a compact oriented irreducible 3 manifold which is neither a graph
MIXED 3 MANIFOLDS ARE VIRTUALLY SPECIAL PIOTR PRZYTYCKI AND DANIEL T. WISE arxiv:1205.6742v2 [math.gr] 24 Jul 2013 Abstract. Let M be a compact oriented irreducible 3 manifold which is neither a graph
The A-B slice problem
 The A-B slice problem Slava Krushkal June 10, 2011 History and motivation: Geometric classification tools in higher dimensions: Surgery: Given an n dimensional Poincaré complex X, is there an n manifold
The A-B slice problem Slava Krushkal June 10, 2011 History and motivation: Geometric classification tools in higher dimensions: Surgery: Given an n dimensional Poincaré complex X, is there an n manifold
We have the following immediate corollary. 1
 1. Thom Spaces and Transversality Definition 1.1. Let π : E B be a real k vector bundle with a Euclidean metric and let E 1 be the set of elements of norm 1. The Thom space T (E) of E is the quotient E/E
1. Thom Spaces and Transversality Definition 1.1. Let π : E B be a real k vector bundle with a Euclidean metric and let E 1 be the set of elements of norm 1. The Thom space T (E) of E is the quotient E/E
THE ASYMPTOTIC BEHAVIOUR OF HEEGAARD GENUS
 THE ASYMPTOTIC BEHAVIOUR OF HEEGAARD GENUS MARC LACKENBY 1. Introduction Heegaard splittings have recently been shown to be related to a number of important conjectures in 3-manifold theory: the virtually
THE ASYMPTOTIC BEHAVIOUR OF HEEGAARD GENUS MARC LACKENBY 1. Introduction Heegaard splittings have recently been shown to be related to a number of important conjectures in 3-manifold theory: the virtually
A 50-Year View of Diffeomorphism Groups
 A 50-Year View of Diffeomorphism Groups Allen Hatcher Question: For a smooth compact manifold M can one determine the homotopy type of its diffeomorphism group Diff(M)? Why this is interesting: Automorphisms
A 50-Year View of Diffeomorphism Groups Allen Hatcher Question: For a smooth compact manifold M can one determine the homotopy type of its diffeomorphism group Diff(M)? Why this is interesting: Automorphisms
Systoles of hyperbolic 3-manifolds
 Math. Proc. Camb. Phil. Soc. (2000), 128, 103 Printed in the United Kingdom 2000 Cambridge Philosophical Society 103 Systoles of hyperbolic 3-manifolds BY COLIN C. ADAMS Department of Mathematics, Williams
Math. Proc. Camb. Phil. Soc. (2000), 128, 103 Printed in the United Kingdom 2000 Cambridge Philosophical Society 103 Systoles of hyperbolic 3-manifolds BY COLIN C. ADAMS Department of Mathematics, Williams
TOPIC PROPOSAL HYPERBOLIC GROUPS AND 3-MANIFOLDS. 1. Introduction
 TOPIC PROPOSAL HYPERBOLIC GROUPS AND 3-MANIFOLDS YAN MARY HE DISCUSSED WITH PROFESSOR DANNY CALEGARI 1. Introduction The theory of hyperbolic groups was introduced and developed by Gromov in the 1980s
TOPIC PROPOSAL HYPERBOLIC GROUPS AND 3-MANIFOLDS YAN MARY HE DISCUSSED WITH PROFESSOR DANNY CALEGARI 1. Introduction The theory of hyperbolic groups was introduced and developed by Gromov in the 1980s
THE THEORY OF NORMAL SURFACES. based on Lecture Notes by Cameron McA. Gordon typeset by Richard P. Kent IV
 THE THEORY OF NORMAL SURFACES based on Lecture Notes by Cameron McA. Gordon typeset by Richard P. Kent IV 1. Introduction When one considers questions like: When are two n-manifolds homeomorphic? When
THE THEORY OF NORMAL SURFACES based on Lecture Notes by Cameron McA. Gordon typeset by Richard P. Kent IV 1. Introduction When one considers questions like: When are two n-manifolds homeomorphic? When
EMBEDDINGS OF TOPOLOGICAL MANIFOLDS
 EMBEDDINGS OF TOPOLOGICAL MANIFOLDS ERIK KJÆR PEDERSEN It is the purpose of this paper to combine the methods of [8] and [9] to prove Haefliger type embedding theorems for topological manifolds. We prove
EMBEDDINGS OF TOPOLOGICAL MANIFOLDS ERIK KJÆR PEDERSEN It is the purpose of this paper to combine the methods of [8] and [9] to prove Haefliger type embedding theorems for topological manifolds. We prove
7.3 Singular Homology Groups
 184 CHAPTER 7. HOMOLOGY THEORY 7.3 Singular Homology Groups 7.3.1 Cycles, Boundaries and Homology Groups We can define the singular p-chains with coefficients in a field K. Furthermore, we can define the
184 CHAPTER 7. HOMOLOGY THEORY 7.3 Singular Homology Groups 7.3.1 Cycles, Boundaries and Homology Groups We can define the singular p-chains with coefficients in a field K. Furthermore, we can define the
Introduction (Lecture 1)
 Introduction (Lecture 1) February 2, 2011 In this course, we will be concerned with variations on the following: Question 1. Let X be a CW complex. When does there exist a homotopy equivalence X M, where
Introduction (Lecture 1) February 2, 2011 In this course, we will be concerned with variations on the following: Question 1. Let X be a CW complex. When does there exist a homotopy equivalence X M, where
Lecture 4: Stabilization
 Lecture 4: Stabilization There are many stabilization processes in topology, and often matters simplify in a stable limit. As a first example, consider the sequence of inclusions (4.1) S 0 S 1 S 2 S 3
Lecture 4: Stabilization There are many stabilization processes in topology, and often matters simplify in a stable limit. As a first example, consider the sequence of inclusions (4.1) S 0 S 1 S 2 S 3
Diffeomorphism Groups of Reducible 3-Manifolds. Allen Hatcher
 Diffeomorphism Groups of Reducible 3-Manifolds Allen Hatcher In a 1979 announcement by César de Sá and Rourke [CR] there is a sketch of an intuitively appealing approach to measuring the difference between
Diffeomorphism Groups of Reducible 3-Manifolds Allen Hatcher In a 1979 announcement by César de Sá and Rourke [CR] there is a sketch of an intuitively appealing approach to measuring the difference between
FUNDAMENTAL GROUPS. Alex Suciu. Northeastern University. Joint work with Thomas Koberda (U. Virginia) arxiv:
 RESIDUAL FINITENESS PROPERTIES OF FUNDAMENTAL GROUPS Alex Suciu Northeastern University Joint work with Thomas Koberda (U. Virginia) arxiv:1604.02010 Number Theory and Algebraic Geometry Seminar Katholieke
RESIDUAL FINITENESS PROPERTIES OF FUNDAMENTAL GROUPS Alex Suciu Northeastern University Joint work with Thomas Koberda (U. Virginia) arxiv:1604.02010 Number Theory and Algebraic Geometry Seminar Katholieke
On the growth of Turaev-Viro 3-manifold invariants
 On the growth of Turaev-Viro 3-manifold invariants E. Kalfagianni (based on work w. R. Detcherry and T. Yang) Michigan State University Redbud Topology Conference, OSU, April 018 E. Kalfagianni (MSU) J
On the growth of Turaev-Viro 3-manifold invariants E. Kalfagianni (based on work w. R. Detcherry and T. Yang) Michigan State University Redbud Topology Conference, OSU, April 018 E. Kalfagianni (MSU) J
Grothendieck s problem for 3-manifold groups
 Grothendieck s problem for 3-manifold groups D. D. Long & A. W. Reid May 12, 2010 1 Introduction For Fritz Grunewald The profinite completion of a group Γ is the inverse limit of the directed system of
Grothendieck s problem for 3-manifold groups D. D. Long & A. W. Reid May 12, 2010 1 Introduction For Fritz Grunewald The profinite completion of a group Γ is the inverse limit of the directed system of
Algebraic Topology Lecture Notes. Jarah Evslin and Alexander Wijns
 Algebraic Topology Lecture Notes Jarah Evslin and Alexander Wijns Abstract We classify finitely generated abelian groups and, using simplicial complex, describe various groups that can be associated to
Algebraic Topology Lecture Notes Jarah Evslin and Alexander Wijns Abstract We classify finitely generated abelian groups and, using simplicial complex, describe various groups that can be associated to
4-DIMENSIONAL LOCALLY CAT(0)-MANIFOLDS WITH NO RIEMANNIAN SMOOTHINGS
 4-DIMENSIONAL LOCALLY CAT(0)-MANIFOLDS WITH NO RIEMANNIAN SMOOTHINGS M. DAVIS, T. JANUSZKIEWICZ, AND J.-F. LAFONT Abstract. We construct examples of 4-dimensional manifolds M supporting a locally CAT(0)-metric,
4-DIMENSIONAL LOCALLY CAT(0)-MANIFOLDS WITH NO RIEMANNIAN SMOOTHINGS M. DAVIS, T. JANUSZKIEWICZ, AND J.-F. LAFONT Abstract. We construct examples of 4-dimensional manifolds M supporting a locally CAT(0)-metric,
DEHN SURGERY AND NEGATIVELY CURVED 3-MANIFOLDS
 DEHN SURGERY AND NEGATIVELY CURVED 3-MANIFOLDS DARYL COOPER AND MARC LACKENBY 1. INTRODUCTION Dehn surgery is perhaps the most common way of constructing 3-manifolds, and yet there remain some profound
DEHN SURGERY AND NEGATIVELY CURVED 3-MANIFOLDS DARYL COOPER AND MARC LACKENBY 1. INTRODUCTION Dehn surgery is perhaps the most common way of constructing 3-manifolds, and yet there remain some profound
Contractibility of the Kakimizu complex and symmetric Seifert surfaces. Śniadeckich 8, Warsaw, Poland
 Contractibility of the Kakimizu complex and symmetric Seifert surfaces Piotr Przytycki a & Jennifer Schultens b a Institute of Mathematics, Polish Academy of Sciences, Śniadeckich 8, 00-956 Warsaw, Poland
Contractibility of the Kakimizu complex and symmetric Seifert surfaces Piotr Przytycki a & Jennifer Schultens b a Institute of Mathematics, Polish Academy of Sciences, Śniadeckich 8, 00-956 Warsaw, Poland
Generalized crossing changes in satellite knots
 Generalized crossing changes in satellite knots Cheryl L. Balm Michigan State University Saturday, December 8, 2012 Generalized crossing changes Introduction Crossing disks and crossing circles Let K be
Generalized crossing changes in satellite knots Cheryl L. Balm Michigan State University Saturday, December 8, 2012 Generalized crossing changes Introduction Crossing disks and crossing circles Let K be
Lecture 4: Knot Complements
 Lecture 4: Knot Complements Notes by Zach Haney January 26, 2016 1 Introduction Here we discuss properties of the knot complement, S 3 \ K, for a knot K. Definition 1.1. A tubular neighborhood V k S 3
Lecture 4: Knot Complements Notes by Zach Haney January 26, 2016 1 Introduction Here we discuss properties of the knot complement, S 3 \ K, for a knot K. Definition 1.1. A tubular neighborhood V k S 3
A Discussion of Thurston s Geometrization Conjecture
 A Discussion of Thurston s Geometrization Conjecture John Zhang, advised by Professor James Morrow June 3, 2014 Contents 1 Introduction and Background 2 2 Discussion of Kneser s Theorem 3 2.1 Definitions....................................
A Discussion of Thurston s Geometrization Conjecture John Zhang, advised by Professor James Morrow June 3, 2014 Contents 1 Introduction and Background 2 2 Discussion of Kneser s Theorem 3 2.1 Definitions....................................
MOM TECHNOLOGY AND VOLUMES OF HYPERBOLIC 3-MANIFOLDS DAVID GABAI, ROBERT MEYERHOFF, AND PETER MILLEY
 1 MOM TECHNOLOGY AND VOLUMES OF HYPERBOLIC 3-MANIFOLDS DAVID GABAI, ROBERT MEYERHOFF, AND PETER MILLEY arxiv:math.gt/0606072 v2 31 Jul 2006 0. Introduction This paper is the first in a series whose goal
1 MOM TECHNOLOGY AND VOLUMES OF HYPERBOLIC 3-MANIFOLDS DAVID GABAI, ROBERT MEYERHOFF, AND PETER MILLEY arxiv:math.gt/0606072 v2 31 Jul 2006 0. Introduction This paper is the first in a series whose goal
Abhijit Champanerkar, David Futer, Ilya Kofman, Walter Neumann, and Jessica S. Purcell
 M ath. Res. Lett. 18 (2011), no. 00, 10001 100NN c International Press 2011 VOLUME BOUNDS FOR GENERALIZED TWISTED TORUS LINKS Abhijit Champanerkar, David Futer, Ilya Kofman, Walter Neumann, and Jessica
M ath. Res. Lett. 18 (2011), no. 00, 10001 100NN c International Press 2011 VOLUME BOUNDS FOR GENERALIZED TWISTED TORUS LINKS Abhijit Champanerkar, David Futer, Ilya Kofman, Walter Neumann, and Jessica
Coxeter Groups and Artin Groups
 Chapter 1 Coxeter Groups and Artin Groups 1.1 Artin Groups Let M be a Coxeter matrix with index set S. defined by M is given by the presentation: A M := s S sts }{{ } = tst }{{ } m s,t factors m s,t The
Chapter 1 Coxeter Groups and Artin Groups 1.1 Artin Groups Let M be a Coxeter matrix with index set S. defined by M is given by the presentation: A M := s S sts }{{ } = tst }{{ } m s,t factors m s,t The
Geometric Estimates from spanning surfaces of knots
 Geometric Estimates from spanning surfaces of knots joint w/ Stephan Burton (MSU) Michigan State University Knots in Hellas, Olymbia, Greece, July 18, 2016 Burton-Kalfagianni (MSU) J 1 / 20 Knot complement:
Geometric Estimates from spanning surfaces of knots joint w/ Stephan Burton (MSU) Michigan State University Knots in Hellas, Olymbia, Greece, July 18, 2016 Burton-Kalfagianni (MSU) J 1 / 20 Knot complement:
ESSENTIAL CLOSED SURFACES IN BOUNDED 3-MANIFOLDS
 JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 10, Number 3, July 1997, Pages 553 563 S 0894-0347(97)00236-1 ESSENTIAL CLOSED SURFACES IN BOUNDED 3-MANIFOLDS D. COOPER, D. D. LONG, AND A. W. REID
JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 10, Number 3, July 1997, Pages 553 563 S 0894-0347(97)00236-1 ESSENTIAL CLOSED SURFACES IN BOUNDED 3-MANIFOLDS D. COOPER, D. D. LONG, AND A. W. REID
Chapter 19 Clifford and the Number of Holes
 Chapter 19 Clifford and the Number of Holes We saw that Riemann denoted the genus by p, a notation which is still frequently used today, in particular for the generalizations of this notion in higher dimensions.
Chapter 19 Clifford and the Number of Holes We saw that Riemann denoted the genus by p, a notation which is still frequently used today, in particular for the generalizations of this notion in higher dimensions.
PRIME KNOTS AND TANGLES
 TRANSACTIONS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 267. Number 1, September 1981 PRIME KNOTS AND TANGLES BY W. B. RAYMOND LICKORISH Abstract. A study is made of a method of proving that a classical
TRANSACTIONS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 267. Number 1, September 1981 PRIME KNOTS AND TANGLES BY W. B. RAYMOND LICKORISH Abstract. A study is made of a method of proving that a classical
Equivalence of the Combinatorial Definition (Lecture 11)
 Equivalence of the Combinatorial Definition (Lecture 11) September 26, 2014 Our goal in this lecture is to complete the proof of our first main theorem by proving the following: Theorem 1. The map of simplicial
Equivalence of the Combinatorial Definition (Lecture 11) September 26, 2014 Our goal in this lecture is to complete the proof of our first main theorem by proving the following: Theorem 1. The map of simplicial
SPHERES AND PROJECTIONS FOR Out(F n )
 SPHERES AND PROJECTIONS FOR Out(F n ) URSULA HAMENSTÄDT AND SEBASTIAN HENSEL Abstract. The outer automorphism group Out(F 2g ) of a free group on 2g generators naturally contains the mapping class group
SPHERES AND PROJECTIONS FOR Out(F n ) URSULA HAMENSTÄDT AND SEBASTIAN HENSEL Abstract. The outer automorphism group Out(F 2g ) of a free group on 2g generators naturally contains the mapping class group
3. Prove or disprove: If a space X is second countable, then every open covering of X contains a countable subcollection covering X.
 Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of South Florida TOPOLOGY QUALIFYING EXAM January 24, 2015 Examiners: Dr. M. Elhamdadi, Dr. M. Saito Instructions: For Ph.D. level, complete at least
Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of South Florida TOPOLOGY QUALIFYING EXAM January 24, 2015 Examiners: Dr. M. Elhamdadi, Dr. M. Saito Instructions: For Ph.D. level, complete at least
Algebra and Topology Special Session
 Algebra and Topology Special Session Australian Mathematical Society Annual Meeting University of Sydney, September 1998. Titles and abstracts of the talks Non-commutative geometry and quantum theory Alan
Algebra and Topology Special Session Australian Mathematical Society Annual Meeting University of Sydney, September 1998. Titles and abstracts of the talks Non-commutative geometry and quantum theory Alan
CHAPTER 1: COMBINATORIAL FOUNDATIONS
 CHAPTER 1: COMBINATORIAL FOUNDATIONS DANNY CALEGARI Abstract. These are notes on 3-manifolds, with an emphasis on the combinatorial theory of immersed and embedded surfaces, which are being transformed
CHAPTER 1: COMBINATORIAL FOUNDATIONS DANNY CALEGARI Abstract. These are notes on 3-manifolds, with an emphasis on the combinatorial theory of immersed and embedded surfaces, which are being transformed
Flows, dynamics and algorithms for 3 manifold groups
 Flows, dynamics and algorithms for 3 manifold groups Tim Susse University of Nebraska 4 March 2017 Joint with Mark Brittenham & Susan Hermiller Groups and the word problem Let G = A R be a finitely presented
Flows, dynamics and algorithms for 3 manifold groups Tim Susse University of Nebraska 4 March 2017 Joint with Mark Brittenham & Susan Hermiller Groups and the word problem Let G = A R be a finitely presented
Lecture on Equivariant Cohomology
 Lecture on Equivariant Cohomology Sébastien Racanière February 20, 2004 I wrote these notes for a hours lecture at Imperial College during January and February. Of course, I tried to track down and remove
Lecture on Equivariant Cohomology Sébastien Racanière February 20, 2004 I wrote these notes for a hours lecture at Imperial College during January and February. Of course, I tried to track down and remove
All roots of unity are detected by the A polynomial
 ISSN 1472-2739 (on-line) 1472-2747 (printed) 207 Algebraic & Geometric Topology Volume 5 (2005) 207 217 Published: 28 March 2005 ATG All roots of unity are detected by the A polynomial Eric Chesebro Abstract
ISSN 1472-2739 (on-line) 1472-2747 (printed) 207 Algebraic & Geometric Topology Volume 5 (2005) 207 217 Published: 28 March 2005 ATG All roots of unity are detected by the A polynomial Eric Chesebro Abstract
Contents. Chapter 1. Introduction Outline of the proof Outline of manuscript Other approaches Acknowledgements 10
 Contents Chapter 1. Introduction 1 1.1. Outline of the proof 4 1.2. Outline of manuscript 8 1.3. Other approaches 8 1.4. Acknowledgements 10 Part 1. GEOMETRIC AND ANALYTIC RESULTS FOR RICCI FLOW WITH SURGERY
Contents Chapter 1. Introduction 1 1.1. Outline of the proof 4 1.2. Outline of manuscript 8 1.3. Other approaches 8 1.4. Acknowledgements 10 Part 1. GEOMETRIC AND ANALYTIC RESULTS FOR RICCI FLOW WITH SURGERY
6. Constructing hyperbolic manifolds
 6. Constructing hyperbolic manifolds Recall that a hyperbolic manifold is a (G, X)-manifold, where X is H n and G = Isom(H n ). Since G is a group of Riemannian isometries, G acts rigidly. Hence, the pseudogroup
6. Constructing hyperbolic manifolds Recall that a hyperbolic manifold is a (G, X)-manifold, where X is H n and G = Isom(H n ). Since G is a group of Riemannian isometries, G acts rigidly. Hence, the pseudogroup
A meridian disk of the solid torus wraps q times around its image disk. Here p =1 and q =2.
 4. HYPERBOLIC DEHN SURGERY A meridian disk of the solid torus wraps q times around its image disk. Here p =1 and q =2. Any three-manifold with a complete codimension-2 hyperbolic foliation has universal
4. HYPERBOLIC DEHN SURGERY A meridian disk of the solid torus wraps q times around its image disk. Here p =1 and q =2. Any three-manifold with a complete codimension-2 hyperbolic foliation has universal
Quasi-Fuchsian surface subgroups of infinite covolume Kleinian groups. Alvin Jay Kerber. A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the
 Quasi-Fuchsian surface subgroups of infinite covolume Kleinian groups by Alvin Jay Kerber A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in
Quasi-Fuchsian surface subgroups of infinite covolume Kleinian groups by Alvin Jay Kerber A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in
Jones polynomials and incompressible surfaces
 Jones polynomials and incompressible surfaces joint with D. Futer and J. Purcell Geometric Topology in Cortona (in honor of Riccardo Benedetti for his 60th birthday), Cortona, Italy, June 3-7, 2013 David
Jones polynomials and incompressible surfaces joint with D. Futer and J. Purcell Geometric Topology in Cortona (in honor of Riccardo Benedetti for his 60th birthday), Cortona, Italy, June 3-7, 2013 David
Discrete groups and the thick thin decomposition
 CHAPTER 5 Discrete groups and the thick thin decomposition Suppose we have a complete hyperbolic structure on an orientable 3-manifold. Then the developing map D : M H 3 is a covering map, by theorem 3.19.
CHAPTER 5 Discrete groups and the thick thin decomposition Suppose we have a complete hyperbolic structure on an orientable 3-manifold. Then the developing map D : M H 3 is a covering map, by theorem 3.19.
BEN KNUDSEN. Conf k (f) Conf k (Y )
 CONFIGURATION SPACES IN ALGEBRAIC TOPOLOGY: LECTURE 2 BEN KNUDSEN We begin our study of configuration spaces by observing a few of their basic properties. First, we note that, if f : X Y is an injective
CONFIGURATION SPACES IN ALGEBRAIC TOPOLOGY: LECTURE 2 BEN KNUDSEN We begin our study of configuration spaces by observing a few of their basic properties. First, we note that, if f : X Y is an injective
On the Diffeomorphism Group of S 1 S 2. Allen Hatcher
 On the Diffeomorphism Group of S 1 S 2 Allen Hatcher This is a revision, written in December 2003, of a paper of the same title that appeared in the Proceedings of the AMS 83 (1981), 427-430. The main
On the Diffeomorphism Group of S 1 S 2 Allen Hatcher This is a revision, written in December 2003, of a paper of the same title that appeared in the Proceedings of the AMS 83 (1981), 427-430. The main
EXOTIC SMOOTH STRUCTURES ON TOPOLOGICAL FIBRE BUNDLES B
 EXOTIC SMOOTH STRUCTURES ON TOPOLOGICAL FIBRE BUNDLES B SEBASTIAN GOETTE, KIYOSHI IGUSA, AND BRUCE WILLIAMS Abstract. When two smooth manifold bundles over the same base are fiberwise tangentially homeomorphic,
EXOTIC SMOOTH STRUCTURES ON TOPOLOGICAL FIBRE BUNDLES B SEBASTIAN GOETTE, KIYOSHI IGUSA, AND BRUCE WILLIAMS Abstract. When two smooth manifold bundles over the same base are fiberwise tangentially homeomorphic,
Stratification of 3 3 Matrices
 Stratification of 3 3 Matrices Meesue Yoo & Clay Shonkwiler March 2, 2006 1 Warmup with 2 2 Matrices { Best matrices of rank 2} = O(2) S 3 ( 2) { Best matrices of rank 1} S 3 (1) 1.1 Viewing O(2) S 3 (
Stratification of 3 3 Matrices Meesue Yoo & Clay Shonkwiler March 2, 2006 1 Warmup with 2 2 Matrices { Best matrices of rank 2} = O(2) S 3 ( 2) { Best matrices of rank 1} S 3 (1) 1.1 Viewing O(2) S 3 (
ACHIRALITY OF KNOTS AND LINKS
 TOPOLOGY AND ITS APPLICATION (to appear). Preprint 1998 ACHIRALITY OF KNOTS AND LINKS Boju Jiang 1, Xiao-Song Lin 2, Shicheng Wang 3 and Ying-Qing Wu 4 We will develop various methods, some are of geometric
TOPOLOGY AND ITS APPLICATION (to appear). Preprint 1998 ACHIRALITY OF KNOTS AND LINKS Boju Jiang 1, Xiao-Song Lin 2, Shicheng Wang 3 and Ying-Qing Wu 4 We will develop various methods, some are of geometric
arxiv: v4 [math.gt] 21 Jan 2018
![arxiv: v4 [math.gt] 21 Jan 2018 arxiv: v4 [math.gt] 21 Jan 2018](/thumbs/89/100571173.jpg) arxiv:1501.02418v4 [math.gt] 21 Jan 2018 STABLE PRESENTATION LENGTH OF 3-MANIFOLD GROUPS KEN ICHI YOSHIDA Abstract We introduce the stable presentation length of a finitely presentable group. The stable
arxiv:1501.02418v4 [math.gt] 21 Jan 2018 STABLE PRESENTATION LENGTH OF 3-MANIFOLD GROUPS KEN ICHI YOSHIDA Abstract We introduce the stable presentation length of a finitely presentable group. The stable
RIMS-1897 On multiframings of 3-manifolds By Tatsuro SHIMIZU December 2018 RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES KYOTO UNIVERSITY, Kyoto, Japan
 RIMS-1897 On multiframings of 3-manifolds By Tatsuro SHIMIZU December 2018 RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES KYOTO UNIVERSITY, Kyoto, Japan On multiframings of 3 manifolds Tatsuro Shimizu 1
RIMS-1897 On multiframings of 3-manifolds By Tatsuro SHIMIZU December 2018 RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES KYOTO UNIVERSITY, Kyoto, Japan On multiframings of 3 manifolds Tatsuro Shimizu 1
SOLUTIONS TO THE FINAL EXAM
 SOLUTIONS TO THE FINAL EXAM Short questions 1 point each) Give a brief definition for each of the following six concepts: 1) normal for topological spaces) 2) path connected 3) homeomorphism 4) covering
SOLUTIONS TO THE FINAL EXAM Short questions 1 point each) Give a brief definition for each of the following six concepts: 1) normal for topological spaces) 2) path connected 3) homeomorphism 4) covering
C-wild knots. Yunlin He
 C-wild knots by Yunlin He A thesis submitted to the Graduate Faculty of Auburn University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the Degree of Master of Science Auburn, Alabama May 5, 2013 Keywords:
C-wild knots by Yunlin He A thesis submitted to the Graduate Faculty of Auburn University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the Degree of Master of Science Auburn, Alabama May 5, 2013 Keywords:
The bumping set and the characteristic submanifold
 The bumping set and the characteristic submanifold Abstract We show here that the Nielsen core of the bumping set of the domain of discontinuity of a Kleinian group Γ is the boundary for the characteristic
The bumping set and the characteristic submanifold Abstract We show here that the Nielsen core of the bumping set of the domain of discontinuity of a Kleinian group Γ is the boundary for the characteristic
The Poincaré Conjecture
 The Poincaré Conjecture COLIN ROURKE The Poincaré Conjecture states that a homotopy 3 sphere is a genuine 3 sphere. It arose from work of Poincaré in 1904 and has attracted a huge amount of attention in
The Poincaré Conjecture COLIN ROURKE The Poincaré Conjecture states that a homotopy 3 sphere is a genuine 3 sphere. It arose from work of Poincaré in 1904 and has attracted a huge amount of attention in
121B: ALGEBRAIC TOPOLOGY. Contents. 6. Poincaré Duality
 121B: ALGEBRAIC TOPOLOGY Contents 6. Poincaré Duality 1 6.1. Manifolds 2 6.2. Orientation 3 6.3. Orientation sheaf 9 6.4. Cap product 11 6.5. Proof for good coverings 15 6.6. Direct limit 18 6.7. Proof
121B: ALGEBRAIC TOPOLOGY Contents 6. Poincaré Duality 1 6.1. Manifolds 2 6.2. Orientation 3 6.3. Orientation sheaf 9 6.4. Cap product 11 6.5. Proof for good coverings 15 6.6. Direct limit 18 6.7. Proof
On the K-category of 3-manifolds for K a wedge of spheres or projective planes
 On the K-category of 3-manifolds for K a wedge of spheres or projective planes J. C. Gómez-Larrañaga F. González-Acuña Wolfgang Heil July 27, 2012 Abstract For a complex K, a closed 3-manifold M is of
On the K-category of 3-manifolds for K a wedge of spheres or projective planes J. C. Gómez-Larrañaga F. González-Acuña Wolfgang Heil July 27, 2012 Abstract For a complex K, a closed 3-manifold M is of
Solution: We can cut the 2-simplex in two, perform the identification and then stitch it back up. The best way to see this is with the picture:
 Samuel Lee Algebraic Topology Homework #6 May 11, 2016 Problem 1: ( 2.1: #1). What familiar space is the quotient -complex of a 2-simplex [v 0, v 1, v 2 ] obtained by identifying the edges [v 0, v 1 ]
Samuel Lee Algebraic Topology Homework #6 May 11, 2016 Problem 1: ( 2.1: #1). What familiar space is the quotient -complex of a 2-simplex [v 0, v 1, v 2 ] obtained by identifying the edges [v 0, v 1 ]
Bianchi Orbifolds of Small Discriminant. A. Hatcher
 Bianchi Orbifolds of Small Discriminant A. Hatcher Let O D be the ring of integers in the imaginary quadratic field Q( D) of discriminant D
Bianchi Orbifolds of Small Discriminant A. Hatcher Let O D be the ring of integers in the imaginary quadratic field Q( D) of discriminant D
Lagrangian knottedness and unknottedness in rational surfaces
 agrangian knottedness and unknottedness in rational surfaces Outline: agrangian knottedness Symplectic geometry of complex projective varieties, D 5, agrangian spheres and Dehn twists agrangian unknottedness
agrangian knottedness and unknottedness in rational surfaces Outline: agrangian knottedness Symplectic geometry of complex projective varieties, D 5, agrangian spheres and Dehn twists agrangian unknottedness
Math 6510 Homework 10
 2.2 Problems 9 Problem. Compute the homology group of the following 2-complexes X: a) The quotient of S 2 obtained by identifying north and south poles to a point b) S 1 (S 1 S 1 ) c) The space obtained
2.2 Problems 9 Problem. Compute the homology group of the following 2-complexes X: a) The quotient of S 2 obtained by identifying north and south poles to a point b) S 1 (S 1 S 1 ) c) The space obtained
