Ideal Gas Law. Deduced from Combination of Gas Relationships: PV = nrt. where R = universal gas constant
|
|
|
- Sharleen Casey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ideal Gas Law Deduced from Combination of Gas Relationships: V 1/P, Boyle's Law V T, Charles's Law V n, Avogadro's Law Therefore, V nt/p or PV nt PV = nrt where R = universal gas constant The empirical Equation of State for an Ideal Gas
2 Boyle s Law (experimental) PV = constant (hyperbolae) T 4 Is T 4 > or < T 1?? Temp T 1
3 Ideal Gas Equation of State
4 Ideal Gas Law PV = nrt where R = universal gas constant R = PV/nT R = atm L mol 1 K 1 R = atm dm 3 mol 1 K 1 R = J mol 1 K 1 (SI unit) Standard molar volume = 22.4 L mol 1 at 0 C and 1 atm Real gases approach ideal gas behavior at low P & high T
5 General Principle!! Energy is distributed among accessible configurations in a random process. The ergodic hypothesis Consider fixed total energy with multiple particles and various possible energies for the particles. Determine the distribution that occupies the largest portion of the available Phase Space. That is the observed distribution.
6 Energy Randomness is the basis* of an exponential distribution of occupied energy levels n(e) A exp[-e/<e>] Average Energy <E> ~ k B T n(e) A exp[-e/k B T] This energy distribution is known as the Boltzmann Distribution. * Shown later when we study statistical mechanics.
7 Maxwell Speed Distribution Law = π 2π k T B 32 1 dn m 4 ue 2 N du mu 2 2k T B 1 dn is the fraction of molecules per unit speed interval N du
8 Maxwell Speed Distribution Law Most probable speed, u dn 2 mp du = 0 for u = u u = mp mp kt m Average speed, <u> or ū ( ) u = u N u du = 0 8kT π m Mean squared speed, <u > ( ) u = u N u du = 0 3kT m Root mean square speed u rms = u = 2 3 kt m
9 Distinguish between System & Surroundings
10 Internal Energy Internal Energy (U) is the sum of all potential and kinetic energy for all particles in a system U is a state function Depends only on current state, not on path U = U final - U initial
11 Internal Energy, Heat, and Work If heat (q) is absorbed by the system, and work (w) is done on the system, the increase in internal energy (U) is given by: U = q (heat absorbed by the system) + w (work done on the system)
12 Reversible and Irreversible Work Reversible or Irreversible Processes Reversible: carried out through a sequence of equilibrium states Irreversible: anything else!
13 Internal Energy (2) U is a state function It depends only on state, not on path to get there U = U final - U initial This means mathematically that du is an exact differential: U = du For now, consider a system of constant composition. U can then be regarded as a function of V, T and P. Because there is an equation of state relating them, any two are sufficient to characterize U. So we could have U(P,V), U(P,T) or U(V,T). f i
14 Enthalpy Defined Enthalpy, H U + PV At Constant P, H = U + P V U = q + w q= q P = U - w, w = -P V q P = U + P V= H At constant V, q = U = H
15 Comparing H and U at constant P H = U + P V 1. Reactions that do not involve gases V 0 and H U 2. Reactions in which n gas = 0 V 0 and H U 3. Reactions in which n gas 0 V 0 and H U
16 Heat Capacity at Constant Volume or Pressure C V = dq V /dt = ( U/ T) V Partial derivative of internal energy with respect to T at constant V C P = dq P /dt = ( H/ T) P Partial derivative of enthalpy with respect to T at constant P Ideal Gas: C P = C V + nr
17 Heat Capacity, C Heat Capacity (J K -1 ) Heat needed to raise T of system by 1 K q = C T Specific Heat Capacity (J K -1 kg -1 ) Heat needed to raise T of 1 kg by 1 K q = C S m T Molar Heat Capacity (J K -1 mol -1 ) Heat needed to raise T of 1 mole by 1 K q = C m n T
18 Endothermic & Exothermic Processes H = H final - H initial H Positive Positive amount of heat absorbed by the system Endothermic Process H Negative Negative amount of heat absorbed (i.e. heat released by the system) Exothermic Process
19 Thermochemical Equations CH 4 (g) + 2 O 2 (g) CO 2 (g) + 2 H 2 O (l) (a combustion reaction) c H = 890 kj Reaction must be balanced Phases must be specified H is an extensive property Sign of H changes when reaction is reversed
20 Standard State The Standard State of an element is defined to be the form in which it is most stable at 25 C and 1 bar pressure Some Standard States of elements: Hg (l) O 2 (g) Cl 2 (g) Ag (s) C (graphite) The standard enthalpy of formation ( f H ) of an element in its standard state is defined to be zero.
21 Enthalpies of Formation The standard enthalpy of formation ( f H ) of a compound is the enthalpy change for the formation of one mole of compound from the elements in their standard state. Designated by superscript o, Ø, or o: H,.. For example, CO 2 : C (graphite) + O 2 (g) CO 2 (g) rxn H = kj/mol Table 2.7 f H CO 2 (g) = kj/mol
22 Enthalpies of Reaction The enthalpy of reaction can be calculated from the enthalpies of formation of the reactants and products rxn H O = f H O (Products) - f H O (Reactants)
23 Example: Find rxn H (using Standard Enthalpies of Formation) CH 4 (g) + 2 O 2 (g) CO 2 (g) + 2 H 2 O (l) f H (from Tables 2.4&5, text): CH 4 (g) kj/mol O 2 (g) 0 CO 2 (g) H 2 O (l) rxn H = (285.8) 0 (-74.6) kj/mol Therefore, rxn H = kj/mol
24 Exam 1 ~ 5 problems (weights given) budget your time Closed book Don t memorize formulas/constants You will be given things you need I would assume that you could derive PV work in an isothermal process. I would not assume that you could derive the Maxwellian distribution. Exam will not be heavily numeric, but will emphasize concepts If a problem seems lengthy, do another problem & come back later Understanding homework will be useful EXAM held in JILA Auditorium, Oct 1, 10 AM
Adiabatic Expansion/Compression
 Adiabatic Expansion/Compression Calculate the cooling in a the reversible adiabatic expansion of an ideal gas. P P 1, 1, T 1 A du q w First Law: Since the process is adiabatic, q = 0. Also w = -p ex d
Adiabatic Expansion/Compression Calculate the cooling in a the reversible adiabatic expansion of an ideal gas. P P 1, 1, T 1 A du q w First Law: Since the process is adiabatic, q = 0. Also w = -p ex d
where R = universal gas constant R = PV/nT R = atm L mol R = atm dm 3 mol 1 K 1 R = J mol 1 K 1 (SI unit)
 Ideal Gas Law PV = nrt where R = universal gas constant R = PV/nT R = 0.0821 atm L mol 1 K 1 R = 0.0821 atm dm 3 mol 1 K 1 R = 8.314 J mol 1 K 1 (SI unit) Standard molar volume = 22.4 L mol 1 at 0 C and
Ideal Gas Law PV = nrt where R = universal gas constant R = PV/nT R = 0.0821 atm L mol 1 K 1 R = 0.0821 atm dm 3 mol 1 K 1 R = 8.314 J mol 1 K 1 (SI unit) Standard molar volume = 22.4 L mol 1 at 0 C and
TODAY 0. Why H = q (if p ext =p=constant and no useful work) 1. Constant Pressure Heat Capacity (what we usually use)
 361 Lec 7 Fri 9sep15 TODAY 0. Why H = q (if p ext =p=constant and no useful work) 1. Constant Pressure Heat Capacity (what we usually use) 2. Heats of Chemical Reactions: r H (mechanics of obtaining from
361 Lec 7 Fri 9sep15 TODAY 0. Why H = q (if p ext =p=constant and no useful work) 1. Constant Pressure Heat Capacity (what we usually use) 2. Heats of Chemical Reactions: r H (mechanics of obtaining from
Chapter 1. The Nature of Physical Chemistry and the Kinetic Theory of Gases
 Chapter 1 The Nature of Physical Chemistry and the Kinetic Theory of Gases Physical chemistry is the application of the methods of physics to chemical problems Work Kinetic and Potential Energy Thermal
Chapter 1 The Nature of Physical Chemistry and the Kinetic Theory of Gases Physical chemistry is the application of the methods of physics to chemical problems Work Kinetic and Potential Energy Thermal
Chapter 5 - Thermochemistry
 Chapter 5 - Thermochemistry Study of energy changes that accompany chemical rx s. I) Nature of Energy Energy / Capacity to do work Mechanical Work w = F x d Heat energy - energy used to cause the temperature
Chapter 5 - Thermochemistry Study of energy changes that accompany chemical rx s. I) Nature of Energy Energy / Capacity to do work Mechanical Work w = F x d Heat energy - energy used to cause the temperature
Gases. Properties of Gases Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases Pressure Boyle s and Charles Law The Ideal Gas Law Gas reactions Partial pressures.
 Gases Properties of Gases Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases Pressure Boyle s and Charles Law The Ideal Gas Law Gas reactions Partial pressures Gases Properties of Gases All elements will form a gas at
Gases Properties of Gases Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases Pressure Boyle s and Charles Law The Ideal Gas Law Gas reactions Partial pressures Gases Properties of Gases All elements will form a gas at
10/1/ st Law of Thermodynamics (Law of Conservation of Energy) & Hess s Law. Learning Targets
 1 st Law of Thermodynamics (Law of Conservation of Energy) & Hess s Law 1 Learning Targets LT 5.02: I can relate temperature to the motions of particles and average kinetic energy. LT 5.03: I can generate
1 st Law of Thermodynamics (Law of Conservation of Energy) & Hess s Law 1 Learning Targets LT 5.02: I can relate temperature to the motions of particles and average kinetic energy. LT 5.03: I can generate
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry
 Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Learning Outcomes: Interconvert energy units Distinguish between the system and the surroundings in thermodynamics Calculate internal energy from heat and work and state sign
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Learning Outcomes: Interconvert energy units Distinguish between the system and the surroundings in thermodynamics Calculate internal energy from heat and work and state sign
CHEMISTRY. Chapter 5 Thermochemistry
 CHEMISTRY The Central Science 8 th Edition Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Dr. Kozet YAPSAKLI The Nature of Energy Kinetic and Potential Energy Potential energy can be converted into kinetic energy. E p = mgh
CHEMISTRY The Central Science 8 th Edition Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Dr. Kozet YAPSAKLI The Nature of Energy Kinetic and Potential Energy Potential energy can be converted into kinetic energy. E p = mgh
Ch. 6 Enthalpy Changes
 Ch. 6 Enthalpy Changes Energy: The capacity to do work. In Physics, there are 2 main types of energy Kinetic (energy of motion) = ½ mv 2 Potential (energy of position due to gravity)= mgh In Chemistry,
Ch. 6 Enthalpy Changes Energy: The capacity to do work. In Physics, there are 2 main types of energy Kinetic (energy of motion) = ½ mv 2 Potential (energy of position due to gravity)= mgh In Chemistry,
CH10007/87. Thermodynamics. Dr Toby Jenkins
 CH10007/87 Thermodynamics Dr Toby Jenkins 1 Objectives To introduce the basic concepts of thermodynamics To apply them to chemical systems To develop competence in thermodynamics calculations 2 Equilibrium
CH10007/87 Thermodynamics Dr Toby Jenkins 1 Objectives To introduce the basic concepts of thermodynamics To apply them to chemical systems To develop competence in thermodynamics calculations 2 Equilibrium
Thermochemistry is the study of the relationships between chemical reactions and energy changes involving heat.
 CHEM134- F18 Dr. Al- Qaisi Chapter 06: Thermodynamics Thermochemistry is the study of the relationships between chemical reactions and energy changes involving heat. Energy is anything that has the capacity
CHEM134- F18 Dr. Al- Qaisi Chapter 06: Thermodynamics Thermochemistry is the study of the relationships between chemical reactions and energy changes involving heat. Energy is anything that has the capacity
Chemistry Chapter 16. Reaction Energy
 Chemistry Reaction Energy Section 16.1.I Thermochemistry Objectives Define temperature and state the units in which it is measured. Define heat and state its units. Perform specific-heat calculations.
Chemistry Reaction Energy Section 16.1.I Thermochemistry Objectives Define temperature and state the units in which it is measured. Define heat and state its units. Perform specific-heat calculations.
CHEM 1105 S10 March 11 & 14, 2014
 CHEM 1105 S10 March 11 & 14, 2014 Today s topics: Thermochemistry (Chapter 6) Basic definitions Calorimetry Enthalpy Thermochemical equations Calculating heats of reaction Hess s Law Energy and Heat Some
CHEM 1105 S10 March 11 & 14, 2014 Today s topics: Thermochemistry (Chapter 6) Basic definitions Calorimetry Enthalpy Thermochemical equations Calculating heats of reaction Hess s Law Energy and Heat Some
First Law of Thermodynamics
 Energy Energy: ability to do work or produce heat. Types of energy 1) Potential energy - energy possessed by objects due to position or arrangement of particles. Forms of potential energy - electrical,
Energy Energy: ability to do work or produce heat. Types of energy 1) Potential energy - energy possessed by objects due to position or arrangement of particles. Forms of potential energy - electrical,
Energy Relationships in Chemical Reactions
 Energy Relationships in Chemical Reactions What is heat? What is a state function? What is enthalpy? Is enthalpy a state function? What does this mean? How can we calculate this? How are the methods the
Energy Relationships in Chemical Reactions What is heat? What is a state function? What is enthalpy? Is enthalpy a state function? What does this mean? How can we calculate this? How are the methods the
L = 6.02 x mol Determine the number of particles and the amount of substance (in moles)
 1.1 The Mole 1.1.1 - Apply the mole concept to substances A mole is the name given to a certain quantity. It represents 6.02 x 10 23 particles. This number is also known as Avogadro's constant, symbolised
1.1 The Mole 1.1.1 - Apply the mole concept to substances A mole is the name given to a certain quantity. It represents 6.02 x 10 23 particles. This number is also known as Avogadro's constant, symbolised
GASES (Chapter 5) Temperature and Pressure, that is, 273 K and 1.00 atm or 760 Torr ) will occupy
 I. Ideal gases. A. Ideal gas law review. GASES (Chapter 5) 1. PV = nrt Ideal gases obey this equation under all conditions. It is a combination ofa. Boyle's Law: P 1/V at constant n and T b. Charles's
I. Ideal gases. A. Ideal gas law review. GASES (Chapter 5) 1. PV = nrt Ideal gases obey this equation under all conditions. It is a combination ofa. Boyle's Law: P 1/V at constant n and T b. Charles's
First Law of Thermodynamics: energy cannot be created or destroyed.
 1 CHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS ANSWERS energy = anything that has the capacity to do work work = force acting over a distance Energy (E) = Work = Force x Distance First Law of Thermodynamics: energy cannot
1 CHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS ANSWERS energy = anything that has the capacity to do work work = force acting over a distance Energy (E) = Work = Force x Distance First Law of Thermodynamics: energy cannot
The following gas laws describes an ideal gas, where
 Alief ISD Chemistry STAAR Review Reporting Category 4: Gases and Thermochemistry C.9.A Describe and calculate the relations between volume, pressure, number of moles, and temperature for an ideal gas as
Alief ISD Chemistry STAAR Review Reporting Category 4: Gases and Thermochemistry C.9.A Describe and calculate the relations between volume, pressure, number of moles, and temperature for an ideal gas as
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics
 Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics Kinetics How fast a rxn. proceeds Equilibrium How far a rxn proceeds towards completion Thermodynamics Study of energy relationships & changes which occur during chemical
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics Kinetics How fast a rxn. proceeds Equilibrium How far a rxn proceeds towards completion Thermodynamics Study of energy relationships & changes which occur during chemical
Thermochemistry. Energy. 1st Law of Thermodynamics. Enthalpy / Calorimetry. Enthalpy of Formation
 THERMOCHEMISTRY Thermochemistry Energy 1st Law of Thermodynamics Enthalpy / Calorimetry Hess' Law Enthalpy of Formation The Nature of Energy Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy Kinetic energy is the energy
THERMOCHEMISTRY Thermochemistry Energy 1st Law of Thermodynamics Enthalpy / Calorimetry Hess' Law Enthalpy of Formation The Nature of Energy Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy Kinetic energy is the energy
H = DATA THAT YOU MAY USE. Units Conventional Volume ml or cm 3 = cm 3 or 10-3 dm 3 Liter (L) = dm 3 Pressure atm = 760 torr = 1.
 DATA THAT YOU MAY USE Units Conventional S.I. Volume ml or cm 3 = cm 3 or 10-3 dm 3 Liter (L) = dm 3 Pressure atm = 760 torr = 1.013 10 5 Pa torr = 133.3 Pa Temperature C 0 C = 73.15 K PV L-atm = 1.013
DATA THAT YOU MAY USE Units Conventional S.I. Volume ml or cm 3 = cm 3 or 10-3 dm 3 Liter (L) = dm 3 Pressure atm = 760 torr = 1.013 10 5 Pa torr = 133.3 Pa Temperature C 0 C = 73.15 K PV L-atm = 1.013
Enthalpy and Adiabatic Changes
 Enthalpy and Adiabatic Changes Chapter 2 of Atkins: The First Law: Concepts Sections 2.5-2.6 of Atkins (7th & 8th editions) Enthalpy Definition of Enthalpy Measurement of Enthalpy Variation of Enthalpy
Enthalpy and Adiabatic Changes Chapter 2 of Atkins: The First Law: Concepts Sections 2.5-2.6 of Atkins (7th & 8th editions) Enthalpy Definition of Enthalpy Measurement of Enthalpy Variation of Enthalpy
10-1 Heat 10-2 Calorimetry 10-3 Enthalpy 10-4 Standard-State Enthalpies 10-5 Bond Enthalpies 10-6 The First Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 10 Thermochemistry 10-1 Heat 10-2 Calorimetry 10-3 Enthalpy 10-4 Standard-State Enthalpies 10-5 Bond Enthalpies 10-6 The First Law of Thermodynamics OFB Chap. 10 1 Chapter 10 Thermochemistry Heat
Chapter 10 Thermochemistry 10-1 Heat 10-2 Calorimetry 10-3 Enthalpy 10-4 Standard-State Enthalpies 10-5 Bond Enthalpies 10-6 The First Law of Thermodynamics OFB Chap. 10 1 Chapter 10 Thermochemistry Heat
Exothermic process is any process that gives off heat transfers thermal energy from the system to the surroundings. H 2 O (l) + energy
 Exothermic process is any process that gives off heat transfers thermal energy from the system to the surroundings. H 2 O (g) H 2 O (l) + energy Endothermic process is any process in which heat has to
Exothermic process is any process that gives off heat transfers thermal energy from the system to the surroundings. H 2 O (g) H 2 O (l) + energy Endothermic process is any process in which heat has to
Chapter 18 Thermal Properties of Matter
 Chapter 18 Thermal Properties of Matter In this section we define the thermodynamic state variables and their relationship to each other, called the equation of state. The system of interest (most of the
Chapter 18 Thermal Properties of Matter In this section we define the thermodynamic state variables and their relationship to each other, called the equation of state. The system of interest (most of the
Lecture 2. Review of Basic Concepts
 Lecture 2 Review of Basic Concepts Thermochemistry Enthalpy H heat content H Changes with all physical and chemical changes H Standard enthalpy (25 C, 1 atm) (H=O for all elements in their standard forms
Lecture 2 Review of Basic Concepts Thermochemistry Enthalpy H heat content H Changes with all physical and chemical changes H Standard enthalpy (25 C, 1 atm) (H=O for all elements in their standard forms
Gases: Their Properties & Behavior. Chapter 09 Slide 1
 9 Gases: Their Properties & Behavior Chapter 09 Slide 1 Gas Pressure 01 Chapter 09 Slide 2 Gas Pressure 02 Units of pressure: atmosphere (atm) Pa (N/m 2, 101,325 Pa = 1 atm) Torr (760 Torr = 1 atm) bar
9 Gases: Their Properties & Behavior Chapter 09 Slide 1 Gas Pressure 01 Chapter 09 Slide 2 Gas Pressure 02 Units of pressure: atmosphere (atm) Pa (N/m 2, 101,325 Pa = 1 atm) Torr (760 Torr = 1 atm) bar
The Nature of Energy. Chapter Six: Kinetic vs. Potential Energy. Energy and Work. Temperature vs. Heat
 The Nature of Energy Chapter Six: THERMOCHEMISTRY Thermodynamics is the study of energy and its transformations. Thermochemistry is the study of the relationship between chemical reactions and energy changes
The Nature of Energy Chapter Six: THERMOCHEMISTRY Thermodynamics is the study of energy and its transformations. Thermochemistry is the study of the relationship between chemical reactions and energy changes
Energy, Heat and Chemical Change
 Energy, Heat and Chemical Change Chemistry 35 Fall 2000 Thermochemistry A part of Thermodynamics dealing with energy changes associated with physical and chemical reactions Why do we care? -will a reaction
Energy, Heat and Chemical Change Chemistry 35 Fall 2000 Thermochemistry A part of Thermodynamics dealing with energy changes associated with physical and chemical reactions Why do we care? -will a reaction
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics Entropy and free energy
 Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics Entropy and free energy Learning goals and key skills: Understand the meaning of spontaneous process, reversible process, irreversible process, and isothermal process.
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics Entropy and free energy Learning goals and key skills: Understand the meaning of spontaneous process, reversible process, irreversible process, and isothermal process.
Outline of the Course
 Outline of the Course 1) Review and Definitions 2) Molecules and their Energies 3) 1 st Law of Thermodynamics 4) 2 nd Law of Thermodynamics 5) Gibbs Free Energy 6) Phase Diagrams and REAL Phenomena 7)
Outline of the Course 1) Review and Definitions 2) Molecules and their Energies 3) 1 st Law of Thermodynamics 4) 2 nd Law of Thermodynamics 5) Gibbs Free Energy 6) Phase Diagrams and REAL Phenomena 7)
Kinetic energy is the energy of motion (of particles). Potential energy involves stored energy (energy locked up in chemical bonds)
 Enthalpy (H) Enthalpy (H) is the total energy amount (Epotential + Ekinetic) of a system during a chemical reaction under constant temperature and pressure conditions. Kinetic energy is the energy of motion
Enthalpy (H) Enthalpy (H) is the total energy amount (Epotential + Ekinetic) of a system during a chemical reaction under constant temperature and pressure conditions. Kinetic energy is the energy of motion
UNIT 15: THERMODYNAMICS
 UNIT 15: THERMODYNAMICS ENTHALPY, DH ENTROPY, DS GIBBS FREE ENERGY, DG ENTHALPY, DH Energy Changes in Reactions Heat is the transfer of thermal energy between two bodies that are at different temperatures.
UNIT 15: THERMODYNAMICS ENTHALPY, DH ENTROPY, DS GIBBS FREE ENERGY, DG ENTHALPY, DH Energy Changes in Reactions Heat is the transfer of thermal energy between two bodies that are at different temperatures.
Measuring and Expressing Enthalpy Changes. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall. Measuring and Expressing Enthalpy Changes. Calorimetry
 Measuring and Expressing Enthalpy Changes A burning match releases heat to its surroundings in all directions. How much heat does this exothermic reaction release? You will learn to measure heat flow in
Measuring and Expressing Enthalpy Changes A burning match releases heat to its surroundings in all directions. How much heat does this exothermic reaction release? You will learn to measure heat flow in
Thermodynamic Processes and Thermochemistry
 General Chemistry Thermodynamic Processes and Thermochemistry 박준원교수 ( 포항공과대학교화학과 ) 이번시간에는! Systems, states, and processes The first law of thermodynamics: internal energy, work, and heat Heat capacity,
General Chemistry Thermodynamic Processes and Thermochemistry 박준원교수 ( 포항공과대학교화학과 ) 이번시간에는! Systems, states, and processes The first law of thermodynamics: internal energy, work, and heat Heat capacity,
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics
 Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics Kinetics How fast a rxn. proceeds Equilibrium How far a rxn proceeds towards completion Thermodynamics Study of energy relationships & changes which occur during chemical
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics Kinetics How fast a rxn. proceeds Equilibrium How far a rxn proceeds towards completion Thermodynamics Study of energy relationships & changes which occur during chemical
Exam 4, Enthalpy and Gases
 CHEM 1100 Dr. Stone November 8, 2017 Name_ G Exam 4, Enthalpy and Gases Equations and constants you may need: ΔE system = q + w PV = nrt R = 0.0821 (L*atm)/(mole*K) w = -PΔV K.E. = 1 2 m *µ 2 rms µ rms=
CHEM 1100 Dr. Stone November 8, 2017 Name_ G Exam 4, Enthalpy and Gases Equations and constants you may need: ΔE system = q + w PV = nrt R = 0.0821 (L*atm)/(mole*K) w = -PΔV K.E. = 1 2 m *µ 2 rms µ rms=
Chapter 6 Problems: 9, 19, 24, 25, 26, 27, 31-33, 37, 39, 43, 45, 47, 48, 53, 55, 57, 59, 65, 67, 73, 78-82, 85, 89, 93
 Chapter 6 Problems: 9, 19, 24, 25, 26, 27, 31-33, 37, 39, 43, 45, 47, 48, 53, 55, 57, 59, 65, 67, 73, 78-82, 85, 89, 93 Chapter 6 Thermochemistry The study of chemical reactions and the energy changes
Chapter 6 Problems: 9, 19, 24, 25, 26, 27, 31-33, 37, 39, 43, 45, 47, 48, 53, 55, 57, 59, 65, 67, 73, 78-82, 85, 89, 93 Chapter 6 Thermochemistry The study of chemical reactions and the energy changes
10-1 Heat 10-2 Calorimetry 10-3 Enthalpy 10-4 Standard-State Enthalpies 10-5 Bond Enthalpies 10-6 The First Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 10 Thermochemistry 10-1 Heat 10-2 Calorimetry 10-3 Enthalpy 10-4 Standard-State Enthalpies 10-5 Bond Enthalpies 10-6 The First Law of Thermodynamics OFB Chap. 10 1 OFB Chap. 10 2 Thermite Reaction
Chapter 10 Thermochemistry 10-1 Heat 10-2 Calorimetry 10-3 Enthalpy 10-4 Standard-State Enthalpies 10-5 Bond Enthalpies 10-6 The First Law of Thermodynamics OFB Chap. 10 1 OFB Chap. 10 2 Thermite Reaction
Thermochemistry: Heat and Chemical Change
 Thermochemistry: Heat and Chemical Change 1 Heat or Thermal Energy (q) Heat is a form of energy Is heat the same as temperature? Heat flows between two objects at different temperatures. Hot Cold 2 Chemical
Thermochemistry: Heat and Chemical Change 1 Heat or Thermal Energy (q) Heat is a form of energy Is heat the same as temperature? Heat flows between two objects at different temperatures. Hot Cold 2 Chemical
Determining the Components of the Rate Equation aa + bb yy + zz
 Determining the Components of the Rate Equation aa + bb yy + zz Rate k[a] [B] The coefficients and components of the rate equation Must be found by experiment Cannot be deduced from stoichiometry Do not
Determining the Components of the Rate Equation aa + bb yy + zz Rate k[a] [B] The coefficients and components of the rate equation Must be found by experiment Cannot be deduced from stoichiometry Do not
I PUC CHEMISTRY CHAPTER - 06 Thermodynamics
 I PUC CHEMISTRY CHAPTER - 06 Thermodynamics One mark questions 1. Define System. 2. Define surroundings. 3. What is an open system? Give one example. 4. What is closed system? Give one example. 5. What
I PUC CHEMISTRY CHAPTER - 06 Thermodynamics One mark questions 1. Define System. 2. Define surroundings. 3. What is an open system? Give one example. 4. What is closed system? Give one example. 5. What
Chapter 5. Thermochemistry
 Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Dr. A. Al-Saadi 1 Preview Introduction to thermochemistry: Potential energy and kinetic energy. Chemical energy. Internal energy, work and heat. Exothermic vs. endothermic reactions.
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Dr. A. Al-Saadi 1 Preview Introduction to thermochemistry: Potential energy and kinetic energy. Chemical energy. Internal energy, work and heat. Exothermic vs. endothermic reactions.
Chapter 6: Thermochemistry
 Chapter 6: Thermochemistry 1. Light the Furnace: The Nature of Energy and Its Transformations a. Thermochemistry is the study of the relationships between chemistry and energy i. This means that we will
Chapter 6: Thermochemistry 1. Light the Furnace: The Nature of Energy and Its Transformations a. Thermochemistry is the study of the relationships between chemistry and energy i. This means that we will
Chapter 8. Thermochemistry
 Chapter 8 Thermochemistry Copyright 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. All rights reserved. Requests for permission to make copies of any part of the work should be mailed to the following address: Permissions Department,
Chapter 8 Thermochemistry Copyright 2001 by Harcourt, Inc. All rights reserved. Requests for permission to make copies of any part of the work should be mailed to the following address: Permissions Department,
Lecture 25 Thermodynamics, Heat and Temp (cont.)
 Lecture 25 Thermodynamics, Heat and Temp (cont.) Heat and temperature Gases & Kinetic theory http://candidchatter.files.wordpress.com/2009/02/hell.jpg Specific Heat Specific Heat: heat capacity per unit
Lecture 25 Thermodynamics, Heat and Temp (cont.) Heat and temperature Gases & Kinetic theory http://candidchatter.files.wordpress.com/2009/02/hell.jpg Specific Heat Specific Heat: heat capacity per unit
Enthalpy. Enthalpy. Enthalpy. Enthalpy. E = q + w. Internal Energy at Constant Volume SYSTEM. heat transfer in (endothermic), +q
 heat transfer in (endothermic), +q heat transfer out (exothermic), -q SYSTEM E = q + w w transfer in (+w) w transfer out (-w) Internal Energy at Constant Volume E = KE + PE ΔE = q + w Because most systems,
heat transfer in (endothermic), +q heat transfer out (exothermic), -q SYSTEM E = q + w w transfer in (+w) w transfer out (-w) Internal Energy at Constant Volume E = KE + PE ΔE = q + w Because most systems,
Thermochemistry Chapter 4
 Thermochemistry Chapter 4 Thermochemistry is the study of energy changes that occur during chemical reactions Focus is on heat and matter transfer between the system and the surroundings Energy The ability
Thermochemistry Chapter 4 Thermochemistry is the study of energy changes that occur during chemical reactions Focus is on heat and matter transfer between the system and the surroundings Energy The ability
Determining the Components of the Rate Equation
 Determining the Components of the Rate Equation aa + bb yy + zz Rate k[a] [B] The coefficients and components of the rate equation Must be found by experiment Cannot be deduced from stoichiometry Do not
Determining the Components of the Rate Equation aa + bb yy + zz Rate k[a] [B] The coefficients and components of the rate equation Must be found by experiment Cannot be deduced from stoichiometry Do not
Guided Notes and Practice- Topi 5.1: Calorimetry and Enthalpy Calculations
 Name: Date: Pd: Guided Notes and Practice- Topi 5.1: Calorimetry and Enthalpy Calculations Endothermic vs. Exothermic 1. Label each ΔH value as being exothermic or endothermic. Thermochemical Equations
Name: Date: Pd: Guided Notes and Practice- Topi 5.1: Calorimetry and Enthalpy Calculations Endothermic vs. Exothermic 1. Label each ΔH value as being exothermic or endothermic. Thermochemical Equations
General Chemistry 1 CHM201 Unit 3 Practice Test
 General Chemistry 1 CHM201 Unit 3 Practice Test 1. Heat is best defined as a. a substance that increases the temperature and causes water to boil. b. a form of potential energy. c. a form of work. d. the
General Chemistry 1 CHM201 Unit 3 Practice Test 1. Heat is best defined as a. a substance that increases the temperature and causes water to boil. b. a form of potential energy. c. a form of work. d. the
Major Concepts Calorimetry (from last time)
 Major Concepts Calorimetry (from last time) Heat capacity Molar heat capacity (per mole) Specific heat capacity (per mass) Standard state enthalpies: Hº Physical Changes Chemical Changes Hess's Law Balancing
Major Concepts Calorimetry (from last time) Heat capacity Molar heat capacity (per mole) Specific heat capacity (per mass) Standard state enthalpies: Hº Physical Changes Chemical Changes Hess's Law Balancing
Useful Information to be provided on the exam: 1 atm = 760 mm Hg = 760 torr = lb/in 2 = 101,325 Pa = kpa. q = m C T. w = -P V.
 Chem 101A Study Questions, Chapters 5 & 6 Name: Review Tues 10/25/16 Due 10/27/16 (Exam 3 date) This is a homework assignment. Please show your work for full credit. If you do work on separate paper, attach
Chem 101A Study Questions, Chapters 5 & 6 Name: Review Tues 10/25/16 Due 10/27/16 (Exam 3 date) This is a homework assignment. Please show your work for full credit. If you do work on separate paper, attach
Ch. 7: Thermochemistry
 Thermodynamics and Thermochemistry Thermodynamics concerns itself with energy and its relationship to the large scale bulk properties of a system that are measurable: Volume, Temperature, Pressure, Heat
Thermodynamics and Thermochemistry Thermodynamics concerns itself with energy and its relationship to the large scale bulk properties of a system that are measurable: Volume, Temperature, Pressure, Heat
Energy Heat Work Heat Capacity Enthalpy
 Energy Heat Work Heat Capacity Enthalpy 1 Prof. Zvi C. Koren 20.07.2010 Thermodynamics vs. Kinetics Thermodynamics Thermo = Thermo + Dynamics E (Note: Absolute E can never be determined by humans!) Can
Energy Heat Work Heat Capacity Enthalpy 1 Prof. Zvi C. Koren 20.07.2010 Thermodynamics vs. Kinetics Thermodynamics Thermo = Thermo + Dynamics E (Note: Absolute E can never be determined by humans!) Can
For more info visit
 Basic Terminology: Terms System Open System Closed System Isolated system Surroundings Boundary State variables State Functions Intensive properties Extensive properties Process Isothermal process Isobaric
Basic Terminology: Terms System Open System Closed System Isolated system Surroundings Boundary State variables State Functions Intensive properties Extensive properties Process Isothermal process Isobaric
Chapter Elements That Exist as Gases at 25 C, 1 atm. 5.2 Pressure basic physics. Gas Properties
 5.1 Elements That Exist as Gases at 25 C, 1 atm Chapter 5 The Gaseous State YOU READ AND BE RESPONSIBLE FOR THIS SECTION! Gaseous compounds include CH 4, NO, NO 2, H 2 S, NH 3, HCl, etc. Gas Properties
5.1 Elements That Exist as Gases at 25 C, 1 atm Chapter 5 The Gaseous State YOU READ AND BE RESPONSIBLE FOR THIS SECTION! Gaseous compounds include CH 4, NO, NO 2, H 2 S, NH 3, HCl, etc. Gas Properties
General Chemistry Review
 General Chemistry Review Helping you remember what you learned, oh, so long ago. Topics (Until we run out of time) The mole Stoichiometry Limiting Reactants Solution Chemistry Molarity Dilution Stoichiometry
General Chemistry Review Helping you remember what you learned, oh, so long ago. Topics (Until we run out of time) The mole Stoichiometry Limiting Reactants Solution Chemistry Molarity Dilution Stoichiometry
Learning Check. How much heat, q, is required to raise the temperature of 1000 kg of iron and 1000 kg of water from 25 C to 75 C?
 Learning Check q = c * m * ΔT How much heat, q, is required to raise the temperature of 1000 kg of iron and 1000 kg of water from 25 C to 75 C? (c water =4.184 J/ C g, c iron =0.450 J/ C g) q Fe = 0.450
Learning Check q = c * m * ΔT How much heat, q, is required to raise the temperature of 1000 kg of iron and 1000 kg of water from 25 C to 75 C? (c water =4.184 J/ C g, c iron =0.450 J/ C g) q Fe = 0.450
BCIT Fall Chem Exam #2
 BCIT Fall 2017 Chem 3310 Exam #2 Name: Attempt all questions in this exam. Read each question carefully and give a complete answer in the space provided. Part marks given for wrong answers with partially
BCIT Fall 2017 Chem 3310 Exam #2 Name: Attempt all questions in this exam. Read each question carefully and give a complete answer in the space provided. Part marks given for wrong answers with partially
Topic 05 Energetics : Heat Change. IB Chemistry T05D01
 Topic 05 Energetics 5.1-5.2: Heat Change IB Chemistry T05D01 5.1 Exothermic and endothermic reactions - 1 hour 5.1.1 Define the terms exothermic reaction, endothermic reaction and standard enthalpy change
Topic 05 Energetics 5.1-5.2: Heat Change IB Chemistry T05D01 5.1 Exothermic and endothermic reactions - 1 hour 5.1.1 Define the terms exothermic reaction, endothermic reaction and standard enthalpy change
Substances that Exist as Gases
 Gases Properties of Gases assume the volume and shape of their containers most compressible of the states of matter mix evenly and completely with other gases much lower density than other forms of matter
Gases Properties of Gases assume the volume and shape of their containers most compressible of the states of matter mix evenly and completely with other gases much lower density than other forms of matter
Enthalpy Chapter 5.3-4,7
 Enthalpy Chapter 5.3-4,7 heat transfer in (endothermic), +q heat transfer out (exothermic), -q SYSTEM E = q + w w transfer in (+w) w transfer out (-w) Internal Energy at Constant Volume E = E K + E P ΔE
Enthalpy Chapter 5.3-4,7 heat transfer in (endothermic), +q heat transfer out (exothermic), -q SYSTEM E = q + w w transfer in (+w) w transfer out (-w) Internal Energy at Constant Volume E = E K + E P ΔE
Thermodynamics - Energy Relationships in Chemical Reactions:
 Thermodynamics - Energy Relationships in Chemical Reactions: energy - The capacity to do work. Types of Energy: radiant-energy from the sun. potential-energy due to an objects position. chemical-energy
Thermodynamics - Energy Relationships in Chemical Reactions: energy - The capacity to do work. Types of Energy: radiant-energy from the sun. potential-energy due to an objects position. chemical-energy
What is thermodynamics? and what can it do for us?
 What is thermodynamics? and what can it do for us? The overall goal of thermodynamics is to describe what happens to a system (anything of interest) when we change the variables that characterized the
What is thermodynamics? and what can it do for us? The overall goal of thermodynamics is to describe what happens to a system (anything of interest) when we change the variables that characterized the
C H E M 1 CHEM 101-GENERAL CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 5 GASES INSTR : FİLİZ ALSHANABLEH
 C H E M 1 CHEM 101-GENERAL CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 5 GASES 0 1 INSTR : FİLİZ ALSHANABLEH CHAPTER 5 GASES Properties of Gases Pressure History and Application of the Gas Laws Partial Pressure Stoichiometry of
C H E M 1 CHEM 101-GENERAL CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 5 GASES 0 1 INSTR : FİLİZ ALSHANABLEH CHAPTER 5 GASES Properties of Gases Pressure History and Application of the Gas Laws Partial Pressure Stoichiometry of
Heat and Thermodynamics. February. 2, Solution of Recitation 2. Consider the first case when air is allowed to expand isothermally.
 Heat and Thermodynamics. February., 0 Solution of Recitation Answer : We have given that, Initial volume of air = = 0.4 m 3 Initial pressure of air = P = 04 kpa = 04 0 3 Pa Final pressure of air = P =
Heat and Thermodynamics. February., 0 Solution of Recitation Answer : We have given that, Initial volume of air = = 0.4 m 3 Initial pressure of air = P = 04 kpa = 04 0 3 Pa Final pressure of air = P =
Chemistry 163B Winter Lectures 2-3. Heat and Work
 Chemistry 163B Winter 2014 Lectures 2-3 Heat and Work Chemistry 163B reserve books 2014 (S&E Library) handout #7 heat capacity (E&R section 2.5) -d q C heat capacity 1 J K dt the amount of heat requires
Chemistry 163B Winter 2014 Lectures 2-3 Heat and Work Chemistry 163B reserve books 2014 (S&E Library) handout #7 heat capacity (E&R section 2.5) -d q C heat capacity 1 J K dt the amount of heat requires
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics Entropy and free energy
 Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics Entropy and free energy Learning goals and key skills: Explain and apply the terms spontaneous process, reversible process, irreversible process, and isothermal process.
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics Entropy and free energy Learning goals and key skills: Explain and apply the terms spontaneous process, reversible process, irreversible process, and isothermal process.
Gases. Chapter 11. Preview. 27-Nov-11
 Chapter 11 Gases Dr. A. Al-Saadi 1 Preview Properties and measurements of gases. Effects of temperature, pressure and volume. Boyle s law. Charles s law, and Avogadro s law. The ideal gas equation. Gas
Chapter 11 Gases Dr. A. Al-Saadi 1 Preview Properties and measurements of gases. Effects of temperature, pressure and volume. Boyle s law. Charles s law, and Avogadro s law. The ideal gas equation. Gas
Chemistry I Practice Exam
 Chemistry I Practice Exam Name Multiple Choice: Choose the best answer that completes each statement. Put all answers on your answer sheet. 1. The mass of one mole of NaCl is a..53 g b. 22.99 g c. 5.44
Chemistry I Practice Exam Name Multiple Choice: Choose the best answer that completes each statement. Put all answers on your answer sheet. 1. The mass of one mole of NaCl is a..53 g b. 22.99 g c. 5.44
Unit 7 Thermochemistry Chemistry 020, R. R. Martin
 Unit 7 Thermochemistry Chemistry 020, R. R. Martin 1. Thermochemistry Heat is a form of energy - which may take many forms: - Kinetic energy due to motion, ½ mv 2 - Potential energy due to position - Electrical
Unit 7 Thermochemistry Chemistry 020, R. R. Martin 1. Thermochemistry Heat is a form of energy - which may take many forms: - Kinetic energy due to motion, ½ mv 2 - Potential energy due to position - Electrical
Kwantlen Polytechnic University Chemistry 1105 S10 Spring Term Test No. 3 Thursday, April 4, 2013
 Kwantlen Polytechnic University Chemistry 1105 S10 Spring Term Test No. 3 Thursday, April 4, 2013 Name: Student Number Instructions: Ensure that this exam contains all eight pages including this page.
Kwantlen Polytechnic University Chemistry 1105 S10 Spring Term Test No. 3 Thursday, April 4, 2013 Name: Student Number Instructions: Ensure that this exam contains all eight pages including this page.
Chapter 11. Thermochemistry. 1. Let s begin by previewing the chapter (Page 292). 2. We will partner read Pages
 Chapter 11 Thermochemistry 1. Let s begin by previewing the chapter (Page 292). 2. We will partner read Pages 293-94 The Flow of energy - heat Thermochemistry concerned with the heat changes that occur
Chapter 11 Thermochemistry 1. Let s begin by previewing the chapter (Page 292). 2. We will partner read Pages 293-94 The Flow of energy - heat Thermochemistry concerned with the heat changes that occur
MCGILL UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF SCIENCE MIDTERM EXAMINATION CHEM 120 MONDAY MARCH 16, :30PM 8:30PM VERSION NUMBER: 1
 MCGILL UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF SCIENCE MIDTERM EXAMINATION CHEM 120 MONDAY MARCH 16, 2009 6:30PM 8:30PM VERSION NUMBER: 1 Instructions: BEFORE YOU BEGIN: Enter your student number and name on the computer
MCGILL UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF SCIENCE MIDTERM EXAMINATION CHEM 120 MONDAY MARCH 16, 2009 6:30PM 8:30PM VERSION NUMBER: 1 Instructions: BEFORE YOU BEGIN: Enter your student number and name on the computer
Properties of Gases. assume the volume and shape of their containers. most compressible of the states of matter
 Gases Properties of Gases assume the volume and shape of their containers most compressible of the states of matter mix evenly and completely with other gases much lower density than other forms of matter
Gases Properties of Gases assume the volume and shape of their containers most compressible of the states of matter mix evenly and completely with other gases much lower density than other forms of matter
. (10 points) A lab worker had three gas cylinders. One she knew contained neon, but the other two had no identifying labels. She allowed all three ga
 Chemistry 50 - Dr. McCoy Answer key for Midquarter Exam 1 February, 1999 100 POINTS 1. (0 points) Consider the combustion of propane [C 3 H 8 (g)] to form H O(g) and CO (g). C 3 H 8 (g) + 5O (g),! 3CO
Chemistry 50 - Dr. McCoy Answer key for Midquarter Exam 1 February, 1999 100 POINTS 1. (0 points) Consider the combustion of propane [C 3 H 8 (g)] to form H O(g) and CO (g). C 3 H 8 (g) + 5O (g),! 3CO
Gases! n Properties! n Kinetic Molecular Theory! n Variables! n The Atmosphere! n Gas Laws!
 Gases n Properties n Kinetic Molecular Theory n Variables n The Atmosphere n Gas Laws Properties of a Gas n No definite shape or volume n Gases expand to fill any container n Thus they take the shape of
Gases n Properties n Kinetic Molecular Theory n Variables n The Atmosphere n Gas Laws Properties of a Gas n No definite shape or volume n Gases expand to fill any container n Thus they take the shape of
LECTURE 4 Variation of enthalpy with temperature
 LECTURE 4 Variation of enthalpy with temperature So far, we can only work at 25 C. Like c v we define a constant pressure heat capacity, c p, as the amount of heat energy needed to raise the temperature
LECTURE 4 Variation of enthalpy with temperature So far, we can only work at 25 C. Like c v we define a constant pressure heat capacity, c p, as the amount of heat energy needed to raise the temperature
Gases and Kinetic Molecular Theory
 1 Gases and Kinetic Molecular Theory 1 CHAPTER GOALS 1. Comparison of Solids, Liquids, and Gases. Composition of the Atmosphere and Some Common Properties of Gases 3. Pressure 4. Boyle s Law: The Volume-Pressure
1 Gases and Kinetic Molecular Theory 1 CHAPTER GOALS 1. Comparison of Solids, Liquids, and Gases. Composition of the Atmosphere and Some Common Properties of Gases 3. Pressure 4. Boyle s Law: The Volume-Pressure
THERMOCHEMISTRY -1. Dr. Sapna Gupta
 THERMOCHEMISTRY -1 Dr. Sapna Gupta THERMODYNAMICS Thermodynamics: Relationship between heat and other forms of energy Thermochemistry: Study of heat absorbed or evolved by chemical reactions. Energy: Capacity
THERMOCHEMISTRY -1 Dr. Sapna Gupta THERMODYNAMICS Thermodynamics: Relationship between heat and other forms of energy Thermochemistry: Study of heat absorbed or evolved by chemical reactions. Energy: Capacity
Chapter 6 Thermochemistry 許富銀
 Chapter 6 Thermochemistry 許富銀 6.1 Chemical Hand Warmers Thermochemistry: the study of the relationships between chemistry and energy Hand warmers use the oxidation of iron as the exothermic reaction: Nature
Chapter 6 Thermochemistry 許富銀 6.1 Chemical Hand Warmers Thermochemistry: the study of the relationships between chemistry and energy Hand warmers use the oxidation of iron as the exothermic reaction: Nature
Quiz I: Thermodynamics
 Quiz I: Thermodynamics SCH4U_2018-2019_V2 NAME: (Total Score: / 30) Multiple Choice (12) 1. What can be deduced from the following reaction profile? A. The reactants are less stable than the products and
Quiz I: Thermodynamics SCH4U_2018-2019_V2 NAME: (Total Score: / 30) Multiple Choice (12) 1. What can be deduced from the following reaction profile? A. The reactants are less stable than the products and
Chapter 15 Thermal Properties of Matter
 Chapter 15 Thermal Properties of Matter To understand the mole and Avogadro's number. To understand equations of state. To study the kinetic theory of ideal gas. To understand heat capacity. To learn and
Chapter 15 Thermal Properties of Matter To understand the mole and Avogadro's number. To understand equations of state. To study the kinetic theory of ideal gas. To understand heat capacity. To learn and
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS. Professor Benjamin G. Levine CEM 182H Lecture 5
 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Professor Benjamin G. Levine CEM 182H Lecture 5 Chemical Equilibrium N 2 + 3 H 2 2 NH 3 Chemical reactions go in both directions Systems started from any initial state
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Professor Benjamin G. Levine CEM 182H Lecture 5 Chemical Equilibrium N 2 + 3 H 2 2 NH 3 Chemical reactions go in both directions Systems started from any initial state
Thermodynamics I - Enthalpy
 Thermodynamics I - Enthalpy Tinoco Chapter 2 Secondary Reference: J.B. Fenn, Engines, Energy and Entropy, Global View Publishing, Pittsburgh, 2003. 1 Thermodynamics CHEM 2880 - Kinetics An essential foundation
Thermodynamics I - Enthalpy Tinoco Chapter 2 Secondary Reference: J.B. Fenn, Engines, Energy and Entropy, Global View Publishing, Pittsburgh, 2003. 1 Thermodynamics CHEM 2880 - Kinetics An essential foundation
CHAPTER 10: THERMOCHEMISTRY
 CHAPTER 10: THERMOCHEMISTRY Definition of heat Calorimetry and relationship between heat and temperature changes Enthalpy Hess s Law Bond enthalpies First Law of Thermodynamics The Zeroth Law Zeroth Law
CHAPTER 10: THERMOCHEMISTRY Definition of heat Calorimetry and relationship between heat and temperature changes Enthalpy Hess s Law Bond enthalpies First Law of Thermodynamics The Zeroth Law Zeroth Law
Thermochemistry Ch. 8
 Definitions I. Energy (E): capacity to do work. II. Heat (q): transfer of energy from a body at a high temp. to a body at a low temp. III. Reaction perspectives: A. System: the focus. B. Surroundings:
Definitions I. Energy (E): capacity to do work. II. Heat (q): transfer of energy from a body at a high temp. to a body at a low temp. III. Reaction perspectives: A. System: the focus. B. Surroundings:
1. State in your own terms what is the first law of thermodynamics, a closed system, an isolated system, surroundings, heat, work, and energy.
 Worksheet 1 1. State in your own terms what is the first law of thermodynamics, a closed system, an isolated system, surroundings, heat, work, and energy. The first law of thermodynamics is the conservation
Worksheet 1 1. State in your own terms what is the first law of thermodynamics, a closed system, an isolated system, surroundings, heat, work, and energy. The first law of thermodynamics is the conservation
- The empirical gas laws (including the ideal gas equation) do not always apply.
 145 At 300 C, ammonium nitrate violently decomposes to produce nitrogen gas, oxygen gas, and water vapor. What is the total volume of gas that would be produced at 1.00 atm by the decomposition of 15.0
145 At 300 C, ammonium nitrate violently decomposes to produce nitrogen gas, oxygen gas, and water vapor. What is the total volume of gas that would be produced at 1.00 atm by the decomposition of 15.0
Chapter 8. Thermochemistry 강의개요. 8.1 Principles of Heat Flow. 2) Magnitude of Heat Flow. 1) State Properties. Basic concepts : study of heat flow
 강의개요 Basic concepts : study of heat flow Chapter 8 Thermochemistry Calorimetry : experimental measurement of the magnitude and direction of heat flow Thermochemical Equations Copyright 2005 연세대학교이학계열일반화학및실험
강의개요 Basic concepts : study of heat flow Chapter 8 Thermochemistry Calorimetry : experimental measurement of the magnitude and direction of heat flow Thermochemical Equations Copyright 2005 연세대학교이학계열일반화학및실험
Thermochemistry. Energy. 1st Law of Thermodynamics. Enthalpy / Calorimetry. Enthalpy of Formation
 Thermochemistry Energy 1st Law of Thermodynamics Enthalpy / Calorimetry Hess' Law Enthalpy of Formation The Nature of Energy Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy Kinetic energy is the energy of motion:
Thermochemistry Energy 1st Law of Thermodynamics Enthalpy / Calorimetry Hess' Law Enthalpy of Formation The Nature of Energy Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy Kinetic energy is the energy of motion:
Chapter 6. Energy Thermodynamics
 Chapter 6 Energy Thermodynamics 1 Energy is... The ability to do work. Conserved. made of heat and work. a state function. independent of the path, or how you get from point A to B. Work is a force acting
Chapter 6 Energy Thermodynamics 1 Energy is... The ability to do work. Conserved. made of heat and work. a state function. independent of the path, or how you get from point A to B. Work is a force acting
ANSWER KEY. Chemistry 25 (Spring term 2016) Midterm Examination
 Name ANSWER KEY Chemistry 25 (Spring term 2016) Midterm Examination 1 Some like it hot 1a (5 pts) The Large Hadron Collider is designed to reach energies of 7 TeV (= 7 x 10 12 ev, with 1 ev = 1.602 x 10-19
Name ANSWER KEY Chemistry 25 (Spring term 2016) Midterm Examination 1 Some like it hot 1a (5 pts) The Large Hadron Collider is designed to reach energies of 7 TeV (= 7 x 10 12 ev, with 1 ev = 1.602 x 10-19
CHEMISTRY Practice Exam #3 - SPRING 2013
 CHEMISTRY 1710 - Practice Exam #3 - SPRING 2013 Section 1 - This section of the exam is multiple choice. Choose the BEST answer from the choices which are given and write the letter for your choice in
CHEMISTRY 1710 - Practice Exam #3 - SPRING 2013 Section 1 - This section of the exam is multiple choice. Choose the BEST answer from the choices which are given and write the letter for your choice in
Chemistry Slide 1 of 33
 Chemistry 17.2 1 of 33 17.2 Measuring and Expressing Enthalpy Changes A burning match releases heat to its surroundings in all directions. How much heat does this exothermic reaction release? You will
Chemistry 17.2 1 of 33 17.2 Measuring and Expressing Enthalpy Changes A burning match releases heat to its surroundings in all directions. How much heat does this exothermic reaction release? You will
This reaction is ENDOTHERMIC. Energy is being transferred from the room/flask/etc. (the SURROUNDINGS) to the reaction itself (the SYSTEM).
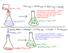 151 This reaction is EXOTHERMIC. Energy is transferred from the reactants and products (the SYSTEM) to the water in the flask, the flask, etc. (the SURROUNDINGS) This reaction is ENDOTHERMIC. Energy is
151 This reaction is EXOTHERMIC. Energy is transferred from the reactants and products (the SYSTEM) to the water in the flask, the flask, etc. (the SURROUNDINGS) This reaction is ENDOTHERMIC. Energy is
Name Chem 161, Section: Group Number: ALE 27. Hess s Law. (Reference: Chapter 6 - Silberberg 5 th edition)
 Name Chem 161, Section: Group Number: ALE 27. Hess s Law (Reference: Chapter 6 - Silberberg 5 th edition) Important!! For answers that involve a calculation you must show your work neatly using dimensional
Name Chem 161, Section: Group Number: ALE 27. Hess s Law (Reference: Chapter 6 - Silberberg 5 th edition) Important!! For answers that involve a calculation you must show your work neatly using dimensional
