Properties of Logarithms. Solving Exponential and Logarithmic Equations. Properties of Logarithms. Properties of Logarithms. ( x)
|
|
|
- Gillian Glenn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Properies of Logrihms Solving Eponenil nd Logrihmic Equions Properies of Logrihms Produc Rule ( ) log mn = log m + log n ( ) log = log + log Properies of Logrihms Quoien Rule log m = logm logn n log7 = log7 log7
2 Properies of Logrihms Power Rule log n m = nlog m log ( ) = log 4 Properies of Logrihms Chnge of Bse Rule log m log m = log g ln log = ln Properies of Logrihms log m = log n m = n ( ) ln + = ln + = 6
3 Properies of Logrihms log = log = log 0 = log = Emple Evlue: ( log )( ) log4 = = log 8 = (log + log 4) log ( 4) 8 Emple Epress s single log: log+ log+ log4 = log + log + log4 = log 4 = log 7 4 = log 6 ( ) 9
4 Emple Epnd erms: ln y z = ln + ln + ln z ln y = ln + ln + ln z ln y 0 Emple Collec erms: ln ln y =ln ln y = ln y = ln y Emple Condense log + log ( ) log ( ) 4 ( ) ( ) = + 4 log log log ( ) = + 4 log log log 4 ( ) ( ) = log log = log 4 4
5 Emple Wrie s he sum nd/or difference of logrihms. Epress ll powers s fcors log + ( ) + log = log log + ( ) ( ) ( ) = + + log log log = log+ log + log ( ) ( ) Solving Eponenil Equions Terms h hve se on one side nd power of h se on he oher side cn e solved using he propery: m n = m= n 4 Emple Solve = = 4 = + + = 4 0 ( )( ) = 0 =, =
6 Prcice Solve = + = + = + = 6 Solving Eponenil Equions Wch for qudric forms where we hve = ( ) We cn ofen fcor epressions conining erms like nd 7 Emple e Wrie in qudric form Fcor e 8= 0 ( ) e e 8= 0 ( e )( e + ) = 4 0 Use Zero Propery e 4 = 0 or e + = 0 Solve for e e = 4 or e = Recll R(e ) >0 Tke he ln of ech side e = 4 = ln 4 8 6
7 Solving Eponenil Equions Generl Guidelines Sep : Isole he eponenil epression Pu your eponenil epression on one side everyhing ouside of he eponenil epression on he oher side of your equion Sep : Tke he nurl log of oh sides The inverse operion of n eponenil epression is log. Mke sure h you do he sme hing o oh sides of your equion o keep hem equl o ech oher 9 Solving Eponenil Equions Sep : Use he properies of logs o pull he ou of he eponen Sep 4: Solve for Now h he vrile is ou of he eponen, solve for he vrile using inverse operions o complee he prolem 0 + Emple ( ) Isole he eponen Tke he log of ech side 0 = + ( 0) = + = log Solve for = log 7
8 Prcice e = 0 Tke he ln of ech side Solve for = ln0 = ln 0 Solving Logrihmic Equions of he Form log = y Sep : Wrie s one log isoled on one side Ge your log on one side everyhing ouside of he log on he oher side of your equion using inverse operions. Also use properies of logs o wrie i so h here is only one log Sep : Use he definiion of logrihms o wrie in eponenil form A reminder h he definiion of logrihms is he logrihmic funcion wih se, where > 0 nd 0, nd is defined s log = y if nd only if y = Solving Logrihmic Equions of he Form log = y Sep : Solve for Now h he vrile is ou of he log, solve for he vrile using inverse operions o complee he prolem Sep 4: Verify he domin This is necessry s he domin of log() is sricly posiive rels 4 8
9 Emple Use properies of log Rewrie s eponen Cross muliply Epnd Solve nd verify domin log ( + 4) log ( + ) = + 4 log = = = + 9 ( ) + 4 = = 9+ 8 = 4 Emple + ln = 4 Surc Propery of log ln = ln ( ) = ln = Muliply y ( ) Wrie in eponenil form = e Add Verify domin { e } = + e + e > Prcice Solve for log = log + ( ) ( ) = ( )( + ) ( )( + ) = log - + log + log0 = log - 0 = = = 0 ( + 4)( ) = 0 = 4, = ( ) ( ) disgrd negive soluion nd = 7 9
10 Solving Mied Equions Eponenil or logrihmic equions h mi ses + = Equions h mi eponenil nd logrihmic epressions + ln = Equions h mi rnscendenl nd lgeric epressions + = Use Grphic Mehod o solve hese mied equions 8 Emple + = 9 Emple + ln = 0 0
11 Prcice + = Newon's Lw of Cooling ( ) = f + ( 0 f ) T T T T e k T0 = emperure ime 0 T = finl emperure (mien) f T 0 T f k = Δ ln T T f = ime from T o T 0 TV Shows like CSI nd Numrs use funcions like he Logisic Funcions nd Newon s Lw of Cooling o solve crimes
12 Forensic Scieniss Forensic scieniss ke he emperure of ded ody les wice, ech mesuremen some ime pr crees d o erpole ck o when he deh 4 Our Prolem A murder vicim is found 8:0 AM nd h he emperure of he ody h ime is 0 o C. One hour ler i ws 8 o C, nd he room in which he murder vicim ly ws consn o C. The norml emperure of humn ody when i is live is 7 o C Wh ws he ime of deh? Our D Deh Discovered Ler Much Ler? 8:0 9:0 7 O C 0 O C 8 O C O C ime? 0 emperure T 0 = 0 T = 8 T f = 6
13 Our equion ecomes ( ) f ( 0 f ) T T T T e k = + = + ( 0 ) e k = + 8e k We mus find k T l T 0 f 0 4 k = ln T T = ln Δ = ln 8 f We hen hve ( ) = + 8e k T = + 8 = + 8 ln( 4) ( e ) ln( 4 ) e = + 8 ln( 4 ) ( e ) 7 I remins o find ou when he murder occurred A he ime of deh, he ody ws 7 o C So we need o solve for 7 = = 8 4 = 8 4 ln = ln = ln ln ( ) = 8.9 ln ( 4) 8 Beginning 8:0, we mus surc.9 hours o deermine he ime of deh 8: = :86 :8.6 6:9 The ime of deh is ou 6:9 AM
A LOG IS AN EXPONENT.
 Ojeives: n nlze nd inerpre he ehvior of rihmi funions, inluding end ehvior nd smpoes. n solve rihmi equions nlill nd grphill. n grph rihmi funions. n deermine he domin nd rnge of rihmi funions. n deermine
Ojeives: n nlze nd inerpre he ehvior of rihmi funions, inluding end ehvior nd smpoes. n solve rihmi equions nlill nd grphill. n grph rihmi funions. n deermine he domin nd rnge of rihmi funions. n deermine
September 20 Homework Solutions
 College of Engineering nd Compuer Science Mechnicl Engineering Deprmen Mechnicl Engineering A Seminr in Engineering Anlysis Fll 7 Number 66 Insrucor: Lrry Creo Sepember Homework Soluions Find he specrum
College of Engineering nd Compuer Science Mechnicl Engineering Deprmen Mechnicl Engineering A Seminr in Engineering Anlysis Fll 7 Number 66 Insrucor: Lrry Creo Sepember Homework Soluions Find he specrum
The solution is often represented as a vector: 2xI + 4X2 + 2X3 + 4X4 + 2X5 = 4 2xI + 4X2 + 3X3 + 3X4 + 3X5 = 4. 3xI + 6X2 + 6X3 + 3X4 + 6X5 = 6.
 [~ o o :- o o ill] i 1. Mrices, Vecors, nd Guss-Jordn Eliminion 1 x y = = - z= The soluion is ofen represened s vecor: n his exmple, he process of eliminion works very smoohly. We cn elimine ll enries
[~ o o :- o o ill] i 1. Mrices, Vecors, nd Guss-Jordn Eliminion 1 x y = = - z= The soluion is ofen represened s vecor: n his exmple, he process of eliminion works very smoohly. We cn elimine ll enries
4.8 Improper Integrals
 4.8 Improper Inegrls Well you ve mde i hrough ll he inegrion echniques. Congrs! Unforunely for us, we sill need o cover one more inegrl. They re clled Improper Inegrls. A his poin, we ve only del wih inegrls
4.8 Improper Inegrls Well you ve mde i hrough ll he inegrion echniques. Congrs! Unforunely for us, we sill need o cover one more inegrl. They re clled Improper Inegrls. A his poin, we ve only del wih inegrls
1.0 Electrical Systems
 . Elecricl Sysems The ypes of dynmicl sysems we will e sudying cn e modeled in erms of lgeric equions, differenil equions, or inegrl equions. We will egin y looking fmilir mhemicl models of idel resisors,
. Elecricl Sysems The ypes of dynmicl sysems we will e sudying cn e modeled in erms of lgeric equions, differenil equions, or inegrl equions. We will egin y looking fmilir mhemicl models of idel resisors,
ENGR 1990 Engineering Mathematics The Integral of a Function as a Function
 ENGR 1990 Engineering Mhemics The Inegrl of Funcion s Funcion Previously, we lerned how o esime he inegrl of funcion f( ) over some inervl y dding he res of finie se of rpezoids h represen he re under
ENGR 1990 Engineering Mhemics The Inegrl of Funcion s Funcion Previously, we lerned how o esime he inegrl of funcion f( ) over some inervl y dding he res of finie se of rpezoids h represen he re under
Chapter Direct Method of Interpolation
 Chper 5. Direc Mehod of Inerpolion Afer reding his chper, you should be ble o:. pply he direc mehod of inerpolion,. sole problems using he direc mehod of inerpolion, nd. use he direc mehod inerpolns o
Chper 5. Direc Mehod of Inerpolion Afer reding his chper, you should be ble o:. pply he direc mehod of inerpolion,. sole problems using he direc mehod of inerpolion, nd. use he direc mehod inerpolns o
MTH 146 Class 11 Notes
 8.- Are of Surfce of Revoluion MTH 6 Clss Noes Suppose we wish o revolve curve C round n is nd find he surfce re of he resuling solid. Suppose f( ) is nonnegive funcion wih coninuous firs derivive on he
8.- Are of Surfce of Revoluion MTH 6 Clss Noes Suppose we wish o revolve curve C round n is nd find he surfce re of he resuling solid. Suppose f( ) is nonnegive funcion wih coninuous firs derivive on he
Section P.1 Notes Page 1 Section P.1 Precalculus and Trigonometry Review
 Secion P Noe Pge Secion P Preclculu nd Trigonomer Review ALGEBRA AND PRECALCULUS Eponen Lw: Emple: 8 Emple: Emple: Emple: b b Emple: 9 EXAMPLE: Simplif: nd wrie wi poiive eponen Fir I will flip e frcion
Secion P Noe Pge Secion P Preclculu nd Trigonomer Review ALGEBRA AND PRECALCULUS Eponen Lw: Emple: 8 Emple: Emple: Emple: b b Emple: 9 EXAMPLE: Simplif: nd wrie wi poiive eponen Fir I will flip e frcion
e t dt e t dt = lim e t dt T (1 e T ) = 1
 Improper Inegrls There re wo ypes of improper inegrls - hose wih infinie limis of inegrion, nd hose wih inegrnds h pproch some poin wihin he limis of inegrion. Firs we will consider inegrls wih infinie
Improper Inegrls There re wo ypes of improper inegrls - hose wih infinie limis of inegrion, nd hose wih inegrnds h pproch some poin wihin he limis of inegrion. Firs we will consider inegrls wih infinie
Chapter 2. Motion along a straight line. 9/9/2015 Physics 218
 Chper Moion long srigh line 9/9/05 Physics 8 Gols for Chper How o describe srigh line moion in erms of displcemen nd erge elociy. The mening of insnneous elociy nd speed. Aerge elociy/insnneous elociy
Chper Moion long srigh line 9/9/05 Physics 8 Gols for Chper How o describe srigh line moion in erms of displcemen nd erge elociy. The mening of insnneous elociy nd speed. Aerge elociy/insnneous elociy
0 for t < 0 1 for t > 0
 8.0 Sep nd del funcions Auhor: Jeremy Orloff The uni Sep Funcion We define he uni sep funcion by u() = 0 for < 0 for > 0 I is clled he uni sep funcion becuse i kes uni sep = 0. I is someimes clled he Heviside
8.0 Sep nd del funcions Auhor: Jeremy Orloff The uni Sep Funcion We define he uni sep funcion by u() = 0 for < 0 for > 0 I is clled he uni sep funcion becuse i kes uni sep = 0. I is someimes clled he Heviside
f t f a f x dx By Lin McMullin f x dx= f b f a. 2
 Accumulion: Thoughs On () By Lin McMullin f f f d = + The gols of he AP* Clculus progrm include he semen, Sudens should undersnd he definie inegrl s he ne ccumulion of chnge. 1 The Topicl Ouline includes
Accumulion: Thoughs On () By Lin McMullin f f f d = + The gols of he AP* Clculus progrm include he semen, Sudens should undersnd he definie inegrl s he ne ccumulion of chnge. 1 The Topicl Ouline includes
Contraction Mapping Principle Approach to Differential Equations
 epl Journl of Science echnology 0 (009) 49-53 Conrcion pping Principle pproch o Differenil Equions Bishnu P. Dhungn Deprmen of hemics, hendr Rn Cmpus ribhuvn Universiy, Khmu epl bsrc Using n eension of
epl Journl of Science echnology 0 (009) 49-53 Conrcion pping Principle pproch o Differenil Equions Bishnu P. Dhungn Deprmen of hemics, hendr Rn Cmpus ribhuvn Universiy, Khmu epl bsrc Using n eension of
Section 4.4 Logarithmic Properties
 Secion. Logarihmic Properies 5 Secion. Logarihmic Properies In he previous secion, we derived wo imporan properies of arihms, which allowed us o solve some asic eponenial and arihmic equaions. Properies
Secion. Logarihmic Properies 5 Secion. Logarihmic Properies In he previous secion, we derived wo imporan properies of arihms, which allowed us o solve some asic eponenial and arihmic equaions. Properies
Section 4.4 Logarithmic Properties
 Secion. Logarihmic Properies 59 Secion. Logarihmic Properies In he previous secion, we derived wo imporan properies of arihms, which allowed us o solve some asic eponenial and arihmic equaions. Properies
Secion. Logarihmic Properies 59 Secion. Logarihmic Properies In he previous secion, we derived wo imporan properies of arihms, which allowed us o solve some asic eponenial and arihmic equaions. Properies
Average & instantaneous velocity and acceleration Motion with constant acceleration
 Physics 7: Lecure Reminders Discussion nd Lb secions sr meeing ne week Fill ou Pink dd/drop form if you need o swich o differen secion h is FULL. Do i TODAY. Homework Ch. : 5, 7,, 3,, nd 6 Ch.: 6,, 3 Submission
Physics 7: Lecure Reminders Discussion nd Lb secions sr meeing ne week Fill ou Pink dd/drop form if you need o swich o differen secion h is FULL. Do i TODAY. Homework Ch. : 5, 7,, 3,, nd 6 Ch.: 6,, 3 Submission
Motion. Part 2: Constant Acceleration. Acceleration. October Lab Physics. Ms. Levine 1. Acceleration. Acceleration. Units for Acceleration.
 Moion Accelerion Pr : Consn Accelerion Accelerion Accelerion Accelerion is he re of chnge of velociy. = v - vo = Δv Δ ccelerion = = v - vo chnge of velociy elpsed ime Accelerion is vecor, lhough in one-dimensionl
Moion Accelerion Pr : Consn Accelerion Accelerion Accelerion Accelerion is he re of chnge of velociy. = v - vo = Δv Δ ccelerion = = v - vo chnge of velociy elpsed ime Accelerion is vecor, lhough in one-dimensionl
Physics 2A HW #3 Solutions
 Chper 3 Focus on Conceps: 3, 4, 6, 9 Problems: 9, 9, 3, 41, 66, 7, 75, 77 Phsics A HW #3 Soluions Focus On Conceps 3-3 (c) The ccelerion due o grvi is he sme for boh blls, despie he fc h he hve differen
Chper 3 Focus on Conceps: 3, 4, 6, 9 Problems: 9, 9, 3, 41, 66, 7, 75, 77 Phsics A HW #3 Soluions Focus On Conceps 3-3 (c) The ccelerion due o grvi is he sme for boh blls, despie he fc h he hve differen
Math 2142 Exam 1 Review Problems. x 2 + f (0) 3! for the 3rd Taylor polynomial at x = 0. To calculate the various quantities:
 Mah 4 Eam Review Problems Problem. Calculae he 3rd Taylor polynomial for arcsin a =. Soluion. Le f() = arcsin. For his problem, we use he formula f() + f () + f ()! + f () 3! for he 3rd Taylor polynomial
Mah 4 Eam Review Problems Problem. Calculae he 3rd Taylor polynomial for arcsin a =. Soluion. Le f() = arcsin. For his problem, we use he formula f() + f () + f ()! + f () 3! for he 3rd Taylor polynomial
5.1-The Initial-Value Problems For Ordinary Differential Equations
 5.-The Iniil-Vlue Problems For Ordinry Differenil Equions Consider solving iniil-vlue problems for ordinry differenil equions: (*) y f, y, b, y. If we know he generl soluion y of he ordinry differenil
5.-The Iniil-Vlue Problems For Ordinry Differenil Equions Consider solving iniil-vlue problems for ordinry differenil equions: (*) y f, y, b, y. If we know he generl soluion y of he ordinry differenil
MATH 124 AND 125 FINAL EXAM REVIEW PACKET (Revised spring 2008)
 MATH 14 AND 15 FINAL EXAM REVIEW PACKET (Revised spring 8) The following quesions cn be used s review for Mh 14/ 15 These quesions re no cul smples of quesions h will pper on he finl em, bu hey will provide
MATH 14 AND 15 FINAL EXAM REVIEW PACKET (Revised spring 8) The following quesions cn be used s review for Mh 14/ 15 These quesions re no cul smples of quesions h will pper on he finl em, bu hey will provide
Honours Introductory Maths Course 2011 Integration, Differential and Difference Equations
 Honours Inroducory Mhs Course 0 Inegrion, Differenil nd Difference Equions Reding: Ching Chper 4 Noe: These noes do no fully cover he meril in Ching, u re men o supplemen your reding in Ching. Thus fr
Honours Inroducory Mhs Course 0 Inegrion, Differenil nd Difference Equions Reding: Ching Chper 4 Noe: These noes do no fully cover he meril in Ching, u re men o supplemen your reding in Ching. Thus fr
IX.1.1 The Laplace Transform Definition 700. IX.1.2 Properties 701. IX.1.3 Examples 702. IX.1.4 Solution of IVP for ODEs 704
 Chper IX The Inegrl Trnform Mehod IX. The plce Trnform November 4, 7 699 IX. THE APACE TRANSFORM IX.. The plce Trnform Definiion 7 IX.. Properie 7 IX..3 Emple 7 IX..4 Soluion of IVP for ODE 74 IX..5 Soluion
Chper IX The Inegrl Trnform Mehod IX. The plce Trnform November 4, 7 699 IX. THE APACE TRANSFORM IX.. The plce Trnform Definiion 7 IX.. Properie 7 IX..3 Emple 7 IX..4 Soluion of IVP for ODE 74 IX..5 Soluion
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( y )
 8. Lengh of Plne Curve The mos fmous heorem in ll of mhemics is he Pyhgoren Theorem. I s formulion s he disnce formul is used o find he lenghs of line segmens in he coordine plne. In his secion you ll
8. Lengh of Plne Curve The mos fmous heorem in ll of mhemics is he Pyhgoren Theorem. I s formulion s he disnce formul is used o find he lenghs of line segmens in he coordine plne. In his secion you ll
3 Motion with constant acceleration: Linear and projectile motion
 3 Moion wih consn ccelerion: Liner nd projecile moion cons, In he precedin Lecure we he considered moion wih consn ccelerion lon he is: Noe h,, cn be posiie nd neie h leds o rie of behiors. Clerl similr
3 Moion wih consn ccelerion: Liner nd projecile moion cons, In he precedin Lecure we he considered moion wih consn ccelerion lon he is: Noe h,, cn be posiie nd neie h leds o rie of behiors. Clerl similr
Mathematics 805 Final Examination Answers
 . 5 poins Se he Weiersrss M-es. Mhemics 85 Finl Eminion Answers Answer: Suppose h A R, nd f n : A R. Suppose furher h f n M n for ll A, nd h Mn converges. Then f n converges uniformly on A.. 5 poins Se
. 5 poins Se he Weiersrss M-es. Mhemics 85 Finl Eminion Answers Answer: Suppose h A R, nd f n : A R. Suppose furher h f n M n for ll A, nd h Mn converges. Then f n converges uniformly on A.. 5 poins Se
REAL ANALYSIS I HOMEWORK 3. Chapter 1
 REAL ANALYSIS I HOMEWORK 3 CİHAN BAHRAN The quesions re from Sein nd Shkrchi s e. Chper 1 18. Prove he following sserion: Every mesurble funcion is he limi.e. of sequence of coninuous funcions. We firs
REAL ANALYSIS I HOMEWORK 3 CİHAN BAHRAN The quesions re from Sein nd Shkrchi s e. Chper 1 18. Prove he following sserion: Every mesurble funcion is he limi.e. of sequence of coninuous funcions. We firs
Chapter 2: Evaluative Feedback
 Chper 2: Evluive Feedbck Evluing cions vs. insrucing by giving correc cions Pure evluive feedbck depends olly on he cion ken. Pure insrucive feedbck depends no ll on he cion ken. Supervised lerning is
Chper 2: Evluive Feedbck Evluing cions vs. insrucing by giving correc cions Pure evluive feedbck depends olly on he cion ken. Pure insrucive feedbck depends no ll on he cion ken. Supervised lerning is
IX.1.1 The Laplace Transform Definition 700. IX.1.2 Properties 701. IX.1.3 Examples 702. IX.1.4 Solution of IVP for ODEs 704
 Chper IX The Inegrl Trnform Mehod IX. The plce Trnform November 6, 8 699 IX. THE APACE TRANSFORM IX.. The plce Trnform Definiion 7 IX.. Properie 7 IX..3 Emple 7 IX..4 Soluion of IVP for ODE 74 IX..5 Soluion
Chper IX The Inegrl Trnform Mehod IX. The plce Trnform November 6, 8 699 IX. THE APACE TRANSFORM IX.. The plce Trnform Definiion 7 IX.. Properie 7 IX..3 Emple 7 IX..4 Soluion of IVP for ODE 74 IX..5 Soluion
PHYSICS 1210 Exam 1 University of Wyoming 14 February points
 PHYSICS 1210 Em 1 Uniersiy of Wyoming 14 Februry 2013 150 poins This es is open-noe nd closed-book. Clculors re permied bu compuers re no. No collborion, consulion, or communicion wih oher people (oher
PHYSICS 1210 Em 1 Uniersiy of Wyoming 14 Februry 2013 150 poins This es is open-noe nd closed-book. Clculors re permied bu compuers re no. No collborion, consulion, or communicion wih oher people (oher
FM Applications of Integration 1.Centroid of Area
 FM Applicions of Inegrion.Cenroid of Are The cenroid of ody is is geomeric cenre. For n ojec mde of uniform meril, he cenroid coincides wih he poin which he ody cn e suppored in perfecly lnced se ie, is
FM Applicions of Inegrion.Cenroid of Are The cenroid of ody is is geomeric cenre. For n ojec mde of uniform meril, he cenroid coincides wih he poin which he ody cn e suppored in perfecly lnced se ie, is
ME 391 Mechanical Engineering Analysis
 Fall 04 ME 39 Mechanical Engineering Analsis Eam # Soluions Direcions: Open noes (including course web posings). No books, compuers, or phones. An calculaor is fair game. Problem Deermine he posiion of
Fall 04 ME 39 Mechanical Engineering Analsis Eam # Soluions Direcions: Open noes (including course web posings). No books, compuers, or phones. An calculaor is fair game. Problem Deermine he posiion of
Introduction to Algebra - Part 2
 Alger Module A Introduction to Alger - Prt Copright This puliction The Northern Alert Institute of Technolog 00. All Rights Reserved. LAST REVISED Oct., 008 Introduction to Alger - Prt Sttement of Prerequisite
Alger Module A Introduction to Alger - Prt Copright This puliction The Northern Alert Institute of Technolog 00. All Rights Reserved. LAST REVISED Oct., 008 Introduction to Alger - Prt Sttement of Prerequisite
Challenge Problems. DIS 203 and 210. March 6, (e 2) k. k(k + 2). k=1. f(x) = k(k + 2) = 1 x k
 Challenge Problems DIS 03 and 0 March 6, 05 Choose one of he following problems, and work on i in your group. Your goal is o convince me ha your answer is correc. Even if your answer isn compleely correc,
Challenge Problems DIS 03 and 0 March 6, 05 Choose one of he following problems, and work on i in your group. Your goal is o convince me ha your answer is correc. Even if your answer isn compleely correc,
Unit 1 Exponentials and Logarithms
 HARTFIELD PRECALCULUS UNIT 1 NOTES PAGE 1 Unit 1 Eponentils nd Logrithms (2) Eponentil Functions (3) The number e (4) Logrithms (5) Specil Logrithms (7) Chnge of Bse Formul (8) Logrithmic Functions (10)
HARTFIELD PRECALCULUS UNIT 1 NOTES PAGE 1 Unit 1 Eponentils nd Logrithms (2) Eponentil Functions (3) The number e (4) Logrithms (5) Specil Logrithms (7) Chnge of Bse Formul (8) Logrithmic Functions (10)
2D Motion WS. A horizontally launched projectile s initial vertical velocity is zero. Solve the following problems with this information.
 Nme D Moion WS The equions of moion h rele o projeciles were discussed in he Projecile Moion Anlsis Acii. ou found h projecile moes wih consn eloci in he horizonl direcion nd consn ccelerion in he ericl
Nme D Moion WS The equions of moion h rele o projeciles were discussed in he Projecile Moion Anlsis Acii. ou found h projecile moes wih consn eloci in he horizonl direcion nd consn ccelerion in he ericl
ON NEW INEQUALITIES OF SIMPSON S TYPE FOR FUNCTIONS WHOSE SECOND DERIVATIVES ABSOLUTE VALUES ARE CONVEX.
 ON NEW INEQUALITIES OF SIMPSON S TYPE FOR FUNCTIONS WHOSE SECOND DERIVATIVES ABSOLUTE VALUES ARE CONVEX. MEHMET ZEKI SARIKAYA?, ERHAN. SET, AND M. EMIN OZDEMIR Asrc. In his noe, we oin new some ineuliies
ON NEW INEQUALITIES OF SIMPSON S TYPE FOR FUNCTIONS WHOSE SECOND DERIVATIVES ABSOLUTE VALUES ARE CONVEX. MEHMET ZEKI SARIKAYA?, ERHAN. SET, AND M. EMIN OZDEMIR Asrc. In his noe, we oin new some ineuliies
Section 3.5 Nonhomogeneous Equations; Method of Undetermined Coefficients
 Secion 3.5 Nonhomogeneous Equaions; Mehod of Undeermined Coefficiens Key Terms/Ideas: Linear Differenial operaor Nonlinear operaor Second order homogeneous DE Second order nonhomogeneous DE Soluion o homogeneous
Secion 3.5 Nonhomogeneous Equaions; Mehod of Undeermined Coefficiens Key Terms/Ideas: Linear Differenial operaor Nonlinear operaor Second order homogeneous DE Second order nonhomogeneous DE Soluion o homogeneous
The order of reaction is defined as the number of atoms or molecules whose concentration change during the chemical reaction.
 www.hechemisryguru.com Re Lw Expression Order of Recion The order of recion is defined s he number of oms or molecules whose concenrion chnge during he chemicl recion. Or The ol number of molecules or
www.hechemisryguru.com Re Lw Expression Order of Recion The order of recion is defined s he number of oms or molecules whose concenrion chnge during he chemicl recion. Or The ol number of molecules or
MAT 266 Calculus for Engineers II Notes on Chapter 6 Professor: John Quigg Semester: spring 2017
 MAT 66 Clculus for Engineers II Noes on Chper 6 Professor: John Quigg Semeser: spring 7 Secion 6.: Inegrion by prs The Produc Rule is d d f()g() = f()g () + f ()g() Tking indefinie inegrls gives [f()g
MAT 66 Clculus for Engineers II Noes on Chper 6 Professor: John Quigg Semeser: spring 7 Secion 6.: Inegrion by prs The Produc Rule is d d f()g() = f()g () + f ()g() Tking indefinie inegrls gives [f()g
Math 2214 Solution Test 1A Spring 2016
 Mah 14 Soluion Tes 1A Spring 016 sec Problem 1: Wha is he larges -inerval for which ( 4) = has a guaraneed + unique soluion for iniial value (-1) = 3 according o he Exisence Uniqueness Theorem? Soluion
Mah 14 Soluion Tes 1A Spring 016 sec Problem 1: Wha is he larges -inerval for which ( 4) = has a guaraneed + unique soluion for iniial value (-1) = 3 according o he Exisence Uniqueness Theorem? Soluion
22.615, MHD Theory of Fusion Systems Prof. Freidberg Lecture 10: The High Beta Tokamak Con d and the High Flux Conserving Tokamak.
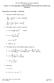 .615, MHD Theory of Fusion Sysems Prof. Freidberg Lecure 1: The High Be Tokmk Con d nd he High Flux Conserving Tokmk Proeries of he High Tokmk 1. Evlue he MHD sfey fcor: ψ B * ( ) 1 3 ρ 1+ ν ρ ρ cosθ *
.615, MHD Theory of Fusion Sysems Prof. Freidberg Lecure 1: The High Be Tokmk Con d nd he High Flux Conserving Tokmk Proeries of he High Tokmk 1. Evlue he MHD sfey fcor: ψ B * ( ) 1 3 ρ 1+ ν ρ ρ cosθ *
dt = C exp (3 ln t 4 ). t 4 W = C exp ( ln(4 t) 3) = C(4 t) 3.
 Mah Rahman Exam Review Soluions () Consider he IVP: ( 4)y 3y + 4y = ; y(3) = 0, y (3) =. (a) Please deermine he longes inerval for which he IVP is guaraneed o have a unique soluion. Soluion: The disconinuiies
Mah Rahman Exam Review Soluions () Consider he IVP: ( 4)y 3y + 4y = ; y(3) = 0, y (3) =. (a) Please deermine he longes inerval for which he IVP is guaraneed o have a unique soluion. Soluion: The disconinuiies
ECE Microwave Engineering. Fall Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of ECE. Notes 10. Waveguides Part 7: Transverse Equivalent Network (TEN)
 EE 537-635 Microwve Engineering Fll 7 Prof. Dvid R. Jcson Dep. of EE Noes Wveguides Pr 7: Trnsverse Equivlen Newor (N) Wveguide Trnsmission Line Model Our gol is o come up wih rnsmission line model for
EE 537-635 Microwve Engineering Fll 7 Prof. Dvid R. Jcson Dep. of EE Noes Wveguides Pr 7: Trnsverse Equivlen Newor (N) Wveguide Trnsmission Line Model Our gol is o come up wih rnsmission line model for
5.2 Exponent Properties Involving Quotients
 5. Eponent Properties Involving Quotients Lerning Objectives Use the quotient of powers property. Use the power of quotient property. Simplify epressions involving quotient properties of eponents. Use
5. Eponent Properties Involving Quotients Lerning Objectives Use the quotient of powers property. Use the power of quotient property. Simplify epressions involving quotient properties of eponents. Use
Solutions to Problems from Chapter 2
 Soluions o Problems rom Chper Problem. The signls u() :5sgn(), u () :5sgn(), nd u h () :5sgn() re ploed respecively in Figures.,b,c. Noe h u h () :5sgn() :5; 8 including, bu u () :5sgn() is undeined..5
Soluions o Problems rom Chper Problem. The signls u() :5sgn(), u () :5sgn(), nd u h () :5sgn() re ploed respecively in Figures.,b,c. Noe h u h () :5sgn() :5; 8 including, bu u () :5sgn() is undeined..5
Chapter 2. First Order Scalar Equations
 Chaper. Firs Order Scalar Equaions We sar our sudy of differenial equaions in he same way he pioneers in his field did. We show paricular echniques o solve paricular ypes of firs order differenial equaions.
Chaper. Firs Order Scalar Equaions We sar our sudy of differenial equaions in he same way he pioneers in his field did. We show paricular echniques o solve paricular ypes of firs order differenial equaions.
1. Find a basis for the row space of each of the following matrices. Your basis should consist of rows of the original matrix.
 Mh 7 Exm - Prcice Prolem Solions. Find sis for he row spce of ech of he following mrices. Yor sis shold consis of rows of he originl mrix. 4 () 7 7 8 () Since we wn sis for he row spce consising of rows
Mh 7 Exm - Prcice Prolem Solions. Find sis for he row spce of ech of he following mrices. Yor sis shold consis of rows of he originl mrix. 4 () 7 7 8 () Since we wn sis for he row spce consising of rows
Physic 231 Lecture 4. Mi it ftd l t. Main points of today s lecture: Example: addition of velocities Trajectories of objects in 2 = =
 Mi i fd l Phsic 3 Lecure 4 Min poins of od s lecure: Emple: ddiion of elociies Trjecories of objecs in dimensions: dimensions: g 9.8m/s downwrds ( ) g o g g Emple: A foobll pler runs he pern gien in he
Mi i fd l Phsic 3 Lecure 4 Min poins of od s lecure: Emple: ddiion of elociies Trjecories of objecs in dimensions: dimensions: g 9.8m/s downwrds ( ) g o g g Emple: A foobll pler runs he pern gien in he
A 1.3 m 2.5 m 2.8 m. x = m m = 8400 m. y = 4900 m 3200 m = 1700 m
 PHYS : Soluions o Chper 3 Home Work. SSM REASONING The displcemen is ecor drwn from he iniil posiion o he finl posiion. The mgniude of he displcemen is he shores disnce beween he posiions. Noe h i is onl
PHYS : Soluions o Chper 3 Home Work. SSM REASONING The displcemen is ecor drwn from he iniil posiion o he finl posiion. The mgniude of he displcemen is he shores disnce beween he posiions. Noe h i is onl
Logarithms. Logarithm is another word for an index or power. POWER. 2 is the power to which the base 10 must be raised to give 100.
 Logrithms. Logrithm is nother word for n inde or power. THIS IS A POWER STATEMENT BASE POWER FOR EXAMPLE : We lred know tht; = NUMBER 10² = 100 This is the POWER Sttement OR 2 is the power to which the
Logrithms. Logrithm is nother word for n inde or power. THIS IS A POWER STATEMENT BASE POWER FOR EXAMPLE : We lred know tht; = NUMBER 10² = 100 This is the POWER Sttement OR 2 is the power to which the
Mathematics Number: Logarithms
 plce of mind F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Deprtment of Curriculum nd Pedgogy Mthemtics Numer: Logrithms Science nd Mthemtics Eduction Reserch Group Supported y UBC Teching nd Lerning Enhncement
plce of mind F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Deprtment of Curriculum nd Pedgogy Mthemtics Numer: Logrithms Science nd Mthemtics Eduction Reserch Group Supported y UBC Teching nd Lerning Enhncement
Chapter 3 Boundary Value Problem
 Chaper 3 Boundary Value Problem A boundary value problem (BVP) is a problem, ypically an ODE or a PDE, which has values assigned on he physical boundary of he domain in which he problem is specified. Le
Chaper 3 Boundary Value Problem A boundary value problem (BVP) is a problem, ypically an ODE or a PDE, which has values assigned on he physical boundary of he domain in which he problem is specified. Le
MATH 31B: MIDTERM 2 REVIEW. x 2 e x2 2x dx = 1. ue u du 2. x 2 e x2 e x2] + C 2. dx = x ln(x) 2 2. ln x dx = x ln x x + C. 2, or dx = 2u du.
![MATH 31B: MIDTERM 2 REVIEW. x 2 e x2 2x dx = 1. ue u du 2. x 2 e x2 e x2] + C 2. dx = x ln(x) 2 2. ln x dx = x ln x x + C. 2, or dx = 2u du. MATH 31B: MIDTERM 2 REVIEW. x 2 e x2 2x dx = 1. ue u du 2. x 2 e x2 e x2] + C 2. dx = x ln(x) 2 2. ln x dx = x ln x x + C. 2, or dx = 2u du.](/thumbs/86/93221008.jpg) MATH 3B: MIDTERM REVIEW JOE HUGHES. Inegraion by Pars. Evaluae 3 e. Soluion: Firs make he subsiuion u =. Then =, hence 3 e = e = ue u Now inegrae by pars o ge ue u = ue u e u + C and subsiue he definiion
MATH 3B: MIDTERM REVIEW JOE HUGHES. Inegraion by Pars. Evaluae 3 e. Soluion: Firs make he subsiuion u =. Then =, hence 3 e = e = ue u Now inegrae by pars o ge ue u = ue u e u + C and subsiue he definiion
Differential Equations
 Mah 21 (Fall 29) Differenial Equaions Soluion #3 1. Find he paricular soluion of he following differenial equaion by variaion of parameer (a) y + y = csc (b) 2 y + y y = ln, > Soluion: (a) The corresponding
Mah 21 (Fall 29) Differenial Equaions Soluion #3 1. Find he paricular soluion of he following differenial equaion by variaion of parameer (a) y + y = csc (b) 2 y + y y = ln, > Soluion: (a) The corresponding
dy dx = xey (a) y(0) = 2 (b) y(1) = 2.5 SOLUTION: See next page
 Assignmen 1 MATH 2270 SOLUTION Please wrie ou complee soluions for each of he following 6 problems (one more will sill be added). You may, of course, consul wih your classmaes, he exbook or oher resources,
Assignmen 1 MATH 2270 SOLUTION Please wrie ou complee soluions for each of he following 6 problems (one more will sill be added). You may, of course, consul wih your classmaes, he exbook or oher resources,
Learning Enhancement Team
 Learning Enhancemen Team Model answers: Exponenial Funcions Exponenial Funcions sudy guide 1 i) The base rae of growh b is equal o 3 You can see his by noicing ha 1b 36 in his sysem, dividing boh sides
Learning Enhancemen Team Model answers: Exponenial Funcions Exponenial Funcions sudy guide 1 i) The base rae of growh b is equal o 3 You can see his by noicing ha 1b 36 in his sysem, dividing boh sides
f(x) dx with An integral having either an infinite limit of integration or an unbounded integrand is called improper. Here are two examples dx x x 2
 Impope Inegls To his poin we hve only consideed inegls f() wih he is of inegion nd b finie nd he inegnd f() bounded (nd in fc coninuous ecep possibly fo finiely mny jump disconinuiies) An inegl hving eihe
Impope Inegls To his poin we hve only consideed inegls f() wih he is of inegion nd b finie nd he inegnd f() bounded (nd in fc coninuous ecep possibly fo finiely mny jump disconinuiies) An inegl hving eihe
Temperature Rise of the Earth
 Avilble online www.sciencedirec.com ScienceDirec Procedi - Socil nd Behviorl Scien ce s 88 ( 2013 ) 220 224 Socil nd Behviorl Sciences Symposium, 4 h Inernionl Science, Socil Science, Engineering nd Energy
Avilble online www.sciencedirec.com ScienceDirec Procedi - Socil nd Behviorl Scien ce s 88 ( 2013 ) 220 224 Socil nd Behviorl Sciences Symposium, 4 h Inernionl Science, Socil Science, Engineering nd Energy
3.1 Exponential Functions and Their Graphs
 . Eponentil Functions nd Their Grphs Sllbus Objective: 9. The student will sketch the grph of eponentil, logistic, or logrithmic function. 9. The student will evlute eponentil or logrithmic epressions.
. Eponentil Functions nd Their Grphs Sllbus Objective: 9. The student will sketch the grph of eponentil, logistic, or logrithmic function. 9. The student will evlute eponentil or logrithmic epressions.
Sections 2.2 & 2.3 Limit of a Function and Limit Laws
 Mah 80 www.imeodare.com Secions. &. Limi of a Funcion and Limi Laws In secion. we saw how is arise when we wan o find he angen o a curve or he velociy of an objec. Now we urn our aenion o is in general
Mah 80 www.imeodare.com Secions. &. Limi of a Funcion and Limi Laws In secion. we saw how is arise when we wan o find he angen o a curve or he velociy of an objec. Now we urn our aenion o is in general
Section 7.1 Area of a Region Between Two Curves
 Section 7.1 Are of Region Between Two Curves White Bord Chllenge The circle elow is inscried into squre: Clcultor 0 cm Wht is the shded re? 400 100 85.841cm White Bord Chllenge Find the re of the region
Section 7.1 Are of Region Between Two Curves White Bord Chllenge The circle elow is inscried into squre: Clcultor 0 cm Wht is the shded re? 400 100 85.841cm White Bord Chllenge Find the re of the region
Math 333 Problem Set #2 Solution 14 February 2003
 Mah 333 Problem Se #2 Soluion 14 February 2003 A1. Solve he iniial value problem dy dx = x2 + e 3x ; 2y 4 y(0) = 1. Soluion: This is separable; we wrie 2y 4 dy = x 2 + e x dx and inegrae o ge The iniial
Mah 333 Problem Se #2 Soluion 14 February 2003 A1. Solve he iniial value problem dy dx = x2 + e 3x ; 2y 4 y(0) = 1. Soluion: This is separable; we wrie 2y 4 dy = x 2 + e x dx and inegrae o ge The iniial
For the reaction, R P, the is given by,
 Dr JADU SAMUEL CHEMICAL KINETICS Inroducion Chemicl ineics is brnch of physicl chemisry, which dels wih he sudy of he re of chemicl recions nd he vrious fcors ffecing i Such sudies lso enble us o elucide
Dr JADU SAMUEL CHEMICAL KINETICS Inroducion Chemicl ineics is brnch of physicl chemisry, which dels wih he sudy of he re of chemicl recions nd he vrious fcors ffecing i Such sudies lso enble us o elucide
An integral having either an infinite limit of integration or an unbounded integrand is called improper. Here are two examples.
 Improper Inegrls To his poin we hve only considered inegrls f(x) wih he is of inegrion nd b finie nd he inegrnd f(x) bounded (nd in fc coninuous excep possibly for finiely mny jump disconinuiies) An inegrl
Improper Inegrls To his poin we hve only considered inegrls f(x) wih he is of inegrion nd b finie nd he inegrnd f(x) bounded (nd in fc coninuous excep possibly for finiely mny jump disconinuiies) An inegrl
P441 Analytical Mechanics - I. Coupled Oscillators. c Alex R. Dzierba
 Lecure 3 Mondy - Deceber 5, 005 Wrien or ls upded: Deceber 3, 005 P44 Anlyicl Mechnics - I oupled Oscillors c Alex R. Dzierb oupled oscillors - rix echnique In Figure we show n exple of wo coupled oscillors,
Lecure 3 Mondy - Deceber 5, 005 Wrien or ls upded: Deceber 3, 005 P44 Anlyicl Mechnics - I oupled Oscillors c Alex R. Dzierb oupled oscillors - rix echnique In Figure we show n exple of wo coupled oscillors,
3D Transformations. Computer Graphics COMP 770 (236) Spring Instructor: Brandon Lloyd 1/26/07 1
 D Trnsformions Compuer Grphics COMP 770 (6) Spring 007 Insrucor: Brndon Lloyd /6/07 Geomery Geomeric eniies, such s poins in spce, exis wihou numers. Coordines re nming scheme. The sme poin cn e descried
D Trnsformions Compuer Grphics COMP 770 (6) Spring 007 Insrucor: Brndon Lloyd /6/07 Geomery Geomeric eniies, such s poins in spce, exis wihou numers. Coordines re nming scheme. The sme poin cn e descried
5.1 - Logarithms and Their Properties
 Chaper 5 Logarihmic Funcions 5.1 - Logarihms and Their Properies Suppose ha a populaion grows according o he formula P 10, where P is he colony size a ime, in hours. When will he populaion be 2500? We
Chaper 5 Logarihmic Funcions 5.1 - Logarihms and Their Properies Suppose ha a populaion grows according o he formula P 10, where P is he colony size a ime, in hours. When will he populaion be 2500? We
than 1. It means in particular that the function is decreasing and approaching the x-
 6 Preclculus Review Grph the functions ) (/) ) log y = b y = Solution () The function y = is n eponentil function with bse smller thn It mens in prticulr tht the function is decresing nd pproching the
6 Preclculus Review Grph the functions ) (/) ) log y = b y = Solution () The function y = is n eponentil function with bse smller thn It mens in prticulr tht the function is decresing nd pproching the
MA 214 Calculus IV (Spring 2016) Section 2. Homework Assignment 1 Solutions
 MA 14 Calculus IV (Spring 016) Secion Homework Assignmen 1 Soluions 1 Boyce and DiPrima, p 40, Problem 10 (c) Soluion: In sandard form he given firs-order linear ODE is: An inegraing facor is given by
MA 14 Calculus IV (Spring 016) Secion Homework Assignmen 1 Soluions 1 Boyce and DiPrima, p 40, Problem 10 (c) Soluion: In sandard form he given firs-order linear ODE is: An inegraing facor is given by
How to Prove the Riemann Hypothesis Author: Fayez Fok Al Adeh.
 How o Prove he Riemnn Hohesis Auhor: Fez Fok Al Adeh. Presiden of he Srin Cosmologicl Socie P.O.Bo,387,Dmscus,Sri Tels:963--77679,735 Emil:hf@scs-ne.org Commens: 3 ges Subj-Clss: Funcionl nlsis, comle
How o Prove he Riemnn Hohesis Auhor: Fez Fok Al Adeh. Presiden of he Srin Cosmologicl Socie P.O.Bo,387,Dmscus,Sri Tels:963--77679,735 Emil:hf@scs-ne.org Commens: 3 ges Subj-Clss: Funcionl nlsis, comle
Direct Current Circuits. February 19, 2014 Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2, Chapter 26 1
 Direc Curren Circuis February 19, 2014 Physics for Scieniss & Engineers 2, Chaper 26 1 Ammeers and Volmeers! A device used o measure curren is called an ammeer! A device used o measure poenial difference
Direc Curren Circuis February 19, 2014 Physics for Scieniss & Engineers 2, Chaper 26 1 Ammeers and Volmeers! A device used o measure curren is called an ammeer! A device used o measure poenial difference
Note: For all questions, answer (E) NOTA means none of the above answers is correct.
 Thea Logarihms & Eponens 0 ΜΑΘ Naional Convenion Noe: For all quesions, answer means none of he above answers is correc.. The elemen C 4 has a half life of 70 ears. There is grams of C 4 in a paricular
Thea Logarihms & Eponens 0 ΜΑΘ Naional Convenion Noe: For all quesions, answer means none of he above answers is correc.. The elemen C 4 has a half life of 70 ears. There is grams of C 4 in a paricular
THE SINE INTEGRAL. x dt t
 THE SINE INTEGRAL As one learns in elemenary calculus, he limi of sin(/ as vanishes is uniy. Furhermore he funcion is even and has an infinie number of zeros locaed a ±n for n1,,3 Is plo looks like his-
THE SINE INTEGRAL As one learns in elemenary calculus, he limi of sin(/ as vanishes is uniy. Furhermore he funcion is even and has an infinie number of zeros locaed a ±n for n1,,3 Is plo looks like his-
A Simple Method to Solve Quartic Equations. Key words: Polynomials, Quartics, Equations of the Fourth Degree INTRODUCTION
 Ausrlin Journl of Bsic nd Applied Sciences, 6(6): -6, 0 ISSN 99-878 A Simple Mehod o Solve Quric Equions Amir Fhi, Poo Mobdersn, Rhim Fhi Deprmen of Elecricl Engineering, Urmi brnch, Islmic Ad Universi,
Ausrlin Journl of Bsic nd Applied Sciences, 6(6): -6, 0 ISSN 99-878 A Simple Mehod o Solve Quric Equions Amir Fhi, Poo Mobdersn, Rhim Fhi Deprmen of Elecricl Engineering, Urmi brnch, Islmic Ad Universi,
fractions Let s Learn to
 5 simple lgebric frctions corne lens pupil retin Norml vision light focused on the retin concve lens Shortsightedness (myopi) light focused in front of the retin Corrected myopi light focused on the retin
5 simple lgebric frctions corne lens pupil retin Norml vision light focused on the retin concve lens Shortsightedness (myopi) light focused in front of the retin Corrected myopi light focused on the retin
22.615, MHD Theory of Fusion Systems Prof. Freidberg Lecture 9: The High Beta Tokamak
 .65, MHD Theory of Fusion Sysems Prof. Freidberg Lecure 9: The High e Tokmk Summry of he Properies of n Ohmic Tokmk. Advnges:. good euilibrium (smll shif) b. good sbiliy ( ) c. good confinemen ( τ nr )
.65, MHD Theory of Fusion Sysems Prof. Freidberg Lecure 9: The High e Tokmk Summry of he Properies of n Ohmic Tokmk. Advnges:. good euilibrium (smll shif) b. good sbiliy ( ) c. good confinemen ( τ nr )
More on Magnetically C Coupled Coils and Ideal Transformers
 Appenix ore on gneiclly C Couple Coils Iel Trnsformers C. Equivlen Circuis for gneiclly Couple Coils A imes, i is convenien o moel mgneiclly couple coils wih n equivlen circui h oes no involve mgneic coupling.
Appenix ore on gneiclly C Couple Coils Iel Trnsformers C. Equivlen Circuis for gneiclly Couple Coils A imes, i is convenien o moel mgneiclly couple coils wih n equivlen circui h oes no involve mgneic coupling.
MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS 1.2
 MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS. Apply lgebric procedures in solving problems Eternlly ssessed 4 credits Electronic technology, such s clcultors or computers, re not permitted in the ssessment of this stndr
MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS. Apply lgebric procedures in solving problems Eternlly ssessed 4 credits Electronic technology, such s clcultors or computers, re not permitted in the ssessment of this stndr
THE DISCRIMINANT & ITS APPLICATIONS
 THE DISCRIMINANT & ITS APPLICATIONS The discriminnt ( Δ ) is the epression tht is locted under the squre root sign in the qudrtic formul i.e. Δ b c. For emple: Given +, Δ () ( )() The discriminnt is used
THE DISCRIMINANT & ITS APPLICATIONS The discriminnt ( Δ ) is the epression tht is locted under the squre root sign in the qudrtic formul i.e. Δ b c. For emple: Given +, Δ () ( )() The discriminnt is used
23.2. Representing Periodic Functions by Fourier Series. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Represening Periodic Funcions by Fourier Series 3. Inroducion In his Secion we show how a periodic funcion can be expressed as a series of sines and cosines. We begin by obaining some sandard inegrals
Represening Periodic Funcions by Fourier Series 3. Inroducion In his Secion we show how a periodic funcion can be expressed as a series of sines and cosines. We begin by obaining some sandard inegrals
INTEGRALS. Exercise 1. Let f : [a, b] R be bounded, and let P and Q be partitions of [a, b]. Prove that if P Q then U(P ) U(Q) and L(P ) L(Q).
![INTEGRALS. Exercise 1. Let f : [a, b] R be bounded, and let P and Q be partitions of [a, b]. Prove that if P Q then U(P ) U(Q) and L(P ) L(Q). INTEGRALS. Exercise 1. Let f : [a, b] R be bounded, and let P and Q be partitions of [a, b]. Prove that if P Q then U(P ) U(Q) and L(P ) L(Q).](/thumbs/78/77677920.jpg) INTEGRALS JOHN QUIGG Eercise. Le f : [, b] R be bounded, nd le P nd Q be priions of [, b]. Prove h if P Q hen U(P ) U(Q) nd L(P ) L(Q). Soluion: Le P = {,..., n }. Since Q is obined from P by dding finiely
INTEGRALS JOHN QUIGG Eercise. Le f : [, b] R be bounded, nd le P nd Q be priions of [, b]. Prove h if P Q hen U(P ) U(Q) nd L(P ) L(Q). Soluion: Le P = {,..., n }. Since Q is obined from P by dding finiely
LAPLACE TRANSFORMS. 1. Basic transforms
 LAPLACE TRANSFORMS. Bic rnform In hi coure, Lplce Trnform will be inroduced nd heir properie exmined; ble of common rnform will be buil up; nd rnform will be ued o olve ome dierenil equion by rnforming
LAPLACE TRANSFORMS. Bic rnform In hi coure, Lplce Trnform will be inroduced nd heir properie exmined; ble of common rnform will be buil up; nd rnform will be ued o olve ome dierenil equion by rnforming
14. The fundamental theorem of the calculus
 4. The funmenl heorem of he clculus V 20 00 80 60 40 20 0 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 v 400 200 0 0 0.2 0.5 0.8 200 400 Figure : () Venriculr volume for subjecs wih cpciies C = 24 ml, C = 20 ml, C = 2 ml n (b) he
4. The funmenl heorem of he clculus V 20 00 80 60 40 20 0 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 v 400 200 0 0 0.2 0.5 0.8 200 400 Figure : () Venriculr volume for subjecs wih cpciies C = 24 ml, C = 20 ml, C = 2 ml n (b) he
Math From Scratch Lesson 34: Isolating Variables
 Mah From Scrach Lesson 34: Isolaing Variables W. Blaine Dowler July 25, 2013 Conens 1 Order of Operaions 1 1.1 Muliplicaion and Addiion..................... 1 1.2 Division and Subracion.......................
Mah From Scrach Lesson 34: Isolaing Variables W. Blaine Dowler July 25, 2013 Conens 1 Order of Operaions 1 1.1 Muliplicaion and Addiion..................... 1 1.2 Division and Subracion.......................
Minimum Squared Error
 Minimum Squred Error LDF: Minimum Squred-Error Procedures Ide: conver o esier nd eer undersood prolem Percepron y i > for ll smples y i solve sysem of liner inequliies MSE procedure y i = i for ll smples
Minimum Squred Error LDF: Minimum Squred-Error Procedures Ide: conver o esier nd eer undersood prolem Percepron y i > for ll smples y i solve sysem of liner inequliies MSE procedure y i = i for ll smples
ON NEW INEQUALITIES OF SIMPSON S TYPE FOR FUNCTIONS WHOSE SECOND DERIVATIVES ABSOLUTE VALUES ARE CONVEX
 Journl of Applied Mhemics, Sisics nd Informics JAMSI), 9 ), No. ON NEW INEQUALITIES OF SIMPSON S TYPE FOR FUNCTIONS WHOSE SECOND DERIVATIVES ABSOLUTE VALUES ARE CONVEX MEHMET ZEKI SARIKAYA, ERHAN. SET
Journl of Applied Mhemics, Sisics nd Informics JAMSI), 9 ), No. ON NEW INEQUALITIES OF SIMPSON S TYPE FOR FUNCTIONS WHOSE SECOND DERIVATIVES ABSOLUTE VALUES ARE CONVEX MEHMET ZEKI SARIKAYA, ERHAN. SET
Minimum Squared Error
 Minimum Squred Error LDF: Minimum Squred-Error Procedures Ide: conver o esier nd eer undersood prolem Percepron y i > 0 for ll smples y i solve sysem of liner inequliies MSE procedure y i i for ll smples
Minimum Squred Error LDF: Minimum Squred-Error Procedures Ide: conver o esier nd eer undersood prolem Percepron y i > 0 for ll smples y i solve sysem of liner inequliies MSE procedure y i i for ll smples
The Contradiction within Equations of Motion with Constant Acceleration
 The Conradicion wihin Equaions of Moion wih Consan Acceleraion Louai Hassan Elzein Basheir (Daed: July 7, 0 This paper is prepared o demonsrae he violaion of rules of mahemaics in he algebraic derivaion
The Conradicion wihin Equaions of Moion wih Consan Acceleraion Louai Hassan Elzein Basheir (Daed: July 7, 0 This paper is prepared o demonsrae he violaion of rules of mahemaics in he algebraic derivaion
Physics 101 Lecture 4 Motion in 2D and 3D
 Phsics 11 Lecure 4 Moion in D nd 3D Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Phsics Deprmen www.ogun.com Vecor nd is componens The componens re he legs of he righ ringle whose hpoenuse is A A A A A n ( θ ) A Acos( θ) A A A nd
Phsics 11 Lecure 4 Moion in D nd 3D Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Phsics Deprmen www.ogun.com Vecor nd is componens The componens re he legs of he righ ringle whose hpoenuse is A A A A A n ( θ ) A Acos( θ) A A A nd
Math 2214 Solution Test 1B Fall 2017
 Mah 14 Soluion Tes 1B Fall 017 Problem 1: A ank has a capaci for 500 gallons and conains 0 gallons of waer wih lbs of sal iniiall. A soluion conaining of 8 lbsgal of sal is pumped ino he ank a 10 galsmin.
Mah 14 Soluion Tes 1B Fall 017 Problem 1: A ank has a capaci for 500 gallons and conains 0 gallons of waer wih lbs of sal iniiall. A soluion conaining of 8 lbsgal of sal is pumped ino he ank a 10 galsmin.
rank Additionally system of equation only independent atfect Gawp (A) possible ( Alb ) easily process form rang A. Proposition with Definition
 Defiion nexivnol numer ler dependen rows mrix sid row Gwp elimion mehod does no fec h numer end process i possile esily red rng fc for mrix form der zz rn rnk wih m dcussion i holds rr o Proposiion ler
Defiion nexivnol numer ler dependen rows mrix sid row Gwp elimion mehod does no fec h numer end process i possile esily red rng fc for mrix form der zz rn rnk wih m dcussion i holds rr o Proposiion ler
3. Renewal Limit Theorems
 Virul Lborories > 14. Renewl Processes > 1 2 3 3. Renewl Limi Theorems In he inroducion o renewl processes, we noed h he rrivl ime process nd he couning process re inverses, in sens The rrivl ime process
Virul Lborories > 14. Renewl Processes > 1 2 3 3. Renewl Limi Theorems In he inroducion o renewl processes, we noed h he rrivl ime process nd he couning process re inverses, in sens The rrivl ime process
Question Details Int Vocab 1 [ ] Question Details Int Vocab 2 [ ]
![Question Details Int Vocab 1 [ ] Question Details Int Vocab 2 [ ] Question Details Int Vocab 1 [ ] Question Details Int Vocab 2 [ ]](/thumbs/92/109283538.jpg) /3/5 Assignmen Previewer 3 Bsic: Definie Inegrls (67795) Due: Wed Apr 5 5 9: AM MDT Quesion 3 5 6 7 8 9 3 5 6 7 8 9 3 5 6 Insrucions Red ody's Noes nd Lerning Gols. Quesion Deils In Vocb [37897] The chnge
/3/5 Assignmen Previewer 3 Bsic: Definie Inegrls (67795) Due: Wed Apr 5 5 9: AM MDT Quesion 3 5 6 7 8 9 3 5 6 7 8 9 3 5 6 Insrucions Red ody's Noes nd Lerning Gols. Quesion Deils In Vocb [37897] The chnge
6. 6 v ; degree = 7; leading coefficient = 6; 7. The expression has 3 terms; t p no; subtracting x from 3x ( 3x x 2x)
 70. a =, r = 0%, = 0. 7. a = 000, r = 0.%, = 00 7. a =, r = 00%, = 7. ( ) = 0,000 0., where = ears 7. ( ) = + 0.0, where = weeks 7 ( ) =,000,000 0., where = das 7 = 77. = 9 7 = 7 geomeric 0. geomeric arihmeic,
70. a =, r = 0%, = 0. 7. a = 000, r = 0.%, = 00 7. a =, r = 00%, = 7. ( ) = 0,000 0., where = ears 7. ( ) = + 0.0, where = weeks 7 ( ) =,000,000 0., where = das 7 = 77. = 9 7 = 7 geomeric 0. geomeric arihmeic,
4.1 - Logarithms and Their Properties
 Chaper 4 Logarihmic Funcions 4.1 - Logarihms and Their Properies Wha is a Logarihm? We define he common logarihm funcion, simply he log funcion, wrien log 10 x log x, as follows: If x is a posiive number,
Chaper 4 Logarihmic Funcions 4.1 - Logarihms and Their Properies Wha is a Logarihm? We define he common logarihm funcion, simply he log funcion, wrien log 10 x log x, as follows: If x is a posiive number,
Hamilton- J acobi Equation: Explicit Formulas In this lecture we try to apply the method of characteristics to the Hamilton-Jacobi equation: u t
 M ah 5 2 7 Fall 2 0 0 9 L ecure 1 0 O c. 7, 2 0 0 9 Hamilon- J acobi Equaion: Explici Formulas In his lecure we ry o apply he mehod of characerisics o he Hamilon-Jacobi equaion: u + H D u, x = 0 in R n
M ah 5 2 7 Fall 2 0 0 9 L ecure 1 0 O c. 7, 2 0 0 9 Hamilon- J acobi Equaion: Explici Formulas In his lecure we ry o apply he mehod of characerisics o he Hamilon-Jacobi equaion: u + H D u, x = 0 in R n
Transformations. Ordered set of numbers: (1,2,3,4) Example: (x,y,z) coordinates of pt in space. Vectors
 Trnformion Ordered e of number:,,,4 Emple:,,z coordine of p in pce. Vecor If, n i i, K, n, i uni ecor Vecor ddiion +w, +, +, + V+w w Sclr roduc,, Inner do roduc α w. w +,.,. The inner produc i SCLR!. w,.,
Trnformion Ordered e of number:,,,4 Emple:,,z coordine of p in pce. Vecor If, n i i, K, n, i uni ecor Vecor ddiion +w, +, +, + V+w w Sclr roduc,, Inner do roduc α w. w +,.,. The inner produc i SCLR!. w,.,
23.5. Half-Range Series. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Half-Range Series 2.5 Inroducion In his Secion we address he following problem: Can we find a Fourier series expansion of a funcion defined over a finie inerval? Of course we recognise ha such a funcion
Half-Range Series 2.5 Inroducion In his Secion we address he following problem: Can we find a Fourier series expansion of a funcion defined over a finie inerval? Of course we recognise ha such a funcion
