Vehicle Dynamics CEE 320. Winter 2006 CEE 320 Steve Muench
|
|
|
- Regina Bishop
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Vehicle Dynamics Steve Muench
2 Outline 1. Resistance a. Aerodynamic b. Rolling c. Grade. Tractive Effort 3. Acceleration 4. Braking Force 5. Stopping Sight Distance (SSD)
3 Main Concepts Resistance Tractive effort Vehicle acceleration Braking Stopping distance F ma + R + R + a rl R g
4 Resistance Resistance is defined as the force impeding vehicle motion 1. What is this force?. Aerodynamic resistance 3. Rolling resistance 4. Grade resistance F ma + R + R + a rl R g
5 Aerodynamic Resistance R a Composed of: 1. Turbulent air flow around vehicle body (85%). Friction of air over vehicle body (1%) 3. Vehicle component resistance, from radiators and air vents (3%) from National Research Council Canada R P a R a ρ ρ C C D D 1 hp 550 A V f A V f ft lb sec 3
6 Rolling Resistance R rl Composed primarily of 1. Resistance from tire deformation ( 90%). Tire penetration and surface compression ( 4%) 3. Tire slippage and air circulation around wheel ( 6%) 4. Wide range of factors affect total rolling resistance 5. Simplifying approximation: R rl f rl W P R f rl rl ft lb 1 hp 550 sec WV f rl V
7 Grade Resistance R g R g W sinθ For small angles, R g W tanθ g sinθ g tanθ g G R g WG tan g θ g R g θ g W θ g
8 Available Tractive Effort The minimum of: 1. Force generated by the engine, F e. Maximum value that is a function of the vehicle s weight distribution and road-tire interaction, F max Available tractive effort min (, F ) F e max
9 Tractive Effort Relationships
10 Engine-Generated Tractive Effort Force F e M e ε 0 η r d F e Engine generated tractive effort reaching wheels (lb) M e Engine torque (ft-lb) ε 0 Gear reduction ratio η d Driveline efficiency r Wheel radius (ft) Power ( ft lb) ft lb torque engine rpm hp 550 π sec 550 sec 60 min
11 Vehicle Speed vs. Engine Speed ( 1 i) πrne V ε 0 V velocity (ft/s) r wheel radius (ft) n e crankshaft rps i driveline slippage ε 0 gear reduction ratio
12 Typical Torque-Power Curves
13 Maximum Tractive Effort Front Wheel Drive Vehicle F max µ W ( l + f h) r 1+ L µ h L rl Rear Wheel Drive Vehicle What about 4WD? F max ( l f h) f µ W L µ h 1 L rl
14 Diagram R a ma h h θg R rlf F bf W f l f W R rlr l r W r F br L θ g
15 Vehicle Acceleration Governing Equation F R γ m ma Mass Factor (accounts for inertia of vehicle s rotating parts) γ ε m 0
16 Example A 1989 Ford 5.0L Mustang Convertible starts on a flat grade from a dead stop as fast as possible. What s the maximum acceleration it can achieve before spinning its wheels? µ 0.40 (wet, bad pavement) 1989 Ford 5.0L Mustang Convertible Torque 300 rpm Curb Weight 3640 Weight Distribution Front 57% Rear 43% Wheelbase in Tire Size P5/60R15 Gear Reduction Ratio 3.8 Driveline efficiency 90% Center of Gravity 0 inches high
17 Braking Force Front axle F bf max µ W l [ + h( µ + f )] r L rl Rear axle F br max µ W l [ h( µ + f )] f L rl
18 Braking Force Ratio BFR l l r f + h h ( µ + f ) rl ( µ + f ) rear rl front Efficiency η b gmax µ
19 Braking Distance Theoretical ignoring air resistance S g ( γ ) b V1 V ( η µ + f ± sinθ ) b rl g Practical Perception d V 1 g V a g ± G For grade 0 d V V a 1 Total d p V1t p d d + s d p
20 Stopping Sight Distance (SSD) Worst-case conditions Poor driver skills Low braking efficiency Wet pavement Perception-reaction time.5 seconds Equation V1 SSD + V1t r a g ± G g
21 Stopping Sight Distance (SSD) from ASSHTO A Policy on Geometric Design of Highways and Streets, 001 Note: this table assumes level grade (G 0)
22 SSD Quick and Dirty 1. Acceleration due to gravity, g 3. ft/sec. There are 1.47 ft/sec per mph 3. Assume G 0 (flat grade) d ( a g ± G) ( 1.47 V ) ( 0) V1 V V V V g d 1.47 V1 t 1. 47Vt p p ( ) a p V d a s Vt p V V 1 in mph a deceleration, 11. ft/s in US customary units t p Conservative perception / reaction time.5 seconds
23
24 Primary References Mannering, F.L.; Kilareski, W.P. and Washburn, S.S. (005). Principles of Highway Engineering and Traffic Analysis, Third Edition). Chapter American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officals (AASHTO). (001). A Policy on Geometric Design of Highways and Streets, Fourth Edition. Washington, D.C.
CE351 Transportation Systems: Planning and Design
 CE351 Transportation Systems: Planning and Design TOPIC: HIGHWAY USERS PERFORMANCE (Part III) 1 ANOUNCEMENT Updated d Schedule on: http://wiki.cecs.pdx.edu/bin/view/main/slidesce 351 Course Outline Introduction
CE351 Transportation Systems: Planning and Design TOPIC: HIGHWAY USERS PERFORMANCE (Part III) 1 ANOUNCEMENT Updated d Schedule on: http://wiki.cecs.pdx.edu/bin/view/main/slidesce 351 Course Outline Introduction
To convert a speed to a velocity. V = Velocity in feet per seconds (ft/sec) S = Speed in miles per hour (mph) = Mathematical Constant
 To convert a speed to a velocity V S ( 1.466) V Velocity in feet per seconds (ft/sec) S Speed in miles per hour (mph) 1.466 Mathematical Constant Example Your driver just had a rear-end accident and says
To convert a speed to a velocity V S ( 1.466) V Velocity in feet per seconds (ft/sec) S Speed in miles per hour (mph) 1.466 Mathematical Constant Example Your driver just had a rear-end accident and says
Overcoming the Limitations of Conservation of Linear Momentum by Including External Impulse
 Overcoming the Limitations of Conservation of Linear Momentum by Including External Impulse March 12, 2008 The University of Tulsa MEPS Lunch Meeting 1 / 40 Motivation The University of Tulsa MEPS Lunch
Overcoming the Limitations of Conservation of Linear Momentum by Including External Impulse March 12, 2008 The University of Tulsa MEPS Lunch Meeting 1 / 40 Motivation The University of Tulsa MEPS Lunch
Assignment 4:Rail Analysis and Stopping/Passing Distances
 CEE 3604: Introduction to Transportation Engineering Fall 2012 Date Due: September 28, 2012 Assignment 4:Rail Analysis and Stopping/Passing Distances Instructor: Trani Problem 1 You are ased to evaluate
CEE 3604: Introduction to Transportation Engineering Fall 2012 Date Due: September 28, 2012 Assignment 4:Rail Analysis and Stopping/Passing Distances Instructor: Trani Problem 1 You are ased to evaluate
Vertical Curve Profile Views. Vertical Alignment Fundamentals. Offsets. Offset Formulas 9/17/2009
 9/17/009 Vertical Alignment Fundamentals Vertical Curve Profile Views CE 3 Transportation Engineering Dr. Ahmed Abdel-Rahim, Ph.D., P.E. Fig. 3.3 Fig. 3.4 Offsets Offsets are vertical distances from initial
9/17/009 Vertical Alignment Fundamentals Vertical Curve Profile Views CE 3 Transportation Engineering Dr. Ahmed Abdel-Rahim, Ph.D., P.E. Fig. 3.3 Fig. 3.4 Offsets Offsets are vertical distances from initial
Today we applied our knowledge of vectors to different kinds of problems.
 DAY 18 Summary of Primary Topics Covered Center of Mass and More Vector Examples Today we applied our knowledge of vectors to different kinds of problems. Working these problems is a matter of taking concepts
DAY 18 Summary of Primary Topics Covered Center of Mass and More Vector Examples Today we applied our knowledge of vectors to different kinds of problems. Working these problems is a matter of taking concepts
Subject: Desert Palisades Specific Plan - Tram Way Access Sight Distance
 Endo Engineering Traffic Engineering Air Quality Studies Noise Assessments July 13, 2015 Mr. Ed Freeman Pinnacle View, LLC P.O. Box 1754 Lake Oswego, OR 97035-0579 Subject: Desert Palisades Specific Plan
Endo Engineering Traffic Engineering Air Quality Studies Noise Assessments July 13, 2015 Mr. Ed Freeman Pinnacle View, LLC P.O. Box 1754 Lake Oswego, OR 97035-0579 Subject: Desert Palisades Specific Plan
Simple Car Dynamics. Outline. Claude Lacoursière HPC2N/VRlab, Umeå Universitet, Sweden, May 18, 2005
 Simple Car Dynamics Claude Lacoursière HPC2N/VRlab, Umeå Universitet, Sweden, and CMLabs Simulations, Montréal, Canada May 18, 2005 Typeset by FoilTEX May 16th 2005 Outline basics of vehicle dynamics different
Simple Car Dynamics Claude Lacoursière HPC2N/VRlab, Umeå Universitet, Sweden, and CMLabs Simulations, Montréal, Canada May 18, 2005 Typeset by FoilTEX May 16th 2005 Outline basics of vehicle dynamics different
(c) McHenry Software. McHenry. Accident Reconstruction. by Raymond R. McHenry Brian G. McHenry. McHenry Training Seminar 2008
 McHenry Training eminar 008 McHenry Accident Reconstruction 008 by Raymond R. McHenry Brian G. McHenry McHenry oftware PO Box 1716 Cary, NC 751 UA (919)-468-966 email: mchenry@mchenrysoftware.com www:
McHenry Training eminar 008 McHenry Accident Reconstruction 008 by Raymond R. McHenry Brian G. McHenry McHenry oftware PO Box 1716 Cary, NC 751 UA (919)-468-966 email: mchenry@mchenrysoftware.com www:
MECH 3140 Final Project
 MECH 3140 Final Project Final presentation will be held December 7-8. The presentation will be the only deliverable for the final project and should be approximately 20-25 minutes with an additional 10
MECH 3140 Final Project Final presentation will be held December 7-8. The presentation will be the only deliverable for the final project and should be approximately 20-25 minutes with an additional 10
Derivation of the Yellow Change Interval Formula
 Derivation of the Yellow Change Interval Formula Brian Ceccarelli, PE; Joseph Shovlin, PhD The yellow change interval formula traffic engineers use to set yellow light durations originated from a paper
Derivation of the Yellow Change Interval Formula Brian Ceccarelli, PE; Joseph Shovlin, PhD The yellow change interval formula traffic engineers use to set yellow light durations originated from a paper
ERRATA AND CLARIFICATIONS Fundamentals of Vehicle Dynamics by Thomas D. Gillespie
 ERRATA AND CLARIFICATIONS Fundamentals of Vehicle Dynamics by Thomas D. Gillespie Page v, Acknowledgements: Typographical error on next to the last line. The fourth name is supposed to read Chuck Houser.
ERRATA AND CLARIFICATIONS Fundamentals of Vehicle Dynamics by Thomas D. Gillespie Page v, Acknowledgements: Typographical error on next to the last line. The fourth name is supposed to read Chuck Houser.
Homework Assignment 4 Root Finding Algorithms The Maximum Velocity of a Car Due: Friday, February 19, 2010 at 12noon
 ME 2016 A Spring Semester 2010 Computing Techniques 3-0-3 Homework Assignment 4 Root Finding Algorithms The Maximum Velocity of a Car Due: Friday, February 19, 2010 at 12noon Description and Outcomes In
ME 2016 A Spring Semester 2010 Computing Techniques 3-0-3 Homework Assignment 4 Root Finding Algorithms The Maximum Velocity of a Car Due: Friday, February 19, 2010 at 12noon Description and Outcomes In
Team-Exercises for DGC 100 Modelica Course
 Team-Exercises for DGC 100 Modelica Course Hubertus Tummescheit United Technologies Research Center, East Hartford, CT 06108. November 4, 2003 Abstract This document is a preliminary version and is going
Team-Exercises for DGC 100 Modelica Course Hubertus Tummescheit United Technologies Research Center, East Hartford, CT 06108. November 4, 2003 Abstract This document is a preliminary version and is going
Uncertainty in the Yellow Change Interval
 Uncertainty in the Yellow Change Interval Abstract The difference between legal and illegal when it comes to running a red light is not black and white. Engineering is never exact. Tolerance is routine
Uncertainty in the Yellow Change Interval Abstract The difference between legal and illegal when it comes to running a red light is not black and white. Engineering is never exact. Tolerance is routine
Homework Assignment 2 Modeling a Drivetrain Model Accuracy Due: Friday, September 16, 2005
 ME 2016 Sections A-B-C-D Fall Semester 2005 Computing Techniques 3-0-3 Homework Assignment 2 Modeling a Drivetrain Model Accuracy Due: Friday, September 16, 2005 Description and Outcomes In this assignment,
ME 2016 Sections A-B-C-D Fall Semester 2005 Computing Techniques 3-0-3 Homework Assignment 2 Modeling a Drivetrain Model Accuracy Due: Friday, September 16, 2005 Description and Outcomes In this assignment,
Derivation of the Yellow Change Interval Formula
 Derivation of the Yellow Change Interval Formula Brian Ceccarelli, Joseph Shovlin The yellow change interval formula traffic engineers use to set yellow light durations originated from a paper written
Derivation of the Yellow Change Interval Formula Brian Ceccarelli, Joseph Shovlin The yellow change interval formula traffic engineers use to set yellow light durations originated from a paper written
Assignment 9. to roll without slipping, how large must F be? Ans: F = R d mgsinθ.
 Assignment 9 1. A heavy cylindrical container is being rolled up an incline as shown, by applying a force parallel to the incline. The static friction coefficient is µ s. The cylinder has radius R, mass
Assignment 9 1. A heavy cylindrical container is being rolled up an incline as shown, by applying a force parallel to the incline. The static friction coefficient is µ s. The cylinder has radius R, mass
Evaluating Hydroplaning Potential of Rutted Highway Pavements
 Evaluating Hydroplaning Potential of Rutted Highway Pavements Longjia CHU a, Tien F. FWA b, Ghim P. ONG c a Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering, National University of Singapore, 119260, Singapore;
Evaluating Hydroplaning Potential of Rutted Highway Pavements Longjia CHU a, Tien F. FWA b, Ghim P. ONG c a Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering, National University of Singapore, 119260, Singapore;
Road Vehicle Dynamics
 Road Vehicle Dynamics Table of Contents: Foreword Preface Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 General 1.2 Vehicle System Classification 1.3 Dynamic System 1.4 Classification of Dynamic System Models 1.5 Constraints,
Road Vehicle Dynamics Table of Contents: Foreword Preface Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 General 1.2 Vehicle System Classification 1.3 Dynamic System 1.4 Classification of Dynamic System Models 1.5 Constraints,
Objectives. Power in Translational Systems 298 CHAPTER 6 POWER
 Objectives Explain the relationship between power and work. Explain the relationship between power, force, and speed for an object in translational motion. Calculate a device s efficiency in terms of the
Objectives Explain the relationship between power and work. Explain the relationship between power, force, and speed for an object in translational motion. Calculate a device s efficiency in terms of the
INTI INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY FOUNDATION IN SCIENCE (CFSI) PHY1203: GENERAL PHYSICS 1 FINAL EXAMINATION: SEPTEMBER 2012 SESSION
 INTI INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY FOUNDATION IN SCIENCE (CFSI) PHY1203: GENERAL PHYSICS 1 FINAL EXAMINATION: SEPTEMBER 2012 SESSION PHY1203(F)/Page 1 of 5 Instructions: This paper consists of FIVE (5) questions.
INTI INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY FOUNDATION IN SCIENCE (CFSI) PHY1203: GENERAL PHYSICS 1 FINAL EXAMINATION: SEPTEMBER 2012 SESSION PHY1203(F)/Page 1 of 5 Instructions: This paper consists of FIVE (5) questions.
Terramechanics V MARYLAND U N I V E R S I T Y O F. Terramechanics V. ENAE 788X - Planetary Surface Robotics
 Terramechanics V Note - I haven t posted the slides from Tuesday because there were a number of typos (and outright mistakes) that were (almost) all corrected on Thursday. This set of slides are the corrected
Terramechanics V Note - I haven t posted the slides from Tuesday because there were a number of typos (and outright mistakes) that were (almost) all corrected on Thursday. This set of slides are the corrected
MODELING OF THE HYDROPLANING PHENOMENON. Ong G P and Fwa T F Department of Civil Engineering National University of Singapore INTRODUCTION
 MODELING OF THE HYDROPLANING PHENOMENON Ong G P and Fwa T F Department of Civil Engineering National University of Singapore INTRODUCTION Hydroplaning is a unique phenomenon in which the water on a wet
MODELING OF THE HYDROPLANING PHENOMENON Ong G P and Fwa T F Department of Civil Engineering National University of Singapore INTRODUCTION Hydroplaning is a unique phenomenon in which the water on a wet
GM VOLT PERFORMANCE SIMULATION
 GM Volt - Vehicle, Motor, Road, and Enironmental Parameters: Enable Generator Only Mode Gear Ratio, Inefficiencies: GR 8 η Max Motor Power: Power max 111 kw.9 axle.9 Battery Energy: Energy P Generator
GM Volt - Vehicle, Motor, Road, and Enironmental Parameters: Enable Generator Only Mode Gear Ratio, Inefficiencies: GR 8 η Max Motor Power: Power max 111 kw.9 axle.9 Battery Energy: Energy P Generator
Closed-form Method to Evaluate Bike Braking Performance
 Human Power ejournal, April 4, 13 Closed-form Method to Evaluate Bike Braking Performance Junghsen Lieh, PhD Professor, Mechanical & Materials Engineering Wright State University, Dayton Ohio 45435 USA
Human Power ejournal, April 4, 13 Closed-form Method to Evaluate Bike Braking Performance Junghsen Lieh, PhD Professor, Mechanical & Materials Engineering Wright State University, Dayton Ohio 45435 USA
Single Stop Transient Thermal Coupled with Structural Analysis and Repeated Braking Analysis with Convective Cooling for Ventilated Rotor
 Single Stop Transient Thermal Coupled with Structural Analysis and Repeated Braking Analysis with Convective Cooling for Ventilated Rotor Tirth Sodagar 1, Avadhoot Ahire 2 1Tirth Sodagar, Student, School
Single Stop Transient Thermal Coupled with Structural Analysis and Repeated Braking Analysis with Convective Cooling for Ventilated Rotor Tirth Sodagar 1, Avadhoot Ahire 2 1Tirth Sodagar, Student, School
Drive-train Basics. Team 1640 Clem McKown - mentor October 2009 (r3)
 Drive-train Basics Team 1640 Clem McKown - mentor October 2009 (r3) Topics What s a Drive-train? Basics Components Propulsion Drivetrain Model Center of Mass Considerations Automobile versus robot tank
Drive-train Basics Team 1640 Clem McKown - mentor October 2009 (r3) Topics What s a Drive-train? Basics Components Propulsion Drivetrain Model Center of Mass Considerations Automobile versus robot tank
Sizing caliper disc brakes can be an easy process.
 Sizing caliper disc brakes can be an easy process. The goal is to determine how much braking tque is required and finding the most cost effective and efficient brake and disc diameter package. Go to the
Sizing caliper disc brakes can be an easy process. The goal is to determine how much braking tque is required and finding the most cost effective and efficient brake and disc diameter package. Go to the
Mechanics. Flight Lessons 1: Basic Flight. Position, starting with 2 dimensions
 Position, starting with 2 dimensions Mechanics We can measure our position forward with positive numbers and backwards with negative numbers. The bike is at 0. Speed (Average) If we take two odometer readings,
Position, starting with 2 dimensions Mechanics We can measure our position forward with positive numbers and backwards with negative numbers. The bike is at 0. Speed (Average) If we take two odometer readings,
A first car following model
 A first car following model CE 391F March 21, 2013 ANNOUNCEMENTS Homework 3 to be posted this weekend Course project abstracts due Tuesday Announcements REVIEW Driver characteristics... Reaction time and
A first car following model CE 391F March 21, 2013 ANNOUNCEMENTS Homework 3 to be posted this weekend Course project abstracts due Tuesday Announcements REVIEW Driver characteristics... Reaction time and
E11 Lecture 13: Motors. Professor Lape Fall 2010
 E11 Lecture 13: Motors Professor Lape Fall 2010 Overview How do electric motors work? Electric motor types and general principles of operation How well does your motor perform? Torque and power output
E11 Lecture 13: Motors Professor Lape Fall 2010 Overview How do electric motors work? Electric motor types and general principles of operation How well does your motor perform? Torque and power output
w = mg Use: g = 10 m/s 2 1 hour = 60 min = 3600 sec
 The exam is closed book and closed notes. Part I: There are 1 multiple choice questions, 1 point each. The answers for the multiple choice questions are to be placed on the SCANTRON form provided. Make
The exam is closed book and closed notes. Part I: There are 1 multiple choice questions, 1 point each. The answers for the multiple choice questions are to be placed on the SCANTRON form provided. Make
CEE 320 Midterm Examination (1 hour)
 Examination (1 hour) Pleae write your name on thi cover. Pleae write you lat name on all other exam page Thi examination i open-book, open-note. There are 5 quetion worth a total of 100 point. Each quetion
Examination (1 hour) Pleae write your name on thi cover. Pleae write you lat name on all other exam page Thi examination i open-book, open-note. There are 5 quetion worth a total of 100 point. Each quetion
Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3 Problem 4 Total
 Name Section THE PENNSYLVANIA STATE UNIVERSITY Department of Engineering Science and Mechanics Engineering Mechanics 12 Final Exam May 5, 2003 8:00 9:50 am (110 minutes) Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3 Problem
Name Section THE PENNSYLVANIA STATE UNIVERSITY Department of Engineering Science and Mechanics Engineering Mechanics 12 Final Exam May 5, 2003 8:00 9:50 am (110 minutes) Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3 Problem
In the equations above, we are assuming that the adhesion coefficient (peak value) of the road surface is minimum
 ME 466 SPRING 017 PERFORMANCE OF ROAD VEHICLES HOMEWORK #4 SOLUTIONS Solution 1: a) F p P i A mc l p η p 50 105 Pa 5. 5 0. 8 π(0.0064 m) 4 380 N (Ans. ) d η i (μ i ) utilized (μ i ) utilized F xi F zi
ME 466 SPRING 017 PERFORMANCE OF ROAD VEHICLES HOMEWORK #4 SOLUTIONS Solution 1: a) F p P i A mc l p η p 50 105 Pa 5. 5 0. 8 π(0.0064 m) 4 380 N (Ans. ) d η i (μ i ) utilized (μ i ) utilized F xi F zi
A NEURAL NETWORK BASED MODEL FOR PREDICTING ACCELERATION AND GRADEABILITY PERFORMANCES OF TRANSIT BUSES
 A NEURAL NETWORK BASED MODEL FOR PREDICTING ACCELERATION AND GRADEABILITY PERFORMANCES OF TRANSIT BUSES Saravanan Muthiah and Bohdan T. Kulakowski Pennsylvania Transportation Institute, The Pennsylvania
A NEURAL NETWORK BASED MODEL FOR PREDICTING ACCELERATION AND GRADEABILITY PERFORMANCES OF TRANSIT BUSES Saravanan Muthiah and Bohdan T. Kulakowski Pennsylvania Transportation Institute, The Pennsylvania
Non-textbook problem #I: Let s start with a schematic side view of the drawbridge and the forces acting on it: F axle θ
 PHY 309 K. Solutions for Problem set # 10. Non-textbook problem #I: Let s start with a schematic side view of the drawbridge and the forces acting on it: F axle θ T mg The bridgeis shown just asit begins
PHY 309 K. Solutions for Problem set # 10. Non-textbook problem #I: Let s start with a schematic side view of the drawbridge and the forces acting on it: F axle θ T mg The bridgeis shown just asit begins
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN GE MECHANICS III FINAL EXAM APRIL 18, 2011 Professor A. Dolovich A CLOSED BOOK EXAMINATION TIME: 3 HOURS
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN GE 226.3 MECHANICS III FINAL EXAM APRIL 18, 2011 Professor A. Dolovich A CLOSED BOOK EXAMINATION TIME: 3 HOURS LAST NAME (printed): FIRST NAME (printed): STUDENT NUMBER: EXAMINATION
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN GE 226.3 MECHANICS III FINAL EXAM APRIL 18, 2011 Professor A. Dolovich A CLOSED BOOK EXAMINATION TIME: 3 HOURS LAST NAME (printed): FIRST NAME (printed): STUDENT NUMBER: EXAMINATION
Estimation of Tire-Road Friction by Tire Rotational Vibration Model
 53 Research Report Estimation of Tire-Road Friction by Tire Rotational Vibration Model Takaji Umeno Abstract Tire-road friction is the most important piece of information used by active safety systems.
53 Research Report Estimation of Tire-Road Friction by Tire Rotational Vibration Model Takaji Umeno Abstract Tire-road friction is the most important piece of information used by active safety systems.
Principles of Engineering Midterm Exam
 Principles of Engineering Midterm Exam Instructions: Respond to all questions below by circling the correct answer, or by writing your answer in the blank space. Use a dark pen/pencil and write neatly
Principles of Engineering Midterm Exam Instructions: Respond to all questions below by circling the correct answer, or by writing your answer in the blank space. Use a dark pen/pencil and write neatly
First Name: Last Name: Section: 1. March 26, 2008 Physics 207 EXAM 2
 First Name: Last Name: Section: 1 March 26, 2008 Physics 207 EXAM 2 Please print your name and section number (or TA s name) clearly on all pages. Show all your work in the space immediately below each
First Name: Last Name: Section: 1 March 26, 2008 Physics 207 EXAM 2 Please print your name and section number (or TA s name) clearly on all pages. Show all your work in the space immediately below each
Engineering Mechanics. Friction in Action
 Engineering Mechanics Friction in Action What is friction? Friction is a retarding force that opposes motion. Friction types: Static friction Kinetic friction Fluid friction Sources of dry friction Dry
Engineering Mechanics Friction in Action What is friction? Friction is a retarding force that opposes motion. Friction types: Static friction Kinetic friction Fluid friction Sources of dry friction Dry
Technical aspects of road time trialing
 Technical aspects of road time trialing Acknowledgements Andrew Coggan,, Ph.D. Kraig Willett, biketechreview.com cyclingnews.com North Chattanooga Cycle Club Excel Sports Cervélo HED Kestrel Litespeed
Technical aspects of road time trialing Acknowledgements Andrew Coggan,, Ph.D. Kraig Willett, biketechreview.com cyclingnews.com North Chattanooga Cycle Club Excel Sports Cervélo HED Kestrel Litespeed
Assignment 4.2 Frictional Forces CONCEPTUAL QUESTIONS: 1. What is the SI unit of the coefficient of friction (μ s or μ k )?
 CONCEPTUAL QUESTIONS: 1. What is the SI unit of the coefficient of friction (μ s or μ k )? 2. Tennis is played on clay, grass, and hard surfaces. Please explain why you think tennis players have or don
CONCEPTUAL QUESTIONS: 1. What is the SI unit of the coefficient of friction (μ s or μ k )? 2. Tennis is played on clay, grass, and hard surfaces. Please explain why you think tennis players have or don
EF 151 Final Exam, Fall, 2011 Page 1 of 11
 EF 5 Final Exam, Fall, 0 Page of Instructions Do not open or turn over the exam until instructed to do so. Name, and section will be written on the st page of the exam after time starts. Do not leave your
EF 5 Final Exam, Fall, 0 Page of Instructions Do not open or turn over the exam until instructed to do so. Name, and section will be written on the st page of the exam after time starts. Do not leave your
PHYSICS 218 Final Exam Fall, 2014
 PHYSICS 18 Final Exam Fall, 014 Name: Signature: E-mail: Section Number: No calculators are allowed in the test. Be sure to put a box around your final answers and clearly indicate your work to your grader.
PHYSICS 18 Final Exam Fall, 014 Name: Signature: E-mail: Section Number: No calculators are allowed in the test. Be sure to put a box around your final answers and clearly indicate your work to your grader.
Chapter 4: Forces. Goals of Period Net Force and Acceleration. Force 1 Force 2
 Chapter 4: Forces Goals of Period 4 Section 4.1: To discuss the effect of net forces acting on objects Section 4.2: To examine the acceleration of falling objects Section 4.3: To describe the frictional
Chapter 4: Forces Goals of Period 4 Section 4.1: To discuss the effect of net forces acting on objects Section 4.2: To examine the acceleration of falling objects Section 4.3: To describe the frictional
Physics for Scientist and Engineers third edition Rotational Motion About a Fixed Axis Problems
 A particular bird s eye can just distinguish objects that subtend an angle no smaller than about 3 E -4 rad, A) How many degrees is this B) How small an object can the bird just distinguish when flying
A particular bird s eye can just distinguish objects that subtend an angle no smaller than about 3 E -4 rad, A) How many degrees is this B) How small an object can the bird just distinguish when flying
ω avg [between t 1 and t 2 ] = ω(t 1) + ω(t 2 ) 2
![ω avg [between t 1 and t 2 ] = ω(t 1) + ω(t 2 ) 2 ω avg [between t 1 and t 2 ] = ω(t 1) + ω(t 2 ) 2](/thumbs/94/120561024.jpg) PHY 302 K. Solutions for problem set #9. Textbook problem 7.10: For linear motion at constant acceleration a, average velocity during some time interval from t 1 to t 2 is the average of the velocities
PHY 302 K. Solutions for problem set #9. Textbook problem 7.10: For linear motion at constant acceleration a, average velocity during some time interval from t 1 to t 2 is the average of the velocities
Electric Vehicle Performance Power and Efficiency
 Electric Vehicle Performance Power and Efficiency 1 Assignment a) Examine measurement guide and electric vehicle (EV) arrangement. b) Drive the route according to teacher s instruction and download measured
Electric Vehicle Performance Power and Efficiency 1 Assignment a) Examine measurement guide and electric vehicle (EV) arrangement. b) Drive the route according to teacher s instruction and download measured
HCTL Open Int. J. of Technology Innovations and Research HCTL Open IJTIR, Volume 3, May 2013 e-issn: ISBN (Print):
 Computation of Power of a Motor in Electric Vehicle under City Traffic and Dynamic Conditions vikas@cpdm.iisc.ernet.in Abstract In this paper author used a novel method to calculate the power of a motor
Computation of Power of a Motor in Electric Vehicle under City Traffic and Dynamic Conditions vikas@cpdm.iisc.ernet.in Abstract In this paper author used a novel method to calculate the power of a motor
Fr h mg rh h. h 2( m)( m) ( (0.800 kg)(9.80 m/s )
 5. We consider the wheel as it leaves the lower floor. The floor no longer exerts a force on the wheel, and the only forces acting are the force F applied horizontally at the axle, the force of gravity
5. We consider the wheel as it leaves the lower floor. The floor no longer exerts a force on the wheel, and the only forces acting are the force F applied horizontally at the axle, the force of gravity
PY205N Spring The vectors a, b, and c. are related by c = a b. The diagram below that best illustrates this relationship is (a) I
 PY205N Spring 2013 Final exam, practice version MODIFIED This practice exam is to help students prepare for the final exam to be given at the end of the semester. Please note that while problems on this
PY205N Spring 2013 Final exam, practice version MODIFIED This practice exam is to help students prepare for the final exam to be given at the end of the semester. Please note that while problems on this
dw dt T (w ( )) i =
 Dan Bolognini & Armen Mkhitarian ECE 492 Motor Controller + Modeling Physics Model Memo 5/11/16 Abstract This memo provides information about the developed physics model for the fully integrated car using
Dan Bolognini & Armen Mkhitarian ECE 492 Motor Controller + Modeling Physics Model Memo 5/11/16 Abstract This memo provides information about the developed physics model for the fully integrated car using
FAA Research on Runway Intersection Grading Criteria
 ENDURING VALUES. INSPIRED PERFORMANCE. FAA Research on Runway Intersection Grading Criteria Injun Song, Ph.D., P.E. November 3, 2016 2016 RPUG, Marriott San Diego Mission Valley Hotel San Diego, California,
ENDURING VALUES. INSPIRED PERFORMANCE. FAA Research on Runway Intersection Grading Criteria Injun Song, Ph.D., P.E. November 3, 2016 2016 RPUG, Marriott San Diego Mission Valley Hotel San Diego, California,
16.07 Dynamics Final Exam
 Name:... Massachusetts Institute of Technology 16.07 Dynamics Final Exam Tuesday, December 20, 2005 Problem 1 (8) Problem 2 (8) Problem 3 (10) Problem 4 (10) Problem 5 (10) Problem 6 (10) Problem 7 (10)
Name:... Massachusetts Institute of Technology 16.07 Dynamics Final Exam Tuesday, December 20, 2005 Problem 1 (8) Problem 2 (8) Problem 3 (10) Problem 4 (10) Problem 5 (10) Problem 6 (10) Problem 7 (10)
Name Period. Algebra 2 Agenda. Week 3.4 Objective Summary Grade
 Name Period Algebra Agenda Week 3.4 Objective Summary Grade Monday January 3, 07 Tuesday January 4, 07 Wednesday January 5, 07 Thursday January 6, 07 Friday January 7, 07 Solving Equations with Radicals
Name Period Algebra Agenda Week 3.4 Objective Summary Grade Monday January 3, 07 Tuesday January 4, 07 Wednesday January 5, 07 Thursday January 6, 07 Friday January 7, 07 Solving Equations with Radicals
16.07 Dynamics. Problem Set 3
 NAME :..................... Massachusetts Institute of Technology 16.07 Dynamics Problem Set 3 Out date: Sept 17, 2007 Due date: Sept 26, 2007 Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3 Problem 4 Study Time Time Spent
NAME :..................... Massachusetts Institute of Technology 16.07 Dynamics Problem Set 3 Out date: Sept 17, 2007 Due date: Sept 26, 2007 Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3 Problem 4 Study Time Time Spent
Analysis of Four Staged Crashes of Passenger Vehicles into a Semi-Trailer
 Institute of Police Technology and Management Analysis of Four Staged Crashes of Passenger Vehicles into a Semi-Trailer Jeremy Daily Russell Strickland Special Problems in Traffic Crash Reconstruction
Institute of Police Technology and Management Analysis of Four Staged Crashes of Passenger Vehicles into a Semi-Trailer Jeremy Daily Russell Strickland Special Problems in Traffic Crash Reconstruction
2. A 10 kg box is being pushed by a 100 N force 30 above the horizontal. The acceleration of the box is 5 m/s 2. What is the value of µ k?
 Physics Whiteboard Forces with Friction 1. A 70 kg block is being pushed across a tabletop with a constant force of 350 N exerted in the direction of travel. If the coefficient of kinetic friction (µ k
Physics Whiteboard Forces with Friction 1. A 70 kg block is being pushed across a tabletop with a constant force of 350 N exerted in the direction of travel. If the coefficient of kinetic friction (µ k
Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Chapter 12 - Practice Questions Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Never remove a radiator cap on a hot engine because a. the
Chapter 12 - Practice Questions Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Never remove a radiator cap on a hot engine because a. the
Important: This test consists of 16 multiple choice problems, each worth 6.25 points.
 Physics 214 Exam 1 Spring 2005 Fill in on the OPSCAN sheet: 1) Name 2) Student identification number 3) Exam number as 01 4) Sign the OPSCAN sheet Important: This test consists of 16 multiple choice problems,
Physics 214 Exam 1 Spring 2005 Fill in on the OPSCAN sheet: 1) Name 2) Student identification number 3) Exam number as 01 4) Sign the OPSCAN sheet Important: This test consists of 16 multiple choice problems,
1 h. Page 1 of 12 FINAL EXAM FORMULAS. Stopping Sight Distance. (2 ) N st U Where N=sample size s=standard deviation t=z value for confidence level
 Page 1 of 12 FINAL EXAM FORMULAS Stopping Sight Distance 2 2 V V d 1.47Vt 1.075 i f a 2 2 Vi Vf d 1.47Vt 30( f 0.01 G) Where d = distance (ft) V = speed (mph) t = time (sec) a=deceleration rate (ft/sec
Page 1 of 12 FINAL EXAM FORMULAS Stopping Sight Distance 2 2 V V d 1.47Vt 1.075 i f a 2 2 Vi Vf d 1.47Vt 30( f 0.01 G) Where d = distance (ft) V = speed (mph) t = time (sec) a=deceleration rate (ft/sec
Vehicle Motion Equations:
 1 Vehicle Motion Equations: v = at + v (2.2.4) x x = v2 2 v 2a (2.2.6) v 2 = v 2 + 2a(x x ) (2.2.6) x = 1 2 at2 + v t + x (2.2.7) D b = x cos α (2.2.10) x = vt D b = v 2 v 2 2g(f G) (2.2.14) e + f s =
1 Vehicle Motion Equations: v = at + v (2.2.4) x x = v2 2 v 2a (2.2.6) v 2 = v 2 + 2a(x x ) (2.2.6) x = 1 2 at2 + v t + x (2.2.7) D b = x cos α (2.2.10) x = vt D b = v 2 v 2 2g(f G) (2.2.14) e + f s =
Driving in Rural Areas. 82 percent of a miles of roadways are rural roads.
 Driving in Rural Areas 82 percent of a miles of roadways are rural roads. Different types of Roadways Rural roads are constructed of many different types of materials. Some are paved Others are not. Different
Driving in Rural Areas 82 percent of a miles of roadways are rural roads. Different types of Roadways Rural roads are constructed of many different types of materials. Some are paved Others are not. Different
Newton s Laws.
 Newton s Laws http://mathsforeurope.digibel.be/images Forces and Equilibrium If the net force on a body is zero, it is in equilibrium. dynamic equilibrium: moving relative to us static equilibrium: appears
Newton s Laws http://mathsforeurope.digibel.be/images Forces and Equilibrium If the net force on a body is zero, it is in equilibrium. dynamic equilibrium: moving relative to us static equilibrium: appears
Acceleration and velocity are related and have a direct impact on the three basic parts of the CNC system.
 Acceleration and velocity are related and have a direct impact on the three basic parts of the CNC system. ACCELERATION Acceleration is a change in velocity with respect to time. The term, in context of
Acceleration and velocity are related and have a direct impact on the three basic parts of the CNC system. ACCELERATION Acceleration is a change in velocity with respect to time. The term, in context of
Energy Correction Factor Collision Force Coefficient of Restitution Damage (Rigid Pole Impact) Damage (Miscellaneous)...
 Table of Contents Acceleration / Deceleration Factor... 5 Equivalent... 5 Stop, From or To... 7 Acceleration... 8 Deceleration... 9 Lateral... 0 Lateral Stability... Acceleration / Deceleration Rate...
Table of Contents Acceleration / Deceleration Factor... 5 Equivalent... 5 Stop, From or To... 7 Acceleration... 8 Deceleration... 9 Lateral... 0 Lateral Stability... Acceleration / Deceleration Rate...
h CIVIL ENGINEERING FLUID MECHANICS section. ± G = percent grade divided by 100 (uphill grade "+")
 FLUID MECHANICS section. TRANSPORTATION U.S. Customary Units a = deceleration rate (ft/sec ) A = absolute value of algebraic difference in grades (%) e = superelevation (%) f = side friction factor ± G
FLUID MECHANICS section. TRANSPORTATION U.S. Customary Units a = deceleration rate (ft/sec ) A = absolute value of algebraic difference in grades (%) e = superelevation (%) f = side friction factor ± G
HSC PHYSICS ONLINE B F BA. repulsion between two negatively charged objects. attraction between a negative charge and a positive charge
 HSC PHYSICS ONLINE DYNAMICS TYPES O ORCES Electrostatic force (force mediated by a field - long range: action at a distance) the attractive or repulsion between two stationary charged objects. AB A B BA
HSC PHYSICS ONLINE DYNAMICS TYPES O ORCES Electrostatic force (force mediated by a field - long range: action at a distance) the attractive or repulsion between two stationary charged objects. AB A B BA
Subject: Triple Physics Unit title: P4.5 Forces (Paper 2) Strand Content Checklist (L) R A G Forces and their interactions
 4.5.3 Forces and elasticity 4.5.2 Work done and energy transfer 4.5.1 Forces and their interactions Subject: Triple Physics Unit title: P4.5 Forces (Paper 2) Strand Content Checklist (L) R A G 1. Identify
4.5.3 Forces and elasticity 4.5.2 Work done and energy transfer 4.5.1 Forces and their interactions Subject: Triple Physics Unit title: P4.5 Forces (Paper 2) Strand Content Checklist (L) R A G 1. Identify
P211 Spring 2004 Form A
 1. A 2 kg block A traveling with a speed of 5 m/s as shown collides with a stationary 4 kg block B. After the collision, A is observed to travel at right angles with respect to the initial direction with
1. A 2 kg block A traveling with a speed of 5 m/s as shown collides with a stationary 4 kg block B. After the collision, A is observed to travel at right angles with respect to the initial direction with
EF 151 Final Exam, Fall, 2010 Page 1 of 9. EF 151 Final Exam, Fall, 2010 Page 2 of 9
 EF 151 Final Exam, Fall, 2010 Page 1 of 9 EF 151 Final Exam, Fall, 2010 Page 2 of 9 Instructions Do not open the exam until instructed to do so. Name, section, and netid will be written on the 1 st page
EF 151 Final Exam, Fall, 2010 Page 1 of 9 EF 151 Final Exam, Fall, 2010 Page 2 of 9 Instructions Do not open the exam until instructed to do so. Name, section, and netid will be written on the 1 st page
Exam 1 Solutions. PHY 2048 Spring 2014 Acosta, Rinzler. Note that there are several variations of some problems, indicated by choices in parentheses.
 Exam 1 Solutions Note that there are several variations of some problems, indicated by choices in parentheses. Problem 1 Let vector a! = 4î + 3 ĵ and vector b! = î + 2 ĵ (or b! = î + 4 ĵ ). What is the
Exam 1 Solutions Note that there are several variations of some problems, indicated by choices in parentheses. Problem 1 Let vector a! = 4î + 3 ĵ and vector b! = î + 2 ĵ (or b! = î + 4 ĵ ). What is the
Physics 53 Exam 3 November 3, 2010 Dr. Alward
 1. When the speed of a rear-drive car (a car that's driven forward by the rear wheels alone) is increasing on a horizontal road the direction of the frictional force on the tires is: A) forward for all
1. When the speed of a rear-drive car (a car that's driven forward by the rear wheels alone) is increasing on a horizontal road the direction of the frictional force on the tires is: A) forward for all
STATICS. Friction VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: Eighth Edition CHAPTER. Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr.
 Eighth E 8 Friction CHAPTER VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University Contents Introduction Laws of Dry Friction.
Eighth E 8 Friction CHAPTER VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University Contents Introduction Laws of Dry Friction.
Tutorial 1 - Drive fundamentals and DC motor characteristics
 University of New South Wales School of Electrical Engineering & elecommunications ELEC4613 ELECRIC DRIVE SYSEMS utorial 1 - Drive fundamentals and DC motor characteristics 1. In the hoist drive system
University of New South Wales School of Electrical Engineering & elecommunications ELEC4613 ELECRIC DRIVE SYSEMS utorial 1 - Drive fundamentals and DC motor characteristics 1. In the hoist drive system
Physics 8 Monday, October 12, 2015
 Physics 8 Monday, October 12, 2015 HW5 will be due Friday. (HW5 is just Ch9 and Ch10 problems.) You re reading Chapter 12 ( torque ) this week, even though in class we re just finishing Ch10 / starting
Physics 8 Monday, October 12, 2015 HW5 will be due Friday. (HW5 is just Ch9 and Ch10 problems.) You re reading Chapter 12 ( torque ) this week, even though in class we re just finishing Ch10 / starting
WHITE PAPER. Winter Tires
 WHITE PAPER Winter Tires WHITE PAPER Introduction According to the Federal Highway Administration accidents caused by winter weather result in 150,000 injuries and 2,000 deaths each year on average. In
WHITE PAPER Winter Tires WHITE PAPER Introduction According to the Federal Highway Administration accidents caused by winter weather result in 150,000 injuries and 2,000 deaths each year on average. In
Midterm 3 Review (Ch 9-14)
 Midterm 3 Review (Ch 9-14) PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by James Pazun Copyright 2008 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson
Midterm 3 Review (Ch 9-14) PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by James Pazun Copyright 2008 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson
SOLUTION di x = y2 dm. rdv. m = a 2 bdx. = 2 3 rpab2. I x = 1 2 rp L0. b 4 a1 - x2 a 2 b. = 4 15 rpab4. Thus, I x = 2 5 mb2. Ans.
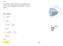 17 4. Determine the moment of inertia of the semiellipsoid with respect to the x axis and express the result in terms of the mass m of the semiellipsoid. The material has a constant density r. y x y a
17 4. Determine the moment of inertia of the semiellipsoid with respect to the x axis and express the result in terms of the mass m of the semiellipsoid. The material has a constant density r. y x y a
EF 151 Final Exam, Fall, 2015 Page 3 of 10
 EF 151 Final Exam, Fall, 2015 Page 3 of 10 Name: Multiple choice questions: 1 point each 1. The acceleration of gravity in mile/min 2 is: a. 1.69x10-6 mile/min 2 b. 21.9 mile/min 2 c. 47.2 mile/min 2 d.
EF 151 Final Exam, Fall, 2015 Page 3 of 10 Name: Multiple choice questions: 1 point each 1. The acceleration of gravity in mile/min 2 is: a. 1.69x10-6 mile/min 2 b. 21.9 mile/min 2 c. 47.2 mile/min 2 d.
Vector Geometry Final Exam Review
 Vector Geometry Final Exam Review Problem 1. Find the center and the radius for the sphere x + 4x 3 + y + z 4y 3 that the center and the radius of a sphere z 7 = 0. Note: Recall x + ax + y + by + z = d
Vector Geometry Final Exam Review Problem 1. Find the center and the radius for the sphere x + 4x 3 + y + z 4y 3 that the center and the radius of a sphere z 7 = 0. Note: Recall x + ax + y + by + z = d
BAD WEATHER DOESN T CAUSE ACCIDENTS
 March 15, 1997 It is with mixed feelings of humor and dismay that persons in the field of traffic safety read frequent headlines in the newspapers--even the largest dailies--blaming the weather for automobile
March 15, 1997 It is with mixed feelings of humor and dismay that persons in the field of traffic safety read frequent headlines in the newspapers--even the largest dailies--blaming the weather for automobile
Physics 111. Lecture 23 (Walker: 10.6, 11.1) Conservation of Energy in Rotation Torque March 30, Kinetic Energy of Rolling Object
 Physics 111 Lecture 3 (Walker: 10.6, 11.1) Conservation of Energy in Rotation Torque March 30, 009 Lecture 3 1/4 Kinetic Energy of Rolling Object Total kinetic energy of a rolling object is the sum of
Physics 111 Lecture 3 (Walker: 10.6, 11.1) Conservation of Energy in Rotation Torque March 30, 009 Lecture 3 1/4 Kinetic Energy of Rolling Object Total kinetic energy of a rolling object is the sum of
Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies: Forces and Accelerations
 Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies: Forces and Accelerations Reference: Beer, Ferdinand P. et al, Vector Mechanics for Engineers : Dynamics, 8 th Edition, Mc GrawHill Hibbeler R.C., Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics,
Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies: Forces and Accelerations Reference: Beer, Ferdinand P. et al, Vector Mechanics for Engineers : Dynamics, 8 th Edition, Mc GrawHill Hibbeler R.C., Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics,
PH 2213 : Chapter 05 Homework Solutions
 PH 2213 : Chapter 05 Homework Solutions Problem 5.4 : The coefficient of static friction between hard rubber and normal street pavement is about 0.90. On how steep a hill (maximum angle) can you leave
PH 2213 : Chapter 05 Homework Solutions Problem 5.4 : The coefficient of static friction between hard rubber and normal street pavement is about 0.90. On how steep a hill (maximum angle) can you leave
DSCC2012-MOVIC
 ASME 212 5th Annual Dynamic Systems and Control Conference joint with the JSME 212 11th Motion and Vibration Conference DSCC212-MOVIC212 October 17-19, 212, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, USA DSCC212-MOVIC212-8535
ASME 212 5th Annual Dynamic Systems and Control Conference joint with the JSME 212 11th Motion and Vibration Conference DSCC212-MOVIC212 October 17-19, 212, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, USA DSCC212-MOVIC212-8535
Chapter 5 Traffic Flow Characteristics
 Chapter 5 Traffic Flow Characteristics 1 Contents 2 Introduction The Nature of Traffic Flow Approaches to Understanding Traffic Flow Parameters Connected with Traffic Flow Categories of Traffic Flow The
Chapter 5 Traffic Flow Characteristics 1 Contents 2 Introduction The Nature of Traffic Flow Approaches to Understanding Traffic Flow Parameters Connected with Traffic Flow Categories of Traffic Flow The
Prediction and Prevention of Tripped Rollovers
 Prediction and Prevention of Tripped Rollovers Final Report Prepared by: Gridsada Phanomchoeng Rajesh Rajamani Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Minnesota CTS 12-33 Technical Report Documentation
Prediction and Prevention of Tripped Rollovers Final Report Prepared by: Gridsada Phanomchoeng Rajesh Rajamani Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Minnesota CTS 12-33 Technical Report Documentation
1. Replace the given system of forces acting on a body as shown in figure 1 by a single force and couple acting at the point A.
 Code No: Z0321 / R07 Set No. 1 I B.Tech - Regular Examinations, June 2009 CLASSICAL MECHANICS ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Mechatronics, Production Engineering and Automobile
Code No: Z0321 / R07 Set No. 1 I B.Tech - Regular Examinations, June 2009 CLASSICAL MECHANICS ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Mechatronics, Production Engineering and Automobile
EQUATIONS OF MOTION: GENERAL PLANE MOTION (Section 17.5) Today s Objectives: Students will be able to analyze the planar kinetics of a rigid body
 EQUATIONS OF MOTION: GENERAL PLANE MOTION (Section 17.5) Today s Objectives: Students will be able to analyze the planar kinetics of a rigid body undergoing general plane motion. APPLICATIONS As the soil
EQUATIONS OF MOTION: GENERAL PLANE MOTION (Section 17.5) Today s Objectives: Students will be able to analyze the planar kinetics of a rigid body undergoing general plane motion. APPLICATIONS As the soil
Question Expected Answers Marks. energy, power and speed underlined. Scale diagram: correct triangle / parallelogram drawn on Fig. 1.
 1 (a)(i) (b) energy, power and speed underlined any error loses this mark vector has magnitude / size vector has a direction Scale diagram: correct triangle / parallelogram drawn on Fig. 1.1 scale stated
1 (a)(i) (b) energy, power and speed underlined any error loses this mark vector has magnitude / size vector has a direction Scale diagram: correct triangle / parallelogram drawn on Fig. 1.1 scale stated
Acceleration due to Gravity
 Acceleration due to Gravity 1 Object To determine the acceleration due to gravity by different methods. 2 Apparatus Balance, ball bearing, clamps, electric timers, meter stick, paper strips, precision
Acceleration due to Gravity 1 Object To determine the acceleration due to gravity by different methods. 2 Apparatus Balance, ball bearing, clamps, electric timers, meter stick, paper strips, precision
+F N = -F g. F g = m٠a g
 Force Normal = F N Force Normal (or the Normal Force, abbreviated F N ) = F N = The contact force exerted by a surface on an object. The word Normal means perpendicular to Therefore, the Normal Force is
Force Normal = F N Force Normal (or the Normal Force, abbreviated F N ) = F N = The contact force exerted by a surface on an object. The word Normal means perpendicular to Therefore, the Normal Force is
Mechanics II. Which of the following relations among the forces W, k, N, and F must be true?
 Mechanics II 1. By applying a force F on a block, a person pulls a block along a rough surface at constant velocity v (see Figure below; directions, but not necessarily magnitudes, are indicated). Which
Mechanics II 1. By applying a force F on a block, a person pulls a block along a rough surface at constant velocity v (see Figure below; directions, but not necessarily magnitudes, are indicated). Which
Physics 106 Sample Common Exam 2, number 2 (Answers on page 6)
 Physics 106 Sample Common Exam 2, number 2 (Answers on page 6) Signature Name (Print): 4 Digit ID: Section: Instructions: Answer all questions. Questions 1 through 12 are multiple choice questions worth
Physics 106 Sample Common Exam 2, number 2 (Answers on page 6) Signature Name (Print): 4 Digit ID: Section: Instructions: Answer all questions. Questions 1 through 12 are multiple choice questions worth
Mechatronics. MANE 4490 Fall 2002 Assignment # 1
 Mechatronics MANE 4490 Fall 2002 Assignment # 1 1. For each of the physical models shown in Figure 1, derive the mathematical model (equation of motion). All displacements are measured from the static
Mechatronics MANE 4490 Fall 2002 Assignment # 1 1. For each of the physical models shown in Figure 1, derive the mathematical model (equation of motion). All displacements are measured from the static
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP PHYSICS GIANCOLI CHAPTER 5: CIRCULAR MOTION; GRAVITATION LSN 5-1: KINEMATICS OF UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION LSN 5-2: DYNAMICS OF UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION LSN 5-3:
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP PHYSICS GIANCOLI CHAPTER 5: CIRCULAR MOTION; GRAVITATION LSN 5-1: KINEMATICS OF UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION LSN 5-2: DYNAMICS OF UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION LSN 5-3:
