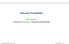
The mousetrap. Figure by MIT OCW.
|
|
|
- Drusilla Heath
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Handout 8: Functionalism The Basic Idea behind various forms of behaviorism (see handout 6) is that to have a mind (or to be in such-and-such mental state) is to (be disposed to) behave in certain ways: how a creature's inner organization produces the behavior is irrelevant to whether it has a mind (or is in such-andsuch mental state). For many reasons -- some of which we have touched on in class -- behaviorism is not a popular view these days. Instead, many philosophers think some kind of functionalism is true. (See Chalmers, pp. 5-6, and Block, Functionalism.) The Basic Idea behind functionalism may be illustrated by the following three examples. Example 1 The mousetrap dead/trapped mouse output mousey input A mousetrap is anything that would respond to mousey input with trapped-mouse output. Provided that this is what something would do, it is a mousetrap no matter what it's made of: a mousetrap can be multiply realized. A mousetrap is the simplest sort of functional kind: the only constraints placed on the internal organization of a mousetrap is that it produce the right inputoutput behavior. So we might say that mousetrap is also a behavioral kind.
2 Example 2 At any one time the vending machine is in two states (the six combinations of the three states M 3, M 2, M 1, with the two states I 1, I 0 ), or else it's shut down. Think of M n as the "n-drinks available state" and I n as the "n-quarters-received state". The causal relations between the inputs (25 ), the output (the dispensing of a Coke, or the illumination of the symbols "25 "), and the various internal states are displayed in the above table: So, if the machine is in state M 2 and state I 0 and receives input of 25, it illuminates the symbols "25 ", and goes into state M 2 and state I 1. If the machine is in state M 2 and state I 1 and receives input of 25, it dispenses a Coke, and goes into state M 1 and state I 1. And so on. A vending machine is also a functional kind, and the table gives a functional theory of a particular machine machine. Like the mousetrap, provided something has internal states that are causally related to each other and to the inputs and outputs as specified by the table (provided, that is, that something has inner states with the appropriate causal roles), it is an instance of this particular vending machine, no matter what it's made of. Notice that to be this kind of vending machine a thing's internal organization must have a particular causal structure. So this vending machine is not a behavioral kind. Behaviorism is a limiting case of functionalism (e.g. things like mousetraps). But what are the states M 3, I 0, etc.? The table tells you everything you need to know. More explicitly: A system S is in M 3 iff S is in the third of five states X 1, X 2, X 3, X 4, X 5, that are related to one another and to the possible inputs and outputs of S as follows: being in X 1 and X 4 and receiving 25 causes S to go into X 2 and remain in X 4 ; being in X 2 and X 4 and receiving 25 causes S to go into X 3 and remain in X 4 ;... being in X 1 and X 5 and receiving 25 causes S to dispense a Coke and to shut down. The Basic Idea of functionalism is that mental states are functional states like M 3 and I 0. They are inner states that can be specified by their causal relations to inputs, outputs, and to each other. (See Putnam, "The nature of mental states".)
3 Example 3 A Toy Functionalist Theory of Pain Toe-Stubbing Icepack on Toe P P, "Ow!" R, "Phew!" R P, "Ow!" R, no output This is a (simplistic!) functionalist theory of pain (in the toe). The mental states of Pain and Relief are those functional states P and R specified by the above table. To be in pain, on this theory, is to have the above causal organization and to be in state P. More explicitly: A system S is in Pain iff S is in the first of two (exclusive) states X and Y that are related to one another and to the possible inputs and outputs of S as follows: being in X and stubbing its toe causes S to remain in X and say "Ow!"; being in X and having an icepack on its toe causes S to go into Y and say "Phew!"; being in Y and stubbing its toe causes S to go into X and say "Ow!"; being in Y and having an icepack on its toe causes S to remain in Y. Functionalism and Physicalism Is functionalism a version of physicalism or materialism? Unfortunately the terminology here can be very confusing: see Block, Functionalism, and contrast Block, "Troubles with functionalism", and Putnam, "The nature of mental states". Although functionalists are happy to concede that minds could be made from "non-physical" components, and in that sense are not physicalists, they invariably think that minds in the actual world are "realized" entirely physically, and in that sense are physicalists. On the standard way of defining 'physicalism' these days, functionalists are physicalists. Representationalism and Computationalism It is important to distinguish the following two theses that are sometimes conflated with functionalism: Representationalism (a.k.a. the representational theory of the mind)
4 Mental states require inner representations: a subject is in such-and-such mental state with representational content that p only if a proper part of the subject has the representational content that p. For example, if the subject believes that snow is white, then according to representationalism some proper part of the subject (part of her brain, presumably) has the representational content that snow is white. (Denied, for instance, by Dennett: see "True believers") [1] Computationalism (a.k.a. the computer model of the mind) A combination of (a) functionalism[2], (b) representationalism, and (c) the idea that mental processes are computational: they involve the algorithmic manipulation of symbols (i.e. the inner representations). Note that computationalism is not committed to the view that a mind is the realization of some Turing machine.[3] Although any algorithmic manipulation of symbols can be carried out by some Turing machine, it's not true that any functional state can be realized in some Turing machine. In other words, if being in a mental state involves having an inner causal organization of some sort, there is no guarantee that a realization of some Turing machine will have the required causal organization. And, on any plausible account of the causal organization required, no Turing machine will do the job. What might be required instead is a machine with a massively parallel architecture. These two theses, and functionalism, come in various degrees of strength: e.g. one might be a functionalist about all mental states, or only about mental states like belief and desire, leaving pain for another kind of theory. So, the relations between representationalism, computationalism, and functionalism, are as follows: Computationalism implies functionalism and representationalism. Neither of the converse implications holds. And neither functionalism nor representationism implies the other. "Troubles with Functionalism" Block's homunculi-head example is supposed to show that functionalism is too "liberal" -- that it counts some things as having minds that do not in fact have them. Imagine a body externally like a human body, say yours, but internally quite different. The neurons from sensory organs are connected to a bank of lights in a hollow cavity in the head. A set of buttons connects to the motor-output neurons. Inside the cavity resides a group of little men. Each has a very simple task: to implement a "square" of an adequate machine table that describes you. On one wall is a bulletin board on which is posted a state card, i.e., a card that bears a symbol designating one of the states specified in the machine table. Here is what the little men do: Suppose the posted card has a 'G' on it... Suppose the light representing input I 17 goes on. One of the G-men has the following as his sole task: when the card reads 'G' and the I 17 light goes on, he presses output button O 191 and changes the state card to 'M'... In spite of the low level of intelligence required of each little man, the system as a whole manages to simulate you because the functional organization they have been trained to realize is yours... (p. 96)
5 Block's homunculus head G-man I 16 I 17 I 18 I 16 I 17 I 18 G M G O 25 K O 191 M O 45 P output H O 8 H O 77 Z O 5 C In a variant, the homunculi are replaced by the citizens of China (pp ). Block's objection is simple: in these examples, the system implemented by homunculi or by the nation of China has exactly the same functional organization as you. So, if functionalism is correct, these systems should share your mental life. But intuitively, the system doesn't have any mental states. It seems especially implausible, Block thinks, that the system could be in any "qualitative" mental states, like being in pain. [1] A restriction here to "explicit" beliefs (and other intentional states) is required (see Block, The mind as..., sect. 3.1) [2] To avoid undue complexity, we are here blurring a distinction that Block makes in section 3 of "The mind as...". The distinction is between functionalism as a partial account of mental states (excluding their representational content), and functionalism as a total account (including representational content). On the second way of using 'functionalism' (this is the way Block uses it in "The mind as..."), it's possible to be a computationalist without being a functionalist. [3] Be sure not to confuse Turing machines in the sense of mathematical objects about which various things are proved, with concrete realizations of Turing machines. But what is the relation between the abstract machine and its concrete realizations? In class, we have been assuming an intuitively correct answer to that question. See Block, "The mind as...", sect. 2.2, and Block, Functionalism.
Minds and Machines spring Functionalism, contd spring 03
 Minds and Machines spring 2003 Functionalism, contd. 1 preliminaries no problem set this week 2 the 3-Coke vending machine initial state s output for 25 input M 3 I 0 25 M 2 I 0 25 M 1 I 0 25 M 3 I 1 M
Minds and Machines spring 2003 Functionalism, contd. 1 preliminaries no problem set this week 2 the 3-Coke vending machine initial state s output for 25 input M 3 I 0 25 M 2 I 0 25 M 1 I 0 25 M 3 I 1 M
Some Thoughts on Computation and Simulation in Cognitive Science
 Some Thoughts on Computation and Simulation in Cognitive Science Markus Peschl ( * ) and Matthias Scheutz ( ** ) ( * ) Department of Philosophy of Science and Social Studies of Science University of Vienna
Some Thoughts on Computation and Simulation in Cognitive Science Markus Peschl ( * ) and Matthias Scheutz ( ** ) ( * ) Department of Philosophy of Science and Social Studies of Science University of Vienna
Replay argument. Abstract. Tanasije Gjorgoski Posted on on 03 April 2006
 Replay argument Tanasije Gjorgoski Posted on http://broodsphilosophy.wordpress.com/, on 03 April 2006 Abstract Before a year or so ago, I was trying to think of an example so I can properly communicate
Replay argument Tanasije Gjorgoski Posted on http://broodsphilosophy.wordpress.com/, on 03 April 2006 Abstract Before a year or so ago, I was trying to think of an example so I can properly communicate
Chapter 2. Mathematical Reasoning. 2.1 Mathematical Models
 Contents Mathematical Reasoning 3.1 Mathematical Models........................... 3. Mathematical Proof............................ 4..1 Structure of Proofs........................ 4.. Direct Method..........................
Contents Mathematical Reasoning 3.1 Mathematical Models........................... 3. Mathematical Proof............................ 4..1 Structure of Proofs........................ 4.. Direct Method..........................
The paradox of knowability, the knower, and the believer
 The paradox of knowability, the knower, and the believer Last time, when discussing the surprise exam paradox, we discussed the possibility that some claims could be true, but not knowable by certain individuals
The paradox of knowability, the knower, and the believer Last time, when discussing the surprise exam paradox, we discussed the possibility that some claims could be true, but not knowable by certain individuals
What Does Quantum Mechanics Suggest About Our Perceptions of Reality?
 What Does Quantum Mechanics Suggest About Our Perceptions of Reality? Quantum mechanics suggests that we perceive at most a tiny sliver of reality. Of course we already knew that! We knew that the visible
What Does Quantum Mechanics Suggest About Our Perceptions of Reality? Quantum mechanics suggests that we perceive at most a tiny sliver of reality. Of course we already knew that! We knew that the visible
The Inductive Proof Template
 CS103 Handout 24 Winter 2016 February 5, 2016 Guide to Inductive Proofs Induction gives a new way to prove results about natural numbers and discrete structures like games, puzzles, and graphs. All of
CS103 Handout 24 Winter 2016 February 5, 2016 Guide to Inductive Proofs Induction gives a new way to prove results about natural numbers and discrete structures like games, puzzles, and graphs. All of
Russell s logicism. Jeff Speaks. September 26, 2007
 Russell s logicism Jeff Speaks September 26, 2007 1 Russell s definition of number............................ 2 2 The idea of reducing one theory to another.................... 4 2.1 Axioms and theories.............................
Russell s logicism Jeff Speaks September 26, 2007 1 Russell s definition of number............................ 2 2 The idea of reducing one theory to another.................... 4 2.1 Axioms and theories.............................
Math 5a Reading Assignments for Sections
 Math 5a Reading Assignments for Sections 4.1 4.5 Due Dates for Reading Assignments Note: There will be a very short online reading quiz (WebWork) on each reading assignment due one hour before class on
Math 5a Reading Assignments for Sections 4.1 4.5 Due Dates for Reading Assignments Note: There will be a very short online reading quiz (WebWork) on each reading assignment due one hour before class on
1 Computational problems
 80240233: Computational Complexity Lecture 1 ITCS, Tsinghua Univesity, Fall 2007 9 October 2007 Instructor: Andrej Bogdanov Notes by: Andrej Bogdanov The aim of computational complexity theory is to study
80240233: Computational Complexity Lecture 1 ITCS, Tsinghua Univesity, Fall 2007 9 October 2007 Instructor: Andrej Bogdanov Notes by: Andrej Bogdanov The aim of computational complexity theory is to study
The Conjunction and Disjunction Theses
 The Conjunction and Disjunction Theses Abstract Rodriguez-Pereyra (2006) argues for the disjunction thesis but against the conjunction thesis. I argue that accepting the disjunction thesis undermines his
The Conjunction and Disjunction Theses Abstract Rodriguez-Pereyra (2006) argues for the disjunction thesis but against the conjunction thesis. I argue that accepting the disjunction thesis undermines his
First-Degree Entailment
 March 5, 2013 Relevance Logics Relevance logics are non-classical logics that try to avoid the paradoxes of material and strict implication: p (q p) p (p q) (p q) (q r) (p p) q p (q q) p (q q) Counterintuitive?
March 5, 2013 Relevance Logics Relevance logics are non-classical logics that try to avoid the paradoxes of material and strict implication: p (q p) p (p q) (p q) (q r) (p p) q p (q q) p (q q) Counterintuitive?
Commentary on Guarini
 University of Windsor Scholarship at UWindsor OSSA Conference Archive OSSA 5 May 14th, 9:00 AM - May 17th, 5:00 PM Commentary on Guarini Andrew Bailey Follow this and additional works at: http://scholar.uwindsor.ca/ossaarchive
University of Windsor Scholarship at UWindsor OSSA Conference Archive OSSA 5 May 14th, 9:00 AM - May 17th, 5:00 PM Commentary on Guarini Andrew Bailey Follow this and additional works at: http://scholar.uwindsor.ca/ossaarchive
65,536 Definitions of Physicalism. David J. Chalmers
 65,536 Definitions of Physicalism David J. Chalmers An Intuitive Definition n Physicalism: n All being is ontologically determined by physical being. Definition Template n Physicalism: n All As of type
65,536 Definitions of Physicalism David J. Chalmers An Intuitive Definition n Physicalism: n All being is ontologically determined by physical being. Definition Template n Physicalism: n All As of type
de Blanc, Peter Ontological Crises in Artificial Agents Value Systems. The Singularity Institute, San Francisco, CA, May 19.
 MIRI MACHINE INTELLIGENCE RESEARCH INSTITUTE Ontological Crises in Artificial Agents Value Systems Peter de Blanc Machine Intelligence Research Institute Abstract Decision-theoretic agents predict and
MIRI MACHINE INTELLIGENCE RESEARCH INSTITUTE Ontological Crises in Artificial Agents Value Systems Peter de Blanc Machine Intelligence Research Institute Abstract Decision-theoretic agents predict and
Unit 4: Computer as a logic machine
 Unit 4: Computer as a logic machine Propositional logic Boolean algebra Logic gates Computer as a logic machine: symbol processor Development of computer The credo of early AI Reference copyright c 2013
Unit 4: Computer as a logic machine Propositional logic Boolean algebra Logic gates Computer as a logic machine: symbol processor Development of computer The credo of early AI Reference copyright c 2013
Philosophy 5340 Epistemology. Topic 3: Analysis, Analytically Basic Concepts, Direct Acquaintance, and Theoretical Terms. Part 2: Theoretical Terms
 Philosophy 5340 Epistemology Topic 3: Analysis, Analytically Basic Concepts, Direct Acquaintance, and Theoretical Terms Part 2: Theoretical Terms 1. What Apparatus Is Available for Carrying out Analyses?
Philosophy 5340 Epistemology Topic 3: Analysis, Analytically Basic Concepts, Direct Acquaintance, and Theoretical Terms Part 2: Theoretical Terms 1. What Apparatus Is Available for Carrying out Analyses?
Triviality Arguments Against Functionalism*
 Triviality Arguments Against Functionalism* Peter Godfrey-Smith Harvard University Philosophical Studies (2008). 1. Introduction Functionalism in the philosophy of mind holds that systems with mental properties
Triviality Arguments Against Functionalism* Peter Godfrey-Smith Harvard University Philosophical Studies (2008). 1. Introduction Functionalism in the philosophy of mind holds that systems with mental properties
Emphasize physical realizability.
 Emphasize physical realizability. The conventional approach is to measure complexity via SPACE & TIME, which are inherently unbounded by their nature. An alternative approach is to count the MATTER & ENERGY
Emphasize physical realizability. The conventional approach is to measure complexity via SPACE & TIME, which are inherently unbounded by their nature. An alternative approach is to count the MATTER & ENERGY
A Note on Turing Machine Design
 CS103 Handout 17 Fall 2013 November 11, 2013 Problem Set 7 This problem explores Turing machines, nondeterministic computation, properties of the RE and R languages, and the limits of RE and R languages.
CS103 Handout 17 Fall 2013 November 11, 2013 Problem Set 7 This problem explores Turing machines, nondeterministic computation, properties of the RE and R languages, and the limits of RE and R languages.
MATH 1130 Exam 1 Review Sheet
 MATH 1130 Exam 1 Review Sheet The Cartesian Coordinate Plane The Cartesian Coordinate Plane is a visual representation of the collection of all ordered pairs (x, y) where x and y are real numbers. This
MATH 1130 Exam 1 Review Sheet The Cartesian Coordinate Plane The Cartesian Coordinate Plane is a visual representation of the collection of all ordered pairs (x, y) where x and y are real numbers. This
P (E) = P (A 1 )P (A 2 )... P (A n ).
 Lecture 9: Conditional probability II: breaking complex events into smaller events, methods to solve probability problems, Bayes rule, law of total probability, Bayes theorem Discrete Structures II (Summer
Lecture 9: Conditional probability II: breaking complex events into smaller events, methods to solve probability problems, Bayes rule, law of total probability, Bayes theorem Discrete Structures II (Summer
TheFourierTransformAndItsApplications-Lecture28
 TheFourierTransformAndItsApplications-Lecture28 Instructor (Brad Osgood):All right. Let me remind you of the exam information as I said last time. I also sent out an announcement to the class this morning
TheFourierTransformAndItsApplications-Lecture28 Instructor (Brad Osgood):All right. Let me remind you of the exam information as I said last time. I also sent out an announcement to the class this morning
Combinatorial-State Automata and Models of Computation
 Trinity University Digital Commons @ Trinity Philosophy Faculty Research Philosophy Department 2012 Combinatorial-State Automata and Models of Computation Curtis Brown Trinity University, cbrown@trinity.edu
Trinity University Digital Commons @ Trinity Philosophy Faculty Research Philosophy Department 2012 Combinatorial-State Automata and Models of Computation Curtis Brown Trinity University, cbrown@trinity.edu
Part I Electrostatics. 1: Charge and Coulomb s Law July 6, 2008
 Part I Electrostatics 1: Charge and Coulomb s Law July 6, 2008 1.1 What is Electric Charge? 1.1.1 History Before 1600CE, very little was known about electric properties of materials, or anything to do
Part I Electrostatics 1: Charge and Coulomb s Law July 6, 2008 1.1 What is Electric Charge? 1.1.1 History Before 1600CE, very little was known about electric properties of materials, or anything to do
Introducing Proof 1. hsn.uk.net. Contents
 Contents 1 1 Introduction 1 What is proof? 1 Statements, Definitions and Euler Diagrams 1 Statements 1 Definitions Our first proof Euler diagrams 4 3 Logical Connectives 5 Negation 6 Conjunction 7 Disjunction
Contents 1 1 Introduction 1 What is proof? 1 Statements, Definitions and Euler Diagrams 1 Statements 1 Definitions Our first proof Euler diagrams 4 3 Logical Connectives 5 Negation 6 Conjunction 7 Disjunction
Paradoxes of special relativity
 Paradoxes of special relativity Today we are turning from metaphysics to physics. As we ll see, certain paradoxes about the nature of space and time result not from philosophical speculation, but from
Paradoxes of special relativity Today we are turning from metaphysics to physics. As we ll see, certain paradoxes about the nature of space and time result not from philosophical speculation, but from
Guide to Proofs on Sets
 CS103 Winter 2019 Guide to Proofs on Sets Cynthia Lee Keith Schwarz I would argue that if you have a single guiding principle for how to mathematically reason about sets, it would be this one: All sets
CS103 Winter 2019 Guide to Proofs on Sets Cynthia Lee Keith Schwarz I would argue that if you have a single guiding principle for how to mathematically reason about sets, it would be this one: All sets
Searle: Proper Names and Intentionality
 Searle: Proper Names and Intentionality Searle s Account Of The Problem In this essay, Searle emphasizes the notion of Intentional content, rather than the cluster of descriptions that Kripke uses to characterize
Searle: Proper Names and Intentionality Searle s Account Of The Problem In this essay, Searle emphasizes the notion of Intentional content, rather than the cluster of descriptions that Kripke uses to characterize
Chapter 8: An Introduction to Probability and Statistics
 Course S3, 200 07 Chapter 8: An Introduction to Probability and Statistics This material is covered in the book: Erwin Kreyszig, Advanced Engineering Mathematics (9th edition) Chapter 24 (not including
Course S3, 200 07 Chapter 8: An Introduction to Probability and Statistics This material is covered in the book: Erwin Kreyszig, Advanced Engineering Mathematics (9th edition) Chapter 24 (not including
Why the Difference Between Quantum and Classical Physics is Irrelevant to the Mind/Body Problem
 Why the Difference Between Quantum and Classical Physics is Irrelevant to the Mind/Body Problem Kirk Ludwig Department of Philosophy University of Florida Gainesville, FL 32611-8545 U.S.A. kludwig@phil.ufl.edu
Why the Difference Between Quantum and Classical Physics is Irrelevant to the Mind/Body Problem Kirk Ludwig Department of Philosophy University of Florida Gainesville, FL 32611-8545 U.S.A. kludwig@phil.ufl.edu
Chapter 3. Cartesian Products and Relations. 3.1 Cartesian Products
 Chapter 3 Cartesian Products and Relations The material in this chapter is the first real encounter with abstraction. Relations are very general thing they are a special type of subset. After introducing
Chapter 3 Cartesian Products and Relations The material in this chapter is the first real encounter with abstraction. Relations are very general thing they are a special type of subset. After introducing
Physicalism decomposed
 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.Oxford, UK and Malden, USAANALAnalysis0003-26382005 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.January 20056513339ArticlesAndreas Hüttemann and David Papineau Physicalism decomposed Physicalism
Blackwell Publishing Ltd.Oxford, UK and Malden, USAANALAnalysis0003-26382005 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.January 20056513339ArticlesAndreas Hüttemann and David Papineau Physicalism decomposed Physicalism
The Philosophy of Physics. Special Relativity and Minkowski Spacetime
 The Philosophy of Physics Lecture Five Special Relativity and Minkowski Spacetime Rob Trueman rob.trueman@york.ac.uk University of York Special Relativity a quick refresher Special Relativity and Minkowski
The Philosophy of Physics Lecture Five Special Relativity and Minkowski Spacetime Rob Trueman rob.trueman@york.ac.uk University of York Special Relativity a quick refresher Special Relativity and Minkowski
A Little Deductive Logic
 A Little Deductive Logic In propositional or sentential deductive logic, we begin by specifying that we will use capital letters (like A, B, C, D, and so on) to stand in for sentences, and we assume that
A Little Deductive Logic In propositional or sentential deductive logic, we begin by specifying that we will use capital letters (like A, B, C, D, and so on) to stand in for sentences, and we assume that
Lecture - 24 Radial Basis Function Networks: Cover s Theorem
 Neural Network and Applications Prof. S. Sengupta Department of Electronic and Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 24 Radial Basis Function Networks:
Neural Network and Applications Prof. S. Sengupta Department of Electronic and Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 24 Radial Basis Function Networks:
PROOF-THEORETIC REDUCTION AS A PHILOSOPHER S TOOL
 THOMAS HOFWEBER PROOF-THEORETIC REDUCTION AS A PHILOSOPHER S TOOL 1. PROOF-THEORETIC REDUCTION AND HILBERT S PROGRAM Hilbert s program in the philosophy of mathematics comes in two parts. One part is a
THOMAS HOFWEBER PROOF-THEORETIC REDUCTION AS A PHILOSOPHER S TOOL 1. PROOF-THEORETIC REDUCTION AND HILBERT S PROGRAM Hilbert s program in the philosophy of mathematics comes in two parts. One part is a
2. Probability. Chris Piech and Mehran Sahami. Oct 2017
 2. Probability Chris Piech and Mehran Sahami Oct 2017 1 Introduction It is that time in the quarter (it is still week one) when we get to talk about probability. Again we are going to build up from first
2. Probability Chris Piech and Mehran Sahami Oct 2017 1 Introduction It is that time in the quarter (it is still week one) when we get to talk about probability. Again we are going to build up from first
Abstract & Applied Linear Algebra (Chapters 1-2) James A. Bernhard University of Puget Sound
 Abstract & Applied Linear Algebra (Chapters 1-2) James A. Bernhard University of Puget Sound Copyright 2018 by James A. Bernhard Contents 1 Vector spaces 3 1.1 Definitions and basic properties.................
Abstract & Applied Linear Algebra (Chapters 1-2) James A. Bernhard University of Puget Sound Copyright 2018 by James A. Bernhard Contents 1 Vector spaces 3 1.1 Definitions and basic properties.................
Lecture notes on Turing machines
 Lecture notes on Turing machines Ivano Ciardelli 1 Introduction Turing machines, introduced by Alan Turing in 1936, are one of the earliest and perhaps the best known model of computation. The importance
Lecture notes on Turing machines Ivano Ciardelli 1 Introduction Turing machines, introduced by Alan Turing in 1936, are one of the earliest and perhaps the best known model of computation. The importance
Astronomy H161 An Introduction to Solar System Astronomy Winter Quarter 2009 Prof. Gaudi Homework #4. Due Monday, February 9 in class
 Name Astronomy H161 An Introduction to Solar System Astronomy Winter Quarter 2009 Prof. Gaudi Homework #4 No late homework will be accepted. Due Monday, February 9 in class Accurate measurements are required
Name Astronomy H161 An Introduction to Solar System Astronomy Winter Quarter 2009 Prof. Gaudi Homework #4 No late homework will be accepted. Due Monday, February 9 in class Accurate measurements are required
The claim that composition is identity is an intuition in search of a formulation.
 Against Composition as Identity KRIS MCDANIEL The claim that composition is identity is an intuition in search of a formulation. The farmer s field is made of six plots, and in some sense is nothing more
Against Composition as Identity KRIS MCDANIEL The claim that composition is identity is an intuition in search of a formulation. The farmer s field is made of six plots, and in some sense is nothing more
Pattern Recognition Prof. P. S. Sastry Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
 Pattern Recognition Prof. P. S. Sastry Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture - 27 Multilayer Feedforward Neural networks with Sigmoidal
Pattern Recognition Prof. P. S. Sastry Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture - 27 Multilayer Feedforward Neural networks with Sigmoidal
Discrete Probability and State Estimation
 6.01, Spring Semester, 2008 Week 12 Course Notes 1 MASSACHVSETTS INSTITVTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.01 Introduction to EECS I Spring Semester, 2008 Week
6.01, Spring Semester, 2008 Week 12 Course Notes 1 MASSACHVSETTS INSTITVTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.01 Introduction to EECS I Spring Semester, 2008 Week
Algorithms and Complexity theory
 Algorithms and Complexity theory Thibaut Barthelemy Some slides kindly provided by Fabien Tricoire University of Vienna WS 2014 Outline 1 Algorithms Overview How to write an algorithm 2 Complexity theory
Algorithms and Complexity theory Thibaut Barthelemy Some slides kindly provided by Fabien Tricoire University of Vienna WS 2014 Outline 1 Algorithms Overview How to write an algorithm 2 Complexity theory
So, what are special sciences? ones that are particularly dear to the author? ( Oh dear. I am touched. Psychology is just, so, well, special!
 Jerry Fodor and his Special Sciences So, what are special sciences? ones that are particularly dear to the author? ( Oh dear. I am touched. Psychology is just, so, well, special! ) The use of special in
Jerry Fodor and his Special Sciences So, what are special sciences? ones that are particularly dear to the author? ( Oh dear. I am touched. Psychology is just, so, well, special! ) The use of special in
In Defense of Jeffrey Conditionalization
 In Defense of Jeffrey Conditionalization Franz Huber Department of Philosophy University of Toronto Please do not cite! December 31, 2013 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Weisberg s Paradox 3 3 Jeffrey Conditionalization
In Defense of Jeffrey Conditionalization Franz Huber Department of Philosophy University of Toronto Please do not cite! December 31, 2013 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Weisberg s Paradox 3 3 Jeffrey Conditionalization
Universalism Entails Extensionalism
 Universalism Entails Extensionalism Achille C. Varzi Department of Philosophy, Columbia University, New York [Final version published in Analysis, 69 (2009), 599 604] 1. Universalism (also known as Conjunctivism,
Universalism Entails Extensionalism Achille C. Varzi Department of Philosophy, Columbia University, New York [Final version published in Analysis, 69 (2009), 599 604] 1. Universalism (also known as Conjunctivism,
COMP3702/7702 Artificial Intelligence Week1: Introduction Russell & Norvig ch.1-2.3, Hanna Kurniawati
 COMP3702/7702 Artificial Intelligence Week1: Introduction Russell & Norvig ch.1-2.3, 3.1-3.3 Hanna Kurniawati Today } What is Artificial Intelligence? } Better know what it is first before committing the
COMP3702/7702 Artificial Intelligence Week1: Introduction Russell & Norvig ch.1-2.3, 3.1-3.3 Hanna Kurniawati Today } What is Artificial Intelligence? } Better know what it is first before committing the
On the scope of diagonal argument and on contradictory equivalence.
 Daniil Teplitskiy, Russia, Saint Petersburg PSI Co. Ltd. 24JUN2011 To my teachers and good people Isaak Perchenok and Rustem Valeyev. To my friend Aleksey Kiselev whose intellectual paradigm underlies
Daniil Teplitskiy, Russia, Saint Petersburg PSI Co. Ltd. 24JUN2011 To my teachers and good people Isaak Perchenok and Rustem Valeyev. To my friend Aleksey Kiselev whose intellectual paradigm underlies
Lecture 1: Introduction Introduction
 Module 1: Signals in Natural Domain Lecture 1: Introduction Introduction The intent of this introduction is to give the reader an idea about Signals and Systems as a field of study and its applications.
Module 1: Signals in Natural Domain Lecture 1: Introduction Introduction The intent of this introduction is to give the reader an idea about Signals and Systems as a field of study and its applications.
The World According to Wolfram
 The World According to Wolfram Basic Summary of NKS- A New Kind of Science is Stephen Wolfram s attempt to revolutionize the theoretical and methodological underpinnings of the universe. Though this endeavor
The World According to Wolfram Basic Summary of NKS- A New Kind of Science is Stephen Wolfram s attempt to revolutionize the theoretical and methodological underpinnings of the universe. Though this endeavor
A Little Deductive Logic
 A Little Deductive Logic In propositional or sentential deductive logic, we begin by specifying that we will use capital letters (like A, B, C, D, and so on) to stand in for sentences, and we assume that
A Little Deductive Logic In propositional or sentential deductive logic, we begin by specifying that we will use capital letters (like A, B, C, D, and so on) to stand in for sentences, and we assume that
Accelerated Observers
 Accelerated Observers In the last few lectures, we ve been discussing the implications that the postulates of special relativity have on the physics of our universe. We ve seen how to compute proper times
Accelerated Observers In the last few lectures, we ve been discussing the implications that the postulates of special relativity have on the physics of our universe. We ve seen how to compute proper times
!t + U " #Q. Solving Physical Problems: Pitfalls, Guidelines, and Advice
 Solving Physical Problems: Pitfalls, Guidelines, and Advice Some Relations in METR 420 There are a relatively small number of mathematical and physical relations that we ve used so far in METR 420 or that
Solving Physical Problems: Pitfalls, Guidelines, and Advice Some Relations in METR 420 There are a relatively small number of mathematical and physical relations that we ve used so far in METR 420 or that
ALBERT EINSTEIN AND THE FABRIC OF TIME by Gevin Giorbran
 ALBERT EINSTEIN AND THE FABRIC OF TIME by Gevin Giorbran Surprising as it may be to most non-scientists and even to some scientists, Albert Einstein concluded in his later years that the past, present,
ALBERT EINSTEIN AND THE FABRIC OF TIME by Gevin Giorbran Surprising as it may be to most non-scientists and even to some scientists, Albert Einstein concluded in his later years that the past, present,
Gödel, Turing, the Undecidability Results and the Nature of Human Mind
 Gödel, Turing, the Undecidability Results and the Nature of Human Mind Riccardo Bruni riccardobruni@hotmail.com Dipartimento di Filosofia Università degli Studi di Firenze (Italy) Computability in Europe
Gödel, Turing, the Undecidability Results and the Nature of Human Mind Riccardo Bruni riccardobruni@hotmail.com Dipartimento di Filosofia Università degli Studi di Firenze (Italy) Computability in Europe
Philosophy of Mathematics Structuralism
 Philosophy of Mathematics Structuralism Owen Griffiths oeg21@cam.ac.uk St John s College, Cambridge 17/11/15 Neo-Fregeanism Last week, we considered recent attempts to revive Fregean logicism. Analytic
Philosophy of Mathematics Structuralism Owen Griffiths oeg21@cam.ac.uk St John s College, Cambridge 17/11/15 Neo-Fregeanism Last week, we considered recent attempts to revive Fregean logicism. Analytic
Series, Parallel, and other Resistance
 EELE 2310 Analysis Lecture 3 Equivalent s Series, Parallel, Delta-to-Wye, Voltage Divider and Current Divider Rules Dr Hala El-Khozondar Series, Parallel, and other Resistance Equivalent s ١ Overview Series,
EELE 2310 Analysis Lecture 3 Equivalent s Series, Parallel, Delta-to-Wye, Voltage Divider and Current Divider Rules Dr Hala El-Khozondar Series, Parallel, and other Resistance Equivalent s ١ Overview Series,
Chapter 1 Review of Equations and Inequalities
 Chapter 1 Review of Equations and Inequalities Part I Review of Basic Equations Recall that an equation is an expression with an equal sign in the middle. Also recall that, if a question asks you to solve
Chapter 1 Review of Equations and Inequalities Part I Review of Basic Equations Recall that an equation is an expression with an equal sign in the middle. Also recall that, if a question asks you to solve
Algorithms for quantum computers. Andrew Childs Department of Combinatorics & Optimization and Institute for Quantum Computing University of Waterloo
 Algorithms for quantum computers Andrew Childs Department of Combinatorics & Optimization and Institute for Quantum Computing University of Waterloo What is a computer? A means for performing calculations
Algorithms for quantum computers Andrew Childs Department of Combinatorics & Optimization and Institute for Quantum Computing University of Waterloo What is a computer? A means for performing calculations
Quadratic Equations Part I
 Quadratic Equations Part I Before proceeding with this section we should note that the topic of solving quadratic equations will be covered in two sections. This is done for the benefit of those viewing
Quadratic Equations Part I Before proceeding with this section we should note that the topic of solving quadratic equations will be covered in two sections. This is done for the benefit of those viewing
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Basic Concepts Paul Dawkins Table of Contents Preface... Basic Concepts... 1 Introduction... 1 Definitions... Direction Fields... 8 Final Thoughts...19 007 Paul Dawkins i http://tutorial.math.lamar.edu/terms.aspx
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Basic Concepts Paul Dawkins Table of Contents Preface... Basic Concepts... 1 Introduction... 1 Definitions... Direction Fields... 8 Final Thoughts...19 007 Paul Dawkins i http://tutorial.math.lamar.edu/terms.aspx
Probability Year 9. Terminology
 Probability Year 9 Terminology Probability measures the chance something happens. Formally, we say it measures how likely is the outcome of an event. We write P(result) as a shorthand. An event is some
Probability Year 9 Terminology Probability measures the chance something happens. Formally, we say it measures how likely is the outcome of an event. We write P(result) as a shorthand. An event is some
SYDE 112, LECTURE 7: Integration by Parts
 SYDE 112, LECTURE 7: Integration by Parts 1 Integration By Parts Consider trying to take the integral of xe x dx. We could try to find a substitution but would quickly grow frustrated there is no substitution
SYDE 112, LECTURE 7: Integration by Parts 1 Integration By Parts Consider trying to take the integral of xe x dx. We could try to find a substitution but would quickly grow frustrated there is no substitution
MITOCW ocw-18_02-f07-lec02_220k
 MITOCW ocw-18_02-f07-lec02_220k The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
MITOCW ocw-18_02-f07-lec02_220k The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free.
Instructor (Brad Osgood)
 TheFourierTransformAndItsApplications-Lecture26 Instructor (Brad Osgood): Relax, but no, no, no, the TV is on. It's time to hit the road. Time to rock and roll. We're going to now turn to our last topic
TheFourierTransformAndItsApplications-Lecture26 Instructor (Brad Osgood): Relax, but no, no, no, the TV is on. It's time to hit the road. Time to rock and roll. We're going to now turn to our last topic
Discrete Probability
 Discrete Probability Mark Muldoon School of Mathematics, University of Manchester M05: Mathematical Methods, January 30, 2007 Discrete Probability - p. 1/38 Overview Mutually exclusive Independent More
Discrete Probability Mark Muldoon School of Mathematics, University of Manchester M05: Mathematical Methods, January 30, 2007 Discrete Probability - p. 1/38 Overview Mutually exclusive Independent More
For True Conditionalizers Weisberg s Paradox is a False Alarm
 For True Conditionalizers Weisberg s Paradox is a False Alarm Franz Huber Department of Philosophy University of Toronto franz.huber@utoronto.ca http://huber.blogs.chass.utoronto.ca/ July 7, 2014; final
For True Conditionalizers Weisberg s Paradox is a False Alarm Franz Huber Department of Philosophy University of Toronto franz.huber@utoronto.ca http://huber.blogs.chass.utoronto.ca/ July 7, 2014; final
Gualtiero Piccinini: Physical Computation: A Mechanistic Account
 Minds & Machines DOI 10.1007/s11023-016-9397-y Gualtiero Piccinini: Physical Computation: A Mechanistic Account Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2015, ix + 313, 35.00, ISBN 9780199658855 Matteo Colombo
Minds & Machines DOI 10.1007/s11023-016-9397-y Gualtiero Piccinini: Physical Computation: A Mechanistic Account Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2015, ix + 313, 35.00, ISBN 9780199658855 Matteo Colombo
For True Conditionalizers Weisberg s Paradox is a False Alarm
 For True Conditionalizers Weisberg s Paradox is a False Alarm Franz Huber Abstract: Weisberg (2009) introduces a phenomenon he terms perceptual undermining He argues that it poses a problem for Jeffrey
For True Conditionalizers Weisberg s Paradox is a False Alarm Franz Huber Abstract: Weisberg (2009) introduces a phenomenon he terms perceptual undermining He argues that it poses a problem for Jeffrey
A Computational Foundation for the Study of Cognition
 A Computational Foundation for the Study of Cognition David J. Chalmers School of Philosophy Australian National University Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia [This paper was written in 1993 but never published
A Computational Foundation for the Study of Cognition David J. Chalmers School of Philosophy Australian National University Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia [This paper was written in 1993 but never published
Complex Numbers For High School Students
 Complex Numbers For High School Students For the Love of Mathematics and Computing Saturday, October 14, 2017 Presented by: Rich Dlin Presented by: Rich Dlin Complex Numbers For High School Students 1
Complex Numbers For High School Students For the Love of Mathematics and Computing Saturday, October 14, 2017 Presented by: Rich Dlin Presented by: Rich Dlin Complex Numbers For High School Students 1
Properties of Arithmetic
 Excerpt from "Prealgebra" 205 AoPS Inc. 4 6 7 4 5 8 22 23 5 7 0 Arithmetic is being able to count up to twenty without taking o your shoes. Mickey Mouse CHAPTER Properties of Arithmetic. Why Start with
Excerpt from "Prealgebra" 205 AoPS Inc. 4 6 7 4 5 8 22 23 5 7 0 Arithmetic is being able to count up to twenty without taking o your shoes. Mickey Mouse CHAPTER Properties of Arithmetic. Why Start with
Properties of Probability
 Econ 325 Notes on Probability 1 By Hiro Kasahara Properties of Probability In statistics, we consider random experiments, experiments for which the outcome is random, i.e., cannot be predicted with certainty.
Econ 325 Notes on Probability 1 By Hiro Kasahara Properties of Probability In statistics, we consider random experiments, experiments for which the outcome is random, i.e., cannot be predicted with certainty.
Durham E-Theses. Physicalism, Mind, and the Ontology of Properties KAIDA, DAISUKE
 Durham E-Theses Physicalism, Mind, and the Ontology of Properties KAIDA, DAISUKE How to cite: KAIDA, DAISUKE (2011) Physicalism, Mind, and the Ontology of Properties, Durham theses, Durham University.
Durham E-Theses Physicalism, Mind, and the Ontology of Properties KAIDA, DAISUKE How to cite: KAIDA, DAISUKE (2011) Physicalism, Mind, and the Ontology of Properties, Durham theses, Durham University.
Math (P)Review Part I:
 Lecture 1: Math (P)Review Part I: Linear Algebra Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Fall 2017 Homework 0.0 (Due Monday!) Exercises will be a bit harder / more rigorous than what you will do for the rest
Lecture 1: Math (P)Review Part I: Linear Algebra Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Fall 2017 Homework 0.0 (Due Monday!) Exercises will be a bit harder / more rigorous than what you will do for the rest
- a reversed conditional; if a conditional is p q, than its converse is q p
 Lesson 5: Inductive and Deductive Reasoning Conditional - a statement that tells if one thing happens, another will follow; stated as if p, then q written as p q; Contrapositive - a type of conditional
Lesson 5: Inductive and Deductive Reasoning Conditional - a statement that tells if one thing happens, another will follow; stated as if p, then q written as p q; Contrapositive - a type of conditional
Reductions in Computability Theory
 Reductions in Computability Theory Prakash Panangaden 9 th November 2015 The concept of reduction is central to computability and complexity theory. The phrase P reduces to Q is often used in a confusing
Reductions in Computability Theory Prakash Panangaden 9 th November 2015 The concept of reduction is central to computability and complexity theory. The phrase P reduces to Q is often used in a confusing
1.3 Rate of Change and Initial Value
 1.3 Rate of Change and Initial Value There are a couple of very important numerical (or quantitative) qualities of functions that we use. We like to know where functions start (initial value) and how steep
1.3 Rate of Change and Initial Value There are a couple of very important numerical (or quantitative) qualities of functions that we use. We like to know where functions start (initial value) and how steep
Chemical Applications of Symmetry and Group Theory Prof. Manabendra Chandra Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur.
 Chemical Applications of Symmetry and Group Theory Prof. Manabendra Chandra Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture 01 Hello and welcome to the course, whose title is Application
Chemical Applications of Symmetry and Group Theory Prof. Manabendra Chandra Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture 01 Hello and welcome to the course, whose title is Application
The Basics COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. chapter. Algebra is a very logical way to solve
 chapter 1 The Basics Algebra is a very logical way to solve problems both theoretically and practically. You need to know a number of things. You already know arithmetic of whole numbers. You will review
chapter 1 The Basics Algebra is a very logical way to solve problems both theoretically and practically. You need to know a number of things. You already know arithmetic of whole numbers. You will review
Lecture 12: Arguments for the absolutist and relationist views of space
 12.1 432018 PHILOSOPHY OF PHYSICS (Spring 2002) Lecture 12: Arguments for the absolutist and relationist views of space Preliminary reading: Sklar, pp. 19-25. Now that we have seen Newton s and Leibniz
12.1 432018 PHILOSOPHY OF PHYSICS (Spring 2002) Lecture 12: Arguments for the absolutist and relationist views of space Preliminary reading: Sklar, pp. 19-25. Now that we have seen Newton s and Leibniz
Introduction to Systems of Equations
 Introduction to Systems of Equations Introduction A system of linear equations is a list of m linear equations in a common set of variables x, x,, x n. a, x + a, x + Ù + a,n x n = b a, x + a, x + Ù + a,n
Introduction to Systems of Equations Introduction A system of linear equations is a list of m linear equations in a common set of variables x, x,, x n. a, x + a, x + Ù + a,n x n = b a, x + a, x + Ù + a,n
Department of Philosophy TCD. Is Physicalism the True Philosophy?
 Department of Philosophy TCD Is Physicalism the True Philosophy? Tom Farrell Department of Philosophy TCD Department of Clinical Medicine RCSI Department of Anatomy RCSI TCD 20 March 2018 Philosophy? Casual
Department of Philosophy TCD Is Physicalism the True Philosophy? Tom Farrell Department of Philosophy TCD Department of Clinical Medicine RCSI Department of Anatomy RCSI TCD 20 March 2018 Philosophy? Casual
Computational Tasks and Models
 1 Computational Tasks and Models Overview: We assume that the reader is familiar with computing devices but may associate the notion of computation with specific incarnations of it. Our first goal is to
1 Computational Tasks and Models Overview: We assume that the reader is familiar with computing devices but may associate the notion of computation with specific incarnations of it. Our first goal is to
SOLUTION: SOLUTION: SOLUTION:
 Convert R and S into nondeterministic finite automata N1 and N2. Given a string s, if we know the states N1 and N2 may reach when s[1...i] has been read, we are able to derive the states N1 and N2 may
Convert R and S into nondeterministic finite automata N1 and N2. Given a string s, if we know the states N1 and N2 may reach when s[1...i] has been read, we are able to derive the states N1 and N2 may
1 Deterministic Turing Machines
 Time and Space Classes Exposition by William Gasarch 1 Deterministic Turing Machines Turing machines are a model of computation. It is believed that anything that can be computed can be computed by a Turing
Time and Space Classes Exposition by William Gasarch 1 Deterministic Turing Machines Turing machines are a model of computation. It is believed that anything that can be computed can be computed by a Turing
Great Theoretical Ideas in Computer Science. Lecture 7: Introduction to Computational Complexity
 15-251 Great Theoretical Ideas in Computer Science Lecture 7: Introduction to Computational Complexity September 20th, 2016 What have we done so far? What will we do next? What have we done so far? > Introduction
15-251 Great Theoretical Ideas in Computer Science Lecture 7: Introduction to Computational Complexity September 20th, 2016 What have we done so far? What will we do next? What have we done so far? > Introduction
Skepticism and Structuralism
 Skepticism and Structuralism Structuralism with respect to space and/or spatial relations is of considerable interest. Consider what I will call the distance relation: x and y stand in this relation just
Skepticism and Structuralism Structuralism with respect to space and/or spatial relations is of considerable interest. Consider what I will call the distance relation: x and y stand in this relation just
1 Deterministic Turing Machines
 Time and Space Classes Exposition by William Gasarch 1 Deterministic Turing Machines Turing machines are a model of computation. It is believed that anything that can be computed can be computed by a Turing
Time and Space Classes Exposition by William Gasarch 1 Deterministic Turing Machines Turing machines are a model of computation. It is believed that anything that can be computed can be computed by a Turing
THE SIMPLE PROOF OF GOLDBACH'S CONJECTURE. by Miles Mathis
 THE SIMPLE PROOF OF GOLDBACH'S CONJECTURE by Miles Mathis miles@mileswmathis.com Abstract Here I solve Goldbach's Conjecture by the simplest method possible. I do this by first calculating probabilites
THE SIMPLE PROOF OF GOLDBACH'S CONJECTURE by Miles Mathis miles@mileswmathis.com Abstract Here I solve Goldbach's Conjecture by the simplest method possible. I do this by first calculating probabilites
What It Feels like to Be in a Superposition
 .. 6... The D y namics b y Itself What It Feels like to Be in a Superposition The trouble with the quantum-mechanical equations of motion, according to Chapter 4 (and according to the conventional wisdom),
.. 6... The D y namics b y Itself What It Feels like to Be in a Superposition The trouble with the quantum-mechanical equations of motion, according to Chapter 4 (and according to the conventional wisdom),
Figure 1: Doing work on a block by pushing it across the floor.
 Work Let s imagine I have a block which I m pushing across the floor, shown in Figure 1. If I m moving the block at constant velocity, then I know that I have to apply a force to compensate the effects
Work Let s imagine I have a block which I m pushing across the floor, shown in Figure 1. If I m moving the block at constant velocity, then I know that I have to apply a force to compensate the effects
Turing Machines Part Three
 Turing Machines Part Three What problems can we solve with a computer? What kind of computer? Very Important Terminology Let M be a Turing machine. M accepts a string w if it enters an accept state when
Turing Machines Part Three What problems can we solve with a computer? What kind of computer? Very Important Terminology Let M be a Turing machine. M accepts a string w if it enters an accept state when
The Evolution and Discovery of the Species of Equality in Euclid s Elements
 From the SelectedWorks of Lee T Nutini 2010 The Evolution and Discovery of the Species of Equality in Euclid s Elements Lee T Nutini Available at: https://works.bepress.com/nutini/2/ Nutini 1 The Evolution
From the SelectedWorks of Lee T Nutini 2010 The Evolution and Discovery of the Species of Equality in Euclid s Elements Lee T Nutini Available at: https://works.bepress.com/nutini/2/ Nutini 1 The Evolution
Basic algebra and graphing for electric circuits
 Basic algebra and graphing for electric circuits This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Basic algebra and graphing for electric circuits This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Solving with Absolute Value
 Solving with Absolute Value Who knew two little lines could cause so much trouble? Ask someone to solve the equation 3x 2 = 7 and they ll say No problem! Add just two little lines, and ask them to solve
Solving with Absolute Value Who knew two little lines could cause so much trouble? Ask someone to solve the equation 3x 2 = 7 and they ll say No problem! Add just two little lines, and ask them to solve
A physical analysis of mechanical computability. Answers
 A physical analysis of mechanical computability Steven Lindell Department of Computer Science Haverford College Answers Most talks: questions answers This talk: answers questions Popular misconception
A physical analysis of mechanical computability Steven Lindell Department of Computer Science Haverford College Answers Most talks: questions answers This talk: answers questions Popular misconception
Is Mind-Brain Interactionism really in trouble?
 "There once was a ghost who opened Einstein's office door... in doing this he thought he could disprove the conservation of energy law." 1 Did he? The law of conservation of energy-mass has had quite an
"There once was a ghost who opened Einstein's office door... in doing this he thought he could disprove the conservation of energy law." 1 Did he? The law of conservation of energy-mass has had quite an
