ECE 3060 VLSI and Advanced Digital Design. Testing
|
|
|
- Bertha Carter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ECE 3060 VLSI and Advanced Digital Design Testing
2 Outline Definitions Faults and Errors Fault models and definitions Fault Detection Undetectable Faults can be used in synthesis Fault Simulation Observability of Faults Design for Testability test point insertion scan registers Built-in Self Test Boundary Scan
3 Test Cost A large percentage (5-40%) of the manufacturing cost of a VLSI chip is due to test Cost is larger for larger circuits more functionality in a "System-on-a-Chip" means more potential faults brute-force "stimulate all possible input vectors" can take centuries or more Mixed-technology test analog, digital on same chip
4 Testing: Definition Testing = experiment in which a system is stimulated and its response analyzed in order to determine if the system will behave correctly under arbitrary input stimulus and prescribed failure mechanisms input stimulus observed response 123 shorts opens failure mechanisms
5 Failure mechanisms Failure mechanisms can be analyzed by looking at how they affect system behaviour at different levels of abstraction messages system level programs/data structures processor level instructions/words instruction set level logic values/words register level logic values logic level Control Data
6 How to Test (1) Stimulate the Integrated Circuit (IC) and observe the response using Automatic Test Equipment (ATE) (2) Run test/diagnostic program on the processor IC (3) Have one or more subsystems test each other by sending and receiving messages
7 Definitions Fault = Defect = Physical failure e.g., shorts, opens, near-open, near-short Error = effect of fault, i.e., incorrect logic value due to fault line stuck-at-0 Error Fault
8 Source of Errors Note that errors may be due to design errors or fabrication errors Design errors: incomplete or inconsistent specification incorrect mappings between different levels of design violations of design rules Fabrication errors: greater than λ error in placement of metal/poly/via/etc. wrong components incorrect wiring shorts caused by improper soldering
9 Permanent always present Intermittent Nature of Faults occurs at regular intervals Transient one time and gone
10 Fault Model Model describes nature of the fault stuck at 0 stuck at 1 stuck open Vdd stuck closed
11 Stuck Closed: Wired-AND or Wired-OR Wired-AND 8a b c d output Wired-OR 8a b c d output
12 Test Evaluation Fault coverage IC with n nodes and z faults coverage = # of faults detected / z Obtained via fault simulation
13 Summary of Definitions Testing: definition experiment in which a system is stimulated and its response analyzed in order to determine if the system will behave correctly under arbitrary input stimulus and prescribed failure mechanisms Faults and Errors Fault = Defect = Physical failure Error = effect of fault, i.e., incorrect logic value Fault Models stuck at 0, stuck at 1, stuck open, stuck closed Fault coverage
14
15
16 Fault Detection x N Z(x) x = input Z(t) = response x N f Z f (x) Test set = {t 1,t 2,, t m } Z(t 1 ), Z(t 2 ),, Z(t m ) Z f (t 1 ), Z f (t 2 ),, Z f (t m ) Definition: t detects f iff Z f (t)!= Z(t)
17 Test Set for Fault f x 1 Z 1 WIRED-OR fault x 2 Z x 2 3 Z 1 = x 1 x 2, Z 2 = x 2 x 3 Z 1f = x 1 (x 2 + x 3 ), Z 2f = x 2 + x 3 t = {0,0,1} detects f Set of all tests that detect f is given by Z(x) Z f (x) = 1
18 Example
19 Example (continued) Note in the example error propogation sensitized path A gate whose output is sensitized to a fault f must have at least one of its inputs sensitized to the fault as well
20 Undetectable Fault a stuck at 1 fault on input a is undetectable
21 Simplification of Previous Circuit can use discovery of an undetectable fault to trigger logic minimizer on circuit with undetectable fault
22 Synthesis and Testability Assumptions combinational circuit single or multiple stuck-at faults Redundancy removal use tests to search for untestable faults and reduce circuit Algorithm: if stuck-at-0 on net y is untestable 8set y = 0 8propagate constant, reducing logic if stuck-at-1 on net y is untestable 8set y = 1 8propagate constant, reducing logic
23 Example
24 Fault Simulation Fault simulation = simulation of the circuit in the presence of faults To evaluate (grade) a test, we use Y = manufacturing yield = probability that a manufactured circuit is defect-free DL = defect level = probability of shipping a defective product d = defect coverage of test DL = 1 - Y 1-d if Y = 0.5 and we desire DL = 0.01 => d = 99% fault coverage
25 Generate initial T = test vectors Evaluate T no Sufficient fault coverage? yes done Modify T
26 Select target fault Generate test no more faults done Fault simulate Discard detected faults Fault simulation target faults during test generation used to construct fault dictionaries
27 Observability Problem Not all faults can be observed right away need to propagate faults to output For n FFs 2 n states 2 n 2 n state sequences While searching for a test sequence, save every sequence that propagates an error to an internal state variable
28 Example suppose y 1 = 0 and y 2 = 0 (if not, another case)
29 Example (continued) solution: test sequence I = (1,1,1) which is 3 cycles!
30 Design for Testability Status (normal, inoperable, degraded) of a device to be determined DFT allows cost-effective development of tests to determine status Controllability setting net y to a 1 (1-controllability) setting net y to a 0 (0-controllability) Observability ability to drive an error from net y to a primary output
31 Test Point Insertion C1. C2 C1 CP0. C2 CP0 for 0-injection C1 CP0 CP1. C2 CP1 for 1-injection Design circuits to be initializable Partition large circuits into smaller subcircuits in order to reduce test cost
32 Scan Registers test N/T = 0 => data loaded from data line Din normal mode N/T = 1 => data loaded from test input D1 test mode 0 1 Din test D Q D2 0 1 N/T CLK 0 1 D Q D Q... Dn 0 1 D Q N/T CLK
33 Scan Register Usage BIST Built-In-Self-Test Boundary Scan
34 Scan Register Usage C1 D0,,D7 C2 replace with C1 D0,,D7 scan reg C2 N/T test N/T = 0 => normal mode N/T = 1 => data loaded serially from test input
35 Fully Integrated Serial Scan n m x z x C1 C1 state ns state ns test_out k k n k scan reg k m z test seq: (x 1,state 1 ),,(x i,state i ) N/T responses: (z 1,ns 1 ),, (z i,ns i ) test set N/T=1, scan state 1 into scan reg. Apply x 1 to input, N/T = 0 next clock edge latches ns 1 set N/T = 1, scan out ns 1 while scanning in x 2 repeat i times
36
37
38
39
Introduction to VLSI Testing
 Introduction to 李昆忠 Kuen-Jong Lee Dept. of Electrical Engineering National Cheng-Kung University Tainan, Taiwan Class Problems to Think How are you going to test A 32 bit adder A 32 bit counter A 32Mb
Introduction to 李昆忠 Kuen-Jong Lee Dept. of Electrical Engineering National Cheng-Kung University Tainan, Taiwan Class Problems to Think How are you going to test A 32 bit adder A 32 bit counter A 32Mb
UMBC. At the system level, DFT includes boundary scan and analog test bus. The DFT techniques discussed focus on improving testability of SAFs.
 Overview Design for testability(dft) makes it possible to: Assure the detection of all faults in a circuit. Reduce the cost and time associated with test development. Reduce the execution time of performing
Overview Design for testability(dft) makes it possible to: Assure the detection of all faults in a circuit. Reduce the cost and time associated with test development. Reduce the execution time of performing
Design for Testability
 Design for Testability Outline Ad Hoc Design for Testability Techniques Method of test points Multiplexing and demultiplexing of test points Time sharing of I/O for normal working and testing modes Partitioning
Design for Testability Outline Ad Hoc Design for Testability Techniques Method of test points Multiplexing and demultiplexing of test points Time sharing of I/O for normal working and testing modes Partitioning
Single Stuck-At Fault Model Other Fault Models Redundancy and Untestable Faults Fault Equivalence and Fault Dominance Method of Boolean Difference
 Single Stuck-At Fault Model Other Fault Models Redundancy and Untestable Faults Fault Equivalence and Fault Dominance Method of Boolean Difference Copyright 1998 Elizabeth M. Rudnick 1 Modeling the effects
Single Stuck-At Fault Model Other Fault Models Redundancy and Untestable Faults Fault Equivalence and Fault Dominance Method of Boolean Difference Copyright 1998 Elizabeth M. Rudnick 1 Modeling the effects
Design for Testability
 Design for Testability Outline Ad Hoc Design for Testability Techniques Method of test points Multiplexing and demultiplexing of test points Time sharing of I/O for normal working and testing modes Partitioning
Design for Testability Outline Ad Hoc Design for Testability Techniques Method of test points Multiplexing and demultiplexing of test points Time sharing of I/O for normal working and testing modes Partitioning
Fault Modeling. Fault Modeling Outline
 Fault Modeling Outline Single Stuck-t Fault Model Other Fault Models Redundancy and Untestable Faults Fault Equivalence and Fault Dominance Method of oolean Difference Copyright 1998 Elizabeth M. Rudnick
Fault Modeling Outline Single Stuck-t Fault Model Other Fault Models Redundancy and Untestable Faults Fault Equivalence and Fault Dominance Method of oolean Difference Copyright 1998 Elizabeth M. Rudnick
Fault Modeling. 李昆忠 Kuen-Jong Lee. Dept. of Electrical Engineering National Cheng-Kung University Tainan, Taiwan. VLSI Testing Class
 Fault Modeling 李昆忠 Kuen-Jong Lee Dept. of Electrical Engineering National Cheng-Kung University Tainan, Taiwan Class Fault Modeling Some Definitions Why Modeling Faults Various Fault Models Fault Detection
Fault Modeling 李昆忠 Kuen-Jong Lee Dept. of Electrical Engineering National Cheng-Kung University Tainan, Taiwan Class Fault Modeling Some Definitions Why Modeling Faults Various Fault Models Fault Detection
VLSI Design I. Defect Mechanisms and Fault Models
 VLSI Design I Defect Mechanisms and Fault Models He s dead Jim... Overview Defects Fault models Goal: You know the difference between design and fabrication defects. You know sources of defects and you
VLSI Design I Defect Mechanisms and Fault Models He s dead Jim... Overview Defects Fault models Goal: You know the difference between design and fabrication defects. You know sources of defects and you
Hardware testing and design for testability. EE 3610 Digital Systems
 EE 3610: Digital Systems 1 Hardware testing and design for testability Introduction A Digital System requires testing before and after it is manufactured 2 Level 1: behavioral modeling and test benches
EE 3610: Digital Systems 1 Hardware testing and design for testability Introduction A Digital System requires testing before and after it is manufactured 2 Level 1: behavioral modeling and test benches
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison. Fall Final Examination
 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison ECE 553: Testing and Testable Design of Digital Systems Fall 2013-2014 Final Examination CLOSED BOOK Kewal K. Saluja Date:
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison ECE 553: Testing and Testable Design of Digital Systems Fall 2013-2014 Final Examination CLOSED BOOK Kewal K. Saluja Date:
Logic BIST. Sungho Kang Yonsei University
 Logic BIST Sungho Kang Yonsei University Outline Introduction Basics Issues Weighted Random Pattern Generation BIST Architectures Deterministic BIST Conclusion 2 Built In Self Test Test/ Normal Input Pattern
Logic BIST Sungho Kang Yonsei University Outline Introduction Basics Issues Weighted Random Pattern Generation BIST Architectures Deterministic BIST Conclusion 2 Built In Self Test Test/ Normal Input Pattern
Chapter 2 Fault Modeling
 Chapter 2 Fault Modeling Jin-Fu Li Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan Outline Why Model Faults? Fault Models (Faults)
Chapter 2 Fault Modeling Jin-Fu Li Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan Outline Why Model Faults? Fault Models (Faults)
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison. Fall Midterm Examination CLOSED BOOK
 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison ECE 553: Testing and Testable Design of Digital Systems Fall 203-204 Midterm Examination CLOSED OOK Kewal K. Saluja Date:
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison ECE 553: Testing and Testable Design of Digital Systems Fall 203-204 Midterm Examination CLOSED OOK Kewal K. Saluja Date:
EECS 579: Logic and Fault Simulation. Simulation
 EECS 579: Logic and Fault Simulation Simulation: Use of computer software models to verify correctness Fault Simulation: Use of simulation for fault analysis and ATPG Circuit description Input data for
EECS 579: Logic and Fault Simulation Simulation: Use of computer software models to verify correctness Fault Simulation: Use of simulation for fault analysis and ATPG Circuit description Input data for
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 23: April 17, 2018 I/O Circuits, Inductive Noise, CLK Generation Lecture Outline! Packaging! Variation and Testing! I/O Circuits! Inductive
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 23: April 17, 2018 I/O Circuits, Inductive Noise, CLK Generation Lecture Outline! Packaging! Variation and Testing! I/O Circuits! Inductive
Outline Fault Simulation
 K.T. Tim Cheng, 4_fault_sim, v. Outline Fault Simulation Applications of fault simulation Fault coverage vs product quality Fault simulation scenarios Fault simulation algorithms Fault sampling K.T. Tim
K.T. Tim Cheng, 4_fault_sim, v. Outline Fault Simulation Applications of fault simulation Fault coverage vs product quality Fault simulation scenarios Fault simulation algorithms Fault sampling K.T. Tim
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison. Fall Midterm Examination CLOSED BOOK
 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison ECE 553: Testing and Testable Design of Digital Systems Fall 2014-2015 Midterm Examination CLOSED BOOK Kewal K. Saluja
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison ECE 553: Testing and Testable Design of Digital Systems Fall 2014-2015 Midterm Examination CLOSED BOOK Kewal K. Saluja
Lecture 5 Fault Modeling
 Lecture 5 Fault Modeling Why model faults? Some real defects in VLSI and PCB Common fault models Stuck-at faults Single stuck-at faults Fault equivalence Fault dominance and checkpoint theorem Classes
Lecture 5 Fault Modeling Why model faults? Some real defects in VLSI and PCB Common fault models Stuck-at faults Single stuck-at faults Fault equivalence Fault dominance and checkpoint theorem Classes
Fault Tolerant Computing CS 530 Fault Modeling. Yashwant K. Malaiya Colorado State University
 CS 530 Fault Modeling Yashwant K. Malaiya Colorado State University 1 Objectives The number of potential defects in a unit under test is extremely large. A fault-model presumes that most of the defects
CS 530 Fault Modeling Yashwant K. Malaiya Colorado State University 1 Objectives The number of potential defects in a unit under test is extremely large. A fault-model presumes that most of the defects
CSE241 VLSI Digital Circuits Winter Lecture 07: Timing II
 CSE241 VLSI Digital Circuits Winter 2003 Lecture 07: Timing II CSE241 L3 ASICs.1 Delay Calculation Cell Fall Cap\Tr 0.05 0.2 0.5 0.01 0.02 0.16 0.30 0.5 2.0 0.04 0.32 0.178 0.08 0.64 0.60 1.20 0.1ns 0.147ns
CSE241 VLSI Digital Circuits Winter 2003 Lecture 07: Timing II CSE241 L3 ASICs.1 Delay Calculation Cell Fall Cap\Tr 0.05 0.2 0.5 0.01 0.02 0.16 0.30 0.5 2.0 0.04 0.32 0.178 0.08 0.64 0.60 1.20 0.1ns 0.147ns
Chapter 7. Sequential Circuits Registers, Counters, RAM
 Chapter 7. Sequential Circuits Registers, Counters, RAM Register - a group of binary storage elements suitable for holding binary info A group of FFs constitutes a register Commonly used as temporary storage
Chapter 7. Sequential Circuits Registers, Counters, RAM Register - a group of binary storage elements suitable for holding binary info A group of FFs constitutes a register Commonly used as temporary storage
IHS 3: Test of Digital Systems R.Ubar, A. Jutman, H-D. Wuttke
 IHS 3: Test of Digital Systems R.Ubar, A. Jutman, H-D. Wuttke Integrierte Hard- und Softwaresysteme RT-Level Design data path and control path on RT-level RT level simulation Functional units (F1,..,F4)
IHS 3: Test of Digital Systems R.Ubar, A. Jutman, H-D. Wuttke Integrierte Hard- und Softwaresysteme RT-Level Design data path and control path on RT-level RT level simulation Functional units (F1,..,F4)
Design for Manufacturability and Power Estimation. Physical issues verification (DSM)
 Design for Manufacturability and Power Estimation Lecture 25 Alessandra Nardi Thanks to Prof. Jan Rabaey and Prof. K. Keutzer Physical issues verification (DSM) Interconnects Signal Integrity P/G integrity
Design for Manufacturability and Power Estimation Lecture 25 Alessandra Nardi Thanks to Prof. Jan Rabaey and Prof. K. Keutzer Physical issues verification (DSM) Interconnects Signal Integrity P/G integrity
S No. Questions Bloom s Taxonomy Level UNIT-I
 GROUP-A (SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS) S No. Questions Bloom s UNIT-I 1 Define oxidation & Classify different types of oxidation Remember 1 2 Explain about Ion implantation Understand 1 3 Describe lithography
GROUP-A (SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS) S No. Questions Bloom s UNIT-I 1 Define oxidation & Classify different types of oxidation Remember 1 2 Explain about Ion implantation Understand 1 3 Describe lithography
Methodology to combine Formal and Fault simulator to measure safety metrics
 Methodology to combine Formal and Fault simulator to measure safety metrics Jain Gaurav, Infineon Technologies AP Pte LTD, Singapore Kadambi Ranga, Infineon Technologies AP Pte LTD, Singapore Bandlamudi
Methodology to combine Formal and Fault simulator to measure safety metrics Jain Gaurav, Infineon Technologies AP Pte LTD, Singapore Kadambi Ranga, Infineon Technologies AP Pte LTD, Singapore Bandlamudi
VLSI Physical Design Prof. Indranil Sengupta Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 VLSI Physical Design Prof. Indranil Sengupta Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 54 Design for Testability So, in the last lecture we talked
VLSI Physical Design Prof. Indranil Sengupta Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 54 Design for Testability So, in the last lecture we talked
T st Cost Reduction LG Electronics Lee Y, ong LG Electronics 2009
 Test Cost Reduction LG Electronics Lee, Yong LG Electronics 2009 Contents Introduction Key factors for test cost reduction in DFT Test vector volume Low cost ATE Test time Reuse a large block Test cost
Test Cost Reduction LG Electronics Lee, Yong LG Electronics 2009 Contents Introduction Key factors for test cost reduction in DFT Test vector volume Low cost ATE Test time Reuse a large block Test cost
Clock signal in digital circuit is responsible for synchronizing the transfer to the data between processing elements.
 1 2 Introduction Clock signal in digital circuit is responsible for synchronizing the transfer to the data between processing elements. Defines the precise instants when the circuit is allowed to change
1 2 Introduction Clock signal in digital circuit is responsible for synchronizing the transfer to the data between processing elements. Defines the precise instants when the circuit is allowed to change
Terminology and Concepts
 Terminology and Concepts Prof. Naga Kandasamy 1 Goals of Fault Tolerance Dependability is an umbrella term encompassing the concepts of reliability, availability, performability, safety, and testability.
Terminology and Concepts Prof. Naga Kandasamy 1 Goals of Fault Tolerance Dependability is an umbrella term encompassing the concepts of reliability, availability, performability, safety, and testability.
FAULT MODELING. Chapter Defects, Errors, and Faults
 Chapter 4 FAULT MODELING... The extreme difficulty of obtaining solutions by conventional mathematical analysis has led in the past to the use of highly unrealistic models simply because they led to equations
Chapter 4 FAULT MODELING... The extreme difficulty of obtaining solutions by conventional mathematical analysis has led in the past to the use of highly unrealistic models simply because they led to equations
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 26 - Faults and Error Correction. Types of Faults in Digital Designs
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 26 - Faults and Error Correction April 25, 2013 John Wawrzynek 1 Types of Faults in Digital Designs Design Bugs (function, timing, power draw) detected and corrected at
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 26 - Faults and Error Correction April 25, 2013 John Wawrzynek 1 Types of Faults in Digital Designs Design Bugs (function, timing, power draw) detected and corrected at
Introduction EE 224: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL CIRCUITS & COMPUTER DESIGN. Lecture 6: Sequential Logic 3 Registers & Counters 5/9/2010
 EE 224: INTROUCTION TO IGITAL CIRCUITS & COMPUTER ESIGN Lecture 6: Sequential Logic 3 Registers & Counters 05/10/2010 Avinash Kodi, kodi@ohio.edu Introduction 2 A Flip-Flop stores one bit of information
EE 224: INTROUCTION TO IGITAL CIRCUITS & COMPUTER ESIGN Lecture 6: Sequential Logic 3 Registers & Counters 05/10/2010 Avinash Kodi, kodi@ohio.edu Introduction 2 A Flip-Flop stores one bit of information
ECE 1767 University of Toronto
 Applications Why Two Fault Simulators Never Agree General Techniques Parallel Pattern Simulation Inactive Fault Removal Critical Path Tracing Fault Sampling Statistical Fault Analysis ECE 767 Fault grading
Applications Why Two Fault Simulators Never Agree General Techniques Parallel Pattern Simulation Inactive Fault Removal Critical Path Tracing Fault Sampling Statistical Fault Analysis ECE 767 Fault grading
Xarxes de distribució del senyal de. interferència electromagnètica, consum, soroll de conmutació.
 Xarxes de distribució del senyal de rellotge. Clock skew, jitter, interferència electromagnètica, consum, soroll de conmutació. (transparències generades a partir de la presentació de Jan M. Rabaey, Anantha
Xarxes de distribució del senyal de rellotge. Clock skew, jitter, interferència electromagnètica, consum, soroll de conmutació. (transparències generades a partir de la presentació de Jan M. Rabaey, Anantha
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 23: April 13, 2017 Variation; I/O Circuits, Inductive Noise Lecture Outline! Design Quality " Variation! Packaging! Variation and Testing!
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 23: April 13, 2017 Variation; I/O Circuits, Inductive Noise Lecture Outline! Design Quality " Variation! Packaging! Variation and Testing!
VLSI Design Verification and Test Simulation CMPE 646. Specification. Design(netlist) True-value Simulator
 Design Verification Simulation used for ) design verification: verify the correctness of the design and 2) test verification. Design verification: Response analysis Specification Design(netlist) Critical
Design Verification Simulation used for ) design verification: verify the correctness of the design and 2) test verification. Design verification: Response analysis Specification Design(netlist) Critical
GMU, ECE 680 Physical VLSI Design 1
 ECE680: Physical VLSI Design Chapter VII Timing Issues in Digital Circuits (chapter 10 in textbook) GMU, ECE 680 Physical VLSI Design 1 Synchronous Timing (Fig. 10 1) CLK In R Combinational 1 R Logic 2
ECE680: Physical VLSI Design Chapter VII Timing Issues in Digital Circuits (chapter 10 in textbook) GMU, ECE 680 Physical VLSI Design 1 Synchronous Timing (Fig. 10 1) CLK In R Combinational 1 R Logic 2
Reduction of Detected Acceptable Faults for Yield Improvement via Error-Tolerance
 Reduction of Detected Acceptable Faults for Yield Improvement via Error-Tolerance Tong-Yu Hsieh and Kuen-Jong Lee Department of Electrical Engineering National Cheng Kung University Tainan, Taiwan 70101
Reduction of Detected Acceptable Faults for Yield Improvement via Error-Tolerance Tong-Yu Hsieh and Kuen-Jong Lee Department of Electrical Engineering National Cheng Kung University Tainan, Taiwan 70101
EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits. Lecture 19: Timing Analysis
 EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits Lecture 19: Timing Analysis Outline Timing parameters Clock nonidealities (skew and jitter) Impact of Clk skew on timing Impact of Clk jitter on timing Flip-flop-
EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits Lecture 19: Timing Analysis Outline Timing parameters Clock nonidealities (skew and jitter) Impact of Clk skew on timing Impact of Clk jitter on timing Flip-flop-
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN. Week 9 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 9 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering TIMING ANALYSIS Overview Circuits do not respond instantaneously to input changes
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 9 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering TIMING ANALYSIS Overview Circuits do not respond instantaneously to input changes
ELEC516 Digital VLSI System Design and Design Automation (spring, 2010) Assignment 4 Reference solution
 ELEC516 Digital VLSI System Design and Design Automation (spring, 010) Assignment 4 Reference solution 1) Pulse-plate 1T DRAM cell a) Timing diagrams for nodes and Y when writing 0 and 1 Timing diagram
ELEC516 Digital VLSI System Design and Design Automation (spring, 010) Assignment 4 Reference solution 1) Pulse-plate 1T DRAM cell a) Timing diagrams for nodes and Y when writing 0 and 1 Timing diagram
DVClub Europe Formal fault analysis for ISO fault metrics on real world designs. Jörg Große Product Manager Functional Safety November 2016
 DVClub Europe Formal fault analysis for ISO 26262 fault metrics on real world designs Jörg Große Product Manager Functional Safety November 2016 Page 1 11/27/2016 Introduction Functional Safety The objective
DVClub Europe Formal fault analysis for ISO 26262 fault metrics on real world designs Jörg Große Product Manager Functional Safety November 2016 Page 1 11/27/2016 Introduction Functional Safety The objective
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2012 Lecture 17: Dynamic Sequential Circuits And Timing Issues
 CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2012 Lecture 17: Dynamic Sequential Circuits And Timing Issues [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan,
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2012 Lecture 17: Dynamic Sequential Circuits And Timing Issues [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan,
CHAPTER 9: SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS
 CHAPTER 9: ASYNCHRONOUS SEUENTIAL CIRCUITS Chapter Objectives 2 Sequential circuits that are not snchronized b a clock Asnchronous circuits Analsis of Asnchronous circuits Snthesis of Asnchronous circuits
CHAPTER 9: ASYNCHRONOUS SEUENTIAL CIRCUITS Chapter Objectives 2 Sequential circuits that are not snchronized b a clock Asnchronous circuits Analsis of Asnchronous circuits Snthesis of Asnchronous circuits
Fault Equivalence, Dominance & Collapsing. Fault Equivalence
 Fault Equivalence, Dominance & ollapsing Definition: If T a is the set of LL TVs which Detect Fault a, and T b is the set of LL TVs which Detect some other Fault b; the Two Faults a, and b are said to
Fault Equivalence, Dominance & ollapsing Definition: If T a is the set of LL TVs which Detect Fault a, and T b is the set of LL TVs which Detect some other Fault b; the Two Faults a, and b are said to
CMPEN 411. Spring Lecture 18: Static Sequential Circuits
 CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2011 Lecture 18: Static Sequential Circuits [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] Sp11
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2011 Lecture 18: Static Sequential Circuits [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] Sp11
Advanced Testing. EE5375 ADD II Prof. MacDonald
 Advanced Testing EE5375 ADD II Prof. MacDonald Functional Testing l Original testing method l Run chip from reset l Tester emulates the outside world l Chip runs functionally with internally generated
Advanced Testing EE5375 ADD II Prof. MacDonald Functional Testing l Original testing method l Run chip from reset l Tester emulates the outside world l Chip runs functionally with internally generated
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 26 Faults and Error Correction. Recap
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 26 Faults and Error Correction Nov. 26, 2013 Prof. Ronald Fearing Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley (slides courtesy of Prof.
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 26 Faults and Error Correction Nov. 26, 2013 Prof. Ronald Fearing Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley (slides courtesy of Prof.
Name: Answers. Mean: 83, Standard Deviation: 12 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q5 Q6 Total. ESE370 Fall 2015
 University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and System Engineering Circuit-Level Modeling, Design, and Optimization for Digital Systems ESE370, Fall 2015 Final Tuesday, December 15 Problem weightings
University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and System Engineering Circuit-Level Modeling, Design, and Optimization for Digital Systems ESE370, Fall 2015 Final Tuesday, December 15 Problem weightings
Timing Issues. Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolić. January 2003
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolić Timing Issues January 2003 1 Synchronous Timing CLK In R Combinational 1 R Logic 2 C in C out Out 2
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolić Timing Issues January 2003 1 Synchronous Timing CLK In R Combinational 1 R Logic 2 C in C out Out 2
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 23 - FFs revisited, FIFOs, ECCs, LSFRs. Cross-coupled NOR gates
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 23 - FFs revisited, FIFOs, ECCs, LSFRs April 16, 2009 John Wawrzynek Spring 2009 EECS150 - Lec24-blocks Page 1 Cross-coupled NOR gates remember, If both R=0 & S=0, then
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 23 - FFs revisited, FIFOs, ECCs, LSFRs April 16, 2009 John Wawrzynek Spring 2009 EECS150 - Lec24-blocks Page 1 Cross-coupled NOR gates remember, If both R=0 & S=0, then
Outline - BIST. Why BIST? Memory BIST Logic BIST pattern generator & response analyzer Scan-based BIST architecture. K.T. Tim Cheng 08_bist, v1.
 1 Outline - BIST Why BIST? Memory BIST Logic BIST pattern generator & response analyzer Scan-based BIST architecture 2 Why Built-In Self Test? TYPES On-Line Self-Test (Concurrent Checking) Functional Self-Test
1 Outline - BIST Why BIST? Memory BIST Logic BIST pattern generator & response analyzer Scan-based BIST architecture 2 Why Built-In Self Test? TYPES On-Line Self-Test (Concurrent Checking) Functional Self-Test
9/18/2008 GMU, ECE 680 Physical VLSI Design
 ECE680: Physical VLSI Design Chapter III CMOS Device, Inverter, Combinational circuit Logic and Layout Part 3 Combinational Logic Gates (textbook chapter 6) 9/18/2008 GMU, ECE 680 Physical VLSI Design
ECE680: Physical VLSI Design Chapter III CMOS Device, Inverter, Combinational circuit Logic and Layout Part 3 Combinational Logic Gates (textbook chapter 6) 9/18/2008 GMU, ECE 680 Physical VLSI Design
Luis Manuel Santana Gallego 31 Investigation and simulation of the clock skew in modern integrated circuits
 Luis Manuel Santana Gallego 31 Investigation and simulation of the clock skew in modern egrated circuits 3. Clock skew 3.1. Definitions For two sequentially adjacent registers, as shown in figure.1, C
Luis Manuel Santana Gallego 31 Investigation and simulation of the clock skew in modern egrated circuits 3. Clock skew 3.1. Definitions For two sequentially adjacent registers, as shown in figure.1, C
Comparing the Effects of Intermittent and Transient Hardware Faults on Programs
 Comparing the Effects of Intermittent and Transient Hardware Faults on Programs Jiesheng Wei, Layali Rashid, Karthik Pattabiraman and Sathish Gopalakrishnan Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering,
Comparing the Effects of Intermittent and Transient Hardware Faults on Programs Jiesheng Wei, Layali Rashid, Karthik Pattabiraman and Sathish Gopalakrishnan Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering,
Chapter 5 CMOS Logic Gate Design
 Chapter 5 CMOS Logic Gate Design Section 5. -To achieve correct operation of integrated logic gates, we need to satisfy 1. Functional specification. Temporal (timing) constraint. (1) In CMOS, incorrect
Chapter 5 CMOS Logic Gate Design Section 5. -To achieve correct operation of integrated logic gates, we need to satisfy 1. Functional specification. Temporal (timing) constraint. (1) In CMOS, incorrect
Fault Tolerant Computing CS 530 Fault Modeling
 CS 53 Fault Modeling Yashwant K. Malaiya Colorado State University Fault Modeling Why fault modeling? Stuck-at / fault model The single fault assumption Bridging and delay faults MOS transistors and CMOS
CS 53 Fault Modeling Yashwant K. Malaiya Colorado State University Fault Modeling Why fault modeling? Stuck-at / fault model The single fault assumption Bridging and delay faults MOS transistors and CMOS
Delay Testing from the Ivory Tower to Tools in the Workshop
 Delay Testing from the Ivory Tower to Tools in the Workshop Einar Johan Aas Department of Electronics and Telecommunications, NTNU Nordic Test Forum, Tallinn, 25. November 2008 Name, title of the presentation
Delay Testing from the Ivory Tower to Tools in the Workshop Einar Johan Aas Department of Electronics and Telecommunications, NTNU Nordic Test Forum, Tallinn, 25. November 2008 Name, title of the presentation
Lecture 25. Dealing with Interconnect and Timing. Digital Integrated Circuits Interconnect
 Lecture 25 Dealing with Interconnect and Timing Administrivia Projects will be graded by next week Project phase 3 will be announced next Tu.» Will be homework-like» Report will be combined poster Today
Lecture 25 Dealing with Interconnect and Timing Administrivia Projects will be graded by next week Project phase 3 will be announced next Tu.» Will be homework-like» Report will be combined poster Today
Stop Watch (System Controller Approach)
 Stop Watch (System Controller Approach) Problem Design a stop watch that can measure times taken for two events Inputs CLK = 6 Hz RESET: Asynchronously reset everything X: comes from push button First
Stop Watch (System Controller Approach) Problem Design a stop watch that can measure times taken for two events Inputs CLK = 6 Hz RESET: Asynchronously reset everything X: comes from push button First
On Random Pattern Testability of Cryptographic VLSI Cores
 On Random Pattern Testability of Cryptographic VLSI Cores A. Schubert, W. Anheier Institut für Theoretische Elektrotechnik und Mikroelektronik (ITEM) University of Bremen P.O. Box 33 04 40, D-28334 Bremen
On Random Pattern Testability of Cryptographic VLSI Cores A. Schubert, W. Anheier Institut für Theoretische Elektrotechnik und Mikroelektronik (ITEM) University of Bremen P.O. Box 33 04 40, D-28334 Bremen
Integrated Circuits & Systems
 Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 18 CMOS Sequential Circuits - 1 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br
Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 18 CMOS Sequential Circuits - 1 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br
Chapter 8. Low-Power VLSI Design Methodology
 VLSI Design hapter 8 Low-Power VLSI Design Methodology Jin-Fu Li hapter 8 Low-Power VLSI Design Methodology Introduction Low-Power Gate-Level Design Low-Power Architecture-Level Design Algorithmic-Level
VLSI Design hapter 8 Low-Power VLSI Design Methodology Jin-Fu Li hapter 8 Low-Power VLSI Design Methodology Introduction Low-Power Gate-Level Design Low-Power Architecture-Level Design Algorithmic-Level
Lecture 16: Circuit Pitfalls
 Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 16: Circuit Pitfalls David Harris Harvey Mudd College Spring 2004 Outline Pitfalls Detective puzzle Given circuit and symptom, diagnose cause and recommend solution
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 16: Circuit Pitfalls David Harris Harvey Mudd College Spring 2004 Outline Pitfalls Detective puzzle Given circuit and symptom, diagnose cause and recommend solution
Lecture Outline. ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals. Total Power. Energy and Power Optimization. Worksheet Problem 1
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 16: March 20, 2018 Energy and Power Optimization, Design Space Exploration Lecture Outline! Energy and Power Optimization " Tradeoffs! Design
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 16: March 20, 2018 Energy and Power Optimization, Design Space Exploration Lecture Outline! Energy and Power Optimization " Tradeoffs! Design
EC 413 Computer Organization
 EC 413 Computer Organization rithmetic Logic Unit (LU) and Register File Prof. Michel. Kinsy Computing: Computer Organization The DN of Modern Computing Computer CPU Memory System LU Register File Disks
EC 413 Computer Organization rithmetic Logic Unit (LU) and Register File Prof. Michel. Kinsy Computing: Computer Organization The DN of Modern Computing Computer CPU Memory System LU Register File Disks
Lecture 7: Logic design. Combinational logic circuits
 /24/28 Lecture 7: Logic design Binary digital circuits: Two voltage levels: and (ground and supply voltage) Built from transistors used as on/off switches Analog circuits not very suitable for generic
/24/28 Lecture 7: Logic design Binary digital circuits: Two voltage levels: and (ground and supply voltage) Built from transistors used as on/off switches Analog circuits not very suitable for generic
UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering. Fault Tolerant Computing ECE 655
 UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Fault Tolerant Computing ECE 655 Part 1 Introduction C. M. Krishna Fall 2006 ECE655/Krishna Part.1.1 Prerequisites Basic courses in
UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS Dept. of Electrical & Computer Engineering Fault Tolerant Computing ECE 655 Part 1 Introduction C. M. Krishna Fall 2006 ECE655/Krishna Part.1.1 Prerequisites Basic courses in
ISSP User Guide CY3207ISSP. Revision C
 CY3207ISSP ISSP User Guide Revision C Cypress Semiconductor 198 Champion Court San Jose, CA 95134-1709 Phone (USA): 800.858.1810 Phone (Intnl): 408.943.2600 http://www.cypress.com Copyrights Copyrights
CY3207ISSP ISSP User Guide Revision C Cypress Semiconductor 198 Champion Court San Jose, CA 95134-1709 Phone (USA): 800.858.1810 Phone (Intnl): 408.943.2600 http://www.cypress.com Copyrights Copyrights
Sequential Logic Worksheet
 Sequential Logic Worksheet Concept Inventory: Notes: D-latch & the Dynamic Discipline D-register Timing constraints for sequential circuits Set-up and hold times for sequential circuits 6.004 Worksheet
Sequential Logic Worksheet Concept Inventory: Notes: D-latch & the Dynamic Discipline D-register Timing constraints for sequential circuits Set-up and hold times for sequential circuits 6.004 Worksheet
Issues on Timing and Clocking
 ECE152B TC 1 Issues on Timing and Clocking X Combinational Logic Z... clock clock clock period ECE152B TC 2 Latch and Flip-Flop L CK CK 1 L1 1 L2 2 CK CK CK ECE152B TC 3 Clocking X Combinational Logic...
ECE152B TC 1 Issues on Timing and Clocking X Combinational Logic Z... clock clock clock period ECE152B TC 2 Latch and Flip-Flop L CK CK 1 L1 1 L2 2 CK CK CK ECE152B TC 3 Clocking X Combinational Logic...
MODULE 5 Chapter 7. Clocked Storage Elements
 MODULE 5 Chapter 7 Clocked Storage Elements 3/9/2015 1 Outline Background Clocked Storage Elements Timing, terminology, classification Static CSEs Latches Registers Dynamic CSEs Latches Registers 3/9/2015
MODULE 5 Chapter 7 Clocked Storage Elements 3/9/2015 1 Outline Background Clocked Storage Elements Timing, terminology, classification Static CSEs Latches Registers Dynamic CSEs Latches Registers 3/9/2015
Dictionary-Less Defect Diagnosis as Real or Surrogate Single Stuck-At Faults. Chidambaram Alagappan
 Dictionary-Less Defect Diagnosis as Real or Surrogate Single Stuck-At Faults by Chidambaram Alagappan A thesis submitted to the Graduate Faculty of Auburn University in partial fulfillment of the requirements
Dictionary-Less Defect Diagnosis as Real or Surrogate Single Stuck-At Faults by Chidambaram Alagappan A thesis submitted to the Graduate Faculty of Auburn University in partial fulfillment of the requirements
 Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET For a complete data sheet, please also download:
Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET For a complete data sheet, please also download:
Lecture 5. MOS Inverter: Switching Characteristics and Interconnection Effects
 Lecture 5 MOS Inverter: Switching Characteristics and Interconnection Effects Introduction C load = (C gd,n + C gd,p + C db,n + C db,p ) + (C int + C g ) Lumped linear capacitance intrinsic cap. extrinsic
Lecture 5 MOS Inverter: Switching Characteristics and Interconnection Effects Introduction C load = (C gd,n + C gd,p + C db,n + C db,p ) + (C int + C g ) Lumped linear capacitance intrinsic cap. extrinsic
Lecture 10: Sequential Networks: Timing and Retiming
 Lecture 10: Sequential Networks: Timing and Retiming CSE 140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Diba Mirza Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering University of California, San Diego
Lecture 10: Sequential Networks: Timing and Retiming CSE 140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Diba Mirza Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering University of California, San Diego
EEC 216 Lecture #3: Power Estimation, Interconnect, & Architecture. Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis
 EEC 216 Lecture #3: Power Estimation, Interconnect, & Architecture Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Outline Announcements Review: PDP, EDP, Intersignal Correlations, Glitching, Top
EEC 216 Lecture #3: Power Estimation, Interconnect, & Architecture Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Outline Announcements Review: PDP, EDP, Intersignal Correlations, Glitching, Top
Structural Delay Testing Under Restricted Scan of Latch-based Pipelines with Time Borrowing
 Structural Delay Testing Under Restricted Scan of Latch-based Pipelines with Borrowing Kun Young Chung and Sandeep K. Gupta University of Southern California, EE Systems Abstract High-speed circuits use
Structural Delay Testing Under Restricted Scan of Latch-based Pipelines with Borrowing Kun Young Chung and Sandeep K. Gupta University of Southern California, EE Systems Abstract High-speed circuits use
CpE358/CS381. Switching Theory and Logical Design. Class 16
 CpE358/CS38 Switching Theory and Logical Design Class 6 CpE358/CS38 Summer- 24 Copyright 24-585 Today Fundamental concepts of digital systems (Mano Chapter ) inary codes, number systems, and arithmetic
CpE358/CS38 Switching Theory and Logical Design Class 6 CpE358/CS38 Summer- 24 Copyright 24-585 Today Fundamental concepts of digital systems (Mano Chapter ) inary codes, number systems, and arithmetic
ECE-470 Digital Design II Memory Test. Memory Cells Per Chip. Failure Mechanisms. Motivation. Test Time in Seconds (Memory Size: n Bits) Fault Types
 ECE-470 Digital Design II Memory Test Motivation Semiconductor memories are about 35% of the entire semiconductor market Memories are the most numerous IPs used in SOC designs Number of bits per chip continues
ECE-470 Digital Design II Memory Test Motivation Semiconductor memories are about 35% of the entire semiconductor market Memories are the most numerous IPs used in SOC designs Number of bits per chip continues
Problem Set 9 Solutions
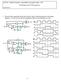 CSE 26 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design - 27 Jon Turner Problem Set 9 Solutions. For each of the sequential circuits shown below, draw in the missing parts of the timing diagrams. You
CSE 26 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design - 27 Jon Turner Problem Set 9 Solutions. For each of the sequential circuits shown below, draw in the missing parts of the timing diagrams. You
ΗΜΥ 307 ΨΗΦΙΑΚΑ ΟΛΟΚΛΗΡΩΜΕΝΑ ΚΥΚΛΩΜΑΤΑ Εαρινό Εξάμηνο 2018
 ΗΜΥ 307 ΨΗΦΙΑΚΑ ΟΛΟΚΛΗΡΩΜΕΝΑ ΚΥΚΛΩΜΑΤΑ Εαρινό Εξάμηνο 2018 ΔΙΑΛΕΞΕΙΣ 12-13: esigning ynamic and Static CMOS Sequential Circuits ΧΑΡΗΣ ΘΕΟΧΑΡΙΔΗΣ (ttheocharides@ucy.ac.cy) (ack: Prof. Mary Jane Irwin and
ΗΜΥ 307 ΨΗΦΙΑΚΑ ΟΛΟΚΛΗΡΩΜΕΝΑ ΚΥΚΛΩΜΑΤΑ Εαρινό Εξάμηνο 2018 ΔΙΑΛΕΞΕΙΣ 12-13: esigning ynamic and Static CMOS Sequential Circuits ΧΑΡΗΣ ΘΕΟΧΑΡΙΔΗΣ (ttheocharides@ucy.ac.cy) (ack: Prof. Mary Jane Irwin and
The Linear-Feedback Shift Register
 EECS 141 S02 Timing Project 2: A Random Number Generator R R R S 0 S 1 S 2 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 The Linear-Feedback Shift Register 1 Project Goal Design a 4-bit LFSR SPEED, SPEED,
EECS 141 S02 Timing Project 2: A Random Number Generator R R R S 0 S 1 S 2 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 The Linear-Feedback Shift Register 1 Project Goal Design a 4-bit LFSR SPEED, SPEED,
UNISONIC TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD L16B45 Preliminary CMOS IC
 UNISONIC TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD L16B45 Preliminary CMOS IC 16-BIT CONSTANT CURRENT LED SINK DRIVER DESCRIPTION The UTC L16B45 is designed for LED displays. UTC L16B45 contains a serial buffer and data latches
UNISONIC TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD L16B45 Preliminary CMOS IC 16-BIT CONSTANT CURRENT LED SINK DRIVER DESCRIPTION The UTC L16B45 is designed for LED displays. UTC L16B45 contains a serial buffer and data latches
Hold Time Illustrations
 Hold Time Illustrations EE213-L09-Sequential Logic.1 Pingqiang, ShanghaiTech, 2018 Hold Time Illustrations EE213-L09-Sequential Logic.2 Pingqiang, ShanghaiTech, 2018 Hold Time Illustrations EE213-L09-Sequential
Hold Time Illustrations EE213-L09-Sequential Logic.1 Pingqiang, ShanghaiTech, 2018 Hold Time Illustrations EE213-L09-Sequential Logic.2 Pingqiang, ShanghaiTech, 2018 Hold Time Illustrations EE213-L09-Sequential
Lecture 9: Clocking, Clock Skew, Clock Jitter, Clock Distribution and some FM
 Lecture 9: Clocking, Clock Skew, Clock Jitter, Clock Distribution and some FM Mark McDermott Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin 9/27/18 VLSI-1 Class Notes Why Clocking?
Lecture 9: Clocking, Clock Skew, Clock Jitter, Clock Distribution and some FM Mark McDermott Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin 9/27/18 VLSI-1 Class Notes Why Clocking?
CARNEGIE MELLON UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING DIGITAL INTEGRATED CIRCUITS FALL 2002
 CARNEGIE MELLON UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING 18-322 DIGITAL INTEGRATED CIRCUITS FALL 2002 Final Examination, Monday Dec. 16, 2002 NAME: SECTION: Time: 180 minutes Closed
CARNEGIE MELLON UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING 18-322 DIGITAL INTEGRATED CIRCUITS FALL 2002 Final Examination, Monday Dec. 16, 2002 NAME: SECTION: Time: 180 minutes Closed
ECE251. VLSI System Design
 ECE251. VLSI System Design Project 4 SRAM Cell and Memory Array Operation Area Memory core 4661 mm 2 (256bit) Row Decoder 204.7 mm 2 Collumn Decoder Overall Design Predecoder 156.1 mm 2 Mux 629.2 mm 2
ECE251. VLSI System Design Project 4 SRAM Cell and Memory Array Operation Area Memory core 4661 mm 2 (256bit) Row Decoder 204.7 mm 2 Collumn Decoder Overall Design Predecoder 156.1 mm 2 Mux 629.2 mm 2
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 17: March 23, 2017 Energy and Power Optimization, Design Space Exploration, Synchronous MOS Logic Lecture Outline! Energy and Power Optimization
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 17: March 23, 2017 Energy and Power Optimization, Design Space Exploration, Synchronous MOS Logic Lecture Outline! Energy and Power Optimization
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI
 DEPARTMENT: ECE MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 6 QUESTION BANK SUBJECT NAME: DIGITAL ELECTRONICS UNIT : Design of Sequential Circuits PART A ( Marks). Draw the logic diagram 4: Multiplexer.(AUC
DEPARTMENT: ECE MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 6 QUESTION BANK SUBJECT NAME: DIGITAL ELECTRONICS UNIT : Design of Sequential Circuits PART A ( Marks). Draw the logic diagram 4: Multiplexer.(AUC
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic Designing Sequential Logic Circuits November 2002 Sequential Logic Inputs Current State COMBINATIONAL
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic Designing Sequential Logic Circuits November 2002 Sequential Logic Inputs Current State COMBINATIONAL
Test Pattern Generator for Built-in Self-Test using Spectral Methods
 Test Pattern Generator for Built-in Self-Test using Spectral Methods Alok S. Doshi and Anand S. Mudlapur Auburn University 2 Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Auburn, AL, USA doshias,anand@auburn.edu
Test Pattern Generator for Built-in Self-Test using Spectral Methods Alok S. Doshi and Anand S. Mudlapur Auburn University 2 Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Auburn, AL, USA doshias,anand@auburn.edu
EE141Microelettronica. CMOS Logic
 Microelettronica CMOS Logic CMOS logic Power consumption in CMOS logic gates Where Does Power Go in CMOS? Dynamic Power Consumption Charging and Discharging Capacitors Short Circuit Currents Short Circuit
Microelettronica CMOS Logic CMOS logic Power consumption in CMOS logic gates Where Does Power Go in CMOS? Dynamic Power Consumption Charging and Discharging Capacitors Short Circuit Currents Short Circuit
EECS 151/251A Homework 5
 EECS 151/251A Homework 5 Due Monday, March 5 th, 2018 Problem 1: Timing The data-path shown below is used in a simple processor. clk rd1 rd2 0 wr regfile 1 0 ALU REG 1 The elements used in the design have
EECS 151/251A Homework 5 Due Monday, March 5 th, 2018 Problem 1: Timing The data-path shown below is used in a simple processor. clk rd1 rd2 0 wr regfile 1 0 ALU REG 1 The elements used in the design have
Lecture 6 Power Zhuo Feng. Z. Feng MTU EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis 2010
 EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Lecture 6 Power Zhuo Feng 6.1 Outline Power and Energy Dynamic Power Static Power 6.2 Power and Energy Power is drawn from a voltage source attached to the V DD
EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Lecture 6 Power Zhuo Feng 6.1 Outline Power and Energy Dynamic Power Static Power 6.2 Power and Energy Power is drawn from a voltage source attached to the V DD
Chapter 5. Digital Design and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition. David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris. Chapter 5 <1>
 Chapter 5 Digital Design and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris Chapter 5 Chapter 5 :: Topics Introduction Arithmetic Circuits umber Systems Sequential Building
Chapter 5 Digital Design and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris Chapter 5 Chapter 5 :: Topics Introduction Arithmetic Circuits umber Systems Sequential Building
DATA SHEET. HEF4031B MSI 64-stage static shift register. For a complete data sheet, please also download: INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET For a complete data sheet, please also download: The IC04 LOCMOS HE4000B Logic Family Specifications HEF, HEC The IC04 LOCMOS HE4000B Logic Package Outlines/Information HEF,
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS DATA SHEET For a complete data sheet, please also download: The IC04 LOCMOS HE4000B Logic Family Specifications HEF, HEC The IC04 LOCMOS HE4000B Logic Package Outlines/Information HEF,
For smaller NRE cost For faster time to market For smaller high-volume manufacturing cost For higher performance
 University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS5 J. Wawrzynek Spring 22 2/22/2. [2 pts] Short Answers. Midterm Exam I a) [2 pts]
University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS5 J. Wawrzynek Spring 22 2/22/2. [2 pts] Short Answers. Midterm Exam I a) [2 pts]
ECE321 Electronics I
 ECE321 Electronics I Lecture 1: Introduction to Digital Electronics Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: ECE Bldg. 230B Office hours: Tuesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: payman@ece.unm.edu Slide: 1 Textbook
ECE321 Electronics I Lecture 1: Introduction to Digital Electronics Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: ECE Bldg. 230B Office hours: Tuesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: payman@ece.unm.edu Slide: 1 Textbook
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT CODE: EC 1354 SUB.NAME : VLSI DESIGN YEAR / SEMESTER: III / VI UNIT I MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY AND
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT CODE: EC 1354 SUB.NAME : VLSI DESIGN YEAR / SEMESTER: III / VI UNIT I MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY AND
