MAE140 Linear Circuits Fall 2016 Final, December 6th Instructions
|
|
|
- Gertrude Harper
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MAE40 Linear Circuits Fall 206 Final, December 6th Instructions. This exam is open book. You may use whatever written materials you choose, including your class notes and textbook. You may use a handheld calculator with no communication capabilities. 2. You have 70 minutes. 3. Do not forget to write your name and student number. 4. This exam has 6 questions, for a total of 60 points and 2 bonus points.
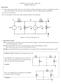
2 i 2 (t) A v C C C v (t) i c i a v B C v x i b v C B D v A (a) (b) Figure : Circuits for Questions and 2. Circuit Equivalence IMPOTANT: All impedances should be given as a ratio of two polynomials! (a) (3 points) Assume zero-initial conditions and find the s-domain equivalent circuit as seen from terminals A and B in Fig. a. First convert the circuit to the s-domain to obtain assuming zero initial conditions: A C B D As seen from A to B we associate the capacitor and resistor: A B which is equivalent to: A Z(s) B (/2 point) Page 2
3 where Z(s) = = s s C = 2s C s C = ( s C 2s C ) (/2 point) (b) (3 points) Assume zero-initial conditions and find the s-domain equivalent circuit as seen from terminals C and B in Fig. a. The circuit has already been converted to the s-domain in part (a). Just notice that the circuit is the same as seen from C to B or from A to B so the answer is the same as in part (a). (3 points) (c) (4 points) Assume a non-zero initial condition v C (0) = V as indicated and repeat parts (a) and (b). Start again by converting to the s-domain but this time consider a non-zero initial condition across the capacitor with polarity matching the circuit diagram: A s C B D The Thevenin equivalent as seen from A to B or C to B will have the same impedances as calculate in parts (a) and (b). To calculate the Thevenin voltage from A to B we can use voltage division: to obtain the equivalent circuit: V T (s) = V AB (s) = 2 s = /2 s 2C (/2 point) Page 3
4 A Z(s) B /2 s 2C To calculate the Thevenin voltage from B to C we note that V T (s) = V CB (s) = V AB (s) = /2 s 2C (/2 point) (/2 point) to obtain the equivalent circuit: C Z(s) /2 s 2C B (/2 point) 2. Circuit Analysis (a) (4 points) Convert the circuit in Fig. b to the s-domain and formulate its nodevoltage equations. Use the node-voltage and labels provided in the figure and clearly indicate the final equations and circuit variable unknowns. Do not assume zero initial conditions. Make sure your final equations only involve nodevoltages. With an eye on node-voltage analysis we convert to the s-domain: I 2 (s) V B (s) Cv x (0) V C (s) V (s) V A (s) Page 4
5 Since V B (s) = 0 and V A (s) is connected to a voltage source so that V A (s) = V (s) we only need to write KCL at node C, which we do by inspection: [ ] ( ) V A (s) = ( I V C (s) 2 (s) Cv x (0) ) The above equations need to be solved for the node voltages V A (s), V B (s) and V C (s). (b) (4 points) Convert the circuit in Fig. b to the s-domain and formulate its meshcurrent equations. Use the mesh-currents and labels provided in the figure and clearly indicate the final equations and circuit variable unknowns. Do not assume zero initial conditions. Make sure your final equations only involve meshcurrents. With an eye on mesh-current analysis we convert to the s-domain: I 2 (s) I c (s) v x(0) s V (s) I a (s) I b (s) Since I 2 (s) is on an external mesh I c (s) = I 2 (s) and we only need to write KVL at meshes a and b, which we do by inspection: [ ] 0 a (s) ( ) I 2 I b (s) V (s) = vx(0) (2 point2) I c (s) s The above equations need to be solved for the mesh currents I a (s), I b (s) and I c (s). Page 5
6 G v ref x v o v ref x v o (a) (b) Figure 2: Circuits for Question 3 (c) (2 points) Express the s-domain voltage V x (s) in terms of the node voltages and mesh currents from parts (a) and (b). From the node voltages: V x (s) = V B (s) V C (s) = V C (s) From the mesh currents: V x (s) = I b(s) I c (s) v x(0) s Page 6
7 3. Wheatstone Bridge The circuits in Fig. 2 are used with strain-gauges to measure small displacements in structures. The displacement causes a change in resistance x indicated in the figure. (a) (5 points) For the circuit in Fig. 2a, show that v 0 x v ref 4 when x is small. Hint: Expand in series about x = 0 and discard higher order terms. v 0 and v 0 can be computed using voltage division, that is: so that v 0 v 0 = x 2 x v ref = x/ 2 x/ v ref, = 2 v ref = v ref 2 v 0 = v 0 v0 = x/ 2 x/ v ref v ref 2 2( x/) (2 x/) x/ = v ref = 2(2 x/) 2(2 x/) v ref When x/ is small v 0 v ref = x/ 2(2 x/) x/ 4 This is the first-order term in the Taylor series. (b) (5 points) For the circuit in Fig. 2b, show that v 0 = x G v ref 2 Hint: Don t get fooled by the drawing; this is simpler than what it seems! The circuit consists of two inverting OpAmp circuits. For clarity label the output of the first OpAmp as in: Page 7
8 G v ref x v o and write for the standard inverting amplifier: v and for the standard inverting summer: v = x v ref v o = G v ref G v Combining the two expressions from where v o = x G v ref G v ref ( ) x = G v ref = x = x G v ref G v ref v o = x G v ref 2 (c) ( point (bonus)) Name one advantage and one disadvantage of each circuit. Circuit (a): advantage: simpler; disadvantage: no way to set the gain; Circuit (b): disadvantage: complex; advantage: gain can be set through G ; ( bonus point) 4. (0 points) OpAmp Design Page 8
9 Design an OpAmp circuit that can be used to amplify the voltage v o shown in the circuit shown in Fig. 2a by a factor K > 0 to produce a voltage v o = Kv 0. Explain how your circuit works. A straightforward solution is to use a subtractor: v 2 v 2 4 v o 3 with which and set so that v o = v 2 2 v =, 2 = K, 3 = K, 4 = (4 points) v o = K K v 2 K K v = K(v 2 v ) In order to avoid loading of the bridge one cannot connect v 2 and v directly to v 0 and v 0. Instead, one should use buffers. The complete circuit would be as follows: v 0 v 0 v K v 2 v o K Page 9
10 v i C v o 5V C v C (t) (a) (b) Figure 3: Circuits for Questions 5 and 6 NOTE TO GADES: Alternative solutions are possible. (3 points) Page 0
11 5. Frequency esponse (a) (3 points) Show that the transfer function T (s) = V o (s)/v i (s) for the circuit in Fig. 3a is: T (s) = s ω a s ω a, ω a = C IMPOTANT: For the rest of this question set ω a = rad/s. Assuming zero initial conditions and converting to the s-domain: V i (s) V o (s) The circuit is a subtractor from which: V o (s) = Z 3 Z 3 Z 4 Z Z 2 Z V i (s) Z 2 Z V i (s) (/2 point) with Z = Z 2 = Z 3 =, Z 4 =. (/2 point) Putting it all together: V o (s) = 2 V i(s) V i(s) ( ) 2s = s V i (s) C = 2s s C s V i (s) C = s C s V i (s) C (/2 point) (/2 point) (b) (3 points) Sketch the magnitude and phase of the frequency response T (jω). Page
12 The frequency response is T (jω) = jω ω a jω ω a Its magnitude is T (jω) = jω ω a jω ω a = ω2 ω 2 a ω2 ω 2 a = (/2 point) for all ω which is constant and equal to for all ω. A sketch should look like: (/2 point) Its phase is T (jω) = jω ω a jω ω a (/2 point) = π tan ω/ω a tan ω/ω a = π 2 tan ω/ω a At ω = ω a = phase is equal to 90 degrees. A sketch should look like: Page 2
13 (/2 point) (c) ( point) Explain what this circuit does based on its frequency response. The circuit preserves the magnitude of all frequencies and shifts the phase from 80 to 0 degrees as ω grows. At ω = ω the shift is equal to 90 degrees. (d) (3 points) Use the frequency response method or a direct calculation to compute the steady-state response of the circuit to an input of the form v i (t) = 2 cos(t)v. Using the frequency response method to calculate the steady state response to an input v i (t) = 2 cos(ωt)v we obtain Substituting ω = ω a = we calculate v SS o (t) = 2 T (jω) cos(ωt T (jω)). T (j) = j j = j from which 6. Circuit with Switch v SS o (t) = 2 cos(t π/2)v. The switch in the circuit in Fig. 3b is kept closed for a long time. At t = 0 the switch is opened. Page 3
14 (a) (3 points) Determine the initial condition at the capacitor at t = 0 and convert the circuit to the s-domain for t 0. Because the circuit has only constant sources we expect that after a long time the capacitor current will be zero, which corresponds to the following circuit: 5V v C (0 ) so that the initial condition on the capacitor can be calculated using voltage division: v C (0 ) = 5V = 2.5V. 2 The s-domain version of the circuit for t 0 should look like: 5 V s I(s) 2.5 s V (b) (5 points) Show that V C (s) v c (t) = e t/(c) V, t 0 The current in the circuit in part (a) is: I(s) = s ( ) = 2.5/ s C Page 4
15 from which Expanding in partial fractions V C (s) = 2.5 s I(s) = 2.5 s 2.5 C s ( ) s C (/2 point) = 2.5 s 2 C s ( ) (/2 point) s C 2.5 s 2 C s ( ) = α s s β s C C (/2 point) where α = lim 2.5 s 2 s 0 s β = lim s C C C 2.5 s 2 C s = C C = 5 (/2 point) = 2.5 C 2 C C = 2.5. (/2 point) Using the Laplace inverse: { α v C (t) = L s β } s C (/2 point) = α βe t/(c) = e t/(c), t 0. (c) (2 points) Calculate the power absorbed by the resistor for t 0. Having calculated the voltage v C (t) we can calculate the voltage across the resistor: v (t) = 5 v C (t) = 2.5 e t/(c) from which p (t) = v (t) 2 = 2.52 e2t/(c). (d) ( point (bonus)) Calculate the total energy delivered by the voltage source after the switch is opened. Page 5
16 From part (b), the current is i(t) = L {I(s)} = 2.5 L { s C so that the power delivered by the source is and the total energy is e(t) = 0 p(τ) dτ = 2.5 } = 2.5 et/(c), t 0. p(t) = 5i(t) = 2.5 et/(c), t 0 Note how it does not depend on! 0 e τ/(c) dτ = 2.5 Ceτ/(C) 0 = 2.5 C. ( bonus point) Page 6
MAE140 - Linear Circuits - Winter 09 Midterm, February 5
 Instructions MAE40 - Linear ircuits - Winter 09 Midterm, February 5 (i) This exam is open book. You may use whatever written materials you choose, including your class notes and textbook. You may use a
Instructions MAE40 - Linear ircuits - Winter 09 Midterm, February 5 (i) This exam is open book. You may use whatever written materials you choose, including your class notes and textbook. You may use a
MAE140 - Linear Circuits - Fall 14 Midterm, November 6
 MAE140 - Linear Circuits - Fall 14 Midterm, November 6 Instructions (i) This exam is open book. You may use whatever written materials you choose, including your class notes and textbook. You may use a
MAE140 - Linear Circuits - Fall 14 Midterm, November 6 Instructions (i) This exam is open book. You may use whatever written materials you choose, including your class notes and textbook. You may use a
ECE 201 Fall 2009 Final Exam
 ECE 01 Fall 009 Final Exam December 16, 009 Division 0101: Tan (11:30am) Division 001: Clark (7:30 am) Division 0301: Elliott (1:30 pm) Instructions 1. DO NOT START UNTIL TOLD TO DO SO.. Write your Name,
ECE 01 Fall 009 Final Exam December 16, 009 Division 0101: Tan (11:30am) Division 001: Clark (7:30 am) Division 0301: Elliott (1:30 pm) Instructions 1. DO NOT START UNTIL TOLD TO DO SO.. Write your Name,
ECE 212H1F Circuit Analysis October 20, :15-19: Reza Iravani 02 Reza Iravani 03 Ali Nabavi-Niaki. (Non-programmable Calculators Allowed)
 Please Print Clearly Last Name: First Name: Student Number: Your Tutorial Section (CIRCLE ONE): 01 Thu 10:00 12:00 HA403 02 Thu 10:00 12:00 GB412 03 Thu 15:00 17:00 GB412 04 Thu 15:00 17:00 SF2202 05 Fri
Please Print Clearly Last Name: First Name: Student Number: Your Tutorial Section (CIRCLE ONE): 01 Thu 10:00 12:00 HA403 02 Thu 10:00 12:00 GB412 03 Thu 15:00 17:00 GB412 04 Thu 15:00 17:00 SF2202 05 Fri
Solved Problems. Electric Circuits & Components. 1-1 Write the KVL equation for the circuit shown.
 Solved Problems Electric Circuits & Components 1-1 Write the KVL equation for the circuit shown. 1-2 Write the KCL equation for the principal node shown. 1-2A In the DC circuit given in Fig. 1, find (i)
Solved Problems Electric Circuits & Components 1-1 Write the KVL equation for the circuit shown. 1-2 Write the KCL equation for the principal node shown. 1-2A In the DC circuit given in Fig. 1, find (i)
Electric Circuits I FINAL EXAMINATION
 EECS:300, Electric Circuits I s6fs_elci7.fm - Electric Circuits I FINAL EXAMINATION Problems Points.. 3. 0 Total 34 Was the exam fair? yes no 5//6 EECS:300, Electric Circuits I s6fs_elci7.fm - Problem
EECS:300, Electric Circuits I s6fs_elci7.fm - Electric Circuits I FINAL EXAMINATION Problems Points.. 3. 0 Total 34 Was the exam fair? yes no 5//6 EECS:300, Electric Circuits I s6fs_elci7.fm - Problem
The equivalent model of a certain op amp is shown in the figure given below, where R 1 = 2.8 MΩ, R 2 = 39 Ω, and A =
 The equivalent model of a certain op amp is shown in the figure given below, where R 1 = 2.8 MΩ, R 2 = 39 Ω, and A = 10 10 4. Section Break Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Understand how real operational
The equivalent model of a certain op amp is shown in the figure given below, where R 1 = 2.8 MΩ, R 2 = 39 Ω, and A = 10 10 4. Section Break Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: Understand how real operational
EE 3120 Electric Energy Systems Study Guide for Prerequisite Test Wednesday, Jan 18, pm, Room TBA
 EE 3120 Electric Energy Systems Study Guide for Prerequisite Test Wednesday, Jan 18, 2006 6-7 pm, Room TBA First retrieve your EE2110 final and other course papers and notes! The test will be closed book
EE 3120 Electric Energy Systems Study Guide for Prerequisite Test Wednesday, Jan 18, 2006 6-7 pm, Room TBA First retrieve your EE2110 final and other course papers and notes! The test will be closed book
Chapter 5. Department of Mechanical Engineering
 Source Transformation By KVL: V s =ir s + v By KCL: i s =i + v/r p is=v s /R s R s =R p V s /R s =i + v/r s i s =i + v/r p Two circuits have the same terminal voltage and current Source Transformation
Source Transformation By KVL: V s =ir s + v By KCL: i s =i + v/r p is=v s /R s R s =R p V s /R s =i + v/r s i s =i + v/r p Two circuits have the same terminal voltage and current Source Transformation
EE-201 Review Exam I. 1. The voltage Vx in the circuit below is: (1) 3V (2) 2V (3) -2V (4) 1V (5) -1V (6) None of above
 EE-201, Review Probs Test 1 page-1 Spring 98 EE-201 Review Exam I Multiple Choice (5 points each, no partial credit.) 1. The voltage Vx in the circuit below is: (1) 3V (2) 2V (3) -2V (4) 1V (5) -1V (6)
EE-201, Review Probs Test 1 page-1 Spring 98 EE-201 Review Exam I Multiple Choice (5 points each, no partial credit.) 1. The voltage Vx in the circuit below is: (1) 3V (2) 2V (3) -2V (4) 1V (5) -1V (6)
Chapter 10 AC Analysis Using Phasors
 Chapter 10 AC Analysis Using Phasors 10.1 Introduction We would like to use our linear circuit theorems (Nodal analysis, Mesh analysis, Thevenin and Norton equivalent circuits, Superposition, etc.) to
Chapter 10 AC Analysis Using Phasors 10.1 Introduction We would like to use our linear circuit theorems (Nodal analysis, Mesh analysis, Thevenin and Norton equivalent circuits, Superposition, etc.) to
ECE Circuit Theory. Final Examination. December 5, 2008
 ECE 212 H1F Pg 1 of 12 ECE 212 - Circuit Theory Final Examination December 5, 2008 1. Policy: closed book, calculators allowed. Show all work. 2. Work in the provided space. 3. The exam has 3 problems
ECE 212 H1F Pg 1 of 12 ECE 212 - Circuit Theory Final Examination December 5, 2008 1. Policy: closed book, calculators allowed. Show all work. 2. Work in the provided space. 3. The exam has 3 problems
MAE140 Linear Circuits Fall 2012 Final, December 13th
 MAE40 Linear Circuit Fall 202 Final, December 3th Intruction. Thi exam i open book. You may ue whatever written material you chooe, including your cla note and textbook. You may ue a hand calculator with
MAE40 Linear Circuit Fall 202 Final, December 3th Intruction. Thi exam i open book. You may ue whatever written material you chooe, including your cla note and textbook. You may ue a hand calculator with
Midterm Exam (closed book/notes) Tuesday, February 23, 2010
 University of California, Berkeley Spring 2010 EE 42/100 Prof. A. Niknejad Midterm Exam (closed book/notes) Tuesday, February 23, 2010 Guidelines: Closed book. You may use a calculator. Do not unstaple
University of California, Berkeley Spring 2010 EE 42/100 Prof. A. Niknejad Midterm Exam (closed book/notes) Tuesday, February 23, 2010 Guidelines: Closed book. You may use a calculator. Do not unstaple
Series & Parallel Resistors 3/17/2015 1
 Series & Parallel Resistors 3/17/2015 1 Series Resistors & Voltage Division Consider the single-loop circuit as shown in figure. The two resistors are in series, since the same current i flows in both
Series & Parallel Resistors 3/17/2015 1 Series Resistors & Voltage Division Consider the single-loop circuit as shown in figure. The two resistors are in series, since the same current i flows in both
Chapter 10: Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis
 Chapter 10: Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 10.6 10.9 Basic Approach Nodal Analysis Mesh Analysis Superposition Theorem Source Transformation Thevenin & Norton Equivalent Circuits
Chapter 10: Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 10.6 10.9 Basic Approach Nodal Analysis Mesh Analysis Superposition Theorem Source Transformation Thevenin & Norton Equivalent Circuits
ECE 202 Fall 2013 Final Exam
 ECE 202 Fall 2013 Final Exam December 12, 2013 Circle your division: Division 0101: Furgason (8:30 am) Division 0201: Bermel (9:30 am) Name (Last, First) Purdue ID # There are 18 multiple choice problems
ECE 202 Fall 2013 Final Exam December 12, 2013 Circle your division: Division 0101: Furgason (8:30 am) Division 0201: Bermel (9:30 am) Name (Last, First) Purdue ID # There are 18 multiple choice problems
Chapter 1W Basic Electromagnetic Concepts
 Chapter 1W Basic Electromagnetic Concepts 1W Basic Electromagnetic Concepts 1W.1 Examples and Problems on Electric Circuits 1W.2 Examples on Magnetic Concepts This chapter includes additional examples
Chapter 1W Basic Electromagnetic Concepts 1W Basic Electromagnetic Concepts 1W.1 Examples and Problems on Electric Circuits 1W.2 Examples on Magnetic Concepts This chapter includes additional examples
UNIT 4 DC EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT AND NETWORK THEOREMS
 UNIT 4 DC EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT AND NETWORK THEOREMS 1.0 Kirchoff s Law Kirchoff s Current Law (KCL) states at any junction in an electric circuit the total current flowing towards that junction is equal
UNIT 4 DC EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT AND NETWORK THEOREMS 1.0 Kirchoff s Law Kirchoff s Current Law (KCL) states at any junction in an electric circuit the total current flowing towards that junction is equal
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals, Biomedical Applications Final Exam Section 3
 EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals, Biomedical Applications Final Exam Section 3 Instructions: Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You may use the equation sheet provided but
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals, Biomedical Applications Final Exam Section 3 Instructions: Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You may use the equation sheet provided but
ECE 212H1F Circuit Analysis October 30, :10-19: Reza Iravani 02 Reza Iravani 03 Piero Triverio. (Non-programmable Calculators Allowed)
 Please Print Clearly Last Name: First Name: Student Number: Your Tutorial Section (CIRCLE ONE): 01 Thu. 9-11 RS211 02 Thu. 9-11 GB119 03 Tue. 10-12 SF2202 04 Tue. 10-12 SF3201 05 Tue. 13-15 GB304 06 Tue.
Please Print Clearly Last Name: First Name: Student Number: Your Tutorial Section (CIRCLE ONE): 01 Thu. 9-11 RS211 02 Thu. 9-11 GB119 03 Tue. 10-12 SF2202 04 Tue. 10-12 SF3201 05 Tue. 13-15 GB304 06 Tue.
ECS 40, Fall 2008 Prof. Chang-Hasnain Test #3 Version A
 ECS 40, Fall 2008 Prof. ChangHasnain Test #3 Version A 10:10 am 11:00 am, Wednesday December 3, 2008 Total Time Allotted: 50 minutes Total Points: 100 1. This is a closed book exam. However, you are allowed
ECS 40, Fall 2008 Prof. ChangHasnain Test #3 Version A 10:10 am 11:00 am, Wednesday December 3, 2008 Total Time Allotted: 50 minutes Total Points: 100 1. This is a closed book exam. However, you are allowed
POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Electrical Engineering Department. EE SOPHOMORE LABORATORY Experiment 2 DC circuits and network theorems
 POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Electrical Engineering Department EE SOPHOMORE LABORATORY Experiment 2 DC circuits and network theorems Modified for Physics 18, Brooklyn College I. Overview of Experiment In this
POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Electrical Engineering Department EE SOPHOMORE LABORATORY Experiment 2 DC circuits and network theorems Modified for Physics 18, Brooklyn College I. Overview of Experiment In this
Solution: Based on the slope of q(t): 20 A for 0 t 1 s dt = 0 for 3 t 4 s. 20 A for 4 t 5 s 0 for t 5 s 20 C. t (s) 20 C. i (A) Fig. P1.
 Problem 1.24 The plot in Fig. P1.24 displays the cumulative charge q(t) that has entered a certain device up to time t. Sketch a plot of the corresponding current i(t). q 20 C 0 1 2 3 4 5 t (s) 20 C Figure
Problem 1.24 The plot in Fig. P1.24 displays the cumulative charge q(t) that has entered a certain device up to time t. Sketch a plot of the corresponding current i(t). q 20 C 0 1 2 3 4 5 t (s) 20 C Figure
Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part II
 Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part II Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part II Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
EE313 Fall 2013 Exam #1 (100 pts) Thursday, September 26, 2013 Name. 1) [6 pts] Convert the following time-domain circuit to the RMS Phasor Domain.
![EE313 Fall 2013 Exam #1 (100 pts) Thursday, September 26, 2013 Name. 1) [6 pts] Convert the following time-domain circuit to the RMS Phasor Domain. EE313 Fall 2013 Exam #1 (100 pts) Thursday, September 26, 2013 Name. 1) [6 pts] Convert the following time-domain circuit to the RMS Phasor Domain.](/thumbs/95/123488230.jpg) Name If you have any questions ask them. Remember to include all units on your answers (V, A, etc). Clearly indicate your answers. All angles must be in the range 0 to +180 or 0 to 180 degrees. 1) [6 pts]
Name If you have any questions ask them. Remember to include all units on your answers (V, A, etc). Clearly indicate your answers. All angles must be in the range 0 to +180 or 0 to 180 degrees. 1) [6 pts]
Electric Circuits II Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis. Dr. Firas Obeidat
 Electric Circuits II Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis Dr. Firas Obeidat 1 Table of Contents 1 2 3 4 5 Nodal Analysis Mesh Analysis Superposition Theorem Source Transformation Thevenin and Norton Equivalent
Electric Circuits II Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis Dr. Firas Obeidat 1 Table of Contents 1 2 3 4 5 Nodal Analysis Mesh Analysis Superposition Theorem Source Transformation Thevenin and Norton Equivalent
3.1 Superposition theorem
 Many electric circuits are complex, but it is an engineer s goal to reduce their complexity to analyze them easily. In the previous chapters, we have mastered the ability to solve networks containing independent
Many electric circuits are complex, but it is an engineer s goal to reduce their complexity to analyze them easily. In the previous chapters, we have mastered the ability to solve networks containing independent
Electric Circuits I. Midterm #1
 The University of Toledo Section number s5ms_elci7.fm - Electric Circuits I Midterm # Problems Points. 3 2. 7 3. 5 Total 5 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo Section number s5ms_elci7.fm
The University of Toledo Section number s5ms_elci7.fm - Electric Circuits I Midterm # Problems Points. 3 2. 7 3. 5 Total 5 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo Section number s5ms_elci7.fm
CHAPTER FOUR CIRCUIT THEOREMS
 4.1 INTRODUCTION CHAPTER FOUR CIRCUIT THEOREMS The growth in areas of application of electric circuits has led to an evolution from simple to complex circuits. To handle the complexity, engineers over
4.1 INTRODUCTION CHAPTER FOUR CIRCUIT THEOREMS The growth in areas of application of electric circuits has led to an evolution from simple to complex circuits. To handle the complexity, engineers over
Design Engineering MEng EXAMINATIONS 2016
 IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Design Engineering MEng EXAMINATIONS 2016 For Internal Students of the Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine This paper is also taken for the relevant examination
IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Design Engineering MEng EXAMINATIONS 2016 For Internal Students of the Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine This paper is also taken for the relevant examination
Homework 2 SJTU233. Part A. Part B. Problem 2. Part A. Problem 1. Find the impedance Zab in the circuit seen in the figure. Suppose that R = 5 Ω.
 Homework 2 SJTU233 Problem 1 Find the impedance Zab in the circuit seen in the figure. Suppose that R = 5 Ω. Express Zab in polar form. Enter your answer using polar notation. Express argument in degrees.
Homework 2 SJTU233 Problem 1 Find the impedance Zab in the circuit seen in the figure. Suppose that R = 5 Ω. Express Zab in polar form. Enter your answer using polar notation. Express argument in degrees.
BFF1303: ELECTRICAL / ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING. Alternating Current Circuits : Basic Law
 BFF1303: ELECTRICAL / ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING Alternating Current Circuits : Basic Law Ismail Mohd Khairuddin, Zulkifil Md Yusof Faculty of Manufacturing Engineering Universiti Malaysia Pahang Alternating
BFF1303: ELECTRICAL / ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING Alternating Current Circuits : Basic Law Ismail Mohd Khairuddin, Zulkifil Md Yusof Faculty of Manufacturing Engineering Universiti Malaysia Pahang Alternating
VI. Transistor amplifiers: Biasing and Small Signal Model
 VI. Transistor amplifiers: iasing and Small Signal Model 6.1 Introduction Transistor amplifiers utilizing JT or FET are similar in design and analysis. Accordingly we will discuss JT amplifiers thoroughly.
VI. Transistor amplifiers: iasing and Small Signal Model 6.1 Introduction Transistor amplifiers utilizing JT or FET are similar in design and analysis. Accordingly we will discuss JT amplifiers thoroughly.
EIT Review. Electrical Circuits DC Circuits. Lecturer: Russ Tatro. Presented by Tau Beta Pi The Engineering Honor Society 10/3/2006 1
 EIT Review Electrical Circuits DC Circuits Lecturer: Russ Tatro Presented by Tau Beta Pi The Engineering Honor Society 10/3/2006 1 Session Outline Basic Concepts Basic Laws Methods of Analysis Circuit
EIT Review Electrical Circuits DC Circuits Lecturer: Russ Tatro Presented by Tau Beta Pi The Engineering Honor Society 10/3/2006 1 Session Outline Basic Concepts Basic Laws Methods of Analysis Circuit
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science : Circuits & Electronics Problem Set #1 Solution
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.2: Circuits & Electronics Problem Set # Solution Exercise. The three resistors form a series connection.
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.2: Circuits & Electronics Problem Set # Solution Exercise. The three resistors form a series connection.
EE292: Fundamentals of ECE
 EE292: Fundamentals of ECE Fall 2012 TTh 10:00-11:15 SEB 1242 Lecture 4 120906 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ee292/ 2 Outline Review Voltage Divider Current Divider Node-Voltage Analysis 3 Network Analysis
EE292: Fundamentals of ECE Fall 2012 TTh 10:00-11:15 SEB 1242 Lecture 4 120906 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ee292/ 2 Outline Review Voltage Divider Current Divider Node-Voltage Analysis 3 Network Analysis
Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part I
 Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part I Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part I Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
Thevenin Norton Equivalencies - GATE Study Material in PDF
 Thevenin Norton Equivalencies - GATE Study Material in PDF In these GATE 2018 Notes, we explain the Thevenin Norton Equivalencies. Thevenin s and Norton s Theorems are two equally valid methods of reducing
Thevenin Norton Equivalencies - GATE Study Material in PDF In these GATE 2018 Notes, we explain the Thevenin Norton Equivalencies. Thevenin s and Norton s Theorems are two equally valid methods of reducing
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 16
 EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 16 Instructions: Write your name and section number on all pages Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You can use
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 16 Instructions: Write your name and section number on all pages Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You can use
Designing Information Devices and Systems I Summer 2017 D. Aranki, F. Maksimovic, V. Swamy Midterm 2. Exam Location: 100 Genetics & Plant Bio
 EECS 16A Designing Information Devices and Systems I Summer 2017 D. Aranki, F. Maksimovic, V. Swamy Midterm 2 Exam Location: 100 Genetics & Plant Bio PINT your student ID: PINT AND SIGN your name:, (last
EECS 16A Designing Information Devices and Systems I Summer 2017 D. Aranki, F. Maksimovic, V. Swamy Midterm 2 Exam Location: 100 Genetics & Plant Bio PINT your student ID: PINT AND SIGN your name:, (last
Lecture 5: Using electronics to make measurements
 Lecture 5: Using electronics to make measurements As physicists, we re not really interested in electronics for its own sake We want to use it to measure something often, something too small to be directly
Lecture 5: Using electronics to make measurements As physicists, we re not really interested in electronics for its own sake We want to use it to measure something often, something too small to be directly
MAE106 Homework 2 - Solution DC Motors & Intro to the frequency domain
 MAE06 Homework 2 - Solution DC Motors & Intro to the frequency domain University of California, Irvine Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Problem You are given the circuit shown in Figure.
MAE06 Homework 2 - Solution DC Motors & Intro to the frequency domain University of California, Irvine Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Problem You are given the circuit shown in Figure.
Electric Circuits I Final Examination
 EECS:300 Electric Circuits I ffs_elci.fm - Electric Circuits I Final Examination Problems Points. 4. 3. Total 38 Was the exam fair? yes no //3 EECS:300 Electric Circuits I ffs_elci.fm - Problem 4 points
EECS:300 Electric Circuits I ffs_elci.fm - Electric Circuits I Final Examination Problems Points. 4. 3. Total 38 Was the exam fair? yes no //3 EECS:300 Electric Circuits I ffs_elci.fm - Problem 4 points
ECE2262 Electric Circuits
 ECE2262 Electric Circuits Equivalence Chapter 5: Circuit Theorems Linearity Superposition Thevenin s and Norton s Theorems Maximum Power Transfer Analysis of Circuits Using Circuit Theorems 1 5. 1 Equivalence
ECE2262 Electric Circuits Equivalence Chapter 5: Circuit Theorems Linearity Superposition Thevenin s and Norton s Theorems Maximum Power Transfer Analysis of Circuits Using Circuit Theorems 1 5. 1 Equivalence
I. Impedance of an R-L circuit.
 I. Impedance of an R-L circuit. [For inductor in an AC Circuit, see Chapter 31, pg. 1024] Consider the R-L circuit shown in Figure: 1. A current i(t) = I cos(ωt) is driven across the circuit using an AC
I. Impedance of an R-L circuit. [For inductor in an AC Circuit, see Chapter 31, pg. 1024] Consider the R-L circuit shown in Figure: 1. A current i(t) = I cos(ωt) is driven across the circuit using an AC
ENGG 225. David Ng. Winter January 9, Circuits, Currents, and Voltages... 5
 ENGG 225 David Ng Winter 2017 Contents 1 January 9, 2017 5 1.1 Circuits, Currents, and Voltages.................... 5 2 January 11, 2017 6 2.1 Ideal Basic Circuit Elements....................... 6 3 January
ENGG 225 David Ng Winter 2017 Contents 1 January 9, 2017 5 1.1 Circuits, Currents, and Voltages.................... 5 2 January 11, 2017 6 2.1 Ideal Basic Circuit Elements....................... 6 3 January
Midterm Exam 2. Prof. Miloš Popović
 Midterm Exam 2 Prof. Miloš Popović 100 min timed, closed book test. Write your name at top of every page (or initials on later pages) Aids: single page (single side) of notes, handheld calculator Work
Midterm Exam 2 Prof. Miloš Popović 100 min timed, closed book test. Write your name at top of every page (or initials on later pages) Aids: single page (single side) of notes, handheld calculator Work
Chapter 2. Engr228 Circuit Analysis. Dr Curtis Nelson
 Chapter 2 Engr228 Circuit Analysis Dr Curtis Nelson Chapter 2 Objectives Understand symbols and behavior of the following circuit elements: Independent voltage and current sources; Dependent voltage and
Chapter 2 Engr228 Circuit Analysis Dr Curtis Nelson Chapter 2 Objectives Understand symbols and behavior of the following circuit elements: Independent voltage and current sources; Dependent voltage and
EE 40: Introduction to Microelectronic Circuits Spring 2008: Midterm 2
 EE 4: Introduction to Microelectronic Circuits Spring 8: Midterm Venkat Anantharam 3/9/8 Total Time Allotted : min Total Points:. This is a closed book exam. However, you are allowed to bring two pages
EE 4: Introduction to Microelectronic Circuits Spring 8: Midterm Venkat Anantharam 3/9/8 Total Time Allotted : min Total Points:. This is a closed book exam. However, you are allowed to bring two pages
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 9
 EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 9 Name: Instructions: Write your name and section number on all pages Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You can
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 9 Name: Instructions: Write your name and section number on all pages Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You can
EE221 - Practice for the Midterm Exam
 EE1 - Practice for the Midterm Exam 1. Consider this circuit and corresponding plot of the inductor current: Determine the values of L, R 1 and R : L = H, R 1 = Ω and R = Ω. Hint: Use the plot to determine
EE1 - Practice for the Midterm Exam 1. Consider this circuit and corresponding plot of the inductor current: Determine the values of L, R 1 and R : L = H, R 1 = Ω and R = Ω. Hint: Use the plot to determine
Chapter 10: Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis
 Chapter 10: Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis 1 Objectives : sinusoidal functions Impedance use phasors to determine the forced response of a circuit subjected to sinusoidal excitation Apply techniques
Chapter 10: Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis 1 Objectives : sinusoidal functions Impedance use phasors to determine the forced response of a circuit subjected to sinusoidal excitation Apply techniques
ECE2262 Electric Circuits. Chapter 5: Circuit Theorems
 ECE2262 Electric Circuits Chapter 5: Circuit Theorems 1 Equivalence Linearity Superposition Thevenin s and Norton s Theorems Maximum Power Transfer Analysis of Circuits Using Circuit Theorems 2 5. 1 Equivalence
ECE2262 Electric Circuits Chapter 5: Circuit Theorems 1 Equivalence Linearity Superposition Thevenin s and Norton s Theorems Maximum Power Transfer Analysis of Circuits Using Circuit Theorems 2 5. 1 Equivalence
Chapter 2 Resistive Circuits
 1. Sole circuits (i.e., find currents and oltages of interest) by combining resistances in series and parallel. 2. Apply the oltage-diision and current-diision principles. 3. Sole circuits by the node-oltage
1. Sole circuits (i.e., find currents and oltages of interest) by combining resistances in series and parallel. 2. Apply the oltage-diision and current-diision principles. 3. Sole circuits by the node-oltage
ECE Spring 2015 Final Exam
 ECE 20100 Spring 2015 Final Exam May 7, 2015 Section (circle below) Jung (1:30) 0001 Qi (12:30) 0002 Peleato (9:30) 0004 Allen (10:30) 0005 Zhu (4:30) 0006 Name PUID Instructions 1. DO NOT START UNTIL
ECE 20100 Spring 2015 Final Exam May 7, 2015 Section (circle below) Jung (1:30) 0001 Qi (12:30) 0002 Peleato (9:30) 0004 Allen (10:30) 0005 Zhu (4:30) 0006 Name PUID Instructions 1. DO NOT START UNTIL
Chapter 5 Objectives
 Chapter 5 Engr228 Circuit Analysis Dr Curtis Nelson Chapter 5 Objectives State and apply the property of linearity State and apply the property of superposition Investigate source transformations Define
Chapter 5 Engr228 Circuit Analysis Dr Curtis Nelson Chapter 5 Objectives State and apply the property of linearity State and apply the property of superposition Investigate source transformations Define
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences E. Alon Final EECS 240 Monday, May 19, 2008 SPRING 2008 You should write your results on the exam
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences E. Alon Final EECS 240 Monday, May 19, 2008 SPRING 2008 You should write your results on the exam
Notes for course EE1.1 Circuit Analysis TOPIC 10 2-PORT CIRCUITS
 Objectives: Introduction Notes for course EE1.1 Circuit Analysis 4-5 Re-examination of 1-port sub-circuits Admittance parameters for -port circuits TOPIC 1 -PORT CIRCUITS Gain and port impedance from -port
Objectives: Introduction Notes for course EE1.1 Circuit Analysis 4-5 Re-examination of 1-port sub-circuits Admittance parameters for -port circuits TOPIC 1 -PORT CIRCUITS Gain and port impedance from -port
Lecture 5: Using electronics to make measurements
 Lecture 5: Using electronics to make measurements As physicists, we re not really interested in electronics for its own sake We want to use it to measure something often, something too small to be directly
Lecture 5: Using electronics to make measurements As physicists, we re not really interested in electronics for its own sake We want to use it to measure something often, something too small to be directly
Basics of Network Theory (Part-I)
 Basics of Network Theory (PartI). A square waveform as shown in figure is applied across mh ideal inductor. The current through the inductor is a. wave of peak amplitude. V 0 0.5 t (m sec) [Gate 987: Marks]
Basics of Network Theory (PartI). A square waveform as shown in figure is applied across mh ideal inductor. The current through the inductor is a. wave of peak amplitude. V 0 0.5 t (m sec) [Gate 987: Marks]
E40M Review - Part 1
 E40M Review Part 1 Topics in Part 1 (Today): KCL, KVL, Power Devices: V and I sources, R Nodal Analysis. Superposition Devices: Diodes, C, L Time Domain Diode, C, L Circuits Topics in Part 2 (Wed): MOSFETs,
E40M Review Part 1 Topics in Part 1 (Today): KCL, KVL, Power Devices: V and I sources, R Nodal Analysis. Superposition Devices: Diodes, C, L Time Domain Diode, C, L Circuits Topics in Part 2 (Wed): MOSFETs,
Georgia Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Midterm-1 Exam (Solution)
 Georgia Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Midterm-1 Exam (Solution) ECE-6414 Spring 2012 Friday, Feb. 17, 2012 Duration: 50min First name Solutions Last name Solutions
Georgia Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Midterm-1 Exam (Solution) ECE-6414 Spring 2012 Friday, Feb. 17, 2012 Duration: 50min First name Solutions Last name Solutions
Module 2. DC Circuit. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 2 DC Circuit Lesson 5 Node-voltage analysis of resistive circuit in the context of dc voltages and currents Objectives To provide a powerful but simple circuit analysis tool based on Kirchhoff s
Module 2 DC Circuit Lesson 5 Node-voltage analysis of resistive circuit in the context of dc voltages and currents Objectives To provide a powerful but simple circuit analysis tool based on Kirchhoff s
ENGR-4300 Spring 2009 Test 2. Name: SOLUTION. Section: 1(MR 8:00) 2(TF 2:00) 3(MR 6:00) (circle one) Question I (20 points): Question II (20 points):
 ENGR43 Test 2 Spring 29 ENGR43 Spring 29 Test 2 Name: SOLUTION Section: 1(MR 8:) 2(TF 2:) 3(MR 6:) (circle one) Question I (2 points): Question II (2 points): Question III (17 points): Question IV (2 points):
ENGR43 Test 2 Spring 29 ENGR43 Spring 29 Test 2 Name: SOLUTION Section: 1(MR 8:) 2(TF 2:) 3(MR 6:) (circle one) Question I (2 points): Question II (2 points): Question III (17 points): Question IV (2 points):
Schedule. ECEN 301 Discussion #20 Exam 2 Review 1. Lab Due date. Title Chapters HW Due date. Date Day Class No. 10 Nov Mon 20 Exam Review.
 Schedule Date Day lass No. 0 Nov Mon 0 Exam Review Nov Tue Title hapters HW Due date Nov Wed Boolean Algebra 3. 3.3 ab Due date AB 7 Exam EXAM 3 Nov Thu 4 Nov Fri Recitation 5 Nov Sat 6 Nov Sun 7 Nov Mon
Schedule Date Day lass No. 0 Nov Mon 0 Exam Review Nov Tue Title hapters HW Due date Nov Wed Boolean Algebra 3. 3.3 ab Due date AB 7 Exam EXAM 3 Nov Thu 4 Nov Fri Recitation 5 Nov Sat 6 Nov Sun 7 Nov Mon
 Network Topology-2 & Dual and Duality Choice of independent branch currents and voltages: The solution of a network involves solving of all branch currents and voltages. We know that the branch current
Network Topology-2 & Dual and Duality Choice of independent branch currents and voltages: The solution of a network involves solving of all branch currents and voltages. We know that the branch current
EECE 2510 Circuits and Signals, Biomedical Applications Final Exam Section 3. Name:
 EECE 2510 Circuits and Signals, Biomedical Applications Final Exam Section 3 Instructions: Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed Scientific calculators are allowed Complete
EECE 2510 Circuits and Signals, Biomedical Applications Final Exam Section 3 Instructions: Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed Scientific calculators are allowed Complete
Designing Information Devices and Systems I Fall 2017 Midterm 2. Exam Location: 150 Wheeler, Last Name: Nguyen - ZZZ
 EECS 16A Designing Information Devices and Systems I Fall 2017 Midterm 2 Exam Location: 150 Wheeler, Last Name: Nguyen - ZZZ PINT your student ID: PINT AND SIGN your name:, (last name) (first name) (signature)
EECS 16A Designing Information Devices and Systems I Fall 2017 Midterm 2 Exam Location: 150 Wheeler, Last Name: Nguyen - ZZZ PINT your student ID: PINT AND SIGN your name:, (last name) (first name) (signature)
Physics 116A Notes Fall 2004
 Physics 116A Notes Fall 2004 David E. Pellett Draft v.0.9 Notes Copyright 2004 David E. Pellett unless stated otherwise. References: Text for course: Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering, second edition,
Physics 116A Notes Fall 2004 David E. Pellett Draft v.0.9 Notes Copyright 2004 David E. Pellett unless stated otherwise. References: Text for course: Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering, second edition,
ELEC 250: LINEAR CIRCUITS I COURSE OVERHEADS. These overheads are adapted from the Elec 250 Course Pack developed by Dr. Fayez Guibaly.
 Elec 250: Linear Circuits I 5/4/08 ELEC 250: LINEAR CIRCUITS I COURSE OVERHEADS These overheads are adapted from the Elec 250 Course Pack developed by Dr. Fayez Guibaly. S.W. Neville Elec 250: Linear Circuits
Elec 250: Linear Circuits I 5/4/08 ELEC 250: LINEAR CIRCUITS I COURSE OVERHEADS These overheads are adapted from the Elec 250 Course Pack developed by Dr. Fayez Guibaly. S.W. Neville Elec 250: Linear Circuits
Two-Port Networks Admittance Parameters CHAPTER16 THE LEARNING GOALS FOR THIS CHAPTER ARE THAT STUDENTS SHOULD BE ABLE TO:
 CHAPTER16 Two-Port Networks THE LEARNING GOALS FOR THIS CHAPTER ARE THAT STUDENTS SHOULD BE ABLE TO: Calculate the admittance, impedance, hybrid, and transmission parameter for two-port networks. Convert
CHAPTER16 Two-Port Networks THE LEARNING GOALS FOR THIS CHAPTER ARE THAT STUDENTS SHOULD BE ABLE TO: Calculate the admittance, impedance, hybrid, and transmission parameter for two-port networks. Convert
QUESTION BANK SUBJECT: NETWORK ANALYSIS (10ES34)
 QUESTION BANK SUBJECT: NETWORK ANALYSIS (10ES34) NOTE: FOR NUMERICAL PROBLEMS FOR ALL UNITS EXCEPT UNIT 5 REFER THE E-BOOK ENGINEERING CIRCUIT ANALYSIS, 7 th EDITION HAYT AND KIMMERLY. PAGE NUMBERS OF
QUESTION BANK SUBJECT: NETWORK ANALYSIS (10ES34) NOTE: FOR NUMERICAL PROBLEMS FOR ALL UNITS EXCEPT UNIT 5 REFER THE E-BOOK ENGINEERING CIRCUIT ANALYSIS, 7 th EDITION HAYT AND KIMMERLY. PAGE NUMBERS OF
= 32.0\cis{38.7} = j Ω. Zab = Homework 2 SJTU233. Part A. Part B. Problem 2. Part A. Problem 1
 Homework 2 SJTU233 Problem 1 Find the impedance Zab in the circuit seen in the figure. Suppose that R = 5 Ω. Express Zab in polar form. Enter your answer using polar notation. Express argument in degrees.
Homework 2 SJTU233 Problem 1 Find the impedance Zab in the circuit seen in the figure. Suppose that R = 5 Ω. Express Zab in polar form. Enter your answer using polar notation. Express argument in degrees.
Circuit Analysis. by John M. Santiago, Jr., PhD FOR. Professor of Electrical and Systems Engineering, Colonel (Ret) USAF. A Wiley Brand FOR-
 Circuit Analysis FOR A Wiley Brand by John M. Santiago, Jr., PhD Professor of Electrical and Systems Engineering, Colonel (Ret) USAF FOR- A Wiley Brand Table of Contents. ' : '" '! " ' ' '... ',. 1 Introduction
Circuit Analysis FOR A Wiley Brand by John M. Santiago, Jr., PhD Professor of Electrical and Systems Engineering, Colonel (Ret) USAF FOR- A Wiley Brand Table of Contents. ' : '" '! " ' ' '... ',. 1 Introduction
Circuit Theorems Overview Linearity Superposition Source Transformation Thévenin and Norton Equivalents Maximum Power Transfer
 Circuit Theorems Overview Linearity Superposition Source Transformation Thévenin and Norton Equivalents Maximum Power Transfer J. McNames Portland State University ECE 221 Circuit Theorems Ver. 1.36 1
Circuit Theorems Overview Linearity Superposition Source Transformation Thévenin and Norton Equivalents Maximum Power Transfer J. McNames Portland State University ECE 221 Circuit Theorems Ver. 1.36 1
4/27 Friday. I have all the old homework if you need to collect them.
 4/27 Friday Last HW: do not need to turn it. Solution will be posted on the web. I have all the old homework if you need to collect them. Final exam: 7-9pm, Monday, 4/30 at Lambert Fieldhouse F101 Calculator
4/27 Friday Last HW: do not need to turn it. Solution will be posted on the web. I have all the old homework if you need to collect them. Final exam: 7-9pm, Monday, 4/30 at Lambert Fieldhouse F101 Calculator
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER APPLICATIONS
 OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER APPLICATIONS 2.1 The Ideal Op Amp (Chapter 2.1) Amplifier Applications 2.2 The Inverting Configuration (Chapter 2.2) 2.3 The Non-inverting Configuration (Chapter 2.3) 2.4 Difference
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER APPLICATIONS 2.1 The Ideal Op Amp (Chapter 2.1) Amplifier Applications 2.2 The Inverting Configuration (Chapter 2.2) 2.3 The Non-inverting Configuration (Chapter 2.3) 2.4 Difference
Designing Information Devices and Systems I Spring 2017 Babak Ayazifar, Vladimir Stojanovic Midterm 2. Exam location: 145 Dwinelle, last SID# 2
 EECS 16A Designing Information Devices and Systems I Spring 2017 Babak Ayazifar, Vladimir Stojanovic Midterm 2 Exam location: 145 Dwinelle, last SID# 2 PRINT your student ID: PRINT AND SIGN your name:,
EECS 16A Designing Information Devices and Systems I Spring 2017 Babak Ayazifar, Vladimir Stojanovic Midterm 2 Exam location: 145 Dwinelle, last SID# 2 PRINT your student ID: PRINT AND SIGN your name:,
Basic RL and RC Circuits R-L TRANSIENTS: STORAGE CYCLE. Engineering Collage Electrical Engineering Dep. Dr. Ibrahim Aljubouri
 st Class Basic RL and RC Circuits The RL circuit with D.C (steady state) The inductor is short time at Calculate the inductor current for circuits shown below. I L E R A I L E R R 3 R R 3 I L I L R 3 R
st Class Basic RL and RC Circuits The RL circuit with D.C (steady state) The inductor is short time at Calculate the inductor current for circuits shown below. I L E R A I L E R R 3 R R 3 I L I L R 3 R
Circuits with Capacitor and Inductor
 Circuits with Capacitor and Inductor We have discussed so far circuits only with resistors. While analyzing it, we came across with the set of algebraic equations. Hereafter we will analyze circuits with
Circuits with Capacitor and Inductor We have discussed so far circuits only with resistors. While analyzing it, we came across with the set of algebraic equations. Hereafter we will analyze circuits with
Chapter 9 Objectives
 Chapter 9 Engr8 Circuit Analysis Dr Curtis Nelson Chapter 9 Objectives Understand the concept of a phasor; Be able to transform a circuit with a sinusoidal source into the frequency domain using phasor
Chapter 9 Engr8 Circuit Analysis Dr Curtis Nelson Chapter 9 Objectives Understand the concept of a phasor; Be able to transform a circuit with a sinusoidal source into the frequency domain using phasor
Chapter 7. Chapter 7
 Chapter 7 Combination circuits Most practical circuits have combinations of series and parallel components. You can frequently simplify analysis by combining series and parallel components. An important
Chapter 7 Combination circuits Most practical circuits have combinations of series and parallel components. You can frequently simplify analysis by combining series and parallel components. An important
San Jose State University Department of Electrical Engineering. Exam 2 Solution. EE 098-MIT 6.002x Fall 2012
 San Jose State University Department of Electrical Engineering Exam Solution EE 98-MIT 6.x Fall 1 losed Book, losed Notes, and no electronic devices. Instructions: There are six problems. Interpretation
San Jose State University Department of Electrical Engineering Exam Solution EE 98-MIT 6.x Fall 1 losed Book, losed Notes, and no electronic devices. Instructions: There are six problems. Interpretation
Voltage Dividers, Nodal, and Mesh Analysis
 Engr228 Lab #2 Voltage Dividers, Nodal, and Mesh Analysis Name Partner(s) Grade /10 Introduction This lab exercise is designed to further your understanding of the use of the lab equipment and to verify
Engr228 Lab #2 Voltage Dividers, Nodal, and Mesh Analysis Name Partner(s) Grade /10 Introduction This lab exercise is designed to further your understanding of the use of the lab equipment and to verify
ECE-202 FINAL April 30, 2018 CIRCLE YOUR DIVISION
 ECE 202 Final, Spring 8 ECE-202 FINAL April 30, 208 Name: (Please print clearly.) Student Email: CIRCLE YOUR DIVISION DeCarlo- 7:30-8:30 DeCarlo-:30-2:45 2025 202 INSTRUCTIONS There are 34 multiple choice
ECE 202 Final, Spring 8 ECE-202 FINAL April 30, 208 Name: (Please print clearly.) Student Email: CIRCLE YOUR DIVISION DeCarlo- 7:30-8:30 DeCarlo-:30-2:45 2025 202 INSTRUCTIONS There are 34 multiple choice
Electronics II. Final Examination
 The University of Toledo f17fs_elct27.fm 1 Electronics II Final Examination Problems Points 1. 11 2. 14 3. 15 Total 40 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo f17fs_elct27.fm 2 Problem 1 11
The University of Toledo f17fs_elct27.fm 1 Electronics II Final Examination Problems Points 1. 11 2. 14 3. 15 Total 40 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo f17fs_elct27.fm 2 Problem 1 11
Chapter 10: Sinusoids and Phasors
 Chapter 10: Sinusoids and Phasors 1. Motivation 2. Sinusoid Features 3. Phasors 4. Phasor Relationships for Circuit Elements 5. Impedance and Admittance 6. Kirchhoff s Laws in the Frequency Domain 7. Impedance
Chapter 10: Sinusoids and Phasors 1. Motivation 2. Sinusoid Features 3. Phasors 4. Phasor Relationships for Circuit Elements 5. Impedance and Admittance 6. Kirchhoff s Laws in the Frequency Domain 7. Impedance
Final Exam. 55:041 Electronic Circuits. The University of Iowa. Fall 2013.
 Final Exam Name: Max: 130 Points Question 1 In the circuit shown, the op-amp is ideal, except for an input bias current I b = 1 na. Further, R F = 10K, R 1 = 100 Ω and C = 1 μf. The switch is opened at
Final Exam Name: Max: 130 Points Question 1 In the circuit shown, the op-amp is ideal, except for an input bias current I b = 1 na. Further, R F = 10K, R 1 = 100 Ω and C = 1 μf. The switch is opened at
Electric Circuits Fall 2015 Solution #5
 RULES: Please try to work on your own. Discussion is permissible, but identical submissions are unacceptable! Please show all intermeate steps: a correct solution without an explanation will get zero cret.
RULES: Please try to work on your own. Discussion is permissible, but identical submissions are unacceptable! Please show all intermeate steps: a correct solution without an explanation will get zero cret.
Problem Set 4 Solutions
 University of California, Berkeley Spring 212 EE 42/1 Prof. A. Niknejad Problem Set 4 Solutions Please note that these are merely suggested solutions. Many of these problems can be approached in different
University of California, Berkeley Spring 212 EE 42/1 Prof. A. Niknejad Problem Set 4 Solutions Please note that these are merely suggested solutions. Many of these problems can be approached in different
Designing Information Devices and Systems II Spring 2016 Anant Sahai and Michel Maharbiz Midterm 2
 EECS 16B Designing Information Devices and Systems II Spring 2016 Anant Sahai and Michel Maharbiz Midterm 2 Exam location: 145 Dwinelle (SIDs ending in 1 and 5) PRINT your student ID: PRINT AND SIGN your
EECS 16B Designing Information Devices and Systems II Spring 2016 Anant Sahai and Michel Maharbiz Midterm 2 Exam location: 145 Dwinelle (SIDs ending in 1 and 5) PRINT your student ID: PRINT AND SIGN your
Lecture #3. Review: Power
 Lecture #3 OUTLINE Power calculations Circuit elements Voltage and current sources Electrical resistance (Ohm s law) Kirchhoff s laws Reading Chapter 2 Lecture 3, Slide 1 Review: Power If an element is
Lecture #3 OUTLINE Power calculations Circuit elements Voltage and current sources Electrical resistance (Ohm s law) Kirchhoff s laws Reading Chapter 2 Lecture 3, Slide 1 Review: Power If an element is
'XNH8QLYHUVLW\ (GPXQG73UDWW-U6FKRRORI(QJLQHHULQJ. ECE 110 Fall Test II. Michael R. Gustafson II
 'XNH8QLYHUVLW\ (GPXQG73UDWW-U6FKRRORI(QJLQHHULQJ ECE 110 Fall 2016 Test II Michael R. Gustafson II Name (please print) In keeping with the Community Standard, I have neither provided nor received any assistance
'XNH8QLYHUVLW\ (GPXQG73UDWW-U6FKRRORI(QJLQHHULQJ ECE 110 Fall 2016 Test II Michael R. Gustafson II Name (please print) In keeping with the Community Standard, I have neither provided nor received any assistance
Experiment #6. Thevenin Equivalent Circuits and Power Transfer
 Experiment #6 Thevenin Equivalent Circuits and Power Transfer Objective: In this lab you will confirm the equivalence between a complicated resistor circuit and its Thevenin equivalent. You will also learn
Experiment #6 Thevenin Equivalent Circuits and Power Transfer Objective: In this lab you will confirm the equivalence between a complicated resistor circuit and its Thevenin equivalent. You will also learn
Chapter 10 Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis Chapter Objectives:
 Chapter 10 Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis Chapter Objectives: Apply previously learn circuit techniques to sinusoidal steady-state analysis. Learn how to apply nodal and mesh analysis in the frequency
Chapter 10 Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis Chapter Objectives: Apply previously learn circuit techniques to sinusoidal steady-state analysis. Learn how to apply nodal and mesh analysis in the frequency
GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL of ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING FINAL EXAM. COURSE: ECE 3084A (Prof. Michaels)
 GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL of ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING FINAL EXAM DATE: 30-Apr-14 COURSE: ECE 3084A (Prof. Michaels) NAME: STUDENT #: LAST, FIRST Write your name on the front page
GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL of ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING FINAL EXAM DATE: 30-Apr-14 COURSE: ECE 3084A (Prof. Michaels) NAME: STUDENT #: LAST, FIRST Write your name on the front page
Electrical Circuits Lab Series RC Circuit Phasor Diagram
 Electrical Circuits Lab. 0903219 Series RC Circuit Phasor Diagram - Simple steps to draw phasor diagram of a series RC circuit without memorizing: * Start with the quantity (voltage or current) that is
Electrical Circuits Lab. 0903219 Series RC Circuit Phasor Diagram - Simple steps to draw phasor diagram of a series RC circuit without memorizing: * Start with the quantity (voltage or current) that is
ECEN 325 Electronics
 ECEN 325 Electronics Introduction Dr. Aydın İlker Karşılayan Texas A&M University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Ohm s Law i R i R v 1 v v 2 v v 1 v 2 v = v 1 v 2 v = v 1 v 2 v = ir
ECEN 325 Electronics Introduction Dr. Aydın İlker Karşılayan Texas A&M University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Ohm s Law i R i R v 1 v v 2 v v 1 v 2 v = v 1 v 2 v = v 1 v 2 v = ir
D is the voltage difference = (V + - V - ).
 1 Operational amplifier is one of the most common electronic building blocks used by engineers. It has two input terminals: V + and V -, and one output terminal Y. It provides a gain A, which is usually
1 Operational amplifier is one of the most common electronic building blocks used by engineers. It has two input terminals: V + and V -, and one output terminal Y. It provides a gain A, which is usually
