United States Patent (19)
|
|
|
- Mavis Briggs
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 United States Patent (19) Tsutsui 11) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,564,284 Jan. 14, 1986 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR EXPOSURE APPARATUS (75 Inventor: Shinji Tsutsui, Yokohama, Japan 73) Assignee: Canon Kabushiki Kaisha, Tokyo, Japan 21 Appl. No.: 741, Filed: Jun. 5, 1985 Related U.S. Application Data 63 Continuation of Ser. No. 531,298, Sep. 12, 1983, aban doned. 30 Foreign Application Priority Data Sep. 12, 1983 JP Japan ) Int. Cl... G03B 27/52; G03B 27/20 52 U.S. Cl /30; 355/53; 355/91 58) Field of Search /78, 79, 91, 125, 355/53, 30; 430/5, 311, 319; 428/65, ) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 4,432,635 2/1984 Mayer /30 4,496,239 1/1985 Isohata et al /30 4,503,335 3/1985 Takahashi /30 X Primary Examiner-L. T. Hix Assistant Examiner-Della Rutledge Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Fitzpatrick, Cella, Harper & Scinto 57 ABSTRACT In a semiconductor exposure apparatus having chucks for holding a mask and a wafer, respectively, the hold ing portion of at least one of the chucks has a coefficient of linear expansion equal to or smaller than the coeffici ent of linear expansion of the bodies held. Particularly, the coefficient of linear expansion of the holding por tion of the chuck should preferably be of a small abso lute value, but even where the absolute value of the coefficient of linear expansion is great, the chucks are usable by providing temperature control. 19 Claims, 3 Drawing Figures PROJECTION OPTICAL SYSTEM VACUUM SOURCE
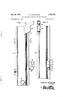
2 U.S. Patent Jan. 14, 1986 Sheet 1 of 2 4,564,284 FIG. I PROJECTION VACUUM 5 SYSTEM SOURCE OPTICAL w S: 6, D, Ag:
3 U.S. Patent Jan. 14, 1986 Sheet 2 of 2 4,564,284 PROJECTION OPTICAL SYSTEM 3 TEMP CONTROL l POWER SOURCE Zazza772 NSle N 2ZZZZYZZZZZZZZZZZ SS NSNNNNN N N N
4 1. SEMCONDUCTOR EXPOSURE APPARATUS This application is a continuation of application Ser. No. 531,298 filed Sept. 12, 1983, now abandoned. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 1. Field of the Invention This invention relates to a semiconductor exposure apparatus used in an integrated circuit manufacturing process and having chucks designed to suppress the magnification error for the pattern of the preceding step when the pattern of a mask is transferred onto a semi conductor wafer. 2. Description of the Prior Art In integrated circuit manufacturing, the step of pro jecting and transferring a mask pattern onto a semicon ductor wafer substrate is done plural times. At this time, it is necessary that the mask pattern of the next step be highly accurately aligned over the entire surface of the wafer relative to the mask pattern transferred onto the wafer in the preceding step. Generally, a semiconductor wafer is adsorbed to a wafer chuck which is a support means for fixedly sup porting the wafer and, once the wafer is held to the wafer chuck, the vacuum is not released until exposure is completed. Heretofore, the wafer chuck has been made of a metal, such as aluminum or stainless steel, which is very sensitive to the thermal expansion and contraction caused by fluctuation of the ambient ten peratures as compared with the wafer. That is, it has been confirmed that when the wafer chuck creates a minute amount of expansion and contraction with the wafer held to the wafer chuck, the wafer also creates expansion and contraction exceeding the elongation. percentage intrinsic to the wafer. For example, let it be assumed that the temperature around the chuck has risen by 0.2 C. from after a silicon wafer has been adsorbed to a wafer chuck made of aluminum until exposure is started, and the temperatures of the wafer and wafer chuck have also risen correspondingly. Here tofore, in such a case, due to the coefficient of linear expansion (2.5X10-6/C.) of the silicon wafer, the amount of expansion of a wafer of 5 inches has been only about 0.06 um and this has been considered to be a negligible amount. At this time, the wafer chuck (whose coefficient of linear expansion is 23x 106/'C) expands to about 0.6 um and the wafer is pulled by the friction force with the chuck and exhibits an amount of elongation approximate thereto. Accordingly, if expo sure is effected in such condition, a magnification error occurs between the pattern of the preceding step and the pattern of the current step and highly accurate alignment of the wafer over the entire surface thereof becomes impossible. In recent years, various methods of highly accurately aligning a mask pattern and a wafer pattern by controlling the temperature of the wafer have been devised. However, if the temperature of the wafer chuck is changed after the wafer has been fixed to the wafer chuck, a great amount of elongation occurs in the wafer chuck which therefore, the wafer is pulled thereby, and has led to the disadvantage that an amount of expansion and contraction greater than necessary OCCS. For this reason, it has been very difficult to achieve highly accurate alignment of the wafer over the entire surface thereof in a case where use is made of a wafer 4,564, chuck made of a metal such as stainless steel or alumi ill. A similar tendency seems to occur not only in the wafer and wafer chuck but also in the mask and mask chuck although there is difference in degree. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION It is an object of the present invention to prevent, after a body such as a mask or a wafer has been vacuum adsorbed or held to a chuck, the held body from creat ing an amount of expansion and contraction exceeding the amount of expansion and contraction by its own temperature change due to a temperature change of the chuck. It is another object of the present invention to pro vide a semiconductor exposure apparatus in which the magnification error for the pattern of the preceding step is suppressed when a mask pattern is transferred onto a wafer. The invention will become fully apparent from the following detailed description thereof taken in conjunc tion with the accompanying drawings. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS FIG. 1 illustrates a projection type semiconductor exposure apparatus which is an embodiment of the pres ent invention. FIG. 2 shows an embodiment of the wafer chuck according to the present invention which has a two piece structure. FIG. 3 shows an example of the arrangement for limiting the temperature of the chuck. DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS Referring to FIG. 1, a photomask 1 and a wafer 2 are vacuum-adsorbed that is, held by a negative pressure to a mask chuck 3 and a wafer chuck 4, respectively, by a vacuum source 6, and the mask pattern of the mask chuck 3 to which a light beam 7 for exposure is applied is projected onto the wafer 2 by a projection optical system 5. Now, embodiments of the chuck of the present inven tion will be shown below. Herein, only a case where the material of the semiconductor wafer is silicon is consid ered. In a first embodiment, ceramics, silicon or Hastelloy A is employed as the material of the wafer chuck. The standard composition of Hastelloy A is Ni55-59%, Mo 18-12%, C % and Fe 18-22%. As regards the coefficients of linear expansion of these materials, the coefficient of linear expansion of ceramics, particularly, silicon nitride (Si3N4) is 3.0x10-6/C. (Industrial Ma terials, (1982)), that of silicon is 2.5x10-6/C. (Physical Constant Table) and that of Hastelloy A is 2.7 x 10-6/ C. (Mechanical Engineering Handbook, 6th Edition), and these are substantially coincident with the coefficient of linear expansion (2.5X 10-6/'C) of silicon wafer. The use of a wafer chuck formed of these materials results in obtainment of the following effect. First, let it be assumed that the wafer is held to the wafer chuck, whereafter the temperature around the chuck is changed by some influence or other and the temperatures of the wafer chuck and the wafer are correspondingly changed. Heretofore, the wafer chuck has been made of aluminum or stainless steel and partic ularly in the case of aluminum, the wafer chuck has a coefficient of linear expansion about ten times as great
5 3 as that of silicon and therefore, even if the temperature change is small, the amount of expansion and contrac tion of the chuck is significant and the wafer also is pulled by the expansion and contraction of the chuck, and such temperature change leads to a magnification error. Accordingly, by using as the material of the wafer chuck the aformentioned material having a coef. ficient of expansion approximate to the coefficient of expansion of the wafer, the amounts of expansion and contraction of the wafer chuck and the wafer are made smaller than the amount of expansion and contraction of the conventional chuck for some temperature change and are made innegligible and, since substantially the same amount of expansion and contraction occurs to the wafer and the chuck simultaneously, the stress by heat does not remain in the wafer due to the expansion and contraction thereof. Further, in an apparatus wherein the temperature of the wafer or the wafer chuck is controlled to purposely achieve the expansion and contraction of the wafer and thereby correct the magnification error, even when a temperature change is imparted to the wafer after being fixed to the wafer chuck, if the wafer chuck is formed of said material, the expansion and contraction of the wafer is not hampered by the chuck and therefore, an accurate preestimate of the amount of expansion and contraction thereof becomes possible and highly accu rate correction of the magnification error becomes pos sible. However, where ceramics or silicon is used for the wafer chuck, it would be very difficult to form the entire chuck of such material because these materials are not easy to machine. However, the entire chuck need not always be formed of a single material, but only the portion thereof which holds the wafer may be formed of a required material and the other portion thereof may be formed of a conventionally used metal, for example, whereby a sufficient effect may be ob itained. Of course, however, the portion of the wafer chuck which holds the wafer must be of a sufficient thickness not to transfer the deformation of the metal to the wafer. An example of the wafer chuck having such two-piece structure is shown in FIG. 2. In FIG. 2, refer ence character 4a designates the metal portion of the wafer chuck and reference character 4b denotes the ceramics portion of the wafer chuck. Description will now be made of a second embodi ment in which the material of the mask chuck is ceram ics or invar. Soda-lime glass, LE-30 or quartz glass is generally used as the material of the photomask, but herein LE-30 and quartz glass will be considered. Among ceramics, the coefficient of linear expansion of silicon carbide (SiC) is 4.0x10-6/ C. (which some what differs depending on the type of crystal and the sintering method) and this is substantially coincident with the coefficient of linear expansion 3.7x10-6/C. of LE-30, and the coefficient of linear expansion of invar is 0.9X 10-6/C. (Mechanical Engineering Hand book, 6th Edition; invar has its coefficient of the com ponents thereof) and this is approximate to the coeffici ent of linear expansion 0.5X 10-6/ C. of quartz glass. The standard composition of invar is C<0.20%, Mn 0.5%, Ni 36% and Fe remainder. Accordingly, by forming the mask chuck by the use of these materials, there is obtained an effect similar to that of the above described first embodiment. Description will now be made of a third embodiment in which super invar, which is a metal of low expansion, 4,564, is used as the material of the mask chuck or the wafer chuck, the coefficient of linear expansion of this mate rial is x 10 6/ C. (Mechanical Engineering Handbook, 6th Edition), which is a very samll value as compared with coefficient of linear expansion of silicon wafer or quartz glass mask. Super invar comprises invar with Co added thereto and its coefficient of linear ex pansion is lowest for Co 5%, Ni31.5% and Fe 63.5%. Therefore, if a mask chuck or a wafer chuck formed of super invar, expansion and contraction will hardly occur in the two chucks even if the ambient tempera ture fluctuates after the mask or the wafer has once been fixed to the chuck and accordingly, the expansion and contraction of the photomask or the wafer substrate fixed thereto by vacuum adsorption will also be sup pressed. Thus, the use of a mask chuck or a wafer chuck formed of super invar makes the expansion and contrac tion of the mask or the wafer very stable for over tem perature and easily prevents occurrence of the magnifi cation error resulting from temperature change. As described above, by a material having an abso lutely low coefficient of linear expansion equal to or smaller than that of the photomask or the wafer being used as the material of the mask chuck or the wafer chuck, the planar expansion and contraction of the mask and wafer resulting from temperature changes is re duced as compared with the conventional case where metal chucks are used, and the magnification error oc curring when a mask pattern is projected and trans ferred onto the wafer becomes smaller and thus, more highly accurate alignment can be achieved over the entire surface of the wafer. In the above-described embodiments, silicon single crystal has typically been used as the material of the semiconductor wafer substrate, but the same concep tion can also apply to other wafer substrates such as GaAs, SoS, quartz substrate, etc. and a sufficient effect can be expected by carrying out the present invention. In the foregoing, description has been made of the embodiments in which the coefficient of linear expan sion of the holding portion of the chuck is of a small absolute value substantially coincident with the coeffi cient of linear expansion of the mask or the wafer, but where the coefficient of linear expansion of the portion of the chuck is of a great absolute value substantially coincident with the coefficient of linear expansion of the mask or the wafer, such chuck can be used by con trolling the temperature of the mask or the wafer. Also, where the coefficient of linear expansion of the adsorbing portion of the chuck is smaller than the coef ficient of linear expansion of the mask or the wafer and the absolute value to that coefficient of linear expansion is of a great absolute value, such chuck is usable by temperature control. Controlling the temperture of the mask or the wafer is useful not only where the coefficient of linear expan sion of the holding portion of the chuck is of a high absolute value, but also where it is of a low absolute value. The above-described temperature control may be effected in a manner as shown, for example, in FIG. 3. FIG. 3 shows a semiconductor exposure apparatus in which only the wafer chuck is temperature-controlled. The wafer chuck 4 fixedly supports the wafer 2 by vacuum and, in the interior thereof, there are provided a heating resistor 9 which is a heating means for making the temperature of the wafer chuck higher by several degrees than the room temperature, a cooling air inlet
6 5 11 and a cooling air outlet 12 for circulating air of nor mal temperature as cooling air, and a platinum tempera ture measuring resistor 8 for detecting the temperature of the interior of the chuck. The mask pattern and the wafer pattern are aligned and at the same time, the magnification errors of the two patterns are read, and the temperature width to be varied is calculated from the values of the magnification errors and the coefficient of linear expansion of the wafer, and then a temperature having this value added to the current temperature of the chuck is set by a tem perature control device 13. Thereafter, the temperature control device 13 is oper ated and the temperature of the wafer chuck is con trolled so that the difference between the temperature detected by the platinum temperature measuring resis tor 8 and the set temperature becomes zero. In FIG. 3, reference numeral 10 designates a radiator plate and reference numeral 14 denotes a power source. In the above-described embodiment, air cooled by a cooling device, instead of the air of normal temperature, may be used as the cooling air. In such case, the cooling speed of the chuck is further increased and the tempera ture control below the room temperature becomes pos sible and therefore, efficient correction of the magnifi cation error in a wider range is possible. The cooling device referred to herein need not al ways have the temperature controlling function, but a sufficient effect may be provided even by a simple cool ing device utilizing, for example, the adiabatic expan sion of air. What we claim is: 1. A semiconductor exposure apparatus having: a mask clutch for holding a mask; and a wafer chuck for holding a wafer; the holding portion of at least one of said chucks having a coefficient of linear expansion substan tially coincident with the coefficient of linear ex pansion of the mask or the wafer held thereby. 2. A semiconductor exposure apparatus according to claim 1, wherein the coefficient of linear expansion of...said holding portion of said chuck has a small absolute value. 3. A semiconductor exposure apparatus according to claim 2, wherein said holding portion includes a ce ramic, 4. A semiconductor exposure apparatus according to claim 2, wherein said holding portion includes silicon. 5. A semiconductor exposure apparatus according to claim 2, wherein said holding portion includes Hastel loy A. 6. A semiconductor exposure apparatus according to claim 2, wherein said holding portion includes invar. 7. A semiconductor exposure apparatus having: mask chuck for holding a mask; and a wafer chuck for holding a wafer; the holding portion of at least one of said chucks having a coefficient of linear expansion smaller than the coefficient of linear expansion of the mask of the wafer held thereby. 8. A seminconductor exposure apparatus according to claim 7, wherein the coefficient of linear expansion of said holding portion of said chuck has a small absolute value. 9. A semiconductor exposure apparatus according to claim 8, wherein said holding portion includes super invar. 10. A semiconductor exposure apparatus having: a mask chuck for holding a mask; 4,564, a wafer chuck for holding a wafer; the holding portion of at least one of said chucks having a coefficient of linear expansion substan tially coincident with the coefficient of linear ex pansion of the mask or the wafer held thereby; and temperature control means for controlling the tem perature of at least one of said chucks. 11. A seminconductor exposure apparatus having: a mask chuck for holding a mask; a wafer chuck for holding a wafer; the holding portion of at least one of said chucks having a coefficient of linear expansion smaller than the coefficient of linear expansion of the mask or the wafer held thereby; and temperature control means for controlling the tem perature of at least one of said chucks. 12. A holding apparatus for holding a seminconduc tor mask or wafer, the apparatus comprising: a chuck for holding the mask or wafer, said chuck including a holding portion having a coefficient of linear expansion substantially coincident with the coefficient of linear expansion of the mask or wafer held thereby; and means for cooperating with said holding portion for applying a megative pressure thereto to hold the mask or wafer on said holding portion. 13. A holding apparatus according to claim 12, fur ther comprising temperature control means for control ling the temperature of said chuck. 14. A holding apparatus for holding a semiconductor mask or wafer, the apparatus comprising: a chuck for holding the mask or wafer, said chuck including a holding portion having a coefficient of linear expansion smaller than the coefficient of linear expansion of the mask or wafer held thereby; and means for cooperating with said chucks to apply a negative pressure to said holding portion to hold the mask or wafer on said holding portion. 15. A holding apparatus according to claim 14, fur ther comprising temperature control means for control ling the temperature of said chuck. 16. A holding apparatus for holding at least one of a semiconductor mask and wafer, said apparatus compris 1ng: a chuck for holding said at least one of said mask and wafer, said chuck including a holding portion hav ing a coefficient of linear expansion substantially coincident with the coefficient of linear expansion of said at least one of said mask and wafer held thereby; and means for securing said at least one of said mask and wafer on said holding portion. 17. A holding apparatus according to claim 16, fur ther comprising temperature control means for control ling the temperature of said chuck. 18. A holding apparatus for holding at least one of a semiconductor mask and wafer, the apparatus compris 1ng: a chuck for holding said at least one of said mask and wafer, said chuck including a holding portion hav ing a coefficient of linear expansion smaller than the coefficient of linear expansion of said at least one of said mask and wafer held thereby; and means for securing one of the mask and wafer on said holding portion. 19. A holding apparatus according to claim 18, fur ther comprising temperature control means for control ling the temperature of said chuck. k sk sk k 2k
7 UNITED STATES PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE CERTIFICATE OF CORRECTION PATENT NO. : 4,564, 284 Page 1 of 2 DATED January 14, 1986 SHINJI TSUTSUI NVENTOR(S) : It is certified that error appears in the above-identified patent and that said Letters Patent is hereby Corrected as shown below: Column 1, line 23, change "adsorbed" to --held-- lines 30-31, change "tem-peratures" to --temperature--; line 49, change "expands to about" to --expands by about-- and change - pulled by the" to --pulled due to the - - line 62, change "which therefore," to --and therefore, --; and line 63, change "and has led" to --which has led--. Column 2, line 37, change "r-adsorbed to" to ---adsorbed, that--. Column 4, line 4, change "samlil" to --Small--; line 9, change "Therefore, if" to --Therefore, in--; line 18, change "for over" to --over--; line 50 change "adsorbing" to --holding --; and line 55, change "temperture" to --temperature--.
8 UNITED STATES PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE CERTIFICATE OF CORRECTION PATENT NO. : 4,564, 284 Page 2 of 2 DATED January 14, 1986 INVENTOR(S) : SHINJI TSUTSUI It is certified that error appears in the above-identified patent and that said Letters Patent is hereby Corrected as shown below: Column 5 line 27, change "temperature controlling" to --temperature-controlling--; line 31, change "What we claim is : " to --What I claim is :- ; line 33, change "a mask clutch" to -- a Imask chuck--; line 59, change "of the wafer" to --Or the wafer-- and line 60, change "A seminconductor" to --A semiconductor -r-. Column 6 line 8, change "A seminconductor" to --A semiconductor -7-; lines 16-17, change "seminconductor" to --semiconductor-r-; and line 24, change "megative" to --negative--. Cover page, --Sep. 16, 1982 JP -- SEAL Attest: 30, change "Sep. 12, 1983 JP" to eigned and escaled this Ninth O ay O f September 1986 Attesting Officer DONALD J. QUIGG Connaissioner of stents and Trademarks
Sep. 2, 1993 (JP) Japan (51 int. Cl... GOR 33/02
 United States Patent (19) Tomita et al. 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MEASURING AMAGNETIC FELD USNGA MAGNETIC FORCE MCROSCOPE BY MAGNETZNG A PROBE AND CORRECTING A DETECTED MAGNETIC FIELD 75) Inventors:
United States Patent (19) Tomita et al. 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MEASURING AMAGNETIC FELD USNGA MAGNETIC FORCE MCROSCOPE BY MAGNETZNG A PROBE AND CORRECTING A DETECTED MAGNETIC FIELD 75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1
 USOO6249200B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1 Stelter et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Jun. 19, 2001 (54) COMBINATION OF MAGNETS FOR 4.673,482 * 6/1987 Setoyama et al.... 204/298
USOO6249200B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1 Stelter et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Jun. 19, 2001 (54) COMBINATION OF MAGNETS FOR 4.673,482 * 6/1987 Setoyama et al.... 204/298
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 OO10407A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0010407 A1 Ker et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LOW-CAPACITANCE BONDING PAD FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
US 2001 OO10407A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0010407 A1 Ker et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LOW-CAPACITANCE BONDING PAD FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Rodov 54 METHOD OF MANUFACTURE OF ZENER DODES (75 Inventor: Vladimir Rodov, Los Angeles, Calif. 73) Assignee: International Rectifier Corporation, Los Angeles, Calif. 21 Appl.
United States Patent (19) Rodov 54 METHOD OF MANUFACTURE OF ZENER DODES (75 Inventor: Vladimir Rodov, Los Angeles, Calif. 73) Assignee: International Rectifier Corporation, Los Angeles, Calif. 21 Appl.
United States Patent (19) Gruaz et al.
 United States Patent (19) Gruaz et al. (54) DEVICE FOR LOCATING AN OBJECT SITUATED CLOSE TO A DETECTION AREA AND A TRANSPARENT KEYBOARD USING SAID DEVICE 75 Inventors: Daniel Gruaz, Montigny le Bretonneux;
United States Patent (19) Gruaz et al. (54) DEVICE FOR LOCATING AN OBJECT SITUATED CLOSE TO A DETECTION AREA AND A TRANSPARENT KEYBOARD USING SAID DEVICE 75 Inventors: Daniel Gruaz, Montigny le Bretonneux;
United States Patent (19) Tanaka
 United States Patent (19) Tanaka 4 CAPACTANCE-VOLTAGE CONVERTER 7 inventor: Katsuaki Tanaka, Sagamihara, Japan 73 Assignee: Iwasaki Tsushinki Kabushiki Kaisha, Japan 22 Filed: May 16, 1973 (21) Appl. No.:
United States Patent (19) Tanaka 4 CAPACTANCE-VOLTAGE CONVERTER 7 inventor: Katsuaki Tanaka, Sagamihara, Japan 73 Assignee: Iwasaki Tsushinki Kabushiki Kaisha, Japan 22 Filed: May 16, 1973 (21) Appl. No.:
United States Patent (19) Ishikawa et al.
 United States Patent (19) Ishikawa et al. 54 NTCTHERMISTOR COMPOSITION BASED ON BARUMTTANATE 75) Inventors: Terunobu Ishikawa; Hideaki Niimi; Yasunobu Yoneda, all of 73 Assignee: Nagaokakyo, Japan Murata
United States Patent (19) Ishikawa et al. 54 NTCTHERMISTOR COMPOSITION BASED ON BARUMTTANATE 75) Inventors: Terunobu Ishikawa; Hideaki Niimi; Yasunobu Yoneda, all of 73 Assignee: Nagaokakyo, Japan Murata
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Fremery et al. 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 28, 1986 54 METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR GAS PRESSURE MEASUREMENT BY THE GAS-FRCTION PRINCIPLE (75) Inventors: Johan
United States Patent (19) Fremery et al. 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 28, 1986 54 METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR GAS PRESSURE MEASUREMENT BY THE GAS-FRCTION PRINCIPLE (75) Inventors: Johan
III. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,143,451 (45. Date of Patent: Sep. 1, Millgard
 United States Patent (19) Millgard 54 METHOD TO MEASURE A TEMPERATURE WITH A PELTER ELEMENT 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: 21) 22 Appl. No.: Filed: Lars O. A. Millgard, Ostersund, Sweden Affairsverket FFV,
United States Patent (19) Millgard 54 METHOD TO MEASURE A TEMPERATURE WITH A PELTER ELEMENT 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: 21) 22 Appl. No.: Filed: Lars O. A. Millgard, Ostersund, Sweden Affairsverket FFV,
I IIIII IIIII lll (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2. (45) Date of Patent:
 I 1111111111111111 11111 1111111111 111111111111111 IIIII IIIII lll111111111111111 US007165566B2 c12) United States Patent Beebe (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jan.23,2007 (54) METHOD
I 1111111111111111 11111 1111111111 111111111111111 IIIII IIIII lll111111111111111 US007165566B2 c12) United States Patent Beebe (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jan.23,2007 (54) METHOD
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0103105 A1 Nakama et al. US 201601031 05A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0103105 A1 Nakama et al. US 201601031 05A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY
(12) United States Patent
 US00928.1819B2 (12) United States Patent Chou et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2016 (54) SOURCE DRIVING CIRCUIT AND RESISTOR RENORMALIZATION METHOD (71) Applicant: Raydium Semiconductor
US00928.1819B2 (12) United States Patent Chou et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2016 (54) SOURCE DRIVING CIRCUIT AND RESISTOR RENORMALIZATION METHOD (71) Applicant: Raydium Semiconductor
United States Patent (19) Kawana et al.
 - United States Patent (19) Kawana et al. (54) METHANOL FUEL CELL 75) Inventors: Hidejiro Kawana; Tatsuo Horiba; Kazuo Iwamoto, all of Hitachi; Kazunori Fujita, Tohkai; Kohki Tamura, Hitachi, all of Japan
- United States Patent (19) Kawana et al. (54) METHANOL FUEL CELL 75) Inventors: Hidejiro Kawana; Tatsuo Horiba; Kazuo Iwamoto, all of Hitachi; Kazunori Fujita, Tohkai; Kohki Tamura, Hitachi, all of Japan
(51) Int. Cl... D06F tank. The liquid level detector includes a first resistance
 US00605O112A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Walker (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2000 54). APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,798,698 8/1998 Politt et al.... 73/291 DETECTING ALIQUID LEVEL IN A SEALED
US00605O112A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Walker (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2000 54). APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,798,698 8/1998 Politt et al.... 73/291 DETECTING ALIQUID LEVEL IN A SEALED
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7825,066 B1
 US00782.5066B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7825,066 B1 Skaggs et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 2, 2010 (54) RAPID FORMALDEHYDE (56) References Cited NEUTRALIZATION USING CHEMICALLY TREATED
US00782.5066B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7825,066 B1 Skaggs et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 2, 2010 (54) RAPID FORMALDEHYDE (56) References Cited NEUTRALIZATION USING CHEMICALLY TREATED
(19) Scott H. Stillinger, Los Gatos, Calif. Oddz0n Products, Campbell, Calif. 60,640 Jun. 11, 1987 Int. Cl'... A63B 37/14
 United States Patent Stillinger 54 (75) (73) 21 22 51 (52) (58 (56) (19) GENERALLY SPHERICAL OBJECT WITH FLOPPY FILAMENTS TO PROMOTE SURE CAPTURE Inventor: Assignee: Appl. No.: Filed: Scott H. Stillinger,
United States Patent Stillinger 54 (75) (73) 21 22 51 (52) (58 (56) (19) GENERALLY SPHERICAL OBJECT WITH FLOPPY FILAMENTS TO PROMOTE SURE CAPTURE Inventor: Assignee: Appl. No.: Filed: Scott H. Stillinger,
(54) (75) (73) (Us) (21) (22) (63) 1, 2007, provisional application No. 60/997,142,?led
 US 20120120398A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0120398 A1 Armani et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 17, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) MICRO-CAVITY GAS AND VAPOR
US 20120120398A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0120398 A1 Armani et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 17, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) MICRO-CAVITY GAS AND VAPOR
High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source.
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source. 7-11-2006 Jonathan Arenberg Northrop Grumman Corporation Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source. 7-11-2006 Jonathan Arenberg Northrop Grumman Corporation Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007191654B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,191,654 B2 Dwyer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR ADJUSTING (56) References Cited MAGNETIC RETURN PATH
(12) United States Patent US007191654B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,191,654 B2 Dwyer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR ADJUSTING (56) References Cited MAGNETIC RETURN PATH
BY ye; v P. April 29, 1969 C. S. KELLEY 3,441,626. TEMPERATURE CONTROL of EXOTHERMIC REACTIONS Filed March 6, 1967 INVENTOR. PRODUCT C. S.
 April 29, 1969 C. S. KELLEY TEMPERATURE CONTROL of EXOTHERMIC REACTIONS Filed March 6, 1967 PRODUCT INVENTOR. C. S. KELLEY BY ye; v P. A 77OAPAWAYS United States Patent Office Patented Apr. 29, 1969 1.
April 29, 1969 C. S. KELLEY TEMPERATURE CONTROL of EXOTHERMIC REACTIONS Filed March 6, 1967 PRODUCT INVENTOR. C. S. KELLEY BY ye; v P. A 77OAPAWAYS United States Patent Office Patented Apr. 29, 1969 1.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,473,187 B1. Manalis (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 29, 2002
 USOO64731.87B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,473,187 B1 Manalis (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 29, 2002 (54) HIGH-SENSITIVITY INTERFEROMETRIC Manalis, et al., Interdigital cantilevers for
USOO64731.87B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,473,187 B1 Manalis (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 29, 2002 (54) HIGH-SENSITIVITY INTERFEROMETRIC Manalis, et al., Interdigital cantilevers for
) USOO A. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994
 ) USOO5363458A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994 54 FIBER OPTIC LIGHT DIFFUSER 5,119,461 6/1992 Beyer et al.... 385/147 5,168,538 12/1992
) USOO5363458A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994 54 FIBER OPTIC LIGHT DIFFUSER 5,119,461 6/1992 Beyer et al.... 385/147 5,168,538 12/1992
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0289056A1 Bergman et al. US 20120289056A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 15, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) SELECTIVE SILICON NITRDEETCH
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0289056A1 Bergman et al. US 20120289056A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 15, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) SELECTIVE SILICON NITRDEETCH
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016O247659A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0247659 A1 OH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2016 (54) ELECTROSTATIC QUADRUPOLE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2016O247659A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0247659 A1 OH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2016 (54) ELECTROSTATIC QUADRUPOLE Publication Classification
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Rajic et al. 54 FTIR SPECTROMETER WITH SOLID-STATE DRIVE SYSTEM 75 Inventors: Slobodan Rajic, Knoxville; Roland D. Seals; Charles M. Egert, both of Oak Ridge, all of Tenn. 73
United States Patent (19) Rajic et al. 54 FTIR SPECTROMETER WITH SOLID-STATE DRIVE SYSTEM 75 Inventors: Slobodan Rajic, Knoxville; Roland D. Seals; Charles M. Egert, both of Oak Ridge, all of Tenn. 73
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7310217B2 (12) United States Patent Takashima et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,310,217 B2 Dec. 18, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CAPACITOR AND MOUNTING STRUCTURE THEREOF (75) Inventors: Hirokazu
USOO7310217B2 (12) United States Patent Takashima et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,310,217 B2 Dec. 18, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CAPACITOR AND MOUNTING STRUCTURE THEREOF (75) Inventors: Hirokazu
IIIHHHHHHHHIIIHIII 5,184,176. United States Patent (19) Unino et al. ARITHMETIC. Feb. 2, mined magnification to form a pattern image on the
 United States Patent (19) Unino et al. (54) PROJECTION EXPOSURE APPARATUS WITH AN ABERRATION COMPENSATION DEVICE OF A PROJECTION LENS (75) Inventors: Yasuyuki Unno, Hadano; Seiji Orii; Masami Yonekawa,
United States Patent (19) Unino et al. (54) PROJECTION EXPOSURE APPARATUS WITH AN ABERRATION COMPENSATION DEVICE OF A PROJECTION LENS (75) Inventors: Yasuyuki Unno, Hadano; Seiji Orii; Masami Yonekawa,
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Jongema 54 PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF SODUM CHILORIDE 75) Inventor: Pieter Jongema, Brummen, Netherlands (73) Assignee: Akzo N.V., Netherlands (21) Appl. No.: 815,090 (22)
United States Patent (19) Jongema 54 PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF SODUM CHILORIDE 75) Inventor: Pieter Jongema, Brummen, Netherlands (73) Assignee: Akzo N.V., Netherlands (21) Appl. No.: 815,090 (22)
United States Patent (19) Namba et al.
 United States Patent (19) Namba et al. 54 PIEZOELECTRIC DEVICE AND METHOD OF MANUFACTURING THE SAME (75) Inventors: Akihiko Namba; Tetsuyoshi Ogura; Yoshihiro Tomita, all of Osaka; Kazuo Eda. Nara, all
United States Patent (19) Namba et al. 54 PIEZOELECTRIC DEVICE AND METHOD OF MANUFACTURING THE SAME (75) Inventors: Akihiko Namba; Tetsuyoshi Ogura; Yoshihiro Tomita, all of Osaka; Kazuo Eda. Nara, all
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent KWOn USOO6943747B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, 2005 (54) SMALL AND OMNI-DIRECTIONAL BICONICAL ANTENNA FOR WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS (75) Inventor: Do-Hoon Kwon,
(12) United States Patent KWOn USOO6943747B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, 2005 (54) SMALL AND OMNI-DIRECTIONAL BICONICAL ANTENNA FOR WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS (75) Inventor: Do-Hoon Kwon,
Si-iö, TH". ()SSS N I. 6-7 Zaf (54) United States Patent (19) Cuff (11 3,968,700. (45) July 13, (21) Appl. No.: 493,748
 United States Patent (19) Cuff (54) DEVICE FOR CONVERTING ROTARY MOTION INTO A UNIDIRECTIONAL LINEAR MOTION 76) Inventor: Calvin I. Cuff, 135 Ocean Ave., Brooklyn, N.Y. 11225 22 Filed: Aug. 1, 1974 (21)
United States Patent (19) Cuff (54) DEVICE FOR CONVERTING ROTARY MOTION INTO A UNIDIRECTIONAL LINEAR MOTION 76) Inventor: Calvin I. Cuff, 135 Ocean Ave., Brooklyn, N.Y. 11225 22 Filed: Aug. 1, 1974 (21)
Paponneau (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 27, 2016
 (12) United States Patent USOO9453899B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9.453,899 B2 Paponneau (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 27, 2016 (54) SYSTEM FOR EFFECTING THE (52) U.S. Cl. ROTATIONAL MOVEMENT OF A SOLAR CPC... G0IS
(12) United States Patent USOO9453899B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9.453,899 B2 Paponneau (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 27, 2016 (54) SYSTEM FOR EFFECTING THE (52) U.S. Cl. ROTATIONAL MOVEMENT OF A SOLAR CPC... G0IS
Electrochemical Deposition of Carbon Nanotubes from Organic Solutions
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Electrochemical Deposition of Carbon Nanotubes from Organic Solutions 7-6-2004 Lee Chow University of Central Florida Elvira Anoshkina University of Central
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Electrochemical Deposition of Carbon Nanotubes from Organic Solutions 7-6-2004 Lee Chow University of Central Florida Elvira Anoshkina University of Central
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110248723A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0248723 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2011 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR HAVING CALIBRATION MECHANISMAND
(19) United States US 20110248723A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0248723 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2011 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR HAVING CALIBRATION MECHANISMAND
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,365,505 B1
 USOO6365505B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,365,505 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 2, 2002 (54) METHOD OF MAKING ASLOT VIA FILLED 6,127,258 A * 10/2000 Watanabe et al... 438/637
USOO6365505B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,365,505 B1 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 2, 2002 (54) METHOD OF MAKING ASLOT VIA FILLED 6,127,258 A * 10/2000 Watanabe et al... 438/637
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2. Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007
 USOO7303925B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2 Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) METHOD OF DETECTING AN ANALYTE (56) References Cited FOR LATERAL FLOW IMMUNOASSAY
USOO7303925B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2 Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) METHOD OF DETECTING AN ANALYTE (56) References Cited FOR LATERAL FLOW IMMUNOASSAY
AA. *alt24& DS. (12) United States Patent US 6,607,370 B2. Aug. 19, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: Fukamachi et al.
 (12) United States Patent Fukamachi et al. USOO660737OB2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,607,370 B2 Aug. 19, 2003 (54) MAGNETIC PUMP (75) Inventors: Masatoshi Fukamachi, Wako (JP); Osamu Sato,
(12) United States Patent Fukamachi et al. USOO660737OB2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,607,370 B2 Aug. 19, 2003 (54) MAGNETIC PUMP (75) Inventors: Masatoshi Fukamachi, Wako (JP); Osamu Sato,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,604,442 B2
 USOO7604442B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,604,442 B2 Motta et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) MULTI-AXIS MACHINE TOOL (58) Field of Classification Search... 409/202, 409/212,
USOO7604442B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,604,442 B2 Motta et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) MULTI-AXIS MACHINE TOOL (58) Field of Classification Search... 409/202, 409/212,
SSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSS 22. 8a 1. United States Patent (19) Maru et al. 11 4,365,007 45) Dec. 21, 1982
 United States Patent (19) Maru et al. (54) FUEL CELL WITH INTERNAL REFORMING (75) Inventors: Hansraj C. Maru, Brookfield Center; Pinakin S. Patel, Danbury, both of Conn. 73 Assignee: Energy Research Corporation,
United States Patent (19) Maru et al. (54) FUEL CELL WITH INTERNAL REFORMING (75) Inventors: Hansraj C. Maru, Brookfield Center; Pinakin S. Patel, Danbury, both of Conn. 73 Assignee: Energy Research Corporation,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,763,928 B2
 USOO7763928B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 2010 (54) MULTI-TIME PROGRAMMABLE MEMORY (58) Field of Classification Search... 257/314321, 257/E29.129,
USOO7763928B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 2010 (54) MULTI-TIME PROGRAMMABLE MEMORY (58) Field of Classification Search... 257/314321, 257/E29.129,
May 2, 1967 H. W. TROLANDER ETAL 3,316,765 EXTENDED RANGE THERMISTOR TEMPERATURE SENSING. Filed Aug. 19, 1965 (,,,,, SR-33-R-N
 May 2, 1967 H. W. TROLANDER ETAL 3,316,7 EXTENDED RANGE THERMISTOR TEMPERATURE SENSING Filed Aug. 19, 19 FG- SR-33-R-N FIG-4 (,,,,, S-CONSTANT CURRENT SOURCE FG-2 INVENTORS HAROY W. TROLANDER 8 By RAY
May 2, 1967 H. W. TROLANDER ETAL 3,316,7 EXTENDED RANGE THERMISTOR TEMPERATURE SENSING Filed Aug. 19, 19 FG- SR-33-R-N FIG-4 (,,,,, S-CONSTANT CURRENT SOURCE FG-2 INVENTORS HAROY W. TROLANDER 8 By RAY
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9633947B2 (12) United States Patent Jacob (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) FOLDED BALLISTC CONDUCTOR INTERCONNECT LINE Applicant:
USOO9633947B2 (12) United States Patent Jacob (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) FOLDED BALLISTC CONDUCTOR INTERCONNECT LINE Applicant:
United States Patent (19) Rex
 United States Patent (19) Rex (54). SOLAR ENERGY COLLECTOR 75) Inventor: Dietrich Rex, Brunswick, Fed. Rep. of Germany 73) Assignee: Erno Raumfahrttechnik GmbH, Bremen, Fed. Rep. of Germany 21) Appl. No.:
United States Patent (19) Rex (54). SOLAR ENERGY COLLECTOR 75) Inventor: Dietrich Rex, Brunswick, Fed. Rep. of Germany 73) Assignee: Erno Raumfahrttechnik GmbH, Bremen, Fed. Rep. of Germany 21) Appl. No.:
United States Patent [19]
![United States Patent [19] United States Patent [19]](/thumbs/76/73521136.jpg) United States Patent [19] Murphy 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US005479716A [11] Patent Number: 5,479,716 [4S] Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 1996 [S4] CAPACITIVE
United States Patent [19] Murphy 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US005479716A [11] Patent Number: 5,479,716 [4S] Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 1996 [S4] CAPACITIVE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,167,752 B1. Raffer (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 2001
 USOO6167752B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Raffer (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 2001 (54) ROTARY VISCOMETER WITH AN AIR (56) References Cited BEARING N U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
USOO6167752B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Raffer (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 2001 (54) ROTARY VISCOMETER WITH AN AIR (56) References Cited BEARING N U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
(54) THERMAL INTERFACE MATERIAL WITH (56) References Cited
 USOO73442B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.3.442 B2 Aug. 7, 2007 (54) THERMAL INTERFACE MATERIAL WITH (56) References Cited CARBON NANOTUBES U.S. PATENT
USOO73442B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.3.442 B2 Aug. 7, 2007 (54) THERMAL INTERFACE MATERIAL WITH (56) References Cited CARBON NANOTUBES U.S. PATENT
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7777214B2 (12) United States Patent Shin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,777,214 B2 Aug. 17, 2010 (54) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY DEVICE WITH A NOVEL ELECTRODE (75) Inventors: Jae-Min Shin,
USOO7777214B2 (12) United States Patent Shin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,777,214 B2 Aug. 17, 2010 (54) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY DEVICE WITH A NOVEL ELECTRODE (75) Inventors: Jae-Min Shin,
- X. (bka III IIII. United States Patent (19) Sobata et al e (2. o
 United States Patent (19) Sobata et al. 54 ACTIVITY CONTROL APPARATUS FOR ZINC PHOSPHATE TREATMENT SOLUTION 75) Inventors: Tamotsu Sobata, Ibaraki; Katsuhiro Takeshita, Hirakata, both of Japan 73) Assignee:
United States Patent (19) Sobata et al. 54 ACTIVITY CONTROL APPARATUS FOR ZINC PHOSPHATE TREATMENT SOLUTION 75) Inventors: Tamotsu Sobata, Ibaraki; Katsuhiro Takeshita, Hirakata, both of Japan 73) Assignee:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013
 US 2013 OOO1573A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0001573 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013 (54) THIN FILM TRANSISTOR AND METHOD OF Publication Classification
US 2013 OOO1573A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0001573 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013 (54) THIN FILM TRANSISTOR AND METHOD OF Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0256036A1 NAKAMURA US 20150256036A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 10, 2015 (54) LAMINATED IRON CORE AND MANUFACTURING METHOD FOR LAMINATED
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0256036A1 NAKAMURA US 20150256036A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 10, 2015 (54) LAMINATED IRON CORE AND MANUFACTURING METHOD FOR LAMINATED
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Harrigan 54 LEVITATION DEVICE 76 Inventor: Roy M. Harrigan, Bromley Mountain Rd., Manchester, Vt. O54 21 22 63 51 (52) 58 Appl. No.: 105,239 Fed: Dec. 19, 1979 Related U.S. Application
United States Patent (19) Harrigan 54 LEVITATION DEVICE 76 Inventor: Roy M. Harrigan, Bromley Mountain Rd., Manchester, Vt. O54 21 22 63 51 (52) 58 Appl. No.: 105,239 Fed: Dec. 19, 1979 Related U.S. Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0158290 A1 MARE-ROSE et al. US 2013 O158290A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 20, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) PRODUCTION OF OXYGENATED
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0158290 A1 MARE-ROSE et al. US 2013 O158290A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 20, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) PRODUCTION OF OXYGENATED
: Y. ti- sk 22N. Sir S. United States Patent (19) Uhri 4,687,061. Aug. 18, Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4 g
 i, a 5 S R 4 g 68 7 6 United States Patent (19) Uhri 8 a g. A 87 OR 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 1987 (54. STIMULATION OF EARTH FORMATIONS SURROUNDING A DEVIATED WELLBORE BYSEQUENTIAL
i, a 5 S R 4 g 68 7 6 United States Patent (19) Uhri 8 a g. A 87 OR 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 1987 (54. STIMULATION OF EARTH FORMATIONS SURROUNDING A DEVIATED WELLBORE BYSEQUENTIAL
United States Patent (19) Sumikawa et al.
 United States Patent (19) Sumikawa et al. 11 3,983,170 (45) Sept. 28, 1976 (54) (75) 73 22 21 52) 51 58) PROCESS FOR THE PURIFICATION OF MALIC ACID Inventors: Shozo Sumikawa, Hofu, Rikichi Maida; Yuriaki
United States Patent (19) Sumikawa et al. 11 3,983,170 (45) Sept. 28, 1976 (54) (75) 73 22 21 52) 51 58) PROCESS FOR THE PURIFICATION OF MALIC ACID Inventors: Shozo Sumikawa, Hofu, Rikichi Maida; Yuriaki
(12) United States Patent
 USOO743665OB2 (12) United States Patent Oguni et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.436,650 B2 Oct. 14, 2008 (54) LAMINATED CERAMIC CAPACITOR (75) Inventors: Toshimi Oguni, Izumo (JP); Hiroyuki
USOO743665OB2 (12) United States Patent Oguni et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.436,650 B2 Oct. 14, 2008 (54) LAMINATED CERAMIC CAPACITOR (75) Inventors: Toshimi Oguni, Izumo (JP); Hiroyuki
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005.0068.047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0068047 A1 Claus (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR Publication Classification DISTINGUISHING
US 2005.0068.047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0068047 A1 Claus (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR Publication Classification DISTINGUISHING
Jinx UDX. (12) United States Patent. 2a2b se 2e2f (10) Patent No.: US 6,365,894 B2. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 2, a2b 2c2d2.
 (12) United States Patent Tadokoro et al. USOO6365894B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,365,894 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 2, 2002 (54) ELECTROMAGNET AND MAGNETIC FIELD GENERATINGAPPARATUS (75) Inventors: Masahiro
(12) United States Patent Tadokoro et al. USOO6365894B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,365,894 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 2, 2002 (54) ELECTROMAGNET AND MAGNETIC FIELD GENERATINGAPPARATUS (75) Inventors: Masahiro
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 2009.0160019A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. o.: US 2009/0160019 A1 Yang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 25, 2009 (54) SEMICODUCTOR CAPACITOR Publication Classification (51)
(19) United States US 2009.0160019A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. o.: US 2009/0160019 A1 Yang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 25, 2009 (54) SEMICODUCTOR CAPACITOR Publication Classification (51)
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7335956B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) CAPACTOR DEVICE WITH VERTICALLY ARRANGED CAPACTOR
USOO7335956B2 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) CAPACTOR DEVICE WITH VERTICALLY ARRANGED CAPACTOR
US 9,214,722 B2 Dec. 15, 2015
 I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US009214 722B2 c12) United States Patent Georgakopoulos et al. (IO) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,214,722 B2
I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US009214 722B2 c12) United States Patent Georgakopoulos et al. (IO) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,214,722 B2
Intelligent Hotspot Connection System
 (19) United States US 2010O246486A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0246486A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2010 (54) INTELLIGENT HOTSPOT CONNECTION SYSTEMIS AND METHODS
(19) United States US 2010O246486A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0246486A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2010 (54) INTELLIGENT HOTSPOT CONNECTION SYSTEMIS AND METHODS
ZZZZZZZZZZYZZZZZZZZZZZZZz6
 USOO5898752A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Van Der Wal (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 1999 54) X-RAY ANALYSIS APPARATUS PROVIDED Primary Examiner-Craig E. Church WITH A DOUBLE COLLIMATOR MASK
USOO5898752A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Van Der Wal (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 1999 54) X-RAY ANALYSIS APPARATUS PROVIDED Primary Examiner-Craig E. Church WITH A DOUBLE COLLIMATOR MASK
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0087941A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0087941 A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 11, 2013 (54) METHOD OF PRODUCING CARBON NANOTUBE SPONGES (75)
(19) United States US 2013 0087941A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0087941 A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 11, 2013 (54) METHOD OF PRODUCING CARBON NANOTUBE SPONGES (75)
56 References Cited UNITED STATES PATENTS 1965, 187 7/1934 Hartman /43 3,483,374 12/1969 Erben /4 3,486,308 12/1969 Burt...
 United States Patent Hochheiser et al. 54) AR PROCESSOR (72) Inventors: Jerome S. Hochheiser; Louis Zer meno, both of Los Angeles, Calif. 73 Assignee: Hochheiser Electronics Corporation, Burband, Calif.
United States Patent Hochheiser et al. 54) AR PROCESSOR (72) Inventors: Jerome S. Hochheiser; Louis Zer meno, both of Los Angeles, Calif. 73 Assignee: Hochheiser Electronics Corporation, Burband, Calif.
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Carter et al. USOO6906789B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2005 (54) MAGNETICALLY LEVITATED AND DRIVEN RETICLE-MASKING BLADE STAGE MECHANISM HAVING SIX DEGREES
(12) United States Patent Carter et al. USOO6906789B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2005 (54) MAGNETICALLY LEVITATED AND DRIVEN RETICLE-MASKING BLADE STAGE MECHANISM HAVING SIX DEGREES
? Ns 54 F2 44. al-f2. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0199986 A1 Miller US 2013 0199986A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) ON EXCHANGE EXOSKELETON
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0199986 A1 Miller US 2013 0199986A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) ON EXCHANGE EXOSKELETON
Zoë 2%lvy Arafa, BY Ace. Aig. / May 28, ,793,758. Aewe// A. Ai//lings/ey. Filed March 28, 1956 MUD AND SAND SEPARATOR FOR WELL, DRILLING
 May 28, 1957 Filed March 28, 1956 Aig. / L. E. BLINGSLEY MUD AND SAND SEPARATOR FOR WELL, DRILLING 26 3 Sheets-Sheet l Aewe// A. Ai//lings/ey INVENTOR. Zoë 2%lvy Arafa, BY Ace May 28, 1957 E, BILLINGSLEY
May 28, 1957 Filed March 28, 1956 Aig. / L. E. BLINGSLEY MUD AND SAND SEPARATOR FOR WELL, DRILLING 26 3 Sheets-Sheet l Aewe// A. Ai//lings/ey INVENTOR. Zoë 2%lvy Arafa, BY Ace May 28, 1957 E, BILLINGSLEY
TEPZZ 89955_A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G01R 15/20 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 899_A T (11) EP 2 899 1 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.07.201 Bulletin 201/31 (1) Int Cl.: G01R 1/20 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 111708.3 (22) Date of
(19) TEPZZ 899_A T (11) EP 2 899 1 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.07.201 Bulletin 201/31 (1) Int Cl.: G01R 1/20 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 111708.3 (22) Date of
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,508,132 B1. Lohr et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 21, 2003
 USOO6508132B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,508,132 B1 Lohr et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 21, 2003 (54) DYNAMIC LOAD CELL APPARATUS 4,478,086 A * 10/1984 Gram... 73/781 5,739,411 A
USOO6508132B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,508,132 B1 Lohr et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 21, 2003 (54) DYNAMIC LOAD CELL APPARATUS 4,478,086 A * 10/1984 Gram... 73/781 5,739,411 A
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O107994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0107994 A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) BIOSENSOR Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
(19) United States US 2015O107994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0107994 A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) BIOSENSOR Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7487686B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7487,686 B2 Feb. 10, 2009 (54) HIGH-PRECISION VORTEX FLOW METER (75) Inventors: An-Bang Wang, Taipei (TW); Ming-Hsun
USOO7487686B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7487,686 B2 Feb. 10, 2009 (54) HIGH-PRECISION VORTEX FLOW METER (75) Inventors: An-Bang Wang, Taipei (TW); Ming-Hsun
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Leonard 54 PREPARATION OF FORMIC ACID BY HYDROLYSIS OF METHYL FORMATE (76) Inventor: Jackson D. Leonard, 7002 Blvd. East, Guttenberg, N.J. 07093 (21) Appl. No. 912,189 22 Filed:
United States Patent (19) Leonard 54 PREPARATION OF FORMIC ACID BY HYDROLYSIS OF METHYL FORMATE (76) Inventor: Jackson D. Leonard, 7002 Blvd. East, Guttenberg, N.J. 07093 (21) Appl. No. 912,189 22 Filed:
in. ION SOURCE \, N. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1 (19) United States 1 N 4
 (19) United States US 20060219890A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0219890 A1 Yamaguchi (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 5, 2006 (54) TIME OF FLIGHT MASS SPECTROMETER (75) Inventor: Shinichi
(19) United States US 20060219890A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0219890 A1 Yamaguchi (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 5, 2006 (54) TIME OF FLIGHT MASS SPECTROMETER (75) Inventor: Shinichi
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,624,640 B2
 USOO662464OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lund et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 23, 2003 (54) CAPACITANCE MEASUREMENT 5,073,757 A * 12/1991 George... 324/677 (75) I nventors: t John Jonn
USOO662464OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lund et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 23, 2003 (54) CAPACITANCE MEASUREMENT 5,073,757 A * 12/1991 George... 324/677 (75) I nventors: t John Jonn
United States Patent (19) Besocke
 United States Patent (19) Besocke 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: 4,686,847 Aug. 18, 1987 54 METHOD AND VIBRATING CAPACITOR APPARATUS FOR ANALYSS OF A SUBSTANCE OR OF AT LEAST ONE COMPONENT OF A
United States Patent (19) Besocke 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: 4,686,847 Aug. 18, 1987 54 METHOD AND VIBRATING CAPACITOR APPARATUS FOR ANALYSS OF A SUBSTANCE OR OF AT LEAST ONE COMPONENT OF A
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Young USOO6419519 B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 16, 2002 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) STRIN RELEF FOR ELECTRICL CONNECTORS Inventor: SSignee:
(12) United States Patent Young USOO6419519 B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 16, 2002 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) STRIN RELEF FOR ELECTRICL CONNECTORS Inventor: SSignee:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 (19) United States US 2001 0042523A1. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0042523 A1 Kesala (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR FEEDING GAS PHASE REACTANT INTO A REACTION
(19) United States US 2001 0042523A1. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0042523 A1 Kesala (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR FEEDING GAS PHASE REACTANT INTO A REACTION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008
 US 2008.0017293A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0017293 A1 Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) AUTOMATICLEVEL ADJUSTMENT FOR Publication Classification
US 2008.0017293A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0017293 A1 Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) AUTOMATICLEVEL ADJUSTMENT FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 20080249323A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0249323 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 9, 2008 (54) SORBITOL CONVERSION PROCESS Publication Classification
US 20080249323A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0249323 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 9, 2008 (54) SORBITOL CONVERSION PROCESS Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070268651A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0268651 A1 TAKASHIMA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 22, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CERAMIC CAPACITOR May 22, 2006 (JP)...
(19) United States US 20070268651A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0268651 A1 TAKASHIMA et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 22, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CERAMIC CAPACITOR May 22, 2006 (JP)...
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140216484A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0216484 A1 Liu (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2014 (54) ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A24F 47/008 (2013.01)
(19) United States US 20140216484A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0216484 A1 Liu (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2014 (54) ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A24F 47/008 (2013.01)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170139281A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0139281 A1 Hou et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 18, 2017 (54) ALIGNMENT METHOD OF FFS TYPE GO2F I/335 (2006.01)
(19) United States US 20170139281A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0139281 A1 Hou et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 18, 2017 (54) ALIGNMENT METHOD OF FFS TYPE GO2F I/335 (2006.01)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090009193A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0009193 A1 Hsiung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 8, 2009 (54) MOISTURE-SENSITIVE ELEMENT WITH AN INTERDIGITAL
(19) United States US 20090009193A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0009193 A1 Hsiung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 8, 2009 (54) MOISTURE-SENSITIVE ELEMENT WITH AN INTERDIGITAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016.0078974A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0078974A1 Jones (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 17, 2016 (54) XRF ANALYZER ROTATIONAL FILTER (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... G2IK
US 2016.0078974A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0078974A1 Jones (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 17, 2016 (54) XRF ANALYZER ROTATIONAL FILTER (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... G2IK
United States Patent (19) Amiet
 United States Patent (19) Amiet 11) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,879,407 Nov. 7, 1989 54 PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF ETHYL TRFLUOROACETATE 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: Louis Amiet, Lyons, France
United States Patent (19) Amiet 11) Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,879,407 Nov. 7, 1989 54 PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF ETHYL TRFLUOROACETATE 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: Louis Amiet, Lyons, France
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1
 USOO731.5677B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2008 (54) DUAL DOPANT DUAL ALPHA MULTIMODE 2006/0285809 A1* 12/2006 Bickham et al.... 385,123
USOO731.5677B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2008 (54) DUAL DOPANT DUAL ALPHA MULTIMODE 2006/0285809 A1* 12/2006 Bickham et al.... 385,123
TEPZZ 95785_A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 978_A_T (11) EP 2 97 81 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.12. Bulletin /2 (21) Application number: 14172928. (1) Int Cl.: F28F 3/04 (06.01) F28F 3/08 (06.01) F28F
(19) TEPZZ 978_A_T (11) EP 2 97 81 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.12. Bulletin /2 (21) Application number: 14172928. (1) Int Cl.: F28F 3/04 (06.01) F28F 3/08 (06.01) F28F
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0295736A1 Wang US 20070295736A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2007 (54) WASTEBASKET OR BN HAVING ROCKING SPRINGS AT BOTTOM (75)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0295736A1 Wang US 20070295736A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2007 (54) WASTEBASKET OR BN HAVING ROCKING SPRINGS AT BOTTOM (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. Suzuki et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 9, 2004
 (19) United States US 2004O173319A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0173319 A1 Suzuki et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) QUARTZ COMPONENT FOR PLASMA (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 2004O173319A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0173319 A1 Suzuki et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) QUARTZ COMPONENT FOR PLASMA (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,261,710 B1
 USOO626171 OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Marianowski (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 17, 2001 (54) SHEET METAL BIPOLAR PLATE DESIGN 5,578,388 11/1996 Faita et al.. FOR POLYMER ELECTROLYTE 5,606,641
USOO626171 OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Marianowski (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 17, 2001 (54) SHEET METAL BIPOLAR PLATE DESIGN 5,578,388 11/1996 Faita et al.. FOR POLYMER ELECTROLYTE 5,606,641
United States Patent (19) (11) 4,420,790 Golke et al. 45) Dec. 13, 1983
 e United States Patent (19) (11) 4,420,790 Golke et al. 45) Dec. 13, 1983 54 HIGH SENSITIVITY VARIABLE 57 ABSTRACT CAPACITANCE TRANSDUCER A semiconductor capacitance transducer includes ad (75) Inventors:,
e United States Patent (19) (11) 4,420,790 Golke et al. 45) Dec. 13, 1983 54 HIGH SENSITIVITY VARIABLE 57 ABSTRACT CAPACITANCE TRANSDUCER A semiconductor capacitance transducer includes ad (75) Inventors:,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Kramer et al. USOO661981 OB2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2003 (54) HALLOWEENTREAT CARRIER INCLUDING GLOW-IN-THE-DARK MATERIAL PUMPKIN DECORATING KIT, AND METHOD
(12) United States Patent Kramer et al. USOO661981 OB2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2003 (54) HALLOWEENTREAT CARRIER INCLUDING GLOW-IN-THE-DARK MATERIAL PUMPKIN DECORATING KIT, AND METHOD
(os) SSO. (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,290 B1. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, (12) United States Patent (54) (75) (73)
 (12) United States Patent HOutSma USOO677929OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,290 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, 2004 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) SEMI PERMANENT BACKUP IRON SIGHT Inventor:
(12) United States Patent HOutSma USOO677929OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,290 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, 2004 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) SEMI PERMANENT BACKUP IRON SIGHT Inventor:
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8680443B2 (12) United States Patent McMillin et al. (54) COMBINED MATERIAL LAYERING TECHNOLOGES FOR ELECTRICHEATERS (75) Inventors: James McMillin, Algonquin, IL (US); Louis P. Steinhauser, St. Louis,MO
USOO8680443B2 (12) United States Patent McMillin et al. (54) COMBINED MATERIAL LAYERING TECHNOLOGES FOR ELECTRICHEATERS (75) Inventors: James McMillin, Algonquin, IL (US); Louis P. Steinhauser, St. Louis,MO
\ 108. (12) United States Patent US 9,502,356 B1. Nov. 22, (45) Date of Patent: NACSSZZNS 27 SCSS ASNZSZCN) 106. (10) Patent No.: 4.
 USOO9502356B1 (12) United States Patent Parvarandeh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 22, 2016 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD WITH PHYSICAL UNCLONABLE FUNCTION (71) Applicant: Maxim Integrated Products,
USOO9502356B1 (12) United States Patent Parvarandeh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 22, 2016 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD WITH PHYSICAL UNCLONABLE FUNCTION (71) Applicant: Maxim Integrated Products,
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 158 (3) EPC
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 158 (3) EPC (11) EP 1 674 509 A1 (43) Date of publication:
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 158 (3) EPC (11) EP 1 674 509 A1 (43) Date of publication:
''. United States Patent (19) Tsikos. 11 4,353,056 45) Oct. 5, the finger under investigation. The sensing member. 21 Appl. No.
 United States Patent (19) Tsikos 54 CAPACITIVE FINGERPRINT SENSOR 75 Inventor: Constantine Tsikos, Pennsauken, N.J 73 Assignee: Siemens Corporation, Iselin, N.J. 21 Appl. No.: 156,571 22 Filed: Jun. 5,
United States Patent (19) Tsikos 54 CAPACITIVE FINGERPRINT SENSOR 75 Inventor: Constantine Tsikos, Pennsauken, N.J 73 Assignee: Siemens Corporation, Iselin, N.J. 21 Appl. No.: 156,571 22 Filed: Jun. 5,
United States Patent (19) Summitsch et al.
 United States Patent (19) Summitsch et al. 54 PROCESS FOR WET ETCHING OF SEMCONDUCTOR WAFERS 75 Inventors: Franz Sumnitsch, Klagenfurt; Gerald Wagner, Velden, both of Austria 73 Assignee: SEZ. Semiconductor-Equipment
United States Patent (19) Summitsch et al. 54 PROCESS FOR WET ETCHING OF SEMCONDUCTOR WAFERS 75 Inventors: Franz Sumnitsch, Klagenfurt; Gerald Wagner, Velden, both of Austria 73 Assignee: SEZ. Semiconductor-Equipment
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.0380.059A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0380059 A1 L0See et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2016 (54) ACTIVE AREA DESIGNS FOR SILICON (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 2016.0380.059A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0380059 A1 L0See et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2016 (54) ACTIVE AREA DESIGNS FOR SILICON (52) U.S. Cl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015 0001700A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0001700 A1 Hartung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 1, 2015 (54) POWER MODULES WITH PARYLENE (52) U.S. Cl. COATING
(19) United States US 2015 0001700A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0001700 A1 Hartung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 1, 2015 (54) POWER MODULES WITH PARYLENE (52) U.S. Cl. COATING
