ON THE USE OF A THEOREM BY V. VÂLCOVICI IN PLANAR MOTION DYNAMICS
|
|
|
- Nancy Lawrence
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE PUBLSHNG HOUSE PROEENGS OF THE ROMNN EMY, Series, OF THE ROMNN EMY Volume 6, Number 1/005, pp ON THE USE OF THEOREM BY V. VÂLOV N PLNR MOTON YNMS Victor BURU *, urel LEU * * epartment of Mechanics, University Politehnica of Bucharest Splaiul ndependentei, 313, sector 6, Bucharest, Romania orresponding author: Victor BURU, vburacu@yahoo.com theorem by V. Vâlcovici that generalizes Koenig s well known angular momentum theorem finds its use in planar motion dynamics. The reference point in this type of motion is the instant center. The advantage in choosing the instant center as the reference point in angular momentum theorems is that unknown constraint forces do not appear in the equations of motions. Key words: relative and absolute angular momentums, instant center, centrodes 1. NTROUTON onsider generally a deformable body S of mass m, occupying at moment t the three dimensional domain () t. We frequently use Koenig s angular momentum theorem K O mo V + K, (1) where K O stands for the angular momentum of the body about fixed point O, V for the velocity of centroid and K for its relative angular momentum about its center of mass ( ) K M vm dm, () () t ( ) v M being the relative velocity of point M with respect to. Koenig s theorem was generalized by V. Vâlcovici [1] by considering instead of an arbitrary point, not necesarily on the body, origin of a frame of reference with axes of constant directions in space: K O mo V + m V + K (3) where ( ) K M vm dm (4) () t ( ) is the relative angular momentum with respect to point ; v M has a similar significance as v ( ) M. The absolute angular momentum in is K M VM dm (5) () t Reccomended by Radu P.VONE, member of the Romanian cademy
2 Victor BURU, urel LEU Since where For KO K + O H, (6) H mv stands for the momentum of the body it follows from (3) and (4) that K m V + K (7) it results K K (8) V. Vâlcovici s relative angular momentum theorem with respect to point is " " m V + K M. (9) Here we identify M as the moment about point of all external forces acting on the body. Note that the absolute angular momentum theorem about the same point is written as " V H + K M. (9') For a rigid body of angular velocity ω and inertia tensor about point, J, we have #### ( ) #### V v, vm v + ω M, vm vm v ω M, #### K #### M ω M (10) d m J ω ( ). RELTVE NGULR MOMENTUM THEOREMS FOR PLNR MOTONS remarkable point in planar motions is the instant center. t is convenient to use the equation of relative angular momentum (9) about the instant center since in many planar motion problems reaction forces concur in this point. This circumstance is not general, but includes the important case of rolling without slipping over a fixed obstacle. However, care must be taken to distinguish as either a point on the space centrode or a point on the body centrode ( ) (fig. 1) since u being the velocity of on the space centrode. M ω M u, M ω M (11).1. Relative angular momentum theorem about, point on the space centrode ( nonmaterial point) Relative angular momentum about point is ( ) K M v dm M ( M ) [ ( ω M u )] J ω m u + m dm ω m u, (1) where J and J M dm represent the inertia moments of the rigid body with respect to axes perpendicular to the plane of motion in and. Equation (9) yields in this case
3 3 On the use of a theorem by V. Vâlcovici in planar motion dynamics m u" + + m " ω + mω d dt m u m u" M (13) Space centrode K u ω K () v M M Body centrode O (fixed) Fig.1 Flat plate in planar motion. t follows from the substitution of the first relation (11) into (13) that Finally we have u ω ω + m " mω d ω + dt M ω d dt (14). (15).. Relative angular momentum theorem about, point on the body centrode material point) ( For a point on a rigid body one can write ( M ) K M v dm M ω M dm J, ( ) [ ( )] ω (16) " K J ω " + ω ", (17) ( J ω) J ω where J is the inertia moment of the rigid with respect to an axis perpendicular to the plane of motion in. Make use of equation (9) replacing by : m a J m " + + ω M. (18) For the acceleration of point one can use the formula [4] n n ρ ρ a ω. (19) n n ρ ρ
4 Victor BURU, urel LEU 4 Here n, n, ρ, ρ stand for the unit vectors of the normals of the centrodes, respectively their curvature radiuses in. 3. EXMPLE We illustrate the use of the two relative angular momentum theorems given above with the example of an excentric roller of mass m, radius r and central moment of inertia J mk rolling without slipping on the inside of a cylindrical surface of radius R > r (fig. ) [3]. O e, ω ϕ", O r R ψ ϕ, θ ϕ, R r R r n n, ρ R, ρ r, Body centrode ψ rr a ϕ" n, R r err ω ϕ" a sin θ, R r ω e + r er cos θ, M mg. ω ( r sin ψ + e sin ϕ) ω θ a O G ϕ Space centrode R Fig. Excentric roller rolling without slipping on the inside of a cylindrical surface ny of the two equations (15) or (18) yields the following equation of motion err ", R r ( k + e + r er cos θ) ϕ " + ϕ" sin θ g( r sin ψ + e sin ϕ) which for small amplitudes is simplified to r + e [ ( ) ] ( R r) k + r e ϕ" g ϕ ". R r 4.1. The relative angular momentum about point is espite the fact that 4. REMRKS K + m ω. (0) is generally a function of time " K + ω " J m, (1)
5 5 On the use of a theorem by V. Vâlcovici in planar motion dynamics that is differentiation of K with respect to time is effective only on the angular velocity ω and not on the moment of inertia J J + m. The explanation resides in the fact that in the general case of formula (17) J is a constant, being a point of the rigid. On the contrary, when we refer to on the space centrode, differentiation of K with respect to time is complete since does not belong to the rigid. 4.. f relation (7) is written with respect to point we have K K. () For planar motions the equality of relative and absolute angular momentums with respect to the, point on the body centrode is valid not only in the centers of mass, but in the instant centers also The following relation is available from [] a ω. (3) u Substitution of (3) into (18) yields a slightly modified form for (18): + m " ω mω ( u ) M. (4) This equation is to be used mainly when the velocity of the instant center on the space centrode can be easily calculated f general formula (6) is written with respect to points and, that is K K + H (5) and since relations (7) and (8) will yield V V K K + m Relation (7) is the equivalent of relation (5) in terms of relative angular momentums. ifferentiation with respect to time of this relation gives (6) (7) " " K K + m. (8) Substitution of (8) into (9) yields m a " + K M. (9) Finally, for a planar motion the issue of distinguishing point being either on the space centrode or on the body centrode does not arise anymore if one replaces in equation (9) with : m a + J ω" M (30) Equation (30) represents a new form for the relative angular momentum theorems with respect to the instant center Equations (15) and (18) have both been obtained in [4] by other considerations. Together with equation (30) they are the main results of this paper.
6 Victor BURU, urel LEU 6 5. ONLUSONS This paper derives equations of planar motion by using a generalization of Koenig s angular momentum theorem. The reference point is the instant center. The advantage of using this point for relative angular momentum theorems is the elimination of the unknown reaction forces from the equations of motion. nstant center must be distinguished either on the space centrode or on the body centrode. Specific equations are derived in each case. However, the two forms are unified in equation (30) that makes no difference regarding the centrode to be considered. REFERENES 1 VÂLOV V., Sur le théorème des moments des quantities de mouvement, omptes rendus, Paris, tome 160, LOTNSK L. G., LURE.., Kurs teoreticeskoi mehaniki, tom pervîi, Moskva, LOTNSK L. G., LURE.., Kurs teoreticeskoi mehaniki, tom vtoroi, Moskva, BURU V., spects géometriques et cinématiques du théorème du moment cinétiques pour le solide rigide ayant un mouvement plan sur plan, Rev. Roum. Sci. Tech. Mec. pl., 37,, 199. Received ecember 0, 004
PLANAR KINETICS OF A RIGID BODY FORCE AND ACCELERATION
 PLANAR KINETICS OF A RIGID BODY FORCE AND ACCELERATION I. Moment of Inertia: Since a body has a definite size and shape, an applied nonconcurrent force system may cause the body to both translate and rotate.
PLANAR KINETICS OF A RIGID BODY FORCE AND ACCELERATION I. Moment of Inertia: Since a body has a definite size and shape, an applied nonconcurrent force system may cause the body to both translate and rotate.
PLANAR KINETIC EQUATIONS OF MOTION (Section 17.2)
 PLANAR KINETIC EQUATIONS OF MOTION (Section 17.2) We will limit our study of planar kinetics to rigid bodies that are symmetric with respect to a fixed reference plane. As discussed in Chapter 16, when
PLANAR KINETIC EQUATIONS OF MOTION (Section 17.2) We will limit our study of planar kinetics to rigid bodies that are symmetric with respect to a fixed reference plane. As discussed in Chapter 16, when
Lecture D20-2D Rigid Body Dynamics: Impulse and Momentum
 J Peraire 1607 Dynamics Fall 004 Version 11 Lecture D0 - D Rigid Body Dynamics: Impulse and Momentum In lecture D9, we saw the principle of impulse and momentum applied to particle motion This principle
J Peraire 1607 Dynamics Fall 004 Version 11 Lecture D0 - D Rigid Body Dynamics: Impulse and Momentum In lecture D9, we saw the principle of impulse and momentum applied to particle motion This principle
5. Plane Kinetics of Rigid Bodies
 5. Plane Kinetics of Rigid Bodies 5.1 Mass moments of inertia 5.2 General equations of motion 5.3 Translation 5.4 Fixed axis rotation 5.5 General plane motion 5.6 Work and energy relations 5.7 Impulse
5. Plane Kinetics of Rigid Bodies 5.1 Mass moments of inertia 5.2 General equations of motion 5.3 Translation 5.4 Fixed axis rotation 5.5 General plane motion 5.6 Work and energy relations 5.7 Impulse
Handout 6: Rotational motion and moment of inertia. Angular velocity and angular acceleration
 1 Handout 6: Rotational motion and moment of inertia Angular velocity and angular acceleration In Figure 1, a particle b is rotating about an axis along a circular path with radius r. The radius sweeps
1 Handout 6: Rotational motion and moment of inertia Angular velocity and angular acceleration In Figure 1, a particle b is rotating about an axis along a circular path with radius r. The radius sweeps
Rigid Body Kinetics :: Virtual Work
 Rigid Body Kinetics :: Virtual Work Work-energy relation for an infinitesimal displacement: du = dt + dv (du :: total work done by all active forces) For interconnected systems, differential change in
Rigid Body Kinetics :: Virtual Work Work-energy relation for an infinitesimal displacement: du = dt + dv (du :: total work done by all active forces) For interconnected systems, differential change in
Rigid Body Kinetics :: Force/Mass/Acc
 Rigid Body Kinetics :: Force/Mass/Acc General Equations of Motion G is the mass center of the body Action Dynamic Response 1 Rigid Body Kinetics :: Force/Mass/Acc Fixed Axis Rotation All points in body
Rigid Body Kinetics :: Force/Mass/Acc General Equations of Motion G is the mass center of the body Action Dynamic Response 1 Rigid Body Kinetics :: Force/Mass/Acc Fixed Axis Rotation All points in body
9 Kinetics of 3D rigid bodies - rotating frames
 9 Kinetics of 3D rigid bodies - rotating frames 9. Consider the two gears depicted in the figure. The gear B of radius R B is fixed to the ground, while the gear A of mass m A and radius R A turns freely
9 Kinetics of 3D rigid bodies - rotating frames 9. Consider the two gears depicted in the figure. The gear B of radius R B is fixed to the ground, while the gear A of mass m A and radius R A turns freely
Rigid bodies - general theory
 Rigid bodies - general theory Kinetic Energy: based on FW-26 Consider a system on N particles with all their relative separations fixed: it has 3 translational and 3 rotational degrees of freedom. Motion
Rigid bodies - general theory Kinetic Energy: based on FW-26 Consider a system on N particles with all their relative separations fixed: it has 3 translational and 3 rotational degrees of freedom. Motion
Oscillatory Motion. Solutions of Selected Problems
 Chapter 15 Oscillatory Motion. Solutions of Selected Problems 15.1 Problem 15.18 (In the text book) A block-spring system oscillates with an amplitude of 3.50 cm. If the spring constant is 250 N/m and
Chapter 15 Oscillatory Motion. Solutions of Selected Problems 15.1 Problem 15.18 (In the text book) A block-spring system oscillates with an amplitude of 3.50 cm. If the spring constant is 250 N/m and
1.1. Rotational Kinematics Description Of Motion Of A Rotating Body
 PHY 19- PHYSICS III 1. Moment Of Inertia 1.1. Rotational Kinematics Description Of Motion Of A Rotating Body 1.1.1. Linear Kinematics Consider the case of linear kinematics; it concerns the description
PHY 19- PHYSICS III 1. Moment Of Inertia 1.1. Rotational Kinematics Description Of Motion Of A Rotating Body 1.1.1. Linear Kinematics Consider the case of linear kinematics; it concerns the description
Physics 121, March 25, Rotational Motion and Angular Momentum. Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Rochester
 Physics 121, March 25, 2008. Rotational Motion and Angular Momentum. Physics 121. March 25, 2008. Course Information Topics to be discussed today: Review of Rotational Motion Rolling Motion Angular Momentum
Physics 121, March 25, 2008. Rotational Motion and Angular Momentum. Physics 121. March 25, 2008. Course Information Topics to be discussed today: Review of Rotational Motion Rolling Motion Angular Momentum
Problem 1. Mathematics of rotations
 Problem 1. Mathematics of rotations (a) Show by algebraic means (i.e. no pictures) that the relationship between ω and is: φ, ψ, θ Feel free to use computer algebra. ω X = φ sin θ sin ψ + θ cos ψ (1) ω
Problem 1. Mathematics of rotations (a) Show by algebraic means (i.e. no pictures) that the relationship between ω and is: φ, ψ, θ Feel free to use computer algebra. ω X = φ sin θ sin ψ + θ cos ψ (1) ω
7 Kinematics and kinetics of planar rigid bodies II
 7 Kinematics and kinetics of planar rigid bodies II 7.1 In-class A rigid circular cylinder of radius a and length h has a hole of radius 0.5a cut out. The density of the cylinder is ρ. Assume that the
7 Kinematics and kinetics of planar rigid bodies II 7.1 In-class A rigid circular cylinder of radius a and length h has a hole of radius 0.5a cut out. The density of the cylinder is ρ. Assume that the
Chapter 9 Notes. x cm =
 Chapter 9 Notes Chapter 8 begins the discussion of rigid bodies, a system of particles with fixed relative positions. Previously we have dealt with translation of a particle: if a rigid body does not rotate
Chapter 9 Notes Chapter 8 begins the discussion of rigid bodies, a system of particles with fixed relative positions. Previously we have dealt with translation of a particle: if a rigid body does not rotate
For a rigid body that is constrained to rotate about a fixed axis, the gravitational torque about the axis is
 Experiment 14 The Physical Pendulum The period of oscillation of a physical pendulum is found to a high degree of accuracy by two methods: theory and experiment. The values are then compared. Theory For
Experiment 14 The Physical Pendulum The period of oscillation of a physical pendulum is found to a high degree of accuracy by two methods: theory and experiment. The values are then compared. Theory For
Lecture D16-2D Rigid Body Kinematics
 J. Peraire 16.07 Dynamics Fall 2004 Version 1.2 Lecture D16-2D Rigid Body Kinematics In this lecture, we will start from the general relative motion concepts introduced in lectures D11 and D12, and then
J. Peraire 16.07 Dynamics Fall 2004 Version 1.2 Lecture D16-2D Rigid Body Kinematics In this lecture, we will start from the general relative motion concepts introduced in lectures D11 and D12, and then
PC 1141 : AY 2012 /13
 NUS Physics Society Past Year Paper Solutions PC 1141 : AY 2012 /13 Compiled by: NUS Physics Society Past Year Solution Team Yeo Zhen Yuan Ryan Goh Published on: November 17, 2015 1. An egg of mass 0.050
NUS Physics Society Past Year Paper Solutions PC 1141 : AY 2012 /13 Compiled by: NUS Physics Society Past Year Solution Team Yeo Zhen Yuan Ryan Goh Published on: November 17, 2015 1. An egg of mass 0.050
N mg N Mg N Figure : Forces acting on particle m and inclined plane M. (b) The equations of motion are obtained by applying the momentum principles to
 .004 MDEING DNMIS ND NTR I I Spring 00 Solutions for Problem Set 5 Problem. Particle slides down movable inclined plane. The inclined plane of mass M is constrained to move parallel to the -axis, and the
.004 MDEING DNMIS ND NTR I I Spring 00 Solutions for Problem Set 5 Problem. Particle slides down movable inclined plane. The inclined plane of mass M is constrained to move parallel to the -axis, and the
Torque and Rotation Lecture 7
 Torque and Rotation Lecture 7 ˆ In this lecture we finally move beyond a simple particle in our mechanical analysis of motion. ˆ Now we consider the so-called rigid body. Essentially, a particle with extension
Torque and Rotation Lecture 7 ˆ In this lecture we finally move beyond a simple particle in our mechanical analysis of motion. ˆ Now we consider the so-called rigid body. Essentially, a particle with extension
SYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
 Chapter Seven SYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION MCQ I 7.1 For which of the following does the centre of mass lie outside the body? (a) A pencil (b) A shotput (c) A dice (d) A bangle 7. Which of
Chapter Seven SYSTEM OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION MCQ I 7.1 For which of the following does the centre of mass lie outside the body? (a) A pencil (b) A shotput (c) A dice (d) A bangle 7. Which of
Handout 7: Torque, angular momentum, rotational kinetic energy and rolling motion. Torque and angular momentum
 Handout 7: Torque, angular momentum, rotational kinetic energy and rolling motion Torque and angular momentum In Figure, in order to turn a rod about a fixed hinge at one end, a force F is applied at a
Handout 7: Torque, angular momentum, rotational kinetic energy and rolling motion Torque and angular momentum In Figure, in order to turn a rod about a fixed hinge at one end, a force F is applied at a
CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 25: Ch.17, Sec.4-5
 1 / 36 CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 25: Ch.17, Sec.4-5 Prof. Albert S. Kim Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Hawaii at Manoa Date: 2 / 36 EQUATIONS OF MOTION: ROTATION
1 / 36 CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 25: Ch.17, Sec.4-5 Prof. Albert S. Kim Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Hawaii at Manoa Date: 2 / 36 EQUATIONS OF MOTION: ROTATION
Cross Product Angular Momentum
 Lecture 21 Chapter 12 Physics I Cross Product Angular Momentum Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi IN THIS CHAPTER, you will continue discussing rotational dynamics
Lecture 21 Chapter 12 Physics I Cross Product Angular Momentum Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi IN THIS CHAPTER, you will continue discussing rotational dynamics
General Physics I. Lecture 10: Rolling Motion and Angular Momentum.
 General Physics I Lecture 10: Rolling Motion and Angular Momentum Prof. WAN, Xin (万歆) 万歆 ) xinwan@zju.edu.cn http://zimp.zju.edu.cn/~xinwan/ Outline Rolling motion of a rigid object: center-of-mass motion
General Physics I Lecture 10: Rolling Motion and Angular Momentum Prof. WAN, Xin (万歆) 万歆 ) xinwan@zju.edu.cn http://zimp.zju.edu.cn/~xinwan/ Outline Rolling motion of a rigid object: center-of-mass motion
16. Rotational Dynamics
 6. Rotational Dynamics A Overview In this unit we will address examples that combine both translational and rotational motion. We will find that we will need both Newton s second law and the rotational
6. Rotational Dynamics A Overview In this unit we will address examples that combine both translational and rotational motion. We will find that we will need both Newton s second law and the rotational
Moments of Inertia (7 pages; 23/3/18)
 Moments of Inertia (7 pages; 3/3/8) () Suppose that an object rotates about a fixed axis AB with angular velocity θ. Considering the object to be made up of particles, suppose that particle i (with mass
Moments of Inertia (7 pages; 3/3/8) () Suppose that an object rotates about a fixed axis AB with angular velocity θ. Considering the object to be made up of particles, suppose that particle i (with mass
DYNAMICS VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies: Energy and Momentum Methods. Seventh Edition CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 7 VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: DYNAMICS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies: Energy and Momentum Methods
CHAPTER 7 VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: DYNAMICS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies: Energy and Momentum Methods
Physics 351, Spring 2015, Final Exam.
 Physics 351, Spring 2015, Final Exam. This closed-book exam has (only) 25% weight in your course grade. You can use one sheet of your own hand-written notes. Please show your work on these pages. The back
Physics 351, Spring 2015, Final Exam. This closed-book exam has (only) 25% weight in your course grade. You can use one sheet of your own hand-written notes. Please show your work on these pages. The back
Problem Solving Session 11 Three Dimensional Rotation and Gyroscopes Solutions
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.01 Problem Solving Session 11 Three Dimensional Rotation and Gyroscopes Solutions W14D3-1 Rotating Skew Rod Solution Consider a simple
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.01 Problem Solving Session 11 Three Dimensional Rotation and Gyroscopes Solutions W14D3-1 Rotating Skew Rod Solution Consider a simple
Chapter 12: Rotation of Rigid Bodies. Center of Mass Moment of Inertia Torque Angular Momentum Rolling Statics
 Chapter 1: Rotation of Rigid Bodies Center of Mass Moment of Inertia Torque Angular Momentum Rolling Statics Translational vs Rotational / / 1/ m x v dx dt a dv dt F ma p mv KE mv Work Fd P Fv / / 1/ I
Chapter 1: Rotation of Rigid Bodies Center of Mass Moment of Inertia Torque Angular Momentum Rolling Statics Translational vs Rotational / / 1/ m x v dx dt a dv dt F ma p mv KE mv Work Fd P Fv / / 1/ I
EQUATIONS OF MOTION: GENERAL PLANE MOTION (Section 17.5) Today s Objectives: Students will be able to analyze the planar kinetics of a rigid body
 EQUATIONS OF MOTION: GENERAL PLANE MOTION (Section 17.5) Today s Objectives: Students will be able to analyze the planar kinetics of a rigid body undergoing general plane motion. APPLICATIONS As the soil
EQUATIONS OF MOTION: GENERAL PLANE MOTION (Section 17.5) Today s Objectives: Students will be able to analyze the planar kinetics of a rigid body undergoing general plane motion. APPLICATIONS As the soil
Conservation of Linear Momentum : If a force F is acting on particle of mass m, then according to Newton s second law of motion, we have F = dp /dt =
 Conservation of Linear Momentum : If a force F is acting on particle of mass m, then according to Newton s second law of motion, we have F = dp /dt = d (mv) /dt where p =mv is linear momentum of particle
Conservation of Linear Momentum : If a force F is acting on particle of mass m, then according to Newton s second law of motion, we have F = dp /dt = d (mv) /dt where p =mv is linear momentum of particle
Classical Mechanics III (8.09) Fall 2014 Assignment 3
 Classical Mechanics III (8.09) Fall 2014 Assignment 3 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Physics Department Due September 29, 2014 September 22, 2014 6:00pm Announcements This week we continue our discussion
Classical Mechanics III (8.09) Fall 2014 Assignment 3 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Physics Department Due September 29, 2014 September 22, 2014 6:00pm Announcements This week we continue our discussion
Qualifying Exam. Aug Part II. Please use blank paper for your work do not write on problems sheets!
 Qualifying Exam Aug. 2015 Part II Please use blank paper for your work do not write on problems sheets! Solve only one problem from each of the four sections Mechanics, Quantum Mechanics, Statistical Physics
Qualifying Exam Aug. 2015 Part II Please use blank paper for your work do not write on problems sheets! Solve only one problem from each of the four sections Mechanics, Quantum Mechanics, Statistical Physics
13. Rigid Body Dynamics II
 University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Classical Dynamics Physics Course Materials 2015 13. Rigid Body Dynamics II Gerhard Müller University of Rhode Island, gmuller@uri.edu Creative Commons License
University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Classical Dynamics Physics Course Materials 2015 13. Rigid Body Dynamics II Gerhard Müller University of Rhode Island, gmuller@uri.edu Creative Commons License
Lecture D10 - Angular Impulse and Momentum
 J. Peraire 6.07 Dynamics Fall 2004 Version.2 Lecture D0 - Angular Impulse and Momentum In addition to the equations of linear impulse and momentum considered in the previous lecture, there is a parallel
J. Peraire 6.07 Dynamics Fall 2004 Version.2 Lecture D0 - Angular Impulse and Momentum In addition to the equations of linear impulse and momentum considered in the previous lecture, there is a parallel
General Definition of Torque, final. Lever Arm. General Definition of Torque 7/29/2010. Units of Chapter 10
 Units of Chapter 10 Determining Moments of Inertia Rotational Kinetic Energy Rotational Plus Translational Motion; Rolling Why Does a Rolling Sphere Slow Down? General Definition of Torque, final Taking
Units of Chapter 10 Determining Moments of Inertia Rotational Kinetic Energy Rotational Plus Translational Motion; Rolling Why Does a Rolling Sphere Slow Down? General Definition of Torque, final Taking
dx n dt =nxn±1 x n dx = n +1 I =Σmr 2 = =r p
 SPSP 3 30 Sept 00 Name Test Group # Remember: Show all your work for full credit. Minimum of 4 steps: Draw a diagram!! What equation are you plugging into? What numbers are you substituting? What is your
SPSP 3 30 Sept 00 Name Test Group # Remember: Show all your work for full credit. Minimum of 4 steps: Draw a diagram!! What equation are you plugging into? What numbers are you substituting? What is your
DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS OPTION B-1A: ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS Essential Idea: The basic laws of mechanics have an extension when equivalent principles are applied to rotation. Actual
DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS OPTION B-1A: ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS Essential Idea: The basic laws of mechanics have an extension when equivalent principles are applied to rotation. Actual
Chapter 10. Rotation of a Rigid Object about a Fixed Axis
 Chapter 10 Rotation of a Rigid Object about a Fixed Axis Angular Position Axis of rotation is the center of the disc Choose a fixed reference line. Point P is at a fixed distance r from the origin. A small
Chapter 10 Rotation of a Rigid Object about a Fixed Axis Angular Position Axis of rotation is the center of the disc Choose a fixed reference line. Point P is at a fixed distance r from the origin. A small
Chapter 11. Angular Momentum
 Chapter 11 Angular Momentum Angular Momentum Angular momentum plays a key role in rotational dynamics. There is a principle of conservation of angular momentum. In analogy to the principle of conservation
Chapter 11 Angular Momentum Angular Momentum Angular momentum plays a key role in rotational dynamics. There is a principle of conservation of angular momentum. In analogy to the principle of conservation
STATICS Chapter 1 Introductory Concepts
 Contents Preface to Adapted Edition... (v) Preface to Third Edition... (vii) List of Symbols and Abbreviations... (xi) PART - I STATICS Chapter 1 Introductory Concepts 1-1 Scope of Mechanics... 1 1-2 Preview
Contents Preface to Adapted Edition... (v) Preface to Third Edition... (vii) List of Symbols and Abbreviations... (xi) PART - I STATICS Chapter 1 Introductory Concepts 1-1 Scope of Mechanics... 1 1-2 Preview
CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 27: Ch.18, Sec.1 5
 1 / 42 CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 27: Ch.18, Sec.1 5 Prof. Albert S. Kim Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Hawaii at Manoa Tuesday, November 27, 2012 2 / 42 KINETIC
1 / 42 CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 27: Ch.18, Sec.1 5 Prof. Albert S. Kim Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Hawaii at Manoa Tuesday, November 27, 2012 2 / 42 KINETIC
CP1 REVISION LECTURE 3 INTRODUCTION TO CLASSICAL MECHANICS. Prof. N. Harnew University of Oxford TT 2017
 CP1 REVISION LECTURE 3 INTRODUCTION TO CLASSICAL MECHANICS Prof. N. Harnew University of Oxford TT 2017 1 OUTLINE : CP1 REVISION LECTURE 3 : INTRODUCTION TO CLASSICAL MECHANICS 1. Angular velocity and
CP1 REVISION LECTURE 3 INTRODUCTION TO CLASSICAL MECHANICS Prof. N. Harnew University of Oxford TT 2017 1 OUTLINE : CP1 REVISION LECTURE 3 : INTRODUCTION TO CLASSICAL MECHANICS 1. Angular velocity and
Physical Dynamics (SPA5304) Lecture Plan 2018
 Physical Dynamics (SPA5304) Lecture Plan 2018 The numbers on the left margin are approximate lecture numbers. Items in gray are not covered this year 1 Advanced Review of Newtonian Mechanics 1.1 One Particle
Physical Dynamics (SPA5304) Lecture Plan 2018 The numbers on the left margin are approximate lecture numbers. Items in gray are not covered this year 1 Advanced Review of Newtonian Mechanics 1.1 One Particle
1. Electricity and Magnetism (Fall 1995, Part 1) A metal sphere has a radius R and a charge Q.
 1. Electricity and Magnetism (Fall 1995, Part 1) A metal sphere has a radius R and a charge Q. (a) Compute the electric part of the Maxwell stress tensor T ij (r) = 1 {E i E j 12 } 4π E2 δ ij both inside
1. Electricity and Magnetism (Fall 1995, Part 1) A metal sphere has a radius R and a charge Q. (a) Compute the electric part of the Maxwell stress tensor T ij (r) = 1 {E i E j 12 } 4π E2 δ ij both inside
Classical Mechanics. FIG. 1. Figure for (a), (b) and (c). FIG. 2. Figure for (d) and (e).
 Classical Mechanics 1. Consider a cylindrically symmetric object with a total mass M and a finite radius R from the axis of symmetry as in the FIG. 1. FIG. 1. Figure for (a), (b) and (c). (a) Show that
Classical Mechanics 1. Consider a cylindrically symmetric object with a total mass M and a finite radius R from the axis of symmetry as in the FIG. 1. FIG. 1. Figure for (a), (b) and (c). (a) Show that
Chapter 8. Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics. 1. Torque. 2. Torque and Equilibrium. 3. Center of Mass and Center of Gravity
 Chapter 8 Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics 1. Torque 2. Torque and Equilibrium 3. Center of Mass and Center of Gravity 4. Torque and angular acceleration 5. Rotational Kinetic energy 6. Angular
Chapter 8 Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics 1. Torque 2. Torque and Equilibrium 3. Center of Mass and Center of Gravity 4. Torque and angular acceleration 5. Rotational Kinetic energy 6. Angular
Chapter 8: Momentum, Impulse, & Collisions. Newton s second law in terms of momentum:
 linear momentum: Chapter 8: Momentum, Impulse, & Collisions Newton s second law in terms of momentum: impulse: Under what SPECIFIC condition is linear momentum conserved? (The answer does not involve collisions.)
linear momentum: Chapter 8: Momentum, Impulse, & Collisions Newton s second law in terms of momentum: impulse: Under what SPECIFIC condition is linear momentum conserved? (The answer does not involve collisions.)
Physics 106a, Caltech 4 December, Lecture 18: Examples on Rigid Body Dynamics. Rotating rectangle. Heavy symmetric top
 Physics 106a, Caltech 4 December, 2018 Lecture 18: Examples on Rigid Body Dynamics I go through a number of examples illustrating the methods of solving rigid body dynamics. In most cases, the problem
Physics 106a, Caltech 4 December, 2018 Lecture 18: Examples on Rigid Body Dynamics I go through a number of examples illustrating the methods of solving rigid body dynamics. In most cases, the problem
1301W.600 Lecture 16. November 6, 2017
 1301W.600 Lecture 16 November 6, 2017 You are Cordially Invited to the Physics Open House Friday, November 17 th, 2017 4:30-8:00 PM Tate Hall, Room B20 Time to apply for a major? Consider Physics!! Program
1301W.600 Lecture 16 November 6, 2017 You are Cordially Invited to the Physics Open House Friday, November 17 th, 2017 4:30-8:00 PM Tate Hall, Room B20 Time to apply for a major? Consider Physics!! Program
Rigid Body Dynamics, SG2150 Solutions to Exam,
 KTH Mechanics 011 10 Calculational problems Rigid Body Dynamics, SG150 Solutions to Eam, 011 10 Problem 1: A slender homogeneous rod of mass m and length a can rotate in a vertical plane about a fied smooth
KTH Mechanics 011 10 Calculational problems Rigid Body Dynamics, SG150 Solutions to Eam, 011 10 Problem 1: A slender homogeneous rod of mass m and length a can rotate in a vertical plane about a fied smooth
Phys 7221 Homework # 8
 Phys 71 Homework # 8 Gabriela González November 15, 6 Derivation 5-6: Torque free symmetric top In a torque free, symmetric top, with I x = I y = I, the angular velocity vector ω in body coordinates with
Phys 71 Homework # 8 Gabriela González November 15, 6 Derivation 5-6: Torque free symmetric top In a torque free, symmetric top, with I x = I y = I, the angular velocity vector ω in body coordinates with
Practice Test 3. Name: Date: ID: A. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Date: _ Practice Test 3 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A wheel rotates about a fixed axis with an initial angular velocity of 20
Name: Date: _ Practice Test 3 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A wheel rotates about a fixed axis with an initial angular velocity of 20
Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics. UCVTS AIT Physics
 Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics UCVTS AIT Physics Angular Position Axis of rotation is the center of the disc Choose a fixed reference line Point P is at a fixed distance r from the origin Angular Position,
Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics UCVTS AIT Physics Angular Position Axis of rotation is the center of the disc Choose a fixed reference line Point P is at a fixed distance r from the origin Angular Position,
Physics 141. Lecture 18. Frank L. H. Wolfs Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Rochester, Lecture 18, Page 1
 Physics 141. Lecture 18. Frank L. H. Wolfs Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Rochester, Lecture 18, Page 1 Physics 141. Lecture 18. Course Information. Topics to be discussed today: A
Physics 141. Lecture 18. Frank L. H. Wolfs Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Rochester, Lecture 18, Page 1 Physics 141. Lecture 18. Course Information. Topics to be discussed today: A
Lecture II: Rigid-Body Physics
 Rigid-Body Motion Previously: Point dimensionless objects moving through a trajectory. Today: Objects with dimensions, moving as one piece. 2 Rigid-Body Kinematics Objects as sets of points. Relative distances
Rigid-Body Motion Previously: Point dimensionless objects moving through a trajectory. Today: Objects with dimensions, moving as one piece. 2 Rigid-Body Kinematics Objects as sets of points. Relative distances
Artificial Intelligence & Neuro Cognitive Systems Fakultät für Informatik. Robot Dynamics. Dr.-Ing. John Nassour J.
 Artificial Intelligence & Neuro Cognitive Systems Fakultät für Informatik Robot Dynamics Dr.-Ing. John Nassour 25.1.218 J.Nassour 1 Introduction Dynamics concerns the motion of bodies Includes Kinematics
Artificial Intelligence & Neuro Cognitive Systems Fakultät für Informatik Robot Dynamics Dr.-Ing. John Nassour 25.1.218 J.Nassour 1 Introduction Dynamics concerns the motion of bodies Includes Kinematics
Chap. 10: Rotational Motion
 Chap. 10: Rotational Motion I. Rotational Kinematics II. Rotational Dynamics - Newton s Law for Rotation III. Angular Momentum Conservation (Chap. 10) 1 Newton s Laws for Rotation n e t I 3 rd part [N
Chap. 10: Rotational Motion I. Rotational Kinematics II. Rotational Dynamics - Newton s Law for Rotation III. Angular Momentum Conservation (Chap. 10) 1 Newton s Laws for Rotation n e t I 3 rd part [N
The Calculus of Vec- tors
 Physics 2460 Electricity and Magnetism I, Fall 2007, Lecture 3 1 The Calculus of Vec- Summary: tors 1. Calculus of Vectors: Limits and Derivatives 2. Parametric representation of Curves r(t) = [x(t), y(t),
Physics 2460 Electricity and Magnetism I, Fall 2007, Lecture 3 1 The Calculus of Vec- Summary: tors 1. Calculus of Vectors: Limits and Derivatives 2. Parametric representation of Curves r(t) = [x(t), y(t),
Rotational & Rigid-Body Mechanics. Lectures 3+4
 Rotational & Rigid-Body Mechanics Lectures 3+4 Rotational Motion So far: point objects moving through a trajectory. Next: moving actual dimensional objects and rotating them. 2 Circular Motion - Definitions
Rotational & Rigid-Body Mechanics Lectures 3+4 Rotational Motion So far: point objects moving through a trajectory. Next: moving actual dimensional objects and rotating them. 2 Circular Motion - Definitions
Part 8: Rigid Body Dynamics
 Document that contains homework problems. Comment out the solutions when printing off for students. Part 8: Rigid Body Dynamics Problem 1. Inertia review Find the moment of inertia for a thin uniform rod
Document that contains homework problems. Comment out the solutions when printing off for students. Part 8: Rigid Body Dynamics Problem 1. Inertia review Find the moment of inertia for a thin uniform rod
Notes on Torque. We ve seen that if we define torque as rfsinθ, and the N 2. i i
 Notes on Torque We ve seen that if we define torque as rfsinθ, and the moment of inertia as N, we end up with an equation mr i= 1 that looks just like Newton s Second Law There is a crucial difference,
Notes on Torque We ve seen that if we define torque as rfsinθ, and the moment of inertia as N, we end up with an equation mr i= 1 that looks just like Newton s Second Law There is a crucial difference,
Rotational Motion and Torque
 Rotational Motion and Torque Introduction to Angular Quantities Sections 8- to 8-2 Introduction Rotational motion deals with spinning objects, or objects rotating around some point. Rotational motion is
Rotational Motion and Torque Introduction to Angular Quantities Sections 8- to 8-2 Introduction Rotational motion deals with spinning objects, or objects rotating around some point. Rotational motion is
First Year Physics: Prelims CP1. Classical Mechanics: Prof. Neville Harnew. Problem Set III : Projectiles, rocket motion and motion in E & B fields
 HT017 First Year Physics: Prelims CP1 Classical Mechanics: Prof Neville Harnew Problem Set III : Projectiles, rocket motion and motion in E & B fields Questions 1-10 are standard examples Questions 11-1
HT017 First Year Physics: Prelims CP1 Classical Mechanics: Prof Neville Harnew Problem Set III : Projectiles, rocket motion and motion in E & B fields Questions 1-10 are standard examples Questions 11-1
Motion in Space. MATH 311, Calculus III. J. Robert Buchanan. Fall Department of Mathematics. J. Robert Buchanan Motion in Space
 Motion in Space MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Background Suppose the position vector of a moving object is given by r(t) = f (t), g(t), h(t), Background
Motion in Space MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2011 Background Suppose the position vector of a moving object is given by r(t) = f (t), g(t), h(t), Background
PLANAR KINETICS OF A RIGID BODY: WORK AND ENERGY Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Define the various ways a force and couple do work.
 PLANAR KINETICS OF A RIGID BODY: WORK AND ENERGY Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Define the various ways a force and couple do work. In-Class Activities: 2. Apply the principle of work
PLANAR KINETICS OF A RIGID BODY: WORK AND ENERGY Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Define the various ways a force and couple do work. In-Class Activities: 2. Apply the principle of work
16.07 Dynamics Final Exam
 Name:... Massachusetts Institute of Technology 16.07 Dynamics Final Exam Tuesday, December 20, 2005 Problem 1 (8) Problem 2 (8) Problem 3 (10) Problem 4 (10) Problem 5 (10) Problem 6 (10) Problem 7 (10)
Name:... Massachusetts Institute of Technology 16.07 Dynamics Final Exam Tuesday, December 20, 2005 Problem 1 (8) Problem 2 (8) Problem 3 (10) Problem 4 (10) Problem 5 (10) Problem 6 (10) Problem 7 (10)
UNIVERSITI TUN HUSSEIN ONN MALAYSIA FINAL EXAMINATION SEMESTER I SESSION 2009/2010
 Aftisse^ UNIVERSITI TUN HUSSEIN ONN MALAYSIA SEMESTER I SESSION 2009/2010 SUBJECT : DYNAMICS SUBJECT CODE : BDA2013 COURSE : 2 BDD DATE : NOVEMBER 2009 DURATION : 2 */ 2 HOURS INSTRUCTION : ANSWER FOUR
Aftisse^ UNIVERSITI TUN HUSSEIN ONN MALAYSIA SEMESTER I SESSION 2009/2010 SUBJECT : DYNAMICS SUBJECT CODE : BDA2013 COURSE : 2 BDD DATE : NOVEMBER 2009 DURATION : 2 */ 2 HOURS INSTRUCTION : ANSWER FOUR
Physics 201. Professor P. Q. Hung. 311B, Physics Building. Physics 201 p. 1/1
 Physics 201 p. 1/1 Physics 201 Professor P. Q. Hung 311B, Physics Building Physics 201 p. 2/1 Rotational Kinematics and Energy Rotational Kinetic Energy, Moment of Inertia All elements inside the rigid
Physics 201 p. 1/1 Physics 201 Professor P. Q. Hung 311B, Physics Building Physics 201 p. 2/1 Rotational Kinematics and Energy Rotational Kinetic Energy, Moment of Inertia All elements inside the rigid
Get Discount Coupons for your Coaching institute and FREE Study Material at Force System
 Get Discount Coupons for your Coaching institute and FEE Study Material at www.pickmycoaching.com Mechanics Force System When a member of forces simultaneously acting on the body, it is known as force
Get Discount Coupons for your Coaching institute and FEE Study Material at www.pickmycoaching.com Mechanics Force System When a member of forces simultaneously acting on the body, it is known as force
Chapter 8 continued. Rotational Dynamics
 Chapter 8 continued Rotational Dynamics 8.4 Rotational Work and Energy Work to accelerate a mass rotating it by angle φ F W = F(cosθ)x x = rφ = Frφ Fr = τ (torque) = τφ r φ s F to x θ = 0 DEFINITION OF
Chapter 8 continued Rotational Dynamics 8.4 Rotational Work and Energy Work to accelerate a mass rotating it by angle φ F W = F(cosθ)x x = rφ = Frφ Fr = τ (torque) = τφ r φ s F to x θ = 0 DEFINITION OF
Rotational Kinetic Energy
 Lecture 17, Chapter 10: Rotational Energy and Angular Momentum 1 Rotational Kinetic Energy Consider a rigid body rotating with an angular velocity ω about an axis. Clearly every point in the rigid body
Lecture 17, Chapter 10: Rotational Energy and Angular Momentum 1 Rotational Kinetic Energy Consider a rigid body rotating with an angular velocity ω about an axis. Clearly every point in the rigid body
CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 33: Ch.19, Sec.1 2
 1 / 36 CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 33: Ch.19, Sec.1 2 Prof. Albert S. Kim Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Hawaii at Manoa Thursday, December 6, 2012 2 / 36 LINEAR
1 / 36 CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 33: Ch.19, Sec.1 2 Prof. Albert S. Kim Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Hawaii at Manoa Thursday, December 6, 2012 2 / 36 LINEAR
CIRCULAR MOTION AND ROTATION
 1. UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION So far we have learned a great deal about linear motion. This section addresses rotational motion. The simplest kind of rotational motion is an object moving in a perfect circle
1. UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION So far we have learned a great deal about linear motion. This section addresses rotational motion. The simplest kind of rotational motion is an object moving in a perfect circle
Chapter 18 KINETICS OF RIGID BODIES IN THREE DIMENSIONS. The two fundamental equations for the motion of a system of particles .
 hapter 18 KINETIS F RIID DIES IN THREE DIMENSINS The to fundamental equations for the motion of a sstem of particles ΣF = ma ΣM = H H provide the foundation for three dimensional analsis, just as the do
hapter 18 KINETIS F RIID DIES IN THREE DIMENSINS The to fundamental equations for the motion of a sstem of particles ΣF = ma ΣM = H H provide the foundation for three dimensional analsis, just as the do
Video 2.1a Vijay Kumar and Ani Hsieh
 Video 2.1a Vijay Kumar and Ani Hsieh Robo3x-1.3 1 Introduction to Lagrangian Mechanics Vijay Kumar and Ani Hsieh University of Pennsylvania Robo3x-1.3 2 Analytical Mechanics Aristotle Galileo Bernoulli
Video 2.1a Vijay Kumar and Ani Hsieh Robo3x-1.3 1 Introduction to Lagrangian Mechanics Vijay Kumar and Ani Hsieh University of Pennsylvania Robo3x-1.3 2 Analytical Mechanics Aristotle Galileo Bernoulli
Physics 121, March 27, Angular Momentum, Torque, and Precession. Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Rochester
 Physics 121, March 27, 2008. Angular Momentum, Torque, and Precession. Physics 121. March 27, 2008. Course Information Quiz Topics to be discussed today: Review of Angular Momentum Conservation of Angular
Physics 121, March 27, 2008. Angular Momentum, Torque, and Precession. Physics 121. March 27, 2008. Course Information Quiz Topics to be discussed today: Review of Angular Momentum Conservation of Angular
General Physics I. Lecture 8: Rotation of a Rigid Object About a Fixed Axis. Prof. WAN, Xin ( 万歆 )
 General Physics I Lecture 8: Rotation of a Rigid Object About a Fixed Axis Prof. WAN, Xin ( 万歆 ) xinwan@zju.edu.cn http://zimp.zju.edu.cn/~xinwan/ New Territory Object In the past, point particle (no rotation,
General Physics I Lecture 8: Rotation of a Rigid Object About a Fixed Axis Prof. WAN, Xin ( 万歆 ) xinwan@zju.edu.cn http://zimp.zju.edu.cn/~xinwan/ New Territory Object In the past, point particle (no rotation,
ME 230: Kinematics and Dynamics Spring 2014 Section AD. Final Exam Review: Rigid Body Dynamics Practice Problem
 ME 230: Kinematics and Dynamics Spring 2014 Section AD Final Exam Review: Rigid Body Dynamics Practice Problem 1. A rigid uniform flat disk of mass m, and radius R is moving in the plane towards a wall
ME 230: Kinematics and Dynamics Spring 2014 Section AD Final Exam Review: Rigid Body Dynamics Practice Problem 1. A rigid uniform flat disk of mass m, and radius R is moving in the plane towards a wall
Afternoon Section. Physics 1210 Exam 2 November 8, ! v = d! r dt. a avg. = v2. ) T 2! w = m g! f s. = v at v 2 1.
 Name Physics 1210 Exam 2 November 8, 2012 Afternoon Section Please write directly on the exam and attach other sheets of work if necessary. Calculators are allowed. No notes or books may be used. Multiple-choice
Name Physics 1210 Exam 2 November 8, 2012 Afternoon Section Please write directly on the exam and attach other sheets of work if necessary. Calculators are allowed. No notes or books may be used. Multiple-choice
Ph1a: Solution to the Final Exam Alejandro Jenkins, Fall 2004
 Ph1a: Solution to the Final Exam Alejandro Jenkins, Fall 2004 Problem 1 (10 points) - The Delivery A crate of mass M, which contains an expensive piece of scientific equipment, is being delivered to Caltech.
Ph1a: Solution to the Final Exam Alejandro Jenkins, Fall 2004 Problem 1 (10 points) - The Delivery A crate of mass M, which contains an expensive piece of scientific equipment, is being delivered to Caltech.
FALL TERM EXAM, PHYS 1211, INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Saturday, 14 December 2013, 1PM to 4 PM, AT 1003
 FALL TERM EXAM, PHYS 1211, INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Saturday, 14 December 2013, 1PM to 4 PM, AT 1003 NAME: STUDENT ID: INSTRUCTION 1. This exam booklet has 14 pages. Make sure none are missing 2. There is
FALL TERM EXAM, PHYS 1211, INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Saturday, 14 December 2013, 1PM to 4 PM, AT 1003 NAME: STUDENT ID: INSTRUCTION 1. This exam booklet has 14 pages. Make sure none are missing 2. There is
CURVILINEAR MOTION: NORMAL AND TANGENTIAL COMPONENTS (12.7)
 19 / 36 CURVILINEAR MOTION: NORMAL AND TANGENTIAL COMPONENTS (12.7) Today s objectives: Students will be able to 1 Determine the normal and tangential components of velocity and acceleration of a particle
19 / 36 CURVILINEAR MOTION: NORMAL AND TANGENTIAL COMPONENTS (12.7) Today s objectives: Students will be able to 1 Determine the normal and tangential components of velocity and acceleration of a particle
Forces Part 1: Newton s Laws
 Forces Part 1: Newton s Laws Last modified: 13/12/2017 Forces Introduction Inertia & Newton s First Law Mass & Momentum Change in Momentum & Force Newton s Second Law Example 1 Newton s Third Law Common
Forces Part 1: Newton s Laws Last modified: 13/12/2017 Forces Introduction Inertia & Newton s First Law Mass & Momentum Change in Momentum & Force Newton s Second Law Example 1 Newton s Third Law Common
3-D Kinetics of Rigid Bodies
 3-D Kinetics of Rigid Bodies Angular Momentum Generalized Newton s second law for the motion for a 3-D mass system Moment eqn for 3-D motion will be different than that obtained for plane motion Consider
3-D Kinetics of Rigid Bodies Angular Momentum Generalized Newton s second law for the motion for a 3-D mass system Moment eqn for 3-D motion will be different than that obtained for plane motion Consider
Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies: Forces and Accelerations
 Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies: Forces and Accelerations Reference: Beer, Ferdinand P. et al, Vector Mechanics for Engineers : Dynamics, 8 th Edition, Mc GrawHill Hibbeler R.C., Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics,
Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies: Forces and Accelerations Reference: Beer, Ferdinand P. et al, Vector Mechanics for Engineers : Dynamics, 8 th Edition, Mc GrawHill Hibbeler R.C., Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics,
RIGID BODY MOTION (Section 16.1)
 RIGID BODY MOTION (Section 16.1) There are cases where an object cannot be treated as a particle. In these cases the size or shape of the body must be considered. Rotation of the body about its center
RIGID BODY MOTION (Section 16.1) There are cases where an object cannot be treated as a particle. In these cases the size or shape of the body must be considered. Rotation of the body about its center
Problem Solving Session 10 Simple Harmonic Oscillator Solutions
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.01 Problem Solving Session 10 Simple Harmonic Oscillator Solutions W13D3-0 Group Problem Gravitational Simple Harmonic Oscillator Two identical
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.01 Problem Solving Session 10 Simple Harmonic Oscillator Solutions W13D3-0 Group Problem Gravitational Simple Harmonic Oscillator Two identical
Chapters 10 & 11: Rotational Dynamics Thursday March 8 th
 Chapters 10 & 11: Rotational Dynamics Thursday March 8 th Review of rotational kinematics equations Review and more on rotational inertia Rolling motion as rotation and translation Rotational kinetic energy
Chapters 10 & 11: Rotational Dynamics Thursday March 8 th Review of rotational kinematics equations Review and more on rotational inertia Rolling motion as rotation and translation Rotational kinetic energy
The University of Melbourne Engineering Mechanics
 The University of Melbourne 436-291 Engineering Mechanics Tutorial Eleven Instantaneous Centre and General Motion Part A (Introductory) 1. (Problem 5/93 from Meriam and Kraige - Dynamics) For the instant
The University of Melbourne 436-291 Engineering Mechanics Tutorial Eleven Instantaneous Centre and General Motion Part A (Introductory) 1. (Problem 5/93 from Meriam and Kraige - Dynamics) For the instant
Advanced Dynamics. - Lecture 4 Lagrange Equations. Paolo Tiso Spring Semester 2017 ETH Zürich
 Advanced Dynamics - Lecture 4 Lagrange Equations Paolo Tiso Spring Semester 2017 ETH Zürich LECTURE OBJECTIVES 1. Derive the Lagrange equations of a system of particles; 2. Show that the equation of motion
Advanced Dynamics - Lecture 4 Lagrange Equations Paolo Tiso Spring Semester 2017 ETH Zürich LECTURE OBJECTIVES 1. Derive the Lagrange equations of a system of particles; 2. Show that the equation of motion
Classical Mechanics Comprehensive Exam Solution
 Classical Mechanics Comprehensive Exam Solution January 31, 011, 1:00 pm 5:pm Solve the following six problems. In the following problems, e x, e y, and e z are unit vectors in the x, y, and z directions,
Classical Mechanics Comprehensive Exam Solution January 31, 011, 1:00 pm 5:pm Solve the following six problems. In the following problems, e x, e y, and e z are unit vectors in the x, y, and z directions,
Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3 Problem 4 Total
 Name Section THE PENNSYLVANIA STATE UNIVERSITY Department of Engineering Science and Mechanics Engineering Mechanics 12 Final Exam May 5, 2003 8:00 9:50 am (110 minutes) Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3 Problem
Name Section THE PENNSYLVANIA STATE UNIVERSITY Department of Engineering Science and Mechanics Engineering Mechanics 12 Final Exam May 5, 2003 8:00 9:50 am (110 minutes) Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3 Problem
Relating Translational and Rotational Variables
 Relating Translational and Rotational Variables Rotational position and distance moved s = θ r (only radian units) Rotational and translational speed d s v = dt v = ω r = ds dt = d θ dt r Relating period
Relating Translational and Rotational Variables Rotational position and distance moved s = θ r (only radian units) Rotational and translational speed d s v = dt v = ω r = ds dt = d θ dt r Relating period
SOLUTION di x = y2 dm. rdv. m = a 2 bdx. = 2 3 rpab2. I x = 1 2 rp L0. b 4 a1 - x2 a 2 b. = 4 15 rpab4. Thus, I x = 2 5 mb2. Ans.
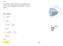 17 4. Determine the moment of inertia of the semiellipsoid with respect to the x axis and express the result in terms of the mass m of the semiellipsoid. The material has a constant density r. y x y a
17 4. Determine the moment of inertia of the semiellipsoid with respect to the x axis and express the result in terms of the mass m of the semiellipsoid. The material has a constant density r. y x y a
Physics 351 Monday, April 3, 2017
 Physics 351 Monday, April 3, 2017 This weekend you read Chapter 11 (coupled oscillators, normal modes, etc.), but it will take us another day or two to finish Chapter 10 in class: Euler angles; Lagrangian
Physics 351 Monday, April 3, 2017 This weekend you read Chapter 11 (coupled oscillators, normal modes, etc.), but it will take us another day or two to finish Chapter 10 in class: Euler angles; Lagrangian
Physics for Scientists and Engineers 4th Edition, 2017
 A Correlation of Physics for Scientists and Engineers 4th Edition, 2017 To the AP Physics C: Mechanics Course Descriptions AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which was not
A Correlation of Physics for Scientists and Engineers 4th Edition, 2017 To the AP Physics C: Mechanics Course Descriptions AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which was not
Dynamics 12e. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd. Chapter 20 3D Kinematics of a Rigid Body
 Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics 12e Chapter 20 3D Kinematics of a Rigid Body Chapter Objectives Kinematics of a body subjected to rotation about a fixed axis and general plane motion. Relative-motion analysis
Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics 12e Chapter 20 3D Kinematics of a Rigid Body Chapter Objectives Kinematics of a body subjected to rotation about a fixed axis and general plane motion. Relative-motion analysis
