Brad Artman Spring Review
|
|
|
- Muriel Randall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Brad Artman Brad Artman Spring Review 2005
2 Passive Spy vs. Spy 1
3 Passive Spy vs. Spy 2
4 Passive Spy vs. Spy SS2 Installation 3
5 2004 Fourier domain imaging condition & migration aliasing Fourier domain time windowing Gather convolution Foward-scattered angle gathers Valhall data 100% accurate ω k propagator Combined Linear/Hyperbolic radon transforms brad@sep.stanford.edu 4
6 FDIC & aliasing I(x, h) ω,z = U(x + h) D (x h) Î(k x, k h ) ω,z = 1 2 Û ( ) kx + k h 2 ( ) ˆD kx k h 2 derivation brad@sep.stanford.edu 5
7 FDIC & aliasing Fourier domain Space domain 6
8 FDIC & aliasing Fourier domain Space domain 7
9 FDIC & aliasing Fourier domain Space domain 8
10 FDIC & aliasing shallow deep 9
11 FDIC & aliasing every 10 th shot all shots 10
12 FDIC & aliasing Î(k x, k h ) = 1 2 Û ( ) kx + k h 2 ( ) ˆD kx k h 2 k x 1 k h Û( 2 2 ) ˆD (0) Û( 1 2 ) ˆD ( 1 2 ) Û(0) ˆD ( 2 0 Û( 1 2 ) ˆD ( 1 2 ) Û(0) ˆD (0) Û( 1 2 ) ˆD ( 1 2 ) 2 ) 1 Û(0) ˆD ( 2 2 ) Û(1 2 ) ˆD ( 1 2 ) Û(2 2 ) ˆD (0) 2 Û( 1 2 ) ˆD ( 3 2 ) Û(2 2 ) ˆD ( 2 2 ) Û(3 2 ) ˆD ( 1 2 ) brad@sep.stanford.edu 11
13 2004 Fourier domain imaging condition & migration aliasing Fourier domain time windowing Gather convolution Foward-scattered angle gathers Valhall data 12
14 Fourier domain time windowing 13
15 Fourier domain time windowing 14
16 2004 Fourier domain imaging condition & migration aliasing Fourier domain time windowing Gather convolution Foward-scattered angle gathers Valhall data 15
17 Gather correlation shot-profile survey sinking passive imaging U z=0 (x r, x s, ω) D z=0 (x r, x s, ω) R z=0 (x r, x s, ω) T z=0 (x r, ω) T z=0 (x r, ω) SSR 1 SSR +1 DSR SSR 1 SSR +1 U z=1 (x r, x s, ω) D z=1 (x r, x s, ω) R z=1 (x r, x s, ω) Tz=1 (x r, ω) T z=1 + (x r, ω) brad@sep.stanford.edu 16
18 Gather correlation Shot-profile=Source-receiver migration R z+1 = DSR R z = DSR U z Dz = (1) = SSR U z SSR Dz = = SSR U z (SSR 1 D z ) = U z+1 Dz+1. brad@sep.stanford.edu 17
19 Gather convolution Image space SRME: M z+1 = DSR M z = DSR U z Uz = (2) = SSR U z SSR Uz = = SSR U z (SSR 1 U z ) = U z+1 Uz+1. brad@sep.stanford.edu 18
20 Migration 19
21 Image-space multiple model 20
22 Migration, subtraction 21
23 Subtraction, migration 22
24 2004 Fourier domain imaging condition & migration aliasing Fourier domain time windowing Gather convolution Foward-scattered angle gathers Valhall data 23
25 Forward-scattered angle gathers 24
26 Forward-scattered angle gathers x (p r + p s ) + z (q r + q s ) h x (p r p s ) h z (q r q s ) = 0, z h x = tan γ and z x = tan α. x (p r p s ) + z (q r q s ) h x (p r + p s ) h z (q r + q s ) = 0, z h x = cot γ a and z x = cot α a. brad@sep.stanford.edu 25
27 2004 Fourier domain imaging condition & migration aliasing Fourier domain time windowing Gather convolution Foward-scattered angle gathers Valhall data 26
28 Valhall 27
29 Valhall 28
30 2005a Valhall passive data Plan-wave decomposition & spectral analysis migrate P,Z, & S components Back-scattered Forward-scattered P-Z summation as U D separation vs. correlation Compare to best-case image Search for earth tremor brad@sep.stanford.edu 29
31 2005b Finish aliasing paper Finish image-space multiple modeling paper Direct migration of Long Beach VSP data Submit multi-offset GPR migration paper 30
32 Thanks contents 31
33 2004 Fourier domain imaging condition & migration aliasing Fourier domain time windowing Gather convolution Foward-scattered angle gathers Valhall data 32
34 Derivation 1 I(x, h) ω,z = U(x r h)d(x s + h) (1) Fourier transform D to ˆD Î(x, h) = U(x h) ˆD(k s )e ik s(x+h) dk s (2) FT all the x s Î(k x, h) = U(x h) ˆD(k s )e ik s(x+h) dk s e ixk x dx (3) brad@sep.stanford.edu 33
35 Derivation 2 Introduce (Sergey inspired) variable flip-flop/reorder Î(k x, h) = ˆD(k s )e ik sh U(x h)e ix(k x k s ) dxdk s Î(k x, h) = ˆD(k s )e ih(2k s k x ) U(x h)e i(x h)(k x k s ) d(x h)dk s (4) Note salient details: Inner integral is FT of U, Î(k x, h) = Û(k x k s ) ˆD(k s )e ih(2k s k x ) dk s (5) brad@sep.stanford.edu 34
36 knowing k h = 2k s k x, Î(k x, h) = 1 2 Derivation 3 Û( k x k h 2 ) ˆD( k x + k h )e ihk hdk h (6) 2 This we see is FT over offset, so the complete FT of the IC is Î(k x, k h ) = 1 x k h 2Û(k ) 2 ˆD( k x + k h ). (7) 2 return brad@sep.stanford.edu 35
Flux-normalized wavefield decomposition and migration of seismic data
 Flux-normalized wavefield decomposition and migration of seismic data Bjørn Ursin 1, Ørjan Pedersen and Børge Arntsen 1 1 NTNU Statoil China, July 011 Overview Wave equation Up-down separation Amplitude
Flux-normalized wavefield decomposition and migration of seismic data Bjørn Ursin 1, Ørjan Pedersen and Børge Arntsen 1 1 NTNU Statoil China, July 011 Overview Wave equation Up-down separation Amplitude
Extended isochron rays in prestack depth (map) migration
 Extended isochron rays in prestack depth (map) migration A.A. Duchkov and M.V. de Hoop Purdue University, 150 N.University st., West Lafayette, IN, 47907 e-mail: aduchkov@purdue.edu (December 15, 2008)
Extended isochron rays in prestack depth (map) migration A.A. Duchkov and M.V. de Hoop Purdue University, 150 N.University st., West Lafayette, IN, 47907 e-mail: aduchkov@purdue.edu (December 15, 2008)
Deconvolution imaging condition for reverse-time migration
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 112, November 11, 2002, pages 83 96 Deconvolution imaging condition for reverse-time migration Alejandro A. Valenciano and Biondo Biondi 1 ABSTRACT The reverse-time
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 112, November 11, 2002, pages 83 96 Deconvolution imaging condition for reverse-time migration Alejandro A. Valenciano and Biondo Biondi 1 ABSTRACT The reverse-time
Biophysics 230: Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Haacke Chapter 11
 Biophysics 230: Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Haacke Chapter 11 Daniel B. Rowe, Ph.D. daniel.rowe@marquette.edu Department of Math, Stat, Comp Sci Marquette University dbrowe@mcw.edu Department of Biophysics
Biophysics 230: Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Haacke Chapter 11 Daniel B. Rowe, Ph.D. daniel.rowe@marquette.edu Department of Math, Stat, Comp Sci Marquette University dbrowe@mcw.edu Department of Biophysics
Fast Algorithms for the Computation of Oscillatory Integrals
 Fast Algorithms for the Computation of Oscillatory Integrals Emmanuel Candès California Institute of Technology EPSRC Symposium Capstone Conference Warwick Mathematics Institute, July 2009 Collaborators
Fast Algorithms for the Computation of Oscillatory Integrals Emmanuel Candès California Institute of Technology EPSRC Symposium Capstone Conference Warwick Mathematics Institute, July 2009 Collaborators
Time and Spatial Series and Transforms
 Time and Spatial Series and Transforms Z- and Fourier transforms Gibbs' phenomenon Transforms and linear algebra Wavelet transforms Reading: Sheriff and Geldart, Chapter 15 Z-Transform Consider a digitized
Time and Spatial Series and Transforms Z- and Fourier transforms Gibbs' phenomenon Transforms and linear algebra Wavelet transforms Reading: Sheriff and Geldart, Chapter 15 Z-Transform Consider a digitized
CS-9645 Introduction to Computer Vision Techniques Winter 2018
 Table of Contents Spectral Analysis...1 Special Functions... 1 Properties of Dirac-delta Functions...1 Derivatives of the Dirac-delta Function... 2 General Dirac-delta Functions...2 Harmonic Analysis...
Table of Contents Spectral Analysis...1 Special Functions... 1 Properties of Dirac-delta Functions...1 Derivatives of the Dirac-delta Function... 2 General Dirac-delta Functions...2 Harmonic Analysis...
BME I5000: Biomedical Imaging
 1 BME I5000: Biomedical Imaging Lecture FT Fourier Transform Review Lucas C. Parra, parra@ccny.cuny.edu Blackboard: http://cityonline.ccny.cuny.edu/ Fourier Transform (1D) The Fourier Transform (FT) is
1 BME I5000: Biomedical Imaging Lecture FT Fourier Transform Review Lucas C. Parra, parra@ccny.cuny.edu Blackboard: http://cityonline.ccny.cuny.edu/ Fourier Transform (1D) The Fourier Transform (FT) is
Hydrogeophysics - Seismics
 Hydrogeophysics - Seismics Matthias Zillmer EOST-ULP p. 1 Table of contents SH polarized shear waves: Seismic source Case study: porosity of an aquifer Seismic velocities for porous media: The Frenkel-Biot-Gassmann
Hydrogeophysics - Seismics Matthias Zillmer EOST-ULP p. 1 Table of contents SH polarized shear waves: Seismic source Case study: porosity of an aquifer Seismic velocities for porous media: The Frenkel-Biot-Gassmann
Ghost Imaging. Josselin Garnier (Université Paris Diderot)
 Grenoble December, 014 Ghost Imaging Josselin Garnier Université Paris Diderot http:/www.josselin-garnier.org General topic: correlation-based imaging with noise sources. Particular application: Ghost
Grenoble December, 014 Ghost Imaging Josselin Garnier Université Paris Diderot http:/www.josselin-garnier.org General topic: correlation-based imaging with noise sources. Particular application: Ghost
Elastic wave-equation migration for laterally varying isotropic and HTI media. Richard A. Bale and Gary F. Margrave
 Elastic wave-equation migration for laterally varying isotropic and HTI media Richard A. Bale and Gary F. Margrave a Outline Introduction Theory Elastic wavefield extrapolation Extension to laterally heterogeneous
Elastic wave-equation migration for laterally varying isotropic and HTI media Richard A. Bale and Gary F. Margrave a Outline Introduction Theory Elastic wavefield extrapolation Extension to laterally heterogeneous
Solutions of differential equations using transforms
 Solutions of differential equations using transforms Process: Take transform of equation and boundary/initial conditions in one variable. Derivatives are turned into multiplication operators. Solve (hopefully
Solutions of differential equations using transforms Process: Take transform of equation and boundary/initial conditions in one variable. Derivatives are turned into multiplication operators. Solve (hopefully
1 Assignment 1: Nonlinear dynamics (due September
 Assignment : Nonlinear dynamics (due September 4, 28). Consider the ordinary differential equation du/dt = cos(u). Sketch the equilibria and indicate by arrows the increase or decrease of the solutions.
Assignment : Nonlinear dynamics (due September 4, 28). Consider the ordinary differential equation du/dt = cos(u). Sketch the equilibria and indicate by arrows the increase or decrease of the solutions.
Explicit extrapolators and common azimuth migration
 Explicit extrapolators and common azimuth migration Eric Dussaud October 9th, 004 Agenda Downward continuation via explicit extrapolation. Design of explicit extrapolators. Design of 1-D convolution operators.
Explicit extrapolators and common azimuth migration Eric Dussaud October 9th, 004 Agenda Downward continuation via explicit extrapolation. Design of explicit extrapolators. Design of 1-D convolution operators.
Downloaded 10/15/15 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Preprocessing in the PS space for on-shore seismic processing: removing ground roll and ghosts without damaging the reflection data Jing Wu and Arthur B. Weglein, M-OSRP, University of Houston SUMMARY
Preprocessing in the PS space for on-shore seismic processing: removing ground roll and ghosts without damaging the reflection data Jing Wu and Arthur B. Weglein, M-OSRP, University of Houston SUMMARY
G52IVG, School of Computer Science, University of Nottingham
 Image Transforms Fourier Transform Basic idea 1 Image Transforms Fourier transform theory Let f(x) be a continuous function of a real variable x. The Fourier transform of f(x) is F ( u) f ( x)exp[ j2πux]
Image Transforms Fourier Transform Basic idea 1 Image Transforms Fourier transform theory Let f(x) be a continuous function of a real variable x. The Fourier transform of f(x) is F ( u) f ( x)exp[ j2πux]
for multicomponent seismic data Wave-equation angle-domain imaging
 Wave-equation angle-domain imaging for multicomponent seismic data Paul Sava and Sergey Fomel Bureau of Economic Geology University of Texas at Austin September 5, 2005 EAGE/SEG Research Workshop on Multicomponent
Wave-equation angle-domain imaging for multicomponent seismic data Paul Sava and Sergey Fomel Bureau of Economic Geology University of Texas at Austin September 5, 2005 EAGE/SEG Research Workshop on Multicomponent
Introduction to Seismology
 1.510 Introduction to Seismology Lecture 5 Feb., 005 1 Introduction At previous lectures, we derived the equation of motion (λ + µ) ( u(x, t)) µ ( u(x, t)) = ρ u(x, t) (1) t This equation of motion can
1.510 Introduction to Seismology Lecture 5 Feb., 005 1 Introduction At previous lectures, we derived the equation of motion (λ + µ) ( u(x, t)) µ ( u(x, t)) = ρ u(x, t) (1) t This equation of motion can
Final Exam May 4, 2016
 1 Math 425 / AMCS 525 Dr. DeTurck Final Exam May 4, 2016 You may use your book and notes on this exam. Show your work in the exam book. Work only the problems that correspond to the section that you prepared.
1 Math 425 / AMCS 525 Dr. DeTurck Final Exam May 4, 2016 You may use your book and notes on this exam. Show your work in the exam book. Work only the problems that correspond to the section that you prepared.
Navier-Stokes equations
 1 Navier-Stokes equations Introduction to spectral methods for the CSC Lunchbytes Seminar Series. Incompressible, hydrodynamic turbulence is described completely by the Navier-Stokes equations where t
1 Navier-Stokes equations Introduction to spectral methods for the CSC Lunchbytes Seminar Series. Incompressible, hydrodynamic turbulence is described completely by the Navier-Stokes equations where t
Notes on Fourier Series and Integrals Fourier Series
 Notes on Fourier Series and Integrals Fourier Series et f(x) be a piecewise linear function on [, ] (This means that f(x) may possess a finite number of finite discontinuities on the interval). Then f(x)
Notes on Fourier Series and Integrals Fourier Series et f(x) be a piecewise linear function on [, ] (This means that f(x) may possess a finite number of finite discontinuities on the interval). Then f(x)
Conformal maps. Lent 2019 COMPLEX METHODS G. Taylor. A star means optional and not necessarily harder.
 Lent 29 COMPLEX METHODS G. Taylor A star means optional and not necessarily harder. Conformal maps. (i) Let f(z) = az + b, with ad bc. Where in C is f conformal? cz + d (ii) Let f(z) = z +. What are the
Lent 29 COMPLEX METHODS G. Taylor A star means optional and not necessarily harder. Conformal maps. (i) Let f(z) = az + b, with ad bc. Where in C is f conformal? cz + d (ii) Let f(z) = z +. What are the
Fourier Approach to Wave Propagation
 Phys 531 Lecture 15 13 October 005 Fourier Approach to Wave Propagation Last time, reviewed Fourier transform Write any function of space/time = sum of harmonic functions e i(k r ωt) Actual waves: harmonic
Phys 531 Lecture 15 13 October 005 Fourier Approach to Wave Propagation Last time, reviewed Fourier transform Write any function of space/time = sum of harmonic functions e i(k r ωt) Actual waves: harmonic
Spectral Methods and Inverse Problems
 Spectral Methods and Inverse Problems Omid Khanmohamadi Department of Mathematics Florida State University Outline Outline 1 Fourier Spectral Methods Fourier Transforms Trigonometric Polynomial Interpolants
Spectral Methods and Inverse Problems Omid Khanmohamadi Department of Mathematics Florida State University Outline Outline 1 Fourier Spectral Methods Fourier Transforms Trigonometric Polynomial Interpolants
MAGIC058 & MATH64062: Partial Differential Equations 1
 MAGIC58 & MATH6462: Partial Differential Equations Section 6 Fourier transforms 6. The Fourier integral formula We have seen from section 4 that, if a function f(x) satisfies the Dirichlet conditions,
MAGIC58 & MATH6462: Partial Differential Equations Section 6 Fourier transforms 6. The Fourier integral formula We have seen from section 4 that, if a function f(x) satisfies the Dirichlet conditions,
Waveform inversion and time-reversal imaging in attenuative TI media
 Waveform inversion and time-reversal imaging in attenuative TI media Tong Bai 1, Tieyuan Zhu 2, Ilya Tsvankin 1, Xinming Wu 3 1. Colorado School of Mines 2. Penn State University 3. University of Texas
Waveform inversion and time-reversal imaging in attenuative TI media Tong Bai 1, Tieyuan Zhu 2, Ilya Tsvankin 1, Xinming Wu 3 1. Colorado School of Mines 2. Penn State University 3. University of Texas
Discrete Fourier Transform
 Last lecture I introduced the idea that any function defined on x 0,..., N 1 could be written a sum of sines and cosines. There are two different reasons why this is useful. The first is a general one,
Last lecture I introduced the idea that any function defined on x 0,..., N 1 could be written a sum of sines and cosines. There are two different reasons why this is useful. The first is a general one,
Photon-atom scattering
 Photon-atom scattering Aussois 005 Part Ohad Assaf and Aharon Gero Technion Photon-atom scattering Complex system: Spin of the photon: dephasing Internal atomic degrees of freedom (Zeeman sublevels): decoherence
Photon-atom scattering Aussois 005 Part Ohad Assaf and Aharon Gero Technion Photon-atom scattering Complex system: Spin of the photon: dephasing Internal atomic degrees of freedom (Zeeman sublevels): decoherence
The Discrete Fourier transform
 453.70 Linear Systems, S.M. Tan, The University of uckland 9- Chapter 9 The Discrete Fourier transform 9. DeÞnition When computing spectra on a computer it is not possible to carry out the integrals involved
453.70 Linear Systems, S.M. Tan, The University of uckland 9- Chapter 9 The Discrete Fourier transform 9. DeÞnition When computing spectra on a computer it is not possible to carry out the integrals involved
Prof. dr. A. Achterberg, Astronomical Dept., IMAPP, Radboud Universiteit
 Prof. dr. A. Achterberg, Astronomical Dept., IMAPP, Radboud Universiteit Central concepts: Phase velocity: velocity with which surfaces of constant phase move Group velocity: velocity with which slow
Prof. dr. A. Achterberg, Astronomical Dept., IMAPP, Radboud Universiteit Central concepts: Phase velocity: velocity with which surfaces of constant phase move Group velocity: velocity with which slow
The discrete and fast Fourier transforms
 The discrete and fast Fourier transforms Marcel Oliver Revised April 7, 1 1 Fourier series We begin by recalling the familiar definition of the Fourier series. For a periodic function u: [, π] C, we define
The discrete and fast Fourier transforms Marcel Oliver Revised April 7, 1 1 Fourier series We begin by recalling the familiar definition of the Fourier series. For a periodic function u: [, π] C, we define
Math 121A: Homework 6 solutions
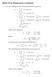 Math A: Homework 6 solutions. (a) The coefficients of the Fourier sine series are given by b n = π f (x) sin nx dx = x(π x) sin nx dx π = (π x) cos nx dx nπ nπ [x(π x) cos nx]π = n ( )(sin nx) dx + π n
Math A: Homework 6 solutions. (a) The coefficients of the Fourier sine series are given by b n = π f (x) sin nx dx = x(π x) sin nx dx π = (π x) cos nx dx nπ nπ [x(π x) cos nx]π = n ( )(sin nx) dx + π n
Green s functions for planarly layered media
 Green s functions for planarly layered media Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.635 lecture notes Introduction: Green s functions The Green s functions is the solution of the wave equation for a point
Green s functions for planarly layered media Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.635 lecture notes Introduction: Green s functions The Green s functions is the solution of the wave equation for a point
The Pseudospectral Method
 The Pseudospectral Method Heiner Igel Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences Ludwig-Maximilians-University Munich Heiner Igel Computational Seismology 1 / 34 Outline 1 Infinite Order Finite Differences
The Pseudospectral Method Heiner Igel Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences Ludwig-Maximilians-University Munich Heiner Igel Computational Seismology 1 / 34 Outline 1 Infinite Order Finite Differences
Wave equation techniques for attenuating multiple reflections
 Wave equation techniques for attenuating multiple reflections Fons ten Kroode a.tenkroode@shell.com Shell Research, Rijswijk, The Netherlands Wave equation techniques for attenuating multiple reflections
Wave equation techniques for attenuating multiple reflections Fons ten Kroode a.tenkroode@shell.com Shell Research, Rijswijk, The Netherlands Wave equation techniques for attenuating multiple reflections
SPECTRAL METHODS: ORTHOGONAL POLYNOMIALS
 SPECTRAL METHODS: ORTHOGONAL POLYNOMIALS 31 October, 2007 1 INTRODUCTION 2 ORTHOGONAL POLYNOMIALS Properties of Orthogonal Polynomials 3 GAUSS INTEGRATION Gauss- Radau Integration Gauss -Lobatto Integration
SPECTRAL METHODS: ORTHOGONAL POLYNOMIALS 31 October, 2007 1 INTRODUCTION 2 ORTHOGONAL POLYNOMIALS Properties of Orthogonal Polynomials 3 GAUSS INTEGRATION Gauss- Radau Integration Gauss -Lobatto Integration
Wave-equation tomography for anisotropic parameters
 Wave-equation tomography for anisotropic parameters Yunyue (Elita) Li and Biondo Biondi ABSTRACT Anisotropic models are recognized as more realistic representations of the subsurface where complex geological
Wave-equation tomography for anisotropic parameters Yunyue (Elita) Li and Biondo Biondi ABSTRACT Anisotropic models are recognized as more realistic representations of the subsurface where complex geological
Poincare wavelet techniques in depth migration
 Proceedings of the International Conference, pp. 104-110 978-1-4673-4419-7/12/$31.00 IEEE 2012 Poincare wavelet techniques in depth migration Evgeny A. Gorodnitskiy, Maria V. Perel Physics Faculty, St.
Proceedings of the International Conference, pp. 104-110 978-1-4673-4419-7/12/$31.00 IEEE 2012 Poincare wavelet techniques in depth migration Evgeny A. Gorodnitskiy, Maria V. Perel Physics Faculty, St.
Reverse Time Shot-Geophone Migration and
 Reverse Time Shot-Geophone Migration and velocity analysis, linearizing, inverse problems, extended models, etc. etc. William W. Symes PIMS Geophysical Inversion Workshop Calgary, Alberta July 2003 www.trip.caam.rice.edu
Reverse Time Shot-Geophone Migration and velocity analysis, linearizing, inverse problems, extended models, etc. etc. William W. Symes PIMS Geophysical Inversion Workshop Calgary, Alberta July 2003 www.trip.caam.rice.edu
MAT 372 K.T.D.D. Final Sınavın Çözümleri N. Course. Question 1 (Canonical Forms). Consider the second order partial differential equation
 OKAN ÜNİVERSİTESİ FEN EDEBİYAT FAKÜTESİ MATEMATİK BÖÜMÜ 1.5. MAT 7 K.T.D.D. Final Sınavın Çözümleri N. Course Question 1 (Canonical Forms). Consider the second order partial differential equation (sin
OKAN ÜNİVERSİTESİ FEN EDEBİYAT FAKÜTESİ MATEMATİK BÖÜMÜ 1.5. MAT 7 K.T.D.D. Final Sınavın Çözümleri N. Course Question 1 (Canonical Forms). Consider the second order partial differential equation (sin
Numerical dispersion and Linearized Saint-Venant Equations
 Numerical dispersion and Linearized Saint-Venant Equations M. Ersoy Basque Center for Applied Mathematics 11 November 2010 Outline of the talk Outline of the talk 1 Introduction 2 The Saint-Venant equations
Numerical dispersion and Linearized Saint-Venant Equations M. Ersoy Basque Center for Applied Mathematics 11 November 2010 Outline of the talk Outline of the talk 1 Introduction 2 The Saint-Venant equations
WAVE PACKETS & SUPERPOSITION
 1 WAVE PACKETS & SUPERPOSITION Reading: Main 9. PH41 Fourier notes 1 x k Non dispersive wave equation x ψ (x,t) = 1 v t ψ (x,t) So far, we know that this equation results from application of Newton s law
1 WAVE PACKETS & SUPERPOSITION Reading: Main 9. PH41 Fourier notes 1 x k Non dispersive wave equation x ψ (x,t) = 1 v t ψ (x,t) So far, we know that this equation results from application of Newton s law
Correlation Functions and Fourier Transforms
 Correlation Functions and Fourier Transforms Introduction The importance of these functions in condensed matter physics Correlation functions (aside convolution) Fourier transforms The diffraction pattern
Correlation Functions and Fourier Transforms Introduction The importance of these functions in condensed matter physics Correlation functions (aside convolution) Fourier transforms The diffraction pattern
A comparison of the imaging conditions and principles in depth migration algorithms
 International Journal of Tomography & Statistics (IJTS), Fall 2006, Vol. 4, No. F06; Int. J. Tomogr. Stat.; 5-16 ISSN 0972-9976; Copyright 2006 by IJTS, ISDER A comparison of the imaging conditions and
International Journal of Tomography & Statistics (IJTS), Fall 2006, Vol. 4, No. F06; Int. J. Tomogr. Stat.; 5-16 ISSN 0972-9976; Copyright 2006 by IJTS, ISDER A comparison of the imaging conditions and
M412 Assignment 9 Solutions
 M4 Assignment 9 Solutions. [ pts] Use separation of variables to show that solutions to the quarter-plane problem can be written in the form u t u xx ; t>,
M4 Assignment 9 Solutions. [ pts] Use separation of variables to show that solutions to the quarter-plane problem can be written in the form u t u xx ; t>,
Stepwise Multiple Elimination using Linear Transforms: An alternative approach to SRME for stacking multiple-free near offsets in the Barents Sea
 : An alternative approach to SRME for stacking multiple-free near offsets in the Barents Sea Anthony Hardwick*, Carl Lang and Bent Kjølhamar, TGS. Summary A novel, de-aliased method called Stepwise Multiple
: An alternative approach to SRME for stacking multiple-free near offsets in the Barents Sea Anthony Hardwick*, Carl Lang and Bent Kjølhamar, TGS. Summary A novel, de-aliased method called Stepwise Multiple
Concepts from linear theory Extra Lecture
 Concepts from linear theory Extra Lecture Ship waves from WW II battleships and a toy boat. Kelvin s (1887) method of stationary phase predicts both. Concepts from linear theory A. Linearize the nonlinear
Concepts from linear theory Extra Lecture Ship waves from WW II battleships and a toy boat. Kelvin s (1887) method of stationary phase predicts both. Concepts from linear theory A. Linearize the nonlinear
Linear Algebra Review (Course Notes for Math 308H - Spring 2016)
 Linear Algebra Review (Course Notes for Math 308H - Spring 2016) Dr. Michael S. Pilant February 12, 2016 1 Background: We begin with one of the most fundamental notions in R 2, distance. Letting (x 1,
Linear Algebra Review (Course Notes for Math 308H - Spring 2016) Dr. Michael S. Pilant February 12, 2016 1 Background: We begin with one of the most fundamental notions in R 2, distance. Letting (x 1,
Seismic Modeling, Migration and Velocity Inversion
 Seismic Modeling, Migration and Velocity Inversion Inverse Scattering Bee Bednar Panorama Technologies, Inc. 14811 St Marys Lane, Suite 150 Houston TX 77079 May 30, 2014 Bee Bednar (Panorama Technologies)
Seismic Modeling, Migration and Velocity Inversion Inverse Scattering Bee Bednar Panorama Technologies, Inc. 14811 St Marys Lane, Suite 150 Houston TX 77079 May 30, 2014 Bee Bednar (Panorama Technologies)
Digital Signal Processing Lecture 10 - Discrete Fourier Transform
 Digital Signal Processing - Discrete Fourier Transform Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Tennessee, Knoxville November 12, 2015 Overview 1 2 3 4 Review - 1 Introduction Discrete-time
Digital Signal Processing - Discrete Fourier Transform Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Tennessee, Knoxville November 12, 2015 Overview 1 2 3 4 Review - 1 Introduction Discrete-time
Nonlinear seismic imaging via reduced order model backprojection
 Nonlinear seismic imaging via reduced order model backprojection Alexander V. Mamonov, Vladimir Druskin 2 and Mikhail Zaslavsky 2 University of Houston, 2 Schlumberger-Doll Research Center Mamonov, Druskin,
Nonlinear seismic imaging via reduced order model backprojection Alexander V. Mamonov, Vladimir Druskin 2 and Mikhail Zaslavsky 2 University of Houston, 2 Schlumberger-Doll Research Center Mamonov, Druskin,
Matrix formulation of adjoint Kirchhoff datuming
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 80, May 15, 2001, pages 1 377 Matrix formulation of adjoint Kirchhoff datuming Dimitri Bevc 1 ABSTRACT I present the matrix formulation of Kirchhoff wave equation datuming
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 80, May 15, 2001, pages 1 377 Matrix formulation of adjoint Kirchhoff datuming Dimitri Bevc 1 ABSTRACT I present the matrix formulation of Kirchhoff wave equation datuming
4 Riesz Kernels. Since the functions k i (ξ) = ξ i. are bounded functions it is clear that R
 4 Riesz Kernels. A natural generalization of the Hilbert transform to higher dimension is mutiplication of the Fourier Transform by homogeneous functions of degree 0, the simplest ones being R i f(ξ) =
4 Riesz Kernels. A natural generalization of the Hilbert transform to higher dimension is mutiplication of the Fourier Transform by homogeneous functions of degree 0, the simplest ones being R i f(ξ) =
Fourier Syntheses, Analyses, and Transforms
 Fourier Syntheses, Analyses, and Transforms http://homepages.utoledo.edu/clind/ The electron density The electron density in a crystal can be described as a periodic function - same contents in each unit
Fourier Syntheses, Analyses, and Transforms http://homepages.utoledo.edu/clind/ The electron density The electron density in a crystal can be described as a periodic function - same contents in each unit
Complex Variables & Integral Transforms
 Complex Variables & Integral Transforms Notes taken by J.Pearson, from a S4 course at the U.Manchester. Lecture delivered by Dr.W.Parnell July 9, 007 Contents 1 Complex Variables 3 1.1 General Relations
Complex Variables & Integral Transforms Notes taken by J.Pearson, from a S4 course at the U.Manchester. Lecture delivered by Dr.W.Parnell July 9, 007 Contents 1 Complex Variables 3 1.1 General Relations
A018 Combining Bandwidth Extension Techniques and Pre-stack Q Inversion for Enhanced Imaging of Intra-basalt Plays
 A018 Combining Bandwidth Extension Techniques and Pre-stack Q Inversion for Enhanced Imaging of Intra-basalt Plays A.J. Hardwick* (TGS), J. Whittaker (University of Leeds) & N. Woodburn (TGS) SUMMARY Extensive
A018 Combining Bandwidth Extension Techniques and Pre-stack Q Inversion for Enhanced Imaging of Intra-basalt Plays A.J. Hardwick* (TGS), J. Whittaker (University of Leeds) & N. Woodburn (TGS) SUMMARY Extensive
The FOCI method of depth migration. Gary Margrave Saleh Al-Saleh Hugh Geiger Michael Lamoureux POTSI
 a The FOCI method of depth migration Gary Margrave Saleh Al-Saleh Hugh Geiger Michael Lamoureux POTSI Outline Wavefield extrapolators and stability A stabilizing Wiener filter FOCI Dual operator tables
a The FOCI method of depth migration Gary Margrave Saleh Al-Saleh Hugh Geiger Michael Lamoureux POTSI Outline Wavefield extrapolators and stability A stabilizing Wiener filter FOCI Dual operator tables
Seismic Waves and Earthquakes A Mathematical Overview
 Seismic Waves and Earthquakes A Mathematical Overview The destruction caused by earthquakes is caused by the seismic waves propagating inside and in particular, near the surface of earth. We describe the
Seismic Waves and Earthquakes A Mathematical Overview The destruction caused by earthquakes is caused by the seismic waves propagating inside and in particular, near the surface of earth. We describe the
MATH243 First Semester 2013/14. Exercises 1
 Complex Functions Dr Anna Pratoussevitch MATH43 First Semester 013/14 Exercises 1 Submit your solutions to questions marked with [HW] in the lecture on Monday 30/09/013 Questions or parts of questions
Complex Functions Dr Anna Pratoussevitch MATH43 First Semester 013/14 Exercises 1 Submit your solutions to questions marked with [HW] in the lecture on Monday 30/09/013 Questions or parts of questions
Musimathics The Mathematical Foundations of Music Volume 2. Gareth Loy. Foreword by John Chowning
 Musimathics The Mathematical Foundations of Music Volume 2 Gareth Loy Foreword by John Chowning The MIT Press Cambridge, Massachusetts London, England ..2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.0..2.3.4 2 2. 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6
Musimathics The Mathematical Foundations of Music Volume 2 Gareth Loy Foreword by John Chowning The MIT Press Cambridge, Massachusetts London, England ..2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.0..2.3.4 2 2. 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6
MATH 3150: PDE FOR ENGINEERS FINAL EXAM (VERSION D) 1. Consider the heat equation in a wire whose diffusivity varies over time: u k(t) 2 x 2
 MATH 35: PDE FOR ENGINEERS FINAL EXAM (VERSION D). Consider the heat equation in a wire whose diffusivity varies over time: u t = u k(t) x where k(t) is some positive function of time. Assume the wire
MATH 35: PDE FOR ENGINEERS FINAL EXAM (VERSION D). Consider the heat equation in a wire whose diffusivity varies over time: u t = u k(t) x where k(t) is some positive function of time. Assume the wire
Traffic flow problems. u t + [uv(u)] x = 0. u 0 x > 1
![Traffic flow problems. u t + [uv(u)] x = 0. u 0 x > 1 Traffic flow problems. u t + [uv(u)] x = 0. u 0 x > 1](/thumbs/88/115962698.jpg) The flow of cars is modelled by the PDE Traffic flow problems u t + [uvu)] x = 1. If vu) = 1 u and x < a) ux, ) = u x 2 x 1 u x > 1 b) ux, ) = u e x, where < u < 1, determine when and where a shock first
The flow of cars is modelled by the PDE Traffic flow problems u t + [uvu)] x = 1. If vu) = 1 u and x < a) ux, ) = u x 2 x 1 u x > 1 b) ux, ) = u e x, where < u < 1, determine when and where a shock first
Prestack exploding reflector modelling and migration for anisotropic media
 Geophysical Prospecting, 015, 63, 10 doi: 10.1111/1365-478.1148 Prestack exploding reflector modelling and migration for anisotropic media T. Alkhalifah Physical Sciences and Engineering, King Abdullah
Geophysical Prospecting, 015, 63, 10 doi: 10.1111/1365-478.1148 Prestack exploding reflector modelling and migration for anisotropic media T. Alkhalifah Physical Sciences and Engineering, King Abdullah
Transient, planar, nonlinear acoustical holography for reconstructing acoustic pressure and particle velocity fields a
 Denver, Colorado NOISE-CON 013 013 August 6-8 Transient, planar, nonlinear acoustical holography for reconstructing acoustic pressure and particle velocity fields a Yaying Niu * Yong-Joe Kim Noise and
Denver, Colorado NOISE-CON 013 013 August 6-8 Transient, planar, nonlinear acoustical holography for reconstructing acoustic pressure and particle velocity fields a Yaying Niu * Yong-Joe Kim Noise and
f(x)e ikx dx. (19.1) ˆf(k)e ikx dk. (19.2)
 9 Fourier transform 9 A first look at the Fourier transform In Math 66 you all studied the Laplace transform, which was used to turn an ordinary differential equation into an algebraic one There are a
9 Fourier transform 9 A first look at the Fourier transform In Math 66 you all studied the Laplace transform, which was used to turn an ordinary differential equation into an algebraic one There are a
Stolt residual migration for converted waves
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 11, September 18, 1, pages 1 6 Stolt residual migration for converted waves Daniel Rosales, Paul Sava, and Biondo Biondi 1 ABSTRACT P S velocity analysis is a new frontier
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 11, September 18, 1, pages 1 6 Stolt residual migration for converted waves Daniel Rosales, Paul Sava, and Biondo Biondi 1 ABSTRACT P S velocity analysis is a new frontier
Review of Fundamental Equations Supplementary notes on Section 1.2 and 1.3
 Review of Fundamental Equations Supplementary notes on Section. and.3 Introduction of the velocity potential: irrotational motion: ω = u = identity in the vector analysis: ϕ u = ϕ Basic conservation principles:
Review of Fundamental Equations Supplementary notes on Section. and.3 Introduction of the velocity potential: irrotational motion: ω = u = identity in the vector analysis: ϕ u = ϕ Basic conservation principles:
Mathematical Methods and its Applications (Solution of assignment-12) Solution 1 From the definition of Fourier transforms, we have.
 For 2 weeks course only Mathematical Methods and its Applications (Solution of assignment-2 Solution From the definition of Fourier transforms, we have F e at2 e at2 e it dt e at2 +(it/a dt ( setting (
For 2 weeks course only Mathematical Methods and its Applications (Solution of assignment-2 Solution From the definition of Fourier transforms, we have F e at2 e at2 e it dt e at2 +(it/a dt ( setting (
2 GOVERNING EQUATIONS
 2 GOVERNING EQUATIONS 9 2 GOVERNING EQUATIONS For completeness we will take a brief moment to review the governing equations for a turbulent uid. We will present them both in physical space coordinates
2 GOVERNING EQUATIONS 9 2 GOVERNING EQUATIONS For completeness we will take a brief moment to review the governing equations for a turbulent uid. We will present them both in physical space coordinates
Fourier Series and Integrals
 Fourier Series and Integrals Fourier Series et f(x) beapiece-wiselinearfunctionon[, ] (Thismeansthatf(x) maypossessa finite number of finite discontinuities on the interval). Then f(x) canbeexpandedina
Fourier Series and Integrals Fourier Series et f(x) beapiece-wiselinearfunctionon[, ] (Thismeansthatf(x) maypossessa finite number of finite discontinuities on the interval). Then f(x) canbeexpandedina
Seismic Imaging. William W. Symes. C. I. M. E. Martina Franca September
 Seismic Imaging William W. Symes C. I. M. E. Martina Franca September 2002 www.trip.caam.rice.edu 1 0 offset (km) -4-3 -2-1 1 2 time (s) 3 4 5 How do you turn lots of this... (field seismogram from the
Seismic Imaging William W. Symes C. I. M. E. Martina Franca September 2002 www.trip.caam.rice.edu 1 0 offset (km) -4-3 -2-1 1 2 time (s) 3 4 5 How do you turn lots of this... (field seismogram from the
Polarimetry of homogeneous half-spaces 1
 Polarimetry of homogeneous half-spaces 1 M. Gilman, E. Smith, S. Tsynkov special thanks to: H. Hong Department of Mathematics North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC Workshop on Symbolic-Numeric Methods
Polarimetry of homogeneous half-spaces 1 M. Gilman, E. Smith, S. Tsynkov special thanks to: H. Hong Department of Mathematics North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC Workshop on Symbolic-Numeric Methods
EXAFS data analysis. Extraction of EXAFS signal
 EXAFS data analysis Extraction of EXAFS signal 1 Experimental EXAFS spectrum Φ x Φ µ (ω) source monochromator sample detectors 1 6 1 5 32 - Ge 1 4 1 3 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 Photon energy hω (kev) 1-1 Ge, 1 K µ
EXAFS data analysis Extraction of EXAFS signal 1 Experimental EXAFS spectrum Φ x Φ µ (ω) source monochromator sample detectors 1 6 1 5 32 - Ge 1 4 1 3 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 Photon energy hω (kev) 1-1 Ge, 1 K µ
Gabor Deconvolution. Gary Margrave and Michael Lamoureux
 Gabor Deconvolution Gary Margrave and Michael Lamoureux = Outline The Gabor idea The continuous Gabor transform The discrete Gabor transform A nonstationary trace model Gabor deconvolution Examples = Gabor
Gabor Deconvolution Gary Margrave and Michael Lamoureux = Outline The Gabor idea The continuous Gabor transform The discrete Gabor transform A nonstationary trace model Gabor deconvolution Examples = Gabor
Rapidity evolution of Wilson lines
 Rapidity evolution of Wilson lines I. Balitsky JLAB & ODU QCD evolution 014 13 May 014 QCD evolution 014 13 May 014 1 / Outline 1 High-energy scattering and Wilson lines High-energy scattering and Wilson
Rapidity evolution of Wilson lines I. Balitsky JLAB & ODU QCD evolution 014 13 May 014 QCD evolution 014 13 May 014 1 / Outline 1 High-energy scattering and Wilson lines High-energy scattering and Wilson
Lecture 3 January 23
 EE 123: Digital Signal Processing Spring 2007 Lecture 3 January 23 Lecturer: Prof. Anant Sahai Scribe: Dominic Antonelli 3.1 Outline These notes cover the following topics: Eigenvectors and Eigenvalues
EE 123: Digital Signal Processing Spring 2007 Lecture 3 January 23 Lecturer: Prof. Anant Sahai Scribe: Dominic Antonelli 3.1 Outline These notes cover the following topics: Eigenvectors and Eigenvalues
MATH 2250 Final Exam Solutions
 MATH 225 Final Exam Solutions Tuesday, April 29, 28, 6: 8:PM Write your name and ID number at the top of this page. Show all your work. You may refer to one double-sided sheet of notes during the exam
MATH 225 Final Exam Solutions Tuesday, April 29, 28, 6: 8:PM Write your name and ID number at the top of this page. Show all your work. You may refer to one double-sided sheet of notes during the exam
Reversible Stolt migration
 Reversible Stolt migration William A. Burnett Robert J. Ferguson ABSTRACT The nonstationary equivalent of the Fourier shift results in a general one-dimensional integral transform that applies to many
Reversible Stolt migration William A. Burnett Robert J. Ferguson ABSTRACT The nonstationary equivalent of the Fourier shift results in a general one-dimensional integral transform that applies to many
Time domain passive seismic processing at Valhall
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 125, January 16, 2007, pages 1?? Time domain passive seismic processing at Valhall Brad Artman ABSTRACT Passive recordings from an array of 2500 four component receiver
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 125, January 16, 2007, pages 1?? Time domain passive seismic processing at Valhall Brad Artman ABSTRACT Passive recordings from an array of 2500 four component receiver
Edinburgh Research Explorer
 Edinburgh Research Explorer Nonlinear Scattering-based Imaging in Elastic Media Citation for published version: Ravasi, M & Curtis, A 213, 'Nonlinear Scattering-based Imaging in Elastic Media' Paper presented
Edinburgh Research Explorer Nonlinear Scattering-based Imaging in Elastic Media Citation for published version: Ravasi, M & Curtis, A 213, 'Nonlinear Scattering-based Imaging in Elastic Media' Paper presented
XGAUPROF. A GIPSY program to fit parameters of a Gauss function, the Gauss-Hermite series or a Voigt line-shape to data from GIPSY sets or ASCII files
 XGAUPROF A GIPSY program to fit parameters of a Gauss function, the Gauss-Hermite series or a Voigt line-shape to data from GIPSY sets or ASCII files M.G.R. Vogelaar May 7, 1999, revision Mar 25, 2012
XGAUPROF A GIPSY program to fit parameters of a Gauss function, the Gauss-Hermite series or a Voigt line-shape to data from GIPSY sets or ASCII files M.G.R. Vogelaar May 7, 1999, revision Mar 25, 2012
Edge Detection. Computer Vision P. Schrater Spring 2003
 Edge Detection Computer Vision P. Schrater Spring 2003 Simplest Model: (Canny) Edge(x) = a U(x) + n(x) U(x)? x=0 Convolve image with U and find points with high magnitude. Choose value by comparing with
Edge Detection Computer Vision P. Schrater Spring 2003 Simplest Model: (Canny) Edge(x) = a U(x) + n(x) U(x)? x=0 Convolve image with U and find points with high magnitude. Choose value by comparing with
A Petroleum Geologist's Guide to Seismic Reflection
 A Petroleum Geologist's Guide to Seismic Reflection William Ashcroft WILEY-BLACKWELL A John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., Publication Contents Preface Acknowledgements xi xiii Part I Basic topics and 2D interpretation
A Petroleum Geologist's Guide to Seismic Reflection William Ashcroft WILEY-BLACKWELL A John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., Publication Contents Preface Acknowledgements xi xiii Part I Basic topics and 2D interpretation
Radiative transfer theory (Pure gas atmosphere)
 Radiative transfer theory (Pure gas atmosphere Bruno Carli Radiative transfer equation The radiative transfer equation states that the specific intensity of radiation I( (defined as the energy flux per
Radiative transfer theory (Pure gas atmosphere Bruno Carli Radiative transfer equation The radiative transfer equation states that the specific intensity of radiation I( (defined as the energy flux per
Research Project Report
 Research Project Report Title: Prediction of pre-critical seismograms from post-critical traces Principal Investigator: Co-principal Investigators: Mrinal Sen Arthur Weglein and Paul Stoffa Final report
Research Project Report Title: Prediction of pre-critical seismograms from post-critical traces Principal Investigator: Co-principal Investigators: Mrinal Sen Arthur Weglein and Paul Stoffa Final report
! Circular Convolution. " Linear convolution with circular convolution. ! Discrete Fourier Transform. " Linear convolution through circular
 Previously ESE 531: Digital Signal Processing Lec 22: April 18, 2017 Fast Fourier Transform (con t)! Circular Convolution " Linear convolution with circular convolution! Discrete Fourier Transform " Linear
Previously ESE 531: Digital Signal Processing Lec 22: April 18, 2017 Fast Fourier Transform (con t)! Circular Convolution " Linear convolution with circular convolution! Discrete Fourier Transform " Linear
Physics III: Final Solutions (Individual and Group)
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology MITES 7 Physics III First and Last Name: Physics III: Final Solutions (Individual and Group Instructor: Mobolaji Williams Teaching Assistant: Rene García (Tuesday
Massachusetts Institute of Technology MITES 7 Physics III First and Last Name: Physics III: Final Solutions (Individual and Group Instructor: Mobolaji Williams Teaching Assistant: Rene García (Tuesday
Complex-beam Migration and Land Depth Tianfei Zhu CGGVeritas, Calgary, Alberta, Canada
 Page 1 of 10 Home Articles Interviews Print Editions Complex-beam Migration and Land Depth Tianfei Zhu CGGVeritas, Calgary, Alberta, Canada DECEMBER 2012 FOCUS ARTICLE Summary Gaussian-beam depth migration
Page 1 of 10 Home Articles Interviews Print Editions Complex-beam Migration and Land Depth Tianfei Zhu CGGVeritas, Calgary, Alberta, Canada DECEMBER 2012 FOCUS ARTICLE Summary Gaussian-beam depth migration
OPAC102. The Acoustic Wave Equation
 OPAC102 The Acoustic Wave Equation Acoustic waves in fluid Acoustic waves constitute one kind of pressure fluctuation that can exist in a compressible fluid. The restoring forces responsible for propagating
OPAC102 The Acoustic Wave Equation Acoustic waves in fluid Acoustic waves constitute one kind of pressure fluctuation that can exist in a compressible fluid. The restoring forces responsible for propagating
Quasi-PDFs and Pseudo-PDFs
 s and s A.V. Radyushkin Physics Department, Old Dominion University & Theory Center, Jefferson Lab 2017 May 23, 2017 Densities and Experimentally, one works with hadrons Theoretically, we work with quarks
s and s A.V. Radyushkin Physics Department, Old Dominion University & Theory Center, Jefferson Lab 2017 May 23, 2017 Densities and Experimentally, one works with hadrons Theoretically, we work with quarks
Lecture 7. 1 Wavepackets and Uncertainty 1. 2 Wavepacket Shape Changes 4. 3 Time evolution of a free wave packet 6. 1 Φ(k)e ikx dk. (1.
 Lecture 7 B. Zwiebach February 8, 06 Contents Wavepackets and Uncertainty Wavepacket Shape Changes 4 3 Time evolution of a free wave packet 6 Wavepackets and Uncertainty A wavepacket is a superposition
Lecture 7 B. Zwiebach February 8, 06 Contents Wavepackets and Uncertainty Wavepacket Shape Changes 4 3 Time evolution of a free wave packet 6 Wavepackets and Uncertainty A wavepacket is a superposition
Cambridge International Examinations CambridgeOrdinaryLevel
 Cambridge International Examinations CambridgeOrdinaryLevel * 2 5 4 0 0 0 9 5 8 5 * ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS 4037/12 Paper1 May/June 2015 2 hours CandidatesanswerontheQuestionPaper. NoAdditionalMaterialsarerequired.
Cambridge International Examinations CambridgeOrdinaryLevel * 2 5 4 0 0 0 9 5 8 5 * ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS 4037/12 Paper1 May/June 2015 2 hours CandidatesanswerontheQuestionPaper. NoAdditionalMaterialsarerequired.
Ratios of harmonic functions
 Ratios of harmonic functions Eugenia Malinnikova NTNU (Trondheim, Norway) joint work with A. Logunov (St.Petersburg/Tel Aviv) Harmonic Analysis, Complex Analysis, Spectral Theory and all that Bedlewo,
Ratios of harmonic functions Eugenia Malinnikova NTNU (Trondheim, Norway) joint work with A. Logunov (St.Petersburg/Tel Aviv) Harmonic Analysis, Complex Analysis, Spectral Theory and all that Bedlewo,
X. Chen More on Sampling
 X. Chen More on Sampling 9 More on Sampling 9.1 Notations denotes the sampling time in second. Ω s = 2π/ and Ω s /2 are, respectively, the sampling frequency and Nyquist frequency in rad/sec. Ω and ω denote,
X. Chen More on Sampling 9 More on Sampling 9.1 Notations denotes the sampling time in second. Ω s = 2π/ and Ω s /2 are, respectively, the sampling frequency and Nyquist frequency in rad/sec. Ω and ω denote,
Th P7 02 A Method to Suppress Salt-related Converted Wave Using 3D Acoustic Modelling
 Th P7 0 A Method to Suppress Salt-related Converted Wave Using 3D Acoustic Modelling J. Kumar* (Petroleum Geo-Services), M. Salem (ENI E&P), D.E. Cegani (ENI E&P) Summary Converted waves can be recorded
Th P7 0 A Method to Suppress Salt-related Converted Wave Using 3D Acoustic Modelling J. Kumar* (Petroleum Geo-Services), M. Salem (ENI E&P), D.E. Cegani (ENI E&P) Summary Converted waves can be recorded
Well-posedness of boundary-value problems for the linear Benjamin-Bona-Mahony equation
 Well-posedness of boundary-value problems for the linear Benjamin-Bona-Mahony equation Vishal Vasan and Bernard Deconinck Department of Applied Mathematics University of Washington Seattle WA 98195 July
Well-posedness of boundary-value problems for the linear Benjamin-Bona-Mahony equation Vishal Vasan and Bernard Deconinck Department of Applied Mathematics University of Washington Seattle WA 98195 July
Devoir 1. Valerio Proietti. November 5, 2014 EXERCISE 1. z f = g. supp g EXERCISE 2
 GÉOMÉTRIE ANALITIQUE COMPLEXE UNIVERSITÉ PARIS-SUD Devoir Valerio Proietti November 5, 04 EXERCISE Thanks to Corollary 3.4 of [, p. ] we know that /πz is a fundamental solution of the operator z on C.
GÉOMÉTRIE ANALITIQUE COMPLEXE UNIVERSITÉ PARIS-SUD Devoir Valerio Proietti November 5, 04 EXERCISE Thanks to Corollary 3.4 of [, p. ] we know that /πz is a fundamental solution of the operator z on C.
Image-space wave-equation tomography in the generalized source domain
 Image-space wave-equation tomography in the generalized source domain Yaxun Tang, Claudio Guerra, and Biondo Biondi ABSTRACT We extend the theory of image-space wave-equation tomography to the generalized
Image-space wave-equation tomography in the generalized source domain Yaxun Tang, Claudio Guerra, and Biondo Biondi ABSTRACT We extend the theory of image-space wave-equation tomography to the generalized
Lecture: Wave-induced Momentum Fluxes: Radiation Stresses
 Chapter 4 Lecture: Wave-induced Momentum Fluxes: Radiation Stresses Here we derive the wave-induced depth-integrated momentum fluxes, otherwise known as the radiation stress tensor S. These are the 2nd-order
Chapter 4 Lecture: Wave-induced Momentum Fluxes: Radiation Stresses Here we derive the wave-induced depth-integrated momentum fluxes, otherwise known as the radiation stress tensor S. These are the 2nd-order
3. Wave equation migration. (i) Reverse time. (ii) Reverse depth
 3. Wave equation migration (i) Reverse time (ii) Reverse depth 1 Reverse time computation of adjoint F [v] : Start with the zero-offset case - easier, but only if you replace it with the exploding reflector
3. Wave equation migration (i) Reverse time (ii) Reverse depth 1 Reverse time computation of adjoint F [v] : Start with the zero-offset case - easier, but only if you replace it with the exploding reflector
