Exercise. Exercise 1.1. MA112 Section : Prepared by Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana 1
|
|
|
- Jared Fox
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MA112 Section : Prepared by Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana 1 Exercise Exercise Find the vertex, focus, and directrix of the parabola and sketch its graph. 1. x = 2y y +x 2 = x 2 = y 4. y 2 = 12x 5. (x+2) 2 = 8(y 3) 6. x 1 = (y +5) 2 7. y 2 +2y +12x+25 = 0 8. y +12x 2x 2 = Find an equation of the parabola. Then find the focus and directrix. 9. y 10. y 2 1 x 1 2 x Find an equation for the parabola that satisfies the given conditions. 11. Vertex (0,0), focus (0, 2) 12. Vertex (0, 0), directrix x = Focus ( 4, 0), directrix x = Focus (3,6), vertex (3,2) 15. Vertex (0,0), axis y = 0, passing through (1, 4) 16. Vertical axis y = 0, passing through ( 2,3), (0,3), and (1,9)
2 MA112 Section : Prepared by Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana Find the vertices and foci of the ellipse and sketch its graph. x y2 5 = x y2 100 = x 2 +y 2 = x 2 +25y 2 = x 2 18x+4y 2 = x 2 +2y 2 6x+4y Find an equation of the ellipse. Then find its foci. 23. y 24. y x 1 2 x Find an equation for the ellipse that satisfies the given conditions. 25. Foci (±2,0), vertices (±5,0) 26. Foci (0,±5), vertices (0,±13) 27. Foci (0,2),(0,6), vertices (0,0),(0,8) 28. Foci (0, 1),(8, 1), vertex (9, 1) 29. Center (2,2), focus (0,2), vertex (5,2) 30. Foci (±2,0), passing through (2,1) 31. Ends of major axis (0,±6), pass through ( 3,2) 32. Foci ( 1,1) and (2, 3), minor axis of length 4
3 MA112 Section : Prepared by Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana Find the vertices, foci, and asymptotes of the hyperbola and sketch its graph. 33. x y2 25 = y 2 16 x2 36 = y 2 x 2 = x 2 4y 2 = y 2 3x 2 4y +12x+8 = x 2 9y 2 +64x 90y = Find an equation for a hyperbola that satisfies the given conditions. 39. Foci (0,±3), vertices (0,±1) 40. Foci (±6,0), vertices (±4,0) 41. Foci (1, 3) and (7, 3), vertices (2, 3) and (7, 3) 42. Foci (2, 2) and (2, 8), vertex (2, 0) and (2, 6) 43. Vertices (±3, 0), asymptotes y = ±2x 44. Foci (2,2) and (6,2), asymptotes y = x 2 and y = 6 x 45. Vertices (0,6) and (6,6), foci 10 units apart 46. Asymptotes y = x 2 and y = x+4, pass through the origin Identify the type of conic section whose equation is given and find the vertices and foci. 47. x 2 = y x 2 = y x 2 = 4y 2y y 2 8y = 6x y 2 +2y = 4x x 2 +4x+y 2 = 0
4 MA112 Section : Prepared by Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana 4 Exercise Let an x y -coordinate system be obtained by rotating an xy-coordinate system through an angle of θ = 60. (a) Find the x y -coordinates of the point whose xy-coordinates are ( 2,6). (b) Find an equation of the curve 3xy +y 2 = 6 in x y -coordinates (c) Sketch the curve in part (b), showing both xy-axes and x y -axes. 2 6 Rotate the coordinate axes to remove the xy-term. Then identify the type of conic and sketch its graph. 2. xy = 9 3. x 2 +4xy 2y 2 6 = 0 4. x xy +3y x 2y = x 2 24xy +16y 2 80x 60y +100 = x 2 72xy +73y 2 +40x+30y 75 = 0 7. Let an x y -coordinate system be obtained by rotating an xy-coordinate system through an angle of θ = 45. Find an equation of the curve 3x 2 +y 2 = 6 in xy-coordinates. 8 9 Show that the graph of the given equation is a parabola. Find its vertex, focus, and directrix. 8. x 2 +2xy +y x 4 2y = x 2 24xy +16y 2 80x 60y +100 = Show that the graph of the given equation is an ellipse. Find its foci, vertices, and the ends of its minor axis x 2 168xy +337y = x xy +21y 2 32x+32 3y 80 = Show that the graph of the given equation is a hyperbola. Find its foci, vertices, and asymptotes. 12. x xy +11y = y 2 52xy 7x x 144 5y +900 = 0
5 MA112 Section : Prepared by Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana 5 Exercise Find the slope of the tangent line to the parametric curve x = t/2, y = t at t = 1 and at t = 1 without eliminating the parameter. 2. Find the slope of the tangent line to the parametric curve x = 3cost, y = 4sint at t = π/4 and at t = 7π/4 without eliminating the parameter. 3 8 Find dy/dx and d 2 y/dx 2 at the given point without eliminating the parameter. 3. x = t, y = 2t+4; t = 1 4. x = 1 2 t2 +1, y = 1 3 t3 t; t = 2 5. x = sect, y = tant; t = π/3 6. x = sinht, y = cosht; t = 0 7. x = θ+cosθ, y = 1+sinθ; θ = π/6 8. x = cosφ, y = 3sinφ; φ = 5π/6 9. (a) Find the equation of the tangent line to the curve x = e t, y = e t at t = 1 without eliminating the parameter. (b) Find the equation of the tangent line in part (a) by eliminating the parameter. 10. (a) Find the equation of the tangent line to the curve x = 2t+4, y = 8t 2 2t+4 at t = 1 without eliminating the parameter. (b) Find the equation of the tangent line in part (a) by eliminating the parameter Find all values of t at which the parametric curve has (a) a horizontal tangent line and (b) a vertical tangent line. 11. x = 2sint, y = 4cost (0 t 2π) 12. x = 2t 3 15t 2 +24t+7, y = t 2 +t+1
6 MA112 Section : Prepared by Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana 6 Exercise Plot the points in polar coordinates. 1. (a) (3,π/4) (b) (5,2π/3) (c) (1,π/2) (d) (4,7π/6) (e) ( 6, π) (f) ( 1,9π/4) 2. (a) (2, π/3) (b) (3/2, 7π/4) (c) ( 3,3π/2) (d) ( 5, π/6) (e) (2,4π/3) (f) (0,π) 3 4 Find the rectangular coordinates of the points whose polar coordinates are given. 3. (a) (6,π/6) (b) (7,2π/3) (c) ( 6, 5π/6) (d) (0, π) (e) (7,17π/6) (f) ( 5,0) 4. (a) ( 2,π/4) (b) (6, π/4) (c) (4,9π/4) (d) (3,0) (e) ( 4, 3π/2) (f) (0,3π) 5. In each part, a point is given in rectangular coordinates. Find two pairs of polar coordinates for the point, one pair satisfying r 0 and 0 θ < 2π, and the second pair satisfying r 0 and 2π < θ 0. (a) ( 5,0) (b) (2 3, 2) (c) (0, 2) (d) ( 8, 8) (e) ( 3,3 3) (f) (1,1) 6. In each part, find polar coordinates satisfying the stated conditions for the point whose rectangular coordinates are ( 3,1). (a) r 0 and 0 θ < 2π (b) r 0 and 0 θ < 2π (c) r 0 and 2π < θ 0 (d) r 0 and π < θ π 7 8 Identify the curve by transforming the given polar equation to rectangular coordinates. 7. (a) r = 2 (b) rsinθ = 4 (c) r = 3cosθ 6 (d) r = 3cosθ +2sinθ 8. (a) r = 5secθ (b) r = 2sinθ (c) r = 4cosθ +4sinθ (d) r = secθtanθ
7 MA112 Section : Prepared by Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana Express the given equations in polar coordinates. 9. (a) x = 3 (b) x 2 +y 2 = 7 (c) x 2 +y 2 +6y = 0 (d) 9xy = (a) y = 3 (b) x 2 +y 2 = 5 (c) x 2 +y 2 +4x = 0 (d) x 2 (x 2 +y 2 ) = y Use the method of Example2.13 to sketch the curve in polar coordinates. 11. r = 2(1+sinθ) 12. r = 1 cosθ Sketch the curve in polar coordinates. 13. θ = π θ = 3π r = r = 4cosθ 17. r = 6sinθ 18. r = 1+sinθ 19. 2r = cosθ 20. r 2 = 2cosθ 21. r = 3(1+sinθ) 22. r = 5 5sinθ 23. r = 4 4cosθ 24. r = 1+2sinθ 25. r = 1 cosθ 26. r = 4+3cosθ 27. r = 2+cosθ 28. r = 3 sinθ 29. r = 3+4cosθ 30. r 5 = 3sinθ 31. r = 5 2cosθ 32. r = 3 4sinθ 33. r 2 = cos2θ 34. r 2 = 9sin2θ 35. r 2 = 16sin2θ 36. r = 4θ (θ 0) 37. r = 4θ (θ 0) 38. r = 4θ 39. r = 2cos2θ 40. r = 3sin2θ 41. r = 9sin4θ 42. r = 2cos3θ 43. Find the highest point on the cardioid r = 1+cosθ. 44. Find the leftmost point on the upper half of the cardioid r = 1+cosθ. Exercise Find the slope of the tangent line to the polar curve for the given value of θ.
8 MA112 Section : Prepared by Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana 8 1. r = 2sinθ; θ = π/6 2. r = 1+cosθ; θ = π/2 3. r = 1/θ; θ = 2 4. r = asec2θ; θ = π/6 5. r = sin3θ; θ = π/4 6. r = 4 3sinθ; θ = π 6 7 Find polar coordinates of all points at which the polar curve has a horizontal or a vertical tangent line. 6. r = a(1+cosθ) 7. r = asinθ 8 13 Use Formula (2.8) to calculate the arc length of the polar curve. 8. The entire circle r = a 9. The entire circle r = 2acosθ 10. The entire cardioid r = a(1 cos θ) 11. r = sin 2 (θ/2) from θ = 0 to θ = π 12. r = e 3θ from θ = 0 to θ = r = sin 3 (θ/3) from θ = 0 to θ = π/2 14. In each part, find the area of the circle by integration. (a) r = 2asinθ (b) r = 2acosθ Find the area of the region described. 15. The region that is enclosed by the cardioid r = 2+2sinθ. 16. The region in the first quadrant within the cardioid r = 1+cosθ. 17. The region enclosed by the rose r = 4cos3θ. 18. The region enclosed by the rose r = 2sin2θ. 19. The region inside the circle r = 3 sin θ and outside the cardioid r = 1 + sin θ. 20. The region outside the cardioid r = 2 2 cos θ and inside the circle r = The region inside the cardioid r = cos θ and outside the circle r = The region inside the rose r = 2acos2θ and outside the circle r = a 2.
9 MA112 Section : Prepared by Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana 9 Exercise A cube of side 4 has its geometric center at the origin and its faces parallel to the coordinate planes. Sketch the cube and give the coordinates of the corners. 2. Suppose that a box has its faces parallel to the coordinate planes and the points (4,2, 2) and ( 6,1,1) are endpoints of a diagonal. Sketch the box and give the coordinates of the remaining six corners. 3. Interpret the graph of x = 1 in the contexts of (a) a number line (b) 2-space (c) 3-space 4. Find the center and radius of the sphere that has (1, 2,4) and (3,4, 12) as endpoints of a diameter. 5. Show that (4,5,2), (1,7,3), and (2,4,5) are vertices of an equilateral triangle. 6. (a) Show that (2,1,6), (4,7,9), and (8,5, 6) are the vertices of a right triangle. (b) Which vertex is at the 90 angle? (c) Find the area of the triangle. 7. Find equations of two spheres that are centered at the origin and are tangent to the sphere of radius 1 centered at (3, 2,4) Describe the surface whose equation is given. 8. x 2 +y 2 +z 2 +10x+4y +2z 19 = 0 9. x 2 +y 2 +z 2 y = x 2 +2y 2 +2z 2 2x 3y +5z 2 = x 2 +y 2 +z 2 +2x 2y +2z +3 = x 2 +y 2 +z 2 3x+4y 8z +25 = x 2 +y 2 +z 2 2x 6y 8z +1 = In each part, sketch the portion of the surface that lies in the first octant. (a) y = x (b) y = z (c) x = z
10 MA112 Section : Prepared by Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana In each part, sketch the graph of the equation in 3-space. (a) x = 1 (b) y = 1 (c) z = In each part, sketch the graph of the equation in 3-space. (a) x 2 +y 2 = 25 (b) y 2 +z 2 = 25 (c) x 2 +z 2 = In each part, sketch the graph of the equation in 3-space. (a) x = y 2 (b) z = x 2 (c) y = z Sketch the surface in 3-space. 18. y = sinx 19. y = e x 20. z = 1 y z = cosx 22. 2x+z = x+3y = x 2 +9z 2 = z = 3 x 26. y 2 4z 2 = yz = If a bug walks on the sphere x 2 +y 2 +z 2 +2x 2y 4z 3 = 0 how close and how far can it get from the origin? 29. Describe the set of all points in 3-space whose coordinates satisfy the inequality x 2 +y 2 +z 2 2x+8z Describe the set of all points in 3-space whose coordinates satisfy the inequality y 2 +z 2 +6y 4z > The distance between a point P(x,y,z) and the point A(1, 2,0) is twice the distance between P and the point B(0,1,1). Show that the set of all such points is a sphere, and find the center and radius of the sphere.
11 MA112 Section : Prepared by Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana 11 Exercise Sketch the vectors with their initial points at the origin. 1. (a) 2,5 (b) 5, 4 (c) 2,0 (d) 5i + 3j (e) 3i 2j (f) 6j 2. (a) 3,7 (b) 6, 2 (c) 0, 8 (d) 4i + 2j (e) 2i j (f) 4i 3. (a) 1, 2,2 (b) 2,2, 1 (c) i+2j+3k (d) 2i+3j k 4. (a) 1,3,2 (b) 3,4,2 (c) 2j k (d) i j+2k 5 6 Find the components of the vector P 1 P (a) P 1 (3,5), P 2 (2,8) (b) P 1 (7, 2), P 2 (0,0) (c) P 1 (5, 2,1), P 2 (2,4,2) 6. (a) P 1 ( 6, 2), P 2 ( 4, 1) (b) P 1 (0,0,0), P 2 ( 1,6,1) (c) P 1 (4,1, 3), P 2 (9,1, 3) 7. (a) Find the terminal point of v = 3i 2j if the initial point is (1, 2). (b) Find the terminal point of v = 3,1,2 if the initial point is (5,0, 1). 8. (a) Find the terminal point of v = 7,6 if the initial point is (2, 1). (b) Find the terminal point of v = i+2j 3k if the initial point is ( 2,1,4) Perform the stated operations on the vectors u, v, and w. 9. u = 3i k, v = i j+2k, w = 3j (a) w v (b) 6u+4w (c) v 2w (d) 4(3u+v) (e) 8(v+w)+2u (f) 3w (v w)
12 MA112 Section : Prepared by Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana u = 2, 1,3, v = 4,0, 2, w = 1,1,3 (a) u w (b) 7v+3w (c) w+v (d) 3(u 7v) (e) 3v 8w (f) 2v (u+w) Find the norm of v. 11. (a) v = 1, 1 (b) v = i+7j (c) v = 1,2,4 (d) v = 3i+2j+k 12. (a) v = 3,4 (b) v = 2i 7j (c) v = 0, 3,0 (d) v = i+j+k 13. Let u = i 3j+2k, v = i+j, and w = 2i+2j 4k. Find (a) u+v (b) u + v (c) 2u +2 v 1 (d) 3u 5v+w (e) w w (f) 1 w w Find the unit vectors that satisfy the stated conditions. 14. (a) Same direction as i + 4j. (b) Oppositely directed to 6i 4j+2k. (c) Same direction as the vector from the point A( 1,0,2) to the point B(3,1,1). 15. (a) Oppositely directed to 3i 4j. (b) Same direction as 2i j 2k. (c) Same direction as the vector from the point A( 3,2) to the point B(1, 1) Find the vectors that satisfy the stated conditions. 16. (a) Oppositely directed to v = 3, 4 and half the length of v. (b) Length 17 and same direction as v = 7,0, (a) Same direction as v = 2i+3j and three times the length of v. (b) Length 2 and oppositely directed to v = 3i + 4j + k. 18. In each part, find the component form of the vector v in 2-space that has the stated length and makes the stated angle θ with the positive x-axis. (a) v = 3; θ = π/4 (b) v = 2; θ = 90 (c) v = 5; θ = 120 (d) v = 1; θ = π
13 MA112 Section : Prepared by Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana Find the component form of v + w and v w in 2-space, given that v = 1, w = 1, v makes an angle of π/6 with the positive x-axis, and w makes an angle of 3π/4 with the positive x-axis. 20. Let u = 1,3, v = 2,1, and w = 4, 1. Find the vector x that satisfies 2u v+x = 7x+w. 21. Let u = 1,1, v = 0,1, and w = 3,4. Find the vector x that satisfies u 2x = x w+3v. 22. Find u and v if u+2v = 3i k and 3u v = i+j+k. 23. Find u and v if u+v = 2, 3 and 3u+2v = 1, In each part, find two unit vectors in 2-space that satisfy the stated condition. (a) Parallel to the line y = 3x + 2 (b) Parallel to the line x+y = 4 (c) Perpendicular to the line y = 5x + 1 Exercise In each part, find the dot product of the vectors and the cosine of the angle between them. (a) u = i+2j, v = 6i 8j (b) u = 7, 3, v = 0,1 (c) u = i 3j+7k, v = 8i 2j 2k (d) u = 3,1,2, v = 4,2, 5 2. In each part use the given information to find u v. (a) u = 1, v = 2, the angle between u and v is π/6. (b) u = 2, v = 3, the angle between u and v is In each part, determine whether u and v make an acute angle, an obtuse angle, or are orthogonal. (a) u = 7i+3j+5k, v = 8i+4j+2k
14 MA112 Section : Prepared by Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana 14 (b) u = 6i+j+3k, v = 4i 6k (c) u = 1,1,1, v = 1,0,0 (d) u = 4,1,6, v = 3,0,2 4. Does the triangle in 3-space with vertices ( 1,2,3), (2, 2,0), and (3,1, 4) have an obtuse angle? Justify your answer. 5. The accompanying figure shows eight vectors that are equally spaced around a circle of radius 1. Find the dot product of v 0 with each of the other seven vectors. v 2 v 3 v 1 v 4 v 0 v 5 v 6 v 7 6. The accompanying figure shows six vectors that are equally spaced around a circle of radius 5. Find the dot product of v 0 with each of the other five vectors. v 2 v 1 v 3 v 0 v 4 v 5 7. (a) Use vectors to show that A(2, 1,1), B(3,2, 1), and C(7,0, 2) are vertices of the right triangle. At which vertex is the right angle? (b) Use vectors to find the interior angles of the triangle with vertices ( 1,0), (2, 1), and (1,4). 8. (a) Show that if v = ai+bj is a vector in 2-space, then the vectors v 1 = bi+aj and v 2 = bi aj are both orthogonal to v. (b) Use the result in part (a) to find two unit vectors that are orthogonal to the vector v = 3i 2j. Sketch the vectors v, v 1, and v 2.
15 MA112 Section : Prepared by Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana Explain why each of the following expressions makes no sense. (a) u (v w) (c) u v (b) (u v)+w (d) k (u+v) 10. True or false? If u v = u w and if u 0, then v = w. Justify your conclusion. 11. Verify part (b) and (c) of Theorem12.7 for the vectors u = 6i j+2k, v = 2i+7j+4k, w = i+j 3k and k = Let u = 1,2, v = 4, 2, and w = 6,0. Find (a) u (7v+w) (c) u (v w) (b) (u w)w (d) ( u v) w 13. Find r so that the vector from the point A(1, 1, 3) to the point B(3, 0, 5) is orthogonal to the vector from A to the point P(r,r,r). 14. Find two unit vectors in 2-space that make an angle of 45 with 4i+3j Find the direction cosines of v. 15. (a) v = i+j k (b) v = 2i 2j+k 16. (a) v = 3i 2j 6k (b) v = 3i 4k 17. In each part, find the vector component of v along b and the vector component of v orthogonal to b. (a) v = 2i j, b = 3i+4j (b) v = 4,5, b = 1, 2 (c) v = 3i 2j, v = 2i+j 18. In each part, find the vector component of v along b and the vector component of v orthogonal to b. (a) v = 2i j+3k, b = i+2j+2k (b) v = 4, 1,7, b = 2,3, 6 (c) v = 3i 2j, v = 2i+j Express the vector v as the sum of a vector parallel to b and a vector orthogonal to b.
16 MA112 Section : Prepared by Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana (a) v = 2i 4j, b = i+j (b) v = 3i+j 2k, b = 2i k (c) v = 4i 2j+6k, b = 2i+j 3k 20. (a) v = 3,5, b = 1,1 (b) v = 2,1,6, b = 0, 2,1 (c) v = 1,4,1, b = 3, 2,5 21. Find the work done by a force F = 3j (pounds) applied to a point that moves on the line from (1,3) to (4,7), Assume that distance is measured in feet. 22. A force F = 4i 6j+k newtons is applied to a point that moves a distance of 15 meters in the direction of the vector i+j+k. How much work is done? 23. A boat travels 100 meters due north while the wind that applies a force of 500 newtons toward the northwest. How much work does the wind do? 24. A box is dragged along the floor by a rope that applies a force of 50 lb at an angle of 60 with the floor. How much work is done moving the box 15 ft?
3. Interpret the graph of x = 1 in the contexts of (a) a number line (b) 2-space (c) 3-space
 MA2: Prepared by Dr. Archara Pacheenburawana Exercise Chapter 3 Exercise 3.. A cube of side 4 has its geometric center at the origin and its faces parallel to the coordinate planes. Sketch the cube and
MA2: Prepared by Dr. Archara Pacheenburawana Exercise Chapter 3 Exercise 3.. A cube of side 4 has its geometric center at the origin and its faces parallel to the coordinate planes. Sketch the cube and
Exam 1 Review SOLUTIONS
 1. True or False (and give a short reason): Exam 1 Review SOLUTIONS (a) If the parametric curve x = f(t), y = g(t) satisfies g (1) = 0, then it has a horizontal tangent line when t = 1. FALSE: To make
1. True or False (and give a short reason): Exam 1 Review SOLUTIONS (a) If the parametric curve x = f(t), y = g(t) satisfies g (1) = 0, then it has a horizontal tangent line when t = 1. FALSE: To make
3. A( 2,0) and B(6, -2), find M 4. A( 3, 7) and M(4,-3), find B. 5. M(4, -9) and B( -10, 11) find A 6. B(4, 8) and M(-2, 5), find A
 Midpoint and Distance Formula Class Work M is the midpoint of A and B. Use the given information to find the missing point. 1. A(4, 2) and B(3, -8), find M 2. A(5, 7) and B( -2, -9), find M 3. A( 2,0)
Midpoint and Distance Formula Class Work M is the midpoint of A and B. Use the given information to find the missing point. 1. A(4, 2) and B(3, -8), find M 2. A(5, 7) and B( -2, -9), find M 3. A( 2,0)
MA 162 FINAL EXAM PRACTICE PROBLEMS Spring Find the angle between the vectors v = 2i + 2j + k and w = 2i + 2j k. C.
 MA 6 FINAL EXAM PRACTICE PROBLEMS Spring. Find the angle between the vectors v = i + j + k and w = i + j k. cos 8 cos 5 cos D. cos 7 E. cos. Find a such that u = i j + ak and v = i + j + k are perpendicular.
MA 6 FINAL EXAM PRACTICE PROBLEMS Spring. Find the angle between the vectors v = i + j + k and w = i + j k. cos 8 cos 5 cos D. cos 7 E. cos. Find a such that u = i j + ak and v = i + j + k are perpendicular.
OHSx XM521 Multivariable Differential Calculus: Homework Solutions 13.1
 OHSx XM521 Multivariable Differential Calculus: Homework Solutions 13.1 (37) If a bug walks on the sphere x 2 + y 2 + z 2 + 2x 2y 4z 3 = 0 how close and how far can it get from the origin? Solution: Complete
OHSx XM521 Multivariable Differential Calculus: Homework Solutions 13.1 (37) If a bug walks on the sphere x 2 + y 2 + z 2 + 2x 2y 4z 3 = 0 how close and how far can it get from the origin? Solution: Complete
Three-Dimensional Space; Vectors
 Chapter 3 Three-Dimensional Space; Vectors 3.1 Rectangular Coordinates in 3-Space; Spheres Rectangular Coordinate Sstems To begin, consider three mutuall perpendicular coordinate lines, called the -ais,
Chapter 3 Three-Dimensional Space; Vectors 3.1 Rectangular Coordinates in 3-Space; Spheres Rectangular Coordinate Sstems To begin, consider three mutuall perpendicular coordinate lines, called the -ais,
Calculus III. George Voutsadakis 1. LSSU Math 251. Lake Superior State University. 1 Mathematics and Computer Science
 Calculus III George Voutsadakis 1 1 Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 251 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) Calculus III January 2016 1 / 76 Outline 1 Parametric Equations,
Calculus III George Voutsadakis 1 1 Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 251 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) Calculus III January 2016 1 / 76 Outline 1 Parametric Equations,
Math 190 (Calculus II) Final Review
 Math 90 (Calculus II) Final Review. Sketch the region enclosed by the given curves and find the area of the region. a. y = 7 x, y = x + 4 b. y = cos ( πx ), y = x. Use the specified method to find the
Math 90 (Calculus II) Final Review. Sketch the region enclosed by the given curves and find the area of the region. a. y = 7 x, y = x + 4 b. y = cos ( πx ), y = x. Use the specified method to find the
Math 259 Winter Solutions to Homework # We will substitute for x and y in the linear equation and then solve for r. x + y = 9.
 Math 59 Winter 9 Solutions to Homework Problems from Pages 5-5 (Section 9.) 18. We will substitute for x and y in the linear equation and then solve for r. x + y = 9 r cos(θ) + r sin(θ) = 9 r (cos(θ) +
Math 59 Winter 9 Solutions to Homework Problems from Pages 5-5 (Section 9.) 18. We will substitute for x and y in the linear equation and then solve for r. x + y = 9 r cos(θ) + r sin(θ) = 9 r (cos(θ) +
3. A( 2,0) and B(6, -2), find M 4. A( 3, 7) and M(4,-3), find B. 5. M(4, -9) and B( -10, 11) find A 6. B(4, 8) and M(-2, 5), find A
 Midpoint and Distance Formula Class Work M is the midpoint of A and B. Use the given information to find the missing point. 1. A(, 2) and B(3, -8), find M 2. A(5, 7) and B( -2, -), find M (3. 5, 3) (1.
Midpoint and Distance Formula Class Work M is the midpoint of A and B. Use the given information to find the missing point. 1. A(, 2) and B(3, -8), find M 2. A(5, 7) and B( -2, -), find M (3. 5, 3) (1.
Conic Sections. Geometry - Conics ~1~ NJCTL.org. Write the following equations in standard form.
 Conic Sections Midpoint and Distance Formula M is the midpoint of A and B. Use the given information to find the missing point. 1. A(, 2) and B(3, -), find M 2. A(5, 7) and B( -2, -), find M 3. A( 2,0)
Conic Sections Midpoint and Distance Formula M is the midpoint of A and B. Use the given information to find the missing point. 1. A(, 2) and B(3, -), find M 2. A(5, 7) and B( -2, -), find M 3. A( 2,0)
Circles. Example 2: Write an equation for a circle if the enpoints of a diameter are at ( 4,5) and (6, 3).
 Conics Unit Ch. 8 Circles Equations of Circles The equation of a circle with center ( hk, ) and radius r units is ( x h) ( y k) r. Example 1: Write an equation of circle with center (8, 3) and radius 6.
Conics Unit Ch. 8 Circles Equations of Circles The equation of a circle with center ( hk, ) and radius r units is ( x h) ( y k) r. Example 1: Write an equation of circle with center (8, 3) and radius 6.
8.1 Solutions to Exercises
 Last edited 9/6/17 8.1 Solutions to Exercises 1. Since the sum of all angles in a triangle is 180, 180 = 70 + 50 + α. Thus α = 60. 10 α B The easiest way to find A and B is to use Law of Sines. sin( )
Last edited 9/6/17 8.1 Solutions to Exercises 1. Since the sum of all angles in a triangle is 180, 180 = 70 + 50 + α. Thus α = 60. 10 α B The easiest way to find A and B is to use Law of Sines. sin( )
Find the rectangular coordinates for each of the following polar coordinates:
 WORKSHEET 13.1 1. Plot the following: 7 3 A. 6, B. 3, 6 4 5 8 D. 6, 3 C., 11 2 E. 5, F. 4, 6 3 Find the rectangular coordinates for each of the following polar coordinates: 5 2 2. 4, 3. 8, 6 3 Given the
WORKSHEET 13.1 1. Plot the following: 7 3 A. 6, B. 3, 6 4 5 8 D. 6, 3 C., 11 2 E. 5, F. 4, 6 3 Find the rectangular coordinates for each of the following polar coordinates: 5 2 2. 4, 3. 8, 6 3 Given the
Distance and Midpoint Formula 7.1
 Distance and Midpoint Formula 7.1 Distance Formula d ( x - x ) ( y - y ) 1 1 Example 1 Find the distance between the points (4, 4) and (-6, -). Example Find the value of a to make the distance = 10 units
Distance and Midpoint Formula 7.1 Distance Formula d ( x - x ) ( y - y ) 1 1 Example 1 Find the distance between the points (4, 4) and (-6, -). Example Find the value of a to make the distance = 10 units
b g 6. P 2 4 π b g b g of the way from A to B. LATE AND ABSENT HOMEWORK IS ACCEPTED UP TO THE TIME OF THE CHAPTER TEST ON ASSIGNMENT DUE
 A Trig/Math Anal Name No LATE AND ABSENT HOMEWORK IS ACCEPTED UP TO THE TIME OF THE CHAPTER TEST ON HW NO. SECTIONS (Brown Book) ASSIGNMENT DUE V 1 1 1/1 Practice Set A V 1 3 Practice Set B #1 1 V B 1
A Trig/Math Anal Name No LATE AND ABSENT HOMEWORK IS ACCEPTED UP TO THE TIME OF THE CHAPTER TEST ON HW NO. SECTIONS (Brown Book) ASSIGNMENT DUE V 1 1 1/1 Practice Set A V 1 3 Practice Set B #1 1 V B 1
3 Inequalities Absolute Values Inequalities and Intervals... 5
 Contents 1 Real Numbers, Exponents, and Radicals 3 1.1 Rationalizing the Denominator................................... 3 1.2 Factoring Polynomials........................................ 3 1.3 Algebraic
Contents 1 Real Numbers, Exponents, and Radicals 3 1.1 Rationalizing the Denominator................................... 3 1.2 Factoring Polynomials........................................ 3 1.3 Algebraic
Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space
 Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space 13.1 3-Dimensional Coordinate System 13.2 Vectors 13.3 The Dot Product 13.4 The Cross Product 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes 13.6 Cylinders and Quadratic
Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space 13.1 3-Dimensional Coordinate System 13.2 Vectors 13.3 The Dot Product 13.4 The Cross Product 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes 13.6 Cylinders and Quadratic
Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space
 Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space 13.1 3-Dimensional Coordinate System 13.2 Vectors 13.3 The Dot Product 13.4 The Cross Product 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes 13.6 Cylinders and Quadratic
Chapter 13: Vectors and the Geometry of Space 13.1 3-Dimensional Coordinate System 13.2 Vectors 13.3 The Dot Product 13.4 The Cross Product 13.5 Equations of Lines and Planes 13.6 Cylinders and Quadratic
AP Calculus (BC) Chapter 10 Test No Calculator Section. Name: Date: Period:
 AP Calculus (BC) Chapter 10 Test No Calculator Section Name: Date: Period: Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions (5 points each; please circle the correct answer.) 1. The graph in the xy-plane represented
AP Calculus (BC) Chapter 10 Test No Calculator Section Name: Date: Period: Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions (5 points each; please circle the correct answer.) 1. The graph in the xy-plane represented
Analytic Geometry MAT 1035
 Analytic Geometry MAT 035 5.09.04 WEEKLY PROGRAM - The first week of the semester, we will introduce the course and given a brief outline. We continue with vectors in R n and some operations including
Analytic Geometry MAT 035 5.09.04 WEEKLY PROGRAM - The first week of the semester, we will introduce the course and given a brief outline. We continue with vectors in R n and some operations including
1 x. II. CHAPTER 2: (A) Graphing Rational Functions: Show Asymptotes using dotted lines, Intercepts, Holes(Coordinates, if any.)
 FINAL REVIEW-014: Before using this review guide be sure to study your test and quizzes from this year. The final will contain big ideas from the first half of the year (chapters 1-) but it will be focused
FINAL REVIEW-014: Before using this review guide be sure to study your test and quizzes from this year. The final will contain big ideas from the first half of the year (chapters 1-) but it will be focused
Analytic Geometry MAT 1035
 Analytic Geometry MAT 035 5.09.04 WEEKLY PROGRAM - The first week of the semester, we will introduce the course and given a brief outline. We continue with vectors in R n and some operations including
Analytic Geometry MAT 035 5.09.04 WEEKLY PROGRAM - The first week of the semester, we will introduce the course and given a brief outline. We continue with vectors in R n and some operations including
MATH Final Review
 MATH 1592 - Final Review 1 Chapter 7 1.1 Main Topics 1. Integration techniques: Fitting integrands to basic rules on page 485. Integration by parts, Theorem 7.1 on page 488. Guidelines for trigonometric
MATH 1592 - Final Review 1 Chapter 7 1.1 Main Topics 1. Integration techniques: Fitting integrands to basic rules on page 485. Integration by parts, Theorem 7.1 on page 488. Guidelines for trigonometric
10.1 Review of Parametric Equations
 10.1 Review of Parametric Equations Recall that often, instead of representing a curve using just x and y (called a Cartesian equation), it is more convenient to define x and y using parametric equations
10.1 Review of Parametric Equations Recall that often, instead of representing a curve using just x and y (called a Cartesian equation), it is more convenient to define x and y using parametric equations
Distance formula: Between (1, 4) and (5, 10) Between (3, 8) and 3, 11) Sketch and write the equation of the following:
 Distance formula: Between (1, 4) and (5, 10) Between (3, 8) and 3, 11) Sketch and write the equation of the following: locus of all points (x,y) that are 5 units from (2,3) locus of all points 3 units
Distance formula: Between (1, 4) and (5, 10) Between (3, 8) and 3, 11) Sketch and write the equation of the following: locus of all points (x,y) that are 5 units from (2,3) locus of all points 3 units
CIRCLES: #1. What is an equation of the circle at the origin and radius 12?
 1 Pre-AP Algebra II Chapter 10 Test Review Standards/Goals: E.3.a.: I can identify conic sections (parabola, circle, ellipse, hyperbola) from their equations in standard form. E.3.b.: I can graph circles
1 Pre-AP Algebra II Chapter 10 Test Review Standards/Goals: E.3.a.: I can identify conic sections (parabola, circle, ellipse, hyperbola) from their equations in standard form. E.3.b.: I can graph circles
ALGEBRA 2 X. Final Exam. Review Packet
 ALGEBRA X Final Exam Review Packet Multiple Choice Match: 1) x + y = r a) equation of a line ) x = 5y 4y+ b) equation of a hyperbola ) 4) x y + = 1 64 9 c) equation of a parabola x y = 1 4 49 d) equation
ALGEBRA X Final Exam Review Packet Multiple Choice Match: 1) x + y = r a) equation of a line ) x = 5y 4y+ b) equation of a hyperbola ) 4) x y + = 1 64 9 c) equation of a parabola x y = 1 4 49 d) equation
Chapter 10: Conic Sections; Polar Coordinates; Parametric Equations
 Chapter 10: Conic Sections; Polar Coordinates; Parametric Equations Section 10.1 Geometry of Parabola, Ellipse, Hyperbola a. Geometric Definition b. Parabola c. Ellipse d. Hyperbola e. Translations f.
Chapter 10: Conic Sections; Polar Coordinates; Parametric Equations Section 10.1 Geometry of Parabola, Ellipse, Hyperbola a. Geometric Definition b. Parabola c. Ellipse d. Hyperbola e. Translations f.
PreCalculus. Curriculum (637 topics additional topics)
 PreCalculus This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular needs.
PreCalculus This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular needs.
Pre-Calculus Final Exam Review Name: May June Use the following schedule to complete the final exam review.
 Pre-Calculus Final Exam Review Name: May June 2015 Use the following schedule to complete the final exam review. Homework will be checked in every day. Late work will NOT be accepted. Homework answers
Pre-Calculus Final Exam Review Name: May June 2015 Use the following schedule to complete the final exam review. Homework will be checked in every day. Late work will NOT be accepted. Homework answers
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS. MATH 233 SOME SOLUTIONS TO EXAM 1 Fall 2018
 DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS MATH SOME SOLUTIONS TO EXAM 1 Fall 018 Version A refers to the regular exam and Version B to the make-up 1. Version A. Find the center
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS MATH SOME SOLUTIONS TO EXAM 1 Fall 018 Version A refers to the regular exam and Version B to the make-up 1. Version A. Find the center
1. Which of the following defines a function f for which f ( x) = f( x) 2. ln(4 2 x) < 0 if and only if
 . Which of the following defines a function f for which f ( ) = f( )? a. f ( ) = + 4 b. f ( ) = sin( ) f ( ) = cos( ) f ( ) = e f ( ) = log. ln(4 ) < 0 if and only if a. < b. < < < < > >. If f ( ) = (
. Which of the following defines a function f for which f ( ) = f( )? a. f ( ) = + 4 b. f ( ) = sin( ) f ( ) = cos( ) f ( ) = e f ( ) = log. ln(4 ) < 0 if and only if a. < b. < < < < > >. If f ( ) = (
Chapter 10 Conics, Parametric Equations, and Polar Coordinates Conics and Calculus
 Chapter 10 Conics, Parametric Equations, and Polar Coordinates 10.1 Conics and Calculus 1. Parabola A parabola is the set of all points x, y ( ) that are equidistant from a fixed line and a fixed point
Chapter 10 Conics, Parametric Equations, and Polar Coordinates 10.1 Conics and Calculus 1. Parabola A parabola is the set of all points x, y ( ) that are equidistant from a fixed line and a fixed point
10.2,3,4. Vectors in 3D, Dot products and Cross Products
 Name: Section: 10.2,3,4. Vectors in 3D, Dot products and Cross Products 1. Sketch the plane parallel to the xy-plane through (2, 4, 2) 2. For the given vectors u and v, evaluate the following expressions.
Name: Section: 10.2,3,4. Vectors in 3D, Dot products and Cross Products 1. Sketch the plane parallel to the xy-plane through (2, 4, 2) 2. For the given vectors u and v, evaluate the following expressions.
Chapter 8. Complex Numbers, Polar Equations, and Parametric Equations. Section 8.1: Complex Numbers. 26. { ± 6i}
 Chapter 8 Complex Numbers, Polar Equations, and Parametric Equations 6. { ± 6i} Section 8.1: Complex Numbers 1. true. true. true 4. true 5. false (Every real number is a complex number. 6. true 7. 4 is
Chapter 8 Complex Numbers, Polar Equations, and Parametric Equations 6. { ± 6i} Section 8.1: Complex Numbers 1. true. true. true 4. true 5. false (Every real number is a complex number. 6. true 7. 4 is
DATE: MATH ANALYSIS 2 CHAPTER 12: VECTORS & DETERMINANTS
 NAME: PERIOD: DATE: MATH ANALYSIS 2 MR. MELLINA CHAPTER 12: VECTORS & DETERMINANTS Sections: v 12.1 Geometric Representation of Vectors v 12.2 Algebraic Representation of Vectors v 12.3 Vector and Parametric
NAME: PERIOD: DATE: MATH ANALYSIS 2 MR. MELLINA CHAPTER 12: VECTORS & DETERMINANTS Sections: v 12.1 Geometric Representation of Vectors v 12.2 Algebraic Representation of Vectors v 12.3 Vector and Parametric
MATH 1020 WORKSHEET 12.1 & 12.2 Vectors in the Plane
 MATH 100 WORKSHEET 1.1 & 1. Vectors in the Plane Find the vector v where u =, 1 and w = 1, given the equation v = u w. Solution. v = u w =, 1 1, =, 1 +, 4 =, 1 4 = 0, 5 Find the magnitude of v = 4, 3 Solution.
MATH 100 WORKSHEET 1.1 & 1. Vectors in the Plane Find the vector v where u =, 1 and w = 1, given the equation v = u w. Solution. v = u w =, 1 1, =, 1 +, 4 =, 1 4 = 0, 5 Find the magnitude of v = 4, 3 Solution.
Chapter 12 Review Vector. MATH 126 (Section 9.5) Vector and Scalar The University of Kansas 1 / 30
 Chapter 12 Review Vector MATH 126 (Section 9.5) Vector and Scalar The University of Kansas 1 / 30 iclicker 1: Let v = PQ where P = ( 2, 5) and Q = (1, 2). Which of the following vectors with the given
Chapter 12 Review Vector MATH 126 (Section 9.5) Vector and Scalar The University of Kansas 1 / 30 iclicker 1: Let v = PQ where P = ( 2, 5) and Q = (1, 2). Which of the following vectors with the given
Precalculus Notes: Unit 6 Vectors, Parametrics, Polars, & Complex Numbers. A: Initial Point (start); B: Terminal Point (end) : ( ) ( )
 Syllabus Objectives: 5.1 The student will explore methods of vector addition and subtraction. 5. The student will develop strategies for computing a vector s direction angle and magnitude given its coordinates.
Syllabus Objectives: 5.1 The student will explore methods of vector addition and subtraction. 5. The student will develop strategies for computing a vector s direction angle and magnitude given its coordinates.
The Distance Formula. The Midpoint Formula
 Math 120 Intermediate Algebra Sec 9.1: Distance Midpoint Formulas The Distance Formula The distance between two points P 1 = (x 1, y 1 ) P 2 = (x 1, y 1 ), denoted by d(p 1, P 2 ), is d(p 1, P 2 ) = (x
Math 120 Intermediate Algebra Sec 9.1: Distance Midpoint Formulas The Distance Formula The distance between two points P 1 = (x 1, y 1 ) P 2 = (x 1, y 1 ), denoted by d(p 1, P 2 ), is d(p 1, P 2 ) = (x
INTEGRAL CALCULUS DIFFERENTIATION UNDER THE INTEGRAL SIGN: Consider an integral involving one parameter and denote it as
 INTEGRAL CALCULUS DIFFERENTIATION UNDER THE INTEGRAL SIGN: Consider an integral involving one parameter and denote it as, where a and b may be constants or functions of. To find the derivative of when
INTEGRAL CALCULUS DIFFERENTIATION UNDER THE INTEGRAL SIGN: Consider an integral involving one parameter and denote it as, where a and b may be constants or functions of. To find the derivative of when
4. Factor the expression completely. Begin by factoring out the lowest power of each common factor: 20x 1/2 + 9x 1/2 + x 3/2
 M180 Final Exam practice 1.Simplify each expression, and eliminate any negative exponents. st 7 4 1 s t. Simplify the expression. Assume that x, y, and z denote any positive real numbers. 3. Rationalize
M180 Final Exam practice 1.Simplify each expression, and eliminate any negative exponents. st 7 4 1 s t. Simplify the expression. Assume that x, y, and z denote any positive real numbers. 3. Rationalize
Quiz 2 Practice Problems
 Quiz Practice Problems Practice problems are similar, both in difficulty and in scope, to the type of problems you will see on the quiz. Problems marked with a are for your entertainment and are not essential.
Quiz Practice Problems Practice problems are similar, both in difficulty and in scope, to the type of problems you will see on the quiz. Problems marked with a are for your entertainment and are not essential.
2018 TAME High School Practice Mathematics Test
 018 TAME High School Practice Mathematics Test (1) Arturo took four exams and made grades of 65, 88, 9 and 75. If Arturo wants to have an average of at least 80, which of the following is the lowest grade
018 TAME High School Practice Mathematics Test (1) Arturo took four exams and made grades of 65, 88, 9 and 75. If Arturo wants to have an average of at least 80, which of the following is the lowest grade
Conic section. Ans: c. Ans: a. Ans: c. Episode:43 Faculty: Prof. A. NAGARAJ. 1. A circle
 Episode:43 Faculty: Prof. A. NAGARAJ Conic section 1. A circle gx fy c 0 is said to be imaginary circle if a) g + f = c b) g + f > c c) g + f < c d) g = f. If (1,-3) is the centre of the circle x y ax
Episode:43 Faculty: Prof. A. NAGARAJ Conic section 1. A circle gx fy c 0 is said to be imaginary circle if a) g + f = c b) g + f > c c) g + f < c d) g = f. If (1,-3) is the centre of the circle x y ax
1.1 Single Variable Calculus versus Multivariable Calculus Rectangular Coordinate Systems... 4
 MATH2202 Notebook 1 Fall 2015/2016 prepared by Professor Jenny Baglivo Contents 1 MATH2202 Notebook 1 3 1.1 Single Variable Calculus versus Multivariable Calculus................... 3 1.2 Rectangular Coordinate
MATH2202 Notebook 1 Fall 2015/2016 prepared by Professor Jenny Baglivo Contents 1 MATH2202 Notebook 1 3 1.1 Single Variable Calculus versus Multivariable Calculus................... 3 1.2 Rectangular Coordinate
Things to Know and Be Able to Do Understand the meaning of equations given in parametric and polar forms, and develop a sketch of the appropriate
 AP Calculus BC Review Chapter (Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates) Things to Know and Be Able to Do Understand the meaning of equations given in parametric and polar forms, and develop a sketch
AP Calculus BC Review Chapter (Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates) Things to Know and Be Able to Do Understand the meaning of equations given in parametric and polar forms, and develop a sketch
Unit #17: Spring Trig Unit. A. First Quadrant Notice how the x-values decrease by while the y-values increase by that same amount.
 Name Unit #17: Spring Trig Unit Notes #1: Basic Trig Review I. Unit Circle A circle with center point and radius. A. First Quadrant Notice how the x-values decrease by while the y-values increase by that
Name Unit #17: Spring Trig Unit Notes #1: Basic Trig Review I. Unit Circle A circle with center point and radius. A. First Quadrant Notice how the x-values decrease by while the y-values increase by that
MATH 32 FALL 2012 FINAL EXAM - PRACTICE EXAM SOLUTIONS
 MATH 3 FALL 0 FINAL EXAM - PRACTICE EXAM SOLUTIONS () You cut a slice from a circular pizza (centered at the origin) with radius 6 along radii at angles 4 and 3 with the positive horizontal axis. (a) (3
MATH 3 FALL 0 FINAL EXAM - PRACTICE EXAM SOLUTIONS () You cut a slice from a circular pizza (centered at the origin) with radius 6 along radii at angles 4 and 3 with the positive horizontal axis. (a) (3
Mixed exercise 3. x y. cosh t sinh t 1 Substituting the values for cosh t and sinht in the equation for the hyperbola H. = θ =
 Mixed exercise x x a Parametric equations: cosθ and sinθ 9 cos θ + sin θ Substituting the values for cos θ and sinθ in the equation for ellipse E gives the Cartesian equation: + 9 b Comparing with the
Mixed exercise x x a Parametric equations: cosθ and sinθ 9 cos θ + sin θ Substituting the values for cos θ and sinθ in the equation for ellipse E gives the Cartesian equation: + 9 b Comparing with the
Alpha Trigonometry Solutions MA National Convention. Answers:
 Answers: 1 A C C D 5 A 6 C 7 B 8 A 9 A 10 A 11 C 1 D 1 E 1 B 15 C 16 C 17 D 18 C 19 B 0 C 1 E A C C 5 E 6 B 7 E 8 D 9 D 0 B 1 Solutions: 1 A Need to check each answer to 1 k60 and 1 (60 ) = 06. C An even
Answers: 1 A C C D 5 A 6 C 7 B 8 A 9 A 10 A 11 C 1 D 1 E 1 B 15 C 16 C 17 D 18 C 19 B 0 C 1 E A C C 5 E 6 B 7 E 8 D 9 D 0 B 1 Solutions: 1 A Need to check each answer to 1 k60 and 1 (60 ) = 06. C An even
Chapter 9 Overview: Parametric and Polar Coordinates
 Chapter 9 Overview: Parametric and Polar Coordinates As we saw briefly last year, there are axis systems other than the Cartesian System for graphing (vector coordinates, polar coordinates, rectangular
Chapter 9 Overview: Parametric and Polar Coordinates As we saw briefly last year, there are axis systems other than the Cartesian System for graphing (vector coordinates, polar coordinates, rectangular
1. Graph each of the given equations, state the domain and range, and specify all intercepts and symmetry. a) y 3x
 MATH 94 Final Exam Review. Graph each of the given equations, state the domain and range, and specify all intercepts and symmetry. a) y x b) y x 4 c) y x 4. Determine whether or not each of the following
MATH 94 Final Exam Review. Graph each of the given equations, state the domain and range, and specify all intercepts and symmetry. a) y x b) y x 4 c) y x 4. Determine whether or not each of the following
MATH 1080 Test 2 -Version A-SOLUTIONS Fall a. (8 pts) Find the exact length of the curve on the given interval.
 MATH 8 Test -Version A-SOLUTIONS Fall 4. Consider the curve defined by y = ln( sec x), x. a. (8 pts) Find the exact length of the curve on the given interval. sec x tan x = = tan x sec x L = + tan x =
MATH 8 Test -Version A-SOLUTIONS Fall 4. Consider the curve defined by y = ln( sec x), x. a. (8 pts) Find the exact length of the curve on the given interval. sec x tan x = = tan x sec x L = + tan x =
( )( ) Algebra 136 Semester 2 Review. ( ) 6. g( h( x) ( ) Name. In 1-6, use the functions below to find the solutions.
 Algebra 136 Semester Review In 1-6, use the functions below to find the solutions. Name f ( x) = 3x x + g( x) = x 3 h( x) = x + 3 1. ( f + h) ( x). ( h g) ( x) 3. h x g ( ) 4. ( gh) ( x). f g( x) ( ) 6.
Algebra 136 Semester Review In 1-6, use the functions below to find the solutions. Name f ( x) = 3x x + g( x) = x 3 h( x) = x + 3 1. ( f + h) ( x). ( h g) ( x) 3. h x g ( ) 4. ( gh) ( x). f g( x) ( ) 6.
11.4 Dot Product Contemporary Calculus 1
 11.4 Dot Product Contemporary Calculus 1 11.4 DOT PRODUCT In the previous sections we looked at the meaning of vectors in two and three dimensions, but the only operations we used were addition and subtraction
11.4 Dot Product Contemporary Calculus 1 11.4 DOT PRODUCT In the previous sections we looked at the meaning of vectors in two and three dimensions, but the only operations we used were addition and subtraction
n4 + 1 n 4 1 ] [5] (b) Find the interval of convergence of the following series 1
![n4 + 1 n 4 1 ] [5] (b) Find the interval of convergence of the following series 1 n4 + 1 n 4 1 ] [5] (b) Find the interval of convergence of the following series 1](/thumbs/82/84773531.jpg) ode No: R05010102 Set No. 1 I B.Tech Supplimentary Examinations, February 2008 MATHEMATIS-I ( ommon to ivil Engineering, Electrical & Electronic Engineering, Mechanical Engineering, Electronics & ommunication
ode No: R05010102 Set No. 1 I B.Tech Supplimentary Examinations, February 2008 MATHEMATIS-I ( ommon to ivil Engineering, Electrical & Electronic Engineering, Mechanical Engineering, Electronics & ommunication
A. Correct! These are the corresponding rectangular coordinates.
 Precalculus - Problem Drill 20: Polar Coordinates No. 1 of 10 1. Find the rectangular coordinates given the point (0, π) in polar (A) (0, 0) (B) (2, 0) (C) (0, 2) (D) (2, 2) (E) (0, -2) A. Correct! These
Precalculus - Problem Drill 20: Polar Coordinates No. 1 of 10 1. Find the rectangular coordinates given the point (0, π) in polar (A) (0, 0) (B) (2, 0) (C) (0, 2) (D) (2, 2) (E) (0, -2) A. Correct! These
1. The positive zero of y = x 2 + 2x 3/5 is, to the nearest tenth, equal to
 SAT II - Math Level Test #0 Solution SAT II - Math Level Test No. 1. The positive zero of y = x + x 3/5 is, to the nearest tenth, equal to (A) 0.8 (B) 0.7 + 1.1i (C) 0.7 (D) 0.3 (E). 3 b b 4ac Using Quadratic
SAT II - Math Level Test #0 Solution SAT II - Math Level Test No. 1. The positive zero of y = x + x 3/5 is, to the nearest tenth, equal to (A) 0.8 (B) 0.7 + 1.1i (C) 0.7 (D) 0.3 (E). 3 b b 4ac Using Quadratic
Math 1720 Final Exam REVIEW Show All work!
 Math 1720 Final Exam REVIEW Show All work! The Final Exam will contain problems/questions that fit into these Course Outcomes (stated on the course syllabus): Upon completion of this course, students will:
Math 1720 Final Exam REVIEW Show All work! The Final Exam will contain problems/questions that fit into these Course Outcomes (stated on the course syllabus): Upon completion of this course, students will:
1. 4 2y 1 2 = x = x 1 2 x + 1 = x x + 1 = x = 6. w = 2. 5 x
 .... VII x + x + = x x x 8 x x = x + a = a + x x = x + x x Solve the absolute value equations.. z = 8. x + 7 =. x =. x =. y = 7 + y VIII Solve the exponential equations.. 0 x = 000. 0 x+ = 00. x+ = 8.
.... VII x + x + = x x x 8 x x = x + a = a + x x = x + x x Solve the absolute value equations.. z = 8. x + 7 =. x =. x =. y = 7 + y VIII Solve the exponential equations.. 0 x = 000. 0 x+ = 00. x+ = 8.
Math 370 Exam 3 Review Name
 Math 370 Exam 3 Review Name The following problems will give you an idea of the concepts covered on the exam. Note that the review questions may not be formatted like those on the exam. You should complete
Math 370 Exam 3 Review Name The following problems will give you an idea of the concepts covered on the exam. Note that the review questions may not be formatted like those on the exam. You should complete
Exam. There are 6 problems. Your 5 best answers count. Please pay attention to the presentation of your work! Best 5
 Department of Mathematical Sciences Instructor: Daiva Pucinskaite Calculus III June, 06 Name: Exam There are 6 problems. Your 5 best answers count. Please pay attention to the presentation of your work!
Department of Mathematical Sciences Instructor: Daiva Pucinskaite Calculus III June, 06 Name: Exam There are 6 problems. Your 5 best answers count. Please pay attention to the presentation of your work!
Conic Sections and Polar Graphing Lab Part 1 - Circles
 MAC 1114 Name Conic Sections and Polar Graphing Lab Part 1 - Circles 1. What is the standard equation for a circle with center at the origin and a radius of k? 3. Consider the circle x + y = 9. a. What
MAC 1114 Name Conic Sections and Polar Graphing Lab Part 1 - Circles 1. What is the standard equation for a circle with center at the origin and a radius of k? 3. Consider the circle x + y = 9. a. What
Study guide for Exam 1. by William H. Meeks III October 26, 2012
 Study guide for Exam 1. by William H. Meeks III October 2, 2012 1 Basics. First we cover the basic definitions and then we go over related problems. Note that the material for the actual midterm may include
Study guide for Exam 1. by William H. Meeks III October 2, 2012 1 Basics. First we cover the basic definitions and then we go over related problems. Note that the material for the actual midterm may include
2. Determine the domain of the function. Verify your result with a graph. f(x) = 25 x 2
 29 April PreCalculus Final Review 1. Find the slope and y-intercept (if possible) of the equation of the line. Sketch the line: y = 3x + 13 2. Determine the domain of the function. Verify your result with
29 April PreCalculus Final Review 1. Find the slope and y-intercept (if possible) of the equation of the line. Sketch the line: y = 3x + 13 2. Determine the domain of the function. Verify your result with
30. (+) Use the unit circle to explain symmetry (odd and even) and periodicity of trigonometric functions. [F-TF]
![30. (+) Use the unit circle to explain symmetry (odd and even) and periodicity of trigonometric functions. [F-TF] 30. (+) Use the unit circle to explain symmetry (odd and even) and periodicity of trigonometric functions. [F-TF]](/thumbs/84/90578705.jpg) Pre-Calculus Curriculum Map (Revised April 2015) Unit Content Standard Unit 1 Unit Circle 29. (+) Use special triangles to determine geometrically the values of sine, cosine, and tangent for and use the
Pre-Calculus Curriculum Map (Revised April 2015) Unit Content Standard Unit 1 Unit Circle 29. (+) Use special triangles to determine geometrically the values of sine, cosine, and tangent for and use the
Short Type Question. Q.1 Discuss the convergence & divergence of the geometric series. Q.6 Test the converegence of the series whose nth term is
 Short Type Question Q.1 Discuss the convergence & divergence of the geometric series. Q.2 Q.3 Q.4 Q.5 Q.6 Test the converegence of the series whose nth term is Q.7 Give the statement of D Alembert ratio
Short Type Question Q.1 Discuss the convergence & divergence of the geometric series. Q.2 Q.3 Q.4 Q.5 Q.6 Test the converegence of the series whose nth term is Q.7 Give the statement of D Alembert ratio
QUESTION BANK ON. CONIC SECTION (Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola)
 QUESTION BANK ON CONIC SECTION (Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola) Question bank on Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) Q. Two mutually perpendicular tangents
QUESTION BANK ON CONIC SECTION (Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola) Question bank on Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) Q. Two mutually perpendicular tangents
HW - Chapter 10 - Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates
 Berkeley City College Due: HW - Chapter 0 - Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates Name Parametric equations and a parameter interval for the motion of a particle in the xy-plane are given. Identify
Berkeley City College Due: HW - Chapter 0 - Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates Name Parametric equations and a parameter interval for the motion of a particle in the xy-plane are given. Identify
Pre Calculus Gary Community School Corporation Unit Planning Map
 UNIT/TIME FRAME STANDARDS Functions and Graphs (6 weeks) PC.F.1: For a function that models a relationship between two quantities, interpret key features of graphs and tables in terms of the quantities,
UNIT/TIME FRAME STANDARDS Functions and Graphs (6 weeks) PC.F.1: For a function that models a relationship between two quantities, interpret key features of graphs and tables in terms of the quantities,
Math 2412 Final Exam Review
 Math 41 Final Exam Review MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Factor and simplify the algebraic expression. 1) (x + 4) /5 - (x + 4) 1/5
Math 41 Final Exam Review MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Factor and simplify the algebraic expression. 1) (x + 4) /5 - (x + 4) 1/5
Review Problems for the Final
 Review Problems for the Final Math -3 5 7 These problems are provided to help you study. The presence of a problem on this handout does not imply that there will be a similar problem on the test. And the
Review Problems for the Final Math -3 5 7 These problems are provided to help you study. The presence of a problem on this handout does not imply that there will be a similar problem on the test. And the
b = 2, c = 3, we get x = 0.3 for the positive root. Ans. (D) x 2-2x - 8 < 0, or (x - 4)(x + 2) < 0, Therefore -2 < x < 4 Ans. (C)
 SAT II - Math Level 2 Test #02 Solution 1. The positive zero of y = x 2 + 2x is, to the nearest tenth, equal to (A) 0.8 (B) 0.7 + 1.1i (C) 0.7 (D) 0.3 (E) 2.2 ± Using Quadratic formula, x =, with a = 1,
SAT II - Math Level 2 Test #02 Solution 1. The positive zero of y = x 2 + 2x is, to the nearest tenth, equal to (A) 0.8 (B) 0.7 + 1.1i (C) 0.7 (D) 0.3 (E) 2.2 ± Using Quadratic formula, x =, with a = 1,
Solutions to old Exam 3 problems
 Solutions to old Exam 3 problems Hi students! I am putting this version of my review for the Final exam review here on the web site, place and time to be announced. Enjoy!! Best, Bill Meeks PS. There are
Solutions to old Exam 3 problems Hi students! I am putting this version of my review for the Final exam review here on the web site, place and time to be announced. Enjoy!! Best, Bill Meeks PS. There are
Ch 9/10/11/12 Exam Review
 Ch 9/0// Exam Review The vector v has initial position P and terminal point Q. Write v in the form ai + bj; that is, find its position vector. ) P = (4, 6); Q = (-6, -) Find the vertex, focus, and directrix
Ch 9/0// Exam Review The vector v has initial position P and terminal point Q. Write v in the form ai + bj; that is, find its position vector. ) P = (4, 6); Q = (-6, -) Find the vertex, focus, and directrix
10.1 Curves Defined by Parametric Equation
 10.1 Curves Defined by Parametric Equation 1. Imagine that a particle moves along the curve C shown below. It is impossible to describe C by an equation of the form y = f (x) because C fails the Vertical
10.1 Curves Defined by Parametric Equation 1. Imagine that a particle moves along the curve C shown below. It is impossible to describe C by an equation of the form y = f (x) because C fails the Vertical
Chapter 1. Topics in Analytic Geometry. 1.1 Conic Sections. Definitions of the Conic Sections
 Chapter 1 Topics in Analtic Geometr 1.1 Conic Sections Circles, ellipses, parabolas, and hperbolas are called conic sections or conics because the can be obtained as intersection of a plane with a double-napped
Chapter 1 Topics in Analtic Geometr 1.1 Conic Sections Circles, ellipses, parabolas, and hperbolas are called conic sections or conics because the can be obtained as intersection of a plane with a double-napped
APPM 1360 Final Exam Spring 2016
 APPM 36 Final Eam Spring 6. 8 points) State whether each of the following quantities converge or diverge. Eplain your reasoning. a) The sequence a, a, a 3,... where a n ln8n) lnn + ) n!) b) ln d c) arctan
APPM 36 Final Eam Spring 6. 8 points) State whether each of the following quantities converge or diverge. Eplain your reasoning. a) The sequence a, a, a 3,... where a n ln8n) lnn + ) n!) b) ln d c) arctan
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 3 2, 5 2 C) - 5 2
 Test Review (chap 0) Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. ) Find the point on the curve x = sin t, y = cos t, -
Test Review (chap 0) Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. ) Find the point on the curve x = sin t, y = cos t, -
Give a geometric description of the set of points in space whose coordinates satisfy the given pair of equations.
 1. Give a geometric description of the set of points in space whose coordinates satisfy the given pair of equations. x + y = 5, z = 4 Choose the correct description. A. The circle with center (0,0, 4)
1. Give a geometric description of the set of points in space whose coordinates satisfy the given pair of equations. x + y = 5, z = 4 Choose the correct description. A. The circle with center (0,0, 4)
which has a check digit of 9. This is consistent with the first nine digits of the ISBN, since
 vector Then the check digit c is computed using the following procedure: 1. Form the dot product. 2. Divide by 11, thereby producing a remainder c that is an integer between 0 and 10, inclusive. The check
vector Then the check digit c is computed using the following procedure: 1. Form the dot product. 2. Divide by 11, thereby producing a remainder c that is an integer between 0 and 10, inclusive. The check
MTH 111, Math for Architects, Exam I, Summer 2013
 Name, ID Math for Architects MTH 111 summer 2013, 1 4 copyright Ayman Badawi 2013 MTH 111, Math for Architects, Exam I, Summer 2013 Ayman Badawi QUESTION 1. Given 12x = y 2 4y 20. Find the vertex, the
Name, ID Math for Architects MTH 111 summer 2013, 1 4 copyright Ayman Badawi 2013 MTH 111, Math for Architects, Exam I, Summer 2013 Ayman Badawi QUESTION 1. Given 12x = y 2 4y 20. Find the vertex, the
Honors Precalculus Chapter 8 Summary Conic Sections- Parabola
 Honors Precalculus Chapter 8 Summary Conic Sections- Parabola Definition: Focal length: y- axis P(x, y) Focal chord: focus Vertex x-axis directrix Focal width/ Latus Rectum: Derivation of equation of parabola:
Honors Precalculus Chapter 8 Summary Conic Sections- Parabola Definition: Focal length: y- axis P(x, y) Focal chord: focus Vertex x-axis directrix Focal width/ Latus Rectum: Derivation of equation of parabola:
CONIC SECTIONS TEST FRIDAY, JANUARY 5 TH
 CONIC SECTIONS TEST FRIDAY, JANUARY 5 TH DAY 1 - CLASSIFYING CONICS 4 Conics Parabola Circle Ellipse Hyperbola DAY 1 - CLASSIFYING CONICS GRAPHICALLY Parabola Ellipse Circle Hyperbola DAY 1 - CLASSIFYING
CONIC SECTIONS TEST FRIDAY, JANUARY 5 TH DAY 1 - CLASSIFYING CONICS 4 Conics Parabola Circle Ellipse Hyperbola DAY 1 - CLASSIFYING CONICS GRAPHICALLY Parabola Ellipse Circle Hyperbola DAY 1 - CLASSIFYING
Name Period. Date: Topic: 9-2 Circles. Standard: G-GPE.1. Objective:
 Name Period Date: Topic: 9-2 Circles Essential Question: If the coefficients of the x 2 and y 2 terms in the equation for a circle were different, how would that change the shape of the graph of the equation?
Name Period Date: Topic: 9-2 Circles Essential Question: If the coefficients of the x 2 and y 2 terms in the equation for a circle were different, how would that change the shape of the graph of the equation?
Find: sinθ. Name: Date:
 Name: Date: 1. Find the exact value of the given trigonometric function of the angle θ shown in the figure. (Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the third side of the triangle.) Find: sinθ c a θ a a =
Name: Date: 1. Find the exact value of the given trigonometric function of the angle θ shown in the figure. (Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the third side of the triangle.) Find: sinθ c a θ a a =
AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB
 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB 1969 1. Consider the following functions defined for all x: f 1 (x) = x, f (x) = xcos x, f 3 (x) = 3e x, f 4 (x) = x - x. Answer the following questions
AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB 1969 1. Consider the following functions defined for all x: f 1 (x) = x, f (x) = xcos x, f 3 (x) = 3e x, f 4 (x) = x - x. Answer the following questions
North Seattle Community College Computer Based Mathematics Instruction Math 102 Test Reviews
 North Seattle Community College Computer Based Mathematics Instruction Math 10 Test Reviews Click on a bookmarked heading on the left to access individual reviews. To print a review, choose print and the
North Seattle Community College Computer Based Mathematics Instruction Math 10 Test Reviews Click on a bookmarked heading on the left to access individual reviews. To print a review, choose print and the
Pre-Calculus Team Questions Florida Regional Competition March C = ( )
 Florida Regional Competition March 08. Given: sin ( ) sin α = for 0 < α
Florida Regional Competition March 08. Given: sin ( ) sin α = for 0 < α
There are two types of multiplication that can be done with vectors: = +.
 Section 7.5: The Dot Product Multiplying Two Vectors using the Dot Product There are two types of multiplication that can be done with vectors: Scalar Multiplication Dot Product The Dot Product of two
Section 7.5: The Dot Product Multiplying Two Vectors using the Dot Product There are two types of multiplication that can be done with vectors: Scalar Multiplication Dot Product The Dot Product of two
+ 4 Ex: y = v = (1, 4) x = 1 Focus: (h, k + ) = (1, 6) L.R. = 8 units We can have parabolas that open sideways too (inverses) x = a (y k) 2 + h
 Unit 7 Notes Parabolas: E: reflectors, microphones, (football game), (Davinci) satellites. Light placed where ras will reflect parallel. This point is the focus. Parabola set of all points in a plane that
Unit 7 Notes Parabolas: E: reflectors, microphones, (football game), (Davinci) satellites. Light placed where ras will reflect parallel. This point is the focus. Parabola set of all points in a plane that
Math 323 Exam 1 Practice Problem Solutions
 Math Exam Practice Problem Solutions. For each of the following curves, first find an equation in x and y whose graph contains the points on the curve. Then sketch the graph of C, indicating its orientation.
Math Exam Practice Problem Solutions. For each of the following curves, first find an equation in x and y whose graph contains the points on the curve. Then sketch the graph of C, indicating its orientation.
MATH 151 Engineering Mathematics I
 MATH 151 Engineering Mathematics I Spring 2018, WEEK 1 JoungDong Kim Week 1 Vectors, The Dot Product, Vector Functions and Parametric Curves. Section 1.1 Vectors Definition. A Vector is a quantity that
MATH 151 Engineering Mathematics I Spring 2018, WEEK 1 JoungDong Kim Week 1 Vectors, The Dot Product, Vector Functions and Parametric Curves. Section 1.1 Vectors Definition. A Vector is a quantity that
8.2 APPLICATIONS TO GEOMETRY
 8.2 APPLICATIONS TO GEOMETRY In Section 8.1, we calculated volumes using slicing and definite integrals. In this section, we use the same method to calculate the volumes of more complicated regions as
8.2 APPLICATIONS TO GEOMETRY In Section 8.1, we calculated volumes using slicing and definite integrals. In this section, we use the same method to calculate the volumes of more complicated regions as
Portable Assisted Study Sequence ALGEBRA IIB
 SCOPE This course is divided into two semesters of study (A & B) comprised of five units each. Each unit teaches concepts and strategies recommended for intermediate algebra students. The second half of
SCOPE This course is divided into two semesters of study (A & B) comprised of five units each. Each unit teaches concepts and strategies recommended for intermediate algebra students. The second half of
11.1 Three-Dimensional Coordinate System
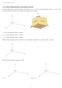 11.1 Three-Dimensional Coordinate System In three dimensions, a point has three coordinates: (x,y,z). The normal orientation of the x, y, and z-axes is shown below. The three axes divide the region into
11.1 Three-Dimensional Coordinate System In three dimensions, a point has three coordinates: (x,y,z). The normal orientation of the x, y, and z-axes is shown below. The three axes divide the region into
Study Guide for Final Exam
 Study Guide for Final Exam. You are supposed to be able to calculate the cross product a b of two vectors a and b in R 3, and understand its geometric meaning. As an application, you should be able to
Study Guide for Final Exam. You are supposed to be able to calculate the cross product a b of two vectors a and b in R 3, and understand its geometric meaning. As an application, you should be able to
Math 1710 Final Review 1 1
 Math 7 Final Review. Use the ɛ δ definition of it to prove 3 (2 2 +)=4. 2. Use the ɛ δ definition of it to prove +7 2 + =3. 3. Use the ɛ-δ definition of it to prove (32 +5 ) = 3. 4. Prove that if f() =
Math 7 Final Review. Use the ɛ δ definition of it to prove 3 (2 2 +)=4. 2. Use the ɛ δ definition of it to prove +7 2 + =3. 3. Use the ɛ-δ definition of it to prove (32 +5 ) = 3. 4. Prove that if f() =
