Chapter 2: Solving Equations and Inequalities
|
|
|
- Bertina Allison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter : Solving Equations and Inequalities Prep Test = = 1 1. (16) = 80 = % = 90(0.01) = = 0.(100%) = % 6. x x 1 ( ) ( ) 1 = (16) = = 6. 10x x (6 x) = 6x 18 + x = 9x 18 Go Figure With the donut on a table, slice the donut parallel to the table. Now cut the halved donut into quarters. Section.1 Concept Review.1 1. Sometimes true The exception is multiplying both sides of an equation by zero.. Always true. Always true. Always true Objective.1.1 Exercises 1. An expression is a combination of numbers, variables, and operation symbols. An equation consists of two expressions set equal to each other. It is important that students note that an equation contains an equals sign; an expression does not.. x = 8 () 8 8 = 8 Yes, is a solution.. b 1 = ( 1) 1 1 No, 1 is not a solution.. m = (1) No, 1 is not a solution. 9. x + = x () + () = 1 Yes, is a solution. 11. a + = a + (0) + (0) = Yes, 0 is a solution. 1. n = n + 10 ( ) + 10 ( ) = 8 Yes, is a solution. 1. z +1 = + z +1 + () No, is not a solution. 1. y 1 = y+ ( 1) 1 ( 1) No, 1 is not a solution. 19. x(x +1) = x + ( + 1) + () No, is not a solution.
2 Chapter : Solving Equations and Inequalities 1. 8t + 1 = Yes, = 1 is a solution.. m + 1 = 10m No, is not a solution.. x x = x (.1) (.1) No,.1 is not a solution. Objective.1. Exercises. The Addition Property of Equations is used to remove a term from one side of an equation by adding the opposite of that term to each side of the equation. 9. The value of x is less than 1. To solve the equation, 1 is subtracted from each side of the 1 equation, and 1 1 < x + = x + = x = The solution is b =11 b + =11+ b =1 The solution is 1. + a =8 + a =8 a = 6 The solution is 6. m + 9 = m +9 9 = 9 m = 6 The solution is 6. n = n + = + n = The solution is. 1. b + = b + = b = 0 The solution is 0.. a = a + = + a = The solution is.. z + 9 = z +9 9 = 9 z = The solution is m = m = 10 m = The solution is x = x = 9 x = 1 The solution is b = b + = + b = The solution is.. = x + = x + = x The solution is.. = m = m = m The solution is = +w 1 = + w 9 = w The solution is = 10 +b +10 = b 1 = b The solution is m + = 1 m + = 1 m = 1 The solution is x 1 = 1 x = The solution is 1.
3 Section y = y = y = 8 = 1 The solution is = n + 1 = n = n 1 = n 6. m + 1 = 1 m = 1 1 m = 1 m = The solution is. 69. x + = x + = x = x = 1 1 The solution is = x = x = x 1 = x The solution is = m = m = m 1 1 = m = m The solution is. 1 = n 1 The solution is.. w +.9 =.801 w = w =1.869 The solution is t = t = t = 0.88 The solution is Objective.1. Exercises 81. If each side of an equation is multiplied by zero, the result is the identity 0 = 0. This does not help find a solution of the equation. 8. The value of x is less than 0. To solve the equation, both sides of the equation are multiplied by the reciprocal of. Therefore, we are 8 multiplying a negative number by a positive number 8 ; the product is negative, or less than y = 8 y = 8 y = The solution is. 8. a = 1 a = 1 a = The solution is. 89. m = 0 m = 0 m = The solution is n = 0 6n 6 = 0 6 n = The solution is.
4 6 Chapter : Solving Equations and Inequalities 9. 18= t 18 = t 9 = t The solution is = x 6 = x 8 = x The solution is x = 0 x = 0 x = 0 The solution is = x = x = x The solution is = y = y 8 = y The solution is m = 1 1m 1 = 1 1 m = 1 The solution is x = 1 x = () x =1 The solution is b = b = (6) b = 18 The solution is 18. t 6 = t = 6( ) t = 18 The solution is c = 8 c = ( 8) c = 6 The solution is d = d = (8) d = 1 The solution is 1. n = n = () n = The solution is. z 8 = z = 8 (9) z = The solution is = y 11. ( 6) = y 9 = y The solution is 9. 9 = y 9 = y 1 = y 1 The solution is. 1. m = 6 m = 6 m = 1 The solution is n +n = 0 n = 0 n = 0 n = The solution is y y = 1 y = 1 y = 1 y = The solution is.
5 Section x 1. =. 1. x 1. =1.(.) x =.8 The solution is a =.00.a. =.00. a =.06 The solution is x =..x. =.. x =.1 The solution is.1. Objective.1. Exercises 1. Employee B s salary is the highest after the raise. Explanations will vary. One possible explanation is: Because each employee receives a % raise, % of the largest original salary will be the largest raise. Adding the largest raise to the largest original salary ensures that the employee will have the largest resulting salary. 1. P(0) =1 0P 0 = 1 0 P = 0. The percent is % (0) = A.0 = A 18% of 0 is (0.1)B = 8 0.1B 0.1 = B = 00 The number is () = A 1 % = 1 9 = A 1 % of is P(1) = 1P 1 = 1 P = 0. The percent is %. 1. (0.60)B = 0.60B 0.60 = 0.60 B = The number is. 19. P(6) = 1 6P 6 = 1 6 P = 1 is 00% of (0.0)B = 1 0.0B 0.0 = B = 00 The number is (0.1)(0)= A.= A 1.% of 0 is.. 1. equal to since 0% 80 = 80% 0 1. Strategy To find the number of seats, solve the basic percent equation using P = 1.11% = and B =,00. The amount is unknown (,00) = A 9. = A 0 seats are reserved for wheelchair accessibility. 19. Strategy To find the total water used, solve the basic percent equation using P = 1.8% = 0.18 and A = 1.. The base is unknown. 0.18B = B = B The total water used gallons a day Strategy To find the percent, solve the basic percent equation using B = 1 and A =. The percent is the unknown. P(1) = 11P 1 = 1 P 0.1 1% of the vacation bill is paid in cash. 16. There is insufficient information to solve this problem. Either the base or the amount must be given.
6 8 Chapter : Solving Equations and Inequalities 16. Strategy To find the percent, solve the basic percent equation using B = = and A = =. The percent is unknown. P() = P = P 0.1 1% of the accidental deaths were not attributed to motor vehicle accidents. 16. Strategy To find the total electricity used, solve the basic percent equation using P = % = 0. and A = 1.. The base is unknown. 0.B = 1. 0.B 0. = B 96.1 The total electricity used for home lighting is 96.1 billion kilowatt-hours a year Strategy To find the simple interest rate, solve the simple interest equation using I = $, P = $100, and t = 8 months = 8 years, for r. 1 I = Prt = (100) r 8 1 = 800r = 800 r = r The annual simple interest rate is 9%. 11. Strategy To find the interest, solve the simple interest equation for each account: First, using P = $1000, r =.% = 0.0, and t = 1 year, for I. Second, using P = = $000, r = 8.% = 0.08, and t = 1 year, for I. Finally, find the total interest by adding the interest earned in each account. I = Prt I = (1000)(0.0)(1) I = I = Prt I = (000)(0.08)(1) I = = $0 Sal earned $0 after one year. 1. The principal for each investment is the same amount. The time the interest accrued is the same for each account. If one account earns 6% and the other earns 9%, the combined interest earned is between 6% and 9%. To find simple interest rate on the combined accounts, solve the simple interest equation for each account: First, using P = $1000, r = 9% = 0.09, and t = 1 year, for I. Second, using P = $1000, r = 6% = 0.06, and t = 1 year, for I. Finally, to find the combined interest rate, add the value of P = = $000, and total the interest earned in both accounts, using the simple interest equation to find r. I = Prt I = (1000)(0.09)(1) I = 90 I = Prt I = (1000)(0.06)(1) I = = (000) r(1) 10 = 000r = r The interest rate earned on the combined accounts is between 6% and 9%. 1. Strategy To find the percent, solve the basic percent equation using B = 0 and A =. The percent is the unknown. P(0) = 0P = 0 0 P = 0.0 There is a % concentration of hydrogen peroxide.
7 Section Strategy To find which brand has the greater concentration, solve the basic percent equation for Apple Dan s using B = and A = 8. The percent is the unknown. Then solve the basic percent equation for the generic brand using B = 0 and A = 9. The percent is the unknown. Compare the percent of concentration. P() = 8 P = 8 P = 0. Apple Dan's P(0) = 9 0 P = P = 0. generic % >.% Apple Dan s has the greater concentration. 19. Strategy To find the amount that is not glycerin, solve the basic percent equation, find the percent that is not glycerin using P = % = 0. and B = 0 g. The amount is unknown. 0.(0) = AA 1. = There is 1. g of cream that is not glycerin Strategy To find the percent, solve the basic percent equation using B = = 00 and A = 0. The percent is unknown. P(00) = 0 00P = P = 0.1 The percent concentration is 1.%. Applying Concepts y 8y = 1 y = 1 y = (1) y = 1 The solution is = 19 x = 19 x 1 x +8 = 19 1 x +8 = 19 x +8 8 = 19 8 x = The solution is. = 6 a a a a = 6 a a = 6 a a = 6 a = 6 a = (6) a = 1 The solution is Strategy To find the cost of the dinner, solve the basic percent equation using P = (100% + 1%)(100% + 6%) = (11%)(106%) = (1.1)(1.06) and A = 9.. The base is unknown. (1.1)(1.06) B = B = B = B = 80 The cost of the dinner was $ If a quantity increases by 100%, then the same quantity is added to itself. The new value will be twice the original value. 19. One equation with a solution of is x = 10.
8 0 Chapter : Solving Equations and Inequalities 19. Students should refer to the two sections of the table, one for single taxpayers and one for married taxpayers filing jointly. The first two columns of a table are used to locate the row containing the taxable income; the last two columns are used to calculate the income tax due. A single taxpayer s taxable income of $,000 falls between $6,0 and $16,0. 1,6 +.0(,000 6,0) = 1, (90) = 1, = 1,. The income tax is $1,.. Section. Concept Review. 1. Always true. Never true First use the Addition Property of Equations to remove the constant term from the left side of the equation. Then use the Multiplication Property of Equations to multiply both sides of the equation by 1 a.. Never true Division by zero is undefined.. Sometimes true If a = c, the equation will have no variables when cx is subtracted from both sides. Objective..1 Exercises 1. x +1 =10 x +1 1 =10 1 x = 9 x = 9 x = The solution is.. a = a + = + a = 1 a = 1 a = 6 The solution is 6.. = x = x = x = x 1 = x The solution is = 9 + z 1 9 = 9 9 +z = z = z 1 = z The solution is x =11 x =11 x = 9 1( x) = 1 9 x = 9 The solution is x = 1 6x = 1 6x = 18 6x = x = The solution is. 1. d + = 1 d + = 1 d = 1 d = 1 d = The solution is. 1. n = n + = + n = 1 n = 1 n = The solution is = 11y = 11y+ 9 9 = 11y 11 = 11y 11 = y The solution is. 19. = 11 n 11= n 8 = n 8 = n = n The solution is. 1. 8x + = 9 8x + = 9 8x = 8x 8 = 8 x = The solution is.
9 Section. 1. x = x + = + x = 6 x = 6 x = 6 The solution is 6.. 9a = 9a = 9a = 9a 9 = 9 a = 9 = 1 The solution is 1.. 6a + = 9 6a + = 9 6a = 6a 6 = 6 a = 6 = The solution is.. 10 = 18x + 10 = 18x + = 18x 18 = 18x = x 1 6 = x. 11= 1+ n 11 1 = 1 1+ n = n = n 1 = n The solution is x = x = 6 9 x = x = x = The solution is x = x = 0 1 x = 1 x = 1 x = 1 The solution is 1.. 8b = 9 8b + = 9 + 8b = 6 8b 8 = 6 8 The solution is x 6 = 1 6 x = x = 18 6 x = x = x = 1 The solution is x + = 9x + = 9x = (9x) = 1 9 (0) x = 0 The solution is 0.. = 9 a 9 = 9 9 a = a = a = a The solution is. b = 6 8 = The solution is.
10 Chapter : Solving Equations and Inequalities. x + = 9 x + = 9 x = 6 x = x = 6 = The solution is. 1 m 1 = 1 m 1 +1 = +1 1 m = 6 1 m = 6 m = 18 The solution is 18. n + =1 n + =1 n = 6 n = (6) n = 8 The solution is b + =10 8. b + = b = b = 8 (6) b = 16 The solution is 16. y = y + = + y = 1 y = y = The solution is.. c 1 = 8 c 1+1 = 8 +1 c = 9 c = (9) c = 1 The solution is 1.. w = 9 w = 9 w = 1 w = ( 1) w =1 The solution is x = x = 1 8 x = x = 8 ( 10) x = 16 The solution is 16. = y = y = y 6 = y The solution is. 6 8 = 1 1 b 8 1 = b 9 10 = 1 b 1 = 1 b 1 = 1 b 1 8 = b 1 The solution is. 8
11 Section. 6. = x + = x + = x () = x 1 = x 1 The solution is y = 9 y = 9 9 y = y = 9 () y = 18 The solution is y +9 + y = y + 9 = y+ 9 9 = 9 y = 1 y = 1 y = The solution is z z = 9 z = 9 z + = 9 + z =1 z = 1 z = The solution is.. b 8b +1 = 6 b +1 = 6 b +1 1 = 6 1 b = b = b = 1 The solution is = n 6 +n 8 = n = n = n 1 = n = n The solution is.. 1.x. = 1. 1.x. +. = x =. 1.x 1. =. 1. x =.9 The solution is =.y =.y =.y.. =.y. 0.8= y The solution is x + = x + = x = 9 x = 9 x = The answer is x =11 x =11 x = 9 x = 9 x = The answer is 0. Objective.. Exercises 8. 6y + = y +1 6y y + = y y +1 y + =1 y + =1 y =1 y = 1 y = The solution is n + =10n n 10n + =10n 10n +11 n + =11 n + =11 n = 8 The solution is a 10 = a + 9a a 10 = a a + 6a 10 = 6a = +10 6a = 1 6a 6 = 1 6 a = The solution is. x = ( ) = 6 = 11 x + x = ( ) + ( ) = 9 6 = = 0
12 Chapter : Solving Equations and Inequalities 91. 1b 1 = b 19 1b b 1 = b b 19 9b 1 = 19 9b 1 +1 = b = 18 9b 9 = 18 9 b = The solution is. 9. a = a 0 a a = a a 0 a = 0 a + = 0 + a = 1 a = 1 a = The solution is. 9. n = 6 n n + n = 6 n + n n = 6 n + = 6 + n =8 n = 8 n = The solution is. 9. y = 16 y y + y = 16 y +y y = 16 y + = 16 + y = 1 y = 1 y = The solution is. 99. m + =m +8 m m + =m m +8 m + =8 m + =8 m = m = m = The solution is d = d + 6d d = d d + d = d + = + d = ( 1)( d) = ( 1)() d = The solution is. 10. a + = a + a a + = a a + a + = a + = a = 0 a = 0 a = 0 The solution is n =16 n 10 n + n =16 n +n 10 n = n =16 10 n = 6 n = 6 n = The solution is. 10. b 10 = b b b 10 = b b 10 = b 10 = b = b The solution is y = y +16 9y y = y y +16 y = 16 y = 16 y = The solution is x = 18 x 8 x +x = 18 x + x 8 + x = x = 18 8 x = 10 The solution is m = 6m m + 6m = 6m +6m m = m = m = 1( ) = 1( ) m = The solution is y 1 = y + 6y y 1 = y y + y 1 = y 1+1 = +1 y = y = y = The solution is.
13 Section x = x 1 10x x = x x 1 x = 1 x + = 1+ x = x = x = The solution is. 1. b = 6 b b + 6 b = 6 b + 6 b 6 b + 6 b = 9 6 b = b = 6 9 () a = a 8a a = a a a = a + = + a = a = a = The solution is. x = 1 1 x + x 1 1 x = 1 1 x 1 1 x x 1 1 x = 8 1 x = x = 1 8 () x = The solution is. c = 1 10 c c c = 1 10 c c = 1 10 c 8 10 c = 10 c 10 ( ) = c 10 = c The solution is 10. b = The solution is. 1..x. =.x.x.x. =.x.x. = 1.8x. 1.8 = 1.8x 1.8 = x The solution is. 19. x = x 8 x x = x x 8 x = 8 x = 8 x = The answer is a = a 6a +a = a +a a = a = a = a = a = 1 The answer is. Objective.. Exercises 1.x + (x +1) = x + x + = x + = x + = x = 1 x = 1 x = The solution is. 1. 9n (n 1) =1 9n 6n + =1 n + =1 n + =1 n =1 n = 1 n = The solution is. x + = ( )+ = 16+ = 1 a a +1 = ( 1) ( 1) +1 = (1) ( 1) +1 = + +1 = 6 +1 =
14 6 Chapter : Solving Equations and Inequalities 1. a (a ) =1 a a + =1 a + =1 a + =1 a = 8 a = 8 a = The solution is. 19. ( y)+ y = 1 10y + y = 1 6y = 1 1 6y = 1 6y = 1 6y 6 = 1 6 y = The solution is x +1 = (x + ) 1 10x +1 = 6x x +1 = 6x x 6x +1 = 6x 6x +9 x +1 = 9 x +1 1 = 9 1 x =8 x = 8 x = The solution is. 1. a = (a + ) a = a 10 a = a a + a = a + a + a = + a = a = The solution is. 1. y = (y ) + y =10y 1+ y =10y 11 y 10y =10y 10y 11 y = 11 y + = 11+ y = y = y = The solution is. 19. [ ( y 1)] = (y +8) [ y +]= 6y + [6 y]= 6y y = 6y y 6y = 6y 6y y = y = 18 18y = 6 18y 18 = 6 18 y = 1 The solution is a +[ + (a 1)] = (a + ) a +[ + a ] = 6a + 8 a + [ 1 +a]= 6a + 8 a +6a = 6a + 8 9a = 6a + 8 9a 6a = 6a 6a + a = 8 a + = 8 + a = 10 a = 10 a = 10 The solution is [ (b + )]= (b + 6) [ b ]= 6b 1 [ b]= 6b + 6b = 6b + 6b + 6b = 6b + 6b +1b = + +1b = + 1b = 1b 1 = 1 b = 1 The solution is x (1.6x) 8 = (1.9x.1) 0.x. x 8 =.x 1..9x 8 =.x 1..9x.x 8 =.x.x x 8 = x 8+ 8 = x =. 8.6x 8.6 =. 8.6 x = 0. The solution is 0.. 8
15 Section. 1. a = (a + ) a = a 10 a = a a + a = a + a + a = + a = a = The answer is z = (z +) z = 1z +1 z 1z = 1z 1z +1 10z = 1 10z + = 1+ 10z = 0 10z 10 = 0 10 z = The answer is 1. Objective.. Exercises a +a = ( ) + ()( ) = 9+ ()( ) = 9 9 = 0 z z = ( ) = = Strategy To find the distance, replace C by and solve for D. C = 1 D = 1 D + = 1 D + = 1 D () = 1 D 168 = D The car will slide 168 ft. 16. Strategy To find the depth, replace P by and solve for D. P = 1 D +1 = 1 D +1 1 = 1 D = 1 D (0) = 1 D 0 = D The depth of the diver is 0 ft. 16. Strategy To find the initial velocity, replace s by 80 and t by and solve for v. s = 16t + vt 80 = 16() +v() 80 = 16() +v 80 = 6 + v 80 6 = v 16 = v 16 = v 8 = v The initial velocity is 8 ft/s. 16. Strategy To find the length, replace H by 66 and solve for L. H =1.L =1.L =1.L =1.L = 1.L L The approximate length of the humerus is 1.8 in Strategy To find the number miles, replace F by 6. and solve for m. F = (m 1) 6. = m = m = m.0 = 0.9m = 0.9m = m The passenger was driven 6 mi. 11. Strategy To find the number of errors, replace S by and W by 90 and solve for e. S = W e e = e 10()= = 90 e 0 90 = e 0 = e 0 = e 8 = e The candidate made 8 errors.
16 8 Chapter : Solving Equations and Inequalities 1. Strategy To find the population, replace P 1 by 8,000, N by 1,100,000, and d by, and solve for P. N =.1P 1P d 1,100,000 =.1(8,000)P 1,100,000 = 10,80P (1,100,000) = 10,80 10,80 10,80P 6 1, P The population is approximately 1,000 people. 1. Strategy To find the break-even point, replace the variables P, C, and F in the cost equation by the given values and solve for x. Px = Cx + F 0x = 16x + 9,0 0x 16x = 16x 16x + 9,0 8x = 9,0 8x 8 = 9,0 8 x = 0 The break-even point is 0 televisions. 1. In the lever-system equation F 1 x = F (d x), x represents the distance from force F 1 to the fulcrum, d represents the length of the lever, and d x represents the distance from the force F to the fulcrum. 19. Strategy To determine whether or not the see-saw is balanced, replace the variables F 1, F, d, and x in the lever system equation by the given values. Evaluate each side of the equation. If it is a true equation, the see-saw is balanced. If it is not a true equation, the see-saw is not balanced. F 1 x = F (d x) 60(.) 0(8.) 10 0(.) 10 The see-saw is not balanced Strategy To find the force when the system balances, replace the variables F 1, x, and d in the lever system equation by the given values and solve for F. F 1 x = F (d x) 100 = F (10 ) 100 = F 8 00 = 8F 00 8 = 8F 8 = F A -lb force must be applied to the other end. 18. Strategy To find the location of the fulcrum when the system balanced, replaces the variables F 1, F, and d in the lever system equation by the given values and solve for x. F 1 x = F (d x) 18x =160(18 x) 18x = x 18x +160x = x +160x 88x = x 88 = x =10 The fulcrum is 10 ft from the 18 lb acrobat. Applying Concepts. 18. (x 1) (6x ) = 9 6x 6x + = 9 6x 6x +1 = No solution
17 Section [(w + ) (w +1)] = (+w) [w+ 8 w 1] = 10+ w [w + ] = 10+ w 9w+ 1= 10+ w 9w w+ 1= 10+ w w w+ 1= 10 w +1 1= 10 1 w = 11 w = 11 w = 11 The solution is To solve, remember Dividend = Quotient Divisor + Remainder,166 = 18 x + 0,166 0 = 18x + 0 0,116 = 18x,116 = 18x = x 191. One possible answer is x 6 = x x = 19. The sentence Solve x (x 1) does not make sense because x (x 1) is not an equation; it is an expression. Equations can be solved. Expressions cannot be solved. 19. Look for the following explanations in your students work. x = x + = + By the addition property of Equations, the same number can be added to each side of the equation without changing the solution of the equation. Add to each side of the equation the opposite of the constant term. x + 0= 9 By the Inverse Property of Addition, the sum of a number and its opposite is 0. x = 9 By the Addition Property of Zero, the sum of a number and zero is the number. x = 9 By the Multiplication Property of Equations, each side of an equation can be multiplied by the same nonzero number without changing the solution of the equation. Multiply each side of the equation by the reciprocal of the coefficient of x. 1x = 1 By the Inverse Property of Multiplication, the product of a number and its reciprocal is 1. x = 1 By the Multiplication Property of One, the product of a number and 1 is the number. Section. Concept Review. 1. Always true. Always true. Always true. Never true The number of dimes is represented by 0 n.
18 0 Chapter : Solving Equations and Inequalities 9. Always true Objective..1 Exercises 1. the unknown number: n The difference between a number and 1 The number is.. the unknown number: n is n 1= n 1 +1= +1 n = seven The product of is negative twenty-one seven and a number n = 1 n = 1 n = The number is.. the unknown number: n Four less than three is times a number n = n + = + n = 9 n = 9 n = The number is.. the unknown number: n five Four times the sum of is twelve twice a number and three ( n + ) = 1 8n +1 = 1 8n +1 1 = 1 1 8n = 0 8n 8 = 0 8 n = 0 The number is the unknown number: n 11. the unknown number: n Twice the difference between a number and twenty-five (n ) = n n 0 = n n n 0 = n n 0 = n The number is the smaller number: n the larger number: 0 n Three times the smaller = 0 n =8 0 n = 0 8 = 1 The smaller number is 8. The larger number is the smaller number: n the larger number: 18 n is three times the number is equal to two times the larger n = (0 n) n = 0 n n +n = 0 n + n n = 0 n The total of three times the smaller and twice the is forty-four larger n +(18 n) = n +6 n = n + 6 = n = 6 n = 8 18 n = 18 8 = 10 The smaller number is 8. The larger number is 10. six times the difference Twelve is between a number and three 1 = 6( n ) 1 = 6n = 6n = 6n 0 6 = 6n 6 = n The number is.
MATH 081. Diagnostic Review Materials PART 2. Chapters 5 to 7 YOU WILL NOT BE GIVEN A DIAGNOSTIC TEST UNTIL THIS MATERIAL IS RETURNED.
 MATH 08 Diagnostic Review Materials PART Chapters 5 to 7 YOU WILL NOT BE GIVEN A DIAGNOSTIC TEST UNTIL THIS MATERIAL IS RETURNED DO NOT WRITE IN THIS MATERIAL Revised Winter 0 PRACTICE TEST: Complete as
MATH 08 Diagnostic Review Materials PART Chapters 5 to 7 YOU WILL NOT BE GIVEN A DIAGNOSTIC TEST UNTIL THIS MATERIAL IS RETURNED DO NOT WRITE IN THIS MATERIAL Revised Winter 0 PRACTICE TEST: Complete as
Chapter 1: Fundamentals of Algebra Lecture notes Math 1010
 Section 1.1: The Real Number System Definition of set and subset A set is a collection of objects and its objects are called members. If all the members of a set A are also members of a set B, then A is
Section 1.1: The Real Number System Definition of set and subset A set is a collection of objects and its objects are called members. If all the members of a set A are also members of a set B, then A is
8.1 Multiplication Properties of Exponents Objectives 1. Use properties of exponents to multiply exponential expressions.
 8.1 Multiplication Properties of Exponents Objectives 1. Use properties of exponents to multiply exponential expressions. 2. Use powers to model real life problems. Multiplication Properties of Exponents
8.1 Multiplication Properties of Exponents Objectives 1. Use properties of exponents to multiply exponential expressions. 2. Use powers to model real life problems. Multiplication Properties of Exponents
Mini Lecture 1.1 Introduction to Algebra: Variables and Mathematical Models
 Mini Lecture. Introduction to Algebra: Variables and Mathematical Models. Evaluate algebraic expressions.. Translate English phrases into algebraic expressions.. Determine whether a number is a solution
Mini Lecture. Introduction to Algebra: Variables and Mathematical Models. Evaluate algebraic expressions.. Translate English phrases into algebraic expressions.. Determine whether a number is a solution
3.3 Dividing Polynomials. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 3.3 Dividing Polynomials Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Long Division of Polynomials Synthetic Division The Remainder and Factor Theorems 2 Dividing Polynomials In this section
3.3 Dividing Polynomials Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Long Division of Polynomials Synthetic Division The Remainder and Factor Theorems 2 Dividing Polynomials In this section
Finding a Percent of a Number (page 216)
 LESSON Name 1 Finding a Percent of a Number (page 216) You already know how to change a percent to a fraction. Rewrite the percent as a fraction with a denominator of 100 and reduce. 25% = 25 100 = 1 5%
LESSON Name 1 Finding a Percent of a Number (page 216) You already know how to change a percent to a fraction. Rewrite the percent as a fraction with a denominator of 100 and reduce. 25% = 25 100 = 1 5%
Solution: Slide 7.1-3
 7.1 Rational Expressions and Functions; Multiplying and Dividing Objectives 1 Define rational expressions. 2 Define rational functions and describe their domains. Define rational expressions. A rational
7.1 Rational Expressions and Functions; Multiplying and Dividing Objectives 1 Define rational expressions. 2 Define rational functions and describe their domains. Define rational expressions. A rational
Seven is less than 11. Four more than seventeen. Four is not equal to three.
 Prealgebra.1: Translations, Simplifying and Evaluating Expressions Words such as,, and indicate addition. Words such as,, and indicate subtraction. Translate each of the following into mathematical symbols.
Prealgebra.1: Translations, Simplifying and Evaluating Expressions Words such as,, and indicate addition. Words such as,, and indicate subtraction. Translate each of the following into mathematical symbols.
2.1 Simplifying Algebraic Expressions
 .1 Simplifying Algebraic Expressions A term is a number or the product of a number and variables raised to powers. The numerical coefficient of a term is the numerical factor. The numerical coefficient
.1 Simplifying Algebraic Expressions A term is a number or the product of a number and variables raised to powers. The numerical coefficient of a term is the numerical factor. The numerical coefficient
Introductory Algebra Final Exam Review
 Introductory Algebra Final Exam Review Note to students: The final exam for this course will consist of 0 multiple-choice questions and a few openended questions. The exam will cover Lessons from your
Introductory Algebra Final Exam Review Note to students: The final exam for this course will consist of 0 multiple-choice questions and a few openended questions. The exam will cover Lessons from your
Mini Lecture 1.1 Introduction to Algebra: Variables and Mathematical Models
 Mini Lecture. Introduction to Algebra: Variables and Mathematical Models. Evaluate algebraic epressions.. Translate English phrases into algebraic epressions.. Determine whether a number is a solution
Mini Lecture. Introduction to Algebra: Variables and Mathematical Models. Evaluate algebraic epressions.. Translate English phrases into algebraic epressions.. Determine whether a number is a solution
Chapter 1: Whole Numbers
 1 Chapter 1: Whole Numbers Prep Test 1. 8 2. 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 9 1 3. a and D; b and E; c and A; d and B; e and F; f and C. 5. fifty Go Figure Section 1.1 On the first trip, the two children row over. The
1 Chapter 1: Whole Numbers Prep Test 1. 8 2. 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 9 1 3. a and D; b and E; c and A; d and B; e and F; f and C. 5. fifty Go Figure Section 1.1 On the first trip, the two children row over. The
Chapter 1: Whole Numbers
 Chapter 1: Whole Numbers Prep Test 1. 8. 1 3 6 7 8 9 1 3. a and D; b and E; c and A; d and B; e and F; f and C.. Fifty Go Figure On the first trip, the two children row over. The second trip, one child
Chapter 1: Whole Numbers Prep Test 1. 8. 1 3 6 7 8 9 1 3. a and D; b and E; c and A; d and B; e and F; f and C.. Fifty Go Figure On the first trip, the two children row over. The second trip, one child
We say that a polynomial is in the standard form if it is written in the order of decreasing exponents of x. Operations on polynomials:
 R.4 Polynomials in one variable A monomial: an algebraic expression of the form ax n, where a is a real number, x is a variable and n is a nonnegative integer. : x,, 7 A binomial is the sum (or difference)
R.4 Polynomials in one variable A monomial: an algebraic expression of the form ax n, where a is a real number, x is a variable and n is a nonnegative integer. : x,, 7 A binomial is the sum (or difference)
Mini Lecture 1.1 Introduction to Algebra: Variables and Mathematical Models
 Mini Lecture. Introduction to Algebra: Variables and Mathematical Models. Evaluate algebraic epressions.. Translate English phrases into algebraic epressions.. Determine whether a number is a solution
Mini Lecture. Introduction to Algebra: Variables and Mathematical Models. Evaluate algebraic epressions.. Translate English phrases into algebraic epressions.. Determine whether a number is a solution
Translate from words to mathematical expressions. Distinguish between simplifying expressions and solving equations.
 Chapter 2 Section 3 2.3 Applications of Linear Equations Objectives 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Translate from words to mathematical expressions. Write equations from given information. Distinguish between simplifying
Chapter 2 Section 3 2.3 Applications of Linear Equations Objectives 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Translate from words to mathematical expressions. Write equations from given information. Distinguish between simplifying
Name: Class: Date: Describe a pattern in each sequence. What are the next two terms of each sequence?
 Class: Date: Unit 3 Practice Test Describe a pattern in each sequence. What are the next two terms of each sequence? 1. 24, 22, 20, 18,... Tell whether the sequence is arithmetic. If it is, what is the
Class: Date: Unit 3 Practice Test Describe a pattern in each sequence. What are the next two terms of each sequence? 1. 24, 22, 20, 18,... Tell whether the sequence is arithmetic. If it is, what is the
Math 101, Basic Algebra. Solving Linear Equations and Inequalities
 Math 101, Basic Algebra Author: Debra Griffin Name Chapter 2 Solving Linear Equations and Inequalities 2.1 Simplifying Algebraic Expressions 2 Terms, coefficients, like terms, combining like terms, simplifying
Math 101, Basic Algebra Author: Debra Griffin Name Chapter 2 Solving Linear Equations and Inequalities 2.1 Simplifying Algebraic Expressions 2 Terms, coefficients, like terms, combining like terms, simplifying
Variable Expression: a collection of numbers, variables, and operations *Expressions DO NOT have signs. Ex: If x = 3 6x = Ex: if y = 9..
 Algebra 1 Chapter 1 Note Packet Name Section 1.1: Variables in Algebra Variable: a letter that is used to represent one or more numbers Ex: x, y, t, etc. (*The most popular one is x ) Variable Values:
Algebra 1 Chapter 1 Note Packet Name Section 1.1: Variables in Algebra Variable: a letter that is used to represent one or more numbers Ex: x, y, t, etc. (*The most popular one is x ) Variable Values:
Prerequisites. Introduction CHAPTER OUTLINE
 Prerequisites 1 Figure 1 Credit: Andreas Kambanls CHAPTER OUTLINE 1.1 Real Numbers: Algebra Essentials 1.2 Exponents and Scientific Notation 1.3 Radicals and Rational Expressions 1.4 Polynomials 1.5 Factoring
Prerequisites 1 Figure 1 Credit: Andreas Kambanls CHAPTER OUTLINE 1.1 Real Numbers: Algebra Essentials 1.2 Exponents and Scientific Notation 1.3 Radicals and Rational Expressions 1.4 Polynomials 1.5 Factoring
ASU Mathematics Placement Test Sample Problems June, 2000
 ASU Mathematics Placement Test Sample Problems June, 000. Evaluate (.5)(0.06). Evaluate (.06) (0.08). Evaluate ( ) 5. Evaluate [ 8 + ( 9) ] 5. Evaluate 7 + ( ) 6. Evaluate ( 8) 7. Evaluate 5 ( 8. Evaluate
ASU Mathematics Placement Test Sample Problems June, 000. Evaluate (.5)(0.06). Evaluate (.06) (0.08). Evaluate ( ) 5. Evaluate [ 8 + ( 9) ] 5. Evaluate 7 + ( ) 6. Evaluate ( 8) 7. Evaluate 5 ( 8. Evaluate
Sect 2.4 Multiplying and Dividing Integers
 55 Sect 2.4 Multiplying and Dividing Integers Objective a: Understanding how to multiply two integers. To see how multiplying and dividing a negative and a positive number works, let s look at some examples.
55 Sect 2.4 Multiplying and Dividing Integers Objective a: Understanding how to multiply two integers. To see how multiplying and dividing a negative and a positive number works, let s look at some examples.
7.12 The student will represent relationships with tables, graphs, rules, and words.
 7.12 The student will represent relationships with tables, graphs, rules, and words. HINTS & NOTES Relation- is a set of ordered pairs. Remember to always start from the origin. Origin is (0,0) Move horizontally
7.12 The student will represent relationships with tables, graphs, rules, and words. HINTS & NOTES Relation- is a set of ordered pairs. Remember to always start from the origin. Origin is (0,0) Move horizontally
Pearson Learning Solutions
 Answers to Selected Exercises CHAPTER REVIEW OF REAL NUMBERS Section.. a. b. c.. a. True b. False c. True d. True. a. b. Ú c.. -0. a. b. c., -, - d.,, -, -, -.,., - e. f.,, -, -,, -.,., -. a. b. c. =.
Answers to Selected Exercises CHAPTER REVIEW OF REAL NUMBERS Section.. a. b. c.. a. True b. False c. True d. True. a. b. Ú c.. -0. a. b. c., -, - d.,, -, -, -.,., - e. f.,, -, -,, -.,., -. a. b. c. =.
Algebra I Notes Unit Two: Variables
 Syllabus Objectives:. The student will use order of operations to evaluate expressions.. The student will evaluate formulas and algebraic expressions using rational numbers (with and without technology).
Syllabus Objectives:. The student will use order of operations to evaluate expressions.. The student will evaluate formulas and algebraic expressions using rational numbers (with and without technology).
Algebra Supplement Homework Packet #1
 Algebra Supplement Homework Packet #1 Day 1: Fill in each blank with one of the words or phrases listed below. Distributive Real Reciprocals Absolute value Opposite Associative Inequality Commutative Whole
Algebra Supplement Homework Packet #1 Day 1: Fill in each blank with one of the words or phrases listed below. Distributive Real Reciprocals Absolute value Opposite Associative Inequality Commutative Whole
4. Based on the table below, what is the joint relative frequency of the people surveyed who do not have a job and have a savings account?
 Name: Period: Date: Algebra 1 Common Semester 1 Final Review Like PS4 1. How many surveyed do not like PS4 and do not like X-Box? 2. What percent of people surveyed like the X-Box, but not the PS4? 3.
Name: Period: Date: Algebra 1 Common Semester 1 Final Review Like PS4 1. How many surveyed do not like PS4 and do not like X-Box? 2. What percent of people surveyed like the X-Box, but not the PS4? 3.
Wahkiakum School District, Pre-EOC Algebra
 Pre-EOC Assessment Algebra1 #2 Wahkiakum School District ALG1 Page 1 1. Order the following numbers from least to greatest: a. 19 2, 3π, 8.7 100, 62 3π, 62, 8.7 10 0, 19 2 b. 62, 8.7 10 0, 3π, 19 2 c.
Pre-EOC Assessment Algebra1 #2 Wahkiakum School District ALG1 Page 1 1. Order the following numbers from least to greatest: a. 19 2, 3π, 8.7 100, 62 3π, 62, 8.7 10 0, 19 2 b. 62, 8.7 10 0, 3π, 19 2 c.
KNOWLEDGE OF NUMBER SENSE, CONCEPTS, AND OPERATIONS
 KNOWLEDGE OF NUMBER SENSE, CONCEPTS, AND OPERATIONS C O M P E T E N C Y 1 KNOWLEDGE OF NUMBER SENSE, CONCEPTS, AND OPERATIONS SKILL 1.1 Compare the relative value of real numbers (e.g., integers, fractions,
KNOWLEDGE OF NUMBER SENSE, CONCEPTS, AND OPERATIONS C O M P E T E N C Y 1 KNOWLEDGE OF NUMBER SENSE, CONCEPTS, AND OPERATIONS SKILL 1.1 Compare the relative value of real numbers (e.g., integers, fractions,
( ) ( ) = Since the numbers have like signs, the quotient is positive = Ê 77. =
 7. Since the numbers have like signs, the quotient is positive. -1-1 = 1 9. Since the numbers have unlike signs, the quotient is negative. 4/ (-4) = 4-4 = -1 61. Since the numbers have unlike signs, the
7. Since the numbers have like signs, the quotient is positive. -1-1 = 1 9. Since the numbers have unlike signs, the quotient is negative. 4/ (-4) = 4-4 = -1 61. Since the numbers have unlike signs, the
Chapter 1. Exercise Set 1.1
 Chapter Exercise Set.. To prepare properly for this class, you need to do all the homework carefully and preview the new material that is to be covered in class.. At least hours of study and homework time
Chapter Exercise Set.. To prepare properly for this class, you need to do all the homework carefully and preview the new material that is to be covered in class.. At least hours of study and homework time
Sect Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, and Division Properties of Equality
 Sect.1 - Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, and Division Properties of Equality Concept #1 Definition of a Linear Equation in One Variable An equation is a statement that two quantities are equal.
Sect.1 - Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, and Division Properties of Equality Concept #1 Definition of a Linear Equation in One Variable An equation is a statement that two quantities are equal.
4. Based on the table below, what is the joint relative frequency of the people surveyed who do not have a job and have a savings account?
 Name: Period: Date: Algebra 1 Common Semester 1 Final Review 1. How many surveyed do not like PS4 and do not like X-Box? 2. What percent of people surveyed like the X-Box, but not the PS4? 3. What is the
Name: Period: Date: Algebra 1 Common Semester 1 Final Review 1. How many surveyed do not like PS4 and do not like X-Box? 2. What percent of people surveyed like the X-Box, but not the PS4? 3. What is the
PRE-ALGEBRA SUMMARY WHOLE NUMBERS
 PRE-ALGEBRA SUMMARY WHOLE NUMBERS Introduction to Whole Numbers and Place Value Digits Digits are the basic symbols of the system 0,,,, 4,, 6, 7, 8, and 9 are digits Place Value The value of a digit in
PRE-ALGEBRA SUMMARY WHOLE NUMBERS Introduction to Whole Numbers and Place Value Digits Digits are the basic symbols of the system 0,,,, 4,, 6, 7, 8, and 9 are digits Place Value The value of a digit in
MATH 0030 Lecture Notes Section 2.1 The Addition Property of Equality Section 2.2 The Multiplication Property of Equality
 MATH 0030 Lecture Notes Section.1 The Addition Property of Equality Section. The Multiplication Property of Equality Introduction Most, but not all, salaries and prices have soared over the decades. To
MATH 0030 Lecture Notes Section.1 The Addition Property of Equality Section. The Multiplication Property of Equality Introduction Most, but not all, salaries and prices have soared over the decades. To
Math Review. for the Quantitative Reasoning measure of the GRE General Test
 Math Review for the Quantitative Reasoning measure of the GRE General Test www.ets.org Overview This Math Review will familiarize you with the mathematical skills and concepts that are important for solving
Math Review for the Quantitative Reasoning measure of the GRE General Test www.ets.org Overview This Math Review will familiarize you with the mathematical skills and concepts that are important for solving
ALGEBRA I END-OF-COURSE EXAM: PRACTICE TEST
 Page 1 ALGEBRA I END-OF-COURSE EXAM: PRACTICE TEST 1. Order the following numbers from least to greatest:, 6, 8.7 10 0, 19 b. 19,, 8.7 100, 6 6, 8.7 10 0,, 19 c. d. 8.7 10 0,, 19, 6, 6, 19, 8.7 100. If
Page 1 ALGEBRA I END-OF-COURSE EXAM: PRACTICE TEST 1. Order the following numbers from least to greatest:, 6, 8.7 10 0, 19 b. 19,, 8.7 100, 6 6, 8.7 10 0,, 19 c. d. 8.7 10 0,, 19, 6, 6, 19, 8.7 100. If
Chapter 1-2 Add and Subtract Integers
 Chapter 1-2 Add and Subtract Integers Absolute Value of a number is its distance from zero on the number line. 5 = 5 and 5 = 5 Adding Numbers with the Same Sign: Add the absolute values and use the sign
Chapter 1-2 Add and Subtract Integers Absolute Value of a number is its distance from zero on the number line. 5 = 5 and 5 = 5 Adding Numbers with the Same Sign: Add the absolute values and use the sign
Chapter 1. Lesson 1.1 Practice Set x 11x = (2 x 11)x = 22x y = 1.35y. 5. 5m + 7 when m = (3) + 7 = = 22
 Chapter 1 Lesson 1.1 Practice Set 1. 2 x 11x = (2 x 11)x = 22x 2. 1.35 y = 1.35y 5. 5m + 7 when m = 3 6. 5(3) + 7 = 15 + 7 = 22 7. 8. 1 c when c = 63 3 1 1 63 63 (63) 21 3 3 1 3 9. $8.15(h) when h = 43
Chapter 1 Lesson 1.1 Practice Set 1. 2 x 11x = (2 x 11)x = 22x 2. 1.35 y = 1.35y 5. 5m + 7 when m = 3 6. 5(3) + 7 = 15 + 7 = 22 7. 8. 1 c when c = 63 3 1 1 63 63 (63) 21 3 3 1 3 9. $8.15(h) when h = 43
Lesson 22: Solving Equations Using Algebra
 Student Outcomes Students use algebra to solve equations (of the form px + q = r and p(x + q) = r, where p, q, and r are specific rational numbers); using techniques of making zero (adding the additive
Student Outcomes Students use algebra to solve equations (of the form px + q = r and p(x + q) = r, where p, q, and r are specific rational numbers); using techniques of making zero (adding the additive
This is a review packet for the entire fall semester of Algebra I at Harrison.
 HARRISON HIGH SCHOOL ALGEBRA I Fall Semester Review Packet This is a review packet for the entire fall semester of Algebra I at Harrison. You are receiving it now so that: you will have plenty of time
HARRISON HIGH SCHOOL ALGEBRA I Fall Semester Review Packet This is a review packet for the entire fall semester of Algebra I at Harrison. You are receiving it now so that: you will have plenty of time
REVIEW Chapter 1 The Real Number System
 REVIEW Chapter The Real Number System In class work: Complete all statements. Solve all exercises. (Section.4) A set is a collection of objects (elements). The Set of Natural Numbers N N = {,,, 4, 5, }
REVIEW Chapter The Real Number System In class work: Complete all statements. Solve all exercises. (Section.4) A set is a collection of objects (elements). The Set of Natural Numbers N N = {,,, 4, 5, }
This is Solving Linear Systems, chapter 4 from the book Beginning Algebra (index.html) (v. 1.0).
 This is Solving Linear Systems, chapter 4 from the book Beginning Algebra (index.html) (v. 1.0). This book is licensed under a Creative Commons by-nc-sa 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/
This is Solving Linear Systems, chapter 4 from the book Beginning Algebra (index.html) (v. 1.0). This book is licensed under a Creative Commons by-nc-sa 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/
Multiplication and Division
 UNIT 3 Multiplication and Division Skaters work as a pair to put on quite a show. Multiplication and division work as a pair to solve many types of problems. 82 UNIT 3 MULTIPLICATION AND DIVISION Isaac
UNIT 3 Multiplication and Division Skaters work as a pair to put on quite a show. Multiplication and division work as a pair to solve many types of problems. 82 UNIT 3 MULTIPLICATION AND DIVISION Isaac
Study Guide for Math 095
 Study Guide for Math 095 David G. Radcliffe November 7, 1994 1 The Real Number System Writing a fraction in lowest terms. 1. Find the largest number that will divide into both the numerator and the denominator.
Study Guide for Math 095 David G. Radcliffe November 7, 1994 1 The Real Number System Writing a fraction in lowest terms. 1. Find the largest number that will divide into both the numerator and the denominator.
Class 7 Integers. Answer the questions. Choose correct answer(s) from the given choices. Fill in the blanks
 ID : in-7-integers [1] Class 7 Integers For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer the questions (1) An integer is divided by 4 and gives a remainder of 3. The resulting quotient is divided
ID : in-7-integers [1] Class 7 Integers For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer the questions (1) An integer is divided by 4 and gives a remainder of 3. The resulting quotient is divided
1. What numbers sum to 10? ex. 1 9,
 Basic Algebra No calculator unless specified otherwise.. What numbers sum to 0? e. 9, 8. 0 8. 6 4. What coin combinations make a dollar? e. 4 quarters. 800/40 0 6. 4 0. Find. 6 7. 7. Find. 8. What time
Basic Algebra No calculator unless specified otherwise.. What numbers sum to 0? e. 9, 8. 0 8. 6 4. What coin combinations make a dollar? e. 4 quarters. 800/40 0 6. 4 0. Find. 6 7. 7. Find. 8. What time
Accelerated Intermediate 2 Summer Math Packet
 Chapter 1: Expressions, Equations, and Functions For Questions 1-2, write an algebraic expression for each verbal expression. 1. the sum of the square of a number and 34 2. the product of 5 and twice a
Chapter 1: Expressions, Equations, and Functions For Questions 1-2, write an algebraic expression for each verbal expression. 1. the sum of the square of a number and 34 2. the product of 5 and twice a
(x + 1)(x 2) = 4. x
 dvanced Integration Techniques: Partial Fractions The method of partial fractions can occasionally make it possible to find the integral of a quotient of rational functions. Partial fractions gives us
dvanced Integration Techniques: Partial Fractions The method of partial fractions can occasionally make it possible to find the integral of a quotient of rational functions. Partial fractions gives us
Part 1 - Pre-Algebra Summary Page 1 of 22 1/19/12
 Part 1 - Pre-Algebra Summary Page 1 of 1/19/1 Table of Contents 1. Numbers... 1.1. NAMES FOR NUMBERS... 1.. PLACE VALUES... 3 1.3. INEQUALITIES... 4 1.4. ROUNDING... 4 1.5. DIVISIBILITY TESTS... 5 1.6.
Part 1 - Pre-Algebra Summary Page 1 of 1/19/1 Table of Contents 1. Numbers... 1.1. NAMES FOR NUMBERS... 1.. PLACE VALUES... 3 1.3. INEQUALITIES... 4 1.4. ROUNDING... 4 1.5. DIVISIBILITY TESTS... 5 1.6.
1.4 Properties of Real Numbers and Algebraic Expressions
 0 CHAPTER Real Numbers and Algebraic Expressions.4 Properties of Real Numbers and Algebraic Expressions S Use Operation and Order Symbols to Write Mathematical Sentences. 2 Identify Identity Numbers and
0 CHAPTER Real Numbers and Algebraic Expressions.4 Properties of Real Numbers and Algebraic Expressions S Use Operation and Order Symbols to Write Mathematical Sentences. 2 Identify Identity Numbers and
Fundamentals of Mathematics I
 Fundamentals of Mathematics I Kent State Department of Mathematical Sciences Fall 2008 Available at: http://www.math.kent.edu/ebooks/10031/book.pdf August 4, 2008 Contents 1 Arithmetic 2 1.1 Real Numbers......................................................
Fundamentals of Mathematics I Kent State Department of Mathematical Sciences Fall 2008 Available at: http://www.math.kent.edu/ebooks/10031/book.pdf August 4, 2008 Contents 1 Arithmetic 2 1.1 Real Numbers......................................................
Chapter 1: Fundamental Concepts
 Chapter : Fundamental Concepts Prep Test. 875 + 9 = 9. 60 58 =. 9(07) = 5,87. 56 9 5. 7.6 6. 7. 68 0 8 08 88 a, c, d are greater than 8. 0.5 7 0.7 0 0.75 89 0.89 00 a and C, b and D, c and A, d and B.
Chapter : Fundamental Concepts Prep Test. 875 + 9 = 9. 60 58 =. 9(07) = 5,87. 56 9 5. 7.6 6. 7. 68 0 8 08 88 a, c, d are greater than 8. 0.5 7 0.7 0 0.75 89 0.89 00 a and C, b and D, c and A, d and B.
Solutions Key Exponential and Radical Functions
 CHAPTER 11 Solutions Key Exponential and Radical Functions xzare YOU READY, PAGE 76 1. B; like terms: terms that contain the same variable raised to the same power. F; square root: one of two equal factors
CHAPTER 11 Solutions Key Exponential and Radical Functions xzare YOU READY, PAGE 76 1. B; like terms: terms that contain the same variable raised to the same power. F; square root: one of two equal factors
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES. ALGEBRA I Part II 1 st Nine Weeks,
 STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES ALGEBRA I Part II 1 st Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 OVERVIEW Algebra I Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES ALGEBRA I Part II 1 st Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 OVERVIEW Algebra I Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource
CHAPTER 2 Solving Equations and Inequalities
 CHAPTER Solving Equations and Inequalities Section. Linear Equations and Problem Solving........... 8 Section. Solving Equations Graphically............... 89 Section. Comple Numbers......................
CHAPTER Solving Equations and Inequalities Section. Linear Equations and Problem Solving........... 8 Section. Solving Equations Graphically............... 89 Section. Comple Numbers......................
KNOWLEDGE OF NUMBER SENSE, CONCEPTS, AND OPERATIONS
 DOMAIN I. COMPETENCY 1.0 MATHEMATICS KNOWLEDGE OF NUMBER SENSE, CONCEPTS, AND OPERATIONS Skill 1.1 Compare the relative value of real numbers (e.g., integers, fractions, decimals, percents, irrational
DOMAIN I. COMPETENCY 1.0 MATHEMATICS KNOWLEDGE OF NUMBER SENSE, CONCEPTS, AND OPERATIONS Skill 1.1 Compare the relative value of real numbers (e.g., integers, fractions, decimals, percents, irrational
Math Analysis Chapter 2 Notes: Polynomial and Rational Functions
 Math Analysis Chapter Notes: Polynomial and Rational Functions Day 13: Section -1 Comple Numbers; Sections - Quadratic Functions -1: Comple Numbers After completing section -1 you should be able to do
Math Analysis Chapter Notes: Polynomial and Rational Functions Day 13: Section -1 Comple Numbers; Sections - Quadratic Functions -1: Comple Numbers After completing section -1 you should be able to do
Write an equation for each relationship. Then make a table of input-output pairs and tell whether the function is proportional.
 Functions Reteaching 41 Math Course, Lesson 41 A function is a rule that identifies a relationship between a set of input numbers and a set of output numbers. A function rule can be described in words,
Functions Reteaching 41 Math Course, Lesson 41 A function is a rule that identifies a relationship between a set of input numbers and a set of output numbers. A function rule can be described in words,
DISTANCE, RATE, AND TIME 7.1.1
 DISTANCE, RATE, AND TIME 7.1.1 Distance (d) equals the product of the rate of speed (r) and the time (t). This relationship is shown below in three forms: d = r!t!!!!!!!!!r = d t!!!!!!!!!t = d r It is
DISTANCE, RATE, AND TIME 7.1.1 Distance (d) equals the product of the rate of speed (r) and the time (t). This relationship is shown below in three forms: d = r!t!!!!!!!!!r = d t!!!!!!!!!t = d r It is
Warm-Up. Use long division to divide 5 into
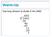 Warm-Up Use long division to divide 5 into 3462. 692 5 3462-30 46-45 12-10 2 Warm-Up Use long division to divide 5 into 3462. Divisor 692 5 3462-30 46-45 12-10 2 Quotient Dividend Remainder Warm-Up Use
Warm-Up Use long division to divide 5 into 3462. 692 5 3462-30 46-45 12-10 2 Warm-Up Use long division to divide 5 into 3462. Divisor 692 5 3462-30 46-45 12-10 2 Quotient Dividend Remainder Warm-Up Use
Chapter 7 - Exponents and Exponential Functions
 Chapter 7 - Exponents and Exponential Functions 7-1: Multiplication Properties of Exponents 7-2: Division Properties of Exponents 7-3: Rational Exponents 7-4: Scientific Notation 7-5: Exponential Functions
Chapter 7 - Exponents and Exponential Functions 7-1: Multiplication Properties of Exponents 7-2: Division Properties of Exponents 7-3: Rational Exponents 7-4: Scientific Notation 7-5: Exponential Functions
ALGEBRA CLAST MATHEMATICS COMPETENCIES
 2 ALGEBRA CLAST MATHEMATICS COMPETENCIES IC1a: IClb: IC2: IC3: IC4a: IC4b: IC: IC6: IC7: IC8: IC9: IIC1: IIC2: IIC3: IIC4: IIIC2: IVC1: IVC2: Add and subtract real numbers Multiply and divide real numbers
2 ALGEBRA CLAST MATHEMATICS COMPETENCIES IC1a: IClb: IC2: IC3: IC4a: IC4b: IC: IC6: IC7: IC8: IC9: IIC1: IIC2: IIC3: IIC4: IIIC2: IVC1: IVC2: Add and subtract real numbers Multiply and divide real numbers
Unit Essential Questions. What are the different representations of exponents? Where do exponents fit into the real number system?
 Unit Essential Questions What are the different representations of exponents? Where do exponents fit into the real number system? How can exponents be used to depict real-world situations? REAL NUMBERS
Unit Essential Questions What are the different representations of exponents? Where do exponents fit into the real number system? How can exponents be used to depict real-world situations? REAL NUMBERS
6 Linear Equations: Real
 www.ck12.org CHAPTER 6 Linear Equations: Real World Applications Chapter Outline 6.1 WRITING EQUATIONS 6.2 RATIOS AND PROPORTIONS 6.3 SCALE AND INDIRECT MEASUREMENT 6.4 PERCENT PROBLEMS Algebra can be
www.ck12.org CHAPTER 6 Linear Equations: Real World Applications Chapter Outline 6.1 WRITING EQUATIONS 6.2 RATIOS AND PROPORTIONS 6.3 SCALE AND INDIRECT MEASUREMENT 6.4 PERCENT PROBLEMS Algebra can be
Basic Property: of Rational Expressions
 Basic Properties of Rational Expressions A rational expression is any expression of the form P Q where P and Q are polynomials and Q 0. In the following properties, no denominator is allowed to be zero.
Basic Properties of Rational Expressions A rational expression is any expression of the form P Q where P and Q are polynomials and Q 0. In the following properties, no denominator is allowed to be zero.
8th Grade Math Definitions
 8th Grade Math Definitions Absolute Value: 1. A number s distance from zero. 2. For any x, is defined as follows: x = x, if x < 0; x, if x 0. Acute Angle: An angle whose measure is greater than 0 and less
8th Grade Math Definitions Absolute Value: 1. A number s distance from zero. 2. For any x, is defined as follows: x = x, if x < 0; x, if x 0. Acute Angle: An angle whose measure is greater than 0 and less
L1 2.1 Long Division of Polynomials and The Remainder Theorem Lesson MHF4U Jensen
 L1 2.1 Long Division of Polynomials and The Remainder Theorem Lesson MHF4U Jensen In this section you will apply the method of long division to divide a polynomial by a binomial. You will also learn to
L1 2.1 Long Division of Polynomials and The Remainder Theorem Lesson MHF4U Jensen In this section you will apply the method of long division to divide a polynomial by a binomial. You will also learn to
addend angle composite number capacity Vocabulary Flash Cards Review Review Review Review Review Review
 addend angle area bar graph capacity composite number cubic units difference A figure formed by two rays with the same endpoint A number to be added to another number. 2 or 3 in the sum 2 + 3. A graph
addend angle area bar graph capacity composite number cubic units difference A figure formed by two rays with the same endpoint A number to be added to another number. 2 or 3 in the sum 2 + 3. A graph
The P/Q Mathematics Study Guide
 The P/Q Mathematics Study Guide Copyright 007 by Lawrence Perez and Patrick Quigley All Rights Reserved Table of Contents Ch. Numerical Operations - Integers... - Fractions... - Proportion and Percent...
The P/Q Mathematics Study Guide Copyright 007 by Lawrence Perez and Patrick Quigley All Rights Reserved Table of Contents Ch. Numerical Operations - Integers... - Fractions... - Proportion and Percent...
Name: Class: Date: ID: A. Identify the hypothesis and conclusion of the statement. Then write the statement in if-then form.
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A 7 Short Answer 1. 12x Write a verbal expression for the algebraic expression. 2. 3 5 + 2 Identify the hypothesis and conclusion of the statement. Then write the statement in if-then
Name: Class: Date: ID: A 7 Short Answer 1. 12x Write a verbal expression for the algebraic expression. 2. 3 5 + 2 Identify the hypothesis and conclusion of the statement. Then write the statement in if-then
1.2 Constructing Models to Solve Problems
 1.2 Constructing Models to Solve Problems In the previous section, we learned how to solve linear equations. In this section, we will put those skills to use in order to solve a variety of application
1.2 Constructing Models to Solve Problems In the previous section, we learned how to solve linear equations. In this section, we will put those skills to use in order to solve a variety of application
Appendix: Synthetic Division
 Appendix: Synthetic Division AP Learning Objectives In this section, we will learn how to: 1. Divide polynomials using synthetic division. Synthetic division is a short form of long division with polynomials.
Appendix: Synthetic Division AP Learning Objectives In this section, we will learn how to: 1. Divide polynomials using synthetic division. Synthetic division is a short form of long division with polynomials.
More Polynomial Equations Section 6.4
 MATH 11009: More Polynomial Equations Section 6.4 Dividend: The number or expression you are dividing into. Divisor: The number or expression you are dividing by. Synthetic division: Synthetic division
MATH 11009: More Polynomial Equations Section 6.4 Dividend: The number or expression you are dividing into. Divisor: The number or expression you are dividing by. Synthetic division: Synthetic division
Practice Set 1.1 Algebraic Expressions and Real Numbers. Translate each English phrase into an algebraic expression. Let x represent the number.
 Practice Set 1.1 Algebraic Expressions and Real Numbers Translate each English phrase into an algebraic expression. Let x represent the number. 1. A number decreased by seven. 1.. Eighteen more than a
Practice Set 1.1 Algebraic Expressions and Real Numbers Translate each English phrase into an algebraic expression. Let x represent the number. 1. A number decreased by seven. 1.. Eighteen more than a
Math Departmental Exit Assessment Review (Student Version)
 Math 008 - Departmental Eit Assessment Review (Student Version) Solve the equation. (Section.) ) ( + ) - 8 = 6-80 - 0 ) + - - 7 = 0-60 - 0 ) 8 + 9 = 9 - - ) - = 60 0-0 -60 ) 0.0 + 0.0(000 - ) = 0.0 0 6000
Math 008 - Departmental Eit Assessment Review (Student Version) Solve the equation. (Section.) ) ( + ) - 8 = 6-80 - 0 ) + - - 7 = 0-60 - 0 ) 8 + 9 = 9 - - ) - = 60 0-0 -60 ) 0.0 + 0.0(000 - ) = 0.0 0 6000
Beginning Algebra. v. 1.0
 Beginning Algebra v. 1.0 Table of Contents About the Author... 1 Acknowledgments... 2 Preface... 3 Chapter 1: Real Numbers and Their Operations... 5 Real Numbers and the Number Line... 6 Adding and Subtracting
Beginning Algebra v. 1.0 Table of Contents About the Author... 1 Acknowledgments... 2 Preface... 3 Chapter 1: Real Numbers and Their Operations... 5 Real Numbers and the Number Line... 6 Adding and Subtracting
L1 2.1 Long Division of Polynomials and The Remainder Theorem Lesson MHF4U Jensen
 L1 2.1 Long Division of Polynomials and The Remainder Theorem Lesson MHF4U Jensen In this section you will apply the method of long division to divide a polynomial by a binomial. You will also learn to
L1 2.1 Long Division of Polynomials and The Remainder Theorem Lesson MHF4U Jensen In this section you will apply the method of long division to divide a polynomial by a binomial. You will also learn to
Name. Unit 1 Worksheets Math 150 College Algebra and Trig
 Name Unit 1 Worksheets Math 10 College Algebra and Trig Revised: Fall 009 Worksheet 1: Integral Eponents Simplify each epression. Write all answers in eponential form. 1. (8 ). ( y). (a b ). y 6. (7 8
Name Unit 1 Worksheets Math 10 College Algebra and Trig Revised: Fall 009 Worksheet 1: Integral Eponents Simplify each epression. Write all answers in eponential form. 1. (8 ). ( y). (a b ). y 6. (7 8
Term Definition Example. 3-D shapes or (3 dimensional) acute angle. addend. algorithm. area of a rectangle. array
 Term Definition Example 3-D shapes or (3 dimensional) an object that has height, width, and depth, like any object in the real world. acute angle an angle that is less than 90 addend a number that is added
Term Definition Example 3-D shapes or (3 dimensional) an object that has height, width, and depth, like any object in the real world. acute angle an angle that is less than 90 addend a number that is added
Algebra 2 Honors: Final Exam Review
 Name: Class: Date: Algebra 2 Honors: Final Exam Review Directions: You may write on this review packet. Remember that this packet is similar to the questions that you will have on your final exam. Attempt
Name: Class: Date: Algebra 2 Honors: Final Exam Review Directions: You may write on this review packet. Remember that this packet is similar to the questions that you will have on your final exam. Attempt
AP Environmental Science Math Prep
 AP Environmental Science Math Prep This year in APES you will hear the two words most dreaded by high school students NO CALCULATORS! That s right, you cannot use a calculator on the AP Environmental Science
AP Environmental Science Math Prep This year in APES you will hear the two words most dreaded by high school students NO CALCULATORS! That s right, you cannot use a calculator on the AP Environmental Science
Algebra 1: Hutschenreuter Chapter 11 Note Packet Ratio and Proportion
 Algebra 1: Hutschenreuter Chapter 11 Note Packet Name 11.1 Ratio and Proportion Proportion: an equation that states that two ratios are equal a c = b 0, d 0 a is to b as c is to d b d Etremes: a and d
Algebra 1: Hutschenreuter Chapter 11 Note Packet Name 11.1 Ratio and Proportion Proportion: an equation that states that two ratios are equal a c = b 0, d 0 a is to b as c is to d b d Etremes: a and d
Chapter 1: Review of Real Numbers
 Chapter : Review of Real Numbers PREP TEST. a..; C....... 7 + + + 9 8 7 8. 9.. + 7. 9. 8.7 7. 9 b. 7.7; D. c..7; A. d. 89.89; B. GO FIGURE If the areas of the known rectangles are,, and, the corresponding
Chapter : Review of Real Numbers PREP TEST. a..; C....... 7 + + + 9 8 7 8. 9.. + 7. 9. 8.7 7. 9 b. 7.7; D. c..7; A. d. 89.89; B. GO FIGURE If the areas of the known rectangles are,, and, the corresponding
Math Workshop Prealgebra/Numerical Skills
 Math Workshop Prealgebra/Numerical Skills Workshop Objective: Once a student successfully completes the Prealgebra Math Workshop, s/he will achieve a basic understanding the material taught in a MAT 060
Math Workshop Prealgebra/Numerical Skills Workshop Objective: Once a student successfully completes the Prealgebra Math Workshop, s/he will achieve a basic understanding the material taught in a MAT 060
Algebra 1 Unit 6: Linear Inequalities and Absolute Value Guided Notes
 Section 6.1: Solving Inequalities by Addition and Subtraction How do we solve the equation: x 12 = 65? How do we solve the equation: x 12 < 65? Graph the solution: Example 1: 12 y 9 Example 2: q + 23
Section 6.1: Solving Inequalities by Addition and Subtraction How do we solve the equation: x 12 = 65? How do we solve the equation: x 12 < 65? Graph the solution: Example 1: 12 y 9 Example 2: q + 23
ALGEBRA 1 CST Questions (2009)
 1 Is the equation 3(x ) = 18 equivalent to 6x 1 = 18? Yes, the equations are equivalent by the ssociative Property of Multiplication. Yes, the equations are equivalent by the ommutative Property of Multiplication.
1 Is the equation 3(x ) = 18 equivalent to 6x 1 = 18? Yes, the equations are equivalent by the ssociative Property of Multiplication. Yes, the equations are equivalent by the ommutative Property of Multiplication.
Polynomial and Rational Functions. Chapter 3
 Polynomial and Rational Functions Chapter 3 Quadratic Functions and Models Section 3.1 Quadratic Functions Quadratic function: Function of the form f(x) = ax 2 + bx + c (a, b and c real numbers, a 0) -30
Polynomial and Rational Functions Chapter 3 Quadratic Functions and Models Section 3.1 Quadratic Functions Quadratic function: Function of the form f(x) = ax 2 + bx + c (a, b and c real numbers, a 0) -30
N= {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,...}
 1.1: Integers and Order of Operations 1. Define the integers 2. Graph integers on a number line. 3. Using inequality symbols < and > 4. Find the absolute value of an integer 5. Perform operations with
1.1: Integers and Order of Operations 1. Define the integers 2. Graph integers on a number line. 3. Using inequality symbols < and > 4. Find the absolute value of an integer 5. Perform operations with
Sail into Summer with Math!
 Sail into Summer with Math! For Students Entering Algebra 1 This summer math booklet was developed to provide students in kindergarten through the eighth grade an opportunity to review grade level math
Sail into Summer with Math! For Students Entering Algebra 1 This summer math booklet was developed to provide students in kindergarten through the eighth grade an opportunity to review grade level math
The first thing we want to do is review basic solving of equations. We will start with linear equations.
 R.1 Equations The first thing we want to do is review basic solving of equations. We will start with linear equations. A few key ideas to remember is when solving equations we are usually trying to get
R.1 Equations The first thing we want to do is review basic solving of equations. We will start with linear equations. A few key ideas to remember is when solving equations we are usually trying to get
Early Start: Worksheet #1 No calculator/phone use (11 16) (17 10)3
 Early Start: Worksheet #1 No calculator/phone use I. Perform the operations; simplify completely. a) 8 ( + 4) ( 7) + ( 1) b) (11 16) (17 10) c) 7 14 6 d) 1 6 5 e) 4 1 + f) 6 9() 10 + 5 5 1 5 4 g) 9 9 +
Early Start: Worksheet #1 No calculator/phone use I. Perform the operations; simplify completely. a) 8 ( + 4) ( 7) + ( 1) b) (11 16) (17 10) c) 7 14 6 d) 1 6 5 e) 4 1 + f) 6 9() 10 + 5 5 1 5 4 g) 9 9 +
Keystone Exam Concept Review. Properties and Order of Operations. Linear Equations and Inequalities Solve the equations. 1)
 Keystone Exam Concept Review Name: Properties and Order of Operations COMMUTATIVE Property of: Addition ASSOCIATIVE Property of: Addition ( ) ( ) IDENTITY Property of Addition ZERO PRODUCT PROPERTY Let
Keystone Exam Concept Review Name: Properties and Order of Operations COMMUTATIVE Property of: Addition ASSOCIATIVE Property of: Addition ( ) ( ) IDENTITY Property of Addition ZERO PRODUCT PROPERTY Let
Grade 7 Mathematics Fall Benchmark Blueprint
 7.NS.1a-d Apply and extend previous understandings of addition and subtraction to add and subtract rational numbers; represent addition and subtraction on a horizontal or vertical number line diagram.
7.NS.1a-d Apply and extend previous understandings of addition and subtraction to add and subtract rational numbers; represent addition and subtraction on a horizontal or vertical number line diagram.
Mini-Lesson 9. Section 9.1: Relations and Functions. Definitions
 9 Section 9.1: Relations and Functions A RELATION is any set of ordered pairs. Definitions A FUNCTION is a relation in which every input value is paired with exactly one output value. Table of Values One
9 Section 9.1: Relations and Functions A RELATION is any set of ordered pairs. Definitions A FUNCTION is a relation in which every input value is paired with exactly one output value. Table of Values One
Glossary. Glossary 981. Hawkes Learning Systems. All rights reserved.
 A Glossary Absolute value The distance a number is from 0 on a number line Acute angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Addends The numbers being added in an addition problem Addition principle
A Glossary Absolute value The distance a number is from 0 on a number line Acute angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Addends The numbers being added in an addition problem Addition principle
6.5 Dividing Polynomials
 Name Class Date 6.5 Dividing Polynomials Essential Question: What are some ways to divide polynomials, and how do you know when the divisor is a factor of the dividend? Explore Evaluating a Polynomial
Name Class Date 6.5 Dividing Polynomials Essential Question: What are some ways to divide polynomials, and how do you know when the divisor is a factor of the dividend? Explore Evaluating a Polynomial
Unit 1: Introduction to Variables
 Section 1.1: Writing Algebraic Expressions Section 1.2: The Story of x Section 1.3: Evaluating Algebraic Expressions Section 1.4: Applications Section 1.5: Geometric Formulas KEY TERMS AND CONCEPTS Look
Section 1.1: Writing Algebraic Expressions Section 1.2: The Story of x Section 1.3: Evaluating Algebraic Expressions Section 1.4: Applications Section 1.5: Geometric Formulas KEY TERMS AND CONCEPTS Look
WORKBOOK. MTH 01 - FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS AND SKILLS IN ARITHMETIC AND ALGEBRA. DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE
 WORKBOOK. MTH 01 - FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS AND SKILLS IN ARITHMETIC AND ALGEBRA. DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Contributors: M. Bates, U. N. Iyer Department of Mathematics and Computer Science,
WORKBOOK. MTH 01 - FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS AND SKILLS IN ARITHMETIC AND ALGEBRA. DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE Contributors: M. Bates, U. N. Iyer Department of Mathematics and Computer Science,
Systems of Equations. Red Company. Blue Company. cost. 30 minutes. Copyright 2003 Hanlonmath 1
 Chapter 6 Systems of Equations Sec. 1 Systems of Equations How many times have you watched a commercial on television touting a product or services as not only the best, but the cheapest? Let s say you
Chapter 6 Systems of Equations Sec. 1 Systems of Equations How many times have you watched a commercial on television touting a product or services as not only the best, but the cheapest? Let s say you
