Impact Analysis of Frontal Car Bumper using Long Fibre Reinforced Thermoplastics
|
|
|
- Noel Jennings
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN , P-ISSN INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at Research Article Impact Analysis of Frontal Car Bumper using Long Fibre Reinforced Thermoplastics Lingam Ramyasree, D.Venkataramaniah and G.Naveen Kumar * Balaji Institute of Engineering and Sciences, Warangal, Telangana, India Department of Mechanical Engineering, CVR College of Engineering, Hyderabad, Telangana, India Accepted 31 May 2015, Available online 02 June 2015, Vol.5, No.3 (June 2015) Abstract The front and rear of the vehicle should be protected in such a manner that low speed collisions will only damage the vehicle slightly, or not at all. In automotive components the use of natural fibers has increased to reduce the weight and increase the strength and safety of the automobile components. Natural Fiber Thermoplastic components in automotive industry can afford the advantages of weight, cost reduction and recyclability, compared to conventional materials. The purpose of this project is to design a bumper which is to improve crashworthiness of the bumper beam. These materials had been studied by impact modeling using Finite Element Analysis software, LS DYNA to determine the energy absorption by analyzing the kinetic energy, displacement and impact force. The selected materials are compared to each other for the design parameters like shape, material and impact condition to validate the crashworthiness. Keywords: LS DYNA, Natural Fibre Thermoplastics. 1. Introduction 1 Automotive bumper beam is a structural component placed behind plastic fascia either in front or rear ends of bumper system mainly to absorb kinetic energy during collision. In low speed collision bumper beam provides protection to occupant from severe injury. Bumper system is designed with the aim to absorb 80% percent of kinetic energy during collision. The main function of a bumper system is to protect the car body and passengers against collision. There are two main components of bumper beam, namely horizontal beam and axial beam or crush box and it is moulded in single piece. The easiest way to do this is simply to download the template, and replace (copy-paste) the content with your own material. however in the mid 80 s, the application of polymer composite material was introduced to replace conventional material such as plastic, aluminium and metal, as it can offer low weight, corrosion free, easier to produce complex shapes, high specific stiffness (stiffness/weight), and high impact energy absorption capacity over its metal counterparts. Furthermore, the use of polymeric based composite material for bumper beam is proposed for the quest of high fuel efficiency in automobiles, and having comparable properties to conventional glass fibers without sacrificing the safety of cars. The *Corresponding author: G.Naveen Kumar; Lingam Ramyasree is a M.Tech Scholar bumper beam is the key structure that helps to absorb the kinetic energy from a high-impact collision and to provide bending resistance in a low-impact collision; therefore the bumper beam is a structural component. The bumper system has to meet deflection and crash stability criteria, established by customers, legislation and insurance companies. 2. Problem Formulation The purpose of this project is to develop a natural fiber reinforced thermoplastic composite as a bumper beam material and to investigate the mechanical, thermal and recycling properties. In the design and analysis the bumper specifications were taken from the standard passenger car, then the modeling of the bumper was done by the PRO E and, then the fine meshing was done by hypermesh software for accurate results. Then the impact loading was applied using LSDYNA to analyze the energy absorbing capacity of the bumper materials. In this research, the various bumper materials like Steel, Aluminum, Glass Mat Thermoplastics (GMT), Sheet Molding Compound (SMC) and Long Fiber Reinforced Thermoplastics (LFRT) were selected for the crash performance of front bumper beam using Finite Element Analysis. These materials were studied by impact modeling to determine the Kinetic Energy, displacement and impact force. The selected materials were compared to each other for the design parameters like shape, material and impact condition International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology, Vol.5, No.3 (June 2015)
2 Simulation was done using Finite Element Analysis software, LS DYNA. 3. Mechanical Properties of Materials The properties of steel, aluminium, GMT and LFRT KLFRT were taken from literature review (Mahmood et al 2008). Material Table 1 Properties of materials Young s modulus (GPa) Poisson ratio Yield strength (GPa) Densit y (Kg/ m 3 ) Steel Aluminium GMT LFRT KLFRT Analysis of Bumper Fig.1 Model 4.1 Development of Mathematical model for frontal Impactor The pendulum is modeled simply as a rigid solid of mass M with an initial velocity of V. The car of equivalent mass M is a rigid solid. Bumper beam stiffness is included in the model as a spring of stiffness K. This stiffness can be identified either experimentally or analytically. From the mechanics of materials, the stiffness of the beam is K= 48EI/L³ when the external loads applied on its center. Here the E is the Young s modulus of the materials, I is the moment of inertia and L the total length of the bumper beam. K B = Load /deflection = F/y (1) The governing differential equation for dynamic system is Mx 1 K B (x 1 -x 2) = 0 (2) Mx 2 K B (x 1 -x 2) = 0 (3) x 1 = 0 (4) x 1 (0) = V (5) x 2 (0) = 0 (6) x 2 (0) = V (7) Linear equations lead to x 1= V/2 t + V/2 2 ὠ sin 2ὠt (8) x 2= V/2 t + V/2 2 ὠ sin 2ὠt (9) t and ὠ stands for time and angular velocity. ὠ = K B/M (10) The total force exerted by the pendulum on bumper can be derived from (8) and (9) as t π/ 2ὠ (11) F=K B(x 1-x 2) (12) F= V K BM/2 sin 2ὠt (13) F max= V K BM/2 (14) Fig.2 Meshed model of impactor and bumper The distance between bumper beam and impactor is 40 mm. LSDYNA software was used for crash analysis. For FMVS velocity of impact barrier selected is 48kmph and for IIHS standard 68 kmph is selected. Crash type was frontal impact. Due to stretch there were residual stresses in bumper beam. From the simulation the bumper beam was shortened in axial direction. The model from PRO-E is imported into HYPERMESH for fine meshing and for analyzing LS DYNA software was used. During impact event when force is zero and that total impact duration, τ s can be expressed as from equation τ s = π/ 2ὠ (15) The equation states mass and velocity in terms of structural loads. Such loads are important for finite element analysis. For different impact velocities and masses of automobile the variation of structural loads can be clearly defined. During impact event the velocity of automobile increases and pendulum velocity decreases. Due to this bumper cannot absorb total kinetic energy of pendulum. During impact the amount of energy absorb U by the bumper can be defined as U = 1/2 K B [(x 1-x 2) max ] 2 (16) 1862 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology, Vol.5, No.3 (June 2015)
3 U = 1/2 F 2 max/ K B = ¼ MV 2 (17) Conservation of energy is used for elastic impact Before impact K.E is converted to elastic energy. Therefore maximum deflection i.e., 1/2mV 12 =1/2 K B [(x 1-x 2) max ] 2 +1/2mV 22 +1/2MV 2 2 (18) Spring constant K B=48EI/L 3 (19) 4.2 Displacement results Table 2 Displacement for different materials Fig.5 Aluminium as per FMVSS LFR KLF Material Steel Aluminium GMT T RT Displacement s (mm) Table 3 Impact Force for different materials Material Steel Aluminium GMT LFRT KLF RT Impact Force (kn) Fig.6 Aluminium as per IIHS 4.3 Distribution of energy for different materials Fig.7 LFRT as per FMVSS Fig.3 Steel as per FMVSS Fig.8 LFRT as per IIHS Fig.4 Steel as per IIHS Fig.9 KLFRT as per FMVSS 1863 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology, Vol.5, No.3 (June 2015)
4 4.5 Impact Force v/s time for different materials Fig.10 KLFRT as per IIHS 4.4 Displacement v/s time for different materials The pendulum collides with bumper at a velocity of 48 km/hr and 64 km/hr. Results were extracted from LSDYNA, according to the FMVS Standard and IIHS standard and comparison of the displacement with respect to time was plotted for the various types of materials. The pendulum hits the bumper with 48km/h velocity and 64km/h. The deflection is an important parameter to check the crashworthiness of the bumper beam material from a comparison of the graphs; it becomes clear that the KLFRT shows an increase in deflection. The deflection is directly proportional to material stiffness and yield strength. So the KLFRT can replace the conventional bumper materials. The maximum displacement of KLFRT was 61.2mm at 6.7ms as per FMVSS, 78.5mm at 6.2 ms as per IIHS. Fig.13 Impact v/s time for different materials (FMVS) Fig.14 Impact v/s time for different materials (IIHS) During collision impact energy is absorbed partly and remaining is converted to plastic deformation. Due to low rigidity, impact force for composites such as LFRT and KLFRT will have longer time interval. The thermoplastic materials will have more energy absorption compared with conventional material which is safe for the vehicle. From the above and due to less impact of collision natural fibre composites used for bumper can replace steel material. Conclusion Fig.11 Displacement v/s time for different materials (FMVS) Bumper was tested for frontal collision using FEA model to prove the ability of material for absorption of energy during collision. 1. This study focuses on comparison with conventional (steel, aluminium) and composite materials such as natural long fibres. 2. FMVSS and IIH standards were considered for impact test of bumper. LS Dyna software was used with various materials and regulations. 3. From the above analysis it is concluded that KLFRT material behaves good compared with other material and during frontal collision of bumper natural fibres have good energy absorption capacity. Fig.12 Displacement v/s time for different materials (IIHS) References Federal automotive standards part bumper standards, pp International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology, Vol.5, No.3 (June 2015)
5 Cheon, S. S., Choi, J. H. and Lee, D.G., (1995) Development of the Composite Bumper Beam for Passenger Cars, Composite Structures, Vol. 32, pp Cheon, S. S., Lim, T. S. and Lee, D. G., (1999), Impact Energy Absorption Characteristics of Glass Fiber Hybrid Composites, Composite Structures, Vol. 46, pp Sapuan, S.M., Maleque, M.A., Hameedullah, M., Suddin, M.N. and Ismail, N. 2004, A note on the conceptual design of polymeric composite automotive bumper system, J. Mater. Production Tech, Vol.159, pp Hosseinzadeh RM, Shokrieh M, and Lessard LB, (2005), Parametric study of automotive composite bumper beams subjected to low-velocity impacts, J. Composite Structure, 68: Marzbanrad JM, Alijanpour M, and Kiasat MS, (2009), Design and analysis of automotive bumper beam in low speed frontal crashes, Thin Walled Structure, 47: Lucital, 2011, Natural fibers in thermoplastic composites review Automotive magazine, pp International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology, Vol.5, No.3 (June 2015)
NONLINEAR STATIC SIMULATION OF AUTOMOTIVE BUMPER OF A PASSENGER CAR IN LOW SPEED IMPACT CRASH SIMULATION
 NONLINEAR STATIC SIMULATION OF AUTOMOTIVE BUMPER OF A PASSENGER CAR IN LOW SPEED IMPACT CRASH SIMULATION Rajshekhar A Kharde 1, S. F. Patil 2 1 M.Tech Student, KLE Dr. M.S Sheshgiri College of Engg & Tech,
NONLINEAR STATIC SIMULATION OF AUTOMOTIVE BUMPER OF A PASSENGER CAR IN LOW SPEED IMPACT CRASH SIMULATION Rajshekhar A Kharde 1, S. F. Patil 2 1 M.Tech Student, KLE Dr. M.S Sheshgiri College of Engg & Tech,
ANALYSIS AND DEVELOPMENT OF ENERGY ABSORBING CRASH BOX
 ANALYSIS AND DEVELOPMENT OF ENERGY ABSORBING CRASH BOX Dhananjay D.Desai 1, Prof.M.A.Kadam 2 1 Student, M.Tech CAD-CAM, Bharati Vidyapeeth Deemed University College of Engineering Pune, Maharashtra, India.
ANALYSIS AND DEVELOPMENT OF ENERGY ABSORBING CRASH BOX Dhananjay D.Desai 1, Prof.M.A.Kadam 2 1 Student, M.Tech CAD-CAM, Bharati Vidyapeeth Deemed University College of Engineering Pune, Maharashtra, India.
IMPACT STRENGTH AND RESPONSE BEHAVIOR OF CFRP GUARDER BELT FOR SIDE COLLISION OF AUTOMOBILES
 IMPACT STRENGTH AND RESPONSE BEHAVIOR OF CFRP GUARDER BELT FOR SIDE COLLISION OF AUTOMOBILES AOKI Y.*, BEN G.**, KIM H. S.* *College of Science & Technology, Nihon University **College of Industrial Technology,
IMPACT STRENGTH AND RESPONSE BEHAVIOR OF CFRP GUARDER BELT FOR SIDE COLLISION OF AUTOMOBILES AOKI Y.*, BEN G.**, KIM H. S.* *College of Science & Technology, Nihon University **College of Industrial Technology,
An orthotropic damage model for crash simulation of composites
 High Performance Structures and Materials III 511 An orthotropic damage model for crash simulation of composites W. Wang 1, F. H. M. Swartjes 1 & M. D. Gan 1 BU Automotive Centre of Lightweight Structures
High Performance Structures and Materials III 511 An orthotropic damage model for crash simulation of composites W. Wang 1, F. H. M. Swartjes 1 & M. D. Gan 1 BU Automotive Centre of Lightweight Structures
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 5, Issue 8, August ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 5, Issue 8, August 2015 1 Optimization of Impact attenuator design using Finite element method for Enhanced Vehicle Safety during collision
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 5, Issue 8, August 2015 1 Optimization of Impact attenuator design using Finite element method for Enhanced Vehicle Safety during collision
COMPARISON OF EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS WITH FEM ONES OF RECTANGULAR CFRP TUBES FOR FRONT SIDE MEMBERS OF AUTOMOBILES
 16 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS COMPARISON OF EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS WITH FEM ONES OF RECTANGULAR CFRP TUBES FOR FRONT SIDE MEMBERS OF AUTOMOBILES Hyoung-Soo Kim*, Goichi Ben**,Yoshio
16 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS COMPARISON OF EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS WITH FEM ONES OF RECTANGULAR CFRP TUBES FOR FRONT SIDE MEMBERS OF AUTOMOBILES Hyoung-Soo Kim*, Goichi Ben**,Yoshio
BEAMS AND PLATES ANALYSIS
 BEAMS AND PLATES ANALYSIS Automotive body structure can be divided into two types: i. Frameworks constructed of beams ii. Panels Classical beam versus typical modern vehicle beam sections Assumptions:
BEAMS AND PLATES ANALYSIS Automotive body structure can be divided into two types: i. Frameworks constructed of beams ii. Panels Classical beam versus typical modern vehicle beam sections Assumptions:
Crash Simulation and Analysis of a Car Body Using ANSYS LS- DYNA
 Failure of Engineering Materials & Structures Code 09 Crash Simulation and Analysis of a Car Body Using ANSYS LS- DYNA Waseem Sarwar 1 and Nasir Hayat 2 1 Student and 2 Professor, Mechanical Engineering
Failure of Engineering Materials & Structures Code 09 Crash Simulation and Analysis of a Car Body Using ANSYS LS- DYNA Waseem Sarwar 1 and Nasir Hayat 2 1 Student and 2 Professor, Mechanical Engineering
Finite Element Models for European Testing: Side Impact Barrier to WG13 Pedestrian Impactors to WG17
 4 th European LS-DYNA Users Conference Occupant II / Pedestrian Safety Finite Element Models for European Testing: Side Impact Barrier to WG13 Pedestrian Impactors to WG17 Trevor Dutton, Arup Solihull,
4 th European LS-DYNA Users Conference Occupant II / Pedestrian Safety Finite Element Models for European Testing: Side Impact Barrier to WG13 Pedestrian Impactors to WG17 Trevor Dutton, Arup Solihull,
Behavior of Tubular Hat Structure Under Three Point Bending
 International Journal of Transportation Engineering and Technology 2016; 2(5-1): 18-24 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com j/ijtet doi: 10.11648/j.ijtet.s.2016020501.14 Behavior of Tubular Hat Structure
International Journal of Transportation Engineering and Technology 2016; 2(5-1): 18-24 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com j/ijtet doi: 10.11648/j.ijtet.s.2016020501.14 Behavior of Tubular Hat Structure
Multi-objective design optimization of a frontal crash energy absorption system for a road-safe vehicle
 Multi-objective design optimization of a frontal crash energy absorption system for a road-safe vehicle Tiago Nunes tiagomenunes@tecnico.ulisboa.pt Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Portugal
Multi-objective design optimization of a frontal crash energy absorption system for a road-safe vehicle Tiago Nunes tiagomenunes@tecnico.ulisboa.pt Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Portugal
SIMPLIFIED MODELING OF THIN-WALLED TUBES WITH OCTAGONAL CROSS SECTION AXIAL CRUSHING. Authors and Correspondance: Abstract:
 SIMPLIFIED MODELING OF THIN-WALLED TUBES WITH OCTAGONAL CROSS SECTION AXIAL CRUSHING Authors and Correspondance: Yucheng Liu, Michael L. Day Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Louisville
SIMPLIFIED MODELING OF THIN-WALLED TUBES WITH OCTAGONAL CROSS SECTION AXIAL CRUSHING Authors and Correspondance: Yucheng Liu, Michael L. Day Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Louisville
VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF E-GLASS FIBRE RESIN MONO LEAF SPRING USED IN LMV
 VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF E-GLASS FIBRE RESIN MONO LEAF SPRING USED IN LMV Mohansing R. Pardeshi 1, Dr. (Prof.) P. K. Sharma 2, Prof. Amit Singh 1 M.tech Research Scholar, 2 Guide & Head, 3 Co-guide & Assistant
VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF E-GLASS FIBRE RESIN MONO LEAF SPRING USED IN LMV Mohansing R. Pardeshi 1, Dr. (Prof.) P. K. Sharma 2, Prof. Amit Singh 1 M.tech Research Scholar, 2 Guide & Head, 3 Co-guide & Assistant
Effect of Specimen Dimensions on Flexural Modulus in a 3-Point Bending Test
 Effect of Specimen Dimensions on Flexural Modulus in a 3-Point Bending Test M. Praveen Kumar 1 and V. Balakrishna Murthy 2* 1 Mechanical Engineering Department, P.V.P. Siddhartha Institute of Technology,
Effect of Specimen Dimensions on Flexural Modulus in a 3-Point Bending Test M. Praveen Kumar 1 and V. Balakrishna Murthy 2* 1 Mechanical Engineering Department, P.V.P. Siddhartha Institute of Technology,
Crash Optimization of Automobile Frontal and Side Structures Using Equivalent Static Loads
 11 th World Congress on Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimisation 7-12, June 2015, Sydney Australia Crash Optimization of Automobile Frontal and Side Structures Using Equivalent Static Loads Youngmyung
11 th World Congress on Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimisation 7-12, June 2015, Sydney Australia Crash Optimization of Automobile Frontal and Side Structures Using Equivalent Static Loads Youngmyung
A Study on the Tube of Integral Propeller Shaft for the Rear-wheel Drive Automobile Using Carbon Composite Fiber
 A Study on the Tube of Integral Propeller Shaft for the Rear-wheel Drive Automobile Using Carbon Composite Fiber Kibong Han Mechatronics Department, Jungwon University, 85 Munmu-ro, Goesan-gun, South Korea.
A Study on the Tube of Integral Propeller Shaft for the Rear-wheel Drive Automobile Using Carbon Composite Fiber Kibong Han Mechatronics Department, Jungwon University, 85 Munmu-ro, Goesan-gun, South Korea.
Design and Finite Element Analysis of Helmeted Head Form in Impact
 , pp.15-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijast.2016.93.02 Design and Finite Element Analysis of Helmeted Head Form in Impact Suddapalli Praneeth Babu* 1 and Dr. Chandana Srinivas 2 1 Mechanical Engineering,
, pp.15-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijast.2016.93.02 Design and Finite Element Analysis of Helmeted Head Form in Impact Suddapalli Praneeth Babu* 1 and Dr. Chandana Srinivas 2 1 Mechanical Engineering,
FIS Specifications for Flex Poles (Edition May 2008) Original Text: German
 FIS Specifications for Flex Poles (Edition May 2008) Original Text: German 1 Field of Application and Basic Information The following FIS specifications for flex poles are intended to ensure that flex
FIS Specifications for Flex Poles (Edition May 2008) Original Text: German 1 Field of Application and Basic Information The following FIS specifications for flex poles are intended to ensure that flex
A Numerical Study on Prediction of BFS in Composite Structures under Ballistic Impact
 VOL. 1, 2015 ISSN 2394 3750 EISSN 2394 3769 SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY A Numerical Study on Prediction of BFS in Composite Structures under Ballistic Impact Bandaru Aswani Kumar 1, Suhail Ahmad 2 1. Research
VOL. 1, 2015 ISSN 2394 3750 EISSN 2394 3769 SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY A Numerical Study on Prediction of BFS in Composite Structures under Ballistic Impact Bandaru Aswani Kumar 1, Suhail Ahmad 2 1. Research
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF DAMAGE IN THERMOPLASTIC COMPOSITE MATERIALS
 5 th European LS-DYNA Users Conference Composites NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF DAMAGE IN THERMOPLASTIC COMPOSITE MATERIALS Kevin Brown 1, Richard Brooks, Nicholas Warrior School of Mechanical, Materials and
5 th European LS-DYNA Users Conference Composites NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF DAMAGE IN THERMOPLASTIC COMPOSITE MATERIALS Kevin Brown 1, Richard Brooks, Nicholas Warrior School of Mechanical, Materials and
ANALYTICAL PENDULUM METHOD USED TO PREDICT THE ROLLOVER BEHAVIOR OF A BODY STRUCTURE
 The 3rd International Conference on Computational Mechanics and Virtual Engineering COMEC 2009 29 30 OCTOBER 2009, Brasov, Romania ANALYTICAL PENDULUM METHOD USED TO PREDICT THE ROLLOVER BEHAVIOR OF A
The 3rd International Conference on Computational Mechanics and Virtual Engineering COMEC 2009 29 30 OCTOBER 2009, Brasov, Romania ANALYTICAL PENDULUM METHOD USED TO PREDICT THE ROLLOVER BEHAVIOR OF A
Rollover Analysis of Passenger Bus as per AIS-031
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 4, Issue 5 (October 2012), PP. 49-59 Rollover Analysis of Passenger Bus as per AIS-031
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 4, Issue 5 (October 2012), PP. 49-59 Rollover Analysis of Passenger Bus as per AIS-031
Crash Analysis of four wheel vehicle for different velocity
 Crash Analysis of four wheel vehicle for different velocity G D Lohith Kumar1, H S Manjunath2, N Shashikanth3, Venkatesh Reddy4 1 Dept of Mechanical Engineering, Dr. Ambedkar Institute of Techn ology Bangalore,
Crash Analysis of four wheel vehicle for different velocity G D Lohith Kumar1, H S Manjunath2, N Shashikanth3, Venkatesh Reddy4 1 Dept of Mechanical Engineering, Dr. Ambedkar Institute of Techn ology Bangalore,
Impact. m k. Natural Period of Vibration τ. Static load Gray area Impact load t > 3 τ. Absorbing energy. Carrying loads
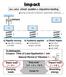 Impact also called shock, sudden or impulsive loading driving a nail with a hammer, automobile collisions. dashpot a) Rapidly moving vehicles crossing a bridge To distinguish: b) Suddenly applied c) Direct
Impact also called shock, sudden or impulsive loading driving a nail with a hammer, automobile collisions. dashpot a) Rapidly moving vehicles crossing a bridge To distinguish: b) Suddenly applied c) Direct
Parametric Studies of Low Velocity Impact on E-glass/Epoxy using Ls-Dyna
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 11, Issue 4 Ver. V (Jul- Aug. 2014), PP 33-39 Parametric Studies of Low Velocity Impact on E-glass/Epoxy
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 11, Issue 4 Ver. V (Jul- Aug. 2014), PP 33-39 Parametric Studies of Low Velocity Impact on E-glass/Epoxy
HVTT 11: Truck Occupant Protection Considerations in Heavy Truck Crashes
 TRUCK OCCUPANT PROTECTION CONSIDERATIONS IN HEAVYVEHICLE CRASHES Peter Hart graduated with a PhD in electrical engineering from Monash University in 1990. He is the principal of Hartwood Consulting Pty
TRUCK OCCUPANT PROTECTION CONSIDERATIONS IN HEAVYVEHICLE CRASHES Peter Hart graduated with a PhD in electrical engineering from Monash University in 1990. He is the principal of Hartwood Consulting Pty
Collapse behaviour and simplified modeling of triangular cross-section columns
 Indian Journal of ngineering & Materials Sciences Vol. 16, April 2009, pp. 71-78 Collapse behaviour and simplified ing of triangular cross-section columns Yucheng Liu* Department of Mechanical ngineering,
Indian Journal of ngineering & Materials Sciences Vol. 16, April 2009, pp. 71-78 Collapse behaviour and simplified ing of triangular cross-section columns Yucheng Liu* Department of Mechanical ngineering,
Crash Pendulum Energy Absorption Test System
 TECHNICAL ARTICLE Crash Pendulum Energy Absorption Test System Mechanical Design and Manufacturing Department, Kocaeli University, Kocaeli, Turkey Keywords Crash, Energy Absorption, Test System, Momentum,
TECHNICAL ARTICLE Crash Pendulum Energy Absorption Test System Mechanical Design and Manufacturing Department, Kocaeli University, Kocaeli, Turkey Keywords Crash, Energy Absorption, Test System, Momentum,
The goal of this study is to define the front crash protocol which responds the best at the following problem:
 CAR TO CAR FRONT CRASH EQUIVALENT PROTOCOL Marc Peru, Marie Estelle Caspar, Richard Zeitouni. PSA Groupe, France Marc Dieudonné, Pierre Couvidat, ACTOAT, France Paper number 17-0282 ABSTRACT The target
CAR TO CAR FRONT CRASH EQUIVALENT PROTOCOL Marc Peru, Marie Estelle Caspar, Richard Zeitouni. PSA Groupe, France Marc Dieudonné, Pierre Couvidat, ACTOAT, France Paper number 17-0282 ABSTRACT The target
Impact Simulation of Extreme Wind Generated Missiles on Radioactive Waste Storage Facilities
 Impact Simulation of Extreme Wind Generated Missiles on Radioactive Waste Storage Facilities Gianluca Barbella Sogin S.p.A. Structural Design Department barbella@sogin.it Rotterdam - october 24, 2013 Outline
Impact Simulation of Extreme Wind Generated Missiles on Radioactive Waste Storage Facilities Gianluca Barbella Sogin S.p.A. Structural Design Department barbella@sogin.it Rotterdam - october 24, 2013 Outline
Dynamic (Vibrational) and Static Structural Analysis of Ladder Frame
 Dynamic (Vibrational) and Static Structural Analysis of Ladder Frame Ketan Gajanan Nalawade 1, Ashish Sabu 2, Baskar P 3 School of Mechanical and building science, VIT University, Vellore-632014, Tamil
Dynamic (Vibrational) and Static Structural Analysis of Ladder Frame Ketan Gajanan Nalawade 1, Ashish Sabu 2, Baskar P 3 School of Mechanical and building science, VIT University, Vellore-632014, Tamil
Sabah Shawkat Cabinet of Structural Engineering Walls carrying vertical loads should be designed as columns. Basically walls are designed in
 Sabah Shawkat Cabinet of Structural Engineering 17 3.6 Shear walls Walls carrying vertical loads should be designed as columns. Basically walls are designed in the same manner as columns, but there are
Sabah Shawkat Cabinet of Structural Engineering 17 3.6 Shear walls Walls carrying vertical loads should be designed as columns. Basically walls are designed in the same manner as columns, but there are
Study on the application of rigid body dynamics in the traffic accident reconstruction. Ming Ni
 Applied Mechanics and Materials Submitted: 2014-10-25 ISSN: 1662-7482, Vol. 707, pp 412-416 Revised: 2014-11-01 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.707.412 Accepted: 2014-11-01 2015 Trans Tech Publications,
Applied Mechanics and Materials Submitted: 2014-10-25 ISSN: 1662-7482, Vol. 707, pp 412-416 Revised: 2014-11-01 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.707.412 Accepted: 2014-11-01 2015 Trans Tech Publications,
Analysis of the Rollover Behavior of the Bus Bodies
 ANALELE UNIVERSITĂłII EFTIMIE MURGU REŞIłA ANUL XVIII, NR. 1, 2011, ISSN 1453-7397 Dan Alexandru Micu, Daniel Mihail Iozsa Analysis of the Rollover Behavior of the Bus Bodies When performing calculations
ANALELE UNIVERSITĂłII EFTIMIE MURGU REŞIłA ANUL XVIII, NR. 1, 2011, ISSN 1453-7397 Dan Alexandru Micu, Daniel Mihail Iozsa Analysis of the Rollover Behavior of the Bus Bodies When performing calculations
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 13, 2008 Professor A. Dolovich
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME 313.3 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 13, 2008 Professor A. Dolovich A CLOSED BOOK EXAMINATION TIME: 3 HOURS For Marker s Use Only LAST NAME (printed): FIRST
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME 313.3 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 13, 2008 Professor A. Dolovich A CLOSED BOOK EXAMINATION TIME: 3 HOURS For Marker s Use Only LAST NAME (printed): FIRST
Anisotropic modeling of short fibers reinforced thermoplastics materials with LS-DYNA
 Anisotropic modeling of short fibers reinforced thermoplastics materials with LS-DYNA Alexandre Hatt 1 1 Faurecia Automotive Seating, Simplified Limited Liability Company 1 Abstract / Summary Polymer thermoplastics
Anisotropic modeling of short fibers reinforced thermoplastics materials with LS-DYNA Alexandre Hatt 1 1 Faurecia Automotive Seating, Simplified Limited Liability Company 1 Abstract / Summary Polymer thermoplastics
Dynamic Response Analysis of Compressor Mounting Bracket of an Automobile Vehicle for Aluminum 6061T6
 Dynamic Response Analysis of Compressor Mounting Bracket of an Automobile Vehicle for Aluminum 6061T6 Rajath J K 1 Dr. L Chandrasagar 2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Dr. Ambedkar Institute of
Dynamic Response Analysis of Compressor Mounting Bracket of an Automobile Vehicle for Aluminum 6061T6 Rajath J K 1 Dr. L Chandrasagar 2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Dr. Ambedkar Institute of
THE HEAD-ON COLLISIONS
 THE HEAD-ON COLLISIONS What is the role of the mass in a head-on collision between two vehicles? What is the role of speed? What is the force produced by each of the two vehicles? Here are some answers
THE HEAD-ON COLLISIONS What is the role of the mass in a head-on collision between two vehicles? What is the role of speed? What is the force produced by each of the two vehicles? Here are some answers
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown.
 D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
Parametric study on the transverse and longitudinal moments of trough type folded plate roofs using ANSYS
 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-4 pp-22-28 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Parametric study on the transverse and longitudinal moments
American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-4 pp-22-28 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Parametric study on the transverse and longitudinal moments
Analysis Of Naca 2412 For Automobile Rear Spoiler Using Composite Material *
 Analysis Of Naca 2412 For Automobile Rear Spoiler Using Composite Material * Kamprasad Chodagudi 1, T.b.s Rao 2 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Analysis Of Naca 2412 For Automobile Rear Spoiler Using Composite Material * Kamprasad Chodagudi 1, T.b.s Rao 2 -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Quasi-static simulation approaches on rollover impact of a bus structure
 Quasi-static simulation approaches on rollover impact of a bus structure DAN ALEXANDRU MICU, MIHAIL DANIEL IOZSA, CORNELIA STAN Automotive Engineering Department University POLITEHNICA of Bucharest 313
Quasi-static simulation approaches on rollover impact of a bus structure DAN ALEXANDRU MICU, MIHAIL DANIEL IOZSA, CORNELIA STAN Automotive Engineering Department University POLITEHNICA of Bucharest 313
Two Tier projects for students in ME 160 class
 ME 160 Introduction to Finite Element Method Spring 2016 Topics for Term Projects by Teams of 2 Students Instructor: Tai Ran Hsu, Professor, Dept. of Mechanical engineering, San Jose State University,
ME 160 Introduction to Finite Element Method Spring 2016 Topics for Term Projects by Teams of 2 Students Instructor: Tai Ran Hsu, Professor, Dept. of Mechanical engineering, San Jose State University,
Experimental Test and Computer Simulation Research on Rollover Impact of a Bus Structure
 Experimental Test and Computer Simulation Research on Rollover Impact of a Bus Structure DAN ALEXANDRU MICU, MIHAIL DANIEL IOZSA, GHEORGHE FRĂȚILĂ Automotive Engineering Department University POLITEHNICA
Experimental Test and Computer Simulation Research on Rollover Impact of a Bus Structure DAN ALEXANDRU MICU, MIHAIL DANIEL IOZSA, GHEORGHE FRĂȚILĂ Automotive Engineering Department University POLITEHNICA
A ROLLOVER TEST OF BUS BODY SECTIONS USING ANSYS
 5 th International Conference Computational Mechanics and Virtual Engineering COMEC 2013 24-25 October 2013, Braşov, Romania A ROLLOVER TEST OF BUS BODY SECTIONS USING ANSYS D.A. Micu, 1, M.D. Iozsa 2,
5 th International Conference Computational Mechanics and Virtual Engineering COMEC 2013 24-25 October 2013, Braşov, Romania A ROLLOVER TEST OF BUS BODY SECTIONS USING ANSYS D.A. Micu, 1, M.D. Iozsa 2,
Simulation of Geometrical Cross-Section for Practical Purposes
 Simulation of Geometrical Cross-Section for Practical Purposes Bhasker R.S. 1, Prasad R. K. 2, Kumar V. 3, Prasad P. 4 123 Department of Mechanical Engineering, R.D. Engineering College, Ghaziabad, UP,
Simulation of Geometrical Cross-Section for Practical Purposes Bhasker R.S. 1, Prasad R. K. 2, Kumar V. 3, Prasad P. 4 123 Department of Mechanical Engineering, R.D. Engineering College, Ghaziabad, UP,
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
 Third E CHAPTER 2 Stress MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. John T. DeWolf Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University and Strain Axial Loading Contents Stress & Strain:
Third E CHAPTER 2 Stress MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. John T. DeWolf Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University and Strain Axial Loading Contents Stress & Strain:
Robust design of an automobile front bumper using design of experiments
 1199 Robust design of an automobile front bumper using design of experiments Kwon-Hee Lee* and Il-Kwon Bang Department of Mechanical Engineering, Dong-A University, Busan, Republic of Korea The manuscript
1199 Robust design of an automobile front bumper using design of experiments Kwon-Hee Lee* and Il-Kwon Bang Department of Mechanical Engineering, Dong-A University, Busan, Republic of Korea The manuscript
SOME RESEARCH ON FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF COMPOSITE MATERIALS
 Mechanical Testing and Diagnosis ISSN 2247 9635, 2012 (II), Volume 3, 79-85 SOME RESEARCH ON FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF COMPOSITE MATERIALS Valeriu DULGHERU, Viorel BOSTAN, Marin GUŢU Technical University
Mechanical Testing and Diagnosis ISSN 2247 9635, 2012 (II), Volume 3, 79-85 SOME RESEARCH ON FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF COMPOSITE MATERIALS Valeriu DULGHERU, Viorel BOSTAN, Marin GUŢU Technical University
UNIT-I STRESS, STRAIN. 1. A Member A B C D is subjected to loading as shown in fig determine the total elongation. Take E= 2 x10 5 N/mm 2
 UNIT-I STRESS, STRAIN 1. A Member A B C D is subjected to loading as shown in fig determine the total elongation. Take E= 2 x10 5 N/mm 2 Young s modulus E= 2 x10 5 N/mm 2 Area1=900mm 2 Area2=400mm 2 Area3=625mm
UNIT-I STRESS, STRAIN 1. A Member A B C D is subjected to loading as shown in fig determine the total elongation. Take E= 2 x10 5 N/mm 2 Young s modulus E= 2 x10 5 N/mm 2 Area1=900mm 2 Area2=400mm 2 Area3=625mm
Post Graduate Diploma in Mechanical Engineering Computational mechanics using finite element method
 9210-220 Post Graduate Diploma in Mechanical Engineering Computational mechanics using finite element method You should have the following for this examination one answer book scientific calculator No
9210-220 Post Graduate Diploma in Mechanical Engineering Computational mechanics using finite element method You should have the following for this examination one answer book scientific calculator No
Chapter 3 Kinetics of Particle: Work & Energy
 Chapter 3 Kinetics of Particle: Work & Energy Dr. Khairul Salleh Basaruddin Applied Mechanics Division School of Mechatronic Engineering Universiti Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP) khsalleh@unimap.edu.my THE WORK
Chapter 3 Kinetics of Particle: Work & Energy Dr. Khairul Salleh Basaruddin Applied Mechanics Division School of Mechatronic Engineering Universiti Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP) khsalleh@unimap.edu.my THE WORK
ANALYSIS AND SIMULATION OF AN AIRPLANE SEAT DURING VERTICAL IMPACTS
 ANALYSIS AND SIMULATION OF AN AIRPLANE SEAT DURING VERTICAL IMPACTS ABSTRACT Luís Carlos das Neves Ferreira luis.neves.ferreira@ist.utl.pt Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Portugal December
ANALYSIS AND SIMULATION OF AN AIRPLANE SEAT DURING VERTICAL IMPACTS ABSTRACT Luís Carlos das Neves Ferreira luis.neves.ferreira@ist.utl.pt Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Portugal December
QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State Hooke s law. 3. Define modular ratio,
QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State Hooke s law. 3. Define modular ratio,
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK. Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV UNIT I STRESS, STRAIN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART A (2 MARKS)
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV UNIT I STRESS, STRAIN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART A (2 MARKS)
Steel Post Load Analysis
 Steel Post Load Analysis Scope The steel posts in 73019022, 73019024, and 73019025, are considered to be traditional building products. According to the 2015 International Building Code, this type of product
Steel Post Load Analysis Scope The steel posts in 73019022, 73019024, and 73019025, are considered to be traditional building products. According to the 2015 International Building Code, this type of product
Lecture #10: Anisotropic plasticity Crashworthiness Basics of shell elements
 Lecture #10: 151-0735: Dynamic behavior of materials and structures Anisotropic plasticity Crashworthiness Basics of shell elements by Dirk Mohr ETH Zurich, Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering,
Lecture #10: 151-0735: Dynamic behavior of materials and structures Anisotropic plasticity Crashworthiness Basics of shell elements by Dirk Mohr ETH Zurich, Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering,
EXPERIMENTAL AND NUMERICAL STUDY OF THE ENERGY ABSORPTION CAPACITY OF PULTRUDED COMPOSITE TUBES
 EXPERIMENTAL AND NUMERICAL STUDY OF THE ENERGY ABSORPTION CAPACITY OF PULTRUDED COMPOSITE TUBES D. Kakogiannis 1, D. Van Hemelrijck 1, J. Wastiels 1, S. Palanivelu 2, W. Van Paepegem 2, K. De Wolf 3, J.
EXPERIMENTAL AND NUMERICAL STUDY OF THE ENERGY ABSORPTION CAPACITY OF PULTRUDED COMPOSITE TUBES D. Kakogiannis 1, D. Van Hemelrijck 1, J. Wastiels 1, S. Palanivelu 2, W. Van Paepegem 2, K. De Wolf 3, J.
Multi Linear Elastic and Plastic Link in SAP2000
 26/01/2016 Marco Donà Multi Linear Elastic and Plastic Link in SAP2000 1 General principles Link object connects two joints, i and j, separated by length L, such that specialized structural behaviour may
26/01/2016 Marco Donà Multi Linear Elastic and Plastic Link in SAP2000 1 General principles Link object connects two joints, i and j, separated by length L, such that specialized structural behaviour may
Lateral Crushing of Square and Rectangular Metallic Tubes under Different Quasi-Static Conditions
 Vol:, No:1, 2 Lateral Crushing of Square and Rectangular Metallic Tubes under Different Quasi-Static Conditions Sajjad Dehghanpour, Ali Yousefi International Science Index, Mechanical and Mechatronics
Vol:, No:1, 2 Lateral Crushing of Square and Rectangular Metallic Tubes under Different Quasi-Static Conditions Sajjad Dehghanpour, Ali Yousefi International Science Index, Mechanical and Mechatronics
EVALUATING DYNAMIC STRESSES OF A PIPELINE
 EVALUATING DYNAMIC STRESSES OF A PIPELINE by K.T. TRUONG Member ASME Mechanical & Piping Division THE ULTRAGEN GROUP LTD 2255 Rue De La Province Longueuil (Quebec) J4G 1G3 This document is provided to
EVALUATING DYNAMIC STRESSES OF A PIPELINE by K.T. TRUONG Member ASME Mechanical & Piping Division THE ULTRAGEN GROUP LTD 2255 Rue De La Province Longueuil (Quebec) J4G 1G3 This document is provided to
Experimental Crash Analysis of a Thin-Walled Box Column Using Cylinder as Web
 Experimental Crash Analysis of a Thin-Walled Box Column Using Cylinder as Web C.P.Santhosh Ananda, R.Gobinath, K.Mathiyazhakan, S.Arulmurugan, P.Lokesh Department of Mechanical Engineering, Nandha College
Experimental Crash Analysis of a Thin-Walled Box Column Using Cylinder as Web C.P.Santhosh Ananda, R.Gobinath, K.Mathiyazhakan, S.Arulmurugan, P.Lokesh Department of Mechanical Engineering, Nandha College
Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2000. Dr. Coates
 Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2 Chapter 6: Mechanical Properties of Metals Dr. Coates 6.2 Concepts of Stress and Strain tension compression shear torsion Tension Tests The specimen is deformed
Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2 Chapter 6: Mechanical Properties of Metals Dr. Coates 6.2 Concepts of Stress and Strain tension compression shear torsion Tension Tests The specimen is deformed
Simulation and Test Validation of Windscreen Subject to Pedestrian Head Impact
 12 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Occupant Safety Simulation and Test Validation of Windscreen Subject to Pedestrian Head Impact Qi Liu, Junyong Liu, Qiang Miao, Dazhi Wang, Xiaodong Tang SAIC
12 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Occupant Safety Simulation and Test Validation of Windscreen Subject to Pedestrian Head Impact Qi Liu, Junyong Liu, Qiang Miao, Dazhi Wang, Xiaodong Tang SAIC
Nonlinear Finite Element Analysis of Airport Approach Lighting Structures under Impact Loading
 8 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Simulation Technology (2) Nonlinear Finite Element Analysis of Airport Approach Lighting Structures under Impact Loading M. Nejad Ensan *1, D.G. Zimcik 1, S.T.
8 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Simulation Technology (2) Nonlinear Finite Element Analysis of Airport Approach Lighting Structures under Impact Loading M. Nejad Ensan *1, D.G. Zimcik 1, S.T.
Solution Derivations for Capa #12
 Solution Derivations for Capa #12 1) A hoop of radius 0.200 m and mass 0.460 kg, is suspended by a point on it s perimeter as shown in the figure. If the hoop is allowed to oscillate side to side as a
Solution Derivations for Capa #12 1) A hoop of radius 0.200 m and mass 0.460 kg, is suspended by a point on it s perimeter as shown in the figure. If the hoop is allowed to oscillate side to side as a
[5] Stress and Strain
![[5] Stress and Strain [5] Stress and Strain](/thumbs/95/123344550.jpg) [5] Stress and Strain Page 1 of 34 [5] Stress and Strain [5.1] Internal Stress of Solids [5.2] Design of Simple Connections (will not be covered in class) [5.3] Deformation and Strain [5.4] Hooke s Law
[5] Stress and Strain Page 1 of 34 [5] Stress and Strain [5.1] Internal Stress of Solids [5.2] Design of Simple Connections (will not be covered in class) [5.3] Deformation and Strain [5.4] Hooke s Law
Mathematical Modelling of Car Crash Test
 REST Journal on Emerging trends in Modelling and Manufacturing Vol:3(3),2017 REST Publisher ISSN: 2455-4537 Website: www.restpublisher.com/journals/jemm Mathematical Modelling of Car Crash Test Abhinav
REST Journal on Emerging trends in Modelling and Manufacturing Vol:3(3),2017 REST Publisher ISSN: 2455-4537 Website: www.restpublisher.com/journals/jemm Mathematical Modelling of Car Crash Test Abhinav
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each.
 GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
Mechanics of Solids. Mechanics Of Solids. Suraj kr. Ray Department of Civil Engineering
 Mechanics Of Solids Suraj kr. Ray (surajjj2445@gmail.com) Department of Civil Engineering 1 Mechanics of Solids is a branch of applied mechanics that deals with the behaviour of solid bodies subjected
Mechanics Of Solids Suraj kr. Ray (surajjj2445@gmail.com) Department of Civil Engineering 1 Mechanics of Solids is a branch of applied mechanics that deals with the behaviour of solid bodies subjected
Energy Considerations
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 4 French, Chapter 3 Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Energy Considerations The force in Hooke s law is = Potential energy can be used to describe conservative
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 4 French, Chapter 3 Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Energy Considerations The force in Hooke s law is = Potential energy can be used to describe conservative
IMPACT TESTT ON MOTORCYCLE HELMET FOR DIFFERENT ANGLES USING FINETE ELEMENT ANALYSIS
 International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 8, Issue 5, May 2017, pp. 280 293, Article ID: IJMET_08_05_030 Available online at http://www.ia aeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtyp
International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 8, Issue 5, May 2017, pp. 280 293, Article ID: IJMET_08_05_030 Available online at http://www.ia aeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtyp
Optimization of Circular Side Door Beam for Crashworthiness Analysis
 Vol. 2 (2012) No. 3 ISSN: 2088-5334 Optimization of Circular Side Door Beam for Crashworthiness Analysis Raja Sharmi Raja Husin 1, Nur Liyana Tajul Lile 2, Sazali Yaacob 2 1 Mechanical Engineering Department,
Vol. 2 (2012) No. 3 ISSN: 2088-5334 Optimization of Circular Side Door Beam for Crashworthiness Analysis Raja Sharmi Raja Husin 1, Nur Liyana Tajul Lile 2, Sazali Yaacob 2 1 Mechanical Engineering Department,
CHAPTER 6 HEAT DISSIPATION AND TEMPERATURE DISTRIBUTION OF BRAKE LINER USING STEADY STATE ANALYSIS
 131 CHAPTER 6 HEAT DISSIPATION AND TEMPERATURE DISTRIBUTION OF BRAKE LINER USING STEADY STATE ANALYSIS 6.1 INTRODUCTION Drum brakes were the first types of brakes used on motor vehicles. Nowadays, over
131 CHAPTER 6 HEAT DISSIPATION AND TEMPERATURE DISTRIBUTION OF BRAKE LINER USING STEADY STATE ANALYSIS 6.1 INTRODUCTION Drum brakes were the first types of brakes used on motor vehicles. Nowadays, over
ISHIK UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF MECHATRONICS ENGINEERING
 ISHIK UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF MECHATRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK FOR THE MECHANICS OF MATERIALS-I 1. A rod 150 cm long and of diameter 2.0 cm is subjected to an axial pull of 20 kn. If the modulus
ISHIK UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF MECHATRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK FOR THE MECHANICS OF MATERIALS-I 1. A rod 150 cm long and of diameter 2.0 cm is subjected to an axial pull of 20 kn. If the modulus
1.050: Beam Elasticity (HW#9)
 1050: Beam Elasticity (HW#9) MIT 1050 (Engineering Mechanics I) Fall 2007 Instructor: Markus J BUEHER Due: November 14, 2007 Team Building and Team Work: We strongly encourage you to form Homework teams
1050: Beam Elasticity (HW#9) MIT 1050 (Engineering Mechanics I) Fall 2007 Instructor: Markus J BUEHER Due: November 14, 2007 Team Building and Team Work: We strongly encourage you to form Homework teams
Class XI Physics. Ch. 9: Mechanical Properties of solids. NCERT Solutions
 Downloaded from Class XI Physics Ch. 9: Mechanical Properties of solids NCERT Solutions Page 242 Question 9.1: A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 10 5 m 2 stretches by the same amount
Downloaded from Class XI Physics Ch. 9: Mechanical Properties of solids NCERT Solutions Page 242 Question 9.1: A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 10 5 m 2 stretches by the same amount
Comparison of crash tests and simulations for various vehicle restraint systems
 Comparison of crash tests and simulations for various vehicle restraint systems C. Goubel ab, E. Di Pasquale c, M. Massenzio a, S. Ronel a a : Université de Lyon, F 69622, Lyon, France ; INRETS, UMR_T946,
Comparison of crash tests and simulations for various vehicle restraint systems C. Goubel ab, E. Di Pasquale c, M. Massenzio a, S. Ronel a a : Université de Lyon, F 69622, Lyon, France ; INRETS, UMR_T946,
VALIDATING DYNAMIC TENSILE MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SHEET STEELS FOR AUTOMOTIVE CRASH APPLICATIONS
 VALIDATING DYNAMIC TENSILE MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SHEET STEELS FOR AUTOMOTIVE CRASH APPLICATIONS AUTHORS: P.K.C. Wood, University of Warwick C.A. Schley, University of Warwick M. Buckley, Jaguar and
VALIDATING DYNAMIC TENSILE MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SHEET STEELS FOR AUTOMOTIVE CRASH APPLICATIONS AUTHORS: P.K.C. Wood, University of Warwick C.A. Schley, University of Warwick M. Buckley, Jaguar and
five Mechanics of Materials 1 ARCHITECTURAL STRUCTURES: FORM, BEHAVIOR, AND DESIGN DR. ANNE NICHOLS SUMMER 2017 lecture
 ARCHITECTURAL STRUCTURES: FORM, BEHAVIOR, AND DESIGN DR. ANNE NICHOLS SUMMER 2017 lecture five mechanics www.carttalk.com of materials Mechanics of Materials 1 Mechanics of Materials MECHANICS MATERIALS
ARCHITECTURAL STRUCTURES: FORM, BEHAVIOR, AND DESIGN DR. ANNE NICHOLS SUMMER 2017 lecture five mechanics www.carttalk.com of materials Mechanics of Materials 1 Mechanics of Materials MECHANICS MATERIALS
Modeling non-isothermal thermoforming of fabricreinforced thermoplastic composites
 Modeling non-isothermal thermoforming of fabricreinforced thermoplastic composites Dominic Schommer, Miro Duhovic, Joachim Hausmann Institut für Verbundwerkstoffe GmbH, Erwin-Schrödinger-Str., Building
Modeling non-isothermal thermoforming of fabricreinforced thermoplastic composites Dominic Schommer, Miro Duhovic, Joachim Hausmann Institut für Verbundwerkstoffe GmbH, Erwin-Schrödinger-Str., Building
Rollover Analysis of Sleeper Coach Bus by Virtual Simulation in LS-DYNA
 Rollover Analysis of Sleeper Coach Bus by Virtual Simulation in LS-DYNA Ajinkya Patil,M-Tech, BVDUCOE, Pune. Prof. S.R. Pawar, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, BVDUCOE, Pune Abstract This paper deals with
Rollover Analysis of Sleeper Coach Bus by Virtual Simulation in LS-DYNA Ajinkya Patil,M-Tech, BVDUCOE, Pune. Prof. S.R. Pawar, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, BVDUCOE, Pune Abstract This paper deals with
SCALING EFFECTS IN THE LOW VELOCITY IMPACT RESPONSE OF FIBRE METAL
 SCALING EFFECTS IN THE LOW VELOCITY IMPACT RESPONSE OF FIBRE METAL LAMINATES J. G. Carrillo 1, S. McKown 1, M. Mujib 1 and W. J. Cantwell 1. R. Day 2 1 Department of Engineering, University of Liverpool,
SCALING EFFECTS IN THE LOW VELOCITY IMPACT RESPONSE OF FIBRE METAL LAMINATES J. G. Carrillo 1, S. McKown 1, M. Mujib 1 and W. J. Cantwell 1. R. Day 2 1 Department of Engineering, University of Liverpool,
Bending Load & Calibration Module
 Bending Load & Calibration Module Objectives After completing this module, students shall be able to: 1) Conduct laboratory work to validate beam bending stress equations. 2) Develop an understanding of
Bending Load & Calibration Module Objectives After completing this module, students shall be able to: 1) Conduct laboratory work to validate beam bending stress equations. 2) Develop an understanding of
Chapter 14 Oscillations. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 14 Oscillations Oscillations of a Spring Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator Simple Harmonic Motion Related to Uniform Circular Motion The Simple Pendulum The Physical
Chapter 14 Oscillations Oscillations of a Spring Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator Simple Harmonic Motion Related to Uniform Circular Motion The Simple Pendulum The Physical
Introduction to Structural Member Properties
 Introduction to Structural Member Properties Structural Member Properties Moment of Inertia (I): a mathematical property of a cross-section (measured in inches 4 or in 4 ) that gives important information
Introduction to Structural Member Properties Structural Member Properties Moment of Inertia (I): a mathematical property of a cross-section (measured in inches 4 or in 4 ) that gives important information
Experimentally Calibrating Cohesive Zone Models for Structural Automotive Adhesives
 Experimentally Calibrating Cohesive Zone Models for Structural Automotive Adhesives Mark Oliver October 19, 2016 Adhesives and Sealants Council Fall Convention contact@veryst.com www.veryst.com Outline
Experimentally Calibrating Cohesive Zone Models for Structural Automotive Adhesives Mark Oliver October 19, 2016 Adhesives and Sealants Council Fall Convention contact@veryst.com www.veryst.com Outline
QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SEMESTER: III SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A
 DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State
DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State
Numerical simulation of the crash behaviour of braided composites
 5th International CFK-Valley Stade Convention Numerical simulation of the crash behaviour of braided composites Stade, Dipl.-Ing. Ralf Matheis Institut für Kraftfahrzeuge RWTH Aachen University #110410
5th International CFK-Valley Stade Convention Numerical simulation of the crash behaviour of braided composites Stade, Dipl.-Ing. Ralf Matheis Institut für Kraftfahrzeuge RWTH Aachen University #110410
1 332 Laboratories 1. 2 Computational Exercises 1 FEA of a Cantilever Beam... 1 Experimental Laboratory: Tensile Testing of Materials...
 1 332 Laboratories Contents 1 332 Laboratories 1 2 Computational Exercises 1 FEA of a Cantilever Beam.......................................... 1 Experimental Laboratory: Tensile Testing of Materials..........................
1 332 Laboratories Contents 1 332 Laboratories 1 2 Computational Exercises 1 FEA of a Cantilever Beam.......................................... 1 Experimental Laboratory: Tensile Testing of Materials..........................
Modal Analysis of Automotive seating System
 Modal Analysis of Automotive seating System Uday M. Jamdade 1, Sandip H. Deshmukh 2, Sanjay S. Deshpande 3 1 Sinhgad college of engineering, pune. 2 Sinhgad college of engineering, Pune 3 Asian academy
Modal Analysis of Automotive seating System Uday M. Jamdade 1, Sandip H. Deshmukh 2, Sanjay S. Deshpande 3 1 Sinhgad college of engineering, pune. 2 Sinhgad college of engineering, Pune 3 Asian academy
PARAMETRIC STUDY OF THE STRUCTURAL CAPACITY OF REINFORCED CONCRETE CONTAINMENT SUBJECTED TO LARGE COMMERICAL AIRCRFAT IMPACT
 Transactions, SMiRT-23, Paper 285 PARAMETRIC STUDY OF THE STRUCTURAL CAPACITY OF REINFORCED CONCRETE CONTAINMENT SUBJECTED TO LARGE COMMERICAL AIRCRFAT IMPACT Marin Kostov 1, Milko Miloshev 2, Zhivko Nikolov
Transactions, SMiRT-23, Paper 285 PARAMETRIC STUDY OF THE STRUCTURAL CAPACITY OF REINFORCED CONCRETE CONTAINMENT SUBJECTED TO LARGE COMMERICAL AIRCRFAT IMPACT Marin Kostov 1, Milko Miloshev 2, Zhivko Nikolov
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
 CHATR Stress MCHANICS OF MATRIALS and Strain Axial Loading Stress & Strain: Axial Loading Suitability of a structure or machine may depend on the deformations in the structure as well as the stresses induced
CHATR Stress MCHANICS OF MATRIALS and Strain Axial Loading Stress & Strain: Axial Loading Suitability of a structure or machine may depend on the deformations in the structure as well as the stresses induced
VIBRATION CONTROL OF RECTANGULAR CROSS-PLY FRP PLATES USING PZT MATERIALS
 Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 12, No. 12 (217) 3398-3411 School of Engineering, Taylor s University VIBRATION CONTROL OF RECTANGULAR CROSS-PLY FRP PLATES USING PZT MATERIALS DILEEP
Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 12, No. 12 (217) 3398-3411 School of Engineering, Taylor s University VIBRATION CONTROL OF RECTANGULAR CROSS-PLY FRP PLATES USING PZT MATERIALS DILEEP
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 PH105-007 Exam 2 VERSION A Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A 1.0-kg block and a 2.0-kg block are pressed together on a horizontal
PH105-007 Exam 2 VERSION A Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A 1.0-kg block and a 2.0-kg block are pressed together on a horizontal
SIMULATION STUDIES ON THE EFFECT OF PROJECTILE NOSE SHAPE IMPACTING ON ALUMINUM PLATES
 Int. J. Mech. Eng. & Rob. Res. 2014 Sivaiah A et al., 2014 Research Paper ISSN 2278 0149 www.ijmerr.com Vol. 3, No. 1, January 2014 2014 IJMERR. All Rights Reserved SIMULATION STUDIES ON THE EFFECT OF
Int. J. Mech. Eng. & Rob. Res. 2014 Sivaiah A et al., 2014 Research Paper ISSN 2278 0149 www.ijmerr.com Vol. 3, No. 1, January 2014 2014 IJMERR. All Rights Reserved SIMULATION STUDIES ON THE EFFECT OF
Finite Element Modeling of an Aluminum Tricycle Frame
 Finite Element Modeling of an Aluminum Tricycle Frame A. Rodríguez, B. Chiné*, and J. A. Ramírez Costa Rica Institute of Technology, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Cartago, Costa Rica *Corresponding
Finite Element Modeling of an Aluminum Tricycle Frame A. Rodríguez, B. Chiné*, and J. A. Ramírez Costa Rica Institute of Technology, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Cartago, Costa Rica *Corresponding
Development of Verification and Validation Procedures for Computer Simulation use in Roadside Safety Applications NCHRP 22-24
 Development of Verification and Validation Procedures for Computer Simulation use in Roadside Safety Applications NCHRP 22-24 PHENOMENA IMPORTANCE RANKING TABLES (PIRTS) Meeting Agenda 1:00-1:15 Introductions/Kick-off
Development of Verification and Validation Procedures for Computer Simulation use in Roadside Safety Applications NCHRP 22-24 PHENOMENA IMPORTANCE RANKING TABLES (PIRTS) Meeting Agenda 1:00-1:15 Introductions/Kick-off
Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy
 Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring 2017-2018 Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy Axial Stress 2 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 3 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 4 Shear Stress
Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring 2017-2018 Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy Axial Stress 2 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 3 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 4 Shear Stress
REGRESSION MODELING FOR STRENGTH AND TOUGHNESS EVALUATION OF HYBRID FIBRE REINFORCED CONCRETE
 REGRESSION MODELING FOR STRENGTH AND TOUGHNESS EVALUATION OF HYBRID FIBRE REINFORCED CONCRETE S. Eswari 1, P. N. Raghunath and S. Kothandaraman 1 1 Department of Civil Engineering, Pondicherry Engineering
REGRESSION MODELING FOR STRENGTH AND TOUGHNESS EVALUATION OF HYBRID FIBRE REINFORCED CONCRETE S. Eswari 1, P. N. Raghunath and S. Kothandaraman 1 1 Department of Civil Engineering, Pondicherry Engineering
