Today s class. Constrained optimization Linear programming. Prof. Jinbo Bi CSE, UConn. Numerical Methods, Fall 2011 Lecture 12
|
|
|
- Dorothy Porter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Today s class Constrained optimization Linear programming 1
2 Midterm Exam 1 Count: 26 Average: 73.2 Median: 72.5 Maximum: Minimum: 45.0 Standard Deviation: Numerical Methods Fall
3 Optimization General optimization problem: p 3
4 Linear Programming General linear programming problem: 4
5 Linear Programming Graphical solutions Limited to two or three dimensions Graph the constraints to determine feasible solution space and then map the objective function on to this space 5
6 Linear Programming Example: 6
7 Linear Programming 7
8 Linear Programming 8
9 Linear Programming Solution at x 1 = 44/9, x 2 = 35/9 Constraints 1 and 2 are binding Constraint 3 is redundant Constraints 4, 5, and 6 are nonbinding 9
10 Linear Programming Possible outcomes Unique solution Alternate solutions Possible if objective function is parallel to one of the constraints No feasible solution Problem is over-constrained Unbounded problems Problem is under-constrained 10
11 Possible outcomes Alternate solutions 11
12 Possible outcomes No feasible solution 12
13 Possible outcomes Unbounded problems 13
14 Extreme points Unique solutions occur at the extreme convex corner points of the feasible solution space The extreme points occur at the intersection of various constraints Since the optimal solution occurs just at the extreme point, we can simplify our search by just looking at extreme points Not every extreme point is feasible 14
15 Transform problem into normal form - i.e. only equality constraints and nonnegativity constraints for all decision variables Add slack variables The slack variables must be positive if the constraints are to be met 15
16 We have more unknowns than equations, so we can t use the linear algebraic methods we used before In general, there are m equations (not counting non-negativity constraints) and n unknowns We re looking for the extreme points In the m equality constraints, set n-m variables to zero, and then solve the m equation, m unknown linear system Problem is that you don t know which of the n-m variables to set to zero 16
17 You could try all the possibilities, but that can get out of hand as n and m get large There are possibilities Many of those choices may not even give you feasible extreme points The Simplex Method offers a more efficient way to quickly identify the feasible extreme points 17
18 Start by setting n-m of the variables to zero. An obvious starting point is the original nonslack variables 18
19 Keep a table that summarizes and tracks all the variables Objective function Constraint functions 19
20 First step is to take our initial starting point and increase one of the variables so that it is non-zero Pick the variable that is going to increase the Z objective the most This column will have the largest positive entry in the Z row. Increase that variable until one of the other values goes negative 20
21 Look at the entry at the intersection of the row and the column we chose above. This is called the pivot element If it is negative, increasing the chosen variable will only make the row basic variable bigger, so it is not restrictive If it is positive, increasing the chosen variable will make row variable smaller, so it is restrictive Divide the constant in the row by the pivot element and that will tell you how much you increase the variable before you hit a constraint restriction Choose the smallest of these values as your pivot element 21
22 Numerical Methods Fall 2010 Lecture Prof. Lei Wang ECE, UConn
23 Numerical Methods Fall 2010 Lecture Prof. Lei Wang ECE, UConn
24 -11 Numerical Methods Fall 2010 Lecture Prof. Lei Wang ECE, UConn
25 -11 Numerical Methods Fall 2010 Lecture Prof. Lei Wang ECE, UConn
26 Numerical Methods Fall 2010 Lecture Prof. Lei Wang ECE, UConn
27 Numerical Methods Fall 2010 Lecture Prof. Lei Wang ECE, UConn
28 Numerical Methods Fall 2010 Lecture Prof. Lei Wang ECE, UConn
29 Numerical Methods Fall 2010 Lecture Prof. Lei Wang ECE, UConn
30 Numerical Methods Fall 2010 Lecture Prof. Lei Wang ECE, UConn
31 Numerical Methods Fall 2010 Lecture Prof. Lei Wang ECE, UConn
32 Numerical Methods Fall 2010 Lecture Prof. Lei Wang ECE, UConn
33 Numerical Methods Fall 2010 Lecture Prof. Lei Wang ECE, UConn
34 Numerical Methods Fall 2010 Lecture Prof. Lei Wang ECE, UConn
35 Numerical Methods Fall 2010 Lecture Prof. Lei Wang ECE, UConn
36 Numerical Methods Fall 2010 Lecture Prof. Lei Wang ECE, UConn
37 Numerical Methods Fall 2010 Lecture Prof. Lei Wang ECE, UConn
38 38
39 39
40 40
41 Linear Programming Simplex Method is the best known algorithm for linear programming problems Can be exponential in the worst case but in practice, is usually polynomial Special cases of linear programming may have faster algorithms 41
42 Next class Numerical Integration Read Chapter PT6 and 21 42
Part III: A Simplex pivot
 MA 3280 Lecture 31 - More on The Simplex Method Friday, April 25, 2014. Objectives: Analyze Simplex examples. We were working on the Simplex tableau The matrix form of this system of equations is called
MA 3280 Lecture 31 - More on The Simplex Method Friday, April 25, 2014. Objectives: Analyze Simplex examples. We were working on the Simplex tableau The matrix form of this system of equations is called
Slide 1 Math 1520, Lecture 10
 Slide 1 Math 1520, Lecture 10 In this lecture, we study the simplex method which is a powerful method for solving maximization/minimization problems developed in the late 1940 s. It has been implemented
Slide 1 Math 1520, Lecture 10 In this lecture, we study the simplex method which is a powerful method for solving maximization/minimization problems developed in the late 1940 s. It has been implemented
ORF 307: Lecture 2. Linear Programming: Chapter 2 Simplex Methods
 ORF 307: Lecture 2 Linear Programming: Chapter 2 Simplex Methods Robert Vanderbei February 8, 2018 Slides last edited on February 8, 2018 http://www.princeton.edu/ rvdb Simplex Method for LP An Example.
ORF 307: Lecture 2 Linear Programming: Chapter 2 Simplex Methods Robert Vanderbei February 8, 2018 Slides last edited on February 8, 2018 http://www.princeton.edu/ rvdb Simplex Method for LP An Example.
Prelude to the Simplex Algorithm. The Algebraic Approach The search for extreme point solutions.
 Prelude to the Simplex Algorithm The Algebraic Approach The search for extreme point solutions. 1 Linear Programming-1 x 2 12 8 (4,8) Max z = 6x 1 + 4x 2 Subj. to: x 1 + x 2
Prelude to the Simplex Algorithm The Algebraic Approach The search for extreme point solutions. 1 Linear Programming-1 x 2 12 8 (4,8) Max z = 6x 1 + 4x 2 Subj. to: x 1 + x 2
MATH 445/545 Test 1 Spring 2016
 MATH 445/545 Test Spring 06 Note the problems are separated into two sections a set for all students and an additional set for those taking the course at the 545 level. Please read and follow all of these
MATH 445/545 Test Spring 06 Note the problems are separated into two sections a set for all students and an additional set for those taking the course at the 545 level. Please read and follow all of these
Summary of the simplex method
 MVE165/MMG631,Linear and integer optimization with applications The simplex method: degeneracy; unbounded solutions; starting solutions; infeasibility; alternative optimal solutions Ann-Brith Strömberg
MVE165/MMG631,Linear and integer optimization with applications The simplex method: degeneracy; unbounded solutions; starting solutions; infeasibility; alternative optimal solutions Ann-Brith Strömberg
4.3 Minimizing & Mixed Constraints
 Mathematics : Mattingly, Fall 6 8 4. Minimizing & Mixed Constraints So far, you have seen how to solve one type of problem: Standard Maximum. The objective function is to be maximized.. Constraints use..
Mathematics : Mattingly, Fall 6 8 4. Minimizing & Mixed Constraints So far, you have seen how to solve one type of problem: Standard Maximum. The objective function is to be maximized.. Constraints use..
CSC Design and Analysis of Algorithms. LP Shader Electronics Example
 CSC 80- Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture (LP) LP Shader Electronics Example The Shader Electronics Company produces two products:.eclipse, a portable touchscreen digital player; it takes hours
CSC 80- Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture (LP) LP Shader Electronics Example The Shader Electronics Company produces two products:.eclipse, a portable touchscreen digital player; it takes hours
Linear Programming, Lecture 4
 Linear Programming, Lecture 4 Corbett Redden October 3, 2016 Simplex Form Conventions Examples Simplex Method To run the simplex method, we start from a Linear Program (LP) in the following standard simplex
Linear Programming, Lecture 4 Corbett Redden October 3, 2016 Simplex Form Conventions Examples Simplex Method To run the simplex method, we start from a Linear Program (LP) in the following standard simplex
Introduction to Operations Research Prof. G. Srinivasan Department of Management Studies Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Introduction to Operations Research Prof. G. Srinivasan Department of Management Studies Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module - 03 Simplex Algorithm Lecture 15 Infeasibility In this class, we
Introduction to Operations Research Prof. G. Srinivasan Department of Management Studies Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module - 03 Simplex Algorithm Lecture 15 Infeasibility In this class, we
(P ) Minimize 4x 1 + 6x 2 + 5x 3 s.t. 2x 1 3x 3 3 3x 2 2x 3 6
 The exam is three hours long and consists of 4 exercises. The exam is graded on a scale 0-25 points, and the points assigned to each question are indicated in parenthesis within the text. Problem 1 Consider
The exam is three hours long and consists of 4 exercises. The exam is graded on a scale 0-25 points, and the points assigned to each question are indicated in parenthesis within the text. Problem 1 Consider
15-780: LinearProgramming
 15-780: LinearProgramming J. Zico Kolter February 1-3, 2016 1 Outline Introduction Some linear algebra review Linear programming Simplex algorithm Duality and dual simplex 2 Outline Introduction Some linear
15-780: LinearProgramming J. Zico Kolter February 1-3, 2016 1 Outline Introduction Some linear algebra review Linear programming Simplex algorithm Duality and dual simplex 2 Outline Introduction Some linear
IE 5531: Engineering Optimization I
 IE 5531: Engineering Optimization I Lecture 5: The Simplex method, continued Prof. John Gunnar Carlsson September 22, 2010 Prof. John Gunnar Carlsson IE 5531: Engineering Optimization I September 22, 2010
IE 5531: Engineering Optimization I Lecture 5: The Simplex method, continued Prof. John Gunnar Carlsson September 22, 2010 Prof. John Gunnar Carlsson IE 5531: Engineering Optimization I September 22, 2010
TIM 206 Lecture 3: The Simplex Method
 TIM 206 Lecture 3: The Simplex Method Kevin Ross. Scribe: Shane Brennan (2006) September 29, 2011 1 Basic Feasible Solutions Have equation Ax = b contain more columns (variables) than rows (constraints),
TIM 206 Lecture 3: The Simplex Method Kevin Ross. Scribe: Shane Brennan (2006) September 29, 2011 1 Basic Feasible Solutions Have equation Ax = b contain more columns (variables) than rows (constraints),
Optimization (168) Lecture 7-8-9
 Optimization (168) Lecture 7-8-9 Jesús De Loera UC Davis, Mathematics Wednesday, April 2, 2012 1 DEGENERACY IN THE SIMPLEX METHOD 2 DEGENERACY z =2x 1 x 2 + 8x 3 x 4 =1 2x 3 x 5 =3 2x 1 + 4x 2 6x 3 x 6
Optimization (168) Lecture 7-8-9 Jesús De Loera UC Davis, Mathematics Wednesday, April 2, 2012 1 DEGENERACY IN THE SIMPLEX METHOD 2 DEGENERACY z =2x 1 x 2 + 8x 3 x 4 =1 2x 3 x 5 =3 2x 1 + 4x 2 6x 3 x 6
AM 121: Intro to Optimization
 AM 121: Intro to Optimization Models and Methods Lecture 6: Phase I, degeneracy, smallest subscript rule. Yiling Chen SEAS Lesson Plan Phase 1 (initialization) Degeneracy and cycling Smallest subscript
AM 121: Intro to Optimization Models and Methods Lecture 6: Phase I, degeneracy, smallest subscript rule. Yiling Chen SEAS Lesson Plan Phase 1 (initialization) Degeneracy and cycling Smallest subscript
4.4 The Simplex Method and the Standard Minimization Problem
 . The Simplex Method and the Standard Minimization Problem Question : What is a standard minimization problem? Question : How is the standard minimization problem related to the dual standard maximization
. The Simplex Method and the Standard Minimization Problem Question : What is a standard minimization problem? Question : How is the standard minimization problem related to the dual standard maximization
Introduction to the Simplex Algorithm Active Learning Module 3
 Introduction to the Simplex Algorithm Active Learning Module 3 J. René Villalobos and Gary L. Hogg Arizona State University Paul M. Griffin Georgia Institute of Technology Background Material Almost any
Introduction to the Simplex Algorithm Active Learning Module 3 J. René Villalobos and Gary L. Hogg Arizona State University Paul M. Griffin Georgia Institute of Technology Background Material Almost any
Answer the following questions: Q1: Choose the correct answer ( 20 Points ):
 Benha University Final Exam. (ختلفات) Class: 2 rd Year Students Subject: Operations Research Faculty of Computers & Informatics Date: - / 5 / 2017 Time: 3 hours Examiner: Dr. El-Sayed Badr Answer the following
Benha University Final Exam. (ختلفات) Class: 2 rd Year Students Subject: Operations Research Faculty of Computers & Informatics Date: - / 5 / 2017 Time: 3 hours Examiner: Dr. El-Sayed Badr Answer the following
Farkas Lemma, Dual Simplex and Sensitivity Analysis
 Summer 2011 Optimization I Lecture 10 Farkas Lemma, Dual Simplex and Sensitivity Analysis 1 Farkas Lemma Theorem 1. Let A R m n, b R m. Then exactly one of the following two alternatives is true: (i) x
Summer 2011 Optimization I Lecture 10 Farkas Lemma, Dual Simplex and Sensitivity Analysis 1 Farkas Lemma Theorem 1. Let A R m n, b R m. Then exactly one of the following two alternatives is true: (i) x
Section Notes 9. IP: Cutting Planes. Applied Math 121. Week of April 12, 2010
 Section Notes 9 IP: Cutting Planes Applied Math 121 Week of April 12, 2010 Goals for the week understand what a strong formulations is. be familiar with the cutting planes algorithm and the types of cuts
Section Notes 9 IP: Cutting Planes Applied Math 121 Week of April 12, 2010 Goals for the week understand what a strong formulations is. be familiar with the cutting planes algorithm and the types of cuts
The augmented form of this LP is the following linear system of equations:
 1 Consider the following LP given in standard form: max z = 5 x_1 + 2 x_2 Subject to 3 x_1 + 2 x_2 2400 x_2 800 2 x_1 1200 x_1, x_2 >= 0 The augmented form of this LP is the following linear system of
1 Consider the following LP given in standard form: max z = 5 x_1 + 2 x_2 Subject to 3 x_1 + 2 x_2 2400 x_2 800 2 x_1 1200 x_1, x_2 >= 0 The augmented form of this LP is the following linear system of
Going from graphic solutions to algebraic
 Going from graphic solutions to algebraic 2 variables: Graph constraints Identify corner points of feasible area Find which corner point has best objective value More variables: Think about constraints
Going from graphic solutions to algebraic 2 variables: Graph constraints Identify corner points of feasible area Find which corner point has best objective value More variables: Think about constraints
1 Review Session. 1.1 Lecture 2
 1 Review Session Note: The following lists give an overview of the material that was covered in the lectures and sections. Your TF will go through these lists. If anything is unclear or you have questions
1 Review Session Note: The following lists give an overview of the material that was covered in the lectures and sections. Your TF will go through these lists. If anything is unclear or you have questions
Professor Alan H. Stein October 31, 2007
 Mathematics 05 Professor Alan H. Stein October 3, 2007 SOLUTIONS. For most maximum problems, the contraints are in the form l(x) k, where l(x) is a linear polynomial and k is a positive constant. Explain
Mathematics 05 Professor Alan H. Stein October 3, 2007 SOLUTIONS. For most maximum problems, the contraints are in the form l(x) k, where l(x) is a linear polynomial and k is a positive constant. Explain
AM 121 Introduction to Optimization: Models and Methods Example Questions for Midterm 1
 AM 121 Introduction to Optimization: Models and Methods Example Questions for Midterm 1 Prof. Yiling Chen Fall 2018 Here are some practice questions to help to prepare for the midterm. The midterm will
AM 121 Introduction to Optimization: Models and Methods Example Questions for Midterm 1 Prof. Yiling Chen Fall 2018 Here are some practice questions to help to prepare for the midterm. The midterm will
Water Resources Systems: Modeling Techniques and Analysis
 INDIAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE Water Resources Systems: Modeling Techniques and Analysis Lecture - 9 Course Instructor : Prof. P. P. MUJUMDAR Department of Civil Engg., IISc. Summary of the previous lecture
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE Water Resources Systems: Modeling Techniques and Analysis Lecture - 9 Course Instructor : Prof. P. P. MUJUMDAR Department of Civil Engg., IISc. Summary of the previous lecture
The Simplex Method for Solving a Linear Program Prof. Stephen Graves
 The Simplex Method for Solving a Linear Program Prof. Stephen Graves Observations from Geometry feasible region is a convex polyhedron an optimum occurs at a corner point possible algorithm - search over
The Simplex Method for Solving a Linear Program Prof. Stephen Graves Observations from Geometry feasible region is a convex polyhedron an optimum occurs at a corner point possible algorithm - search over
REVISION SHEET DECISION MATHS 2 DECISION ANALYSIS
 REVISION SHEET DECISION MATHS 2 DECISION ANALYSIS The main ideas are covered in AQA Edexcel MEI OCR D2 Before the exam you should know The meaning of the different kinds of node. Be able to construct a
REVISION SHEET DECISION MATHS 2 DECISION ANALYSIS The main ideas are covered in AQA Edexcel MEI OCR D2 Before the exam you should know The meaning of the different kinds of node. Be able to construct a
CS Algorithms and Complexity
 CS 50 - Algorithms and Complexity Linear Programming, the Simplex Method, and Hard Problems Sean Anderson 2/15/18 Portland State University Table of contents 1. The Simplex Method 2. The Graph Problem
CS 50 - Algorithms and Complexity Linear Programming, the Simplex Method, and Hard Problems Sean Anderson 2/15/18 Portland State University Table of contents 1. The Simplex Method 2. The Graph Problem
Michælmas 2012 Operations Research III/IV 1
 Michælmas 2012 Operations Research III/IV 1 An inventory example A company makes windsurfing boards and has orders for 40, 60, 75 and 25 boards respectively over the next four production quarters. All
Michælmas 2012 Operations Research III/IV 1 An inventory example A company makes windsurfing boards and has orders for 40, 60, 75 and 25 boards respectively over the next four production quarters. All
Review Solutions, Exam 2, Operations Research
 Review Solutions, Exam 2, Operations Research 1. Prove the weak duality theorem: For any x feasible for the primal and y feasible for the dual, then... HINT: Consider the quantity y T Ax. SOLUTION: To
Review Solutions, Exam 2, Operations Research 1. Prove the weak duality theorem: For any x feasible for the primal and y feasible for the dual, then... HINT: Consider the quantity y T Ax. SOLUTION: To
Lesson 27 Linear Programming; The Simplex Method
 Lesson Linear Programming; The Simplex Method Math 0 April 9, 006 Setup A standard linear programming problem is to maximize the quantity c x + c x +... c n x n = c T x subject to constraints a x + a x
Lesson Linear Programming; The Simplex Method Math 0 April 9, 006 Setup A standard linear programming problem is to maximize the quantity c x + c x +... c n x n = c T x subject to constraints a x + a x
Math Models of OR: Some Definitions
 Math Models of OR: Some Definitions John E. Mitchell Department of Mathematical Sciences RPI, Troy, NY 12180 USA September 2018 Mitchell Some Definitions 1 / 20 Active constraints Outline 1 Active constraints
Math Models of OR: Some Definitions John E. Mitchell Department of Mathematical Sciences RPI, Troy, NY 12180 USA September 2018 Mitchell Some Definitions 1 / 20 Active constraints Outline 1 Active constraints
1. (7pts) Find the points of intersection, if any, of the following planes. 3x + 9y + 6z = 3 2x 6y 4z = 2 x + 3y + 2z = 1
 Math 125 Exam 1 Version 1 February 20, 2006 1. (a) (7pts) Find the points of intersection, if any, of the following planes. Solution: augmented R 1 R 3 3x + 9y + 6z = 3 2x 6y 4z = 2 x + 3y + 2z = 1 3 9
Math 125 Exam 1 Version 1 February 20, 2006 1. (a) (7pts) Find the points of intersection, if any, of the following planes. Solution: augmented R 1 R 3 3x + 9y + 6z = 3 2x 6y 4z = 2 x + 3y + 2z = 1 3 9
Simplex Method for LP (II)
 Simplex Method for LP (II) Xiaoxi Li Wuhan University Sept. 27, 2017 (week 4) Operations Research (Li, X.) Simplex Method for LP (II) Sept. 27, 2017 (week 4) 1 / 31 Organization of this lecture Contents:
Simplex Method for LP (II) Xiaoxi Li Wuhan University Sept. 27, 2017 (week 4) Operations Research (Li, X.) Simplex Method for LP (II) Sept. 27, 2017 (week 4) 1 / 31 Organization of this lecture Contents:
Optimisation and Operations Research
 Optimisation and Operations Research Lecture 22: Linear Programming Revisited Matthew Roughan http://www.maths.adelaide.edu.au/matthew.roughan/ Lecture_notes/OORII/ School
Optimisation and Operations Research Lecture 22: Linear Programming Revisited Matthew Roughan http://www.maths.adelaide.edu.au/matthew.roughan/ Lecture_notes/OORII/ School
Standard Form An LP is in standard form when: All variables are non-negativenegative All constraints are equalities Putting an LP formulation into sta
 Chapter 4 Linear Programming: The Simplex Method An Overview of the Simplex Method Standard Form Tableau Form Setting Up the Initial Simplex Tableau Improving the Solution Calculating the Next Tableau
Chapter 4 Linear Programming: The Simplex Method An Overview of the Simplex Method Standard Form Tableau Form Setting Up the Initial Simplex Tableau Improving the Solution Calculating the Next Tableau
1 Overview. 2 Extreme Points. AM 221: Advanced Optimization Spring 2016
 AM 22: Advanced Optimization Spring 206 Prof. Yaron Singer Lecture 7 February 7th Overview In the previous lectures we saw applications of duality to game theory and later to learning theory. In this lecture
AM 22: Advanced Optimization Spring 206 Prof. Yaron Singer Lecture 7 February 7th Overview In the previous lectures we saw applications of duality to game theory and later to learning theory. In this lecture
36106 Managerial Decision Modeling Linear Decision Models: Part II
 1 36106 Managerial Decision Modeling Linear Decision Models: Part II Kipp Martin University of Chicago Booth School of Business January 20, 2014 Reading and Excel Files Reading (Powell and Baker): Sections
1 36106 Managerial Decision Modeling Linear Decision Models: Part II Kipp Martin University of Chicago Booth School of Business January 20, 2014 Reading and Excel Files Reading (Powell and Baker): Sections
ORF 523 Final Exam, Spring 2016
 Name: Princeton University ORF 523 Final Exam, Spring 2016 Thursday, May 5, 9am, to Tuesday, May 10, 11am Instructor: A.A. Ahmadi AI: G. Hall 1. Please write out and sign the following pledge on top of
Name: Princeton University ORF 523 Final Exam, Spring 2016 Thursday, May 5, 9am, to Tuesday, May 10, 11am Instructor: A.A. Ahmadi AI: G. Hall 1. Please write out and sign the following pledge on top of
MA 162: Finite Mathematics - Section 3.3/4.1
 MA 162: Finite Mathematics - Section 3.3/4.1 Fall 2014 Ray Kremer University of Kentucky October 6, 2014 Announcements: Homework 3.3 due Tuesday at 6pm. Homework 4.1 due Friday at 6pm. Exam scores were
MA 162: Finite Mathematics - Section 3.3/4.1 Fall 2014 Ray Kremer University of Kentucky October 6, 2014 Announcements: Homework 3.3 due Tuesday at 6pm. Homework 4.1 due Friday at 6pm. Exam scores were
Understanding the Simplex algorithm. Standard Optimization Problems.
 Understanding the Simplex algorithm. Ma 162 Spring 2011 Ma 162 Spring 2011 February 28, 2011 Standard Optimization Problems. A standard maximization problem can be conveniently described in matrix form
Understanding the Simplex algorithm. Ma 162 Spring 2011 Ma 162 Spring 2011 February 28, 2011 Standard Optimization Problems. A standard maximization problem can be conveniently described in matrix form
Notes on Simplex Algorithm
 Notes on Simplex Algorithm CS 9 Staff October 8, 7 Until now, we have represented the problems geometrically, and solved by finding a corner and moving around Now we learn an algorithm to solve this without
Notes on Simplex Algorithm CS 9 Staff October 8, 7 Until now, we have represented the problems geometrically, and solved by finding a corner and moving around Now we learn an algorithm to solve this without
Section 4.1 Solving Systems of Linear Inequalities
 Section 4.1 Solving Systems of Linear Inequalities Question 1 How do you graph a linear inequality? Question 2 How do you graph a system of linear inequalities? Question 1 How do you graph a linear inequality?
Section 4.1 Solving Systems of Linear Inequalities Question 1 How do you graph a linear inequality? Question 2 How do you graph a system of linear inequalities? Question 1 How do you graph a linear inequality?
In Chapters 3 and 4 we introduced linear programming
 SUPPLEMENT The Simplex Method CD3 In Chapters 3 and 4 we introduced linear programming and showed how models with two variables can be solved graphically. We relied on computer programs (WINQSB, Excel,
SUPPLEMENT The Simplex Method CD3 In Chapters 3 and 4 we introduced linear programming and showed how models with two variables can be solved graphically. We relied on computer programs (WINQSB, Excel,
2 3 x = 6 4. (x 1) 6
 Solutions to Math 201 Final Eam from spring 2007 p. 1 of 16 (some of these problem solutions are out of order, in the interest of saving paper) 1. given equation: 1 2 ( 1) 1 3 = 4 both sides 6: 6 1 1 (
Solutions to Math 201 Final Eam from spring 2007 p. 1 of 16 (some of these problem solutions are out of order, in the interest of saving paper) 1. given equation: 1 2 ( 1) 1 3 = 4 both sides 6: 6 1 1 (
Civil Engineering Systems Analysis Lecture XII. Instructor: Prof. Naveen Eluru Department of Civil Engineering and Applied Mechanics
 Civil Engineering Systems Analysis Lecture XII Instructor: Prof. Naveen Eluru Department of Civil Engineering and Applied Mechanics Today s Learning Objectives Dual Midterm 2 Let us look at a complex case
Civil Engineering Systems Analysis Lecture XII Instructor: Prof. Naveen Eluru Department of Civil Engineering and Applied Mechanics Today s Learning Objectives Dual Midterm 2 Let us look at a complex case
CPS 616 ITERATIVE IMPROVEMENTS 10-1
 CPS 66 ITERATIVE IMPROVEMENTS 0 - APPROACH Algorithm design technique for solving optimization problems Start with a feasible solution Repeat the following step until no improvement can be found: change
CPS 66 ITERATIVE IMPROVEMENTS 0 - APPROACH Algorithm design technique for solving optimization problems Start with a feasible solution Repeat the following step until no improvement can be found: change
Simplex Method in different guises
 Simplex Method in different guises The Furniture problem Max 0x + 0x 2 + 20x, subject to x 0, 8x + x 2 + 2x 48, 4x + 2x 2 +.x 20, 2x +.x 2 +.x 8. Canonical form: slack variables s = (s, s 2, s ) 0. Constraints
Simplex Method in different guises The Furniture problem Max 0x + 0x 2 + 20x, subject to x 0, 8x + x 2 + 2x 48, 4x + 2x 2 +.x 20, 2x +.x 2 +.x 8. Canonical form: slack variables s = (s, s 2, s ) 0. Constraints
Motivating examples Introduction to algorithms Simplex algorithm. On a particular example General algorithm. Duality An application to game theory
 Instructor: Shengyu Zhang 1 LP Motivating examples Introduction to algorithms Simplex algorithm On a particular example General algorithm Duality An application to game theory 2 Example 1: profit maximization
Instructor: Shengyu Zhang 1 LP Motivating examples Introduction to algorithms Simplex algorithm On a particular example General algorithm Duality An application to game theory 2 Example 1: profit maximization
Introduction to optimization
 Introduction to optimization Geir Dahl CMA, Dept. of Mathematics and Dept. of Informatics University of Oslo 1 / 24 The plan 1. The basic concepts 2. Some useful tools (linear programming = linear optimization)
Introduction to optimization Geir Dahl CMA, Dept. of Mathematics and Dept. of Informatics University of Oslo 1 / 24 The plan 1. The basic concepts 2. Some useful tools (linear programming = linear optimization)
Notes taken by Graham Taylor. January 22, 2005
 CSC4 - Linear Programming and Combinatorial Optimization Lecture : Different forms of LP. The algebraic objects behind LP. Basic Feasible Solutions Notes taken by Graham Taylor January, 5 Summary: We first
CSC4 - Linear Programming and Combinatorial Optimization Lecture : Different forms of LP. The algebraic objects behind LP. Basic Feasible Solutions Notes taken by Graham Taylor January, 5 Summary: We first
IE 400: Principles of Engineering Management. Simplex Method Continued
 IE 400: Principles of Engineering Management Simplex Method Continued 1 Agenda Simplex for min problems Alternative optimal solutions Unboundedness Degeneracy Big M method Two phase method 2 Simplex for
IE 400: Principles of Engineering Management Simplex Method Continued 1 Agenda Simplex for min problems Alternative optimal solutions Unboundedness Degeneracy Big M method Two phase method 2 Simplex for
3 The Simplex Method. 3.1 Basic Solutions
 3 The Simplex Method 3.1 Basic Solutions In the LP of Example 2.3, the optimal solution happened to lie at an extreme point of the feasible set. This was not a coincidence. Consider an LP in general form,
3 The Simplex Method 3.1 Basic Solutions In the LP of Example 2.3, the optimal solution happened to lie at an extreme point of the feasible set. This was not a coincidence. Consider an LP in general form,
Optimization Methods in Management Science
 Optimization Methods in Management Science MIT 15.05 Recitation 8 TAs: Giacomo Nannicini, Ebrahim Nasrabadi At the end of this recitation, students should be able to: 1. Derive Gomory cut from fractional
Optimization Methods in Management Science MIT 15.05 Recitation 8 TAs: Giacomo Nannicini, Ebrahim Nasrabadi At the end of this recitation, students should be able to: 1. Derive Gomory cut from fractional
1. Algebraic and geometric treatments Consider an LP problem in the standard form. x 0. Solutions to the system of linear equations
 The Simplex Method Most textbooks in mathematical optimization, especially linear programming, deal with the simplex method. In this note we study the simplex method. It requires basically elementary linear
The Simplex Method Most textbooks in mathematical optimization, especially linear programming, deal with the simplex method. In this note we study the simplex method. It requires basically elementary linear
CO 250 Final Exam Guide
 Spring 2017 CO 250 Final Exam Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS richardwu.ca CO 250 Final Exam Guide Introduction to Optimization Kanstantsin Pashkovich Spring 2017 University of Waterloo Last Revision: March 4,
Spring 2017 CO 250 Final Exam Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS richardwu.ca CO 250 Final Exam Guide Introduction to Optimization Kanstantsin Pashkovich Spring 2017 University of Waterloo Last Revision: March 4,
IE 5531 Midterm #2 Solutions
 IE 5531 Midterm #2 s Prof. John Gunnar Carlsson November 9, 2011 Before you begin: This exam has 9 pages and a total of 5 problems. Make sure that all pages are present. To obtain credit for a problem,
IE 5531 Midterm #2 s Prof. John Gunnar Carlsson November 9, 2011 Before you begin: This exam has 9 pages and a total of 5 problems. Make sure that all pages are present. To obtain credit for a problem,
Topic: Primal-Dual Algorithms Date: We finished our discussion of randomized rounding and began talking about LP Duality.
 CS787: Advanced Algorithms Scribe: Amanda Burton, Leah Kluegel Lecturer: Shuchi Chawla Topic: Primal-Dual Algorithms Date: 10-17-07 14.1 Last Time We finished our discussion of randomized rounding and
CS787: Advanced Algorithms Scribe: Amanda Burton, Leah Kluegel Lecturer: Shuchi Chawla Topic: Primal-Dual Algorithms Date: 10-17-07 14.1 Last Time We finished our discussion of randomized rounding and
Linear Programming Duality
 Summer 2011 Optimization I Lecture 8 1 Duality recap Linear Programming Duality We motivated the dual of a linear program by thinking about the best possible lower bound on the optimal value we can achieve
Summer 2011 Optimization I Lecture 8 1 Duality recap Linear Programming Duality We motivated the dual of a linear program by thinking about the best possible lower bound on the optimal value we can achieve
The Simplex Algorithm and Goal Programming
 The Simplex Algorithm and Goal Programming In Chapter 3, we saw how to solve two-variable linear programming problems graphically. Unfortunately, most real-life LPs have many variables, so a method is
The Simplex Algorithm and Goal Programming In Chapter 3, we saw how to solve two-variable linear programming problems graphically. Unfortunately, most real-life LPs have many variables, so a method is
ORF 522. Linear Programming and Convex Analysis
 ORF 5 Linear Programming and Convex Analysis Initial solution and particular cases Marco Cuturi Princeton ORF-5 Reminder: Tableaux At each iteration, a tableau for an LP in standard form keeps track of....................
ORF 5 Linear Programming and Convex Analysis Initial solution and particular cases Marco Cuturi Princeton ORF-5 Reminder: Tableaux At each iteration, a tableau for an LP in standard form keeps track of....................
Operations Research Lecture 2: Linear Programming Simplex Method
 Operations Research Lecture 2: Linear Programming Simplex Method Notes taken by Kaiquan Xu@Business School, Nanjing University Mar 10th 2016 1 Geometry of LP 1.1 Graphical Representation and Solution Example
Operations Research Lecture 2: Linear Programming Simplex Method Notes taken by Kaiquan Xu@Business School, Nanjing University Mar 10th 2016 1 Geometry of LP 1.1 Graphical Representation and Solution Example
Math 354 Summer 2004 Solutions to review problems for Midterm #1
 Solutions to review problems for Midterm #1 First: Midterm #1 covers Chapter 1 and 2. In particular, this means that it does not explicitly cover linear algebra. Also, I promise there will not be any proofs.
Solutions to review problems for Midterm #1 First: Midterm #1 covers Chapter 1 and 2. In particular, this means that it does not explicitly cover linear algebra. Also, I promise there will not be any proofs.
Yinyu Ye, MS&E, Stanford MS&E310 Lecture Note #06. The Simplex Method
 The Simplex Method Yinyu Ye Department of Management Science and Engineering Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305, U.S.A. http://www.stanford.edu/ yyye (LY, Chapters 2.3-2.5, 3.1-3.4) 1 Geometry of Linear
The Simplex Method Yinyu Ye Department of Management Science and Engineering Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305, U.S.A. http://www.stanford.edu/ yyye (LY, Chapters 2.3-2.5, 3.1-3.4) 1 Geometry of Linear
Ω R n is called the constraint set or feasible set. x 1
 1 Chapter 5 Linear Programming (LP) General constrained optimization problem: minimize subject to f(x) x Ω Ω R n is called the constraint set or feasible set. any point x Ω is called a feasible point We
1 Chapter 5 Linear Programming (LP) General constrained optimization problem: minimize subject to f(x) x Ω Ω R n is called the constraint set or feasible set. any point x Ω is called a feasible point We
CHAPTER 2. The Simplex Method
 CHAPTER 2 The Simplex Method In this chapter we present the simplex method as it applies to linear programming problems in standard form. 1. An Example We first illustrate how the simplex method works
CHAPTER 2 The Simplex Method In this chapter we present the simplex method as it applies to linear programming problems in standard form. 1. An Example We first illustrate how the simplex method works
The Simplex Algorithm
 8.433 Combinatorial Optimization The Simplex Algorithm October 6, 8 Lecturer: Santosh Vempala We proved the following: Lemma (Farkas). Let A R m n, b R m. Exactly one of the following conditions is true:.
8.433 Combinatorial Optimization The Simplex Algorithm October 6, 8 Lecturer: Santosh Vempala We proved the following: Lemma (Farkas). Let A R m n, b R m. Exactly one of the following conditions is true:.
Lecture 2: The Simplex method
 Lecture 2 1 Linear and Combinatorial Optimization Lecture 2: The Simplex method Basic solution. The Simplex method (standardform, b>0). 1. Repetition of basic solution. 2. One step in the Simplex algorithm.
Lecture 2 1 Linear and Combinatorial Optimization Lecture 2: The Simplex method Basic solution. The Simplex method (standardform, b>0). 1. Repetition of basic solution. 2. One step in the Simplex algorithm.
The simplex algorithm
 The simplex algorithm The simplex algorithm is the classical method for solving linear programs. Its running time is not polynomial in the worst case. It does yield insight into linear programs, however,
The simplex algorithm The simplex algorithm is the classical method for solving linear programs. Its running time is not polynomial in the worst case. It does yield insight into linear programs, however,
Lecture 11: Post-Optimal Analysis. September 23, 2009
 Lecture : Post-Optimal Analysis September 23, 2009 Today Lecture Dual-Simplex Algorithm Post-Optimal Analysis Chapters 4.4 and 4.5. IE 30/GE 330 Lecture Dual Simplex Method The dual simplex method will
Lecture : Post-Optimal Analysis September 23, 2009 Today Lecture Dual-Simplex Algorithm Post-Optimal Analysis Chapters 4.4 and 4.5. IE 30/GE 330 Lecture Dual Simplex Method The dual simplex method will
MATH 445/545 Homework 2: Due March 3rd, 2016
 MATH 445/545 Homework 2: Due March 3rd, 216 Answer the following questions. Please include the question with the solution (write or type them out doing this will help you digest the problem). I do not
MATH 445/545 Homework 2: Due March 3rd, 216 Answer the following questions. Please include the question with the solution (write or type them out doing this will help you digest the problem). I do not
Linear Programming: Simplex
 Linear Programming: Simplex Stephen J. Wright 1 2 Computer Sciences Department, University of Wisconsin-Madison. IMA, August 2016 Stephen Wright (UW-Madison) Linear Programming: Simplex IMA, August 2016
Linear Programming: Simplex Stephen J. Wright 1 2 Computer Sciences Department, University of Wisconsin-Madison. IMA, August 2016 Stephen Wright (UW-Madison) Linear Programming: Simplex IMA, August 2016
The Simplex Algorithm: Technicalities 1
 1/45 The Simplex Algorithm: Technicalities 1 Adrian Vetta 1 This presentation is based upon the book Linear Programming by Vasek Chvatal 2/45 Two Issues Here we discuss two potential problems with the
1/45 The Simplex Algorithm: Technicalities 1 Adrian Vetta 1 This presentation is based upon the book Linear Programming by Vasek Chvatal 2/45 Two Issues Here we discuss two potential problems with the
c) Place the Coefficients from all Equations into a Simplex Tableau, labeled above with variables indicating their respective columns
 BUILDING A SIMPLEX TABLEAU AND PROPER PIVOT SELECTION Maximize : 15x + 25y + 18 z s. t. 2x+ 3y+ 4z 60 4x+ 4y+ 2z 100 8x+ 5y 80 x 0, y 0, z 0 a) Build Equations out of each of the constraints above by introducing
BUILDING A SIMPLEX TABLEAU AND PROPER PIVOT SELECTION Maximize : 15x + 25y + 18 z s. t. 2x+ 3y+ 4z 60 4x+ 4y+ 2z 100 8x+ 5y 80 x 0, y 0, z 0 a) Build Equations out of each of the constraints above by introducing
Optimization 4. GAME THEORY
 Optimization GAME THEORY DPK Easter Term Saddle points of two-person zero-sum games We consider a game with two players Player I can choose one of m strategies, indexed by i =,, m and Player II can choose
Optimization GAME THEORY DPK Easter Term Saddle points of two-person zero-sum games We consider a game with two players Player I can choose one of m strategies, indexed by i =,, m and Player II can choose
OPRE 6201 : 3. Special Cases
 OPRE 6201 : 3. Special Cases 1 Initialization: The Big-M Formulation Consider the linear program: Minimize 4x 1 +x 2 3x 1 +x 2 = 3 (1) 4x 1 +3x 2 6 (2) x 1 +2x 2 3 (3) x 1, x 2 0. Notice that there are
OPRE 6201 : 3. Special Cases 1 Initialization: The Big-M Formulation Consider the linear program: Minimize 4x 1 +x 2 3x 1 +x 2 = 3 (1) 4x 1 +3x 2 6 (2) x 1 +2x 2 3 (3) x 1, x 2 0. Notice that there are
Advanced Mathematical Programming IE417. Lecture 24. Dr. Ted Ralphs
 Advanced Mathematical Programming IE417 Lecture 24 Dr. Ted Ralphs IE417 Lecture 24 1 Reading for This Lecture Sections 11.2-11.2 IE417 Lecture 24 2 The Linear Complementarity Problem Given M R p p and
Advanced Mathematical Programming IE417 Lecture 24 Dr. Ted Ralphs IE417 Lecture 24 1 Reading for This Lecture Sections 11.2-11.2 IE417 Lecture 24 2 The Linear Complementarity Problem Given M R p p and
An introductory example
 CS1 Lecture 9 An introductory example Suppose that a company that produces three products wishes to decide the level of production of each so as to maximize profits. Let x 1 be the amount of Product 1
CS1 Lecture 9 An introductory example Suppose that a company that produces three products wishes to decide the level of production of each so as to maximize profits. Let x 1 be the amount of Product 1
1. Introduce slack variables for each inequaility to make them equations and rewrite the objective function in the form ax by cz... + P = 0.
 3.4 Simplex Method If a linear programming problem has more than 2 variables, solving graphically is not the way to go. Instead, we ll use a more methodical, numeric process called the Simplex Method.
3.4 Simplex Method If a linear programming problem has more than 2 variables, solving graphically is not the way to go. Instead, we ll use a more methodical, numeric process called the Simplex Method.
LINEAR PROGRAMMING 2. In many business and policy making situations the following type of problem is encountered:
 LINEAR PROGRAMMING 2 In many business and policy making situations the following type of problem is encountered: Maximise an objective subject to (in)equality constraints. Mathematical programming provides
LINEAR PROGRAMMING 2 In many business and policy making situations the following type of problem is encountered: Maximise an objective subject to (in)equality constraints. Mathematical programming provides
IE 5531: Engineering Optimization I
 IE 5531: Engineering Optimization I Lecture 7: Duality and applications Prof. John Gunnar Carlsson September 29, 2010 Prof. John Gunnar Carlsson IE 5531: Engineering Optimization I September 29, 2010 1
IE 5531: Engineering Optimization I Lecture 7: Duality and applications Prof. John Gunnar Carlsson September 29, 2010 Prof. John Gunnar Carlsson IE 5531: Engineering Optimization I September 29, 2010 1
Chapter 1 Linear Programming. Paragraph 5 Duality
 Chapter 1 Linear Programming Paragraph 5 Duality What we did so far We developed the 2-Phase Simplex Algorithm: Hop (reasonably) from basic solution (bs) to bs until you find a basic feasible solution
Chapter 1 Linear Programming Paragraph 5 Duality What we did so far We developed the 2-Phase Simplex Algorithm: Hop (reasonably) from basic solution (bs) to bs until you find a basic feasible solution
February 22, Introduction to the Simplex Algorithm
 15.53 February 22, 27 Introduction to the Simplex Algorithm 1 Quotes for today Give a man a fish and you feed him for a day. Teach him how to fish and you feed him for a lifetime. -- Lao Tzu Give a man
15.53 February 22, 27 Introduction to the Simplex Algorithm 1 Quotes for today Give a man a fish and you feed him for a day. Teach him how to fish and you feed him for a lifetime. -- Lao Tzu Give a man
Summary of the simplex method
 MVE165/MMG630, The simplex method; degeneracy; unbounded solutions; infeasibility; starting solutions; duality; interpretation Ann-Brith Strömberg 2012 03 16 Summary of the simplex method Optimality condition:
MVE165/MMG630, The simplex method; degeneracy; unbounded solutions; infeasibility; starting solutions; duality; interpretation Ann-Brith Strömberg 2012 03 16 Summary of the simplex method Optimality condition:
The Simplex Method: An Example
 The Simplex Method: An Example Our first step is to introduce one more new variable, which we denote by z. The variable z is define to be equal to 4x 1 +3x 2. Doing this will allow us to have a unified
The Simplex Method: An Example Our first step is to introduce one more new variable, which we denote by z. The variable z is define to be equal to 4x 1 +3x 2. Doing this will allow us to have a unified
"SYMMETRIC" PRIMAL-DUAL PAIR
 "SYMMETRIC" PRIMAL-DUAL PAIR PRIMAL Minimize cx DUAL Maximize y T b st Ax b st A T y c T x y Here c 1 n, x n 1, b m 1, A m n, y m 1, WITH THE PRIMAL IN STANDARD FORM... Minimize cx Maximize y T b st Ax
"SYMMETRIC" PRIMAL-DUAL PAIR PRIMAL Minimize cx DUAL Maximize y T b st Ax b st A T y c T x y Here c 1 n, x n 1, b m 1, A m n, y m 1, WITH THE PRIMAL IN STANDARD FORM... Minimize cx Maximize y T b st Ax
Slack Variable. Max Z= 3x 1 + 4x 2 + 5X 3. Subject to: X 1 + X 2 + X x 1 + 4x 2 + X X 1 + X 2 + 4X 3 10 X 1 0, X 2 0, X 3 0
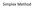 Simplex Method Slack Variable Max Z= 3x 1 + 4x 2 + 5X 3 Subject to: X 1 + X 2 + X 3 20 3x 1 + 4x 2 + X 3 15 2X 1 + X 2 + 4X 3 10 X 1 0, X 2 0, X 3 0 Standard Form Max Z= 3x 1 +4x 2 +5X 3 + 0S 1 + 0S 2
Simplex Method Slack Variable Max Z= 3x 1 + 4x 2 + 5X 3 Subject to: X 1 + X 2 + X 3 20 3x 1 + 4x 2 + X 3 15 2X 1 + X 2 + 4X 3 10 X 1 0, X 2 0, X 3 0 Standard Form Max Z= 3x 1 +4x 2 +5X 3 + 0S 1 + 0S 2
Lecture slides by Kevin Wayne
 LINEAR PROGRAMMING I a refreshing example standard form fundamental questions geometry linear algebra simplex algorithm Lecture slides by Kevin Wayne Last updated on 7/25/17 11:09 AM Linear programming
LINEAR PROGRAMMING I a refreshing example standard form fundamental questions geometry linear algebra simplex algorithm Lecture slides by Kevin Wayne Last updated on 7/25/17 11:09 AM Linear programming
MA 0090 Section 21 - Slope-Intercept Wednesday, October 31, Objectives: Review the slope of the graph of an equation in slope-intercept form.
 MA 0090 Section 21 - Slope-Intercept Wednesday, October 31, 2018 Objectives: Review the slope of the graph of an equation in slope-intercept form. Last time, we looked at the equation Slope (1) y = 2x
MA 0090 Section 21 - Slope-Intercept Wednesday, October 31, 2018 Objectives: Review the slope of the graph of an equation in slope-intercept form. Last time, we looked at the equation Slope (1) y = 2x
Finite Mathematics : A Business Approach
 Finite Mathematics : A Business Approach Dr. Brian Travers and Prof. James Lampes Second Edition Cover Art by Stephanie Oxenford Additional Editing by John Gambino Contents What You Should Already Know
Finite Mathematics : A Business Approach Dr. Brian Travers and Prof. James Lampes Second Edition Cover Art by Stephanie Oxenford Additional Editing by John Gambino Contents What You Should Already Know
Chap6 Duality Theory and Sensitivity Analysis
 Chap6 Duality Theory and Sensitivity Analysis The rationale of duality theory Max 4x 1 + x 2 + 5x 3 + 3x 4 S.T. x 1 x 2 x 3 + 3x 4 1 5x 1 + x 2 + 3x 3 + 8x 4 55 x 1 + 2x 2 + 3x 3 5x 4 3 x 1 ~x 4 0 If we
Chap6 Duality Theory and Sensitivity Analysis The rationale of duality theory Max 4x 1 + x 2 + 5x 3 + 3x 4 S.T. x 1 x 2 x 3 + 3x 4 1 5x 1 + x 2 + 3x 3 + 8x 4 55 x 1 + 2x 2 + 3x 3 5x 4 3 x 1 ~x 4 0 If we
AM 121: Intro to Optimization Models and Methods
 AM 121: Intro to Optimization Models and Methods Fall 2017 Lecture 2: Intro to LP, Linear algebra review. Yiling Chen SEAS Lecture 2: Lesson Plan What is an LP? Graphical and algebraic correspondence Problems
AM 121: Intro to Optimization Models and Methods Fall 2017 Lecture 2: Intro to LP, Linear algebra review. Yiling Chen SEAS Lecture 2: Lesson Plan What is an LP? Graphical and algebraic correspondence Problems
Linear Programming: Simplex Method CHAPTER The Simplex Tableau; Pivoting
 CHAPTER 5 Linear Programming: 5.1. The Simplex Tableau; Pivoting Simplex Method In this section we will learn how to prepare a linear programming problem in order to solve it by pivoting using a matrix
CHAPTER 5 Linear Programming: 5.1. The Simplex Tableau; Pivoting Simplex Method In this section we will learn how to prepare a linear programming problem in order to solve it by pivoting using a matrix
Chapter 5 Linear Programming (LP)
 Chapter 5 Linear Programming (LP) General constrained optimization problem: minimize f(x) subject to x R n is called the constraint set or feasible set. any point x is called a feasible point We consider
Chapter 5 Linear Programming (LP) General constrained optimization problem: minimize f(x) subject to x R n is called the constraint set or feasible set. any point x is called a feasible point We consider
The Avis-Kalunzy Algorithm is designed to find a basic feasible solution (BFS) of a given set of constraints. Its input: A R m n and b R m such that
 Lecture 4 Avis-Kaluzny and the Simplex Method Last time, we discussed some applications of Linear Programming, such as Max-Flow, Matching, and Vertex-Cover. The broad range of applications to Linear Programming
Lecture 4 Avis-Kaluzny and the Simplex Method Last time, we discussed some applications of Linear Programming, such as Max-Flow, Matching, and Vertex-Cover. The broad range of applications to Linear Programming
III. Linear Programming
 III. Linear Programming Thomas Sauerwald Easter 2017 Outline Introduction Standard and Slack Forms Formulating Problems as Linear Programs Simplex Algorithm Finding an Initial Solution III. Linear Programming
III. Linear Programming Thomas Sauerwald Easter 2017 Outline Introduction Standard and Slack Forms Formulating Problems as Linear Programs Simplex Algorithm Finding an Initial Solution III. Linear Programming
Math Models of OR: Handling Upper Bounds in Simplex
 Math Models of OR: Handling Upper Bounds in Simplex John E. Mitchell Department of Mathematical Sciences RPI, Troy, NY 280 USA September 208 Mitchell Handling Upper Bounds in Simplex / 8 Introduction Outline
Math Models of OR: Handling Upper Bounds in Simplex John E. Mitchell Department of Mathematical Sciences RPI, Troy, NY 280 USA September 208 Mitchell Handling Upper Bounds in Simplex / 8 Introduction Outline
Dr. Maddah ENMG 500 Engineering Management I 10/21/07
 Dr. Maddah ENMG 500 Engineering Management I 10/21/07 Computational Procedure of the Simplex Method The optimal solution of a general LP problem is obtained in the following steps: Step 1. Express the
Dr. Maddah ENMG 500 Engineering Management I 10/21/07 Computational Procedure of the Simplex Method The optimal solution of a general LP problem is obtained in the following steps: Step 1. Express the
