Physics 23 Fall 1998 Lab 4 - The Hydrogen Spectrum
|
|
|
- Rudolph Hicks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Physics 3 Fall 998 Lab 4 - The Hydrogen Spectrum Theory In the late 800's, it was known that when a gas is excited by means of an electric discharge and the light emitted is viewed through a diffraction grating, the spectrum observed consists not of a continuous band of light, but of individual lines with well defined wavelengths. Experiments had also shown that the wavelengths of the lines were characteristic of the chemical element emitting the light. They were an atomic fingerprint which somehow resulted from the internal structure of the atom. In 885 Johann Balmer discovered a formula which accurately gave the wavelengths of a group of lines emitted by the simplest atom, atomic hydrogen. It was λ = R - n () where λ is the wavelength of the emitted light, R is a constant called the Rydberg constant (R =.097 x 0 7 m - ) and n is an integer greater than (n = 3,4,5,...). This formula, however, was entirely empirical. It could be used to accurately predict the values of the observed wavelengths, but it could not explain why only those specific wavelengths occurred. In 93 Niels Bohr succeeded in producing a theory for the structure of the hydrogen atom which explained the sharp line spectrum and gave the proper wavelengths. In so doing, however, he had to reject certain basic classical ideas and replace them with quantum ideas. Like the classical planetary atom, Bohr's hydrogen atom consisted of a nucleus with charge + orbited by a single electron with charge -, but contrary to classical theory the electron was restricted to only certain discrete orbits with energies given by E n = E n = ev n. () The lowest energy, the ground state, occurred when n =. Bohr postulated that while in these allowed orbits (called stationary states), the electrons do not radiate energy even though they are constantly accelerating. According to the Bohr theory, the hydrogen atom normally is in an unexcited condition with the electron in the ground state. However, when energy is added to the atom (for example, by means of an electrical discharge ), the atom can exist in an excited state with the electron being found in a higher energy level. Because the electron has only certain allowed energies, energy can be added to the atom only in discrete amounts. The amount added must be equal to the energy difference between the ground state and the energy of the orbit to which the electron goes. Once the atom has been excited to a higher energy level, it relaxes back to a lower level and eventually to
2 the ground state by giving off energy in the form of photons. The energy of the photon emitted must again correspond to the energy difference between the two orbital energies. This produces the emission spectrum characteristic of the hydrogen atom. Suppose, for example, a hydrogen atom originally in the ground state is excited in the electrical discharge to the n = 3 state and then relaxes to the n = state by emitting a photon. Energy conservation requires that the energy of the photon hν be equal to the energy difference between the levels n = 3 and n =, hν = E 3 - E = E - 3. (3) If we let ν = c/λ, equation (3) can be rewritten in terms of the wavelength of the photon, λ = E hc - 3 (4) which is consistent with equation () if R = E /hc. When evaluated, this equation gives a wavelength of Å, the observed wavelength of the H α line of the hydrogen spectrum. If, in turn, the 3 in equation (4) is replaced by n = 4 and n = 5, the expression correctly gives the wavelengths of the H β and H γ lines. Equation (4) can be generalized by replacing the by n f (the number of the final energy level) and the 3 by n i (the number of the initial energy level), λ = E hc n - f n i. (5) It can be shown that the constant E /hc is numerically equal to the Rydberg constant. Making the substitution, we see that equation (5) has the same mathematical form as the Balmer formula and the significance of the Balmer formula becomes clear. It gives the wavelengths of the photons given off when an electron relaxes from a higher energy state to the n = state. To obtain the wavelengths of the photons given off when an electron relaxes to the n = state, we need only replace n f by and let n =, 3, 4, etc. This set of lines falls in the ultraviolet region and is called the Lyman series. Other series of lines can be found by a similar process. Figure (top of next page) shows some of the transitions for the first three spectral series for hydrogen. Only lines with n = in the final state (the Balmer series) are in the visible region of the spectrum and these are the lines we will observe in this experiment. The Bohr theory is a semiclassical theory that has been found to be of limited value in
3 understanding the energy levels of more complicated atoms. For the hydrogen atom, however, calculations derived from it give quite accurate results. Figure References The following should be reviewed before coming to lab:. Serway chapter 3 pp. -30 (on reserve in Kresge). Beiser chapter 4 pp Experimental Purpose Bohr's theory of the structure of the hydrogen atom predicts that the energies of the photons of light emitted by excited atomic hydrogen are given by the expression hν = E n - f n i where h is Planck's constant, ν is the frequency of the emitted light, E is the energy of the ground state of the hydrogen atom, n i is the number of the initial energy state and n f is the number of the final energy state. The purpose of this laboratory is to check the validity of this prediction. This will be done by measuring the wavelengths of the H, H β and H γ lines of the hydrogen emission spectrum using a grating spectrometer. The measured wavelengths will then be used to compute the energy of the photons producing those lines and those energies will be compared to the energies predicted by the Bohr theory for the hydrogen atom.
4 Procedure The apparatus used in this laboratory consists of a hydrogen discharge tube with power supply and a grating spectrometer as shown in figure at the bottom of this page. The hydrogen atoms in the discharge tube are excited by means of an electrical current and the light emitted is passed through the diffraction grating of the spectrometer which disperses it into its component wavelengths. The individual lines can be viewed through the observation arm of the spectrometer. Each line can be precisely located using crosshairs in the eye piece of the observation arm. The angle at which the lines appear is read off a scale on the base of the spectrometer. The diffraction grating used is a multiple slit system one inch wide with approximately 6000 slits/cm. (The exact value is given on each grating). For any multiple slit system, the angular location θ of the maxima for light of wavelength λ is given by the expression mλ = d sin θ, m = 0, ±, ±... (6) where d is the distance between the slits and m is the order of the maximum.. In this experiment, we will be concerned only with the first order spectrum (m = ) which simplifies equation (6) to λ = d sin θ. (7) Once the angle θ for a specific spectral line has been measured, with d known for the grating, the wavelength of the line can be computed from equation (7). When the wavelength is known, the energy of the photons producing that line can be calculated and compared to those predicted by Bohr theory. Figure CAUTION: The power supply produces dangerous voltages. Do not touch the metal connectors on the power supply when the power supply is turned on.
5 . Make certain the diffraction grating on the spectrometer is level (using three leveling screws under the grating platform) and is in a plane which is perpendicular (both horizontally and vertically) to the light exiting the arm containing the entrance slits. Do not touch the optical surfaces of the grating. Always handle it by the edges. Make sure the hydrogen discharge tube is securely in the power supply. Do not touch the thin, light emitting portion of the tube. Plug in the crosshairs illuminator. Turn on the power supply and turn off the lights in the room. Position the thin portion of the discharge tube so that it is just in front of the entrance slit to the spectrometer. Position the observation arm so that it is in line with the arm containing the entrance slit. You should see the bright pink central maximum in the eyepiece. The thickness of the line can be changed by opening or closing the entrance slit with the knob next to the entrance slit. Adjust the slit opening until a thin line is obtained. The spectrometer optics can be focused by moving the eyepiece in and out in its holder. Focus the spectrometer so that both the observed line and the crosshairs can be clearly seen. [Note: with some of the spectrometers it may be impossible to have both the line and the crosshairs in perfect focus. In that case, focus them so that the crosshairs are clearly visible and the line is as focused as possible.]. Swing the observation arm to one side and set the crosshairs on the hydrogen red line (the H α line). There is a fine position adjustment on the lower part of the observation arm which can be used to accurately position the crosshairs. [Note that the line has a finite thickness and the crosshairs can be placed on either edge or in the middle of the line. Where on the line the crosshairs are positioned does not matter as long as you position the crosshairs in the same way each time you make a measurement (why?).] If the crosshairs can not be seen, rotate the crosshair illuminator until just enough light is let into the eyepiece so that both the line and the crosshairs become visible. An alternative method of making the crosshairs visible is to shine a flashlight at an angle on the lens where the light from the grating enters the observation arm. If neither of these methods works or if the line is washed out by the increased light, it may be necessary to open the entrance slit a little more. The angle scale on the base of the spectrometer is divided into two parts, a fixed part containing the degree markings and a movable vernier scale. Each degree on the fixed scale is divided into two parts each representing thirty minutes of a degree. The vernier scale is divided into thirty equal divisions each representing one minute of a degree. A magnifying glass is provided on the spectrometer to assist you in reading the scales. The scales are read in the following way. a. Determine in which degree division on the fixed scale the zero line on the vernier scale is falling. This gives you the whole degree of the angle being measured. b. Determine in which half of the degree the zero line on the vernier scale is falling.
6 c. Determine which line on the vernier scale exactly lines up with a line on the fixed scale. If the zero on the vernier scale is in the first half of the degree, then the minute measurement is simply the value of the line on the vernier scale which lined up with the line on the fixed scale. If the zero on the vernier scale is in the second half of the degree, then the minute measurement is the value of the line on the vernier scale which lined up with the line on the fixed scale plus thirty minutes. Record the angle to the nearest minute. Repeat this step for the red line on the other side of the central maximum. Compute θ by finding the difference between the two angles and dividing by. This method of measuring θ increases the accuracy the measurement (why?). 3. Repeat step for the hydrogen green line (the H β line) and the hydrogen violet line (the H γ line). 4. Compute λ, ν and E for each line. 5. The H α corresponds to the n = 3 to n = transition, the H β to the n = 4 to n = transition and the H γ to the n = 5 to n = transition. Compute the theoretical wavelengths and energies as predicted by the Bohr theory and compare them to the experimentally measured values. Compute the percent deviation of the experimental values from the theoretical values. 6. There are discharge tubes containing other gases available in the lab. Observe the spectra of at least two other gases and compare them to the hydrogen spectrum. Choose one gas from each of the following groups: Group Group Hg iodine He N Ne H 0 vapor Ar CAUTION: Do not attempt to change the discharge tube without first turning off the high voltage power supply. After a short period of use, the discharge tube becomes quite hot. Allow a few minutes for it to cool before changing it. Store the hydrogen tube in its cylindrical storage container while you are looking at the other gases. When you are done looking at a specific gas, please make sure to put it back into its own cylindrical storage container and return to the main storage box.
7 7. Put the hydrogen spectrum tube back into the power supply leaving the power supply off when you have done so. Unplug the crosshair illuminator. Lab Report Follow the usual lab notebook format. Your lab report should include the answers to all of the questions asked in the introduction or procedure, all raw and derived data, and an estimate of the magnitude and sources of error in any data recorded. When answering any question or when giving any comparison or explanation, always refer to specific data to support your statements. For this lab also include the following:. a table summarizing all measurements made;. all computations made; 3. a table summarizing the final results - theoretical values vs experimental values; and 4. a listing of the similarities and differences noted between the hydrogen spectrum and the other spectra observed, with a discussion of what conclusions you can draw from those observations.
Physics 24, Spring 2007 Lab 2 - Complex Spectra
 Physics 24, Spring 2007 Lab 2 - Complex Spectra Theory The optical spectra of isolated atoms consist of discrete, unequally spaced lines. This fact could not be understood on the basis of classical atomic
Physics 24, Spring 2007 Lab 2 - Complex Spectra Theory The optical spectra of isolated atoms consist of discrete, unequally spaced lines. This fact could not be understood on the basis of classical atomic
Any first year text, sections on atomic structure, spectral lines and spectrometers
 Physics 33 Experiment 5 Atomic Spectra References Any first year text, sections on atomic structure, spectral lines and spectrometers Any modern physics text, eg F.K. Richtmeyer, E.H. Kennard and J.N.
Physics 33 Experiment 5 Atomic Spectra References Any first year text, sections on atomic structure, spectral lines and spectrometers Any modern physics text, eg F.K. Richtmeyer, E.H. Kennard and J.N.
The Quantum Model of the Hydrogen Atom
 Physics 109 Science 1 Experiment 1 1 The Quantum Model of the Hydrogen Atom In this experiment you will use a spectrometer to determine the wavelengths of the visible lines of atomic hydrogen. The goal
Physics 109 Science 1 Experiment 1 1 The Quantum Model of the Hydrogen Atom In this experiment you will use a spectrometer to determine the wavelengths of the visible lines of atomic hydrogen. The goal
Atomic Spectra. d sin θ = mλ (1)
 Atomic Spectra Objectives: To measure the wavelengths of visible light emitted by atomic hydrogen and verify that the measured wavelengths obey the empirical Rydberg formula. To observe emission spectra
Atomic Spectra Objectives: To measure the wavelengths of visible light emitted by atomic hydrogen and verify that the measured wavelengths obey the empirical Rydberg formula. To observe emission spectra
high energy state for the electron in the atom low energy state for the electron in the atom
 Atomic Spectra Objectives The objectives of this experiment are to: 1) Build and calibrate a simple spectroscope capable of measuring wavelengths of visible light. 2) Measure several wavelengths of light
Atomic Spectra Objectives The objectives of this experiment are to: 1) Build and calibrate a simple spectroscope capable of measuring wavelengths of visible light. 2) Measure several wavelengths of light
EXPERIMENT 12 THE GRATING SPECTROMETER AND ATOMIC SPECTRA
 OBJECTIVES Learn the theory of the grating spectrometer Observe the spectrum of mercury and hydrogen Measure the grating constant of a diffraction grating Measure the Rydberg Constant EXPERIMENT THE GRATING
OBJECTIVES Learn the theory of the grating spectrometer Observe the spectrum of mercury and hydrogen Measure the grating constant of a diffraction grating Measure the Rydberg Constant EXPERIMENT THE GRATING
HYDROGEN SPECTRUM. Figure 1 shows the energy level scheme for the hydrogen atom as calculated from equation. Figure 1 Figure 2
 15 Jul 04 Hydrogen.1 HYDROGEN SPECTRUM In this experiment the wavelengths of the visible emission lines of hydrogen (Balmer series) will be measured and compared to the values predicted by Bohr s quantum
15 Jul 04 Hydrogen.1 HYDROGEN SPECTRUM In this experiment the wavelengths of the visible emission lines of hydrogen (Balmer series) will be measured and compared to the values predicted by Bohr s quantum
Physics 1CL OPTICAL SPECTROSCOPY Spring 2010
 Introduction In this lab, you will use a diffraction grating to split up light into the various colors which make up the different wavelengths of the visible electromagnetic spectrum. You will assemble
Introduction In this lab, you will use a diffraction grating to split up light into the various colors which make up the different wavelengths of the visible electromagnetic spectrum. You will assemble
Observation of Atomic Spectra
 Observation of Atomic Spectra Introduction In this experiment you will observe and measure the wavelengths of different colors of light emitted by atoms. You will first observe light emitted from excited
Observation of Atomic Spectra Introduction In this experiment you will observe and measure the wavelengths of different colors of light emitted by atoms. You will first observe light emitted from excited
Lab 5: Spectroscopy & the Hydrogen Atom Phy248 Spring 2009
 Lab 5: Spectroscopy & the Hydrogen Atom Phy248 Spring 2009 Name Section Return this spreadsheet to your TA that will use it to score your lab. To receive full credit you must use complete sentences and
Lab 5: Spectroscopy & the Hydrogen Atom Phy248 Spring 2009 Name Section Return this spreadsheet to your TA that will use it to score your lab. To receive full credit you must use complete sentences and
PC1144 Physics IV. Atomic Spectra
 PC1144 Physics IV Atomic Spectra 1 Objectives Investigate how well the visible light wavelengths of hydrogen predicted by the Bohr theory agree with experimental values. Determine an experimental value
PC1144 Physics IV Atomic Spectra 1 Objectives Investigate how well the visible light wavelengths of hydrogen predicted by the Bohr theory agree with experimental values. Determine an experimental value
The Emission Spectra of Light
 The Emission Spectra of Light Objectives: Theory: 1.... measured the wavelength limits of the color bands in the visible spectrum, 2.... measured the wavelengths of the emission lines of the hydrogen Balmer
The Emission Spectra of Light Objectives: Theory: 1.... measured the wavelength limits of the color bands in the visible spectrum, 2.... measured the wavelengths of the emission lines of the hydrogen Balmer
Atomic Emission Spectra
 Atomic Emission Spectra Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are as follows: To build and calibrate a simple meter-stick spectroscope that is capable of measuring wavelengths of visible light.
Atomic Emission Spectra Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are as follows: To build and calibrate a simple meter-stick spectroscope that is capable of measuring wavelengths of visible light.
Lab 10: Spectroscopy & the Hydrogen Atom Phy208 Fall 2008
 Lab 10: Spectroscopy & the Hydrogen Atom Phy208 Fall 2008 Name Section This sheet is the lab document your TA will use to score your lab. It is to be turned in at the end of lab. To receive full credit
Lab 10: Spectroscopy & the Hydrogen Atom Phy208 Fall 2008 Name Section This sheet is the lab document your TA will use to score your lab. It is to be turned in at the end of lab. To receive full credit
ATOMIC SPECTRA. Objective:
 1 ATOMIC SPECTRA Objective: To measure the wavelengths of visible light emitted by atomic hydrogen and verify the measured wavelengths against those predicted by quantum theory. To identify an unknown
1 ATOMIC SPECTRA Objective: To measure the wavelengths of visible light emitted by atomic hydrogen and verify the measured wavelengths against those predicted by quantum theory. To identify an unknown
Ph 3455/MSE 3255 Experiment 2: Atomic Spectra
 Ph 3455/MSE 3255 Experiment 2: Atomic Spectra Background Reading: Tipler, Llewellyn pp. 163-165 Apparatus: Spectrometer, sodium lamp, hydrogen lamp, mercury lamp, diffraction grating, watchmaker eyeglass,
Ph 3455/MSE 3255 Experiment 2: Atomic Spectra Background Reading: Tipler, Llewellyn pp. 163-165 Apparatus: Spectrometer, sodium lamp, hydrogen lamp, mercury lamp, diffraction grating, watchmaker eyeglass,
The Spectrophotometer and Atomic Spectra of Hydrogen Physics 246
 The Spectrophotometer and Atomic Spectra of Hydrogen Physics 46 Introduction: When heated sufficiently, most elements emit light. With a spectrometer, the emitted light can be broken down into its various
The Spectrophotometer and Atomic Spectra of Hydrogen Physics 46 Introduction: When heated sufficiently, most elements emit light. With a spectrometer, the emitted light can be broken down into its various
Spectrum of Hydrogen. Physics 227 Lab
 Introduction In today's lab you will be dealing with an area of physics called quantum mechanics. The only quantum mechanical idea that you will be using today is that electrons in an atom can exist only
Introduction In today's lab you will be dealing with an area of physics called quantum mechanics. The only quantum mechanical idea that you will be using today is that electrons in an atom can exist only
PHYS General Physics II Lab The Balmer Series for Hydrogen Source. c = speed of light = 3 x 10 8 m/s
 PHYS 1040 - General Physics II Lab The Balmer Series for Hydrogen Source Purpose: The purpose of this experiment is to analyze the emission of light from a hydrogen source and measure and the wavelengths
PHYS 1040 - General Physics II Lab The Balmer Series for Hydrogen Source Purpose: The purpose of this experiment is to analyze the emission of light from a hydrogen source and measure and the wavelengths
NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY PHYSICS DEPARTMENT. Physics 211 E&M and Quantum Physics Spring Lab #9: Diffraction Spectroscopy
 NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY PHYSICS DEPARTMENT Physics 211 E&M and Quantum Physics Spring 2018 Lab #9: Diffraction Spectroscopy Lab Writeup Due: Mon/Wed/Thu/Fri, April 30/ May 2/3/4, 2018 Background All
NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY PHYSICS DEPARTMENT Physics 211 E&M and Quantum Physics Spring 2018 Lab #9: Diffraction Spectroscopy Lab Writeup Due: Mon/Wed/Thu/Fri, April 30/ May 2/3/4, 2018 Background All
The Grating Spectrometer and Atomic Spectra
 PHY 192 Grating Spectrometer 1 The Grating Spectrometer and Atomic Spectra Introduction In the previous experiment diffraction and interference were discussed and at the end a diffraction grating was introduced.
PHY 192 Grating Spectrometer 1 The Grating Spectrometer and Atomic Spectra Introduction In the previous experiment diffraction and interference were discussed and at the end a diffraction grating was introduced.
The Grating Spectrometer and Atomic Spectra
 PHY 192 Grating Spectrometer Spring 2012 1 The Grating Spectrometer and Atomic Spectra Introduction In the previous experiment diffraction and interference were discussed and at the end a diffraction grating
PHY 192 Grating Spectrometer Spring 2012 1 The Grating Spectrometer and Atomic Spectra Introduction In the previous experiment diffraction and interference were discussed and at the end a diffraction grating
ATOMIC SPECTRA. To identify elements through their emission spectra. Apparatus: spectrometer, spectral tubes, power supply, incandescent lamp.
 ATOMIC SPECTRA Objective: To measure the wavelengths of visible light emitted by atomic hydrogen and verify the measured wavelengths against those predicted by quantum theory. To identify elements through
ATOMIC SPECTRA Objective: To measure the wavelengths of visible light emitted by atomic hydrogen and verify the measured wavelengths against those predicted by quantum theory. To identify elements through
Experiment 7: Spectrum of the Hydrogen Atom
 Experiment 7: Spectrum of the Hydrogen Nate Saffold nas2173@columbia.edu Office Hour: Mondays, 5:30-6:30PM INTRO TO EXPERIMENTAL PHYS-LAB 1493/1494/2699 Introduction The physics behind: The spectrum of
Experiment 7: Spectrum of the Hydrogen Nate Saffold nas2173@columbia.edu Office Hour: Mondays, 5:30-6:30PM INTRO TO EXPERIMENTAL PHYS-LAB 1493/1494/2699 Introduction The physics behind: The spectrum of
THE DIFFRACTION GRATING SPECTROMETER
 Purpose Theory THE DIFFRACTION GRATING SPECTROMETER a. To study diffraction of light using a diffraction grating spectrometer b. To measure the wavelengths of certain lines in the spectrum of the mercury
Purpose Theory THE DIFFRACTION GRATING SPECTROMETER a. To study diffraction of light using a diffraction grating spectrometer b. To measure the wavelengths of certain lines in the spectrum of the mercury
Physics 1C OPTICAL SPECTROSCOPY Rev. 2-AH. Introduction
 Introduction In this lab you will use a diffraction grating to split up light into its various colors (like a rainbow). You will assemble a spectrometer, incorporating the diffraction grating. A spectrometer
Introduction In this lab you will use a diffraction grating to split up light into its various colors (like a rainbow). You will assemble a spectrometer, incorporating the diffraction grating. A spectrometer
Emission Spectrum of Atomic Gases. Prelab Questions
 Emission Spectrum of Atomic Gases Prelab Questions Before this coming to this lab, please review your text for the physics of the spectrum of visible light and of diffraction grating spectrometer.. Which
Emission Spectrum of Atomic Gases Prelab Questions Before this coming to this lab, please review your text for the physics of the spectrum of visible light and of diffraction grating spectrometer.. Which
HYDROGEN SPECTRUM = 2
 MP6 OBJECT 3 HYDROGEN SPECTRUM MP6. The object o this experiment is to observe some o the lines in the emission spectrum o hydrogen, and to compare their experimentally determined wavelengths with those
MP6 OBJECT 3 HYDROGEN SPECTRUM MP6. The object o this experiment is to observe some o the lines in the emission spectrum o hydrogen, and to compare their experimentally determined wavelengths with those
Experiment 24: Spectroscopy
 Experiment 24: Spectroscopy Figure 24.1: Spectroscopy EQUIPMENT High Voltage Power Supply Incandescent Light Source (3) Gas Discharge Tubes: 1. Helium 2. Hydrogen 3. Unknown Element Spectrometer Felt (1)
Experiment 24: Spectroscopy Figure 24.1: Spectroscopy EQUIPMENT High Voltage Power Supply Incandescent Light Source (3) Gas Discharge Tubes: 1. Helium 2. Hydrogen 3. Unknown Element Spectrometer Felt (1)
Emission Spectroscopy
 Objectives Emission Spectroscopy Observe spectral lines from a hydrogen gas discharge tube Determine the initial and final energy levels for the electronic transitions associated with the visible portion
Objectives Emission Spectroscopy Observe spectral lines from a hydrogen gas discharge tube Determine the initial and final energy levels for the electronic transitions associated with the visible portion
Stellar Astrophysics: The Interaction of Light and Matter
 Stellar Astrophysics: The Interaction of Light and Matter The Photoelectric Effect Methods of electron emission Thermionic emission: Application of heat allows electrons to gain enough energy to escape
Stellar Astrophysics: The Interaction of Light and Matter The Photoelectric Effect Methods of electron emission Thermionic emission: Application of heat allows electrons to gain enough energy to escape
EXPERIMENT 17: Atomic Emission
 EXPERIMENT 17: Atomic Emission PURPOSE: To construct an energy level diagram of the hydrogen atom To identify an element from its line spectrum. PRINCIPLES: White light, such as emitted by the sun or an
EXPERIMENT 17: Atomic Emission PURPOSE: To construct an energy level diagram of the hydrogen atom To identify an element from its line spectrum. PRINCIPLES: White light, such as emitted by the sun or an
10. Wavelength measurement using prism spectroscopy
 Spk 0. Wavelength measurement using prism spectroscopy 0. Introduction The study of emitted spectra of electromagnetic waves by excited atoms makes for one of the most important methods to investigate
Spk 0. Wavelength measurement using prism spectroscopy 0. Introduction The study of emitted spectra of electromagnetic waves by excited atoms makes for one of the most important methods to investigate
University of Massachusetts, Amherst
 PHYSICS 286: Modern Physics Laboratory SPRING 2010 (A. Dinsmore and K. Kumar) Feb 2009 Experiment 4: THE FRANCK HERTZ EXPERIMENT Electronic Excitations of a Gas, and Evidence for the Quantization of Atomic
PHYSICS 286: Modern Physics Laboratory SPRING 2010 (A. Dinsmore and K. Kumar) Feb 2009 Experiment 4: THE FRANCK HERTZ EXPERIMENT Electronic Excitations of a Gas, and Evidence for the Quantization of Atomic
THE UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS PHYS2041 ATOMIC SPECTROSCOPY
 THE UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS PHYS2041 ATOMIC SPECTROSCOPY Warning: The mercury spectral lamps emit UV radiation. Do not stare into the lamp. Avoid exposure where possible. Introduction
THE UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS PHYS2041 ATOMIC SPECTROSCOPY Warning: The mercury spectral lamps emit UV radiation. Do not stare into the lamp. Avoid exposure where possible. Introduction
LAB 12 ATOMIC SPECTRA
 217 Name Date Partners LAB 12 ATOMIC SPECTRA OBJECTIVES Review the quantum nature of light and how light photons are produced in atoms. Learn to use an optical spectrometer to measure light wavelengths.
217 Name Date Partners LAB 12 ATOMIC SPECTRA OBJECTIVES Review the quantum nature of light and how light photons are produced in atoms. Learn to use an optical spectrometer to measure light wavelengths.
Laboratory #29: Spectrometer
 INDIANA UNIVERSITY, DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS, P309 LABORATORY Laboratory #29: Spectrometer Goal: Learn to adjust an optical spectrometer, use a transmission grating to measure known spectral lines of mercury,
INDIANA UNIVERSITY, DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS, P309 LABORATORY Laboratory #29: Spectrometer Goal: Learn to adjust an optical spectrometer, use a transmission grating to measure known spectral lines of mercury,
Chemistry 212 ATOMIC SPECTROSCOPY
 Chemistry 212 ATOMIC SPECTROSCOPY The emission and absorption of light energy of particular wavelengths by atoms and molecules is a common phenomenon. The emissions/absorptions are characteristic for each
Chemistry 212 ATOMIC SPECTROSCOPY The emission and absorption of light energy of particular wavelengths by atoms and molecules is a common phenomenon. The emissions/absorptions are characteristic for each
Atomic Spectra 1. Name Date Partners ATOMIC SPECTRA
 Atomic Spectra 1 Name Date Partners ATOMIC SPECTRA Sodium Mercury Lithium Hydrogen Atomic line spectra are characteristic for every element. These are emission spectra (without color). OBJECTIVES Review
Atomic Spectra 1 Name Date Partners ATOMIC SPECTRA Sodium Mercury Lithium Hydrogen Atomic line spectra are characteristic for every element. These are emission spectra (without color). OBJECTIVES Review
Exercise 5: The electromagnetic spectrum and spectroscopy
 Physics 223 Name: Exercise 5: The electromagnetic spectrum and spectroscopy Objectives: Experience an example of a discovery exercise Predict and confirm the relationship between measured quantities Using
Physics 223 Name: Exercise 5: The electromagnetic spectrum and spectroscopy Objectives: Experience an example of a discovery exercise Predict and confirm the relationship between measured quantities Using
APAS Laboratory { PAGE } Spectroscopy SPECTROSCOPY
 SPECTROSCOPY SYNOPSIS: In this lab you will eplore different types of emission spectra, calibrate a spectrometer using the spectrum of a known element, and use your calibration to identify an unknown element.
SPECTROSCOPY SYNOPSIS: In this lab you will eplore different types of emission spectra, calibrate a spectrometer using the spectrum of a known element, and use your calibration to identify an unknown element.
DISPERSION OF A GLASS PRISM
 PH2 page 1 DISPERSION OF A GLASS PRISM OBJECTIVE The objective of this experiment is to analyze the emission spectrum of helium and to analyze the dispersion of a glass prism by measuring the index of
PH2 page 1 DISPERSION OF A GLASS PRISM OBJECTIVE The objective of this experiment is to analyze the emission spectrum of helium and to analyze the dispersion of a glass prism by measuring the index of
Experiment #9. Atomic Emission Spectroscopy
 Introduction Experiment #9. Atomic Emission Spectroscopy Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction of light with matter. This interaction can be in the form of the absorption or the emission of electromagnetic
Introduction Experiment #9. Atomic Emission Spectroscopy Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction of light with matter. This interaction can be in the form of the absorption or the emission of electromagnetic
Atomic Spectra for Atoms and Ions. Light is made up of different wavelengths
 Atomic Spectra for Atoms and Ions What will you be doing in lab next week? Recording the line spectra of several different substances in discharge tubes. Recording the line spectra of several ions from
Atomic Spectra for Atoms and Ions What will you be doing in lab next week? Recording the line spectra of several different substances in discharge tubes. Recording the line spectra of several ions from
E. K. A. ADVANCED PHYSICS LABORATORY PHYSICS 3081, 4051 FRAUNHOFER DIFFRACTION
 E. K. A. ADVANCED PHYSICS LABORATORY PHYSICS 3081, 4051 FRAUNHOFER DIFFRACTION References for Fraunhofer Diffraction 1. Jenkins and White Fundamentals of Optics. Chapters on Fraunhofer diffraction and
E. K. A. ADVANCED PHYSICS LABORATORY PHYSICS 3081, 4051 FRAUNHOFER DIFFRACTION References for Fraunhofer Diffraction 1. Jenkins and White Fundamentals of Optics. Chapters on Fraunhofer diffraction and
EXPERIMENT 14. The Atomic Spectrum of Hydrogen
 Name: Laboratory Section: Laboratory Section Date: Partners Names: Grade: Last Revised on March 18, 2003 EXPERIMENT 14 The Atomic Spectrum of Hydrogen 0. Pre-Laboratory Work [2 pts] 1. You will be using
Name: Laboratory Section: Laboratory Section Date: Partners Names: Grade: Last Revised on March 18, 2003 EXPERIMENT 14 The Atomic Spectrum of Hydrogen 0. Pre-Laboratory Work [2 pts] 1. You will be using
Laboratory Exercise. Quantum Mechanics
 Laboratory Exercise Quantum Mechanics Exercise 1 Atomic Spectrum of Hydrogen INTRODUCTION You have no doubt been exposed many times to the Bohr model of the atom. You may have even learned of the connection
Laboratory Exercise Quantum Mechanics Exercise 1 Atomic Spectrum of Hydrogen INTRODUCTION You have no doubt been exposed many times to the Bohr model of the atom. You may have even learned of the connection
Chapter 8. Spectroscopy. 8.1 Purpose. 8.2 Introduction
 Chapter 8 Spectroscopy 8.1 Purpose In the experiment atomic spectra will be investigated. The spectra of three know materials will be observed. The composition of an unknown material will be determined.
Chapter 8 Spectroscopy 8.1 Purpose In the experiment atomic spectra will be investigated. The spectra of three know materials will be observed. The composition of an unknown material will be determined.
ASTRO Fall 2012 LAB #7: The Electromagnetic Spectrum
 ASTRO 1050 - Fall 2012 LAB #7: The Electromagnetic Spectrum ABSTRACT Astronomers rely on light to convey almost all of the information we have on distant astronomical objects. In addition to measuring
ASTRO 1050 - Fall 2012 LAB #7: The Electromagnetic Spectrum ABSTRACT Astronomers rely on light to convey almost all of the information we have on distant astronomical objects. In addition to measuring
Atomic emission spectra experiment
 Atomic emission spectra experiment Contents 1 Overview 1 2 Equipment 1 3 Measuring the grating spacing using the sodium D-lines 4 4 Measurement of hydrogen lines and the Rydberg Constant 5 5 Measurement
Atomic emission spectra experiment Contents 1 Overview 1 2 Equipment 1 3 Measuring the grating spacing using the sodium D-lines 4 4 Measurement of hydrogen lines and the Rydberg Constant 5 5 Measurement
Diffraction Gratings, Atomic Spectra. Prof. Shawhan (substituting for Prof. Hall) November 14, 2016
 Diffraction Gratings, Atomic Spectra Prof. Shawhan (substituting for Prof. Hall) November 14, 2016 1 Increase number of slits: 2 Visual Comparisons 3 4 8 2 Diffraction Grating Note: despite the name, this
Diffraction Gratings, Atomic Spectra Prof. Shawhan (substituting for Prof. Hall) November 14, 2016 1 Increase number of slits: 2 Visual Comparisons 3 4 8 2 Diffraction Grating Note: despite the name, this
PHYSICS 122/124 Lab EXPERIMENT NO. 9 ATOMIC SPECTRA
 PHYSICS 1/14 Lab EXPERIMENT NO. 9 ATOMIC SPECTRA The purpose of this laboratory is to study energy levels of the Hydrogen atom by observing the spectrum of emitted light when Hydrogen atoms make transitions
PHYSICS 1/14 Lab EXPERIMENT NO. 9 ATOMIC SPECTRA The purpose of this laboratory is to study energy levels of the Hydrogen atom by observing the spectrum of emitted light when Hydrogen atoms make transitions
Lab report 30 EXPERIMENT 4. REFRACTION OF LIGHT
 30 EXPERIMENT 4. REFRACTION OF LIGHT Lab report Go to your course homepage on Sakai (Resources, Lab templates) to access the online lab report worksheet for this experiment. The worksheet has to be completed
30 EXPERIMENT 4. REFRACTION OF LIGHT Lab report Go to your course homepage on Sakai (Resources, Lab templates) to access the online lab report worksheet for this experiment. The worksheet has to be completed
Atomic Spectra & Electron Energy Levels
 CHM151LL: ATOMIC SPECTRA & ELECTRON ENERGY LEVELS 1 Atomic Spectra & Electron Energy Levels OBJECTIVES: To measure the wavelength of visible light emitted by excited atoms to calculate the energy of that
CHM151LL: ATOMIC SPECTRA & ELECTRON ENERGY LEVELS 1 Atomic Spectra & Electron Energy Levels OBJECTIVES: To measure the wavelength of visible light emitted by excited atoms to calculate the energy of that
The Photoelectric Effect
 Stellar Astrophysics: The Interaction of Light and Matter The Photoelectric Effect Methods of electron emission Thermionic emission: Application of heat allows electrons to gain enough energy to escape
Stellar Astrophysics: The Interaction of Light and Matter The Photoelectric Effect Methods of electron emission Thermionic emission: Application of heat allows electrons to gain enough energy to escape
10.1 Introduction: The Bohr Hydrogen Atom
 Chapter 10 Experiment 8: The Spectral Nature of Light 10.1 Introduction: The Bohr Hydrogen Atom Historical Aside The 19 th century was a golden age of science. We could explain everything we observed.
Chapter 10 Experiment 8: The Spectral Nature of Light 10.1 Introduction: The Bohr Hydrogen Atom Historical Aside The 19 th century was a golden age of science. We could explain everything we observed.
Optics. Measuring the line spectra of inert gases and metal vapors using a prism spectrometer. LD Physics Leaflets P
 Optics Spectrometer Prism spectrometer LD Physics Leaflets P5.7.1.1 Measuring the line spectra of inert gases and metal vapors using a prism spectrometer Objects of the experiment Adjusting the prism spectrometer.
Optics Spectrometer Prism spectrometer LD Physics Leaflets P5.7.1.1 Measuring the line spectra of inert gases and metal vapors using a prism spectrometer Objects of the experiment Adjusting the prism spectrometer.
Diffraction of light by a grating
 (ta initials) first name (print) last name (print) brock id (ab17cd) (lab date) Experiment 5 Diffraction of light by a grating In this Experiment you will learn the geometical analysis of a diffraction
(ta initials) first name (print) last name (print) brock id (ab17cd) (lab date) Experiment 5 Diffraction of light by a grating In this Experiment you will learn the geometical analysis of a diffraction
The Hydrogen Spectrum
 1 The Hydrogen Spectrum PHYS 1301 F98 Prof. T.E. Coan Last edit: 6 Aug 98 Introduction In last week's laboratory experiment on diffraction, you should have noticed that the light from the mercury discharge
1 The Hydrogen Spectrum PHYS 1301 F98 Prof. T.E. Coan Last edit: 6 Aug 98 Introduction In last week's laboratory experiment on diffraction, you should have noticed that the light from the mercury discharge
Optical Spectroscopy and Atomic Structure. PHYS 0219 Optical Spectroscopy and Atomic Structure 1
 Optical Spectroscopy and Atomic Structure PHYS 0219 Optical Spectroscopy and Atomic Structure 1 Optical Spectroscopy and Atomic Structure This experiment has four parts: 1. Spectroscope Setup - Your lab
Optical Spectroscopy and Atomic Structure PHYS 0219 Optical Spectroscopy and Atomic Structure 1 Optical Spectroscopy and Atomic Structure This experiment has four parts: 1. Spectroscope Setup - Your lab
Chapter 28. Atomic Physics
 Chapter 28 Atomic Physics Sir Joseph John Thomson J. J. Thomson 1856-1940 Discovered the electron Did extensive work with cathode ray deflections 1906 Nobel Prize for discovery of electron Early Models
Chapter 28 Atomic Physics Sir Joseph John Thomson J. J. Thomson 1856-1940 Discovered the electron Did extensive work with cathode ray deflections 1906 Nobel Prize for discovery of electron Early Models
Physics 476LW Advanced Physics Laboratory Atomic Spectroscopy
 Physics 476LW Atomic Spectroscopy 1 Introduction The description of atomic spectra and the Rutherford-Geiger-Marsden experiment were the most significant precursors of the so-called Bohr planetary model
Physics 476LW Atomic Spectroscopy 1 Introduction The description of atomic spectra and the Rutherford-Geiger-Marsden experiment were the most significant precursors of the so-called Bohr planetary model
n(λ) = c/v(λ). Figure 1: Dispersion curves for some common optical glass types.
 Physics 2310 Lab 2: The Dispersion of Optical Glass Dr. Michael Pierce (Univ. of Wyoming) Based on a lab by Dr. M. Kruger (Univ. of Missouri, Kansas City) Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to introduce
Physics 2310 Lab 2: The Dispersion of Optical Glass Dr. Michael Pierce (Univ. of Wyoming) Based on a lab by Dr. M. Kruger (Univ. of Missouri, Kansas City) Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to introduce
EXPERIMENT #5 The Franck-Hertz Experiment: Electron Collisions with Mercury
 EXPERIMENT #5 The Franck-Hertz Experiment: Electron Collisions with Mercury GOALS Physics Measure the energy difference between the ground state and the first excited state in mercury atoms, and conclude
EXPERIMENT #5 The Franck-Hertz Experiment: Electron Collisions with Mercury GOALS Physics Measure the energy difference between the ground state and the first excited state in mercury atoms, and conclude
Chapter 7. Quantum Theory and Atomic Structure
 Chapter 7 Quantum Theory and Atomic Structure Outline 1. The Nature of Light 2. Atomic Spectra 3. The Wave-Particle Duality of Matter and Energy 4. The Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom 3 September
Chapter 7 Quantum Theory and Atomic Structure Outline 1. The Nature of Light 2. Atomic Spectra 3. The Wave-Particle Duality of Matter and Energy 4. The Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom 3 September
Practical 1P4 Energy Levels and Band Gaps
 Practical 1P4 Energy Levels and Band Gaps What you should learn from this practical Science This practical illustrates some of the points from the lecture course on Elementary Quantum Mechanics and Bonding
Practical 1P4 Energy Levels and Band Gaps What you should learn from this practical Science This practical illustrates some of the points from the lecture course on Elementary Quantum Mechanics and Bonding
AS 101: Day Lab #2 Summer Spectroscopy
 Spectroscopy Goals To see light dispersed into its constituent colors To study how temperature, light intensity, and light color are related To see spectral lines from different elements in emission and
Spectroscopy Goals To see light dispersed into its constituent colors To study how temperature, light intensity, and light color are related To see spectral lines from different elements in emission and
Atomic Spectra HISTORY AND THEORY
 Atomic Spectra HISTORY AND THEORY When atoms of a gas are excited (by high voltage, for instance) they will give off light. Each element (in fact, each isotope) gives off a characteristic atomic spectrum,
Atomic Spectra HISTORY AND THEORY When atoms of a gas are excited (by high voltage, for instance) they will give off light. Each element (in fact, each isotope) gives off a characteristic atomic spectrum,
Atomic Spectra. Eric Reichwein David Steinberg Department of Physics University of California, Santa Cruz. August 30, 2012
 Atomic Spectra Eric Reichwein David Steinberg Department of Physics University of California, Santa Cruz August 30, 0 Abstract To observe helium spectral lines we used a spectrometer. From a table of known
Atomic Spectra Eric Reichwein David Steinberg Department of Physics University of California, Santa Cruz August 30, 0 Abstract To observe helium spectral lines we used a spectrometer. From a table of known
Rydberg constant from atomic spectra of gases
 Page 1 of 8 Rydberg constant from atomic spectra of gases Objective - Calibrating a prism spectrometer to convert the scale readings in wavelengths of spectral lines. - Observing the Balmer series of atomic
Page 1 of 8 Rydberg constant from atomic spectra of gases Objective - Calibrating a prism spectrometer to convert the scale readings in wavelengths of spectral lines. - Observing the Balmer series of atomic
PHY Atomic Spectra
 Page 1 of 6 PHY 124 - Atomic Spectra The purpose of this laboratory is to study transitions between energy levels of the hydrogen atom by observing the spectrum of light emitted when the atoms make transitions
Page 1 of 6 PHY 124 - Atomic Spectra The purpose of this laboratory is to study transitions between energy levels of the hydrogen atom by observing the spectrum of light emitted when the atoms make transitions
Physics 1CL OPTICAL SPECTROSCOPY Spring 2009
 Introduction In this lab, you will use a diffraction grating to split up light into the various colors which make up the different wavelengths of the visible electromagnetic spectrum. You will assemble
Introduction In this lab, you will use a diffraction grating to split up light into the various colors which make up the different wavelengths of the visible electromagnetic spectrum. You will assemble
Earlier we learned that hot, opaque objects produce continuous spectra of radiation of different wavelengths.
 Section7: The Bohr Atom Earlier we learned that hot, opaque objects produce continuous spectra of radiation of different wavelengths. Continuous Spectrum Everyone has seen the spectrum produced when white
Section7: The Bohr Atom Earlier we learned that hot, opaque objects produce continuous spectra of radiation of different wavelengths. Continuous Spectrum Everyone has seen the spectrum produced when white
UNIT : QUANTUM THEORY AND THE ATOM
 Name St.No. Date(YY/MM/DD) / / Section UNIT 102-10: QUANTUM THEORY AND THE ATOM OBJECTIVES Atomic Spectra for Hydrogen, Mercury and Neon. 1. To observe various atomic spectra with a diffraction grating
Name St.No. Date(YY/MM/DD) / / Section UNIT 102-10: QUANTUM THEORY AND THE ATOM OBJECTIVES Atomic Spectra for Hydrogen, Mercury and Neon. 1. To observe various atomic spectra with a diffraction grating
Different energy levels
 Different energy levels In the microscopic world energy is discrete www.cgrahamphysics.com Review Atomic electrons can only exist in certain discrete energy levels Light is made of photons When e s lose
Different energy levels In the microscopic world energy is discrete www.cgrahamphysics.com Review Atomic electrons can only exist in certain discrete energy levels Light is made of photons When e s lose
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA - SANTA CRUZ DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS PHYS 133 PROFESSOR: SHER. Atomic Spectra. Benjamin Stahl
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA - SANTA CRUZ DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS PHYS 133 PROFESSOR: SHER Atomic Spectra Benjamin Stahl Lab Partners: Aaron Lopez & Dillon Teal April 2, 2014 Abstract As an introduction to spectroscopy,
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA - SANTA CRUZ DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS PHYS 133 PROFESSOR: SHER Atomic Spectra Benjamin Stahl Lab Partners: Aaron Lopez & Dillon Teal April 2, 2014 Abstract As an introduction to spectroscopy,
Atomic spectra of one and two-electron systems
 Atomic spectra of one and two-electron systems Key Words Term symbol, Selection rule, Fine structure, Atomic spectra, Sodium D-line, Hund s rules, Russell-Saunders coupling, j-j coupling, Spin-orbit coupling,
Atomic spectra of one and two-electron systems Key Words Term symbol, Selection rule, Fine structure, Atomic spectra, Sodium D-line, Hund s rules, Russell-Saunders coupling, j-j coupling, Spin-orbit coupling,
Practical 1P4 Energy Levels and Band Gaps
 Practical 1P4 Energy Levels and Band Gaps What you should learn from this practical Science This practical illustrates some of the points from the lecture course on Elementary Quantum Mechanics and Bonding
Practical 1P4 Energy Levels and Band Gaps What you should learn from this practical Science This practical illustrates some of the points from the lecture course on Elementary Quantum Mechanics and Bonding
CSUS Department of Chemistry Experiment 9 Chem. 1A
 CSUS Department of Chemistry xperiment 9 Chem. 1A xp. 9 PR-Lab ASSIGNMNT Name: Lab Section (1) Use equation (2) [see the discussion on the next page] to calculate the energies of the ten lowest states
CSUS Department of Chemistry xperiment 9 Chem. 1A xp. 9 PR-Lab ASSIGNMNT Name: Lab Section (1) Use equation (2) [see the discussion on the next page] to calculate the energies of the ten lowest states
Quantum Theory of the Atom
 The Wave Nature of Light Quantum Theory of the Atom Electromagnetic radiation carries energy = radiant energy some forms are visible light, x rays, and radio waves Wavelength ( λ) is the distance between
The Wave Nature of Light Quantum Theory of the Atom Electromagnetic radiation carries energy = radiant energy some forms are visible light, x rays, and radio waves Wavelength ( λ) is the distance between
THE ATOMIC SPECTRUM OF HYDROGEN
 THE ATOMIC SPECTRUM OF HYDROGEN When atoms are excited, either in an electric discharge or with heat, they tend to give off light. The light is emitted only at certain wavelengths that are characteristic
THE ATOMIC SPECTRUM OF HYDROGEN When atoms are excited, either in an electric discharge or with heat, they tend to give off light. The light is emitted only at certain wavelengths that are characteristic
Lab: Excited Electrons
 Part A: EMISSION SPECTROSCOPY Lab: Excited Electrons According to the Bohr atomic model, electrons orbit the nucleus within specific energy levels. These levels are defined by unique amounts of energy.
Part A: EMISSION SPECTROSCOPY Lab: Excited Electrons According to the Bohr atomic model, electrons orbit the nucleus within specific energy levels. These levels are defined by unique amounts of energy.
The energy of the emitted light (photons) is given by the difference in energy between the initial and final states of hydrogen atom.
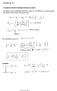 Lecture 20-21 Page 1 Lectures 20-21 Transitions between hydrogen stationary states The energy of the emitted light (photons) is given by the difference in energy between the initial and final states of
Lecture 20-21 Page 1 Lectures 20-21 Transitions between hydrogen stationary states The energy of the emitted light (photons) is given by the difference in energy between the initial and final states of
Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom
 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom Electron Discharge tube (circa 1900 s) There is something ( cathode rays ) which is emitted by the cathode and causes glowing Unlike light, these rays are deflected
Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom Electron Discharge tube (circa 1900 s) There is something ( cathode rays ) which is emitted by the cathode and causes glowing Unlike light, these rays are deflected
Introduction. Procedure and Data
 Introduction The spectrum is the entire range over which some measurable property of a physical system of phenomenon can vary. Systems that have spectrums include sound frequency, electromagnetic radiation
Introduction The spectrum is the entire range over which some measurable property of a physical system of phenomenon can vary. Systems that have spectrums include sound frequency, electromagnetic radiation
PHYSICS 116 SPECTROSCOPY: DETERMINATION OF THE WAVELENGTH OF LIGHT
 Name Date Lab Time Lab TA PHYSICS 116 SPECTROSCOPY: DETERMINATION OF THE WAVELENGTH OF LIGHT I. PURPOSE To use a diffraction grating to investigate the spectra produced by several unknown gas discharge
Name Date Lab Time Lab TA PHYSICS 116 SPECTROSCOPY: DETERMINATION OF THE WAVELENGTH OF LIGHT I. PURPOSE To use a diffraction grating to investigate the spectra produced by several unknown gas discharge
EXPERIMENT 12 THE WAVELENGTH OF LIGHT; THE DIFFRACTION GRATING
 EXPERIMENT 12 THE WAVELENGTH OF LIGHT; THE DIFFRACTION GRATING INTRODUCTION: One of the most fascinating chapters in the history of physics has been the search for an understanding of the true nature of
EXPERIMENT 12 THE WAVELENGTH OF LIGHT; THE DIFFRACTION GRATING INTRODUCTION: One of the most fascinating chapters in the history of physics has been the search for an understanding of the true nature of
Physics 1C Lecture 29B
 Physics 1C Lecture 29B Emission Spectra! The easiest gas to analyze is hydrogen gas.! Four prominent visible lines were observed, as well as several ultraviolet lines.! In 1885, Johann Balmer, found a
Physics 1C Lecture 29B Emission Spectra! The easiest gas to analyze is hydrogen gas.! Four prominent visible lines were observed, as well as several ultraviolet lines.! In 1885, Johann Balmer, found a
Spectroscopy. Materials Diffraction grating Grating tube Spectrometer Incandescent light source
 Name: Date: Spectroscopy Hazards: The power supply used to run the lights is HIGH VOLTAGE. You should not need to change any tubes, but if you do please call the instructor over for assistance, and turn
Name: Date: Spectroscopy Hazards: The power supply used to run the lights is HIGH VOLTAGE. You should not need to change any tubes, but if you do please call the instructor over for assistance, and turn
EMISSION SPECTROSCOPY
 IFM The Department of Physics, Chemistry and Biology LAB 57 EMISSION SPECTROSCOPY NAME PERSONAL NUMBER DATE APPROVED I. OBJECTIVES - Understand the principle of atomic emission spectra. - Know how to acquire
IFM The Department of Physics, Chemistry and Biology LAB 57 EMISSION SPECTROSCOPY NAME PERSONAL NUMBER DATE APPROVED I. OBJECTIVES - Understand the principle of atomic emission spectra. - Know how to acquire
Department of Physics, Colorado State University PH 425 Advanced Physics Laboratory The Zeeman Effect. 1 Introduction. 2 Origin of the Zeeman Effect
 Department of Physics, Colorado State University PH 425 Advanced Physics Laboratory The Zeeman Effect (a) CAUTION: Do not look directly at the mercury light source. It is contained in a quartz tube. The
Department of Physics, Colorado State University PH 425 Advanced Physics Laboratory The Zeeman Effect (a) CAUTION: Do not look directly at the mercury light source. It is contained in a quartz tube. The
where n = (an integer) =
 5.111 Lecture Summary #5 Readings for today: Section 1.3 (1.6 in 3 rd ed) Atomic Spectra, Section 1.7 up to equation 9b (1.5 up to eq. 8b in 3 rd ed) Wavefunctions and Energy Levels, Section 1.8 (1.7 in
5.111 Lecture Summary #5 Readings for today: Section 1.3 (1.6 in 3 rd ed) Atomic Spectra, Section 1.7 up to equation 9b (1.5 up to eq. 8b in 3 rd ed) Wavefunctions and Energy Levels, Section 1.8 (1.7 in
Quantum Physics Objective: Apparatus:
 1 Quantum Physics Objective: 1. To measure the wavelengths of visible light emitted by atomic hydrogen and verify the measured wavelengths against those predicted by quantum theory. To identify an unknown
1 Quantum Physics Objective: 1. To measure the wavelengths of visible light emitted by atomic hydrogen and verify the measured wavelengths against those predicted by quantum theory. To identify an unknown
E n = n h ν. The oscillators must absorb or emit energy in discrete multiples of the fundamental quantum of energy given by.
 Planck s s Radiation Law Planck made two modifications to the classical theory The oscillators (of electromagnetic origin) can only have certain discrete energies determined by E n = n h ν with n is an
Planck s s Radiation Law Planck made two modifications to the classical theory The oscillators (of electromagnetic origin) can only have certain discrete energies determined by E n = n h ν with n is an
ATOMIC MODELS. Models are formulated to fit the available data. Atom was known to have certain size. Atom was known to be neutral.
 ATOMIC MODELS Models are formulated to fit the available data. 1900 Atom was known to have certain size. Atom was known to be neutral. Atom was known to give off electrons. THOMPSON MODEL To satisfy the
ATOMIC MODELS Models are formulated to fit the available data. 1900 Atom was known to have certain size. Atom was known to be neutral. Atom was known to give off electrons. THOMPSON MODEL To satisfy the
What are the energies (J) and wavelengths (in nm) for these colors? Color Energy wavelength. Rev. F11 Page 1 of 5
 Exp. 8 Pre Lab ASSIGNMENT Name: Lab Section Score: / 10 (1) Use the equations [see the discussion on the next page] to calculate the energies of the 6 lowest states for the hydrogen atom, and enter your
Exp. 8 Pre Lab ASSIGNMENT Name: Lab Section Score: / 10 (1) Use the equations [see the discussion on the next page] to calculate the energies of the 6 lowest states for the hydrogen atom, and enter your
Pre-lab Quiz/PHYS 224. Your name Lab section
 Pre-lab Quiz/PHYS 224 THE DIFFRACTION GRATING AND THE OPTICAL SPECTRUM Your name Lab section 1. What are the goals of this experiment? 2. If the period of a diffraction grating is d = 1,000 nm, where the
Pre-lab Quiz/PHYS 224 THE DIFFRACTION GRATING AND THE OPTICAL SPECTRUM Your name Lab section 1. What are the goals of this experiment? 2. If the period of a diffraction grating is d = 1,000 nm, where the
Particle nature of light & Quantization
 Particle nature of light & Quantization A quantity is quantized if its possible values are limited to a discrete set. An example from classical physics is the allowed frequencies of standing waves on a
Particle nature of light & Quantization A quantity is quantized if its possible values are limited to a discrete set. An example from classical physics is the allowed frequencies of standing waves on a
Because light behaves like a wave, we can describe it in one of two ways by its wavelength or by its frequency.
 Light We can use different terms to describe light: Color Wavelength Frequency Light is composed of electromagnetic waves that travel through some medium. The properties of the medium determine how light
Light We can use different terms to describe light: Color Wavelength Frequency Light is composed of electromagnetic waves that travel through some medium. The properties of the medium determine how light
DAY LABORATORY EXERCISE: SPECTROSCOPY
 AS101 - Day Laboratory: Spectroscopy Page 1 DAY LABORATORY EXERCISE: SPECTROSCOPY Goals: To see light dispersed into its constituent colors To study how temperature, light intensity, and light color are
AS101 - Day Laboratory: Spectroscopy Page 1 DAY LABORATORY EXERCISE: SPECTROSCOPY Goals: To see light dispersed into its constituent colors To study how temperature, light intensity, and light color are
