Sub-harmonic resonance in a nearly pre-loaded mechanical oscillator
|
|
|
- Grant Floyd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nonlinear Dyn (27) 5: DOI.7/s y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sub-harmonic resonance in a nearly pre-loaded mechanical oscillator Chengwu Duan Todd E. Rook Rajendra Singh Received: 7 February 26 / Accepted: November 26 / Published online: 2 January 27 C Science + Business Media B.V. 27 Abstract In this paper, the sub-harmonic resonance of a single degree of freedom system with a nearly preloaded non-linearity (gain-changing clearance) is studied. First, a new perturbation approach is incorporated in the traditional multi-term harmonic balance method to calculate the sub-harmonic resonance. Our approach significantly reduces the work as it computes the sub-harmonic responses with just one run. Initial guesses in the vicinity of sub-harmonic regime are relaxed compared to prior approaches. Second, a parametric study is conducted to examine the occurrence and characteristics of sub-harmonic resonance. The possibility of the sub-harmonic occurrence increases with an increase of dynamic excitation or the stiffness ratio. For instance, our analysis shows that the subharmonic resonance typically occurs when the mean load is close to the stiffness transition point. In the extreme case, a very small excitation would generate a sub-harmonic resonance. With a higher mean load, the resonant peak appears at lower frequencies as a result of the reduced equivalent stiffness. Finally, our analytical formulation is successfully validated using numerical integration results. C. Duan T. E. Rook R. Singh ( ) Acoustics and Dynamics Laboratory, Department of Mechanical Engineering and The Center for Automotive Research, The Ohio State University, 2 West 9th Avenue, Columbus, OH 432, USA singh.3@osu.edu Keywords Sub-harmonic resonance. Mechanical oscillator. Discontinuous non-linearity Abbreviations MHBM multi-term harmonic balance method max maximum value min minimum value rms root mean square Introduction Mechanical oscillators with dual-staged piecewise linear stiffness characteristics (as shown in Fig. ) have received considerable inquiry since their dynamic responses exhibit strong nonlinear characteristics depending on the mean and dynamic loads [ 7]. Taking α as the ratio of first and second stage stiffness elements, one could study various cases of α. Geometrically, two extreme cases of α exist: (i) α = for the gap or backlash element and (ii) α = for the true preload case. When the system degenerates from nonlinear to linear (α =.) case from two extreme ends, the in-between regimes are categorized as the clearance non-linearity ( α<.) and nearly pre-loaded non-linearity (. <α< ). However, much attention has focused on the backlash or gap non-linearity or on the clearance non-linearity case. For instance, Padmanabhan and Singh [3, 4] examined the nonlinear frequency responses of a gear pair with backlash. Kim et al. [5] further extended the specific gear pair
2 64 Nonlinear Dyn (27) 5: f(x) K and, x ( α) x c f ( x) = α x x + ( α) x c x > x c x x c,α (, ) x < x c αk x c x Rewrite the above in a compact form as, (2a) ( ) α f ( x) = x + [ x x c x + x c ] (2b) 2 f ( x) = x + ( α) ( x x c)sgn( x x c ) ( x + x c )sgn( x + x c ) 2 (2c) Fig. Nearly pre-loaded non-linearity with α between. and formulation to a more general problem. In a recent paper, Duan and Singh [6] studied the α = case. Further, super-harmonic resonances have been examined (primarily for the case when α varies between and.), as evident from the work of Kim et al. [5] and Padmanabhan and Singh [4]. Yet, it seems that the nearly pre-loaded case, when α varies between. and, has not received much attention. Gelb and Vander Velde [7] have defined this as a gain-changing non-linearity and have provided a solution at the primary harmonic by employing the well-known describing function method. But, sub-harmonics in such a system have never been examined though Padmanabhan and Singh [6] investigated them for α = case. Therefore, the chief goal of this paper is to analytically and computationally examine sub-harmonic responses, for the mechanical oscillator with α greater than.. 2 Problem formulation Consider a single degree of freedom system with mass M, viscous damping C and piece-wise linear function f ( x) (of Fig. ) where K is the second stage stiffness. Further, apply the mean load F m and harmonic force of amplitude F p as shown below where x = d x/d t. M x + C x + Kf( x) = F m + F p sin( ω t) () Here, sgn( ) is the triple-valued signum function. Further, Equation () is non-dimensionalized by introducing the following dimensionless parameters and taking α x c as characteristic displacement. ω n = K / M, (3a) = ω/ ω n, τ = ω n t, x = x/(α x c ), (3b) (3c) (3d) ς = C/2 K M, (3e) F m = F m /( K α x c ), F p = F p /( K α x c ). (3f) (3g) Thus, we obtain the governing equation in the following form where () represents d() /dτ. x + 2ς x + f (x) = F m + F p sin( τ) (4) By choosing α x c as characteristic displacement (assuming that α is not infinity), the initial operating point can be easily identified since F m =. would exactly correspond to the transition from the first to the second stage. A new perturbation approach will be introduced in this article for the calculation of sub-harmonics when α varies between and. In particular, effects of F m, F p and α on the occurrence of sub-harmonic resonances will be investigated. We will however focus on the second sub-harmonic resonance for the sake of brevity.
3 Nonlinear Dyn (27) 5: Finally our analytical formulation will be validated using numerical solutions. 3 Calculation of sub-harmonic resonance 3. Multi-term harmonic balance method Multi-term harmonic balance method (MHBM) has been widely used for nonlinear problem. For instance, refer to [5] for detailed mathematical formulation. Recently, Duan and Singh [6] developed an indirect MHBM for the pre-load type non-linearity when α =. The fundamental principle of HBM is to represent periodic excitation and response by a truncated harmonic series, as shown below; refer to the list of symbols (Appendix A) for the identification of symbols. N h ( ) n x(τ) = a o + a 2n sin τ n= ( ) n + a 2n cos τ. (5a) N h ( ) n f (x(τ)) = c o + c 2n sin τ n= + c 2n cos N h F (τ) = q + q 2m sin (m τ) m= ( ) n τ. (5b) + q 2m cos (m τ) (5c) Or in discrete matrix form, ( ) 2 ( ) ΓΔ 2 a + 2ς ΓΔa + Ɣc = ƔQ (6) Here Γ is an operator digitizing the continuous data, Δ is to perform derivation function, a is Fourier coefficients of nonlinear response x(τ), c is coefficients for f (x(τ)), Q contains coefficients of excitation. sin ( ) cos ( ) sin ( ) 2 sin ( Γ =.. τ τ ) sin ( τ N ) τ cos ( τ ). cos ( τ ) N τ sin ( 2 τ ). sin ( 2 τ ) N Δ = [ ] ( ) cos Nh τ ( ) cos Nh τ. (7b)... [ ] Nh N h and is sub-harmonic index. In the case when the second sub-harmonics are sought, = 2. Further, since excitation is known, Q is written as: Q = [ F m F p ] T (8) Here F p is 2th element of the input vector. By introducing a pseudo inverse of Γ + = (Γ T Γ) Γ T,we obtain the following residual that is to be minimized: Θ(a, ) = ( ) 2 Δ 2 a + 2ς, (7a).. ( ) cos Nh τ N ( ) Δa + c Q (9) The coefficients a can be obtained through a Newton Raphson iteration scheme from a certain starting point and initial guess of a. A frequency sweep can be conducted by implementing a continuation scheme in conjunction with the Newton Raphson iteration. Subsequently, the stability of the converged periodic responses can be determined by Hill s method as in [5]. This particular method would work fine for the limiting case when α. Conversely when α., we will encounter numerical stiffness problem as a result of poor-conditioned Jacobian contributed by f / x in a manner similar to the pre-loaded problem [6]. J = a = ( ) 2 Δ 2 + 2ς ( ) Δ + c a c f = Γ+ a x Γ (a) (b)
4 642 Nonlinear Dyn (27) 5: In indirect MHBM [6], the force-displacement relationship in Fig. is inverted (viz. f (x) x( f )) and the residual is reformulated as (c, ). The periodic nonlinear force becomes the independent variable while the periodic displacement is calculated from the inverted force-displacement relationship. ( ) β x( f ) = f + [ f f c f + f c ] () 2 where β = /α and f c = αx c. Taking periodic f as the main solution target, the Jacobian is redefined as, J = Θ c = [ ( ) 2 Δ 2 + 2ς ( ) ] Δ a +EI (2) c Here, EI is an (2N n +) (2N h +) identity matrix. In this way, we successfully convert the calculation of f / x to x/ f by defining: a x = Γ+ Γ. (3) c f 3.2 Excitation perturbation for sub-harmonic calculation To identify and then calculate a sub-harmonic resonance, Kim et al. [5] first ran the MBHM using = and noted whether there were any unstable harmonic regimes beyond primary resonance. Should there exist such an unstable region, a second frequency sweep with = 2 can be used to calculate the second subharmonic resonance. However, the responses at subharmonic regime are typically very complex (and not well understood) and consequently the calculation is highly sensitive to the choice of initial guess of a.for example, an inappropriate a can lead to the same results as = case thereby failing to latch onto the sub-harmonic branch. For this reason, this approach would involve a certain amount of trial and error work to find a proper initial guess of a and thus we refer to this as the initial guess approach. To overcome the above-mentioned difficulty, we propose a new excitation perturbation method in this study. Namely, a perturbation item is to be artificially included in the excitation. For example, for the th sub-harmonics, we write the input excitation as: ( ) F(τ) = F m + ε sin τ + F p sin ( τ) (4a) Therefore for the 2nd-subharmonic, Q = [F m ε F p ] T (4b) Note that the perturbation term ε shall be very small, for instance ε = ( 4 3 )F p. A higher value of ε is not recommended as it would couple the non-linear sub-harmonic response and the linear response excited by the second harmonic term. With this perturbation item, the sub-harmonic resonance can be effectively triggered and the sensitivity of initial guess as experienced in the aforementioned conventional approach is remarkably reduced. Consequently, the sub-harmonics could be calculated with just one run of frequency sweep. Also, the initial guess is not a serious issue for our approach as long as is reasonably far away from the primary resonance whose upper limit (assuming the system always operates within the stiff stage) can be easily defined as max( prim ) = α. Another scenario that requires careful treatment is when an isolated subharmonic branch would occur, as we will discuss later. Figure 2 compares the results of initial guess approach, excitation perturbation approach and a numerical integration scheme using Runge-Kutta with adaptive size control [8]. Excellent agreement is clearly observed between these three approaches. Note that the excitation perturbation approach takes only one run to complete the response characteristics. 4 Results and discussion For clearance type non-linearity where α [, ), Kim et al. found that the crossing of mean operating point from the stiff to the compliant stage plays an important role [5]. For instance, they found a 2nd subharmonic resonance occurs when the separation between the crossing point c and primary resonance p is sufficiently far, i.e. ( c p ) > p. Following this criterion, they stated if the mean operating point x m ( ) always staying within the compliant stage and thus ( c p ) =, then a sub-harmonic resonance could exist. But, as evident from Fig. 3, this criterion no longer holds for the case when α>. Following their
5 Nonlinear Dyn (27) 5: Fig. 2 Comparison of Calculation Results, given α = 2, ς =.5, F m =.8 and F p =.85. (a) Primary and Sub-harmonic Resonances. (b) Enlarged View of Sub-harmonic Resonance. Key: : stable solution of MHBM first run;, unstable solution of MHBM first run; : stable solution of initial guess approach with MHBM second run; +++: Unstable solution of initial guess approach with MHBM second run; : stable solution of excitation perturbation approach; : unstable solution f excitation perturbation approach; : numerical integration with Runge-Kutta scheme (a) (b) initial guess approach and running the MHBM with = 2, a sub-harmonic resonant peak is clearly seen in Fig. 3 but ( c p ) < p. Note that x max, x m and x min stand for maximum, mean and minimum responses respectively at each. As indicated by x m, the system behaves nonlinearly in the primary resonance regime, and there is dynamic crossover between the first and second stage. In such case, the primary resonant frequency is a combined effect of the stiff first stage and the compliant second stage. Consequently, the system shows softening characteristics and the resultant p is lower than α. To study the occurrence of sub-harmonic resonance, parametric study is conducted. For the dimensionless system of Equation (4), F m, F p and α can sufficiently describe the system, assuming a light damping ratio of
6 644 Nonlinear Dyn (27) 5: x max x 4 2 x m x min p =.2 c = Fig. 3 Sub-harmonic Resonance given α = 3, ς =.5, F m =.7 and F p =.85. Key:, MHBM result with = ;, MHBM initial guess approach with = 2;, transition point value;, mean operation x m ( ) Fig. 4 Effect of F m on the occurrence of sub-resonance given α = 8 and F p =.75. Key:, stable response;, unstable response δ rms δ rms δ rms F m =.5 F m =.7 F m =.9 δ rms δ rms F m =. F m = ς =.5. First, we study the effect of F m on the subharmonic resonance. In Fig. 4, when F m starts from.5, no sub-harmonic resonance is found. As F m moves closer to the transition point (viz. F m =.), for example F m =.7,.9, a 2nd sub-harmonic resonance is clearly observed. Also, a 2nd sub-harmonic resonance occurs even when the starting mean operating point x m is close enough to the transition point, for example, F m =.. Here x m is defined as follows: { Fm /α F m. x m = F m +. α F α m >. (5)
7 Nonlinear Dyn (27) 5: Note that we focus on the positive definite mean load cases in this article. Since the non-linear forcedisplacement relationship is an odd function as shown in Fig., the system dynamics for a negative mean load could be symmetrically mapped. In the extreme case when F m =., even a small excitation F p will generate sub-harmonic resonance. For example in Fig. 5, an active 2nd sub-harmonic peak occurs although F p is as small as.. Further, it is noted that the sub-harmonic peak frequency decreases with an increase of F m. For example, as F m increases from.7 to., the sub-harmonic peak frequency decreases from Fig. 5 Sub-harmonic Resonance when F m =.givenα = 8 and F p =.. Key:, MHBM result;, Numerical integration result Fig. 6 Comparison of Equivalent Stiffness. Key:, F m =.7;, F m =.9; +++, F m =. 4 3 K e
8 646 Nonlinear Dyn (27) 5: (a) Fig. 7 Effect of F p on Sub-harmonic Resonance given α = 4. (a) For F m =.8. Key:, F p =.4;, F p =.6;, F p =.8;, F p =.,, unstable solutions. (b) For (b) F m =.2. Key:, F p =.6;, F p =.8;, F p =.;, F p =.2,, unstable solutions
9 Nonlinear Dyn (27) 5: = 2.95 to This could be explained by an effective stiffness K e concept. K e = N N N ( f (x) f (x) N )(x x N ) N (x x N )(x x N ) (6) Here N is the arithmetic average of N discrete points calculated by MHBM. As presented in (6), this is indeed an unbiased covariance calculation []. Figure 6 compares K e of three F m in the sub-harmonic resonance regime. As seen, a higher F m generally has lower K e in the sub-harmonic resonant regime. Note that the.44 α = α = α = (a) (b) Fig. 8 Effect of α on Sub-harmonic Resonance given F m =.8 and F p =.5. (a) Frequency responses. (b) Enlarged view of isolated branch. Key:, stable solution;, unstable solution
10 648 Nonlinear Dyn (27) 5: resonant peak response is actually a joint effect of the whole regime rather than K e at a specific. For this reason, although at some frequencies the effective stiffness K e (with higher F m ) is larger than that for lower F m, the overall effect across the frequency range yields a lower peak frequency. Physically, with lower F m, system operates more in the first stage with higher stiffness that results in a higher sub-harmonic resonant peak frequency. Next, the effect of F p is investigated. Figure 7a shows the results when x m stays in the first (stiffer) stage (F m < ) and 7b in the second (compliant) stage (F m > ). As is shown, in both cases as F p increases, the root-mean-square response also increases as a result of enhanced excitation. In either case, there is a slightly downshifting of peak frequency as F p increases. Though the calculation of K e would help in examining this frequency shifting phenomena, similar to the previous discussion, we provide an intuitive yet sensible explanation here. Although an increase of F p is symmetric around F m and thus x m in terms of excitation force, the asymmetric nature of the piecewise linear system introduces different duty-cycles of stiffer and compliant stages. As a matter of fact, the periodic response of piecewise linear system is a combination of two transient responses within stiff and compliant stages, referring to the piecewise solution strategy [9]. Theoretically, the higher the stiffness (or frequency) is, the shorter the response (decay) time is. Consequently, although an increase in the dynamic excitation F p is symmetric around F m, the enhanced response is not symmetric as a result of the asymmetric non-linearity. Thus, the proportion of time that the system operates within the stiff stage shall be smaller than in the compliant side within one period of response. Therefore an increase in F p would decrease the peak frequency. Finally, we examine the effect of α value. Figure 8 shows a cascading plot of frequency response in the sub-harmonic resonance regime. It is evident that the sub-harmonic tends to take place with an increase in α. It is because when α is higher, the transition point./α is smaller. Further, a higher stiffness would enlarge the dynamic response (as contributed by F p ) at higher frequency. Therefore, it is easier for the system to go through the transition point. Since such transition indicates a switch from linear to nonlinear system behavior, a higher transition frequency would introduce more complicated system dynamics such as sub-harmonic resonance. Further, it is noted that as sub-harmonic resonance first appears when α = 4, an isolated closedloop sub-harmonic branch is found. Because the system initiates in the first (stiffer) stage (F m < ), the system trends to soften up as it moves in the second region; hence the resonance branch in Fig. 8a tilts to the left. As discussed earlier in Section 3, the excitation perturbation approach cannot be directly applied in this α = 2 α= 4.4 α = Fig. 9 Effect of α on Sub-harmonic Resonance given F m =.5 and F p =.5. Key:, stable solution;, unstable solution
11 Nonlinear Dyn (27) 5: case. As shown in Fig. 8b, the closed-loop branch is totally isolated from the lower locus. The excitation perturbation approach, taking the adjacent points as initial guess for next calculation, cannot take the jump. Rather, the initial guess approach must be used by taking a trial and error process to find the appropriate initial conditions. Figure 9 also shows a similar trend: a higher α would bring sub-harmonic resonance more easily. Because the system initiates within the second (compliant) stage (F m > ), the system stiffens up as it expands into the first region; hence the resonance branch in Fig. 9 tilts to the right, typical for a hardening nonlinearity. 5 Conclusion In this study, we studied the sub-harmonic resonance of a mechanical oscillator with a nearly pre-loaded non-linearity. Several contributions to the state-of-art emerge. First, with a new excitation perturbation approach, we have successfully applied MHBM to calculate the sub-harmonic resonances. Our approach has significantly reduced the work by computing the subharmonic responses with just one run. Initial guesses in the vicinity of sub-harmonic regime are relaxed compared to previous approach. Second, effects of F m, F p and α on the occurrence and characteristics of subharmonic resonances have been examined. Our analysis shows that the sub-harmonic resonance typically happens when F m is close to the transition point. In the extreme case, a very small F p would be sufficient to excite a sub-harmonic resonance. For a higher F m, the resonant peak appears in lower frequency as a result of reduced equivalent stiffness. The possibility of the subharmonic occurrence also increases as an increase of F p or α. Finally our analytical formulations have been validated using numerical integration results. Future work would focus on analytical study of sub-harmonic resonances in multi-degree of freedom systems with preload type nonlinearity. Appendix A: List of symbols C F M N K viscous damping coefficient force mass number of integration points stiffness t time x displacement ω excitation frequency (rad/s) ε perturbation dimensionless frequency τ dimensionless time ζ damping ratio differential operator matrix Ɣ discrete Fourier transform matrix Subscripts c crossing e equivalent m mean load n natural frequency or index p fluctuating component or primary initial or starting Superscripts - dimensional variable or parameter first derivative with respect to dimensionless time second derivative with respect to dimensionless time inverse + pseudo inverse T transpose Operator arithmetic averaging References. Comparin, R.J., Singh, R.: Nonlinear frequency response characteristics of an impact pair. J. Sound Vib. 34(2), 9 4 (989) 2. Choi, H.S., Lou, J.Y.K.: Nonlinear behavior and chaotic motions of an SDOF system with piecewise non-linear stiffness. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 26, (99) 3. Padmanabhan, C., Singh, R.: Dynamics of a piecewise nonlinear system subject to dual harmonic excitation using parametric continuation. J. Sound Vib. 84(5), (995) 4. Padmanabhan, C., Singh, R.: Analysis of periodically forced non-linear Hill s oscillator with application to a Geared system. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 99(), (996) 5. Kim, T.C., Rook, T.E., Singh, R.: Super- and sub-harmonic response calculations for a torsional system with clearance non-linearity using harmonic balance method. J. Sound Vib. 28(3 5), (25) 6. Duan, C., Singh, R.: Dynamic analysis of preload nonlinearity in a mechanical oscillator. J. Sound Vib. (accepted for publication) (26)
12 65 Nonlinear Dyn (27) 5: Gelb, A., Vander Velde, W.E.: Multiple-Input Describing Functions and Non-linear System Design. McGraw-Hill, New York, USA (968) 8. Dormand, J.R., Prince, P.J.: A family of embedded Runge Kutta formulae. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 6(), 9 26 (98) 9. Duan, C., Singh, R.: Dynamics of a 3DOF torsional system with a dry friction controlled path. J. Sound Vib. 289(4 5), (26). Rook, T.E., Singh, R.: Dynamic analysis of a reverse idler gear pair with concurrent clearances. J. Sound Vib. 82(2), (995)
ARTICLE IN PRESS. Journal of Sound and Vibration
 Journal of Sound and Vibration 325 (29) 499 56 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Sound and Vibration journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jsvi Rapid Communication Forced vibrations
Journal of Sound and Vibration 325 (29) 499 56 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Sound and Vibration journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jsvi Rapid Communication Forced vibrations
Limitations of smoothening functions for automotive vibro-impact problems
 Shock and Vibration 18 (2011) 397 406 397 DOI 10.3233/SAV-2010-0582 IOS Press Limitations of smoothening functions for automotive vibro-impact problems Zhiwei Zhang a,, Rajendra Singh b and Ashley R. Crowther
Shock and Vibration 18 (2011) 397 406 397 DOI 10.3233/SAV-2010-0582 IOS Press Limitations of smoothening functions for automotive vibro-impact problems Zhiwei Zhang a,, Rajendra Singh b and Ashley R. Crowther
2.034: Nonlinear Dynamics and Waves. Term Project: Nonlinear dynamics of piece-wise linear oscillators Mostafa Momen
 2.034: Nonlinear Dynamics and Waves Term Project: Nonlinear dynamics of piece-wise linear oscillators Mostafa Momen May 2015 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 1 Nonlinear dynamics of piece-wise linear
2.034: Nonlinear Dynamics and Waves Term Project: Nonlinear dynamics of piece-wise linear oscillators Mostafa Momen May 2015 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 1 Nonlinear dynamics of piece-wise linear
Modeling of Automotive Gear Rattle Phenomenon: State of the Art
 Modeling of Automotive Gear Rattle Phenomenon: State of the Art Chandramouli Padmanabhan, Todd E. Rook, and Rajendra Singh The Ohio State Univ. ABSTRACT The sources of gear rattle in automotive transmission
Modeling of Automotive Gear Rattle Phenomenon: State of the Art Chandramouli Padmanabhan, Todd E. Rook, and Rajendra Singh The Ohio State Univ. ABSTRACT The sources of gear rattle in automotive transmission
Anatomy of a Real-Life Non-Linear Device: Hydraulic Engine Mount
 Anatomy of a Real-Life Non-Linear Device: Hydraulic Engine Mount Rajendra Singh and Song He Acoustics and Dynamics Laboratory, Department of Mechanical Engineering and
Anatomy of a Real-Life Non-Linear Device: Hydraulic Engine Mount Rajendra Singh and Song He Acoustics and Dynamics Laboratory, Department of Mechanical Engineering and
An improved brake squeal source model in the presence of kinematic and friction nonlinearities
 An improved brake squeal source model in the presence of kinematic and friction nonlinearities Osman Taha Sen, Jason T. Dreyer, and Rajendra Singh 3 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Istanbul Technical
An improved brake squeal source model in the presence of kinematic and friction nonlinearities Osman Taha Sen, Jason T. Dreyer, and Rajendra Singh 3 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Istanbul Technical
Hardening nonlinearity effects on forced vibration of viscoelastic dynamical systems to external step perturbation field
 Int. J. Adv. Appl. Math. and Mech. 3(2) (215) 16 32 (ISSN: 2347-2529) IJAAMM Journal homepage: www.ijaamm.com International Journal of Advances in Applied Mathematics and Mechanics Hardening nonlinearity
Int. J. Adv. Appl. Math. and Mech. 3(2) (215) 16 32 (ISSN: 2347-2529) IJAAMM Journal homepage: www.ijaamm.com International Journal of Advances in Applied Mathematics and Mechanics Hardening nonlinearity
PERIODIC RESPONSE OF MECHANICAL SYSTEMS WITH LOCAL NON-LINEARITIES USING AN ENHANCED GALERKIN TECHNIQUE
 Journal of Sound and Vibration (1996) 194(2), 243 263 PERIODIC RESPONSE OF MECHANICAL SYSTEMS WITH LOCAL NON-LINEARITIES USING AN ENHANCED GALERKIN TECHNIQUE T. J. ROYSTON and R. SINGH Acoustics and Dynamics
Journal of Sound and Vibration (1996) 194(2), 243 263 PERIODIC RESPONSE OF MECHANICAL SYSTEMS WITH LOCAL NON-LINEARITIES USING AN ENHANCED GALERKIN TECHNIQUE T. J. ROYSTON and R. SINGH Acoustics and Dynamics
Chapter 2 PARAMETRIC OSCILLATOR
 CHAPTER- Chapter PARAMETRIC OSCILLATOR.1 Introduction A simple pendulum consists of a mass m suspended from a string of length L which is fixed at a pivot P. When simple pendulum is displaced to an initial
CHAPTER- Chapter PARAMETRIC OSCILLATOR.1 Introduction A simple pendulum consists of a mass m suspended from a string of length L which is fixed at a pivot P. When simple pendulum is displaced to an initial
Construction of Semianalytical Solutions to Spur Gear Dynamics Given Periodic Mesh Stiffness and Sliding Friction Functions
 Song He Acoustics and Dynamics Laboratory, Department of Mechanical Engineering, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 430 e-mail: he.8@osu.edu Todd Rook Goodrich Aerospace, 0 Waco Street, Troy, OH 45373
Song He Acoustics and Dynamics Laboratory, Department of Mechanical Engineering, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 430 e-mail: he.8@osu.edu Todd Rook Goodrich Aerospace, 0 Waco Street, Troy, OH 45373
Use of Full Spectrum Cascade for Rotor Rub Identification
 Use of Full Spectrum Cascade for Rotor Rub Identification T. H. Patel 1, A. K. Darpe 2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi 110016, India. 1 Research scholar, 2 Assistant
Use of Full Spectrum Cascade for Rotor Rub Identification T. H. Patel 1, A. K. Darpe 2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi 110016, India. 1 Research scholar, 2 Assistant
DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A REVERSE-IDLER GEAR PAIR WITH CONCURRENT CLEARANCES
 Journal of Sound and Vibration (1995) 182(2), 303 322 DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A REVERSE-IDLER GEAR PAIR WITH CONCURRENT CLEARANCES Acoustics & Dynamics Laboratory, Department of Mechanical Engineering, The
Journal of Sound and Vibration (1995) 182(2), 303 322 DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF A REVERSE-IDLER GEAR PAIR WITH CONCURRENT CLEARANCES Acoustics & Dynamics Laboratory, Department of Mechanical Engineering, The
Insight into brake squeal source mechanism considering kinematic nonlinearity and pad-disc separation
 Insight into brake squeal source mechanism considering kinematic nonlinearity and pad-disc separation Osman Taha Sen a Department of Mechanical Engineering, Istanbul Technical University, Istanbul, 34469,
Insight into brake squeal source mechanism considering kinematic nonlinearity and pad-disc separation Osman Taha Sen a Department of Mechanical Engineering, Istanbul Technical University, Istanbul, 34469,
Improving convergence of incremental harmonic balance method using homotopy analysis method
 Acta Mech Sin (2009) 25:707 712 DOI 10.1007/s10409-009-0256-4 RESEARCH PAPER Improving convergence of incremental harmonic balance method using homotopy analysis method Yanmao Chen Jike Liu Received: 10
Acta Mech Sin (2009) 25:707 712 DOI 10.1007/s10409-009-0256-4 RESEARCH PAPER Improving convergence of incremental harmonic balance method using homotopy analysis method Yanmao Chen Jike Liu Received: 10
Dynamics of Rotor Systems with Clearance and Weak Pedestals in Full Contact
 Paper ID No: 23 Dynamics of Rotor Systems with Clearance and Weak Pedestals in Full Contact Dr. Magnus Karlberg 1, Dr. Martin Karlsson 2, Prof. Lennart Karlsson 3 and Ass. Prof. Mats Näsström 4 1 Department
Paper ID No: 23 Dynamics of Rotor Systems with Clearance and Weak Pedestals in Full Contact Dr. Magnus Karlberg 1, Dr. Martin Karlsson 2, Prof. Lennart Karlsson 3 and Ass. Prof. Mats Näsström 4 1 Department
8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7)
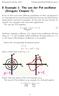 8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7) So far we have seen some different possibilities of what can happen in two-dimensional systems (local and global attractors and bifurcations)
8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7) So far we have seen some different possibilities of what can happen in two-dimensional systems (local and global attractors and bifurcations)
Response of A Hard Duffing Oscillator to Harmonic Excitation An Overview
 INDIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, KHRGPUR 710, DECEMBER 8-0, 00 1 Response of Hard Duffing Oscillator to Harmonic Excitation n Overview.K. Mallik Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology
INDIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, KHRGPUR 710, DECEMBER 8-0, 00 1 Response of Hard Duffing Oscillator to Harmonic Excitation n Overview.K. Mallik Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology
Period-One Rotating Solutions of Horizontally Excited Pendulum Based on Iterative Harmonic Balance
 Advances in Pure Mathematics, 015, 5, 413-47 Published Online June 015 in Scies. http://www.scirp.org/journal/apm http://dx.doi.org/10.436/apm.015.58041 Period-One otating Solutions of Horizontally Excited
Advances in Pure Mathematics, 015, 5, 413-47 Published Online June 015 in Scies. http://www.scirp.org/journal/apm http://dx.doi.org/10.436/apm.015.58041 Period-One otating Solutions of Horizontally Excited
Existence of super-harmonics in quarter-vehicle system responses with nonlinear inertia hydraulic track mount given sinusoidal force excitation
 Journal of Sound and Vibration 313 (8) 367 374 Rapid Communication JOURNAL OF SOUND AND VIBRATION Existence of super-harmonics in quarter-vehicle system responses with nonlinear inertia hydraulic track
Journal of Sound and Vibration 313 (8) 367 374 Rapid Communication JOURNAL OF SOUND AND VIBRATION Existence of super-harmonics in quarter-vehicle system responses with nonlinear inertia hydraulic track
Suppression of the primary resonance vibrations of a forced nonlinear system using a dynamic vibration absorber
 Suppression of the primary resonance vibrations of a forced nonlinear system using a dynamic vibration absorber J.C. Ji, N. Zhang Faculty of Engineering, University of Technology, Sydney PO Box, Broadway,
Suppression of the primary resonance vibrations of a forced nonlinear system using a dynamic vibration absorber J.C. Ji, N. Zhang Faculty of Engineering, University of Technology, Sydney PO Box, Broadway,
Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics
 Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics Volume 19, 13 http://acousticalsociety.org/ ICA 13 Montreal Montreal, Canada - 7 June 13 Signal Processing in Acoustics Session 1pSPc: Miscellaneous Topics in Signal
Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics Volume 19, 13 http://acousticalsociety.org/ ICA 13 Montreal Montreal, Canada - 7 June 13 Signal Processing in Acoustics Session 1pSPc: Miscellaneous Topics in Signal
In-Plane and Out-of-Plane Dynamic Responses of Elastic Cables under External and Parametric Excitations
 Applied Mathematics 5, 5(6): -4 DOI:.59/j.am.556. In-Plane and Out-of-Plane Dynamic Responses of Elastic Cables under External and Parametric Excitations Usama H. Hegazy Department of Mathematics, Faculty
Applied Mathematics 5, 5(6): -4 DOI:.59/j.am.556. In-Plane and Out-of-Plane Dynamic Responses of Elastic Cables under External and Parametric Excitations Usama H. Hegazy Department of Mathematics, Faculty
Bifurcation Trees of Periodic Motions to Chaos in a Parametric, Quadratic Nonlinear Oscillator
 International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, Vol. 24, No. 5 (2014) 1450075 (28 pages) c World Scientific Publishing Company DOI: 10.1142/S0218127414500758 Bifurcation Trees of Periodic Motions to Chaos
International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, Vol. 24, No. 5 (2014) 1450075 (28 pages) c World Scientific Publishing Company DOI: 10.1142/S0218127414500758 Bifurcation Trees of Periodic Motions to Chaos
Development of a test apparatus that consistently generates squeak to rate squeak propensity of a pair of materials
 Development of a test apparatus that consistently generates squeak to rate squeak propensity of a pair of materials Gil Jun LEE 1 ; Jay KIM 2 1, 2 Department of Mechanical and Materials Engineering, University
Development of a test apparatus that consistently generates squeak to rate squeak propensity of a pair of materials Gil Jun LEE 1 ; Jay KIM 2 1, 2 Department of Mechanical and Materials Engineering, University
A Harmonic Balance Approach for Large-Scale Problems in Nonlinear Structural Dynamics
 A Harmonic Balance Approach for Large-Scale Problems in Nonlinear Structural Dynamics Allen R, PhD Candidate Peter J Attar, Assistant Professor University of Oklahoma Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering
A Harmonic Balance Approach for Large-Scale Problems in Nonlinear Structural Dynamics Allen R, PhD Candidate Peter J Attar, Assistant Professor University of Oklahoma Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering
Strategies for Modeling Friction in Gear Dynamics
 Manish Vaishya Rajendra Singh e-mail: singh.3@osu.edu Department of Mechanical Engineering, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 43210-1107 Strategies for Modeling Friction in Gear Dynamics Sliding
Manish Vaishya Rajendra Singh e-mail: singh.3@osu.edu Department of Mechanical Engineering, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 43210-1107 Strategies for Modeling Friction in Gear Dynamics Sliding
Research Article Approximate Super- and Sub-harmonic Response of a Multi-DOFs System with Local Cubic Nonlinearities under Resonance
 Journal of Applied Mathematics Volume 212, Article ID 53148, 22 pages doi:1155/212/53148 Research Article Approximate Super- and Sub-harmonic Response of a Multi-DOFs System with Local Cubic Nonlinearities
Journal of Applied Mathematics Volume 212, Article ID 53148, 22 pages doi:1155/212/53148 Research Article Approximate Super- and Sub-harmonic Response of a Multi-DOFs System with Local Cubic Nonlinearities
Steady state forced response of a mechanical oscillator with combined parametric excitation and clearance type non-linearity
 Steady state forced response of a mechanical oscillator with combined parametric excitation and clearance type non-linearity G.W. Blankenship, A. Kahraman To cite this version: G.W. Blankenship, A. Kahraman.
Steady state forced response of a mechanical oscillator with combined parametric excitation and clearance type non-linearity G.W. Blankenship, A. Kahraman To cite this version: G.W. Blankenship, A. Kahraman.
Nonharmonic Forcing of an Inverted Pendulum
 Nonharmonic Forcing of an Inverted Pendulum Robert M. Hayward a,,, Samuel Shapero a,, Yiwei Cheng a,3 a Georgia Institute of Technology Abstract The harmonically driven pendulum has been investigated thoroughly
Nonharmonic Forcing of an Inverted Pendulum Robert M. Hayward a,,, Samuel Shapero a,, Yiwei Cheng a,3 a Georgia Institute of Technology Abstract The harmonically driven pendulum has been investigated thoroughly
SAMCEF For ROTORS. Chapter 1 : Physical Aspects of rotor dynamics. This document is the property of SAMTECH S.A. MEF A, Page 1
 SAMCEF For ROTORS Chapter 1 : Physical Aspects of rotor dynamics This document is the property of SAMTECH S.A. MEF 101-01-A, Page 1 Table of Contents rotor dynamics Introduction Rotating parts Gyroscopic
SAMCEF For ROTORS Chapter 1 : Physical Aspects of rotor dynamics This document is the property of SAMTECH S.A. MEF 101-01-A, Page 1 Table of Contents rotor dynamics Introduction Rotating parts Gyroscopic
Vibro-Impact Energy Analysis of a Geared System with Piecewise-Type Nonlinearities Using Various Parameter Values
 Energies 2015, 8, 8924-8944; doi:10.3390/en8088924 Article OPEN ACCESS energies ISSN 1996-1073 www.mdpi.com/journal/energies Vibro-Impact Energy Analysis of a Geared System with Piecewise-Type Nonlinearities
Energies 2015, 8, 8924-8944; doi:10.3390/en8088924 Article OPEN ACCESS energies ISSN 1996-1073 www.mdpi.com/journal/energies Vibro-Impact Energy Analysis of a Geared System with Piecewise-Type Nonlinearities
Clearly the passage of an eigenvalue through to the positive real half plane leads to a qualitative change in the phase portrait, i.e.
 Bifurcations We have already seen how the loss of stiffness in a linear oscillator leads to instability. In a practical situation the stiffness may not degrade in a linear fashion, and instability may
Bifurcations We have already seen how the loss of stiffness in a linear oscillator leads to instability. In a practical situation the stiffness may not degrade in a linear fashion, and instability may
CALCULATION OF NONLINEAR VIBRATIONS OF PIECEWISE-LINEAR SYSTEMS USING THE SHOOTING METHOD
 Vietnam Journal of Mechanics, VAST, Vol. 34, No. 3 (2012), pp. 157 167 CALCULATION OF NONLINEAR VIBRATIONS OF PIECEWISE-LINEAR SYSTEMS USING THE SHOOTING METHOD Nguyen Van Khang, Hoang Manh Cuong, Nguyen
Vietnam Journal of Mechanics, VAST, Vol. 34, No. 3 (2012), pp. 157 167 CALCULATION OF NONLINEAR VIBRATIONS OF PIECEWISE-LINEAR SYSTEMS USING THE SHOOTING METHOD Nguyen Van Khang, Hoang Manh Cuong, Nguyen
Nonlinear Normal Modes: Theoretical Curiosity or Practical Concept?
 Nonlinear Normal Modes: Theoretical Curiosity or Practical Concept? Gaëtan Kerschen Space Structures and Systems Lab Structural Dynamics Research Group University of Liège Linear Modes: A Key Concept Clear
Nonlinear Normal Modes: Theoretical Curiosity or Practical Concept? Gaëtan Kerschen Space Structures and Systems Lab Structural Dynamics Research Group University of Liège Linear Modes: A Key Concept Clear
Periodic Skeletons of Nonlinear Dynamical Systems in the Problems of Global Bifurcation Analysis
 Periodic Skeletons of Nonlinear Dynamical Systems in the Problems of Global Bifurcation Analysis M Zakrzhevsky, I Schukin, A Klokov and E Shilvan PERIODIC SKELETONS OF NONLINEAR DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS IN THE
Periodic Skeletons of Nonlinear Dynamical Systems in the Problems of Global Bifurcation Analysis M Zakrzhevsky, I Schukin, A Klokov and E Shilvan PERIODIC SKELETONS OF NONLINEAR DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS IN THE
Effects of viscosity and varying gravity on liquid sloshing in a carrier subjected to external excitations
 Int. J. Dynam. Control (204) 2:52 532 DOI 0.007/s40435-04-0072-y Effects of viscosity and varying gravity on liquid sloshing in a carrier subjected to external excitations Liming Dai Xiaojie Wang Received:
Int. J. Dynam. Control (204) 2:52 532 DOI 0.007/s40435-04-0072-y Effects of viscosity and varying gravity on liquid sloshing in a carrier subjected to external excitations Liming Dai Xiaojie Wang Received:
ME 563 HOMEWORK # 7 SOLUTIONS Fall 2010
 ME 563 HOMEWORK # 7 SOLUTIONS Fall 2010 PROBLEM 1: Given the mass matrix and two undamped natural frequencies for a general two degree-of-freedom system with a symmetric stiffness matrix, find the stiffness
ME 563 HOMEWORK # 7 SOLUTIONS Fall 2010 PROBLEM 1: Given the mass matrix and two undamped natural frequencies for a general two degree-of-freedom system with a symmetric stiffness matrix, find the stiffness
2:2:1 Resonance in the Quasiperiodic Mathieu Equation
 Nonlinear Dynamics 31: 367 374, 003. 003 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. ::1 Resonance in the Quasiperiodic Mathieu Equation RICHARD RAND Department of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics,
Nonlinear Dynamics 31: 367 374, 003. 003 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. ::1 Resonance in the Quasiperiodic Mathieu Equation RICHARD RAND Department of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics,
Comparative Analysis of Time Steps Distribution in Runge-Kutta Algorithms
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 3, Issue 1, January-212 1 Comparative Analysis of Steps Distribution in Runge-Kutta Algorithms Salau, T.A.O., Ajide, O.O. Abstract This
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 3, Issue 1, January-212 1 Comparative Analysis of Steps Distribution in Runge-Kutta Algorithms Salau, T.A.O., Ajide, O.O. Abstract This
Nonlinear Stability and Bifurcation of Multi-D.O.F. Chatter System in Grinding Process
 Key Engineering Materials Vols. -5 (6) pp. -5 online at http://www.scientific.net (6) Trans Tech Publications Switzerland Online available since 6//5 Nonlinear Stability and Bifurcation of Multi-D.O.F.
Key Engineering Materials Vols. -5 (6) pp. -5 online at http://www.scientific.net (6) Trans Tech Publications Switzerland Online available since 6//5 Nonlinear Stability and Bifurcation of Multi-D.O.F.
Effect of the Tooth Surface Waviness on the Dynamics and Structure-Borne Noise of a Spur Gear Pair
 2013-01-1877 Published 05/13/2013 Copyright 2013 SAE International doi:10.4271/2013-01-1877 saepcmech.saejournals.org Effect of the Tooth Surface Waviness on the Dynamics and Structure-Borne Noise of a
2013-01-1877 Published 05/13/2013 Copyright 2013 SAE International doi:10.4271/2013-01-1877 saepcmech.saejournals.org Effect of the Tooth Surface Waviness on the Dynamics and Structure-Borne Noise of a
In this lecture you will learn the following
 Module 9 : Forced Vibration with Harmonic Excitation; Undamped Systems and resonance; Viscously Damped Systems; Frequency Response Characteristics and Phase Lag; Systems with Base Excitation; Transmissibility
Module 9 : Forced Vibration with Harmonic Excitation; Undamped Systems and resonance; Viscously Damped Systems; Frequency Response Characteristics and Phase Lag; Systems with Base Excitation; Transmissibility
Strange dynamics of bilinear oscillator close to grazing
 Strange dynamics of bilinear oscillator close to grazing Ekaterina Pavlovskaia, James Ing, Soumitro Banerjee and Marian Wiercigroch Centre for Applied Dynamics Research, School of Engineering, King s College,
Strange dynamics of bilinear oscillator close to grazing Ekaterina Pavlovskaia, James Ing, Soumitro Banerjee and Marian Wiercigroch Centre for Applied Dynamics Research, School of Engineering, King s College,
Solution of a Quadratic Non-Linear Oscillator by Elliptic Homotopy Averaging Method
 Math. Sci. Lett. 4, No. 3, 313-317 (215) 313 Mathematical Sciences Letters An International Journal http://dx.doi.org/1.12785/msl/4315 Solution of a Quadratic Non-Linear Oscillator by Elliptic Homotopy
Math. Sci. Lett. 4, No. 3, 313-317 (215) 313 Mathematical Sciences Letters An International Journal http://dx.doi.org/1.12785/msl/4315 Solution of a Quadratic Non-Linear Oscillator by Elliptic Homotopy
Final Exam Solution Dynamics :45 12:15. Problem 1 Bateau
 Final Exam Solution Dynamics 2 191157140 31-01-2013 8:45 12:15 Problem 1 Bateau Bateau is a trapeze act by Cirque du Soleil in which artists perform aerial maneuvers on a boat shaped structure. The boat
Final Exam Solution Dynamics 2 191157140 31-01-2013 8:45 12:15 Problem 1 Bateau Bateau is a trapeze act by Cirque du Soleil in which artists perform aerial maneuvers on a boat shaped structure. The boat
Compound Damped Pendulum: An Example
 Compound Damped Pendulum: An Example Temple H. Fay Department of Mathematical Technology 1 Tshwane University of Technology Pretoria, South Africa thf ay@hotmail:com Abstract: In this article, we use an
Compound Damped Pendulum: An Example Temple H. Fay Department of Mathematical Technology 1 Tshwane University of Technology Pretoria, South Africa thf ay@hotmail:com Abstract: In this article, we use an
Chapter 23: Principles of Passive Vibration Control: Design of absorber
 Chapter 23: Principles of Passive Vibration Control: Design of absorber INTRODUCTION The term 'vibration absorber' is used for passive devices attached to the vibrating structure. Such devices are made
Chapter 23: Principles of Passive Vibration Control: Design of absorber INTRODUCTION The term 'vibration absorber' is used for passive devices attached to the vibrating structure. Such devices are made
Approximate step response of a nonlinear hydraulic mount using a simplified linear model
 Journal of Sound and Vibration 99 (007) 656 663 Short Communication JOURNAL OF SOUND AND VIBRATION Approximate step response of a nonlinear hydraulic mount using a simplified linear model Song He, Rajendra
Journal of Sound and Vibration 99 (007) 656 663 Short Communication JOURNAL OF SOUND AND VIBRATION Approximate step response of a nonlinear hydraulic mount using a simplified linear model Song He, Rajendra
ANNEX A: ANALYSIS METHODOLOGIES
 ANNEX A: ANALYSIS METHODOLOGIES A.1 Introduction Before discussing supplemental damping devices, this annex provides a brief review of the seismic analysis methods used in the optimization algorithms considered
ANNEX A: ANALYSIS METHODOLOGIES A.1 Introduction Before discussing supplemental damping devices, this annex provides a brief review of the seismic analysis methods used in the optimization algorithms considered
Application of a novel method to identify multi-axis joint properties
 Application of a novel method to identify multi-axis joint properties Scott Noll, Jason Dreyer, and Rajendra Singh The Ohio State University, 219 W. 19 th Avenue, Columbus, Ohio 4321 USA ABSTRACT This
Application of a novel method to identify multi-axis joint properties Scott Noll, Jason Dreyer, and Rajendra Singh The Ohio State University, 219 W. 19 th Avenue, Columbus, Ohio 4321 USA ABSTRACT This
Solution of Cubic-Quintic Duffing Oscillators using Harmonic Balance Method
 Malaysian Journal of Mathematical Sciences 10(S) February: 181 192 (2016) Special Issue: The 3 rd International Conference on Mathematical Applications in Engineering 2014 (ICMAE 14) MALAYSIAN JOURNAL
Malaysian Journal of Mathematical Sciences 10(S) February: 181 192 (2016) Special Issue: The 3 rd International Conference on Mathematical Applications in Engineering 2014 (ICMAE 14) MALAYSIAN JOURNAL
Solutions of Nonlinear Oscillators by Iteration Perturbation Method
 Inf. Sci. Lett. 3, No. 3, 91-95 2014 91 Information Sciences Letters An International Journal http://dx.doi.org/10.12785/isl/030301 Solutions of Nonlinear Oscillators by Iteration Perturbation Method A.
Inf. Sci. Lett. 3, No. 3, 91-95 2014 91 Information Sciences Letters An International Journal http://dx.doi.org/10.12785/isl/030301 Solutions of Nonlinear Oscillators by Iteration Perturbation Method A.
Abstract: Complex responses observed in an experimental, nonlinear, moored structural
 AN INDEPENDENT-FLOW-FIELD MODEL FOR A SDOF NONLINEAR STRUCTURAL SYSTEM, PART II: ANALYSIS OF COMPLEX RESPONSES Huan Lin e-mail: linh@engr.orst.edu Solomon C.S. Yim e-mail: solomon.yim@oregonstate.edu Ocean
AN INDEPENDENT-FLOW-FIELD MODEL FOR A SDOF NONLINEAR STRUCTURAL SYSTEM, PART II: ANALYSIS OF COMPLEX RESPONSES Huan Lin e-mail: linh@engr.orst.edu Solomon C.S. Yim e-mail: solomon.yim@oregonstate.edu Ocean
DYNAMICS OF ASYMMETRIC NONLINEAR VIBRATION ABSORBER
 8 Journal of Marine Science and Technology, Vol. 11, No. 1, pp. 8-19 (2003) DYNAMICS OF ASYMMETRIC NONLINEAR VIBRATION ABSORBER Chiou-Fong Chung and Chiang-Nan Chang* Key words: bifurcation, absorber,
8 Journal of Marine Science and Technology, Vol. 11, No. 1, pp. 8-19 (2003) DYNAMICS OF ASYMMETRIC NONLINEAR VIBRATION ABSORBER Chiou-Fong Chung and Chiang-Nan Chang* Key words: bifurcation, absorber,
NONLINEAR NORMAL MODES OF COUPLED SELF-EXCITED OSCILLATORS
 NONLINEAR NORMAL MODES OF COUPLED SELF-EXCITED OSCILLATORS Jerzy Warminski 1 1 Department of Applied Mechanics, Lublin University of Technology, Lublin, Poland, j.warminski@pollub.pl Abstract: The main
NONLINEAR NORMAL MODES OF COUPLED SELF-EXCITED OSCILLATORS Jerzy Warminski 1 1 Department of Applied Mechanics, Lublin University of Technology, Lublin, Poland, j.warminski@pollub.pl Abstract: The main
34 Imperfections 34 1
 34 Imperfections 34 1 Chapter 34: IMPERFECTIONS TABLE OF CONTENTS Page 34.1 No Body is Perfect................... 34 3 34.2 Imperfection Sources................. 34 3 34.2.1 Physical Imperfections..............
34 Imperfections 34 1 Chapter 34: IMPERFECTIONS TABLE OF CONTENTS Page 34.1 No Body is Perfect................... 34 3 34.2 Imperfection Sources................. 34 3 34.2.1 Physical Imperfections..............
Lab #2: Digital Simulation of Torsional Disk Systems in LabVIEW
 Lab #2: Digital Simulation of Torsional Disk Systems in LabVIEW Objective The purpose of this lab is to increase your familiarity with LabVIEW, increase your mechanical modeling prowess, and give you simulation
Lab #2: Digital Simulation of Torsional Disk Systems in LabVIEW Objective The purpose of this lab is to increase your familiarity with LabVIEW, increase your mechanical modeling prowess, and give you simulation
Transactions on the Built Environment vol 22, 1996 WIT Press, ISSN
 A shock damage potential approach to shock testing D.H. Trepess Mechanical Subject Group, School of Engineering, Coventry University, Coventry CVl 5FB, UK A shock damage (excitation capacity) approach
A shock damage potential approach to shock testing D.H. Trepess Mechanical Subject Group, School of Engineering, Coventry University, Coventry CVl 5FB, UK A shock damage (excitation capacity) approach
Implementation Issues for the Virtual Spring
 Implementation Issues for the Virtual Spring J. S. Freudenberg EECS 461 Embedded Control Systems 1 Introduction One of the tasks in Lab 4 is to attach the haptic wheel to a virtual reference position with
Implementation Issues for the Virtual Spring J. S. Freudenberg EECS 461 Embedded Control Systems 1 Introduction One of the tasks in Lab 4 is to attach the haptic wheel to a virtual reference position with
Identification Methods for Structural Systems. Prof. Dr. Eleni Chatzi Lecture March, 2016
 Prof. Dr. Eleni Chatzi Lecture 4-09. March, 2016 Fundamentals Overview Multiple DOF Systems State-space Formulation Eigenvalue Analysis The Mode Superposition Method The effect of Damping on Structural
Prof. Dr. Eleni Chatzi Lecture 4-09. March, 2016 Fundamentals Overview Multiple DOF Systems State-space Formulation Eigenvalue Analysis The Mode Superposition Method The effect of Damping on Structural
DYNAMICS OF UNSYMMETRIC PIECEWISE-LINEAR/NON-LINEAR SYSTEMS USING FINITE ELEMENTS IN TIME
 DYNAMICS OF UNSYMMETRIC PIECEWISE-LINEAR/NON-LINEAR SYSTEMS USING FINITE ELEMENTS IN TIME Yu Wang Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Maryland, 5401 Wilkens Avenue, Baltimore, Maryland
DYNAMICS OF UNSYMMETRIC PIECEWISE-LINEAR/NON-LINEAR SYSTEMS USING FINITE ELEMENTS IN TIME Yu Wang Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Maryland, 5401 Wilkens Avenue, Baltimore, Maryland
Design and Analysis of a Simple Nonlinear Vibration Absorber
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 78-1684,p-ISSN: 30-334X, Volume 11, Issue Ver. VI (Mar- Apr. 014), PP 84-90 Design and Analysis of a Simple Nonlinear Vibration Absorber
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 78-1684,p-ISSN: 30-334X, Volume 11, Issue Ver. VI (Mar- Apr. 014), PP 84-90 Design and Analysis of a Simple Nonlinear Vibration Absorber
NON-LINEAR ATTENUATION EFFECTS ON SOILS DYNAMIC RESPONSE EVALUATION *
 1 NON-LINEAR ATTENUATION EFFECTS ON SOILS DYNAMIC RESPONSE EVALUATION * Dinu BRATOSIN 1 The object of this paper is to estimate the structural attenuation in geological site materials with the aid of the
1 NON-LINEAR ATTENUATION EFFECTS ON SOILS DYNAMIC RESPONSE EVALUATION * Dinu BRATOSIN 1 The object of this paper is to estimate the structural attenuation in geological site materials with the aid of the
Dynamics of a 3dof torsional system with a dry friction controlled path
 Journal of Sound and Vibration 289 (26) 657 688 JOURNAL OF SOUND AND VIBRATION www.elsevier.com/locate/jsvi Dynamics of a 3dof torsional system with a dry friction controlled path Chengwu Duan, Rajendra
Journal of Sound and Vibration 289 (26) 657 688 JOURNAL OF SOUND AND VIBRATION www.elsevier.com/locate/jsvi Dynamics of a 3dof torsional system with a dry friction controlled path Chengwu Duan, Rajendra
ENGINEERING MECHANICS 2012 pp Svratka, Czech Republic, May 14 17, 2012 Paper #6
 . 18 m 12 th International Conference ENGINEERING MECHANICS 12 pp. 255 261 Svratka, Czech Republic, May 14 17, 12 Paper #6 RESONANCE BEHAVIOUR OF SPHERICAL PENDULUM INFLUENCE OF DAMPING C. Fischer, J.
. 18 m 12 th International Conference ENGINEERING MECHANICS 12 pp. 255 261 Svratka, Czech Republic, May 14 17, 12 Paper #6 RESONANCE BEHAVIOUR OF SPHERICAL PENDULUM INFLUENCE OF DAMPING C. Fischer, J.
NONLINEAR DYNAMICS OF ONE-WAY CLUTCHES AND DRY FRICTION TENSIONERS IN BELT-PULLEY SYSTEMS DISSERTATION
 NONLINEAR DYNAMICS OF ONE-WAY CLUTCHES AND DRY FRICTION TENSIONERS IN BELT-PULLEY SYSTEMS DISSERTATION Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements of the Degree Doctor of Philosophy in the Graduate
NONLINEAR DYNAMICS OF ONE-WAY CLUTCHES AND DRY FRICTION TENSIONERS IN BELT-PULLEY SYSTEMS DISSERTATION Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements of the Degree Doctor of Philosophy in the Graduate
Active Vibration Control for A Bilinear System with Nonlinear Velocity Time-delayed Feedback
 Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering Vol III, WCE, July - 5,, London, U.K. Active Vibration Control for A Bilinear System with Nonlinear Velocity Time-delayed Feedback X. Gao, Q. Chen Abstract
Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering Vol III, WCE, July - 5,, London, U.K. Active Vibration Control for A Bilinear System with Nonlinear Velocity Time-delayed Feedback X. Gao, Q. Chen Abstract
The Stick-Slip Vibration and Bifurcation of a Vibro-Impact System with Dry Friction
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 308 The Open Mechanical Engineering Journal, 2014, 8, 308-313 Open Access The Stick-Slip Vibration and Bifurcation of a Vibro-Impact System with Dry
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 308 The Open Mechanical Engineering Journal, 2014, 8, 308-313 Open Access The Stick-Slip Vibration and Bifurcation of a Vibro-Impact System with Dry
OPTIMIZATION OF PASSIVE AND ACTIVE NON-LINEAR VIBRATION MOUNTING SYSTEMS BASED ON VIBRATORY POWER TRANSMISSION
 Journal of Sound and Vibration (1996) 194(3), 295 316 OPTIMIZATION OF PASSIVE AND ACTIVE NON-LINEAR VIBRATION MOUNTING SYSTEMS BASED ON VIBRATORY POWER TRANSMISSION T. J. ROYSTON AND R. SINGH Acoustics
Journal of Sound and Vibration (1996) 194(3), 295 316 OPTIMIZATION OF PASSIVE AND ACTIVE NON-LINEAR VIBRATION MOUNTING SYSTEMS BASED ON VIBRATORY POWER TRANSMISSION T. J. ROYSTON AND R. SINGH Acoustics
Methods for the Simulation of Dynamic Phasor Models in Power Systems
 Using Frequency-Matched Numerical Integration Methods for the Simulation of Dynamic Phasor Models in Power Systems Turhan Demiray, Student, IEEE and Göran Andersson, Fellow, IEEE Abstract In this paper
Using Frequency-Matched Numerical Integration Methods for the Simulation of Dynamic Phasor Models in Power Systems Turhan Demiray, Student, IEEE and Göran Andersson, Fellow, IEEE Abstract In this paper
Lecture 5 Classical Control Overview III. Dr. Radhakant Padhi Asst. Professor Dept. of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Science - Bangalore
 Lecture 5 Classical Control Overview III Dr. Radhakant Padhi Asst. Professor Dept. of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Science - Bangalore A Fundamental Problem in Control Systems Poles of open
Lecture 5 Classical Control Overview III Dr. Radhakant Padhi Asst. Professor Dept. of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Science - Bangalore A Fundamental Problem in Control Systems Poles of open
Boundary element methods in the prediction of the acoustic damping of ship whipping vibrations
 ANZIAM J. 45 (E) ppc845 C856, 2004 C845 Boundary element methods in the prediction of the acoustic damping of ship whipping vibrations D. S. Holloway G. A. Thomas M. R. Davis (Received 8 August 2003) Abstract
ANZIAM J. 45 (E) ppc845 C856, 2004 C845 Boundary element methods in the prediction of the acoustic damping of ship whipping vibrations D. S. Holloway G. A. Thomas M. R. Davis (Received 8 August 2003) Abstract
Nonlinear Normal Modes of a Curved Beam and its Response to Random Loading
 Nonlinear Normal Modes of a Curved Beam and its Response to Random Loading Christopher I. VanDamme and Matthew S. Allen 2 Graduate Student; e-mail: cvandamme@wisc.edu 2 Associate Professor; e-mail: matt.allen@wisc.edu
Nonlinear Normal Modes of a Curved Beam and its Response to Random Loading Christopher I. VanDamme and Matthew S. Allen 2 Graduate Student; e-mail: cvandamme@wisc.edu 2 Associate Professor; e-mail: matt.allen@wisc.edu
Theory of bifurcation amplifiers utilizing the nonlinear dynamical response of an optically damped mechanical oscillator
 Theory of bifurcation amplifiers utilizing the nonlinear dynamical response of an optically damped mechanical oscillator Research on optomechanical systems is of relevance to gravitational wave detection
Theory of bifurcation amplifiers utilizing the nonlinear dynamical response of an optically damped mechanical oscillator Research on optomechanical systems is of relevance to gravitational wave detection
Analysis of Tensioner Induced Coupling in Serpentine Belt Drive Systems
 2008-01-1371 of Tensioner Induced Coupling in Serpentine Belt Drive Systems Copyright 2007 SAE International R. P. Neward and S. Boedo Department of Mechanical Engineering, Rochester Institute of Technology
2008-01-1371 of Tensioner Induced Coupling in Serpentine Belt Drive Systems Copyright 2007 SAE International R. P. Neward and S. Boedo Department of Mechanical Engineering, Rochester Institute of Technology
Prof. Dr. Erol KURT Nonlinear Problems in Piezoelectric Harvesters
 Prof. Dr. Erol KURT Nonlinear Problems in Piezoelectric Harvesters 1 This chapter focuses on the nonlinear problems in the piezoelectric harvester systems under the magnetic field. In this manner, the
Prof. Dr. Erol KURT Nonlinear Problems in Piezoelectric Harvesters 1 This chapter focuses on the nonlinear problems in the piezoelectric harvester systems under the magnetic field. In this manner, the
NUMERICAL STUDY OF INTRINSIC FEATURES OF ISOLAS IN A 2-DOF NONLINEAR SYSTEM
 NUMERICAL STUDY OF INTRINSIC FEATURES OF ISOLAS IN A 2-DOF NONLINEAR SYSTEM T. Detroux 1, J.P. Noël 1, L. Masset 1, G. Kerschen 1, L.N. Virgin 2 1 Space Structures and Systems Lab., Department of Aerospace
NUMERICAL STUDY OF INTRINSIC FEATURES OF ISOLAS IN A 2-DOF NONLINEAR SYSTEM T. Detroux 1, J.P. Noël 1, L. Masset 1, G. Kerschen 1, L.N. Virgin 2 1 Space Structures and Systems Lab., Department of Aerospace
DETC98/PTG-5788 VIBRO-ACOUSTIC STUDIES OF TRANSMISSION CASING STRUCTURES
 Proceedings of DETC98: 1998 ASME Design Engineering Technical Conference September 13-16, 1998, Atlanta, GA DETC98/PTG-5788 VIBRO-ACOUSTIC STUDIES O TRANSMISSION CASING STRUCTURES D. Crimaldi Graduate
Proceedings of DETC98: 1998 ASME Design Engineering Technical Conference September 13-16, 1998, Atlanta, GA DETC98/PTG-5788 VIBRO-ACOUSTIC STUDIES O TRANSMISSION CASING STRUCTURES D. Crimaldi Graduate
Spontaneous Speed Reversals in Stepper Motors
 Spontaneous Speed Reversals in Stepper Motors Marc Bodson University of Utah Electrical & Computer Engineering 50 S Central Campus Dr Rm 3280 Salt Lake City, UT 84112, U.S.A. Jeffrey S. Sato & Stephen
Spontaneous Speed Reversals in Stepper Motors Marc Bodson University of Utah Electrical & Computer Engineering 50 S Central Campus Dr Rm 3280 Salt Lake City, UT 84112, U.S.A. Jeffrey S. Sato & Stephen
Reliability-based Design Optimization of Nonlinear Energy Sinks
 th World Congress on Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 7 th - th, June, Sydney Australia Reliability-based Design Optimization of Nonlinear Energy Sinks Ethan Boroson and Samy Missoum University
th World Congress on Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 7 th - th, June, Sydney Australia Reliability-based Design Optimization of Nonlinear Energy Sinks Ethan Boroson and Samy Missoum University
Transient Squeal Analysis of a Non Steady State Manoeuvre
 Journal of Mechanics Engineering and Automation 7 (2017) 269-277 doi: 10.17265/2159-5275/2017.05.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Transient Squeal Analysis of a Non Steady State Manoeuvre Oliver Stump 1,2, Maximilian
Journal of Mechanics Engineering and Automation 7 (2017) 269-277 doi: 10.17265/2159-5275/2017.05.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Transient Squeal Analysis of a Non Steady State Manoeuvre Oliver Stump 1,2, Maximilian
Dynamical behaviour of a controlled vibro-impact system
 Vol 17 No 7, July 2008 c 2008 Chin. Phys. Soc. 1674-1056/2008/17(07)/2446-05 Chinese Physics B and IOP Publishing Ltd Dynamical behaviour of a controlled vibro-impact system Wang Liang( ), Xu Wei( ), and
Vol 17 No 7, July 2008 c 2008 Chin. Phys. Soc. 1674-1056/2008/17(07)/2446-05 Chinese Physics B and IOP Publishing Ltd Dynamical behaviour of a controlled vibro-impact system Wang Liang( ), Xu Wei( ), and
Simple Identification of Nonlinear Modal Parameters Using Wavelet Transform
 Proceedings of the 9 th ISSM achen, 7 th -9 th October 4 1 Simple Identification of Nonlinear Modal Parameters Using Wavelet Transform Tegoeh Tjahjowidodo, Farid l-bender, Hendrik Van Brussel Mechanical
Proceedings of the 9 th ISSM achen, 7 th -9 th October 4 1 Simple Identification of Nonlinear Modal Parameters Using Wavelet Transform Tegoeh Tjahjowidodo, Farid l-bender, Hendrik Van Brussel Mechanical
Statistical Study of Complex Eigenvalues in Stochastic Systems
 Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 2(3): 233-238, 2010 ISSN: 2040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2010 Submitted Date: March 08, 2010 Accepted Date: March 24, 2010 Published
Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 2(3): 233-238, 2010 ISSN: 2040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2010 Submitted Date: March 08, 2010 Accepted Date: March 24, 2010 Published
Finite element analysis of rotating structures
 Finite element analysis of rotating structures Dr. Louis Komzsik Chief Numerical Analyst Siemens PLM Software Why do rotor dynamics with FEM? Very complex structures with millions of degrees of freedom
Finite element analysis of rotating structures Dr. Louis Komzsik Chief Numerical Analyst Siemens PLM Software Why do rotor dynamics with FEM? Very complex structures with millions of degrees of freedom
Simulating Two-Dimensional Stick-Slip Motion of a Rigid Body using a New Friction Model
 Proceedings of the 2 nd World Congress on Mechanical, Chemical, and Material Engineering (MCM'16) Budapest, Hungary August 22 23, 2016 Paper No. ICMIE 116 DOI: 10.11159/icmie16.116 Simulating Two-Dimensional
Proceedings of the 2 nd World Congress on Mechanical, Chemical, and Material Engineering (MCM'16) Budapest, Hungary August 22 23, 2016 Paper No. ICMIE 116 DOI: 10.11159/icmie16.116 Simulating Two-Dimensional
Dynamics of structures
 Dynamics of structures 2.Vibrations: single degree of freedom system Arnaud Deraemaeker (aderaema@ulb.ac.be) 1 Outline of the chapter *One degree of freedom systems in real life Hypothesis Examples *Response
Dynamics of structures 2.Vibrations: single degree of freedom system Arnaud Deraemaeker (aderaema@ulb.ac.be) 1 Outline of the chapter *One degree of freedom systems in real life Hypothesis Examples *Response
Two models for the parametric forcing of a nonlinear oscillator
 Nonlinear Dyn (007) 50:147 160 DOI 10.1007/s11071-006-9148-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Two models for the parametric forcing of a nonlinear oscillator Nazha Abouhazim Mohamed Belhaq Richard H. Rand Received: 3
Nonlinear Dyn (007) 50:147 160 DOI 10.1007/s11071-006-9148-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Two models for the parametric forcing of a nonlinear oscillator Nazha Abouhazim Mohamed Belhaq Richard H. Rand Received: 3
3.1 Centrifugal Pendulum Vibration Absorbers: Centrifugal pendulum vibration absorbers are a type of tuned dynamic absorber used for the reduction of
 3.1 Centrifugal Pendulum Vibration Absorbers: Centrifugal pendulum vibration absorbers are a type of tuned dynamic absorber used for the reduction of torsional vibrations in rotating and reciprocating
3.1 Centrifugal Pendulum Vibration Absorbers: Centrifugal pendulum vibration absorbers are a type of tuned dynamic absorber used for the reduction of torsional vibrations in rotating and reciprocating
Analytic solution of simplified Cardan s shaft model
 Applied and Computational Mechanics 8 (2014) 215 228 Analytic solution of simplified Cardan s shaft model M. Zají cek a,, J. Dupal a a Faculty of Applied Sciences, University of West Bohemia, Univerzitní
Applied and Computational Mechanics 8 (2014) 215 228 Analytic solution of simplified Cardan s shaft model M. Zají cek a,, J. Dupal a a Faculty of Applied Sciences, University of West Bohemia, Univerzitní
Research Article Stability Analysis of Journal Bearing: Dynamic Characteristics
 Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 9(1): 47-52, 2015 DOI:10.19026/rjaset.9.1375 ISSN: 2040-7459; e-issn: 2040-7467 2015 Maxwell Scientific Publication Corp. Submitted: July
Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 9(1): 47-52, 2015 DOI:10.19026/rjaset.9.1375 ISSN: 2040-7459; e-issn: 2040-7467 2015 Maxwell Scientific Publication Corp. Submitted: July
Estimating the Degree of Nonlinearity in Transient Responses with Zeroed Early Time Fast Fourier Transforms
 Estimating the Degree of Nonlinearity in Transient Responses with Zeroed Early Time Fast Fourier Transforms Matthew S. Allen Department of Engineering Physics University of Wisconsin-Madison Randall L.
Estimating the Degree of Nonlinearity in Transient Responses with Zeroed Early Time Fast Fourier Transforms Matthew S. Allen Department of Engineering Physics University of Wisconsin-Madison Randall L.
Structural Dynamics Lecture 2. Outline of Lecture 2. Single-Degree-of-Freedom Systems (cont.)
 Outline of Single-Degree-of-Freedom Systems (cont.) Linear Viscous Damped Eigenvibrations. Logarithmic decrement. Response to Harmonic and Periodic Loads. 1 Single-Degreee-of-Freedom Systems (cont.). Linear
Outline of Single-Degree-of-Freedom Systems (cont.) Linear Viscous Damped Eigenvibrations. Logarithmic decrement. Response to Harmonic and Periodic Loads. 1 Single-Degreee-of-Freedom Systems (cont.). Linear
EFFECT OF SLIDING FRICTION ON SPUR AND HELICAL GEAR DYNAMICS AND VIBRO-ACOUSTICS DISSERTATION. the Degree Doctor of Philosophy in the Graduate School
 EFFECT OF SLIDING FRICTION ON SPUR AND HELICAL GEAR DYNAMICS AND VIBRO-ACOUSTICS DISSERTATION Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Doctor of Philosophy in the Graduate School
EFFECT OF SLIDING FRICTION ON SPUR AND HELICAL GEAR DYNAMICS AND VIBRO-ACOUSTICS DISSERTATION Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Doctor of Philosophy in the Graduate School
Theoretical Manual Theoretical background to the Strand7 finite element analysis system
 Theoretical Manual Theoretical background to the Strand7 finite element analysis system Edition 1 January 2005 Strand7 Release 2.3 2004-2005 Strand7 Pty Limited All rights reserved Contents Preface Chapter
Theoretical Manual Theoretical background to the Strand7 finite element analysis system Edition 1 January 2005 Strand7 Release 2.3 2004-2005 Strand7 Pty Limited All rights reserved Contents Preface Chapter
Transitioning to Chaos in a Simple Mechanical Oscillator
 Transitioning to Chaos in a Simple Mechanical Oscillator Hwan Bae Physics Department, The College of Wooster, Wooster, Ohio 69, USA (Dated: May 9, 8) We vary the magnetic damping, driver frequency, and
Transitioning to Chaos in a Simple Mechanical Oscillator Hwan Bae Physics Department, The College of Wooster, Wooster, Ohio 69, USA (Dated: May 9, 8) We vary the magnetic damping, driver frequency, and
COMPOSITE MATERIAL WITH NEGATIVE STIFFNESS INCLUSION FOR VIBRATION DAMPING: THE EFFECT OF A NONLINEAR BISTABLE ELEMENT
 11 th International Conference on Vibration Problems Z. Dimitrovová et.al. (eds.) Lisbon, Portugal, 9 12 September 2013 COMPOSITE MATERIAL WITH NEGATIVE STIFFNESS INCLUSION FOR VIBRATION DAMPING: THE EFFECT
11 th International Conference on Vibration Problems Z. Dimitrovová et.al. (eds.) Lisbon, Portugal, 9 12 September 2013 COMPOSITE MATERIAL WITH NEGATIVE STIFFNESS INCLUSION FOR VIBRATION DAMPING: THE EFFECT
NON-LINEAR ATTENUATION IN SOILS AND ROCKS
 THE PUBLISHING HOUSE PROCEEDINGS OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY, Series A, OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY Volume 7, Number 3/6, pp. - NON-LINEAR ATTENUATION IN SOILS AND ROCKS Dinu BRATOSIN Institute of Solid Mechanics
THE PUBLISHING HOUSE PROCEEDINGS OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY, Series A, OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY Volume 7, Number 3/6, pp. - NON-LINEAR ATTENUATION IN SOILS AND ROCKS Dinu BRATOSIN Institute of Solid Mechanics
A derivative-free nonmonotone line search and its application to the spectral residual method
 IMA Journal of Numerical Analysis (2009) 29, 814 825 doi:10.1093/imanum/drn019 Advance Access publication on November 14, 2008 A derivative-free nonmonotone line search and its application to the spectral
IMA Journal of Numerical Analysis (2009) 29, 814 825 doi:10.1093/imanum/drn019 Advance Access publication on November 14, 2008 A derivative-free nonmonotone line search and its application to the spectral
Vibration Testing. an excitation source a device to measure the response a digital signal processor to analyze the system response
 Vibration Testing For vibration testing, you need an excitation source a device to measure the response a digital signal processor to analyze the system response i) Excitation sources Typically either
Vibration Testing For vibration testing, you need an excitation source a device to measure the response a digital signal processor to analyze the system response i) Excitation sources Typically either
