StatPatternRecognition: A C++ Package for Multivariate Classification of HEP Data. Ilya Narsky, Caltech
|
|
|
- Colin Underwood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 StatPatternRecognition: A C++ Package for Multivariate Classification of HEP Data Ilya Narsky, Caltech
2 Motivation Introduction advanced classification tools in a convenient C++ package for HEP researchers Description of math formalism: I. Narsky, physics/5743, StatPatternRecognition: A C++ Package for Statistical Analysis of High Energy Physics Data I. Narsky, physics/5757, Optimization of Signal Significance by Bagging Decision Trees Practical instructions: README included in the package Ilya Narsky Phystat 25 2
3 Classifiers: Binary split Implemented Methods Linear and quadratic discriminant analysis Decision trees Bump hunting algorithm (PRIM, Friedman & Fisher) AdaBoost Bagging and random forest algorithms AdaBoost and Bagger are capable of boosting/bagging any classifier implemented in the package Methods of general use: Bootstrap Calculation of data moments (mean, covariance, kurtosis) Test of zero correlation for variables with a joint elliptical distribution Ilya Narsky Phystat 25 3
4 Linear and Quadratic Discriminant Analysis Separation of a bivariate Gaussian from uniform background by quadratic discriminant analysis. Each class density is a multivariate Gaussian f k ( x) = exp d k k µ / 2 2 k (2π ) Σ / 2 k Look at the log-ratio of two class probabilities: log f f 2 ( x) ( x) Assume => linear Fisher Don t assume => Σ 2 quadratic Fisher T ( x µ ) Σ ( x ) T ( Σ µ Σ ) x ( Σ Σ )x = C + x µ Σ T = Σ 2 Σ = 2 Ilya Narsky Phystat 25 4
5 Decision trees in StatPatternRecognition S, B S = S +S 2 B = B +B 2 S, B S 2, B 2 StatPatternRecognition allows the user to supply an arbitrary criterion for tree optimization by providing an implementation to the abstract C++ interface. At the moment, following criteria are implemented: Conventional: Gini index, crossentropy, and correctly classified fraction of events. Physics: signal purity, S/ S+B, 9% Bayesian UL, and 2*( S+B- B). Conventional decision tree, e.g., CART: - Each split minimizes Gini index: Gini = SB S + B - The tree spends 5% of time finding clean signal nodes and 5% of time finding clean background nodes. + Decision tree in StatPatternRecognition: - Each split maximizes signal significance: Signif = max S S, + B S2B2 S + B 2 S 2 S B 2
6 Decision Trees: An Idealistic Example -5 Separation of two bivariate Gaussians from uniform background by decision trees optimizing various figures of merit: true signal signal significance (top right) signal significance signal purity (bottom left) Gini index (bottom right) True signal is shown in the top left signal purity Ilya Narsky - - Gini index Phystat 25 6
7 Bump hunting true signal purity bump hunter 2 pts/node peel=.7 Algorithm finds a box in the multidimensional space in two stages: shrinkage: reduce the box size; peel parameter = max fraction of points that can be peeled off in one iteration expansion Above: The bump hunter finds two tiny signal peaks on top of uniform background (right). Full signal+background distribution (left). Ilya Narsky Phystat 25 7
8 Method for combining classifiers Applies classifiers sequentially: enhances weights of misclassified events computes relative weight of each classifier Iterate as long as e<.5 Final decision: weighted vote of all classifiers AdaBoost iteration iteration : K : weight of () w i = / N; i =,..., N f ( K ) ( x) : classifier ε correctly classified events : misclassified events : C f ( x) = β K = K f ( K ) ( x) K K : = w w ( K ) i misclassified β ( K ) i ( K ) i K w < ( K ) wi = 2( ε K ) ( K ) wi = 2ε K ε K = log ε K.5 Ilya Narsky Phystat 25 8
9 Bagging (Bootstrap AGGregatING) Algorithm: draw a bootstrap replica of the training sample train a new classifier on this replica classify new data by the majority vote of the built classifiers Parallel algorithm: uses classifiers built on independently-drawn bootstrap replicas Random forest: A more generic version of bagging sample not only from training events but also from input dimensions for now SPR bootstraps all input dimensions (you can t choose how many you include)
10 AdaBoost and Bagging: An Idealistic Example true signal accepted signal Separation of two bivariate Gaussians from uniform background by boosted binary splits. Background is uniform on -<x<; -<y<. Ilya Narsky. classifier output accepted background Separation of two bivariate Gaussians from uniform background by bagged trees. Background is uniform on -<x<; -<y<. Phystat 25
11 Why boosted and bagged decision trees are good? The best off-the-shelf method for classification in many dimensions. Unlike kernel-based methods, methods based on local averaging and nearest-neighbor methods, trees do not suffer from the curse of dimensionality. CPU time generally scales linearly with dimensionality. Training mechanism is robust. Can deal with strongly correlated inputs mixed input types (continuous and discrete) Ilya Narsky Phystat 25
12 Bbar B Physics Examples - All results shown for test data. Separation of B gln from combined background at BaBar by bagged decision trees optimizing the signal significance with input variables. Time needed to train bagged trees on 5k events = several hours. Gives a 25% improvement in the signal significance compared to the method originally used by the analysts. 5 signal background B/Bbar tagging at BaBar by boosted decision trees with 35 input variables. Time needed to train 5 boosted trees on 5k events = + day. At the moment, gives a somewhat worse B/Bbar separation than the clever algorithm that builds 9 neural nets on low-dimensional subtaggers and then combines them. But first results showed promise classifier output
13 Physics Examples - 2 (D data from Harrison Prosper) All results shown for test data. ppbar Wbb ppbar tqb Separation of ppbar tqb from ppbar Wbb by bagged decision trees in dimensions. Time needed to train 2 decision trees on 5 events = several minutes. ppbar Wbb ppbar tqb Separation of ppbar tqb from ppbar Wbb by boosted binary splits in dimensions. Time needed to train binary splits on 5 events = seconds.
14 Installation and use outside BaBar Send to Get a copy of the package Edit SprExperiment.hh to remove reference to BaBar.hh (one line) Provide a Makefile that resolves references to CLHEP headers and CERN libraries Either provide your own implementation of SprTupleWriter (depends on BaBar-specific histogramming utils) or replace it with SprAsciiWriter provided in the package You are ready to go! Feedback is very much appreciated Ilya Narsky Phystat 25 4
StatPatternRecognition: User Guide. Ilya Narsky, Caltech
 StatPatternRecognition: User Guide, Caltech Also see http://www.slac.stanford.edu/bfroot/www/organization/collabmtgs/2005/detsep05/wed4/narsky.pdf BaBar Meeting, December 2005 2 Classifiers in StatPatternRecognition
StatPatternRecognition: User Guide, Caltech Also see http://www.slac.stanford.edu/bfroot/www/organization/collabmtgs/2005/detsep05/wed4/narsky.pdf BaBar Meeting, December 2005 2 Classifiers in StatPatternRecognition
arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.data-an] 20 Jul 2005
![arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.data-an] 20 Jul 2005 arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.data-an] 20 Jul 2005](/thumbs/82/86788180.jpg) StatPatternRecognition: A C++ Package for Statistical Analysis of High Energy Physics Data Ilya Narsky arxiv:physics/57143v1 [physics.data-an] 2 Jul 25 California Institute of Technology (Dated: February
StatPatternRecognition: A C++ Package for Statistical Analysis of High Energy Physics Data Ilya Narsky arxiv:physics/57143v1 [physics.data-an] 2 Jul 25 California Institute of Technology (Dated: February
Multivariate statistical methods and data mining in particle physics
 Multivariate statistical methods and data mining in particle physics RHUL Physics www.pp.rhul.ac.uk/~cowan Academic Training Lectures CERN 16 19 June, 2008 1 Outline Statement of the problem Some general
Multivariate statistical methods and data mining in particle physics RHUL Physics www.pp.rhul.ac.uk/~cowan Academic Training Lectures CERN 16 19 June, 2008 1 Outline Statement of the problem Some general
Advanced statistical methods for data analysis Lecture 1
 Advanced statistical methods for data analysis Lecture 1 RHUL Physics www.pp.rhul.ac.uk/~cowan Universität Mainz Klausurtagung des GK Eichtheorien exp. Tests... Bullay/Mosel 15 17 September, 2008 1 Outline
Advanced statistical methods for data analysis Lecture 1 RHUL Physics www.pp.rhul.ac.uk/~cowan Universität Mainz Klausurtagung des GK Eichtheorien exp. Tests... Bullay/Mosel 15 17 September, 2008 1 Outline
Harrison B. Prosper. Bari Lectures
 Harrison B. Prosper Florida State University Bari Lectures 30, 31 May, 1 June 2016 Lectures on Multivariate Methods Harrison B. Prosper Bari, 2016 1 h Lecture 1 h Introduction h Classification h Grid Searches
Harrison B. Prosper Florida State University Bari Lectures 30, 31 May, 1 June 2016 Lectures on Multivariate Methods Harrison B. Prosper Bari, 2016 1 h Lecture 1 h Introduction h Classification h Grid Searches
Data Mining und Maschinelles Lernen
 Data Mining und Maschinelles Lernen Ensemble Methods Bias-Variance Trade-off Basic Idea of Ensembles Bagging Basic Algorithm Bagging with Costs Randomization Random Forests Boosting Stacking Error-Correcting
Data Mining und Maschinelles Lernen Ensemble Methods Bias-Variance Trade-off Basic Idea of Ensembles Bagging Basic Algorithm Bagging with Costs Randomization Random Forests Boosting Stacking Error-Correcting
Ensembles. Léon Bottou COS 424 4/8/2010
 Ensembles Léon Bottou COS 424 4/8/2010 Readings T. G. Dietterich (2000) Ensemble Methods in Machine Learning. R. E. Schapire (2003): The Boosting Approach to Machine Learning. Sections 1,2,3,4,6. Léon
Ensembles Léon Bottou COS 424 4/8/2010 Readings T. G. Dietterich (2000) Ensemble Methods in Machine Learning. R. E. Schapire (2003): The Boosting Approach to Machine Learning. Sections 1,2,3,4,6. Léon
Algorithm-Independent Learning Issues
 Algorithm-Independent Learning Issues Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr CS 551, Spring 2007 c 2007, Selim Aksoy Introduction We have seen many learning
Algorithm-Independent Learning Issues Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr CS 551, Spring 2007 c 2007, Selim Aksoy Introduction We have seen many learning
TDT4173 Machine Learning
 TDT4173 Machine Learning Lecture 9 Learning Classifiers: Bagging & Boosting Norwegian University of Science and Technology Helge Langseth IT-VEST 310 helgel@idi.ntnu.no 1 TDT4173 Machine Learning Outline
TDT4173 Machine Learning Lecture 9 Learning Classifiers: Bagging & Boosting Norwegian University of Science and Technology Helge Langseth IT-VEST 310 helgel@idi.ntnu.no 1 TDT4173 Machine Learning Outline
CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning. Final Review. Henry Chai 12/4/18
 CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning Final Review Henry Chai 12/4/18 Overfitting Overfitting is fitting the training data more than is warranted Fitting noise rather than signal 2 Estimating! "#$
CSE 417T: Introduction to Machine Learning Final Review Henry Chai 12/4/18 Overfitting Overfitting is fitting the training data more than is warranted Fitting noise rather than signal 2 Estimating! "#$
Statistical Methods for Particle Physics Lecture 2: statistical tests, multivariate methods
 Statistical Methods for Particle Physics Lecture 2: statistical tests, multivariate methods www.pp.rhul.ac.uk/~cowan/stat_aachen.html Graduierten-Kolleg RWTH Aachen 10-14 February 2014 Glen Cowan Physics
Statistical Methods for Particle Physics Lecture 2: statistical tests, multivariate methods www.pp.rhul.ac.uk/~cowan/stat_aachen.html Graduierten-Kolleg RWTH Aachen 10-14 February 2014 Glen Cowan Physics
Data Mining Classification: Basic Concepts and Techniques. Lecture Notes for Chapter 3. Introduction to Data Mining, 2nd Edition
 Data Mining Classification: Basic Concepts and Techniques Lecture Notes for Chapter 3 by Tan, Steinbach, Karpatne, Kumar 1 Classification: Definition Given a collection of records (training set ) Each
Data Mining Classification: Basic Concepts and Techniques Lecture Notes for Chapter 3 by Tan, Steinbach, Karpatne, Kumar 1 Classification: Definition Given a collection of records (training set ) Each
CSCI-567: Machine Learning (Spring 2019)
 CSCI-567: Machine Learning (Spring 2019) Prof. Victor Adamchik U of Southern California Mar. 19, 2019 March 19, 2019 1 / 43 Administration March 19, 2019 2 / 43 Administration TA3 is due this week March
CSCI-567: Machine Learning (Spring 2019) Prof. Victor Adamchik U of Southern California Mar. 19, 2019 March 19, 2019 1 / 43 Administration March 19, 2019 2 / 43 Administration TA3 is due this week March
CS 484 Data Mining. Classification 7. Some slides are from Professor Padhraic Smyth at UC Irvine
 CS 484 Data Mining Classification 7 Some slides are from Professor Padhraic Smyth at UC Irvine Bayesian Belief networks Conditional independence assumption of Naïve Bayes classifier is too strong. Allows
CS 484 Data Mining Classification 7 Some slides are from Professor Padhraic Smyth at UC Irvine Bayesian Belief networks Conditional independence assumption of Naïve Bayes classifier is too strong. Allows
Multivariate statistical methods and data mining in particle physics Lecture 4 (19 June, 2008)
 Multivariate statistical methods and data mining in particle physics Lecture 4 (19 June, 2008) RHUL Physics www.pp.rhul.ac.uk/~cowan Academic Training Lectures CERN 16 19 June, 2008 1 Outline Statement
Multivariate statistical methods and data mining in particle physics Lecture 4 (19 June, 2008) RHUL Physics www.pp.rhul.ac.uk/~cowan Academic Training Lectures CERN 16 19 June, 2008 1 Outline Statement
CS534 Machine Learning - Spring Final Exam
 CS534 Machine Learning - Spring 2013 Final Exam Name: You have 110 minutes. There are 6 questions (8 pages including cover page). If you get stuck on one question, move on to others and come back to the
CS534 Machine Learning - Spring 2013 Final Exam Name: You have 110 minutes. There are 6 questions (8 pages including cover page). If you get stuck on one question, move on to others and come back to the
Boosting. Ryan Tibshirani Data Mining: / April Optional reading: ISL 8.2, ESL , 10.7, 10.13
 Boosting Ryan Tibshirani Data Mining: 36-462/36-662 April 25 2013 Optional reading: ISL 8.2, ESL 10.1 10.4, 10.7, 10.13 1 Reminder: classification trees Suppose that we are given training data (x i, y
Boosting Ryan Tibshirani Data Mining: 36-462/36-662 April 25 2013 Optional reading: ISL 8.2, ESL 10.1 10.4, 10.7, 10.13 1 Reminder: classification trees Suppose that we are given training data (x i, y
TDT4173 Machine Learning
 TDT4173 Machine Learning Lecture 3 Bagging & Boosting + SVMs Norwegian University of Science and Technology Helge Langseth IT-VEST 310 helgel@idi.ntnu.no 1 TDT4173 Machine Learning Outline 1 Ensemble-methods
TDT4173 Machine Learning Lecture 3 Bagging & Boosting + SVMs Norwegian University of Science and Technology Helge Langseth IT-VEST 310 helgel@idi.ntnu.no 1 TDT4173 Machine Learning Outline 1 Ensemble-methods
Statistical Methods for Particle Physics Lecture 2: multivariate methods
 Statistical Methods for Particle Physics Lecture 2: multivariate methods http://indico.ihep.ac.cn/event/4902/ istep 2015 Shandong University, Jinan August 11-19, 2015 Glen Cowan ( 谷林 科恩 ) Physics Department
Statistical Methods for Particle Physics Lecture 2: multivariate methods http://indico.ihep.ac.cn/event/4902/ istep 2015 Shandong University, Jinan August 11-19, 2015 Glen Cowan ( 谷林 科恩 ) Physics Department
Chapter 14 Combining Models
 Chapter 14 Combining Models T-61.62 Special Course II: Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning Spring 27 Laboratory of Computer and Information Science TKK April 3th 27 Outline Independent Mixing Coefficients
Chapter 14 Combining Models T-61.62 Special Course II: Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning Spring 27 Laboratory of Computer and Information Science TKK April 3th 27 Outline Independent Mixing Coefficients
Machine Learning Ensemble Learning I Hamid R. Rabiee Jafar Muhammadi, Alireza Ghasemi Spring /
 Machine Learning Ensemble Learning I Hamid R. Rabiee Jafar Muhammadi, Alireza Ghasemi Spring 2015 http://ce.sharif.edu/courses/93-94/2/ce717-1 / Agenda Combining Classifiers Empirical view Theoretical
Machine Learning Ensemble Learning I Hamid R. Rabiee Jafar Muhammadi, Alireza Ghasemi Spring 2015 http://ce.sharif.edu/courses/93-94/2/ce717-1 / Agenda Combining Classifiers Empirical view Theoretical
Multivariate Analysis Techniques in HEP
 Multivariate Analysis Techniques in HEP Jan Therhaag IKTP Institutsseminar, Dresden, January 31 st 2013 Multivariate analysis in a nutshell Neural networks: Defeating the black box Boosted Decision Trees:
Multivariate Analysis Techniques in HEP Jan Therhaag IKTP Institutsseminar, Dresden, January 31 st 2013 Multivariate analysis in a nutshell Neural networks: Defeating the black box Boosted Decision Trees:
Support Vector Machines
 Support Vector Machines Hypothesis Space variable size deterministic continuous parameters Learning Algorithm linear and quadratic programming eager batch SVMs combine three important ideas Apply optimization
Support Vector Machines Hypothesis Space variable size deterministic continuous parameters Learning Algorithm linear and quadratic programming eager batch SVMs combine three important ideas Apply optimization
Learning with multiple models. Boosting.
 CS 2750 Machine Learning Lecture 21 Learning with multiple models. Boosting. Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 5329 Sennott Square Learning with multiple models: Approach 2 Approach 2: use multiple models
CS 2750 Machine Learning Lecture 21 Learning with multiple models. Boosting. Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 5329 Sennott Square Learning with multiple models: Approach 2 Approach 2: use multiple models
EXAM IN STATISTICAL MACHINE LEARNING STATISTISK MASKININLÄRNING
 EXAM IN STATISTICAL MACHINE LEARNING STATISTISK MASKININLÄRNING DATE AND TIME: June 9, 2018, 09.00 14.00 RESPONSIBLE TEACHER: Andreas Svensson NUMBER OF PROBLEMS: 5 AIDING MATERIAL: Calculator, mathematical
EXAM IN STATISTICAL MACHINE LEARNING STATISTISK MASKININLÄRNING DATE AND TIME: June 9, 2018, 09.00 14.00 RESPONSIBLE TEACHER: Andreas Svensson NUMBER OF PROBLEMS: 5 AIDING MATERIAL: Calculator, mathematical
Neural Networks and Ensemble Methods for Classification
 Neural Networks and Ensemble Methods for Classification NEURAL NETWORKS 2 Neural Networks A neural network is a set of connected input/output units (neurons) where each connection has a weight associated
Neural Networks and Ensemble Methods for Classification NEURAL NETWORKS 2 Neural Networks A neural network is a set of connected input/output units (neurons) where each connection has a weight associated
Frank C Porter and Ilya Narsky: Statistical Analysis Techniques in Particle Physics Chap. c /9/9 page 331 le-tex
 Frank C Porter and Ilya Narsky: Statistical Analysis Techniques in Particle Physics Chap. c15 2013/9/9 page 331 le-tex 331 15 Ensemble Learning The expression ensemble learning refers to a broad class
Frank C Porter and Ilya Narsky: Statistical Analysis Techniques in Particle Physics Chap. c15 2013/9/9 page 331 le-tex 331 15 Ensemble Learning The expression ensemble learning refers to a broad class
FINAL: CS 6375 (Machine Learning) Fall 2014
 FINAL: CS 6375 (Machine Learning) Fall 2014 The exam is closed book. You are allowed a one-page cheat sheet. Answer the questions in the spaces provided on the question sheets. If you run out of room for
FINAL: CS 6375 (Machine Learning) Fall 2014 The exam is closed book. You are allowed a one-page cheat sheet. Answer the questions in the spaces provided on the question sheets. If you run out of room for
Advanced statistical methods for data analysis Lecture 2
 Advanced statistical methods for data analysis Lecture 2 RHUL Physics www.pp.rhul.ac.uk/~cowan Universität Mainz Klausurtagung des GK Eichtheorien exp. Tests... Bullay/Mosel 15 17 September, 2008 1 Outline
Advanced statistical methods for data analysis Lecture 2 RHUL Physics www.pp.rhul.ac.uk/~cowan Universität Mainz Klausurtagung des GK Eichtheorien exp. Tests... Bullay/Mosel 15 17 September, 2008 1 Outline
Statistics and learning: Big Data
 Statistics and learning: Big Data Learning Decision Trees and an Introduction to Boosting Sébastien Gadat Toulouse School of Economics February 2017 S. Gadat (TSE) SAD 2013 1 / 30 Keywords Decision trees
Statistics and learning: Big Data Learning Decision Trees and an Introduction to Boosting Sébastien Gadat Toulouse School of Economics February 2017 S. Gadat (TSE) SAD 2013 1 / 30 Keywords Decision trees
Variance Reduction and Ensemble Methods
 Variance Reduction and Ensemble Methods Nicholas Ruozzi University of Texas at Dallas Based on the slides of Vibhav Gogate and David Sontag Last Time PAC learning Bias/variance tradeoff small hypothesis
Variance Reduction and Ensemble Methods Nicholas Ruozzi University of Texas at Dallas Based on the slides of Vibhav Gogate and David Sontag Last Time PAC learning Bias/variance tradeoff small hypothesis
Bagging and Other Ensemble Methods
 Bagging and Other Ensemble Methods Sargur N. Srihari srihari@buffalo.edu 1 Regularization Strategies 1. Parameter Norm Penalties 2. Norm Penalties as Constrained Optimization 3. Regularization and Underconstrained
Bagging and Other Ensemble Methods Sargur N. Srihari srihari@buffalo.edu 1 Regularization Strategies 1. Parameter Norm Penalties 2. Norm Penalties as Constrained Optimization 3. Regularization and Underconstrained
Multivariate Methods in Statistical Data Analysis
 Multivariate Methods in Statistical Data Analysis Web-Site: http://tmva.sourceforge.net/ See also: "TMVA - Toolkit for Multivariate Data Analysis, A. Hoecker, P. Speckmayer, J. Stelzer, J. Therhaag, E.
Multivariate Methods in Statistical Data Analysis Web-Site: http://tmva.sourceforge.net/ See also: "TMVA - Toolkit for Multivariate Data Analysis, A. Hoecker, P. Speckmayer, J. Stelzer, J. Therhaag, E.
BAGGING PREDICTORS AND RANDOM FOREST
 BAGGING PREDICTORS AND RANDOM FOREST DANA KANER M.SC. SEMINAR IN STATISTICS, MAY 2017 BAGIGNG PREDICTORS / LEO BREIMAN, 1996 RANDOM FORESTS / LEO BREIMAN, 2001 THE ELEMENTS OF STATISTICAL LEARNING (CHAPTERS
BAGGING PREDICTORS AND RANDOM FOREST DANA KANER M.SC. SEMINAR IN STATISTICS, MAY 2017 BAGIGNG PREDICTORS / LEO BREIMAN, 1996 RANDOM FORESTS / LEO BREIMAN, 2001 THE ELEMENTS OF STATISTICAL LEARNING (CHAPTERS
Analysis Techniques Multivariate Methods
 Analysis Techniques Multivariate Methods Harrison B. Prosper NEPPSR 007 Outline hintroduction hsignal/background Discrimination hfisher Discriminant hsupport Vector Machines hnaïve Bayes hbayesian Neural
Analysis Techniques Multivariate Methods Harrison B. Prosper NEPPSR 007 Outline hintroduction hsignal/background Discrimination hfisher Discriminant hsupport Vector Machines hnaïve Bayes hbayesian Neural
1 Handling of Continuous Attributes in C4.5. Algorithm
 .. Spring 2009 CSC 466: Knowledge Discovery from Data Alexander Dekhtyar.. Data Mining: Classification/Supervised Learning Potpourri Contents 1. C4.5. and continuous attributes: incorporating continuous
.. Spring 2009 CSC 466: Knowledge Discovery from Data Alexander Dekhtyar.. Data Mining: Classification/Supervised Learning Potpourri Contents 1. C4.5. and continuous attributes: incorporating continuous
The exam is closed book, closed notes except your one-page cheat sheet.
 CS 189 Fall 2015 Introduction to Machine Learning Final Please do not turn over the page before you are instructed to do so. You have 2 hours and 50 minutes. Please write your initials on the top-right
CS 189 Fall 2015 Introduction to Machine Learning Final Please do not turn over the page before you are instructed to do so. You have 2 hours and 50 minutes. Please write your initials on the top-right
Universität Potsdam Institut für Informatik Lehrstuhl Maschinelles Lernen. Decision Trees. Tobias Scheffer
 Universität Potsdam Institut für Informatik Lehrstuhl Maschinelles Lernen Decision Trees Tobias Scheffer Decision Trees One of many applications: credit risk Employed longer than 3 months Positive credit
Universität Potsdam Institut für Informatik Lehrstuhl Maschinelles Lernen Decision Trees Tobias Scheffer Decision Trees One of many applications: credit risk Employed longer than 3 months Positive credit
HEP Data Mining with TMVA
 HEP Data Mining with TMVA ToolKit for Multivariate Analysis with ROOT Andreas Hoecker ( * ) (CERN) Seminar, IFJ Krakow, Feb 27, 2007 ( * ) on behalf of J. Stelzer, F. Tegenfeldt, H.+K. Voss, and many other
HEP Data Mining with TMVA ToolKit for Multivariate Analysis with ROOT Andreas Hoecker ( * ) (CERN) Seminar, IFJ Krakow, Feb 27, 2007 ( * ) on behalf of J. Stelzer, F. Tegenfeldt, H.+K. Voss, and many other
Statistical Machine Learning from Data
 Samy Bengio Statistical Machine Learning from Data 1 Statistical Machine Learning from Data Ensembles Samy Bengio IDIAP Research Institute, Martigny, Switzerland, and Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne
Samy Bengio Statistical Machine Learning from Data 1 Statistical Machine Learning from Data Ensembles Samy Bengio IDIAP Research Institute, Martigny, Switzerland, and Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne
ECE 5424: Introduction to Machine Learning
 ECE 5424: Introduction to Machine Learning Topics: Ensemble Methods: Bagging, Boosting PAC Learning Readings: Murphy 16.4;; Hastie 16 Stefan Lee Virginia Tech Fighting the bias-variance tradeoff Simple
ECE 5424: Introduction to Machine Learning Topics: Ensemble Methods: Bagging, Boosting PAC Learning Readings: Murphy 16.4;; Hastie 16 Stefan Lee Virginia Tech Fighting the bias-variance tradeoff Simple
PATTERN CLASSIFICATION
 PATTERN CLASSIFICATION Second Edition Richard O. Duda Peter E. Hart David G. Stork A Wiley-lnterscience Publication JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. New York Chichester Weinheim Brisbane Singapore Toronto CONTENTS
PATTERN CLASSIFICATION Second Edition Richard O. Duda Peter E. Hart David G. Stork A Wiley-lnterscience Publication JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. New York Chichester Weinheim Brisbane Singapore Toronto CONTENTS
CS7267 MACHINE LEARNING
 CS7267 MACHINE LEARNING ENSEMBLE LEARNING Ref: Dr. Ricardo Gutierrez-Osuna at TAMU, and Aarti Singh at CMU Mingon Kang, Ph.D. Computer Science, Kennesaw State University Definition of Ensemble Learning
CS7267 MACHINE LEARNING ENSEMBLE LEARNING Ref: Dr. Ricardo Gutierrez-Osuna at TAMU, and Aarti Singh at CMU Mingon Kang, Ph.D. Computer Science, Kennesaw State University Definition of Ensemble Learning
W vs. QCD Jet Tagging at the Large Hadron Collider
 W vs. QCD Jet Tagging at the Large Hadron Collider Bryan Anenberg: anenberg@stanford.edu; CS229 December 13, 2013 Problem Statement High energy collisions of protons at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC)
W vs. QCD Jet Tagging at the Large Hadron Collider Bryan Anenberg: anenberg@stanford.edu; CS229 December 13, 2013 Problem Statement High energy collisions of protons at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC)
Final Overview. Introduction to ML. Marek Petrik 4/25/2017
 Final Overview Introduction to ML Marek Petrik 4/25/2017 This Course: Introduction to Machine Learning Build a foundation for practice and research in ML Basic machine learning concepts: max likelihood,
Final Overview Introduction to ML Marek Petrik 4/25/2017 This Course: Introduction to Machine Learning Build a foundation for practice and research in ML Basic machine learning concepts: max likelihood,
Statistical Methods in Particle Physics
 Statistical Methods in Particle Physics 8. Multivariate Analysis Prof. Dr. Klaus Reygers (lectures) Dr. Sebastian Neubert (tutorials) Heidelberg University WS 2017/18 Multi-Variate Classification Consider
Statistical Methods in Particle Physics 8. Multivariate Analysis Prof. Dr. Klaus Reygers (lectures) Dr. Sebastian Neubert (tutorials) Heidelberg University WS 2017/18 Multi-Variate Classification Consider
CART Classification and Regression Trees Trees can be viewed as basis expansions of simple functions. f(x) = c m 1(x R m )
 CART Classification and Regression Trees Trees can be viewed as basis expansions of simple functions with R 1,..., R m R p disjoint. f(x) = M c m 1(x R m ) m=1 The CART algorithm is a heuristic, adaptive
CART Classification and Regression Trees Trees can be viewed as basis expansions of simple functions with R 1,..., R m R p disjoint. f(x) = M c m 1(x R m ) m=1 The CART algorithm is a heuristic, adaptive
Motivating the Covariance Matrix
 Motivating the Covariance Matrix Raúl Rojas Computer Science Department Freie Universität Berlin January 2009 Abstract This note reviews some interesting properties of the covariance matrix and its role
Motivating the Covariance Matrix Raúl Rojas Computer Science Department Freie Universität Berlin January 2009 Abstract This note reviews some interesting properties of the covariance matrix and its role
EXAM IN STATISTICAL MACHINE LEARNING STATISTISK MASKININLÄRNING
 EXAM IN STATISTICAL MACHINE LEARNING STATISTISK MASKININLÄRNING DATE AND TIME: August 30, 2018, 14.00 19.00 RESPONSIBLE TEACHER: Niklas Wahlström NUMBER OF PROBLEMS: 5 AIDING MATERIAL: Calculator, mathematical
EXAM IN STATISTICAL MACHINE LEARNING STATISTISK MASKININLÄRNING DATE AND TIME: August 30, 2018, 14.00 19.00 RESPONSIBLE TEACHER: Niklas Wahlström NUMBER OF PROBLEMS: 5 AIDING MATERIAL: Calculator, mathematical
Linear Models for Classification
 Linear Models for Classification Oliver Schulte - CMPT 726 Bishop PRML Ch. 4 Classification: Hand-written Digit Recognition CHINE INTELLIGENCE, VOL. 24, NO. 24, APRIL 2002 x i = t i = (0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0,
Linear Models for Classification Oliver Schulte - CMPT 726 Bishop PRML Ch. 4 Classification: Hand-written Digit Recognition CHINE INTELLIGENCE, VOL. 24, NO. 24, APRIL 2002 x i = t i = (0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0,
Machine learning comes from Bayesian decision theory in statistics. There we want to minimize the expected value of the loss function.
 Bayesian learning: Machine learning comes from Bayesian decision theory in statistics. There we want to minimize the expected value of the loss function. Let y be the true label and y be the predicted
Bayesian learning: Machine learning comes from Bayesian decision theory in statistics. There we want to minimize the expected value of the loss function. Let y be the true label and y be the predicted
Holdout and Cross-Validation Methods Overfitting Avoidance
 Holdout and Cross-Validation Methods Overfitting Avoidance Decision Trees Reduce error pruning Cost-complexity pruning Neural Networks Early stopping Adjusting Regularizers via Cross-Validation Nearest
Holdout and Cross-Validation Methods Overfitting Avoidance Decision Trees Reduce error pruning Cost-complexity pruning Neural Networks Early stopping Adjusting Regularizers via Cross-Validation Nearest
Evidence for Single Top Quark Production. Reinhard Schwienhorst
 Evidence for Single Top Quark Production Reinhard Schwienhorst MSU high energy seminar, 1/9/2007 Outline Motivation Preparation Optimized Event Analysis Sensitivity Cross section measurement Vtb Conclusions/Outlook
Evidence for Single Top Quark Production Reinhard Schwienhorst MSU high energy seminar, 1/9/2007 Outline Motivation Preparation Optimized Event Analysis Sensitivity Cross section measurement Vtb Conclusions/Outlook
CSE 151 Machine Learning. Instructor: Kamalika Chaudhuri
 CSE 151 Machine Learning Instructor: Kamalika Chaudhuri Ensemble Learning How to combine multiple classifiers into a single one Works well if the classifiers are complementary This class: two types of
CSE 151 Machine Learning Instructor: Kamalika Chaudhuri Ensemble Learning How to combine multiple classifiers into a single one Works well if the classifiers are complementary This class: two types of
Final Exam, Spring 2006
 070 Final Exam, Spring 2006. Write your name and your email address below. Name: Andrew account: 2. There should be 22 numbered pages in this exam (including this cover sheet). 3. You may use any and all
070 Final Exam, Spring 2006. Write your name and your email address below. Name: Andrew account: 2. There should be 22 numbered pages in this exam (including this cover sheet). 3. You may use any and all
Boosting. CAP5610: Machine Learning Instructor: Guo-Jun Qi
 Boosting CAP5610: Machine Learning Instructor: Guo-Jun Qi Weak classifiers Weak classifiers Decision stump one layer decision tree Naive Bayes A classifier without feature correlations Linear classifier
Boosting CAP5610: Machine Learning Instructor: Guo-Jun Qi Weak classifiers Weak classifiers Decision stump one layer decision tree Naive Bayes A classifier without feature correlations Linear classifier
Applied Multivariate and Longitudinal Data Analysis
 Applied Multivariate and Longitudinal Data Analysis Discriminant analysis and classification Ana-Maria Staicu SAS Hall 5220; 919-515-0644; astaicu@ncsu.edu 1 Consider the examples: An online banking service
Applied Multivariate and Longitudinal Data Analysis Discriminant analysis and classification Ana-Maria Staicu SAS Hall 5220; 919-515-0644; astaicu@ncsu.edu 1 Consider the examples: An online banking service
The exam is closed book, closed notes except your one-page (two sides) or two-page (one side) crib sheet.
 CS 189 Spring 013 Introduction to Machine Learning Final You have 3 hours for the exam. The exam is closed book, closed notes except your one-page (two sides) or two-page (one side) crib sheet. Please
CS 189 Spring 013 Introduction to Machine Learning Final You have 3 hours for the exam. The exam is closed book, closed notes except your one-page (two sides) or two-page (one side) crib sheet. Please
Gradient Boosting (Continued)
 Gradient Boosting (Continued) David Rosenberg New York University April 4, 2016 David Rosenberg (New York University) DS-GA 1003 April 4, 2016 1 / 31 Boosting Fits an Additive Model Boosting Fits an Additive
Gradient Boosting (Continued) David Rosenberg New York University April 4, 2016 David Rosenberg (New York University) DS-GA 1003 April 4, 2016 1 / 31 Boosting Fits an Additive Model Boosting Fits an Additive
Final Exam, Machine Learning, Spring 2009
 Name: Andrew ID: Final Exam, 10701 Machine Learning, Spring 2009 - The exam is open-book, open-notes, no electronics other than calculators. - The maximum possible score on this exam is 100. You have 3
Name: Andrew ID: Final Exam, 10701 Machine Learning, Spring 2009 - The exam is open-book, open-notes, no electronics other than calculators. - The maximum possible score on this exam is 100. You have 3
Bagging. Ryan Tibshirani Data Mining: / April Optional reading: ISL 8.2, ESL 8.7
 Bagging Ryan Tibshirani Data Mining: 36-462/36-662 April 23 2013 Optional reading: ISL 8.2, ESL 8.7 1 Reminder: classification trees Our task is to predict the class label y {1,... K} given a feature vector
Bagging Ryan Tibshirani Data Mining: 36-462/36-662 April 23 2013 Optional reading: ISL 8.2, ESL 8.7 1 Reminder: classification trees Our task is to predict the class label y {1,... K} given a feature vector
Ensembles of Classifiers.
 Ensembles of Classifiers www.biostat.wisc.edu/~dpage/cs760/ 1 Goals for the lecture you should understand the following concepts ensemble bootstrap sample bagging boosting random forests error correcting
Ensembles of Classifiers www.biostat.wisc.edu/~dpage/cs760/ 1 Goals for the lecture you should understand the following concepts ensemble bootstrap sample bagging boosting random forests error correcting
arxiv: v1 [stat.ml] 24 Nov 2016
![arxiv: v1 [stat.ml] 24 Nov 2016 arxiv: v1 [stat.ml] 24 Nov 2016](/thumbs/92/109412189.jpg) EPJ Web of Conferences will be set by the publisher DOI: will be set by the publisher c Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 28 arxiv:6.8256v [stat.ml] 24 Nov 26 The Algorithm: Anomaly Detection
EPJ Web of Conferences will be set by the publisher DOI: will be set by the publisher c Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 28 arxiv:6.8256v [stat.ml] 24 Nov 26 The Algorithm: Anomaly Detection
Oliver Dürr. Statistisches Data Mining (StDM) Woche 11. Institut für Datenanalyse und Prozessdesign Zürcher Hochschule für Angewandte Wissenschaften
 Statistisches Data Mining (StDM) Woche 11 Oliver Dürr Institut für Datenanalyse und Prozessdesign Zürcher Hochschule für Angewandte Wissenschaften oliver.duerr@zhaw.ch Winterthur, 29 November 2016 1 Multitasking
Statistisches Data Mining (StDM) Woche 11 Oliver Dürr Institut für Datenanalyse und Prozessdesign Zürcher Hochschule für Angewandte Wissenschaften oliver.duerr@zhaw.ch Winterthur, 29 November 2016 1 Multitasking
Machine Learning, Fall 2009: Midterm
 10-601 Machine Learning, Fall 009: Midterm Monday, November nd hours 1. Personal info: Name: Andrew account: E-mail address:. You are permitted two pages of notes and a calculator. Please turn off all
10-601 Machine Learning, Fall 009: Midterm Monday, November nd hours 1. Personal info: Name: Andrew account: E-mail address:. You are permitted two pages of notes and a calculator. Please turn off all
Ensemble Methods and Random Forests
 Ensemble Methods and Random Forests Vaishnavi S May 2017 1 Introduction We have seen various analysis for classification and regression in the course. One of the common methods to reduce the generalization
Ensemble Methods and Random Forests Vaishnavi S May 2017 1 Introduction We have seen various analysis for classification and regression in the course. One of the common methods to reduce the generalization
Artificial Intelligence Roman Barták
 Artificial Intelligence Roman Barták Department of Theoretical Computer Science and Mathematical Logic Introduction We will describe agents that can improve their behavior through diligent study of their
Artificial Intelligence Roman Barták Department of Theoretical Computer Science and Mathematical Logic Introduction We will describe agents that can improve their behavior through diligent study of their
Data Mining. Linear & nonlinear classifiers. Hamid Beigy. Sharif University of Technology. Fall 1396
 Data Mining Linear & nonlinear classifiers Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1396 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Data Mining Fall 1396 1 / 31 Table of contents 1 Introduction
Data Mining Linear & nonlinear classifiers Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1396 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Data Mining Fall 1396 1 / 31 Table of contents 1 Introduction
Last updated: Oct 22, 2012 LINEAR CLASSIFIERS. J. Elder CSE 4404/5327 Introduction to Machine Learning and Pattern Recognition
 Last updated: Oct 22, 2012 LINEAR CLASSIFIERS Problems 2 Please do Problem 8.3 in the textbook. We will discuss this in class. Classification: Problem Statement 3 In regression, we are modeling the relationship
Last updated: Oct 22, 2012 LINEAR CLASSIFIERS Problems 2 Please do Problem 8.3 in the textbook. We will discuss this in class. Classification: Problem Statement 3 In regression, we are modeling the relationship
Statistical Data Analysis Stat 2: Monte Carlo Method, Statistical Tests
 Statistical Data Analysis Stat 2: Monte Carlo Method, Statistical Tests London Postgraduate Lectures on Particle Physics; University of London MSci course PH4515 Glen Cowan Physics Department Royal Holloway,
Statistical Data Analysis Stat 2: Monte Carlo Method, Statistical Tests London Postgraduate Lectures on Particle Physics; University of London MSci course PH4515 Glen Cowan Physics Department Royal Holloway,
Midterm Exam Solutions, Spring 2007
 1-71 Midterm Exam Solutions, Spring 7 1. Personal info: Name: Andrew account: E-mail address:. There should be 16 numbered pages in this exam (including this cover sheet). 3. You can use any material you
1-71 Midterm Exam Solutions, Spring 7 1. Personal info: Name: Andrew account: E-mail address:. There should be 16 numbered pages in this exam (including this cover sheet). 3. You can use any material you
ABC random forest for parameter estimation. Jean-Michel Marin
 ABC random forest for parameter estimation Jean-Michel Marin Université de Montpellier Institut Montpelliérain Alexander Grothendieck (IMAG) Institut de Biologie Computationnelle (IBC) Labex Numev! joint
ABC random forest for parameter estimation Jean-Michel Marin Université de Montpellier Institut Montpelliérain Alexander Grothendieck (IMAG) Institut de Biologie Computationnelle (IBC) Labex Numev! joint
UVA CS 4501: Machine Learning
 UVA CS 4501: Machine Learning Lecture 21: Decision Tree / Random Forest / Ensemble Dr. Yanjun Qi University of Virginia Department of Computer Science Where are we? è Five major sections of this course
UVA CS 4501: Machine Learning Lecture 21: Decision Tree / Random Forest / Ensemble Dr. Yanjun Qi University of Virginia Department of Computer Science Where are we? è Five major sections of this course
VBM683 Machine Learning
 VBM683 Machine Learning Pinar Duygulu Slides are adapted from Dhruv Batra Bias is the algorithm's tendency to consistently learn the wrong thing by not taking into account all the information in the data
VBM683 Machine Learning Pinar Duygulu Slides are adapted from Dhruv Batra Bias is the algorithm's tendency to consistently learn the wrong thing by not taking into account all the information in the data
Classification: The rest of the story
 U NIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS AT URBANA-CHAMPAIGN CS598 Machine Learning for Signal Processing Classification: The rest of the story 3 October 2017 Today s lecture Important things we haven t covered yet Fisher
U NIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS AT URBANA-CHAMPAIGN CS598 Machine Learning for Signal Processing Classification: The rest of the story 3 October 2017 Today s lecture Important things we haven t covered yet Fisher
Introduction to Machine Learning Midterm, Tues April 8
 Introduction to Machine Learning 10-701 Midterm, Tues April 8 [1 point] Name: Andrew ID: Instructions: You are allowed a (two-sided) sheet of notes. Exam ends at 2:45pm Take a deep breath and don t spend
Introduction to Machine Learning 10-701 Midterm, Tues April 8 [1 point] Name: Andrew ID: Instructions: You are allowed a (two-sided) sheet of notes. Exam ends at 2:45pm Take a deep breath and don t spend
Discriminant Analysis and Statistical Pattern Recognition
 Discriminant Analysis and Statistical Pattern Recognition GEOFFREY J. McLACHLAN Department of Mathematics The University of Queensland St. Lucia, Queensland, Australia A Wiley-Interscience Publication
Discriminant Analysis and Statistical Pattern Recognition GEOFFREY J. McLACHLAN Department of Mathematics The University of Queensland St. Lucia, Queensland, Australia A Wiley-Interscience Publication
Classification Ensemble That Maximizes the Area Under Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve (AUC)
 Classification Ensemble That Maximizes the Area Under Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve (AUC) Eunsik Park 1 and Y-c Ivan Chang 2 1 Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea 2 Academia Sinica, Taipei,
Classification Ensemble That Maximizes the Area Under Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve (AUC) Eunsik Park 1 and Y-c Ivan Chang 2 1 Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea 2 Academia Sinica, Taipei,
Support Vector Machine, Random Forests, Boosting Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes. December 2, 2012
 Support Vector Machine, Random Forests, Boosting Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes December 2, 2012 1 / 1 Neural networks Neural network Another classifier (or regression technique)
Support Vector Machine, Random Forests, Boosting Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes December 2, 2012 1 / 1 Neural networks Neural network Another classifier (or regression technique)
Nearest Neighbors Methods for Support Vector Machines
 Nearest Neighbors Methods for Support Vector Machines A. J. Quiroz, Dpto. de Matemáticas. Universidad de Los Andes joint work with María González-Lima, Universidad Simón Boĺıvar and Sergio A. Camelo, Universidad
Nearest Neighbors Methods for Support Vector Machines A. J. Quiroz, Dpto. de Matemáticas. Universidad de Los Andes joint work with María González-Lima, Universidad Simón Boĺıvar and Sergio A. Camelo, Universidad
Curve Fitting Re-visited, Bishop1.2.5
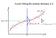 Curve Fitting Re-visited, Bishop1.2.5 Maximum Likelihood Bishop 1.2.5 Model Likelihood differentiation p(t x, w, β) = Maximum Likelihood N N ( t n y(x n, w), β 1). (1.61) n=1 As we did in the case of the
Curve Fitting Re-visited, Bishop1.2.5 Maximum Likelihood Bishop 1.2.5 Model Likelihood differentiation p(t x, w, β) = Maximum Likelihood N N ( t n y(x n, w), β 1). (1.61) n=1 As we did in the case of the
Final Exam, Fall 2002
 15-781 Final Exam, Fall 22 1. Write your name and your andrew email address below. Name: Andrew ID: 2. There should be 17 pages in this exam (excluding this cover sheet). 3. If you need more room to work
15-781 Final Exam, Fall 22 1. Write your name and your andrew email address below. Name: Andrew ID: 2. There should be 17 pages in this exam (excluding this cover sheet). 3. If you need more room to work
CS4495/6495 Introduction to Computer Vision. 8C-L3 Support Vector Machines
 CS4495/6495 Introduction to Computer Vision 8C-L3 Support Vector Machines Discriminative classifiers Discriminative classifiers find a division (surface) in feature space that separates the classes Several
CS4495/6495 Introduction to Computer Vision 8C-L3 Support Vector Machines Discriminative classifiers Discriminative classifiers find a division (surface) in feature space that separates the classes Several
Introduction to Machine Learning
 Introduction to Machine Learning Thomas G. Dietterich tgd@eecs.oregonstate.edu 1 Outline What is Machine Learning? Introduction to Supervised Learning: Linear Methods Overfitting, Regularization, and the
Introduction to Machine Learning Thomas G. Dietterich tgd@eecs.oregonstate.edu 1 Outline What is Machine Learning? Introduction to Supervised Learning: Linear Methods Overfitting, Regularization, and the
Lectures in AstroStatistics: Topics in Machine Learning for Astronomers
 Lectures in AstroStatistics: Topics in Machine Learning for Astronomers Jessi Cisewski Yale University American Astronomical Society Meeting Wednesday, January 6, 2016 1 Statistical Learning - learning
Lectures in AstroStatistics: Topics in Machine Learning for Astronomers Jessi Cisewski Yale University American Astronomical Society Meeting Wednesday, January 6, 2016 1 Statistical Learning - learning
Learning theory. Ensemble methods. Boosting. Boosting: history
 Learning theory Probability distribution P over X {0, 1}; let (X, Y ) P. We get S := {(x i, y i )} n i=1, an iid sample from P. Ensemble methods Goal: Fix ɛ, δ (0, 1). With probability at least 1 δ (over
Learning theory Probability distribution P over X {0, 1}; let (X, Y ) P. We get S := {(x i, y i )} n i=1, an iid sample from P. Ensemble methods Goal: Fix ɛ, δ (0, 1). With probability at least 1 δ (over
Part I Week 7 Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes
 Part I Week 7 Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes Support Vector Machine, Random Forests, Boosting December 2, 2012 1 / 1 2 / 1 Neural networks Artificial Neural networks: Networks
Part I Week 7 Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes Support Vector Machine, Random Forests, Boosting December 2, 2012 1 / 1 2 / 1 Neural networks Artificial Neural networks: Networks
Machine Learning Lecture 5
 Machine Learning Lecture 5 Linear Discriminant Functions 26.10.2017 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Course Outline Fundamentals Bayes Decision Theory
Machine Learning Lecture 5 Linear Discriminant Functions 26.10.2017 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Course Outline Fundamentals Bayes Decision Theory
1 Handling of Continuous Attributes in C4.5. Algorithm
 .. Spring 2009 CSC 466: Knowledge Discovery from Data Alexander Dekhtyar.. Data Mining: Classification/Supervised Learning Potpourri Contents 1. C4.5. and continuous attributes: incorporating continuous
.. Spring 2009 CSC 466: Knowledge Discovery from Data Alexander Dekhtyar.. Data Mining: Classification/Supervised Learning Potpourri Contents 1. C4.5. and continuous attributes: incorporating continuous
Part I. Linear Discriminant Analysis. Discriminant analysis. Discriminant analysis
 Week 5 Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes Part I Linear Discriminant Analysis October 29, 2012 1 / 1 2 / 1 Nearest centroid rule Suppose we break down our data matrix as by the
Week 5 Based in part on slides from textbook, slides of Susan Holmes Part I Linear Discriminant Analysis October 29, 2012 1 / 1 2 / 1 Nearest centroid rule Suppose we break down our data matrix as by the
ECE 5984: Introduction to Machine Learning
 ECE 5984: Introduction to Machine Learning Topics: Ensemble Methods: Bagging, Boosting Readings: Murphy 16.4; Hastie 16 Dhruv Batra Virginia Tech Administrativia HW3 Due: April 14, 11:55pm You will implement
ECE 5984: Introduction to Machine Learning Topics: Ensemble Methods: Bagging, Boosting Readings: Murphy 16.4; Hastie 16 Dhruv Batra Virginia Tech Administrativia HW3 Due: April 14, 11:55pm You will implement
CART Classification and Regression Trees Trees can be viewed as basis expansions of simple functions
 CART Classification and Regression Trees Trees can be viewed as basis expansions of simple functions f (x) = M c m 1(x R m ) m=1 with R 1,..., R m R p disjoint. The CART algorithm is a heuristic, adaptive
CART Classification and Regression Trees Trees can be viewed as basis expansions of simple functions f (x) = M c m 1(x R m ) m=1 with R 1,..., R m R p disjoint. The CART algorithm is a heuristic, adaptive
Lossless Online Bayesian Bagging
 Lossless Online Bayesian Bagging Herbert K. H. Lee ISDS Duke University Box 90251 Durham, NC 27708 herbie@isds.duke.edu Merlise A. Clyde ISDS Duke University Box 90251 Durham, NC 27708 clyde@isds.duke.edu
Lossless Online Bayesian Bagging Herbert K. H. Lee ISDS Duke University Box 90251 Durham, NC 27708 herbie@isds.duke.edu Merlise A. Clyde ISDS Duke University Box 90251 Durham, NC 27708 clyde@isds.duke.edu
REGRESSION TREE CREDIBILITY MODEL
 LIQUN DIAO AND CHENGGUO WENG Department of Statistics and Actuarial Science, University of Waterloo Advances in Predictive Analytics Conference, Waterloo, Ontario Dec 1, 2017 Overview Statistical }{{ Method
LIQUN DIAO AND CHENGGUO WENG Department of Statistics and Actuarial Science, University of Waterloo Advances in Predictive Analytics Conference, Waterloo, Ontario Dec 1, 2017 Overview Statistical }{{ Method
Classification Methods II: Linear and Quadratic Discrimminant Analysis
 Classification Methods II: Linear and Quadratic Discrimminant Analysis Rebecca C. Steorts, Duke University STA 325, Chapter 4 ISL Agenda Linear Discrimminant Analysis (LDA) Classification Recall that linear
Classification Methods II: Linear and Quadratic Discrimminant Analysis Rebecca C. Steorts, Duke University STA 325, Chapter 4 ISL Agenda Linear Discrimminant Analysis (LDA) Classification Recall that linear
6.867 Machine Learning
 6.867 Machine Learning Problem Set 2 Due date: Wednesday October 6 Please address all questions and comments about this problem set to 6867-staff@csail.mit.edu. You will need to use MATLAB for some of
6.867 Machine Learning Problem Set 2 Due date: Wednesday October 6 Please address all questions and comments about this problem set to 6867-staff@csail.mit.edu. You will need to use MATLAB for some of
Discriminative Learning and Big Data
 AIMS-CDT Michaelmas 2016 Discriminative Learning and Big Data Lecture 2: Other loss functions and ANN Andrew Zisserman Visual Geometry Group University of Oxford http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~vgg Lecture
AIMS-CDT Michaelmas 2016 Discriminative Learning and Big Data Lecture 2: Other loss functions and ANN Andrew Zisserman Visual Geometry Group University of Oxford http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~vgg Lecture
Measurement of the. Maren Ugland. Bergen group meeting
 Measurement of the B µµ BF s Maren Ugland Bergen group meeting - 25.11.2009 Introduction Neutral B-meson decays to two leptons are very sensitive to new physics. Since B s 0 l + l - involves a flavor changing
Measurement of the B µµ BF s Maren Ugland Bergen group meeting - 25.11.2009 Introduction Neutral B-meson decays to two leptons are very sensitive to new physics. Since B s 0 l + l - involves a flavor changing
Machine Learning. Ensemble Methods. Manfred Huber
 Machine Learning Ensemble Methods Manfred Huber 2015 1 Bias, Variance, Noise Classification errors have different sources Choice of hypothesis space and algorithm Training set Noise in the data The expected
Machine Learning Ensemble Methods Manfred Huber 2015 1 Bias, Variance, Noise Classification errors have different sources Choice of hypothesis space and algorithm Training set Noise in the data The expected
