Statistical NLP Spring A Discriminative Approach
|
|
|
- Barry Bates
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Statistical NLP Spring 2008 Lecture 6: Classification Dan Klein UC Berkeley A Discriminative Approach View WSD as a discrimination task (regression, really) P(sense context:jail, context:county, context:feeding, local-context:jail, local-context:meals subcat:np, direct-object-head:meals,.) Have to estimate multinomial (over senses) where there are a huge number of things to condition on History is too complex to think about this as a smoothing / backoff problem Many feature-based classification techniques out there We tend to need ones that output distributions over classes (why?) 1
2 Feature Representations d Washington County jail served 11,166 meals last month - a figure that translates to feeding some 120 people three times daily for 31 days. Features are indicator functions f i which count the occurrences of certain patterns in the input We map each input to a vector of feature predicate counts { fi( d)} context:jail = 1 context:county = 1 context:feeding = 1 context:game = 0 local-context:jail = 1 local-context:meals = 1 subcat:np = 1 subcat:pp = 0 object-head:meals = 1 object-head:ball = 0 Example: Text Classification We want to classify documents into categories DOCUMENT win the election win the game see a movie CATEGORY POLITICS SPORTS OTHER Classically, do this on the basis of words in the document, but other information sources are potentially relevant: Document length Average word length Document s source Document layout 2
3 Some Definitions Sometimes, we want Y to depend on x INPUTS OUTPUT SPACE OUTPUTS TRUE OUTPUTS FEATURE VECTORS Either x is implicit, or y contains x win the election SPORTS, POLITICS, OTHER SPORTS POLITICS SPORTS win POLITICS election POLITICS win Block Feature Vectors Sometimes, we think of the input as having features, which are multiplied by outputs to form the candidates win the election win election 3
4 Non-Block Feature Vectors Sometimes the features of candidates cannot be decomposed in this regular way Example: a parse tree s features may be the productions present in the tree N NP NP N S S VP VP V N V N Different candidates will thus often share features We ll return to the non-block case later NP N V S NP VP V N NP N VP VP N Linear Models: Scoring In a linear model, each feature gets a weight w We compare hypotheses on the basis of their linear scores: 4
5 Linear Models: Prediction Rule The linear prediction rule: We ve said nothing about where weights come from! Binary Decision Rule Heavily studied case: binary classification Simplifed: only class 1 has features Decision rule is a hyperplane One side will be class 1 Other side will be class 0 money 2 SPAM 1 BIAS : -3 free : 4 money : 2 the : 0... HAM free 5
6 Multiclass Decision Rule If more than two classes: Highest score wins Boundaries are more complex Harder to visualize There are other ways: e.g. reconcile pairwise decisions Learning Classifier Weights Two broad approaches to learning weights Generative: work with a probabilistic model of the data, weights are (log) local conditional probabilities Advantages: learning weights is easy, smoothing is wellunderstood, backed by understanding of modeling Discriminative: set weights based on some errorrelated criterion Advantages: error-driven, often weights which are good for classification aren t the ones which best describe the data We ll mainly talk about the latter 6
7 Example: Stoplights Lights Working Reality Lights Broken P(g,r,w) = 3/7 P(r,g,w) = 3/7 P(r,r,b) = 1/7 NB Model Working? NS EW NB FACTORS: P(w) = 6/7 P(r w) = 1/2 P(g w) = 1/2 P(b) = 1/7 P(r b) = 1 P(g b) = 0 Example: Stoplights What does the model say when both lights are red? P(b,r,r) = (1/7)(1)(1) = 1/7 = 4/28 P(w,r,r) = (6/7)(1/2)(1/2) = 6/28 = 6/28 P(w r,r) = 6/10! We ll guess that (r,r) indicates lights are working Imagine if P(b) were boosted higher, to 1/2: P(b,r,r) = (1/2)(1)(1) = 1/2 = 4/8 P(w,r,r) = (1/2)(1/2)(1/2) = 1/8 = 1/8 P(w r,r) = 1/5! Non-generative values can give better classification 7
8 Linear Models: Naïve-Bayes (Multinomial) Naïve-Bayes is a linear model, where: y d 1 d 2 d n How to pick weights? Goal: choose best vector w given training data For now, we mean best for classification The ideal: the weights which have greatest test set accuracy / F1 / whatever But, don t have the test set Must compute weights from training set Maybe we want weights which give best training set accuracy? Hard discontinuous optimization problem May not (does not) generalize to test set Easy to overfit Though, min-error training for MT does exactly this. 8
9 Minimize Training Error? A loss function declares how costly each mistake is E.g. 0 loss for correct label, 1 loss for wrong label Can weight mistakes differently (e.g. false positives worse than false negatives or Hamming distance over structured labels) We could, in principle, minimize training loss: This is a hard, discontinuous optimization problem Linear Models: Perceptron The perceptron algorithm Iteratively processes the training set, reacting to training errors Can be thought of as trying to drive down training error The (online) perceptron algorithm: Start with zero weights Visit training instances one by one Try to classify If correct, no change! If wrong: adjust weights 9
10 Examples: Perceptron Separable Case Examples: Perceptron Separable Case 10
11 Perceptrons and Separability A data set is separable if some parameters classify it perfectly Separable Convergence: if training data separable, perceptron will separate (binary case) Mistake Bound: the maximum number of mistakes (binary case) related to the margin or degree of separability Non-Separable Examples: Perceptron Non-Separable Case 11
12 Examples: Perceptron Non-Separable Case Issues with Perceptrons Overtraining: test / held-out accuracy usually rises, then falls Overtraining isn t quite as bad as overfitting, but is similar Regularization: if the data isn t separable, weights often thrash around Averaging weight vectors over time can help (averaged perceptron) [Freund & Schapire 99, Collins 02] Mediocre generalization: finds a barely separating solution 12
13 Problems with Perceptrons Perceptron goal : separate the training data 1. This may be an entire feasible space 2. Or it may be impossible Linear Separators Which of these linear separators is optimal? 13
14 Objective Functions What do we want from our weights? Depends! So far: minimize (training) errors: This is the zero-one loss Discontinuous, minimizing is NP-complete Not really what we want anyway Maximum entropy and SVMs have other objectives related to zero-one loss Linear Models: Maximum Entropy Maximum entropy (logistic regression) Use the scores as probabilities: Make positive Normalize Maximize the (log) conditional likelihood of training data 14
15 Derivative for Maximum Entropy Total count of feature n in correct candidates Expected count of feature n in predicted candidates Expected Counts y i P(y x i, w) x i s meal, jail, jail, term, food prison.8.4 The weight for the contextword:jail and cat:prison feature: actual = 1 empirical = 1.2 The optimum parameters are the ones for which each feature s predicted expectation equals its empirical expectation. The optimum distribution is: Always unique (but parameters may not be unique) Always exists (if features counts are from actual data). 15
16 Maximum Entropy II Motivation for maximum entropy: Connection to maximum entropy principle (sort of) Might want to do a good job of being uncertain on noisy cases in practice, though, posteriors are pretty peaked Regularization (smoothing) Maximum Entropy Separators 16
17 Maximum Entropy Separators Maximum Entropy 17
18 Example: NER Smoothing Because of smoothing, the more common prefixes have larger weights even though entire-word features are more specific. State Word Tag Sig Local Context Prev Other at IN x Cur??? Grace NNP Xx Next??? Road NNP Xx Feature Weights Feature Type Feature PERS Previous word at Current word Grace 0.03 Beginning bigram <G 0.45 Current POS tag NNP 0.47 Prev and cur tags IN NNP Previous state Other Current signature Xx 0.80 Prev state, cur sig O-Xx 0.68 Prev-cur-next sig x-xx-xx P. state - p-cur sig O-x-Xx Total: LOC Log-Loss If we view maxent as a minimization problem: This minimizes the log loss on each example One view: log loss is an upper bound on zero-one loss 18
19 Derivative for Maximum Entropy Big weights are bad Expected count of feature n in predicted candidates Total count of feature n in correct candidates Unconstrained Optimization The maxent objective is an unconstrained optimization problem Basic idea: move uphill from current guess Gradient ascent / descent follows the gradient incrementally At local optimum, derivative vector is zero Will converge if step sizes are small enough, but not efficient All we need is to be able to evaluate the function and its derivative 19
20 Convexity The maxent objective is nicely behaved: Differentiable (so many ways to optimize) Convex (so no local optima) Convex Non-Convex Convexity guarantees a single, global maximum value because any higher points are greedily reachable Unconstrained Optimization Once we have a function f, we can find a local optimum by iteratively following the gradient For convex functions, a local optimum will be global Basic gradient ascent isn t very efficient, but there are simple enhancements which take into account previous gradients: conjugate gradient, L-BFGs There are special-purpose optimization techniques for maxent, like iterative scaling, but they aren t better 20
21 Classification Margin (Binary) Distance of x i to separator is its margin, m i Examples closest to the hyperplane are support vectors Marginγof the separator is the minimum m γ m Classification Margin For each example x i and possible mistaken candidate y, we avoid that mistake by a margin m i (y) (with zero-one loss) Margin γ of the entire separator is the minimum m It is also the largest γ for which the following constraints hold 21
22 Maximum Margin Separable SVMs: find the max-margin w Can stick this into Matlab and (slowly) get an SVM Won t work (well) if non-separable Why Max Margin? Why do this? Various arguments: Solution depends only on the boundary cases, or support vectors (but remember how this diagram is broken!) Solution robust to movement of support vectors Sparse solutions (features not in support vectors get zero weight) Generalization bound arguments Works well in practice for many problems Support vectors 22
23 Max Margin / Small Norm Reformulation: find the smallest w which separates data Remember this condition? γ scales linearly in w, so if w isn t constrained, we can take any separating w and scale up our margin Instead of fixing the scale of w, we can fix γ = 1 Gamma to w 23
24 Soft Margin Classification What if the training set is not linearly separable? Slack variablesξ i can be added to allow misclassification of difficult or noisy examples, resulting in a soft margin classifier ξ i ξ i Maximum Margin Non-separable SVMs Add slack to the constraints Make objective pay (linearly) for slack: C is called the capacity of the SVM the smoothing knob Learning: Can still stick this into Matlab if you want Constrained optimization is hard; better methods! We ll come back to this later 24
25 Maximum Margin Remember SVMs We had a constrained minimization but we can solve for ξ i Giving 25
26 Hinge Loss Consider the per-instance objective: This is called the hinge loss Unlike maxent / log loss, you stop gaining objective once the true label wins by enough You can start from here and derive the SVM objective Plot really only right in binary case Max vs Soft-Max Margin SVMs: Maxent: You can make this zero but not this one Very similar! Both try to make the true score better than a function of the other scores The SVM tries to beat the augmented runner-up The Maxent classifier tries to beat the soft-max 26
27 Loss Functions: Comparison Zero-One Loss Hinge Log Separators: Comparison 27
Natural Language Processing. Classification. Features. Some Definitions. Classification. Feature Vectors. Classification I. Dan Klein UC Berkeley
 Natural Language Processing Classification Classification I Dan Klein UC Berkeley Classification Automatically make a decision about inputs Example: document category Example: image of digit digit Example:
Natural Language Processing Classification Classification I Dan Klein UC Berkeley Classification Automatically make a decision about inputs Example: document category Example: image of digit digit Example:
Statistical NLP Spring 2010
 Statistical NLP Spring 2010 Lecture 5: WSD / Maxent Dan Klein UC Berkeley Unsupervised Learning with EM Goal, learn parameters without observing labels y y y θ x x x x x x x x x 1 EM: More Formally Hard
Statistical NLP Spring 2010 Lecture 5: WSD / Maxent Dan Klein UC Berkeley Unsupervised Learning with EM Goal, learn parameters without observing labels y y y θ x x x x x x x x x 1 EM: More Formally Hard
Classification. Statistical NLP Spring Example: Text Classification. Some Definitions. Block Feature Vectors.
 tatistical NLP pring 0 Lecture : Classification Dan Klein UC Berkeley Classification Automatically make a decision about inputs Example: document category Example: image of digit digit Example: image of
tatistical NLP pring 0 Lecture : Classification Dan Klein UC Berkeley Classification Automatically make a decision about inputs Example: document category Example: image of digit digit Example: image of
Natural Language Processing. Classification. Margin. Linear Models: Perceptron. Issues with Perceptrons. Problems with Perceptrons.
 Natural Language Processing Classification Classification II Dan Klein UC Berkeley Linear Models: Perceptron The perceptron algorithm Iteratively processes the training set, reacting to training errors
Natural Language Processing Classification Classification II Dan Klein UC Berkeley Linear Models: Perceptron The perceptron algorithm Iteratively processes the training set, reacting to training errors
Algorithms for NLP. Classification II. Taylor Berg-Kirkpatrick CMU Slides: Dan Klein UC Berkeley
 Algorithms for NLP Classification II Taylor Berg-Kirkpatrick CMU Slides: Dan Klein UC Berkeley Minimize Training Error? A loss function declares how costly each mistake is E.g. 0 loss for correct label,
Algorithms for NLP Classification II Taylor Berg-Kirkpatrick CMU Slides: Dan Klein UC Berkeley Minimize Training Error? A loss function declares how costly each mistake is E.g. 0 loss for correct label,
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence. Outline
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Lecture 21: Perceptrons Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley Many slides adapted from Dan Klein. Outline Generative vs. Discriminative Binary Linear Classifiers Perceptron Multi-class
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Lecture 21: Perceptrons Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley Many slides adapted from Dan Klein. Outline Generative vs. Discriminative Binary Linear Classifiers Perceptron Multi-class
EE 511 Online Learning Perceptron
 Slides adapted from Ali Farhadi, Mari Ostendorf, Pedro Domingos, Carlos Guestrin, and Luke Zettelmoyer, Kevin Jamison EE 511 Online Learning Perceptron Instructor: Hanna Hajishirzi hannaneh@washington.edu
Slides adapted from Ali Farhadi, Mari Ostendorf, Pedro Domingos, Carlos Guestrin, and Luke Zettelmoyer, Kevin Jamison EE 511 Online Learning Perceptron Instructor: Hanna Hajishirzi hannaneh@washington.edu
Learning: Binary Perceptron. Examples: Perceptron. Separable Case. In the space of feature vectors
 Linear Classifiers CS 88 Artificial Intelligence Perceptrons and Logistic Regression Pieter Abbeel & Dan Klein University of California, Berkeley Feature Vectors Some (Simplified) Biology Very loose inspiration
Linear Classifiers CS 88 Artificial Intelligence Perceptrons and Logistic Regression Pieter Abbeel & Dan Klein University of California, Berkeley Feature Vectors Some (Simplified) Biology Very loose inspiration
Text Classification. CS5740: Natural Language Processing Spring Instructor: Yoav Artzi
 CS5740: Natural Language Processing Spring 2018 Text Classification Instructor: Yoav Artzi Slides adapted from Dan Klein, Dan Jurafsky, Chris Manning, Michael Collins, Luke Zettlemoyer, Yejin Choi, and
CS5740: Natural Language Processing Spring 2018 Text Classification Instructor: Yoav Artzi Slides adapted from Dan Klein, Dan Jurafsky, Chris Manning, Michael Collins, Luke Zettlemoyer, Yejin Choi, and
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Lecture 23: Perceptrons 11/20/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley 1 General Naïve Bayes A general naive Bayes model: C E 1 E 2 E n We only specify how each feature depends
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Lecture 23: Perceptrons 11/20/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley 1 General Naïve Bayes A general naive Bayes model: C E 1 E 2 E n We only specify how each feature depends
General Naïve Bayes. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall Example: Overfitting. Example: OCR. Example: Spam Filtering. Example: Spam Filtering
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 General Naïve Bayes A general naive Bayes model: C Lecture 23: Perceptrons 11/20/2008 E 1 E 2 E n Dan Klein UC Berkeley We only specify how each feature depends
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 General Naïve Bayes A general naive Bayes model: C Lecture 23: Perceptrons 11/20/2008 E 1 E 2 E n Dan Klein UC Berkeley We only specify how each feature depends
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011 Lecture 22: Perceptrons and More! 11/15/2011 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Errors, and What to Do Examples of errors Dear GlobalSCAPE Customer, GlobalSCAPE has partnered
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011 Lecture 22: Perceptrons and More! 11/15/2011 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Errors, and What to Do Examples of errors Dear GlobalSCAPE Customer, GlobalSCAPE has partnered
Errors, and What to Do. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall What to Do About Errors. Later On. Some (Simplified) Biology
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011 Lecture 22: Perceptrons and More! 11/15/2011 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Errors, and What to Do Examples of errors Dear GlobalSCAPE Customer, GlobalSCAPE has partnered
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2011 Lecture 22: Perceptrons and More! 11/15/2011 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Errors, and What to Do Examples of errors Dear GlobalSCAPE Customer, GlobalSCAPE has partnered
MIRA, SVM, k-nn. Lirong Xia
 MIRA, SVM, k-nn Lirong Xia Linear Classifiers (perceptrons) Inputs are feature values Each feature has a weight Sum is the activation activation w If the activation is: Positive: output +1 Negative, output
MIRA, SVM, k-nn Lirong Xia Linear Classifiers (perceptrons) Inputs are feature values Each feature has a weight Sum is the activation activation w If the activation is: Positive: output +1 Negative, output
Machine Learning for NLP
 Machine Learning for NLP Uppsala University Department of Linguistics and Philology Slides borrowed from Ryan McDonald, Google Research Machine Learning for NLP 1(50) Introduction Linear Classifiers Classifiers
Machine Learning for NLP Uppsala University Department of Linguistics and Philology Slides borrowed from Ryan McDonald, Google Research Machine Learning for NLP 1(50) Introduction Linear Classifiers Classifiers
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence. Machine Learning
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Review of Machine Learning (ML) DISCLAIMER: It is insufficient to simply study these slides, they are merely meant as a quick refresher of the high-level ideas covered.
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Review of Machine Learning (ML) DISCLAIMER: It is insufficient to simply study these slides, they are merely meant as a quick refresher of the high-level ideas covered.
Machine Learning for NLP
 Machine Learning for NLP Linear Models Joakim Nivre Uppsala University Department of Linguistics and Philology Slides adapted from Ryan McDonald, Google Research Machine Learning for NLP 1(26) Outline
Machine Learning for NLP Linear Models Joakim Nivre Uppsala University Department of Linguistics and Philology Slides adapted from Ryan McDonald, Google Research Machine Learning for NLP 1(26) Outline
Support vector machines Lecture 4
 Support vector machines Lecture 4 David Sontag New York University Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Vibhav Gogate, and Carlos Guestrin Q: What does the Perceptron mistake bound tell us? Theorem: The
Support vector machines Lecture 4 David Sontag New York University Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Vibhav Gogate, and Carlos Guestrin Q: What does the Perceptron mistake bound tell us? Theorem: The
CS 343: Artificial Intelligence
 CS 343: Artificial Intelligence Perceptrons Prof. Scott Niekum The University of Texas at Austin [These slides based on those of Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley. All CS188
CS 343: Artificial Intelligence Perceptrons Prof. Scott Niekum The University of Texas at Austin [These slides based on those of Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley. All CS188
CSEP%517% Natural%Language%Processing% Autumn%2013%
 CSEP%517% Natural%Language%Processing% Autumn%2013% Text Classification Luke Zettlemoyer - University of Washington [Many slides from Dan Klein and Michael Collins] Overview: Classification! Classification
CSEP%517% Natural%Language%Processing% Autumn%2013% Text Classification Luke Zettlemoyer - University of Washington [Many slides from Dan Klein and Michael Collins] Overview: Classification! Classification
Introduction to Logistic Regression and Support Vector Machine
 Introduction to Logistic Regression and Support Vector Machine guest lecturer: Ming-Wei Chang CS 446 Fall, 2009 () / 25 Fall, 2009 / 25 Before we start () 2 / 25 Fall, 2009 2 / 25 Before we start Feel
Introduction to Logistic Regression and Support Vector Machine guest lecturer: Ming-Wei Chang CS 446 Fall, 2009 () / 25 Fall, 2009 / 25 Before we start () 2 / 25 Fall, 2009 2 / 25 Before we start Feel
Machine Learning. Hal Daumé III. Computer Science University of Maryland CS 421: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 8 May 2012
 Machine Learning Hal Daumé III Computer Science University of Maryland me@hal3.name CS 421 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 8 May 2012 g 1 Many slides courtesy of Dan Klein, Stuart Russell, or Andrew
Machine Learning Hal Daumé III Computer Science University of Maryland me@hal3.name CS 421 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence 8 May 2012 g 1 Many slides courtesy of Dan Klein, Stuart Russell, or Andrew
CS 5522: Artificial Intelligence II
 CS 5522: Artificial Intelligence II Perceptrons Instructor: Alan Ritter Ohio State University [These slides were adapted from CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley. All materials available at http://ai.berkeley.edu.]
CS 5522: Artificial Intelligence II Perceptrons Instructor: Alan Ritter Ohio State University [These slides were adapted from CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley. All materials available at http://ai.berkeley.edu.]
From Binary to Multiclass Classification. CS 6961: Structured Prediction Spring 2018
 From Binary to Multiclass Classification CS 6961: Structured Prediction Spring 2018 1 So far: Binary Classification We have seen linear models Learning algorithms Perceptron SVM Logistic Regression Prediction
From Binary to Multiclass Classification CS 6961: Structured Prediction Spring 2018 1 So far: Binary Classification We have seen linear models Learning algorithms Perceptron SVM Logistic Regression Prediction
Mark your answers ON THE EXAM ITSELF. If you are not sure of your answer you may wish to provide a brief explanation.
 CS 189 Spring 2015 Introduction to Machine Learning Midterm You have 80 minutes for the exam. The exam is closed book, closed notes except your one-page crib sheet. No calculators or electronic items.
CS 189 Spring 2015 Introduction to Machine Learning Midterm You have 80 minutes for the exam. The exam is closed book, closed notes except your one-page crib sheet. No calculators or electronic items.
Algorithms for NLP. Classifica(on III. Taylor Berg- Kirkpatrick CMU Slides: Dan Klein UC Berkeley
 Algorithms for NLP Classifica(on III Taylor Berg- Kirkpatrick CMU Slides: Dan Klein UC Berkeley Objec(ve Func(ons What do we want from our weights? Depends! So far: minimize (training) errors: This is
Algorithms for NLP Classifica(on III Taylor Berg- Kirkpatrick CMU Slides: Dan Klein UC Berkeley Objec(ve Func(ons What do we want from our weights? Depends! So far: minimize (training) errors: This is
Stochastic Gradient Descent
 Stochastic Gradient Descent Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington October 9, 2013 1 Logistic Regression Logistic function (or Sigmoid): Learn P(Y X) directly Assume a particular
Stochastic Gradient Descent Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington October 9, 2013 1 Logistic Regression Logistic function (or Sigmoid): Learn P(Y X) directly Assume a particular
Support Vector Machines
 Support Vector Machines Jordan Boyd-Graber University of Colorado Boulder LECTURE 7 Slides adapted from Tom Mitchell, Eric Xing, and Lauren Hannah Jordan Boyd-Graber Boulder Support Vector Machines 1 of
Support Vector Machines Jordan Boyd-Graber University of Colorado Boulder LECTURE 7 Slides adapted from Tom Mitchell, Eric Xing, and Lauren Hannah Jordan Boyd-Graber Boulder Support Vector Machines 1 of
Perceptron. Subhransu Maji. CMPSCI 689: Machine Learning. 3 February February 2015
 Perceptron Subhransu Maji CMPSCI 689: Machine Learning 3 February 2015 5 February 2015 So far in the class Decision trees Inductive bias: use a combination of small number of features Nearest neighbor
Perceptron Subhransu Maji CMPSCI 689: Machine Learning 3 February 2015 5 February 2015 So far in the class Decision trees Inductive bias: use a combination of small number of features Nearest neighbor
CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining. MLE and MAP Fall 2017
 CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining MLE and MAP Fall 2017 Assignment 3: Admin 1 late day to hand in tonight, 2 late days for Wednesday. Assignment 4: Due Friday of next week. Last Time: Multi-Class
CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining MLE and MAP Fall 2017 Assignment 3: Admin 1 late day to hand in tonight, 2 late days for Wednesday. Assignment 4: Due Friday of next week. Last Time: Multi-Class
Logistic Regression Logistic
 Case Study 1: Estimating Click Probabilities L2 Regularization for Logistic Regression Machine Learning/Statistics for Big Data CSE599C1/STAT592, University of Washington Carlos Guestrin January 10 th,
Case Study 1: Estimating Click Probabilities L2 Regularization for Logistic Regression Machine Learning/Statistics for Big Data CSE599C1/STAT592, University of Washington Carlos Guestrin January 10 th,
Logistic Regression. Machine Learning Fall 2018
 Logistic Regression Machine Learning Fall 2018 1 Where are e? We have seen the folloing ideas Linear models Learning as loss minimization Bayesian learning criteria (MAP and MLE estimation) The Naïve Bayes
Logistic Regression Machine Learning Fall 2018 1 Where are e? We have seen the folloing ideas Linear models Learning as loss minimization Bayesian learning criteria (MAP and MLE estimation) The Naïve Bayes
Max Margin-Classifier
 Max Margin-Classifier Oliver Schulte - CMPT 726 Bishop PRML Ch. 7 Outline Maximum Margin Criterion Math Maximizing the Margin Non-Separable Data Kernels and Non-linear Mappings Where does the maximization
Max Margin-Classifier Oliver Schulte - CMPT 726 Bishop PRML Ch. 7 Outline Maximum Margin Criterion Math Maximizing the Margin Non-Separable Data Kernels and Non-linear Mappings Where does the maximization
Lecture 4: Training a Classifier
 Lecture 4: Training a Classifier Roger Grosse 1 Introduction Now that we ve defined what binary classification is, let s actually train a classifier. We ll approach this problem in much the same way as
Lecture 4: Training a Classifier Roger Grosse 1 Introduction Now that we ve defined what binary classification is, let s actually train a classifier. We ll approach this problem in much the same way as
Lecture 9: Large Margin Classifiers. Linear Support Vector Machines
 Lecture 9: Large Margin Classifiers. Linear Support Vector Machines Perceptrons Definition Perceptron learning rule Convergence Margin & max margin classifiers (Linear) support vector machines Formulation
Lecture 9: Large Margin Classifiers. Linear Support Vector Machines Perceptrons Definition Perceptron learning rule Convergence Margin & max margin classifiers (Linear) support vector machines Formulation
Ad Placement Strategies
 Case Study : Estimating Click Probabilities Intro Logistic Regression Gradient Descent + SGD AdaGrad Machine Learning for Big Data CSE547/STAT548, University of Washington Emily Fox January 7 th, 04 Ad
Case Study : Estimating Click Probabilities Intro Logistic Regression Gradient Descent + SGD AdaGrad Machine Learning for Big Data CSE547/STAT548, University of Washington Emily Fox January 7 th, 04 Ad
Case Study 1: Estimating Click Probabilities. Kakade Announcements: Project Proposals: due this Friday!
 Case Study 1: Estimating Click Probabilities Intro Logistic Regression Gradient Descent + SGD Machine Learning for Big Data CSE547/STAT548, University of Washington Sham Kakade April 4, 017 1 Announcements:
Case Study 1: Estimating Click Probabilities Intro Logistic Regression Gradient Descent + SGD Machine Learning for Big Data CSE547/STAT548, University of Washington Sham Kakade April 4, 017 1 Announcements:
Machine Learning for Structured Prediction
 Machine Learning for Structured Prediction Grzegorz Chrupa la National Centre for Language Technology School of Computing Dublin City University NCLT Seminar Grzegorz Chrupa la (DCU) Machine Learning for
Machine Learning for Structured Prediction Grzegorz Chrupa la National Centre for Language Technology School of Computing Dublin City University NCLT Seminar Grzegorz Chrupa la (DCU) Machine Learning for
Gaussian and Linear Discriminant Analysis; Multiclass Classification
 Gaussian and Linear Discriminant Analysis; Multiclass Classification Professor Ameet Talwalkar Slide Credit: Professor Fei Sha Professor Ameet Talwalkar CS260 Machine Learning Algorithms October 13, 2015
Gaussian and Linear Discriminant Analysis; Multiclass Classification Professor Ameet Talwalkar Slide Credit: Professor Fei Sha Professor Ameet Talwalkar CS260 Machine Learning Algorithms October 13, 2015
CS6375: Machine Learning Gautam Kunapuli. Support Vector Machines
 Gautam Kunapuli Example: Text Categorization Example: Develop a model to classify news stories into various categories based on their content. sports politics Use the bag-of-words representation for this
Gautam Kunapuli Example: Text Categorization Example: Develop a model to classify news stories into various categories based on their content. sports politics Use the bag-of-words representation for this
ML4NLP Multiclass Classification
 ML4NLP Multiclass Classification CS 590NLP Dan Goldwasser Purdue University dgoldwas@purdue.edu Social NLP Last week we discussed the speed-dates paper. Interesting perspective on NLP problems- Can we
ML4NLP Multiclass Classification CS 590NLP Dan Goldwasser Purdue University dgoldwas@purdue.edu Social NLP Last week we discussed the speed-dates paper. Interesting perspective on NLP problems- Can we
Machine Learning: Chenhao Tan University of Colorado Boulder LECTURE 9
 Machine Learning: Chenhao Tan University of Colorado Boulder LECTURE 9 Slides adapted from Jordan Boyd-Graber Machine Learning: Chenhao Tan Boulder 1 of 39 Recap Supervised learning Previously: KNN, naïve
Machine Learning: Chenhao Tan University of Colorado Boulder LECTURE 9 Slides adapted from Jordan Boyd-Graber Machine Learning: Chenhao Tan Boulder 1 of 39 Recap Supervised learning Previously: KNN, naïve
Classification CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology. M. Soleymani Fall 2012
 Classification CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2012 Topics Discriminant functions Logistic regression Perceptron Generative models Generative vs. discriminative
Classification CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2012 Topics Discriminant functions Logistic regression Perceptron Generative models Generative vs. discriminative
Announcements - Homework
 Announcements - Homework Homework 1 is graded, please collect at end of lecture Homework 2 due today Homework 3 out soon (watch email) Ques 1 midterm review HW1 score distribution 40 HW1 total score 35
Announcements - Homework Homework 1 is graded, please collect at end of lecture Homework 2 due today Homework 3 out soon (watch email) Ques 1 midterm review HW1 score distribution 40 HW1 total score 35
Introduction to Machine Learning
 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning: Jordan Boyd-Graber University of Maryland SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES Slides adapted from Tom Mitchell, Eric Xing, and Lauren Hannah Machine Learning: Jordan
Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning: Jordan Boyd-Graber University of Maryland SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES Slides adapted from Tom Mitchell, Eric Xing, and Lauren Hannah Machine Learning: Jordan
Algorithms for NLP. Language Modeling III. Taylor Berg-Kirkpatrick CMU Slides: Dan Klein UC Berkeley
 Algorithms for NLP Language Modeling III Taylor Berg-Kirkpatrick CMU Slides: Dan Klein UC Berkeley Announcements Office hours on website but no OH for Taylor until next week. Efficient Hashing Closed address
Algorithms for NLP Language Modeling III Taylor Berg-Kirkpatrick CMU Slides: Dan Klein UC Berkeley Announcements Office hours on website but no OH for Taylor until next week. Efficient Hashing Closed address
CSC 411 Lecture 17: Support Vector Machine
 CSC 411 Lecture 17: Support Vector Machine Ethan Fetaya, James Lucas and Emad Andrews University of Toronto CSC411 Lec17 1 / 1 Today Max-margin classification SVM Hard SVM Duality Soft SVM CSC411 Lec17
CSC 411 Lecture 17: Support Vector Machine Ethan Fetaya, James Lucas and Emad Andrews University of Toronto CSC411 Lec17 1 / 1 Today Max-margin classification SVM Hard SVM Duality Soft SVM CSC411 Lec17
CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining
 CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining MLE and MAP Original version of these slides by Mark Schmidt, with modifications by Mike Gelbart. 1 Admin Assignment 4: Due tonight. Assignment 5: Will be released
CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining MLE and MAP Original version of these slides by Mark Schmidt, with modifications by Mike Gelbart. 1 Admin Assignment 4: Due tonight. Assignment 5: Will be released
Applied Machine Learning Lecture 5: Linear classifiers, continued. Richard Johansson
 Applied Machine Learning Lecture 5: Linear classifiers, continued Richard Johansson overview preliminaries logistic regression training a logistic regression classifier side note: multiclass linear classifiers
Applied Machine Learning Lecture 5: Linear classifiers, continued Richard Johansson overview preliminaries logistic regression training a logistic regression classifier side note: multiclass linear classifiers
Machine Learning Lecture 5
 Machine Learning Lecture 5 Linear Discriminant Functions 26.10.2017 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Course Outline Fundamentals Bayes Decision Theory
Machine Learning Lecture 5 Linear Discriminant Functions 26.10.2017 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Course Outline Fundamentals Bayes Decision Theory
Linear & nonlinear classifiers
 Linear & nonlinear classifiers Machine Learning Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1394 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Linear & nonlinear classifiers Fall 1394 1 / 34 Table
Linear & nonlinear classifiers Machine Learning Hamid Beigy Sharif University of Technology Fall 1394 Hamid Beigy (Sharif University of Technology) Linear & nonlinear classifiers Fall 1394 1 / 34 Table
18.9 SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES
 744 Chapter 8. Learning from Examples is the fact that each regression problem will be easier to solve, because it involves only the examples with nonzero weight the examples whose kernels overlap the
744 Chapter 8. Learning from Examples is the fact that each regression problem will be easier to solve, because it involves only the examples with nonzero weight the examples whose kernels overlap the
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring Today
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2006 Lecture 9: Naïve Bayes 2/14/2006 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides from either Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore Bayes rule Today Expectations and utilities Naïve
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Spring 2006 Lecture 9: Naïve Bayes 2/14/2006 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Many slides from either Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore Bayes rule Today Expectations and utilities Naïve
Naïve Bayes, Maxent and Neural Models
 Naïve Bayes, Maxent and Neural Models CMSC 473/673 UMBC Some slides adapted from 3SLP Outline Recap: classification (MAP vs. noisy channel) & evaluation Naïve Bayes (NB) classification Terminology: bag-of-words
Naïve Bayes, Maxent and Neural Models CMSC 473/673 UMBC Some slides adapted from 3SLP Outline Recap: classification (MAP vs. noisy channel) & evaluation Naïve Bayes (NB) classification Terminology: bag-of-words
Linear Classifiers and the Perceptron
 Linear Classifiers and the Perceptron William Cohen February 4, 2008 1 Linear classifiers Let s assume that every instance is an n-dimensional vector of real numbers x R n, and there are only two possible
Linear Classifiers and the Perceptron William Cohen February 4, 2008 1 Linear classifiers Let s assume that every instance is an n-dimensional vector of real numbers x R n, and there are only two possible
SVAN 2016 Mini Course: Stochastic Convex Optimization Methods in Machine Learning
 SVAN 2016 Mini Course: Stochastic Convex Optimization Methods in Machine Learning Mark Schmidt University of British Columbia, May 2016 www.cs.ubc.ca/~schmidtm/svan16 Some images from this lecture are
SVAN 2016 Mini Course: Stochastic Convex Optimization Methods in Machine Learning Mark Schmidt University of British Columbia, May 2016 www.cs.ubc.ca/~schmidtm/svan16 Some images from this lecture are
Logistic Regression. Some slides adapted from Dan Jurfasky and Brendan O Connor
 Logistic Regression Some slides adapted from Dan Jurfasky and Brendan O Connor Naïve Bayes Recap Bag of words (order independent) Features are assumed independent given class P (x 1,...,x n c) =P (x 1
Logistic Regression Some slides adapted from Dan Jurfasky and Brendan O Connor Naïve Bayes Recap Bag of words (order independent) Features are assumed independent given class P (x 1,...,x n c) =P (x 1
Logistic Regression & Neural Networks
 Logistic Regression & Neural Networks CMSC 723 / LING 723 / INST 725 Marine Carpuat Slides credit: Graham Neubig, Jacob Eisenstein Logistic Regression Perceptron & Probabilities What if we want a probability
Logistic Regression & Neural Networks CMSC 723 / LING 723 / INST 725 Marine Carpuat Slides credit: Graham Neubig, Jacob Eisenstein Logistic Regression Perceptron & Probabilities What if we want a probability
Lecture 4: Training a Classifier
 Lecture 4: Training a Classifier Roger Grosse 1 Introduction Now that we ve defined what binary classification is, let s actually train a classifier. We ll approach this problem in much the same way as
Lecture 4: Training a Classifier Roger Grosse 1 Introduction Now that we ve defined what binary classification is, let s actually train a classifier. We ll approach this problem in much the same way as
Perceptron (Theory) + Linear Regression
 10601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Perceptron (Theory) Linear Regression Matt Gormley Lecture 6 Feb. 5, 2018 1 Q&A
10601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Perceptron (Theory) Linear Regression Matt Gormley Lecture 6 Feb. 5, 2018 1 Q&A
Kernel Methods and Support Vector Machines
 Kernel Methods and Support Vector Machines Oliver Schulte - CMPT 726 Bishop PRML Ch. 6 Support Vector Machines Defining Characteristics Like logistic regression, good for continuous input features, discrete
Kernel Methods and Support Vector Machines Oliver Schulte - CMPT 726 Bishop PRML Ch. 6 Support Vector Machines Defining Characteristics Like logistic regression, good for continuous input features, discrete
Multiclass Classification-1
 CS 446 Machine Learning Fall 2016 Oct 27, 2016 Multiclass Classification Professor: Dan Roth Scribe: C. Cheng Overview Binary to multiclass Multiclass SVM Constraint classification 1 Introduction Multiclass
CS 446 Machine Learning Fall 2016 Oct 27, 2016 Multiclass Classification Professor: Dan Roth Scribe: C. Cheng Overview Binary to multiclass Multiclass SVM Constraint classification 1 Introduction Multiclass
Machine learning comes from Bayesian decision theory in statistics. There we want to minimize the expected value of the loss function.
 Bayesian learning: Machine learning comes from Bayesian decision theory in statistics. There we want to minimize the expected value of the loss function. Let y be the true label and y be the predicted
Bayesian learning: Machine learning comes from Bayesian decision theory in statistics. There we want to minimize the expected value of the loss function. Let y be the true label and y be the predicted
Optimization and Gradient Descent
 Optimization and Gradient Descent INFO-4604, Applied Machine Learning University of Colorado Boulder September 12, 2017 Prof. Michael Paul Prediction Functions Remember: a prediction function is the function
Optimization and Gradient Descent INFO-4604, Applied Machine Learning University of Colorado Boulder September 12, 2017 Prof. Michael Paul Prediction Functions Remember: a prediction function is the function
Linear Models for Classification: Discriminative Learning (Perceptron, SVMs, MaxEnt)
 Linear Models for Classification: Discriminative Learning (Perceptron, SVMs, MaxEnt) Nathan Schneider (some slides borrowed from Chris Dyer) ENLP 12 February 2018 23 Outline Words, probabilities Features,
Linear Models for Classification: Discriminative Learning (Perceptron, SVMs, MaxEnt) Nathan Schneider (some slides borrowed from Chris Dyer) ENLP 12 February 2018 23 Outline Words, probabilities Features,
Midterm Review CS 6375: Machine Learning. Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas
 Midterm Review CS 6375: Machine Learning Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas Machine Learning Supervised Learning Unsupervised Learning Reinforcement Learning Parametric Y Continuous Non-parametric
Midterm Review CS 6375: Machine Learning Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas Machine Learning Supervised Learning Unsupervised Learning Reinforcement Learning Parametric Y Continuous Non-parametric
Deep Learning for Computer Vision
 Deep Learning for Computer Vision Lecture 4: Curse of Dimensionality, High Dimensional Feature Spaces, Linear Classifiers, Linear Regression, Python, and Jupyter Notebooks Peter Belhumeur Computer Science
Deep Learning for Computer Vision Lecture 4: Curse of Dimensionality, High Dimensional Feature Spaces, Linear Classifiers, Linear Regression, Python, and Jupyter Notebooks Peter Belhumeur Computer Science
Warm up: risk prediction with logistic regression
 Warm up: risk prediction with logistic regression Boss gives you a bunch of data on loans defaulting or not: {(x i,y i )} n i= x i 2 R d, y i 2 {, } You model the data as: P (Y = y x, w) = + exp( yw T
Warm up: risk prediction with logistic regression Boss gives you a bunch of data on loans defaulting or not: {(x i,y i )} n i= x i 2 R d, y i 2 {, } You model the data as: P (Y = y x, w) = + exp( yw T
CS 446 Machine Learning Fall 2016 Nov 01, Bayesian Learning
 CS 446 Machine Learning Fall 206 Nov 0, 206 Bayesian Learning Professor: Dan Roth Scribe: Ben Zhou, C. Cervantes Overview Bayesian Learning Naive Bayes Logistic Regression Bayesian Learning So far, we
CS 446 Machine Learning Fall 206 Nov 0, 206 Bayesian Learning Professor: Dan Roth Scribe: Ben Zhou, C. Cervantes Overview Bayesian Learning Naive Bayes Logistic Regression Bayesian Learning So far, we
9/12/17. Types of learning. Modeling data. Supervised learning: Classification. Supervised learning: Regression. Unsupervised learning: Clustering
 Types of learning Modeling data Supervised: we know input and targets Goal is to learn a model that, given input data, accurately predicts target data Unsupervised: we know the input only and want to make
Types of learning Modeling data Supervised: we know input and targets Goal is to learn a model that, given input data, accurately predicts target data Unsupervised: we know the input only and want to make
Linear discriminant functions
 Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Discriminative learning Discriminative vs generative Generative learning assumes knowledge of the distribution governing the data Discriminative
Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Discriminative learning Discriminative vs generative Generative learning assumes knowledge of the distribution governing the data Discriminative
Lecture 3: Multiclass Classification
 Lecture 3: Multiclass Classification Kai-Wei Chang CS @ University of Virginia kw@kwchang.net Some slides are adapted from Vivek Skirmar and Dan Roth CS6501 Lecture 3 1 Announcement v Please enroll in
Lecture 3: Multiclass Classification Kai-Wei Chang CS @ University of Virginia kw@kwchang.net Some slides are adapted from Vivek Skirmar and Dan Roth CS6501 Lecture 3 1 Announcement v Please enroll in
Linear smoother. ŷ = S y. where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x))
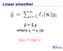 Linear smoother ŷ = S y where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x)) 2 Online Learning: LMS and Perceptrons Partially adapted from slides by Ryan Gabbard and Mitch Marcus (and lots original slides by
Linear smoother ŷ = S y where s ij = s ij (x) e.g. s ij = diag(l i (x)) 2 Online Learning: LMS and Perceptrons Partially adapted from slides by Ryan Gabbard and Mitch Marcus (and lots original slides by
ECE521 Lecture7. Logistic Regression
 ECE521 Lecture7 Logistic Regression Outline Review of decision theory Logistic regression A single neuron Multi-class classification 2 Outline Decision theory is conceptually easy and computationally hard
ECE521 Lecture7 Logistic Regression Outline Review of decision theory Logistic regression A single neuron Multi-class classification 2 Outline Decision theory is conceptually easy and computationally hard
Jeff Howbert Introduction to Machine Learning Winter
 Classification / Regression Support Vector Machines Jeff Howbert Introduction to Machine Learning Winter 2012 1 Topics SVM classifiers for linearly separable classes SVM classifiers for non-linearly separable
Classification / Regression Support Vector Machines Jeff Howbert Introduction to Machine Learning Winter 2012 1 Topics SVM classifiers for linearly separable classes SVM classifiers for non-linearly separable
CS6375: Machine Learning Gautam Kunapuli. Decision Trees
 Gautam Kunapuli Example: Restaurant Recommendation Example: Develop a model to recommend restaurants to users depending on their past dining experiences. Here, the features are cost (x ) and the user s
Gautam Kunapuli Example: Restaurant Recommendation Example: Develop a model to recommend restaurants to users depending on their past dining experiences. Here, the features are cost (x ) and the user s
A short introduction to supervised learning, with applications to cancer pathway analysis Dr. Christina Leslie
 A short introduction to supervised learning, with applications to cancer pathway analysis Dr. Christina Leslie Computational Biology Program Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center http://cbio.mskcc.org/leslielab
A short introduction to supervised learning, with applications to cancer pathway analysis Dr. Christina Leslie Computational Biology Program Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center http://cbio.mskcc.org/leslielab
Midterm Review CS 7301: Advanced Machine Learning. Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas
 Midterm Review CS 7301: Advanced Machine Learning Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas Supervised Learning Issues in supervised learning What makes learning hard Point Estimation: MLE vs Bayesian
Midterm Review CS 7301: Advanced Machine Learning Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas Supervised Learning Issues in supervised learning What makes learning hard Point Estimation: MLE vs Bayesian
Machine Learning And Applications: Supervised Learning-SVM
 Machine Learning And Applications: Supervised Learning-SVM Raphaël Bournhonesque École Normale Supérieure de Lyon, Lyon, France raphael.bournhonesque@ens-lyon.fr 1 Supervised vs unsupervised learning Machine
Machine Learning And Applications: Supervised Learning-SVM Raphaël Bournhonesque École Normale Supérieure de Lyon, Lyon, France raphael.bournhonesque@ens-lyon.fr 1 Supervised vs unsupervised learning Machine
Classification Logistic Regression
 Announcements: Classification Logistic Regression Machine Learning CSE546 Sham Kakade University of Washington HW due on Friday. Today: Review: sub-gradients,lasso Logistic Regression October 3, 26 Sham
Announcements: Classification Logistic Regression Machine Learning CSE546 Sham Kakade University of Washington HW due on Friday. Today: Review: sub-gradients,lasso Logistic Regression October 3, 26 Sham
Logistic Regression. COMP 527 Danushka Bollegala
 Logistic Regression COMP 527 Danushka Bollegala Binary Classification Given an instance x we must classify it to either positive (1) or negative (0) class We can use {1,-1} instead of {1,0} but we will
Logistic Regression COMP 527 Danushka Bollegala Binary Classification Given an instance x we must classify it to either positive (1) or negative (0) class We can use {1,-1} instead of {1,0} but we will
Ad Placement Strategies
 Case Study 1: Estimating Click Probabilities Tackling an Unknown Number of Features with Sketching Machine Learning for Big Data CSE547/STAT548, University of Washington Emily Fox 2014 Emily Fox January
Case Study 1: Estimating Click Probabilities Tackling an Unknown Number of Features with Sketching Machine Learning for Big Data CSE547/STAT548, University of Washington Emily Fox 2014 Emily Fox January
Logistic Regression Introduction to Machine Learning. Matt Gormley Lecture 9 Sep. 26, 2018
 10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Logistic Regression Matt Gormley Lecture 9 Sep. 26, 2018 1 Reminders Homework 3:
10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Logistic Regression Matt Gormley Lecture 9 Sep. 26, 2018 1 Reminders Homework 3:
CSE446: Clustering and EM Spring 2017
 CSE446: Clustering and EM Spring 2017 Ali Farhadi Slides adapted from Carlos Guestrin, Dan Klein, and Luke Zettlemoyer Clustering systems: Unsupervised learning Clustering Detect patterns in unlabeled
CSE446: Clustering and EM Spring 2017 Ali Farhadi Slides adapted from Carlos Guestrin, Dan Klein, and Luke Zettlemoyer Clustering systems: Unsupervised learning Clustering Detect patterns in unlabeled
Lecture 14 : Online Learning, Stochastic Gradient Descent, Perceptron
 CS446: Machine Learning, Fall 2017 Lecture 14 : Online Learning, Stochastic Gradient Descent, Perceptron Lecturer: Sanmi Koyejo Scribe: Ke Wang, Oct. 24th, 2017 Agenda Recap: SVM and Hinge loss, Representer
CS446: Machine Learning, Fall 2017 Lecture 14 : Online Learning, Stochastic Gradient Descent, Perceptron Lecturer: Sanmi Koyejo Scribe: Ke Wang, Oct. 24th, 2017 Agenda Recap: SVM and Hinge loss, Representer
Classification II: Decision Trees and SVMs
 Classification II: Decision Trees and SVMs Digging into Data: Jordan Boyd-Graber February 25, 2013 Slides adapted from Tom Mitchell, Eric Xing, and Lauren Hannah Digging into Data: Jordan Boyd-Graber ()
Classification II: Decision Trees and SVMs Digging into Data: Jordan Boyd-Graber February 25, 2013 Slides adapted from Tom Mitchell, Eric Xing, and Lauren Hannah Digging into Data: Jordan Boyd-Graber ()
Dan Roth 461C, 3401 Walnut
 CIS 519/419 Applied Machine Learning www.seas.upenn.edu/~cis519 Dan Roth danroth@seas.upenn.edu http://www.cis.upenn.edu/~danroth/ 461C, 3401 Walnut Slides were created by Dan Roth (for CIS519/419 at Penn
CIS 519/419 Applied Machine Learning www.seas.upenn.edu/~cis519 Dan Roth danroth@seas.upenn.edu http://www.cis.upenn.edu/~danroth/ 461C, 3401 Walnut Slides were created by Dan Roth (for CIS519/419 at Penn
ECE521 week 3: 23/26 January 2017
 ECE521 week 3: 23/26 January 2017 Outline Probabilistic interpretation of linear regression - Maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) - Maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimation Bias-variance trade-off Linear
ECE521 week 3: 23/26 January 2017 Outline Probabilistic interpretation of linear regression - Maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) - Maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimation Bias-variance trade-off Linear
Classification and Regression Trees
 Classification and Regression Trees Ryan P Adams So far, we have primarily examined linear classifiers and regressors, and considered several different ways to train them When we ve found the linearity
Classification and Regression Trees Ryan P Adams So far, we have primarily examined linear classifiers and regressors, and considered several different ways to train them When we ve found the linearity
Support Vector Machines
 Support Vector Machines Le Song Machine Learning I CSE 6740, Fall 2013 Naïve Bayes classifier Still use Bayes decision rule for classification P y x = P x y P y P x But assume p x y = 1 is fully factorized
Support Vector Machines Le Song Machine Learning I CSE 6740, Fall 2013 Naïve Bayes classifier Still use Bayes decision rule for classification P y x = P x y P y P x But assume p x y = 1 is fully factorized
Minimax risk bounds for linear threshold functions
 CS281B/Stat241B (Spring 2008) Statistical Learning Theory Lecture: 3 Minimax risk bounds for linear threshold functions Lecturer: Peter Bartlett Scribe: Hao Zhang 1 Review We assume that there is a probability
CS281B/Stat241B (Spring 2008) Statistical Learning Theory Lecture: 3 Minimax risk bounds for linear threshold functions Lecturer: Peter Bartlett Scribe: Hao Zhang 1 Review We assume that there is a probability
Introduction to AI Learning Bayesian networks. Vibhav Gogate
 Introduction to AI Learning Bayesian networks Vibhav Gogate Inductive Learning in a nutshell Given: Data Examples of a function (X, F(X)) Predict function F(X) for new examples X Discrete F(X): Classification
Introduction to AI Learning Bayesian networks Vibhav Gogate Inductive Learning in a nutshell Given: Data Examples of a function (X, F(X)) Predict function F(X) for new examples X Discrete F(X): Classification
Math for Machine Learning Open Doors to Data Science and Artificial Intelligence. Richard Han
 Math for Machine Learning Open Doors to Data Science and Artificial Intelligence Richard Han Copyright 05 Richard Han All rights reserved. CONTENTS PREFACE... - INTRODUCTION... LINEAR REGRESSION... 4 LINEAR
Math for Machine Learning Open Doors to Data Science and Artificial Intelligence Richard Han Copyright 05 Richard Han All rights reserved. CONTENTS PREFACE... - INTRODUCTION... LINEAR REGRESSION... 4 LINEAR
MIDTERM SOLUTIONS: FALL 2012 CS 6375 INSTRUCTOR: VIBHAV GOGATE
 MIDTERM SOLUTIONS: FALL 2012 CS 6375 INSTRUCTOR: VIBHAV GOGATE March 28, 2012 The exam is closed book. You are allowed a double sided one page cheat sheet. Answer the questions in the spaces provided on
MIDTERM SOLUTIONS: FALL 2012 CS 6375 INSTRUCTOR: VIBHAV GOGATE March 28, 2012 The exam is closed book. You are allowed a double sided one page cheat sheet. Answer the questions in the spaces provided on
Brief Introduction to Machine Learning
 Brief Introduction to Machine Learning Yuh-Jye Lee Lab of Data Science and Machine Intelligence Dept. of Applied Math. at NCTU August 29, 2016 1 / 49 1 Introduction 2 Binary Classification 3 Support Vector
Brief Introduction to Machine Learning Yuh-Jye Lee Lab of Data Science and Machine Intelligence Dept. of Applied Math. at NCTU August 29, 2016 1 / 49 1 Introduction 2 Binary Classification 3 Support Vector
Support Vector Machines
 Two SVM tutorials linked in class website (please, read both): High-level presentation with applications (Hearst 1998) Detailed tutorial (Burges 1998) Support Vector Machines Machine Learning 10701/15781
Two SVM tutorials linked in class website (please, read both): High-level presentation with applications (Hearst 1998) Detailed tutorial (Burges 1998) Support Vector Machines Machine Learning 10701/15781
Midterm. Introduction to Machine Learning. CS 189 Spring Please do not open the exam before you are instructed to do so.
 CS 89 Spring 07 Introduction to Machine Learning Midterm Please do not open the exam before you are instructed to do so. The exam is closed book, closed notes except your one-page cheat sheet. Electronic
CS 89 Spring 07 Introduction to Machine Learning Midterm Please do not open the exam before you are instructed to do so. The exam is closed book, closed notes except your one-page cheat sheet. Electronic
Machine Learning Lecture 7
 Course Outline Machine Learning Lecture 7 Fundamentals (2 weeks) Bayes Decision Theory Probability Density Estimation Statistical Learning Theory 23.05.2016 Discriminative Approaches (5 weeks) Linear Discriminant
Course Outline Machine Learning Lecture 7 Fundamentals (2 weeks) Bayes Decision Theory Probability Density Estimation Statistical Learning Theory 23.05.2016 Discriminative Approaches (5 weeks) Linear Discriminant
Machine Learning Practice Page 2 of 2 10/28/13
 Machine Learning 10-701 Practice Page 2 of 2 10/28/13 1. True or False Please give an explanation for your answer, this is worth 1 pt/question. (a) (2 points) No classifier can do better than a naive Bayes
Machine Learning 10-701 Practice Page 2 of 2 10/28/13 1. True or False Please give an explanation for your answer, this is worth 1 pt/question. (a) (2 points) No classifier can do better than a naive Bayes
