EE 330 Lecture 14. Devices in Semiconductor Processes. Diodes Capacitors MOSFETs
|
|
|
- Lilian Miles
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EE 330 Lecture 14 Devices in Semiconuctor Processes Dioes Capacitors MOSFETs
2 Reminer: Exam 1 Friay Feb 16 Stuents may bring one page of notes (front an back) but no electronic ata storage or remote access HW Assignment ue on We of next week at en of class perio (no late HW accepte) Review session: Thursay Feb 15 6:00 p.m. Rm 1016 Coover
3 Review from Last Lecture Basic Devices an Device Moels Resistor Dioe Capacitor MOSFET BJT
4 Review from Last Lecture Analysis of Nonlinear Circuits (Circuits with one or more nonlinear evices) What analysis tools or methos can be use? KCL? KVL? Superposition? Noal Analysis Mesh Analysis Two-Port Subcircuits Voltage Divier? Current Divier? Thevenin an Norton Equivalent Circuits?
5 Review from Last Lecture Dioe Moels I (amps) Dioe Characteristics V (volts) I (amps) Dioe Characteristics V (volts) Dioe Characteristics I D I (amps) V (volts) V D Which moel shoul be use? The simplest moel that will give acceptable results in the analysis of a circuit
6 Review from Last Lecture Piecewise Linear Moels Dioe Moel Summary I = 0 if V < 0 V =0 if I > 0 I D V D Dioe Characteristics I = 0 if V < 0.6V V =0.6V if I > 0 I (amps) V (volts) Dioe Equation I = 0 if V < 0.6 V =0.6+I R if I > 0 I (amps) Dioe Characteristics V (volts) V Vt I = I e -1 S
7 Review from Last Lecture Piecewise Linear Moels I = 0 if V < 0 Dioe Moel Summary V =0 if I > 0 I = 0 if V < 0.6V V =0.6V if I > 0 I = 0 if V < 0.6 V =0.6+I R if I > 0 Dioe Equation V Vt I = IS e -1 When is the ieal moel aequate? When it oesn t make much ifference whether V =0V or V =0.6V When is the secon piecewise-linear moel aequate? When it oesn t make much ifference whether V =0.6V or V =0.7V
8 Valiate Moel Select Moel Example: Determine I OUT for the following circuit 10K I OUT 12V D 1 Solution: Strategy: 1. Assume PWL moel with V D =0.6V, R D =0 2. Guess state of ioe (ON) 3. Analyze circuit with moel 4. Valiate state of guess in step 2 (verify the if conition in moel) 5. Assume PWL with V D =0.7V 6. Guess state of ioe (ON) 7. Analyze circuit with moel 8. Valiate state of guess in step 6 (verify the if conition in moel) 9. Show ifference between results using these two moels is small 10. If ifference is not small, must use a ifferent moel
9 Solution: 1. Assume PWL moel with V D =0.6V, R D =0 2. Guess state of ioe (ON) 10K I OUT 12V 0.6V 3. Analyze circuit with moel 12V-0.6V I = 1. 14mA OUT 10K 4. Valiate state of guess in step 2 To valiate state, must show I D >0 I =I D OUT =1.14mA>0
10 Solution: 5. Assume PWL moel with V D =0.7V, R D =0 6. Guess state of ioe (ON) 10K I OUT 12V 0.7V 7. Analyze circuit with moel 12V-0.7V I = 1. 13mA OUT 10K 8. Valiate state of guess in step 6 To valiate state, must show I D >0 I =I D OUT =1.13mA>0
11 Solution: 9. Show ifference between results using these two moels is small I =1.14mA an I =1.13 ma are close OUT OUT Thus, can conclue IOUT 1.14mA
12 Example: Determine I OUT for the following circuit 10K 0.8V I OUT D 1 Solution: Strategy: 1. Assume PWL moel with V D =0.6V, R D =0 2. Guess state of ioe (ON) 3. Analyze circuit with moel 4. Valiate state of guess in step 2 5. Assume PWL with V D =0.7V 6. Guess state of ioe (ON) 7. Analyze circuit with moel 8. Valiate state of guess in step 6 9. Show ifference between results using these two moels is small 10. If ifference is not small, must use a ifferent moel
13 Solution: 1. Assume PWL moel with V D =0.6V, R D =0 2. Guess state of ioe (ON) 10K 0.8V I OUT 0.6V 3. Analyze circuit with moel V I = OUT 10K 20 A 4. Valiate state of guess in step 2 To valiate state, must show I D >0 I =I =20A>0 D OUT
14 Solution: 5. Assume PWL moel with V D =0.7V, R D =0 6. Guess state of ioe (ON) 10K 0.8V I OUT 0.7V 7. Analyze circuit with moel 0.8V-0.7V I = OUT 10K 10 A 8. Valiate state of guess in step 6 To valiate state, must show I D >0 I =I =10A>0 D OUT
15 Solution: 9. Show ifference between results using these two moels is small I =10A an I =20A are not close OUT OUT 10. If ifference is not small, must use a ifferent moel Thus must use ioe equation to moel the evice I I OUT OUT 0.8-V = 10K =I e S V V D t D 0.8V 10K V D I OUT 0.6V Solve simultaneously, assume V t =25mV, I S =1fA Solving these two equations by iteration, obtain V D = V an I OUT =18.60μA
16 Use of Piecewise Moels for Nonlinear Devices when Analyzing Electronic Circuits Process: Observations: 1. Guess state of the evice 2. Analyze circuit 3. Verify State 4. Repeat steps 1 to 3 if verification fails 5. Verify moel (if necessary) o Analysis generally simplifie ramatically (particularly if piecewise moel is linear) o Approach applicable to wie variety of nonlinear evices o Close-form solutions give insight into performance of circuit o Usually much faster than solving the nonlinear circuit irectly o Wrong guesses in the state of the evice o not compromise solution (verification will fail) o Helps to guess right the first time o Moel is often not necessary with most nonlinear evices
17 Use of Piecewise Moels for Nonlinear Devices when Analyzing Electronic Circuits Process: 1. Guess state of the evice 2. Analyze circuit 3. Verify State 4. Repeat steps 1 to 3 if verification fails 5. Verify moel (if necessary) What about nonlinear circuits (using piecewise moels) with time-varying inputs? 1K V out 80Vsin500t D 1 1K Same process except state verification (step 3) may inclue a range where solution is vali
18 Example: Determine V OUT for V IN =80sin500t 1K 80Vsin500t V IN D 1 V out 1K Guess D 1 ON (will use ieal ioe moel) 1K V IN I D D 1 V out 1K V OUT =V IN =80sin(500t) Vali for I D >0 Thus vali for V IN > 0 I D VIN 1K
19 Example: Determine V OUT for V IN =80sin500t 1K 80Vsin500t V IN D 1 V out 1K Guess D 1 OFF (will use ieal ioe moel) 1K V IN V D D 1 V out 1K V OUT =V IN /2=40sin(500t) Vali for V D <0 V VD 2 Thus vali for V IN < 0 IN
20 Example: Determine V OUT for V IN =80sin500t 1K 80Vsin500t V IN D 1 V out 1K Thus overall solution V IN 80V V OUT 80sin 500t for VIN 0 40sin 500t forvin 0 t V OUT 80V t -40V
21 Use of Piecewise Moels for Nonlinear Devices when Analyzing Electronic Circuits Process: 1. Guess state of the evice 2. Analyze circuit 3. Verify State 4. Repeat steps 1 to 3 if verification fails 5. Verify moel (if necessary) What about circuits (using piecewise moels) with multiple nonlinear evices? 1K 20V V out 80V D 1 D 2 Guess state for each evice (multiple combinations possible) 4K
22 Example: Obtain V OUT 1K 20V V out 80V D 1 D 2 4K
23 Example: Obtain V OUT 1K 20V V out 80V D 1 D 2 Guess D 1 an D 2 on 4K 1K 20V V out 80V D I D1 1 I D2 D 2 I V OUT =-20V Vali for I D1 >0 an I D2 >0 D2 20V 5mA 0 4K 80V I D1 I D2 85mA 0 1K 4K Since valiates, solution is vali
24 Types of Dioes pn junction ioes I I I I I I V V V V V V Signal or Rectifier Pin or Photo Light Emitting LED Laser Dioe Metal-semiconuctor junction ioes Zener Varactor or Varicap V I V I V I Schottky Barrier
25 Basic Devices an Device Moels Resistor Dioe Capacitor MOSFET BJT
26 Capacitors Types Parallel Plate Fringe Junction
27 Parallel Plate Capacitors con 2 con 1 A 1 A 2 C insulator A = area of intersection of A 1 & A 2 One (top) plate intentionally C A size smaller to etermine C
28 Parallel Plate Capacitors If C Cap unit area where C C C ε A C ε A
29 Fringe Capacitors C C ε A A is the area where the two plates are parallel Only a single layer is neee to make fringe capacitors
30 Fringe Capacitors C
31 Junction Capacitor Capacitance C C 1 jo V φ p C A A D B n n for V FB φ 2 φ B 0.6V n ; 0.5 B C epletion region V D Note: is voltage epenent -capacitance is voltage epenent -usually parasitic caps -varicaps or varactor ioes exploit voltage ep. of C
32 Capacitance Junction Capacitor C Cj0A V D V D C C 1 jo V φ A D B n for V FB φ B 0.6V n ; 0.5 φ 2 B Voltage epenence is substantial
33 Basic Devices an Device Moels Resistor Dioe Capacitor MOSFET BJT
34 n-channel MOSFET Poly n-active Gate oxie p-sub
35 n-channel MOSFET Source Gate L Drain W L EFF Bulk
36 n-channel MOSFET Poly Gate oxie n-active p-sub epletion region (electrically inuce)
37 n-channel MOSFET Operation an Moel V DS V GS I D V BS I B I G Apply small V GS (V DS an V BS assume to be small) Depletion region electrically inuce in channel Terme cutoff region of operation I D =0 I G =0 I B =0
38 n-channel MOSFET Operation an Moel V DS V GS I D V BS I B I G Increase V GS (V DS an V BS assume to be small) Depletion region in channel becomes larger I D =0 I G =0 I B =0
39 n-channel MOSFET Operation an Moel V DS V GS I D V BS I B I G I D =0 I G =0 I B =0 Moel in Cutoff Region
40 n-channel MOSFET Operation an Moel V DS Critical value of V GS that creates inversion layer terme threshol voltage, V T ) V BS I B V GS I G I D (V DS an V BS small) Increase V GS more Inversion layer forms in channel Inversion layer will support current flow from D to S Channel behaves as thin-film resistor I D R CH =V DS I G =0 I B =0
41 Trioe Region of Operation I D I G V DS R CH V DS V GS I B V BS = 0 For V DS small I I R D G CH L W W μcox L I 0 B 1 VGS VT COX V GS V T V DS Behaves as a resistor between rain an source Moel in Deep Trioe Region
42 Trioe Region of Operation I D I G R CH V GS I B V BS = 0 R CH For V DS small L W 1 VGS VT COX Resistor is controlle by the voltage V GS Terme a Voltage Controlle Resistor (VCR)
43 n-channel MOSFET Operation an Moel V DS V GS I D V BS I B I G (V DS an V BS small) Increase V GS more Inversion layer in channel thickens R CH will ecrease Terme ohmic or trioe region of operation I D R CH =V DS I G =0 I B =0
44 n-channel MOSFET Operation an Moel V DS V GS I D V BS I B I G (V BS small) Increase V DS Inversion layer thins near rain I D =? I I G =0 D no longer linearly epenent upon V DS Still terme ohmic or trioe region of operation I B =0
45 Trioe Region of Operation I D I G V DS V GS I B V BS = 0 R For V DS larger CH L W 1 VGS VT COX I I D G μc I B OX 0 W L V GS V T V 2 DS V DS Moel in Trioe Region
46 En of Lecture 14
EE 330 Lecture 15. Devices in Semiconductor Processes. Diodes Capacitors MOSFETs
 EE 330 Lecture 15 evices in Semiconuctor Processes ioes Capacitors MOSFETs Review from Last Lecture Basic evices an evice Moels Resistor ioe Capacitor MOSFET BJT Review from Last Lecture Review from Last
EE 330 Lecture 15 evices in Semiconuctor Processes ioes Capacitors MOSFETs Review from Last Lecture Basic evices an evice Moels Resistor ioe Capacitor MOSFET BJT Review from Last Lecture Review from Last
EE 330 Lecture 13. Devices in Semiconductor Processes. Diodes Capacitors Transistors
 EE 330 Lecture 13 evices in Semiconuctor Processes ioes Capacitors Transistors Review from Last Lecture pn Junctions Physical Bounary Separating n-type an p-type regions Extens farther into n-type region
EE 330 Lecture 13 evices in Semiconuctor Processes ioes Capacitors Transistors Review from Last Lecture pn Junctions Physical Bounary Separating n-type an p-type regions Extens farther into n-type region
EE 330 Lecture 12. Devices in Semiconductor Processes. Diodes
 EE 330 Lecture 12 evices in Semiconuctor Processes ioes Review from Last Lecture http://www.ayah.com/perioic/mages/perioic%20table.png Review from Last Lecture Review from Last Lecture Silicon opants in
EE 330 Lecture 12 evices in Semiconuctor Processes ioes Review from Last Lecture http://www.ayah.com/perioic/mages/perioic%20table.png Review from Last Lecture Review from Last Lecture Silicon opants in
EE 330 Lecture 22. Small Signal Modelling Operating Points for Amplifier Applications Amplification with Transistor Circuits
 EE 330 Lecture 22 Small Signal Modelling Operating Points for Amplifier Applications Amplification with Transistor Circuits Exam 2 Friday March 9 Exam 3 Friday April 13 Review Session for Exam 2: 6:00
EE 330 Lecture 22 Small Signal Modelling Operating Points for Amplifier Applications Amplification with Transistor Circuits Exam 2 Friday March 9 Exam 3 Friday April 13 Review Session for Exam 2: 6:00
EE 330 Lecture 13. Devices in Semiconductor Processes. Diodes
 EE 330 Lecture 13 evices in Semiconductor Processes iodes Exam 1 Friday Sept 22 Students may bring 1 page of notes Next weeks HW assignment due on Wed Sept 20 at beginning of class No 5:00 p.m extension
EE 330 Lecture 13 evices in Semiconductor Processes iodes Exam 1 Friday Sept 22 Students may bring 1 page of notes Next weeks HW assignment due on Wed Sept 20 at beginning of class No 5:00 p.m extension
EE 330 Lecture 12. Devices in Semiconductor Processes. Resistors Diodes
 EE 330 Lecture 12 evices in Semiconductor Processes Resistors iodes Exam 1 Friday Feb 16 Students may bring 1 page of notes HW assignment of week of Feb 11 due on Wed Sfeb 14 at beginning of class No 5:00
EE 330 Lecture 12 evices in Semiconductor Processes Resistors iodes Exam 1 Friday Feb 16 Students may bring 1 page of notes HW assignment of week of Feb 11 due on Wed Sfeb 14 at beginning of class No 5:00
EE105 - Fall 2006 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits. Some Administrative Issues
 EE105 - Fall 006 Microelectronic evices and Circuits Prof. Jan M. Rabaey (jan@eecs Lecture 8: MOS Small Signal Model Some Administrative Issues REIEW Session Next Week Tu Sept 6 6:00-7:30pm; 060 alley
EE105 - Fall 006 Microelectronic evices and Circuits Prof. Jan M. Rabaey (jan@eecs Lecture 8: MOS Small Signal Model Some Administrative Issues REIEW Session Next Week Tu Sept 6 6:00-7:30pm; 060 alley
EE105 - Fall 2006 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits
 EE105 - Fall 2006 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Jan M. Rabaey (jan@eecs) Lecture 7: MOS Transistor Some Administrative Issues Lab 2 this week Hw 2 due on We Hw 3 will be posted same day MIDTERM
EE105 - Fall 2006 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Jan M. Rabaey (jan@eecs) Lecture 7: MOS Transistor Some Administrative Issues Lab 2 this week Hw 2 due on We Hw 3 will be posted same day MIDTERM
EE 330. Lecture 35. Parasitic Capacitances in MOS Devices
 EE 330 Lecture 35 Parasitic Capacitances in MOS Devices Exam 2 Wed Oct 24 Exam 3 Friday Nov 16 Review from Last Lecture Cascode Configuration Discuss V CC gm1 gm1 I B VCC V OUT g02 g01 A - β β VXX Q 2
EE 330 Lecture 35 Parasitic Capacitances in MOS Devices Exam 2 Wed Oct 24 Exam 3 Friday Nov 16 Review from Last Lecture Cascode Configuration Discuss V CC gm1 gm1 I B VCC V OUT g02 g01 A - β β VXX Q 2
EE 434 Lecture 12. Process Flow (wrap up) Device Modeling in Semiconductor Processes
 EE 434 Lecture 12 Process Flow (wrap up) Device Modeling in Semiconductor Processes Quiz 6 How have process engineers configured a process to assure that the thickness of the gate oxide for the p-channel
EE 434 Lecture 12 Process Flow (wrap up) Device Modeling in Semiconductor Processes Quiz 6 How have process engineers configured a process to assure that the thickness of the gate oxide for the p-channel
EE 435. Lecture 37. Parasitic Capacitances in MOS Devices. String DAC Parasitic Capacitances
 EE 435 Lecture 37 Parasitic Capacitances in MOS Devices String DAC Parasitic Capacitances Parasitic Capacitors in MOSFET (will initially consider two) Parasitic Capacitors in MOSFET C GCH Parasitic Capacitors
EE 435 Lecture 37 Parasitic Capacitances in MOS Devices String DAC Parasitic Capacitances Parasitic Capacitors in MOSFET (will initially consider two) Parasitic Capacitors in MOSFET C GCH Parasitic Capacitors
EE 330 Lecture 17. MOSFET Modeling CMOS Process Flow
 EE 330 Lecture 17 MOSFET Modeling CMOS Process Flow Review from Last Lecture Limitations of Existing Models V DD V OUT V OUT V DD?? V IN V OUT V IN V IN V DD Switch-Level Models V DD Simple square-law
EE 330 Lecture 17 MOSFET Modeling CMOS Process Flow Review from Last Lecture Limitations of Existing Models V DD V OUT V OUT V DD?? V IN V OUT V IN V IN V DD Switch-Level Models V DD Simple square-law
CMOS Devices. PN junctions and diodes NMOS and PMOS transistors Resistors Capacitors Inductors Bipolar transistors
 CMOS Devices PN junctions and diodes NMOS and PMOS transistors Resistors Capacitors Inductors Bipolar transistors PN Junctions Diffusion causes depletion region D.R. is insulator and establishes barrier
CMOS Devices PN junctions and diodes NMOS and PMOS transistors Resistors Capacitors Inductors Bipolar transistors PN Junctions Diffusion causes depletion region D.R. is insulator and establishes barrier
EE 230 Lecture 33. Nonlinear Circuits and Nonlinear Devices. Diode BJT MOSFET
 EE 230 Lecture 33 Nonlinear Circuits and Nonlinear Devices Diode BJT MOSFET Review from Last Time: n-channel MOSFET Source Gate L Drain W L EFF Poly Gate oxide n-active p-sub depletion region (electrically
EE 230 Lecture 33 Nonlinear Circuits and Nonlinear Devices Diode BJT MOSFET Review from Last Time: n-channel MOSFET Source Gate L Drain W L EFF Poly Gate oxide n-active p-sub depletion region (electrically
Lecture 15: MOS Transistor models: Body effects, SPICE models. Context. In the last lecture, we discussed the modes of operation of a MOS FET:
 Lecture 15: MOS Transistor models: Body effects, SPICE models Context In the last lecture, we discussed the modes of operation of a MOS FET: oltage controlled resistor model I- curve (Square-Law Model)
Lecture 15: MOS Transistor models: Body effects, SPICE models Context In the last lecture, we discussed the modes of operation of a MOS FET: oltage controlled resistor model I- curve (Square-Law Model)
Lecture 9 MOSFET(II) MOSFET I V CHARACTERISTICS(contd.)
 Lecture 9 MOSFET(II) MOSFET I V CHARACTERISTICS(contd.) Outline 1. The saturation region 2. Backgate characteristics Reading Assignment: Howe and Sodini, Chapter 4, Section 4.4 6.012 Spring 2009 Lecture
Lecture 9 MOSFET(II) MOSFET I V CHARACTERISTICS(contd.) Outline 1. The saturation region 2. Backgate characteristics Reading Assignment: Howe and Sodini, Chapter 4, Section 4.4 6.012 Spring 2009 Lecture
EE105 - Fall 2005 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits
 EE105 - Fall 005 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits ecture 7 MOS Transistor Announcements Homework 3, due today Homework 4 due next week ab this week Reading: Chapter 4 1 ecture Material ast lecture
EE105 - Fall 005 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits ecture 7 MOS Transistor Announcements Homework 3, due today Homework 4 due next week ab this week Reading: Chapter 4 1 ecture Material ast lecture
MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics
 ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics ECEN 454 Facts about Transistors So far, we have treated transistors as ideal switches An ON transistor passes
ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics ECEN 454 Facts about Transistors So far, we have treated transistors as ideal switches An ON transistor passes
Lecture 11: MOS Transistor
 Lecture 11: MOS Transistor Prof. Niknejad Lecture Outline Review: MOS Capacitors Regions MOS Capacitors (3.8 3.9) CV Curve Threshold Voltage MOS Transistors (4.1 4.3): Overview Cross-section and layout
Lecture 11: MOS Transistor Prof. Niknejad Lecture Outline Review: MOS Capacitors Regions MOS Capacitors (3.8 3.9) CV Curve Threshold Voltage MOS Transistors (4.1 4.3): Overview Cross-section and layout
EE 330 Lecture 16. Devices in Semiconductor Processes. MOS Transistors
 EE 330 Lecture 16 Devices in Semiconductor Processes MOS Transistors Review from Last Time Model Summary I D I V DS V S I B V BS = 0 0 VS VT W VDS ID = μcox VS VT VDS VS V VDS VS VT L T < W μc ( V V )
EE 330 Lecture 16 Devices in Semiconductor Processes MOS Transistors Review from Last Time Model Summary I D I V DS V S I B V BS = 0 0 VS VT W VDS ID = μcox VS VT VDS VS V VDS VS VT L T < W μc ( V V )
EE 330 Lecture 16. MOSFET Modeling CMOS Process Flow
 EE 330 Lecture 16 MOSFET Modeling CMOS Process Flow Model Extensions 300 Id 250 200 150 100 50 300 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 Vds Existing Model 250 200 Id 150 100 50 Slope is not 0 0 0 1 2 3 4 Actual Device Vds Model
EE 330 Lecture 16 MOSFET Modeling CMOS Process Flow Model Extensions 300 Id 250 200 150 100 50 300 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 Vds Existing Model 250 200 Id 150 100 50 Slope is not 0 0 0 1 2 3 4 Actual Device Vds Model
Lecture 3: CMOS Transistor Theory
 Lecture 3: CMOS Transistor Theory Outline Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics pmos I-V Characteristics Gate and Diffusion Capacitance 2 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
Lecture 3: CMOS Transistor Theory Outline Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics pmos I-V Characteristics Gate and Diffusion Capacitance 2 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
EE 330 Lecture 16. MOS Device Modeling p-channel n-channel comparisons Model consistency and relationships CMOS Process Flow
 EE 330 Lecture 16 MOS Device Modeling p-channel n-channel comparisons Model consistency and relationships CMOS Process Flow Review from Last Time Operation Regions by Applications Id I D 300 250 200 150
EE 330 Lecture 16 MOS Device Modeling p-channel n-channel comparisons Model consistency and relationships CMOS Process Flow Review from Last Time Operation Regions by Applications Id I D 300 250 200 150
Class 05: Device Physics II
 Topics: 1. Introduction 2. NFET Model and Cross Section with Parasitics 3. NFET as a Capacitor 4. Capacitance vs. Voltage Curves 5. NFET as a Capacitor - Band Diagrams at V=0 6. NFET as a Capacitor - Accumulation
Topics: 1. Introduction 2. NFET Model and Cross Section with Parasitics 3. NFET as a Capacitor 4. Capacitance vs. Voltage Curves 5. NFET as a Capacitor - Band Diagrams at V=0 6. NFET as a Capacitor - Accumulation
Introduction and Background
 Analog CMOS Integrated Circuit Design Introduction and Background Dr. Jawdat Abu-Taha Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Islamic University of Gaza jtaha@iugaza.edu.ps 1 Marking Assignments
Analog CMOS Integrated Circuit Design Introduction and Background Dr. Jawdat Abu-Taha Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Islamic University of Gaza jtaha@iugaza.edu.ps 1 Marking Assignments
EE 230 Lecture 31. THE MOS TRANSISTOR Model Simplifcations THE Bipolar Junction TRANSISTOR
 EE 23 Lecture 3 THE MOS TRANSISTOR Model Simplifcations THE Bipolar Junction TRANSISTOR Quiz 3 Determine I X. Assume W=u, L=2u, V T =V, uc OX = - 4 A/V 2, λ= And the number is? 3 8 5 2? 6 4 9 7 Quiz 3
EE 23 Lecture 3 THE MOS TRANSISTOR Model Simplifcations THE Bipolar Junction TRANSISTOR Quiz 3 Determine I X. Assume W=u, L=2u, V T =V, uc OX = - 4 A/V 2, λ= And the number is? 3 8 5 2? 6 4 9 7 Quiz 3
EECS240 Spring Today s Lecture. Lecture 2: CMOS Technology and Passive Devices. Lingkai Kong EECS. EE240 CMOS Technology
 EECS240 Spring 2013 Lecture 2: CMOS Technology and Passive Devices Lingkai Kong EECS Today s Lecture EE240 CMOS Technology Passive devices Motivation Resistors Capacitors (Inductors) Next time: MOS transistor
EECS240 Spring 2013 Lecture 2: CMOS Technology and Passive Devices Lingkai Kong EECS Today s Lecture EE240 CMOS Technology Passive devices Motivation Resistors Capacitors (Inductors) Next time: MOS transistor
EEC 118 Lecture #2: MOSFET Structure and Basic Operation. Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parkhurst Intel Corporation
 EEC 118 Lecture #2: MOSFET Structure and Basic Operation Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parkhurst Intel Corporation Announcements Lab 1 this week, report due next week Bring
EEC 118 Lecture #2: MOSFET Structure and Basic Operation Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parkhurst Intel Corporation Announcements Lab 1 this week, report due next week Bring
Lecture 4: CMOS Transistor Theory
 Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 4: CMOS Transistor Theory David Harris, Harvey Mudd College Kartik Mohanram and Steven Levitan University of Pittsburgh Outline q Introduction q MOS Capacitor q
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 4: CMOS Transistor Theory David Harris, Harvey Mudd College Kartik Mohanram and Steven Levitan University of Pittsburgh Outline q Introduction q MOS Capacitor q
Lecture 11: J-FET and MOSFET
 ENE 311 Lecture 11: J-FET and MOSFET FETs vs. BJTs Similarities: Amplifiers Switching devices Impedance matching circuits Differences: FETs are voltage controlled devices. BJTs are current controlled devices.
ENE 311 Lecture 11: J-FET and MOSFET FETs vs. BJTs Similarities: Amplifiers Switching devices Impedance matching circuits Differences: FETs are voltage controlled devices. BJTs are current controlled devices.
Chapter 13 Small-Signal Modeling and Linear Amplification
 Chapter 13 Small-Signal Modeling and Linear Amplification Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 1/4/12 Chap 13-1 Chapter Goals Understanding of concepts related to: Transistors
Chapter 13 Small-Signal Modeling and Linear Amplification Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 1/4/12 Chap 13-1 Chapter Goals Understanding of concepts related to: Transistors
Chapter 6: Field-Effect Transistors
 Chapter 6: Field-Effect Transistors slamic University of Gaza Dr. Talal Skaik FETs vs. BJTs Similarities: Amplifiers Switching devices mpedance matching circuits Differences: FETs are voltage controlled
Chapter 6: Field-Effect Transistors slamic University of Gaza Dr. Talal Skaik FETs vs. BJTs Similarities: Amplifiers Switching devices mpedance matching circuits Differences: FETs are voltage controlled
SECTION: Circle one: Alam Lundstrom. ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: Spring 2016 April 18, 2016 M. A. Alam and M.S. Lundstrom Purdue University
 NAME: PUID: SECTION: Circle one: Alam Lundstrom ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: April 18, 2016 M A Alam and MS Lundstrom Purdue University This is a closed book exam You may use a calculator and the formula
NAME: PUID: SECTION: Circle one: Alam Lundstrom ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: April 18, 2016 M A Alam and MS Lundstrom Purdue University This is a closed book exam You may use a calculator and the formula
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 26. MOSFET Small Signal Modelling
 ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 26 MOSFET Small Signal Modelling Lecture Outline MOSFET small signal behavior will be considered in the same way as for the diode and BJT Capacitances will be considered
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 26 MOSFET Small Signal Modelling Lecture Outline MOSFET small signal behavior will be considered in the same way as for the diode and BJT Capacitances will be considered
Lecture contents. Metal-semiconductor contact
 1 Lecture contents Metal-semiconuctor contact Electrostatics: Full epletion approimation Electrostatics: Eact electrostatic solution Current Methos for barrier measurement Junctions: general approaches,
1 Lecture contents Metal-semiconuctor contact Electrostatics: Full epletion approimation Electrostatics: Eact electrostatic solution Current Methos for barrier measurement Junctions: general approaches,
Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Lecture 13 - Linear Equivalent Circuits - Outline Announcements Exam Two -
 6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Lecture 13 Linear Equivalent Circuits Outline Announcements Exam Two Coming next week, Nov. 5, 7:309:30 p.m. Review Subthreshold operation of MOSFETs Review Large
6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Lecture 13 Linear Equivalent Circuits Outline Announcements Exam Two Coming next week, Nov. 5, 7:309:30 p.m. Review Subthreshold operation of MOSFETs Review Large
MOS Transistor Theory
 CHAPTER 3 MOS Transistor Theory Outline 2 1. Introduction 2. Ideal I-V Characteristics 3. Nonideal I-V Effects 4. C-V Characteristics 5. DC Transfer Characteristics 6. Switch-level RC Delay Models MOS
CHAPTER 3 MOS Transistor Theory Outline 2 1. Introduction 2. Ideal I-V Characteristics 3. Nonideal I-V Effects 4. C-V Characteristics 5. DC Transfer Characteristics 6. Switch-level RC Delay Models MOS
FIELD-EFFECT TRANSISTORS
 FIEL-EFFECT TRANSISTORS 1 Semiconductor review 2 The MOS capacitor 2 The enhancement-type N-MOS transistor 3 I-V characteristics of enhancement MOSFETS 4 The output characteristic of the MOSFET in saturation
FIEL-EFFECT TRANSISTORS 1 Semiconductor review 2 The MOS capacitor 2 The enhancement-type N-MOS transistor 3 I-V characteristics of enhancement MOSFETS 4 The output characteristic of the MOSFET in saturation
EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices
 EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices Professor Ali Javey 10/02/2007 MS Junctions, Lecture 2 MOS Cap, Lecture 1 Reading: finish chapter14, start chapter16 Announcements Professor Javey will hold his OH at
EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices Professor Ali Javey 10/02/2007 MS Junctions, Lecture 2 MOS Cap, Lecture 1 Reading: finish chapter14, start chapter16 Announcements Professor Javey will hold his OH at
Lecture 10 MOSFET (III) MOSFET Equivalent Circuit Models
 Lecture 10 MOSFET (III) MOSFET Equivalent Circuit Models Outline Lowfrequency smallsignal equivalent circuit model Highfrequency smallsignal equivalent circuit model Reading Assignment: Howe and Sodini;
Lecture 10 MOSFET (III) MOSFET Equivalent Circuit Models Outline Lowfrequency smallsignal equivalent circuit model Highfrequency smallsignal equivalent circuit model Reading Assignment: Howe and Sodini;
MOS Transistor Theory
 MOS Transistor Theory So far, we have viewed a MOS transistor as an ideal switch (digital operation) Reality: less than ideal EE 261 Krish Chakrabarty 1 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
MOS Transistor Theory So far, we have viewed a MOS transistor as an ideal switch (digital operation) Reality: less than ideal EE 261 Krish Chakrabarty 1 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
Lecture 10 MOSFET (III) MOSFET Equivalent Circuit Models
 Lecture 1 MOSFET (III) MOSFET Equivalent Circuit Models Outline Lowfrequency smallsignal equivalent circuit model Highfrequency smallsignal equivalent circuit model Reading Assignment: Howe and Sodini;
Lecture 1 MOSFET (III) MOSFET Equivalent Circuit Models Outline Lowfrequency smallsignal equivalent circuit model Highfrequency smallsignal equivalent circuit model Reading Assignment: Howe and Sodini;
MOSFET Capacitance Model
 MOSFET Capacitance Model So far we discussed the MOSFET DC models. In real circuit operation, the device operates under time varying terminal voltages and the device operation can be described by: 1 small
MOSFET Capacitance Model So far we discussed the MOSFET DC models. In real circuit operation, the device operates under time varying terminal voltages and the device operation can be described by: 1 small
EE 330 Lecture 25. Amplifier Biasing (precursor) Two-Port Amplifier Model
 EE 330 Lecture 25 Amplifier Biasing (precursor) Two-Port Amplifier Model Review from Last Lecture Exam Schedule Exam 2 Friday March 24 Review from Last Lecture Graphical Analysis and Interpretation 2 OX
EE 330 Lecture 25 Amplifier Biasing (precursor) Two-Port Amplifier Model Review from Last Lecture Exam Schedule Exam 2 Friday March 24 Review from Last Lecture Graphical Analysis and Interpretation 2 OX
Module 2. DC Circuit. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur
 Moule 2 DC Circuit Lesson 9 Analysis of c resistive network in presence of one non-linear element Objectives To unerstan the volt (V ) ampere ( A ) characteristics of linear an nonlinear elements. Concept
Moule 2 DC Circuit Lesson 9 Analysis of c resistive network in presence of one non-linear element Objectives To unerstan the volt (V ) ampere ( A ) characteristics of linear an nonlinear elements. Concept
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 5: January 25, 2018 MOS Operating Regions, pt. 1 Lecture Outline! 3 Regions of operation for MOSFET " Subthreshold " Linear " Saturation!
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 5: January 25, 2018 MOS Operating Regions, pt. 1 Lecture Outline! 3 Regions of operation for MOSFET " Subthreshold " Linear " Saturation!
ESE370: Circuit-Level Modeling, Design, and Optimization for Digital Systems. Today. Refinement. Last Time. No Field. Body Contact
 ESE370: Circuit-Level Modeling, Design, and Optimization for Digital Systems Day 10: September 6, 01 MOS Transistor Basics Today MOS Transistor Topology Threshold Operating Regions Resistive Saturation
ESE370: Circuit-Level Modeling, Design, and Optimization for Digital Systems Day 10: September 6, 01 MOS Transistor Basics Today MOS Transistor Topology Threshold Operating Regions Resistive Saturation
Lecture 13 MOSFET as an amplifier with an introduction to MOSFET small-signal model and small-signal schematics. Lena Peterson
 Lecture 13 MOSFET as an amplifier with an introduction to MOSFET small-signal model and small-signal schematics Lena Peterson 2015-10-13 Outline (1) Why is the CMOS inverter gain not infinite? Large-signal
Lecture 13 MOSFET as an amplifier with an introduction to MOSFET small-signal model and small-signal schematics Lena Peterson 2015-10-13 Outline (1) Why is the CMOS inverter gain not infinite? Large-signal
Lecture 210 Physical Aspects of ICs (12/15/01) Page 210-1
 Lecture 210 Physical Aspects of ICs (12/15/01) Page 210-1 LECTURE 210 PHYSICAL ASPECTS OF ICs (READING: Text-Sec. 2.5, 2.6, 2.8) INTRODUCTION Objective Illustrate the physical aspects of integrated circuits
Lecture 210 Physical Aspects of ICs (12/15/01) Page 210-1 LECTURE 210 PHYSICAL ASPECTS OF ICs (READING: Text-Sec. 2.5, 2.6, 2.8) INTRODUCTION Objective Illustrate the physical aspects of integrated circuits
EE 330 Lecture 16. MOSFET Modeling CMOS Process Flow
 EE 330 Lecture 16 MOFET Modeling CMO Process Flow Review from Last Lecture Limitations of Existing Models V V OUT V OUT V?? V IN V OUT V IN V IN V witch-level Models V imple square-law Model Logic ate
EE 330 Lecture 16 MOFET Modeling CMO Process Flow Review from Last Lecture Limitations of Existing Models V V OUT V OUT V?? V IN V OUT V IN V IN V witch-level Models V imple square-law Model Logic ate
Lecture 23: Negative Resistance Osc, Differential Osc, and VCOs
 EECS 142 Lecture 23: Negative Resistance Osc, Differential Osc, and VCOs Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley Copyright c 2005 by Ali M. Niknejad A. M. Niknejad University of California,
EECS 142 Lecture 23: Negative Resistance Osc, Differential Osc, and VCOs Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley Copyright c 2005 by Ali M. Niknejad A. M. Niknejad University of California,
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits. 3. MOS Transistors
 ECE 342 Electronic Circuits 3. MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jschutt@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2 to
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits 3. MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jschutt@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2 to
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 23. The MOSFET Square Law Model
 ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 23 The MOSFET Square Law Model Lecture Outline As with the diode and bipolar, have looked at basic structure of the MOSFET and now turn to derivation of a current
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 23 The MOSFET Square Law Model Lecture Outline As with the diode and bipolar, have looked at basic structure of the MOSFET and now turn to derivation of a current
EE105 Fall 2014 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits. NMOS Transistor Capacitances: Saturation Region
 EE105 Fall 014 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Ming C. Wu wu@eecs.berkeley.edu 511 Sutardja Dai Hall (SDH) 1 NMOS Transistor Capacitances: Saturation Region Drain no longer connected to channel
EE105 Fall 014 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Ming C. Wu wu@eecs.berkeley.edu 511 Sutardja Dai Hall (SDH) 1 NMOS Transistor Capacitances: Saturation Region Drain no longer connected to channel
Chapter 10 AC Analysis Using Phasors
 Chapter 10 AC Analysis Using Phasors 10.1 Introduction We would like to use our linear circuit theorems (Nodal analysis, Mesh analysis, Thevenin and Norton equivalent circuits, Superposition, etc.) to
Chapter 10 AC Analysis Using Phasors 10.1 Introduction We would like to use our linear circuit theorems (Nodal analysis, Mesh analysis, Thevenin and Norton equivalent circuits, Superposition, etc.) to
Charge Storage in the MOS Structure. The Inverted MOS Capacitor (V GB > V Tn )
 The Inverted MO Capacitor (V > V Tn ) We consider the surface potential as Þxed (ÒpinnedÓ) at φ s,max = - φ p φ(x).5 V. V V ox Charge torage in the MO tructure Three regions of operation: Accumulation:
The Inverted MO Capacitor (V > V Tn ) We consider the surface potential as Þxed (ÒpinnedÓ) at φ s,max = - φ p φ(x).5 V. V V ox Charge torage in the MO tructure Three regions of operation: Accumulation:
EE 435. Lecture 22. Offset Voltages
 EE 435 Lecture Offset Voltages . Review from last lecture. Offset Voltage Definition: The input-referred offset voltage is the differential dc input voltage that must be applied to obtain the desired output
EE 435 Lecture Offset Voltages . Review from last lecture. Offset Voltage Definition: The input-referred offset voltage is the differential dc input voltage that must be applied to obtain the desired output
Section 12: Intro to Devices
 Section 12: Intro to Devices Extensive reading materials on reserve, including Robert F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals EE143 Ali Javey Bond Model of Electrons and Holes Si Si Si Si Si Si Si
Section 12: Intro to Devices Extensive reading materials on reserve, including Robert F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals EE143 Ali Javey Bond Model of Electrons and Holes Si Si Si Si Si Si Si
Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory
 Instructor s Resource Manual to accompany Electronic Devices an Circuit Theory Tenth Eition Robert L. Boylesta Louis Nashelsky Upper Sale River, New Jersey Columbus, Ohio Copyright 2009 by Pearson Eucation,
Instructor s Resource Manual to accompany Electronic Devices an Circuit Theory Tenth Eition Robert L. Boylesta Louis Nashelsky Upper Sale River, New Jersey Columbus, Ohio Copyright 2009 by Pearson Eucation,
MOSFET. Id-Vd curve. I DS Transfer curve V G. Lec. 8. Vd=1V. Saturation region. V Th
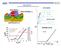 MOSFET Id-Vd curve Saturation region I DS Transfer curve Vd=1V V Th V G 1 0 < V GS < V T V GS > V T V Gs >V T & Small V D > 0 I DS WQ inv WC v WC i V V VDS V V G i T G n T L n I D g V D (g conductance
MOSFET Id-Vd curve Saturation region I DS Transfer curve Vd=1V V Th V G 1 0 < V GS < V T V GS > V T V Gs >V T & Small V D > 0 I DS WQ inv WC v WC i V V VDS V V G i T G n T L n I D g V D (g conductance
Charge-Storage Elements: Base-Charging Capacitance C b
 Charge-Storage Elements: Base-Charging Capacitance C b * Minority electrons are stored in the base -- this charge q NB is a function of the base-emitter voltage * base is still neutral... majority carriers
Charge-Storage Elements: Base-Charging Capacitance C b * Minority electrons are stored in the base -- this charge q NB is a function of the base-emitter voltage * base is still neutral... majority carriers
The Devices. Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic. July 30, 2002
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The Devices July 30, 2002 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The Devices July 30, 2002 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
Chapter 10 Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis Chapter Objectives:
 Chapter 10 Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis Chapter Objectives: Apply previously learn circuit techniques to sinusoidal steady-state analysis. Learn how to apply nodal and mesh analysis in the frequency
Chapter 10 Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis Chapter Objectives: Apply previously learn circuit techniques to sinusoidal steady-state analysis. Learn how to apply nodal and mesh analysis in the frequency
JFET Operating Characteristics: V GS = 0 V 14. JFET Operating Characteristics: V GS = 0 V 15
 J Operating Characteristics: V GS = 0 V 14 V GS = 0 and V DS increases from 0 to a more positive voltage: Gate and Source terminals: at the same potential Drain: at positive potential => reverse biased
J Operating Characteristics: V GS = 0 V 14 V GS = 0 and V DS increases from 0 to a more positive voltage: Gate and Source terminals: at the same potential Drain: at positive potential => reverse biased
The Gradual Channel Approximation for the MOSFET:
 6.01 - Electronic Devices and Circuits Fall 003 The Gradual Channel Approximation for the MOSFET: We are modeling the terminal characteristics of a MOSFET and thus want i D (v DS, v GS, v BS ), i B (v
6.01 - Electronic Devices and Circuits Fall 003 The Gradual Channel Approximation for the MOSFET: We are modeling the terminal characteristics of a MOSFET and thus want i D (v DS, v GS, v BS ), i B (v
Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors
 Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 5/5/11 Chap 4-1 Chapter Goals Describe operation of MOSFETs. Define FET characteristics in operation
Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 5/5/11 Chap 4-1 Chapter Goals Describe operation of MOSFETs. Define FET characteristics in operation
Practice 3: Semiconductors
 Practice 3: Semiconductors Digital Electronic Circuits Semester A 2012 VLSI Fabrication Process VLSI Very Large Scale Integration The ability to fabricate many devices on a single substrate within a given
Practice 3: Semiconductors Digital Electronic Circuits Semester A 2012 VLSI Fabrication Process VLSI Very Large Scale Integration The ability to fabricate many devices on a single substrate within a given
Quantitative MOSFET. Step 1. Connect the MOS capacitor results for the electron charge in the inversion layer Q N to the drain current.
 Quantitative MOSFET Step 1. Connect the MOS capacitor results for the electron charge in the inversion layer Q N to the drain current. V DS _ n source polysilicon gate y = y * 0 x metal interconnect to
Quantitative MOSFET Step 1. Connect the MOS capacitor results for the electron charge in the inversion layer Q N to the drain current. V DS _ n source polysilicon gate y = y * 0 x metal interconnect to
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic. The Devices. July 30, Devices.
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The July 30, 2002 1 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The July 30, 2002 1 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
MOSFET Physics: The Long Channel Approximation
 MOSFET Physics: The ong Channel Approximation A basic n-channel MOSFET (Figure 1) consists of two heavily-doped n-type regions, the Source and Drain, that comprise the main terminals of the device. The
MOSFET Physics: The ong Channel Approximation A basic n-channel MOSFET (Figure 1) consists of two heavily-doped n-type regions, the Source and Drain, that comprise the main terminals of the device. The
MOSFET: Introduction
 E&CE 437 Integrated VLSI Systems MOS Transistor 1 of 30 MOSFET: Introduction Metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) or MOS is widely used for implementing digital designs Its major
E&CE 437 Integrated VLSI Systems MOS Transistor 1 of 30 MOSFET: Introduction Metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) or MOS is widely used for implementing digital designs Its major
EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices
 EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices Professor Ali Javey 10/30/2007 MOSFETs Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 17, 19 Announcements The next HW set is due on Thursday. Midterm 2 is next week!!!! Threshold and Subthreshold
EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices Professor Ali Javey 10/30/2007 MOSFETs Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 17, 19 Announcements The next HW set is due on Thursday. Midterm 2 is next week!!!! Threshold and Subthreshold
6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits
 Page 1 of 12 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits FINAL EXAMINATION Open book. Notes: 1. Unless
Page 1 of 12 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits FINAL EXAMINATION Open book. Notes: 1. Unless
FET Inrush Protection
 FET Inrush Protection Chris Pavlina https://semianalog.com 2015-11-23 CC0 1.0 Universal Abstract It is possible to use a simple one-transistor FET circuit to provie inrush protection for low voltage DC
FET Inrush Protection Chris Pavlina https://semianalog.com 2015-11-23 CC0 1.0 Universal Abstract It is possible to use a simple one-transistor FET circuit to provie inrush protection for low voltage DC
Long Channel MOS Transistors
 Long Channel MOS Transistors The theory developed for MOS capacitor (HO #2) can be directly extended to Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect transistors (MOSFET) by considering the following structure:
Long Channel MOS Transistors The theory developed for MOS capacitor (HO #2) can be directly extended to Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect transistors (MOSFET) by considering the following structure:
MOS Transistor Theory MOSFET Symbols Current Characteristics of MOSFET. MOS Symbols and Characteristics. nmos Enhancement Transistor
 MOS Transistor Theory MOSFET Symbols Current Characteristics of MOSFET Calculation of t and Important 2 nd Order Effects SmallSignal Signal MOSFET Model Summary Material from: CMOS LSI Design By Weste
MOS Transistor Theory MOSFET Symbols Current Characteristics of MOSFET Calculation of t and Important 2 nd Order Effects SmallSignal Signal MOSFET Model Summary Material from: CMOS LSI Design By Weste
Extensive reading materials on reserve, including
 Section 12: Intro to Devices Extensive reading materials on reserve, including Robert F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals EE143 Ali Javey Bond Model of Electrons and Holes Si Si Si Si Si Si Si
Section 12: Intro to Devices Extensive reading materials on reserve, including Robert F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals EE143 Ali Javey Bond Model of Electrons and Holes Si Si Si Si Si Si Si
Biasing the CE Amplifier
 Biasing the CE Amplifier Graphical approach: plot I C as a function of the DC base-emitter voltage (note: normally plot vs. base current, so we must return to Ebers-Moll): I C I S e V BE V th I S e V th
Biasing the CE Amplifier Graphical approach: plot I C as a function of the DC base-emitter voltage (note: normally plot vs. base current, so we must return to Ebers-Moll): I C I S e V BE V th I S e V th
EE 330 Lecture 18. Small-signal Model (very preliminary) Bulk CMOS Process Flow
 EE 330 Lecture 18 Small-signal Model (very preliminary) Bulk CMOS Process Flow Review from Last Lecture How many models of the MOSFET do we have? Switch-level model (2) Square-law model Square-law model
EE 330 Lecture 18 Small-signal Model (very preliminary) Bulk CMOS Process Flow Review from Last Lecture How many models of the MOSFET do we have? Switch-level model (2) Square-law model Square-law model
! MOS Capacitances. " Extrinsic. " Intrinsic. ! Lumped Capacitance Model. ! First Order Capacitor Summary. ! Capacitance Implications
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 7: February, 07 MOS SPICE Models, MOS Parasitic Details Lecture Outline! MOS Capacitances " Extrinsic " Intrinsic! Lumped Capacitance Model!
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 7: February, 07 MOS SPICE Models, MOS Parasitic Details Lecture Outline! MOS Capacitances " Extrinsic " Intrinsic! Lumped Capacitance Model!
Field effect = Induction of an electronic charge due to an electric field Example: Planar capacitor
 JFETs AND MESFETs Introduction Field effect = Induction of an electronic charge due to an electric field Example: Planar capacitor Why would an FET made of a planar capacitor with two metal plates, as
JFETs AND MESFETs Introduction Field effect = Induction of an electronic charge due to an electric field Example: Planar capacitor Why would an FET made of a planar capacitor with two metal plates, as
Lecture #27. The Short Channel Effect (SCE)
 Lecture #27 ANNOUNCEMENTS Design Project: Your BJT design should meet the performance specifications to within 10% at both 300K and 360K. ( β dc > 45, f T > 18 GHz, V A > 9 V and V punchthrough > 9 V )
Lecture #27 ANNOUNCEMENTS Design Project: Your BJT design should meet the performance specifications to within 10% at both 300K and 360K. ( β dc > 45, f T > 18 GHz, V A > 9 V and V punchthrough > 9 V )
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits. Lecture 6 MOS Transistors
 ECE 342 Electronic Circuits Lecture 6 MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits Lecture 6 MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2
ECE 205: Intro Elec & Electr Circuits
 ECE 205: Intro Elec & Electr Circuits Final Exam Study Guide Version 1.00 Created by Charles Feng http://www.fenguin.net ECE 205: Intro Elec & Electr Circuits Final Exam Study Guide 1 Contents 1 Introductory
ECE 205: Intro Elec & Electr Circuits Final Exam Study Guide Version 1.00 Created by Charles Feng http://www.fenguin.net ECE 205: Intro Elec & Electr Circuits Final Exam Study Guide 1 Contents 1 Introductory
6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits
 Page 1 of 10 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Exam No. 2 Thursday, November 5, 2009 7:30 to
Page 1 of 10 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Exam No. 2 Thursday, November 5, 2009 7:30 to
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 13. Diode Small Signal Modeling
 ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 13 iode Small Signal Modeling Lecture Outline Last few lectures have dealt exclusively with modeling and important effects in static (dc) operation ifferent modeling
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 13 iode Small Signal Modeling Lecture Outline Last few lectures have dealt exclusively with modeling and important effects in static (dc) operation ifferent modeling
EE141. EE141-Spring 2006 Digital Integrated Circuits. Administrative Stuff. Class Material. Flash Memory. Read-Only Memory Cells MOS OR ROM
 EE141-pring 2006 igital Integrated Circuits Lecture 29 Flash memory Administrative tuff reat job on projects and posters! Homework #10 due today Lab reports due this week Friday lab in 353 Final exam May
EE141-pring 2006 igital Integrated Circuits Lecture 29 Flash memory Administrative tuff reat job on projects and posters! Homework #10 due today Lab reports due this week Friday lab in 353 Final exam May
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 23, 2018 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Penn ESE 570 Spring 2018 Khanna Lecture Outline! CMOS Process Enhancements! Semiconductor
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 23, 2018 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Penn ESE 570 Spring 2018 Khanna Lecture Outline! CMOS Process Enhancements! Semiconductor
ECE321 Electronics I
 ECE321 Electronics I Lecture 4: Physics of Semiconductor iodes Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: ECE Bldg. 230B Office hours: Tuesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: pzarkesh.unm.edu Slide: 1 Review of Last
ECE321 Electronics I Lecture 4: Physics of Semiconductor iodes Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: ECE Bldg. 230B Office hours: Tuesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: pzarkesh.unm.edu Slide: 1 Review of Last
Figure 1: MOSFET symbols.
 c Copyright 2008. W. Marshall Leach, Jr., Professor, Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. The MOSFET Device Symbols Whereas the JFET has a diode junction between
c Copyright 2008. W. Marshall Leach, Jr., Professor, Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. The MOSFET Device Symbols Whereas the JFET has a diode junction between
EE 435. Lecture 22. Offset Voltages Common Mode Feedback
 EE 435 Lecture Offset Voltages Common Mode Feedback Review from last lecture Offset Voltage Two types of offset voltage: Systematic Offset Voltage Random Offset Voltage V ICQ Definition: The output offset
EE 435 Lecture Offset Voltages Common Mode Feedback Review from last lecture Offset Voltage Two types of offset voltage: Systematic Offset Voltage Random Offset Voltage V ICQ Definition: The output offset
MOS Transistors. Prof. Krishna Saraswat. Department of Electrical Engineering Stanford University Stanford, CA
 MOS Transistors Prof. Krishna Saraswat Department of Electrical Engineering S Stanford, CA 94305 saraswat@stanford.edu 1 1930: Patent on the Field-Effect Transistor! Julius Lilienfeld filed a patent describing
MOS Transistors Prof. Krishna Saraswat Department of Electrical Engineering S Stanford, CA 94305 saraswat@stanford.edu 1 1930: Patent on the Field-Effect Transistor! Julius Lilienfeld filed a patent describing
Lecture 12: MOSFET Devices
 Lecture 12: MOSFET Devices Gu-Yeon Wei Division of Engineering and Applied Sciences Harvard University guyeon@eecs.harvard.edu Wei 1 Overview Reading S&S: Chapter 5.1~5.4 Supplemental Reading Background
Lecture 12: MOSFET Devices Gu-Yeon Wei Division of Engineering and Applied Sciences Harvard University guyeon@eecs.harvard.edu Wei 1 Overview Reading S&S: Chapter 5.1~5.4 Supplemental Reading Background
P. R. Nelson 1 ECE418 - VLSI. Midterm Exam. Solutions
 P. R. Nelson 1 ECE418 - VLSI Midterm Exam Solutions 1. (8 points) Draw the cross-section view for A-A. The cross-section view is as shown below.. ( points) Can you tell which of the metal1 regions is the
P. R. Nelson 1 ECE418 - VLSI Midterm Exam Solutions 1. (8 points) Draw the cross-section view for A-A. The cross-section view is as shown below.. ( points) Can you tell which of the metal1 regions is the
Studio 3 Review MOSFET as current source Small V DS : Resistor (value controlled by V GS ) Large V DS : Current source (value controlled by V GS )
 Studio 3 Review MOSFET as current source Small V DS : Resistor (value controlled by V GS ) Large V DS : Current source (value controlled by V GS ) 1 Simulation Review: Circuit Fixed V GS, Sweep V DS I
Studio 3 Review MOSFET as current source Small V DS : Resistor (value controlled by V GS ) Large V DS : Current source (value controlled by V GS ) 1 Simulation Review: Circuit Fixed V GS, Sweep V DS I
VLSI Design and Simulation
 VLSI Design and Simulation Performance Characterization Topics Performance Characterization Resistance Estimation Capacitance Estimation Inductance Estimation Performance Characterization Inverter Voltage
VLSI Design and Simulation Performance Characterization Topics Performance Characterization Resistance Estimation Capacitance Estimation Inductance Estimation Performance Characterization Inverter Voltage
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 7: February 4, 2016 MOS SPICE Models, MOS Parasitic Details Lecture Outline! MOS Capacitances " Extrinsic " Intrinsic! Lumped Capacitance
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 7: February 4, 2016 MOS SPICE Models, MOS Parasitic Details Lecture Outline! MOS Capacitances " Extrinsic " Intrinsic! Lumped Capacitance
EE 230 Lecture 20. Nonlinear Op Amp Applications. The Comparator Nonlinear Analysis Methods
 EE 230 Lecture 20 Nonlinear Op Amp Applications The Comparator Nonlinear Analysis Methods Quiz 14 What is the major purpose of compensation when designing an operatinal amplifier? And the number is? 1
EE 230 Lecture 20 Nonlinear Op Amp Applications The Comparator Nonlinear Analysis Methods Quiz 14 What is the major purpose of compensation when designing an operatinal amplifier? And the number is? 1
6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Spring 2005
 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Spring 2005 May 16, 2005 Final Exam (200 points) -OPEN BOOK- Problem NAME RECITATION TIME 1 2 3 4 5 Total General guidelines (please read carefully before starting):
6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Spring 2005 May 16, 2005 Final Exam (200 points) -OPEN BOOK- Problem NAME RECITATION TIME 1 2 3 4 5 Total General guidelines (please read carefully before starting):
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET )
 Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
