Paragraph Proof, Two-Column Proof, Construction Proof, and Flow Chart Proof
|
|
|
- Harvey Russell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 .3 Forms of Proof Paragraph Proof, Two-Column Proof, Construction Proof, and Flow Chart Proof Learning Goals Key Terms In this lesson, you will: Use the addition and subtraction properties of equality. Use the reflexive, substitution, and transitive properties. Write a paragraph proof. Prove theorems involving angles. Complete a two-column proof. Perform a construction proof. Complete a flow chart proof. Addition Property of Equality Subtraction Property of Equality Reflexive Property Substitution Property Transitive Property flow chart proof two-column proof paragraph proof construction proof Right Angle Congruence Theorem Congruent Supplement Theorem Congruent Complement Theorem Vertical Angle Theorem Have you ever heard the famous phrase, The proof is in the pudding? If you stop to think about what this phrase means, you might be left scratching your head! The phrase used now is actually a shortened version of the original phrase, The proof of the pudding is in the eating. This phrase meant that the pudding recipe may appear to be delicious, include fresh ingredients, and may even look delicious after it is made. However, the only way to really prove that the pudding is delicious is by eating it! Today it is used to imply that the quality or truth of something can only be determined by putting it into action. For example, you don t know how good an idea is until you actually test the idea. Can you think of any other popular phrases that don t seem to make sense? Perhaps you should do a little research to find out where these phrases came from. 153
2 Problem 1 Properties of Real Numbers in Geometry Many properties of real numbers can be applied in geometry. These properties are important when making conjectures and proving new theorems. The Addition Property of Equality states: If a, b, and c are real numbers and a 5 b, then a 1 c 5 b 1 c. The Addition Property of Equality can be applied to angle measures, segment measures, and distances. If m 1 5 m, then m 1 1 m 3 5 m 1 m 3. If m AB 5 m CD, then m AB 1 m EF 5 m CD 1 m EF. If AB 5 CD, then AB 1 EF 5 CD 1 EF. 1. Sketch a diagram and write a statement that applies the Addition Property of Equality to angle measures.. Sketch a diagram and write a statement that applies the Addition Property of Equality to segment measures. 154 Chapter Introduction to Proof
3 The Subtraction Property of Equality states: If a, b, and c are real numbers and a 5 b, then a c 5 b c. The Subtraction Property of Equality can be applied to angle measures, segment measures, and distances. If m 1 5 m, then m 1 m 3 5 m m 3. _ If m AB 5 m CD, then m AB m EF 5 m CD m EF. If AB 5 CD, then AB EF 5 CD EF. 3. Sketch a diagram and write a statement that applies the Subtraction Property of Equality to angle measures. 4. Sketch a diagram and write a statement that applies the Subtraction Property of Equality to segment measures..3 Paragraph Proof, Two-Column Proof, Construction Proof, and Flow Chart Proof 155
4 The Reflexive Property states: If a is a real number, then a 5 a. The Reflexive Property can be applied to angle measures, segment measures, distances, congruent angles, and congruent segments. m 1 5 m 1 m AB 5 m AB AB 5 AB Congruent angles: 1 1 Congruent segments: AB AB 5. Sketch a diagram and write a statement that applies the Reflexive Property to angles. 6. Sketch a diagram and write a statement that applies the Reflexive Property to segments. 156 Chapter Introduction to Proof
5 The Substitution Property states: If a and b are real numbers and a 5 b, then a can be substituted for b. The Substitution Property can be applied to angle measures, segment measures, and distances. If m and m 5 56, then m 1 5 m. If m AB 5 4 mm and m CD 5 4 mm, then m AB 5 m CD. If AB 5 1 ft and CD 5 1 ft, then AB 5 CD. 7. Sketch a diagram and write a statement that applies the Substitution Property to angles. 8. Sketch a diagram and write a statement that applies the Substitution Property to segments..3 Paragraph Proof, Two-Column Proof, Construction Proof, and Flow Chart Proof 157
6 The Transitive Property states: If a, b, and c are real numbers, a 5 b, and b 5 c, then a 5 c. The Transitive Property can be applied to angle measures, segment measures, distances, congruent angles, and congruent segments. If m 1 5 m and m 5 m 3, then m 1 5 m 3. If m AB 5 m CD and m CD 5 m EF, then m AB 5 m EF. If AB 5 CD and CD 5 EF, then AB 5 EF. Congruent angles: If 1 and 3, then 1 3. Congruent segments: If AB CD and CD EF, then AB EF. 9. Sketch a diagram and write a statement that applies the Transitive Property to angles. Sometimes mathematical properties can seem obvious. So, why do we need them? When you learn about proofs, you will need these properties to justify your statements and conclusions. 10. Sketch a diagram and write a statement that applies the Transitive Property to congruent segments. 158 Chapter Introduction to Proof
Paragraph Proof, Two-Column Proof, Construction Proof, and Flow Chart Proof
 .3 Forms of Proof Paragraph Proof, Two-Column Proof, Construction Proof, and Flow Chart Proof Learning Goals Key Terms In this lesson, you will: Use the addition and subtraction properties of equality.
.3 Forms of Proof Paragraph Proof, Two-Column Proof, Construction Proof, and Flow Chart Proof Learning Goals Key Terms In this lesson, you will: Use the addition and subtraction properties of equality.
2-5 Algebraic Proof. Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz. Holt McDougal Geometry
 2-5 Algebraic Proof Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Geometry Warm Up Solve each equation. 1. 3x + 5 = 17 4. x = 4 2. r 3.5 = 8.7 r = 12.2 3. 4t 7 = 8t + 3 t = 5 2 n = 38 5. 2(y 5) 20 = 0 y = 15
2-5 Algebraic Proof Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Geometry Warm Up Solve each equation. 1. 3x + 5 = 17 4. x = 4 2. r 3.5 = 8.7 r = 12.2 3. 4t 7 = 8t + 3 t = 5 2 n = 38 5. 2(y 5) 20 = 0 y = 15
Algebraic Proof. Warm Up Solve each equation. Agenda: Warm-Up/Pull SG Algebraic Proofs Notes Practice Proofs. 1. 3x + 5 = 17.
 Warm Up Solve each equation. 1. 3x + 5 = 17 4. x = 4 2. r 3.5 = 8.7 r = 12.2 3. 4t 7 = 8t + 3 t = 5 2 n = 38 Agenda: Warm-Up/Pull SG Algebraic Proofs Notes Practice Proofs 5. 2(y 5) 20 = 0 y = 15 Essential
Warm Up Solve each equation. 1. 3x + 5 = 17 4. x = 4 2. r 3.5 = 8.7 r = 12.2 3. 4t 7 = 8t + 3 t = 5 2 n = 38 Agenda: Warm-Up/Pull SG Algebraic Proofs Notes Practice Proofs 5. 2(y 5) 20 = 0 y = 15 Essential
2-5 Algebraic Proof. Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz. Holt McDougal Geometry
 2-5 Algebraic Proof Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Geometry Bellringer Solve each equation. 1. 3x + 5 = 17 4. x = 4 2. r 3.5 = 8.7 r = 12.2 3. 4t 7 = 8t + 3 t = 5 2 n = 38 5. 2(y 5) 20 = 0 y =
2-5 Algebraic Proof Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Geometry Bellringer Solve each equation. 1. 3x + 5 = 17 4. x = 4 2. r 3.5 = 8.7 r = 12.2 3. 4t 7 = 8t + 3 t = 5 2 n = 38 5. 2(y 5) 20 = 0 y =
Introduction to Proof 2
 Introduction to Proof The popular game Sudoku seems so simple but requires the use of logic to come up with a solution..1 A Little Dash of Logic Foundations for Proof........................ 135. And Now
Introduction to Proof The popular game Sudoku seems so simple but requires the use of logic to come up with a solution..1 A Little Dash of Logic Foundations for Proof........................ 135. And Now
2-1 Using Inductive Reasoning to Make Conjectures
 CHAPTER 2 Chapter Review 2-1 Using Inductive Reasoning to Make Conjectures Find the next term in each pattern. 1. 6, 12, 18,... 2. January, April, July,... 3. The table shows the score on a reaction time
CHAPTER 2 Chapter Review 2-1 Using Inductive Reasoning to Make Conjectures Find the next term in each pattern. 1. 6, 12, 18,... 2. January, April, July,... 3. The table shows the score on a reaction time
2-6 Algebraic Proof. State the property that justifies each statement. 1. If m 1 = m 2 and m 2 = m 3, then m 1 = m 3. SOLUTION:
 State the property that justifies each 1. If m 1 = m 2 and m 2 = m 3, then m 1 = m 3. There are two parts to the hypotheses. "If m 1 = m 2 and m 2 = m 3, then m 1 = m 3. "The end of the first part of the
State the property that justifies each 1. If m 1 = m 2 and m 2 = m 3, then m 1 = m 3. There are two parts to the hypotheses. "If m 1 = m 2 and m 2 = m 3, then m 1 = m 3. "The end of the first part of the
Unit 1: Introduction to Proof
 Unit 1: Introduction to Proof Prove geometric theorems both formally and informally using a variety of methods. G.CO.9 Prove and apply theorems about lines and angles. Theorems include but are not restricted
Unit 1: Introduction to Proof Prove geometric theorems both formally and informally using a variety of methods. G.CO.9 Prove and apply theorems about lines and angles. Theorems include but are not restricted
LESSON 2 5 CHAPTER 2 OBJECTIVES
 LESSON 2 5 CHAPTER 2 OBJECTIVES POSTULATE a statement that describes a fundamental relationship between the basic terms of geometry. THEOREM a statement that can be proved true. PROOF a logical argument
LESSON 2 5 CHAPTER 2 OBJECTIVES POSTULATE a statement that describes a fundamental relationship between the basic terms of geometry. THEOREM a statement that can be proved true. PROOF a logical argument
2.2 Day 1: Date: Geometry
 2.2 Day 1: Date: Geometry A Conditional Statement is an statement. The is the part following if. The is the part following then. Ex 1). What are the hypothesis and the conclusion of the conditional statement?
2.2 Day 1: Date: Geometry A Conditional Statement is an statement. The is the part following if. The is the part following then. Ex 1). What are the hypothesis and the conclusion of the conditional statement?
Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 2 7) CCSS Then/Now Postulate 2.10: Protractor Postulate Postulate 2.11: Angle Addition Postulate Example 1: Use the
 Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 2 7) CCSS Then/Now Postulate 2.10: Protractor Postulate Postulate 2.11: Angle Addition Postulate Example 1: Use the Angle Addition Postulate Theorems 2.3 and 2.4 Example
Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 2 7) CCSS Then/Now Postulate 2.10: Protractor Postulate Postulate 2.11: Angle Addition Postulate Example 1: Use the Angle Addition Postulate Theorems 2.3 and 2.4 Example
2.6 algebraic proofs. September 13, algebraic proofs ink.notebook. Page 71. Page 72 Page 70. Page 73. Standards. 2.
 2.6 algebraic proofs ink.notebook September 13, 2017 Page 71 Page 72 Page 70 2.6 algebraic proofs Page 73 Lesson Objectives Standards Lesson Notes 2.6 Algebraic Proofs Press the tabs to view details. 1
2.6 algebraic proofs ink.notebook September 13, 2017 Page 71 Page 72 Page 70 2.6 algebraic proofs Page 73 Lesson Objectives Standards Lesson Notes 2.6 Algebraic Proofs Press the tabs to view details. 1
Chapter 2: Reasoning and Proof
 Name: Chapter 2: Reasoning and Proof Guided Notes Geometry Fall Semester 2.1 Use Inductive Reasoning CH. 2 Guided Notes, page 2 Term Definition Example conjecture An unproven statement that is based on
Name: Chapter 2: Reasoning and Proof Guided Notes Geometry Fall Semester 2.1 Use Inductive Reasoning CH. 2 Guided Notes, page 2 Term Definition Example conjecture An unproven statement that is based on
2-1. Inductive Reasoning and Conjecture. Lesson 2-1. What You ll Learn. Active Vocabulary
 2-1 Inductive Reasoning and Conjecture What You ll Learn Scan Lesson 2-1. List two headings you would use to make an outline of this lesson. 1. Active Vocabulary 2. New Vocabulary Fill in each blank with
2-1 Inductive Reasoning and Conjecture What You ll Learn Scan Lesson 2-1. List two headings you would use to make an outline of this lesson. 1. Active Vocabulary 2. New Vocabulary Fill in each blank with
Geometry Study Guide. Name: Class: Date: Matching
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Geometry Study Guide Matching Match each vocabulary term with its definition. a. conjecture e. biconditional statement b. inductive reasoning f. hypothesis c. deductive reasoning
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Geometry Study Guide Matching Match each vocabulary term with its definition. a. conjecture e. biconditional statement b. inductive reasoning f. hypothesis c. deductive reasoning
Over Lesson 2 7 Justify the statement with a property of equality or a property of congruence. Justify the statement with a property of equality or a
 Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 2 7) CCSS Then/Now Postulate 2.10: Protractor Postulate Postulate 2.11: Angle Addition Postulate Example 1: Use the Angle Addition Postulate Theorems 2.3 and 2.4 Example
Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 2 7) CCSS Then/Now Postulate 2.10: Protractor Postulate Postulate 2.11: Angle Addition Postulate Example 1: Use the Angle Addition Postulate Theorems 2.3 and 2.4 Example
Geometry - Chapter 2 Earn-A-Try Test
 Name: Geometry - Chapter 2 Earn-A-Try Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Use CAPITAL letters only!! Ex: A,B,C,D; Not a,b,c,d. 1. Write a
Name: Geometry - Chapter 2 Earn-A-Try Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Use CAPITAL letters only!! Ex: A,B,C,D; Not a,b,c,d. 1. Write a
GEOMETRY. 2.5 Proving Statements about Segments and Angles
 GEOMETRY 2.5 Proving Statements about Segments and Angles ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can I prove a geometric statement? REVIEW! Today we are starting proofs. This means we will be using ALL of the theorems
GEOMETRY 2.5 Proving Statements about Segments and Angles ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can I prove a geometric statement? REVIEW! Today we are starting proofs. This means we will be using ALL of the theorems
2-6 Geometric Proof. Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz. Holt Geometry
 2-6 Geometric Proof Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Warm Up Determine whether each statement is true or false. If false, give a counterexample. 1. It two angles are complementary, then they are
2-6 Geometric Proof Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Warm Up Determine whether each statement is true or false. If false, give a counterexample. 1. It two angles are complementary, then they are
Chapter 2 Segment Measurement and Coordinate Graphing
 Geometry Concepts Chapter 2 Segment Measurement and Coordinate Graphing 2.2 Find length segments (1.3) 2.3 Compare lengths of segments (1.3) 2.3 Find midpoints of segments (1.7) 2.5 Calculate coordinates
Geometry Concepts Chapter 2 Segment Measurement and Coordinate Graphing 2.2 Find length segments (1.3) 2.3 Compare lengths of segments (1.3) 2.3 Find midpoints of segments (1.7) 2.5 Calculate coordinates
Section 2-1. Chapter 2. Make Conjectures. Example 1. Reasoning and Proof. Inductive Reasoning and Conjecture
 Chapter 2 Reasoning and Proof Section 2-1 Inductive Reasoning and Conjecture Make Conjectures Inductive reasoning - reasoning that uses a number of specific examples to arrive at a conclusion Conjecture
Chapter 2 Reasoning and Proof Section 2-1 Inductive Reasoning and Conjecture Make Conjectures Inductive reasoning - reasoning that uses a number of specific examples to arrive at a conclusion Conjecture
Geometry Unit 2 Notes Logic, Reasoning and Proof
 Geometry Unit 2 Notes Logic, Reasoning and Proof Review Vocab.: Complementary, Supplementary and Vertical angles. Syllabus Objective: 2.1 - The student will differentiate among definitions, postulates,
Geometry Unit 2 Notes Logic, Reasoning and Proof Review Vocab.: Complementary, Supplementary and Vertical angles. Syllabus Objective: 2.1 - The student will differentiate among definitions, postulates,
NAME DATE PERIOD. Inductive Reasoning and Conjecture. Make a conjecture based on the given information. Draw a figure to illustrate your conjecture.
 2-1 NAME DATE PERIOD Skills Practice Inductive Reasoning and Conjecture Make a conjecture about the next item in each sequence. 1. 2. 4, 1, 2, 5, 8 3. 6, 1 1, 5, 9 2 2,4 4. 2, 4, 8, 16, 32 Make a conjecture
2-1 NAME DATE PERIOD Skills Practice Inductive Reasoning and Conjecture Make a conjecture about the next item in each sequence. 1. 2. 4, 1, 2, 5, 8 3. 6, 1 1, 5, 9 2 2,4 4. 2, 4, 8, 16, 32 Make a conjecture
2.8 Proving angle relationships cont. ink.notebook. September 20, page 84 page cont. page 86. page 85. Standards. Cont.
 2.8 Proving angle relationships cont. ink.notebook page 84 page 83 2.8 cont. page 85 page 86 Lesson Objectives Standards Lesson Notes 2.8 Proving Angle Relationships Cont. Press the tabs to view details.
2.8 Proving angle relationships cont. ink.notebook page 84 page 83 2.8 cont. page 85 page 86 Lesson Objectives Standards Lesson Notes 2.8 Proving Angle Relationships Cont. Press the tabs to view details.
HONORS GEOMETRY CHAPTER 2 WORKBOOK
 HONORS GEOMETRY CHAPTER 2 WORKBOOK FALL 2016 Chapter 2 Miscellaneous: The Structure of Geometry Vocabulary Definition Example Elements: 1. Deductive Structure Postulate (axiom) Example: Definitions Reversed:
HONORS GEOMETRY CHAPTER 2 WORKBOOK FALL 2016 Chapter 2 Miscellaneous: The Structure of Geometry Vocabulary Definition Example Elements: 1. Deductive Structure Postulate (axiom) Example: Definitions Reversed:
Geometry Unit 2 Notes Logic, Reasoning and Proof
 Geometry Unit Notes Logic, Reasoning and Proof Review Vocab.: Complementary, Supplementary and Vertical angles. Syllabus Objective:. - The student will justify conjectures and solve problem using inductive
Geometry Unit Notes Logic, Reasoning and Proof Review Vocab.: Complementary, Supplementary and Vertical angles. Syllabus Objective:. - The student will justify conjectures and solve problem using inductive
Chapter 2. Reasoning and Proof
 Chapter 2 Reasoning and Proof 2.1 Inductive Reasoning 2.2 Analyze Conditional Statements 2.3 Apply Deductive Reasoning 2.4 Use Postulates and Diagrams 2.5 Algebraic Proofs 2.6 Segments and Angles Proofs
Chapter 2 Reasoning and Proof 2.1 Inductive Reasoning 2.2 Analyze Conditional Statements 2.3 Apply Deductive Reasoning 2.4 Use Postulates and Diagrams 2.5 Algebraic Proofs 2.6 Segments and Angles Proofs
Geometry Unit 2 Notes Logic, Reasoning and Proof
 Geometry Unit Notes Logic, Reasoning and Proof Review Vocab.: Complementary, Supplementary and Vertical angles. Syllabus Objective:. - The student will justify conjectures and solve problem using inductive
Geometry Unit Notes Logic, Reasoning and Proof Review Vocab.: Complementary, Supplementary and Vertical angles. Syllabus Objective:. - The student will justify conjectures and solve problem using inductive
Inductive Reasoning. Courage is resistance to fear, mastery of fear, not absence of fear. Mark Twain
 Inductive Reasoning Courage is resistance to fear, mastery of fear, not absence of fear. Mark Twain Inductive Reasoning O Inductive Reasoning is the process of observing a pattern and making a conjecture
Inductive Reasoning Courage is resistance to fear, mastery of fear, not absence of fear. Mark Twain Inductive Reasoning O Inductive Reasoning is the process of observing a pattern and making a conjecture
GEOMETRY UNIT 1 WORKBOOK. CHAPTER 2 Reasoning and Proof
 GEOMETRY UNIT 1 WORKBOOK CHAPTER 2 Reasoning and Proof 1 2 Notes 5 : Using postulates and diagrams, make valid conclusions about points, lines, and planes. I) Reminder: Rules that are accepted without
GEOMETRY UNIT 1 WORKBOOK CHAPTER 2 Reasoning and Proof 1 2 Notes 5 : Using postulates and diagrams, make valid conclusions about points, lines, and planes. I) Reminder: Rules that are accepted without
Angle-Side-Angle Congruence Theorem
 ngle to the Left of Me, ngle to the Right of Me ngle-side-ngle ongruence Theorem. Learning Goals In this lesson, you will: Explore the ngle-side-ngle ongruence Theorem using constructions. Explore the
ngle to the Left of Me, ngle to the Right of Me ngle-side-ngle ongruence Theorem. Learning Goals In this lesson, you will: Explore the ngle-side-ngle ongruence Theorem using constructions. Explore the
If two sides of a triangle are congruent, then it is an isosceles triangle.
 1. What is the hypothesis of the conditional statement If two sides of a triangle are congruent, then it is an isosceles triangle. two sides of a triangle are congruent it is an isosceles triangle If two
1. What is the hypothesis of the conditional statement If two sides of a triangle are congruent, then it is an isosceles triangle. two sides of a triangle are congruent it is an isosceles triangle If two
Name: Class: Date: B. The twentieth term is A. D. There is not enough information.
 Class: Date: Chapter 2 Review 1. Based on the pattern, what are the next two terms of the sequence? 9, 15, 21, 27,... A. 33, 972 B. 39, 45 C. 162, 972 D. 33, 39 2. What conjecture can you make about the
Class: Date: Chapter 2 Review 1. Based on the pattern, what are the next two terms of the sequence? 9, 15, 21, 27,... A. 33, 972 B. 39, 45 C. 162, 972 D. 33, 39 2. What conjecture can you make about the
Adding and Subtracting Terms
 Adding and Subtracting Terms 1.6 OBJECTIVES 1.6 1. Identify terms and like terms 2. Combine like terms 3. Add algebraic expressions 4. Subtract algebraic expressions To find the perimeter of (or the distance
Adding and Subtracting Terms 1.6 OBJECTIVES 1.6 1. Identify terms and like terms 2. Combine like terms 3. Add algebraic expressions 4. Subtract algebraic expressions To find the perimeter of (or the distance
Homework 10: p.147: 17-41, 45
 2-4B: Writing Proofs Homework 10: p.147: 17-41, 45 Learning Objectives: Analyze figures to identify and use postulates about points, lines and planes Analyze and construct viable arguments in several proof
2-4B: Writing Proofs Homework 10: p.147: 17-41, 45 Learning Objectives: Analyze figures to identify and use postulates about points, lines and planes Analyze and construct viable arguments in several proof
10.1 Tangents to Circles. Geometry Mrs. Spitz Spring 2005
 10.1 Tangents to Circles Geometry Mrs. Spitz Spring 2005 Objectives/Assignment Identify segments and lines related to circles. Use properties of a tangent to a circle. Assignment: Chapter 10 Definitions
10.1 Tangents to Circles Geometry Mrs. Spitz Spring 2005 Objectives/Assignment Identify segments and lines related to circles. Use properties of a tangent to a circle. Assignment: Chapter 10 Definitions
Segment Measurement, Midpoints, & Congruence
 Lesson 2 Lesson 2, page 1 Glencoe Geometry Chapter 1.4 & 1.5 Segment Measurement, Midpoints, & Congruence Last time, we looked at points, lines, and planes. Today we are going to further investigate lines,
Lesson 2 Lesson 2, page 1 Glencoe Geometry Chapter 1.4 & 1.5 Segment Measurement, Midpoints, & Congruence Last time, we looked at points, lines, and planes. Today we are going to further investigate lines,
2.1 If Then Statements
 Chapter Deductive Reasoning Learn deductive logic Do your first - column proof New Theorems and Postulates **PUT YOUR LAWYER HAT ON!!. If Then Statements Recognize the hypothesis and conclusion of an ifthen
Chapter Deductive Reasoning Learn deductive logic Do your first - column proof New Theorems and Postulates **PUT YOUR LAWYER HAT ON!!. If Then Statements Recognize the hypothesis and conclusion of an ifthen
Lesson 2-6: Graphs of Absolute Value Equations
 Where we re headed today Today we re going to take the net graphing step we ll learn how to graph absolute value equations. Here are the three things you are going to need to be able to do: 1. Match an
Where we re headed today Today we re going to take the net graphing step we ll learn how to graph absolute value equations. Here are the three things you are going to need to be able to do: 1. Match an
Lesson 9.1 Skills Practice
 Lesson 9.1 Skills Practice Name Date Earth Measure Introduction to Geometry and Geometric Constructions Vocabulary Write the term that best completes the statement. 1. means to have the same size, shape,
Lesson 9.1 Skills Practice Name Date Earth Measure Introduction to Geometry and Geometric Constructions Vocabulary Write the term that best completes the statement. 1. means to have the same size, shape,
Segment Measurement, Midpoints, & Congruence
 Lesson 2 Lesson 2, page 1 Glencoe Geometry Chapter 1.4 & 1.5 Segment Measurement, Midpoints, & Congruence Last time, we looked at points, lines, and planes. Today we are going to further investigate lines,
Lesson 2 Lesson 2, page 1 Glencoe Geometry Chapter 1.4 & 1.5 Segment Measurement, Midpoints, & Congruence Last time, we looked at points, lines, and planes. Today we are going to further investigate lines,
Comparing Multiple Representations of Functions
 Are All Functions Created Equal? Comparing Multiple Representations of Functions 1.3 Learning Goals In this lesson, you will: Identify equivalent forms of functions in various representations. Model situations
Are All Functions Created Equal? Comparing Multiple Representations of Functions 1.3 Learning Goals In this lesson, you will: Identify equivalent forms of functions in various representations. Model situations
Chapter 2. Reasoning and Proof
 Chapter 2 Reasoning and Proof 2.1 Use Inductive Reasoning Objective: Describe patterns and use deductive reasoning. Essential Question: How do you use inductive reasoning in mathematics? Common Core: CC.9-12.G.CO.9
Chapter 2 Reasoning and Proof 2.1 Use Inductive Reasoning Objective: Describe patterns and use deductive reasoning. Essential Question: How do you use inductive reasoning in mathematics? Common Core: CC.9-12.G.CO.9
GH Chapter 2 Test Review-includes Constructions
 Name: Class: Date: Show All Work. Test will include 2 proofs from the proof practice worksheet assigned week of 9/8. GH Chapter 2 Test Review-includes Constructions ID: A 1. What is the value of x? State
Name: Class: Date: Show All Work. Test will include 2 proofs from the proof practice worksheet assigned week of 9/8. GH Chapter 2 Test Review-includes Constructions ID: A 1. What is the value of x? State
GEOMETRY CHAPTER 2 REVIEW / PRACTICE TEST
 GEOMETRY CHAPTER 2 REVIEW / PRACTICE TEST Name: Date: Hour: SECTION 1: Rewrite the conditional statement in If-Then Form. Then write its Converse, Inverse, and Contrapositive. 1) Adjacent angles share
GEOMETRY CHAPTER 2 REVIEW / PRACTICE TEST Name: Date: Hour: SECTION 1: Rewrite the conditional statement in If-Then Form. Then write its Converse, Inverse, and Contrapositive. 1) Adjacent angles share
CMA Geometry Unit 1 Introduction Week 2 Notes
 CMA Geometry Unit 1 Introduction Week 2 Notes Assignment: 9. Defined Terms: Definitions betweenness of points collinear points coplanar points space bisector of a segment length of a segment line segment
CMA Geometry Unit 1 Introduction Week 2 Notes Assignment: 9. Defined Terms: Definitions betweenness of points collinear points coplanar points space bisector of a segment length of a segment line segment
Algebra, Part I. x m x = n xm i x n = x m n = 1
 Lesson 7 Algebra, Part I Rules and Definitions Rules Additive property of equality: If a, b, and c represent real numbers, and if a=b, then a + c = b + c. Also, c + a = c + b Multiplicative property of
Lesson 7 Algebra, Part I Rules and Definitions Rules Additive property of equality: If a, b, and c represent real numbers, and if a=b, then a + c = b + c. Also, c + a = c + b Multiplicative property of
Mr. Northcutt's Math Classes Class Presentation
 Mr. Northcutt's Math Classes Class Presentation October 2, 2009 (22) Transition Math Math 1 Math 2 1 Transition Math Daily Summary Announcement(s): Retests: Can take a retest is you work with me or Ms.
Mr. Northcutt's Math Classes Class Presentation October 2, 2009 (22) Transition Math Math 1 Math 2 1 Transition Math Daily Summary Announcement(s): Retests: Can take a retest is you work with me or Ms.
The following statements are conditional: Underline each hypothesis and circle each conclusion.
 Geometry Unit 2 Reasoning and Proof 2-1 Conditional Statements Conditional Statement a statement which has a hypothesis and conclusion, often called an if-then statement. Conditional statements are contain
Geometry Unit 2 Reasoning and Proof 2-1 Conditional Statements Conditional Statement a statement which has a hypothesis and conclusion, often called an if-then statement. Conditional statements are contain
GEOMETRY. 2.4 Algebraic Reasoning
 GEOMETRY 2.4 Algebraic Reasoning 2.4 ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can algebraic properties help you solve an equation? GOALS Use properties from algebra. Use properties to justify statements. ADDITION PROPERTY
GEOMETRY 2.4 Algebraic Reasoning 2.4 ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can algebraic properties help you solve an equation? GOALS Use properties from algebra. Use properties to justify statements. ADDITION PROPERTY
Name. A Farmer s Fields
 Student #1 3 triangles $150 2 triangles 6 triangles $100 $300 6 triangles $300 3 triangles $150 1 triangle $50 2 triangles $100 1 triangle $50 I put it in triangles $ 50.00 50 50 50 150 24 1200.00 x 2
Student #1 3 triangles $150 2 triangles 6 triangles $100 $300 6 triangles $300 3 triangles $150 1 triangle $50 2 triangles $100 1 triangle $50 I put it in triangles $ 50.00 50 50 50 150 24 1200.00 x 2
Geometry Unit 1 Segment 3 Practice Questions
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ Geometry Unit 1 Segment 3 Practice Questions Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Based on the pattern, what are the
Name: Class: _ Date: _ Geometry Unit 1 Segment 3 Practice Questions Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Based on the pattern, what are the
ACTIVITY 15 Continued Lesson 15-2
 Continued PLAN Pacing: 1 class period Chunking the Lesson Examples A, B Try These A B #1 2 Example C Lesson Practice TEACH Bell-Ringer Activity Read the introduction with students and remind them of the
Continued PLAN Pacing: 1 class period Chunking the Lesson Examples A, B Try These A B #1 2 Example C Lesson Practice TEACH Bell-Ringer Activity Read the introduction with students and remind them of the
Geometry Blizzard Bag Day 1
 Name: Class: Date: Geometry Blizzard Bag Day 1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Draw and label a pair of opposite rays FG and FH. a. c.
Name: Class: Date: Geometry Blizzard Bag Day 1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Draw and label a pair of opposite rays FG and FH. a. c.
Chapter 03 Test. 1 Complete the congruence statement. A B C D. 2 Complete the congruence statement. A B C D
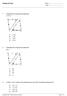 hapter 03 Test Name: ate: 1 omplete the congruence statement. 2 omplete the congruence statement. 3 If, which of the following can you NOT conclude as being true? opyright 2005-2006 by Pearson Education
hapter 03 Test Name: ate: 1 omplete the congruence statement. 2 omplete the congruence statement. 3 If, which of the following can you NOT conclude as being true? opyright 2005-2006 by Pearson Education
Toss 1. Fig.1. 2 Heads 2 Tails Heads/Tails (H, H) (T, T) (H, T) Fig.2
 1 Basic Probabilities The probabilities that we ll be learning about build from the set theory that we learned last class, only this time, the sets are specifically sets of events. What are events? Roughly,
1 Basic Probabilities The probabilities that we ll be learning about build from the set theory that we learned last class, only this time, the sets are specifically sets of events. What are events? Roughly,
Geometry. Unit 2- Reasoning and Proof. Name:
 Geometry Unit 2- Reasoning and Proof Name: 1 Geometry Chapter 2 Reasoning and Proof ***In order to get full credit for your assignments they must me done on time and you must SHOW ALL WORK. *** 1. (2-1)
Geometry Unit 2- Reasoning and Proof Name: 1 Geometry Chapter 2 Reasoning and Proof ***In order to get full credit for your assignments they must me done on time and you must SHOW ALL WORK. *** 1. (2-1)
Chapter Start Thinking. 3.1 Warm Up. 1. Sample answer: 3. CG. 5. Sample answer: FE and FG. 6. Sample answer: D. 3.
 7. ( x + )( x 7) 8. ( x )( x + ) 9. ( x 7)( x + ) 0. ( x 5)( x ). ( x )( x ). ( x + )( x 9) Chapter. Start Thinking B. ( x + )( x ). ( x + )( x ) 5. ( x + 5)( x 5) 6. ( x )( x + ) A C 7. ( x 5)( x 7) 8.
7. ( x + )( x 7) 8. ( x )( x + ) 9. ( x 7)( x + ) 0. ( x 5)( x ). ( x )( x ). ( x + )( x 9) Chapter. Start Thinking B. ( x + )( x ). ( x + )( x ) 5. ( x + 5)( x 5) 6. ( x )( x + ) A C 7. ( x 5)( x 7) 8.
2.4 Algebraic and Congruence Properties
 2.4 Algebraic and Congruence Properties Learning Objectives Understand basic properties of equality and congruence. Solve equations and justify each step in the solution. Use a 2-column format to prove
2.4 Algebraic and Congruence Properties Learning Objectives Understand basic properties of equality and congruence. Solve equations and justify each step in the solution. Use a 2-column format to prove
Test Review: Geometry L2 Period 1 and 3 Test Date: Friday November 6
 Test Review: Geometry L2 Period 1 and 3 Test Date: Friday November 6 Things it would be a good idea to know: 1) All terms, definitions, properties, postulates, theorems from Unit 1 and Unit 2 2) How to
Test Review: Geometry L2 Period 1 and 3 Test Date: Friday November 6 Things it would be a good idea to know: 1) All terms, definitions, properties, postulates, theorems from Unit 1 and Unit 2 2) How to
Chapter 2. Reasoning and Proof
 Chapter 2 Reasoning and Proof 2.1 Use Inductive Reasoning Objective: Describe patterns and use deductive reasoning. Essential Question: How do you use inductive reasoning in mathematics? Common Core: CC.9-12.G.CO.9
Chapter 2 Reasoning and Proof 2.1 Use Inductive Reasoning Objective: Describe patterns and use deductive reasoning. Essential Question: How do you use inductive reasoning in mathematics? Common Core: CC.9-12.G.CO.9
Geometry/Trig Name: Date: Lesson 1-11 Writing the Equation of a Perpendicular Bisector
 Name: Date: Lesson 1-11 Writing the Equation of a Perpendicular Bisector Learning Goals: #14: How do I write the equation of a perpendicular bisector? Warm-up What is the equation of a line that passes
Name: Date: Lesson 1-11 Writing the Equation of a Perpendicular Bisector Learning Goals: #14: How do I write the equation of a perpendicular bisector? Warm-up What is the equation of a line that passes
Instructional Goal Terminal Objective Assessment Item Students will generate twocolumn
 eport Two Objectives Instructional Goal Terminal Objective ssessment Item Students will generate twocolumn geometric proofs. PS Given a statement to be proven, a diagram, and a given statement student
eport Two Objectives Instructional Goal Terminal Objective ssessment Item Students will generate twocolumn geometric proofs. PS Given a statement to be proven, a diagram, and a given statement student
Unit 5, Lesson 4.3 Proving the Pythagorean Theorem using Similarity
 Unit 5, Lesson 4.3 Proving the Pythagorean Theorem using Similarity Geometry includes many definitions and statements. Once a statement has been shown to be true, it is called a theorem. Theorems, like
Unit 5, Lesson 4.3 Proving the Pythagorean Theorem using Similarity Geometry includes many definitions and statements. Once a statement has been shown to be true, it is called a theorem. Theorems, like
Chapter 2: Geometric Reasoning Review
 Geometry B Name: Date: Block: Chapter 2: Geometric Reasoning Review Show all work to receive full credit. This will be collected. 1) What is the next item in the pattern? 1, 2, 4, 8,... 2) Find the next
Geometry B Name: Date: Block: Chapter 2: Geometric Reasoning Review Show all work to receive full credit. This will be collected. 1) What is the next item in the pattern? 1, 2, 4, 8,... 2) Find the next
Geometry First Semester Exam Review
 Geometry First Semester Exam Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Name three points that are collinear. a. points T, Q, and R c. points
Geometry First Semester Exam Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Name three points that are collinear. a. points T, Q, and R c. points
1-2 Measuring and Constructing Segments
 1-2 Measuring and Constructing Segments Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Objectives Use length and midpoint of a segment. Construct midpoints and congruent segments. Vocabulary coordinate midpoint
1-2 Measuring and Constructing Segments Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Objectives Use length and midpoint of a segment. Construct midpoints and congruent segments. Vocabulary coordinate midpoint
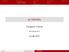 = (, ) V λ (1) λ λ ( + + ) P = [ ( ), (1)] ( ) ( ) = ( ) ( ) ( 0 ) ( 0 ) = ( 0 ) ( 0 ) 0 ( 0 ) ( ( 0 )) ( ( 0 )) = ( ( 0 )) ( ( 0 )) ( + ( 0 )) ( + ( 0 )) = ( + ( 0 )) ( ( 0 )) P V V V V V P V P V V V
= (, ) V λ (1) λ λ ( + + ) P = [ ( ), (1)] ( ) ( ) = ( ) ( ) ( 0 ) ( 0 ) = ( 0 ) ( 0 ) 0 ( 0 ) ( ( 0 )) ( ( 0 )) = ( ( 0 )) ( ( 0 )) ( + ( 0 )) ( + ( 0 )) = ( + ( 0 )) ( ( 0 )) P V V V V V P V P V V V
Lesson. Warm Up deductive 2. D. 3. I will go to the store; Law of Detachment. Lesson Practice 31
 Warm Up 1. deductive 2. D b. a and b intersect 1 and 2 are supplementary 2 and 3 are supplementary 3. I will go to the store; Law of Detachment Lesson Practice a. 1. 1 and 2 are. 2. 1 and 3 are. 3. m 1
Warm Up 1. deductive 2. D b. a and b intersect 1 and 2 are supplementary 2 and 3 are supplementary 3. I will go to the store; Law of Detachment Lesson Practice a. 1. 1 and 2 are. 2. 1 and 3 are. 3. m 1
UNIT 1: SIMILARITY, CONGRUENCE, AND PROOFS. 1) Figure A'B'C'D'F' is a dilation of figure ABCDF by a scale factor of 1. 2 centered at ( 4, 1).
 EOCT Practice Items 1) Figure A'B'C'D'F' is a dilation of figure ABCDF by a scale factor of 1. 2 centered at ( 4, 1). The dilation is Which statement is true? A. B. C. D. AB B' C' A' B' BC AB BC A' B'
EOCT Practice Items 1) Figure A'B'C'D'F' is a dilation of figure ABCDF by a scale factor of 1. 2 centered at ( 4, 1). The dilation is Which statement is true? A. B. C. D. AB B' C' A' B' BC AB BC A' B'
Find the next item in the pattern below. The red square moves in the counterclockwise direction. The next figure is.
 CHAPTER 2 Study Guide: Review Organizer Objective: Help students organize and review key concepts and skills presented in Chapter 2. Online Edition Multilingual Glossary Countdown Week 4 Vocabulary biconditional
CHAPTER 2 Study Guide: Review Organizer Objective: Help students organize and review key concepts and skills presented in Chapter 2. Online Edition Multilingual Glossary Countdown Week 4 Vocabulary biconditional
Transversals. What is a proof? A proof is logical argument in which each statement you make is backed up by a statement that is accepted true.
 Chapter 2: Angles, Parallel Lines and Transversals Lesson 2.1: Writing a Proof Getting Ready: Your math teacher asked you to solve the equation: 4x 3 = 2x + 25. What is a proof? A proof is logical argument
Chapter 2: Angles, Parallel Lines and Transversals Lesson 2.1: Writing a Proof Getting Ready: Your math teacher asked you to solve the equation: 4x 3 = 2x + 25. What is a proof? A proof is logical argument
Unit 1 Lesson 6: Seeing Structure in Expressions
 Unit 1 Lesson 6: Seeing Structure in Expressions Objective: Students will be able to use inductive reasoning to try to solve problems that are puzzle like in nature. CCSS: A.SSE.1.b, A.SSE.2 Example Problems
Unit 1 Lesson 6: Seeing Structure in Expressions Objective: Students will be able to use inductive reasoning to try to solve problems that are puzzle like in nature. CCSS: A.SSE.1.b, A.SSE.2 Example Problems
Lesson 8: Graphs of Simple Non Linear Functions
 Student Outcomes Students examine the average rate of change for non linear functions and learn that, unlike linear functions, non linear functions do not have a constant rate of change. Students determine
Student Outcomes Students examine the average rate of change for non linear functions and learn that, unlike linear functions, non linear functions do not have a constant rate of change. Students determine
Introduction to Vector Spaces Linear Algebra, Fall 2008
 Introduction to Vector Spaces Linear Algebra, Fall 2008 1 Echoes Consider the set P of polynomials with real coefficients, which includes elements such as 7x 3 4 3 x + π and 3x4 2x 3. Now we can add, subtract,
Introduction to Vector Spaces Linear Algebra, Fall 2008 1 Echoes Consider the set P of polynomials with real coefficients, which includes elements such as 7x 3 4 3 x + π and 3x4 2x 3. Now we can add, subtract,
Lecture The Definite Integral (1 of 2) MTH 124
 We now begin our study of the integral or anti-derivative. Up to this point we have explored how to calculate the rate of change of a quantity. We now consider a related problem. That is, given the rate
We now begin our study of the integral or anti-derivative. Up to this point we have explored how to calculate the rate of change of a quantity. We now consider a related problem. That is, given the rate
Questions. Exercise (1)
 Questions Exercise (1) (1) hoose the correct answer: 1) The acute angle supplements. angle. a) acute b) obtuse c) right d) reflex 2) The right angle complements angle whose measure is. a) 0 b) 45 c) 90
Questions Exercise (1) (1) hoose the correct answer: 1) The acute angle supplements. angle. a) acute b) obtuse c) right d) reflex 2) The right angle complements angle whose measure is. a) 0 b) 45 c) 90
Assignment Assignment for Lesson 6.1
 Assignment Assignment for Lesson.1 Name Date Constructing Congruent Triangles or Not Constructing Triangles In each exercise, do the following. a. Use the given information to construct a triangle. b.
Assignment Assignment for Lesson.1 Name Date Constructing Congruent Triangles or Not Constructing Triangles In each exercise, do the following. a. Use the given information to construct a triangle. b.
HW Set #1: Problems #1-8 For #1-4, choose the best answer for each multiple choice question.
 Geometry Homework Worksheets: Chapter 2 HW Set #1: Problems #1-8 For #1-4, choose the best answer for each multiple choice question. 1. Which of the following statements is/are always true? I. adjacent
Geometry Homework Worksheets: Chapter 2 HW Set #1: Problems #1-8 For #1-4, choose the best answer for each multiple choice question. 1. Which of the following statements is/are always true? I. adjacent
CHAPTER 3. Congruences. Congruence: definitions and properties
 CHAPTER 3 Congruences Part V of PJE Congruence: definitions and properties Definition. (PJE definition 19.1.1) Let m > 0 be an integer. Integers a and b are congruent modulo m if m divides a b. We write
CHAPTER 3 Congruences Part V of PJE Congruence: definitions and properties Definition. (PJE definition 19.1.1) Let m > 0 be an integer. Integers a and b are congruent modulo m if m divides a b. We write
Neutral Geometry. October 25, c 2009 Charles Delman
 Neutral Geometry October 25, 2009 c 2009 Charles Delman Taking Stock: where we have been; where we are going Set Theory & Logic Terms of Geometry: points, lines, incidence, betweenness, congruence. Incidence
Neutral Geometry October 25, 2009 c 2009 Charles Delman Taking Stock: where we have been; where we are going Set Theory & Logic Terms of Geometry: points, lines, incidence, betweenness, congruence. Incidence
Day 1 Inductive Reasoning and Conjectures
 Formal Geometry Chapter 2 Logic and Proofs Day 1 Inductive Reasoning and Conjectures Objectives: SWBAT form a conjecture, and check it SWBAT use counterexamples to disprove a conjecture Logic the use of
Formal Geometry Chapter 2 Logic and Proofs Day 1 Inductive Reasoning and Conjectures Objectives: SWBAT form a conjecture, and check it SWBAT use counterexamples to disprove a conjecture Logic the use of
Inductive Reasoning. Inductive Reasoning. Inductive Reasoning. Inductive Reasoning. Logic (with Truth Tables) If-Then Statements
 Intro to Proofs (t-charts and paragraph) www.njctl.org Table of Contents When asked a question you don't know the answer to: 1) You can take a known to be true. Using conjecture is Contents Bob is taller
Intro to Proofs (t-charts and paragraph) www.njctl.org Table of Contents When asked a question you don't know the answer to: 1) You can take a known to be true. Using conjecture is Contents Bob is taller
(b) Follow-up visits: December, May, October, March. (c ) 10, 4, -2, -8,..
 Geometry Honors - Chapter 2 Reasoning and Proof Section 2-1 Inductive Reasoning and Conjecture I can explore inductive and deductive reasoning. I can find counterexamples to disprove conjectures. I can
Geometry Honors - Chapter 2 Reasoning and Proof Section 2-1 Inductive Reasoning and Conjecture I can explore inductive and deductive reasoning. I can find counterexamples to disprove conjectures. I can
7 th Grade Math Scope and Sequence Student Outcomes (Objectives Skills/Verbs)
 own discovery of the Big BIG IDEA: How are different types of numbers used to represent real life situations? Why is it necessary to have different types of numbers for different situations? Pg 762 1-4(no
own discovery of the Big BIG IDEA: How are different types of numbers used to represent real life situations? Why is it necessary to have different types of numbers for different situations? Pg 762 1-4(no
Elijah Helps A Poor Widow 1 Kings 17:8-24
 Lesson 098 Elijah Helps A Poor Widow 1 Kings 17:8-24 MEMORY VERSE 1 KIN GS 17:15 S o she went away and did according to the word of Elijah; and she and he and her household ate for m any days. WHAT YOU
Lesson 098 Elijah Helps A Poor Widow 1 Kings 17:8-24 MEMORY VERSE 1 KIN GS 17:15 S o she went away and did according to the word of Elijah; and she and he and her household ate for m any days. WHAT YOU
1-2 Measuring and Constructing Segments
 Warm Up Simplify. 1. 7 ( 3) 10 2. 1 ( 13) 12 3. 7 1 8 Solve each equation. 4. 2x + 3 = 9x 11 5. 3x = 4x 5 2 5 6. How many numbers are there between and? Infinitely many Standard U1S2 Use length and midpoint
Warm Up Simplify. 1. 7 ( 3) 10 2. 1 ( 13) 12 3. 7 1 8 Solve each equation. 4. 2x + 3 = 9x 11 5. 3x = 4x 5 2 5 6. How many numbers are there between and? Infinitely many Standard U1S2 Use length and midpoint
Q1: Lesson 6 Parallel Lines Handouts Page 1
 6.1 Warmup Per ate Instructions: Justify each statement using your Vocab/Theorems ook. If!! =!! and!! = 50, then!! = 50. P F S If!" is rotated 180 around point F, then!"!" If!!"# +!!"# = 180, then!"# is
6.1 Warmup Per ate Instructions: Justify each statement using your Vocab/Theorems ook. If!! =!! and!! = 50, then!! = 50. P F S If!" is rotated 180 around point F, then!"!" If!!"# +!!"# = 180, then!"# is
32. SOLVING LINEAR EQUATIONS IN ONE VARIABLE
 get the complete book: /getfulltextfullbook.htm 32. SOLVING LINEAR EQUATIONS IN ONE VARIABLE classifying families of sentences In mathematics, it is common to group together sentences of the same type
get the complete book: /getfulltextfullbook.htm 32. SOLVING LINEAR EQUATIONS IN ONE VARIABLE classifying families of sentences In mathematics, it is common to group together sentences of the same type
Cumulative Test. 101 Holt Geometry. Name Date Class
 Choose the best answer. 1. Which of PQ and QR contains P? A PQ only B QR only C Both D Neither. K is between J and L. JK 3x, and KL x 1. If JL 16, what is JK? F 7 H 9 G 8 J 13 3. SU bisects RST. If mrst
Choose the best answer. 1. Which of PQ and QR contains P? A PQ only B QR only C Both D Neither. K is between J and L. JK 3x, and KL x 1. If JL 16, what is JK? F 7 H 9 G 8 J 13 3. SU bisects RST. If mrst
We have seen that the symbols,,, and can guide the logical
 CHAPTER 7 Quantified Statements We have seen that the symbols,,, and can guide the logical flow of algorithms. We have learned how to use them to deconstruct many English sentences into a symbolic form.
CHAPTER 7 Quantified Statements We have seen that the symbols,,, and can guide the logical flow of algorithms. We have learned how to use them to deconstruct many English sentences into a symbolic form.
Unit 5: Congruency. Part 1 of 3: Intro to Congruency & Proof Pieces. Lessons 5-1 through 5-4
 Name: Geometry Period Unit 5: Congruency Part 1 of 3: Intro to Congruency & Proof Pieces Lessons 5-1 through 5-4 In this unit you must bring the following materials with you to class every day: Please
Name: Geometry Period Unit 5: Congruency Part 1 of 3: Intro to Congruency & Proof Pieces Lessons 5-1 through 5-4 In this unit you must bring the following materials with you to class every day: Please
UNIT 1: SIMILARITY, CONGRUENCE, AND PROOFS. 1) Figure A'B'C'D'F' is a dilation of figure ABCDF by a scale factor of 1. 2 centered at ( 4, 1).
 1) Figure A'B'C'D'F' is a dilation of figure ABCDF by a scale factor of 1. 2 centered at ( 4, 1). The dilation is Which statement is true? A. B. C. D. AB B' C' A' B' BC AB BC A' B' B' C' AB BC A' B' D'
1) Figure A'B'C'D'F' is a dilation of figure ABCDF by a scale factor of 1. 2 centered at ( 4, 1). The dilation is Which statement is true? A. B. C. D. AB B' C' A' B' BC AB BC A' B' B' C' AB BC A' B' D'
Common Segments Theorem (Flowchart Proof)
 Common Segments Theorem (Flowchart Proof) Below is a flow proof proving the Common Segments Theorem. The Common Segments Theorem states that if a segment is combined with two congruent segments then the
Common Segments Theorem (Flowchart Proof) Below is a flow proof proving the Common Segments Theorem. The Common Segments Theorem states that if a segment is combined with two congruent segments then the
Ch 2 Practice. Multiple Choice
 Ch 2 Practice Multiple Choice 1. For the conditional statement, write the converse and a biconditional statement. If a figure is a right triangle with sides a, b, and c, then a 2 + b 2 = c 2. a. Converse:
Ch 2 Practice Multiple Choice 1. For the conditional statement, write the converse and a biconditional statement. If a figure is a right triangle with sides a, b, and c, then a 2 + b 2 = c 2. a. Converse:
Algebraic Expressions Combining Like Terms
 LESSON 2 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Today I am: combining like terms. Algebraic Expressions Combining Like Terms So that I can: simplify polynomial expressions. 2ft 3fttht5h 5ft 6h I ll know I have it when I
LESSON 2 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Today I am: combining like terms. Algebraic Expressions Combining Like Terms So that I can: simplify polynomial expressions. 2ft 3fttht5h 5ft 6h I ll know I have it when I
1-2 Measuring and Constructing Segments
 1-2 Measuring and Constructing Segments Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Objectives Use length and midpoint of a segment. Construct midpoints and congruent segments. Vocabulary coordinate midpoint distance
1-2 Measuring and Constructing Segments Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Objectives Use length and midpoint of a segment. Construct midpoints and congruent segments. Vocabulary coordinate midpoint distance
Geometry CP Review WS
 Geometry CP 2.1-2.5 Review WS Name 1. a) Use inductive reasoning to sketch the fourth figure in each pattern. Figure 4 b) How many squares are in the next object? 2. Use inductive reasoning to write the
Geometry CP 2.1-2.5 Review WS Name 1. a) Use inductive reasoning to sketch the fourth figure in each pattern. Figure 4 b) How many squares are in the next object? 2. Use inductive reasoning to write the
Modular Arithmetic Instructor: Marizza Bailey Name:
 Modular Arithmetic Instructor: Marizza Bailey Name: 1. Introduction to Modular Arithmetic If someone asks you what day it is 145 days from now, what would you answer? Would you count 145 days, or find
Modular Arithmetic Instructor: Marizza Bailey Name: 1. Introduction to Modular Arithmetic If someone asks you what day it is 145 days from now, what would you answer? Would you count 145 days, or find
3. Understand The Laws of Detachment and Syllogism 4. Appreciate a simple Ham Sandwich.
 Lesson 4 Lesson 4, page 1 of 8 Glencoe Geometry Chapter 2.2 and 2.3 If-Then Statements & Deductive Reasoning By the end of this lesson, you should be able to 1. Write a statement in if-then Form. 2. To
Lesson 4 Lesson 4, page 1 of 8 Glencoe Geometry Chapter 2.2 and 2.3 If-Then Statements & Deductive Reasoning By the end of this lesson, you should be able to 1. Write a statement in if-then Form. 2. To
