Large-Scale Feature Learning with Spike-and-Slab Sparse Coding
|
|
|
- Lora Reeves
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Large-Scale Feature Learning with Spike-and-Slab Sparse Coding Ian J. Goodfellow, Aaron Courville, Yoshua Bengio ICML 2012 Presented by Xin Yuan January 17,
2 Outline Contributions Spike-and-Slab Sparse Coding (S3C) Model Algorithm: Variational EM for S3C Results 2
3 Contributions Introduce a new feature learning and extraction procedure based on a factor model, Spike-and-Slab Sparse Coding (S3C). Overcome two major scaling challenges. 1) Scale inference in the spike-and-slab coding model to work for the large problem sizes required for object recognition. 2) Use the enhanced regularization properties of spikeand-slab sparse coding to scale object recognition techniques to work with large numbers of classes and small amounts of labeled data. 3
4 The Spike-and-Slab Sparse Coding Model 1. Latent binary spike variables 2. Latent real-valued slab variables, 3. Real-valued D-dimensional visible vector : the logistic sigmoid function : a set of biases on the spike variables : governs the linear dependence of s on h. : the element-wise product of h and s. : governs the linear dependence of v on s. The columns of W have unit norm. and are diagonal precision matrices. The state of a hidden unit is best understood as 4
5 Comparison to Sparse Coding 1. One can derive the S3C model from sparse coding by replacing the factorial Cauchy or Laplace prior with a spike-and-slab prior. 2. One drawback of sparse coding is that the latent variables are not merely encouraged to be sparse; they are encouraged to remain close to 0, even when they are active. S3C uses b and s. 3. Another drawback of sparse coding is that the factors are not actually sparse in the generative distribution. 4. Sparse coding is also difficult to integrate into a deep generative model of data such as natural images. 5
6 Comparison to Restricted Boltzmann Machines Energy based model: S3C moves from an undirected ssrbm model to the directed graphical model. A variant of the Effects: 1. Partition function 2. Posterior 3. Prior 6
7 Review of RBM(1) A restricted Boltzmann machine (RBM) is a generative stochastic neural network that can learn a probability distribution over its set of inputs. RBMs are a variant of Boltzmann machines, with the restriction that their neurons must form a bipartite graph: they have input units, corresponding to features of their inputs, hidden units that are trained, and each connection in an RBM must connect a visible unit to a hidden unit. RBMs have found applications in dimensionality reduction, classification, collaborative filtering and topic modeling. They can be trained in either supervised or unsupervised ways, depending on the task. Diagram of a restricted Boltzmann machine with three visible units and four hidden units (no bias units). 7
8 Review of RBM(2) A joint conguration, (v; h) of the visible and hidden units has an energy given by: The network assigns a probability to every possible pair of a visible and a hidden vector via this energy function: The probability that the network assigns to a visible vector, Geoffrey Hinton (2010). A Practical Guide to Training Restricted Boltzmann Machines. UTML TR , University of Toronto. 8
9 Effects: from Undirected Modeling to Directed Modeling 1. Partition function The partition function becomes tractable. 2. Posterior RBMs have a factorial posterior, but S3C and sparse coding have a complicated posterior due to the explaining away effect. Being able to selectively activate a small set of features that cooperate to explain the input likely provides S3C a major advantage in discriminative capability. 3. Prior S3C introduces a factorial prior. This probably makes it a poor generative model, but this is not a problem for the purpose of feature discovery. 9
10 Variational EM for S3C A variant of the EM algorithm 1) E-step, compute a variational approximation to the posterior rather than the posterior itself. 2) M-step, a closed-form solution. Online learning with small gradient steps on the M-step objective worked better in practice. The goal of the variational E-step is to maximize the energy functional with respect to a distribution Q over the unobserved variables. Selecting Q that minimizes the KL divergence: is drawn from a restricted family of distributions. This family can be chosen to ensure that Q is tractable. 10
11 Parallel Updates to All Units (1) 1) Start each iteration by partially minimizing the KL divergence with respect to The terms of the KL divergence that depend on make up a quadratic function so this can be minimized via conjugate gradient descent. Implement conjugate gradient descent efficiently by using the R-operator to perform Hessian vector products rather than computing the entire Hessian explicitly. This step is guaranteed to improve the KL divergence on each iteration. 2) Next update in parallel, shrinking the update by a damping coefficient. This approach is not guaranteed to decrease the KL divergence on each iteration but it is a widely applied approach. Pearlmutter, B. A. (1994). Fast exact multiplication by the Hessian. Neural Computation, 6(1),
12 Parallel Updates to All Units (2) Replace the conjugate gradient update to with a more heuristic approach. In practice faster convergence, reaching equally good solutions. Use a parallel damped update on much like. An additional heuristic modication to the update rule which is made necessary by the unbounded nature of. Clip the update to so that if has the opposite sign from, its magnitude is at most. This prevents a case where multiple mutually inhibitory s units inhibit each other so strongly that rather than being driven to 0 they change sign and actually increase in magnitude. This case is a failure mode of the parallel updates that can result in amplifying without bound if clipping is not used. 12
13 13
14 14
15 15
16 Performance Results 16
17 17
18 18
19 Classification Results 19
20 CIFAR-100 Classification Results The CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 are labeled subsets of the 80 million tiny images dataset. They were collected by Alex Krizhevsky, Vinod Nair, and Geoffrey Hinton. The CIFAR-10 dataset consists of x32 colour images in 10 classes, with 6000 images per class. There are training images and test images. The CIFAR-100 has 100 classes containing 600 images each. There are 500 training images and 100 testing images per class. The 100 classes in the CIFAR-100 are grouped into 20 superclasses. Each image comes with a "fine" label (the class to which it belongs) and a "coarse" label (the superclass to which it belongs). 20
21 Transfer Learning Challenge NIPS 2011 Workshop on Challenges in Learning Hierarchical Models. Dataset: 32x32 color images, including 100,000 unlabeled examples, 50,000 labeled examples of 100 object classes not present in the test set, and 120 labeled examples of 10 object classes present in the test set. Results: A test set accuracy of 48.6 %. This approach disregards the 50,000 labels and treats this transfer learning problem as a semisupervised learning problem. Experimented with some transfer learning techniques but the transferfree approach performed best on leave-one-out cross-validation on the 120 example training set, so we chose to enter the transfer-free technique in the challenge. 21
A graph contains a set of nodes (vertices) connected by links (edges or arcs)
 BOLTZMANN MACHINES Generative Models Graphical Models A graph contains a set of nodes (vertices) connected by links (edges or arcs) In a probabilistic graphical model, each node represents a random variable,
BOLTZMANN MACHINES Generative Models Graphical Models A graph contains a set of nodes (vertices) connected by links (edges or arcs) In a probabilistic graphical model, each node represents a random variable,
Unsupervised Learning
 CS 3750 Advanced Machine Learning hkc6@pitt.edu Unsupervised Learning Data: Just data, no labels Goal: Learn some underlying hidden structure of the data P(, ) P( ) Principle Component Analysis (Dimensionality
CS 3750 Advanced Machine Learning hkc6@pitt.edu Unsupervised Learning Data: Just data, no labels Goal: Learn some underlying hidden structure of the data P(, ) P( ) Principle Component Analysis (Dimensionality
Deep Learning Srihari. Deep Belief Nets. Sargur N. Srihari
 Deep Belief Nets Sargur N. Srihari srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu Topics 1. Boltzmann machines 2. Restricted Boltzmann machines 3. Deep Belief Networks 4. Deep Boltzmann machines 5. Boltzmann machines for continuous
Deep Belief Nets Sargur N. Srihari srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu Topics 1. Boltzmann machines 2. Restricted Boltzmann machines 3. Deep Belief Networks 4. Deep Boltzmann machines 5. Boltzmann machines for continuous
Joint Training of Partially-Directed Deep Boltzmann Machines
 Joint Training of Partially-Directed Deep Boltzmann Machines Ian J. Goodfellow goodfeli@iro.umontreal.ca Aaron Courville aaron.courville@umontreal.ca Yoshua Bengio Département d Informatique et de Recherche
Joint Training of Partially-Directed Deep Boltzmann Machines Ian J. Goodfellow goodfeli@iro.umontreal.ca Aaron Courville aaron.courville@umontreal.ca Yoshua Bengio Département d Informatique et de Recherche
UNSUPERVISED LEARNING
 UNSUPERVISED LEARNING Topics Layer-wise (unsupervised) pre-training Restricted Boltzmann Machines Auto-encoders LAYER-WISE (UNSUPERVISED) PRE-TRAINING Breakthrough in 2006 Layer-wise (unsupervised) pre-training
UNSUPERVISED LEARNING Topics Layer-wise (unsupervised) pre-training Restricted Boltzmann Machines Auto-encoders LAYER-WISE (UNSUPERVISED) PRE-TRAINING Breakthrough in 2006 Layer-wise (unsupervised) pre-training
Deep unsupervised learning
 Deep unsupervised learning Advanced data-mining Yongdai Kim Department of Statistics, Seoul National University, South Korea Unsupervised learning In machine learning, there are 3 kinds of learning paradigm.
Deep unsupervised learning Advanced data-mining Yongdai Kim Department of Statistics, Seoul National University, South Korea Unsupervised learning In machine learning, there are 3 kinds of learning paradigm.
Greedy Layer-Wise Training of Deep Networks
 Greedy Layer-Wise Training of Deep Networks Yoshua Bengio, Pascal Lamblin, Dan Popovici, Hugo Larochelle NIPS 2007 Presented by Ahmed Hefny Story so far Deep neural nets are more expressive: Can learn
Greedy Layer-Wise Training of Deep Networks Yoshua Bengio, Pascal Lamblin, Dan Popovici, Hugo Larochelle NIPS 2007 Presented by Ahmed Hefny Story so far Deep neural nets are more expressive: Can learn
Reading Group on Deep Learning Session 4 Unsupervised Neural Networks
 Reading Group on Deep Learning Session 4 Unsupervised Neural Networks Jakob Verbeek & Daan Wynen 206-09-22 Jakob Verbeek & Daan Wynen Unsupervised Neural Networks Outline Autoencoders Restricted) Boltzmann
Reading Group on Deep Learning Session 4 Unsupervised Neural Networks Jakob Verbeek & Daan Wynen 206-09-22 Jakob Verbeek & Daan Wynen Unsupervised Neural Networks Outline Autoencoders Restricted) Boltzmann
How to do backpropagation in a brain
 How to do backpropagation in a brain Geoffrey Hinton Canadian Institute for Advanced Research & University of Toronto & Google Inc. Prelude I will start with three slides explaining a popular type of deep
How to do backpropagation in a brain Geoffrey Hinton Canadian Institute for Advanced Research & University of Toronto & Google Inc. Prelude I will start with three slides explaining a popular type of deep
Lecture 16 Deep Neural Generative Models
 Lecture 16 Deep Neural Generative Models CMSC 35246: Deep Learning Shubhendu Trivedi & Risi Kondor University of Chicago May 22, 2017 Approach so far: We have considered simple models and then constructed
Lecture 16 Deep Neural Generative Models CMSC 35246: Deep Learning Shubhendu Trivedi & Risi Kondor University of Chicago May 22, 2017 Approach so far: We have considered simple models and then constructed
Bias-Variance Trade-Off in Hierarchical Probabilistic Models Using Higher-Order Feature Interactions
 - Trade-Off in Hierarchical Probabilistic Models Using Higher-Order Feature Interactions Simon Luo The University of Sydney Data61, CSIRO simon.luo@data61.csiro.au Mahito Sugiyama National Institute of
- Trade-Off in Hierarchical Probabilistic Models Using Higher-Order Feature Interactions Simon Luo The University of Sydney Data61, CSIRO simon.luo@data61.csiro.au Mahito Sugiyama National Institute of
Restricted Boltzmann Machines for Collaborative Filtering
 Restricted Boltzmann Machines for Collaborative Filtering Authors: Ruslan Salakhutdinov Andriy Mnih Geoffrey Hinton Benjamin Schwehn Presentation by: Ioan Stanculescu 1 Overview The Netflix prize problem
Restricted Boltzmann Machines for Collaborative Filtering Authors: Ruslan Salakhutdinov Andriy Mnih Geoffrey Hinton Benjamin Schwehn Presentation by: Ioan Stanculescu 1 Overview The Netflix prize problem
Stochastic Gradient Estimate Variance in Contrastive Divergence and Persistent Contrastive Divergence
 ESANN 0 proceedings, European Symposium on Artificial Neural Networks, Computational Intelligence and Machine Learning. Bruges (Belgium), 7-9 April 0, idoc.com publ., ISBN 97-7707-. Stochastic Gradient
ESANN 0 proceedings, European Symposium on Artificial Neural Networks, Computational Intelligence and Machine Learning. Bruges (Belgium), 7-9 April 0, idoc.com publ., ISBN 97-7707-. Stochastic Gradient
Gaussian Cardinality Restricted Boltzmann Machines
 Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence Gaussian Cardinality Restricted Boltzmann Machines Cheng Wan, Xiaoming Jin, Guiguang Ding and Dou Shen School of Software, Tsinghua
Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence Gaussian Cardinality Restricted Boltzmann Machines Cheng Wan, Xiaoming Jin, Guiguang Ding and Dou Shen School of Software, Tsinghua
Learning Deep Architectures
 Learning Deep Architectures Yoshua Bengio, U. Montreal Microsoft Cambridge, U.K. July 7th, 2009, Montreal Thanks to: Aaron Courville, Pascal Vincent, Dumitru Erhan, Olivier Delalleau, Olivier Breuleux,
Learning Deep Architectures Yoshua Bengio, U. Montreal Microsoft Cambridge, U.K. July 7th, 2009, Montreal Thanks to: Aaron Courville, Pascal Vincent, Dumitru Erhan, Olivier Delalleau, Olivier Breuleux,
Measuring the Usefulness of Hidden Units in Boltzmann Machines with Mutual Information
 Measuring the Usefulness of Hidden Units in Boltzmann Machines with Mutual Information Mathias Berglund, Tapani Raiko, and KyungHyun Cho Department of Information and Computer Science Aalto University
Measuring the Usefulness of Hidden Units in Boltzmann Machines with Mutual Information Mathias Berglund, Tapani Raiko, and KyungHyun Cho Department of Information and Computer Science Aalto University
Deep learning / Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio and Aaron Courville. - Cambridge, MA ; London, Spis treści
 Deep learning / Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio and Aaron Courville. - Cambridge, MA ; London, 2017 Spis treści Website Acknowledgments Notation xiii xv xix 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Who Should Read This Book?
Deep learning / Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio and Aaron Courville. - Cambridge, MA ; London, 2017 Spis treści Website Acknowledgments Notation xiii xv xix 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Who Should Read This Book?
Need for Deep Networks Perceptron. Can only model linear functions. Kernel Machines. Non-linearity provided by kernels
 Need for Deep Networks Perceptron Can only model linear functions Kernel Machines Non-linearity provided by kernels Need to design appropriate kernels (possibly selecting from a set, i.e. kernel learning)
Need for Deep Networks Perceptron Can only model linear functions Kernel Machines Non-linearity provided by kernels Need to design appropriate kernels (possibly selecting from a set, i.e. kernel learning)
Need for Deep Networks Perceptron. Can only model linear functions. Kernel Machines. Non-linearity provided by kernels
 Need for Deep Networks Perceptron Can only model linear functions Kernel Machines Non-linearity provided by kernels Need to design appropriate kernels (possibly selecting from a set, i.e. kernel learning)
Need for Deep Networks Perceptron Can only model linear functions Kernel Machines Non-linearity provided by kernels Need to design appropriate kernels (possibly selecting from a set, i.e. kernel learning)
Representational Power of Restricted Boltzmann Machines and Deep Belief Networks. Nicolas Le Roux and Yoshua Bengio Presented by Colin Graber
 Representational Power of Restricted Boltzmann Machines and Deep Belief Networks Nicolas Le Roux and Yoshua Bengio Presented by Colin Graber Introduction Representational abilities of functions with some
Representational Power of Restricted Boltzmann Machines and Deep Belief Networks Nicolas Le Roux and Yoshua Bengio Presented by Colin Graber Introduction Representational abilities of functions with some
ECE521 Lectures 9 Fully Connected Neural Networks
 ECE521 Lectures 9 Fully Connected Neural Networks Outline Multi-class classification Learning multi-layer neural networks 2 Measuring distance in probability space We learnt that the squared L2 distance
ECE521 Lectures 9 Fully Connected Neural Networks Outline Multi-class classification Learning multi-layer neural networks 2 Measuring distance in probability space We learnt that the squared L2 distance
STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning
 STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@utstat.toronto.edu! http://www.utstat.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Sidney Smith Hall, Room 6002 Lecture 3 Linear
STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@utstat.toronto.edu! http://www.utstat.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Sidney Smith Hall, Room 6002 Lecture 3 Linear
COMP9444 Neural Networks and Deep Learning 11. Boltzmann Machines. COMP9444 c Alan Blair, 2017
 COMP9444 Neural Networks and Deep Learning 11. Boltzmann Machines COMP9444 17s2 Boltzmann Machines 1 Outline Content Addressable Memory Hopfield Network Generative Models Boltzmann Machine Restricted Boltzmann
COMP9444 Neural Networks and Deep Learning 11. Boltzmann Machines COMP9444 17s2 Boltzmann Machines 1 Outline Content Addressable Memory Hopfield Network Generative Models Boltzmann Machine Restricted Boltzmann
Part 2. Representation Learning Algorithms
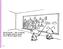 53 Part 2 Representation Learning Algorithms 54 A neural network = running several logistic regressions at the same time If we feed a vector of inputs through a bunch of logis;c regression func;ons, then
53 Part 2 Representation Learning Algorithms 54 A neural network = running several logistic regressions at the same time If we feed a vector of inputs through a bunch of logis;c regression func;ons, then
STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning
 STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@utstat.toronto.edu! http://www.utstat.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Sidney Smith Hall, Room 6002 Lecture 7 Approximate
STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@utstat.toronto.edu! http://www.utstat.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Sidney Smith Hall, Room 6002 Lecture 7 Approximate
Learning Energy-Based Models of High-Dimensional Data
 Learning Energy-Based Models of High-Dimensional Data Geoffrey Hinton Max Welling Yee-Whye Teh Simon Osindero www.cs.toronto.edu/~hinton/energybasedmodelsweb.htm Discovering causal structure as a goal
Learning Energy-Based Models of High-Dimensional Data Geoffrey Hinton Max Welling Yee-Whye Teh Simon Osindero www.cs.toronto.edu/~hinton/energybasedmodelsweb.htm Discovering causal structure as a goal
The Origin of Deep Learning. Lili Mou Jan, 2015
 The Origin of Deep Learning Lili Mou Jan, 2015 Acknowledgment Most of the materials come from G. E. Hinton s online course. Outline Introduction Preliminary Boltzmann Machines and RBMs Deep Belief Nets
The Origin of Deep Learning Lili Mou Jan, 2015 Acknowledgment Most of the materials come from G. E. Hinton s online course. Outline Introduction Preliminary Boltzmann Machines and RBMs Deep Belief Nets
Chapter 20. Deep Generative Models
 Peng et al.: Deep Learning and Practice 1 Chapter 20 Deep Generative Models Peng et al.: Deep Learning and Practice 2 Generative Models Models that are able to Provide an estimate of the probability distribution
Peng et al.: Deep Learning and Practice 1 Chapter 20 Deep Generative Models Peng et al.: Deep Learning and Practice 2 Generative Models Models that are able to Provide an estimate of the probability distribution
Knowledge Extraction from DBNs for Images
 Knowledge Extraction from DBNs for Images Son N. Tran and Artur d Avila Garcez Department of Computer Science City University London Contents 1 Introduction 2 Knowledge Extraction from DBNs 3 Experimental
Knowledge Extraction from DBNs for Images Son N. Tran and Artur d Avila Garcez Department of Computer Science City University London Contents 1 Introduction 2 Knowledge Extraction from DBNs 3 Experimental
Learning Deep Architectures for AI. Part II - Vijay Chakilam
 Learning Deep Architectures for AI - Yoshua Bengio Part II - Vijay Chakilam Limitations of Perceptron x1 W, b 0,1 1,1 y x2 weight plane output =1 output =0 There is no value for W and b such that the model
Learning Deep Architectures for AI - Yoshua Bengio Part II - Vijay Chakilam Limitations of Perceptron x1 W, b 0,1 1,1 y x2 weight plane output =1 output =0 There is no value for W and b such that the model
Deep Learning. What Is Deep Learning? The Rise of Deep Learning. Long History (in Hind Sight)
 CSCE 636 Neural Networks Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe Deep Learning What Is Deep Learning? Learning higher level abstractions/representations from data. Motivation: how the brain represents sensory information
CSCE 636 Neural Networks Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe Deep Learning What Is Deep Learning? Learning higher level abstractions/representations from data. Motivation: how the brain represents sensory information
Deep Learning Basics Lecture 8: Autoencoder & DBM. Princeton University COS 495 Instructor: Yingyu Liang
 Deep Learning Basics Lecture 8: Autoencoder & DBM Princeton University COS 495 Instructor: Yingyu Liang Autoencoder Autoencoder Neural networks trained to attempt to copy its input to its output Contain
Deep Learning Basics Lecture 8: Autoencoder & DBM Princeton University COS 495 Instructor: Yingyu Liang Autoencoder Autoencoder Neural networks trained to attempt to copy its input to its output Contain
ECE521 week 3: 23/26 January 2017
 ECE521 week 3: 23/26 January 2017 Outline Probabilistic interpretation of linear regression - Maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) - Maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimation Bias-variance trade-off Linear
ECE521 week 3: 23/26 January 2017 Outline Probabilistic interpretation of linear regression - Maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) - Maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimation Bias-variance trade-off Linear
arxiv: v2 [cs.ne] 22 Feb 2013
![arxiv: v2 [cs.ne] 22 Feb 2013 arxiv: v2 [cs.ne] 22 Feb 2013](/thumbs/76/74046790.jpg) Sparse Penalty in Deep Belief Networks: Using the Mixed Norm Constraint arxiv:1301.3533v2 [cs.ne] 22 Feb 2013 Xanadu C. Halkias DYNI, LSIS, Universitè du Sud, Avenue de l Université - BP20132, 83957 LA
Sparse Penalty in Deep Belief Networks: Using the Mixed Norm Constraint arxiv:1301.3533v2 [cs.ne] 22 Feb 2013 Xanadu C. Halkias DYNI, LSIS, Universitè du Sud, Avenue de l Université - BP20132, 83957 LA
Speaker Representation and Verification Part II. by Vasileios Vasilakakis
 Speaker Representation and Verification Part II by Vasileios Vasilakakis Outline -Approaches of Neural Networks in Speaker/Speech Recognition -Feed-Forward Neural Networks -Training with Back-propagation
Speaker Representation and Verification Part II by Vasileios Vasilakakis Outline -Approaches of Neural Networks in Speaker/Speech Recognition -Feed-Forward Neural Networks -Training with Back-propagation
Learning Tetris. 1 Tetris. February 3, 2009
 Learning Tetris Matt Zucker Andrew Maas February 3, 2009 1 Tetris The Tetris game has been used as a benchmark for Machine Learning tasks because its large state space (over 2 200 cell configurations are
Learning Tetris Matt Zucker Andrew Maas February 3, 2009 1 Tetris The Tetris game has been used as a benchmark for Machine Learning tasks because its large state space (over 2 200 cell configurations are
Jakub Hajic Artificial Intelligence Seminar I
 Jakub Hajic Artificial Intelligence Seminar I. 11. 11. 2014 Outline Key concepts Deep Belief Networks Convolutional Neural Networks A couple of questions Convolution Perceptron Feedforward Neural Network
Jakub Hajic Artificial Intelligence Seminar I. 11. 11. 2014 Outline Key concepts Deep Belief Networks Convolutional Neural Networks A couple of questions Convolution Perceptron Feedforward Neural Network
TUTORIAL PART 1 Unsupervised Learning
 TUTORIAL PART 1 Unsupervised Learning Marc'Aurelio Ranzato Department of Computer Science Univ. of Toronto ranzato@cs.toronto.edu Co-organizers: Honglak Lee, Yoshua Bengio, Geoff Hinton, Yann LeCun, Andrew
TUTORIAL PART 1 Unsupervised Learning Marc'Aurelio Ranzato Department of Computer Science Univ. of Toronto ranzato@cs.toronto.edu Co-organizers: Honglak Lee, Yoshua Bengio, Geoff Hinton, Yann LeCun, Andrew
Deep Boltzmann Machines
 Deep Boltzmann Machines Ruslan Salakutdinov and Geoffrey E. Hinton Amish Goel University of Illinois Urbana Champaign agoel10@illinois.edu December 2, 2016 Ruslan Salakutdinov and Geoffrey E. Hinton Amish
Deep Boltzmann Machines Ruslan Salakutdinov and Geoffrey E. Hinton Amish Goel University of Illinois Urbana Champaign agoel10@illinois.edu December 2, 2016 Ruslan Salakutdinov and Geoffrey E. Hinton Amish
Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning
 Christopher M. Bishop Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning ÖSpri inger Contents Preface Mathematical notation Contents vii xi xiii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Example: Polynomial Curve Fitting 4 1.2 Probability
Christopher M. Bishop Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning ÖSpri inger Contents Preface Mathematical notation Contents vii xi xiii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Example: Polynomial Curve Fitting 4 1.2 Probability
Recent Advances in Bayesian Inference Techniques
 Recent Advances in Bayesian Inference Techniques Christopher M. Bishop Microsoft Research, Cambridge, U.K. research.microsoft.com/~cmbishop SIAM Conference on Data Mining, April 2004 Abstract Bayesian
Recent Advances in Bayesian Inference Techniques Christopher M. Bishop Microsoft Research, Cambridge, U.K. research.microsoft.com/~cmbishop SIAM Conference on Data Mining, April 2004 Abstract Bayesian
Importance Reweighting Using Adversarial-Collaborative Training
 Importance Reweighting Using Adversarial-Collaborative Training Yifan Wu yw4@andrew.cmu.edu Tianshu Ren tren@andrew.cmu.edu Lidan Mu lmu@andrew.cmu.edu Abstract We consider the problem of reweighting a
Importance Reweighting Using Adversarial-Collaborative Training Yifan Wu yw4@andrew.cmu.edu Tianshu Ren tren@andrew.cmu.edu Lidan Mu lmu@andrew.cmu.edu Abstract We consider the problem of reweighting a
Based on the original slides of Hung-yi Lee
 Based on the original slides of Hung-yi Lee Google Trends Deep learning obtains many exciting results. Can contribute to new Smart Services in the Context of the Internet of Things (IoT). IoT Services
Based on the original slides of Hung-yi Lee Google Trends Deep learning obtains many exciting results. Can contribute to new Smart Services in the Context of the Internet of Things (IoT). IoT Services
Chapter 16. Structured Probabilistic Models for Deep Learning
 Peng et al.: Deep Learning and Practice 1 Chapter 16 Structured Probabilistic Models for Deep Learning Peng et al.: Deep Learning and Practice 2 Structured Probabilistic Models way of using graphs to describe
Peng et al.: Deep Learning and Practice 1 Chapter 16 Structured Probabilistic Models for Deep Learning Peng et al.: Deep Learning and Practice 2 Structured Probabilistic Models way of using graphs to describe
The connection of dropout and Bayesian statistics
 The connection of dropout and Bayesian statistics Interpretation of dropout as approximate Bayesian modelling of NN http://mlg.eng.cam.ac.uk/yarin/thesis/thesis.pdf Dropout Geoffrey Hinton Google, University
The connection of dropout and Bayesian statistics Interpretation of dropout as approximate Bayesian modelling of NN http://mlg.eng.cam.ac.uk/yarin/thesis/thesis.pdf Dropout Geoffrey Hinton Google, University
Restricted Boltzmann Machines
 Restricted Boltzmann Machines http://deeplearning4.org/rbm-mnist-tutorial.html Slides from Hugo Larochelle, Geoffrey Hinton, and Yoshua Bengio CSC321: Intro to Machine Learning and Neural Networks, Winter
Restricted Boltzmann Machines http://deeplearning4.org/rbm-mnist-tutorial.html Slides from Hugo Larochelle, Geoffrey Hinton, and Yoshua Bengio CSC321: Intro to Machine Learning and Neural Networks, Winter
Deep Learning: Self-Taught Learning and Deep vs. Shallow Architectures. Lecture 04
 Deep Learning: Self-Taught Learning and Deep vs. Shallow Architectures Lecture 04 Razvan C. Bunescu School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science bunescu@ohio.edu Self-Taught Learning 1. Learn
Deep Learning: Self-Taught Learning and Deep vs. Shallow Architectures Lecture 04 Razvan C. Bunescu School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science bunescu@ohio.edu Self-Taught Learning 1. Learn
Replicated Softmax: an Undirected Topic Model. Stephen Turner
 Replicated Softmax: an Undirected Topic Model Stephen Turner 1. Introduction 2. Replicated Softmax: A Generative Model of Word Counts 3. Evaluating Replicated Softmax as a Generative Model 4. Experimental
Replicated Softmax: an Undirected Topic Model Stephen Turner 1. Introduction 2. Replicated Softmax: A Generative Model of Word Counts 3. Evaluating Replicated Softmax as a Generative Model 4. Experimental
Machine Learning Basics
 Security and Fairness of Deep Learning Machine Learning Basics Anupam Datta CMU Spring 2019 Image Classification Image Classification Image classification pipeline Input: A training set of N images, each
Security and Fairness of Deep Learning Machine Learning Basics Anupam Datta CMU Spring 2019 Image Classification Image Classification Image classification pipeline Input: A training set of N images, each
Reading Group on Deep Learning Session 1
 Reading Group on Deep Learning Session 1 Stephane Lathuiliere & Pablo Mesejo 2 June 2016 1/31 Contents Introduction to Artificial Neural Networks to understand, and to be able to efficiently use, the popular
Reading Group on Deep Learning Session 1 Stephane Lathuiliere & Pablo Mesejo 2 June 2016 1/31 Contents Introduction to Artificial Neural Networks to understand, and to be able to efficiently use, the popular
Deep Learning Autoencoder Models
 Deep Learning Autoencoder Models Davide Bacciu Dipartimento di Informatica Università di Pisa Intelligent Systems for Pattern Recognition (ISPR) Generative Models Wrap-up Deep Learning Module Lecture Generative
Deep Learning Autoencoder Models Davide Bacciu Dipartimento di Informatica Università di Pisa Intelligent Systems for Pattern Recognition (ISPR) Generative Models Wrap-up Deep Learning Module Lecture Generative
Deep Learning. What Is Deep Learning? The Rise of Deep Learning. Long History (in Hind Sight)
 CSCE 636 Neural Networks Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe Deep Learning What Is Deep Learning? Learning higher level abstractions/representations from data. Motivation: how the brain represents sensory information
CSCE 636 Neural Networks Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe Deep Learning What Is Deep Learning? Learning higher level abstractions/representations from data. Motivation: how the brain represents sensory information
A Spike and Slab Restricted Boltzmann Machine
 Aaron Courville James Bergstra Yoshua Bengio DIRO, Université de Montréal, Montréal, Québec, Canada {courvila,bergstrj,bengioy}@iro.umontreal.ca Abstract We introduce the spike and slab Restricted Boltzmann
Aaron Courville James Bergstra Yoshua Bengio DIRO, Université de Montréal, Montréal, Québec, Canada {courvila,bergstrj,bengioy}@iro.umontreal.ca Abstract We introduce the spike and slab Restricted Boltzmann
Deep Belief Networks are compact universal approximators
 1 Deep Belief Networks are compact universal approximators Nicolas Le Roux 1, Yoshua Bengio 2 1 Microsoft Research Cambridge 2 University of Montreal Keywords: Deep Belief Networks, Universal Approximation
1 Deep Belief Networks are compact universal approximators Nicolas Le Roux 1, Yoshua Bengio 2 1 Microsoft Research Cambridge 2 University of Montreal Keywords: Deep Belief Networks, Universal Approximation
Au-delà de la Machine de Boltzmann Restreinte. Hugo Larochelle University of Toronto
 Au-delà de la Machine de Boltzmann Restreinte Hugo Larochelle University of Toronto Introduction Restricted Boltzmann Machines (RBMs) are useful feature extractors They are mostly used to initialize deep
Au-delà de la Machine de Boltzmann Restreinte Hugo Larochelle University of Toronto Introduction Restricted Boltzmann Machines (RBMs) are useful feature extractors They are mostly used to initialize deep
Study Notes on the Latent Dirichlet Allocation
 Study Notes on the Latent Dirichlet Allocation Xugang Ye 1. Model Framework A word is an element of dictionary {1,,}. A document is represented by a sequence of words: =(,, ), {1,,}. A corpus is a collection
Study Notes on the Latent Dirichlet Allocation Xugang Ye 1. Model Framework A word is an element of dictionary {1,,}. A document is represented by a sequence of words: =(,, ), {1,,}. A corpus is a collection
Summary and discussion of: Dropout Training as Adaptive Regularization
 Summary and discussion of: Dropout Training as Adaptive Regularization Statistics Journal Club, 36-825 Kirstin Early and Calvin Murdock November 21, 2014 1 Introduction Multi-layered (i.e. deep) artificial
Summary and discussion of: Dropout Training as Adaptive Regularization Statistics Journal Club, 36-825 Kirstin Early and Calvin Murdock November 21, 2014 1 Introduction Multi-layered (i.e. deep) artificial
Undirected Graphical Models
 Outline Hong Chang Institute of Computing Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences Machine Learning Methods (Fall 2012) Outline Outline I 1 Introduction 2 Properties Properties 3 Generative vs. Conditional
Outline Hong Chang Institute of Computing Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences Machine Learning Methods (Fall 2012) Outline Outline I 1 Introduction 2 Properties Properties 3 Generative vs. Conditional
Deep Generative Models. (Unsupervised Learning)
 Deep Generative Models (Unsupervised Learning) CEng 783 Deep Learning Fall 2017 Emre Akbaş Reminders Next week: project progress demos in class Describe your problem/goal What you have done so far What
Deep Generative Models (Unsupervised Learning) CEng 783 Deep Learning Fall 2017 Emre Akbaş Reminders Next week: project progress demos in class Describe your problem/goal What you have done so far What
Improved Local Coordinate Coding using Local Tangents
 Improved Local Coordinate Coding using Local Tangents Kai Yu NEC Laboratories America, 10081 N. Wolfe Road, Cupertino, CA 95129 Tong Zhang Rutgers University, 110 Frelinghuysen Road, Piscataway, NJ 08854
Improved Local Coordinate Coding using Local Tangents Kai Yu NEC Laboratories America, 10081 N. Wolfe Road, Cupertino, CA 95129 Tong Zhang Rutgers University, 110 Frelinghuysen Road, Piscataway, NJ 08854
Learning Deep Architectures for AI. Part I - Vijay Chakilam
 Learning Deep Architectures for AI - Yoshua Bengio Part I - Vijay Chakilam Chapter 0: Preliminaries Neural Network Models The basic idea behind the neural network approach is to model the response as a
Learning Deep Architectures for AI - Yoshua Bengio Part I - Vijay Chakilam Chapter 0: Preliminaries Neural Network Models The basic idea behind the neural network approach is to model the response as a
9/12/17. Types of learning. Modeling data. Supervised learning: Classification. Supervised learning: Regression. Unsupervised learning: Clustering
 Types of learning Modeling data Supervised: we know input and targets Goal is to learn a model that, given input data, accurately predicts target data Unsupervised: we know the input only and want to make
Types of learning Modeling data Supervised: we know input and targets Goal is to learn a model that, given input data, accurately predicts target data Unsupervised: we know the input only and want to make
Course Structure. Psychology 452 Week 12: Deep Learning. Chapter 8 Discussion. Part I: Deep Learning: What and Why? Rufus. Rufus Processed By Fetch
 Psychology 452 Week 12: Deep Learning What Is Deep Learning? Preliminary Ideas (that we already know!) The Restricted Boltzmann Machine (RBM) Many Layers of RBMs Pros and Cons of Deep Learning Course Structure
Psychology 452 Week 12: Deep Learning What Is Deep Learning? Preliminary Ideas (that we already know!) The Restricted Boltzmann Machine (RBM) Many Layers of RBMs Pros and Cons of Deep Learning Course Structure
An efficient way to learn deep generative models
 An efficient way to learn deep generative models Geoffrey Hinton Canadian Institute for Advanced Research & Department of Computer Science University of Toronto Joint work with: Ruslan Salakhutdinov, Yee-Whye
An efficient way to learn deep generative models Geoffrey Hinton Canadian Institute for Advanced Research & Department of Computer Science University of Toronto Joint work with: Ruslan Salakhutdinov, Yee-Whye
Lecture 12. Neural Networks Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen
 Advanced Machine Learning Lecture 12 Neural Networks 10.12.2015 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de/ leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de This Lecture: Advanced Machine Learning Regression
Advanced Machine Learning Lecture 12 Neural Networks 10.12.2015 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de/ leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de This Lecture: Advanced Machine Learning Regression
Introduction to Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
 Introduction to Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) nojunk@snu.ac.kr http://mipal.snu.ac.kr Department of Transdisciplinary Studies Seoul National University, Korea Jan. 2016 Many slides are from Fei-Fei
Introduction to Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) nojunk@snu.ac.kr http://mipal.snu.ac.kr Department of Transdisciplinary Studies Seoul National University, Korea Jan. 2016 Many slides are from Fei-Fei
(Feed-Forward) Neural Networks Dr. Hajira Jabeen, Prof. Jens Lehmann
 (Feed-Forward) Neural Networks 2016-12-06 Dr. Hajira Jabeen, Prof. Jens Lehmann Outline In the previous lectures we have learned about tensors and factorization methods. RESCAL is a bilinear model for
(Feed-Forward) Neural Networks 2016-12-06 Dr. Hajira Jabeen, Prof. Jens Lehmann Outline In the previous lectures we have learned about tensors and factorization methods. RESCAL is a bilinear model for
OPTIMIZATION METHODS IN DEEP LEARNING
 Tutorial outline OPTIMIZATION METHODS IN DEEP LEARNING Based on Deep Learning, chapter 8 by Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio and Aaron Courville Presented By Nadav Bhonker Optimization vs Learning Surrogate
Tutorial outline OPTIMIZATION METHODS IN DEEP LEARNING Based on Deep Learning, chapter 8 by Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio and Aaron Courville Presented By Nadav Bhonker Optimization vs Learning Surrogate
Introduction to Restricted Boltzmann Machines
 Introduction to Restricted Boltzmann Machines Ilija Bogunovic and Edo Collins EPFL {ilija.bogunovic,edo.collins}@epfl.ch October 13, 2014 Introduction Ingredients: 1. Probabilistic graphical models (undirected,
Introduction to Restricted Boltzmann Machines Ilija Bogunovic and Edo Collins EPFL {ilija.bogunovic,edo.collins}@epfl.ch October 13, 2014 Introduction Ingredients: 1. Probabilistic graphical models (undirected,
Neural Networks Lecturer: J. Matas Authors: J. Matas, B. Flach, O. Drbohlav
 Neural Networks 30.11.2015 Lecturer: J. Matas Authors: J. Matas, B. Flach, O. Drbohlav 1 Talk Outline Perceptron Combining neurons to a network Neural network, processing input to an output Learning Cost
Neural Networks 30.11.2015 Lecturer: J. Matas Authors: J. Matas, B. Flach, O. Drbohlav 1 Talk Outline Perceptron Combining neurons to a network Neural network, processing input to an output Learning Cost
Modeling Documents with a Deep Boltzmann Machine
 Modeling Documents with a Deep Boltzmann Machine Nitish Srivastava, Ruslan Salakhutdinov & Geoffrey Hinton UAI 2013 Presented by Zhe Gan, Duke University November 14, 2014 1 / 15 Outline Replicated Softmax
Modeling Documents with a Deep Boltzmann Machine Nitish Srivastava, Ruslan Salakhutdinov & Geoffrey Hinton UAI 2013 Presented by Zhe Gan, Duke University November 14, 2014 1 / 15 Outline Replicated Softmax
A summary of Deep Learning without Poor Local Minima
 A summary of Deep Learning without Poor Local Minima by Kenji Kawaguchi MIT oral presentation at NIPS 2016 Learning Supervised (or Predictive) learning Learn a mapping from inputs x to outputs y, given
A summary of Deep Learning without Poor Local Minima by Kenji Kawaguchi MIT oral presentation at NIPS 2016 Learning Supervised (or Predictive) learning Learn a mapping from inputs x to outputs y, given
Deep Feedforward Networks
 Deep Feedforward Networks Liu Yang March 30, 2017 Liu Yang Short title March 30, 2017 1 / 24 Overview 1 Background A general introduction Example 2 Gradient based learning Cost functions Output Units 3
Deep Feedforward Networks Liu Yang March 30, 2017 Liu Yang Short title March 30, 2017 1 / 24 Overview 1 Background A general introduction Example 2 Gradient based learning Cost functions Output Units 3
Convolutional Neural Networks II. Slides from Dr. Vlad Morariu
 Convolutional Neural Networks II Slides from Dr. Vlad Morariu 1 Optimization Example of optimization progress while training a neural network. (Loss over mini-batches goes down over time.) 2 Learning rate
Convolutional Neural Networks II Slides from Dr. Vlad Morariu 1 Optimization Example of optimization progress while training a neural network. (Loss over mini-batches goes down over time.) 2 Learning rate
arxiv: v1 [cs.lg] 9 Nov 2015
![arxiv: v1 [cs.lg] 9 Nov 2015 arxiv: v1 [cs.lg] 9 Nov 2015](/thumbs/85/91366127.jpg) HOW FAR CAN WE GO WITHOUT CONVOLUTION: IM- PROVING FULLY-CONNECTED NETWORKS Zhouhan Lin & Roland Memisevic Université de Montréal Canada {zhouhan.lin, roland.memisevic}@umontreal.ca arxiv:1511.02580v1
HOW FAR CAN WE GO WITHOUT CONVOLUTION: IM- PROVING FULLY-CONNECTED NETWORKS Zhouhan Lin & Roland Memisevic Université de Montréal Canada {zhouhan.lin, roland.memisevic}@umontreal.ca arxiv:1511.02580v1
Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder. Canberra February June 2018
 Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder Research Group and College of Engineering and Computer Science Canberra February June 218 Outlines Overview Introduction Linear Algebra Probability Linear Regression 1
Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder Research Group and College of Engineering and Computer Science Canberra February June 218 Outlines Overview Introduction Linear Algebra Probability Linear Regression 1
Self Supervised Boosting
 Self Supervised Boosting Max Welling, Richard S. Zemel, and Geoffrey E. Hinton Department of omputer Science University of Toronto 1 King s ollege Road Toronto, M5S 3G5 anada Abstract Boosting algorithms
Self Supervised Boosting Max Welling, Richard S. Zemel, and Geoffrey E. Hinton Department of omputer Science University of Toronto 1 King s ollege Road Toronto, M5S 3G5 anada Abstract Boosting algorithms
Discriminative Learning of Sum-Product Networks. Robert Gens Pedro Domingos
 Discriminative Learning of Sum-Product Networks Robert Gens Pedro Domingos X1 X1 X1 X1 X2 X2 X2 X2 X3 X3 X3 X3 X4 X4 X4 X4 X5 X5 X5 X5 X6 X6 X6 X6 Distributions X 1 X 1 X 1 X 1 X 2 X 2 X 2 X 2 X 3 X 3
Discriminative Learning of Sum-Product Networks Robert Gens Pedro Domingos X1 X1 X1 X1 X2 X2 X2 X2 X3 X3 X3 X3 X4 X4 X4 X4 X5 X5 X5 X5 X6 X6 X6 X6 Distributions X 1 X 1 X 1 X 1 X 2 X 2 X 2 X 2 X 3 X 3
How to do backpropagation in a brain. Geoffrey Hinton Canadian Institute for Advanced Research & University of Toronto
 1 How to do backpropagation in a brain Geoffrey Hinton Canadian Institute for Advanced Research & University of Toronto What is wrong with back-propagation? It requires labeled training data. (fixed) Almost
1 How to do backpropagation in a brain Geoffrey Hinton Canadian Institute for Advanced Research & University of Toronto What is wrong with back-propagation? It requires labeled training data. (fixed) Almost
Restricted Boltzmann Machines
 Restricted Boltzmann Machines Boltzmann Machine(BM) A Boltzmann machine extends a stochastic Hopfield network to include hidden units. It has binary (0 or 1) visible vector unit x and hidden (latent) vector
Restricted Boltzmann Machines Boltzmann Machine(BM) A Boltzmann machine extends a stochastic Hopfield network to include hidden units. It has binary (0 or 1) visible vector unit x and hidden (latent) vector
Learning to Disentangle Factors of Variation with Manifold Learning
 Learning to Disentangle Factors of Variation with Manifold Learning Scott Reed Kihyuk Sohn Yuting Zhang Honglak Lee University of Michigan, Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 08
Learning to Disentangle Factors of Variation with Manifold Learning Scott Reed Kihyuk Sohn Yuting Zhang Honglak Lee University of Michigan, Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 08
Collaborative Filtering Applied to Educational Data Mining
 Journal of Machine Learning Research (200) Submitted ; Published Collaborative Filtering Applied to Educational Data Mining Andreas Töscher commendo research 8580 Köflach, Austria andreas.toescher@commendo.at
Journal of Machine Learning Research (200) Submitted ; Published Collaborative Filtering Applied to Educational Data Mining Andreas Töscher commendo research 8580 Köflach, Austria andreas.toescher@commendo.at
Cardinality Restricted Boltzmann Machines
 Cardinality Restricted Boltzmann Machines Kevin Swersky Daniel Tarlow Ilya Sutskever Dept. of Computer Science University of Toronto [kswersky,dtarlow,ilya]@cs.toronto.edu Ruslan Salakhutdinov, Richard
Cardinality Restricted Boltzmann Machines Kevin Swersky Daniel Tarlow Ilya Sutskever Dept. of Computer Science University of Toronto [kswersky,dtarlow,ilya]@cs.toronto.edu Ruslan Salakhutdinov, Richard
WHY ARE DEEP NETS REVERSIBLE: A SIMPLE THEORY,
 WHY ARE DEEP NETS REVERSIBLE: A SIMPLE THEORY, WITH IMPLICATIONS FOR TRAINING Sanjeev Arora, Yingyu Liang & Tengyu Ma Department of Computer Science Princeton University Princeton, NJ 08540, USA {arora,yingyul,tengyu}@cs.princeton.edu
WHY ARE DEEP NETS REVERSIBLE: A SIMPLE THEORY, WITH IMPLICATIONS FOR TRAINING Sanjeev Arora, Yingyu Liang & Tengyu Ma Department of Computer Science Princeton University Princeton, NJ 08540, USA {arora,yingyul,tengyu}@cs.princeton.edu
Maxout Networks. Hien Quoc Dang
 Maxout Networks Hien Quoc Dang Outline Introduction Maxout Networks Description A Universal Approximator & Proof Experiments with Maxout Why does Maxout work? Conclusion 10/12/13 Hien Quoc Dang Machine
Maxout Networks Hien Quoc Dang Outline Introduction Maxout Networks Description A Universal Approximator & Proof Experiments with Maxout Why does Maxout work? Conclusion 10/12/13 Hien Quoc Dang Machine
Fundamentals of Computational Neuroscience 2e
 Fundamentals of Computational Neuroscience 2e January 1, 2010 Chapter 10: The cognitive brain Hierarchical maps and attentive vision A. Ventral visual pathway B. Layered cortical maps Receptive field size
Fundamentals of Computational Neuroscience 2e January 1, 2010 Chapter 10: The cognitive brain Hierarchical maps and attentive vision A. Ventral visual pathway B. Layered cortical maps Receptive field size
Neural Networks Learning the network: Backprop , Fall 2018 Lecture 4
 Neural Networks Learning the network: Backprop 11-785, Fall 2018 Lecture 4 1 Recap: The MLP can represent any function The MLP can be constructed to represent anything But how do we construct it? 2 Recap:
Neural Networks Learning the network: Backprop 11-785, Fall 2018 Lecture 4 1 Recap: The MLP can represent any function The MLP can be constructed to represent anything But how do we construct it? 2 Recap:
Fast Inference and Learning for Modeling Documents with a Deep Boltzmann Machine
 Fast Inference and Learning for Modeling Documents with a Deep Boltzmann Machine Nitish Srivastava nitish@cs.toronto.edu Ruslan Salahutdinov rsalahu@cs.toronto.edu Geoffrey Hinton hinton@cs.toronto.edu
Fast Inference and Learning for Modeling Documents with a Deep Boltzmann Machine Nitish Srivastava nitish@cs.toronto.edu Ruslan Salahutdinov rsalahu@cs.toronto.edu Geoffrey Hinton hinton@cs.toronto.edu
Neural Networks. Mark van Rossum. January 15, School of Informatics, University of Edinburgh 1 / 28
 1 / 28 Neural Networks Mark van Rossum School of Informatics, University of Edinburgh January 15, 2018 2 / 28 Goals: Understand how (recurrent) networks behave Find a way to teach networks to do a certain
1 / 28 Neural Networks Mark van Rossum School of Informatics, University of Edinburgh January 15, 2018 2 / 28 Goals: Understand how (recurrent) networks behave Find a way to teach networks to do a certain
Empirical Analysis of the Divergence of Gibbs Sampling Based Learning Algorithms for Restricted Boltzmann Machines
 Empirical Analysis of the Divergence of Gibbs Sampling Based Learning Algorithms for Restricted Boltzmann Machines Asja Fischer and Christian Igel Institut für Neuroinformatik Ruhr-Universität Bochum,
Empirical Analysis of the Divergence of Gibbs Sampling Based Learning Algorithms for Restricted Boltzmann Machines Asja Fischer and Christian Igel Institut für Neuroinformatik Ruhr-Universität Bochum,
Lecture 5: Logistic Regression. Neural Networks
 Lecture 5: Logistic Regression. Neural Networks Logistic regression Comparison with generative models Feed-forward neural networks Backpropagation Tricks for training neural networks COMP-652, Lecture
Lecture 5: Logistic Regression. Neural Networks Logistic regression Comparison with generative models Feed-forward neural networks Backpropagation Tricks for training neural networks COMP-652, Lecture
ARestricted Boltzmann machine (RBM) [1] is a probabilistic
![ARestricted Boltzmann machine (RBM) [1] is a probabilistic ARestricted Boltzmann machine (RBM) [1] is a probabilistic](/thumbs/90/102816372.jpg) 1 Matrix Product Operator Restricted Boltzmann Machines Cong Chen, Kim Batselier, Ching-Yun Ko, and Ngai Wong chencong@eee.hku.hk, k.batselier@tudelft.nl, cyko@eee.hku.hk, nwong@eee.hku.hk arxiv:1811.04608v1
1 Matrix Product Operator Restricted Boltzmann Machines Cong Chen, Kim Batselier, Ching-Yun Ko, and Ngai Wong chencong@eee.hku.hk, k.batselier@tudelft.nl, cyko@eee.hku.hk, nwong@eee.hku.hk arxiv:1811.04608v1
Deep Neural Networks
 Deep Neural Networks DT2118 Speech and Speaker Recognition Giampiero Salvi KTH/CSC/TMH giampi@kth.se VT 2015 1 / 45 Outline State-to-Output Probability Model Artificial Neural Networks Perceptron Multi
Deep Neural Networks DT2118 Speech and Speaker Recognition Giampiero Salvi KTH/CSC/TMH giampi@kth.se VT 2015 1 / 45 Outline State-to-Output Probability Model Artificial Neural Networks Perceptron Multi
Robust Classification using Boltzmann machines by Vasileios Vasilakakis
 Robust Classification using Boltzmann machines by Vasileios Vasilakakis The scope of this report is to propose an architecture of Boltzmann machines that could be used in the context of classification,
Robust Classification using Boltzmann machines by Vasileios Vasilakakis The scope of this report is to propose an architecture of Boltzmann machines that could be used in the context of classification,
RAGAV VENKATESAN VIJETHA GATUPALLI BAOXIN LI NEURAL DATASET GENERALITY
 RAGAV VENKATESAN VIJETHA GATUPALLI BAOXIN LI NEURAL DATASET GENERALITY SIFT HOG ALL ABOUT THE FEATURES DAISY GABOR AlexNet GoogleNet CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORKS VGG-19 ResNet FEATURES COMES FROM DATA
RAGAV VENKATESAN VIJETHA GATUPALLI BAOXIN LI NEURAL DATASET GENERALITY SIFT HOG ALL ABOUT THE FEATURES DAISY GABOR AlexNet GoogleNet CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORKS VGG-19 ResNet FEATURES COMES FROM DATA
Neural Networks. William Cohen [pilfered from: Ziv; Geoff Hinton; Yoshua Bengio; Yann LeCun; Hongkak Lee - NIPs 2010 tutorial ]
![Neural Networks. William Cohen [pilfered from: Ziv; Geoff Hinton; Yoshua Bengio; Yann LeCun; Hongkak Lee - NIPs 2010 tutorial ] Neural Networks. William Cohen [pilfered from: Ziv; Geoff Hinton; Yoshua Bengio; Yann LeCun; Hongkak Lee - NIPs 2010 tutorial ]](/thumbs/88/117565192.jpg) Neural Networks William Cohen 10-601 [pilfered from: Ziv; Geoff Hinton; Yoshua Bengio; Yann LeCun; Hongkak Lee - NIPs 2010 tutorial ] WHAT ARE NEURAL NETWORKS? William s notation Logis;c regression + 1
Neural Networks William Cohen 10-601 [pilfered from: Ziv; Geoff Hinton; Yoshua Bengio; Yann LeCun; Hongkak Lee - NIPs 2010 tutorial ] WHAT ARE NEURAL NETWORKS? William s notation Logis;c regression + 1
RegML 2018 Class 8 Deep learning
 RegML 2018 Class 8 Deep learning Lorenzo Rosasco UNIGE-MIT-IIT June 18, 2018 Supervised vs unsupervised learning? So far we have been thinking of learning schemes made in two steps f(x) = w, Φ(x) F, x
RegML 2018 Class 8 Deep learning Lorenzo Rosasco UNIGE-MIT-IIT June 18, 2018 Supervised vs unsupervised learning? So far we have been thinking of learning schemes made in two steps f(x) = w, Φ(x) F, x
Active and Semi-supervised Kernel Classification
 Active and Semi-supervised Kernel Classification Zoubin Ghahramani Gatsby Computational Neuroscience Unit University College London Work done in collaboration with Xiaojin Zhu (CMU), John Lafferty (CMU),
Active and Semi-supervised Kernel Classification Zoubin Ghahramani Gatsby Computational Neuroscience Unit University College London Work done in collaboration with Xiaojin Zhu (CMU), John Lafferty (CMU),
Sum-Product Networks: A New Deep Architecture
 Sum-Product Networks: A New Deep Architecture Pedro Domingos Dept. Computer Science & Eng. University of Washington Joint work with Hoifung Poon 1 Graphical Models: Challenges Bayesian Network Markov Network
Sum-Product Networks: A New Deep Architecture Pedro Domingos Dept. Computer Science & Eng. University of Washington Joint work with Hoifung Poon 1 Graphical Models: Challenges Bayesian Network Markov Network
Mixing Rates for the Gibbs Sampler over Restricted Boltzmann Machines
 Mixing Rates for the Gibbs Sampler over Restricted Boltzmann Machines Christopher Tosh Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of California, San Diego ctosh@cs.ucsd.edu Abstract The
Mixing Rates for the Gibbs Sampler over Restricted Boltzmann Machines Christopher Tosh Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of California, San Diego ctosh@cs.ucsd.edu Abstract The
