min3x 1 + 4x 2 + 5x 3 2x 1 + 2x 2 + x 3 6 x 1 + 2x 2 + 3x 3 5 x 1, x 2, x 3 0.
|
|
|
- Edgar Moore
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ex-.-. Foundations of Operations Research Prof. E. Amaldi. Dual simplex algorithm Given the linear program minx + x + x x + x + x 6 x + x + x x, x, x. solve it via the dual simplex algorithm. Describe the advantages of the algorithm when compared to the primal simplex algorithm.. Branch-and-Bound Given the integer linear program max z = x + x x + x 6 x + x 9 x, x, integer solve it via the Branch-and-Bound method (solving graphically the continuous relaxation of each subproblem encountered in the enumeration tree). Branch on the fractional variable with fractional value closest to. Among the set of active nodes, pick that with the most promising bound.. Branch-and-Bound for - knapsack A bank has million Euro, which can be invested into stocks of four companies (,,, and ). The table reports, for each company, the net revenue and the amount of money that must be invested into it. Company Revenue 6 8 Money 7 Given an integer linear programming formulation for the probelm of choosing a set of companies that maximizes the total revenue. Observe that no partial investment can be done, i.e., for each company we can either invest into it or not. Solve the problem with the Branch-and-Bound algorithm. Show that the solution to each continuous relaxation can be found with a greedy algorithm. Document prepared by L. Liberti, S. Bosio, S. Coniglio, and C. Iuliano. Translation to English by S. Coniglio
2 ex-.-. Foundations of Operations Research Prof. E. Amaldi. Cutting plane algorithm Given the integer linear program min x x x + 6x 9 x + x x, x solve it via Gomory s cutting plane method., integer Document prepared by L. Liberti, S. Bosio, S. Coniglio, and C. Iuliano. Translation to English by S. Coniglio
3 ex-.-. Foundations of Operations Research Prof. E. Amaldi Solution. Dual simplex algorithm We reduce the problem to its canonical form, by changing the direction of the constraints (so that they become constraints) and introducing the nonnegative slack variables x e x. We obtain the tableau x x x x x z x x which basic solution is x = (,,, 6, ). Observe that, since all the variables must be nonnegative, this solution is not feasible. Since the reduced costs are also nonnegative, the dual solution associated to this tableau is dual feasible. We apply the dual simplex algorithm. Both basic variables x and x have a negative value. By Bland s rule, we let x leave the basis (since it has smaller index). To choose the variable x s that enters the basis, we consider the ratio between the reduced costs c j for nonbasic variables x j s and the respective coefficient a ij in row i (where x i is the variable that is leaving the basis, which is x in this example), only considering the columns where a ij <. The varible to chose is that which minimizes the absolute value of such ratio, i.e. that of index { } cj s = arg min j n ā rj : ā rj <. In our example, the ratios are /, / and /. Therefore, x enters the basis. Pivot is performed in the highlighted element x x x x x z x x We obtain the tableau x x x x x z -9 7/ / x / -/ x - - -/ -/ Observe that the objective function value has increased (we are considering a minimization problem). This is due to the fact that we are considering a sequence, decreasing in objective function value, of superoptimal solutions, which are dual feasible but not primal feasible. When primal feasibility is achieved, the algorithm halts. Document prepared by L. Liberti, S. Bosio, S. Coniglio, and C. Iuliano. Translation to English by S. Coniglio
4 ex-.-. Foundations of Operations Research Prof. E. Amaldi Variable x leaves the basis (as it s the only variable with negative value). Variable x, which minimized the ratios /, (7/)/(/), and (/)/(/), enters the basis. We obtain the tableau x x x x x z - x - - x / / - The associated basic solution is both primal and dual feasible, and therefore optimal for both problems.. Branch-and-Bound The enumeration tree is reported in Figure. The graphical solution of each subproblem is reported. The subproblems are solved in the following order: P, P, P, P, P, P6, P7. Note that when the optimal value z of a subproblem is fractional, we can round the upper bound given by the subproblem to z. For instance, in P we obtain the bound =. After solving P7, we observe that P6 yields an integer solution which is worse than that of P7, which is therefore discarded. We also observe that P yields an upper bound which is smaller than the value of the best feasible solution found (in P7). The node is therefore pruned. The optimal solution (found in P7) is x = (, ), of value z =. Document prepared by L. Liberti, S. Bosio, S. Coniglio, and C. Iuliano. Translation to English by S. Coniglio
5 ex-.-. Foundations of Operations Research Prof. E. Amaldi () () P: x = () () { x = x + 6 x = x + x = ( 9, ), z =. x x () () () () () () P: x = () () { x = x + 6 x = x = (, ), z =.. < : stop P: x = () () { x = x + x = x = (, ), z =. x x () () () () () P: x = () () { x = x + () P: infeasible () () x = x = (, ) 7, z = 7. x x () () () () () P6: x = () () x = (, ), z =. () () () P7: x = () () x = (, ), z =. Figure : Enumeration tree for problem. Document prepared by L. Liberti, S. Bosio, S. Coniglio, and C. Iuliano. Translation to English by S. Coniglio
6 ex-.-. Foundations of Operations Research Prof. E. Amaldi. Branch-and-Bound for - knapsack The integer linear programming formulation for the problem is max6x + x + x + 8x x + 7x + x + x x, x, x, x {, }. An optimal solution to its linear relaxation can be found as follows. First, sort the ratios between revenues and costs, obtaining (6/, /7, /, 8/) = (.,.,,.66) Then, put to all the variables according to the ordering, until variable i : i<i c i B, and i<i c i + c i > B. Let x i =, and let all the other variables be equivalent to zero. c i B P i<i c i For instance, at node we have: x =, (it uses units), x = (7 units), x = (/=/ units). Since, at each branching iteration, we set a variable either to or, this method can be applied in any node of the enumeration tree, by fixing the approriate variables. The enumeration tree is given in Figure. Some observations: The index t indicates the order by which the subproblems are solved. l ordine di risoluzione dei problemi. Since all variables are integer, whenever a subproblem yields a solution with fractional value, we round it to z. The lower bounds (LB) is not computed at each node (to do this, a heuristic should be applied). We update it whenever a subproblem yields a feasible solution. Note that this value is NOT related to the specific subproblem, as it depends only on the iteration. Indeed, at each iteration t, LB corresponds to the value of the best feasible solution found in any part of the enumeration tree. For instance, in subproblem we find a feasible solution of value z = 6. Since it is the first that is found and LB still has the initial value of +, we set LB to 6. In subproblem 6 an integer solution is found and the node is pruned by feasibility. Subproblem 7 is infeasible, since x = x = x = require a budget of 6 >. The node is pruned by infeasibility. Subproblem 8 yields an upper bound of z = 8 which is strictly smaller than the current LB of. The node is pruned by bound. The same happens for subproblem 9, where z = The upper bound is z =, which is strictly smaller than the current LB of value. Node 9 is pruned by bound. The final optimal solution, which is found in node 9, is x = (,,, ), of value. Document prepared by L. Liberti, S. Bosio, S. Coniglio, and C. Iuliano. Translation to English by S. Coniglio 6
7 ex-.-. Foundations of Operations Research Prof. E. Amaldi t = z = x = (,,,) UB= LB= t = 7 x = x = z = + z = + x = (,,, ) 7 x = (, t = 7,,) UB= UB= LB= LB=+ 8 z = 8 x = (,,,) UB=8 LB= x = x = x = x = 9 z = x = (, 6 7,,) UB= LB= t = 8 t = 9 z = 6 x = (,,,) UB=6 LB=6 6 7 z = x = (,,,) UB= LB=, Ottimo z = + x = (,,,) UB= LB=6 t = t = x = x = Not feasible t = t = 6 Figure : Enumeration tree for problem.. Cutting plane algorithm The continuous relaxation of the the problem at hand, reduced to standard form, reads min x x x + 6x + x = 9 x + x + x = x, x, x, x, were x, x are slack variables. We solve it via the primal simplex method. The initial feasible basic solution is x B = (x, x ). We obtain the following sequence of tableaus, where the pivot element is denoted by the symbol. Document prepared by L. Liberti, S. Bosio, S. Coniglio, and C. Iuliano. Translation to English by S. Coniglio 7
8 ex-.-. Foundations of Operations Research Prof. E. Amaldi x x x x x x x x 6 6 x x x x 7 The optimal solution to the relaxation is x = (, ), where x = x = (see Figure ). x () () Figure : Graphical solution to problem. We derive a Gomory cut from the first row of the optimal tableau x + x + x =. The cut is defined as x i + j F ā ij x j b i, () where F is the set of the indices of the nonbasic variables and i is the index of the basic variable corresponding to the tableau row that is chosen. We obtain the cut x (see Figure (constraint ()). The cut is to be added to the tableau. Note that, in the current form, it is not a function of the nonbasic variables x, x. Instead of adding it to the tableau and performing some pivot operations to restore the correct for of the tableau, we can write the fractional form of the cut. We obtain by taking the ith row of the optimal tableau x i + j F ā ij x j = b i and subtracting from it the cut (), obtaining (ā ij ā ij )x j ( b i b i ). j F In our case, we have x + x Document prepared by L. Liberti, S. Bosio, S. Coniglio, and C. Iuliano. Translation to English by S. Coniglio 8
9 ex-.-. Foundations of Operations Research Prof. E. Amaldi which, by introducing a surplus variable x becomes x + x x =. Observe that x only occurs in the new row. Therefore, it is directly added to the set of basic variables. We multiply the cut by -, obtaining x x + x =. We obtain the new tableau x x x x x 7 x x () () () Figure : First Gomory cut for problem. We reoptimize the tableau via the dual simplex algorithm. We perform pivoting on the highlighted element x x x x x 7 obtaining the tableau Document prepared by L. Liberti, S. Bosio, S. Coniglio, and C. Iuliano. Translation to English by S. Coniglio 9
10 ex-.-. Foundations of Operations Research Prof. E. Amaldi x x x x x with a solution x = (, ). Since it is not integer, we perform another iteration of the cutting plane method. We pick the second row x x + x =, from which we deduce the Gomory cut x x + x which, in the space of the original variable, amounts to x, x è x + x 7. Its fractional version is x + x. x () () x x () () Figure : Last Gomory cut for problem. We obtain the tableau x x x x x x 6 Performing the pivot operation Document prepared by L. Liberti, S. Bosio, S. Coniglio, and C. Iuliano. Translation to English by S. Coniglio
11 ex-.-. Foundations of Operations Research Prof. E. Amaldi x x x x x x 6 we obtain the tableau x x x x x x 6 8 which yields the integer solution x = (, ), shown in Figure (together with the last Gomory cut that was added). Document prepared by L. Liberti, S. Bosio, S. Coniglio, and C. Iuliano. Translation to English by S. Coniglio
maxz = 3x 1 +4x 2 2x 1 +x 2 6 2x 1 +3x 2 9 x 1,x 2
 ex-5.-5. Foundations of Operations Research Prof. E. Amaldi 5. Branch-and-Bound Given the integer linear program maxz = x +x x +x 6 x +x 9 x,x integer solve it via the Branch-and-Bound method (solving
ex-5.-5. Foundations of Operations Research Prof. E. Amaldi 5. Branch-and-Bound Given the integer linear program maxz = x +x x +x 6 x +x 9 x,x integer solve it via the Branch-and-Bound method (solving
IP Cut Homework from J and B Chapter 9: 14, 15, 16, 23, 24, You wish to solve the IP below with a cutting plane technique.
 IP Cut Homework from J and B Chapter 9: 14, 15, 16, 23, 24, 31 14. You wish to solve the IP below with a cutting plane technique. Maximize 4x 1 + 2x 2 + x 3 subject to 14x 1 + 10x 2 + 11x 3 32 10x 1 +
IP Cut Homework from J and B Chapter 9: 14, 15, 16, 23, 24, 31 14. You wish to solve the IP below with a cutting plane technique. Maximize 4x 1 + 2x 2 + x 3 subject to 14x 1 + 10x 2 + 11x 3 32 10x 1 +
21. Solve the LP given in Exercise 19 using the big-m method discussed in Exercise 20.
 Extra Problems for Chapter 3. Linear Programming Methods 20. (Big-M Method) An alternative to the two-phase method of finding an initial basic feasible solution by minimizing the sum of the artificial
Extra Problems for Chapter 3. Linear Programming Methods 20. (Big-M Method) An alternative to the two-phase method of finding an initial basic feasible solution by minimizing the sum of the artificial
2.13 Maximum flow with a strictly positive initial feasible flow
 ex-.-. Foundations of Operations Research Prof. E. Amaldi. Maximum flow and minimum cut iven the following network with capacities on the arcs find a maximum (feasible) flow from node to node, and determine
ex-.-. Foundations of Operations Research Prof. E. Amaldi. Maximum flow and minimum cut iven the following network with capacities on the arcs find a maximum (feasible) flow from node to node, and determine
Slack Variable. Max Z= 3x 1 + 4x 2 + 5X 3. Subject to: X 1 + X 2 + X x 1 + 4x 2 + X X 1 + X 2 + 4X 3 10 X 1 0, X 2 0, X 3 0
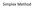 Simplex Method Slack Variable Max Z= 3x 1 + 4x 2 + 5X 3 Subject to: X 1 + X 2 + X 3 20 3x 1 + 4x 2 + X 3 15 2X 1 + X 2 + 4X 3 10 X 1 0, X 2 0, X 3 0 Standard Form Max Z= 3x 1 +4x 2 +5X 3 + 0S 1 + 0S 2
Simplex Method Slack Variable Max Z= 3x 1 + 4x 2 + 5X 3 Subject to: X 1 + X 2 + X 3 20 3x 1 + 4x 2 + X 3 15 2X 1 + X 2 + 4X 3 10 X 1 0, X 2 0, X 3 0 Standard Form Max Z= 3x 1 +4x 2 +5X 3 + 0S 1 + 0S 2
The Simplex Method. Lecture 5 Standard and Canonical Forms and Setting up the Tableau. Lecture 5 Slide 1. FOMGT 353 Introduction to Management Science
 The Simplex Method Lecture 5 Standard and Canonical Forms and Setting up the Tableau Lecture 5 Slide 1 The Simplex Method Formulate Constrained Maximization or Minimization Problem Convert to Standard
The Simplex Method Lecture 5 Standard and Canonical Forms and Setting up the Tableau Lecture 5 Slide 1 The Simplex Method Formulate Constrained Maximization or Minimization Problem Convert to Standard
Sensitivity Analysis
 Dr. Maddah ENMG 500 /9/07 Sensitivity Analysis Changes in the RHS (b) Consider an optimal LP solution. Suppose that the original RHS (b) is changed from b 0 to b new. In the following, we study the affect
Dr. Maddah ENMG 500 /9/07 Sensitivity Analysis Changes in the RHS (b) Consider an optimal LP solution. Suppose that the original RHS (b) is changed from b 0 to b new. In the following, we study the affect
Standard Form An LP is in standard form when: All variables are non-negativenegative All constraints are equalities Putting an LP formulation into sta
 Chapter 4 Linear Programming: The Simplex Method An Overview of the Simplex Method Standard Form Tableau Form Setting Up the Initial Simplex Tableau Improving the Solution Calculating the Next Tableau
Chapter 4 Linear Programming: The Simplex Method An Overview of the Simplex Method Standard Form Tableau Form Setting Up the Initial Simplex Tableau Improving the Solution Calculating the Next Tableau
where X is the feasible region, i.e., the set of the feasible solutions.
 3.5 Branch and Bound Consider a generic Discrete Optimization problem (P) z = max{c(x) : x X }, where X is the feasible region, i.e., the set of the feasible solutions. Branch and Bound is a general semi-enumerative
3.5 Branch and Bound Consider a generic Discrete Optimization problem (P) z = max{c(x) : x X }, where X is the feasible region, i.e., the set of the feasible solutions. Branch and Bound is a general semi-enumerative
Operations Research Lecture 6: Integer Programming
 Operations Research Lecture 6: Integer Programming Notes taken by Kaiquan Xu@Business School, Nanjing University May 12th 2016 1 Integer programming (IP) formulations The integer programming (IP) is the
Operations Research Lecture 6: Integer Programming Notes taken by Kaiquan Xu@Business School, Nanjing University May 12th 2016 1 Integer programming (IP) formulations The integer programming (IP) is the
Foundations of Operations Research
 Solved exercises for the course of Foundations of Operations Research Roberto Cordone The dual simplex method Given the following LP problem: maxz = 5x 1 +8x 2 x 1 +x 2 6 5x 1 +9x 2 45 x 1,x 2 0 1. solve
Solved exercises for the course of Foundations of Operations Research Roberto Cordone The dual simplex method Given the following LP problem: maxz = 5x 1 +8x 2 x 1 +x 2 6 5x 1 +9x 2 45 x 1,x 2 0 1. solve
Simplex Method for LP (II)
 Simplex Method for LP (II) Xiaoxi Li Wuhan University Sept. 27, 2017 (week 4) Operations Research (Li, X.) Simplex Method for LP (II) Sept. 27, 2017 (week 4) 1 / 31 Organization of this lecture Contents:
Simplex Method for LP (II) Xiaoxi Li Wuhan University Sept. 27, 2017 (week 4) Operations Research (Li, X.) Simplex Method for LP (II) Sept. 27, 2017 (week 4) 1 / 31 Organization of this lecture Contents:
Section Notes 9. Midterm 2 Review. Applied Math / Engineering Sciences 121. Week of December 3, 2018
 Section Notes 9 Midterm 2 Review Applied Math / Engineering Sciences 121 Week of December 3, 2018 The following list of topics is an overview of the material that was covered in the lectures and sections
Section Notes 9 Midterm 2 Review Applied Math / Engineering Sciences 121 Week of December 3, 2018 The following list of topics is an overview of the material that was covered in the lectures and sections
Section Notes 9. IP: Cutting Planes. Applied Math 121. Week of April 12, 2010
 Section Notes 9 IP: Cutting Planes Applied Math 121 Week of April 12, 2010 Goals for the week understand what a strong formulations is. be familiar with the cutting planes algorithm and the types of cuts
Section Notes 9 IP: Cutting Planes Applied Math 121 Week of April 12, 2010 Goals for the week understand what a strong formulations is. be familiar with the cutting planes algorithm and the types of cuts
Foundations of Operations Research
 Solved exercises for the course of Foundations of Operations Research Roberto Cordone Gomory cuts Given the ILP problem maxf = 4x 1 +3x 2 2x 1 +x 2 11 x 1 +2x 2 6 x 1,x 2 N solve it with the Gomory cutting
Solved exercises for the course of Foundations of Operations Research Roberto Cordone Gomory cuts Given the ILP problem maxf = 4x 1 +3x 2 2x 1 +x 2 11 x 1 +2x 2 6 x 1,x 2 N solve it with the Gomory cutting
MATH 445/545 Homework 2: Due March 3rd, 2016
 MATH 445/545 Homework 2: Due March 3rd, 216 Answer the following questions. Please include the question with the solution (write or type them out doing this will help you digest the problem). I do not
MATH 445/545 Homework 2: Due March 3rd, 216 Answer the following questions. Please include the question with the solution (write or type them out doing this will help you digest the problem). I do not
The use of shadow price is an example of sensitivity analysis. Duality theory can be applied to do other kind of sensitivity analysis:
 Sensitivity analysis The use of shadow price is an example of sensitivity analysis. Duality theory can be applied to do other kind of sensitivity analysis: Changing the coefficient of a nonbasic variable
Sensitivity analysis The use of shadow price is an example of sensitivity analysis. Duality theory can be applied to do other kind of sensitivity analysis: Changing the coefficient of a nonbasic variable
(includes both Phases I & II)
 (includes both Phases I & II) Dennis ricker Dept of Mechanical & Industrial Engineering The University of Iowa Revised Simplex Method 09/23/04 page 1 of 22 Minimize z=3x + 5x + 4x + 7x + 5x + 4x subject
(includes both Phases I & II) Dennis ricker Dept of Mechanical & Industrial Engineering The University of Iowa Revised Simplex Method 09/23/04 page 1 of 22 Minimize z=3x + 5x + 4x + 7x + 5x + 4x subject
Lecture 11: Post-Optimal Analysis. September 23, 2009
 Lecture : Post-Optimal Analysis September 23, 2009 Today Lecture Dual-Simplex Algorithm Post-Optimal Analysis Chapters 4.4 and 4.5. IE 30/GE 330 Lecture Dual Simplex Method The dual simplex method will
Lecture : Post-Optimal Analysis September 23, 2009 Today Lecture Dual-Simplex Algorithm Post-Optimal Analysis Chapters 4.4 and 4.5. IE 30/GE 330 Lecture Dual Simplex Method The dual simplex method will
The Simplex Method. Formulate Constrained Maximization or Minimization Problem. Convert to Standard Form. Convert to Canonical Form
 The Simplex Method 1 The Simplex Method Formulate Constrained Maximization or Minimization Problem Convert to Standard Form Convert to Canonical Form Set Up the Tableau and the Initial Basic Feasible Solution
The Simplex Method 1 The Simplex Method Formulate Constrained Maximization or Minimization Problem Convert to Standard Form Convert to Canonical Form Set Up the Tableau and the Initial Basic Feasible Solution
Part 1. The Review of Linear Programming
 In the name of God Part 1. The Review of Linear Programming 1.5. Spring 2010 Instructor: Dr. Masoud Yaghini Outline Introduction Formulation of the Dual Problem Primal-Dual Relationship Economic Interpretation
In the name of God Part 1. The Review of Linear Programming 1.5. Spring 2010 Instructor: Dr. Masoud Yaghini Outline Introduction Formulation of the Dual Problem Primal-Dual Relationship Economic Interpretation
F 1 F 2 Daily Requirement Cost N N N
 Chapter 5 DUALITY 5. The Dual Problems Every linear programming problem has associated with it another linear programming problem and that the two problems have such a close relationship that whenever
Chapter 5 DUALITY 5. The Dual Problems Every linear programming problem has associated with it another linear programming problem and that the two problems have such a close relationship that whenever
Math Models of OR: Sensitivity Analysis
 Math Models of OR: Sensitivity Analysis John E. Mitchell Department of Mathematical Sciences RPI, Troy, NY 8 USA October 8 Mitchell Sensitivity Analysis / 9 Optimal tableau and pivot matrix Outline Optimal
Math Models of OR: Sensitivity Analysis John E. Mitchell Department of Mathematical Sciences RPI, Troy, NY 8 USA October 8 Mitchell Sensitivity Analysis / 9 Optimal tableau and pivot matrix Outline Optimal
(includes both Phases I & II)
 Minimize z=3x 5x 4x 7x 5x 4x subject to 2x x2 x4 3x6 0 x 3x3 x4 3x5 2x6 2 4x2 2x3 3x4 x5 5 and x 0 j, 6 2 3 4 5 6 j ecause of the lack of a slack variable in each constraint, we must use Phase I to find
Minimize z=3x 5x 4x 7x 5x 4x subject to 2x x2 x4 3x6 0 x 3x3 x4 3x5 2x6 2 4x2 2x3 3x4 x5 5 and x 0 j, 6 2 3 4 5 6 j ecause of the lack of a slack variable in each constraint, we must use Phase I to find
Simplex tableau CE 377K. April 2, 2015
 CE 377K April 2, 2015 Review Reduced costs Basic and nonbasic variables OUTLINE Review by example: simplex method demonstration Outline Example You own a small firm producing construction materials for
CE 377K April 2, 2015 Review Reduced costs Basic and nonbasic variables OUTLINE Review by example: simplex method demonstration Outline Example You own a small firm producing construction materials for
min 4x 1 5x 2 + 3x 3 s.t. x 1 + 2x 2 + x 3 = 10 x 1 x 2 6 x 1 + 3x 2 + x 3 14
 The exam is three hours long and consists of 4 exercises. The exam is graded on a scale 0-25 points, and the points assigned to each question are indicated in parenthesis within the text. If necessary,
The exam is three hours long and consists of 4 exercises. The exam is graded on a scale 0-25 points, and the points assigned to each question are indicated in parenthesis within the text. If necessary,
Integer Programming. The focus of this chapter is on solution techniques for integer programming models.
 Integer Programming Introduction The general linear programming model depends on the assumption of divisibility. In other words, the decision variables are allowed to take non-negative integer as well
Integer Programming Introduction The general linear programming model depends on the assumption of divisibility. In other words, the decision variables are allowed to take non-negative integer as well
9.1 Linear Programs in canonical form
 9.1 Linear Programs in canonical form LP in standard form: max (LP) s.t. where b i R, i = 1,..., m z = j c jx j j a ijx j b i i = 1,..., m x j 0 j = 1,..., n But the Simplex method works only on systems
9.1 Linear Programs in canonical form LP in standard form: max (LP) s.t. where b i R, i = 1,..., m z = j c jx j j a ijx j b i i = 1,..., m x j 0 j = 1,..., n But the Simplex method works only on systems
(P ) Minimize 4x 1 + 6x 2 + 5x 3 s.t. 2x 1 3x 3 3 3x 2 2x 3 6
 The exam is three hours long and consists of 4 exercises. The exam is graded on a scale 0-25 points, and the points assigned to each question are indicated in parenthesis within the text. Problem 1 Consider
The exam is three hours long and consists of 4 exercises. The exam is graded on a scale 0-25 points, and the points assigned to each question are indicated in parenthesis within the text. Problem 1 Consider
CSC Design and Analysis of Algorithms. LP Shader Electronics Example
 CSC 80- Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture (LP) LP Shader Electronics Example The Shader Electronics Company produces two products:.eclipse, a portable touchscreen digital player; it takes hours
CSC 80- Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture (LP) LP Shader Electronics Example The Shader Electronics Company produces two products:.eclipse, a portable touchscreen digital player; it takes hours
Chap6 Duality Theory and Sensitivity Analysis
 Chap6 Duality Theory and Sensitivity Analysis The rationale of duality theory Max 4x 1 + x 2 + 5x 3 + 3x 4 S.T. x 1 x 2 x 3 + 3x 4 1 5x 1 + x 2 + 3x 3 + 8x 4 55 x 1 + 2x 2 + 3x 3 5x 4 3 x 1 ~x 4 0 If we
Chap6 Duality Theory and Sensitivity Analysis The rationale of duality theory Max 4x 1 + x 2 + 5x 3 + 3x 4 S.T. x 1 x 2 x 3 + 3x 4 1 5x 1 + x 2 + 3x 3 + 8x 4 55 x 1 + 2x 2 + 3x 3 5x 4 3 x 1 ~x 4 0 If we
The dual simplex method with bounds
 The dual simplex method with bounds Linear programming basis. Let a linear programming problem be given by min s.t. c T x Ax = b x R n, (P) where we assume A R m n to be full row rank (we will see in the
The dual simplex method with bounds Linear programming basis. Let a linear programming problem be given by min s.t. c T x Ax = b x R n, (P) where we assume A R m n to be full row rank (we will see in the
23. Cutting planes and branch & bound
 CS/ECE/ISyE 524 Introduction to Optimization Spring 207 8 23. Cutting planes and branch & bound ˆ Algorithms for solving MIPs ˆ Cutting plane methods ˆ Branch and bound methods Laurent Lessard (www.laurentlessard.com)
CS/ECE/ISyE 524 Introduction to Optimization Spring 207 8 23. Cutting planes and branch & bound ˆ Algorithms for solving MIPs ˆ Cutting plane methods ˆ Branch and bound methods Laurent Lessard (www.laurentlessard.com)
Special cases of linear programming
 Special cases of linear programming Infeasible solution Multiple solution (infinitely many solution) Unbounded solution Degenerated solution Notes on the Simplex tableau 1. The intersection of any basic
Special cases of linear programming Infeasible solution Multiple solution (infinitely many solution) Unbounded solution Degenerated solution Notes on the Simplex tableau 1. The intersection of any basic
Introduction to Integer Linear Programming
 Lecture 7/12/2006 p. 1/30 Introduction to Integer Linear Programming Leo Liberti, Ruslan Sadykov LIX, École Polytechnique liberti@lix.polytechnique.fr sadykov@lix.polytechnique.fr Lecture 7/12/2006 p.
Lecture 7/12/2006 p. 1/30 Introduction to Integer Linear Programming Leo Liberti, Ruslan Sadykov LIX, École Polytechnique liberti@lix.polytechnique.fr sadykov@lix.polytechnique.fr Lecture 7/12/2006 p.
4. Duality and Sensitivity
 4. Duality and Sensitivity For every instance of an LP, there is an associated LP known as the dual problem. The original problem is known as the primal problem. There are two de nitions of the dual pair
4. Duality and Sensitivity For every instance of an LP, there is an associated LP known as the dual problem. The original problem is known as the primal problem. There are two de nitions of the dual pair
Points: The first problem is worth 10 points, the others are worth 15. Maximize z = x y subject to 3x y 19 x + 7y 10 x + y = 100.
 Math 5 Summer Points: The first problem is worth points, the others are worth 5. Midterm # Solutions Find the dual of the following linear programming problem. Maximize z = x y x y 9 x + y x + y = x, y
Math 5 Summer Points: The first problem is worth points, the others are worth 5. Midterm # Solutions Find the dual of the following linear programming problem. Maximize z = x y x y 9 x + y x + y = x, y
Week_4: simplex method II
 Week_4: simplex method II 1 1.introduction LPs in which all the constraints are ( ) with nonnegative right-hand sides offer a convenient all-slack starting basic feasible solution. Models involving (=)
Week_4: simplex method II 1 1.introduction LPs in which all the constraints are ( ) with nonnegative right-hand sides offer a convenient all-slack starting basic feasible solution. Models involving (=)
Written Exam Linear and Integer Programming (DM545)
 Written Exam Linear and Integer Programming (DM545) Department of Mathematics and Computer Science University of Southern Denmark Monday, June 22, 2015, 10:00 14:00, Festsalen, Niels Bohr Allé 1 The exam
Written Exam Linear and Integer Programming (DM545) Department of Mathematics and Computer Science University of Southern Denmark Monday, June 22, 2015, 10:00 14:00, Festsalen, Niels Bohr Allé 1 The exam
SOLVING INTEGER LINEAR PROGRAMS. 1. Solving the LP relaxation. 2. How to deal with fractional solutions?
 SOLVING INTEGER LINEAR PROGRAMS 1. Solving the LP relaxation. 2. How to deal with fractional solutions? Integer Linear Program: Example max x 1 2x 2 0.5x 3 0.2x 4 x 5 +0.6x 6 s.t. x 1 +2x 2 1 x 1 + x 2
SOLVING INTEGER LINEAR PROGRAMS 1. Solving the LP relaxation. 2. How to deal with fractional solutions? Integer Linear Program: Example max x 1 2x 2 0.5x 3 0.2x 4 x 5 +0.6x 6 s.t. x 1 +2x 2 1 x 1 + x 2
(tree searching technique) (Boolean formulas) satisfying assignment: (X 1, X 2 )
 Algorithms Chapter 5: The Tree Searching Strategy - Examples 1 / 11 Chapter 5: The Tree Searching Strategy 1. Ex 5.1Determine the satisfiability of the following Boolean formulas by depth-first search
Algorithms Chapter 5: The Tree Searching Strategy - Examples 1 / 11 Chapter 5: The Tree Searching Strategy 1. Ex 5.1Determine the satisfiability of the following Boolean formulas by depth-first search
Example. 1 Rows 1,..., m of the simplex tableau remain lexicographically positive
 3.4 Anticycling Lexicographic order In this section we discuss two pivoting rules that are guaranteed to avoid cycling. These are the lexicographic rule and Bland s rule. Definition A vector u R n is lexicographically
3.4 Anticycling Lexicographic order In this section we discuss two pivoting rules that are guaranteed to avoid cycling. These are the lexicographic rule and Bland s rule. Definition A vector u R n is lexicographically
Summary of the simplex method
 MVE165/MMG630, The simplex method; degeneracy; unbounded solutions; infeasibility; starting solutions; duality; interpretation Ann-Brith Strömberg 2012 03 16 Summary of the simplex method Optimality condition:
MVE165/MMG630, The simplex method; degeneracy; unbounded solutions; infeasibility; starting solutions; duality; interpretation Ann-Brith Strömberg 2012 03 16 Summary of the simplex method Optimality condition:
Math Models of OR: Some Definitions
 Math Models of OR: Some Definitions John E. Mitchell Department of Mathematical Sciences RPI, Troy, NY 12180 USA September 2018 Mitchell Some Definitions 1 / 20 Active constraints Outline 1 Active constraints
Math Models of OR: Some Definitions John E. Mitchell Department of Mathematical Sciences RPI, Troy, NY 12180 USA September 2018 Mitchell Some Definitions 1 / 20 Active constraints Outline 1 Active constraints
The Dual Simplex Algorithm
 p. 1 The Dual Simplex Algorithm Primal optimal (dual feasible) and primal feasible (dual optimal) bases The dual simplex tableau, dual optimality and the dual pivot rules Classical applications of linear
p. 1 The Dual Simplex Algorithm Primal optimal (dual feasible) and primal feasible (dual optimal) bases The dual simplex tableau, dual optimality and the dual pivot rules Classical applications of linear
Introduction to Mathematical Programming IE406. Lecture 21. Dr. Ted Ralphs
 Introduction to Mathematical Programming IE406 Lecture 21 Dr. Ted Ralphs IE406 Lecture 21 1 Reading for This Lecture Bertsimas Sections 10.2, 10.3, 11.1, 11.2 IE406 Lecture 21 2 Branch and Bound Branch
Introduction to Mathematical Programming IE406 Lecture 21 Dr. Ted Ralphs IE406 Lecture 21 1 Reading for This Lecture Bertsimas Sections 10.2, 10.3, 11.1, 11.2 IE406 Lecture 21 2 Branch and Bound Branch
9.5 THE SIMPLEX METHOD: MIXED CONSTRAINTS
 SECTION 9.5 THE SIMPLEX METHOD: MIXED CONSTRAINTS 557 9.5 THE SIMPLEX METHOD: MIXED CONSTRAINTS In Sections 9. and 9., you looked at linear programming problems that occurred in standard form. The constraints
SECTION 9.5 THE SIMPLEX METHOD: MIXED CONSTRAINTS 557 9.5 THE SIMPLEX METHOD: MIXED CONSTRAINTS In Sections 9. and 9., you looked at linear programming problems that occurred in standard form. The constraints
Systems Analysis in Construction
 Systems Analysis in Construction CB312 Construction & Building Engineering Department- AASTMT by A h m e d E l h a k e e m & M o h a m e d S a i e d 3. Linear Programming Optimization Simplex Method 135
Systems Analysis in Construction CB312 Construction & Building Engineering Department- AASTMT by A h m e d E l h a k e e m & M o h a m e d S a i e d 3. Linear Programming Optimization Simplex Method 135
3.10 Column generation method
 3.10 Column generation method Many relevant decision-making (discrete optimization) problems can be formulated as ILP problems with a very large (exponential) number of variables. Examples: cutting stock,
3.10 Column generation method Many relevant decision-making (discrete optimization) problems can be formulated as ILP problems with a very large (exponential) number of variables. Examples: cutting stock,
If the above problem is hard to solve, we might try to break it into smaller problems which are easier to solve.
 8 Branch and Bound 8.1 Divide and Conquer uppose that we would like to solve the problem { z = max c T x : x. If the above problem is hard to solve, we might try to break it into smaller problems which
8 Branch and Bound 8.1 Divide and Conquer uppose that we would like to solve the problem { z = max c T x : x. If the above problem is hard to solve, we might try to break it into smaller problems which
The simplex algorithm
 The simplex algorithm The simplex algorithm is the classical method for solving linear programs. Its running time is not polynomial in the worst case. It does yield insight into linear programs, however,
The simplex algorithm The simplex algorithm is the classical method for solving linear programs. Its running time is not polynomial in the worst case. It does yield insight into linear programs, however,
1 Review Session. 1.1 Lecture 2
 1 Review Session Note: The following lists give an overview of the material that was covered in the lectures and sections. Your TF will go through these lists. If anything is unclear or you have questions
1 Review Session Note: The following lists give an overview of the material that was covered in the lectures and sections. Your TF will go through these lists. If anything is unclear or you have questions
"SYMMETRIC" PRIMAL-DUAL PAIR
 "SYMMETRIC" PRIMAL-DUAL PAIR PRIMAL Minimize cx DUAL Maximize y T b st Ax b st A T y c T x y Here c 1 n, x n 1, b m 1, A m n, y m 1, WITH THE PRIMAL IN STANDARD FORM... Minimize cx Maximize y T b st Ax
"SYMMETRIC" PRIMAL-DUAL PAIR PRIMAL Minimize cx DUAL Maximize y T b st Ax b st A T y c T x y Here c 1 n, x n 1, b m 1, A m n, y m 1, WITH THE PRIMAL IN STANDARD FORM... Minimize cx Maximize y T b st Ax
AM 121: Intro to Optimization
 AM 121: Intro to Optimization Models and Methods Lecture 6: Phase I, degeneracy, smallest subscript rule. Yiling Chen SEAS Lesson Plan Phase 1 (initialization) Degeneracy and cycling Smallest subscript
AM 121: Intro to Optimization Models and Methods Lecture 6: Phase I, degeneracy, smallest subscript rule. Yiling Chen SEAS Lesson Plan Phase 1 (initialization) Degeneracy and cycling Smallest subscript
Ω R n is called the constraint set or feasible set. x 1
 1 Chapter 5 Linear Programming (LP) General constrained optimization problem: minimize subject to f(x) x Ω Ω R n is called the constraint set or feasible set. any point x Ω is called a feasible point We
1 Chapter 5 Linear Programming (LP) General constrained optimization problem: minimize subject to f(x) x Ω Ω R n is called the constraint set or feasible set. any point x Ω is called a feasible point We
to work with) can be solved by solving their LP relaxations with the Simplex method I Cutting plane algorithms, e.g., Gomory s fractional cutting
 Summary so far z =max{c T x : Ax apple b, x 2 Z n +} I Modeling with IP (and MIP, and BIP) problems I Formulation for a discrete set that is a feasible region of an IP I Alternative formulations for the
Summary so far z =max{c T x : Ax apple b, x 2 Z n +} I Modeling with IP (and MIP, and BIP) problems I Formulation for a discrete set that is a feasible region of an IP I Alternative formulations for the
AM 121: Intro to Optimization Models and Methods Fall 2018
 AM 121: Intro to Optimization Models and Methods Fall 2018 Lecture 5: The Simplex Method Yiling Chen Harvard SEAS Lesson Plan This lecture: Moving towards an algorithm for solving LPs Tableau. Adjacent
AM 121: Intro to Optimization Models and Methods Fall 2018 Lecture 5: The Simplex Method Yiling Chen Harvard SEAS Lesson Plan This lecture: Moving towards an algorithm for solving LPs Tableau. Adjacent
Linear Programming Duality P&S Chapter 3 Last Revised Nov 1, 2004
 Linear Programming Duality P&S Chapter 3 Last Revised Nov 1, 2004 1 In this section we lean about duality, which is another way to approach linear programming. In particular, we will see: How to define
Linear Programming Duality P&S Chapter 3 Last Revised Nov 1, 2004 1 In this section we lean about duality, which is another way to approach linear programming. In particular, we will see: How to define
Relation of Pure Minimum Cost Flow Model to Linear Programming
 Appendix A Page 1 Relation of Pure Minimum Cost Flow Model to Linear Programming The Network Model The network pure minimum cost flow model has m nodes. The external flows given by the vector b with m
Appendix A Page 1 Relation of Pure Minimum Cost Flow Model to Linear Programming The Network Model The network pure minimum cost flow model has m nodes. The external flows given by the vector b with m
CPS 616 ITERATIVE IMPROVEMENTS 10-1
 CPS 66 ITERATIVE IMPROVEMENTS 0 - APPROACH Algorithm design technique for solving optimization problems Start with a feasible solution Repeat the following step until no improvement can be found: change
CPS 66 ITERATIVE IMPROVEMENTS 0 - APPROACH Algorithm design technique for solving optimization problems Start with a feasible solution Repeat the following step until no improvement can be found: change
MAT016: Optimization
 MAT016: Optimization M.El Ghami e-mail: melghami@ii.uib.no URL: http://www.ii.uib.no/ melghami/ March 29, 2011 Outline for today The Simplex method in matrix notation Managing a production facility The
MAT016: Optimization M.El Ghami e-mail: melghami@ii.uib.no URL: http://www.ii.uib.no/ melghami/ March 29, 2011 Outline for today The Simplex method in matrix notation Managing a production facility The
56:270 Final Exam - May
 @ @ 56:270 Linear Programming @ @ Final Exam - May 4, 1989 @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ Select any 7 of the 9 problems below: (1.) ANALYSIS OF MPSX OUTPUT: Please refer to the attached materials on the
@ @ 56:270 Linear Programming @ @ Final Exam - May 4, 1989 @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ @ Select any 7 of the 9 problems below: (1.) ANALYSIS OF MPSX OUTPUT: Please refer to the attached materials on the
Lecture 23 Branch-and-Bound Algorithm. November 3, 2009
 Branch-and-Bound Algorithm November 3, 2009 Outline Lecture 23 Modeling aspect: Either-Or requirement Special ILPs: Totally unimodular matrices Branch-and-Bound Algorithm Underlying idea Terminology Formal
Branch-and-Bound Algorithm November 3, 2009 Outline Lecture 23 Modeling aspect: Either-Or requirement Special ILPs: Totally unimodular matrices Branch-and-Bound Algorithm Underlying idea Terminology Formal
Dual Basic Solutions. Observation 5.7. Consider LP in standard form with A 2 R m n,rank(a) =m, and dual LP:
 Dual Basic Solutions Consider LP in standard form with A 2 R m n,rank(a) =m, and dual LP: Observation 5.7. AbasisB yields min c T x max p T b s.t. A x = b s.t. p T A apple c T x 0 aprimalbasicsolutiongivenbyx
Dual Basic Solutions Consider LP in standard form with A 2 R m n,rank(a) =m, and dual LP: Observation 5.7. AbasisB yields min c T x max p T b s.t. A x = b s.t. p T A apple c T x 0 aprimalbasicsolutiongivenbyx
Worked Examples for Chapter 5
 Worked Examples for Chapter 5 Example for Section 5.2 Construct the primal-dual table and the dual problem for the following linear programming model fitting our standard form. Maximize Z = 5 x 1 + 4 x
Worked Examples for Chapter 5 Example for Section 5.2 Construct the primal-dual table and the dual problem for the following linear programming model fitting our standard form. Maximize Z = 5 x 1 + 4 x
IE 400 Principles of Engineering Management. The Simplex Algorithm-I: Set 3
 IE 4 Principles of Engineering Management The Simple Algorithm-I: Set 3 So far, we have studied how to solve two-variable LP problems graphically. However, most real life problems have more than two variables!
IE 4 Principles of Engineering Management The Simple Algorithm-I: Set 3 So far, we have studied how to solve two-variable LP problems graphically. However, most real life problems have more than two variables!
1. Algebraic and geometric treatments Consider an LP problem in the standard form. x 0. Solutions to the system of linear equations
 The Simplex Method Most textbooks in mathematical optimization, especially linear programming, deal with the simplex method. In this note we study the simplex method. It requires basically elementary linear
The Simplex Method Most textbooks in mathematical optimization, especially linear programming, deal with the simplex method. In this note we study the simplex method. It requires basically elementary linear
Integer Programming. Wolfram Wiesemann. December 6, 2007
 Integer Programming Wolfram Wiesemann December 6, 2007 Contents of this Lecture Revision: Mixed Integer Programming Problems Branch & Bound Algorithms: The Big Picture Solving MIP s: Complete Enumeration
Integer Programming Wolfram Wiesemann December 6, 2007 Contents of this Lecture Revision: Mixed Integer Programming Problems Branch & Bound Algorithms: The Big Picture Solving MIP s: Complete Enumeration
3.10 Column generation method
 3.10 Column generation method Many relevant decision-making problems can be formulated as ILP problems with a very large (exponential) number of variables. Examples: cutting stock, crew scheduling, vehicle
3.10 Column generation method Many relevant decision-making problems can be formulated as ILP problems with a very large (exponential) number of variables. Examples: cutting stock, crew scheduling, vehicle
TIM 206 Lecture 3: The Simplex Method
 TIM 206 Lecture 3: The Simplex Method Kevin Ross. Scribe: Shane Brennan (2006) September 29, 2011 1 Basic Feasible Solutions Have equation Ax = b contain more columns (variables) than rows (constraints),
TIM 206 Lecture 3: The Simplex Method Kevin Ross. Scribe: Shane Brennan (2006) September 29, 2011 1 Basic Feasible Solutions Have equation Ax = b contain more columns (variables) than rows (constraints),
Written Exam Linear and Integer Programming (DM554)
 Written Exam Linear and Integer Programming (DM554) Department of Mathematics and Computer Science University of Southern Denmark Monday, June 22, 2015, 10:00 14:00, Festsalen, Niels Bohr Allé 1 The exam
Written Exam Linear and Integer Programming (DM554) Department of Mathematics and Computer Science University of Southern Denmark Monday, June 22, 2015, 10:00 14:00, Festsalen, Niels Bohr Allé 1 The exam
CS Algorithms and Complexity
 CS 50 - Algorithms and Complexity Linear Programming, the Simplex Method, and Hard Problems Sean Anderson 2/15/18 Portland State University Table of contents 1. The Simplex Method 2. The Graph Problem
CS 50 - Algorithms and Complexity Linear Programming, the Simplex Method, and Hard Problems Sean Anderson 2/15/18 Portland State University Table of contents 1. The Simplex Method 2. The Graph Problem
3 The Simplex Method. 3.1 Basic Solutions
 3 The Simplex Method 3.1 Basic Solutions In the LP of Example 2.3, the optimal solution happened to lie at an extreme point of the feasible set. This was not a coincidence. Consider an LP in general form,
3 The Simplex Method 3.1 Basic Solutions In the LP of Example 2.3, the optimal solution happened to lie at an extreme point of the feasible set. This was not a coincidence. Consider an LP in general form,
Metode Kuantitatif Bisnis. Week 4 Linear Programming Simplex Method - Minimize
 Metode Kuantitatif Bisnis Week 4 Linear Programming Simplex Method - Minimize Outlines Solve Linear Programming Model Using Graphic Solution Solve Linear Programming Model Using Simplex Method (Maximize)
Metode Kuantitatif Bisnis Week 4 Linear Programming Simplex Method - Minimize Outlines Solve Linear Programming Model Using Graphic Solution Solve Linear Programming Model Using Simplex Method (Maximize)
4.6 Linear Programming duality
 4.6 Linear Programming duality To any minimization (maximization) LP we can associate a closely related maximization (minimization) LP Different spaces and objective functions but in general same optimal
4.6 Linear Programming duality To any minimization (maximization) LP we can associate a closely related maximization (minimization) LP Different spaces and objective functions but in general same optimal
Chapter 5 Linear Programming (LP)
 Chapter 5 Linear Programming (LP) General constrained optimization problem: minimize f(x) subject to x R n is called the constraint set or feasible set. any point x is called a feasible point We consider
Chapter 5 Linear Programming (LP) General constrained optimization problem: minimize f(x) subject to x R n is called the constraint set or feasible set. any point x is called a feasible point We consider
TRANSPORTATION PROBLEMS
 Chapter 6 TRANSPORTATION PROBLEMS 61 Transportation Model Transportation models deal with the determination of a minimum-cost plan for transporting a commodity from a number of sources to a number of destinations
Chapter 6 TRANSPORTATION PROBLEMS 61 Transportation Model Transportation models deal with the determination of a minimum-cost plan for transporting a commodity from a number of sources to a number of destinations
ECE 307 Techniques for Engineering Decisions
 ECE 7 Techniques for Engineering Decisions Introduction to the Simple Algorithm George Gross Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign ECE 7 5 9 George
ECE 7 Techniques for Engineering Decisions Introduction to the Simple Algorithm George Gross Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign ECE 7 5 9 George
Yinyu Ye, MS&E, Stanford MS&E310 Lecture Note #06. The Simplex Method
 The Simplex Method Yinyu Ye Department of Management Science and Engineering Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305, U.S.A. http://www.stanford.edu/ yyye (LY, Chapters 2.3-2.5, 3.1-3.4) 1 Geometry of Linear
The Simplex Method Yinyu Ye Department of Management Science and Engineering Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305, U.S.A. http://www.stanford.edu/ yyye (LY, Chapters 2.3-2.5, 3.1-3.4) 1 Geometry of Linear
IE 5531: Engineering Optimization I
 IE 5531: Engineering Optimization I Lecture 5: The Simplex method, continued Prof. John Gunnar Carlsson September 22, 2010 Prof. John Gunnar Carlsson IE 5531: Engineering Optimization I September 22, 2010
IE 5531: Engineering Optimization I Lecture 5: The Simplex method, continued Prof. John Gunnar Carlsson September 22, 2010 Prof. John Gunnar Carlsson IE 5531: Engineering Optimization I September 22, 2010
Optimization Methods in Management Science
 Optimization Methods in Management Science MIT 15.05 Recitation 8 TAs: Giacomo Nannicini, Ebrahim Nasrabadi At the end of this recitation, students should be able to: 1. Derive Gomory cut from fractional
Optimization Methods in Management Science MIT 15.05 Recitation 8 TAs: Giacomo Nannicini, Ebrahim Nasrabadi At the end of this recitation, students should be able to: 1. Derive Gomory cut from fractional
Optimization Exercise Set n.5 :
 Optimization Exercise Set n.5 : Prepared by S. Coniglio translated by O. Jabali 2016/2017 1 5.1 Airport location In air transportation, usually there is not a direct connection between every pair of airports.
Optimization Exercise Set n.5 : Prepared by S. Coniglio translated by O. Jabali 2016/2017 1 5.1 Airport location In air transportation, usually there is not a direct connection between every pair of airports.
OPRE 6201 : 3. Special Cases
 OPRE 6201 : 3. Special Cases 1 Initialization: The Big-M Formulation Consider the linear program: Minimize 4x 1 +x 2 3x 1 +x 2 = 3 (1) 4x 1 +3x 2 6 (2) x 1 +2x 2 3 (3) x 1, x 2 0. Notice that there are
OPRE 6201 : 3. Special Cases 1 Initialization: The Big-M Formulation Consider the linear program: Minimize 4x 1 +x 2 3x 1 +x 2 = 3 (1) 4x 1 +3x 2 6 (2) x 1 +2x 2 3 (3) x 1, x 2 0. Notice that there are
In Chapters 3 and 4 we introduced linear programming
 SUPPLEMENT The Simplex Method CD3 In Chapters 3 and 4 we introduced linear programming and showed how models with two variables can be solved graphically. We relied on computer programs (WINQSB, Excel,
SUPPLEMENT The Simplex Method CD3 In Chapters 3 and 4 we introduced linear programming and showed how models with two variables can be solved graphically. We relied on computer programs (WINQSB, Excel,
MATH2070 Optimisation
 MATH2070 Optimisation Linear Programming Semester 2, 2012 Lecturer: I.W. Guo Lecture slides courtesy of J.R. Wishart Review The standard Linear Programming (LP) Problem Graphical method of solving LP problem
MATH2070 Optimisation Linear Programming Semester 2, 2012 Lecturer: I.W. Guo Lecture slides courtesy of J.R. Wishart Review The standard Linear Programming (LP) Problem Graphical method of solving LP problem
OPERATIONS RESEARCH. Michał Kulej. Business Information Systems
 OPERATIONS RESEARCH Michał Kulej Business Information Systems The development of the potential and academic programmes of Wrocław University of Technology Project co-financed by European Union within European
OPERATIONS RESEARCH Michał Kulej Business Information Systems The development of the potential and academic programmes of Wrocław University of Technology Project co-financed by European Union within European
Note 3: LP Duality. If the primal problem (P) in the canonical form is min Z = n (1) then the dual problem (D) in the canonical form is max W = m (2)
 Note 3: LP Duality If the primal problem (P) in the canonical form is min Z = n j=1 c j x j s.t. nj=1 a ij x j b i i = 1, 2,..., m (1) x j 0 j = 1, 2,..., n, then the dual problem (D) in the canonical
Note 3: LP Duality If the primal problem (P) in the canonical form is min Z = n j=1 c j x j s.t. nj=1 a ij x j b i i = 1, 2,..., m (1) x j 0 j = 1, 2,..., n, then the dual problem (D) in the canonical
Linear Programming, Lecture 4
 Linear Programming, Lecture 4 Corbett Redden October 3, 2016 Simplex Form Conventions Examples Simplex Method To run the simplex method, we start from a Linear Program (LP) in the following standard simplex
Linear Programming, Lecture 4 Corbett Redden October 3, 2016 Simplex Form Conventions Examples Simplex Method To run the simplex method, we start from a Linear Program (LP) in the following standard simplex
UNIVERSITY of LIMERICK
 UNIVERSITY of LIMERICK OLLSCOIL LUIMNIGH Department of Mathematics & Statistics Faculty of Science and Engineering END OF SEMESTER ASSESSMENT PAPER MODULE CODE: MS4303 SEMESTER: Spring 2018 MODULE TITLE:
UNIVERSITY of LIMERICK OLLSCOIL LUIMNIGH Department of Mathematics & Statistics Faculty of Science and Engineering END OF SEMESTER ASSESSMENT PAPER MODULE CODE: MS4303 SEMESTER: Spring 2018 MODULE TITLE:
Fundamental Theorems of Optimization
 Fundamental Theorems of Optimization 1 Fundamental Theorems of Math Prog. Maximizing a concave function over a convex set. Maximizing a convex function over a closed bounded convex set. 2 Maximizing Concave
Fundamental Theorems of Optimization 1 Fundamental Theorems of Math Prog. Maximizing a concave function over a convex set. Maximizing a convex function over a closed bounded convex set. 2 Maximizing Concave
4.5 Simplex method. min z = c T x s.v. Ax = b. LP in standard form
 4.5 Simplex method min z = c T x s.v. Ax = b x 0 LP in standard form Examine a sequence of basic feasible solutions with non increasing objective function value until an optimal solution is reached or
4.5 Simplex method min z = c T x s.v. Ax = b x 0 LP in standard form Examine a sequence of basic feasible solutions with non increasing objective function value until an optimal solution is reached or
Gestion de la production. Book: Linear Programming, Vasek Chvatal, McGill University, W.H. Freeman and Company, New York, USA
 Gestion de la production Book: Linear Programming, Vasek Chvatal, McGill University, W.H. Freeman and Company, New York, USA 1 Contents 1 Integer Linear Programming 3 1.1 Definitions and notations......................................
Gestion de la production Book: Linear Programming, Vasek Chvatal, McGill University, W.H. Freeman and Company, New York, USA 1 Contents 1 Integer Linear Programming 3 1.1 Definitions and notations......................................
Week 3: Simplex Method I
 Week 3: Simplex Method I 1 1. Introduction The simplex method computations are particularly tedious and repetitive. It attempts to move from one corner point of the solution space to a better corner point
Week 3: Simplex Method I 1 1. Introduction The simplex method computations are particularly tedious and repetitive. It attempts to move from one corner point of the solution space to a better corner point
Integer Linear Programming
 Integer Linear Programming Solution : cutting planes and Branch and Bound Hugues Talbot Laboratoire CVN April 13, 2018 IP Resolution Gomory s cutting planes Solution branch-and-bound General method Resolution
Integer Linear Programming Solution : cutting planes and Branch and Bound Hugues Talbot Laboratoire CVN April 13, 2018 IP Resolution Gomory s cutting planes Solution branch-and-bound General method Resolution
Optimization Exercise Set n. 4 :
 Optimization Exercise Set n. 4 : Prepared by S. Coniglio and E. Amaldi translated by O. Jabali 2018/2019 1 4.1 Airport location In air transportation, usually there is not a direct connection between every
Optimization Exercise Set n. 4 : Prepared by S. Coniglio and E. Amaldi translated by O. Jabali 2018/2019 1 4.1 Airport location In air transportation, usually there is not a direct connection between every
CO350 Linear Programming Chapter 8: Degeneracy and Finite Termination
 CO350 Linear Programming Chapter 8: Degeneracy and Finite Termination 27th June 2005 Chapter 8: Finite Termination 1 The perturbation method Recap max c T x (P ) s.t. Ax = b x 0 Assumption: B is a feasible
CO350 Linear Programming Chapter 8: Degeneracy and Finite Termination 27th June 2005 Chapter 8: Finite Termination 1 The perturbation method Recap max c T x (P ) s.t. Ax = b x 0 Assumption: B is a feasible
AM 121 Introduction to Optimization: Models and Methods Example Questions for Midterm 1
 AM 121 Introduction to Optimization: Models and Methods Example Questions for Midterm 1 Prof. Yiling Chen Fall 2018 Here are some practice questions to help to prepare for the midterm. The midterm will
AM 121 Introduction to Optimization: Models and Methods Example Questions for Midterm 1 Prof. Yiling Chen Fall 2018 Here are some practice questions to help to prepare for the midterm. The midterm will
March 13, Duality 3
 15.53 March 13, 27 Duality 3 There are concepts much more difficult to grasp than duality in linear programming. -- Jim Orlin The concept [of nonduality], often described in English as "nondualism," is
15.53 March 13, 27 Duality 3 There are concepts much more difficult to grasp than duality in linear programming. -- Jim Orlin The concept [of nonduality], often described in English as "nondualism," is
Section Notes 8. Integer Programming II. Applied Math 121. Week of April 5, expand your knowledge of big M s and logical constraints.
 Section Notes 8 Integer Programming II Applied Math 121 Week of April 5, 2010 Goals for the week understand IP relaxations be able to determine the relative strength of formulations understand the branch
Section Notes 8 Integer Programming II Applied Math 121 Week of April 5, 2010 Goals for the week understand IP relaxations be able to determine the relative strength of formulations understand the branch
1 Column Generation and the Cutting Stock Problem
 1 Column Generation and the Cutting Stock Problem In the linear programming approach to the traveling salesman problem we used the cutting plane approach. The cutting plane approach is appropriate when
1 Column Generation and the Cutting Stock Problem In the linear programming approach to the traveling salesman problem we used the cutting plane approach. The cutting plane approach is appropriate when
