f(w) w z =R z a 0 a n a nz n Liouville s theorem, we see that Q is constant, which implies that P is constant, which is a contradiction.
|
|
|
- Arthur Heath
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Theorem [Liouville s Theorem] Every bouded etire fuctio is costat. Proof. Let f be a etire fuctio. Suppose that there is M R such that M for ay z C. The for ay z C ad R > 0 f (z) f(w) 2πi (w z) 2 dw. f(w) w z R For w { w z R}, f(w) M. Thus, (w z) 2 R 2 R 2 f (z) M L({ z w R}) 2π R2 2π M R 2 2πR M R. Sice this holds for ay R > 0, we get f (z) 0 for ay z C. Thus, f is costat. Theorem Suppose that there exists costat C, M > 0 ad k N such that Prove that f is a polyomial of degree k. C z k, if z M. Proof. We left this as a homework problem. Hit: Use the Cauchy itegral formula to estimate f (k+) (z) usig the Jorda curve J { z R} with R M ad R > z. The let R. Theorem [Fudametal Theorem of Algebra] Ay o-costat polyomial has a root i C. Proof. Let P (z) a 0 + a z + a z be a o-costat polyomial with a 0. Suppose P has o zero i C. The Q(z) /P (z) is holomorphic i C. We will show that Q is bouded o C. This requires a careful estimatio. We fid that P (z) a z + a a z + + a 0 z, as z. Thus, there is R > 0 such that P (z) a z /2 for z > R. This the implies that Q(z) 2 a z 2 a R if z > R. Sice Q is cotiuous o the compact set D(0, R), it is bouded o this set. So there is M 0 > 0 such that Q(z) M 0 if z R. Let M 2 max{m 0, a R }. The Q(z) M for ay z C. So Q is a bouded etire fuctio. Applyig Liouville s theorem, we see that Q is costat, which implies that P is costat, which is a cotradictio. Theorem Suppose f is cotiuous o a domai U, ad satisfies that for ay closed path γ i U, γ f 0. The f is aalytic. Proof. From a theorem we studied, f has a primitive F i U. Such F is holomorphic, which is also aalytic. So f F is also aalytic i U. 43
2 4.2 Lauret Series We will cosider the series of the form z, where (z ) Z is a sequece of complex umbers. The series coverges if ad oly if the followig two series both coverge: z, ad the sum z is defied to be z z, z z + The Lauret series (cetered at 0) is of the form a z, where a, Z, are complex umbers. It coverges iff the followig two series both coverges: a z, a z. The first is a power series. The secod ca also be trasferred to a power series: a z z. a (/z). Suppose the radius of a z is R +, ad the radius of a w is R. The a z coverges whe z < R + ad /z < R, i.e., /R < z < R +. Suppose that /R < R +. Let R R +, r /R, ad let A be the aulus {r < z < R}. Let f + (z) a z, g (w) a w, ad f (z) g (/z). The f + is holomorphic i D(0, R + ) D(0, R) ad g is holomorphic i D(0, R ). So f is holomorphic i { z > /R } { z > r}, ad f f + + f is holomorphic i A. Moreover, we have f +(z) a z ad g (w) a w. Usig chai rule, we get f (z) g ( z ) z 2 Thus, the derivative of f f + + f is a z f (z) a z. k ka k z k. 48
3 Theorem Let r < R [0, ]. Suppose that f is holomorphic o A {z : r < z < R}. The f has a Lauret expasio: where a z, z A, a dz, Z, r < t < R. (4.) 2πi z t z+ Proof. First, from Cauchy s theorem, the value of each a does ot deped o t. Let z 0 A. Pick s < S (r, R) such that s < z 0 < S. Let ε mi{ z 0 s, S z 0 }/2 > 0. Let J { z S}, J 2 { z s}, ad J 3 { ε}. The J 2 ad J 3 lie iside J. The fuctio z z 0 is holomorphic o J, J 2, J 3, ad the domai bouded by these circles. From Cauchy s Theorem ad Cauchy s itegral formula, Now we expad z z 0 J dz usig J 2 dz J 3 dz 2πif(z 0 ). /z z 0 /z z0 z +, z J. /z 0 z/z 0 J k0 z k+ 0 z k k z 0 z +, z J 2. The first holds because z 0 /z < for z J. The secod holds because z/z 0 < for z J 2. Thus, 2πif(z 0 ) dz dz J J 2 z 0 z0 dz + z+ z + dz. J 2 If the ifiite sums exchage with the lie itegrals, we have 2πif(z 0 ) ( J ) z + dz z0 + ( J 2 ) z + dz z0 2πia z 0. (4.2) It remais to show that the ifiite sums exchage with the lie itegrals. Note that, for z J, z 0 z 0 z + f J R +, 49
4 ad from z 0 /R <, we fid that For z J 2, ad from z 0 /r >, we fid that z 0 f J R + f J R z 0 z 0 z + f J2 r +, z 0 f J2 r + f J 2 r k From compariso priciple, we justify the step i (4.2). ( z0 ) <. R ( r ) k <. z 0 Similarly, if f is holomorphic i A {r < < R}, the f has a Lauret series expasio i A: a ( ), where a dz, Z, r < t < R. 2πi z z 0 t ( ) + Usually, we do ot use (4.) to compute the coefficiets. O the cotrary, we use other methods to fid the coefficiets, ad use (4.) to compute the itegral. For example, from the power series of e z, we fid that e /z z /! 0 z ( )!, z 0. the coefficiets for e /z are a 0 whe > 0, ad a /( )! whe 0. The series coverges i the aulus {0 < z < }. The we ca compute z r e /z z + dz 2πia 2πi( )!, 0. Other examples appear i the above proof. We used two ways to expad z z 0 : /z z 0 /z z0 ; (4.3) z+ /z 0 z/z 0 z k k0 z k+ 0 k z0. (4.4) z+ 50
5 The first coverges o {z : z > z 0 }. The secod coverges o {z : z < z 0 }. Suppose a z z + b z z 2, ad z < z 2. The f is holomorphic o C \ {z, z 2 }. To fid the Lauret series of f i { z > z 2 }, we expad both /(z z ) ad /(z z 2 ) usig (4.3). To fid the Lauret series of f i { z < z }, we expad both /(z z ) ad /(z z 2 ) usig (4.4). To fid the Lauret series of f i { z < z < z 2 }, we expad /(z z ) usig (4.3), ad expad /(z z 2 ) usig (4.4). Example. Let Fid the Lauret series for f: (a) i { z < 2}; (b) i (z 2)(z 5). {2 < z < 5}; (c) i { z > 5}. First, we may write ad b /3. We have Thus, i { z < 2}, i {2 < z < 5}, a z 2 + /3 z 2 /6 z/2 6 /3 /3 /z z 2 2/z b z 5. Solvig a liear equatio, we fid that a /3 ( z 2) z, z < 2; 6 2 3z /3 z 5 /5 z/5 5 /3 z 5 /(3z) 5/z 3z ( 2 ) 2, z > 2; z 3z+ ( z 5) z 5, z < 5; 5 ( 5 ) 5, z > 5. z 3z+ ( )z ; 2 3z + + z 5 5 ; ad i { z > 5}, 2 /3 + 5 /3 z +. If we kow the Lauret series for f: a z, the the Lauret series for z m is a z +m, the Lauret series for f(/z) is a z, ad the Lauret series for f(z m ) is a z m. 5
6 4.3 Isolated Sigularities Suppose f is holomorphic i U, z 0 U, but there is r > 0 such that D(z 0, r)\{z 0 } U. The we say that z 0 is a isolated sigularity of f. The f has a Lauret expasio i {0 < z z 0 < r}: where a ( ), (4.5) a dz, Z, t (0, r). (4.6) 2πi z z 0 t ( ) + Case : a 0 for all N. The (4.5) becomes the usual power series a (z z 0 ), which coverges to a holomorphic fuctio i { < r}. Thus, if we defie f(z 0 ) a 0, the f is holomorphic i U {z 0 }. I this case, we call z 0 a removable sigularity. Case 2: Not all a, N, equal to 0, ad there are oly fiitely may ozero a. We may fid m N such that a m 0 ad a 0 for > m. I this case, we call z 0 a pole of f of order m. We fid that z 0 is a removable sigularity of g(z) : ( ) m, ad g(z 0 ) a m 0. A pole of order is called a simple pole. Case 3: There are ifiitely may ozero a, N. I this case, we call z 0 a essetial sigularity of f. For ay m N, z 0 is still a (essetial) sigularity of ( ) m. Defiitio The series a ( ) is called the pricipal part at z 0 of f. Suppose there is m Z such that a m 0 ad for all < m, a 0. This meas that z 0 is either a removable sigularity or a pole, ad f is ot costat 0 ear z 0. I this case, we say that the order of f at z 0 is m, ad write ord z0 f m. We see that ord z0 f m if ad oly if there is a holomorphic fuctio g i D(z 0, r) with g(z 0 ) 0 such that ( ) m g(z). If m 0, z 0 is removable. If m, z 0 is a zero of f after removig the sigularity, ad we say that z 0 is a zero of f of order m. A zero of order is called a simple zero. Sice a f () (z 0 )!, z 0 is a zero of order m iff f (k) (z 0 ) 0 for 0 k m ad f (m) (z 0 ) 0. If m < 0, z 0 is a pole of f of order m. Note that if f ad g are holomorphic at z 0, ad if f(z 0 ), g(z 0 ) 0, the h fg ad h 2 f/g are both holomorphic at z 0, ad h (z 0 ), h 2 (z 0 ) 0. So we have ord z0 (f f 2 ) ord z0 f + ord z0 f 2, ord z0 (f /f 2 ) ord z0 f ord z0 f 2. Examples. Sice ord 0 z ord 0 si z, we have ord 0 /z ord 0 / si z, which implies that 0 is a simple pole of /z ad / si z. From ord 0 si z/z ord 0 si z ord 0 z 0, we see that 0 is a removable sigularity of si z/z. After removig the sigularity 0, we exted si z/z to a etire fuctio. 52
7 Defiitio Let U be a ope set. Suppose that S U has o accumulatio poit i U. If f is holomorphic i U \ S, ad each z 0 S is a pole of f, the we say that f is meromorphic o U. A meromorphic fuctio may be costructed by the quotiet of two holomorphic fuctios. Suppose f ad g are holomorphic i a domai U such that g is ot costat 0. Let Z deote the set of zeros of g. The Z has o accumulatio poit i U. Let h f/g. The h is holomorphic i U \ Z. Every z Z is either a removable sigularity or a pole of h depedig o whether ord z f ord z g. By extedig h to the removable sigularities, we obtai a meromorphic fuctio o U. Examples. ta z si z cos z cos z ad cot z si z are meromorphic i C. For ta z, sice the zeroes of cos z are kπ + π/2, k Z, which are simple because cos z si z 0 at kπ + π/2, ad sice si(kπ +π/2) 0, we fid that every kπ +π/2 is a simple pole of ta z. Similarly, cot z is also a meromorphic fuctio i C, whose poles are kπ, k Z, ad every pole is simple. The quotiet of two polyomials is also a meromorphic fuctio i C, which is called a ratioal fuctio. Now we describe the behavior of f ear a isolated sigularity of each kid. Theorem If f is bouded i D(z 0, r) \ {z 0 }, the z 0 is a removable sigularity of f. Proof. Suppose M o D(z 0, r) \ {z 0 }. From (4.6), we see that, for ay t (0, r), a 2π f z z 0 tt L({ t}) Mt, Z. If, the t 0 as t 0, which implies that a 0 for. 53
j=1 dz Res(f, z j ) = 1 d k 1 dz k 1 (z c)k f(z) Res(f, c) = lim z c (k 1)! Res g, c = f(c) g (c)
 Problem. Compute the itegrals C r d for Z, where C r = ad r >. Recall that C r has the couter-clockwise orietatio. Solutio: We will use the idue Theorem to solve this oe. We could istead use other (perhaps
Problem. Compute the itegrals C r d for Z, where C r = ad r >. Recall that C r has the couter-clockwise orietatio. Solutio: We will use the idue Theorem to solve this oe. We could istead use other (perhaps
Notes 8 Singularities
 ECE 6382 Fall 27 David R. Jackso Notes 8 Sigularities Notes are from D. R. Wilto, Dept. of ECE Sigularity A poit s is a sigularity of the fuctio f () if the fuctio is ot aalytic at s. (The fuctio does
ECE 6382 Fall 27 David R. Jackso Notes 8 Sigularities Notes are from D. R. Wilto, Dept. of ECE Sigularity A poit s is a sigularity of the fuctio f () if the fuctio is ot aalytic at s. (The fuctio does
Dupuy Complex Analysis Spring 2016 Homework 02
 Dupuy Complex Aalysis Sprig 206 Homework 02. (CUNY, Fall 2005) Let D be the closed uit disc. Let g be a sequece of aalytic fuctios covergig uiformly to f o D. (a) Show that g coverges. Solutio We have
Dupuy Complex Aalysis Sprig 206 Homework 02. (CUNY, Fall 2005) Let D be the closed uit disc. Let g be a sequece of aalytic fuctios covergig uiformly to f o D. (a) Show that g coverges. Solutio We have
APPM 4360/5360 Exam #2 Solutions Spring 2015
 APPM 436/536 Exam # Solutios Sprig 5 O the frot of your bluebook, write your ame ad make a gradig table. You re allowed oe sheet (letter-sized, frot ad back of otes. You are ot allowed to use textbooks,
APPM 436/536 Exam # Solutios Sprig 5 O the frot of your bluebook, write your ame ad make a gradig table. You re allowed oe sheet (letter-sized, frot ad back of otes. You are ot allowed to use textbooks,
Analytic Continuation
 Aalytic Cotiuatio The stadard example of this is give by Example Let h (z) = 1 + z + z 2 + z 3 +... kow to coverge oly for z < 1. I fact h (z) = 1/ (1 z) for such z. Yet H (z) = 1/ (1 z) is defied for
Aalytic Cotiuatio The stadard example of this is give by Example Let h (z) = 1 + z + z 2 + z 3 +... kow to coverge oly for z < 1. I fact h (z) = 1/ (1 z) for such z. Yet H (z) = 1/ (1 z) is defied for
Solutions to Homework 1
 Solutios to Homework MATH 36. Describe geometrically the sets of poits z i the complex plae defied by the followig relatios /z = z () Re(az + b) >, where a, b (2) Im(z) = c, with c (3) () = = z z = z 2.
Solutios to Homework MATH 36. Describe geometrically the sets of poits z i the complex plae defied by the followig relatios /z = z () Re(az + b) >, where a, b (2) Im(z) = c, with c (3) () = = z z = z 2.
Sequences and Series of Functions
 Chapter 6 Sequeces ad Series of Fuctios 6.1. Covergece of a Sequece of Fuctios Poitwise Covergece. Defiitio 6.1. Let, for each N, fuctio f : A R be defied. If, for each x A, the sequece (f (x)) coverges
Chapter 6 Sequeces ad Series of Fuctios 6.1. Covergece of a Sequece of Fuctios Poitwise Covergece. Defiitio 6.1. Let, for each N, fuctio f : A R be defied. If, for each x A, the sequece (f (x)) coverges
PRELIM PROBLEM SOLUTIONS
 PRELIM PROBLEM SOLUTIONS THE GRAD STUDENTS + KEN Cotets. Complex Aalysis Practice Problems 2. 2. Real Aalysis Practice Problems 2. 4 3. Algebra Practice Problems 2. 8. Complex Aalysis Practice Problems
PRELIM PROBLEM SOLUTIONS THE GRAD STUDENTS + KEN Cotets. Complex Aalysis Practice Problems 2. 2. Real Aalysis Practice Problems 2. 4 3. Algebra Practice Problems 2. 8. Complex Aalysis Practice Problems
Section 11.8: Power Series
 Sectio 11.8: Power Series 1. Power Series I this sectio, we cosider geeralizig the cocept of a series. Recall that a series is a ifiite sum of umbers a. We ca talk about whether or ot it coverges ad i
Sectio 11.8: Power Series 1. Power Series I this sectio, we cosider geeralizig the cocept of a series. Recall that a series is a ifiite sum of umbers a. We ca talk about whether or ot it coverges ad i
MATH301 Real Analysis (2008 Fall) Tutorial Note #7. k=1 f k (x) converges pointwise to S(x) on E if and
 MATH01 Real Aalysis (2008 Fall) Tutorial Note #7 Sequece ad Series of fuctio 1: Poitwise Covergece ad Uiform Covergece Part I: Poitwise Covergece Defiitio of poitwise covergece: A sequece of fuctios f
MATH01 Real Aalysis (2008 Fall) Tutorial Note #7 Sequece ad Series of fuctio 1: Poitwise Covergece ad Uiform Covergece Part I: Poitwise Covergece Defiitio of poitwise covergece: A sequece of fuctios f
MAT1026 Calculus II Basic Convergence Tests for Series
 MAT026 Calculus II Basic Covergece Tests for Series Egi MERMUT 202.03.08 Dokuz Eylül Uiversity Faculty of Sciece Departmet of Mathematics İzmir/TURKEY Cotets Mootoe Covergece Theorem 2 2 Series of Real
MAT026 Calculus II Basic Covergece Tests for Series Egi MERMUT 202.03.08 Dokuz Eylül Uiversity Faculty of Sciece Departmet of Mathematics İzmir/TURKEY Cotets Mootoe Covergece Theorem 2 2 Series of Real
Math 210A Homework 1
 Math 0A Homework Edward Burkard Exercise. a) State the defiitio of a aalytic fuctio. b) What are the relatioships betwee aalytic fuctios ad the Cauchy-Riema equatios? Solutio. a) A fuctio f : G C is called
Math 0A Homework Edward Burkard Exercise. a) State the defiitio of a aalytic fuctio. b) What are the relatioships betwee aalytic fuctios ad the Cauchy-Riema equatios? Solutio. a) A fuctio f : G C is called
Chapter 8. Euler s Gamma function
 Chapter 8 Euler s Gamma fuctio The Gamma fuctio plays a importat role i the fuctioal equatio for ζ(s that we will derive i the ext chapter. I the preset chapter we have collected some properties of the
Chapter 8 Euler s Gamma fuctio The Gamma fuctio plays a importat role i the fuctioal equatio for ζ(s that we will derive i the ext chapter. I the preset chapter we have collected some properties of the
lim za n n = z lim a n n.
 Lecture 6 Sequeces ad Series Defiitio 1 By a sequece i a set A, we mea a mappig f : N A. It is customary to deote a sequece f by {s } where, s := f(). A sequece {z } of (complex) umbers is said to be coverget
Lecture 6 Sequeces ad Series Defiitio 1 By a sequece i a set A, we mea a mappig f : N A. It is customary to deote a sequece f by {s } where, s := f(). A sequece {z } of (complex) umbers is said to be coverget
Chapter 10: Power Series
 Chapter : Power Series 57 Chapter Overview: Power Series The reaso series are part of a Calculus course is that there are fuctios which caot be itegrated. All power series, though, ca be itegrated because
Chapter : Power Series 57 Chapter Overview: Power Series The reaso series are part of a Calculus course is that there are fuctios which caot be itegrated. All power series, though, ca be itegrated because
Solutions to Exercises 4.1
 Sectio 4. Sequeces ad Series of Complex Numbers 73 Solutios to Exercises 4.. We have a e i π as. So a by the squeee theorem or by applyig, Sec. 4.. 5. We have cosh i cos see 5, Sec..6. Hece a cosh i cos
Sectio 4. Sequeces ad Series of Complex Numbers 73 Solutios to Exercises 4.. We have a e i π as. So a by the squeee theorem or by applyig, Sec. 4.. 5. We have cosh i cos see 5, Sec..6. Hece a cosh i cos
62. Power series Definition 16. (Power series) Given a sequence {c n }, the series. c n x n = c 0 + c 1 x + c 2 x 2 + c 3 x 3 +
 62. Power series Defiitio 16. (Power series) Give a sequece {c }, the series c x = c 0 + c 1 x + c 2 x 2 + c 3 x 3 + is called a power series i the variable x. The umbers c are called the coefficiets of
62. Power series Defiitio 16. (Power series) Give a sequece {c }, the series c x = c 0 + c 1 x + c 2 x 2 + c 3 x 3 + is called a power series i the variable x. The umbers c are called the coefficiets of
Solutions for Math 411 Assignment #8 1
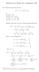 Solutios for Math Assigmet #8 A8. Fid the Lauret series of f() 3 2 + i (a) { < }; (b) { < < }; (c) { < 2 < 3}; (d) {0 < + < 2}. Solutio. We write f() as a sum of partial fractios: f() 3 2 + ( ) 2 ( + )
Solutios for Math Assigmet #8 A8. Fid the Lauret series of f() 3 2 + i (a) { < }; (b) { < < }; (c) { < 2 < 3}; (d) {0 < + < 2}. Solutio. We write f() as a sum of partial fractios: f() 3 2 + ( ) 2 ( + )
SCORE. Exam 2. MA 114 Exam 2 Fall 2017
 Exam Name: Sectio ad/or TA: Do ot remove this aswer page you will retur the whole exam. You will be allowed two hours to complete this test. No books or otes may be used. You may use a graphig calculator
Exam Name: Sectio ad/or TA: Do ot remove this aswer page you will retur the whole exam. You will be allowed two hours to complete this test. No books or otes may be used. You may use a graphig calculator
Theorem [Mean Value Theorem for Harmonic Functions] Let u be harmonic on D(z 0, R). Then for any r (0, R), u(z 0 ) = 1 z z 0 r
![Theorem [Mean Value Theorem for Harmonic Functions] Let u be harmonic on D(z 0, R). Then for any r (0, R), u(z 0 ) = 1 z z 0 r Theorem [Mean Value Theorem for Harmonic Functions] Let u be harmonic on D(z 0, R). Then for any r (0, R), u(z 0 ) = 1 z z 0 r](/thumbs/77/75527144.jpg) 2. A harmonic conjugate always exists locally: if u is a harmonic function in an open set U, then for any disk D(z 0, r) U, there is f, which is analytic in D(z 0, r) and satisfies that Re f u. Since such
2. A harmonic conjugate always exists locally: if u is a harmonic function in an open set U, then for any disk D(z 0, r) U, there is f, which is analytic in D(z 0, r) and satisfies that Re f u. Since such
n n 2 n n + 1 +
 Istructor: Marius Ioescu 1. Let a =. (5pts) (a) Prove that for every ε > 0 there is N 1 such that a +1 a < ε if N. Solutio: Let ε > 0. The a +1 a < ε is equivalet with + 1 < ε. Simplifyig, this iequality
Istructor: Marius Ioescu 1. Let a =. (5pts) (a) Prove that for every ε > 0 there is N 1 such that a +1 a < ε if N. Solutio: Let ε > 0. The a +1 a < ε is equivalet with + 1 < ε. Simplifyig, this iequality
Power Series: A power series about the center, x = 0, is a function of x of the form
 You are familiar with polyomial fuctios, polyomial that has ifiitely may terms. 2 p ( ) a0 a a 2 a. A power series is just a Power Series: A power series about the ceter, = 0, is a fuctio of of the form
You are familiar with polyomial fuctios, polyomial that has ifiitely may terms. 2 p ( ) a0 a a 2 a. A power series is just a Power Series: A power series about the ceter, = 0, is a fuctio of of the form
MAS111 Convergence and Continuity
 MAS Covergece ad Cotiuity Key Objectives At the ed of the course, studets should kow the followig topics ad be able to apply the basic priciples ad theorems therei to solvig various problems cocerig covergece
MAS Covergece ad Cotiuity Key Objectives At the ed of the course, studets should kow the followig topics ad be able to apply the basic priciples ad theorems therei to solvig various problems cocerig covergece
Ma 530 Introduction to Power Series
 Ma 530 Itroductio to Power Series Please ote that there is material o power series at Visual Calculus. Some of this material was used as part of the presetatio of the topics that follow. What is a Power
Ma 530 Itroductio to Power Series Please ote that there is material o power series at Visual Calculus. Some of this material was used as part of the presetatio of the topics that follow. What is a Power
Math Solutions to homework 6
 Math 175 - Solutios to homework 6 Cédric De Groote November 16, 2017 Problem 1 (8.11 i the book): Let K be a compact Hermitia operator o a Hilbert space H ad let the kerel of K be {0}. Show that there
Math 175 - Solutios to homework 6 Cédric De Groote November 16, 2017 Problem 1 (8.11 i the book): Let K be a compact Hermitia operator o a Hilbert space H ad let the kerel of K be {0}. Show that there
Chapter 8. Euler s Gamma function
 Chapter 8 Euler s Gamma fuctio The Gamma fuctio plays a importat role i the fuctioal equatio for ζ(s) that we will derive i the ext chapter. I the preset chapter we have collected some properties of the
Chapter 8 Euler s Gamma fuctio The Gamma fuctio plays a importat role i the fuctioal equatio for ζ(s) that we will derive i the ext chapter. I the preset chapter we have collected some properties of the
Topics. Homework Problems. MATH 301 Introduction to Analysis Chapter Four Sequences. 1. Definition of convergence of sequences.
 MATH 301 Itroductio to Aalysis Chapter Four Sequeces Topics 1. Defiitio of covergece of sequeces. 2. Fidig ad provig the limit of sequeces. 3. Bouded covergece theorem: Theorem 4.1.8. 4. Theorems 4.1.13
MATH 301 Itroductio to Aalysis Chapter Four Sequeces Topics 1. Defiitio of covergece of sequeces. 2. Fidig ad provig the limit of sequeces. 3. Bouded covergece theorem: Theorem 4.1.8. 4. Theorems 4.1.13
Continuous Functions
 Cotiuous Fuctios Q What does it mea for a fuctio to be cotiuous at a poit? Aswer- I mathematics, we have a defiitio that cosists of three cocepts that are liked i a special way Cosider the followig defiitio
Cotiuous Fuctios Q What does it mea for a fuctio to be cotiuous at a poit? Aswer- I mathematics, we have a defiitio that cosists of three cocepts that are liked i a special way Cosider the followig defiitio
Lecture Notes for Analysis Class
 Lecture Notes for Aalysis Class Topological Spaces A topology for a set X is a collectio T of subsets of X such that: (a) X ad the empty set are i T (b) Uios of elemets of T are i T (c) Fiite itersectios
Lecture Notes for Aalysis Class Topological Spaces A topology for a set X is a collectio T of subsets of X such that: (a) X ad the empty set are i T (b) Uios of elemets of T are i T (c) Fiite itersectios
Solutions for Math 411 Assignment #2 1
 Solutios for Math 4 Assigmet #2 A2. For each of the followig fuctios f : C C, fid where f(z is complex differetiable ad where f(z is aalytic. You must justify your aswer. (a f(z = e x2 y 2 (cos(2xy + i
Solutios for Math 4 Assigmet #2 A2. For each of the followig fuctios f : C C, fid where f(z is complex differetiable ad where f(z is aalytic. You must justify your aswer. (a f(z = e x2 y 2 (cos(2xy + i
MATH 31B: MIDTERM 2 REVIEW
 MATH 3B: MIDTERM REVIEW JOE HUGHES. Evaluate x (x ) (x 3).. Partial Fractios Solutio: The umerator has degree less tha the deomiator, so we ca use partial fractios. Write x (x ) (x 3) = A x + A (x ) +
MATH 3B: MIDTERM REVIEW JOE HUGHES. Evaluate x (x ) (x 3).. Partial Fractios Solutio: The umerator has degree less tha the deomiator, so we ca use partial fractios. Write x (x ) (x 3) = A x + A (x ) +
SUMMARY OF SEQUENCES AND SERIES
 SUMMARY OF SEQUENCES AND SERIES Importat Defiitios, Results ad Theorems for Sequeces ad Series Defiitio. A sequece {a } has a limit L ad we write lim a = L if for every ɛ > 0, there is a correspodig iteger
SUMMARY OF SEQUENCES AND SERIES Importat Defiitios, Results ad Theorems for Sequeces ad Series Defiitio. A sequece {a } has a limit L ad we write lim a = L if for every ɛ > 0, there is a correspodig iteger
1 lim. f(x) sin(nx)dx = 0. n sin(nx)dx
 Problem A. Calculate ta(.) to 4 decimal places. Solutio: The power series for si(x)/ cos(x) is x + x 3 /3 + (2/5)x 5 +. Puttig x =. gives ta(.) =.3. Problem 2A. Let f : R R be a cotiuous fuctio. Show that
Problem A. Calculate ta(.) to 4 decimal places. Solutio: The power series for si(x)/ cos(x) is x + x 3 /3 + (2/5)x 5 +. Puttig x =. gives ta(.) =.3. Problem 2A. Let f : R R be a cotiuous fuctio. Show that
SOLUTIONS TO EXAM 3. Solution: Note that this defines two convergent geometric series with respective radii r 1 = 2/5 < 1 and r 2 = 1/5 < 1.
 SOLUTIONS TO EXAM 3 Problem Fid the sum of the followig series 2 + ( ) 5 5 2 5 3 25 2 2 This series diverges Solutio: Note that this defies two coverget geometric series with respective radii r 2/5 < ad
SOLUTIONS TO EXAM 3 Problem Fid the sum of the followig series 2 + ( ) 5 5 2 5 3 25 2 2 This series diverges Solutio: Note that this defies two coverget geometric series with respective radii r 2/5 < ad
CHAPTER 5. Theory and Solution Using Matrix Techniques
 A SERIES OF CLASS NOTES FOR 2005-2006 TO INTRODUCE LINEAR AND NONLINEAR PROBLEMS TO ENGINEERS, SCIENTISTS, AND APPLIED MATHEMATICIANS DE CLASS NOTES 3 A COLLECTION OF HANDOUTS ON SYSTEMS OF ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL
A SERIES OF CLASS NOTES FOR 2005-2006 TO INTRODUCE LINEAR AND NONLINEAR PROBLEMS TO ENGINEERS, SCIENTISTS, AND APPLIED MATHEMATICIANS DE CLASS NOTES 3 A COLLECTION OF HANDOUTS ON SYSTEMS OF ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL
The z-transform. 7.1 Introduction. 7.2 The z-transform Derivation of the z-transform: x[n] = z n LTI system, h[n] z = re j
![The z-transform. 7.1 Introduction. 7.2 The z-transform Derivation of the z-transform: x[n] = z n LTI system, h[n] z = re j The z-transform. 7.1 Introduction. 7.2 The z-transform Derivation of the z-transform: x[n] = z n LTI system, h[n] z = re j](/thumbs/82/85448534.jpg) The -Trasform 7. Itroductio Geeralie the complex siusoidal represetatio offered by DTFT to a represetatio of complex expoetial sigals. Obtai more geeral characteristics for discrete-time LTI systems. 7.
The -Trasform 7. Itroductio Geeralie the complex siusoidal represetatio offered by DTFT to a represetatio of complex expoetial sigals. Obtai more geeral characteristics for discrete-time LTI systems. 7.
4x 2. (n+1) x 3 n+1. = lim. 4x 2 n+1 n3 n. n 4x 2 = lim = 3
 Exam Problems (x. Give the series (, fid the values of x for which this power series coverges. Also =0 state clearly what the radius of covergece is. We start by settig up the Ratio Test: x ( x x ( x x
Exam Problems (x. Give the series (, fid the values of x for which this power series coverges. Also =0 state clearly what the radius of covergece is. We start by settig up the Ratio Test: x ( x x ( x x
Notes 12 Asymptotic Series
 ECE 6382 Fall 207 David R. Jackso otes 2 Asymptotic Series Asymptotic Series A asymptotic series (as ) is of the form a ( ) f as = 0 or f a + a a + + ( ) 2 0 2 ote the asymptotically equal to sig. The
ECE 6382 Fall 207 David R. Jackso otes 2 Asymptotic Series Asymptotic Series A asymptotic series (as ) is of the form a ( ) f as = 0 or f a + a a + + ( ) 2 0 2 ote the asymptotically equal to sig. The
(A sequence also can be thought of as the list of function values attained for a function f :ℵ X, where f (n) = x n for n 1.) x 1 x N +k x N +4 x 3
 MATH 337 Sequeces Dr. Neal, WKU Let X be a metric space with distace fuctio d. We shall defie the geeral cocept of sequece ad limit i a metric space, the apply the results i particular to some special
MATH 337 Sequeces Dr. Neal, WKU Let X be a metric space with distace fuctio d. We shall defie the geeral cocept of sequece ad limit i a metric space, the apply the results i particular to some special
We are mainly going to be concerned with power series in x, such as. (x)} converges - that is, lims N n
 Review of Power Series, Power Series Solutios A power series i x - a is a ifiite series of the form c (x a) =c +c (x a)+(x a) +... We also call this a power series cetered at a. Ex. (x+) is cetered at
Review of Power Series, Power Series Solutios A power series i x - a is a ifiite series of the form c (x a) =c +c (x a)+(x a) +... We also call this a power series cetered at a. Ex. (x+) is cetered at
It is often useful to approximate complicated functions using simpler ones. We consider the task of approximating a function by a polynomial.
 Taylor Polyomials ad Taylor Series It is ofte useful to approximate complicated fuctios usig simpler oes We cosider the task of approximatig a fuctio by a polyomial If f is at least -times differetiable
Taylor Polyomials ad Taylor Series It is ofte useful to approximate complicated fuctios usig simpler oes We cosider the task of approximatig a fuctio by a polyomial If f is at least -times differetiable
. Then g is holomorphic and bounded in U. So z 0 is a removable singularity of g. Since f(z) = w 0 + 1
 Now we describe the behavior of f near an isolated singularity of each kind. We will always assume that z 0 is a singularity of f, and f is holomorphic on D(z 0, r) \ {z 0 }. Theorem 4.2.. z 0 is a removable
Now we describe the behavior of f near an isolated singularity of each kind. We will always assume that z 0 is a singularity of f, and f is holomorphic on D(z 0, r) \ {z 0 }. Theorem 4.2.. z 0 is a removable
CHAPTER 10 INFINITE SEQUENCES AND SERIES
 CHAPTER 10 INFINITE SEQUENCES AND SERIES 10.1 Sequeces 10.2 Ifiite Series 10.3 The Itegral Tests 10.4 Compariso Tests 10.5 The Ratio ad Root Tests 10.6 Alteratig Series: Absolute ad Coditioal Covergece
CHAPTER 10 INFINITE SEQUENCES AND SERIES 10.1 Sequeces 10.2 Ifiite Series 10.3 The Itegral Tests 10.4 Compariso Tests 10.5 The Ratio ad Root Tests 10.6 Alteratig Series: Absolute ad Coditioal Covergece
Real Variables II Homework Set #5
 Real Variables II Homework Set #5 Name: Due Friday /0 by 4pm (at GOS-4) Istructios: () Attach this page to the frot of your homework assigmet you tur i (or write each problem before your solutio). () Please
Real Variables II Homework Set #5 Name: Due Friday /0 by 4pm (at GOS-4) Istructios: () Attach this page to the frot of your homework assigmet you tur i (or write each problem before your solutio). () Please
Math 113, Calculus II Winter 2007 Final Exam Solutions
 Math, Calculus II Witer 7 Fial Exam Solutios (5 poits) Use the limit defiitio of the defiite itegral ad the sum formulas to compute x x + dx The check your aswer usig the Evaluatio Theorem Solutio: I this
Math, Calculus II Witer 7 Fial Exam Solutios (5 poits) Use the limit defiitio of the defiite itegral ad the sum formulas to compute x x + dx The check your aswer usig the Evaluatio Theorem Solutio: I this
Generalizing the DTFT. The z Transform. Complex Exponential Excitation. The Transfer Function. Systems Described by Difference Equations
 Geeraliig the DTFT The Trasform M. J. Roberts - All Rights Reserved. Edited by Dr. Robert Akl 1 The forward DTFT is defied by X e jω = x e jω i which = Ω is discrete-time radia frequecy, a real variable.
Geeraliig the DTFT The Trasform M. J. Roberts - All Rights Reserved. Edited by Dr. Robert Akl 1 The forward DTFT is defied by X e jω = x e jω i which = Ω is discrete-time radia frequecy, a real variable.
Zeros of Polynomials
 Math 160 www.timetodare.com 4.5 4.6 Zeros of Polyomials I these sectios we will study polyomials algebraically. Most of our work will be cocered with fidig the solutios of polyomial equatios of ay degree
Math 160 www.timetodare.com 4.5 4.6 Zeros of Polyomials I these sectios we will study polyomials algebraically. Most of our work will be cocered with fidig the solutios of polyomial equatios of ay degree
3. Z Transform. Recall that the Fourier transform (FT) of a DT signal xn [ ] is ( ) [ ] = In order for the FT to exist in the finite magnitude sense,
![3. Z Transform. Recall that the Fourier transform (FT) of a DT signal xn [ ] is ( ) [ ] = In order for the FT to exist in the finite magnitude sense, 3. Z Transform. Recall that the Fourier transform (FT) of a DT signal xn [ ] is ( ) [ ] = In order for the FT to exist in the finite magnitude sense,](/thumbs/82/85448051.jpg) 3. Z Trasform Referece: Etire Chapter 3 of text. Recall that the Fourier trasform (FT) of a DT sigal x [ ] is ω ( ) [ ] X e = j jω k = xe I order for the FT to exist i the fiite magitude sese, S = x [
3. Z Trasform Referece: Etire Chapter 3 of text. Recall that the Fourier trasform (FT) of a DT sigal x [ ] is ω ( ) [ ] X e = j jω k = xe I order for the FT to exist i the fiite magitude sese, S = x [
PLEASE MARK YOUR ANSWERS WITH AN X, not a circle! 1. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 3. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 5. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 7. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e)
 Math 0560, Exam 3 November 6, 07 The Hoor Code is i effect for this examiatio. All work is to be your ow. No calculators. The exam lasts for hour ad 5 mi. Be sure that your ame is o every page i case pages
Math 0560, Exam 3 November 6, 07 The Hoor Code is i effect for this examiatio. All work is to be your ow. No calculators. The exam lasts for hour ad 5 mi. Be sure that your ame is o every page i case pages
MATH 312 Midterm I(Spring 2015)
 MATH 3 Midterm I(Sprig 05) Istructor: Xiaowei Wag Feb 3rd, :30pm-3:50pm, 05 Problem (0 poits). Test for covergece:.. 3.. p, p 0. (coverges for p < ad diverges for p by ratio test.). ( coverges, sice (log
MATH 3 Midterm I(Sprig 05) Istructor: Xiaowei Wag Feb 3rd, :30pm-3:50pm, 05 Problem (0 poits). Test for covergece:.. 3.. p, p 0. (coverges for p < ad diverges for p by ratio test.). ( coverges, sice (log
Math 113 Exam 3 Practice
 Math Exam Practice Exam 4 will cover.-., 0. ad 0.. Note that eve though. was tested i exam, questios from that sectios may also be o this exam. For practice problems o., refer to the last review. This
Math Exam Practice Exam 4 will cover.-., 0. ad 0.. Note that eve though. was tested i exam, questios from that sectios may also be o this exam. For practice problems o., refer to the last review. This
f(x)g(x) dx is an inner product on D.
 Ark9: Exercises for MAT2400 Fourier series The exercises o this sheet cover the sectios 4.9 to 4.13. They are iteded for the groups o Thursday, April 12 ad Friday, March 30 ad April 13. NB: No group o
Ark9: Exercises for MAT2400 Fourier series The exercises o this sheet cover the sectios 4.9 to 4.13. They are iteded for the groups o Thursday, April 12 ad Friday, March 30 ad April 13. NB: No group o
Arkansas Tech University MATH 2924: Calculus II Dr. Marcel B. Finan
 Arkasas Tech Uiversity MATH 94: Calculus II Dr Marcel B Fia 85 Power Series Let {a } =0 be a sequece of umbers The a power series about x = a is a series of the form a (x a) = a 0 + a (x a) + a (x a) +
Arkasas Tech Uiversity MATH 94: Calculus II Dr Marcel B Fia 85 Power Series Let {a } =0 be a sequece of umbers The a power series about x = a is a series of the form a (x a) = a 0 + a (x a) + a (x a) +
1.3 Convergence Theorems of Fourier Series. k k k k. N N k 1. With this in mind, we state (without proof) the convergence of Fourier series.
 .3 Covergece Theorems of Fourier Series I this sectio, we preset the covergece of Fourier series. A ifiite sum is, by defiitio, a limit of partial sums, that is, a cos( kx) b si( kx) lim a cos( kx) b si(
.3 Covergece Theorems of Fourier Series I this sectio, we preset the covergece of Fourier series. A ifiite sum is, by defiitio, a limit of partial sums, that is, a cos( kx) b si( kx) lim a cos( kx) b si(
Real Analysis Fall 2004 Take Home Test 1 SOLUTIONS. < ε. Hence lim
 Real Aalysis Fall 004 Take Home Test SOLUTIONS. Use the defiitio of a limit to show that (a) lim si = 0 (b) Proof. Let ε > 0 be give. Defie N >, where N is a positive iteger. The for ε > N, si 0 < si
Real Aalysis Fall 004 Take Home Test SOLUTIONS. Use the defiitio of a limit to show that (a) lim si = 0 (b) Proof. Let ε > 0 be give. Defie N >, where N is a positive iteger. The for ε > N, si 0 < si
3.2 Properties of Division 3.3 Zeros of Polynomials 3.4 Complex and Rational Zeros of Polynomials
 Math 60 www.timetodare.com 3. Properties of Divisio 3.3 Zeros of Polyomials 3.4 Complex ad Ratioal Zeros of Polyomials I these sectios we will study polyomials algebraically. Most of our work will be cocered
Math 60 www.timetodare.com 3. Properties of Divisio 3.3 Zeros of Polyomials 3.4 Complex ad Ratioal Zeros of Polyomials I these sectios we will study polyomials algebraically. Most of our work will be cocered
TERMWISE DERIVATIVES OF COMPLEX FUNCTIONS
 TERMWISE DERIVATIVES OF COMPLEX FUNCTIONS This writeup proves a result that has as oe cosequece that ay complex power series ca be differetiated term-by-term withi its disk of covergece The result has
TERMWISE DERIVATIVES OF COMPLEX FUNCTIONS This writeup proves a result that has as oe cosequece that ay complex power series ca be differetiated term-by-term withi its disk of covergece The result has
Read carefully the instructions on the answer book and make sure that the particulars required are entered on each answer book.
 THE UNIVERSITY OF WARWICK FIRST YEAR EXAMINATION: Jauary 2009 Aalysis I Time Allowed:.5 hours Read carefully the istructios o the aswer book ad make sure that the particulars required are etered o each
THE UNIVERSITY OF WARWICK FIRST YEAR EXAMINATION: Jauary 2009 Aalysis I Time Allowed:.5 hours Read carefully the istructios o the aswer book ad make sure that the particulars required are etered o each
INEQUALITIES BJORN POONEN
 INEQUALITIES BJORN POONEN 1 The AM-GM iequality The most basic arithmetic mea-geometric mea (AM-GM) iequality states simply that if x ad y are oegative real umbers, the (x + y)/2 xy, with equality if ad
INEQUALITIES BJORN POONEN 1 The AM-GM iequality The most basic arithmetic mea-geometric mea (AM-GM) iequality states simply that if x ad y are oegative real umbers, the (x + y)/2 xy, with equality if ad
University of Colorado Denver Dept. Math. & Stat. Sciences Applied Analysis Preliminary Exam 13 January 2012, 10:00 am 2:00 pm. Good luck!
 Uiversity of Colorado Dever Dept. Math. & Stat. Scieces Applied Aalysis Prelimiary Exam 13 Jauary 01, 10:00 am :00 pm Name: The proctor will let you read the followig coditios before the exam begis, ad
Uiversity of Colorado Dever Dept. Math. & Stat. Scieces Applied Aalysis Prelimiary Exam 13 Jauary 01, 10:00 am :00 pm Name: The proctor will let you read the followig coditios before the exam begis, ad
Section 1.4. Power Series
 Sectio.4. Power Series De itio. The fuctio de ed by f (x) (x a) () c 0 + c (x a) + c 2 (x a) 2 + c (x a) + ::: is called a power series cetered at x a with coe ciet sequece f g :The domai of this fuctio
Sectio.4. Power Series De itio. The fuctio de ed by f (x) (x a) () c 0 + c (x a) + c 2 (x a) 2 + c (x a) + ::: is called a power series cetered at x a with coe ciet sequece f g :The domai of this fuctio
Exponential Functions and Taylor Series
 MATH 4530: Aalysis Oe Expoetial Fuctios ad Taylor Series James K. Peterso Departmet of Biological Scieces ad Departmet of Mathematical Scieces Clemso Uiversity March 29, 2017 MATH 4530: Aalysis Oe Outlie
MATH 4530: Aalysis Oe Expoetial Fuctios ad Taylor Series James K. Peterso Departmet of Biological Scieces ad Departmet of Mathematical Scieces Clemso Uiversity March 29, 2017 MATH 4530: Aalysis Oe Outlie
Quiz No. 1. ln n n. 1. Define: an infinite sequence A function whose domain is N 2. Define: a convergent sequence A sequence that has a limit
 Quiz No.. Defie: a ifiite sequece A fuctio whose domai is N 2. Defie: a coverget sequece A sequece that has a limit 3. Is this sequece coverget? Why or why ot? l Yes, it is coverget sice L=0 by LHR. INFINITE
Quiz No.. Defie: a ifiite sequece A fuctio whose domai is N 2. Defie: a coverget sequece A sequece that has a limit 3. Is this sequece coverget? Why or why ot? l Yes, it is coverget sice L=0 by LHR. INFINITE
Chapter 1. Complex Numbers. Dr. Pulak Sahoo
 Chapter 1 Complex Numbers BY Dr. Pulak Sahoo Assistat Professor Departmet of Mathematics Uiversity Of Kalyai West Begal, Idia E-mail : sahoopulak1@gmail.com 1 Module-2: Stereographic Projectio 1 Euler
Chapter 1 Complex Numbers BY Dr. Pulak Sahoo Assistat Professor Departmet of Mathematics Uiversity Of Kalyai West Begal, Idia E-mail : sahoopulak1@gmail.com 1 Module-2: Stereographic Projectio 1 Euler
AP Calculus Chapter 9: Infinite Series
 AP Calculus Chapter 9: Ifiite Series 9. Sequeces a, a 2, a 3, a 4, a 5,... Sequece: A fuctio whose domai is the set of positive itegers = 2 3 4 a = a a 2 a 3 a 4 terms of the sequece Begi with the patter
AP Calculus Chapter 9: Ifiite Series 9. Sequeces a, a 2, a 3, a 4, a 5,... Sequece: A fuctio whose domai is the set of positive itegers = 2 3 4 a = a a 2 a 3 a 4 terms of the sequece Begi with the patter
Dirichlet s Theorem on Arithmetic Progressions
 Dirichlet s Theorem o Arithmetic Progressios Athoy Várilly Harvard Uiversity, Cambridge, MA 0238 Itroductio Dirichlet s theorem o arithmetic progressios is a gem of umber theory. A great part of its beauty
Dirichlet s Theorem o Arithmetic Progressios Athoy Várilly Harvard Uiversity, Cambridge, MA 0238 Itroductio Dirichlet s theorem o arithmetic progressios is a gem of umber theory. A great part of its beauty
Beyond simple iteration of a single function, or even a finite sequence of functions, results
 A Primer o the Elemetary Theory of Ifiite Compositios of Complex Fuctios Joh Gill Sprig 07 Abstract: Elemetary meas ot requirig the complex fuctios be holomorphic Theorem proofs are fairly simple ad are
A Primer o the Elemetary Theory of Ifiite Compositios of Complex Fuctios Joh Gill Sprig 07 Abstract: Elemetary meas ot requirig the complex fuctios be holomorphic Theorem proofs are fairly simple ad are
[ 11 ] z of degree 2 as both degree 2 each. The degree of a polynomial in n variables is the maximum of the degrees of its terms.
![[ 11 ] z of degree 2 as both degree 2 each. The degree of a polynomial in n variables is the maximum of the degrees of its terms. [ 11 ] z of degree 2 as both degree 2 each. The degree of a polynomial in n variables is the maximum of the degrees of its terms.](/thumbs/82/84777652.jpg) [ 11 ] 1 1.1 Polyomial Fuctios 1 Algebra Ay fuctio f ( x) ax a1x... a1x a0 is a polyomial fuctio if ai ( i 0,1,,,..., ) is a costat which belogs to the set of real umbers ad the idices,, 1,...,1 are atural
[ 11 ] 1 1.1 Polyomial Fuctios 1 Algebra Ay fuctio f ( x) ax a1x... a1x a0 is a polyomial fuctio if ai ( i 0,1,,,..., ) is a costat which belogs to the set of real umbers ad the idices,, 1,...,1 are atural
6.003 Homework #3 Solutions
 6.00 Homework # Solutios Problems. Complex umbers a. Evaluate the real ad imagiary parts of j j. π/ Real part = Imagiary part = 0 e Euler s formula says that j = e jπ/, so jπ/ j π/ j j = e = e. Thus the
6.00 Homework # Solutios Problems. Complex umbers a. Evaluate the real ad imagiary parts of j j. π/ Real part = Imagiary part = 0 e Euler s formula says that j = e jπ/, so jπ/ j π/ j j = e = e. Thus the
Ma 4121: Introduction to Lebesgue Integration Solutions to Homework Assignment 5
 Ma 42: Itroductio to Lebesgue Itegratio Solutios to Homework Assigmet 5 Prof. Wickerhauser Due Thursday, April th, 23 Please retur your solutios to the istructor by the ed of class o the due date. You
Ma 42: Itroductio to Lebesgue Itegratio Solutios to Homework Assigmet 5 Prof. Wickerhauser Due Thursday, April th, 23 Please retur your solutios to the istructor by the ed of class o the due date. You
Math 113 Exam 4 Practice
 Math Exam 4 Practice Exam 4 will cover.-.. This sheet has three sectios. The first sectio will remid you about techiques ad formulas that you should kow. The secod gives a umber of practice questios for
Math Exam 4 Practice Exam 4 will cover.-.. This sheet has three sectios. The first sectio will remid you about techiques ad formulas that you should kow. The secod gives a umber of practice questios for
Fall 2013 MTH431/531 Real analysis Section Notes
 Fall 013 MTH431/531 Real aalysis Sectio 8.1-8. Notes Yi Su 013.11.1 1. Defiitio of uiform covergece. We look at a sequece of fuctios f (x) ad study the coverget property. Notice we have two parameters
Fall 013 MTH431/531 Real aalysis Sectio 8.1-8. Notes Yi Su 013.11.1 1. Defiitio of uiform covergece. We look at a sequece of fuctios f (x) ad study the coverget property. Notice we have two parameters
COMM 602: Digital Signal Processing
 COMM 60: Digital Sigal Processig Lecture 4 -Properties of LTIS Usig Z-Trasform -Iverse Z-Trasform Properties of LTIS Usig Z-Trasform Properties of LTIS Usig Z-Trasform -ve +ve Properties of LTIS Usig Z-Trasform
COMM 60: Digital Sigal Processig Lecture 4 -Properties of LTIS Usig Z-Trasform -Iverse Z-Trasform Properties of LTIS Usig Z-Trasform Properties of LTIS Usig Z-Trasform -ve +ve Properties of LTIS Usig Z-Trasform
} is said to be a Cauchy sequence provided the following condition is true.
 Math 4200, Fial Exam Review I. Itroductio to Proofs 1. Prove the Pythagorea theorem. 2. Show that 43 is a irratioal umber. II. Itroductio to Logic 1. Costruct a truth table for the statemet ( p ad ~ r
Math 4200, Fial Exam Review I. Itroductio to Proofs 1. Prove the Pythagorea theorem. 2. Show that 43 is a irratioal umber. II. Itroductio to Logic 1. Costruct a truth table for the statemet ( p ad ~ r
CHAPTER 1 SEQUENCES AND INFINITE SERIES
 CHAPTER SEQUENCES AND INFINITE SERIES SEQUENCES AND INFINITE SERIES (0 meetigs) Sequeces ad limit of a sequece Mootoic ad bouded sequece Ifiite series of costat terms Ifiite series of positive terms Alteratig
CHAPTER SEQUENCES AND INFINITE SERIES SEQUENCES AND INFINITE SERIES (0 meetigs) Sequeces ad limit of a sequece Mootoic ad bouded sequece Ifiite series of costat terms Ifiite series of positive terms Alteratig
PAPER : IIT-JAM 2010
 MATHEMATICS-MA (CODE A) Q.-Q.5: Oly oe optio is correct for each questio. Each questio carries (+6) marks for correct aswer ad ( ) marks for icorrect aswer.. Which of the followig coditios does NOT esure
MATHEMATICS-MA (CODE A) Q.-Q.5: Oly oe optio is correct for each questio. Each questio carries (+6) marks for correct aswer ad ( ) marks for icorrect aswer.. Which of the followig coditios does NOT esure
n=1 a n is the sequence (s n ) n 1 n=1 a n converges to s. We write a n = s, n=1 n=1 a n
 Series. Defiitios ad first properties A series is a ifiite sum a + a + a +..., deoted i short by a. The sequece of partial sums of the series a is the sequece s ) defied by s = a k = a +... + a,. k= Defiitio
Series. Defiitios ad first properties A series is a ifiite sum a + a + a +..., deoted i short by a. The sequece of partial sums of the series a is the sequece s ) defied by s = a k = a +... + a,. k= Defiitio
1. (25 points) Use the limit definition of the definite integral and the sum formulas 1 to compute
 Math, Calculus II Fial Eam Solutios. 5 poits) Use the limit defiitio of the defiite itegral ad the sum formulas to compute 4 d. The check your aswer usig the Evaluatio Theorem. ) ) Solutio: I this itegral,
Math, Calculus II Fial Eam Solutios. 5 poits) Use the limit defiitio of the defiite itegral ad the sum formulas to compute 4 d. The check your aswer usig the Evaluatio Theorem. ) ) Solutio: I this itegral,
Chapter 6 Infinite Series
 Chapter 6 Ifiite Series I the previous chapter we cosidered itegrals which were improper i the sese that the iterval of itegratio was ubouded. I this chapter we are goig to discuss a topic which is somewhat
Chapter 6 Ifiite Series I the previous chapter we cosidered itegrals which were improper i the sese that the iterval of itegratio was ubouded. I this chapter we are goig to discuss a topic which is somewhat
Assignment 5: Solutions
 McGill Uiversity Departmet of Mathematics ad Statistics MATH 54 Aalysis, Fall 05 Assigmet 5: Solutios. Let y be a ubouded sequece of positive umbers satisfyig y + > y for all N. Let x be aother sequece
McGill Uiversity Departmet of Mathematics ad Statistics MATH 54 Aalysis, Fall 05 Assigmet 5: Solutios. Let y be a ubouded sequece of positive umbers satisfyig y + > y for all N. Let x be aother sequece
f t dt. Write the third-degree Taylor polynomial for G
 AP Calculus BC Homework - Chapter 8B Taylor, Maclauri, ad Power Series # Taylor & Maclauri Polyomials Critical Thikig Joural: (CTJ: 5 pts.) Discuss the followig questios i a paragraph: What does it mea
AP Calculus BC Homework - Chapter 8B Taylor, Maclauri, ad Power Series # Taylor & Maclauri Polyomials Critical Thikig Joural: (CTJ: 5 pts.) Discuss the followig questios i a paragraph: What does it mea
Exponential Functions and Taylor Series
 Expoetial Fuctios ad Taylor Series James K. Peterso Departmet of Biological Scieces ad Departmet of Mathematical Scieces Clemso Uiversity March 29, 207 Outlie Revistig the Expoetial Fuctio Taylor Series
Expoetial Fuctios ad Taylor Series James K. Peterso Departmet of Biological Scieces ad Departmet of Mathematical Scieces Clemso Uiversity March 29, 207 Outlie Revistig the Expoetial Fuctio Taylor Series
The type of limit that is used to find TANGENTS and VELOCITIES gives rise to the central idea in DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS, the DERIVATIVE.
 NOTES : LIMITS AND DERIVATIVES Name: Date: Period: Iitial: LESSON.1 THE TANGENT AND VELOCITY PROBLEMS Pre-Calculus Mathematics Limit Process Calculus The type of it that is used to fid TANGENTS ad VELOCITIES
NOTES : LIMITS AND DERIVATIVES Name: Date: Period: Iitial: LESSON.1 THE TANGENT AND VELOCITY PROBLEMS Pre-Calculus Mathematics Limit Process Calculus The type of it that is used to fid TANGENTS ad VELOCITIES
Complex Analysis Spring 2001 Homework I Solution
 Complex Aalysis Sprig 2001 Homework I Solutio 1. Coway, Chapter 1, sectio 3, problem 3. Describe the set of poits satisfyig the equatio z a z + a = 2c, where c > 0 ad a R. To begi, we see from the triagle
Complex Aalysis Sprig 2001 Homework I Solutio 1. Coway, Chapter 1, sectio 3, problem 3. Describe the set of poits satisfyig the equatio z a z + a = 2c, where c > 0 ad a R. To begi, we see from the triagle
A collocation method for singular integral equations with cosecant kernel via Semi-trigonometric interpolation
 Iteratioal Joural of Mathematics Research. ISSN 0976-5840 Volume 9 Number 1 (017) pp. 45-51 Iteratioal Research Publicatio House http://www.irphouse.com A collocatio method for sigular itegral equatios
Iteratioal Joural of Mathematics Research. ISSN 0976-5840 Volume 9 Number 1 (017) pp. 45-51 Iteratioal Research Publicatio House http://www.irphouse.com A collocatio method for sigular itegral equatios
Definition 4.2. (a) A sequence {x n } in a Banach space X is a basis for X if. unique scalars a n (x) such that x = n. a n (x) x n. (4.
 4. BASES I BAACH SPACES 39 4. BASES I BAACH SPACES Sice a Baach space X is a vector space, it must possess a Hamel, or vector space, basis, i.e., a subset {x γ } γ Γ whose fiite liear spa is all of X ad
4. BASES I BAACH SPACES 39 4. BASES I BAACH SPACES Sice a Baach space X is a vector space, it must possess a Hamel, or vector space, basis, i.e., a subset {x γ } γ Γ whose fiite liear spa is all of X ad
Math 61CM - Solutions to homework 3
 Math 6CM - Solutios to homework 3 Cédric De Groote October 2 th, 208 Problem : Let F be a field, m 0 a fixed oegative iteger ad let V = {a 0 + a x + + a m x m a 0,, a m F} be the vector space cosistig
Math 6CM - Solutios to homework 3 Cédric De Groote October 2 th, 208 Problem : Let F be a field, m 0 a fixed oegative iteger ad let V = {a 0 + a x + + a m x m a 0,, a m F} be the vector space cosistig
(a) (b) All real numbers. (c) All real numbers. (d) None. to show the. (a) 3. (b) [ 7, 1) (c) ( 7, 1) (d) At x = 7. (a) (b)
 Chapter 0 Review 597. E; a ( + )( + ) + + S S + S + + + + + + S lim + l. D; a diverges by the Itegral l k Test sice d lim [(l ) ], so k l ( ) does ot coverge absolutely. But it coverges by the Alteratig
Chapter 0 Review 597. E; a ( + )( + ) + + S S + S + + + + + + S lim + l. D; a diverges by the Itegral l k Test sice d lim [(l ) ], so k l ( ) does ot coverge absolutely. But it coverges by the Alteratig
MATH 10550, EXAM 3 SOLUTIONS
 MATH 155, EXAM 3 SOLUTIONS 1. I fidig a approximate solutio to the equatio x 3 +x 4 = usig Newto s method with iitial approximatio x 1 = 1, what is x? Solutio. Recall that x +1 = x f(x ) f (x ). Hece,
MATH 155, EXAM 3 SOLUTIONS 1. I fidig a approximate solutio to the equatio x 3 +x 4 = usig Newto s method with iitial approximatio x 1 = 1, what is x? Solutio. Recall that x +1 = x f(x ) f (x ). Hece,
Seunghee Ye Ma 8: Week 5 Oct 28
 Week 5 Summary I Sectio, we go over the Mea Value Theorem ad its applicatios. I Sectio 2, we will recap what we have covered so far this term. Topics Page Mea Value Theorem. Applicatios of the Mea Value
Week 5 Summary I Sectio, we go over the Mea Value Theorem ad its applicatios. I Sectio 2, we will recap what we have covered so far this term. Topics Page Mea Value Theorem. Applicatios of the Mea Value
Fundamental Theorem of Algebra. Yvonne Lai March 2010
 Fudametal Theorem of Algebra Yvoe Lai March 010 We prove the Fudametal Theorem of Algebra: Fudametal Theorem of Algebra. Let f be a o-costat polyomial with real coefficiets. The f has at least oe complex
Fudametal Theorem of Algebra Yvoe Lai March 010 We prove the Fudametal Theorem of Algebra: Fudametal Theorem of Algebra. Let f be a o-costat polyomial with real coefficiets. The f has at least oe complex
Solving equations (incl. radical equations) involving these skills, but ultimately solvable by factoring/quadratic formula (no complex roots)
 Evet A: Fuctios ad Algebraic Maipulatio Factorig Square of a sum: ( a + b) = a + ab + b Square of a differece: ( a b) = a ab + b Differece of squares: a b = ( a b )(a + b ) Differece of cubes: a 3 b 3
Evet A: Fuctios ad Algebraic Maipulatio Factorig Square of a sum: ( a + b) = a + ab + b Square of a differece: ( a b) = a ab + b Differece of squares: a b = ( a b )(a + b ) Differece of cubes: a 3 b 3
x x x Using a second Taylor polynomial with remainder, find the best constant C so that for x 0,
 Math Activity 9( Due with Fial Eam) Usig first ad secod Taylor polyomials with remaider, show that for, 8 Usig a secod Taylor polyomial with remaider, fid the best costat C so that for, C 9 The th Derivative
Math Activity 9( Due with Fial Eam) Usig first ad secod Taylor polyomials with remaider, show that for, 8 Usig a secod Taylor polyomial with remaider, fid the best costat C so that for, C 9 The th Derivative
d) If the sequence of partial sums converges to a limit L, we say that the series converges and its
 Ifiite Series. Defiitios & covergece Defiitio... Let {a } be a sequece of real umbers. a) A expressio of the form a + a +... + a +... is called a ifiite series. b) The umber a is called as the th term
Ifiite Series. Defiitios & covergece Defiitio... Let {a } be a sequece of real umbers. a) A expressio of the form a + a +... + a +... is called a ifiite series. b) The umber a is called as the th term
Sequences. A Sequence is a list of numbers written in order.
 Sequeces A Sequece is a list of umbers writte i order. {a, a 2, a 3,... } The sequece may be ifiite. The th term of the sequece is the th umber o the list. O the list above a = st term, a 2 = 2 d term,
Sequeces A Sequece is a list of umbers writte i order. {a, a 2, a 3,... } The sequece may be ifiite. The th term of the sequece is the th umber o the list. O the list above a = st term, a 2 = 2 d term,
Chapter 3. z-transform
 Chapter 3 -Trasform 3.0 Itroductio The -Trasform has the same role as that played by the Laplace Trasform i the cotiuous-time theorem. It is a liear operator that is useful for aalyig LTI systems such
Chapter 3 -Trasform 3.0 Itroductio The -Trasform has the same role as that played by the Laplace Trasform i the cotiuous-time theorem. It is a liear operator that is useful for aalyig LTI systems such
Math 140A Elementary Analysis Homework Questions 3-1
 Math 0A Elemetary Aalysis Homework Questios -.9 Limits Theorems for Sequeces Suppose that lim x =, lim y = 7 ad that all y are o-zero. Detarime the followig limits: (a) lim(x + y ) (b) lim y x y Let s
Math 0A Elemetary Aalysis Homework Questios -.9 Limits Theorems for Sequeces Suppose that lim x =, lim y = 7 ad that all y are o-zero. Detarime the followig limits: (a) lim(x + y ) (b) lim y x y Let s
Ma 530 Infinite Series I
 Ma 50 Ifiite Series I Please ote that i additio to the material below this lecture icorporated material from the Visual Calculus web site. The material o sequeces is at Visual Sequeces. (To use this li
Ma 50 Ifiite Series I Please ote that i additio to the material below this lecture icorporated material from the Visual Calculus web site. The material o sequeces is at Visual Sequeces. (To use this li
Quiz. Use either the RATIO or ROOT TEST to determine whether the series is convergent or not.
 Quiz. Use either the RATIO or ROOT TEST to determie whether the series is coverget or ot. e .6 POWER SERIES Defiitio. A power series i about is a series of the form c 0 c a c a... c a... a 0 c a where
Quiz. Use either the RATIO or ROOT TEST to determie whether the series is coverget or ot. e .6 POWER SERIES Defiitio. A power series i about is a series of the form c 0 c a c a... c a... a 0 c a where
Math 132, Fall 2009 Exam 2: Solutions
 Math 3, Fall 009 Exam : Solutios () a) ( poits) Determie for which positive real umbers p, is the followig improper itegral coverget, ad for which it is diverget. Evaluate the itegral for each value of
Math 3, Fall 009 Exam : Solutios () a) ( poits) Determie for which positive real umbers p, is the followig improper itegral coverget, ad for which it is diverget. Evaluate the itegral for each value of
