Primer in Special Relativity and Electromagnetic Equations (Lecture 13)
|
|
|
- Naomi Carson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Primer in Special Relativity and Electromagnetic Equations (Lecture 13) January 29, /441
2 Lecture outline We will review the relativistic transformation for time-space coordinates, frequency, and electromagnetic field. 213/441
3 Maxwell s equations Classical electrodynamics in vacuum is governed by the Maxwell equations. In the SI system of units, the equations are D = ρ B = 0 E = B t H = j + D t where ρ is the charge density, j is the current density, with (13.1) D = ɛ 0 E, H = B/µ 0. B is called the magnetic induction, and H is called the magnetic field. The equations are linear: the sum of two solutions, E 1, B 1 and E 2, B 2, is also a solution corresponding to the sum of densities ρ 1 + ρ 2, j 1 + j /441
4 Point charge For a point charge moving along a trajectory r = r 0 (t), ρ(r, t) = qδ(r r 0 (t)), j(r, t) = qv(t)δ(r r 0 (t)), (13.2) with v(t) = dr 0 (t)/dt. Proper boundary conditions should be specified in each particular case. On a surface of a good conducting metal the boundary condition requires that the tangential component of the electric field is equal to zero, E t S = /441
5 SI units We will use the SI system of units (sometimes energy in ev). To convert an equation written in SI variables to the corresponding equation in Gaussian variables, replace according to the following table (from Jackson s book): Quantity SI Gaussian Velocity of light (µ 0 ɛ 0 ) 1/2 c Electric field, potential E, φ E 4πɛ0, φ 4πɛ0 Charge density, current q, ρ, j q 4πɛ 0, ρ 4πɛ 0, j 4πɛ 0 Magnetic induction B B µ0 4π We introduce the vacuum impedance Z 0, µ0 Z 0 = 377 Ohm. (13.3) ɛ 0 In CGS units Z 0 = 4π/c. 216/441
6 Wave equations In free space with no charges and currents field components satisfy the wave equation 1 2 f c 2 t 2 2 f x 2 2 f y 2 2 f z 2 = 0. (13.4) A particular solution of this equation is a sinusoidal wave characterized by frequency ω and wave number k and propagating in the direction of unit vector n: where A is a constant and ω = ck. f = A sin(ωt kn r), (13.5) 217/441
7 Vector and scalar potentials It is often convenient to express the fields in terms of the vector potential A and the scalar potential φ: E = φ A t B = A (13.6) Substituting these equations into Maxwell s equations, we find that the second and the third equations are satisfied identically. We only need to take care of the first and the fourth equations. 218/441
8 Energy balance and the Poynting theorem The electromagnetic field has an energy and momentum associated with it. The energy density of the field (energy per unit volume) is The Poynting vector u = 1 2 (E D + H B) = ɛ 0 2 (E 2 + c 2 B 2 ). (13.7) S = E H (13.8) gives the energy flow (energy per unit area per unit time) in the electromagnetic field. 219/441
9 Energy balance and the Poynting theorem A n V Consider charges that move inside a volume V enclosed by a surface A. The Poynting theorem states t V udv = V j EdV n SdA, A (13.9) where n is the unit vector normal to the surface and directed outward. The LHS of this equation is the rate of change of the electromagnetic energy. The first term on the right hand side is the work done by the electric field. The second term describes the electromagnetic energy flow from the volume through the enclosing surface. 220/441
10 Photons The quantum view on the radiation is that the electromagnetic field is represented by photons. Each photon carries the energy hω and the momentum hk, where the vector k is the wave number which points to the direction of propagation of the radiation, h = J sec is the Planck constant divided by 2π, and k = ω/c. 221/441
11 Lorentz transformation and matrices Consider two coordinate systems, K and K. The system K is moving with velocity v in the z direction relative to the system K. The coordinates of an event in both systems are related by the Lorentz transformation x = x, y = y, z = γ(z + βct ), t = γ(t + βz /c), (13.10) where β = v/c, and γ = 1/ 1 β 2. The vector (ct, r) = (ct, x, y, z) is called a 4-vector, and the above transformation is valid for any 4-vector quantity. 222/441
12 Lorentz transformation and matrices We will often deal with ultrarelativistic particles, which means that γ 1. In this limit, a useful approximation is β = 1 1 γ γ 2. (13.11) The Lorentz transformation (13.10) can also be written in the matrix notation x x x y z = y 0 0 γ cβγ z = L y z t 0 0 γ t t βγ c. (13.12) 223/441
13 Lorentz transformation and matrices The advantage of using matrices is that they can be consecutively applied in several steps. Here is an example: we want to generate a matrix which corresponds to a moving coordinate system along the x axis. 224/441
14 Lorentz transformation and matrices Let us rotate K system by 90 degrees around the y axis, in such a way that the new x axis is equal to the old z. The rotated frame is denoted by K and the y y y y x x V V M L M -1 rot rot x z z x z z coordinate transformation from K to K is given by x = z, z = x, or in matrix notation M rot = (13.13) /441
15 Lorentz transformation and matrices A new frame K is moving along along the z axis and we then use the Lorentz transformation L to transform from K to K. Finally, we transform from K to the lab frame K using the matrix Mrot 1. The sequence of these transformations is given by the product (M rot ) 1 L M rot = γ 0 0 γβc γβ/c 0 0 γ. (13.14) This result, of course, can be easily obtained directly from the original transformation by exchanging x z. 226/441
16 Lorentz contraction and time dilation Two events occurring in the moving frame at the same point and separated by the time interval t will be measured by the lab observes as separated by t, t = γ t. (13.15) This is the effect of relativistic time dilation. An object of length l aligned in the moving frame with the z axis will have the length l in the lab frame: l = l γ. (13.16) This is the effect of relativistic contraction. The length in the direction transverse to the motion is not changed. 227/441
17 Doppler effect Consider a wave propagating in a moving frame K. It has the time-space dependence: cos(ω t k r ), (13.17) where ω is the frequency and k is the wavenumber of the wave in the moving frame. What kind of time-space dependence an observer in the frame K would see? We need to make a Lorentz transformation of coordinates and time to get cos(ω t k r ) = cos(ω γ(t βz/c) k x x k y y k z γ(z βct)) = cos(γ(ω + k z βc)t k x x k y y γ(k z + ω β/c)z). (13.18) 228/441
18 Doppler effect We see that in the K frame this process is also a wave with the frequency and wavenumber cos(ωt kr), (13.19) k x = k x, k y = k y, The object (ω, ck) is a 4-vector. k z = γ(k z + βω /c), ω = γ(ω + βck z ). (13.20) The result ω = γ(ω + k z βc) matches E = γ(e + p z βc), and similarly for k z and p z. 229/441
19 Doppler effect The above transformation is valid for any type of waves (electromagnetic, acoustic, plasma waves, etc.) Now let us apply it to electromagnetic waves in vacuum. For those waves we know that ω = ck. (13.21) Assume that an electromagnetic wave propagates at angle θ in the frame K cos θ = k z k, (13.22) and has a frequency ω in that frame. What is the angle θ and the frequency ω of this wave in the lab frame? 230/441
20 Doppler effect We can always choose the coordinate system such that k = (0, k y, k z ), then tan θ = k y k z = k y γ(k z + βω /c) = sin θ γ(cos θ + β). (13.23) In the limit γ 1 almost all angles θ (except for those very close to π) are transformed to angles θ 1/γ. This explains why radiation of an ultrarelativistic beams goes mostly in the forward direction, within an angle of the order of 1/γ. 231/441
21 Doppler effect For the frequency, a convenient formula relates ω with ω and θ (not θ ). To derive it, we use first the inverse Lorentz transformation which gives ω = γ(ω βck z ) = γ(ω βck cos θ), (13.24) ω = ω γ(1 β cos θ). (13.25) Using β 1 1/2γ 2 and cos θ = 1 θ 2 /2, we obtain ω = 2γω 1 + γ 2 θ 2. (13.26) The radiation in the forward direction (θ = 0) gets a factor 2γ in the frequency. 232/441
22 Lorentz transformation of fields The electromagnetic field is transformed from K to K according to following equations E z = E z, E = γ ( E v B ), ( B z = B z, B = γ B + 1 ) c 2 v E, (13.27) where E and B are the components of the electric and magnetic fields perpendicular to the velocity v: E = (E x, E y ), B = (B x, B y ). 233/441
23 Lorentz transformation of fields The electromagnetic potentials (φ/c, A) are transformed exactly as the 4-vector (ct, r): A x = A x, A y = A y, ( A z = γ A z + v c 2 φ ), φ = γ(φ + va z), (13.28) 234/441
24 Lorentz transformation and photons It is often convenient, even in classical electrodynamics, to consider electromagnetic radiation as a collection of photons. How do we transform photon properties from K to K? The answer is simple: the wavevector k and the frequency of each photon ω is transformed as described above. The number of photons is a relativistic invariant it is the same in all frames. 235/441
Module II: Relativity and Electrodynamics
 Module II: Relativity and Electrodynamics Lecture 2: Lorentz transformations of observables Amol Dighe TIFR, Mumbai Outline Length, time, velocity, acceleration Transformations of electric and magnetic
Module II: Relativity and Electrodynamics Lecture 2: Lorentz transformations of observables Amol Dighe TIFR, Mumbai Outline Length, time, velocity, acceleration Transformations of electric and magnetic
FYS 3120: Classical Mechanics and Electrodynamics
 FYS 3120: Classical Mechanics and Electrodynamics Formula Collection Spring semester 2014 1 Analytical Mechanics The Lagrangian L = L(q, q, t), (1) is a function of the generalized coordinates q = {q i
FYS 3120: Classical Mechanics and Electrodynamics Formula Collection Spring semester 2014 1 Analytical Mechanics The Lagrangian L = L(q, q, t), (1) is a function of the generalized coordinates q = {q i
Lecture notes on Classical Mechanics and Electromagnetism in Accelerator Physics
 G. Stupakov Revision 20 Lecture notes on Classical Mechanics and Electromagnetism in Accelerator Physics The US Particle Accelerator School June 13-24, 2011 Melville, New York 2011 Contents 1 Preliminaries
G. Stupakov Revision 20 Lecture notes on Classical Mechanics and Electromagnetism in Accelerator Physics The US Particle Accelerator School June 13-24, 2011 Melville, New York 2011 Contents 1 Preliminaries
Electrodynamics I Final Exam - Part A - Closed Book KSU 2005/12/12 Electro Dynamic
 Electrodynamics I Final Exam - Part A - Closed Book KSU 2005/12/12 Name Electro Dynamic Instructions: Use SI units. Short answers! No derivations here, just state your responses clearly. 1. (2) Write an
Electrodynamics I Final Exam - Part A - Closed Book KSU 2005/12/12 Name Electro Dynamic Instructions: Use SI units. Short answers! No derivations here, just state your responses clearly. 1. (2) Write an
Plane electromagnetic waves and Gaussian beams (Lecture 17)
 Plane electromagnetic waves and Gaussian beams (Lecture 17) February 2, 2016 305/441 Lecture outline In this lecture we will study electromagnetic field propagating in space free of charges and currents.
Plane electromagnetic waves and Gaussian beams (Lecture 17) February 2, 2016 305/441 Lecture outline In this lecture we will study electromagnetic field propagating in space free of charges and currents.
E & M Qualifier. January 11, To insure that the your work is graded correctly you MUST:
 E & M Qualifier 1 January 11, 2017 To insure that the your work is graded correctly you MUST: 1. use only the blank answer paper provided, 2. use only the reference material supplied (Schaum s Guides),
E & M Qualifier 1 January 11, 2017 To insure that the your work is graded correctly you MUST: 1. use only the blank answer paper provided, 2. use only the reference material supplied (Schaum s Guides),
Postulates of Special Relativity
 Relativity Relativity - Seen as an intricate theory that is necessary when dealing with really high speeds - Two charged initially stationary particles: Electrostatic force - In another, moving reference
Relativity Relativity - Seen as an intricate theory that is necessary when dealing with really high speeds - Two charged initially stationary particles: Electrostatic force - In another, moving reference
Electromagnetism. Christopher R Prior. ASTeC Intense Beams Group Rutherford Appleton Laboratory
 lectromagnetism Christopher R Prior Fellow and Tutor in Mathematics Trinity College, Oxford ASTeC Intense Beams Group Rutherford Appleton Laboratory Contents Review of Maxwell s equations and Lorentz Force
lectromagnetism Christopher R Prior Fellow and Tutor in Mathematics Trinity College, Oxford ASTeC Intense Beams Group Rutherford Appleton Laboratory Contents Review of Maxwell s equations and Lorentz Force
Transformations. 1 The Lorentz Transformation. 2 Velocity Transformation
 Transformations 1 The Lorentz Transformation In the last lecture we obtained the relativistic transformations for space/time between inertial frames. These transformations follow mainly from the postulate
Transformations 1 The Lorentz Transformation In the last lecture we obtained the relativistic transformations for space/time between inertial frames. These transformations follow mainly from the postulate
Accelerator Physics NMI and Synchrotron Radiation. G. A. Krafft Old Dominion University Jefferson Lab Lecture 16
 Accelerator Physics NMI and Synchrotron Radiation G. A. Krafft Old Dominion University Jefferson Lab Lecture 16 Graduate Accelerator Physics Fall 17 Oscillation Frequency nq I n i Z c E Re Z 1 mode has
Accelerator Physics NMI and Synchrotron Radiation G. A. Krafft Old Dominion University Jefferson Lab Lecture 16 Graduate Accelerator Physics Fall 17 Oscillation Frequency nq I n i Z c E Re Z 1 mode has
PH 253 Exam I Solutions
 PH 253 Exam I Solutions. An electron and a proton are each accelerated starting from rest through a potential difference of 0.0 million volts (0 7 V). Find the momentum (in MeV/c) and kinetic energy (in
PH 253 Exam I Solutions. An electron and a proton are each accelerated starting from rest through a potential difference of 0.0 million volts (0 7 V). Find the momentum (in MeV/c) and kinetic energy (in
Lorentz Transformations
 Lorentz Transformations 1 The Lorentz Transformation In the last lecture the relativistic transformations for space/time between inertial frames was obtained. These transformations esentially follow from
Lorentz Transformations 1 The Lorentz Transformation In the last lecture the relativistic transformations for space/time between inertial frames was obtained. These transformations esentially follow from
Chapter 2 Undulator Radiation
 Chapter 2 Undulator Radiation 2.1 Magnetic Field of a Planar Undulator The motion of an electron in a planar undulator magnet is shown schematically in Fig. 2.1. The undulator axis is along the direction
Chapter 2 Undulator Radiation 2.1 Magnetic Field of a Planar Undulator The motion of an electron in a planar undulator magnet is shown schematically in Fig. 2.1. The undulator axis is along the direction
Physics 504, Lecture 22 April 19, Frequency and Angular Distribution
 Last Latexed: April 16, 010 at 11:56 1 Physics 504, Lecture April 19, 010 Copyright c 009 by Joel A Shapiro 1 Freuency and Angular Distribution We have found the expression for the power radiated in a
Last Latexed: April 16, 010 at 11:56 1 Physics 504, Lecture April 19, 010 Copyright c 009 by Joel A Shapiro 1 Freuency and Angular Distribution We have found the expression for the power radiated in a
Chapter 2 Radiation of an Accelerated Charge
 Chapter 2 Radiation of an Accelerated Charge Whatever the energy source and whatever the object, (but with the notable exception of neutrino emission that we will not consider further, and that of gravitational
Chapter 2 Radiation of an Accelerated Charge Whatever the energy source and whatever the object, (but with the notable exception of neutrino emission that we will not consider further, and that of gravitational
Radiative Processes in Astrophysics
 Radiative Processes in Astrophysics 6. Relativistic Covariance & Kinematics Eline Tolstoy http://www.astro.rug.nl/~etolstoy/astroa07/ Practise, practise, practise... mid-term, 31st may, 9.15-11am As we
Radiative Processes in Astrophysics 6. Relativistic Covariance & Kinematics Eline Tolstoy http://www.astro.rug.nl/~etolstoy/astroa07/ Practise, practise, practise... mid-term, 31st may, 9.15-11am As we
Particles and Deep Inelastic Scattering
 Particles and Deep Inelastic Scattering Heidi Schellman University HUGS - JLab - June 2010 June 2010 HUGS 1 Course Outline 1. Really basic stuff 2. How we detect particles 3. Basics of 2 2 scattering 4.
Particles and Deep Inelastic Scattering Heidi Schellman University HUGS - JLab - June 2010 June 2010 HUGS 1 Course Outline 1. Really basic stuff 2. How we detect particles 3. Basics of 2 2 scattering 4.
Special relativity and light RL 4.1, 4.9, 5.4, (6.7)
 Special relativity and light RL 4.1, 4.9, 5.4, (6.7) First: Bremsstrahlung recap Braking radiation, free-free emission Important in hot plasma (e.g. coronae) Most relevant: thermal Bremsstrahlung What
Special relativity and light RL 4.1, 4.9, 5.4, (6.7) First: Bremsstrahlung recap Braking radiation, free-free emission Important in hot plasma (e.g. coronae) Most relevant: thermal Bremsstrahlung What
The relativistic Doppler effect: when a zero frequency shift or a red shift exists for sources approaching the observer
 The relativistic Doppler effect: when a zero frequency shift or a red shift exists for sources approaching the observer Changbiao Wang * ShangGang Group, 70 Huntington Road, Apartment, New Haven, CT 065,
The relativistic Doppler effect: when a zero frequency shift or a red shift exists for sources approaching the observer Changbiao Wang * ShangGang Group, 70 Huntington Road, Apartment, New Haven, CT 065,
Covariant Formulation of Electrodynamics
 Chapter 7. Covariant Formulation of Electrodynamics Notes: Most of the material presented in this chapter is taken from Jackson, Chap. 11, and Rybicki and Lightman, Chap. 4. Starting with this chapter,
Chapter 7. Covariant Formulation of Electrodynamics Notes: Most of the material presented in this chapter is taken from Jackson, Chap. 11, and Rybicki and Lightman, Chap. 4. Starting with this chapter,
Relativistic Transformations
 Relativistic Transformations Lecture 7 1 The Lorentz transformation In the last lecture we obtained the relativistic transformations for space/time between inertial frames. These transformations follow
Relativistic Transformations Lecture 7 1 The Lorentz transformation In the last lecture we obtained the relativistic transformations for space/time between inertial frames. These transformations follow
Examples - Lecture 8. 1 GPS System
 Examples - Lecture 8 1 GPS System The global positioning system, GPS, was established in 1973, and has been updated almost yearly. The GPS calculates postion on the earth s surface by accurately measuring
Examples - Lecture 8 1 GPS System The global positioning system, GPS, was established in 1973, and has been updated almost yearly. The GPS calculates postion on the earth s surface by accurately measuring
Covariant Formulation of Electrodynamics
 Chapter 7. Covariant Formulation of Electrodynamics Notes: Most of the material presented in this chapter is taken from Jackson, Chap. 11, and Rybicki and Lightman, Chap. 4. Starting with this chapter,
Chapter 7. Covariant Formulation of Electrodynamics Notes: Most of the material presented in this chapter is taken from Jackson, Chap. 11, and Rybicki and Lightman, Chap. 4. Starting with this chapter,
Special Relativity. Christopher R. Prior. Accelerator Science and Technology Centre Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, U.K.
 Special Relativity Christopher R. Prior Fellow and Tutor in Mathematics Trinity College, Oxford Accelerator Science and Technology Centre Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, U.K. The principle of special relativity
Special Relativity Christopher R. Prior Fellow and Tutor in Mathematics Trinity College, Oxford Accelerator Science and Technology Centre Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, U.K. The principle of special relativity
4/13/2015. Outlines CHAPTER 12 ELECTRODYNAMICS & RELATIVITY. 1. The special theory of relativity. 2. Relativistic Mechanics
 CHAPTER 12 ELECTRODYNAMICS & RELATIVITY Lee Chow Department of Physics University of Central Florida Orlando, FL 32816 Outlines 1. The special theory of relativity 2. Relativistic Mechanics 3. Relativistic
CHAPTER 12 ELECTRODYNAMICS & RELATIVITY Lee Chow Department of Physics University of Central Florida Orlando, FL 32816 Outlines 1. The special theory of relativity 2. Relativistic Mechanics 3. Relativistic
Vectors in Special Relativity
 Chapter 2 Vectors in Special Relativity 2.1 Four - vectors A four - vector is a quantity with four components which changes like spacetime coordinates under a coordinate transformation. We will write the
Chapter 2 Vectors in Special Relativity 2.1 Four - vectors A four - vector is a quantity with four components which changes like spacetime coordinates under a coordinate transformation. We will write the
Covariant electrodynamics
 Lecture 9 Covariant electrodynamics WS2010/11: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics 1 Consider Lorentz transformations pseudo-orthogonal transformations in 4-dimentional vector space (Minkowski
Lecture 9 Covariant electrodynamics WS2010/11: Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics 1 Consider Lorentz transformations pseudo-orthogonal transformations in 4-dimentional vector space (Minkowski
Basics of Radiation Fields
 Basics of Radiation Fields Initial questions: How could you estimate the distance to a radio source in our galaxy if you don t have a parallax? We are now going to shift gears a bit. In order to understand
Basics of Radiation Fields Initial questions: How could you estimate the distance to a radio source in our galaxy if you don t have a parallax? We are now going to shift gears a bit. In order to understand
Solutions to problem set 6
 Solutions to problem set 6 Donal O Connell February 3, 006 1 Problem 1 (a) The Lorentz transformations are just t = γ(t vx) (1) x = γ(x vt). () In S, the length δx is at the points x = 0 and x = δx for
Solutions to problem set 6 Donal O Connell February 3, 006 1 Problem 1 (a) The Lorentz transformations are just t = γ(t vx) (1) x = γ(x vt). () In S, the length δx is at the points x = 0 and x = δx for
Covariant Electromagnetic Fields
 Chapter 8 Covariant Electromagnetic Fields 8. Introduction The electromagnetic field was the original system that obeyed the principles of relativity. In fact, Einstein s original articulation of relativity
Chapter 8 Covariant Electromagnetic Fields 8. Introduction The electromagnetic field was the original system that obeyed the principles of relativity. In fact, Einstein s original articulation of relativity
Overthrows a basic assumption of classical physics - that lengths and time intervals are absolute quantities, i.e., the same for all observes.
 Relativistic Electrodynamics An inertial frame = coordinate system where Newton's 1st law of motion - the law of inertia - is true. An inertial frame moves with constant velocity with respect to any other
Relativistic Electrodynamics An inertial frame = coordinate system where Newton's 1st law of motion - the law of inertia - is true. An inertial frame moves with constant velocity with respect to any other
Inflation, vacua and the end of the Universe
 Inflation, 10 500 vacua and the end of the Universe Homework Problems: 1-7 (15 points) 1-10 (25 points) 2-9 (20 points) 2-13 (20 points) from Spacetime Physics Physics 311 Special Relativity Lecture 4:
Inflation, 10 500 vacua and the end of the Universe Homework Problems: 1-7 (15 points) 1-10 (25 points) 2-9 (20 points) 2-13 (20 points) from Spacetime Physics Physics 311 Special Relativity Lecture 4:
Electrodynamics HW Problems 06 EM Waves
 Electrodynamics HW Problems 06 EM Waves 1. Energy in a wave on a string 2. Traveling wave on a string 3. Standing wave 4. Spherical traveling wave 5. Traveling EM wave 6. 3- D electromagnetic plane wave
Electrodynamics HW Problems 06 EM Waves 1. Energy in a wave on a string 2. Traveling wave on a string 3. Standing wave 4. Spherical traveling wave 5. Traveling EM wave 6. 3- D electromagnetic plane wave
Chapter Three: Propagation of light waves
 Chapter Three Propagation of Light Waves CHAPTER OUTLINE 3.1 Maxwell s Equations 3.2 Physical Significance of Maxwell s Equations 3.3 Properties of Electromagnetic Waves 3.4 Constitutive Relations 3.5
Chapter Three Propagation of Light Waves CHAPTER OUTLINE 3.1 Maxwell s Equations 3.2 Physical Significance of Maxwell s Equations 3.3 Properties of Electromagnetic Waves 3.4 Constitutive Relations 3.5
Instructor: Sudipta Mukherji, Institute of Physics, Bhubaneswar
 Chapter 1 Lorentz and Poincare Instructor: Sudipta Mukherji, Institute of Physics, Bhubaneswar 1.1 Lorentz Transformation Consider two inertial frames S and S, where S moves with a velocity v with respect
Chapter 1 Lorentz and Poincare Instructor: Sudipta Mukherji, Institute of Physics, Bhubaneswar 1.1 Lorentz Transformation Consider two inertial frames S and S, where S moves with a velocity v with respect
Electromagnetic Waves
 May 7, 2008 1 1 J.D.Jackson, Classical Electrodynamics, 2nd Edition, Section 7 Maxwell Equations In a region of space where there are no free sources (ρ = 0, J = 0), Maxwell s equations reduce to a simple
May 7, 2008 1 1 J.D.Jackson, Classical Electrodynamics, 2nd Edition, Section 7 Maxwell Equations In a region of space where there are no free sources (ρ = 0, J = 0), Maxwell s equations reduce to a simple
Special Theory of Relativity
 June 17, 2008 1 1 J.D.Jackson, Classical Electrodynamics, 3rd Edition, Chapter 11 Introduction Einstein s theory of special relativity is based on the assumption (which might be a deep-rooted superstition
June 17, 2008 1 1 J.D.Jackson, Classical Electrodynamics, 3rd Edition, Chapter 11 Introduction Einstein s theory of special relativity is based on the assumption (which might be a deep-rooted superstition
(a) Show that the amplitudes of the reflected and transmitted waves, corrrect to first order
 Problem 1. A conducting slab A plane polarized electromagnetic wave E = E I e ikz ωt is incident normally on a flat uniform sheet of an excellent conductor (σ ω) having thickness D. Assume that in space
Problem 1. A conducting slab A plane polarized electromagnetic wave E = E I e ikz ωt is incident normally on a flat uniform sheet of an excellent conductor (σ ω) having thickness D. Assume that in space
1 Fundamentals. 1.1 Overview. 1.2 Units: Physics 704 Spring 2018
 Physics 704 Spring 2018 1 Fundamentals 1.1 Overview The objective of this course is: to determine and fields in various physical systems and the forces and/or torques resulting from them. The domain of
Physics 704 Spring 2018 1 Fundamentals 1.1 Overview The objective of this course is: to determine and fields in various physical systems and the forces and/or torques resulting from them. The domain of
Electromagnetic. G. A. Krafft Jefferson Lab Jefferson Lab Professor of Physics Old Dominion University Physics 804 Electromagnetic Theory II
 Physics 704/804 Electromagnetic Theory II G. A. Krafft Jefferson Lab Jefferson Lab Professor of Physics Old Dominion University 04-13-10 4-Vectors and Proper Time Any set of four quantities that transform
Physics 704/804 Electromagnetic Theory II G. A. Krafft Jefferson Lab Jefferson Lab Professor of Physics Old Dominion University 04-13-10 4-Vectors and Proper Time Any set of four quantities that transform
Review and Notation (Special relativity)
 Review and Notation (Special relativity) December 30, 2016 7:35 PM Special Relativity: i) The principle of special relativity: The laws of physics must be the same in any inertial reference frame. In particular,
Review and Notation (Special relativity) December 30, 2016 7:35 PM Special Relativity: i) The principle of special relativity: The laws of physics must be the same in any inertial reference frame. In particular,
Special Relativity. Chris Prior. Trinity College Oxford. and
 Special Relativity Chris Prior ASTeC RAL Trinity College Oxford and 1 Overview The principle of special relativity Lorentz transformation and consequences Space-time 4-vectors: position, velocity, momentum,
Special Relativity Chris Prior ASTeC RAL Trinity College Oxford and 1 Overview The principle of special relativity Lorentz transformation and consequences Space-time 4-vectors: position, velocity, momentum,
1 Tensors and relativity
 Physics 705 1 Tensors and relativity 1.1 History Physical laws should not depend on the reference frame used to describe them. This idea dates back to Galileo, who recognized projectile motion as free
Physics 705 1 Tensors and relativity 1.1 History Physical laws should not depend on the reference frame used to describe them. This idea dates back to Galileo, who recognized projectile motion as free
The Helmholtz Decomposition and the Coulomb Gauge
 The Helmholtz Decomposition and the Coulomb Gauge 1 Problem Kirk T. McDonald Joseph Henry Laboratories, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544 (April 17, 2008; updated February 7, 2015 Helmholtz showed
The Helmholtz Decomposition and the Coulomb Gauge 1 Problem Kirk T. McDonald Joseph Henry Laboratories, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544 (April 17, 2008; updated February 7, 2015 Helmholtz showed
The Four-Frequency of Light. William O. Straub Pasadena, California June 28, 2014
 The Four-Frequency of Light William O. Straub Pasadena, Califnia 91104 June 28, 2014 Abstract A basic overview of the photon four-frequency is given, demonstrating its use in the explanation of the aberration
The Four-Frequency of Light William O. Straub Pasadena, Califnia 91104 June 28, 2014 Abstract A basic overview of the photon four-frequency is given, demonstrating its use in the explanation of the aberration
Astrophysical Radiation Processes
 PHY3145 Topics in Theoretical Physics Astrophysical Radiation Processes 3: Relativistic effects I Dr. J. Hatchell, Physics 407, J.Hatchell@exeter.ac.uk Course structure 1. Radiation basics. Radiative transfer.
PHY3145 Topics in Theoretical Physics Astrophysical Radiation Processes 3: Relativistic effects I Dr. J. Hatchell, Physics 407, J.Hatchell@exeter.ac.uk Course structure 1. Radiation basics. Radiative transfer.
Radiated Power Distribution in the Far Zone of a Moving System
 1 Problem Radiated Power Distribution in the Far Zone of a Moving System Kirk T. McDonald Joseph Henry Laboratories, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544 (April 24, 1979; updated April 28, 2017) Show
1 Problem Radiated Power Distribution in the Far Zone of a Moving System Kirk T. McDonald Joseph Henry Laboratories, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544 (April 24, 1979; updated April 28, 2017) Show
8.20 MIT Introduction to Special Relativity IAP 2005 Tentative Outline
 8.20 MIT Introduction to Special Relativity IAP 2005 Tentative Outline 1 Main Headings I Introduction and relativity pre Einstein II Einstein s principle of relativity and a new concept of spacetime III
8.20 MIT Introduction to Special Relativity IAP 2005 Tentative Outline 1 Main Headings I Introduction and relativity pre Einstein II Einstein s principle of relativity and a new concept of spacetime III
1 Lagrangian for a continuous system
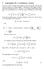 Lagrangian for a continuous system Let s start with an example from mechanics to get the big idea. The physical system of interest is a string of length and mass per unit length fixed at both ends, and
Lagrangian for a continuous system Let s start with an example from mechanics to get the big idea. The physical system of interest is a string of length and mass per unit length fixed at both ends, and
Mechanics Physics 151
 Mechanics Physics 151 Lecture 15 Special Relativity (Chapter 7) What We Did Last Time Defined Lorentz transformation Linear transformation of 4-vectors that conserve the length in Minkowski space Derived
Mechanics Physics 151 Lecture 15 Special Relativity (Chapter 7) What We Did Last Time Defined Lorentz transformation Linear transformation of 4-vectors that conserve the length in Minkowski space Derived
2. Special Relativity (SR) explicit Lorentz transformations Particles with m > 0 can always be seen as boosted from their rest frame
 2. Special Relativity (SR) explicit Lorentz transformations Particles with m > 0 can always be seen as boosted from their rest frame in frame O we see the particle as p µ = (E, p) =. (E,p,0,0) in its rest
2. Special Relativity (SR) explicit Lorentz transformations Particles with m > 0 can always be seen as boosted from their rest frame in frame O we see the particle as p µ = (E, p) =. (E,p,0,0) in its rest
Chapter 11. Special Relativity
 Chapter 11 Special Relativity Note: Please also consult the fifth) problem list associated with this chapter In this chapter, Latin indices are used for space coordinates only eg, i = 1,2,3, etc), while
Chapter 11 Special Relativity Note: Please also consult the fifth) problem list associated with this chapter In this chapter, Latin indices are used for space coordinates only eg, i = 1,2,3, etc), while
Examples. Figure 1: The figure shows the geometry of the GPS system
 Examples 1 GPS System The global positioning system was established in 1973, and has been updated almost yearly. The GPS calcualtes postion on the earth ssurface by accurately measuring timing signals
Examples 1 GPS System The global positioning system was established in 1973, and has been updated almost yearly. The GPS calcualtes postion on the earth ssurface by accurately measuring timing signals
Field Theory exam II Solutions
 Field Theory exam II Solutions Problem 1 (a) Consider point charges, one with charge q located at x 1 = (1, 0, 1), and the other one with charge q at x = (1, 0, 1). Compute the multipole moments q lm in
Field Theory exam II Solutions Problem 1 (a) Consider point charges, one with charge q located at x 1 = (1, 0, 1), and the other one with charge q at x = (1, 0, 1). Compute the multipole moments q lm in
Simultaneity, Time Dilation, and Length Contraction Using Minkowski Diagrams and Lorentz Transformations
 Simultaneity, Time Dilation, and Length Contraction Using Minkowski Diagrams and Lorentz Transformations Dr. Russell L. Herman January 25, 2008 (modified: January 17, 2018) Abstract In these notes we present
Simultaneity, Time Dilation, and Length Contraction Using Minkowski Diagrams and Lorentz Transformations Dr. Russell L. Herman January 25, 2008 (modified: January 17, 2018) Abstract In these notes we present
Chapter-1 Relativity Part I RADIATION
 Chapter-1 Relativity Part I RADIATION Radiation implies the transfer of energy from one place to another. - Electromagnetic Radiation - Light - Particle and Cosmic Radiation photons, protons, neutrons,
Chapter-1 Relativity Part I RADIATION Radiation implies the transfer of energy from one place to another. - Electromagnetic Radiation - Light - Particle and Cosmic Radiation photons, protons, neutrons,
Physics 214 Midterm Exam Solutions Winter 2017
 Physics 14 Midterm Exam Solutions Winter 017 1. A linearly polarized electromagnetic wave, polarized in the ˆx direction, is traveling in the ẑ-direction in a dielectric medium of refractive index n 1.
Physics 14 Midterm Exam Solutions Winter 017 1. A linearly polarized electromagnetic wave, polarized in the ˆx direction, is traveling in the ẑ-direction in a dielectric medium of refractive index n 1.
MIT Course 8.033, Fall 2006, Relativistic Kinematics Max Tegmark Last revised October
 MIT Course 8.33, Fall 6, Relativistic Kinematics Max Tegmark Last revised October 17 6 Topics Lorentz transformations toolbox formula summary inverse composition (v addition) boosts as rotations the invariant
MIT Course 8.33, Fall 6, Relativistic Kinematics Max Tegmark Last revised October 17 6 Topics Lorentz transformations toolbox formula summary inverse composition (v addition) boosts as rotations the invariant
Fundamental Concepts of Particle Accelerators III : High-Energy Beam Dynamics (2) Koji TAKATA KEK. Accelerator Course, Sokendai. Second Term, JFY2012
 .... Fundamental Concepts of Particle Accelerators III : High-Energy Beam Dynamics (2) Koji TAKATA KEK koji.takata@kek.jp http://research.kek.jp/people/takata/home.html Accelerator Course, Sokendai Second
.... Fundamental Concepts of Particle Accelerators III : High-Energy Beam Dynamics (2) Koji TAKATA KEK koji.takata@kek.jp http://research.kek.jp/people/takata/home.html Accelerator Course, Sokendai Second
Particle Notes. Ryan D. Reece
 Particle Notes Ryan D. Reece July 9, 2007 Chapter 1 Preliminaries 1.1 Overview of Special Relativity 1.1.1 Lorentz Boosts Searches in the later part 19th century for the coordinate transformation that
Particle Notes Ryan D. Reece July 9, 2007 Chapter 1 Preliminaries 1.1 Overview of Special Relativity 1.1.1 Lorentz Boosts Searches in the later part 19th century for the coordinate transformation that
A Brief Introduction to Relativistic Quantum Mechanics
 A Brief Introduction to Relativistic Quantum Mechanics Hsin-Chia Cheng, U.C. Davis 1 Introduction In Physics 215AB, you learned non-relativistic quantum mechanics, e.g., Schrödinger equation, E = p2 2m
A Brief Introduction to Relativistic Quantum Mechanics Hsin-Chia Cheng, U.C. Davis 1 Introduction In Physics 215AB, you learned non-relativistic quantum mechanics, e.g., Schrödinger equation, E = p2 2m
University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics. Electricity and Magnetism PhD Qualifying Examination
 University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics Electricity and Magnetism PhD Qualifying Examination January 8, 216 (Friday) 9: am - 12: noon Full credit can be achieved from completely correct
University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics Electricity and Magnetism PhD Qualifying Examination January 8, 216 (Friday) 9: am - 12: noon Full credit can be achieved from completely correct
Selected electrostatic problems (Lecture 14)
 Selected electrostatic problems (Lecture 14) February 1, 2016 236/441 Lecture outline In this lecture, we demonstrate how to solve several electrostatic problems related to calculation of the fields generated
Selected electrostatic problems (Lecture 14) February 1, 2016 236/441 Lecture outline In this lecture, we demonstrate how to solve several electrostatic problems related to calculation of the fields generated
Lecture 9: Macroscopic Quantum Model
 Lecture 9: Macroscopic Quantum Model Outline 1. Development of Quantum Mechanics 2. Schrödinger's Equation Free particle With forces With Electromagnetic force 3. Physical meaning of Wavefunction Probability
Lecture 9: Macroscopic Quantum Model Outline 1. Development of Quantum Mechanics 2. Schrödinger's Equation Free particle With forces With Electromagnetic force 3. Physical meaning of Wavefunction Probability
E&M. 1 Capacitors. January 2009
 E&M January 2009 1 Capacitors Consider a spherical capacitor which has the space between its plates filled with a dielectric of permittivity ɛ. The inner sphere has radius r 1 and the outer sphere has
E&M January 2009 1 Capacitors Consider a spherical capacitor which has the space between its plates filled with a dielectric of permittivity ɛ. The inner sphere has radius r 1 and the outer sphere has
Special Relativity and Electromagnetism
 1/32 Special Relativity and Electromagnetism Jonathan Gratus Cockcroft Postgraduate Lecture Series October 2016 Introduction 10:30 11:40 14:00? Monday SR EM Tuesday SR EM Seminar Four lectures is clearly
1/32 Special Relativity and Electromagnetism Jonathan Gratus Cockcroft Postgraduate Lecture Series October 2016 Introduction 10:30 11:40 14:00? Monday SR EM Tuesday SR EM Seminar Four lectures is clearly
Lecture 15 Notes: 07 / 26. The photoelectric effect and the particle nature of light
 Lecture 15 Notes: 07 / 26 The photoelectric effect and the particle nature of light When diffraction of light was discovered, it was assumed that light was purely a wave phenomenon, since waves, but not
Lecture 15 Notes: 07 / 26 The photoelectric effect and the particle nature of light When diffraction of light was discovered, it was assumed that light was purely a wave phenomenon, since waves, but not
2nd Year Electromagnetism 2012:.Exam Practice
 2nd Year Electromagnetism 2012:.Exam Practice These are sample questions of the type of question that will be set in the exam. They haven t been checked the way exam questions are checked so there may
2nd Year Electromagnetism 2012:.Exam Practice These are sample questions of the type of question that will be set in the exam. They haven t been checked the way exam questions are checked so there may
Lecture: Lorentz Invariant Dynamics
 Chapter 5 Lecture: Lorentz Invariant Dynamics In the preceding chapter we introduced the Minkowski metric and covariance with respect to Lorentz transformations between inertial systems. This was shown
Chapter 5 Lecture: Lorentz Invariant Dynamics In the preceding chapter we introduced the Minkowski metric and covariance with respect to Lorentz transformations between inertial systems. This was shown
Electricity & Magnetism Qualifier
 Electricity & Magnetism Qualifier For each problem state what system of units you are using. 1. Imagine that a spherical balloon is being filled with a charged gas in such a way that the rate of charge
Electricity & Magnetism Qualifier For each problem state what system of units you are using. 1. Imagine that a spherical balloon is being filled with a charged gas in such a way that the rate of charge
Set 5: Classical E&M and Plasma Processes
 Set 5: Classical E&M and Plasma Processes Maxwell Equations Classical E&M defined by the Maxwell Equations (fields sourced by matter) and the Lorentz force (matter moved by fields) In cgs (gaussian) units
Set 5: Classical E&M and Plasma Processes Maxwell Equations Classical E&M defined by the Maxwell Equations (fields sourced by matter) and the Lorentz force (matter moved by fields) In cgs (gaussian) units
Chapter 12. Electrodynamics and Relativity. Does the principle of relativity apply to the laws of electrodynamics?
 Chapter 12. Electrodynamics and Relativity Does the principle of relativity apply to the laws of electrodynamics? 12.1 The Special Theory of Relativity Does the principle of relativity apply to the laws
Chapter 12. Electrodynamics and Relativity Does the principle of relativity apply to the laws of electrodynamics? 12.1 The Special Theory of Relativity Does the principle of relativity apply to the laws
9 Wave solution of Maxwells equations.
 9 Wave solution of Maxwells equations. Contents 9.1 Wave solution: Plane waves 9.2 Scalar Spherical waves 9.3 Cylindrical waves 9.4 Momentum and energy of the electromagnetic field Keywords: Plane, cylindrical
9 Wave solution of Maxwells equations. Contents 9.1 Wave solution: Plane waves 9.2 Scalar Spherical waves 9.3 Cylindrical waves 9.4 Momentum and energy of the electromagnetic field Keywords: Plane, cylindrical
Synchrotron Radiation Reflection from Outer Wall of Vacuum Chamber
 , YerPhI Synchrotron Radiation Reflection from Outer Wall of Vacuum Chamber M.A. Aginian, S.G. Arutunian, E.G.Lazareva, A.V. Margaryan Yerevan Physics Institute The presentation is devoted to the eightieth
, YerPhI Synchrotron Radiation Reflection from Outer Wall of Vacuum Chamber M.A. Aginian, S.G. Arutunian, E.G.Lazareva, A.V. Margaryan Yerevan Physics Institute The presentation is devoted to the eightieth
Introduction to electron and photon beam physics. Zhirong Huang SLAC and Stanford University
 Introduction to electron and photon beam physics Zhirong Huang SLAC and Stanford University August 03, 2015 Lecture Plan Electron beams (1.5 hrs) Photon or radiation beams (1 hr) References: 1. J. D. Jackson,
Introduction to electron and photon beam physics Zhirong Huang SLAC and Stanford University August 03, 2015 Lecture Plan Electron beams (1.5 hrs) Photon or radiation beams (1 hr) References: 1. J. D. Jackson,
Chapter 2: The Special Theory of Relativity. A reference fram is inertial if Newton s laws are valid in that frame.
 Chapter 2: The Special Theory of Relativity What is a reference frame? A reference fram is inertial if Newton s laws are valid in that frame. If Newton s laws are valid in one reference frame, they are
Chapter 2: The Special Theory of Relativity What is a reference frame? A reference fram is inertial if Newton s laws are valid in that frame. If Newton s laws are valid in one reference frame, they are
Electromagnetic Wave Propagation Lecture 3: Plane waves in isotropic and bianisotropic media
 Electromagnetic Wave Propagation Lecture 3: Plane waves in isotropic and bianisotropic media Daniel Sjöberg Department of Electrical and Information Technology September 2016 Outline 1 Plane waves in lossless
Electromagnetic Wave Propagation Lecture 3: Plane waves in isotropic and bianisotropic media Daniel Sjöberg Department of Electrical and Information Technology September 2016 Outline 1 Plane waves in lossless
Lecture 3. Experimental Methods & Feynman Diagrams
 Lecture 3 Experimental Methods & Feynman Diagrams Natural Units & the Planck Scale Review of Relativistic Kinematics Cross-Sections, Matrix Elements & Phase Space Decay Rates, Lifetimes & Branching Fractions
Lecture 3 Experimental Methods & Feynman Diagrams Natural Units & the Planck Scale Review of Relativistic Kinematics Cross-Sections, Matrix Elements & Phase Space Decay Rates, Lifetimes & Branching Fractions
Physics 4183 Electricity and Magnetism II. Covariant Formulation of Electrodynamics-1
 Physics 4183 Electricity and Magnetism II Covariant Formulation of Electrodynamics 1 Introduction Having briefly discussed the origins of relativity, the Lorentz transformations, 4-vectors and tensors,
Physics 4183 Electricity and Magnetism II Covariant Formulation of Electrodynamics 1 Introduction Having briefly discussed the origins of relativity, the Lorentz transformations, 4-vectors and tensors,
Maxwell s equations. based on S-54. electric field charge density. current density
 Maxwell s equations based on S-54 Our next task is to find a quantum field theory description of spin-1 particles, e.g. photons. Classical electrodynamics is governed by Maxwell s equations: electric field
Maxwell s equations based on S-54 Our next task is to find a quantum field theory description of spin-1 particles, e.g. photons. Classical electrodynamics is governed by Maxwell s equations: electric field
(Dated: September 3, 2015)
 DOPPLER TRANSFORMATION AS EIGENVALUES OF LORENTZ TRANSFORMATION Louai Hassan Elzein Basheir 1 Physics College, Khartoum University, Sudan. P.O. Box: 7725 - Zip Code: 11123 (Dated: September 3, 215) This
DOPPLER TRANSFORMATION AS EIGENVALUES OF LORENTZ TRANSFORMATION Louai Hassan Elzein Basheir 1 Physics College, Khartoum University, Sudan. P.O. Box: 7725 - Zip Code: 11123 (Dated: September 3, 215) This
Relativity. An explanation of Brownian motion in terms of atoms. An explanation of the photoelectric effect ==> Quantum Theory
 Relativity Relativity In 1905 Albert Einstein published five articles in Annalen Der Physik that had a major effect upon our understanding of physics. They included:- An explanation of Brownian motion
Relativity Relativity In 1905 Albert Einstein published five articles in Annalen Der Physik that had a major effect upon our understanding of physics. They included:- An explanation of Brownian motion
Classical Mechanics/Electricity and Magnetism. Preliminary Exam. August 20, :00-15:00 in P-121
 Classical Mechanics/Electricity and Magnetism Preliminary Exam August 20, 2008 09:00-15:00 in P-121 Answer THREE (3) questions from each of the TWO (2) sections A and B for a total of SIX (6) solutions.
Classical Mechanics/Electricity and Magnetism Preliminary Exam August 20, 2008 09:00-15:00 in P-121 Answer THREE (3) questions from each of the TWO (2) sections A and B for a total of SIX (6) solutions.
B(r) = µ 0a 2 J r 2ρ 2
 28 S8 Covariant Electromagnetism: Problems Questions marked with an asterisk are more difficult.. Eliminate B instead of H from the standard Maxwell equations. Show that the effective source terms are
28 S8 Covariant Electromagnetism: Problems Questions marked with an asterisk are more difficult.. Eliminate B instead of H from the standard Maxwell equations. Show that the effective source terms are
Electromagnetic (EM) Waves
 Electromagnetic (EM) Waves Short review on calculus vector Outline A. Various formulations of the Maxwell equation: 1. In a vacuum 2. In a vacuum without source charge 3. In a medium 4. In a dielectric
Electromagnetic (EM) Waves Short review on calculus vector Outline A. Various formulations of the Maxwell equation: 1. In a vacuum 2. In a vacuum without source charge 3. In a medium 4. In a dielectric
Typical anisotropies introduced by geometry (not everything is spherically symmetric) temperature gradients magnetic fields electrical fields
 Lecture 6: Polarimetry 1 Outline 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Fundamentals of Polarized Light 3 Descriptions of Polarized Light Polarized Light in the Universe Polarization indicates anisotropy
Lecture 6: Polarimetry 1 Outline 1 Polarized Light in the Universe 2 Fundamentals of Polarized Light 3 Descriptions of Polarized Light Polarized Light in the Universe Polarization indicates anisotropy
Electromagnetic Wave Propagation Lecture 1: Maxwell s equations
 Electromagnetic Wave Propagation Lecture 1: Maxwell s equations Daniel Sjöberg Department of Electrical and Information Technology September 3, 2013 Outline 1 Maxwell s equations 2 Vector analysis 3 Boundary
Electromagnetic Wave Propagation Lecture 1: Maxwell s equations Daniel Sjöberg Department of Electrical and Information Technology September 3, 2013 Outline 1 Maxwell s equations 2 Vector analysis 3 Boundary
Self field of a relativistic beam (Lecture 15)
 Self field of a relativistic beam (Lecture 15) February 1, 2016 259/441 Lecture outline We will study the electromagnetic field of a bunch of charged particles moving with relativistic velocity along a
Self field of a relativistic beam (Lecture 15) February 1, 2016 259/441 Lecture outline We will study the electromagnetic field of a bunch of charged particles moving with relativistic velocity along a
1 Fundamentals of laser energy absorption
 1 Fundamentals of laser energy absorption 1.1 Classical electromagnetic-theory concepts 1.1.1 Electric and magnetic properties of materials Electric and magnetic fields can exert forces directly on atoms
1 Fundamentals of laser energy absorption 1.1 Classical electromagnetic-theory concepts 1.1.1 Electric and magnetic properties of materials Electric and magnetic fields can exert forces directly on atoms
Classical Field Theory
 April 13, 2010 Field Theory : Introduction A classical field theory is a physical theory that describes the study of how one or more physical fields interact with matter. The word classical is used in
April 13, 2010 Field Theory : Introduction A classical field theory is a physical theory that describes the study of how one or more physical fields interact with matter. The word classical is used in
Electromagnetic energy and momentum
 Electromagnetic energy and momentum Conservation of energy: the Poynting vector In previous chapters of Jackson we have seen that the energy density of the electric eq. 4.89 in Jackson and magnetic eq.
Electromagnetic energy and momentum Conservation of energy: the Poynting vector In previous chapters of Jackson we have seen that the energy density of the electric eq. 4.89 in Jackson and magnetic eq.
Energy during a burst of deceleration
 Problem 1. Energy during a burst of deceleration A particle of charge e moves at constant velocity, βc, for t < 0. During the short time interval, 0 < t < t its velocity remains in the same direction but
Problem 1. Energy during a burst of deceleration A particle of charge e moves at constant velocity, βc, for t < 0. During the short time interval, 0 < t < t its velocity remains in the same direction but
Problem Set # 2 SOLUTIONS
 Wissink P640 Subatomic Physics I Fall 007 Problem Set # SOLUTIONS 1. Easy as π! (a) Consider the decay of a charged pion, the π +, that is at rest in the laboratory frame. Most charged pions decay according
Wissink P640 Subatomic Physics I Fall 007 Problem Set # SOLUTIONS 1. Easy as π! (a) Consider the decay of a charged pion, the π +, that is at rest in the laboratory frame. Most charged pions decay according
Covarient Formulation Lecture 8
 Covarient Formulation Lecture 8 1 Covarient Notation We use a 4-D space represented by the Cartesian coordinates, x 0 (orx 4 ), x 1, x 2, x 3. The components describe a vector (tensor of rank 1) in this
Covarient Formulation Lecture 8 1 Covarient Notation We use a 4-D space represented by the Cartesian coordinates, x 0 (orx 4 ), x 1, x 2, x 3. The components describe a vector (tensor of rank 1) in this
Classical Scattering
 Classical Scattering Daniele Colosi Mathematical Physics Seminar Daniele Colosi (IMATE) Classical Scattering 27.03.09 1 / 38 Contents 1 Generalities 2 Classical particle scattering Scattering cross sections
Classical Scattering Daniele Colosi Mathematical Physics Seminar Daniele Colosi (IMATE) Classical Scattering 27.03.09 1 / 38 Contents 1 Generalities 2 Classical particle scattering Scattering cross sections
Physics 218 Practice Final Exam
 Physics 218 Practice Final Exam Spring 2004 If this were a real exam, you would be reminded here of the exam rules: You may consult only two pages of formulas and constants and a calculator while taking
Physics 218 Practice Final Exam Spring 2004 If this were a real exam, you would be reminded here of the exam rules: You may consult only two pages of formulas and constants and a calculator while taking
The Lorentz Transformation
 The Lorentz Transformation This is a derivation of the Lorentz transformation of Special Relativity. The basic idea is to derive a relationship between the spacetime coordinates, y, z, t as seen by observer
The Lorentz Transformation This is a derivation of the Lorentz transformation of Special Relativity. The basic idea is to derive a relationship between the spacetime coordinates, y, z, t as seen by observer
Electromagnetic Induction Faraday s Law Lenz s Law Self-Inductance RL Circuits Energy in a Magnetic Field Mutual Inductance
 Lesson 7 Electromagnetic Induction Faraday s Law Lenz s Law Self-Inductance RL Circuits Energy in a Magnetic Field Mutual Inductance Oscillations in an LC Circuit The RLC Circuit Alternating Current Electromagnetic
Lesson 7 Electromagnetic Induction Faraday s Law Lenz s Law Self-Inductance RL Circuits Energy in a Magnetic Field Mutual Inductance Oscillations in an LC Circuit The RLC Circuit Alternating Current Electromagnetic
CHARGED PARTICLE MOTION IN CONSTANT AND UNIFORM ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS
 CHARGED PARTICLE MOTION IN CONSTANT AND UNIFORM ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS In this and in the following two chapters we investigate the motion of charged particles in the presence of electric and magnetic
CHARGED PARTICLE MOTION IN CONSTANT AND UNIFORM ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS In this and in the following two chapters we investigate the motion of charged particles in the presence of electric and magnetic
by M.W. Evans, British Civil List (
 Derivation of relativity and the Sagnac Effect from the rotation of the Minkowski and other metrics of the ECE Orbital Theorem: the effect of rotation on spectra. by M.W. Evans, British Civil List (www.aias.us)
Derivation of relativity and the Sagnac Effect from the rotation of the Minkowski and other metrics of the ECE Orbital Theorem: the effect of rotation on spectra. by M.W. Evans, British Civil List (www.aias.us)
