Modeling Dynamic Production Systems with Network Structure
|
|
|
- Myrtle Cory Walters
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Iranian Journal of Mathematical Sciences and Informatics Vol. 12, No. 1 (2017), pp DOI: /ijmsi Modeling Dynamic Production Systems with Network Structure F. Koushki Department of Electrical, Biomedical and Mechatronics Engineering, Qazvin Branch, Islamic Azad University, Qazvin, Iran. fkoushki@gmail.com Abstract. This paper deals with the problem of optimizing two-stage structure decision making units (DMUs) where the activity and the performance of two-stage DMU in one period effect on its efficiency in the next period. To evaluate such systems the effect of activities in one period on ones in the next term must be considered. To do so, here a dynamic DEA approach presented to measure the performance of such network units. According to the results of proposed dynamic model the inefficiencies of DMUs improve considerably. Additionally, in models which measure efficiency score, undesirable outputs are mostly treated as inputs, which do not reflect the true production process. This paper proposes an alternative method in dealing with bad outputs. Statistical analysis of sub-efficiencies, i.e. efficiency score of each stage, during all periods represents useful information about the total performance of the stage over all periods. Keywords: Data envelopment analysis (DEA), Network DEA, Bad outputs, Dynamic DEA, Sub-efficiency Mathematics subject classification: 90C05, 90B10, 90C Introduction Data envelopment analysis (DEA) is a nonparametric technique based on mathematical programming to evaluate performance of homogenous multi input/output decision making units. In decision-making units, which use multiple Received 24 August 2013; Accepted 28 September 2015 c 2017 Academic Center for Education, Culture and Research TMU 13
2 14 F. Koushki inputs to produce multiple outputs, managers make decisions about how to use, integrate and process the inputs and resources. In traditional DEA models, the efficiency of DMUs measured by assuming that the inputs are used to produce only final outputs. In contrast, some production systems have a network structure, such as when production by one division or sub-process results in an intermediate output that is an input to another sub-process. In these cases, managers are likely to glean more information from sub-process or divisional efficiency measures than from firm level efficiency measures. Botti et al. [3] use DEA to estimate the efficiency of French hotel chains. They found that the plural form of organization consisting of a mixture of company-owned subsidiaries and franchised units was more efficient than hotel chains dominated by franchises and hotel chains dominated by company owned subsidiaries. There are many decision making units with network structure in which the outputs of one division or sub-process are the inputs to another sub-process. Färe and Primont [8], first time, applied a DEA approach to evaluate performance of multi-plant firms as multi-stage structure DMUs. Färe and Grosskopf [6, 7] suggested models to measure efficiency score of multi-stage DMUs in static and dynamic cases. In dynamic case, activities of DMU in one period effect on ones in the next period. There have been many studies dealing with systems with two-stage structure. Wang et al. [16] proposed a DEA model to measure efficiency score of twostage structure DMUs without consideration of intermediate products. Seiford and Zhu [15] extended their approach and applied modified model to assess the efficiency of the top 55 US commercial banks. Chen and Zhu [4] improved models presented by Seiford and Zhu with consideration the intermediate products to project two-stage structure DMUs on efficient frontier. Kao and Hwang [11] evaluated efficiency score of two-stage DMU as product of efficiencies of its stages. Chen et al. [5] measured the efficiency score of two-stage structure DMU as a weighted mean of efficiency scores of stages. Aslani et al. [2] proposed radial basis function neural networks with the K-means clustering method for evaluation of bank branches. Yang et al. [18] presented a non-linear programming to measure efficiency of two-member supply chains, as two-stage DMUs. Paradi et al. [13] developed a two-stage DEA approach for simultaneously benchmarking the performance of operating units and a modified slacks-based measure model to aggregate the obtained efficiency scores from stage one and generate a composite performance index for each unit. Fukuyama and Mirdehghan [9] proposed slack-based network approach for identifying the efficiency status of each DMU and its divisions. Amirteimoori [1] and Liu [12] proposed DEA approaches for performance assessment of two-stage decision process in existence of imperfect outputs and Fuzzy data respectively. Wang et al. [17]
3 Modeling Dynamic Production Systems with Network Structure 15 utilized the network DEA approach to evaluate the efficiencies of major Chinese commercial banks. Banks have two-stage structure in which labor, physical capital, and financial equity capital are inputs of the first stage to raise deposits, which are as intermediate output. In the second stage, deposits are used to produce loans and security investments as the outputs of this stage. Bad loans produced in one period might limit the way labor, physical capital, and equity capital are able to produce deposits in the next period. It means that performance of DMU in one period effect on its performance in the next period. Therefore, a dynamic model is required to evaluate such systems. In this paper, a dynamic DEA approach is presented to measure the performance of such network units. In models which evaluate DMUs, the bad outputs mostly are treated as inputs so that the true production process is not reflected. Here an alternative method is considered in dealing with bad outputs. In section 2, some preliminaries of two-stage structure DMUs are given; additionally, non-redial dynamic model to measure inefficiency, for several periods, of whole DMU process at each period and during all periods is proposed. In proposed dynamic model, bad outputs are treated properly. In section 3, the superiority of the dynamic model over the traditional separation model,which measures inefficiency of DMU in each period separately without considering the relation between the periods, is demonstrated during an illustrative example. Statistical analysis of efficiency scores of each stage, named sub-efficiencies, during all periods is presented in section Dynamic Model Let x j, y j, b j and be the N-dimensional input, M-dimensional final output, L-dimensional bad output vectors and vector of variables associated with intermediate output, respectively, of DMU j, j = 1,..., J. Deposits are considered as an intermediate output from stage 1 and an input to stage 2.The network slacks-based inefficiency [10] is defined as follows { 1 N s n n=1 N NSBI(x 0, y 0, b 0 ) = max s,s +,s #,λ 1,λ 2 x 0 = x j λ 1 j + s, y 0 = x n + 1 M M m=1 3 y j λ 2 j s +, b 0 = s + m + 1 L s # l l=1 y m L b l b j λ 2 j + s #
4 16 F. Koushki z j λ 1 j z 0, z j λ 2 j z 0 λ 1 j = 1, λ 2 j = 1 } λ 1 j 0, λ 2 j 0, s 0, s + 0, s # 0 (2.1) λ 1, λ 2 are vectors of intensity variables for the two stages. The production of bad loans in one period might limit the way labor, physical capital, and equity capital are able to produce deposits in the next period. In addition, the profit earned by bank activities in one period, makes the financial capital increase in the next period. This paper improves static model (2.1) and uses a dynamic model to measure the inefficiency of DMU 0 at each term and the overall inefficiency, in which the effects of activities at each term on the next term are considered. At each term t, the whole profit earned by bank activities will increase the financial capital at the next term. Let p t be the value of whole profit at term t. Suppose x t 01 indicates the financial capital in the input vector of DMU 0 at term t.hence, at term t, t = 2,..., T, this value will be x t 01 + p t 1.The whole profit earned in each term, is a proportion of the financial capital in that term. Thus, we have p t = αx t 01 0 < α < 1. The bad outputs at each term t, are nonperforming loans with borrowers unable to make full or even partial repayment. Therefore, bad outputs at term t, b t 0, make financial capital reduce as much as L l=1 bt 01 at the next term. At term t, t = 2,..., T, this value will be x t 01 L l=1 bt Previous models do not reflect the true production process, as they consider bad outputs as inputs. Here, another method is considered to treat bad outputs as follow calculations: Let b sr = max j {b jr } r = 1,..., L; Then, find u r r = 1,..., L such that b sr = b sr + u r r = 1,..., L Then let b jr = b jr + u r j = 1,..., J... r = 1,..., L. According to the above method, the values of b are desirable outputs and the increment of them is favorite and results in decrease of the values of b as bad outputs. In addition, deposits as the outputs of the first stage are the inputs to the second stage. This continuity and series relationship between two stages implies that J λ1 j Z j = J λ2 j Z j instead of inequalities J z jλ 1 j z 0, J z jλ 2 j z 0 in model (2.1).
5 Modeling Dynamic Production Systems with Network Structure 17 Therefore, the network slacks-based overall inefficiency is defined as follows: 1 N s t n max 1 T w t N x t + 1 M s +t m n=1 0n M y t + 1 L s #t l m=1 0m L bt l=1 0l T 3 t=1 s.t. x 1 jλ 11 j + s 1 = x 1 0 x t j 1λ1t j x t jnλ 1t j + s t 1 = x t 01 + p t 1 L l=1 b t 1 0l t = 2,..., T + s t n = x t 0n n = 2,..., N t = 2,..., T y t jλ 2t j + s +t = y t 0 t = 1,..., T b t jλ 2t j + s #t = b t 0 t = 1,..., T z t jλ 1t j = z t λ 2t j λ 1t j = 1 t = 1,..., T λ 2t j = 1 t = 1,..., T t = 1,..., T λ 1t 0, λ 2t 0 t = 1,..., T S t 0, S +t 0, S #t 0 t = 1,..., T (2.2) w t is the weight of term t,which is determined by manager with attention to the importance of term t, satisfying T t=1 wt = T In this model we assume that data is independent of passing the time. Otherwise a( rate of interest per term should ) be considered in modeling. Let {λ t }, {s t }, {s +t }, {s #t } be an optimal solution. We define the inefficiency score for DMU 0 at term by β t 0 = 1 N N n=1 s t n x t 0n + 1 M M m=1 3 s +t m y t 0m + 1 L L l=1 s #t l bt 01
6 18 F. Koushki The overall inefficiency is the weighted average of the term efficiencies as described below: β 0 = 1 T T t=1 w t β t 0 If all optimal solutions satisfy β t 0 = 0, then DMU 0 is efficient for the term t. This implies that the optimal slacks for the term are all zero. If β 0 = 0, then DMU 0 is overall efficient and all optimal slacks are zero. Thus we have: Theorem 2.1. DMU 0 is overall efficient, if and only if it is efficient for all terms. The term inefficiencies and the overall inefficiency satisfy the following optimality property. Theorem 2.2. If for two DMUs a and b, their terms of inefficiencies satisfy the inequality βa t βb t ( t), then it holds that β a βb. Addition to assumptions, if there exists a term t such that βa t > βb t, then we have the strict inequality βa > βb. Proof. From the definition of overall inefficiency, this theorem holds. We define the projected of DMU 0 as follows: x 1 0 = x 1 0 s 1 x t 01 = x t 01 + p t 1 L l 1 b t 1 01 s t 1 t = 2,..., T x t 0n = x t 0n s t n n = 2,..., N t = 2,..., T ȳ t 0 = y t 0 + s +t b t 0 = b t 0 + s #t t = 1,..., T t = 1,..., T Theorem 2.3. The projected DMU 0 is overall efficient. Proof. We evaluate the overall efficiency of the projected DMU.
7 Let have: Modeling Dynamic Production Systems with Network Structure 19 ( } } } }) { λt, { s t, { s +t, { s #t x 1 0 = x 1 0 λ 11 j x t 01 + p t 1 x t 0n = ȳ t 0 = b t 0 = L l=1 + s 1 b t 1 01 = x t jl λ 1t j be an optimal solution. + s t 1 t = 2,..., T x t jn λ 1t j + s t n = 2,..., N t = 2,..., T yj t 2t λ j s +t b t 2t j λ j s #t t = 1,..., T t = 1,..., T Then we Replacing x 1 0, x t 01 + p t 1 L l=1 bt 1 01, xt 0n, ȳ t 0 and bt 0, we have: x 1 0 = x t 01 + p t 1 x t 0n = y t 0 = b t 0 = 1 x 1 λ1 j + s 1 + s 1 L l=1 b t 1 01 = x t jl λ 1t j + s t 1 + s t 1 t = 2,..., T x t λ 1 t jn j + s t n + s t n n = 2,..., N t = 2,..., T yj t 2t λ j s +t s + t b t 2t j λ j s #t s # t t = 1,..., T t = 1,..., T Considering this expression we have the overall inefficiency, β 0 = 1 T T w t 1 [ 1 3 N t=1 N n=1 + 1 M s t n M m=1 + s t n x t 0n s +t m + s +t m y t 0m + 1 L L l=1 s #t l + s #t ] l. bt 01 If any member of ({ s t }, { s +t }, { s #t } is positive, then it holds that β0 > β0. This contradicts the optimality of β0. Thus, we have s t = 0, s +t = 0 and s #t = 0, t.
8 20 F. Koushki Hence the projected DMU is overall efficient. 3. An Illustrative Example The data, which is drawn from 20 branches of some bank, is shown in tables 1 and 2. Inputs to the first stage are financial capital (x 1 ), personnel cost (x 2 ), official cost (x 3 ), and rent cost (x 4 ). The intermediate output of the first stage is raised funds (z). In the second stage, the desirable output is all assets associated with business activities (y) and the undesirable output is sum of all loans to bankrupt borrowers and the balance of non-accrual delinquent loans (b). All data is in billion. x 1 j1 x 1 j2 x 1 j3 x 1 j4 yj 1 p j b 1 j z 1 j Table 1. Data The values of b associated with bad outputs calculated in table 3. We assign weights of one for each term and use the dynamic model for 2 terms. α is considered in interval [0.02,0.14]. Here GAMS is used to estimate each inefficiency measure. To clarify features of dynamic model, the results are compared with those of separate model, in table 5, which measures inefficiency score separately for
9 Modeling Dynamic Production Systems with Network Structure 21 x 2 j1 x 2 j2 x 2 j3 x 2 j4 yj 2 b 2 j z 2 j Table 2. Data each term. Over all inefficiency of separate model is calculated as an average of term efficiencies during the two terms. Bank activities in each term affect the inputs of the next term; thus they affect the performance of the next term. In dynamic model, the effects of each term activities are considered. The results of dynamic model in table 4 show that by considering the effects of each term activities on the next term, the inefficiencies of DMUs improve considerably. 4. Sub-efficiencies Statistical Analysis Financial capital, personnel cost, official cost, and rent cost are inputs to stage 1. Deposits are produced as an output from stage 1 and an input to stage 2. The desirable output is all assets associated with business activities and the undesirable output is sum of all loans to bankrupt borrowers and the balance of non-accrual delinquent loans. Thus we can associate an efficiency score with each stage, considering their input and output respectively, named sub-efficiency and is given by following SBM models for stage 1 and stage 2, respectively:
10 22 F. Koushki b1 j b2 j Table 3. Translated outputs 1 1 N θ1 n=1 N = min s.t. θ 2 = min s.t Q Q q=1 S # n x n0 S # q z q0 λ 1 jx j + S # = X 0 λ 1 jz j + S #+ = Z 0 S #, S #+, λ 1 0 (4.1) M M m=1 1 1 Q Q q=1 λ 2 jz j + S = Z 0 λ 2 jy j S + = Y 0 λ 2 j b j S + = b 0 S q Z q0 S + m y m0 + 1 L L l=1 S + l bl0 S, S +, S +, λ 2 0 (4.2)
11 Modeling Dynamic Production Systems with Network Structure 23 Overall inefficiency Term inefficiency t 1 t Table 4. Results of dynamic model Let θk t1 be the sub-efficiency score of stage 1 of DMU k in term t and θ k 1 be the mean value of such scores all over the T terms. Thus the DMU with larger mean value has more performance in stage 1 all over T terms. Let k 1 be the standard deviation value of sub-efficiencies of stage 1of DMU k all over T terms. Large k 1 is not desirable since it denotes that the sub-efficiencies are unstable during T terms so that larger standard deviation represents more dispersion in sub-efficiencies of DMU k during T terms. The coefficient variation value associated with sub-efficiencies of stage 1 of DMU k all over T terms obtained by cvk 1 = 1 k θ k 1. According to above argument, the value of 1 cv 1 k = θ 1 k 1 k can be interpreted as an efficiency indicator of stage 1 of DMU k all over T terms. The same argument can be considered for stage 2 sub-efficiencies during T terms.
12 24 F. Koushki Overall inefficiency Term inefficiency t 1 t Table 5. Results of separate model The mean, standard deviation, and coefficient variation values of sub-efficiencies of each of 2 stages of 10 branches of some bank all over 9 terms calculated in table 6. Branches 1 and 2 are sub-efficient in each stage in every term. θ k 1 k 1 cvk 1 θ k 2 k 2 cvk Table 6. Sub-efficiencies statistical indicators Branches 3 and 8 are sub-efficient in stage 1 in every term; Branch 3 has the least and branch 8 has the most sub-efficiency instability in stage 2 between branches 3 to 10 all over 9 terms.
13 Modeling Dynamic Production Systems with Network Structure 25 Branch 9 has the least and branch 7 has the most sub-efficiency instability in stage 1 between branches 4,5,7,9. In addition branch 9 has the least value of coefficient variation in stage 1 between branches 4,5,7,9 all over 9 terms that implies this branch has the best total performance in stage 1 between these branches. Similarly, branch 3has the best total performance in stage 2 between branches 3 to 10 all over 9 terms. 5. Conclusion This paper has considered the production systems in which inputs in the first stage produce intermediate outputs transformed in the second stage of production to final outputs. Bank production process has such network structure in which bad loans are considered as an undesirable output of the second stage. These bad loans are as a constraining factor to the first stage in the subsequent period. This paper has modeled such network production systems by using a dynamic model to measure the inefficiency at each term and the overall inefficiency while the effects of outputs in one term on the inputs of the next term are considered. In models that measure efficiency, the bad outputs are mostly treated as inputs so that the true production process is not reflected. Here an alternative method is considered in dealing with bad outputs. The superiority of the dynamic model over the traditional separation model has been demonstrated during an illustrative example. The statistical analysis of efficiency scores for every DMU stage, which named sub-efficiencies, represents useful information about the total performance of the stage over all periods. Standard deviation value of such sub-efficiencies implies the instability amount of efficiencies of each stage over all periods. The converse of coefficient variation value of such subefficiencies over all periods shows the total performance of each stage over all terms. Acknowledgments I would like to thank the referee for his/her helpful remarks which have contributed to improve the presentation of the paper. References 1. A. Amirteimoori, ADEA two-stage decision processes with shared resources, Central European Journal of Operations Research,21, (2013), G. Aslani, S.H. Momeni-Masuleh, A. Malek, F. Ghorbani, Bank efficiency evaluation using a neural network-dea method, Iranian Journal of Mathematical Sciences and Information, 4(2), (2009), L. Botti, W. Briec, G. Cliquet, Plural forms versus franchise and company-owned systems: a DEA approach of hotel chain performance, Omega, The International Journal of Management Science, 37, (2009),
14 26 F. Koushki 4. Y. Chen, J. Zhu, Measuring information technologys indirect impact on firm performance, Information Technology and Management, 5(12), (2004), Y. Chen, W.D. Cook, N. Li, J.Zhu, Additive efficiency decomposition in two-stage DEA, European Journal of Operational Research, 196, (2009), R. Färe, S. Grosskopf, Productivity and intermediate products: a Frontier approach, Economics Letters, 50(1), (1996), R. Färe, S. Grosskopf, w. Gerald, Network Dea, Modeling data irregularities and structural complexities in data envelopment analysis, Springer US, (2007), R. Färe, D. Primont, Efficiency measures for multi plant firms, Operations Research Letters, 3, (1984), H. Fukuyama, S.M. Mirdehghan, Identifying the efficiency status in network DEA, European Journal of Operational Research, 220(1), (2012), H. Fukuyama, L. Wiliam, A.Weber, Slacks-based inefficiency measure for a two-stage system with bad outputs, Omega, 38, (2010), C. Kao, S.N. Hwang, Efficiency decomposition in two-stage data envelopment analysis: An application to non-life insurance companies in Taiwan, European Journal of Operational Research, 185(1), (2008), S.T. Liu, Fuzzy efficiency ranking in fuzzy two-stage data envelopment analysis, Optimization Letters, (2013). 13. J.C. Paradi, S. Rouatt, H. Zhu, Two-stage evaluation of bank branch efficiency using data envelopment analysis, Omega, 39(1), (2011), M. Saraj, N. Safaei, Integrating goal programming, Taylor Series, Kuhn-Tucker conditions, and penalty function approaches to solve linear fractional bi-level programming problems, Iranian Journal of Mathematical Sciences and Information, 10(1), (2015). 15. L.M. Seiford, J.Zhu, Profitability and marketability of the top 55 US commercial banks, MANAGE SCI, 45(9), (1999), C.H. Wang, R. Gopal, S. Zionts, Use of data envelopment analysis in assessing information technology impact on firm performance, Annals of Operations Research, 73, (1997), K. Wang, W. Huang, J. Wu, Y.N. Liu, Efficiency measures of the Chinese commercial banking system using an additive two-stage DEA, Omega, (2014), F. Yang, D.Wu, L. Liang, G.Bi, D.D. Wu, Supply chain DEA: production possibility set and performance evaluation model, Annals of Operations Research, 185, (2011),
Research Article A Data Envelopment Analysis Approach to Supply Chain Efficiency
 Advances in Decision Sciences Volume 2011, Article ID 608324, 8 pages doi:10.1155/2011/608324 Research Article A Data Envelopment Analysis Approach to Supply Chain Efficiency Alireza Amirteimoori and Leila
Advances in Decision Sciences Volume 2011, Article ID 608324, 8 pages doi:10.1155/2011/608324 Research Article A Data Envelopment Analysis Approach to Supply Chain Efficiency Alireza Amirteimoori and Leila
European Journal of Operational Research
 European Journal of Operational Research 207 (200) 22 29 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect European Journal of Operational Research journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ejor Interfaces with
European Journal of Operational Research 207 (200) 22 29 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect European Journal of Operational Research journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ejor Interfaces with
Groups performance ranking based on inefficiency sharing
 Available online at http://ijim.srbiau.ac.ir/ Int. J. Industrial Mathematics (ISSN 2008-5621) Vol. 5, No. 4, 2013 Article ID IJIM-00350, 9 pages Research Article Groups performance ranking based on inefficiency
Available online at http://ijim.srbiau.ac.ir/ Int. J. Industrial Mathematics (ISSN 2008-5621) Vol. 5, No. 4, 2013 Article ID IJIM-00350, 9 pages Research Article Groups performance ranking based on inefficiency
Measuring the efficiency of assembled printed circuit boards with undesirable outputs using Two-stage Data Envelopment Analysis
 Measuring the efficiency of assembled printed circuit boards with undesirable outputs using Two-stage ata Envelopment Analysis Vincent Charles CENTRUM Católica, Graduate School of Business, Pontificia
Measuring the efficiency of assembled printed circuit boards with undesirable outputs using Two-stage ata Envelopment Analysis Vincent Charles CENTRUM Católica, Graduate School of Business, Pontificia
PRIORITIZATION METHOD FOR FRONTIER DMUs: A DISTANCE-BASED APPROACH
 PRIORITIZATION METHOD FOR FRONTIER DMUs: A DISTANCE-BASED APPROACH ALIREZA AMIRTEIMOORI, GHOLAMREZA JAHANSHAHLOO, AND SOHRAB KORDROSTAMI Received 7 October 2003 and in revised form 27 May 2004 In nonparametric
PRIORITIZATION METHOD FOR FRONTIER DMUs: A DISTANCE-BASED APPROACH ALIREZA AMIRTEIMOORI, GHOLAMREZA JAHANSHAHLOO, AND SOHRAB KORDROSTAMI Received 7 October 2003 and in revised form 27 May 2004 In nonparametric
A New Method for Optimization of Inefficient Cost Units In The Presence of Undesirable Outputs
 Available online at http://ijim.srbiau.ac.ir/ Int. J. Industrial Mathematics (ISSN 2008-5621) Vol. 10, No. 4, 2018 Article ID IJIM-01173, 8 pages Research Article A New Method for Optimization of Inefficient
Available online at http://ijim.srbiau.ac.ir/ Int. J. Industrial Mathematics (ISSN 2008-5621) Vol. 10, No. 4, 2018 Article ID IJIM-01173, 8 pages Research Article A New Method for Optimization of Inefficient
Chapter 2 Network DEA Pitfalls: Divisional Efficiency and Frontier Projection
 Chapter 2 Network DEA Pitfalls: Divisional Efficiency and Frontier Projection Yao Chen, Wade D. Cook, Chiang Kao, and Joe Zhu Abstract Recently network DEA models have been developed to examine the efficiency
Chapter 2 Network DEA Pitfalls: Divisional Efficiency and Frontier Projection Yao Chen, Wade D. Cook, Chiang Kao, and Joe Zhu Abstract Recently network DEA models have been developed to examine the efficiency
Symmetric Error Structure in Stochastic DEA
 Available online at http://ijim.srbiau.ac.ir Int. J. Industrial Mathematics (ISSN 2008-5621) Vol. 4, No. 4, Year 2012 Article ID IJIM-00191, 9 pages Research Article Symmetric Error Structure in Stochastic
Available online at http://ijim.srbiau.ac.ir Int. J. Industrial Mathematics (ISSN 2008-5621) Vol. 4, No. 4, Year 2012 Article ID IJIM-00191, 9 pages Research Article Symmetric Error Structure in Stochastic
A Slacks-base Measure of Super-efficiency for Dea with Negative Data
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 4(12): 6197-6210, 2010 ISSN 1991-8178 A Slacks-base Measure of Super-efficiency for Dea with Negative Data 1 F. Hosseinzadeh Lotfi, 2 A.A. Noora, 3 G.R.
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 4(12): 6197-6210, 2010 ISSN 1991-8178 A Slacks-base Measure of Super-efficiency for Dea with Negative Data 1 F. Hosseinzadeh Lotfi, 2 A.A. Noora, 3 G.R.
Data Envelopment Analysis within Evaluation of the Efficiency of Firm Productivity
 Data Envelopment Analysis within Evaluation of the Efficiency of Firm Productivity Michal Houda Department of Applied Mathematics and Informatics Faculty of Economics, University of South Bohemia in Česé
Data Envelopment Analysis within Evaluation of the Efficiency of Firm Productivity Michal Houda Department of Applied Mathematics and Informatics Faculty of Economics, University of South Bohemia in Česé
Finding the strong defining hyperplanes of production possibility set with constant returns to scale using the linear independent vectors
 Rafati-Maleki et al., Cogent Mathematics & Statistics (28), 5: 447222 https://doi.org/.8/233835.28.447222 APPLIED & INTERDISCIPLINARY MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Finding the strong defining hyperplanes
Rafati-Maleki et al., Cogent Mathematics & Statistics (28), 5: 447222 https://doi.org/.8/233835.28.447222 APPLIED & INTERDISCIPLINARY MATHEMATICS RESEARCH ARTICLE Finding the strong defining hyperplanes
Classifying inputs and outputs in data envelopment analysis
 European Journal of Operational Research 180 (2007) 692 699 Decision Support Classifying inputs and outputs in data envelopment analysis Wade D. Cook a, *, Joe Zhu b a Department of Management Science,
European Journal of Operational Research 180 (2007) 692 699 Decision Support Classifying inputs and outputs in data envelopment analysis Wade D. Cook a, *, Joe Zhu b a Department of Management Science,
Ranking Decision Making Units with Negative and Positive Input and Output
 Int. J. Research in Industrial Engineering, pp. 69-74 Volume 3, Number 3, 2014 International Journal of Research in Industrial Engineering www.nvlscience.com Ranking Decision Making Units with Negative
Int. J. Research in Industrial Engineering, pp. 69-74 Volume 3, Number 3, 2014 International Journal of Research in Industrial Engineering www.nvlscience.com Ranking Decision Making Units with Negative
Modeling undesirable factors in efficiency evaluation
 European Journal of Operational Research142 (2002) 16 20 Continuous Optimization Modeling undesirable factors in efficiency evaluation Lawrence M. Seiford a, Joe Zhu b, * www.elsevier.com/locate/dsw a
European Journal of Operational Research142 (2002) 16 20 Continuous Optimization Modeling undesirable factors in efficiency evaluation Lawrence M. Seiford a, Joe Zhu b, * www.elsevier.com/locate/dsw a
Determination of Economic Optimal Strategy for Increment of the Electricity Supply Industry in Iran by DEA
 International Mathematical Forum, 2, 2007, no. 64, 3181-3189 Determination of Economic Optimal Strategy for Increment of the Electricity Supply Industry in Iran by DEA KH. Azizi Department of Management,
International Mathematical Forum, 2, 2007, no. 64, 3181-3189 Determination of Economic Optimal Strategy for Increment of the Electricity Supply Industry in Iran by DEA KH. Azizi Department of Management,
MULTI-COMPONENT RETURNS TO SCALE: A DEA-BASED APPROACH
 Int. J. Contemp. Math. Sci., Vol. 1, 2006, no. 12, 583-590 MULTI-COMPONENT RETURNS TO SCALE: A DEA-BASED APPROACH Alireza Amirteimoori 1 Department of Mathematics P.O. Box: 41335-3516 Islamic Azad University,
Int. J. Contemp. Math. Sci., Vol. 1, 2006, no. 12, 583-590 MULTI-COMPONENT RETURNS TO SCALE: A DEA-BASED APPROACH Alireza Amirteimoori 1 Department of Mathematics P.O. Box: 41335-3516 Islamic Azad University,
Author Copy. A modified super-efficiency DEA model for infeasibility. WD Cook 1,LLiang 2,YZha 2 and J Zhu 3
 Journal of the Operational Research Society (2009) 60, 276 --281 2009 Operational Research Society Ltd. All rights reserved. 0160-5682/09 www.palgrave-journals.com/jors/ A modified super-efficiency DEA
Journal of the Operational Research Society (2009) 60, 276 --281 2009 Operational Research Society Ltd. All rights reserved. 0160-5682/09 www.palgrave-journals.com/jors/ A modified super-efficiency DEA
Developing a Data Envelopment Analysis Methodology for Supplier Selection in the Presence of Fuzzy Undesirable Factors
 Available online at http://ijim.srbiau.ac.ir Int. J. Industrial Mathematics (ISSN 2008-5621) Vol. 4, No. 3, Year 2012 Article ID IJIM-00225, 10 pages Research Article Developing a Data Envelopment Analysis
Available online at http://ijim.srbiau.ac.ir Int. J. Industrial Mathematics (ISSN 2008-5621) Vol. 4, No. 3, Year 2012 Article ID IJIM-00225, 10 pages Research Article Developing a Data Envelopment Analysis
Selective Measures under Constant and Variable Returns-To- Scale Assumptions
 ISBN 978-93-86878-06-9 9th International Conference on Business, Management, Law and Education (BMLE-17) Kuala Lumpur (Malaysia) Dec. 14-15, 2017 Selective Measures under Constant and Variable Returns-To-
ISBN 978-93-86878-06-9 9th International Conference on Business, Management, Law and Education (BMLE-17) Kuala Lumpur (Malaysia) Dec. 14-15, 2017 Selective Measures under Constant and Variable Returns-To-
Indian Institute of Management Calcutta. Working Paper Series. WPS No. 787 September 2016
 Indian Institute of Management Calcutta Working Paper Series WPS No. 787 September 2016 Improving DEA efficiency under constant sum of inputs/outputs and Common weights Sanjeet Singh Associate Professor
Indian Institute of Management Calcutta Working Paper Series WPS No. 787 September 2016 Improving DEA efficiency under constant sum of inputs/outputs and Common weights Sanjeet Singh Associate Professor
A ratio-based method for ranking production units in profit efficiency measurement
 Math Sci (2016) 10:211 217 DOI 10.1007/s40096-016-0195-8 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A ratio-based method for ranking production units in profit efficiency measurement Roza Azizi 1 Reza Kazemi Matin 1 Gholam R.
Math Sci (2016) 10:211 217 DOI 10.1007/s40096-016-0195-8 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A ratio-based method for ranking production units in profit efficiency measurement Roza Azizi 1 Reza Kazemi Matin 1 Gholam R.
NEGATIVE DATA IN DEA: A SIMPLE PROPORTIONAL DISTANCE FUNCTION APPROACH. Kristiaan Kerstens*, Ignace Van de Woestyne**
 Document de travail du LEM 2009-06 NEGATIVE DATA IN DEA: A SIMPLE PROPORTIONAL DISTANCE FUNCTION APPROACH Kristiaan Kerstens*, Ignace Van de Woestyne** *IÉSEG School of Management, CNRS-LEM (UMR 8179)
Document de travail du LEM 2009-06 NEGATIVE DATA IN DEA: A SIMPLE PROPORTIONAL DISTANCE FUNCTION APPROACH Kristiaan Kerstens*, Ignace Van de Woestyne** *IÉSEG School of Management, CNRS-LEM (UMR 8179)
AN IMPROVED APPROACH FOR MEASUREMENT EFFICIENCY OF DEA AND ITS STABILITY USING LOCAL VARIATIONS
 Bulletin of Mathematics Vol. 05, No. 01 (2013), pp. 27 42. AN IMPROVED APPROACH FOR MEASUREMENT EFFICIENCY OF DEA AND ITS STABILITY USING LOCAL VARIATIONS Isnaini Halimah Rambe, M. Romi Syahputra, Herman
Bulletin of Mathematics Vol. 05, No. 01 (2013), pp. 27 42. AN IMPROVED APPROACH FOR MEASUREMENT EFFICIENCY OF DEA AND ITS STABILITY USING LOCAL VARIATIONS Isnaini Halimah Rambe, M. Romi Syahputra, Herman
Chance Constrained Data Envelopment Analysis The Productive Efficiency of Units with Stochastic Outputs
 Chance Constrained Data Envelopment Analysis The Productive Efficiency of Units with Stochastic Outputs Michal Houda Department of Applied Mathematics and Informatics ROBUST 2016, September 11 16, 2016
Chance Constrained Data Envelopment Analysis The Productive Efficiency of Units with Stochastic Outputs Michal Houda Department of Applied Mathematics and Informatics ROBUST 2016, September 11 16, 2016
Novel Models for Obtaining the Closest Weak and Strong Efficient Projections in Data Envelopment Analysis
 Bol. Soc. Paran. Mat. (3s.) v. 00 0 (0000):????. c SPM ISSN21751188 on line ISSN00378712 in press SPM: www.spm.uem.br/bspm doi:10.5269/bspm.41096 Novel Models for Obtaining the Closest Weak and Strong
Bol. Soc. Paran. Mat. (3s.) v. 00 0 (0000):????. c SPM ISSN21751188 on line ISSN00378712 in press SPM: www.spm.uem.br/bspm doi:10.5269/bspm.41096 Novel Models for Obtaining the Closest Weak and Strong
Data Envelopment Analysis and its aplications
 Data Envelopment Analysis and its aplications VŠB-Technical University of Ostrava Czech Republic 13. Letní škola aplikované informatiky Bedřichov Content Classic Special - for the example The aim to calculate
Data Envelopment Analysis and its aplications VŠB-Technical University of Ostrava Czech Republic 13. Letní škola aplikované informatiky Bedřichov Content Classic Special - for the example The aim to calculate
A DIMENSIONAL DECOMPOSITION APPROACH TO IDENTIFYING EFFICIENT UNITS IN LARGE-SCALE DEA MODELS
 Pekka J. Korhonen Pyry-Antti Siitari A DIMENSIONAL DECOMPOSITION APPROACH TO IDENTIFYING EFFICIENT UNITS IN LARGE-SCALE DEA MODELS HELSINKI SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS WORKING PAPERS W-421 Pekka J. Korhonen Pyry-Antti
Pekka J. Korhonen Pyry-Antti Siitari A DIMENSIONAL DECOMPOSITION APPROACH TO IDENTIFYING EFFICIENT UNITS IN LARGE-SCALE DEA MODELS HELSINKI SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS WORKING PAPERS W-421 Pekka J. Korhonen Pyry-Antti
A METHOD FOR SOLVING 0-1 MULTIPLE OBJECTIVE LINEAR PROGRAMMING PROBLEM USING DEA
 Journal of the Operations Research Society of Japan 2003, Vol. 46, No. 2, 189-202 2003 The Operations Research Society of Japan A METHOD FOR SOLVING 0-1 MULTIPLE OBJECTIVE LINEAR PROGRAMMING PROBLEM USING
Journal of the Operations Research Society of Japan 2003, Vol. 46, No. 2, 189-202 2003 The Operations Research Society of Japan A METHOD FOR SOLVING 0-1 MULTIPLE OBJECTIVE LINEAR PROGRAMMING PROBLEM USING
Further discussion on linear production functions and DEA
 European Journal of Operational Research 127 (2000) 611±618 www.elsevier.com/locate/dsw Theory and Methodology Further discussion on linear production functions and DEA Joe Zhu * Department of Management,
European Journal of Operational Research 127 (2000) 611±618 www.elsevier.com/locate/dsw Theory and Methodology Further discussion on linear production functions and DEA Joe Zhu * Department of Management,
Joint Use of Factor Analysis (FA) and Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) for Ranking of Data Envelopment Analysis
 Joint Use of Factor Analysis () and Data Envelopment Analysis () for Ranking of Data Envelopment Analysis Reza Nadimi, Fariborz Jolai Abstract This article combines two techniques: data envelopment analysis
Joint Use of Factor Analysis () and Data Envelopment Analysis () for Ranking of Data Envelopment Analysis Reza Nadimi, Fariborz Jolai Abstract This article combines two techniques: data envelopment analysis
Interest Rate Liberalization and Capital Misallocation 1
 Interest Rate Liberalization and Capital Misallocation 1 Zheng Liu 1 Pengfei Wang 2 Zhiwei Xu 3 1 Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco 2 Hong Kong University of Science and Technology 3 Shanghai Jiao
Interest Rate Liberalization and Capital Misallocation 1 Zheng Liu 1 Pengfei Wang 2 Zhiwei Xu 3 1 Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco 2 Hong Kong University of Science and Technology 3 Shanghai Jiao
A buyer - seller game model for selection and negotiation of purchasing bids on interval data
 International Mathematical Forum, 1, 2006, no. 33, 1645-1657 A buyer - seller game model for selection and negotiation of purchasing bids on interval data G. R. Jahanshahloo, F. Hosseinzadeh Lotfi 1, S.
International Mathematical Forum, 1, 2006, no. 33, 1645-1657 A buyer - seller game model for selection and negotiation of purchasing bids on interval data G. R. Jahanshahloo, F. Hosseinzadeh Lotfi 1, S.
The profit function system with output- and input- specific technical efficiency
 The profit function system with output- and input- specific technical efficiency Mike G. Tsionas December 19, 2016 Abstract In a recent paper Kumbhakar and Lai (2016) proposed an output-oriented non-radial
The profit function system with output- and input- specific technical efficiency Mike G. Tsionas December 19, 2016 Abstract In a recent paper Kumbhakar and Lai (2016) proposed an output-oriented non-radial
Economic Policy and Equality of Opportunity
 Economic Policy and Equality of Opportunity Sang Yoon (Tim) Lee 1 Ananth Seshdari 2 1 University of Mannheim 2 University of Wisconsin October 25, 2014 Normative Ethics and Welfare Economics Redistributive
Economic Policy and Equality of Opportunity Sang Yoon (Tim) Lee 1 Ananth Seshdari 2 1 University of Mannheim 2 University of Wisconsin October 25, 2014 Normative Ethics and Welfare Economics Redistributive
Department of Economics Working Paper Series
 Department of Economics Working Paper Series Comparing Input- and Output-Oriented Measures of Technical Efficiency to Determine Local Returns to Scale in DEA Models Subhash C. Ray University of Connecticut
Department of Economics Working Paper Series Comparing Input- and Output-Oriented Measures of Technical Efficiency to Determine Local Returns to Scale in DEA Models Subhash C. Ray University of Connecticut
A Data Envelopment Analysis Based Approach for Target Setting and Resource Allocation: Application in Gas Companies
 A Data Envelopment Analysis Based Approach for Target Setting and Resource Allocation: Application in Gas Companies Azam Mottaghi, Ali Ebrahimnejad, Reza Ezzati and Esmail Khorram Keywords: power. Abstract
A Data Envelopment Analysis Based Approach for Target Setting and Resource Allocation: Application in Gas Companies Azam Mottaghi, Ali Ebrahimnejad, Reza Ezzati and Esmail Khorram Keywords: power. Abstract
PRIORITIZATION METHOD FOR FRONTIER DMUs: A DISTANCE-BASED APPROACH
 PRIORITIZATION METHOD FOR FRONTIER DMUs: A DISTANCE-BASED APPROACH ALIREZA AMIRTEIMOORI, GHOLAMREZA JAHANSHAHLOO, AND SOHRAB KORDROSTAMI Received 7 October 2003 and in revised form 27 May 2004 In nonparametric
PRIORITIZATION METHOD FOR FRONTIER DMUs: A DISTANCE-BASED APPROACH ALIREZA AMIRTEIMOORI, GHOLAMREZA JAHANSHAHLOO, AND SOHRAB KORDROSTAMI Received 7 October 2003 and in revised form 27 May 2004 In nonparametric
A Fuzzy Data Envelopment Analysis Approach based on Parametric Programming
 INT J COMPUT COMMUN, ISSN 1841-9836 8(4:594-607, August, 013. A Fuzzy Data Envelopment Analysis Approach based on Parametric Programming S.H. Razavi, H. Amoozad, E.K. Zavadskas, S.S. Hashemi Seyed Hossein
INT J COMPUT COMMUN, ISSN 1841-9836 8(4:594-607, August, 013. A Fuzzy Data Envelopment Analysis Approach based on Parametric Programming S.H. Razavi, H. Amoozad, E.K. Zavadskas, S.S. Hashemi Seyed Hossein
INEFFICIENCY EVALUATION WITH AN ADDITIVE DEA MODEL UNDER IMPRECISE DATA, AN APPLICATION ON IAUK DEPARTMENTS
 Journal of the Operations Research Society of Japan 2007, Vol. 50, No. 3, 163-177 INEFFICIENCY EVALUATION WITH AN ADDITIVE DEA MODEL UNDER IMPRECISE DATA, AN APPLICATION ON IAUK DEPARTMENTS Reza Kazemi
Journal of the Operations Research Society of Japan 2007, Vol. 50, No. 3, 163-177 INEFFICIENCY EVALUATION WITH AN ADDITIVE DEA MODEL UNDER IMPRECISE DATA, AN APPLICATION ON IAUK DEPARTMENTS Reza Kazemi
Centre for Efficiency and Productivity Analysis
 Centre for Efficiency and Productivity Analysis Working Paper Series No. WP04/2018 Profit Efficiency, DEA, FDH and Big Data Valentin Zelenyuk Date: June 2018 School of Economics University of Queensland
Centre for Efficiency and Productivity Analysis Working Paper Series No. WP04/2018 Profit Efficiency, DEA, FDH and Big Data Valentin Zelenyuk Date: June 2018 School of Economics University of Queensland
Equivalent Standard DEA Models to Provide Super-Efficiency Scores
 Second Revision MS 5035 Equivalent Standard DEA Models to Provide Super-Efficiency Scores C.A.K. Lovell 1 and A.P.B. Rouse 2 1 Department of Economics 2 Department of Accounting and Finance Terry College
Second Revision MS 5035 Equivalent Standard DEA Models to Provide Super-Efficiency Scores C.A.K. Lovell 1 and A.P.B. Rouse 2 1 Department of Economics 2 Department of Accounting and Finance Terry College
Measuring performance of a three-stage structure using data envelopment analysis and Stackelberg game
 Journal of ndustrial and Systems Engineering Vol., No., pp. 5-7 Spring (April) 9 Measuring performance of a three-stage structure using data envelopment analysis and Stackelberg game Ehsan Vaezi, Seyyed
Journal of ndustrial and Systems Engineering Vol., No., pp. 5-7 Spring (April) 9 Measuring performance of a three-stage structure using data envelopment analysis and Stackelberg game Ehsan Vaezi, Seyyed
Subhash C Ray Department of Economics University of Connecticut Storrs CT
 CATEGORICAL AND AMBIGUOUS CHARACTERIZATION OF RETUNS TO SCALE PROPERTIES OF OBSERVED INPUT-OUTPUT BUNDLES IN DATA ENVELOPMENT ANALYSIS Subhash C Ray Department of Economics University of Connecticut Storrs
CATEGORICAL AND AMBIGUOUS CHARACTERIZATION OF RETUNS TO SCALE PROPERTIES OF OBSERVED INPUT-OUTPUT BUNDLES IN DATA ENVELOPMENT ANALYSIS Subhash C Ray Department of Economics University of Connecticut Storrs
The flow of funds in a who-to-whom framework: balance-sheet interlinkages and propagation of quantity shocks
 The flow of funds in a who-to-whom framework: balance-sheet interlinkages and propagation of quantity shocks C Girón (*) European Central Bank (**) How financial systems work: evidence from financial accounts
The flow of funds in a who-to-whom framework: balance-sheet interlinkages and propagation of quantity shocks C Girón (*) European Central Bank (**) How financial systems work: evidence from financial accounts
Project investment decision-making based on inventory financing with stochastic demand
 31 2 2016 4 JOURNAL OF SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Vol.31 No.2 Apr. 2016 1,2, 1,2, 1,2, 1,2 (1., 400044; 2., 400044) :,,.,.,,,,. : : F253.4 : A : 1000 5781(2016)02 0227 07 doi: 10.13383/j.cnki.jse.2016.02.008
31 2 2016 4 JOURNAL OF SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Vol.31 No.2 Apr. 2016 1,2, 1,2, 1,2, 1,2 (1., 400044; 2., 400044) :,,.,.,,,,. : : F253.4 : A : 1000 5781(2016)02 0227 07 doi: 10.13383/j.cnki.jse.2016.02.008
Sensitivity and Stability Analysis in Uncertain Data Envelopment (DEA)
 Sensitivity and Stability Analysis in Uncertain Data Envelopment (DEA) eilin Wen a,b, Zhongfeng Qin c, Rui Kang b a State Key Laboratory of Virtual Reality Technology and Systems b Department of System
Sensitivity and Stability Analysis in Uncertain Data Envelopment (DEA) eilin Wen a,b, Zhongfeng Qin c, Rui Kang b a State Key Laboratory of Virtual Reality Technology and Systems b Department of System
Revenue Malmquist Index with Variable Relative Importance as a Function of Time in Different PERIOD and FDH Models of DEA
 Revenue Malmquist Index with Variable Relative Importance as a Function of Time in Different PERIOD and FDH Models of DEA Mohammad Ehsanifar, Golnaz Mohammadi Department of Industrial Management and Engineering
Revenue Malmquist Index with Variable Relative Importance as a Function of Time in Different PERIOD and FDH Models of DEA Mohammad Ehsanifar, Golnaz Mohammadi Department of Industrial Management and Engineering
EFFICIENCY ANALYSIS UNDER CONSIDERATION OF SATISFICING LEVELS
 EFFICIENCY ANALYSIS UNDER CONSIDERATION OF SATISFICING LEVELS FOR OUTPUT QUANTITIES [004-0236] Malte L. Peters, University of Duisburg-Essen, Campus Essen Stephan Zelewski, University of Duisburg-Essen,
EFFICIENCY ANALYSIS UNDER CONSIDERATION OF SATISFICING LEVELS FOR OUTPUT QUANTITIES [004-0236] Malte L. Peters, University of Duisburg-Essen, Campus Essen Stephan Zelewski, University of Duisburg-Essen,
Two-stage network DEA: when intermediate measures can be treated as outputs from the second stage
 Journal of the Operational Research Society (2015) 66, 1868 1877 2015 Operational Research Society Ltd. All rights reserved. 0160-5682/15 www.palgrave-journals.com/jors/ Two-stage network DEA: when intermediate
Journal of the Operational Research Society (2015) 66, 1868 1877 2015 Operational Research Society Ltd. All rights reserved. 0160-5682/15 www.palgrave-journals.com/jors/ Two-stage network DEA: when intermediate
Fuzzy efficiency: Multiplier and enveloping CCR models
 Available online at http://ijim.srbiau.ac.ir/ Int. J. Industrial Mathematics (ISSN 28-5621) Vol. 8, No. 1, 216 Article ID IJIM-484, 8 pages Research Article Fuzzy efficiency: Multiplier and enveloping
Available online at http://ijim.srbiau.ac.ir/ Int. J. Industrial Mathematics (ISSN 28-5621) Vol. 8, No. 1, 216 Article ID IJIM-484, 8 pages Research Article Fuzzy efficiency: Multiplier and enveloping
SECOND ORDER DUALITY IN MULTIOBJECTIVE PROGRAMMING
 Journal of Applied Analysis Vol. 4, No. (2008), pp. 3-48 SECOND ORDER DUALITY IN MULTIOBJECTIVE PROGRAMMING I. AHMAD and Z. HUSAIN Received November 0, 2006 and, in revised form, November 6, 2007 Abstract.
Journal of Applied Analysis Vol. 4, No. (2008), pp. 3-48 SECOND ORDER DUALITY IN MULTIOBJECTIVE PROGRAMMING I. AHMAD and Z. HUSAIN Received November 0, 2006 and, in revised form, November 6, 2007 Abstract.
Environmental investment and firm performance: A network approach
 Environmental investment and firm performance: A network approach Moriah Bostian 1 Rolf Färe 2 Shawna Grosskopf 2 Tommy Lundgren 3 1 Department of Economics, Lewis & Clark College and University of Turku
Environmental investment and firm performance: A network approach Moriah Bostian 1 Rolf Färe 2 Shawna Grosskopf 2 Tommy Lundgren 3 1 Department of Economics, Lewis & Clark College and University of Turku
CHAPTER 3 THE METHOD OF DEA, DDF AND MLPI
 CHAPTER 3 THE METHOD OF DEA, DDF AD MLP 3.1 ntroduction As has been discussed in the literature review chapter, in any organization, technical efficiency can be determined in order to measure the performance.
CHAPTER 3 THE METHOD OF DEA, DDF AD MLP 3.1 ntroduction As has been discussed in the literature review chapter, in any organization, technical efficiency can be determined in order to measure the performance.
Properties of Inefficiency Indexes on Input, Output Space
 Properties of Inefficiency Indexes on Input, Output Space by R. Robert Russell University of California, Riverside, and University of New South Wales and William Schworm University of New South Wales September
Properties of Inefficiency Indexes on Input, Output Space by R. Robert Russell University of California, Riverside, and University of New South Wales and William Schworm University of New South Wales September
A New Group Data Envelopment Analysis Method for Ranking Design Requirements in Quality Function Deployment
 Available online at http://ijim.srbiau.ac.ir/ Int. J. Industrial Mathematics (ISSN 2008-5621) Vol. 9, No. 4, 2017 Article ID IJIM-00833, 10 pages Research Article A New Group Data Envelopment Analysis
Available online at http://ijim.srbiau.ac.ir/ Int. J. Industrial Mathematics (ISSN 2008-5621) Vol. 9, No. 4, 2017 Article ID IJIM-00833, 10 pages Research Article A New Group Data Envelopment Analysis
USING LEXICOGRAPHIC PARAMETRIC PROGRAMMING FOR IDENTIFYING EFFICIENT UNITS IN DEA
 Pekka J. Korhonen Pyry-Antti Siitari USING LEXICOGRAPHIC PARAMETRIC PROGRAMMING FOR IDENTIFYING EFFICIENT UNITS IN DEA HELSINKI SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS WORKING PAPERS W-381 Pekka J. Korhonen Pyry-Antti Siitari
Pekka J. Korhonen Pyry-Antti Siitari USING LEXICOGRAPHIC PARAMETRIC PROGRAMMING FOR IDENTIFYING EFFICIENT UNITS IN DEA HELSINKI SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS WORKING PAPERS W-381 Pekka J. Korhonen Pyry-Antti Siitari
30E00300 Productivity and Efficiency Analysis Abolfazl Keshvari, Ph.D.
 30E00300 Productivity and Efficiency Analysis 2016 Abolfazl Keshvari, Ph.D. abolfazl.keshvari@aalto.fi Mathematics and statistics We need to know some basics of math and stat What is a function, and its
30E00300 Productivity and Efficiency Analysis 2016 Abolfazl Keshvari, Ph.D. abolfazl.keshvari@aalto.fi Mathematics and statistics We need to know some basics of math and stat What is a function, and its
Data envelopment analysis
 15 Data envelopment analysis The purpose of data envelopment analysis (DEA) is to compare the operating performance of a set of units such as companies, university departments, hospitals, bank branch offices,
15 Data envelopment analysis The purpose of data envelopment analysis (DEA) is to compare the operating performance of a set of units such as companies, university departments, hospitals, bank branch offices,
Lamar Institute of Technology Quarterly Cash Statement For the Quarter Ended May 31, 2010
 Quarterly Cash Statement For the Quarter Ended May 31, 2010 Fund 0287 Treasury Bonds Fund Group Demand Texpool State Treasury Securities lemo's) Total $ $ $ $ $ $ Educational and General 2,414,131.60 2,414,131.60
Quarterly Cash Statement For the Quarter Ended May 31, 2010 Fund 0287 Treasury Bonds Fund Group Demand Texpool State Treasury Securities lemo's) Total $ $ $ $ $ $ Educational and General 2,414,131.60 2,414,131.60
UCLA Recent Work. Title. Permalink. Authors. Publication Date. Measuring Eco-inefficiency: A New Frontier Approach
 UCLA Recent Work Title Measuring Eco-inefficiency: A New Frontier Approach Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/3r22v65j Authors Chen, Chien-Ming Delmas, Magali A Publication Date 2011-01-19 escholarship.org
UCLA Recent Work Title Measuring Eco-inefficiency: A New Frontier Approach Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/3r22v65j Authors Chen, Chien-Ming Delmas, Magali A Publication Date 2011-01-19 escholarship.org
The Comparison of Stochastic and Deterministic DEA Models
 The International Scientific Conference INPROFORUM 2015, November 5-6, 2015, České Budějovice, 140-145, ISBN 978-80-7394-536-7. The Comparison of Stochastic and Deterministic DEA Models Michal Houda, Jana
The International Scientific Conference INPROFORUM 2015, November 5-6, 2015, České Budějovice, 140-145, ISBN 978-80-7394-536-7. The Comparison of Stochastic and Deterministic DEA Models Michal Houda, Jana
Graph Convergence for H(, )-co-accretive Mapping with over-relaxed Proximal Point Method for Solving a Generalized Variational Inclusion Problem
 Iranian Journal of Mathematical Sciences and Informatics Vol. 12, No. 1 (2017), pp 35-46 DOI: 10.7508/ijmsi.2017.01.004 Graph Convergence for H(, )-co-accretive Mapping with over-relaxed Proximal Point
Iranian Journal of Mathematical Sciences and Informatics Vol. 12, No. 1 (2017), pp 35-46 DOI: 10.7508/ijmsi.2017.01.004 Graph Convergence for H(, )-co-accretive Mapping with over-relaxed Proximal Point
LITERATURE REVIEW. Chapter 2
 Chapter 2 LITERATURE REVIEW This chapter reviews literature in the areas of productivity and performance measurement using mathematical programming and multi-level planning for resource allocation and
Chapter 2 LITERATURE REVIEW This chapter reviews literature in the areas of productivity and performance measurement using mathematical programming and multi-level planning for resource allocation and
H. Zareamoghaddam, Z. Zareamoghaddam. (Received 3 August 2013, accepted 14 March 2014)
 ISSN 1749-3889 (print 1749-3897 (online International Journal of Nonlinear Science Vol.17(2014 No.2pp.128-134 A New Algorithm for Fuzzy Linear Regression with Crisp Inputs and Fuzzy Output H. Zareamoghaddam
ISSN 1749-3889 (print 1749-3897 (online International Journal of Nonlinear Science Vol.17(2014 No.2pp.128-134 A New Algorithm for Fuzzy Linear Regression with Crisp Inputs and Fuzzy Output H. Zareamoghaddam
STRUCTURE Of ECONOMICS A MATHEMATICAL ANALYSIS
 THIRD EDITION STRUCTURE Of ECONOMICS A MATHEMATICAL ANALYSIS Eugene Silberberg University of Washington Wing Suen University of Hong Kong I Us Irwin McGraw-Hill Boston Burr Ridge, IL Dubuque, IA Madison,
THIRD EDITION STRUCTURE Of ECONOMICS A MATHEMATICAL ANALYSIS Eugene Silberberg University of Washington Wing Suen University of Hong Kong I Us Irwin McGraw-Hill Boston Burr Ridge, IL Dubuque, IA Madison,
1) Standards and Methodology for the Evaluation of Financial Statements 2) Letter of Credit Instructions
 TO: IATA Travel Agencies DATE: 29 th January 2016 REFERENCE: Annual Financial Review Preparation - Agency Risk Management Guideline About In preparation for your agency s upcoming annual financial review,
TO: IATA Travel Agencies DATE: 29 th January 2016 REFERENCE: Annual Financial Review Preparation - Agency Risk Management Guideline About In preparation for your agency s upcoming annual financial review,
Sensitivity and Stability Analysis in DEA on Interval Data by Using MOLP Methods
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 3, 2009, no. 18, 891-908 Sensitivity and Stability Analysis in DEA on Interval Data by Using MOLP Methods Z. Ghelej beigi a1, F. Hosseinzadeh Lotfi b, A.A. Noora c M.R.
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 3, 2009, no. 18, 891-908 Sensitivity and Stability Analysis in DEA on Interval Data by Using MOLP Methods Z. Ghelej beigi a1, F. Hosseinzadeh Lotfi b, A.A. Noora c M.R.
M. R. Grasselli. Research in Options - IMPA, December 2, 2015
 Mathematics and Statistics, McMaster University and The Fields Institute Joint with Gael Giraud (AFD, CNRS, CES) Research in Options - IMPA, December 2, 2015 The book Opening salvo To put it bluntly, the
Mathematics and Statistics, McMaster University and The Fields Institute Joint with Gael Giraud (AFD, CNRS, CES) Research in Options - IMPA, December 2, 2015 The book Opening salvo To put it bluntly, the
Testing the Validity of the Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Index in the World Economic Forum with Classical and Fuzzy Data Envelopment Analyses
 PTiR 2013;4;121-128 121 Hatice Ozkoc, Hakan Bakan, Ercan Baldemi r Muğla Sitki Koçman Üniversitesi, Turkey Testing the Validity of the Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Index in the World Economic Forum
PTiR 2013;4;121-128 121 Hatice Ozkoc, Hakan Bakan, Ercan Baldemi r Muğla Sitki Koçman Üniversitesi, Turkey Testing the Validity of the Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Index in the World Economic Forum
Microeconomic Theory. Microeconomic Theory. Everyday Economics. The Course:
 The Course: Microeconomic Theory This is the first rigorous course in microeconomic theory This is a course on economic methodology. The main goal is to teach analytical tools that will be useful in other
The Course: Microeconomic Theory This is the first rigorous course in microeconomic theory This is a course on economic methodology. The main goal is to teach analytical tools that will be useful in other
Angelo Zago University of Verona - Italy
 Quality Estimation and Wine Industry Competitiveness Angelo Zago University of Verona - Italy Davis, August 9, 2007 Work in progress 1. Motivation Measuring and evaluating the quality attributes of raw
Quality Estimation and Wine Industry Competitiveness Angelo Zago University of Verona - Italy Davis, August 9, 2007 Work in progress 1. Motivation Measuring and evaluating the quality attributes of raw
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 Implementation of A Log-Linear Poisson Regression Model to Estimate the Odds of Being Technically Efficient in DEA Setting: The Case of Hospitals in Oman By Parakramaweera Sunil Dharmapala Dept. of Operations
Implementation of A Log-Linear Poisson Regression Model to Estimate the Odds of Being Technically Efficient in DEA Setting: The Case of Hospitals in Oman By Parakramaweera Sunil Dharmapala Dept. of Operations
Cecilio Mar-Molinero, Diego Prior, Maria-Manuela Segovia & Fabiola Portillo
 On centralized resource utilization and its reallocation by using DEA Cecilio Mar-Molinero, Diego Prior, Maria-Manuela Segovia & Fabiola Portillo Annals of Operations Research ISSN 0254-5330 Volume 221
On centralized resource utilization and its reallocation by using DEA Cecilio Mar-Molinero, Diego Prior, Maria-Manuela Segovia & Fabiola Portillo Annals of Operations Research ISSN 0254-5330 Volume 221
M. R. Grasselli. QMF, Sydney, December 16, Mathematics and Statistics, McMaster University Joint with Gaël Giraud (AFD, CNRS, ENPC)
 Mathematics and Statistics, McMaster University Joint with Gaël Giraud (AFD, CNRS, ENPC) QMF, Sydney, December 16, 2016 The book Opening salvo To put it bluntly, the discipline of economics has yet to
Mathematics and Statistics, McMaster University Joint with Gaël Giraud (AFD, CNRS, ENPC) QMF, Sydney, December 16, 2016 The book Opening salvo To put it bluntly, the discipline of economics has yet to
Mainor Ülemiste AS. Interim Report July September
 Mainor Ülemiste AS Interim Report July September 2018 http://mainorulemiste.ee/opiku/ Main Events in the 3Q 2018 Mainor Ülemiste s subsidiary concluded a loan agreement in amount of 10,7 million euros
Mainor Ülemiste AS Interim Report July September 2018 http://mainorulemiste.ee/opiku/ Main Events in the 3Q 2018 Mainor Ülemiste s subsidiary concluded a loan agreement in amount of 10,7 million euros
Sensitivity and Stability Radius in Data Envelopment Analysis
 Available online at http://ijim.srbiau.ac.ir Int. J. Industrial Mathematics Vol. 1, No. 3 (2009) 227-234 Sensitivity and Stability Radius in Data Envelopment Analysis A. Gholam Abri a, N. Shoja a, M. Fallah
Available online at http://ijim.srbiau.ac.ir Int. J. Industrial Mathematics Vol. 1, No. 3 (2009) 227-234 Sensitivity and Stability Radius in Data Envelopment Analysis A. Gholam Abri a, N. Shoja a, M. Fallah
Optimal weights in DEA models with weight restrictions
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository Optimal weights in DEA models with weight restrictions This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an author. Citation:
Loughborough University Institutional Repository Optimal weights in DEA models with weight restrictions This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an author. Citation:
Suggested Solutions to Homework #3 Econ 511b (Part I), Spring 2004
 Suggested Solutions to Homework #3 Econ 5b (Part I), Spring 2004. Consider an exchange economy with two (types of) consumers. Type-A consumers comprise fraction λ of the economy s population and type-b
Suggested Solutions to Homework #3 Econ 5b (Part I), Spring 2004. Consider an exchange economy with two (types of) consumers. Type-A consumers comprise fraction λ of the economy s population and type-b
Source: US. Bureau of Economic Analysis Shaded areas indicate US recessions research.stlouisfed.org
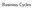 Business Cycles 0 Real Gross Domestic Product 18,000 16,000 (Billions of Chained 2009 Dollars) 14,000 12,000 10,000 8,000 6,000 4,000 2,000 1940 1960 1980 2000 Source: US. Bureau of Economic Analysis Shaded
Business Cycles 0 Real Gross Domestic Product 18,000 16,000 (Billions of Chained 2009 Dollars) 14,000 12,000 10,000 8,000 6,000 4,000 2,000 1940 1960 1980 2000 Source: US. Bureau of Economic Analysis Shaded
LOCATIONAL PREFERENCES OF FDI FIRMS IN TURKEY
 LOCATIONAL PREFERENCES OF FDI FIRMS IN TURKEY Prof. Dr. Lale BERKÖZ Assist. Prof. Dr.S. SenceTÜRK I.T.U. Faculty of Architecture Istanbul/TURKEY E-mail: lberkoz@itu.edu.tr INTRODUCTION Foreign direct investment
LOCATIONAL PREFERENCES OF FDI FIRMS IN TURKEY Prof. Dr. Lale BERKÖZ Assist. Prof. Dr.S. SenceTÜRK I.T.U. Faculty of Architecture Istanbul/TURKEY E-mail: lberkoz@itu.edu.tr INTRODUCTION Foreign direct investment
Research Article An Optimization Model of the Single-Leg Air Cargo Space Control Based on Markov Decision Process
 Applied Mathematics Volume 2012, Article ID 235706, 7 pages doi:10.1155/2012/235706 Research Article An Optimization Model of the Single-Leg Air Cargo Space Control Based on Markov Decision Process Chun-rong
Applied Mathematics Volume 2012, Article ID 235706, 7 pages doi:10.1155/2012/235706 Research Article An Optimization Model of the Single-Leg Air Cargo Space Control Based on Markov Decision Process Chun-rong
How to Measure Interconnectedness between Banks, Insurers and Financial Conglomerates?
 How to Measure Interconnectedness between Banks, Insurers and Financial Conglomerates? G. Hauton 1 JC. Héam 2 1 ACPR 2 ACPR, CREST 3 rd EBA Policy Research Workshop, November 2014, London. The views expressed
How to Measure Interconnectedness between Banks, Insurers and Financial Conglomerates? G. Hauton 1 JC. Héam 2 1 ACPR 2 ACPR, CREST 3 rd EBA Policy Research Workshop, November 2014, London. The views expressed
Prediction of A CRS Frontier Function and A Transformation Function for A CCR DEA Using EMBEDED PCA
 03 (03) -5 Available online at www.ispacs.com/dea Volume: 03, Year 03 Article ID: dea-0006, 5 Pages doi:0.5899/03/dea-0006 Research Article Data Envelopment Analysis and Decision Science Prediction of
03 (03) -5 Available online at www.ispacs.com/dea Volume: 03, Year 03 Article ID: dea-0006, 5 Pages doi:0.5899/03/dea-0006 Research Article Data Envelopment Analysis and Decision Science Prediction of
GARP and Afriat s Theorem Production
 GARP and Afriat s Theorem Production Econ 2100 Fall 2017 Lecture 8, September 21 Outline 1 Generalized Axiom of Revealed Preferences 2 Afriat s Theorem 3 Production Sets and Production Functions 4 Profits
GARP and Afriat s Theorem Production Econ 2100 Fall 2017 Lecture 8, September 21 Outline 1 Generalized Axiom of Revealed Preferences 2 Afriat s Theorem 3 Production Sets and Production Functions 4 Profits
Do Financial Factors Drive Aggregate Productivity? Evidence from Indian Manufacturing Establishments
 Do Financial Factors Drive Aggregate Productivity? Evidence from Indian Manufacturing Establishments N. Aaron Pancost University of Chicago January 29, 2016 Motivation Does financial development increase
Do Financial Factors Drive Aggregate Productivity? Evidence from Indian Manufacturing Establishments N. Aaron Pancost University of Chicago January 29, 2016 Motivation Does financial development increase
The Difference Approach to Productivity Measurement and Exact Indicators November 25, 2017
 1 The Difference Approach to Productivity Measurement and Exact Indicators November 25, 2017 Erwin Diewert and Kevin J. Fox, 1 Discussion Paper 17-08, Vancouver School of Economics, University of British
1 The Difference Approach to Productivity Measurement and Exact Indicators November 25, 2017 Erwin Diewert and Kevin J. Fox, 1 Discussion Paper 17-08, Vancouver School of Economics, University of British
OPERATIONS RESEARCH. Michał Kulej. Business Information Systems
 OPERATIONS RESEARCH Michał Kulej Business Information Systems The development of the potential and academic programmes of Wrocław University of Technology Project co-financed by European Union within European
OPERATIONS RESEARCH Michał Kulej Business Information Systems The development of the potential and academic programmes of Wrocław University of Technology Project co-financed by European Union within European
More Technical Efficiency and Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA)
 More Technical Efficiency and Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) based on OnFront, Reference Guide Coelli, et al., Introduction to Efficiency and Productivity Springer, 2005, Ch 6. April 22, 2008 Technology:
More Technical Efficiency and Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) based on OnFront, Reference Guide Coelli, et al., Introduction to Efficiency and Productivity Springer, 2005, Ch 6. April 22, 2008 Technology:
Financial Frictions and Credit Spreads. Ke Pang Pierre L. Siklos Wilfrid Laurier University
 Financial Frictions and Credit Spreads Ke Pang Pierre L. Siklos Wilfrid Laurier University 1 Modelling Challenges Considerable work underway to incorporate a role for financial frictions the financial
Financial Frictions and Credit Spreads Ke Pang Pierre L. Siklos Wilfrid Laurier University 1 Modelling Challenges Considerable work underway to incorporate a role for financial frictions the financial
1 The Basic RBC Model
 IHS 2016, Macroeconomics III Michael Reiter Ch. 1: Notes on RBC Model 1 1 The Basic RBC Model 1.1 Description of Model Variables y z k L c I w r output level of technology (exogenous) capital at end of
IHS 2016, Macroeconomics III Michael Reiter Ch. 1: Notes on RBC Model 1 1 The Basic RBC Model 1.1 Description of Model Variables y z k L c I w r output level of technology (exogenous) capital at end of
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION FOR LBB REPORTING:
 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION FOR LBB REPORTING: Lamar Insitute of Technology book balance of Local Funds in the State Treasury for the Quarter Ending on August 31, 2006 was $ 1,961,286.98 Quarterly Investment
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION FOR LBB REPORTING: Lamar Insitute of Technology book balance of Local Funds in the State Treasury for the Quarter Ending on August 31, 2006 was $ 1,961,286.98 Quarterly Investment
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION FOR LBB REPORTING:
 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION FOR LBB REPORTING: Lamar Insitute of Technology book balance of Local Funds in the State Treasury for the Quarter Ending on February 29, 2008 was $ 3,458,061.57 Quarterly Investment
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION FOR LBB REPORTING: Lamar Insitute of Technology book balance of Local Funds in the State Treasury for the Quarter Ending on February 29, 2008 was $ 3,458,061.57 Quarterly Investment
u(c t, x t+1 ) = c α t + x α t+1
 Review Questions: Overlapping Generations Econ720. Fall 2017. Prof. Lutz Hendricks 1 A Savings Function Consider the standard two-period household problem. The household receives a wage w t when young
Review Questions: Overlapping Generations Econ720. Fall 2017. Prof. Lutz Hendricks 1 A Savings Function Consider the standard two-period household problem. The household receives a wage w t when young
ECON 581: Growth with Overlapping Generations. Instructor: Dmytro Hryshko
 ECON 581: Growth with Overlapping Generations Instructor: Dmytro Hryshko Readings Acemoglu, Chapter 9. Motivation Neoclassical growth model relies on the representative household. OLG models allow for
ECON 581: Growth with Overlapping Generations Instructor: Dmytro Hryshko Readings Acemoglu, Chapter 9. Motivation Neoclassical growth model relies on the representative household. OLG models allow for
EFFICIENCY ASSESSMENT OF WASTEWATER TREATMENT PLANTS: A DATA ENVELOPMENT ANALYSIS APPROACH INTEGRATING TECHNICAL, ECONOMICAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES
 EFFICIENCY ASSESSMENT OF WASTEWATER TREATMENT PLANTS: A DATA ENVELOPMENT ANALYSIS APPROACH INTEGRATING TECHNICAL, ECONOMICAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES Lledó Castellet Viciano, María Molinos-Senante b, Vicent
EFFICIENCY ASSESSMENT OF WASTEWATER TREATMENT PLANTS: A DATA ENVELOPMENT ANALYSIS APPROACH INTEGRATING TECHNICAL, ECONOMICAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES Lledó Castellet Viciano, María Molinos-Senante b, Vicent
A Generalization of Discounted Central Limit Theorem and its Berry-Esseen Analogue
 Journal of Statistical Theory and Applications, Vol. 13, No. 4 (December 2014), 289-295 A Generalization of Discounted Central Limit Theorem and its Berry-Esseen Analogue B. Amiri Aghbilagh 1, Z. Shishebor
Journal of Statistical Theory and Applications, Vol. 13, No. 4 (December 2014), 289-295 A Generalization of Discounted Central Limit Theorem and its Berry-Esseen Analogue B. Amiri Aghbilagh 1, Z. Shishebor
Technical Appendix for Financial Business Cycles
 Technical Appendix for Financial usiness Cycles Matteo Iacoviello Federal Reserve oard December 4, 05 This appendix contains some of the derivations for the paper Financial usiness Cycles.. The Extended
Technical Appendix for Financial usiness Cycles Matteo Iacoviello Federal Reserve oard December 4, 05 This appendix contains some of the derivations for the paper Financial usiness Cycles.. The Extended
AMASES Lista delle riviste ritenute di interesse per la ricerca nell'ambito della Matematica Applicata alle Scienze Economiche e Sociali
 AMASES Lista delle riviste ritenute di interesse per la ricerca nell'ambito della Matematica Applicata alle Scienze Economiche e Sociali 24 Gennaio 2010 ISI SCIMAGOJR Mathscinet Zentralblatt Econlit 4OR
AMASES Lista delle riviste ritenute di interesse per la ricerca nell'ambito della Matematica Applicata alle Scienze Economiche e Sociali 24 Gennaio 2010 ISI SCIMAGOJR Mathscinet Zentralblatt Econlit 4OR
Bubbles and Credit Constraints
 Bubbles and Credit Constraints Miao and Wang ECON 101 Miao and Wang (2008) Bubbles and Credit Constraints 1 / 14 Bubbles Bubble Growth Ḃ B g or eventually they get bigger than the economy, where g is the
Bubbles and Credit Constraints Miao and Wang ECON 101 Miao and Wang (2008) Bubbles and Credit Constraints 1 / 14 Bubbles Bubble Growth Ḃ B g or eventually they get bigger than the economy, where g is the
A Unifying Framework for Farrell Profit Efficiency Measurement
 A Unifying Framework for Farrell Profit Efficiency Measurement Rolf Färe a, Xinju He b, Sungko Li b, Valentin Zelenyuk c Abstract Measuring profit efficiency is a challenging task and many different approaches
A Unifying Framework for Farrell Profit Efficiency Measurement Rolf Färe a, Xinju He b, Sungko Li b, Valentin Zelenyuk c Abstract Measuring profit efficiency is a challenging task and many different approaches
