Markov Chains and Related Matters
|
|
|
- Vincent Weaver
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Markov Chains and Related Matters 2 :9 3 4 : The four nodes are called states. The numbers on the arrows are called transition probabilities. For example if we are in state, there is a probability of going to state 3 and a probability of going to state 2. There would be no probability of staying in state or going to state 4. (These are allowed in Markov chains, but my example just doesn t have them.) The sum of the outgoing numbers from any state sum to. Q520 Markov Chains
2 These Get Applied in Many Settings What do IU undergrads do between 6PM and midnight? 2 :9 3 4 : = study 2 = eat 3 = make phone call 4 =watchtv Q520 Markov Chains 2
3 Related Model: Automata a b 2 b a a a 3 Let s declare to be the start state. a b 4 We have indicated 4 as the accepting state. Then we read in words, following any paths of arrows we like, starting in and hoping to get 4. Some words accepted: aa, aaa, aabababababababa. Some words not accepted: bb, a, any word not ending in a. Q520 Markov Chains 3
4 Markov Chains and Related Matters 2 :9 3 4 : What we have here are probabilities instead of atomic letters like a, b, c. We also don t have starting or accepting state. However, it is possible and useful to have these extra features of top of Markov chains, as we ll see. Q520 Markov Chains 4
5 State Vectors Suppose we have a large number of IU students, and we measure their state by a random variable X. Let s say that the value space V (X) is f 2 3 4g, with = study 2 = eat 3 = make phone call 4 =watchtv We have probabilities like Pr (X = ), Pr (X = 2), etc. These P will be numbers between 0 and, and Pr (X = i) =. i Definition A state vector for X is a vector x = (x ::: x n ) of numbers between 0 and which sum to. Q520 Markov Chains 5
6 The Evolution of State Vectors Suppose our original state vector x is (:2 :3 : )..2.3 :9..4 : A good way to think about a Markov chain is that we have a large number of individuals making choices with no memory, and independent of each other. We want to go from x to x. How should we get X? For, we would have ()(:3) + ()(:) = :5 + :04 = :9. Q520 Markov Chains 6
7 The Evolution of State Vectors We call our original state vector x 0.Sox 0 is (:2 :3 : ). Then we do the calculations:.9.44 :9.6.4 : We get x = (:9 4 :3 :06). Continuing, we want to get x 2, x 3, :::, x 3225, :::, x n, :::. Q520 Markov Chains 7
8 State Vectors and Markov Chains We ll discuss formulas soon, but first let s remember that state vectors come from random variables. This means that in addition to the state variables x 0 x ::: x n :::we also have random variables X 0 X ::: X n :::. These have an important independence property: Pr (X n jx ::: X n ) = Pr (X n jx n ): () In formally, what happens at time n only depends on time n and not on anything further back. This Markov property in () formalizes the idea that we are modeling a system with no memory. In sophisticated books, a Markov chain is defined to be the sequence of random variables, and then the picture is a specification of it. Q520 Markov Chains 8
9 Markov Chains and Related Matters There are two ways to turn a Markov Chain into a matrix: 2 :9 3 4 : or :9 0 : 0 :9 : Q520 Markov Chains 9
10 Matrices, continued or :9 0 : 0 :9 : The first way, the rows add to. The second way, the columns do. We always write a i j for the entries in a matrix A, withtherow index first. On the left p i j is the probability of going from state i to state j. On the right p i j is the prob of going from state j to state i. The two matrices are transposes of each other. One has to be careful in reading books and papers, because both kinds of matrices are used. Q520 Markov Chains 0
11 Markov Chains and Related Matters Even more, one has to be careful in writing! Cf. Textbook, Chapter 0: both conventions seem to be in use! To make life easier for us, we ll call P the one on the left, and P t the one on the right. So the rows of P add to. Remember that we started with a state vector x 0 = (:2 :3 : ). To get x, we multiply matrices: x = x 0 P In more detail, x = (:2 :3 : ) :9 : 0 Q520 Markov Chains
12 Markov Chains, continued The general formula is x n+ = x n P, where the operation here is matrix multiplication. We could also work with P t, and here what we would do is to multiply on the right by the transpose of x n : x t n+ = P t x t n : For example, we would get x t by multiplying P t x t : 0 0 :2 0 0 :9 :3 0 :9 = 4 0 : : :3 :06 Q520 Markov Chains 2
13 Regular Markov Chains Here is one of the main facts about Markov Chains. We say that a Markov chain is regular if for each pair of states i and j, it is possible to go from i to j following non-zero arrows. Our example chain is regular, but we ll soon see one which is not. Then, there is a unique long-term state vector x with the following properties:. x P = x :sox is stable. 2. In terms of the transpose, P t (x ) t = (x ) t. 3. No matter what the starting x 0 is, the sequence x 0 x ::: x n ::: will converge to x in an appropriate sense. 4. We can find x by solving a set of linear equations. Q520 Markov Chains 3
14 How to find x In our example, let s write x as (w x y z). It will be easier to work with the transpose P t and to solve We want to solve :9 0 w x = 0 w x 0 : y y z z When we multiply out the left side, we get 0 0w + x + y + z w + 0x + 0y + :9z w + x + 0y + :z 0w + 0x + y + 0z 0 w = x y z Q520 Markov Chains 4
15 Solving it, continued So we would have to solve 0w + x + y + z = w w + 0x + 0y + :9z = x w + x + 0y + :z = y 0w + 0x + y + 0z = z This is four linear equations in four unknowns, and it has a unique solution by our theorem. The easiest way to get the solution is to use a program like Matlab. Q520 Markov Chains 5
16 A Non-Regular Chain Flip a fain coin forever, stopping when you get a Heads. What s the probability that the first H is on an even numbered flip? = an even number of T s and no H. 2 = an odd number of T s and no H. 3 = H after an an even number of all T flips 4 = H after an an odd number of all T flips We start with x 0 = ( 0 0 0), and we want to know the long term distribution. Q520 Markov Chains 6
Getting Started with Communications Engineering. Rows first, columns second. Remember that. R then C. 1
 1 Rows first, columns second. Remember that. R then C. 1 A matrix is a set of real or complex numbers arranged in a rectangular array. They can be any size and shape (provided they are rectangular). A
1 Rows first, columns second. Remember that. R then C. 1 A matrix is a set of real or complex numbers arranged in a rectangular array. They can be any size and shape (provided they are rectangular). A
MA 1128: Lecture 08 03/02/2018. Linear Equations from Graphs And Linear Inequalities
 MA 1128: Lecture 08 03/02/2018 Linear Equations from Graphs And Linear Inequalities Linear Equations from Graphs Given a line, we would like to be able to come up with an equation for it. I ll go over
MA 1128: Lecture 08 03/02/2018 Linear Equations from Graphs And Linear Inequalities Linear Equations from Graphs Given a line, we would like to be able to come up with an equation for it. I ll go over
[Disclaimer: This is not a complete list of everything you need to know, just some of the topics that gave people difficulty.]
![[Disclaimer: This is not a complete list of everything you need to know, just some of the topics that gave people difficulty.] [Disclaimer: This is not a complete list of everything you need to know, just some of the topics that gave people difficulty.]](/thumbs/82/86615903.jpg) Math 43 Review Notes [Disclaimer: This is not a complete list of everything you need to know, just some of the topics that gave people difficulty Dot Product If v (v, v, v 3 and w (w, w, w 3, then the
Math 43 Review Notes [Disclaimer: This is not a complete list of everything you need to know, just some of the topics that gave people difficulty Dot Product If v (v, v, v 3 and w (w, w, w 3, then the
Section 1.2. Row Reduction and Echelon Forms
 Section 1.2 Row Reduction and Echelon Forms Row Echelon Form Let s come up with an algorithm for turning an arbitrary matrix into a solved matrix. What do we mean by solved? A matrix is in row echelon
Section 1.2 Row Reduction and Echelon Forms Row Echelon Form Let s come up with an algorithm for turning an arbitrary matrix into a solved matrix. What do we mean by solved? A matrix is in row echelon
Basic Linear Algebra in MATLAB
 Basic Linear Algebra in MATLAB 9.29 Optional Lecture 2 In the last optional lecture we learned the the basic type in MATLAB is a matrix of double precision floating point numbers. You learned a number
Basic Linear Algebra in MATLAB 9.29 Optional Lecture 2 In the last optional lecture we learned the the basic type in MATLAB is a matrix of double precision floating point numbers. You learned a number
Vectors Picturing vectors Properties of vectors Linear combination Span. Vectors. Math 4A Scharlemann. 9 January /31
 1/31 Vectors Math 4A Scharlemann 9 January 2015 2/31 CELL PHONES OFF 3/31 An m-vector [column vector, vector in R m ] is an m 1 matrix: a 1 a 2 a = a 3. a m 3/31 An m-vector [column vector, vector in R
1/31 Vectors Math 4A Scharlemann 9 January 2015 2/31 CELL PHONES OFF 3/31 An m-vector [column vector, vector in R m ] is an m 1 matrix: a 1 a 2 a = a 3. a m 3/31 An m-vector [column vector, vector in R
A Series Transformations
 .3 Constructing Rotations We re halfway through the transformations and our next one, the rotation, gives a congruent image just like the reflection did. Just remember that a series of transformations
.3 Constructing Rotations We re halfway through the transformations and our next one, the rotation, gives a congruent image just like the reflection did. Just remember that a series of transformations
Methods for Solving Linear Systems Part 2
 Methods for Solving Linear Systems Part 2 We have studied the properties of matrices and found out that there are more ways that we can solve Linear Systems. In Section 7.3, we learned that we can use
Methods for Solving Linear Systems Part 2 We have studied the properties of matrices and found out that there are more ways that we can solve Linear Systems. In Section 7.3, we learned that we can use
Properties of Arithmetic
 Excerpt from "Prealgebra" 205 AoPS Inc. 4 6 7 4 5 8 22 23 5 7 0 Arithmetic is being able to count up to twenty without taking o your shoes. Mickey Mouse CHAPTER Properties of Arithmetic. Why Start with
Excerpt from "Prealgebra" 205 AoPS Inc. 4 6 7 4 5 8 22 23 5 7 0 Arithmetic is being able to count up to twenty without taking o your shoes. Mickey Mouse CHAPTER Properties of Arithmetic. Why Start with
An Intuitive Introduction to Motivic Homotopy Theory Vladimir Voevodsky
 What follows is Vladimir Voevodsky s snapshot of his Fields Medal work on motivic homotopy, plus a little philosophy and from my point of view the main fun of doing mathematics Voevodsky (2002). Voevodsky
What follows is Vladimir Voevodsky s snapshot of his Fields Medal work on motivic homotopy, plus a little philosophy and from my point of view the main fun of doing mathematics Voevodsky (2002). Voevodsky
M. Matrices and Linear Algebra
 M. Matrices and Linear Algebra. Matrix algebra. In section D we calculated the determinants of square arrays of numbers. Such arrays are important in mathematics and its applications; they are called matrices.
M. Matrices and Linear Algebra. Matrix algebra. In section D we calculated the determinants of square arrays of numbers. Such arrays are important in mathematics and its applications; they are called matrices.
ELE2120 Digital Circuits and Systems. Tutorial Note 10
 ELE2120 Digital Circuits and Systems Tutorial Note 10 Outline 1. 1. Sequential Circuit Design 2. 2. Design procedure: a complete example illustration Sequential circuit analysis & design In sequential
ELE2120 Digital Circuits and Systems Tutorial Note 10 Outline 1. 1. Sequential Circuit Design 2. 2. Design procedure: a complete example illustration Sequential circuit analysis & design In sequential
MATH3200, Lecture 31: Applications of Eigenvectors. Markov Chains and Chemical Reaction Systems
 Lecture 31: Some Applications of Eigenvectors: Markov Chains and Chemical Reaction Systems Winfried Just Department of Mathematics, Ohio University April 9 11, 2018 Review: Eigenvectors and left eigenvectors
Lecture 31: Some Applications of Eigenvectors: Markov Chains and Chemical Reaction Systems Winfried Just Department of Mathematics, Ohio University April 9 11, 2018 Review: Eigenvectors and left eigenvectors
Chapter 14. From Randomness to Probability. Copyright 2012, 2008, 2005 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 14 From Randomness to Probability Copyright 2012, 2008, 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Dealing with Random Phenomena A random phenomenon is a situation in which we know what outcomes could happen,
Chapter 14 From Randomness to Probability Copyright 2012, 2008, 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Dealing with Random Phenomena A random phenomenon is a situation in which we know what outcomes could happen,
Solutions to Selected Questions from Denis Sevee s Vector Geometry. (Updated )
 Solutions to Selected Questions from Denis Sevee s Vector Geometry. (Updated 24--27) Denis Sevee s Vector Geometry notes appear as Chapter 5 in the current custom textbook used at John Abbott College for
Solutions to Selected Questions from Denis Sevee s Vector Geometry. (Updated 24--27) Denis Sevee s Vector Geometry notes appear as Chapter 5 in the current custom textbook used at John Abbott College for
Chapter 2. Ma 322 Fall Ma 322. Sept 23-27
 Chapter 2 Ma 322 Fall 2013 Ma 322 Sept 23-27 Summary ˆ Matrices and their Operations. ˆ Special matrices: Zero, Square, Identity. ˆ Elementary Matrices, Permutation Matrices. ˆ Voodoo Principle. What is
Chapter 2 Ma 322 Fall 2013 Ma 322 Sept 23-27 Summary ˆ Matrices and their Operations. ˆ Special matrices: Zero, Square, Identity. ˆ Elementary Matrices, Permutation Matrices. ˆ Voodoo Principle. What is
Announcements Wednesday, October 25
 Announcements Wednesday, October 25 The midterm will be returned in recitation on Friday. The grade breakdown is posted on Piazza. You can pick it up from me in office hours before then. Keep tabs on your
Announcements Wednesday, October 25 The midterm will be returned in recitation on Friday. The grade breakdown is posted on Piazza. You can pick it up from me in office hours before then. Keep tabs on your
THE NULLSPACE OF A: SOLVING AX = 0 3.2
 32 The Nullspace of A: Solving Ax = 0 11 THE NULLSPACE OF A: SOLVING AX = 0 32 This section is about the space of solutions to Ax = 0 The matrix A can be square or rectangular One immediate solution is
32 The Nullspace of A: Solving Ax = 0 11 THE NULLSPACE OF A: SOLVING AX = 0 32 This section is about the space of solutions to Ax = 0 The matrix A can be square or rectangular One immediate solution is
1 Last time: determinants
 1 Last time: determinants Let n be a positive integer If A is an n n matrix, then its determinant is the number det A = Π(X, A)( 1) inv(x) X S n where S n is the set of n n permutation matrices Π(X, A)
1 Last time: determinants Let n be a positive integer If A is an n n matrix, then its determinant is the number det A = Π(X, A)( 1) inv(x) X S n where S n is the set of n n permutation matrices Π(X, A)
Bayesian Networks 3 D-separation. D-separation
 ayesian Networks 3 D-separation 1 D-separation iven a graph, we would like to read off independencies The converse is easier to think about: when does an independence statement not hold? g. when can X
ayesian Networks 3 D-separation 1 D-separation iven a graph, we would like to read off independencies The converse is easier to think about: when does an independence statement not hold? g. when can X
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2009
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2009 Lecture 14: Bayes Nets 10/13/2009 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Announcements Assignments P3 due yesterday W2 due Thursday W1 returned in front (after lecture) Midterm
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2009 Lecture 14: Bayes Nets 10/13/2009 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Announcements Assignments P3 due yesterday W2 due Thursday W1 returned in front (after lecture) Midterm
P (A) = P (B) = P (C) = P (D) =
 STAT 145 CHAPTER 12 - PROBABILITY - STUDENT VERSION The probability of a random event, is the proportion of times the event will occur in a large number of repititions. For example, when flipping a coin,
STAT 145 CHAPTER 12 - PROBABILITY - STUDENT VERSION The probability of a random event, is the proportion of times the event will occur in a large number of repititions. For example, when flipping a coin,
Dot Products, Transposes, and Orthogonal Projections
 Dot Products, Transposes, and Orthogonal Projections David Jekel November 13, 2015 Properties of Dot Products Recall that the dot product or standard inner product on R n is given by x y = x 1 y 1 + +
Dot Products, Transposes, and Orthogonal Projections David Jekel November 13, 2015 Properties of Dot Products Recall that the dot product or standard inner product on R n is given by x y = x 1 y 1 + +
Exam 2 Solutions. (a) Is W closed under addition? Why or why not? W is not closed under addition. For example,
 Exam 2 Solutions. Let V be the set of pairs of real numbers (x, y). Define the following operations on V : (x, y) (x, y ) = (x + x, xx + yy ) r (x, y) = (rx, y) Check if V together with and satisfy properties
Exam 2 Solutions. Let V be the set of pairs of real numbers (x, y). Define the following operations on V : (x, y) (x, y ) = (x + x, xx + yy ) r (x, y) = (rx, y) Check if V together with and satisfy properties
Chapter 4. Solving Systems of Equations. Chapter 4
 Solving Systems of Equations 3 Scenarios for Solutions There are three general situations we may find ourselves in when attempting to solve systems of equations: 1 The system could have one unique solution.
Solving Systems of Equations 3 Scenarios for Solutions There are three general situations we may find ourselves in when attempting to solve systems of equations: 1 The system could have one unique solution.
The Matrix Vector Product and the Matrix Product
 The Matrix Vector Product and the Matrix Product As we have seen a matrix is just a rectangular array of scalars (real numbers) The size of a matrix indicates its number of rows and columns A matrix with
The Matrix Vector Product and the Matrix Product As we have seen a matrix is just a rectangular array of scalars (real numbers) The size of a matrix indicates its number of rows and columns A matrix with
PageRank: The Math-y Version (Or, What To Do When You Can t Tear Up Little Pieces of Paper)
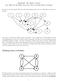 PageRank: The Math-y Version (Or, What To Do When You Can t Tear Up Little Pieces of Paper) In class, we saw this graph, with each node representing people who are following each other on Twitter: Our
PageRank: The Math-y Version (Or, What To Do When You Can t Tear Up Little Pieces of Paper) In class, we saw this graph, with each node representing people who are following each other on Twitter: Our
Class President: A Network Approach to Popularity. Due July 18, 2014
 Class President: A Network Approach to Popularity Due July 8, 24 Instructions. Due Fri, July 8 at :59 PM 2. Work in groups of up to 3 3. Type up the report, and submit as a pdf on D2L 4. Attach the code
Class President: A Network Approach to Popularity Due July 8, 24 Instructions. Due Fri, July 8 at :59 PM 2. Work in groups of up to 3 3. Type up the report, and submit as a pdf on D2L 4. Attach the code
Sequential Circuit Analysis
 Sequential Circuit Analysis Last time we started talking about latches and flip-flops, which are basic one-bit memory units. Today we ll talk about sequential circuit analysis and design. First, we ll
Sequential Circuit Analysis Last time we started talking about latches and flip-flops, which are basic one-bit memory units. Today we ll talk about sequential circuit analysis and design. First, we ll
Markov Chains. CS70 Summer Lecture 6B. David Dinh 26 July UC Berkeley
 Markov Chains CS70 Summer 2016 - Lecture 6B David Dinh 26 July 2016 UC Berkeley Agenda Quiz is out! Due: Friday at noon. What are Markov Chains? State machine and matrix representations. Hitting Time 1
Markov Chains CS70 Summer 2016 - Lecture 6B David Dinh 26 July 2016 UC Berkeley Agenda Quiz is out! Due: Friday at noon. What are Markov Chains? State machine and matrix representations. Hitting Time 1
Notes on Mathematics Groups
 EPGY Singapore Quantum Mechanics: 2007 Notes on Mathematics Groups A group, G, is defined is a set of elements G and a binary operation on G; one of the elements of G has particularly special properties
EPGY Singapore Quantum Mechanics: 2007 Notes on Mathematics Groups A group, G, is defined is a set of elements G and a binary operation on G; one of the elements of G has particularly special properties
IEOR 6711: Professor Whitt. Introduction to Markov Chains
 IEOR 6711: Professor Whitt Introduction to Markov Chains 1. Markov Mouse: The Closed Maze We start by considering how to model a mouse moving around in a maze. The maze is a closed space containing nine
IEOR 6711: Professor Whitt Introduction to Markov Chains 1. Markov Mouse: The Closed Maze We start by considering how to model a mouse moving around in a maze. The maze is a closed space containing nine
Linear Algebra review Powers of a diagonalizable matrix Spectral decomposition
 Linear Algebra review Powers of a diagonalizable matrix Spectral decomposition Prof. Tesler Math 283 Fall 2016 Also see the separate version of this with Matlab and R commands. Prof. Tesler Diagonalizing
Linear Algebra review Powers of a diagonalizable matrix Spectral decomposition Prof. Tesler Math 283 Fall 2016 Also see the separate version of this with Matlab and R commands. Prof. Tesler Diagonalizing
Algebra 8.6 Simple Equations
 Algebra 8.6 Simple Equations 1. Introduction Let s talk about the truth: 2 = 2 This is a true statement What else can we say about 2 that is true? Eample 1 2 = 2 1+ 1= 2 2 1= 2 4 1 = 2 2 4 2 = 2 4 = 4
Algebra 8.6 Simple Equations 1. Introduction Let s talk about the truth: 2 = 2 This is a true statement What else can we say about 2 that is true? Eample 1 2 = 2 1+ 1= 2 2 1= 2 4 1 = 2 2 4 2 = 2 4 = 4
Lecture 10: Powers of Matrices, Difference Equations
 Lecture 10: Powers of Matrices, Difference Equations Difference Equations A difference equation, also sometimes called a recurrence equation is an equation that defines a sequence recursively, i.e. each
Lecture 10: Powers of Matrices, Difference Equations Difference Equations A difference equation, also sometimes called a recurrence equation is an equation that defines a sequence recursively, i.e. each
STA Module 4 Probability Concepts. Rev.F08 1
 STA 2023 Module 4 Probability Concepts Rev.F08 1 Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Compute probabilities for experiments having equally likely outcomes. 2. Interpret
STA 2023 Module 4 Probability Concepts Rev.F08 1 Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Compute probabilities for experiments having equally likely outcomes. 2. Interpret
Synchronous Sequential Circuit Design
 Synchronous Sequential Circuit Design 1 Sequential circuit design In sequential circuit design, we turn some description into a working circuit We first make a state table or diagram to express the computation
Synchronous Sequential Circuit Design 1 Sequential circuit design In sequential circuit design, we turn some description into a working circuit We first make a state table or diagram to express the computation
Section 29: What s an Inverse?
 Section 29: What s an Inverse? Our investigations in the last section showed that all of the matrix operations had an identity element. The identity element for addition is, for obvious reasons, called
Section 29: What s an Inverse? Our investigations in the last section showed that all of the matrix operations had an identity element. The identity element for addition is, for obvious reasons, called
Answers in blue. If you have questions or spot an error, let me know. 1. Find all matrices that commute with A =. 4 3
 Answers in blue. If you have questions or spot an error, let me know. 3 4. Find all matrices that commute with A =. 4 3 a b If we set B = and set AB = BA, we see that 3a + 4b = 3a 4c, 4a + 3b = 3b 4d,
Answers in blue. If you have questions or spot an error, let me know. 3 4. Find all matrices that commute with A =. 4 3 a b If we set B = and set AB = BA, we see that 3a + 4b = 3a 4c, 4a + 3b = 3b 4d,
RECURSION EQUATION FOR
 Math 46 Lecture 8 Infinite Horizon discounted reward problem From the last lecture: The value function of policy u for the infinite horizon problem with discount factor a and initial state i is W i, u
Math 46 Lecture 8 Infinite Horizon discounted reward problem From the last lecture: The value function of policy u for the infinite horizon problem with discount factor a and initial state i is W i, u
Algebra Year 10. Language
 Algebra Year 10 Introduction In Algebra we do Maths with numbers, but some of those numbers are not known. They are represented with letters, and called unknowns, variables or, most formally, literals.
Algebra Year 10 Introduction In Algebra we do Maths with numbers, but some of those numbers are not known. They are represented with letters, and called unknowns, variables or, most formally, literals.
Markov Chains and Pandemics
 Markov Chains and Pandemics Caleb Dedmore and Brad Smith December 8, 2016 Page 1 of 16 Abstract Markov Chain Theory is a powerful tool used in statistical analysis to make predictions about future events
Markov Chains and Pandemics Caleb Dedmore and Brad Smith December 8, 2016 Page 1 of 16 Abstract Markov Chain Theory is a powerful tool used in statistical analysis to make predictions about future events
LS.1 Review of Linear Algebra
 LS. LINEAR SYSTEMS LS.1 Review of Linear Algebra In these notes, we will investigate a way of handling a linear system of ODE s directly, instead of using elimination to reduce it to a single higher-order
LS. LINEAR SYSTEMS LS.1 Review of Linear Algebra In these notes, we will investigate a way of handling a linear system of ODE s directly, instead of using elimination to reduce it to a single higher-order
Systems of equation and matrices
 Systems of equation and matrices Jean-Luc Bouchot jean-luc.bouchot@drexel.edu February 23, 2013 Warning This is a work in progress. I can not ensure it to be mistake free at the moment. It is also lacking
Systems of equation and matrices Jean-Luc Bouchot jean-luc.bouchot@drexel.edu February 23, 2013 Warning This is a work in progress. I can not ensure it to be mistake free at the moment. It is also lacking
MAT Mathematics in Today's World
 MAT 1000 Mathematics in Today's World Last Time We discussed the four rules that govern probabilities: 1. Probabilities are numbers between 0 and 1 2. The probability an event does not occur is 1 minus
MAT 1000 Mathematics in Today's World Last Time We discussed the four rules that govern probabilities: 1. Probabilities are numbers between 0 and 1 2. The probability an event does not occur is 1 minus
Section 6.3. Matrices and Systems of Equations
 Section 6.3 Matrices and Systems of Equations Introduction Definitions A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers. Definitions A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers. For example: [ 4 7 π 3 2 5 Definitions
Section 6.3 Matrices and Systems of Equations Introduction Definitions A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers. Definitions A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers. For example: [ 4 7 π 3 2 5 Definitions
The matrix will only be consistent if the last entry of row three is 0, meaning 2b 3 + b 2 b 1 = 0.
 ) Find all solutions of the linear system. Express the answer in vector form. x + 2x + x + x 5 = 2 2x 2 + 2x + 2x + x 5 = 8 x + 2x + x + 9x 5 = 2 2 Solution: Reduce the augmented matrix [ 2 2 2 8 ] to
) Find all solutions of the linear system. Express the answer in vector form. x + 2x + x + x 5 = 2 2x 2 + 2x + 2x + x 5 = 8 x + 2x + x + 9x 5 = 2 2 Solution: Reduce the augmented matrix [ 2 2 2 8 ] to
Math 54 HW 4 solutions
 Math 54 HW 4 solutions 2.2. Section 2.2 (a) False: Recall that performing a series of elementary row operations A is equivalent to multiplying A by a series of elementary matrices. Suppose that E,...,
Math 54 HW 4 solutions 2.2. Section 2.2 (a) False: Recall that performing a series of elementary row operations A is equivalent to multiplying A by a series of elementary matrices. Suppose that E,...,
Getting Started with Communications Engineering
 1 Linear algebra is the algebra of linear equations: the term linear being used in the same sense as in linear functions, such as: which is the equation of a straight line. y ax c (0.1) Of course, if we
1 Linear algebra is the algebra of linear equations: the term linear being used in the same sense as in linear functions, such as: which is the equation of a straight line. y ax c (0.1) Of course, if we
Math Lecture 26 : The Properties of Determinants
 Math 2270 - Lecture 26 : The Properties of Determinants Dylan Zwick Fall 202 The lecture covers section 5. from the textbook. The determinant of a square matrix is a number that tells you quite a bit about
Math 2270 - Lecture 26 : The Properties of Determinants Dylan Zwick Fall 202 The lecture covers section 5. from the textbook. The determinant of a square matrix is a number that tells you quite a bit about
Markov Chains Handout for Stat 110
 Markov Chains Handout for Stat 0 Prof. Joe Blitzstein (Harvard Statistics Department) Introduction Markov chains were first introduced in 906 by Andrey Markov, with the goal of showing that the Law of
Markov Chains Handout for Stat 0 Prof. Joe Blitzstein (Harvard Statistics Department) Introduction Markov chains were first introduced in 906 by Andrey Markov, with the goal of showing that the Law of
MITOCW ocw f99-lec05_300k
 MITOCW ocw-18.06-f99-lec05_300k This is lecture five in linear algebra. And, it will complete this chapter of the book. So the last section of this chapter is two point seven that talks about permutations,
MITOCW ocw-18.06-f99-lec05_300k This is lecture five in linear algebra. And, it will complete this chapter of the book. So the last section of this chapter is two point seven that talks about permutations,
MATH Mathematics for Agriculture II
 MATH 10240 Mathematics for Agriculture II Academic year 2018 2019 UCD School of Mathematics and Statistics Contents Chapter 1. Linear Algebra 1 1. Introduction to Matrices 1 2. Matrix Multiplication 3
MATH 10240 Mathematics for Agriculture II Academic year 2018 2019 UCD School of Mathematics and Statistics Contents Chapter 1. Linear Algebra 1 1. Introduction to Matrices 1 2. Matrix Multiplication 3
Solution Set 3, Fall '12
 Solution Set 3, 86 Fall '2 Do Problem 5 from 32 [ 3 5 Solution (a) A = Only one elimination step is needed to produce the 2 6 echelon form The pivot is the in row, column, and the entry to eliminate is
Solution Set 3, 86 Fall '2 Do Problem 5 from 32 [ 3 5 Solution (a) A = Only one elimination step is needed to produce the 2 6 echelon form The pivot is the in row, column, and the entry to eliminate is
Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Systems of Linear Equations
 What is a linear equation? Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Systems of Linear Equations We are now going to discuss solving systems of two or more linear equations with two variables. Recall that solving an equation
What is a linear equation? Sections 6.1 and 6.2: Systems of Linear Equations We are now going to discuss solving systems of two or more linear equations with two variables. Recall that solving an equation
Probabilistic Models
 Bayes Nets 1 Probabilistic Models Models describe how (a portion of) the world works Models are always simplifications May not account for every variable May not account for all interactions between variables
Bayes Nets 1 Probabilistic Models Models describe how (a portion of) the world works Models are always simplifications May not account for every variable May not account for all interactions between variables
To factor an expression means to write it as a product of factors instead of a sum of terms. The expression 3x
 Factoring trinomials In general, we are factoring ax + bx + c where a, b, and c are real numbers. To factor an expression means to write it as a product of factors instead of a sum of terms. The expression
Factoring trinomials In general, we are factoring ax + bx + c where a, b, and c are real numbers. To factor an expression means to write it as a product of factors instead of a sum of terms. The expression
Lecture 2. When we studied dimensional analysis in the last lecture, I defined speed. The average speed for a traveling object is quite simply
 Lecture 2 Speed Displacement Average velocity Instantaneous velocity Cutnell+Johnson: chapter 2.1-2.2 Most physics classes start by studying the laws describing how things move around. This study goes
Lecture 2 Speed Displacement Average velocity Instantaneous velocity Cutnell+Johnson: chapter 2.1-2.2 Most physics classes start by studying the laws describing how things move around. This study goes
Announcements Wednesday, August 30
 Announcements Wednesday, August 30 WeBWorK due on Friday at 11:59pm. The first quiz is on Friday, during recitation. It covers through Monday s material. Quizzes mostly test your understanding of the homework.
Announcements Wednesday, August 30 WeBWorK due on Friday at 11:59pm. The first quiz is on Friday, during recitation. It covers through Monday s material. Quizzes mostly test your understanding of the homework.
Markov chains and the number of occurrences of a word in a sequence ( , 11.1,2,4,6)
 Markov chains and the number of occurrences of a word in a sequence (4.5 4.9,.,2,4,6) Prof. Tesler Math 283 Fall 208 Prof. Tesler Markov Chains Math 283 / Fall 208 / 44 Locating overlapping occurrences
Markov chains and the number of occurrences of a word in a sequence (4.5 4.9,.,2,4,6) Prof. Tesler Math 283 Fall 208 Prof. Tesler Markov Chains Math 283 / Fall 208 / 44 Locating overlapping occurrences
Determinants and Scalar Multiplication
 Properties of Determinants In the last section, we saw how determinants interact with the elementary row operations. There are other operations on matrices, though, such as scalar multiplication, matrix
Properties of Determinants In the last section, we saw how determinants interact with the elementary row operations. There are other operations on matrices, though, such as scalar multiplication, matrix
Roberto s Notes on Linear Algebra Chapter 4: Matrix Algebra Section 4. Matrix products
 Roberto s Notes on Linear Algebra Chapter 4: Matrix Algebra Section 4 Matrix products What you need to know already: The dot product of vectors Basic matrix operations. Special types of matrices What you
Roberto s Notes on Linear Algebra Chapter 4: Matrix Algebra Section 4 Matrix products What you need to know already: The dot product of vectors Basic matrix operations. Special types of matrices What you
12. Perturbed Matrices
 MAT334 : Applied Linear Algebra Mike Newman, winter 208 2. Perturbed Matrices motivation We want to solve a system Ax = b in a context where A and b are not known exactly. There might be experimental errors,
MAT334 : Applied Linear Algebra Mike Newman, winter 208 2. Perturbed Matrices motivation We want to solve a system Ax = b in a context where A and b are not known exactly. There might be experimental errors,
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Lecture 14: Bayes Nets 10/14/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley 1 1 Announcements Midterm 10/21! One page note sheet Review sessions Friday and Sunday (similar) OHs on
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Lecture 14: Bayes Nets 10/14/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley 1 1 Announcements Midterm 10/21! One page note sheet Review sessions Friday and Sunday (similar) OHs on
Finite Mathematics : A Business Approach
 Finite Mathematics : A Business Approach Dr. Brian Travers and Prof. James Lampes Second Edition Cover Art by Stephanie Oxenford Additional Editing by John Gambino Contents What You Should Already Know
Finite Mathematics : A Business Approach Dr. Brian Travers and Prof. James Lampes Second Edition Cover Art by Stephanie Oxenford Additional Editing by John Gambino Contents What You Should Already Know
Algebra Year 9. Language
 Algebra Year 9 Introduction In Algebra we do Maths with numbers, but some of those numbers are not known. They are represented with letters, and called unknowns, variables or, most formally, literals.
Algebra Year 9 Introduction In Algebra we do Maths with numbers, but some of those numbers are not known. They are represented with letters, and called unknowns, variables or, most formally, literals.
SECTION 2.3: LONG AND SYNTHETIC POLYNOMIAL DIVISION
 2.25 SECTION 2.3: LONG AND SYNTHETIC POLYNOMIAL DIVISION PART A: LONG DIVISION Ancient Example with Integers 2 4 9 8 1 In general: dividend, f divisor, d We can say: 9 4 = 2 + 1 4 By multiplying both sides
2.25 SECTION 2.3: LONG AND SYNTHETIC POLYNOMIAL DIVISION PART A: LONG DIVISION Ancient Example with Integers 2 4 9 8 1 In general: dividend, f divisor, d We can say: 9 4 = 2 + 1 4 By multiplying both sides
Linear Algebra review Powers of a diagonalizable matrix Spectral decomposition
 Linear Algebra review Powers of a diagonalizable matrix Spectral decomposition Prof. Tesler Math 283 Fall 2018 Also see the separate version of this with Matlab and R commands. Prof. Tesler Diagonalizing
Linear Algebra review Powers of a diagonalizable matrix Spectral decomposition Prof. Tesler Math 283 Fall 2018 Also see the separate version of this with Matlab and R commands. Prof. Tesler Diagonalizing
Exercise Set Suppose that A, B, C, D, and E are matrices with the following sizes: A B C D E
 Determine the size of a given matrix. Identify the row vectors and column vectors of a given matrix. Perform the arithmetic operations of matrix addition, subtraction, scalar multiplication, and multiplication.
Determine the size of a given matrix. Identify the row vectors and column vectors of a given matrix. Perform the arithmetic operations of matrix addition, subtraction, scalar multiplication, and multiplication.
Announcements Wednesday, August 30
 Announcements Wednesday, August 30 WeBWorK due on Friday at 11:59pm. The first quiz is on Friday, during recitation. It covers through Monday s material. Quizzes mostly test your understanding of the homework.
Announcements Wednesday, August 30 WeBWorK due on Friday at 11:59pm. The first quiz is on Friday, during recitation. It covers through Monday s material. Quizzes mostly test your understanding of the homework.
Confidence Intervals. - simply, an interval for which we have a certain confidence.
 Confidence Intervals I. What are confidence intervals? - simply, an interval for which we have a certain confidence. - for example, we are 90% certain that an interval contains the true value of something
Confidence Intervals I. What are confidence intervals? - simply, an interval for which we have a certain confidence. - for example, we are 90% certain that an interval contains the true value of something
Roberto s Notes on Linear Algebra Chapter 9: Orthogonality Section 2. Orthogonal matrices
 Roberto s Notes on Linear Algebra Chapter 9: Orthogonality Section 2 Orthogonal matrices What you need to know already: What orthogonal and orthonormal bases for subspaces are. What you can learn here:
Roberto s Notes on Linear Algebra Chapter 9: Orthogonality Section 2 Orthogonal matrices What you need to know already: What orthogonal and orthonormal bases for subspaces are. What you can learn here:
MATH 118 FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE
 MATH 118 FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE Recommendations: 1. Take the Final Practice Exam and take note of questions 2. Use this study guide as you take the tests and cross off what you know well 3. Take the Practice
MATH 118 FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE Recommendations: 1. Take the Final Practice Exam and take note of questions 2. Use this study guide as you take the tests and cross off what you know well 3. Take the Practice
Chapter 1 Review of Equations and Inequalities
 Chapter 1 Review of Equations and Inequalities Part I Review of Basic Equations Recall that an equation is an expression with an equal sign in the middle. Also recall that, if a question asks you to solve
Chapter 1 Review of Equations and Inequalities Part I Review of Basic Equations Recall that an equation is an expression with an equal sign in the middle. Also recall that, if a question asks you to solve
Chapter 1: Systems of linear equations and matrices. Section 1.1: Introduction to systems of linear equations
 Chapter 1: Systems of linear equations and matrices Section 1.1: Introduction to systems of linear equations Definition: A linear equation in n variables can be expressed in the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2
Chapter 1: Systems of linear equations and matrices Section 1.1: Introduction to systems of linear equations Definition: A linear equation in n variables can be expressed in the form a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2
Latches. October 13, 2003 Latches 1
 Latches The second part of CS231 focuses on sequential circuits, where we add memory to the hardware that we ve already seen. Our schedule will be very similar to before: We first show how primitive memory
Latches The second part of CS231 focuses on sequential circuits, where we add memory to the hardware that we ve already seen. Our schedule will be very similar to before: We first show how primitive memory
Week-5. Sequential Circuit Design. Acknowledgement: Most of the following slides are adapted from Prof. Kale's slides at UIUC, USA.
 Week-5 Sequential Circuit Design Acknowledgement: Most of the following slides are adapted from Prof. Kale's slides at UIUC, USA. Storing a value: SR = 00 What if S = 0 and R = 0? The equations on the
Week-5 Sequential Circuit Design Acknowledgement: Most of the following slides are adapted from Prof. Kale's slides at UIUC, USA. Storing a value: SR = 00 What if S = 0 and R = 0? The equations on the
Steve Smith Tuition: Maths Notes
 Maths Notes : Discrete Random Variables Version. Steve Smith Tuition: Maths Notes e iπ + = 0 a + b = c z n+ = z n + c V E + F = Discrete Random Variables Contents Intro The Distribution of Probabilities
Maths Notes : Discrete Random Variables Version. Steve Smith Tuition: Maths Notes e iπ + = 0 a + b = c z n+ = z n + c V E + F = Discrete Random Variables Contents Intro The Distribution of Probabilities
base 2 4 The EXPONENT tells you how many times to write the base as a factor. Evaluate the following expressions in standard notation.
 EXPONENTIALS Exponential is a number written with an exponent. The rules for exponents make computing with very large or very small numbers easier. Students will come across exponentials in geometric sequences
EXPONENTIALS Exponential is a number written with an exponent. The rules for exponents make computing with very large or very small numbers easier. Students will come across exponentials in geometric sequences
P (E) = P (A 1 )P (A 2 )... P (A n ).
 Lecture 9: Conditional probability II: breaking complex events into smaller events, methods to solve probability problems, Bayes rule, law of total probability, Bayes theorem Discrete Structures II (Summer
Lecture 9: Conditional probability II: breaking complex events into smaller events, methods to solve probability problems, Bayes rule, law of total probability, Bayes theorem Discrete Structures II (Summer
Stochastic Processes
 qmc082.tex. Version of 30 September 2010. Lecture Notes on Quantum Mechanics No. 8 R. B. Griffiths References: Stochastic Processes CQT = R. B. Griffiths, Consistent Quantum Theory (Cambridge, 2002) DeGroot
qmc082.tex. Version of 30 September 2010. Lecture Notes on Quantum Mechanics No. 8 R. B. Griffiths References: Stochastic Processes CQT = R. B. Griffiths, Consistent Quantum Theory (Cambridge, 2002) DeGroot
MAC Module 2 Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices II. Learning Objectives. Upon completing this module, you should be able to :
 MAC 0 Module Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices II Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to :. Find the inverse of a square matrix.. Determine whether a matrix is invertible..
MAC 0 Module Systems of Linear Equations and Matrices II Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to :. Find the inverse of a square matrix.. Determine whether a matrix is invertible..
I&C 6N. Computational Linear Algebra
 I&C 6N Computational Linear Algebra 1 Lecture 1: Scalars and Vectors What is a scalar? Computer representation of a scalar Scalar Equality Scalar Operations Addition and Multiplication What is a vector?
I&C 6N Computational Linear Algebra 1 Lecture 1: Scalars and Vectors What is a scalar? Computer representation of a scalar Scalar Equality Scalar Operations Addition and Multiplication What is a vector?
Solutions to Exam I MATH 304, section 6
 Solutions to Exam I MATH 304, section 6 YOU MUST SHOW ALL WORK TO GET CREDIT. Problem 1. Let A = 1 2 5 6 1 2 5 6 3 2 0 0 1 3 1 1 2 0 1 3, B =, C =, I = I 0 0 0 1 1 3 4 = 4 4 identity matrix. 3 1 2 6 0
Solutions to Exam I MATH 304, section 6 YOU MUST SHOW ALL WORK TO GET CREDIT. Problem 1. Let A = 1 2 5 6 1 2 5 6 3 2 0 0 1 3 1 1 2 0 1 3, B =, C =, I = I 0 0 0 1 1 3 4 = 4 4 identity matrix. 3 1 2 6 0
Matrices, Row Reduction of Matrices
 Matrices, Row Reduction of Matrices October 9, 014 1 Row Reduction and Echelon Forms In the previous section, we saw a procedure for solving systems of equations It is simple in that it consists of only
Matrices, Row Reduction of Matrices October 9, 014 1 Row Reduction and Echelon Forms In the previous section, we saw a procedure for solving systems of equations It is simple in that it consists of only
A primer on matrices
 A primer on matrices Stephen Boyd August 4, 2007 These notes describe the notation of matrices, the mechanics of matrix manipulation, and how to use matrices to formulate and solve sets of simultaneous
A primer on matrices Stephen Boyd August 4, 2007 These notes describe the notation of matrices, the mechanics of matrix manipulation, and how to use matrices to formulate and solve sets of simultaneous
Sometimes the domains X and Z will be the same, so this might be written:
 II. MULTIVARIATE CALCULUS The first lecture covered functions where a single input goes in, and a single output comes out. Most economic applications aren t so simple. In most cases, a number of variables
II. MULTIVARIATE CALCULUS The first lecture covered functions where a single input goes in, and a single output comes out. Most economic applications aren t so simple. In most cases, a number of variables
18.06 Problem Set 3 Due Wednesday, 27 February 2008 at 4 pm in
 8.6 Problem Set 3 Due Wednesday, 27 February 28 at 4 pm in 2-6. Problem : Do problem 7 from section 2.7 (pg. 5) in the book. Solution (2+3+3+2 points) a) False. One example is when A = [ ] 2. 3 4 b) False.
8.6 Problem Set 3 Due Wednesday, 27 February 28 at 4 pm in 2-6. Problem : Do problem 7 from section 2.7 (pg. 5) in the book. Solution (2+3+3+2 points) a) False. One example is when A = [ ] 2. 3 4 b) False.
Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
 Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors MAT 67L, Laboratory III Contents Instructions (1) Read this document. (2) The questions labeled Experiments are not graded, and should not be turned in. They are designed for
Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors MAT 67L, Laboratory III Contents Instructions (1) Read this document. (2) The questions labeled Experiments are not graded, and should not be turned in. They are designed for
Proofs, Strings, and Finite Automata. CS154 Chris Pollett Feb 5, 2007.
 Proofs, Strings, and Finite Automata CS154 Chris Pollett Feb 5, 2007. Outline Proofs and Proof Strategies Strings Finding proofs Example: For every graph G, the sum of the degrees of all the nodes in G
Proofs, Strings, and Finite Automata CS154 Chris Pollett Feb 5, 2007. Outline Proofs and Proof Strategies Strings Finding proofs Example: For every graph G, the sum of the degrees of all the nodes in G
MAT 1302B Mathematical Methods II
 MAT 1302B Mathematical Methods II Alistair Savage Mathematics and Statistics University of Ottawa Winter 2015 Lecture 19 Alistair Savage (uottawa) MAT 1302B Mathematical Methods II Winter 2015 Lecture
MAT 1302B Mathematical Methods II Alistair Savage Mathematics and Statistics University of Ottawa Winter 2015 Lecture 19 Alistair Savage (uottawa) MAT 1302B Mathematical Methods II Winter 2015 Lecture
Eigenvalues and eigenvectors
 Roberto s Notes on Linear Algebra Chapter 0: Eigenvalues and diagonalization Section Eigenvalues and eigenvectors What you need to know already: Basic properties of linear transformations. Linear systems
Roberto s Notes on Linear Algebra Chapter 0: Eigenvalues and diagonalization Section Eigenvalues and eigenvectors What you need to know already: Basic properties of linear transformations. Linear systems
Chapter 29 out of 37 from Discrete Mathematics for Neophytes: Number Theory, Probability, Algorithms, and Other Stuff by J. M.
 29 Markov Chains Definition of a Markov Chain Markov chains are one of the most fun tools of probability; they give a lot of power for very little effort. We will restrict ourselves to finite Markov chains.
29 Markov Chains Definition of a Markov Chain Markov chains are one of the most fun tools of probability; they give a lot of power for very little effort. We will restrict ourselves to finite Markov chains.
Matrices and Vectors
 Matrices and Vectors James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University November 11, 2013 Outline 1 Matrices and Vectors 2 Vector Details 3 Matrix
Matrices and Vectors James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University November 11, 2013 Outline 1 Matrices and Vectors 2 Vector Details 3 Matrix
Probabilistic Models. Models describe how (a portion of) the world works
 Probabilistic Models Models describe how (a portion of) the world works Models are always simplifications May not account for every variable May not account for all interactions between variables All models
Probabilistic Models Models describe how (a portion of) the world works Models are always simplifications May not account for every variable May not account for all interactions between variables All models
Sec 2.1 The Real Number Line. Opposites: Two numbers that are the same distance from the origin (zero), but on opposite sides of the origin.
 Algebra 1 Chapter 2 Note Packet Name Sec 2.1 The Real Number Line Real Numbers- All the numbers on the number line, not just whole number integers (decimals, fractions and mixed numbers, square roots,
Algebra 1 Chapter 2 Note Packet Name Sec 2.1 The Real Number Line Real Numbers- All the numbers on the number line, not just whole number integers (decimals, fractions and mixed numbers, square roots,
Determinants and Scalar Multiplication
 Invertibility and Properties of Determinants In a previous section, we saw that the trace function, which calculates the sum of the diagonal entries of a square matrix, interacts nicely with the operations
Invertibility and Properties of Determinants In a previous section, we saw that the trace function, which calculates the sum of the diagonal entries of a square matrix, interacts nicely with the operations
CS 5522: Artificial Intelligence II
 CS 5522: Artificial Intelligence II Bayes Nets Instructor: Alan Ritter Ohio State University [These slides were adapted from CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley. All materials available at http://ai.berkeley.edu.]
CS 5522: Artificial Intelligence II Bayes Nets Instructor: Alan Ritter Ohio State University [These slides were adapted from CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley. All materials available at http://ai.berkeley.edu.]
Lecture 8: A Crash Course in Linear Algebra
 Math/CS 120: Intro. to Math Professor: Padraic Bartlett Lecture 8: A Crash Course in Linear Algebra Week 9 UCSB 2014 Qué sed de saber cuánto! Pablo Neruda, Oda a los Números 1 Linear Algebra In the past
Math/CS 120: Intro. to Math Professor: Padraic Bartlett Lecture 8: A Crash Course in Linear Algebra Week 9 UCSB 2014 Qué sed de saber cuánto! Pablo Neruda, Oda a los Números 1 Linear Algebra In the past
Row Reduction
 Row Reduction 1-12-2015 Row reduction (or Gaussian elimination) is the process of using row operations to reduce a matrix to row reduced echelon form This procedure is used to solve systems of linear equations,
Row Reduction 1-12-2015 Row reduction (or Gaussian elimination) is the process of using row operations to reduce a matrix to row reduced echelon form This procedure is used to solve systems of linear equations,
