Working Mathematically SAMPLE ACTIVITIES. for the Stage 4 Mathematics Syllabus
|
|
|
- Alexander Thomas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Working Mathematically SAMPLE ACTIVITIES for the Stage 4 Mathematics Syllabus
2 NS4.2 Number Part A Activity 3-2 The size of a number The temperature felt by bare skin is determined not only by the temperature of the air but also by the speed of the wind. This temperature is called the wind chill. The table below shows how wind chill (measured in C) varies with air temperature and wind speed. Wind speed (km/h) Air temperature ( C) When a cross-country skier set out from the clubhouse one morning, the air temperature was -35 C and the wind speed was 10 km/h. What was the wind chill when he set out? In the afternoon, the air temperature rose by 5 C and the wind speed rose by 30 km/h. What was the wind chill then? Mark this number line with the morning and afternoon wind chill: Did the wind chill rise or fall? In some places, people need to know changes in temperature and wind speed to avoid being frostbitten. At this Golf and Country Club, people go cross-country skiing in the winter but sometimes it can get too dangerous to be outside. Use the number line below to find the difference between the following temperatures: 1) 0.2 C and 3.2 C = 3) -0.2 C and -3.2 C = 2) -0.2 C and 3.2 C = 4) 0.2 C and -3.2 C = , McMaster & Mitchelmore 35 ISBN
3 NS4.2 Number Part A Activity 3-3 Patterns in times tables Below is the 3 times table and a column graph of this times table. The horizontal axis (across) shows the number that is multiplied by 3. The vertical axis (up and down) shows the answer to the multiplication. Rule a line that goes through the end point of each column in the graph below. The relationship between the number that is multiplied and the result of the multiplication is a linear relationship because the results lie in a straight line. 3 x 1 = 3 3 x 2 = 6 3 x 3 = 9 3 x 4 =12 3 x 5 =15 3 x 6 =18 3 x 7 = 21 3 x 8 = 24 3 x 9 = 27 3 x10= 30 3 x11= 33 3 x12= 36 Result Number multiplied by 3 Why do the answers to the multiplications above keep going up by 3? Write answers to each multiplication below. Then graph your results. 4 x 5 = 4 x 4 = 4 x 3 = 4 x 2 = 4 x 1 = 4 x 0 = 4 x (-1) = 4 x (-2) = 4 x (-3) = 4 x (-4) = 4 x (-5) = The answers to the multiplications above keep going down by 4. Why do you think they do this? , McMaster & Mitchelmore 49 ISBN
4 NS4.2 Number Part A Activity 3-3 Answer these multiplications: 3 x 5 = 5 x 3 = 4 x (-5) = (-5) x 4 = Does the order of the two numbers being multiplied matter? Use this fact to answer the multiplications below. Then graph your results. (-5) x 5 = (-5) x 4 = (-5) x 3 = (-5) x 2 = (-5) x 1 = (-5) x 0 = (-5) x (-1) = (-5) x (-2) = (-5) x (-3) = (-5) x (-4) = (-5) x (-5) = In the (-5) times table above, the numbers keep going The opposite of multiplication is division. (-5) x 4 = (-20) so (-20) 4 = and (-20) (-5) = (-5) x (-4) = so 20 (-4) = and 20 (-5) = by Complete the following sentences by writing positive or negative. When a positive number is multiplied or divided by a positive number, the answer is a number. When a positive number is multiplied or divided by a negative number, the answer is a number. When a negative number is multiplied or divided by a positive number, the answer is a number. When a negative number is multiplied or divided by a negative number, the answer is a number. Answer the following questions. 1) (-4) + 4 = 5) (-4) x 4 = 9) (-4) 4 = 2) (-4) - 4 = 6) 4(-4) = 10) (-4) (-4) = 3) (-4) - (-4) = 7) (-4) x (-4) = 11) 4 x (-4) (-4) = 4) (-4) + (-4) = 8) 4 (-4) = 12) (-4) x (-4) x (-4) = 2008, McMaster & Mitchelmore 50 ISBN
5 NS4.2 Number Part A Activity 3-3 Make these calculations: (-1.2) x 0.5 = (-1.2) x (-0.5) = (-1.2) x 1.0 = (-1.2) x (-1.0) = (-1.2) x 1.5 = (-1.2) x (-1.5) = Plot your answers as columns on the graph below. Then rule a line that goes through the end point of each column From your graph, find the approximate values of (-1.2) x 1.4 = (-1.2) x (-1.15) = (-1.2) x 0.65 = (-1.2) x (-0.9) = Check your answers by making these calculations in the space below. 2008, McMaster & Mitchelmore 51 ISBN
6 NS4.3 Number Part A Activity 5-4 Common multiples Sand timers These are sand timers (also called hourglasses). The time they measure is the time it takes for the sand to fall from the top bulb, through the narrow tube, into the bottom bulb. Once all the sand has fallen to the bottom bulb, the timer can be quickly turned over in order to measure the same time again One of the timers measures 5 minutes. So by using it over and over again, it measures multiples of 5 minutes. Lightly shade all the boxes in this number chart that have multiples of 5 written in them. The other timer measures multiples of 7 minutes. Use a different type of shading to shade all the boxes in this chart that have multiples of 7 written in them. Circle all the numbers in the chart that have been shaded twice. If the time taken to turn over a sand timer doesn t count, what time intervals (up to 96 minutes) can be measured by either the 5 minute timer or the 7 minute timer? How could you get your answer from looking at the number chart? How could you get your answer from the numbers 5 and 7? The time intervals that can be measured by either the 5 minute timer or the 7 minute timer are common multiples of 5 and 7. A common multiple of two (or more) numbers is any number which is a multiple of all the given numbers. Write down three other common multiples of 5 and 7: How many common multiples of 5 and 7 are there? 2008, McMaster & Mitchelmore 80 ISBN
7 NS4.1 Number Part A Activity 6-4 Fractions and percentages The bar below represents one whole. One whole is 100%. Using a sharp pencil and ruler, carefully divide the height of the first bar to mark the fractions listed in the table. By ruling a line straight across to the second bar, you can then find out what each fraction is as a percentage. Write your answers (to the nearest 1%) in the table. The first fraction in the table has been done for you. 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% Fraction Percentage 10% 0% 2008, McMaster & Mitchelmore 103 ISBN
8 NS4.3 Number Part B Activity 8-1 Absolute and relative comparisons A life span is the length of a life. In wealthy countries, humans have an average life span of about 80 years. The average life span of humans and various other species are shown in the table and the column graph below. 110 Average Life Spans 100 SPECIES Average Life Span Turtles 100 Humans 80 Elephants 40 Giraffes 25 Horses 20 Cats 12 Dogs 12 Pigs 10 Rabbits 5 Age (years) Rabbits Pigs Dogs Cats Horses Giraffes Elephants Humans Turtles If a person when they reach about 40 is considered to be middle-aged, - at about what age would a turtle become middle-aged? - at about what age would a giraffe become middle-aged? - at about what age would an elephant become middle-aged? On the graph above, mark the beginning of middle-age for each species by drawing a blue line across each column. How did you decide where to put your marks? 2008, McMaster & Mitchelmore 2 ISBN
9 NS4.3 Number Part B Activity 8-1 If a girl and her horse are both 10 years old, they are the same age in an absolute sense. This is called an absolute comparison. If a girl and her horse have just reached middle-age, they are the same age in a relative sense. This is called a relative comparison. It is a relative comparison because their age is related to their life span. This 50 year old man has a 15 year old horse. In an absolute sense, which is older (the horse or the man)? On the graph on the previous page, use a pencil to: mark the position of a 15 year old horse on the horse column mark the position of a 50 year old man on the human column. Which is older in a relative sense, the horse or the man? How could you tell this by comparing fractions? How could you tell this from looking at the graph on the previous page? If a horse is 15 years old, what is its relative turtle age? what is its relative human age? what is its relative elephant age? what is its relative dog age? what is its relative pig age? What is the relative turtle age of: a 10 year old horse? a 10 year old elephant? a 10 year old pig? a 10 year old giraffe? a 10 year old human? 2008, McMaster & Mitchelmore 3 ISBN
10 NS4.3 Number Part B Activity 8-6 Inverse fractions In his job, Ken needs to carry a laptop computer with him. His current laptop is too heavy. He wants to buy something lighter. Ken s current laptop weighs 3.6 kg. He sees an advertisement for a notebook weighing 2.4 kg and a subnotebook weighing only 900 g. To compare the weight of the notebook with the weight of his laptop, Ken wrote the relationship as a fraction. Is this a relative or absolute comparison (See Activity 8-1)? Weight of notebook = 2.4 = 24 = 2 Weight of laptop So the notebook is 2 thirds of the weight of the laptop. To calculate the weight of the laptop as a fraction of the weight of the notebook, the weight of the notebook becomes the denominator. Weight of laptop = 3.6 = 36 = 3 Weight of notebook = 1 1 So the laptop is 3 halves of the weight of the notebook. 2 2 So in other words, the laptop is 1½ times the weight of the notebook. The fractions calculated above (ie. 2 and 3 ) are inverses of each other. 3 2 They are inverses because in their simplest form, the numerator of the first fraction is the denominator of the second fraction and vice versa. The inverse of a fraction is also called its reciprocal. What is the product of 2 and 3? (Hint: Multiply them together.) 3 2 Do all pairs of inverse fractions have the same product? Calculate the weight of the subnotebook as a fraction of the weight of Ken s laptop. (Note: You must use the same units for both values.) The subnotebook is of the weight of the laptop. Calculate the weight of Ken s laptop as a fraction of the weight of the subnotebook. Write this fraction in its simplest form. The laptop is times the weight of the subnotebook. (Hint: 4 = 4) , McMaster & Mitchelmore 13 ISBN
11 NS4.3 Number Part B Activity 9-6 Percentage increases and decreases Café tips Darren and Nadina work together in a café. The have agreed to share the tips they receive equally between them. One day Nadina received $25 in tips and Darren received $20 in tips. Calculate the amount that Darren received as a percentage of the amount that Nadina received. So Darren received % of what Nadina received. Calculate the amount that Nadina received as a percentage of the amount that Darren received. So Nadina received % of what Darren received. The dashed line drawn across the bar diagram shows the amount they should each have when their tips are divided equally between them. Nadina s tips: $25 Darren s tips: $20 What is the difference between Nadina s tips and Darren s tips? $ To share the tips equally between them, what amount should Nadina give Darren? $ Calculate this amount as a percentage of Nadina s tips. So Nadina s amount will decrease by % As a result of the sharing, Darren s amount increased by $. Calculate this amount as a percentage of Darren s tips. So Darren s amount will increase by % Why is the percentage decrease in Nadina s amount smaller than the percentage increase in Darren s amount? 2008, McMaster & Mitchelmore 31 ISBN
12 NS4.3 Number Part B Activity 9-6 Length and area Roy made a guinea pig cage by wiring together 4 mesh panels he found at the tip. It has a square base because the 4 side panels are all the same length. Now Roy s looking for more panels so he can make another guinea pig cage. The base of the original guinea pig cage is shown in this diagram. The sides are each 1 m long. What is the perimeter of the base? What is the area of the base? When Roy went to find some more panels, he could only find panels that were 20% longer or 20% shorter than the ones he used before. What was the length of one of the longer panels? What was the length of one of the shorter panels? If he made a square cage using the longer panels, what would be the perimeter of the base? what would be the area of the base? Compared to the original cage, calculate the percentage increase in the perimeter. 1 m calculate the percentage increase in the area of the base. If he made a square cage using the shorter panels, what would be the perimeter of the base? what would be the area of the base? Compared to the original cage, calculate the percentage decrease in the perimeter. calculate the percentage decrease in the area of the base. If the original panel had been a different length (eg 2 m instead of 1 m) and the new panels had been 20% shorter or 20% longer than this, would the percentage results be the same as your answers above? Why or why not? 2008, McMaster & Mitchelmore 32 ISBN
13 NS4.3 Number Part B Activity 10-2 Equivalent rates Gerty the garden snail always travels at a constant speed. In other words, her speed does not change. Gerty finished a 10 cm snail race in 20 seconds. Calculate Gerty s speed in centimetres per second. Speed = cm/s = cm/s This means that Gerty travels cm in 1 second. How many centimetres does Gerty travel in 2 seconds? So Gerty s speed could also be expressed as cm/2s. How many centimetres does Gerty travel in 6 seconds? So Gerty s speed could also be expressed as cm/6s. Gerty s speed is constant. So these rates are equivalent (ie. the same): 0.5 cm/s = cm/2s = cm/6s How many centimetres does Gerty travel in 60 seconds? cm So Gerty s speed could also be expressed as cm/60s or cm/min. How many centimetres does Gerty travel in an hour? So Gerty s speed could also be expressed as cm/h. Gerty s speed is constant. So these rates are also equivalent: 0.5 cm/s = cm/min = cm/h. As the unit of time (in the denominator) gets larger, does the distance travelled in this unit of time get larger or smaller? How many millimetres does Gerty travel in 1 hour? mm/h How many metres does Gerty travel in 1 hour? m/h How many kilometres does Gerty travel in 1 hour? km/h So 1800 cm/h = mm/h = m/h = km/h. As the unit of distance (in the numerator) gets larger, does the number of these units travelled in the time get larger or smaller? Hilda the house mouse runs constantly at 12 km/h. What is her speed in metres per hour? Calculate her speed in m/s (to 1 decimal place). Speed = = = = m/h 2008, McMaster & Mitchelmore 48 ISBN cm cm cm
14 NS4.3 Number Part B Activity 10-3 Inverse rates Resources required: a calculator. Birth rate In 2008, the Australian Bureau of Statistics estimated that children were being born in Australia at the rate of births per second. It doesn t make much sense to talk about a fraction of a birth, so they decided to express the same value in a different way births/second is births per 1 second births per 1 second = 87 births per seconds = 1 birth per seconds. 87 This is 1 birth every seconds (to the nearest second). Notice that: 87 is the inverse of So the number of births per second is the inverse of the number of seconds per birth. Without first converting births/second to a fraction, how could you calculate the number of seconds/birth? Draw the button(s) on your calculator that can you use to find the inverse of a decimal. The inverse is also called the reciprocal. Water use efficiency Farmer Fred was concerned about the rising cost of the irrigation water he needed to produce his rice crop. So Fred tried to reduce the amount of water he required to grow each tonne of rice. The table below shows the amount of rice Fred produced in each of the next 5 years and the quantity of irrigation water he used to produce it. Calculate his water use efficiency (WUE) as the tonnes of rice he produced per megalitre of water he used. Then calculate his WUE as the megalitres of water he used per tonne of rice he produced. Year Rice produced (t) Water used (ML) WUE (t/ml) Did Fred s use of irrigation water become more efficient? WUE (ML/t) 2008, McMaster & Mitchelmore 49 ISBN
15 NS4.3 Number Part B Activity 10-7 Multiplying and dividing rates Russell (who lives in Australia) and his brother Randall (who lives in the United States) want to compare the fuel efficiency of their vehicles. In Australia, fuel efficiency is usually measured as the number of litres of petrol needed to drive 100 km. In the United States it is usually measured as the number of miles you can travel for every gallon of petrol. Russell and Randall each measured the amount of petrol needed to refill their tank after travelling a measured distance. Russell drove his Land Rover 500 km before he needed to refill his tank with 70 L of petrol. Calculate the number of litres Russell used per 100 km. Fuel efficiency = = L per 100 km Randall drove his Chevrolet 4WD 400 miles before he needed to refill his tank with 25 gallons of petrol. Calculate the number of miles Randall travelled per gallon of petrol. Fuel efficiency = = mpg (miles per gallon) To find out whose vehicle was more fuel efficient, they had to use a common unit of measurement. Russell decided to convert Randall s mpg into L per 100 km. A mile is 1.61 km. A gallon is 3.8 L. Fuel efficiency of Randall s vehicle = mpg = x km per gallon = x km per L = x lots of 100 km per L = lots of 100 km per L (to 4 d.p.) = L per 100 km (to 1 d.p.) Whose vehicle was the more fuel efficient? Calculate how many km Randall could drive on one of his tanks of petrol. Distance Randall could drive = km = km 2008, McMaster & Mitchelmore 58 ISBN
16
Test B. Calculator allowed. Mathematics test KEY STAGE LEVELS. First name. Middle name. Last name. School. DfE number. For marker s use only
 2012 Ma KEY STAGE 2 LEVELS 3 5 Mathematics test Test B Calculator allowed First name Middle name Last name 2012 School DfE number For marker s use only Page 5 7 9 11 Marks 13 15 17 19 21 23 Total 2012
2012 Ma KEY STAGE 2 LEVELS 3 5 Mathematics test Test B Calculator allowed First name Middle name Last name 2012 School DfE number For marker s use only Page 5 7 9 11 Marks 13 15 17 19 21 23 Total 2012
GCSE Mathematics Calculator Foundation Tier Free Practice Set 1 1 hour 30 minutes ANSWERS. Marks shown in brackets for each question (2)
 MathsMadeEasy 3 GCSE Mathematics Calculator Foundation Tier Free Practice Set 1 1 hour 30 minutes ANSWERS Marks shown in brackets for each question Grade Boundaries C D E F G 76 60 47 33 20 Legend used
MathsMadeEasy 3 GCSE Mathematics Calculator Foundation Tier Free Practice Set 1 1 hour 30 minutes ANSWERS Marks shown in brackets for each question Grade Boundaries C D E F G 76 60 47 33 20 Legend used
CONTENTS Page Rounding 3 Addition 4 Subtraction 6 Multiplication 7 Division 10 Order of operations (BODMAS)
 CONTENTS Page Rounding 3 Addition 4 Subtraction 6 Multiplication 7 Division 10 Order of operations (BODMAS) 12 Formulae 13 Time 14 Fractions 17 Percentages 19 Ratio and Proportion 23 Information Handling
CONTENTS Page Rounding 3 Addition 4 Subtraction 6 Multiplication 7 Division 10 Order of operations (BODMAS) 12 Formulae 13 Time 14 Fractions 17 Percentages 19 Ratio and Proportion 23 Information Handling
GCSE Mathematics Non Calculator Foundation Tier Free Practice Set 1 1 hour 30 minutes ANSWERS. Marks shown in brackets for each question (2)
 MathsMadeEasy 3 GCSE Mathematics Non Calculator Foundation Tier Free Practice Set 1 1 hour 30 minutes ANSWERS Marks shown in brackets for each question Grade Boundaries C D E F G 76 60 47 33 20 Legend
MathsMadeEasy 3 GCSE Mathematics Non Calculator Foundation Tier Free Practice Set 1 1 hour 30 minutes ANSWERS Marks shown in brackets for each question Grade Boundaries C D E F G 76 60 47 33 20 Legend
Calculating methods. Addition. Multiplication. Th H T U Th H T U = Example
 1 Addition Calculating methods Example 534 + 2678 Place the digits in the correct place value columns with the numbers under each other. Th H T U Begin adding in the units column. 5 3 4 + 12 16 17 8 4+8
1 Addition Calculating methods Example 534 + 2678 Place the digits in the correct place value columns with the numbers under each other. Th H T U Begin adding in the units column. 5 3 4 + 12 16 17 8 4+8
Home NAME:... FORM:... MATHS TOOLKIT Year 6
 NAME:... FORM:... MATHS TOOLKIT 017 018 Year 6 Click on the topic of choice Contents Number... 4 Revision of Four Operations... 4 Multiplication and Division of Decimals... 5 Long Multiplication... 7 Long
NAME:... FORM:... MATHS TOOLKIT 017 018 Year 6 Click on the topic of choice Contents Number... 4 Revision of Four Operations... 4 Multiplication and Division of Decimals... 5 Long Multiplication... 7 Long
Odd numbers 4 2 = 4 X 4 = 16
 Even numbers Square numbers 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 1 2 = 1 x 1 = 1 2 divides exactly into every even number. 2 2 = 2 x 2 = 4 3 2 = 3 x 3 = 9 Odd numbers 4 2 = 4 X 4 = 16 5 2 = 5 X 5 = 25 1, 3, 5, 7, 11, 6
Even numbers Square numbers 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 1 2 = 1 x 1 = 1 2 divides exactly into every even number. 2 2 = 2 x 2 = 4 3 2 = 3 x 3 = 9 Odd numbers 4 2 = 4 X 4 = 16 5 2 = 5 X 5 = 25 1, 3, 5, 7, 11, 6
NUMERACY TOOLKIT TOOLKIT NUMERACY
 NUMERACY TOOLKIT TOOLKIT NUMERACY Addition Calculating methods Example 534 + 2678 Place the digits in the correct place value columns with the numbers under each other. Th H T U Begin adding in the units
NUMERACY TOOLKIT TOOLKIT NUMERACY Addition Calculating methods Example 534 + 2678 Place the digits in the correct place value columns with the numbers under each other. Th H T U Begin adding in the units
2015 Predicted Paper 1(2)
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number 2015 Predicted Paper 1 Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Higher Tier Paper Reference 1MA0/1H You must have: Ruler graduated
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number 2015 Predicted Paper 1 Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Higher Tier Paper Reference 1MA0/1H You must have: Ruler graduated
Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number
 GCSE MATHEMATICS Sample Assessment Materials 69 Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 0 GCSE MATHEMATICS COMPONENT 2 Calculator-Allowed Mathematics Higher Tier SPECIMEN PAPER 2 hours 15 minutes
GCSE MATHEMATICS Sample Assessment Materials 69 Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 0 GCSE MATHEMATICS COMPONENT 2 Calculator-Allowed Mathematics Higher Tier SPECIMEN PAPER 2 hours 15 minutes
Mathematics A *P45840A0124* Pearson Edexcel GCSE P45840A. Paper 2 (Calculator) Higher Tier. Friday 6 November 2015 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Mathematics A Paper 2 (Calculator) Friday 6 November 2015 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Mathematics A Paper 2 (Calculator) Friday 6 November 2015 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper
Paper reference. 5504/04 Edexcel GCSE Mathematics A 1387 Paper 4 (Calculator) Intermediate Tier. Tuesday 9 November 2004 Morning Time: 2 hours
 Centre No Paper reference Candidate No 5 5 0 4 / 0 4 Surname Signature Initial(s) Paper References(s) 5504/04 Edexcel GCSE Mathematics A 1387 Paper 4 (Calculator) Intermediate Tier Tuesday 9 November 2004
Centre No Paper reference Candidate No 5 5 0 4 / 0 4 Surname Signature Initial(s) Paper References(s) 5504/04 Edexcel GCSE Mathematics A 1387 Paper 4 (Calculator) Intermediate Tier Tuesday 9 November 2004
STRAND C: Measurement. UNIT C1 Units of Measurement: Text. Contents. Section. C1.1 Units and Measuring. C1.2 Upper and Lower Bounds
 STRAND C: Measurement C1 Units of Measurement Text Contents Section C1.1 Units and Measuring * C1.2 Upper and Lower Bounds C1.3 Estimating Areas C1.4 Conversion of Units C1 Units of Measurement C1.1 Units
STRAND C: Measurement C1 Units of Measurement Text Contents Section C1.1 Units and Measuring * C1.2 Upper and Lower Bounds C1.3 Estimating Areas C1.4 Conversion of Units C1 Units of Measurement C1.1 Units
GCSE Mathematics Practice Tests: Set 4
 GCSE Mathematics Practice Tests: Set 4 Paper 2H (Calculator) Time: 1 hour 30 minutes You should have: Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, pair of compasses, pen, HB pencil, eraser,
GCSE Mathematics Practice Tests: Set 4 Paper 2H (Calculator) Time: 1 hour 30 minutes You should have: Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, pair of compasses, pen, HB pencil, eraser,
MATHEMATICS Standard Grade - General Level
 General Mathematics - Practice Examination G Please note the format of this practice examination is the same as the current format. The paper timings are the same, as are the marks allocated. Calculators
General Mathematics - Practice Examination G Please note the format of this practice examination is the same as the current format. The paper timings are the same, as are the marks allocated. Calculators
Measurement Year 11. Rounding
 Measurement Year 11 Rounding Do not round early. Students should carry all decimal places in working until the end of their calculations. They should then give their answers sensibly rounded. An answer
Measurement Year 11 Rounding Do not round early. Students should carry all decimal places in working until the end of their calculations. They should then give their answers sensibly rounded. An answer
Applications of Mathematics Unit 2: Applications 2
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Applications of Mathematics Unit 2: Applications 2 Practice paper Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Higher Tier Paper Reference
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Applications of Mathematics Unit 2: Applications 2 Practice paper Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Higher Tier Paper Reference
Position and Displacement
 Position and Displacement Ch. in your text book Objectives Students will be able to: ) Explain the difference between a scalar and a vector quantity ) Explain the difference between total distance traveled
Position and Displacement Ch. in your text book Objectives Students will be able to: ) Explain the difference between a scalar and a vector quantity ) Explain the difference between total distance traveled
Day 1. Mental Arithmetic Questions. 1. What number is five cubed? 2. A circle has radius r. What is the formula for the area of the circle?
 Mental Arithmetic Questions 1. What number is five cubed? KS3 MATHEMATICS 10 4 10 Level 6 Questions Day 1 2. A circle has radius r. What is the formula for the area of the circle? 3. Jenny and Mark share
Mental Arithmetic Questions 1. What number is five cubed? KS3 MATHEMATICS 10 4 10 Level 6 Questions Day 1 2. A circle has radius r. What is the formula for the area of the circle? 3. Jenny and Mark share
Materials for assessing adult numeracy
 Materials for assessing adult numeracy Number Task Write this number in figures. Two hundred and seventy two thousand four hundred and twenty nine. In which of these numbers is the 7 worth seventy? Write
Materials for assessing adult numeracy Number Task Write this number in figures. Two hundred and seventy two thousand four hundred and twenty nine. In which of these numbers is the 7 worth seventy? Write
Measurement with Reasoning
 compare, describe and solve practical problems for: * lengths and heights [e.g. long/short, longer/shorter, tall/short, double/half] * mass/weight [e.g. heavy/light, heavier than, lighter than] * capacity
compare, describe and solve practical problems for: * lengths and heights [e.g. long/short, longer/shorter, tall/short, double/half] * mass/weight [e.g. heavy/light, heavier than, lighter than] * capacity
You must have: Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, compasses, pen, HB pencil, eraser, calculator. Tracing paper may be used.
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Centre Number Mathematics B Paper 1R Candidate Number Monday 8 January 2018 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Paper Reference 4MB0/01R
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Centre Number Mathematics B Paper 1R Candidate Number Monday 8 January 2018 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Paper Reference 4MB0/01R
Mathematics Paper 3 (Calculator)
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) Centre Number Candidate Number Mathematics Paper 3 (Calculator) Specimen Papers Set 2 Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Foundation
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) Centre Number Candidate Number Mathematics Paper 3 (Calculator) Specimen Papers Set 2 Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Foundation
Learning Outcome 4 Measurement
 Maths in Context Learning Outcome 4 Measurement Exercise Book Learning Outcome 4 Exercise 1 Select the most appropriate metric units for measuring each item. 1. The height of a person: (A) mm (B) cm (c)
Maths in Context Learning Outcome 4 Measurement Exercise Book Learning Outcome 4 Exercise 1 Select the most appropriate metric units for measuring each item. 1. The height of a person: (A) mm (B) cm (c)
8 LEVELS 5 7 PAPER. Paper 2. Year 8 mathematics test. Calculator allowed. First name. Last name. Class. Date YEAR
 Ma YEAR 8 LEVELS 5 7 PAPER 2 Year 8 mathematics test Paper 2 Calculator allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your details in the spaces
Ma YEAR 8 LEVELS 5 7 PAPER 2 Year 8 mathematics test Paper 2 Calculator allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your details in the spaces
Mathematics A *P43380A0132* Pearson Edexcel GCSE P43380A. Paper 2 (Calculator) Foundation Tier. Friday 13 June 2014 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Mathematics A Paper 2 (Calculator) Friday 13 June 2014 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Candidate Number Foundation Tier Paper
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Mathematics A Paper 2 (Calculator) Friday 13 June 2014 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Candidate Number Foundation Tier Paper
Maths Revision. Book 2. Name:.
 Maths Revision Book 2 Name:. Number Fractions Calculating with Fractions Addition 6 + 4 2 2 Subtraction 2 Subtract wholes first 0 2 + 9 2 2 2 Change one whole into thirds 9 2 + + 2 7 2 2 Multiplication
Maths Revision Book 2 Name:. Number Fractions Calculating with Fractions Addition 6 + 4 2 2 Subtraction 2 Subtract wholes first 0 2 + 9 2 2 2 Change one whole into thirds 9 2 + + 2 7 2 2 Multiplication
GCSE style questions arranged by topic
 Write your name here Surname Other names In the style of: Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Mathematics Bounds GCSE style questions arranged by topic Higher Tier Paper Reference 1MA0/2H
Write your name here Surname Other names In the style of: Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Mathematics Bounds GCSE style questions arranged by topic Higher Tier Paper Reference 1MA0/2H
MEP Primary Practice Book 5b a) Use a ruler to draw the required parts of this 10 cm line segment. i) ii) iii) iv) 1 unit
 Use a ruler to draw the required parts of this 0 cm line segment. i) ii) iii) iv) unit 8 00 00 0 cm b) Express the fractions in hundredths and percentages. i) iii) = ii) = 8 00 iv) 00 Use the diagrams
Use a ruler to draw the required parts of this 0 cm line segment. i) ii) iii) iv) unit 8 00 00 0 cm b) Express the fractions in hundredths and percentages. i) iii) = ii) = 8 00 iv) 00 Use the diagrams
The pairs of terms: mass and weight, volume and capacity, are used interchangeably at this stage.
 MEASUREMENT 2014 and 2006 COMPARISON PROGRESSION DOCUMENT YEAR 1 NC 2014 Programme of study (statutory requirements) NC 2014 Notes and Guidance (non-statutory) PNS 2006 Compare, describe and solve practical
MEASUREMENT 2014 and 2006 COMPARISON PROGRESSION DOCUMENT YEAR 1 NC 2014 Programme of study (statutory requirements) NC 2014 Notes and Guidance (non-statutory) PNS 2006 Compare, describe and solve practical
Book 5. The wee Maths Book. Growth. Grow your brain. N4 Numeracy. of Big Brain. Guaranteed to make your brain grow, just add some effort and hard work
 Grow your brain N4 Numeracy Book 5 The wee Maths Book of Big Brain Growth Guaranteed to make your brain grow, just add some effort and hard work Don t be afraid if you don t know how to do it, yet! It
Grow your brain N4 Numeracy Book 5 The wee Maths Book of Big Brain Growth Guaranteed to make your brain grow, just add some effort and hard work Don t be afraid if you don t know how to do it, yet! It
Pre-Lab 0.2 Reading: Measurement
 Name Block Pre-Lab 0.2 Reading: Measurement section 1 Description and Measurement Before You Read Weight, height, and length are common measurements. List at least five things you can measure. What You
Name Block Pre-Lab 0.2 Reading: Measurement section 1 Description and Measurement Before You Read Weight, height, and length are common measurements. List at least five things you can measure. What You
Paper Reference. Mathematics A 1387 Paper 2 (Calculator) Foundation Tier Monday 11 June 2007 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
 Centre No. Paper Reference Surname Initial(s) Candidate No. 5 5 2 1 0 2 Signature Paper Reference(s) 5521/02 Edexcel GCSE Mathematics A 1387 Paper 2 (Calculator) Foundation Tier Monday 11 June 2007 Morning
Centre No. Paper Reference Surname Initial(s) Candidate No. 5 5 2 1 0 2 Signature Paper Reference(s) 5521/02 Edexcel GCSE Mathematics A 1387 Paper 2 (Calculator) Foundation Tier Monday 11 June 2007 Morning
General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier June Time allowed 1 hour 30 minutes
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Pages Mark Mathematics General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier June 2015
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Pages Mark Mathematics General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier June 2015
Trades Math Practice Assessment Test
 Trades Math Practice Assessment Test Please leave 2 or 3 digits after the decimal point rounding is optional Calculators ARE allowed For full marks, you MUST include units in your answer e.g. 2 ft. or
Trades Math Practice Assessment Test Please leave 2 or 3 digits after the decimal point rounding is optional Calculators ARE allowed For full marks, you MUST include units in your answer e.g. 2 ft. or
Applications of Mathematics
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Applications of Mathematics Unit 2: Applications 2 For Approved Pilot Centres ONLY Higher Tier Friday 14 June 2013 Morning
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Applications of Mathematics Unit 2: Applications 2 For Approved Pilot Centres ONLY Higher Tier Friday 14 June 2013 Morning
MATHEMATICS Component 2 Calculator-Allowed Mathematics HIGHER TIER
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE C300UB0-1 S18-C300UB0-1 MATHEMATICS Component 2 Calculator-Allowed Mathematics HIGHER TIER THURSDAY, 7 JUNE 2018 MORNING 2 hours 15 minutes For
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE C300UB0-1 S18-C300UB0-1 MATHEMATICS Component 2 Calculator-Allowed Mathematics HIGHER TIER THURSDAY, 7 JUNE 2018 MORNING 2 hours 15 minutes For
Intermediate Tier Tuesday 7 November 2006 Morning Time: 2 hours
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference 5 5 2 3 0 3 Paper Reference(s) 5523/03 Edexcel GCSE Mathematics A 1387 Paper 3 (Non-Calculator) Intermediate Tier Tuesday 7 November 2006 Morning Time: 2 hours
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference 5 5 2 3 0 3 Paper Reference(s) 5523/03 Edexcel GCSE Mathematics A 1387 Paper 3 (Non-Calculator) Intermediate Tier Tuesday 7 November 2006 Morning Time: 2 hours
You must have: Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, compasses, pen, HB pencil, eraser, calculator. Tracing paper may be used.
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Certificate Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 1F Friday 10 January 2014 Morning Time: 2 hours Centre Number Candidate Number
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Certificate Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 1F Friday 10 January 2014 Morning Time: 2 hours Centre Number Candidate Number
WORKSHEET General 2 Mathematics
 WORKSHEET General 2 Mathematics Topic Areas: Algebra and Modelling AM5 Non linear relationships Exponential/Quadratic (Projectile) Inverse Perimeter/Area problem Teacher: PETER HARGRAVES Source: HSC exam
WORKSHEET General 2 Mathematics Topic Areas: Algebra and Modelling AM5 Non linear relationships Exponential/Quadratic (Projectile) Inverse Perimeter/Area problem Teacher: PETER HARGRAVES Source: HSC exam
Area and Volume 1. Circumference and Area of a Circle. Area of a Trapezium. and Measures. Geometry. Key Point. Key Point.
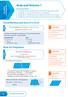 Geometry and Measures Area and Volume 1 You must be able to: Recall and use the formulae for the circumference and area of a circle Recall and use the formula for the area of a trapezium Recall and use
Geometry and Measures Area and Volume 1 You must be able to: Recall and use the formulae for the circumference and area of a circle Recall and use the formula for the area of a trapezium Recall and use
Paper Reference. Mathematics A Paper 3 (Non-Calculator) Intermediate Tier. Tuesday 7 November 2006 Morning Time: 2 hours
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference 5 5 2 3 0 3 Paper Reference(s) 5523/03 Edexcel GCSE Mathematics A 1387 Paper 3 (Non-Calculator) Intermediate Tier Tuesday 7 November 2006 Morning Time: 2 hours
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference 5 5 2 3 0 3 Paper Reference(s) 5523/03 Edexcel GCSE Mathematics A 1387 Paper 3 (Non-Calculator) Intermediate Tier Tuesday 7 November 2006 Morning Time: 2 hours
Accuracy and Precision Making measurements is an important skill in science.
 Motion Physics Unit Physics is the scientific study of matter and energy and how they interact. topic such as motion, light, electricity, and heat strong rules about using numbers in math Accuracy and
Motion Physics Unit Physics is the scientific study of matter and energy and how they interact. topic such as motion, light, electricity, and heat strong rules about using numbers in math Accuracy and
Paper 2. Mathematics test. Calculator allowed. satspapers.org. First name. Last name. School KEY STAGE TIER
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIER 5 7 2003 Mathematics test Paper 2 Calculator allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your
Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIER 5 7 2003 Mathematics test Paper 2 Calculator allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your
Physical Quantities- Measurements and Units
 Physical Quantities- Measurements and Units Key Words to measure base length depth kilogram metre measurement (-s) derived width volume tonne mass magnitude unit area intensive extensive matter scientific
Physical Quantities- Measurements and Units Key Words to measure base length depth kilogram metre measurement (-s) derived width volume tonne mass magnitude unit area intensive extensive matter scientific
Appendix B: Skills Handbook
 Appendix B: Skills Handbook Effective communication is an important part of science. To avoid confusion when measuring and doing mathematical calculations, there are accepted conventions and practices
Appendix B: Skills Handbook Effective communication is an important part of science. To avoid confusion when measuring and doing mathematical calculations, there are accepted conventions and practices
Mathematics A *P49304A0128* Pearson Edexcel GCSE P49304A. Paper 2 (Calculator) Higher Tier. Thursday 9 June 2016 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Mathematics A Paper 2 (Calculator) Thursday 9 June 2016 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper Reference
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Mathematics A Paper 2 (Calculator) Thursday 9 June 2016 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Candidate Number Higher Tier Paper Reference
Mathematics Paper 2 (Calculator)
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) Centre Number Candidate Number Mathematics Paper 2 (Calculator) Specimen Papers Set 2 Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Higher
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) Centre Number Candidate Number Mathematics Paper 2 (Calculator) Specimen Papers Set 2 Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Higher
Measurement Year 10. The topic Measurement includes units because any size has no meaning without the units. Every answer must include the units used.
 Measurement Year 10 The topic Measurement includes units because any size has no meaning without the units. Every answer must include the units used. Precision and Estimation In general students should
Measurement Year 10 The topic Measurement includes units because any size has no meaning without the units. Every answer must include the units used. Precision and Estimation In general students should
MATHEMATICS NUMERACY UNIT 2: CALCULATOR-ALLOWED INTERMEDIATE TIER
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE NEW 3310U40-1 S17-3310U40-1 MATHEMATICS NUMERACY UNIT 2: CALCULATOR-ALLOWED INTERMEDIATE TIER THURSDAY, 8 JUNE 2017 MORNING 1 hour 45 minutes For
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE NEW 3310U40-1 S17-3310U40-1 MATHEMATICS NUMERACY UNIT 2: CALCULATOR-ALLOWED INTERMEDIATE TIER THURSDAY, 8 JUNE 2017 MORNING 1 hour 45 minutes For
Area and Volume 2. Circles. Trapeziums. and Measures. Geometry. Key Point. Key Point. Key Point
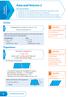 Geometry and Measures Area and Volume 2 You must be able to: Recall and use the formulae for the circumference and area of a circle Recall and use the formula for the area of a trapezium Recall and use
Geometry and Measures Area and Volume 2 You must be able to: Recall and use the formulae for the circumference and area of a circle Recall and use the formula for the area of a trapezium Recall and use
Methods in Mathematics
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Methods in Mathematics Unit 2: Methods 2 For Approved Pilot Centres ONLY Foundation Tier Tuesday 13 November 2012 Morning
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Methods in Mathematics Unit 2: Methods 2 For Approved Pilot Centres ONLY Foundation Tier Tuesday 13 November 2012 Morning
43603F. General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier June Unit 3. (JUN F01) WMP/Jun12/43603F F
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier June 2012 Pages 3 4 5 Mark Mathematics
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier June 2012 Pages 3 4 5 Mark Mathematics
PLC Papers. Created For:
 PLC Papers Created For: Compare Fractions, Decimals and Percentages 2 Grade 4 Objective: Compare quantities by calculating equivalent fractions, decimals and percentages. Question 1 Write down three-quarters
PLC Papers Created For: Compare Fractions, Decimals and Percentages 2 Grade 4 Objective: Compare quantities by calculating equivalent fractions, decimals and percentages. Question 1 Write down three-quarters
4306/1F. General Certificate of Secondary Education November MATHEMATICS (SPECIFICATION A) 4306/1F Foundation Tier Paper 1 Non-calculator
 Surname Other Names For Examiner s Use Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Secondary Education November 2009 MATHEMATICS (SPECIFICATION A) 4306/1F Foundation Tier
Surname Other Names For Examiner s Use Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Secondary Education November 2009 MATHEMATICS (SPECIFICATION A) 4306/1F Foundation Tier
Paper 2. Mathematics test. Calculator allowed. First name. Last name. School. Pupil number KEY STAGE TIER
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIER 6 8 2002 Mathematics test Paper 2 Calculator allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your
Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIER 6 8 2002 Mathematics test Paper 2 Calculator allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your
THOUGHTS AND CROSSES. TOPIC: volume and surface area
 THOUGHTS ND CROSSES TOPIC: volume and surface area * * block of wood, 9cm by 11cm by 12cm, has a hole of radius 2.5cm drilled out. Calculate the mass of the wood if the density is pepper pot consists of
THOUGHTS ND CROSSES TOPIC: volume and surface area * * block of wood, 9cm by 11cm by 12cm, has a hole of radius 2.5cm drilled out. Calculate the mass of the wood if the density is pepper pot consists of
Measurement COMPARING AND ESTIMATING Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6
 compare, describe and solve practical problems for: * lengths and heights [e.g. long/short, longer/shorter, tall/short, double/half] * mass/weight [e.g. heavy/light, heavier than, lighter than] * capacity
compare, describe and solve practical problems for: * lengths and heights [e.g. long/short, longer/shorter, tall/short, double/half] * mass/weight [e.g. heavy/light, heavier than, lighter than] * capacity
NS8-1 Factors and Multiples
 NS- Factors and Multiples The multiples of a number are the numbers you say when counting by that number. is a multiple of both and 0 is a multiple of both 0 and = 0 = 0 and are both factors of 0 and are
NS- Factors and Multiples The multiples of a number are the numbers you say when counting by that number. is a multiple of both and 0 is a multiple of both 0 and = 0 = 0 and are both factors of 0 and are
First Practice Test 2 Levels 5-7 Calculator allowed
 Mathematics First Practice Test 2 Levels 5-7 Calculator allowed First name Last name School Remember The test is 1 hour long. You may use a calculator for any question in this test. You will need: pen,
Mathematics First Practice Test 2 Levels 5-7 Calculator allowed First name Last name School Remember The test is 1 hour long. You may use a calculator for any question in this test. You will need: pen,
Wednesday 8 November 2017 Morning Time allowed: 1 hour 30 minutes
 Oxford Cambridge and RSA GCSE (9 1) Mathematics J560/03 Paper 3 (Foundation Tier) F Wednesday 8 November 2017 Morning Time allowed: 1 hour 30 minutes *6932107064* You may use: A scientific or graphical
Oxford Cambridge and RSA GCSE (9 1) Mathematics J560/03 Paper 3 (Foundation Tier) F Wednesday 8 November 2017 Morning Time allowed: 1 hour 30 minutes *6932107064* You may use: A scientific or graphical
You must have: Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, compasses, pen, HB pencil, eraser, calculator. Tracing paper may be used.
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 1F Centre Number Monday 9 January 2017 Morning Time: 2 hours Candidate Number Foundation Tier Paper Reference
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 1F Centre Number Monday 9 January 2017 Morning Time: 2 hours Candidate Number Foundation Tier Paper Reference
GCSE Mathematics Non Calculator Foundation Tier Free Practice Set 5 1 hour 30 minutes ANSWERS
 MathsMadeEasy 3 GCSE Mathematics Non Calculator Foundation Tier Free Practice Set 5 1 hour 30 minutes ANSWERS Marks shown in brackets for each question Typical Grade Boundaries C D E F G 76 60 47 33 20
MathsMadeEasy 3 GCSE Mathematics Non Calculator Foundation Tier Free Practice Set 5 1 hour 30 minutes ANSWERS Marks shown in brackets for each question Typical Grade Boundaries C D E F G 76 60 47 33 20
You must have: Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, compasses, pen, HB pencil, eraser, calculator. Tracing paper may be used.
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 2FR Thursday 9 June 2016 Morning Time: 2 hours Centre Number Candidate Number Foundation Tier Paper Reference
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 2FR Thursday 9 June 2016 Morning Time: 2 hours Centre Number Candidate Number Foundation Tier Paper Reference
PLC Papers. Created For:
 PLC Papers Created For: Compound Units 2 Grade 5 Objective: Convert standard compound units in numerical and algebraic contexts. Question 1. Ben goes on holiday to Hong Kong. In Hong Kong, Ben sees a camera
PLC Papers Created For: Compound Units 2 Grade 5 Objective: Convert standard compound units in numerical and algebraic contexts. Question 1. Ben goes on holiday to Hong Kong. In Hong Kong, Ben sees a camera
Allows us to work with very large or small numbers more easily. All numbers are a product of 10.
 Unit 1: Measurements Scientific Notation : Allows us to work with very large or small numbers more easily. All numbers are a product of 10. M x 10n M= signif. digit [ 1 < M < 10 ] n = an integer move the
Unit 1: Measurements Scientific Notation : Allows us to work with very large or small numbers more easily. All numbers are a product of 10. M x 10n M= signif. digit [ 1 < M < 10 ] n = an integer move the
A1 Further Worksheet 1
 Cambridge Essentials Mathematics Extension 7 A1 Further Worksheet 1 A1 Further Worksheet 1 1 Here is a puzzle. Each symbol stands for a number. The column on the right shows the total of each row. For
Cambridge Essentials Mathematics Extension 7 A1 Further Worksheet 1 A1 Further Worksheet 1 1 Here is a puzzle. Each symbol stands for a number. The column on the right shows the total of each row. For
Mathematics *P48148RA0124* P48148RA. Paper 2 (Calculator) Higher Tier. Pearson Edexcel Level 1 / Level 2 GCSE (9 1)
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Level 1 / Level 2 GCSE (9 1) Centre Number Mathematics Paper 2 (Calculator) Thursday 8 June 2017 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Candidate Number
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Level 1 / Level 2 GCSE (9 1) Centre Number Mathematics Paper 2 (Calculator) Thursday 8 June 2017 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Candidate Number
Day What number is five cubed? 2. A circle has radius r. What is the formula for the area of the circle?
 Mental Arithmetic Questions 1. What number is five cubed? KS3 MATHEMATICS 10 4 10 Level 7 Questions Day 1 2. A circle has radius r. What is the formula for the area of the circle? 3. Jenny and Mark share
Mental Arithmetic Questions 1. What number is five cubed? KS3 MATHEMATICS 10 4 10 Level 7 Questions Day 1 2. A circle has radius r. What is the formula for the area of the circle? 3. Jenny and Mark share
Notes: The Number System (6.NS.1 8)
 Notes: The Number System (6.NS. 8) Adding Fractions ) Find a common denominator. (LCM) ) Convert the fractions.(equivalent Denominators) ) Add the numerators and keep the denominator. ) Simplify. 6 8 9
Notes: The Number System (6.NS. 8) Adding Fractions ) Find a common denominator. (LCM) ) Convert the fractions.(equivalent Denominators) ) Add the numerators and keep the denominator. ) Simplify. 6 8 9
GCSE style questions arranged by topic
 Write your name here Surname Other names In the style of: Pearson Edecel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) Centre Number Candidate Number Mathematics Algebra Model Answers GCSE style questions arranged by topic
Write your name here Surname Other names In the style of: Pearson Edecel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) Centre Number Candidate Number Mathematics Algebra Model Answers GCSE style questions arranged by topic
Unit 3: Number, Algebra, Geometry 2 (Calculator)
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Mathematics B Unit 3: Number, Algebra, Geometry 2 (Calculator) Tuesday 8 November 2016 Morning Time: 1 hour
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Mathematics B Unit 3: Number, Algebra, Geometry 2 (Calculator) Tuesday 8 November 2016 Morning Time: 1 hour
Neston High School Mathematics Faculty Homework Booklet
 Neston High School Mathematics Faculty Homework Booklet Year: 11 Scheme: Higher Homework Sheet 1 Week Commencing: 11 th December 2017 1: The number of bacteria doubles in size every 3 hours. If C11: Find
Neston High School Mathematics Faculty Homework Booklet Year: 11 Scheme: Higher Homework Sheet 1 Week Commencing: 11 th December 2017 1: The number of bacteria doubles in size every 3 hours. If C11: Find
? 4. Like number bonds, a formula is useful because it helps us know what operation to use depending on which pieces of information we have.
 UNIT SIX DECIMALS LESSON 168 PROBLEM-SOLVING You ve covered quite a distance in your journey through our number system, from whole numbers through fractions, to decimals. Today s math mysteries all have
UNIT SIX DECIMALS LESSON 168 PROBLEM-SOLVING You ve covered quite a distance in your journey through our number system, from whole numbers through fractions, to decimals. Today s math mysteries all have
You must have: Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, compasses, pen, HB pencil, eraser, calculator. Tracing paper may be used.
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel International GCSE Centre Number Mathematics B Paper 1R Candidate Number Friday 10 May 2013 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Paper Reference 4MB0/01R You
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel International GCSE Centre Number Mathematics B Paper 1R Candidate Number Friday 10 May 2013 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Paper Reference 4MB0/01R You
Home NAME:... FORM:... MATHS TOOLKIT Year 5. Copyright 2017 Dulwich Prep London
 NAME:... FORM:... MATHS TOOLKIT 2017 2018 Year 5 Copyright 2017 Dulwich Prep London YEAR 5 OVERVIEW Home Contents Number... 5 Addition and Subtraction... 5 Multiplication and Division... 6 Place Value
NAME:... FORM:... MATHS TOOLKIT 2017 2018 Year 5 Copyright 2017 Dulwich Prep London YEAR 5 OVERVIEW Home Contents Number... 5 Addition and Subtraction... 5 Multiplication and Division... 6 Place Value
NATIONAL 5 MATHEMATICS. Unit 1 Assessment Revision
 NATIONAL 5 MATHEMATICS Unit 1 Assessment Revision Volume, Changing the Subject, Equations & Inequations, Simultaneous Equations, Fractions & Percentages, Arcs & Sectors Mr Miscandlon gw13miscandlondavid@glow.sch.uk
NATIONAL 5 MATHEMATICS Unit 1 Assessment Revision Volume, Changing the Subject, Equations & Inequations, Simultaneous Equations, Fractions & Percentages, Arcs & Sectors Mr Miscandlon gw13miscandlondavid@glow.sch.uk
AREA AND VOLUME TRAPEZOIDAL RULE
 AREA AND VOLUME TRAPEZOIDAL RULE Ratio and Proportion Table of Contents LCOL New Course 2017 LCOL Paper 1 Question 5 (a) 2017 LCOL Paper 1 Question 5 (b) 2014 LCOL Sample Paper 2 Question 5 2013 LCOL Paper
AREA AND VOLUME TRAPEZOIDAL RULE Ratio and Proportion Table of Contents LCOL New Course 2017 LCOL Paper 1 Question 5 (a) 2017 LCOL Paper 1 Question 5 (b) 2014 LCOL Sample Paper 2 Question 5 2013 LCOL Paper
General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier
 Centre Number Surname Other Names Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Examiner s Initials Candidate Signature Pages Mark General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier 3 4-5 GCSE Mathematics
Centre Number Surname Other Names Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Examiner s Initials Candidate Signature Pages Mark General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier 3 4-5 GCSE Mathematics
Algebra. CLCnet. Page Topic Title. Revision Websites. GCSE Revision 2006/7 - Mathematics. Add your favourite websites and school software here.
 Section 2 Page Topic Title 54-57 12. Basic algebra 58-61 13. Solving equations 62-64 14. Forming and solving equations from written information 65-67 15. Trial and improvement 68-72 16. Formulae 73-76
Section 2 Page Topic Title 54-57 12. Basic algebra 58-61 13. Solving equations 62-64 14. Forming and solving equations from written information 65-67 15. Trial and improvement 68-72 16. Formulae 73-76
GCSE MATHEMATICS 43603F. Foundation Tier Unit 3 Geometry and Algebra. Morning. (NOV F01) WMP/Nov16/E4. Materials.
 Please write clearly in block capitals. Centre number Candidate number Surname Forename(s) Candidate signature GCSE F MATHEMATICS Foundation Tier Unit 3 Geometry and Algebra Tuesday 8 November 2016 Morning
Please write clearly in block capitals. Centre number Candidate number Surname Forename(s) Candidate signature GCSE F MATHEMATICS Foundation Tier Unit 3 Geometry and Algebra Tuesday 8 November 2016 Morning
Numeric Reasoning. Robert Lakeland & Carl Nugent. Contents
 Year 11 Mathematics IAS 1.1 Numeric Reasoning Robert Lakeland & Carl Nugent Contents Achievement Standard.................................................. 2 Prime Numbers.......................................................
Year 11 Mathematics IAS 1.1 Numeric Reasoning Robert Lakeland & Carl Nugent Contents Achievement Standard.................................................. 2 Prime Numbers.......................................................
GOZO COLLEGE BOYS SECONDARY SCHOOL
 GOZO COLLEGE BOYS SECONDARY SCHOOL Embracing Diversity Half Yearly Exams 2013-2014 Subject: Form: Time: Mathematics (Main Paper) 4 Scheme B 1 hr 40 mins Name: Class: Instructions to Candidates Calculators
GOZO COLLEGE BOYS SECONDARY SCHOOL Embracing Diversity Half Yearly Exams 2013-2014 Subject: Form: Time: Mathematics (Main Paper) 4 Scheme B 1 hr 40 mins Name: Class: Instructions to Candidates Calculators
Unit 2 - Motion. Chapter 3 - Distance and Speed. Unit 2 - Motion 1 / 76
 Unit 2 - Motion Chapter 3 - Distance and Speed Unit 2 - Motion 1 / 76 Precision and Accuracy Precision is a measure of how closely individual measurements agree with one another. Accuracy refers to how
Unit 2 - Motion Chapter 3 - Distance and Speed Unit 2 - Motion 1 / 76 Precision and Accuracy Precision is a measure of how closely individual measurements agree with one another. Accuracy refers to how
Materials for assessing adult numeracy
 Materials for assessing adult numeracy Number Task The population of Wales is approximately Write this in numbers in the box. million. What is the value of the 7 in this number? Write your answer in words.
Materials for assessing adult numeracy Number Task The population of Wales is approximately Write this in numbers in the box. million. What is the value of the 7 in this number? Write your answer in words.
MEP: Primary Project. R: Calculations C: Ratio and proportion. Direct proportion. Graphs E: Problems. Activity Notes
 R: Calculations C: Ratio and proportion. Direct proportion. Graphs E: Problems Week Lesson Plan Factorisation Factorise these numbers in your exercise book and list their positive factors. T sets a time
R: Calculations C: Ratio and proportion. Direct proportion. Graphs E: Problems Week Lesson Plan Factorisation Factorise these numbers in your exercise book and list their positive factors. T sets a time
ALGEBRA QUESTIONS SIMPLIFYING, FACTORISING & EXPANDING EXPRESSIONS. 1. Simplify: i 2x + 3x ii h h h h h iii 2m 3n
 ALGEBRA QUESTIONS SIMPLIFYING, FACTORISING & EXPANDING EXPRESSIONS 1. Simplify: i 2x + 3x ii h h h h h iii 2m 3n iv 2(x + 3) + 5(x - 3) v. 2(3x + 4) 3(4x 5) vi. (2xy 3 ) 5 2. (a) Work out the value of
ALGEBRA QUESTIONS SIMPLIFYING, FACTORISING & EXPANDING EXPRESSIONS 1. Simplify: i 2x + 3x ii h h h h h iii 2m 3n iv 2(x + 3) + 5(x - 3) v. 2(3x + 4) 3(4x 5) vi. (2xy 3 ) 5 2. (a) Work out the value of
Baldragon Academy National 4 Maths Checklist
 Baldragon Academy National 4 Maths Checklist Contents: Page Numeracy Number..2 Measure.4 Statistics...6 Expressions and Formulae Algebra..8 Geometry.....9 Statistics..11 Relationships Linear Equations
Baldragon Academy National 4 Maths Checklist Contents: Page Numeracy Number..2 Measure.4 Statistics...6 Expressions and Formulae Algebra..8 Geometry.....9 Statistics..11 Relationships Linear Equations
The Celsius temperature scale is based on the freezing point and the boiling point of water. 12 degrees Celsius below zero would be written as
 Prealgebra, Chapter 2 - Integers, Introductory Algebra 2.1 Integers In the real world, numbers are used to represent real things, such as the height of a building, the cost of a car, the temperature of
Prealgebra, Chapter 2 - Integers, Introductory Algebra 2.1 Integers In the real world, numbers are used to represent real things, such as the height of a building, the cost of a car, the temperature of
Direct and Inverse Proportion
 Advance Topic Direct and Inverse Proportion 12.1 Introduction to Proportions We come across many such situations in our day-to-day life, where we need to see variation in one quantity bringing in variation
Advance Topic Direct and Inverse Proportion 12.1 Introduction to Proportions We come across many such situations in our day-to-day life, where we need to see variation in one quantity bringing in variation
Exam Question Bank. Name Class
 M7 Exam Question Bank Name Class 1 1. Lisa worked this out on her calculator 29.8 3.9 19.8 7.9 This is what her calculator showed 2.03030303 Write down a calculation Lisa could do in her head to check
M7 Exam Question Bank Name Class 1 1. Lisa worked this out on her calculator 29.8 3.9 19.8 7.9 This is what her calculator showed 2.03030303 Write down a calculation Lisa could do in her head to check
The total time traveled divided by the total time taken to travel it. Average speed =
 Unit 3: Motion V = d t Average speed The total time traveled divided by the total time taken to travel it Mathematically: Average speed = Total Distance Travelled Total Time Traveled So just how fast were
Unit 3: Motion V = d t Average speed The total time traveled divided by the total time taken to travel it Mathematically: Average speed = Total Distance Travelled Total Time Traveled So just how fast were
Learn to read, tell the time and write the time from analogue clocks
 OpenStax-CNX module: m30507 1 Learn to read, tell the time and write the time from analogue clocks Siyavula Uploaders This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution
OpenStax-CNX module: m30507 1 Learn to read, tell the time and write the time from analogue clocks Siyavula Uploaders This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution
Wednesday 15 January 2014 Morning Time: 2 hours
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Certificate Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 2F Centre Number Wednesday 15 January 2014 Morning Time: 2 hours Candidate Number
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Certificate Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Mathematics A Paper 2F Centre Number Wednesday 15 January 2014 Morning Time: 2 hours Candidate Number
Instructions. Information. Advice
 Instructions Use black ink or ball-point pen. Fill in the boxes at the top of this page with your name, centre number and candidate number. Answer all questions. Answer the questions in the spaces provided
Instructions Use black ink or ball-point pen. Fill in the boxes at the top of this page with your name, centre number and candidate number. Answer all questions. Answer the questions in the spaces provided
Unit 5 Practice Problems. 1. Tom had. of a carrot cake today. How much of one whole carrot. of a carrot cake last night and
 UNIT PRACTICE PROBLEMS 8: Use the diagrams given to represent the values in the addition problem and find the sum. Then perform the operation and represent the sum using the symbolic representation of
UNIT PRACTICE PROBLEMS 8: Use the diagrams given to represent the values in the addition problem and find the sum. Then perform the operation and represent the sum using the symbolic representation of
Paper 2. Calculator allowed. Mathematics test. First name. Last name. School. Remember KEY STAGE 3 TIER 5 7. satspapers.org
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 5 7 Paper 2 Calculator allowed First name Last name School 2009 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You may use a calculator for any question in this test. You will need:
Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 5 7 Paper 2 Calculator allowed First name Last name School 2009 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You may use a calculator for any question in this test. You will need:
40 mins NUMERACY. year. Use 2B or HB pencil only SESSION 2. Time available for students to complete test: 40 minutes
 NUMERACY NON-calculator year 9 204 40 mins SESSION 2 Time available for students to complete test: 40 minutes Use 2B or HB pencil only Australian Curriculum, Assessment and Reporting Authority, 204 This
NUMERACY NON-calculator year 9 204 40 mins SESSION 2 Time available for students to complete test: 40 minutes Use 2B or HB pencil only Australian Curriculum, Assessment and Reporting Authority, 204 This
Introductory Physics, High School Learning Standards for a Full First-Year Course
 Introductory Physics, High School Learning Standards for a Full First-Year Course I. C O N T E N T S T A N D A R D S Central Concept: Newton s laws of motion and gravitation describe and predict the motion
Introductory Physics, High School Learning Standards for a Full First-Year Course I. C O N T E N T S T A N D A R D S Central Concept: Newton s laws of motion and gravitation describe and predict the motion
MATHEMATICS. Equipment. Y5 Measuring. Standard metric units of measurement. Paper, pencil, ruler. MathsGoGoGo Home Use Only
 MATHEMATICS Y5 Measuring 5601 Standard metric units of measurement Paper, pencil, ruler. Equipment Maths Go Go Go 5601 Standard metric units of measurement. Page 2 Concepts Children should know and use
MATHEMATICS Y5 Measuring 5601 Standard metric units of measurement Paper, pencil, ruler. Equipment Maths Go Go Go 5601 Standard metric units of measurement. Page 2 Concepts Children should know and use
