Synchrotron Radiation, magnetic fields and cosmic rays
|
|
|
- Bertram Lee
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Synchrotron Radiation, magnetic fields and cosmic rays Giuseppe Di Bernardo 1 in collaboration with Evoli, C., Gaggero, D., Grasso, D. 1 Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics bernardo@mpa-garching.mpg.de Planck Conference Ferrara, December 05, 2014
2 The Synchrotron Emission of the Galaxy quick overview of recent models in view of PLANCK results e.g., the pre-launch PSM, in Delabrouille, J., et al., A&A (2013) They use the template 408 MHz Haslam, and extrapolate in frequency to the Planck ν-channels, assuming (i) a spectral index β s 3.0 (i.e., n epeq9e p, p 3), or (ii) using a β s map derived by combining the 408 MHz and WMAP 23 GHz data (see e.g., Miville-Dechenes et al. 2008) e.g., Fauvet, L., et al., A&A (2012) analytical spatial distribution n epr, zq9 expp r{r scale q{rcoshp2z{z scale qs (Drimmel & Spergel (2001)), with an uniform CRE spectrum and β s 3.45pÑ p 4!!q, and the HAMMURABI code (Waelkens et al., 2009) to compute RMs and synchrotron sky maps. e.g., GALPROP results (Strong, A.W., Orlando, E., Jaffe, T.J., A&A (2011) they based on a physical CRE model, accounting for a double broken power-law source spectrum (w/o extra-component), and uniform diffusion coefficient, and a continuous source distribution (see also Orlando E. contribution in the Poster session) Giuseppe Di Bernardo, in collaboration Planck Conference with Evoli, Ferrara, C.,, December Gaggero, 05, 2014 D.,, Grasso, D. (MPA) 2 / 23
3 The Synchrotron Emission of the Galaxy A Multi-Wavelength Analysis using DRAGON Evoli, C., et al., JCAP (2008); Gaggero, D., et al., PRL (2013) ( Fixing diffusion models against CR nuclei data DRAGON is a new numerical code aiming to solve the diffusion equation of CRs in the Galaxy environment. DRAGON features: position dependent, anisotropic diffusion; independent injection spectra for each nuclear species; interfaced with GAMMASKY to calculate diffuse gamma and synchrotron emissions; interfaced with DarkSUSY to calculate DM contribution... (other major codes, GALPROP, PICARD). The positron-excess... the role of astrophysical galactic extra-component seems more likely than exotic ones (DM annihilation/decay). Plot from Di Bernardo G., et al., See also e.g., Grasso et al., APP 32 (2009), Serpico, P., PRD, 79 (2009), Hooper, D., et al., JCAP 1 (2009): incomplete list of papers! Giuseppe Di Bernardo, in collaboration Planck Conference with Evoli, Ferrara, C.,, December Gaggero, 05, 2014 D.,, Grasso, D. (MPA) 3 / 23
4 The Synchrotron Emission of the Galaxy To Probe the Low Energy Lis of e` ` e using DRAGON + GAMMASKY results from Di Bernardo G., Evoli, C., Gaggero D., Grasso, D., and Maccione, L., JCAP 3 (2013) Sky region: 40 l 340, 10 b T[K] ν[mhz] Radio data GMF - KRA Model KRA Model - w/o break KOL Model - w/o break Below 20 GeV... the e` ` e may not be representative of the physical conditions of the rest of the Galaxy; the solar modulation reshapes the e` ` e Lis ν [MHz] Giuseppe Di Bernardo, in collaboration Planck Conference with Evoli, Ferrara, C.,, December Gaggero, 05, 2014 D.,, Grasso, D. (MPA) 4 / 23
5 The Synchrotron Emission of the Galaxy To Probe the Low Energy Lis of e` ` e using DRAGON + GAMMASKY results from Di Bernardo G., et al., JCAP 3 (2013) Sky region: 40 l 340, 10 b T[K] ν[mhz] Radio data GMF - KRA Model KRA Model - w/o break KOL Model - w/o break KRA Model - only 2 nd Below 100 MHz... the radio spectrum is dominated by secondary e` ` e ; KOL Model - only 2 nd ν [MHz] Giuseppe Di Bernardo, in collaboration Planck Conference with Evoli, Ferrara, C.,, December Gaggero, 05, 2014 D.,, Grasso, D. (MPA) 5 / 23
6 The Synchrotron Emission of the Galaxy To Probe the Low Energy Lis of e` ` e using DRAGON + GAMMASKY results from Di Bernardo G., et al., JCAP 3 (2013) T[K] ν[mhz] Sky region: 40 l 340, 10 b 45 χ 2 KRA = 2.6 χ 2 KOL = 1.9 γ(e ) kra = 1.6 γ(e ) kol = 2.0 Below 100 MHz Radio data GMF Total - KRA Model model Below the 100 radio MHz spectrum... is dominated KRA Total Model - KOL -model w/o break by secondary e` ` e ; the radio spectrum is dominated KOL Model - w/o break 10 5 GMF - KRA Model the ν-radio data are reproduced by secondary e` ` e ; only 2 nd only imposing a sharp break to KRA Model - w/o break the e spectrum below 4GeV KOL KRA Model - only 2 nd (see also e.g., Orlando E., & Strong, A. (2013); 10 5 Bringmann, T. et al (2012); Jaffe et al ν [MHz] (2011)). Giuseppe Di Bernardo, in collaboration Planck Conference with Evoli, Ferrara, C.,, December Gaggero, 05, 2014 D.,, Grasso, D. (MPA) 5 / 23
7 The Synchrotron Emission of the Galaxy To Probe the Low Energy Lis of e` ` e using DRAGON + GAMMASKY results from Di Bernardo G., et al., JCAP 3 (2013) T[K] ν[mhz] Sky region: 40 l 340, 10 b 45 χ 2 KRA = 2.6 χ 2 KOL = 1.9 γ(e ) kra = 1.6 γ(e ) kol = 2.0 a few more details Radio data Total - KRA model regular GMF: B Total - KOL model disc 2µG, B halo 4µG (Pshirkov et al. 2012); 10 5 GMF - KRA Model random MF: KRA Model - w/o break B ranpzq 7.6 ˆ exp p z{z tqµg, KRA Model - only 2 nd (see Han, Ferriere and 10 4 Manchester, 2004); Dpzq9B 1 ran 9 exp pz{ztq. ν [MHz] Giuseppe Di Bernardo, in collaboration Planck Conference with Evoli, Ferrara, C.,, December Gaggero, 05, 2014 D.,, Grasso, D. (MPA) 6 / 23
8 Giuseppe Di Bernardo, in collaboration Planck Conference with Evoli, Ferrara, C.,, December Gaggero, 05, 2014 D.,, Grasso, D. (MPA) 7 / 23 The Synchrotron Emission of the Galaxy The Halo Height: a Cornerstone in Modern Astro-Particle Physics results from Di Bernardo G., et al., JCAP 3 (2013) The magnetic halo height... for a given propagation set up, the synchrotron flux depends only on the random field normalization B ran(z = 0) and on z t, the scale-height of the diffusion region. Bran 2 pz 0q9z MHz dark grey 3σ ÞÑ zt ą 4 kpc; light grey 5σ ÞÑ zt ą 3 kpc; For an exponential profile of the random MF we constraint the halo height using the RM data
9 The Synchrotron Emission of the Galaxy The Latitude Profile: the Global Environment results from Di Bernardo G., et al., JCAP 3 (2013) 10 9 Sky region: 40 l ν = 408 MHz χ 2 zt=2 = 2.8 χ 2 zt=4 = 2.2 χ 2 zt=8 = 0.9 χ 2 zt=16 = 0.5 T[K] ν[mhz] Radio data 40 l 100 Thin halos are excluded at 3 σ... KRA Model, zt = 2 kpc KRA Model, zt = 4 kpc complementary probe of the vertical CRE distribution; KRA Model, zt = 8 kpc KRA set up at different halo KRA Model, zt = 16 kpc heights reproducing well the synchrotron spectrum; latitude [deg] thick halos are favoured! Giuseppe Di Bernardo, in collaboration Planck Conference with Evoli, Ferrara, C.,, December Gaggero, 05, 2014 D.,, Grasso, D. (MPA) 8 / 23
10 How do the Large Scale Structures Influence the Observables? 8 Faucher-Giguère and Kaspi TABLE 2 Spiral Arm Parameters The effects of the spiral arm pattern We live in an inter-arm region: most of the CR sources lie in the arms; high energy CRE cross through larger distances than what expected in a smooth model, where no spiral arm structure is taken into account; more severe energy losses (via IC & Synchrotron): steepening; no steep injection: compatible with 1 st Fermi acceleration mechanism The spiral arm structure...[see e.g., Faucher-Giguere & Kaspi, 2007] Arm Number Name k r0 θ0 (rad) (kpc) (rad) Isolated neutron stars are thought to be formed in core- These mark the deaths of massive, short-lived Population I stars associated with the arms of spiral galaxies. It is thus expected that the birth sites of isolated pulsars will be highly correlated with spiral arms. In fact, Kramer et al. (2003a, see especially their Figure 5) note that following the PM survey, the spiral structure is now clearly vis- birth sites of isolated pulsars ðñ spiral arms; collapse supernova events. pulsars progenitors traced by four major arm centroids: θprq9lnpr{r 0q ` θ 0 1 Norma Carina-Sagittarius Perseus Crux-Scutum Note. The numerical values differ from those given by Wainscoat et al. (1992) due to differences between the coordinate systems used in that paper and in this one. θ =arctan(y/x), and x =(x, y, z) Spiral Arm Structure Fig. 3. Example of a simulated initial distribution of pulsars in the xy plane. Each point represents the birth position of a ible in the distribution Planck Conference in longitudes Ferrara, of December young 05, pulsar 2014 projected onto the plane. The location of the9 Sun / 23 Giuseppe Di Bernardo, in collaboration with Evoli, C.,, Gaggero, D.,, Grasso, D. (MPA)
11 Giuseppe Di Bernardo, in collaboration Planck Conference with Evoli, Ferrara, C.,, December Gaggero, 05, 2014 D.,, Grasso, D. (MPA) 10 / 23 The effects of the spiral arm pattern 2D vs. 3D face-on 1 GeV on the plane Y[kpc] X[kpc] Electron density, Ee =1GeV,z=0 Y[kpc] X[kpc] Electron density, Ee =1GeV,z=0 DRAGON 3D mode (from Gaggero, D., et al. PRL, 111 (2013)) sources distributed in the spiral arms [as in e.g., Faucher-Giguere & Kaspi, 2007; see also Blasi & Amato, JCAP I&II (2012)]; distances between arms» 1 kpc: IC & Synchrotron radiative losses
12 Giuseppe Di Bernardo, in collaboration Planck Conference with Evoli, Ferrara, C.,, December Gaggero, 05, 2014 D.,, Grasso, D. (MPA) 11 / 23 The effects of the spiral arm pattern 2D vs. 3D face-on 100 GeV on the plane Y[kpc] X[kpc] Electron density, Ee =100GeV,z=0 DRAGON 3D mode (from Gaggero, D., et al. PRL, 111 (2013)) sources distributed in the spiral arms [as in e.g., Faucher-Giguere & Kaspi, 2007; see also Blasi & Amato, JCAP I&II (2012)]; distances between arms» 1 kpc: IC & Synchrotron radiative losses; energy losses in the inter-arm region change dramatically the e ` e` spectra above 20 GeV
13 The effects of the spiral arm pattern 2D vs. 3D radial distribution in the z-plane at different energies (1 GeV, 100 GeV and 1 TeV) Giuseppe Di Bernardo, in collaboration Planck Conference with Evoli, Ferrara,C.,, December Gaggero, 05, 2014 D.,, Grasso, D. (MPA)12 / 23
14 The effects of the spiral arm pattern 2D vs. 3D radial distribution at energy of 50 GeV (normalized) electron density no spiral arm pattern; spiral arm pattern profile x [kpc] Giuseppe Di Bernardo, in collaboration Planck Conference with Evoli, Ferrara, C.,, December Gaggero, 05, 2014 D.,, Grasso, D. (MPA) 13 / 23
15 Giuseppe Di Bernardo, in collaboration Planck Conference with Evoli, Ferrara, C.,, December Gaggero, 05, 2014 D.,, Grasso, D. (MPA) 14 / 23 3D Modelling of Pamela and Ams-02 data results from Gaggero, D., et al., PRD 89 (2014) Astrophysical galactic extra-component Γpe q 2.5, and Γpe q 1.7; Wtotppq «10 57, W totpe q «10 55, W totpe q «10 54, W SNR «10 58 rgev{myrs; purple (red): Ecut 10 TeV; blue (orange): Ecut 1 TeV
16 3D Modelling of Synchrotron Ia. 408 MHz Brightness Temperature Maps: Preliminary Results DRAGON + GAMMASKY Giuseppe Di Bernardo, in collaboration Planck Conference with Evoli, Ferrara, C.,, December Gaggero, 05, 2014 D.,, Grasso, D. (MPA) 15 / 23 Brightness ν = 408 MHz Brightness ν = 408 MHz 10 T[K] 1000 Brightness ν = 408 MHz 10 T[K] 1000 Intensity T Ipνqc 2 {2ν 2 k B 10 T[K] 1000 in clockwise order... Drimmel and Spergel (2001); GAMMASKY + CRE w/o arms; GAMMASKY + CRE w/ arms.
17 3D Modelling of Synchrotron Ib. 408 MHz Brightness Temperature Residuals: Preliminary Results DRAGON + GAMMASKY Giuseppe Di Bernardo, in collaboration Planck Conference with Evoli, Ferrara, C.,, December Gaggero, 05, 2014 D.,, Grasso, D. (MPA) 16 / 23 Brightness ν = 408 MHz Brightness ν = 408 MHz 10 T[K] 1000 ν = 408 MHz - full sky 10 T[K] 1000 Residuals -50 T/T [%] 50 S no arms p408q Sarms p408q Sarms p408q
18 3D Modelling of Synchrotron II. Spectral Index Maps from 408 MHz to 23 GHz: Preliminary Results DRAGON + GAMMASKY Giuseppe Di Bernardo, in collaboration Planck Conference with Evoli, Ferrara, C.,, December Gaggero, 05, 2014 D.,, Grasso, D. (MPA) 17 / 23 Synchrotron Spectral index Synchrotron Spectral index βs Synchrotron Spectral index βs Spνq9pν{ν 0 q βs β s logps 23{S 408q βs in clockwise order... CRE by Drimmel and Spergel (2001); GAMMASKY + GAMMASKY CRE w/o arms; GAMMASKY + GAMMASKY CRE w/ arms.
19 3D Modelling of Synchrotron III. The Longitude Profile near the Plane: Preliminary Results DRAGON + GAMMASKY Brightness temperature, T [mk] Sky region: b < ν = 23 GHz WMAP K-band, 9yr 3D KRA model - w/ arms 3D KRA model - w/o arms Drimmel & Spergel longitude [deg] Giuseppe Di Bernardo, in collaboration Planck Conference with Evoli, Ferrara, C.,, December Gaggero, 05, 2014 D.,, Grasso, D. (MPA) 18 / 23
20 3D Modelling of Synchrotron IVa. Polarization Maps at 30 GHz: Preliminary Results DRAGON + GAMMASKY (following the scheme as in HAMMURABI, Waelkens et al., 2009) Synchrotron polarization, Stokes I Synchrotron polarization, Stokes P [mk] 5 Synchrotron polarization, Stokes I D&S vs. 3D CRE ɛ I ɛ K ` ɛ ; ɛ P ɛ K ɛ ; GMF: Pshirkov [mk] 5 Synchrotron polarization, Stokes P [mk] [mk] 5 Giuseppe Di Bernardo, in collaboration Planck Conference with Evoli, Ferrara, C.,, December Gaggero, 05, 2014 D.,, Grasso, D. (MPA) 19 / 23
21 3D Modelling of Synchrotron IVb. Polarization Maps at 30 GHz: Preliminary Results DRAGON + GAMMASKY (following the scheme as in HAMMURABI, Waelkens et al., 2009) Synchrotron polarization, Stokes I Synchrotron polarization, Stokes P [mk] 0.1 Synchrotron polarization, Stokes I D&S vs. 3D CRE ɛ I ɛ K ` ɛ ; ɛ P ɛ K ɛ ; GMF: Spiral [mk] 0.1 Synchrotron polarization, Stokes P [mk] [mk] 0.1 Giuseppe Di Bernardo, in collaboration Planck Conference with Evoli, Ferrara, C.,, December Gaggero, 05, 2014 D.,, Grasso, D. (MPA) 20 / 23
22 Conclusions More effort is needed Giuseppe Di Bernardo, in collaboration Planck Conference with Evoli, Ferrara, C.,, December Gaggero, 05, 2014 D.,, Grasso, D. (MPA) 21 / 23 Multichannel analysis! We exploited the galactic diffuse synchrotron emission as a way to measure the low energy LIS spectrum of CRE; The synchrotron emission, conversely to the common 10 Be{ 9 Be constraint, offers instead a much more direct probe of the magnetic halo height, z t. The spatial and energy distribution of CRE is largely affected by the spiral arm pattern for energy around (and above) 50GeV : that reflects drastically on the angular distribution and the spectral index map of the synchrotron emission; DRAGON: a suitable tool for most CR analysis; GAMMASKY will be soon complete of all relevant components (free-free emission, all Stokes parameters... etc) γ-fermi-lat, CRs and Planck data, simultaneously (see Ensslin s talk).
23 Backup slides Giuseppe Di Bernardo, in collaboration Planck Conference with Evoli, Ferrara, C.,, December Gaggero, 05, 2014 D.,, Grasso, D. (MPA) 22 / 23
24 The Interstellar Medium Turbulence and Transport of CRs Giuseppe Di Bernardo, in collaboration Planck Conference with Evoli, Ferrara, C.,, December Gaggero, 05, 2014 D.,, Grasso, D. (MPA) 23 / 23 The legacy of Kolmogorov pu qu: distorsions of the velocity field (eddies); Onset of turbulence: Re " 1; Energy cascade process: 9ɛ pδu 3 L {Lq; (HD) Kolmogorov s law: WK pkq9 k 5{3 (Alfvnic eddies elongated along the MF); (MHD) Kraichnan s law: WIK pkq9 k 3{2 (fast modes). In the Quasi Linear Theory... kres Ω{vµ; τsca Ω 1 pk res W pk res q{b 2 0 {4πq 1 ; D 1{3vrL {F; F pk res W pk res q{b 2 0 {4πq; ş dkw pkq δb 2 {4π; W pkqdk k 2`δ dk; DpRq 9 R δ ; (HD) Kolmogorov s law: δ 1{3; (MHD) Kraichnan s law: δ 1{2; The ISM is turbulent... on scales ranging from AUs to kpc, with an embedded magnetic field taht influences almost all of its properties. MHD turbulence is accepted to be of key importance for the propagation and acceleration of Cosmic Rays.
High and low energy puzzles in the AMS-02 positron fraction results
 High and low energy puzzles in the AMS-02 positron fraction results Dario Grasso (INFN, Pisa) D. Gaggero (SISSA), L.Maccione (MPI, Munich), C. Evoli(DESY), G. Di Bernardo (Göteborg) AMS-02 positron fraction
High and low energy puzzles in the AMS-02 positron fraction results Dario Grasso (INFN, Pisa) D. Gaggero (SISSA), L.Maccione (MPI, Munich), C. Evoli(DESY), G. Di Bernardo (Göteborg) AMS-02 positron fraction
Gamma-ray and neutrino diffuse emissions of the Galaxy above the TeV
 Gamma-ray and neutrino diffuse emissions of the Galaxy above the TeV (with spatial dependent CR transport) D. Grasso (INFN, Pisa) with D. Gaggero, A. Marinelli, A. Urbano, M. Valli IceCube recent results
Gamma-ray and neutrino diffuse emissions of the Galaxy above the TeV (with spatial dependent CR transport) D. Grasso (INFN, Pisa) with D. Gaggero, A. Marinelli, A. Urbano, M. Valli IceCube recent results
The High-Energy Interstellar Medium
 The High-Energy Interstellar Medium Andy Strong MPE Garching on behalf of Fermi-LAT collaboration Cosmic Ray Interactions: Bridging High and Low Energy Astrophysics Lorentz Centre Workshop March 14-18
The High-Energy Interstellar Medium Andy Strong MPE Garching on behalf of Fermi-LAT collaboration Cosmic Ray Interactions: Bridging High and Low Energy Astrophysics Lorentz Centre Workshop March 14-18
Interstellar gamma rays. New insights from Fermi. Andy Strong. on behalf of Fermi-LAT collaboration. COSPAR Scientific Assembly, Bremen, July 2010
 Interstellar gamma rays New insights from Fermi Andy Strong on behalf of Fermi-LAT collaboration COSPAR Scientific Assembly, Bremen, July 2010 Session E110: ' The next generation of ground-based Cerenkov
Interstellar gamma rays New insights from Fermi Andy Strong on behalf of Fermi-LAT collaboration COSPAR Scientific Assembly, Bremen, July 2010 Session E110: ' The next generation of ground-based Cerenkov
Dark Matter searches with radio observations
 Marco Taoso Dpt. of Physics and Astronomy UBC Vancouver Dark Matter searches with radio observations IDM 2012 Chicago, 23-27 July Search for DM with astrophysical observations Gamma- rays Microwave Radio
Marco Taoso Dpt. of Physics and Astronomy UBC Vancouver Dark Matter searches with radio observations IDM 2012 Chicago, 23-27 July Search for DM with astrophysical observations Gamma- rays Microwave Radio
Searching for Dark Matter in the Galactic Center with Fermi LAT: Challenges
 Searching for Dark Matter in the Galactic Center with Fermi LAT: Challenges Simona Murgia University of California, Irvine Debates on the Nature of Dark Matter Sackler 2014 19-22 May 2014 arxiv:0908.0195
Searching for Dark Matter in the Galactic Center with Fermi LAT: Challenges Simona Murgia University of California, Irvine Debates on the Nature of Dark Matter Sackler 2014 19-22 May 2014 arxiv:0908.0195
Galactic radio loops. Philipp Mertsch with Subir Sarkar. The Radio Synchrotron Background Workshop, University of Richmond 21 July 2017
 Galactic radio loops Philipp Mertsch with Subir Sarkar The Radio Synchrotron Background Workshop, University of Richmond 21 July 2017 Foregrounds in B-modes Adam et al., arxiv:1502.01588 1409.5738 (Planck
Galactic radio loops Philipp Mertsch with Subir Sarkar The Radio Synchrotron Background Workshop, University of Richmond 21 July 2017 Foregrounds in B-modes Adam et al., arxiv:1502.01588 1409.5738 (Planck
Astrophysical issues in the cosmic ray e spectra: Have we seen dark matter annihilation?
 Astrophysical issues +/ in the cosmic ray e spectra: Have we seen dark matter annihilation? Julien Lavalle Department of Theoretical Physics University of Torino and INFN Collab: Torino: R. Lineros, F.
Astrophysical issues +/ in the cosmic ray e spectra: Have we seen dark matter annihilation? Julien Lavalle Department of Theoretical Physics University of Torino and INFN Collab: Torino: R. Lineros, F.
Cosmic ray electrons from here and there (the Galactic scale)
 Cosmic ray electrons from here and there (the Galactic scale) Julien Lavalle Department of Theoretical Physics Torino University and INFN Outline: (i) local electrons (ii) comments on synchrotron [based
Cosmic ray electrons from here and there (the Galactic scale) Julien Lavalle Department of Theoretical Physics Torino University and INFN Outline: (i) local electrons (ii) comments on synchrotron [based
Astro2020 Science White Paper Prospects for the detection of synchrotron halos around middle-age pulsars
 Astro2020 Science White Paper Prospects for the detection of synchrotron halos around middle-age pulsars Thematic Areas: Planetary Systems Star and Planet Formation Formation and Evolution of Compact Objects
Astro2020 Science White Paper Prospects for the detection of synchrotron halos around middle-age pulsars Thematic Areas: Planetary Systems Star and Planet Formation Formation and Evolution of Compact Objects
Dark Matter Electron Anisotropy: A universal upper limit
 Seminari teorici del venerdì Enrico Borriello Università degli Studi di Napoli Federico II & INFN Sezione di Napoli Dark Matter Electron Anisotropy: A universal upper limit Based on Borriello, Maccione,
Seminari teorici del venerdì Enrico Borriello Università degli Studi di Napoli Federico II & INFN Sezione di Napoli Dark Matter Electron Anisotropy: A universal upper limit Based on Borriello, Maccione,
Indirect dark matter detection and the Galactic Center GeV Excess
 Image Credit: Springel et al. 2008 Indirect dark matter detection and the Galactic Center GeV Excess Jennifer Siegal-Gaskins Caltech Image Credit: Springel et al. 2008 Jennifer Siegal-Gaskins Caltech Image
Image Credit: Springel et al. 2008 Indirect dark matter detection and the Galactic Center GeV Excess Jennifer Siegal-Gaskins Caltech Image Credit: Springel et al. 2008 Jennifer Siegal-Gaskins Caltech Image
Instituto de Fisica Teórica, IFT-CSIC Madrid. Marco Taoso. DM and the Galactic Center GeV excess
 Instituto de Fisica Teórica, IFT-CSIC Madrid Marco Taoso DM and the Galactic Center GeV excess Frontier Objects in Astrophysics and Particle Physics Vulcano Workshop 26-05- 2016 How and where to look for
Instituto de Fisica Teórica, IFT-CSIC Madrid Marco Taoso DM and the Galactic Center GeV excess Frontier Objects in Astrophysics and Particle Physics Vulcano Workshop 26-05- 2016 How and where to look for
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 17 Nov 2008
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 17 Nov 2008 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 17 Nov 2008](/thumbs/91/106443029.jpg) Dark Matter Annihilation in the light of EGRET, HEAT, WMAP, INTEGRAL and ROSAT arxiv:0811.v1 [astro-ph 1 Nov 008 Institut für Experimentelle Kernphysik, Universiät Karlsruhe E-mail: gebauer@ekp.uni-karlsruhe.de
Dark Matter Annihilation in the light of EGRET, HEAT, WMAP, INTEGRAL and ROSAT arxiv:0811.v1 [astro-ph 1 Nov 008 Institut für Experimentelle Kernphysik, Universiät Karlsruhe E-mail: gebauer@ekp.uni-karlsruhe.de
Indirect Dark Matter constraints with radio observations
 Indirect Dark Matter constraints with radio observations In collaboration with E.Borriello and G.Miele, University of Naples Federico II Alessandro Cuoco, Institute for Physics and Astronomy University
Indirect Dark Matter constraints with radio observations In collaboration with E.Borriello and G.Miele, University of Naples Federico II Alessandro Cuoco, Institute for Physics and Astronomy University
Properties of Elementary Particle Fluxes in Cosmic Rays. TeVPA Aug. 7, Yuan-Hann Chang National Central University, Taiwan
 Properties of Elementary Particle Fluxes in Cosmic Rays TeVPA Aug. 7, 2017 Yuan-Hann Chang National Central University, Taiwan Elementary Particles in Space There are hundreds of different kinds of charged
Properties of Elementary Particle Fluxes in Cosmic Rays TeVPA Aug. 7, 2017 Yuan-Hann Chang National Central University, Taiwan Elementary Particles in Space There are hundreds of different kinds of charged
Large-Scale Structure of the Galactic Magnetic Field. Marijke Haverkorn & Jo-Anne Brown NRAO/UC-Berkeley University of Calgary
 Large-Scale Structure of the Galactic Magnetic Field Marijke Haverkorn & Jo-Anne Brown NRAO/UC-Berkeley University of Calgary Outline On the Large-Scale Structure of the GMF... Why do we care? What do
Large-Scale Structure of the Galactic Magnetic Field Marijke Haverkorn & Jo-Anne Brown NRAO/UC-Berkeley University of Calgary Outline On the Large-Scale Structure of the GMF... Why do we care? What do
THE WMAP HAZE: PARTICLE PHYSICS ASTROPHYSICS VERSUS. Greg Dobler. Harvard/CfA July 14 th, TeV09
 THE WMAP HAZE: PARTICLE PHYSICS VERSUS ASTROPHYSICS Greg Dobler Harvard/CfA July 14 th, 2009 - TeV09 THE WMAP HAZE: PARTICLE PHYSICS VERSUS ASTROPHYSICS Doug Finkbeiner (CfA) Dan Hooper (FNAL) Gabrijela
THE WMAP HAZE: PARTICLE PHYSICS VERSUS ASTROPHYSICS Greg Dobler Harvard/CfA July 14 th, 2009 - TeV09 THE WMAP HAZE: PARTICLE PHYSICS VERSUS ASTROPHYSICS Doug Finkbeiner (CfA) Dan Hooper (FNAL) Gabrijela
a cosmic- ray propagation and gamma-ray code
 GALPROP: a cosmic- ray propagation and gamma-ray code A. Strong, MPE Garching Tools for SUSY, Annecy, June 28 2006 The basis: cosmic-ray production & propagation in the Galaxy intergalactic space HALO
GALPROP: a cosmic- ray propagation and gamma-ray code A. Strong, MPE Garching Tools for SUSY, Annecy, June 28 2006 The basis: cosmic-ray production & propagation in the Galaxy intergalactic space HALO
Seeing the moon shadow in CRs
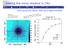 Seeing the moon shadow in CRs and using the Earth field as a spectrometer Tibet III Amenomori et al. arxiv:0810.3757 see also ARGO-YBJ results Bartoli et. al, arxiv:1107.4887 Milargo: 100% coverage r owe
Seeing the moon shadow in CRs and using the Earth field as a spectrometer Tibet III Amenomori et al. arxiv:0810.3757 see also ARGO-YBJ results Bartoli et. al, arxiv:1107.4887 Milargo: 100% coverage r owe
The Inner Region of the Milky Way Galaxy in High Energy Gamma Rays
 The Inner Region of the Milky Way Galaxy in High Energy Gamma Rays Simona Murgia, SLAC-KIPAC for the Fermi LAT Collaboration UCLA Dark Matter 2012 Marina del Rey 22-24 February 2012 arxiv:0908.0195 Gamma
The Inner Region of the Milky Way Galaxy in High Energy Gamma Rays Simona Murgia, SLAC-KIPAC for the Fermi LAT Collaboration UCLA Dark Matter 2012 Marina del Rey 22-24 February 2012 arxiv:0908.0195 Gamma
Measurement of CR anisotropies with the AMS detector on the ISS
 Measurement of CR anisotropies with the AMS detector on the ISS J. Casaus ( CIEMAT Spain ) on behalf of the AMS Collaboration Origin of excess of positrons Positron fraction shows an excess above 10 GeV
Measurement of CR anisotropies with the AMS detector on the ISS J. Casaus ( CIEMAT Spain ) on behalf of the AMS Collaboration Origin of excess of positrons Positron fraction shows an excess above 10 GeV
Troy A. Porter Stanford University
 High-Energy Gamma-Rays from the Milky Way: 3D Spatial Models for the CR and Radiation Field Densities Troy A. Porter Stanford University What is GALPROP? Tool for modelling and interpreting cosmic-ray
High-Energy Gamma-Rays from the Milky Way: 3D Spatial Models for the CR and Radiation Field Densities Troy A. Porter Stanford University What is GALPROP? Tool for modelling and interpreting cosmic-ray
² The universe observed ² Relativistic world models ² Reconstructing the thermal history ² Big bang nucleosynthesis ² Dark matter: astrophysical
 ² The universe observed ² Relativistic world models ² Reconstructing the thermal history ² Big bang nucleosynthesis ² Dark matter: astrophysical observations ² Dark matter: relic particles ² Dark matter:
² The universe observed ² Relativistic world models ² Reconstructing the thermal history ² Big bang nucleosynthesis ² Dark matter: astrophysical observations ² Dark matter: relic particles ² Dark matter:
Testing a DM explanation of the positron excess with the Inverse Compton scattering
 Testing a DM explanation of the positron excess with the Inverse Compton scattering Gabrijela Zaharijaš Oskar Klein Center, Stockholm University Work with A. Sellerholm, L. Bergstrom, J. Edsjo on behalf
Testing a DM explanation of the positron excess with the Inverse Compton scattering Gabrijela Zaharijaš Oskar Klein Center, Stockholm University Work with A. Sellerholm, L. Bergstrom, J. Edsjo on behalf
The Inner Region of the Milky Way Galaxy in High Energy Gamma Rays
 The Inner Region of the Milky Way Galaxy in High Energy Gamma Rays Simona Murgia, SLAC-KIPAC for the Fermi LAT Collaboration Dark Matter Signatures in the Gamma-ray Sky Austin, Texas 7-8 May 2012 arxiv:0908.0195
The Inner Region of the Milky Way Galaxy in High Energy Gamma Rays Simona Murgia, SLAC-KIPAC for the Fermi LAT Collaboration Dark Matter Signatures in the Gamma-ray Sky Austin, Texas 7-8 May 2012 arxiv:0908.0195
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 29 Oct 2012
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 29 Oct 2012 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 29 Oct 2012](/thumbs/93/117943116.jpg) Draft version September 10, 2018 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 THE GALACTIC MAGNETIC FIELD Ronnie Jansson and Glennys R. Farrar Center for Cosmology and Particle Physics, Department
Draft version September 10, 2018 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 THE GALACTIC MAGNETIC FIELD Ronnie Jansson and Glennys R. Farrar Center for Cosmology and Particle Physics, Department
Radio Continuum: Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields. Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn
 Radio Continuum: Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn Synchrotron emission Beam angle: Ψ/2=1/γ=E o /E Radio continuum tools to study GeV Cosmic ray electrons (CRE) Synchrotron spectrum:
Radio Continuum: Cosmic Rays & Magnetic Fields Rainer Beck MPIfR Bonn Synchrotron emission Beam angle: Ψ/2=1/γ=E o /E Radio continuum tools to study GeV Cosmic ray electrons (CRE) Synchrotron spectrum:
Sep. 13, JPS meeting
 Recent Results on Cosmic-Rays by Fermi-LAT Sep. 13, 2010 @ JPS meeting Tsunefumi Mizuno (Hiroshima Univ.) On behalf of the Fermi-LAT collaboration 1 Outline Introduction Direct measurement of CRs CRs in
Recent Results on Cosmic-Rays by Fermi-LAT Sep. 13, 2010 @ JPS meeting Tsunefumi Mizuno (Hiroshima Univ.) On behalf of the Fermi-LAT collaboration 1 Outline Introduction Direct measurement of CRs CRs in
Implication of AMS-02 positron fraction measurement. Qiang Yuan
 Implication of AMS-02 positron fraction measurement Qiang Yuan (yuanq@ihep.ac.cn) Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences Collaborated with Xiaojun Bi, Guo-Ming Chen, Yi-Qing Guo,
Implication of AMS-02 positron fraction measurement Qiang Yuan (yuanq@ihep.ac.cn) Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences Collaborated with Xiaojun Bi, Guo-Ming Chen, Yi-Qing Guo,
Constraining Dark Matter annihilation with the Fermi-LAT isotropic gamma-ray background
 Constraining Dark Matter annihilation with the Fermi-LAT isotropic gamma-ray background Fiorenza Donato @ Physics Dept., Un. Torino The gamma-ray sky - Minneapolis, October 10, 2013 Plan of my talk What
Constraining Dark Matter annihilation with the Fermi-LAT isotropic gamma-ray background Fiorenza Donato @ Physics Dept., Un. Torino The gamma-ray sky - Minneapolis, October 10, 2013 Plan of my talk What
Gamma-ray emission at the base of the Fermi bubbles. Dmitry Malyshev, Laura Herold Erlangen Center for Astroparticle Physics
 Gamma-ray emission at the base of the Fermi bubbles Dmitry Malyshev, Laura Herold Erlangen Center for Astroparticle Physics On behalf of the Fermi-LAT collaboration TeVPA 2018, Berlin Fermi bubbles surprise
Gamma-ray emission at the base of the Fermi bubbles Dmitry Malyshev, Laura Herold Erlangen Center for Astroparticle Physics On behalf of the Fermi-LAT collaboration TeVPA 2018, Berlin Fermi bubbles surprise
Gamma rays from Galactic pulsars: high- and lowlatitude
 Francesca Calore Gamma rays from Galactic pulsars: high- and lowlatitude emission Conca Specchiulla, 8th September 2014 based on: F. Calore, M. Di Mauro & F. Donato, arxiv:1406.2706 F. Calore, I. Cholis
Francesca Calore Gamma rays from Galactic pulsars: high- and lowlatitude emission Conca Specchiulla, 8th September 2014 based on: F. Calore, M. Di Mauro & F. Donato, arxiv:1406.2706 F. Calore, I. Cholis
A New View of the High-Energy γ-ray Sky with the Fermi Telescope
 A New View of the High-Energy γ-ray Sky with the Fermi Telescope Aurelien Bouvier KIPAC/SLAC, Stanford University On behalf of the Fermi collaboration SNOWPAC, 2010 The Fermi observatory Launch: June 11
A New View of the High-Energy γ-ray Sky with the Fermi Telescope Aurelien Bouvier KIPAC/SLAC, Stanford University On behalf of the Fermi collaboration SNOWPAC, 2010 The Fermi observatory Launch: June 11
Cosmic Ray Excess From Multi-Component Dark Matter
 Cosmic Ray Excess From Multi-Component Dark Matter Da Huang Physics Department, NTHU @ LeCosPA PRD89, 055021(2014) [arxiv: 1312.0366] PRD91, 095006 (2015) [arxiv: 1411.4450] Mod. Phys. Lett. A 30 (2015)
Cosmic Ray Excess From Multi-Component Dark Matter Da Huang Physics Department, NTHU @ LeCosPA PRD89, 055021(2014) [arxiv: 1312.0366] PRD91, 095006 (2015) [arxiv: 1411.4450] Mod. Phys. Lett. A 30 (2015)
Dark Matter searches with astrophysics
 Marco Taoso IPhT CEA-Saclay Dark Matter searches with astrophysics IAP 24 February 2013 The cosmological pie Non baryonic Dark Matter dominates the matter content of the Universe Motivation to search for
Marco Taoso IPhT CEA-Saclay Dark Matter searches with astrophysics IAP 24 February 2013 The cosmological pie Non baryonic Dark Matter dominates the matter content of the Universe Motivation to search for
Galactic Diffuse Gamma-Ray Emission
 Galactic Diffuse Gamma-Ray Emission The Bright Gamma-Ray Sky 7 th AGILE Workshop 29 Sep - 1 Oct, 2009 Stanley D. Hunter NASA/GSFC stanley.d.hunter@nasa.gov Galactic Diffuse Emission The beginning: OSO
Galactic Diffuse Gamma-Ray Emission The Bright Gamma-Ray Sky 7 th AGILE Workshop 29 Sep - 1 Oct, 2009 Stanley D. Hunter NASA/GSFC stanley.d.hunter@nasa.gov Galactic Diffuse Emission The beginning: OSO
Hunting for Dark Matter in Anisotropies of Gamma-ray Sky: Theory and First Observational Results from Fermi-LAT
 Hunting for Dark Matter in Anisotropies of Gamma-ray Sky: Theory and First Observational Results from Fermi-LAT Eiichiro Komatsu (Texas Cosmology Center, Univ. of Texas at Austin) MPA Seminar, September
Hunting for Dark Matter in Anisotropies of Gamma-ray Sky: Theory and First Observational Results from Fermi-LAT Eiichiro Komatsu (Texas Cosmology Center, Univ. of Texas at Austin) MPA Seminar, September
Mattia Di Mauro. Fermi-LAT point source population studies and origin of the Fermi-LAT gamma-ray background. Trieste, May, 3, 2016
 Fermi-LAT point source population studies and origin of the Fermi-LAT gamma-ray background Mattia Di Mauro On behalf of the Fermi- LAT Collaboration 1 Trieste, May, 3, 2016 THE ISOTROPIC GAMMA RAY BACKGROUND
Fermi-LAT point source population studies and origin of the Fermi-LAT gamma-ray background Mattia Di Mauro On behalf of the Fermi- LAT Collaboration 1 Trieste, May, 3, 2016 THE ISOTROPIC GAMMA RAY BACKGROUND
Constraining primordial magnetic fields with observations
 Constraining primordial magnetic fields with observations Kerstin Kunze (University of Salamanca and IUFFyM) KK PRD 83 (2011) 023006; PRD 85 (2012) 083004; PRD 87 (2013) 103005; PRD 89 (2014) 103016, arxiv:1703.03650
Constraining primordial magnetic fields with observations Kerstin Kunze (University of Salamanca and IUFFyM) KK PRD 83 (2011) 023006; PRD 85 (2012) 083004; PRD 87 (2013) 103005; PRD 89 (2014) 103016, arxiv:1703.03650
The Galactic diffuse gamma ray emission in the energy range 30 TeV 3 PeV
 The Galactic diffuse gamma ray emission in the energy range 30 TeV 3 PeV Mount Rainier by Will Christiansen Silvia Vernetto & Paolo Lipari 35th ICRC 12-20 July 2017 - Busan - South Korea Gamma ray astronomy
The Galactic diffuse gamma ray emission in the energy range 30 TeV 3 PeV Mount Rainier by Will Christiansen Silvia Vernetto & Paolo Lipari 35th ICRC 12-20 July 2017 - Busan - South Korea Gamma ray astronomy
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 29 Jan 2015
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 29 Jan 2015 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 29 Jan 2015](/thumbs/81/82871468.jpg) arxiv:1501.07485v1 [astro-ph.he] 29 Jan 2015 Fitting the Fermi-LAT GeV excess: on the importance of the propagation of electrons from dark matter UPMC-CNRS, UMR7095, Institut d Astrophysique de Paris,
arxiv:1501.07485v1 [astro-ph.he] 29 Jan 2015 Fitting the Fermi-LAT GeV excess: on the importance of the propagation of electrons from dark matter UPMC-CNRS, UMR7095, Institut d Astrophysique de Paris,
Topics. 1. Towards a unified picture of CRs production and propagation: 2. AMS-02 good candidates for Dark Matter space search
 Nicolò Masi Bologna University and INFN - 31 May 2016 Topics 1. Towards a unified picture of CRs production and propagation: Astrophysical uncertainties with GALPROP Local Interstellar Spectra: AMS-02
Nicolò Masi Bologna University and INFN - 31 May 2016 Topics 1. Towards a unified picture of CRs production and propagation: Astrophysical uncertainties with GALPROP Local Interstellar Spectra: AMS-02
Using the Fermi-LAT to Search for Indirect Signals from Dark Matter Annihilation
 Using the Fermi-LAT to Search for Indirect Signals from Dark Matter Annihilation Tim Linden UC - Santa Cruz Representing the Fermi-LAT Collaboration with acknowledgements to: Brandon Anderson, Elliott
Using the Fermi-LAT to Search for Indirect Signals from Dark Matter Annihilation Tim Linden UC - Santa Cruz Representing the Fermi-LAT Collaboration with acknowledgements to: Brandon Anderson, Elliott
Galactic cosmic rays propagation
 Galactic cosmic rays propagation Side view of the Galaxy The Solar system is 8.5 kpc away from the galactic center. One pc is 3.10 18 cm, so we are at a distance of 2.55 10 17 km and the light from it
Galactic cosmic rays propagation Side view of the Galaxy The Solar system is 8.5 kpc away from the galactic center. One pc is 3.10 18 cm, so we are at a distance of 2.55 10 17 km and the light from it
A New Method for Characterizing Unresolved Point Sources: applications to Fermi Gamma-Ray Data
 A New Method for Characterizing Unresolved Point Sources: applications to Fermi Gamma-Ray Data Ben Safdi Massachusetts Institute of Technology 2015 B.S., S. Lee, M. Lisanti, and B.S., S. Lee, M. Lisanti,
A New Method for Characterizing Unresolved Point Sources: applications to Fermi Gamma-Ray Data Ben Safdi Massachusetts Institute of Technology 2015 B.S., S. Lee, M. Lisanti, and B.S., S. Lee, M. Lisanti,
Magnetic Fields in the Milky Way
 Magnetic Fields in the Milky Way Wolfgang Reich Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie Bonn Why is the Galactic B-field of interest? highest spatial resolution of B-fields clarify its role in spiral galaxies
Magnetic Fields in the Milky Way Wolfgang Reich Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie Bonn Why is the Galactic B-field of interest? highest spatial resolution of B-fields clarify its role in spiral galaxies
Cosmic Ray Electrons and GC Observations with H.E.S.S.
 Cosmic Ray Electrons and GC Observations with H.E.S.S. Christopher van Eldik (for the H.E.S.S. Collaboration) MPI für Kernphysik, Heidelberg, Germany TeVPA '09, SLAC, July 2009 The Centre of the Milky
Cosmic Ray Electrons and GC Observations with H.E.S.S. Christopher van Eldik (for the H.E.S.S. Collaboration) MPI für Kernphysik, Heidelberg, Germany TeVPA '09, SLAC, July 2009 The Centre of the Milky
Fundamental Physics with GeV Gamma Rays
 Stefano Profumo UC Santa Cruz Santa Cruz Institute for Particle Physics T.A.S.C. [Theoretical Astrophysics, Santa Cruz] Fundamental Physics with GeV Gamma Rays Based on: Kamionkowski & SP, 0810.3233 (subm.
Stefano Profumo UC Santa Cruz Santa Cruz Institute for Particle Physics T.A.S.C. [Theoretical Astrophysics, Santa Cruz] Fundamental Physics with GeV Gamma Rays Based on: Kamionkowski & SP, 0810.3233 (subm.
Cosmic rays in the local interstellar medium
 Cosmic rays in the local interstellar medium Igor V. Moskalenko Igor V. Moskalenko/NASA-GSFC 1 LMC (Magellanic Cloud Emission Nuclear Data-2004/09/28, Line Survey: Smith, Points) Santa Fe R - H G - [S
Cosmic rays in the local interstellar medium Igor V. Moskalenko Igor V. Moskalenko/NASA-GSFC 1 LMC (Magellanic Cloud Emission Nuclear Data-2004/09/28, Line Survey: Smith, Points) Santa Fe R - H G - [S
High-Energy GammaRays toward the. Galactic Centre. Troy A. Porter Stanford University
 High-Energy GammaRays toward the Galactic Centre Troy A. Porter Stanford University Fermi LAT 5-Year Sky Map > 1 GeV Galactic Plane Galactic Centre Point Sources Diffuse γ-ray emission produced by cosmic
High-Energy GammaRays toward the Galactic Centre Troy A. Porter Stanford University Fermi LAT 5-Year Sky Map > 1 GeV Galactic Plane Galactic Centre Point Sources Diffuse γ-ray emission produced by cosmic
Subir Sarkar
 Trinity 2016 Oxford ² The universe observed ² Relativistic world models ² Reconstructing the thermal history ² Big bang nucleosynthesis ² Dark matter: astrophysical observations ² Dark matter: relic particles
Trinity 2016 Oxford ² The universe observed ² Relativistic world models ² Reconstructing the thermal history ² Big bang nucleosynthesis ² Dark matter: astrophysical observations ² Dark matter: relic particles
Galactic cosmic nuclei and leptons with USINE
 Galactic cosmic nuclei and leptons with USINE a, David Maurin b a LPTHE, CNRS & UPMC, 4 Place Jussieu, F-75252 Paris France b LPSC, UGA & CNRS/IN2P3, 53 avenue des Martyrs, 38026 Grenoble France E-mail:
Galactic cosmic nuclei and leptons with USINE a, David Maurin b a LPTHE, CNRS & UPMC, 4 Place Jussieu, F-75252 Paris France b LPSC, UGA & CNRS/IN2P3, 53 avenue des Martyrs, 38026 Grenoble France E-mail:
Spectra of Cosmic Rays
 Spectra of Cosmic Rays Flux of relativistic charged particles [nearly exactly isotropic] Particle density Power-Law Energy spectra Exponent (p, Nuclei) : Why power laws? (constraint on the dynamics of
Spectra of Cosmic Rays Flux of relativistic charged particles [nearly exactly isotropic] Particle density Power-Law Energy spectra Exponent (p, Nuclei) : Why power laws? (constraint on the dynamics of
Galactic diffuse neutrino component in the astrophysical excess measured by the IceCube experiment
 IL NUOVO CIMENTO 40 C (2017) 140 DOI 10.1393/ncc/i2017-17140-4 Colloquia: SciNeGHE 2016 Galactic diffuse neutrino component in the astrophysical excess measured by the IceCube experiment D. Grasso( 1 ),
IL NUOVO CIMENTO 40 C (2017) 140 DOI 10.1393/ncc/i2017-17140-4 Colloquia: SciNeGHE 2016 Galactic diffuse neutrino component in the astrophysical excess measured by the IceCube experiment D. Grasso( 1 ),
Production of Secondary Cosmic Rays in Supernova Remnants
 Production of Secondary Cosmic Rays in Supernova Remnants E. G. Berezhko, Yu. G. Shafer Institute of Cosmophysical Research and Aeronomy, 31 Lenin Ave., 677891 Yakutsk, Russia E-mail: ksenofon@ikfia.sbras.ru
Production of Secondary Cosmic Rays in Supernova Remnants E. G. Berezhko, Yu. G. Shafer Institute of Cosmophysical Research and Aeronomy, 31 Lenin Ave., 677891 Yakutsk, Russia E-mail: ksenofon@ikfia.sbras.ru
Gamma-ray and neutrino diffuse emissions of the Galaxy above the TeV
 Gamma-ray and neutrino diffuse emissions of the Galaxy above the TeV Daniele Gaggero SISSA and INFN, via Bonomea 265, I-34136 Trieste, Italy E-mail: daniele.gaggero@sissa.it arxiv:1507.07796v1 [astro-ph.he]
Gamma-ray and neutrino diffuse emissions of the Galaxy above the TeV Daniele Gaggero SISSA and INFN, via Bonomea 265, I-34136 Trieste, Italy E-mail: daniele.gaggero@sissa.it arxiv:1507.07796v1 [astro-ph.he]
Primordial B-modes: Foreground modelling and constraints
 Primordial B-modes: Foreground modelling and constraints Carlo Contaldi Imperial College London Model Polarisation Amplitude 40 60-180 160 140 120 100 20 80 0 60 40 20 0-20 -40-60 -80-100 -120-140 -160-20
Primordial B-modes: Foreground modelling and constraints Carlo Contaldi Imperial College London Model Polarisation Amplitude 40 60-180 160 140 120 100 20 80 0 60 40 20 0-20 -40-60 -80-100 -120-140 -160-20
Quest for New Physics
 Stefano Profumo UC Santa Cruz Santa Cruz Institute for Particle Physics T.A.S.C. [Theoretical Astrophysics in Santa Cruz] Cosmic Rays and the Quest for New Physics Scineghe 2010, Trieste, Italy Thursday,
Stefano Profumo UC Santa Cruz Santa Cruz Institute for Particle Physics T.A.S.C. [Theoretical Astrophysics in Santa Cruz] Cosmic Rays and the Quest for New Physics Scineghe 2010, Trieste, Italy Thursday,
Lecture 13 Interstellar Magnetic Fields
 Lecture 13 Interstellar Magnetic Fields 1. Introduction. Synchrotron radiation 3. Faraday rotation 4. Zeeman effect 5. Polarization of starlight 6. Summary of results References Zweibel & Heiles, Nature
Lecture 13 Interstellar Magnetic Fields 1. Introduction. Synchrotron radiation 3. Faraday rotation 4. Zeeman effect 5. Polarization of starlight 6. Summary of results References Zweibel & Heiles, Nature
Fermi: Highlights of GeV Gamma-ray Astronomy
 Fermi: Highlights of GeV Gamma-ray Astronomy Dave Thompson NASA GSFC On behalf of the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Large Area Telescope Collaboration Neutrino Oscillation Workshop Otranto, Lecce, Italy
Fermi: Highlights of GeV Gamma-ray Astronomy Dave Thompson NASA GSFC On behalf of the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Large Area Telescope Collaboration Neutrino Oscillation Workshop Otranto, Lecce, Italy
W.R. Webber. New Mexico State University, Astronomy Department, Las Cruces, NM 88003, USA
 A Galactic Cosmic Ray Electron Spectrum at Energies from 2 MeV to 2 TeV That Fits Voyager 5-60 MeV Data at Low Energies and PAMELA and AMS-2 Data at 10 GeV Using an Electron Source Spectrum ~E -2.25 A
A Galactic Cosmic Ray Electron Spectrum at Energies from 2 MeV to 2 TeV That Fits Voyager 5-60 MeV Data at Low Energies and PAMELA and AMS-2 Data at 10 GeV Using an Electron Source Spectrum ~E -2.25 A
DM subhalos: The obser vational challenge
 DM subhalos: The obser vational challenge Hannes-S. Zechlin and Dieter Horns Inst. f. Experimentalphysik, Universität Hamburg, Germany July 26th, 2012 DM subhalos in the Milky Way concordance cosmology
DM subhalos: The obser vational challenge Hannes-S. Zechlin and Dieter Horns Inst. f. Experimentalphysik, Universität Hamburg, Germany July 26th, 2012 DM subhalos in the Milky Way concordance cosmology
Fermi measurements of diffuse gamma-ray emission: results at the first-year milestone
 SciNeGHE 2009 Assisi, October 7th Fermi measurements of diffuse gamma-ray emission: results at the first-year milestone Luigi Tibaldo luigi.tibaldo@pd.infn.it INFN Sezione di Padova Dip. di Fisica G. Galilei,
SciNeGHE 2009 Assisi, October 7th Fermi measurements of diffuse gamma-ray emission: results at the first-year milestone Luigi Tibaldo luigi.tibaldo@pd.infn.it INFN Sezione di Padova Dip. di Fisica G. Galilei,
White dwarf pulsar as Possible Cosmic Ray Electron-Positron Factories
 White dwarf pulsar as Possible Cosmic Ray Electron-Positron Factories 2010 7/9 Kazumi Kashiyama (Kyoto University) Kunihito Ioka & Norita Kawanaka (KEK) arxiv:1009.1141 (submitted to PRD) http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/news/topstory/2007/whitedwarf_pulsar.html
White dwarf pulsar as Possible Cosmic Ray Electron-Positron Factories 2010 7/9 Kazumi Kashiyama (Kyoto University) Kunihito Ioka & Norita Kawanaka (KEK) arxiv:1009.1141 (submitted to PRD) http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/news/topstory/2007/whitedwarf_pulsar.html
Cosmic Ray panorama. Pamela.roma2.infn.it PAMELA (2012) Experimental challenges : e + /p ~ 10-3 e + /e - ~ 10-1
 1912 1932 Cosmic Ray panorama http::// Pamela.roma2.infn.it PAMELA (2012) Experimental challenges : e + /p ~ 10-3 e + /e - ~ 10-1 Pamela : < 0.1 evt year/gev Flux E α α 2.7 / 3.3 Statistical precision
1912 1932 Cosmic Ray panorama http::// Pamela.roma2.infn.it PAMELA (2012) Experimental challenges : e + /p ~ 10-3 e + /e - ~ 10-1 Pamela : < 0.1 evt year/gev Flux E α α 2.7 / 3.3 Statistical precision
Supernova Remnants and Cosmic. Rays
 Stars: Their Life and Afterlife Supernova Remnants and Cosmic 68 th Rays Brian Humensky Series, Compton Lecture #5 November 8, 2008 th Series, Compton Lecture #5 Outline Evolution of Supernova Remnants
Stars: Their Life and Afterlife Supernova Remnants and Cosmic 68 th Rays Brian Humensky Series, Compton Lecture #5 November 8, 2008 th Series, Compton Lecture #5 Outline Evolution of Supernova Remnants
The Large Area Telescope on-board of the Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope Mission
 The Large Area Telescope on-board of the Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope Mission 1 Outline Mainly from 2009 ApJ 697 1071 The Pair Conversion Telescope The Large Area Telescope Charged Background and Events
The Large Area Telescope on-board of the Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Telescope Mission 1 Outline Mainly from 2009 ApJ 697 1071 The Pair Conversion Telescope The Large Area Telescope Charged Background and Events
The Egret Excess, an Example of Combining Tools
 The Egret Excess, an Example of Combining Tools Institut für Experimentelle Kernphysik, Universität Karlsruhe TOOLS 2006-26th - 28th June 2006 - Annecy Outline Spectral Fit to EGRET data Problems: Rotation
The Egret Excess, an Example of Combining Tools Institut für Experimentelle Kernphysik, Universität Karlsruhe TOOLS 2006-26th - 28th June 2006 - Annecy Outline Spectral Fit to EGRET data Problems: Rotation
Cosmic rays and the diffuse gamma-ray emission
 Cosmic rays and the diffuse gamma-ray emission Dipartimento di Fisica, Torino University and INFN Sezione di Torino via P. Giuria 1, 10125 Torino, Italy E-mail: donato@to.infn.it The diffuse γ-ray emission
Cosmic rays and the diffuse gamma-ray emission Dipartimento di Fisica, Torino University and INFN Sezione di Torino via P. Giuria 1, 10125 Torino, Italy E-mail: donato@to.infn.it The diffuse γ-ray emission
Evidence of Stochastic Acceleration of Secondary. Antiprotons by Supernova Remnants! Ilias Cholis, 08/09/2017
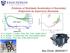 C [ ] -4 Evidence of Stochastic Acceleration of Secondary 2.2 1.0 2.0 1.8 1.6 1.4 1.2 C k p p Φ /Φ ratio fit Antiprotons by Supernova Remnants! 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0-6 - 1 k [ GV ] -1 AMS-02 PAMELA Fermi
C [ ] -4 Evidence of Stochastic Acceleration of Secondary 2.2 1.0 2.0 1.8 1.6 1.4 1.2 C k p p Φ /Φ ratio fit Antiprotons by Supernova Remnants! 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0-6 - 1 k [ GV ] -1 AMS-02 PAMELA Fermi
Spatial Profile of the Emission from Pulsar Wind Nebulae with steady-state 1D Modeling
 Spatial Profile of the Emission from Pulsar Wind Nebulae with steady-state 1D Modeling Wataru Ishizaki ( Department of Physics, Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo ) Abstract The pulsar
Spatial Profile of the Emission from Pulsar Wind Nebulae with steady-state 1D Modeling Wataru Ishizaki ( Department of Physics, Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo ) Abstract The pulsar
The 2 Icecube PeV events [A. ] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
![The 2 Icecube PeV events [A. ] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23 The 2 Icecube PeV events [A. ] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23](/thumbs/92/110652138.jpg) The 2 Icecube PeV events [A. Schuhkraft@NOW2012 ] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran 2012 1 / 23 The 2 Icecube PeV events [A. Schuhkraft@NOW2012 ] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU
The 2 Icecube PeV events [A. Schuhkraft@NOW2012 ] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran 2012 1 / 23 The 2 Icecube PeV events [A. Schuhkraft@NOW2012 ] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU
New results from the AMS experiment on the International Space Station. Henning Gast RWTH Aachen
 New results from the AMS experiment on the International Space Station Henning Gast RWTH Aachen 1 Questions to AMS-02: Are there galaxies made of anti-matter in the Universe? What is the nature of Dark
New results from the AMS experiment on the International Space Station Henning Gast RWTH Aachen 1 Questions to AMS-02: Are there galaxies made of anti-matter in the Universe? What is the nature of Dark
Constraints on cosmic-ray origin from gamma-ray observations of supernova remnants
 Constraints on cosmic-ray origin from gamma-ray observations of supernova remnants Marianne Lemoine-Goumard (CENBG, Université Bordeaux, CNRS-IN2P3, France) On behalf of the Fermi-LAT and HESS Collaborations
Constraints on cosmic-ray origin from gamma-ray observations of supernova remnants Marianne Lemoine-Goumard (CENBG, Université Bordeaux, CNRS-IN2P3, France) On behalf of the Fermi-LAT and HESS Collaborations
Dark Matter in the Universe
 Dark Matter in the Universe NTNU Trondheim [] Experimental anomalies: WMAP haze: synchrotron radiation from the GC Experimental anomalies: WMAP haze: synchrotron radiation from the GC Integral: positron
Dark Matter in the Universe NTNU Trondheim [] Experimental anomalies: WMAP haze: synchrotron radiation from the GC Experimental anomalies: WMAP haze: synchrotron radiation from the GC Integral: positron
Particle acceleration and pulsars
 Meudon, nov. 2013 p. 1/17 Particle acceleration and pulsars Fabrice Mottez LUTH - Obs. Paris-Meudon - CNRS - Univ. Paris Diderot Meudon, nov. 2013 p. 2/17 Pulsars (PSR) and pulsar wind nebulae (PWNe) Mostly
Meudon, nov. 2013 p. 1/17 Particle acceleration and pulsars Fabrice Mottez LUTH - Obs. Paris-Meudon - CNRS - Univ. Paris Diderot Meudon, nov. 2013 p. 2/17 Pulsars (PSR) and pulsar wind nebulae (PWNe) Mostly
Remnants and Pulsar Wind
 High Energy Supernova Remnants and Pulsar Wind Nebulae F. Giordano Dipartimento Interateneo di Fisica and INFN Sez. Bari For the Fermi-LAT Collaboration Scineghe 2010 The Afterlife of a star IC443 Crab
High Energy Supernova Remnants and Pulsar Wind Nebulae F. Giordano Dipartimento Interateneo di Fisica and INFN Sez. Bari For the Fermi-LAT Collaboration Scineghe 2010 The Afterlife of a star IC443 Crab
Recent Observations of Supernova Remnants
 1 Recent Observations of Supernova Remnants with VERITAS Tülün Ergin (U. of Massachusetts Amherst, MA) on behalf of the VERITAS Collaboration (http://veritas.sao.arizona.edu) 2 Contents Supernova Remnants
1 Recent Observations of Supernova Remnants with VERITAS Tülün Ergin (U. of Massachusetts Amherst, MA) on behalf of the VERITAS Collaboration (http://veritas.sao.arizona.edu) 2 Contents Supernova Remnants
Uri Keshet / CfA Impact of upcoming high-energy astrophysics experiments Workshop, KAVLI, October 2008
 Uri Keshet / CfA Impact of upcoming high-energy astrophysics experiments Workshop, KAVLI, October 008 Impact of upcoming high-energy astrophysics experiments Workshop, KAVLI, October 008 Relaxed, cool
Uri Keshet / CfA Impact of upcoming high-energy astrophysics experiments Workshop, KAVLI, October 008 Impact of upcoming high-energy astrophysics experiments Workshop, KAVLI, October 008 Relaxed, cool
Supernova Remnants and GLAST
 SLAC-PUB-14797 Supernova Remnants and GLAST Patrick Slane Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Abstract. It has long been speculated that supernova remnants represent a major source of cosmic rays
SLAC-PUB-14797 Supernova Remnants and GLAST Patrick Slane Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Abstract. It has long been speculated that supernova remnants represent a major source of cosmic rays
Measurement of the CR e+/e- ratio with ground-based instruments
 Measurement of the CR e+/e- ratio with ground-based instruments Pierre Colin Max-Planck-Institut für Physik CR Moon shadow MPP retreat - 21 January 2014 Cosmic ray electrons Observation: Above the atmosphere:
Measurement of the CR e+/e- ratio with ground-based instruments Pierre Colin Max-Planck-Institut für Physik CR Moon shadow MPP retreat - 21 January 2014 Cosmic ray electrons Observation: Above the atmosphere:
Cosmic Ray Transport (in the Galaxy) Luke Drury. Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies Institiúid Ard-Léinn Bhaile Átha Cliath
 Cosmic Ray Transport (in the Galaxy) Luke Drury Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies Institiúid Ard-Léinn Bhaile Átha Cliath 1 A few disclaimers and preliminary remarks! Not my main field of research
Cosmic Ray Transport (in the Galaxy) Luke Drury Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies Institiúid Ard-Léinn Bhaile Átha Cliath 1 A few disclaimers and preliminary remarks! Not my main field of research
PERSPECTIVES of HIGH ENERGY NEUTRINO ASTRONOMY. Paolo Lipari Vulcano 27 may 2006
 PERSPECTIVES of HIGH ENERGY NEUTRINO ASTRONOMY Paolo Lipari Vulcano 27 may 2006 High Energy Neutrino Astrophysics will CERTAINLY become an essential field in a New Multi-Messenger Astrophysics What is
PERSPECTIVES of HIGH ENERGY NEUTRINO ASTRONOMY Paolo Lipari Vulcano 27 may 2006 High Energy Neutrino Astrophysics will CERTAINLY become an essential field in a New Multi-Messenger Astrophysics What is
Using Pulsars to study the Magnetic Field in The Milky way
 Using Pulsars to study the Magnetic Field in The Milky way Dipanjan Mitra ( MPIFR Bonn) R. Wielebinski ( MPIFR Bonn) M. Kramer ( Jodrell Bank) A. Jessner ( MPIFR Bonn) MPIFR, Bonn (24 th April 2003) To
Using Pulsars to study the Magnetic Field in The Milky way Dipanjan Mitra ( MPIFR Bonn) R. Wielebinski ( MPIFR Bonn) M. Kramer ( Jodrell Bank) A. Jessner ( MPIFR Bonn) MPIFR, Bonn (24 th April 2003) To
THE MAGIC TELESCOPES. Major Atmospheric Gamma Imaging Cherenkov Telescopes
 THE MAGIC TELESCOPES Observatorio del Roque de los Muchachos, La Palma (2200 m a.s.l.) System of two 17 m Cherenkov Telescopes for VHE γ-ray astronomy MAGIC-I operational since 2004, Stereo system since
THE MAGIC TELESCOPES Observatorio del Roque de los Muchachos, La Palma (2200 m a.s.l.) System of two 17 m Cherenkov Telescopes for VHE γ-ray astronomy MAGIC-I operational since 2004, Stereo system since
Cosmic Ray Anomalies from the MSSM?
 Cosmic Ray Anomalies from the MSSM? Randy Cotta (Stanford/SLAC) In collaboration with: J.A. Conley (Bonn) J.S. Gainer (ANL/NU) J.L. Hewett (SLAC) T.G. Rizzo (SLAC) Based on: 0812.0980 0903.4409 1007.5520
Cosmic Ray Anomalies from the MSSM? Randy Cotta (Stanford/SLAC) In collaboration with: J.A. Conley (Bonn) J.S. Gainer (ANL/NU) J.L. Hewett (SLAC) T.G. Rizzo (SLAC) Based on: 0812.0980 0903.4409 1007.5520
The VERITAS Dark M atter and Astroparticle Programs. Benjamin Zitzer For The VERITAS Collaboration
 The VERITAS Dark M atter and Astroparticle Programs Benjamin Zitzer For The VERITAS Collaboration Introduction to VERITAS Array of four IACTs in Southern AZ, USA Employs ~100 Scientists in five countries
The VERITAS Dark M atter and Astroparticle Programs Benjamin Zitzer For The VERITAS Collaboration Introduction to VERITAS Array of four IACTs in Southern AZ, USA Employs ~100 Scientists in five countries
High energy radiation from molecular clouds (illuminated by a supernova remnant
 High energy radiation from molecular clouds (illuminated by a supernova remnant A. Marcowith (L.P.T.A. Montpellier) collaboration with S. Gabici (D.I.A.S.) 1 Outlook Introduction: Scientific interests.
High energy radiation from molecular clouds (illuminated by a supernova remnant A. Marcowith (L.P.T.A. Montpellier) collaboration with S. Gabici (D.I.A.S.) 1 Outlook Introduction: Scientific interests.
Cosmic Rays, Photons and Neutrinos
 Cosmic Rays, Photons and Neutrinos Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Introduction Outline Plan of the lectures: Cosmic rays Galactic cosmic rays Basic observations Acceleration Supernova remnants Problems
Cosmic Rays, Photons and Neutrinos Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Introduction Outline Plan of the lectures: Cosmic rays Galactic cosmic rays Basic observations Acceleration Supernova remnants Problems
Tentative observation of a gamma-ray line at the Fermi Large Area Telescope
 Tentative observation of a gamma-ray line at the Fermi Large Area Telescope arxiv:1203.1312 with T. Bringmann, X. Huang, A. Ibarra, S. Vogl (accepted for JCAP), arxiv:1204.2797 (accepted for JCAP) Christoph
Tentative observation of a gamma-ray line at the Fermi Large Area Telescope arxiv:1203.1312 with T. Bringmann, X. Huang, A. Ibarra, S. Vogl (accepted for JCAP), arxiv:1204.2797 (accepted for JCAP) Christoph
EXCESS OF VHE COSMIC RAYS IN THE CENTRAL 100 PC OF THE MILKY WAY. Léa Jouvin, A. Lemière and R. Terrier
 1 EXCESS OF VHE COSMIC RAYS IN THE CENTRAL 100 PC OF THE MILKY WAY Léa Jouvin, A. Lemière and R. Terrier 2 Excess of VHE cosmic rays (CRs) γ-ray count map Matter traced by CS 150 pc After subtracting the
1 EXCESS OF VHE COSMIC RAYS IN THE CENTRAL 100 PC OF THE MILKY WAY Léa Jouvin, A. Lemière and R. Terrier 2 Excess of VHE cosmic rays (CRs) γ-ray count map Matter traced by CS 150 pc After subtracting the
LATE DECAYING TWO-COMPONENT DARK MATTER (LD2DM) CAN EXPLAIN THE AMS-02 POSITRON EXCESS
 LATE DECAYING TWO-COMPONENT DARK MATTER (LD2DM) CAN EXPLAIN THE AMS-02 POSITRON EXCESS (WITH A FEW BONUS FEATURES!) (BASED ON 1609.04821 W/ P. RALEGANKAR AND V. RENTALA) JATAN BUCH (BROWN U.) 1 THE DARK
LATE DECAYING TWO-COMPONENT DARK MATTER (LD2DM) CAN EXPLAIN THE AMS-02 POSITRON EXCESS (WITH A FEW BONUS FEATURES!) (BASED ON 1609.04821 W/ P. RALEGANKAR AND V. RENTALA) JATAN BUCH (BROWN U.) 1 THE DARK
A few grams of matter in a bright world
 A few grams of matter in a bright world Benjamin Rouillé d Orfeuil (LAL) Fellow Collaborators: D. Allard, C. Lachaud & E. Parizot (APC) A. V. Olinto (University of Chicago) February 12 th 2013 LAL All
A few grams of matter in a bright world Benjamin Rouillé d Orfeuil (LAL) Fellow Collaborators: D. Allard, C. Lachaud & E. Parizot (APC) A. V. Olinto (University of Chicago) February 12 th 2013 LAL All
ON PROBABLE CONTRIBUTION OF NEARBY SOURCES TO ANISOTROPY AND SPECTRUM OF COSMIC RAYS AT TEV-PEV-ENERGIES
 ON PROBABLE CONTRIBUTION OF NEARBY SOURCES TO ANISOTROPY AND SPECTRUM OF COSMIC RAYS AT TEV-PEV-ENERGIES SVESHNIKOVA L.G. 1, STRELNIKOVA O.N. 1, PTUSKIN V.S. 3 1 Lomonosov Moscow State University, SINP,
ON PROBABLE CONTRIBUTION OF NEARBY SOURCES TO ANISOTROPY AND SPECTRUM OF COSMIC RAYS AT TEV-PEV-ENERGIES SVESHNIKOVA L.G. 1, STRELNIKOVA O.N. 1, PTUSKIN V.S. 3 1 Lomonosov Moscow State University, SINP,
observation of Galactic sources
 AGILE observation of Galactic sources Andrea Giuliani Istituto Astrofisica Spaziale e Fisica Cosmica, Milano ( INAF ) on behalf of the AGILE Team Summary of the Presentation The AGILE Mission The diffuse
AGILE observation of Galactic sources Andrea Giuliani Istituto Astrofisica Spaziale e Fisica Cosmica, Milano ( INAF ) on behalf of the AGILE Team Summary of the Presentation The AGILE Mission The diffuse
Dark matter annihilations and decays after the AMS-02 positron measurements
 Dark matter annihilations and decays after the AMS-02 positron measurements Anna S. Lamperstorfer Technische Universität München SISSA - International School for Advanced Studies of Trieste Workshop The
Dark matter annihilations and decays after the AMS-02 positron measurements Anna S. Lamperstorfer Technische Universität München SISSA - International School for Advanced Studies of Trieste Workshop The
Signals from Dark Matter Indirect Detection
 Signals from Dark Matter Indirect Detection Indirect Search for Dark Matter Christian Sander Institut für Experimentelle Kernphysik, Universität Karlsruhe, Germany 2nd Symposium On Neutrinos and Dark Matter
Signals from Dark Matter Indirect Detection Indirect Search for Dark Matter Christian Sander Institut für Experimentelle Kernphysik, Universität Karlsruhe, Germany 2nd Symposium On Neutrinos and Dark Matter
f (R) Cosmology and Dark Matter
 f (R) Cosmology and Dark Matter Dark side of the Universe Kyoto, December 14-18, 2015 G. Lambiase Università di Salerno Dipartimento di Fisica E.R. Caianiello & INFN - Naples Italy in collaboration with
f (R) Cosmology and Dark Matter Dark side of the Universe Kyoto, December 14-18, 2015 G. Lambiase Università di Salerno Dipartimento di Fisica E.R. Caianiello & INFN - Naples Italy in collaboration with
Particle acceleration during the gamma-ray flares of the Crab Nebular
 Particle acceleration during the gamma-ray flares of the Crab Nebular SLAC Accelerator seminar SLAC 15 June 2011 R. Buehler for the LAT collaboration and A. Tennant, E. Costa, D. Horns, C. Ferrigno, A.
Particle acceleration during the gamma-ray flares of the Crab Nebular SLAC Accelerator seminar SLAC 15 June 2011 R. Buehler for the LAT collaboration and A. Tennant, E. Costa, D. Horns, C. Ferrigno, A.
