Mathwithsheppard.weebly.com
|
|
|
- Gerald Barnett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
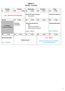
1 Unit #: Powers and Polynomials Unit Outline: Date Lesson Title Assignment Completed.1 Introduction to Algebra. Discovering the Exponent Laws Part 1. Discovering the Exponent Laws Part. Multiplying and Dividing Polynomials Mid Unit Test àlesson.1 to..5 Collecting Like Terms.6 Adding and Subtracting Polynomials.7 Multiplying a Polynomial by a Monomial Mid Unit Test à Lessons.5 to.7.8 Simplifying Algebraic Expressions Part 1.9 Simplifying Algebraic Expressions Part *** Final Algebra Test Mathwithsheppard.weebly.com 1
2 .1 Introduction to Algebra Learning Goals: By the end of this lesson, you will be able to: What is algebra? Learning algebra is like learning another language. By learning algebra, mathematical models of realworld situations can be created and solved! In algebra, letters are often used to represent numbers. Visualizing Algebra: x x x x+x (x)(x) Vocabulary à Term: à Variable: à Coefficient: à Constant: Draw the following algebraic terms: x x Vocabulary à Like Terms: Come up with some examples!
3 Terms can be added and/or subtracted together to form polynomials. Important: Polynomials are in simplest form when they contain no like terms. Vocabulary à Polynomial: à Trinomial: à Binomial: à Monomial: ***Polynomials are in standard form when they are written with exponents highest à lowest. Practice Problems: 1. State the coefficient and variable(s) in each term a) 15x b) -y c) -w Coefficient: Coefficient: Coefficient: Variable: Variable: Variable:. Circle the constant term in each polynomial. a) x + x + b) y 5 c) a + 5a
4 . Draw a model of each of the following. a) x b) -x c) x + 1 d) x - e)x f) x Writing Algebraic Expression Writing algebraic expressions from word problems is a very important skill in mathematics. 1. Seven times a number plus three. Seven times the square of a number plus three. Three quarters of a number. A gym membership costs $5 upfront, then $10 per month 5. The sum of a number and seven 6. The difference between seven and a number 8. times a number plus seven
5 Assignment.1: Introduction to Algebra 1. Sketch models to represent each of the following algebraic expressions. a) x b) x c) y d) 5x. For each term, identify the coefficient and the variable. a) x b) 5p c) m n d) g h e) y 5 f) p q 5 g) ab h) 0.6r s. Classify each polynomial by type. a) x + 1 b) p p + c) b d d) 6 + gh 5 e) y 5 y + y f) x y + g) ab b h) 6p q. We read as squared and as cubed. Sketch models that show why this makes sense. 5. Write an algebraic expression for each phrase. a) double a number b) triple a number c) quadruple a number d) one half of a number e) one third of a number f) one quarter of a number g) 6 more than a number h) a number increased by h) increased by a number j) 5 decreased by a number k) 7 less than a number l) a number decreased by 6 6. Write an algebraic expression for each phrase. a) more than triple a number b) half a number, less 5 c) quadruple a number decreased by 1 d) less than double a number 7. Sate the problems that are in standard form. If it is not in standard form, re-write in standard form. a. x 11x b. + x + x + x c. x + 17x + x d. 1+ x + x 8. Given: x 5x x + 1 a) How many terms are there? b) What is the coefficient of the rd term? c) What is the constant? 5
6 . Discovering the Exponent Laws Part 1 Learning Goals: By the end of this lesson, you will be able to: Investigation #1: Multiplication of Powers Product Expanded Form Single Power x y m a x = ( x x x x) ( x x x) y = ( y y y y y) ( y y y y y y) 5 6 m = = 5 6 t w h p a = = t = = w = = 7 h = = 8 5 x p = = a b x = = 7 = x 11 = y Complete this statement: When multiplying powers with the same base. Challenge: cd cd = ( c c d d d) ( c c c c d d d d d) = cd k j k j = = 5 pq pq = = vz vz = = 5 gt gt = = 5 abc abc = = 5 6
7 Investigation #: Division of Powers Product Expanded Form Single Power x y m x 7 y 5 x x x x x x x = x x x y y y y y = y y m = = 6 = x = y a a = = 6 t t = = x a b x = Complete this statement: When DIVIDING powers with the same base Challenge: cd cd c c c c c c c d d d = c c c c d d 7 = cd k j k j = = 8 5 pq pq = = 6 vz vz = = 5 8 gt gt = = 6 5 abc abc = = 7 6 7
8 Let s Review: a 1 = a 0 = x y = x y = a 5 a = a 5 a = a 5 b 6 a b = b 5 b 5 = Consolidation: a) ( x 7 )( x ) b) ( a 5 b )( a b ) b) x 6 ( x y )( x y 5 ) x 5 y 5 Confirm your answers by writing the expressions in standard form. (When it doubt, write it out) 8
9 Assignment. Discovering the Exponent Laws Part 1 1. Write each expression as a single power. a) 7 7 b) 5 c) 5 5 d) e) ( ) ( ) f) ( 1) ( 1) ( 1) g) h). Evaluate each expression in question 1.. Write each expression as a single power. a) b) c) d) 8 5 e) ( 9) 7 ( 9) 6 f) g)( 0.) ( 0.) h). Evaluate each expression in question. 5. Simplify. a) b 5 b b) p p c) w 5 w d) x 8 x e) a b 5 ab f) m n m n g) p 6 q 5 p q h) xy y 6. Simplify each of the following, write as a single power if possible. a) b) a 7 a 1 c) c c 8 d) d 7 d 9 e) x x 8 f) w 10 w 100 g) a 6 b 5 h) 10 a 10 b i) g 1 g 19 g 11 j) k) l) Explain why it is necessary for the bases to be the same in order to apply the multiplication and division principles for exponents, use examples in your explanations. Enrichment: Write as a single power 9
10 Warm Up:. Discovering the Exponent Laws Part Evaluate by writing the expanding form Simplify using the exponent principles. Investigation : Power of a Power Product ( ) Expanded Form x = ( x x x x) ( x x x x) ( ) y = ( y y y) ( y y y) ( y y y) ( y y y) ( m ) = = ( g ) 5 = = ( t ) = = a ( x ) b = = 8 = x Single Power 1 = y Do these using your SHORTCUT! ( m ) 5 = When simplifying POWERS OF POWERS. 8 ( q ) 6 = ( ) 5 ab = ( x y z ) 6! # " a b $ & % 10
11 '! )# ( )" x $ & %! # " *, +, x 5 $ & % Let s Review: There are still two more: Example: (xy) = Example a b = Practice Problems: Simplify a) (x y ) b) (5xy) c) (x y ) d)! " # $ % &!# $ " e) %' ( & % + ) 5 * &, f)! # " x 5 $ & % Exponent Rules can only be used when. 11
12 Practice: Simplify ( x 5 y ) a) (n ) (n ) b) xy c) ( x y ) xy Extension: Determine the value that makes each statement true a) =? b) 7 =? c) 5? = 6 0 1
13 Assignment. Discovering the Exponent Laws Part 1. Simplify each expression using exponent laws. 5 9 a) ( ) b) ( 5 ) 5 c) ( ) 7 d) ( 7 ) 5 e) f) ( ) 7. Simplify each expression using exponent laws. a) ( x ) 5 b) ( 5 ) 5 c) ( ) 7 d) ( 7 ) 5 7 e) ( a ) 5 f) ( x ) 5 g) ( x ) h) ( ) y i) y ( ) ( x ) 5 j) ( x x x ) 5 k) ( s t ) 5 l) ( x y 5 ) 6 m) a b n) x y. Simplify each expression using exponent laws. 1 6 y x 8 5 o) 5 a b a b a) (m 5 ) b) (k ) k c) g 5 g 5 g 7 d) (a 6 ) (a 5 ) e) (gh ) f) k m (k ) g) (g 5 h ) gh 6 h*). Show that 10 is the same as 9 5 using your understanding of exponent. 5. Determine the value of the exponent that makes each expression true. a) 7 =? b) (-15) 7 = (-5)? c) 6? = bd bd ( bd ) 6. Evaluate for a = 5 and b =. Are the expressions equal? If not, which expression has the lesser value? a) a + b or a + b b) a b or (ab) 1
14 . Multiplying and Dividing Monomials Warm Up: After marking a quiz, a teacher recorded the most common errors made by the students. In each case, identify the error made by the student and provide the correct simplification. a) 1 5 b) ( ) = = c) d) ( 5a b) = 5a b = Multiplying Monomials x y xy When in doubt, write it out. MULTIPLYING MONOMIALS (6x y 6 z)(xy ) 1
15 Practice Problems: Multiply the following monomials. a) ( x)( x) b) ( 5m n) m ( ) c) ( 6z)( x y) d) ( 7mn )( mn ) e) 7 x ( 15 x ) f) ( mnp )( 8n) DIVIDING MONOMIALS 81a b 5 c 18a b 5 c Practice Problems: Divide the following monomials. a) 10x b) 5x 16m n mn c) 8x y 16xy 5 15
16 e) x yz 1 xyz 5 5 d) ( 15mp) ( 5p) f) x x Challenge Questions: 5 6x y a) 8y ( )( 5 6x y 9x y ) b) x y 16
17 Assignment. Multiplying and Dividing Monomials 1. Multiplying Monomials: Simplify each expression using exponent laws. a) ( b)( b) b) ( 6b) d) 5 x( 5x) e) ( b ) ( b ) 5 5 g) ( b )( b ) h) 5 ( y )( 6x )( y ) 6 j) 7 ( a ) 5 c) ( b)( b ) f) ( x)( x ) x i) 5x ( ) a k) ( 5 x)( x)( x) l) ( x )( x)( x) m) ( a b )( ab ) n) ( xy)( 5y ) o) a ( a)( 5a ) 5 p) 7m n ( m )( 6n) q) x ( x y )( 8y) r) 8x y ( x y )( x y ). Dividing Monomials: Simplify each expression using exponent laws. Fractions must be in lowest terms no decimals! a) 9x b) 8y 5 c) y 1n 18n 6 5 d) g) j) 5z 5z 5x 7 0x y 7 8 y 1 7x 6 y 6x y ( )( x y) e) h) 7t 9t 9a a b b 5 7m ( 5n ) k) 9 5m n 8 f) x 6x 7 5 9x ( y ) i) 11 81( x ) y ( 5x) ( 5y ) l) ( 5x y ). Write an expression to represent the area of the following shapes. a) xy b) x 1 m 17
18 . Determine the volume of the cube shown. 5. Determine the volume of the following shapes. 6. Write an expression to represent the volume of the following shape. 7. The volume of a box is 6a 5 b. The length of the box is a and the width of the box is 8b. Determine the height of the box. 18
19 . 5 Collecting Like Terms Warm Up: Draw a model to represent x, x, and x Illustrate and explain the difference between a) x and x. b) x and x Start to fill out the FISHBONE diagram (next page) with the following definitions: ü Variable ü Coefficient ü Constant ü Like Terms ü Polynomial 19
20 0 Powers and Polynomials
21 Representing Polynomials Algebra Tiles are often used to represent polynomials. Algebra tiles can help you visualize equivalent algebraic expressions and/or equations. Represent the following polynomials with algebra tiles a) x + 1 b) x x c) x x + d) x 5 Like and Unlike Terms Like terms have the same set of variable bases and corresponding exponents. Examples: Represent each of the following sets with algebra tiles a) x and -5x b) -6x and 9x c) xy and 5xy Did you notice how algebra tiles with the same size and shape represent like terms? Define and give an example of Unlike Terms - 1
22 Collecting Like Terms Algebraic expressions that contain like terms can be simplified by combining each group of like terms. Examples: x + x 9x 6x 1x y - 5x y Why can t you simplify? x + x x 7 6x y + 5xy Practice Problems: Simplify 1) 7x + 5 x ) 6w + 11w + 8w 15w ) 6x + 5 (-7x) ) (-1x) 5 7x 11 5) x (-x) + 7 (-x ) + x 7 6) 11a b 1ab
23 Assignment. 5: Collecting Like Terms 1. Are the terms in each pair like or unlike? a) 5a and a b) x and x c) p and p d) ab and ab e) b and b f) 6a b and a b g) 9pq and p q h) x y and x y. Simplify. a) + v + 5v 10 b) 7a b a b c) 8k k 5k + + k d) x x + 8x + 5x e) 1 m 8 m + m f) 6y + y + 10 y 6 y. Simplify. a) a + 6b + b + a b) x + xy + y + 5x xy y c) m m m + m d) x + xy + y x + xy y. Simplify: a) w w + 1 w w b) a 1 5 b a b 5. Find the perimeter of each figure below. a) b) n
24 .6 Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Warm Up: Determine a simplified expression the perimeter of the following rectangle. Give an example of A monomial A binomial A trinomial A constant term ACTIVITY: Adding Polynomials Use tiles and two different colours to record your solution. Create zero pairs if you are adding positive & negative tiles. Draw the tiles under each polynomial & write answer in chart. Compare with neighbor. **compare with a neighbor.
25 To separate one polynomial from another, often brackets are used: Evaluate: (x + 5x 1) + (x x) USING TILES: WITHOUT TILES: Practice Problems: Simplify. Choose your method! a. (y 7) + ( y+ ) b. ( a + a) + (6a + 10 a) + (5a+ 1) PROBLEM SOLVING: The measures of two sides of a triangle are given. P is the perimeter. Find the measure of the third side. P = x + 5x + 5 x + x 5 x + x + 6 Enrichment: Determine the polynomial that must be added to x xy + 6y to get: 6x 6xy + 8y Create two three-term polynomials that when they are combined you get a -term polynomial 5
26 Subtracting Polynomials Review: Subtracting is the same as the. This same idea can be used to subtract polynomials. Ex. (x + x + 5) - (x + x + ) Ex. Try without tiles: (7b b 1) (b 5b 6) +. Practice Problems: Simplify (choose your method). a. (x ) (x+ 9) b. (5z 1 z) ( z 8) c. 1 (x 5x 1) + d. (8x + 7 x) (x ) ( 5x+ 9) 6
27 Assignment.6 Adding and Subtracting Polynomials 1. Add. a) (y + 6y 5) + ( 7y + y ) b) ( n + n + ) + ( 1 7n + n) c) (m + m) + ( 10m m ) d) ( d + ) + ( 7d + d). For each shape below, write the perimeter as a sum of polynomials and in simplest form. i) ii) iii) iv). Subtract. a) (x + ) (5x + ) b) ( 8w) (7w + 1) c) (x + x ) (x + x ) d) ( 9z z ) (z z ). A student subtracted (y + 5y + ) (y + y + ) like this: = y 5y y y = y y 5y y = y 8y a) Explain why the student s solution is incorrect. b) What is the correct answer? Show your work. 5. The difference between two polynomials is (5x + ). One of the two polynomials is (x + 1 x ). What is the other polynomial? Explain how you found your answer. 6. Subtract. a) (mn 5m 7) ( 6n + m + 1) b) (a + b a + b ) ( a + 8b + a b) c) (xy x 5y + y ) (6y + 9y xy) 7. The sum of the perimeters of two shapes is represented by 1x + y. The perimeter of one shape is represented by x y. Determine an expression for the perimeter of the other shape. Show your work. 8. A rectangular field has a perimeter of 10a 6 meters. The width is a meters. Determine an expression for the length of this field. 7
28 .7 Multiplying a Polynomial by a Monomial Warm Up: Simplify a) (b) b) (6h) c) (b ) d) (x ) e) ( y ) f) ( f) Simplify. a) (6k ) + (k + ) Simplify 5 a) a a b) (a + 1) (a + ) b) 6xy x y 7 c) (b 6) ( 5b) + (b + ) c) ( xy 5 )(x y ) d) 5 (9 y ) d) (m + m + 1) (m + m 6) e) 8bd bd ( bd ) 8
29 The Distributive Property The property known as the distributive property is also known as expanding. We are making sure EVERY TERM in bracket gets multiplied. Distributive Property: ab ( + c) = ab+ ac With an integer. a) (g + ) b) 7(q + ) c) (t 1) d) ( w 5) With a variable.. Example 1) Simplify: x(x+ 5) Practice Problems: Expand. a) b(b + 1) b) p(p + ) c) r( 5r + ) d) w(w 1) 9
30 With a variable and coefficient. Example ) Expand (9 x x ) x. Practice Problems: Simplify. 6 a) y( y + y ) b) 5 z (z 1) c) x ( x x+ 9) d) ( a 1) 11 a Example ) Simplify (b b + ) + 5b(b + ) Practice Problems: Expand and simplify. a) -(p ) + 6(p + 1) b) [ (6 t) + 5t] c) 5m(m + 5) (m m 7) 0
31 Assignment.7 Multiplying a Polynomial by a monomial 1. Determine each product. a) (a + ) b) (d + d)( ) c) (c c + ) d) ( n + n 1)(6) e) ( 5m + 6m + 7). Here is a student s solution for a multiplication question. ( 5k k )( ) = (5k ) (k) () = 10k k 6 a) Explain why the student s solution is incorrect. b) What is the correct answer? Show your work.. Expand. a) (x + x ) b) (m m + 5) c) (b b ) d) 5c(c 6c 1) e) h( h ) f) (n + n + )( ) g) (5t t)( t) h) (w + w 5)(w). Write a simplified expression for the area of the following rectangles a) b) 5. Expand a) x (x + ) b) n(n ) c) 5m(m + m) d) (y y )y e) pq(p + q) f) d(d d + 1) g) (t + t )(-t) h) a b(a b ) 6. Simplify a) (x + ) (x + ) b) a(a + b ) b(a + ab) c) p(p ) + 6(p + p ) d) x(x y ) + y(6x + y) Enrichment: Do some research to learn how to multiply a binomial by a binomial (or a polynomial) a) (x + 1)(x ) b) (x 5)(x ) c) (x y)(5x + y) 1
32 .8 Simplifying Algebraic Expressions Solve the following word problems. Include your steps and a clear and thorough solution. 1. The area of a rectangle is represented by the other side? 6 6x y. One side is represented by 6x y. What is the length of..
33 .
34 Assignment.8 - Simplifying Algebraic Expressions Simplify 1) p q + p + + 5q 1 ) 5x y + 1xy 8x 1xy ) 5 y + y 8y 9y 1 ) x + x 7x (-5x ) 5) 5(a b) + (-b a) 6) (x + y) 5(-y + x) 7) -b(5a b) + (-ab 5b ) 8) x(x - y) (-x - xy) 9) -(x + y) + 5(-6y x ) 10) -(7xy - 11y ) y(-x + y) 11) ( x) - (-5 1x) 1) 7( - x) 6(8-1x) 1) 15) x y y + x 1) 1 x y x + y ) s t s t a b a b 18) 6 [ ( x y) ] + 19) (x y) [ (x y)] 0) 7 { x [ x (x 1) ]} ( ) 1) 5x (x + 6) " # x 1 + x $ % { } ) a a ( b + a ) ) [ x ( y w) ] [ x (y w) ] ) 6b { 5a [ a + ( b a) ]} + + 5) x x + x! + 5 6) A triangle has sides of length a centimeters, 7b centimeters, and 5a + centimeters. What is the perimeter of the triangle? 7) A rectangle has sides of length 7x meters and x + meters. What is the perimeter of the rectangle? 8) A square has a side of length 9x inches. Each side is shortened by inches. What is the perimeter of the new smaller square? 9) A triangle has sides of length a 5 feet, a + 8 feet, and 9a + feet. Each side is doubled in length. What is the perimeter of the new enlarged triangle? 0) Subtract four times the quantity x + 5 from three times the quantity 7x 8.
35 Possible Test Questions 1. If x =, what is the value of x + 5x? a 1 b 7 c d 51. Simplify the following expression: x(x + ) 5x a 6x 5x + b 6x 6x c 15x 5x d 6x + x. Simplify the following algebraic expression: a a b b a b 6 a b a b c a b d a b. Tim shows the steps he took in simplifying the following algebraic expression: In which step did Tim make an error? a Step 1 b Step c Step d Step = Step 1 = Step = Step 5. Sabeeta expands and simplifies the expression below. (x 5x) + x(7 + x) Which expression is equivalent to the one above? a 6x + x b 10x + 18x c 10x 8x d 8x = 1 Step 1) x + ( 1) (+5x) ( 6) ) ( 5a + 6) + (8a 7) ) (b ) (b 8) ) y(y 5) 5) (x + 6) (x + ) 6) 1 x ( ) + 9x +1 ( ) 7) m(m 5) (m m 1) 8) [(p + ) p] 6 ( x y) x ( y + w) x + (y w) 9) [ + ] 10) [ ] [ ] 5
Collecting Like Terms
 MPM1D Unit 2: Algebra Lesson 5 Learning goal: how to simplify algebraic expressions by collecting like terms. Date: Collecting Like Terms WARM-UP Example 1: Simplify each expression using exponent laws.
MPM1D Unit 2: Algebra Lesson 5 Learning goal: how to simplify algebraic expressions by collecting like terms. Date: Collecting Like Terms WARM-UP Example 1: Simplify each expression using exponent laws.
Something that can have different values at different times. A variable is usually represented by a letter in algebraic expressions.
 Lesson Objectives: Students will be able to define, recognize and use the following terms in the context of polynomials: o Constant o Variable o Monomial o Binomial o Trinomial o Polynomial o Numerical
Lesson Objectives: Students will be able to define, recognize and use the following terms in the context of polynomials: o Constant o Variable o Monomial o Binomial o Trinomial o Polynomial o Numerical
I CAN classify polynomials by degree and by the number of terms.
 13-1 Polynomials I CAN classify polynomials by degree and by the number of terms. 13-1 Polynomials Insert Lesson Title Here Vocabulary monomial polynomial binomial trinomial degree of a polynomial 13-1
13-1 Polynomials I CAN classify polynomials by degree and by the number of terms. 13-1 Polynomials Insert Lesson Title Here Vocabulary monomial polynomial binomial trinomial degree of a polynomial 13-1
Chapter 5: Exponents and Polynomials
 Chapter 5: Exponents and Polynomials 5.1 Multiplication with Exponents and Scientific Notation 5.2 Division with Exponents 5.3 Operations with Monomials 5.4 Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials 5.5
Chapter 5: Exponents and Polynomials 5.1 Multiplication with Exponents and Scientific Notation 5.2 Division with Exponents 5.3 Operations with Monomials 5.4 Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials 5.5
5.1 Modelling Polynomials
 5.1 Modelling Polynomials FOCUS Model, write, and classify polynomials. In arithmetic, we use Base Ten Blocks to model whole numbers. How would you model the number 234? In algebra, we use algebra tiles
5.1 Modelling Polynomials FOCUS Model, write, and classify polynomials. In arithmetic, we use Base Ten Blocks to model whole numbers. How would you model the number 234? In algebra, we use algebra tiles
2.1 Intro to Algebra
 MFM1P Unit 2: Algebra Lesson 1 Date: Learning goal: I understand polynomial terminology and can create algebraic expressions. 2.1 Intro to Algebra What is algebra? Learning algebra is like learning another
MFM1P Unit 2: Algebra Lesson 1 Date: Learning goal: I understand polynomial terminology and can create algebraic expressions. 2.1 Intro to Algebra What is algebra? Learning algebra is like learning another
Unit 13: Polynomials and Exponents
 Section 13.1: Polynomials Section 13.2: Operations on Polynomials Section 13.3: Properties of Exponents Section 13.4: Multiplication of Polynomials Section 13.5: Applications from Geometry Section 13.6:
Section 13.1: Polynomials Section 13.2: Operations on Polynomials Section 13.3: Properties of Exponents Section 13.4: Multiplication of Polynomials Section 13.5: Applications from Geometry Section 13.6:
Algebraic Expressions
 Algebraic Expressions 1. Expressions are formed from variables and constants. 2. Terms are added to form expressions. Terms themselves are formed as product of factors. 3. Expressions that contain exactly
Algebraic Expressions 1. Expressions are formed from variables and constants. 2. Terms are added to form expressions. Terms themselves are formed as product of factors. 3. Expressions that contain exactly
Unit 3 Factors & Products
 1 Unit 3 Factors & Products General Outcome: Develop algebraic reasoning and number sense. Specific Outcomes: 3.1 Demonstrate an understanding of factors of whole number by determining the: o prime factors
1 Unit 3 Factors & Products General Outcome: Develop algebraic reasoning and number sense. Specific Outcomes: 3.1 Demonstrate an understanding of factors of whole number by determining the: o prime factors
Math 10 - Unit 5 Final Review - Polynomials
 Class: Date: Math 10 - Unit 5 Final Review - Polynomials Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Factor the binomial 44a + 99a 2. a. a(44 + 99a)
Class: Date: Math 10 - Unit 5 Final Review - Polynomials Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Factor the binomial 44a + 99a 2. a. a(44 + 99a)
Why It s Important. What You ll Learn
 How could you solve this problem? Denali and Mahala weed the borders on the north and south sides of their rectangular yard. Denali starts first and has weeded m on the south side when Mahala says he should
How could you solve this problem? Denali and Mahala weed the borders on the north and south sides of their rectangular yard. Denali starts first and has weeded m on the south side when Mahala says he should
MATHEMATICS 9 CHAPTER 7 MILLER HIGH SCHOOL MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT NAME: DATE: BLOCK: TEACHER: Miller High School Mathematics Page 1
 MATHEMATICS 9 CHAPTER 7 NAME: DATE: BLOCK: TEACHER: MILLER HIGH SCHOOL MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT Miller High School Mathematics Page 1 Day 1: Creating expressions with algebra tiles 1. Determine the multiplication
MATHEMATICS 9 CHAPTER 7 NAME: DATE: BLOCK: TEACHER: MILLER HIGH SCHOOL MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT Miller High School Mathematics Page 1 Day 1: Creating expressions with algebra tiles 1. Determine the multiplication
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
 Chapter 7 Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency Simplify the expression. 1. 5x 6 + 3x. 3t + 7 3t 4 3. 8s 4 + 4s 6 5s 4. 9m + 3 + m 3 + 5m 5. 4 3p 7 3p 4 1 z 1 + 4 6. ( ) 7. 6( x + ) 4 8. 3( h + 4) 3( h
Chapter 7 Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency Simplify the expression. 1. 5x 6 + 3x. 3t + 7 3t 4 3. 8s 4 + 4s 6 5s 4. 9m + 3 + m 3 + 5m 5. 4 3p 7 3p 4 1 z 1 + 4 6. ( ) 7. 6( x + ) 4 8. 3( h + 4) 3( h
Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 1 Lesson 3. Polynomials
 Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 1 Lesson 3 Suggested time: 150 min Polynomials What s important in this lesson: You will use algebra tiles to learn how to add/subtract polynomials. Problems are provided
Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 1 Lesson 3 Suggested time: 150 min Polynomials What s important in this lesson: You will use algebra tiles to learn how to add/subtract polynomials. Problems are provided
CHAPTER 1 POLYNOMIALS
 1 CHAPTER 1 POLYNOMIALS 1.1 Removing Nested Symbols of Grouping Simplify. 1. 4x + 3( x ) + 4( x + 1). ( ) 3x + 4 5 x 3 + x 3. 3 5( y 4) + 6 y ( y + 3) 4. 3 n ( n + 5) 4 ( n + 8) 5. ( x + 5) x + 3( x 6)
1 CHAPTER 1 POLYNOMIALS 1.1 Removing Nested Symbols of Grouping Simplify. 1. 4x + 3( x ) + 4( x + 1). ( ) 3x + 4 5 x 3 + x 3. 3 5( y 4) + 6 y ( y + 3) 4. 3 n ( n + 5) 4 ( n + 8) 5. ( x + 5) x + 3( x 6)
6-5 Multiplying Polynomials
 6-5 Multiplying Polynomials Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 1 Warm Up Evaluate. 1.3 2 3.10 2 Simplify. 9 2.2 4 16 100 4.2 3 2 4 6. (5 3 ) 2 2 7 5. y 5 y 4 5 6 7.(x 2 ) 4 y 9 x 8 8. 4(x
6-5 Multiplying Polynomials Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 1 Warm Up Evaluate. 1.3 2 3.10 2 Simplify. 9 2.2 4 16 100 4.2 3 2 4 6. (5 3 ) 2 2 7 5. y 5 y 4 5 6 7.(x 2 ) 4 y 9 x 8 8. 4(x
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 7-1 Integer Exponents
 7A Evaluating Expressions with Zero and Negative Exponents Zero Exponent: Any nonzero number raised to the zero power is. 4 0 Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 7-1 Integer Exponents Negative Exponent:
7A Evaluating Expressions with Zero and Negative Exponents Zero Exponent: Any nonzero number raised to the zero power is. 4 0 Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 7-1 Integer Exponents Negative Exponent:
Classifying Polynomials. Simplifying Polynomials
 1 Classifying Polynomials A polynomial is an algebraic expression with one or more unlike terms linked together by + or **Polynomials can be classified by the number of terms they have: A monomial has
1 Classifying Polynomials A polynomial is an algebraic expression with one or more unlike terms linked together by + or **Polynomials can be classified by the number of terms they have: A monomial has
To Find the Product of Monomials. ax m bx n abx m n. Let s look at an example in which we multiply two monomials. (3x 2 y)(2x 3 y 5 )
 5.4 E x a m p l e 1 362SECTION 5.4 OBJECTIVES 1. Find the product of a monomial and a polynomial 2. Find the product of two polynomials 3. Square a polynomial 4. Find the product of two binomials that
5.4 E x a m p l e 1 362SECTION 5.4 OBJECTIVES 1. Find the product of a monomial and a polynomial 2. Find the product of two polynomials 3. Square a polynomial 4. Find the product of two binomials that
5.1 The Language of Mathematics
 5. The Language of Mathematics Prescribed Learning Outcomes (PLO s): Use mathematical terminology (variables, degree, number of terms, coefficients, constant terms) to describe polynomials. Identify different
5. The Language of Mathematics Prescribed Learning Outcomes (PLO s): Use mathematical terminology (variables, degree, number of terms, coefficients, constant terms) to describe polynomials. Identify different
Algebra I. Polynomials.
 1 Algebra I Polynomials 2015 11 02 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents Definitions of Monomials, Polynomials and Degrees Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Multiplying a Polynomial by a Monomial Multiplying
1 Algebra I Polynomials 2015 11 02 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents Definitions of Monomials, Polynomials and Degrees Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Multiplying a Polynomial by a Monomial Multiplying
review To find the coefficient of all the terms in 15ab + 60bc 17ca: Coefficient of ab = 15 Coefficient of bc = 60 Coefficient of ca = -17
 1. Revision Recall basic terms of algebraic expressions like Variable, Constant, Term, Coefficient, Polynomial etc. The coefficients of the terms in 4x 2 5xy + 6y 2 are Coefficient of 4x 2 is 4 Coefficient
1. Revision Recall basic terms of algebraic expressions like Variable, Constant, Term, Coefficient, Polynomial etc. The coefficients of the terms in 4x 2 5xy + 6y 2 are Coefficient of 4x 2 is 4 Coefficient
Algebra I Polynomials
 Slide 1 / 217 Slide 2 / 217 Algebra I Polynomials 2014-04-24 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 217 Table of Contents Definitions of Monomials, Polynomials and Degrees Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Multiplying
Slide 1 / 217 Slide 2 / 217 Algebra I Polynomials 2014-04-24 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 217 Table of Contents Definitions of Monomials, Polynomials and Degrees Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Multiplying
Polynomials 370 UNIT 10 WORKING WITH POLYNOMIALS. The railcars are linked together.
 UNIT 10 Working with Polynomials The railcars are linked together. 370 UNIT 10 WORKING WITH POLYNOMIALS Just as a train is built from linking railcars together, a polynomial is built by bringing terms
UNIT 10 Working with Polynomials The railcars are linked together. 370 UNIT 10 WORKING WITH POLYNOMIALS Just as a train is built from linking railcars together, a polynomial is built by bringing terms
Lesson 3: Polynomials and Exponents, Part 1
 Lesson 2: Introduction to Variables Assessment Lesson 3: Polynomials and Exponents, Part 1 When working with algebraic expressions, variables raised to a power play a major role. In this lesson, we look
Lesson 2: Introduction to Variables Assessment Lesson 3: Polynomials and Exponents, Part 1 When working with algebraic expressions, variables raised to a power play a major role. In this lesson, we look
LESSON 6.2 POLYNOMIAL OPERATIONS I
 LESSON 6.2 POLYNOMIAL OPERATIONS I Overview In business, people use algebra everyday to find unknown quantities. For example, a manufacturer may use algebra to determine a product s selling price in order
LESSON 6.2 POLYNOMIAL OPERATIONS I Overview In business, people use algebra everyday to find unknown quantities. For example, a manufacturer may use algebra to determine a product s selling price in order
POLYNOMIAL: A polynomial is a or the
 MONOMIALS: CC Math I Standards: Unit 6 POLYNOMIALS: INTRODUCTION EXAMPLES: A number 4 y a 1 x y A variable NON-EXAMPLES: Variable as an exponent A sum x x 3 The product of variables 5a The product of numbers
MONOMIALS: CC Math I Standards: Unit 6 POLYNOMIALS: INTRODUCTION EXAMPLES: A number 4 y a 1 x y A variable NON-EXAMPLES: Variable as an exponent A sum x x 3 The product of variables 5a The product of numbers
Math 9 Homework & Notebook
 Math 9 Homework & Notebook Name: Block: Teacher: Miss Zukowski Date Submitted: / / 2018 Unit # : Submission Checklist: (make sure you have included all components for full marks) Cover page & Assignment
Math 9 Homework & Notebook Name: Block: Teacher: Miss Zukowski Date Submitted: / / 2018 Unit # : Submission Checklist: (make sure you have included all components for full marks) Cover page & Assignment
Chapter Six. Polynomials. Properties of Exponents Algebraic Expressions Addition, Subtraction, and Multiplication Factoring Solving by Factoring
 Chapter Six Polynomials Properties of Exponents Algebraic Expressions Addition, Subtraction, and Multiplication Factoring Solving by Factoring Properties of Exponents The properties below form the basis
Chapter Six Polynomials Properties of Exponents Algebraic Expressions Addition, Subtraction, and Multiplication Factoring Solving by Factoring Properties of Exponents The properties below form the basis
Lesson 10.1 Polynomials
 Lesson 10.1 Polynomials Objectives Classify polynomials. Use algebra tiles to add polynomials. Add and subtract polynomials. A contractor is buying paint to cover the interior of two cubical storage tanks.
Lesson 10.1 Polynomials Objectives Classify polynomials. Use algebra tiles to add polynomials. Add and subtract polynomials. A contractor is buying paint to cover the interior of two cubical storage tanks.
For Your Notebook E XAMPLE 1. Factor when b and c are positive KEY CONCEPT. CHECK (x 1 9)(x 1 2) 5 x 2 1 2x 1 9x Factoring x 2 1 bx 1 c
 9.5 Factor x2 1 bx 1 c Before You factored out the greatest common monomial factor. Now You will factor trinomials of the form x 2 1 bx 1 c. Why So you can find the dimensions of figures, as in Ex. 61.
9.5 Factor x2 1 bx 1 c Before You factored out the greatest common monomial factor. Now You will factor trinomials of the form x 2 1 bx 1 c. Why So you can find the dimensions of figures, as in Ex. 61.
What is a constant? A Constant is a number representing a quantity or value that does not change.
 Worksheet -: Algebraic Expressions What is a constant? A Constant is a number representing a quantity or value that does not change. What is a variable? A variable is a letter or symbol representing a
Worksheet -: Algebraic Expressions What is a constant? A Constant is a number representing a quantity or value that does not change. What is a variable? A variable is a letter or symbol representing a
Algebra 1 Unit 6B Factoring
 Algebra 1 Unit 6B Factoring Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 9 A Day 10 B Day 11 A Day 12 B Day 13 A Day Test Exponents and Polynomials Factor GCF and Trinomials box method Factoring Trinomials
Algebra 1 Unit 6B Factoring Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 9 A Day 10 B Day 11 A Day 12 B Day 13 A Day Test Exponents and Polynomials Factor GCF and Trinomials box method Factoring Trinomials
Math 101 Study Session Spring 2016 Test 4 Chapter 10, Chapter 11 Chapter 12 Section 1, and Chapter 12 Section 2
 Math 101 Study Session Spring 2016 Test 4 Chapter 10, Chapter 11 Chapter 12 Section 1, and Chapter 12 Section 2 April 11, 2016 Chapter 10 Section 1: Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials A monomial is
Math 101 Study Session Spring 2016 Test 4 Chapter 10, Chapter 11 Chapter 12 Section 1, and Chapter 12 Section 2 April 11, 2016 Chapter 10 Section 1: Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials A monomial is
Chapter 3: Section 3.1: Factors & Multiples of Whole Numbers
 Chapter 3: Section 3.1: Factors & Multiples of Whole Numbers Prime Factor: a prime number that is a factor of a number. The first 15 prime numbers are: 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43,
Chapter 3: Section 3.1: Factors & Multiples of Whole Numbers Prime Factor: a prime number that is a factor of a number. The first 15 prime numbers are: 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43,
Polynomials Practice Test
 Name: Class: Date: Polynomials Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. From the list, which terms are like 7x? 7x 2, 6x, 5, 8x, 7x,
Name: Class: Date: Polynomials Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. From the list, which terms are like 7x? 7x 2, 6x, 5, 8x, 7x,
How could you express algebraically, the total amount of money he earned for the three days?
 UNIT 4 POLYNOMIALS Math 11 Unit 4 Introduction p. 1 of 1 A. Algebraic Skills Unit 4 Polynomials Introduction Problem: Derrek has a part time job changing tires. He gets paid the same amount for each tire
UNIT 4 POLYNOMIALS Math 11 Unit 4 Introduction p. 1 of 1 A. Algebraic Skills Unit 4 Polynomials Introduction Problem: Derrek has a part time job changing tires. He gets paid the same amount for each tire
5.1, 5.2, 5.3 Properites of Exponents last revised 6/7/2014. c = Properites of Exponents. *Simplify each of the following:
 48 5.1, 5.2, 5.3 Properites of Exponents last revised 6/7/2014 Properites of Exponents 1. x a x b = x a+b *Simplify each of the following: a. x 4 x 8 = b. x 5 x 7 x = 2. xa xb = xa b c. 5 6 5 11 = d. x14
48 5.1, 5.2, 5.3 Properites of Exponents last revised 6/7/2014 Properites of Exponents 1. x a x b = x a+b *Simplify each of the following: a. x 4 x 8 = b. x 5 x 7 x = 2. xa xb = xa b c. 5 6 5 11 = d. x14
Beginning Algebra MAT0024C. Professor Sikora. Professor M. J. Sikora ~ Valencia Community College
 Beginning Algebra Professor Sikora MAT002C POLYNOMIALS 6.1 Positive Integer Exponents x n = x x x x x [n of these x factors] base exponent Numerical: Ex: - = where as Ex: (-) = Ex: - = and Ex: (-) = Rule:
Beginning Algebra Professor Sikora MAT002C POLYNOMIALS 6.1 Positive Integer Exponents x n = x x x x x [n of these x factors] base exponent Numerical: Ex: - = where as Ex: (-) = Ex: - = and Ex: (-) = Rule:
Algebraic Expressions
 ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS 229 Algebraic Expressions Chapter 12 12.1 INTRODUCTION We have already come across simple algebraic expressions like x + 3, y 5, 4x + 5, 10y 5 and so on. In Class VI, we have seen
ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS 229 Algebraic Expressions Chapter 12 12.1 INTRODUCTION We have already come across simple algebraic expressions like x + 3, y 5, 4x + 5, 10y 5 and so on. In Class VI, we have seen
Chapter 5 Simplifying Formulas and Solving Equations
 Chapter 5 Simplifying Formulas and Solving Equations Look at the geometry formula for Perimeter of a rectangle P = L W L W. Can this formula be written in a simpler way? If it is true, that we can simplify
Chapter 5 Simplifying Formulas and Solving Equations Look at the geometry formula for Perimeter of a rectangle P = L W L W. Can this formula be written in a simpler way? If it is true, that we can simplify
Name: Class: IM8 Block:
 Name: Block: Class: IM8 Investigation 1: Mathematical Properties and Order of Operations Mathematical Properties 2 Practice Level 1: Write the name of the property shown in the examples below. 1. 4 + 5
Name: Block: Class: IM8 Investigation 1: Mathematical Properties and Order of Operations Mathematical Properties 2 Practice Level 1: Write the name of the property shown in the examples below. 1. 4 + 5
Algebraic Expressions and Identities
 ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS AND IDENTITIES 137 Algebraic Expressions and Identities CHAPTER 9 9.1 What are Expressions? In earlier classes, we have already become familiar with what algebraic expressions (or
ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS AND IDENTITIES 137 Algebraic Expressions and Identities CHAPTER 9 9.1 What are Expressions? In earlier classes, we have already become familiar with what algebraic expressions (or
Adding and Subtracting Terms
 Adding and Subtracting Terms 1.6 OBJECTIVES 1.6 1. Identify terms and like terms 2. Combine like terms 3. Add algebraic expressions 4. Subtract algebraic expressions To find the perimeter of (or the distance
Adding and Subtracting Terms 1.6 OBJECTIVES 1.6 1. Identify terms and like terms 2. Combine like terms 3. Add algebraic expressions 4. Subtract algebraic expressions To find the perimeter of (or the distance
Math 10-C Polynomials Concept Sheets
 Math 10-C Polynomials Concept Sheets Concept 1: Polynomial Intro & Review A polynomial is a mathematical expression with one or more terms in which the exponents are whole numbers and the coefficients
Math 10-C Polynomials Concept Sheets Concept 1: Polynomial Intro & Review A polynomial is a mathematical expression with one or more terms in which the exponents are whole numbers and the coefficients
Unit 1 Foundations of Algebra
 1 Unit 1 Foundations of Algebra Real Number System 2 A. Real Number System 1. Counting Numbers (Natural Numbers) {1,2,3,4, } 2. Whole Numbers { 0,1,2,3,4, } 3. Integers - Negative and Positive Whole Numbers
1 Unit 1 Foundations of Algebra Real Number System 2 A. Real Number System 1. Counting Numbers (Natural Numbers) {1,2,3,4, } 2. Whole Numbers { 0,1,2,3,4, } 3. Integers - Negative and Positive Whole Numbers
MATH 60 Course Notebook Chapter #1
 MATH 60 Course Notebook Chapter #1 Integers and Real Numbers Before we start the journey into Algebra, we need to understand more about the numbers and number concepts, which form the foundation of Algebra.
MATH 60 Course Notebook Chapter #1 Integers and Real Numbers Before we start the journey into Algebra, we need to understand more about the numbers and number concepts, which form the foundation of Algebra.
Name: 4-1 P a g e Teacher:
 Name: 4-1 Teacher: P a g e Problem 5: What Drinking Box Design Is Most Efficient MPM1D1 Grade 9 Academic Mathematics: Principles of Mathematics Tool Number Lesson Title & Topics Topics Homework 1 Exponents
Name: 4-1 Teacher: P a g e Problem 5: What Drinking Box Design Is Most Efficient MPM1D1 Grade 9 Academic Mathematics: Principles of Mathematics Tool Number Lesson Title & Topics Topics Homework 1 Exponents
Remember, you may not use a calculator when you take the assessment test.
 Elementary Algebra problems you can use for practice. Remember, you may not use a calculator when you take the assessment test. Use these problems to help you get up to speed. Perform the indicated operation.
Elementary Algebra problems you can use for practice. Remember, you may not use a calculator when you take the assessment test. Use these problems to help you get up to speed. Perform the indicated operation.
LESSON 6.2 POLYNOMIAL OPERATIONS I
 LESSON 6. POLYNOMIAL OPERATIONS I LESSON 6. POLYNOMIALS OPERATIONS I 63 OVERVIEW Here's what you'll learn in this lesson: Adding and Subtracting a. Definition of polynomial, term, and coefficient b. Evaluating
LESSON 6. POLYNOMIAL OPERATIONS I LESSON 6. POLYNOMIALS OPERATIONS I 63 OVERVIEW Here's what you'll learn in this lesson: Adding and Subtracting a. Definition of polynomial, term, and coefficient b. Evaluating
Northwood High School Algebra 2/Honors Algebra 2 Summer Review Packet
 Northwood High School Algebra 2/Honors Algebra 2 Summer Review Packet This assignment should serve as a review of the Algebra 1 skills necessary for success. Our hope is that this review will keep your
Northwood High School Algebra 2/Honors Algebra 2 Summer Review Packet This assignment should serve as a review of the Algebra 1 skills necessary for success. Our hope is that this review will keep your
Algebraic Expressions and Identities
 9 Algebraic Epressions and Identities introduction In previous classes, you have studied the fundamental concepts of algebra, algebraic epressions and their addition and subtraction. In this chapter, we
9 Algebraic Epressions and Identities introduction In previous classes, you have studied the fundamental concepts of algebra, algebraic epressions and their addition and subtraction. In this chapter, we
Exponents and Polynomials. (5) Page 459 #15 43 Second Column; Page 466 #6 30 Fourth Column
 Algebra Name: Date: Period: # Exponents and Polynomials (1) Page 453 #22 59 Left (2) Page 453 #25 62 Right (3) Page 459 #5 29 Odd (4) Page 459 #14 42 First Column; Page 466 #3 27 First Column (5) Page
Algebra Name: Date: Period: # Exponents and Polynomials (1) Page 453 #22 59 Left (2) Page 453 #25 62 Right (3) Page 459 #5 29 Odd (4) Page 459 #14 42 First Column; Page 466 #3 27 First Column (5) Page
7-7 Multiplying Polynomials
 Example 1: Multiplying Monomials A. (6y 3 )(3y 5 ) (6y 3 )(3y 5 ) (6 3)(y 3 y 5 ) 18y 8 Group factors with like bases together. B. (3mn 2 ) (9m 2 n) Example 1C: Multiplying Monomials Group factors with
Example 1: Multiplying Monomials A. (6y 3 )(3y 5 ) (6y 3 )(3y 5 ) (6 3)(y 3 y 5 ) 18y 8 Group factors with like bases together. B. (3mn 2 ) (9m 2 n) Example 1C: Multiplying Monomials Group factors with
LESSON 9.1 ROOTS AND RADICALS
 LESSON 9.1 ROOTS AND RADICALS LESSON 9.1 ROOTS AND RADICALS 67 OVERVIEW Here s what you ll learn in this lesson: Square Roots and Cube Roots a. Definition of square root and cube root b. Radicand, radical
LESSON 9.1 ROOTS AND RADICALS LESSON 9.1 ROOTS AND RADICALS 67 OVERVIEW Here s what you ll learn in this lesson: Square Roots and Cube Roots a. Definition of square root and cube root b. Radicand, radical
Mathematics. Algebra I (PreAP, Pt. 1, Pt. 2) Curriculum Guide. Revised 2016
 Mathematics Algebra I (PreAP, Pt. 1, Pt. ) Curriculum Guide Revised 016 Intentionally Left Blank Introduction The Mathematics Curriculum Guide serves as a guide for teachers when planning instruction and
Mathematics Algebra I (PreAP, Pt. 1, Pt. ) Curriculum Guide Revised 016 Intentionally Left Blank Introduction The Mathematics Curriculum Guide serves as a guide for teachers when planning instruction and
LESSON 16 More Complicated Evaluations
 72 Lesson 16 27. 2 2 + 2 3 2. (1) 3 5 4 2 3 3 1 9 1 5 29. The length of PQ is 5 yards. The length of QR is yards. Find PR. (1) 3 P Q R 30. Find the surface area of this right rectangular prism. Dimensions
72 Lesson 16 27. 2 2 + 2 3 2. (1) 3 5 4 2 3 3 1 9 1 5 29. The length of PQ is 5 yards. The length of QR is yards. Find PR. (1) 3 P Q R 30. Find the surface area of this right rectangular prism. Dimensions
Adding and Subtracting Polynomials
 Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Polynomial A monomial or sum of monomials. Binomials and Trinomial are also polynomials. Binomials are sum of two monomials Trinomials are sum of three monomials Degree
Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Polynomial A monomial or sum of monomials. Binomials and Trinomial are also polynomials. Binomials are sum of two monomials Trinomials are sum of three monomials Degree
mn 3 17x 2 81y 4 z Polynomials 32,457 Polynomials Part 1 Algebra (MS) Definitions of Monomials, Polynomials and Degrees Table of Contents
 Table of ontents Polynomials efinitions of Monomials, Polynomials and egrees dding and Subtracting Polynomials Multiplying Monomials ividing by Monomials Mulitplying a Polynomial by a Monomial Multiplying
Table of ontents Polynomials efinitions of Monomials, Polynomials and egrees dding and Subtracting Polynomials Multiplying Monomials ividing by Monomials Mulitplying a Polynomial by a Monomial Multiplying
Unit # 4 : Polynomials
 Name: Block: Teacher: Miss Zukowski Date Submitted: / / 2018 Unit # 4 : Polynomials Submission Checklist: (make sure you have included all components for full marks) Cover page & Assignment Log Class Notes
Name: Block: Teacher: Miss Zukowski Date Submitted: / / 2018 Unit # 4 : Polynomials Submission Checklist: (make sure you have included all components for full marks) Cover page & Assignment Log Class Notes
Controlling the Population
 Lesson.1 Skills Practice Name Date Controlling the Population Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Vocabulary Match each definition with its corresponding term. 1. polynomial a. a polynomial with only 1
Lesson.1 Skills Practice Name Date Controlling the Population Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Vocabulary Match each definition with its corresponding term. 1. polynomial a. a polynomial with only 1
Algebraic expression is formed from variables and constants using different operations. NCERT
 UNIT 10 ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS (A) Main Concepts and Results Algebraic expression is formed from variables and constants using different operations. Expressions are made up of terms. A term is the product
UNIT 10 ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS (A) Main Concepts and Results Algebraic expression is formed from variables and constants using different operations. Expressions are made up of terms. A term is the product
Secondary Math 2H Unit 3 Notes: Factoring and Solving Quadratics
 Secondary Math H Unit 3 Notes: Factoring and Solving Quadratics 3.1 Factoring out the Greatest Common Factor (GCF) Factoring: The reverse of multiplying. It means figuring out what you would multiply together
Secondary Math H Unit 3 Notes: Factoring and Solving Quadratics 3.1 Factoring out the Greatest Common Factor (GCF) Factoring: The reverse of multiplying. It means figuring out what you would multiply together
Dividing Polynomials
 3-3 3-3 Dividing Polynomials Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 2 Warm Up Divide using long division. 1. 161 7 2. 12.18 2.1 23 5.8 Divide. 3. 4. 6x + 15y 3 7a 2 ab a 2x + 5y 7a b Objective
3-3 3-3 Dividing Polynomials Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 2 Warm Up Divide using long division. 1. 161 7 2. 12.18 2.1 23 5.8 Divide. 3. 4. 6x + 15y 3 7a 2 ab a 2x + 5y 7a b Objective
Answers (Lesson 11-1)
 Answers (Lesson -) Lesson - - Study Guide and Intervention Product Property of Square Roots The Product Property of Square Roots and prime factorization can be used to simplify expressions involving irrational
Answers (Lesson -) Lesson - - Study Guide and Intervention Product Property of Square Roots The Product Property of Square Roots and prime factorization can be used to simplify expressions involving irrational
Review for Mastery. Integer Exponents. Zero Exponents Negative Exponents Negative Exponents in the Denominator. Definition.
 LESSON 6- Review for Mastery Integer Exponents Remember that means 8. The base is, the exponent is positive. Exponents can also be 0 or negative. Zero Exponents Negative Exponents Negative Exponents in
LESSON 6- Review for Mastery Integer Exponents Remember that means 8. The base is, the exponent is positive. Exponents can also be 0 or negative. Zero Exponents Negative Exponents Negative Exponents in
LESSON 8.1 RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS I
 LESSON 8. RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS I LESSON 8. RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS I 7 OVERVIEW Here is what you'll learn in this lesson: Multiplying and Dividing a. Determining when a rational expression is undefined Almost
LESSON 8. RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS I LESSON 8. RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS I 7 OVERVIEW Here is what you'll learn in this lesson: Multiplying and Dividing a. Determining when a rational expression is undefined Almost
PREFACE. Synergy for Success in Mathematics 8 is designed for Grade 8 students. The textbook contains
 Synergy for Success in Mathematics 8 is designed for Grade 8 students. The textbook contains all the required learning competencies and is supplemented with some additional topics for enrichment. Lessons
Synergy for Success in Mathematics 8 is designed for Grade 8 students. The textbook contains all the required learning competencies and is supplemented with some additional topics for enrichment. Lessons
= The algebraic expression is 3x 2 x The algebraic expression is x 2 + x. 3. The algebraic expression is x 2 2x.
 Chapter 7 Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency (p. 335) 1. 3x 7 x = 3x x 7 = (3 )x 7 = 5x 7. 4r 6 9r 1 = 4r 9r 6 1 = (4 9)r 6 1 = 5r 5 3. 5t 3 t 4 8t = 5t t 8t 3 4 = ( 5 1 8)t 3 4 = ()t ( 1) = t 1 4. 3(s
Chapter 7 Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency (p. 335) 1. 3x 7 x = 3x x 7 = (3 )x 7 = 5x 7. 4r 6 9r 1 = 4r 9r 6 1 = (4 9)r 6 1 = 5r 5 3. 5t 3 t 4 8t = 5t t 8t 3 4 = ( 5 1 8)t 3 4 = ()t ( 1) = t 1 4. 3(s
The product is 8a 11 b 6. Simplify. 3a 3 b 12 27a 3 b 12 64x 6 b 3. y 10 n 28 x (y 5 ) 2 2. (n 7 ) 4 3. (x 2 ) 5 (x 3 )
 Answers (Lesson 8-) Lesson 8-8- 6- Study Guide and Intervention Multiplying Monomials Multiply Monomials A monomial is a number, a variable, or a product of a number and one or more variables. An expression
Answers (Lesson 8-) Lesson 8-8- 6- Study Guide and Intervention Multiplying Monomials Multiply Monomials A monomial is a number, a variable, or a product of a number and one or more variables. An expression
When you square a binomial, you can apply the FOIL method to find the product. You can also apply the following rules as a short cut.
 Squaring a Binomial When you square a binomial, you can apply the FOIL method to find the product. You can also apply the following rules as a short cut. Solve. (x 3) 2 Step 1 Square the first term. Rules
Squaring a Binomial When you square a binomial, you can apply the FOIL method to find the product. You can also apply the following rules as a short cut. Solve. (x 3) 2 Step 1 Square the first term. Rules
Unit 2-1: Factoring and Solving Quadratics. 0. I can add, subtract and multiply polynomial expressions
 CP Algebra Unit -1: Factoring and Solving Quadratics NOTE PACKET Name: Period Learning Targets: 0. I can add, subtract and multiply polynomial expressions 1. I can factor using GCF.. I can factor by grouping.
CP Algebra Unit -1: Factoring and Solving Quadratics NOTE PACKET Name: Period Learning Targets: 0. I can add, subtract and multiply polynomial expressions 1. I can factor using GCF.. I can factor by grouping.
Algebra I Lesson 6 Monomials and Polynomials (Grades 9-12) Instruction 6-1 Multiplying Polynomials
 In algebra, we deal with different types of expressions. Grouping them helps us to learn rules and concepts easily. One group of expressions is called polynomials. In a polynomial, the powers are whole
In algebra, we deal with different types of expressions. Grouping them helps us to learn rules and concepts easily. One group of expressions is called polynomials. In a polynomial, the powers are whole
MAFS Algebra 1. Polynomials. Day 15 - Student Packet
 MAFS Algebra 1 Polynomials Day 15 - Student Packet Day 15: Polynomials MAFS.91.A-SSE.1., MAFS.91.A-SSE..3a,b, MAFS.91.A-APR..3, MAFS.91.F-IF.3.7c I CAN rewrite algebraic expressions in different equivalent
MAFS Algebra 1 Polynomials Day 15 - Student Packet Day 15: Polynomials MAFS.91.A-SSE.1., MAFS.91.A-SSE..3a,b, MAFS.91.A-APR..3, MAFS.91.F-IF.3.7c I CAN rewrite algebraic expressions in different equivalent
SECTION 1.4 PolyNomiAls feet. Figure 1. A = s 2 = (2x) 2 = 4x 2 A = 2 (2x) 3 _ 2 = 1 _ = 3 _. A = lw = x 1. = x
 SECTION 1.4 PolyNomiAls 4 1 learning ObjeCTIveS In this section, you will: Identify the degree and leading coefficient of polynomials. Add and subtract polynomials. Multiply polynomials. Use FOIL to multiply
SECTION 1.4 PolyNomiAls 4 1 learning ObjeCTIveS In this section, you will: Identify the degree and leading coefficient of polynomials. Add and subtract polynomials. Multiply polynomials. Use FOIL to multiply
Words to Review. Give an example of the vocabulary word. Numerical expression. Variable. Evaluate a variable expression. Variable expression
 1 Words to Review Give an example of the vocabulary word. Numerical expression 5 12 Variable x Variable expression 3x 1 Verbal model Distance Rate p Time Evaluate a variable expression Evaluate the expression
1 Words to Review Give an example of the vocabulary word. Numerical expression 5 12 Variable x Variable expression 3x 1 Verbal model Distance Rate p Time Evaluate a variable expression Evaluate the expression
Real Numbers. Real numbers are divided into two types, rational numbers and irrational numbers
 Real Numbers Real numbers are divided into two types, rational numbers and irrational numbers I. Rational Numbers: Any number that can be expressed as the quotient of two integers. (fraction). Any number
Real Numbers Real numbers are divided into two types, rational numbers and irrational numbers I. Rational Numbers: Any number that can be expressed as the quotient of two integers. (fraction). Any number
POLYNOMIAL ADDITION AND MULTIPLICATION
 Topic 23: Polynomial addition and multiplication 377 POLYNOMIAL ADDITION AND MULTIPLICATION Lesson 23.1 Introduction to polynomials 23.1 OPENER The Bradley family has decided to build a house in a new
Topic 23: Polynomial addition and multiplication 377 POLYNOMIAL ADDITION AND MULTIPLICATION Lesson 23.1 Introduction to polynomials 23.1 OPENER The Bradley family has decided to build a house in a new
Algebra is a part of mathematics in which numbers and letters are used. Numbers and letters are combined by the arithmetic operations.
 Colegio Herma. Maths. Bilingual Department by Isabel Martos Martínez. 2013 WHAT IS ALGEBRA? Algebra is a part of mathematics in which numbers and letters are used. Numbers and letters are combined by the
Colegio Herma. Maths. Bilingual Department by Isabel Martos Martínez. 2013 WHAT IS ALGEBRA? Algebra is a part of mathematics in which numbers and letters are used. Numbers and letters are combined by the
LESSON #1: VARIABLES, TERMS, AND EXPRESSIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 1 LESSON #1: VARIABLES, TERMS, AND EXPRESSIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Mathematics has developed a language all to itself in order to clarify concepts and remove ambiguity from the analysis of problems.
1 LESSON #1: VARIABLES, TERMS, AND EXPRESSIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Mathematics has developed a language all to itself in order to clarify concepts and remove ambiguity from the analysis of problems.
1.3 Algebraic Expressions. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 1.3 Algebraic Expressions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Multiplying Algebraic Expressions Special Product Formulas Factoring Common Factors
1.3 Algebraic Expressions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Multiplying Algebraic Expressions Special Product Formulas Factoring Common Factors
Polynomial comes from poly- (meaning "many") and -nomial (in this case meaning "term")... so it says "many terms
 Polynomials Polynomial comes from poly- (meaning "many") and -nomial (in this case meaning "term")... so it says "many terms Polynomials A polynomial looks like this: Term A number, a variable, or the
Polynomials Polynomial comes from poly- (meaning "many") and -nomial (in this case meaning "term")... so it says "many terms Polynomials A polynomial looks like this: Term A number, a variable, or the
Properties of Real Numbers
 Pre-Algebra Properties of Real Numbers Identity Properties Addition: Multiplication: Commutative Properties Addition: Multiplication: Associative Properties Inverse Properties Distributive Properties Properties
Pre-Algebra Properties of Real Numbers Identity Properties Addition: Multiplication: Commutative Properties Addition: Multiplication: Associative Properties Inverse Properties Distributive Properties Properties
Never leave a NEGATIVE EXPONENT or a ZERO EXPONENT in an answer in simplest form!!!!!
 1 ICM Unit 0 Algebra Rules Lesson 1 Rules of Exponents RULE EXAMPLE EXPLANANTION a m a n = a m+n A) x x 6 = B) x 4 y 8 x 3 yz = When multiplying with like bases, keep the base and add the exponents. a
1 ICM Unit 0 Algebra Rules Lesson 1 Rules of Exponents RULE EXAMPLE EXPLANANTION a m a n = a m+n A) x x 6 = B) x 4 y 8 x 3 yz = When multiplying with like bases, keep the base and add the exponents. a
Example #3: 14 (5 + 2) 6 = = then add = 1 x (-3) then. = 1.5 = add
 Grade 9 Curricular content Operations with rational numbers (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division and order of operations) -incudes brackets and exponents (exponent laws) -exponents includes
Grade 9 Curricular content Operations with rational numbers (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division and order of operations) -incudes brackets and exponents (exponent laws) -exponents includes
Which of the following expressions are monomials?
 9 1 Stud Guide Pages 382 387 Polnomials The epressions, 6, 5a 2, and 10cd 3 are eamples of monomials. A monomial is a number, a variable, or a product of numbers and variables. An eponents in a monomial
9 1 Stud Guide Pages 382 387 Polnomials The epressions, 6, 5a 2, and 10cd 3 are eamples of monomials. A monomial is a number, a variable, or a product of numbers and variables. An eponents in a monomial
A field trips costs $800 for the charter bus plus $10 per student for x students. The cost per student is represented by: 10x x
 LEARNING STRATEGIES: Activate Prior Knowledge, Shared Reading, Think/Pair/Share, Note Taking, Group Presentation, Interactive Word Wall A field trips costs $800 for the charter bus plus $10 per student
LEARNING STRATEGIES: Activate Prior Knowledge, Shared Reading, Think/Pair/Share, Note Taking, Group Presentation, Interactive Word Wall A field trips costs $800 for the charter bus plus $10 per student
27 Wyner Math 2 Spring 2019
 27 Wyner Math 2 Spring 2019 CHAPTER SIX: POLYNOMIALS Review January 25 Test February 8 Thorough understanding and fluency of the concepts and methods in this chapter is a cornerstone to success in the
27 Wyner Math 2 Spring 2019 CHAPTER SIX: POLYNOMIALS Review January 25 Test February 8 Thorough understanding and fluency of the concepts and methods in this chapter is a cornerstone to success in the
LESSON 6.3 POLYNOMIAL OPERATIONS II
 LESSON 6.3 POLYNOMIAL OPERATIONS II LESSON 6.3 POLYNOMIALS OPERATIONS II 277 OVERVIEW Here's what you'll learn in this lesson: Multiplying Binomials a. Multiplying binomials by the FOIL method b. Perfect
LESSON 6.3 POLYNOMIAL OPERATIONS II LESSON 6.3 POLYNOMIALS OPERATIONS II 277 OVERVIEW Here's what you'll learn in this lesson: Multiplying Binomials a. Multiplying binomials by the FOIL method b. Perfect
Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz. Holt McDougal Algebra 2
 Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 2 Warm Up Factor each expression. 1. 3x 6y 2. a 2 b 2 3(x 2y) (a + b)(a b) Find each product. 3. (x 1)(x + 3) 4. (a + 1)(a 2 + 1) x 2 + 2x 3 a 3 + a 2 +
Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Algebra 2 Warm Up Factor each expression. 1. 3x 6y 2. a 2 b 2 3(x 2y) (a + b)(a b) Find each product. 3. (x 1)(x + 3) 4. (a + 1)(a 2 + 1) x 2 + 2x 3 a 3 + a 2 +
VARIABLES, TERMS, AND EXPRESSIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 Name: Date: VARIABLES, TERMS, AND EXPRESSIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Mathematics has developed a language all to itself in order to clarify concepts and remove ambiguity from the analysis of problems.
Name: Date: VARIABLES, TERMS, AND EXPRESSIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Mathematics has developed a language all to itself in order to clarify concepts and remove ambiguity from the analysis of problems.
Multiplication of Polynomials
 Summary 391 Chapter 5 SUMMARY Section 5.1 A polynomial in x is defined by a finite sum of terms of the form ax n, where a is a real number and n is a whole number. a is the coefficient of the term. n is
Summary 391 Chapter 5 SUMMARY Section 5.1 A polynomial in x is defined by a finite sum of terms of the form ax n, where a is a real number and n is a whole number. a is the coefficient of the term. n is
= 9 = x + 8 = = -5x 19. For today: 2.5 (Review) and. 4.4a (also review) Objectives:
 Math 65 / Notes & Practice #1 / 20 points / Due. / Name: Home Work Practice: Simplify the following expressions by reducing the fractions: 16 = 4 = 8xy =? = 9 40 32 38x 64 16 Solve the following equations
Math 65 / Notes & Practice #1 / 20 points / Due. / Name: Home Work Practice: Simplify the following expressions by reducing the fractions: 16 = 4 = 8xy =? = 9 40 32 38x 64 16 Solve the following equations
Note: A file Algebra Unit 09 Practice X Patterns can be useful to prepare students to quickly find sum and product.
 Note: This unit can be used as needed (review or introductory) to practice operations on polynomials. Math Background Previously, you Identified monomials and their characteristics Applied the laws of
Note: This unit can be used as needed (review or introductory) to practice operations on polynomials. Math Background Previously, you Identified monomials and their characteristics Applied the laws of
POLYNOMIAL EXPRESSIONS PART 1
 POLYNOMIAL EXPRESSIONS PART 1 A polynomial is an expression that is a sum of one or more terms. Each term consists of one or more variables multiplied by a coefficient. Coefficients can be negative, so
POLYNOMIAL EXPRESSIONS PART 1 A polynomial is an expression that is a sum of one or more terms. Each term consists of one or more variables multiplied by a coefficient. Coefficients can be negative, so
MATH 0960 ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA FOR COLLEGE STUDENTS (8 TH EDITION) BY ANGEL & RUNDE Course Outline
 MATH 0960 ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA FOR COLLEGE STUDENTS (8 TH EDITION) BY ANGEL & RUNDE Course Outline 1. Real Numbers (33 topics) 1.3 Fractions (pg. 27: 1-75 odd) A. Simplify fractions. B. Change mixed numbers
MATH 0960 ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA FOR COLLEGE STUDENTS (8 TH EDITION) BY ANGEL & RUNDE Course Outline 1. Real Numbers (33 topics) 1.3 Fractions (pg. 27: 1-75 odd) A. Simplify fractions. B. Change mixed numbers
Unit 1 Notes. Polynomials
 Unit 1 Notes 1 Day Number Date Topic Problem Set 1 Wed. Sept. Operations with Signed Numbers and Order of Operations Pre-Unit Review PS (1 ) Thurs. Sept. Working with Exponents Start Exponent Laws P.S.
Unit 1 Notes 1 Day Number Date Topic Problem Set 1 Wed. Sept. Operations with Signed Numbers and Order of Operations Pre-Unit Review PS (1 ) Thurs. Sept. Working with Exponents Start Exponent Laws P.S.
Using Proportions to Solve Percent Problems (page 562)
 LESSON Name 81 Using Proportions to Solve Percent Problems (page 562) Percent problems can be solved using proportions. Make and complete a percent box. (The total is always 100.) 1. Write in the known
LESSON Name 81 Using Proportions to Solve Percent Problems (page 562) Percent problems can be solved using proportions. Make and complete a percent box. (The total is always 100.) 1. Write in the known
Algebra. Practice Pack
 Algebra Practice Pack WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents Unit 1: Algebra Basics Practice 1 What Are Negative and Positive Numbers?... 1 Practice 2 Larger and Smaller Numbers................ 2 Practice
Algebra Practice Pack WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents Unit 1: Algebra Basics Practice 1 What Are Negative and Positive Numbers?... 1 Practice 2 Larger and Smaller Numbers................ 2 Practice
Virginia Unit-Specific Learning Pathways. Grades 6-Algebra I: Standards of Learning
 BUI L T F O VIR R G INIA 2014 2015 Virginia -Specific Learning Pathways Grades 6-Algebra I: Standards of Learning Table of Contents Grade 6...3 Grade 7...6 Grade 8...9 Algebra I... 11 Grade 6 Virginia
BUI L T F O VIR R G INIA 2014 2015 Virginia -Specific Learning Pathways Grades 6-Algebra I: Standards of Learning Table of Contents Grade 6...3 Grade 7...6 Grade 8...9 Algebra I... 11 Grade 6 Virginia
