Polynomial Functions and Their Graphs
|
|
|
- Mariah Johns
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Polyomial Fuctios ad Their Graphs I this sectio we begi the study of fuctios defied by polyomial expressios. Polyomial ad ratioal fuctios are the most commo fuctios used to model data, ad are used extesively i mathematical models of productio costs, cosumer demads, wildlife maagemet, biological processes, ad may other scietific studies. Usig these fuctios ad their graphs, predictios regardig future treds ca be made. Polyomial Fuctios ad Their Graphs: Before we start lookig at polyomials, we should kow some commo termiology. Defiitio: A polyomial of degree is a fuctio of the form P x = a x + a x + + a x + a where a 0. The umbers a0, a1, a,..., a are called the coefficiets of the polyomial. The umber a 0 is the costat coefficiet or costat term. The umber a, the coefficiet of the highest power is the leadig coefficiet, ad the term ax is the leadig term. Notice that a polyomial is usually writte i descedig powers of the variable, ad the degree of a polyomial is the power of the leadig term. For istace 3 P x = 4x x + 5 is a polyomial of degree 3. Also, if a polyomial cosists of just a sigle term, such as Q x = 7x, the it is called a moomial. 4 Graphs of Polyomials: Polyomials of degree 0 ad 1 are liear equatios, ad their graphs are straight lies. Polyomials of degree are quadratic equatios, ad their graphs are parabolas. As the degree of the polyomial icreases beyod, the umber of possible shapes the graph ca be icreases. However, the graph of a polyomial fuctio is always a smooth cotiuous curve (o breaks, gaps, or sharp corers). Moomials of the form P x = x are the simplest polyomials.
2 As the figure suggest, the graph of P( x) x = has the same geeral shape as y x = whe 3 is eve, ad the same geeral shape as y = x whe is odd. However, as the degree becomes larger, the graphs become flatter aroud the origi ad steeper elsewhere. Trasformatios of Moomials: Whe graphig certai polyomial fuctios, we ca use the graphs of moomials we already kow, ad trasform them usig the techiques we leared earlier. 3 Example 1: Sketch the graph of the fuctio P( x) x of a appropriate fuctio of the form y itercepts o the graph. = + by trasformig the graph x =. Idicate all x- ad y- Based o the trasformatio techiques, we kow the graph of 3 3 P( x) = x + is the reflectio of the graph of y = x i the x-axis, shifted vertically up uits. Thus, Most polyomial fuctios caot be graphed usig trasformatios though. For istace i the polyomial fuctio 3 5 R x = x x + 1,
3 we caot determie easily what fuctio s graph we should perform trasformatios o to graph R ( x ). Therefore, we will eed a ew method for fidig the graphs of more complex polyomials. Ed Behavior of Polyomials: The ed behavior of a polyomial is a descriptio of what happes as x becomes large i the positive or egative directio. To describe ed behavior, we use the followig otatio: x meas x becomes large i the positive directio x meas x becomes large i the egative directio For example, the moomial y x 3 = has the ed behavior y as x ad y as x The ed behavior of a polyomial graph is determied by the term of highest degree. For 5 istace, the polyomial f x = 3x 4x + has the same ed behavior as f ( x) = 3x 5 because both are polyomials of degree 5.
4 Example : Determie the ed behavior of the polyomial 6 4 Q x = 6x 4x + x 3. Sice Q has eve degree ad positive leadig coefficiet, it has the followig ed behavior: y as x ad y as x Usig Zeros to Graph Polyomials: P 0 Defiitio: If is a polyomial ad c is a umber such that P c =, the we say that c is a zero of P. The followig are equivalet ways of sayig the same thig. 1. c is a zero of P. x = c is a root of the equatio P( x ) = 0 3. x c is a factor of P( x ) Whe graphig a polyomial, we wat to fid the roots of the polyomial equatio P x =. To do this, we factor the polyomial ad the use the Zero-Product Property 0 (Sectio 3.3). Remember that if P( c ) = 0, the the graph of y P( x) at x = c, so the x-itercepts of the graph are the zeros of the fuctio. Example 3: Fid the zeros of the polyomial Step 1: First we must factor R to get Step : Sice 4 = ( 4)( 3) R x x x x is a factor of x 3 is a factor of R( x) x x R x = x 7x+ 1. = has a x-itercept R x = x 7x+ 1, 4 is a zero of R, ad sice = 7 + 1, 3 is a zero of R. The followig theorem ad its cosequeces will be used to help us graph polyomials. Itermediate Value Theorem for Polyomials: If P is a polyomial fuctio ad P( a ) ad P( b ) have opposite sigs, P( c ) = 0 the there exists at least oe value c betwee a ad b for which. The figure below graphically demostrates this theorem.
5 Oe importat cosequece of this theorem is that betwee ay two successive zeros, the values of a polyomial are either all positive or all egative. That is, betwee two successive zeros the graph of a polyomial lies etirely above or etirely below the x- axis. So, to sketch the graph of P, we first fid all the zeros of P. The we choose test poits P x is betwee (ad to the right ad left of) successive zeros to determie whether positive or egative o each iterval determied by the zeros. Guidelies for Graphig Polyomial Fuctios: 1. Zeros: Factor the polyomial to fid all its real zeros; these are the x-itercepts of the graph.. Test Poits: Make a table of values for the polyomial. Iclude test poits to determie whether the graph of the polyomial lies above or below the x-axis o the itervals determied by the zeros. Iclude the y-itercept i the table 3. Ed Behavior: Determie the ed behavior of the polyomial. 4. Graph: Plot the itercepts ad other poits you foud i the table. Sketch a smooth curve that passes through these poits ad exhibits the required ed behavior.
6 Example 4: Sketch the graph of the fuctio P x = x+ 1 x graph shows all itercepts ad exhibits the proper ed behavior. Step 1: First we must fid all the real zeros of P( x ). Sice = ( + 1)( ) P x x x. Make sure your is already factored, it is easy to see the zeros are x = 1 ad x =. Therefore, the x-itercepts are x = 1 ad x =. Step : Now we will make a table of values of P( x ), makig sure we choose test poits betwee (ad to the left ad right of ) successive zeros, ad iclude the y-itercept, P 0 = 4. Step 3: Next we determie the ed behavior. If we expad P, we get P x = x x +4. Sice P is of odd degree (degree 3) ad its 3 leadig coefficiet is positive, it has the followig ed behavior: y as x ad y as x
7 Example 4 (Cotiued): Step 4: Fially, we plot the poits from the table ad coect the poits by a smooth curve to complete the graph. Example 5: Sketch the graph of the fuctio 4 Q x = x 4x. Make sure your graph shows all itercepts ad exhibits the proper ed behavior. Step 1: I order to fid all the real zeros of Q( x ), we must first factor it completely. 4 = 4 Q x x x x ( x 4) = = x ( x+ )( x ) Factor x Differece of Squares Step : Sice Q( x) x ( x )( x ) = + the zeros are x = 0, x = ad x =. Thus, the x-itercepts are x = 0, x = ad x =.
8 Example 5 (Cotiued): Step 3: Now we will make a table of values of Q( x ), makig sure we choose test poits betwee (ad to the left ad right of) successive zeros, ad iclude the y-itercept, Q 0 = 0. Step 4: Next we determie the ed behavior. Sice Q is of eve degree (degree 4) ad its leadig coefficiet is positive, it has the followig ed behavior: y as x ad y as x Step 5: Fially, we plot the poits from the table ad coect the poits by a smooth curve to complete the graph.
9 By examiig Example 4 ad Example 5, otice that whe c is a zero of P, ad the correspodig factor ( x c) occurs exactly m times i the factorizatio of P, the graph crosses the x-axis at c if m is odd ad does ot cross the x-axis if m is eve. Example 6: Sketch the graph of the fuctio R( x) ( x ) ( x 1) ( x ) = + +. Make sure your graph shows all itercepts ad exhibits the proper ed behavior. Step 1: The real zeros of R( x) = ( x ) ( x+ 1) ( x+ ) x = 1 are x =, ad x =. These are the x-itercepts of the graph.
10 Example 6 (Cotiued): Step : Now we will make a table of values of R ( x ), makig sure we choose test poits betwee (ad to the left ad right of) R 0 = 8. successive zeros, ad the y-itercept, Step 3: Sice R is of odd degree (degree 5) ad its leadig coefficiet is egative, it has the followig ed behavior: y as x ad y as x Step 4: Fially, we plot the poits from the table ad coect the poits by a smooth curve to complete the graph.
Quadratic Functions. Before we start looking at polynomials, we should know some common terminology.
 Quadratic Fuctios I this sectio we begi the study of fuctios defied by polyomial expressios. Polyomial ad ratioal fuctios are the most commo fuctios used to model data, ad are used extesively i mathematical
Quadratic Fuctios I this sectio we begi the study of fuctios defied by polyomial expressios. Polyomial ad ratioal fuctios are the most commo fuctios used to model data, ad are used extesively i mathematical
Polynomial Functions. New Section 1 Page 1. A Polynomial function of degree n is written is the form:
 New Sectio 1 Page 1 A Polyomial fuctio of degree is writte is the form: 1 P x a x a x a x a x a x a 1 1 0 where is a o-egative iteger expoet ad a 0 ca oly take o values where a, a, a,..., a, a. 0 1 1.
New Sectio 1 Page 1 A Polyomial fuctio of degree is writte is the form: 1 P x a x a x a x a x a x a 1 1 0 where is a o-egative iteger expoet ad a 0 ca oly take o values where a, a, a,..., a, a. 0 1 1.
x c the remainder is Pc ().
 Algebra, Polyomial ad Ratioal Fuctios Page 1 K.Paulk Notes Chapter 3, Sectio 3.1 to 3.4 Summary Sectio Theorem Notes 3.1 Zeros of a Fuctio Set the fuctio to zero ad solve for x. The fuctio is zero at these
Algebra, Polyomial ad Ratioal Fuctios Page 1 K.Paulk Notes Chapter 3, Sectio 3.1 to 3.4 Summary Sectio Theorem Notes 3.1 Zeros of a Fuctio Set the fuctio to zero ad solve for x. The fuctio is zero at these
Unit 4: Polynomial and Rational Functions
 48 Uit 4: Polyomial ad Ratioal Fuctios Polyomial Fuctios A polyomial fuctio y px ( ) is a fuctio of the form p( x) ax + a x + a x +... + ax + ax+ a 1 1 1 0 where a, a 1,..., a, a1, a0are real costats ad
48 Uit 4: Polyomial ad Ratioal Fuctios Polyomial Fuctios A polyomial fuctio y px ( ) is a fuctio of the form p( x) ax + a x + a x +... + ax + ax+ a 1 1 1 0 where a, a 1,..., a, a1, a0are real costats ad
Properties and Tests of Zeros of Polynomial Functions
 Properties ad Tests of Zeros of Polyomial Fuctios The Remaider ad Factor Theorems: Sythetic divisio ca be used to fid the values of polyomials i a sometimes easier way tha substitutio. This is show by
Properties ad Tests of Zeros of Polyomial Fuctios The Remaider ad Factor Theorems: Sythetic divisio ca be used to fid the values of polyomials i a sometimes easier way tha substitutio. This is show by
Zeros of Polynomials
 Math 160 www.timetodare.com 4.5 4.6 Zeros of Polyomials I these sectios we will study polyomials algebraically. Most of our work will be cocered with fidig the solutios of polyomial equatios of ay degree
Math 160 www.timetodare.com 4.5 4.6 Zeros of Polyomials I these sectios we will study polyomials algebraically. Most of our work will be cocered with fidig the solutios of polyomial equatios of ay degree
CALCULUS BASIC SUMMER REVIEW
 CALCULUS BASIC SUMMER REVIEW NAME rise y y y Slope of a o vertical lie: m ru Poit Slope Equatio: y y m( ) The slope is m ad a poit o your lie is, ). ( y Slope-Itercept Equatio: y m b slope= m y-itercept=
CALCULUS BASIC SUMMER REVIEW NAME rise y y y Slope of a o vertical lie: m ru Poit Slope Equatio: y y m( ) The slope is m ad a poit o your lie is, ). ( y Slope-Itercept Equatio: y m b slope= m y-itercept=
Continuous Functions
 Cotiuous Fuctios Q What does it mea for a fuctio to be cotiuous at a poit? Aswer- I mathematics, we have a defiitio that cosists of three cocepts that are liked i a special way Cosider the followig defiitio
Cotiuous Fuctios Q What does it mea for a fuctio to be cotiuous at a poit? Aswer- I mathematics, we have a defiitio that cosists of three cocepts that are liked i a special way Cosider the followig defiitio
3.2 Properties of Division 3.3 Zeros of Polynomials 3.4 Complex and Rational Zeros of Polynomials
 Math 60 www.timetodare.com 3. Properties of Divisio 3.3 Zeros of Polyomials 3.4 Complex ad Ratioal Zeros of Polyomials I these sectios we will study polyomials algebraically. Most of our work will be cocered
Math 60 www.timetodare.com 3. Properties of Divisio 3.3 Zeros of Polyomials 3.4 Complex ad Ratioal Zeros of Polyomials I these sectios we will study polyomials algebraically. Most of our work will be cocered
TEACHER CERTIFICATION STUDY GUIDE
 COMPETENCY 1. ALGEBRA SKILL 1.1 1.1a. ALGEBRAIC STRUCTURES Kow why the real ad complex umbers are each a field, ad that particular rigs are ot fields (e.g., itegers, polyomial rigs, matrix rigs) Algebra
COMPETENCY 1. ALGEBRA SKILL 1.1 1.1a. ALGEBRAIC STRUCTURES Kow why the real ad complex umbers are each a field, ad that particular rigs are ot fields (e.g., itegers, polyomial rigs, matrix rigs) Algebra
September 2012 C1 Note. C1 Notes (Edexcel) Copyright - For AS, A2 notes and IGCSE / GCSE worksheets 1
 September 0 s (Edecel) Copyright www.pgmaths.co.uk - For AS, A otes ad IGCSE / GCSE worksheets September 0 Copyright www.pgmaths.co.uk - For AS, A otes ad IGCSE / GCSE worksheets September 0 Copyright
September 0 s (Edecel) Copyright www.pgmaths.co.uk - For AS, A otes ad IGCSE / GCSE worksheets September 0 Copyright www.pgmaths.co.uk - For AS, A otes ad IGCSE / GCSE worksheets September 0 Copyright
Curve Sketching Handout #5 Topic Interpretation Rational Functions
 Curve Sketchig Hadout #5 Topic Iterpretatio Ratioal Fuctios A ratioal fuctio is a fuctio f that is a quotiet of two polyomials. I other words, p ( ) ( ) f is a ratioal fuctio if p ( ) ad q ( ) are polyomials
Curve Sketchig Hadout #5 Topic Iterpretatio Ratioal Fuctios A ratioal fuctio is a fuctio f that is a quotiet of two polyomials. I other words, p ( ) ( ) f is a ratioal fuctio if p ( ) ad q ( ) are polyomials
A sequence of numbers is a function whose domain is the positive integers. We can see that the sequence
 Sequeces A sequece of umbers is a fuctio whose domai is the positive itegers. We ca see that the sequece,, 2, 2, 3, 3,... is a fuctio from the positive itegers whe we write the first sequece elemet as
Sequeces A sequece of umbers is a fuctio whose domai is the positive itegers. We ca see that the sequece,, 2, 2, 3, 3,... is a fuctio from the positive itegers whe we write the first sequece elemet as
Infinite Sequences and Series
 Chapter 6 Ifiite Sequeces ad Series 6.1 Ifiite Sequeces 6.1.1 Elemetary Cocepts Simply speakig, a sequece is a ordered list of umbers writte: {a 1, a 2, a 3,...a, a +1,...} where the elemets a i represet
Chapter 6 Ifiite Sequeces ad Series 6.1 Ifiite Sequeces 6.1.1 Elemetary Cocepts Simply speakig, a sequece is a ordered list of umbers writte: {a 1, a 2, a 3,...a, a +1,...} where the elemets a i represet
Section 11.8: Power Series
 Sectio 11.8: Power Series 1. Power Series I this sectio, we cosider geeralizig the cocept of a series. Recall that a series is a ifiite sum of umbers a. We ca talk about whether or ot it coverges ad i
Sectio 11.8: Power Series 1. Power Series I this sectio, we cosider geeralizig the cocept of a series. Recall that a series is a ifiite sum of umbers a. We ca talk about whether or ot it coverges ad i
P.3 Polynomials and Special products
 Precalc Fall 2016 Sectios P.3, 1.2, 1.3, P.4, 1.4, P.2 (radicals/ratioal expoets), 1.5, 1.6, 1.7, 1.8, 1.1, 2.1, 2.2 I Polyomial defiitio (p. 28) a x + a x +... + a x + a x 1 1 0 1 1 0 a x + a x +... +
Precalc Fall 2016 Sectios P.3, 1.2, 1.3, P.4, 1.4, P.2 (radicals/ratioal expoets), 1.5, 1.6, 1.7, 1.8, 1.1, 2.1, 2.2 I Polyomial defiitio (p. 28) a x + a x +... + a x + a x 1 1 0 1 1 0 a x + a x +... +
Ma 530 Introduction to Power Series
 Ma 530 Itroductio to Power Series Please ote that there is material o power series at Visual Calculus. Some of this material was used as part of the presetatio of the topics that follow. What is a Power
Ma 530 Itroductio to Power Series Please ote that there is material o power series at Visual Calculus. Some of this material was used as part of the presetatio of the topics that follow. What is a Power
62. Power series Definition 16. (Power series) Given a sequence {c n }, the series. c n x n = c 0 + c 1 x + c 2 x 2 + c 3 x 3 +
 62. Power series Defiitio 16. (Power series) Give a sequece {c }, the series c x = c 0 + c 1 x + c 2 x 2 + c 3 x 3 + is called a power series i the variable x. The umbers c are called the coefficiets of
62. Power series Defiitio 16. (Power series) Give a sequece {c }, the series c x = c 0 + c 1 x + c 2 x 2 + c 3 x 3 + is called a power series i the variable x. The umbers c are called the coefficiets of
6.3 Testing Series With Positive Terms
 6.3. TESTING SERIES WITH POSITIVE TERMS 307 6.3 Testig Series With Positive Terms 6.3. Review of what is kow up to ow I theory, testig a series a i for covergece amouts to fidig the i= sequece of partial
6.3. TESTING SERIES WITH POSITIVE TERMS 307 6.3 Testig Series With Positive Terms 6.3. Review of what is kow up to ow I theory, testig a series a i for covergece amouts to fidig the i= sequece of partial
CHAPTER 10 INFINITE SEQUENCES AND SERIES
 CHAPTER 10 INFINITE SEQUENCES AND SERIES 10.1 Sequeces 10.2 Ifiite Series 10.3 The Itegral Tests 10.4 Compariso Tests 10.5 The Ratio ad Root Tests 10.6 Alteratig Series: Absolute ad Coditioal Covergece
CHAPTER 10 INFINITE SEQUENCES AND SERIES 10.1 Sequeces 10.2 Ifiite Series 10.3 The Itegral Tests 10.4 Compariso Tests 10.5 The Ratio ad Root Tests 10.6 Alteratig Series: Absolute ad Coditioal Covergece
Sequences A sequence of numbers is a function whose domain is the positive integers. We can see that the sequence
 Sequeces A sequece of umbers is a fuctio whose domai is the positive itegers. We ca see that the sequece 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3,... is a fuctio from the positive itegers whe we write the first sequece elemet
Sequeces A sequece of umbers is a fuctio whose domai is the positive itegers. We ca see that the sequece 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3,... is a fuctio from the positive itegers whe we write the first sequece elemet
MAT 271 Project: Partial Fractions for certain rational functions
 MAT 7 Project: Partial Fractios for certai ratioal fuctios Prerequisite kowledge: partial fractios from MAT 7, a very good commad of factorig ad complex umbers from Precalculus. To complete this project,
MAT 7 Project: Partial Fractios for certai ratioal fuctios Prerequisite kowledge: partial fractios from MAT 7, a very good commad of factorig ad complex umbers from Precalculus. To complete this project,
The picture in figure 1.1 helps us to see that the area represents the distance traveled. Figure 1: Area represents distance travelled
 1 Lecture : Area Area ad distace traveled Approximatig area by rectagles Summatio The area uder a parabola 1.1 Area ad distace Suppose we have the followig iformatio about the velocity of a particle, how
1 Lecture : Area Area ad distace traveled Approximatig area by rectagles Summatio The area uder a parabola 1.1 Area ad distace Suppose we have the followig iformatio about the velocity of a particle, how
Lesson 10: Limits and Continuity
 www.scimsacademy.com Lesso 10: Limits ad Cotiuity SCIMS Academy 1 Limit of a fuctio The cocept of limit of a fuctio is cetral to all other cocepts i calculus (like cotiuity, derivative, defiite itegrals
www.scimsacademy.com Lesso 10: Limits ad Cotiuity SCIMS Academy 1 Limit of a fuctio The cocept of limit of a fuctio is cetral to all other cocepts i calculus (like cotiuity, derivative, defiite itegrals
, then cv V. Differential Equations Elements of Lineaer Algebra Name: Consider the differential equation. and y2 cos( kx)
 Cosider the differetial equatio y '' k y 0 has particular solutios y1 si( kx) ad y cos( kx) I geeral, ay liear combiatio of y1 ad y, cy 1 1 cy where c1, c is also a solutio to the equatio above The reaso
Cosider the differetial equatio y '' k y 0 has particular solutios y1 si( kx) ad y cos( kx) I geeral, ay liear combiatio of y1 ad y, cy 1 1 cy where c1, c is also a solutio to the equatio above The reaso
REVISION SHEET FP1 (MEI) ALGEBRA. Identities In mathematics, an identity is a statement which is true for all values of the variables it contains.
 The mai ideas are: Idetities REVISION SHEET FP (MEI) ALGEBRA Before the exam you should kow: If a expressio is a idetity the it is true for all values of the variable it cotais The relatioships betwee
The mai ideas are: Idetities REVISION SHEET FP (MEI) ALGEBRA Before the exam you should kow: If a expressio is a idetity the it is true for all values of the variable it cotais The relatioships betwee
G r a d e 1 1 P r e - C a l c u l u s M a t h e m a t i c s ( 3 0 S )
 G r a d e 1 1 P r e - C a l c u l u s M a t h e m a t i c s ( 3 0 S ) Grade 11 Pre-Calculus Mathematics (30S) is desiged for studets who ited to study calculus ad related mathematics as part of post-secodary
G r a d e 1 1 P r e - C a l c u l u s M a t h e m a t i c s ( 3 0 S ) Grade 11 Pre-Calculus Mathematics (30S) is desiged for studets who ited to study calculus ad related mathematics as part of post-secodary
Some examples of vector spaces
 Roberto s Notes o Liear Algebra Chapter 11: Vector spaces Sectio 2 Some examples of vector spaces What you eed to kow already: The te axioms eeded to idetify a vector space. What you ca lear here: Some
Roberto s Notes o Liear Algebra Chapter 11: Vector spaces Sectio 2 Some examples of vector spaces What you eed to kow already: The te axioms eeded to idetify a vector space. What you ca lear here: Some
AP Calculus Chapter 9: Infinite Series
 AP Calculus Chapter 9: Ifiite Series 9. Sequeces a, a 2, a 3, a 4, a 5,... Sequece: A fuctio whose domai is the set of positive itegers = 2 3 4 a = a a 2 a 3 a 4 terms of the sequece Begi with the patter
AP Calculus Chapter 9: Ifiite Series 9. Sequeces a, a 2, a 3, a 4, a 5,... Sequece: A fuctio whose domai is the set of positive itegers = 2 3 4 a = a a 2 a 3 a 4 terms of the sequece Begi with the patter
n m CHAPTER 3 RATIONAL EXPONENTS AND RADICAL FUNCTIONS 3-1 Evaluate n th Roots and Use Rational Exponents Real nth Roots of a n th Root of a
 CHAPTER RATIONAL EXPONENTS AND RADICAL FUNCTIONS Big IDEAS: 1) Usig ratioal expoets ) Performig fuctio operatios ad fidig iverse fuctios ) Graphig radical fuctios ad solvig radical equatios Sectio: Essetial
CHAPTER RATIONAL EXPONENTS AND RADICAL FUNCTIONS Big IDEAS: 1) Usig ratioal expoets ) Performig fuctio operatios ad fidig iverse fuctios ) Graphig radical fuctios ad solvig radical equatios Sectio: Essetial
II. Descriptive Statistics D. Linear Correlation and Regression. 1. Linear Correlation
 II. Descriptive Statistics D. Liear Correlatio ad Regressio I this sectio Liear Correlatio Cause ad Effect Liear Regressio 1. Liear Correlatio Quatifyig Liear Correlatio The Pearso product-momet correlatio
II. Descriptive Statistics D. Liear Correlatio ad Regressio I this sectio Liear Correlatio Cause ad Effect Liear Regressio 1. Liear Correlatio Quatifyig Liear Correlatio The Pearso product-momet correlatio
REVISION SHEET FP1 (MEI) ALGEBRA. Identities In mathematics, an identity is a statement which is true for all values of the variables it contains.
 the Further Mathematics etwork wwwfmetworkorguk V 07 The mai ideas are: Idetities REVISION SHEET FP (MEI) ALGEBRA Before the exam you should kow: If a expressio is a idetity the it is true for all values
the Further Mathematics etwork wwwfmetworkorguk V 07 The mai ideas are: Idetities REVISION SHEET FP (MEI) ALGEBRA Before the exam you should kow: If a expressio is a idetity the it is true for all values
A.1 Algebra Review: Polynomials/Rationals. Definitions:
 MATH 040 Notes: Uit 0 Page 1 A.1 Algera Review: Polyomials/Ratioals Defiitios: A polyomial is a sum of polyomial terms. Polyomial terms are epressios formed y products of costats ad variales with whole
MATH 040 Notes: Uit 0 Page 1 A.1 Algera Review: Polyomials/Ratioals Defiitios: A polyomial is a sum of polyomial terms. Polyomial terms are epressios formed y products of costats ad variales with whole
We will conclude the chapter with the study a few methods and techniques which are useful
 Chapter : Coordiate geometry: I this chapter we will lear about the mai priciples of graphig i a dimesioal (D) Cartesia system of coordiates. We will focus o drawig lies ad the characteristics of the graphs
Chapter : Coordiate geometry: I this chapter we will lear about the mai priciples of graphig i a dimesioal (D) Cartesia system of coordiates. We will focus o drawig lies ad the characteristics of the graphs
Taylor Series (BC Only)
 Studet Study Sessio Taylor Series (BC Oly) Taylor series provide a way to fid a polyomial look-alike to a o-polyomial fuctio. This is doe by a specific formula show below (which should be memorized): Taylor
Studet Study Sessio Taylor Series (BC Oly) Taylor series provide a way to fid a polyomial look-alike to a o-polyomial fuctio. This is doe by a specific formula show below (which should be memorized): Taylor
MA Lesson 26 Notes Graphs of Rational Functions (Asymptotes) Limits at infinity
 MA 1910 Lesso 6 Notes Graphs of Ratioal Fuctios (Asymptotes) Limits at ifiity Defiitio of a Ratioal Fuctio: If P() ad Q() are both polyomial fuctios, Q() 0, the the fuctio f below is called a Ratioal Fuctio.
MA 1910 Lesso 6 Notes Graphs of Ratioal Fuctios (Asymptotes) Limits at ifiity Defiitio of a Ratioal Fuctio: If P() ad Q() are both polyomial fuctios, Q() 0, the the fuctio f below is called a Ratioal Fuctio.
Apply change-of-basis formula to rewrite x as a linear combination of eigenvectors v j.
 Eigevalue-Eigevector Istructor: Nam Su Wag eigemcd Ay vector i real Euclidea space of dimesio ca be uiquely epressed as a liear combiatio of liearly idepedet vectors (ie, basis) g j, j,,, α g α g α g α
Eigevalue-Eigevector Istructor: Nam Su Wag eigemcd Ay vector i real Euclidea space of dimesio ca be uiquely epressed as a liear combiatio of liearly idepedet vectors (ie, basis) g j, j,,, α g α g α g α
Chapter 10: Power Series
 Chapter : Power Series 57 Chapter Overview: Power Series The reaso series are part of a Calculus course is that there are fuctios which caot be itegrated. All power series, though, ca be itegrated because
Chapter : Power Series 57 Chapter Overview: Power Series The reaso series are part of a Calculus course is that there are fuctios which caot be itegrated. All power series, though, ca be itegrated because
Math 312 Lecture Notes One Dimensional Maps
 Math 312 Lecture Notes Oe Dimesioal Maps Warre Weckesser Departmet of Mathematics Colgate Uiversity 21-23 February 25 A Example We begi with the simplest model of populatio growth. Suppose, for example,
Math 312 Lecture Notes Oe Dimesioal Maps Warre Weckesser Departmet of Mathematics Colgate Uiversity 21-23 February 25 A Example We begi with the simplest model of populatio growth. Suppose, for example,
Algebra II Notes Unit Seven: Powers, Roots, and Radicals
 Syllabus Objectives: 7. The studets will use properties of ratioal epoets to simplify ad evaluate epressios. 7.8 The studet will solve equatios cotaiig radicals or ratioal epoets. b a, the b is the radical.
Syllabus Objectives: 7. The studets will use properties of ratioal epoets to simplify ad evaluate epressios. 7.8 The studet will solve equatios cotaiig radicals or ratioal epoets. b a, the b is the radical.
The type of limit that is used to find TANGENTS and VELOCITIES gives rise to the central idea in DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS, the DERIVATIVE.
 NOTES : LIMITS AND DERIVATIVES Name: Date: Period: Iitial: LESSON.1 THE TANGENT AND VELOCITY PROBLEMS Pre-Calculus Mathematics Limit Process Calculus The type of it that is used to fid TANGENTS ad VELOCITIES
NOTES : LIMITS AND DERIVATIVES Name: Date: Period: Iitial: LESSON.1 THE TANGENT AND VELOCITY PROBLEMS Pre-Calculus Mathematics Limit Process Calculus The type of it that is used to fid TANGENTS ad VELOCITIES
Polynomial and Rational Functions. Polynomial functions and Their Graphs. Polynomial functions and Their Graphs. Examples
 Polomial ad Ratioal Fuctios Polomial fuctios ad Their Graphs Math 44 Precalculus Polomial ad Ratioal Fuctios Polomial Fuctios ad Their Graphs Polomial fuctios ad Their Graphs A Polomial of degree is a
Polomial ad Ratioal Fuctios Polomial fuctios ad Their Graphs Math 44 Precalculus Polomial ad Ratioal Fuctios Polomial Fuctios ad Their Graphs Polomial fuctios ad Their Graphs A Polomial of degree is a
Problem Cosider the curve give parametrically as x = si t ad y = + cos t for» t» ß: (a) Describe the path this traverses: Where does it start (whe t =
 Mathematics Summer Wilso Fial Exam August 8, ANSWERS Problem 1 (a) Fid the solutio to y +x y = e x x that satisfies y() = 5 : This is already i the form we used for a first order liear differetial equatio,
Mathematics Summer Wilso Fial Exam August 8, ANSWERS Problem 1 (a) Fid the solutio to y +x y = e x x that satisfies y() = 5 : This is already i the form we used for a first order liear differetial equatio,
Maximum and Minimum Values
 Sec 4.1 Maimum ad Miimum Values A. Absolute Maimum or Miimum / Etreme Values A fuctio Similarly, f has a Absolute Maimum at c if c f f has a Absolute Miimum at c if c f f for every poit i the domai. f
Sec 4.1 Maimum ad Miimum Values A. Absolute Maimum or Miimum / Etreme Values A fuctio Similarly, f has a Absolute Maimum at c if c f f has a Absolute Miimum at c if c f f for every poit i the domai. f
RADICAL EXPRESSION. If a and x are real numbers and n is a positive integer, then x is an. n th root theorems: Example 1 Simplify
 Example 1 Simplify 1.2A Radical Operatios a) 4 2 b) 16 1 2 c) 16 d) 2 e) 8 1 f) 8 What is the relatioship betwee a, b, c? What is the relatioship betwee d, e, f? If x = a, the x = = th root theorems: RADICAL
Example 1 Simplify 1.2A Radical Operatios a) 4 2 b) 16 1 2 c) 16 d) 2 e) 8 1 f) 8 What is the relatioship betwee a, b, c? What is the relatioship betwee d, e, f? If x = a, the x = = th root theorems: RADICAL
Lecture 6 Chi Square Distribution (χ 2 ) and Least Squares Fitting
 Lecture 6 Chi Square Distributio (χ ) ad Least Squares Fittig Chi Square Distributio (χ ) Suppose: We have a set of measuremets {x 1, x, x }. We kow the true value of each x i (x t1, x t, x t ). We would
Lecture 6 Chi Square Distributio (χ ) ad Least Squares Fittig Chi Square Distributio (χ ) Suppose: We have a set of measuremets {x 1, x, x }. We kow the true value of each x i (x t1, x t, x t ). We would
The Growth of Functions. Theoretical Supplement
 The Growth of Fuctios Theoretical Supplemet The Triagle Iequality The triagle iequality is a algebraic tool that is ofte useful i maipulatig absolute values of fuctios. The triagle iequality says that
The Growth of Fuctios Theoretical Supplemet The Triagle Iequality The triagle iequality is a algebraic tool that is ofte useful i maipulatig absolute values of fuctios. The triagle iequality says that
is also known as the general term of the sequence
 Lesso : Sequeces ad Series Outlie Objectives: I ca determie whether a sequece has a patter. I ca determie whether a sequece ca be geeralized to fid a formula for the geeral term i the sequece. I ca determie
Lesso : Sequeces ad Series Outlie Objectives: I ca determie whether a sequece has a patter. I ca determie whether a sequece ca be geeralized to fid a formula for the geeral term i the sequece. I ca determie
We are mainly going to be concerned with power series in x, such as. (x)} converges - that is, lims N n
 Review of Power Series, Power Series Solutios A power series i x - a is a ifiite series of the form c (x a) =c +c (x a)+(x a) +... We also call this a power series cetered at a. Ex. (x+) is cetered at
Review of Power Series, Power Series Solutios A power series i x - a is a ifiite series of the form c (x a) =c +c (x a)+(x a) +... We also call this a power series cetered at a. Ex. (x+) is cetered at
Lecture 6 Chi Square Distribution (χ 2 ) and Least Squares Fitting
 Lecture 6 Chi Square Distributio (χ ) ad Least Squares Fittig Chi Square Distributio (χ ) Suppose: We have a set of measuremets {x 1, x, x }. We kow the true value of each x i (x t1, x t, x t ). We would
Lecture 6 Chi Square Distributio (χ ) ad Least Squares Fittig Chi Square Distributio (χ ) Suppose: We have a set of measuremets {x 1, x, x }. We kow the true value of each x i (x t1, x t, x t ). We would
CHAPTER I: Vector Spaces
 CHAPTER I: Vector Spaces Sectio 1: Itroductio ad Examples This first chapter is largely a review of topics you probably saw i your liear algebra course. So why cover it? (1) Not everyoe remembers everythig
CHAPTER I: Vector Spaces Sectio 1: Itroductio ad Examples This first chapter is largely a review of topics you probably saw i your liear algebra course. So why cover it? (1) Not everyoe remembers everythig
Topic 9: Sampling Distributions of Estimators
 Topic 9: Samplig Distributios of Estimators Course 003, 2016 Page 0 Samplig distributios of estimators Sice our estimators are statistics (particular fuctios of radom variables), their distributio ca be
Topic 9: Samplig Distributios of Estimators Course 003, 2016 Page 0 Samplig distributios of estimators Sice our estimators are statistics (particular fuctios of radom variables), their distributio ca be
SNAP Centre Workshop. Basic Algebraic Manipulation
 SNAP Cetre Workshop Basic Algebraic Maipulatio 8 Simplifyig Algebraic Expressios Whe a expressio is writte i the most compact maer possible, it is cosidered to be simplified. Not Simplified: x(x + 4x)
SNAP Cetre Workshop Basic Algebraic Maipulatio 8 Simplifyig Algebraic Expressios Whe a expressio is writte i the most compact maer possible, it is cosidered to be simplified. Not Simplified: x(x + 4x)
(A sequence also can be thought of as the list of function values attained for a function f :ℵ X, where f (n) = x n for n 1.) x 1 x N +k x N +4 x 3
 MATH 337 Sequeces Dr. Neal, WKU Let X be a metric space with distace fuctio d. We shall defie the geeral cocept of sequece ad limit i a metric space, the apply the results i particular to some special
MATH 337 Sequeces Dr. Neal, WKU Let X be a metric space with distace fuctio d. We shall defie the geeral cocept of sequece ad limit i a metric space, the apply the results i particular to some special
1 Generating functions for balls in boxes
 Math 566 Fall 05 Some otes o geeratig fuctios Give a sequece a 0, a, a,..., a,..., a geeratig fuctio some way of represetig the sequece as a fuctio. There are may ways to do this, with the most commo ways
Math 566 Fall 05 Some otes o geeratig fuctios Give a sequece a 0, a, a,..., a,..., a geeratig fuctio some way of represetig the sequece as a fuctio. There are may ways to do this, with the most commo ways
REAL ANALYSIS II: PROBLEM SET 1 - SOLUTIONS
 REAL ANALYSIS II: PROBLEM SET 1 - SOLUTIONS 18th Feb, 016 Defiitio (Lipschitz fuctio). A fuctio f : R R is said to be Lipschitz if there exists a positive real umber c such that for ay x, y i the domai
REAL ANALYSIS II: PROBLEM SET 1 - SOLUTIONS 18th Feb, 016 Defiitio (Lipschitz fuctio). A fuctio f : R R is said to be Lipschitz if there exists a positive real umber c such that for ay x, y i the domai
Northwest High School s Algebra 2/Honors Algebra 2 Summer Review Packet
 Northwest High School s Algebra /Hoors Algebra Summer Review Packet This packet is optioal! It will NOT be collected for a grade et school year! This packet has bee desiged to help you review various mathematical
Northwest High School s Algebra /Hoors Algebra Summer Review Packet This packet is optioal! It will NOT be collected for a grade et school year! This packet has bee desiged to help you review various mathematical
Statistics 511 Additional Materials
 Cofidece Itervals o mu Statistics 511 Additioal Materials This topic officially moves us from probability to statistics. We begi to discuss makig ifereces about the populatio. Oe way to differetiate probability
Cofidece Itervals o mu Statistics 511 Additioal Materials This topic officially moves us from probability to statistics. We begi to discuss makig ifereces about the populatio. Oe way to differetiate probability
Essential Question How can you recognize an arithmetic sequence from its graph?
 . Aalyzig Arithmetic Sequeces ad Series COMMON CORE Learig Stadards HSF-IF.A.3 HSF-BF.A. HSF-LE.A. Essetial Questio How ca you recogize a arithmetic sequece from its graph? I a arithmetic sequece, the
. Aalyzig Arithmetic Sequeces ad Series COMMON CORE Learig Stadards HSF-IF.A.3 HSF-BF.A. HSF-LE.A. Essetial Questio How ca you recogize a arithmetic sequece from its graph? I a arithmetic sequece, the
10.1 Sequences. n term. We will deal a. a n or a n n. ( 1) n ( 1) n 1 2 ( 1) a =, 0 0,,,,, ln n. n an 2. n term.
 0. Sequeces A sequece is a list of umbers writte i a defiite order: a, a,, a, a is called the first term, a is the secod term, ad i geeral eclusively with ifiite sequeces ad so each term Notatio: the sequece
0. Sequeces A sequece is a list of umbers writte i a defiite order: a, a,, a, a is called the first term, a is the secod term, ad i geeral eclusively with ifiite sequeces ad so each term Notatio: the sequece
In algebra one spends much time finding common denominators and thus simplifying rational expressions. For example:
 74 The Method of Partial Fractios I algebra oe speds much time fidig commo deomiators ad thus simplifyig ratioal epressios For eample: + + + 6 5 + = + = = + + + + + ( )( ) 5 It may the seem odd to be watig
74 The Method of Partial Fractios I algebra oe speds much time fidig commo deomiators ad thus simplifyig ratioal epressios For eample: + + + 6 5 + = + = = + + + + + ( )( ) 5 It may the seem odd to be watig
ECE-S352 Introduction to Digital Signal Processing Lecture 3A Direct Solution of Difference Equations
 ECE-S352 Itroductio to Digital Sigal Processig Lecture 3A Direct Solutio of Differece Equatios Discrete Time Systems Described by Differece Equatios Uit impulse (sample) respose h() of a DT system allows
ECE-S352 Itroductio to Digital Sigal Processig Lecture 3A Direct Solutio of Differece Equatios Discrete Time Systems Described by Differece Equatios Uit impulse (sample) respose h() of a DT system allows
Chapter 6 Infinite Series
 Chapter 6 Ifiite Series I the previous chapter we cosidered itegrals which were improper i the sese that the iterval of itegratio was ubouded. I this chapter we are goig to discuss a topic which is somewhat
Chapter 6 Ifiite Series I the previous chapter we cosidered itegrals which were improper i the sese that the iterval of itegratio was ubouded. I this chapter we are goig to discuss a topic which is somewhat
3. Z Transform. Recall that the Fourier transform (FT) of a DT signal xn [ ] is ( ) [ ] = In order for the FT to exist in the finite magnitude sense,
![3. Z Transform. Recall that the Fourier transform (FT) of a DT signal xn [ ] is ( ) [ ] = In order for the FT to exist in the finite magnitude sense, 3. Z Transform. Recall that the Fourier transform (FT) of a DT signal xn [ ] is ( ) [ ] = In order for the FT to exist in the finite magnitude sense,](/thumbs/82/85448051.jpg) 3. Z Trasform Referece: Etire Chapter 3 of text. Recall that the Fourier trasform (FT) of a DT sigal x [ ] is ω ( ) [ ] X e = j jω k = xe I order for the FT to exist i the fiite magitude sese, S = x [
3. Z Trasform Referece: Etire Chapter 3 of text. Recall that the Fourier trasform (FT) of a DT sigal x [ ] is ω ( ) [ ] X e = j jω k = xe I order for the FT to exist i the fiite magitude sese, S = x [
6 Integers Modulo n. integer k can be written as k = qn + r, with q,r, 0 r b. So any integer.
 6 Itegers Modulo I Example 2.3(e), we have defied the cogruece of two itegers a,b with respect to a modulus. Let us recall that a b (mod ) meas a b. We have proved that cogruece is a equivalece relatio
6 Itegers Modulo I Example 2.3(e), we have defied the cogruece of two itegers a,b with respect to a modulus. Let us recall that a b (mod ) meas a b. We have proved that cogruece is a equivalece relatio
x x x Using a second Taylor polynomial with remainder, find the best constant C so that for x 0,
 Math Activity 9( Due with Fial Eam) Usig first ad secod Taylor polyomials with remaider, show that for, 8 Usig a secod Taylor polyomial with remaider, fid the best costat C so that for, C 9 The th Derivative
Math Activity 9( Due with Fial Eam) Usig first ad secod Taylor polyomials with remaider, show that for, 8 Usig a secod Taylor polyomial with remaider, fid the best costat C so that for, C 9 The th Derivative
a is some real number (called the coefficient) other
 Precalculus Notes for Sectio.1 Liear/Quadratic Fuctios ad Modelig http://www.schooltube.com/video/77e0a939a3344194bb4f Defiitios: A moomial is a term of the form tha zero ad is a oegative iteger. a where
Precalculus Notes for Sectio.1 Liear/Quadratic Fuctios ad Modelig http://www.schooltube.com/video/77e0a939a3344194bb4f Defiitios: A moomial is a term of the form tha zero ad is a oegative iteger. a where
The z-transform. 7.1 Introduction. 7.2 The z-transform Derivation of the z-transform: x[n] = z n LTI system, h[n] z = re j
![The z-transform. 7.1 Introduction. 7.2 The z-transform Derivation of the z-transform: x[n] = z n LTI system, h[n] z = re j The z-transform. 7.1 Introduction. 7.2 The z-transform Derivation of the z-transform: x[n] = z n LTI system, h[n] z = re j](/thumbs/82/85448534.jpg) The -Trasform 7. Itroductio Geeralie the complex siusoidal represetatio offered by DTFT to a represetatio of complex expoetial sigals. Obtai more geeral characteristics for discrete-time LTI systems. 7.
The -Trasform 7. Itroductio Geeralie the complex siusoidal represetatio offered by DTFT to a represetatio of complex expoetial sigals. Obtai more geeral characteristics for discrete-time LTI systems. 7.
Most text will write ordinary derivatives using either Leibniz notation 2 3. y + 5y= e and y y. xx tt t
 Itroductio to Differetial Equatios Defiitios ad Termiolog Differetial Equatio: A equatio cotaiig the derivatives of oe or more depedet variables, with respect to oe or more idepedet variables, is said
Itroductio to Differetial Equatios Defiitios ad Termiolog Differetial Equatio: A equatio cotaiig the derivatives of oe or more depedet variables, with respect to oe or more idepedet variables, is said
Polynomials with Rational Roots that Differ by a Non-zero Constant. Generalities
 Polyomials with Ratioal Roots that Differ by a No-zero Costat Philip Gibbs The problem of fidig two polyomials P(x) ad Q(x) of a give degree i a sigle variable x that have all ratioal roots ad differ by
Polyomials with Ratioal Roots that Differ by a No-zero Costat Philip Gibbs The problem of fidig two polyomials P(x) ad Q(x) of a give degree i a sigle variable x that have all ratioal roots ad differ by
MATH 304: MIDTERM EXAM SOLUTIONS
 MATH 304: MIDTERM EXAM SOLUTIONS [The problems are each worth five poits, except for problem 8, which is worth 8 poits. Thus there are 43 possible poits.] 1. Use the Euclidea algorithm to fid the greatest
MATH 304: MIDTERM EXAM SOLUTIONS [The problems are each worth five poits, except for problem 8, which is worth 8 poits. Thus there are 43 possible poits.] 1. Use the Euclidea algorithm to fid the greatest
Linear Regression Analysis. Analysis of paired data and using a given value of one variable to predict the value of the other
 Liear Regressio Aalysis Aalysis of paired data ad usig a give value of oe variable to predict the value of the other 5 5 15 15 1 1 5 5 1 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 3 4 5 6 7 8 Liear Regressio Aalysis E: The chirp rate
Liear Regressio Aalysis Aalysis of paired data ad usig a give value of oe variable to predict the value of the other 5 5 15 15 1 1 5 5 1 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 3 4 5 6 7 8 Liear Regressio Aalysis E: The chirp rate
Section 11.6 Absolute and Conditional Convergence, Root and Ratio Tests
 Sectio.6 Absolute ad Coditioal Covergece, Root ad Ratio Tests I this chapter we have see several examples of covergece tests that oly apply to series whose terms are oegative. I this sectio, we will lear
Sectio.6 Absolute ad Coditioal Covergece, Root ad Ratio Tests I this chapter we have see several examples of covergece tests that oly apply to series whose terms are oegative. I this sectio, we will lear
Addition: Property Name Property Description Examples. a+b = b+a. a+(b+c) = (a+b)+c
 Notes for March 31 Fields: A field is a set of umbers with two (biary) operatios (usually called additio [+] ad multiplicatio [ ]) such that the followig properties hold: Additio: Name Descriptio Commutativity
Notes for March 31 Fields: A field is a set of umbers with two (biary) operatios (usually called additio [+] ad multiplicatio [ ]) such that the followig properties hold: Additio: Name Descriptio Commutativity
Math 128A: Homework 1 Solutions
 Math 8A: Homework Solutios Due: Jue. Determie the limits of the followig sequeces as. a) a = +. lim a + = lim =. b) a = + ). c) a = si4 +6) +. lim a = lim = lim + ) [ + ) ] = [ e ] = e 6. Observe that
Math 8A: Homework Solutios Due: Jue. Determie the limits of the followig sequeces as. a) a = +. lim a + = lim =. b) a = + ). c) a = si4 +6) +. lim a = lim = lim + ) [ + ) ] = [ e ] = e 6. Observe that
Section 5.5. Infinite Series: The Ratio Test
 Differece Equatios to Differetial Equatios Sectio 5.5 Ifiite Series: The Ratio Test I the last sectio we saw that we could demostrate the covergece of a series a, where a 0 for all, by showig that a approaches
Differece Equatios to Differetial Equatios Sectio 5.5 Ifiite Series: The Ratio Test I the last sectio we saw that we could demostrate the covergece of a series a, where a 0 for all, by showig that a approaches
IP Reference guide for integer programming formulations.
 IP Referece guide for iteger programmig formulatios. by James B. Orli for 15.053 ad 15.058 This documet is iteded as a compact (or relatively compact) guide to the formulatio of iteger programs. For more
IP Referece guide for iteger programmig formulatios. by James B. Orli for 15.053 ad 15.058 This documet is iteded as a compact (or relatively compact) guide to the formulatio of iteger programs. For more
Sequences and Series of Functions
 Chapter 6 Sequeces ad Series of Fuctios 6.1. Covergece of a Sequece of Fuctios Poitwise Covergece. Defiitio 6.1. Let, for each N, fuctio f : A R be defied. If, for each x A, the sequece (f (x)) coverges
Chapter 6 Sequeces ad Series of Fuctios 6.1. Covergece of a Sequece of Fuctios Poitwise Covergece. Defiitio 6.1. Let, for each N, fuctio f : A R be defied. If, for each x A, the sequece (f (x)) coverges
C. Complex Numbers. x 6x + 2 = 0. This equation was known to have three real roots, given by simple combinations of the expressions
 C. Complex Numbers. Complex arithmetic. Most people thik that complex umbers arose from attempts to solve quadratic equatios, but actually it was i coectio with cubic equatios they first appeared. Everyoe
C. Complex Numbers. Complex arithmetic. Most people thik that complex umbers arose from attempts to solve quadratic equatios, but actually it was i coectio with cubic equatios they first appeared. Everyoe
a 3, a 4, ... are the terms of the sequence. The number a n is the nth term of the sequence, and the entire sequence is denoted by a n
 60_090.qxd //0 : PM Page 59 59 CHAPTER 9 Ifiite Series Sectio 9. EXPLORATION Fidig Patters Describe a patter for each of the followig sequeces. The use your descriptio to write a formula for the th term
60_090.qxd //0 : PM Page 59 59 CHAPTER 9 Ifiite Series Sectio 9. EXPLORATION Fidig Patters Describe a patter for each of the followig sequeces. The use your descriptio to write a formula for the th term
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Solids of Rotation:
 Slide 1 Solids of Rotatio: The Eggplat Experiece Suz Atik Palo Alto High School Palo Alto, Ca EdD; NBCT, AYA Math satik@pausd.org May thaks to my colleague, Kathy Weiss, NBCT, AYA Math, who origially desiged
Slide 1 Solids of Rotatio: The Eggplat Experiece Suz Atik Palo Alto High School Palo Alto, Ca EdD; NBCT, AYA Math satik@pausd.org May thaks to my colleague, Kathy Weiss, NBCT, AYA Math, who origially desiged
(3) If you replace row i of A by its sum with a multiple of another row, then the determinant is unchanged! Expand across the i th row:
 Math 5-4 Tue Feb 4 Cotiue with sectio 36 Determiats The effective way to compute determiats for larger-sized matrices without lots of zeroes is to ot use the defiitio, but rather to use the followig facts,
Math 5-4 Tue Feb 4 Cotiue with sectio 36 Determiats The effective way to compute determiats for larger-sized matrices without lots of zeroes is to ot use the defiitio, but rather to use the followig facts,
(Figure 2.9), we observe x. and we write. (b) as x, x 1. and we write. We say that the line y 0 is a horizontal asymptote of the graph of f.
 The symbol for ifiity ( ) does ot represet a real umber. We use to describe the behavior of a fuctio whe the values i its domai or rage outgrow all fiite bouds. For eample, whe we say the limit of f as
The symbol for ifiity ( ) does ot represet a real umber. We use to describe the behavior of a fuctio whe the values i its domai or rage outgrow all fiite bouds. For eample, whe we say the limit of f as
Math 113 Exam 3 Practice
 Math Exam Practice Exam 4 will cover.-., 0. ad 0.. Note that eve though. was tested i exam, questios from that sectios may also be o this exam. For practice problems o., refer to the last review. This
Math Exam Practice Exam 4 will cover.-., 0. ad 0.. Note that eve though. was tested i exam, questios from that sectios may also be o this exam. For practice problems o., refer to the last review. This
Topic 9: Sampling Distributions of Estimators
 Topic 9: Samplig Distributios of Estimators Course 003, 2018 Page 0 Samplig distributios of estimators Sice our estimators are statistics (particular fuctios of radom variables), their distributio ca be
Topic 9: Samplig Distributios of Estimators Course 003, 2018 Page 0 Samplig distributios of estimators Sice our estimators are statistics (particular fuctios of radom variables), their distributio ca be
Section 13.3 Area and the Definite Integral
 Sectio 3.3 Area ad the Defiite Itegral We ca easily fid areas of certai geometric figures usig well-kow formulas: However, it is t easy to fid the area of a regio with curved sides: METHOD: To evaluate
Sectio 3.3 Area ad the Defiite Itegral We ca easily fid areas of certai geometric figures usig well-kow formulas: However, it is t easy to fid the area of a regio with curved sides: METHOD: To evaluate
Chapter 9 - CD companion 1. A Generic Implementation; The Common-Merge Amplifier. 1 τ is. ω ch. τ io
 Chapter 9 - CD compaio CHAPTER NINE CD-9.2 CD-9.2. Stages With Voltage ad Curret Gai A Geeric Implemetatio; The Commo-Merge Amplifier The advaced method preseted i the text for approximatig cutoff frequecies
Chapter 9 - CD compaio CHAPTER NINE CD-9.2 CD-9.2. Stages With Voltage ad Curret Gai A Geeric Implemetatio; The Commo-Merge Amplifier The advaced method preseted i the text for approximatig cutoff frequecies
Practice Problems: Taylor and Maclaurin Series
 Practice Problems: Taylor ad Maclauri Series Aswers. a) Start by takig derivatives util a patter develops that lets you to write a geeral formula for the -th derivative. Do t simplify as you go, because
Practice Problems: Taylor ad Maclauri Series Aswers. a) Start by takig derivatives util a patter develops that lets you to write a geeral formula for the -th derivative. Do t simplify as you go, because
Topic 9: Sampling Distributions of Estimators
 Topic 9: Samplig Distributios of Estimators Course 003, 2018 Page 0 Samplig distributios of estimators Sice our estimators are statistics (particular fuctios of radom variables), their distributio ca be
Topic 9: Samplig Distributios of Estimators Course 003, 2018 Page 0 Samplig distributios of estimators Sice our estimators are statistics (particular fuctios of radom variables), their distributio ca be
Areas and Distances. We can easily find areas of certain geometric figures using well-known formulas:
 Areas ad Distaces We ca easily fid areas of certai geometric figures usig well-kow formulas: However, it is t easy to fid the area of a regio with curved sides: METHOD: To evaluate the area of the regio
Areas ad Distaces We ca easily fid areas of certai geometric figures usig well-kow formulas: However, it is t easy to fid the area of a regio with curved sides: METHOD: To evaluate the area of the regio
SECTION 1.5 : SUMMATION NOTATION + WORK WITH SEQUENCES
 SECTION 1.5 : SUMMATION NOTATION + WORK WITH SEQUENCES Read Sectio 1.5 (pages 5 9) Overview I Sectio 1.5 we lear to work with summatio otatio ad formulas. We will also itroduce a brief overview of sequeces,
SECTION 1.5 : SUMMATION NOTATION + WORK WITH SEQUENCES Read Sectio 1.5 (pages 5 9) Overview I Sectio 1.5 we lear to work with summatio otatio ad formulas. We will also itroduce a brief overview of sequeces,
1 Approximating Integrals using Taylor Polynomials
 Seughee Ye Ma 8: Week 7 Nov Week 7 Summary This week, we will lear how we ca approximate itegrals usig Taylor series ad umerical methods. Topics Page Approximatig Itegrals usig Taylor Polyomials. Defiitios................................................
Seughee Ye Ma 8: Week 7 Nov Week 7 Summary This week, we will lear how we ca approximate itegrals usig Taylor series ad umerical methods. Topics Page Approximatig Itegrals usig Taylor Polyomials. Defiitios................................................
Introduction to Signals and Systems, Part V: Lecture Summary
 EEL33: Discrete-Time Sigals ad Systems Itroductio to Sigals ad Systems, Part V: Lecture Summary Itroductio to Sigals ad Systems, Part V: Lecture Summary So far we have oly looked at examples of o-recursive
EEL33: Discrete-Time Sigals ad Systems Itroductio to Sigals ad Systems, Part V: Lecture Summary Itroductio to Sigals ad Systems, Part V: Lecture Summary So far we have oly looked at examples of o-recursive
4.1 Sigma Notation and Riemann Sums
 0 the itegral. Sigma Notatio ad Riema Sums Oe strategy for calculatig the area of a regio is to cut the regio ito simple shapes, calculate the area of each simple shape, ad the add these smaller areas
0 the itegral. Sigma Notatio ad Riema Sums Oe strategy for calculatig the area of a regio is to cut the regio ito simple shapes, calculate the area of each simple shape, ad the add these smaller areas
Math 120 Answers for Homework 23
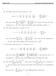 Math 0 Aswers for Homewor. (a) The Taylor series for cos(x) aroud a 0 is cos(x) x! + x4 4! x6 6! + x8 8! x0 0! + ( ) ()! x ( ) π ( ) ad so the series ()! ()! (π) is just the series for cos(x) evaluated
Math 0 Aswers for Homewor. (a) The Taylor series for cos(x) aroud a 0 is cos(x) x! + x4 4! x6 6! + x8 8! x0 0! + ( ) ()! x ( ) π ( ) ad so the series ()! ()! (π) is just the series for cos(x) evaluated
Definitions and Theorems. where x are the decision variables. c, b, and a are constant coefficients.
 Defiitios ad Theorems Remember the scalar form of the liear programmig problem, Miimize, Subject to, f(x) = c i x i a 1i x i = b 1 a mi x i = b m x i 0 i = 1,2,, where x are the decisio variables. c, b,
Defiitios ad Theorems Remember the scalar form of the liear programmig problem, Miimize, Subject to, f(x) = c i x i a 1i x i = b 1 a mi x i = b m x i 0 i = 1,2,, where x are the decisio variables. c, b,
Math 113, Calculus II Winter 2007 Final Exam Solutions
 Math, Calculus II Witer 7 Fial Exam Solutios (5 poits) Use the limit defiitio of the defiite itegral ad the sum formulas to compute x x + dx The check your aswer usig the Evaluatio Theorem Solutio: I this
Math, Calculus II Witer 7 Fial Exam Solutios (5 poits) Use the limit defiitio of the defiite itegral ad the sum formulas to compute x x + dx The check your aswer usig the Evaluatio Theorem Solutio: I this
Math 2784 (or 2794W) University of Connecticut
 ORDERS OF GROWTH PAT SMITH Math 2784 (or 2794W) Uiversity of Coecticut Date: Mar. 2, 22. ORDERS OF GROWTH. Itroductio Gaiig a ituitive feel for the relative growth of fuctios is importat if you really
ORDERS OF GROWTH PAT SMITH Math 2784 (or 2794W) Uiversity of Coecticut Date: Mar. 2, 22. ORDERS OF GROWTH. Itroductio Gaiig a ituitive feel for the relative growth of fuctios is importat if you really
AP Calculus BC Review Applications of Derivatives (Chapter 4) and f,
 AP alculus B Review Applicatios of Derivatives (hapter ) Thigs to Kow ad Be Able to Do Defiitios of the followig i terms of derivatives, ad how to fid them: critical poit, global miima/maima, local (relative)
AP alculus B Review Applicatios of Derivatives (hapter ) Thigs to Kow ad Be Able to Do Defiitios of the followig i terms of derivatives, ad how to fid them: critical poit, global miima/maima, local (relative)
Math 61CM - Solutions to homework 3
 Math 6CM - Solutios to homework 3 Cédric De Groote October 2 th, 208 Problem : Let F be a field, m 0 a fixed oegative iteger ad let V = {a 0 + a x + + a m x m a 0,, a m F} be the vector space cosistig
Math 6CM - Solutios to homework 3 Cédric De Groote October 2 th, 208 Problem : Let F be a field, m 0 a fixed oegative iteger ad let V = {a 0 + a x + + a m x m a 0,, a m F} be the vector space cosistig
