ENGI 5708 Design of Civil Engineering Systems
|
|
|
- Lizbeth Chase
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ENGI 5708 Design of Civil Engineering Systems Lecture 10: Sensitivity Analysis Shawn Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. Assistant Professor Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Memorial University of Newfoundland
2 Lecture 10 Objective to understand parameters influencing sensitivity of LP problems S. Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. ENGI 5708 Civil Engineering Systems Lecture 10
3 Motivation for Sensitivity Analysis Model Idealization Abstraction of reality, linearization Relationship between variables, constraints, coefficients Scope extent, system hierarchy Quantifiable fact or importance Subjectivity Uncertainty Natural variability or volatility Regulations, economics, resources Mechanisms Poor or incomplete understanding of processes Data Bias, error or sample size S. Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. ENGI 5708 Civil Engineering Systems Lecture 10
4 What is Sensitivity Analysis? Tool for Decision Making Heuristic analysis Trial and error What if scenario analysis Assess importance of possible events (i.e. change in parameter value) and probable outcomes from these changes or variability S. Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. ENGI 5708 Civil Engineering Systems Lecture 10
5 Why Conduct Sensitivity Analysis? Rank Assessment Screening tool Identify key elements and parameters Increase or decrease model complexity Focus effort and resources Model advancement or refinement Test optimal solution robustness Identify critical parameters Establish thresholds (upper/lower bounds) Contingency planning Impact to optimal solution or decision making? Set conditions for changes in strategy S. Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. ENGI 5708 Civil Engineering Systems Lecture 10
6 Sensitivity Analysis Constraint Equation Coefficient (a mn ) Right-Hand Side Constraints (C m ) Objective Function Coefficient (k n ) Add New Decision Variables Add Constraint Equations Objective Function or Merit Function (Non-$) N ( ) Z = f x = k x N n n n n= 1 n= 1 min or max Constraint Equations M M N ( ) g x = a x, =, C m n mn n m m= 1 m= 1n= S. Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. ENGI 5708 Civil Engineering Systems Lecture 10
7 Constraint Equation Coefficient Possible Variation Volume, production rate or yield of a process or resource Example 6-01 Clay volume, blending time or storage capacity per unit volume of product Impact Constraint equation slope region Basic feasible solutions F A E D C B Example S. Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. ENGI 5708 Civil Engineering Systems Lecture 10
8 Constraint Equation Coefficient (cont.) Example 6-01 Double HYDIT blending time 5 x + 5 x x + 5 x Example S. Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. ENGI 5708 Civil Engineering Systems Lecture 10
9 Constraint Equation Coefficient (cont.) Example 6-01 Double FILIT blending time 5x + 5x 50 5x + 10x Example S. Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. ENGI 5708 Civil Engineering Systems Lecture 10
10 Right-Hand Side Constraint Possible Variation Maximum capacity, resource availability, usage or time Example 6-01 Total clay volume, blending time or storage capacity Impact Constraint equation shift region Basic feasible solutions F A E D C B Example S. Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. ENGI 5708 Civil Engineering Systems Lecture 10
11 Right-Hand Side Constraint (cont.) Example 6-01 Increase total available blending time to 70 hrs 5 x + 5 x 50 5x + 5 x Example S. Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. ENGI 5708 Civil Engineering Systems Lecture 10
12 Right-Hand Side Constraint (cont.) Example 6-01 Decrease total available blending time to 30 hrs 5 x + 5 x 50 5x + 5 x Example S. Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. ENGI 5708 Civil Engineering Systems Lecture 10
13 Right-Hand Side Constraint (cont.) Binding Constraints If binding then RHS limits value of obj. function 2x1+ 4x2 28 5x1+ 5x2 50 x1 8 x2 6 x, x F A E D Example 6-01 Unique Optimal Solution x 1 = 6; x 2 = 4 C B Z = 140x + 160x S. Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. ENGI 5708 Civil Engineering Systems Lecture 10
14 Right-Hand Side Constraint (cont.) Binding Constraints Reduced cost coefficients Clay Volume { } B s, x, x, s s s s = Example 6-01 D = x = 4 s + s = = x s s s s s Z = s 24s Blending Time 1 2 Unique Optimal Solution x 1 = 6; x 2 = S. Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. ENGI 5708 Civil Engineering Systems Lecture 10 F A E D C B
15 Right-Hand Side Constraint (cont.) Non-Binding Constraints Look at basic variables { } B s, x, x, s s s s D = x = 4 s + s = = x s s s s s Z = s 24s HYDIT Storage = Example 6-01 FILIT Storage 1 2 Unique Optimal Solution x 1 = 6; x 2 = S. Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. ENGI 5708 Civil Engineering Systems Lecture 10 F A E D Increasing storage capacity has no effect on strategy C B
16 Right-Hand Side Constraint (cont.) Shadow Prices or Dual Resource Prices Reduced cost coefficients Tolerable range on variability? ll constraint line thru adjacent vertex Clay Volume Z = s 24s Blending Time S. Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. ENGI 5708 Civil Engineering Systems Lecture 10 F A E G D Example 6-01 Unique Optimal Solution x 1 = 6; x 2 = 4 C B H
17 Right-Hand Side Constraint (cont.) Shadow Prices or Dual Resource Prices 2x1+ 4x2 28 5x + 5x Clay Volume Blending Time x1 8 x 2 6 HYDIT Storage FILIT Storage Resource Wabash Red Clay Blending Time HYDIT Curing Vat Capacity FILIT Curing Vat Capacity Current RHS Optimal Usage Lower Range 24 m 3 28 m 3 28 m 3 (C 8,2) 50 hr 50 hr 40 hr (E 2,6) 6 m 3 8 m 3 6 m 3 (D 6,4) 4 m 3 6 m 3 4 m 3 (D 6,4) Allowable Decrease Upper Range 4 m 3 32 m 3 (G 4,6) 10 hr 55 hr (H 8,3) Allowable Increase Shadow Price 4 m 3 $10 5 hr $24 2 m 3 Unlimited $0 2 m 3 Unlimited $ S. Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. ENGI 5708 Civil Engineering Systems Lecture 10
18 Right-Hand Side Constraint (cont.) Shadow Prices or Dual Resource Shadow price implications If unit price of clay $10/t then purchase If supplier failed to deliver clay then for this range the compensation price is $10/t Vat capacity provides no improved profits Resource Wabash Red Clay Blending Time HYDIT Curing Vat Capacity FILIT Curing Vat Capacity Optimal Usage Allowable Decrease Allowable Increase Shadow Price 28 m 3 4 m 3 4 m 3 $10 50 hr 10 hr 5 hr $24 6 m 3 2 m 3 Unlimited $0 4 m 3 2 m 3 Unlimited $ S. Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. ENGI 5708 Civil Engineering Systems Lecture 10
19 Objective Function Possible Variation Unit cost or profit Unit gain or loss Impact Objective function slope Optimal solution 2 1 Increasing HYDIT Profit Increasing FILIT Profit S. Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. ENGI 5708 Civil Engineering Systems Lecture 10
20 Reading List Pike, R.W. (2001). Optimization for Engineering Systems. Arsham (2007). Linear Programming. Arsham (2007). Linear Programming S. Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. ENGI 5708 Civil Engineering Systems Lecture 10
21 References ReVelle, C.S., E.E. Whitlatch, Jr. and J.R. Wright (2004). Civil and Environmental Systems Engineering 2 nd Edition, Pearson Prentice Hall ISBN S. Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. ENGI 5708 Civil Engineering Systems Lecture 10
ENGI 5708 Design of Civil Engineering Systems
 ENGI 5708 Design of Civil Engineering Systems Lecture 04: Graphical Solution Methods Part 1 Shawn Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. Assistant Professor Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Memorial University
ENGI 5708 Design of Civil Engineering Systems Lecture 04: Graphical Solution Methods Part 1 Shawn Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. Assistant Professor Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Memorial University
ENGI 5708 Design of Civil Engineering Systems
 ENGI 5708 Design of Civil Engineering Systems Lecture 09: Characteristics of Simplex Algorithm Solutions Shawn Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. Assistant Professor Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Memorial
ENGI 5708 Design of Civil Engineering Systems Lecture 09: Characteristics of Simplex Algorithm Solutions Shawn Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. Assistant Professor Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Memorial
ENGI 1313 Mechanics I
 ENGI 1313 Mechanics I Lecture 25: Equilibrium of a Rigid Body Shawn Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. Assistant Professor Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Memorial University of Newfoundland spkenny@engr.mun.ca
ENGI 1313 Mechanics I Lecture 25: Equilibrium of a Rigid Body Shawn Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. Assistant Professor Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Memorial University of Newfoundland spkenny@engr.mun.ca
Introduction to sensitivity analysis
 Introduction to sensitivity analysis BSAD 0 Dave Novak Summer 0 Overview Introduction to sensitivity analysis Range of optimality Range of feasibility Source: Anderson et al., 0 Quantitative Methods for
Introduction to sensitivity analysis BSAD 0 Dave Novak Summer 0 Overview Introduction to sensitivity analysis Range of optimality Range of feasibility Source: Anderson et al., 0 Quantitative Methods for
ENGI 1313 Mechanics I
 ENGI 1313 Mechanics I Lecture 01: Course Introduction and General Principles Shawn Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. Assistant Professor Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Memorial University of Newfoundland
ENGI 1313 Mechanics I Lecture 01: Course Introduction and General Principles Shawn Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. Assistant Professor Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Memorial University of Newfoundland
ENGI 1313 Mechanics I
 ENGI 1313 Mechanics I Lecture 43: Course Material Review Shawn Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. ssistant Professor aculty of Engineering and pplied Science Memorial University of Newfoundland spkenny@engr.mun.ca inal
ENGI 1313 Mechanics I Lecture 43: Course Material Review Shawn Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. ssistant Professor aculty of Engineering and pplied Science Memorial University of Newfoundland spkenny@engr.mun.ca inal
Introduction to LP. Types of Linear Programming. There are five common types of decisions in which LP may play a role
 Linear Programming RK Jana Lecture Outline Introduction to Linear Programming (LP) Historical Perspective Model Formulation Graphical Solution Method Simplex Method Introduction to LP Continued Today many
Linear Programming RK Jana Lecture Outline Introduction to Linear Programming (LP) Historical Perspective Model Formulation Graphical Solution Method Simplex Method Introduction to LP Continued Today many
Linear programming Dr. Arturo S. Leon, BSU (Spring 2010)
 Linear programming (Adapted from Chapter 13 Supplement, Operations and Management, 5 th edition by Roberta Russell & Bernard W. Taylor, III., Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. This presentation also
Linear programming (Adapted from Chapter 13 Supplement, Operations and Management, 5 th edition by Roberta Russell & Bernard W. Taylor, III., Copyright 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. This presentation also
9/23/ S. Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. Lecture Goals. Reading List. Students will be able to: Lecture 09 Soil Retaining Structures
 Lecture 09 Soil Retaining Structures Shawn Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. Assistant Professor Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Memorial University of Newfoundland spkenny@mun.ca Lecture Goals Students
Lecture 09 Soil Retaining Structures Shawn Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. Assistant Professor Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Memorial University of Newfoundland spkenny@mun.ca Lecture Goals Students
Linear Programming: Sensitivity Analysis
 Linear Programming: Sensitivity Analysis Riset Operasi 1 3-1 Chapter Topic Sensitivity Analysis 3-2 Beaver Creek Pottery Example Sensitivity Analysis (1 of 4) Sensitivity analysis determines the effect
Linear Programming: Sensitivity Analysis Riset Operasi 1 3-1 Chapter Topic Sensitivity Analysis 3-2 Beaver Creek Pottery Example Sensitivity Analysis (1 of 4) Sensitivity analysis determines the effect
Introduction to the Simplex Algorithm Active Learning Module 3
 Introduction to the Simplex Algorithm Active Learning Module 3 J. René Villalobos and Gary L. Hogg Arizona State University Paul M. Griffin Georgia Institute of Technology Background Material Almost any
Introduction to the Simplex Algorithm Active Learning Module 3 J. René Villalobos and Gary L. Hogg Arizona State University Paul M. Griffin Georgia Institute of Technology Background Material Almost any
SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS IN LINEAR PROGRAMING: SOME CASES AND LECTURE NOTES
 SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS IN LINEAR PROGRAMING: SOME CASES AND LECTURE NOTES Samih Antoine Azar, Haigazian University CASE DESCRIPTION This paper presents case studies and lecture notes on a specific constituent
SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS IN LINEAR PROGRAMING: SOME CASES AND LECTURE NOTES Samih Antoine Azar, Haigazian University CASE DESCRIPTION This paper presents case studies and lecture notes on a specific constituent
Sensitivity Analysis and Duality in LP
 Sensitivity Analysis and Duality in LP Xiaoxi Li EMS & IAS, Wuhan University Oct. 13th, 2016 (week vi) Operations Research (Li, X.) Sensitivity Analysis and Duality in LP Oct. 13th, 2016 (week vi) 1 /
Sensitivity Analysis and Duality in LP Xiaoxi Li EMS & IAS, Wuhan University Oct. 13th, 2016 (week vi) Operations Research (Li, X.) Sensitivity Analysis and Duality in LP Oct. 13th, 2016 (week vi) 1 /
LINEAR PROGRAMMING: A GEOMETRIC APPROACH. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 3 LINEAR PROGRAMMING: A GEOMETRIC APPROACH Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.4 Sensitivity Analysis Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Sensitivity Analysis In this section,
3 LINEAR PROGRAMMING: A GEOMETRIC APPROACH Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.4 Sensitivity Analysis Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Sensitivity Analysis In this section,
Ch.03 Solving LP Models. Management Science / Prof. Bonghyun Ahn
 Ch.03 Solving LP Models Management Science / Prof. Bonghyun Ahn Chapter Topics Computer Solution Sensitivity Analysis 2 Computer Solution Early linear programming used lengthy manual mathematical solution
Ch.03 Solving LP Models Management Science / Prof. Bonghyun Ahn Chapter Topics Computer Solution Sensitivity Analysis 2 Computer Solution Early linear programming used lengthy manual mathematical solution
Special cases of linear programming
 Special cases of linear programming Infeasible solution Multiple solution (infinitely many solution) Unbounded solution Degenerated solution Notes on the Simplex tableau 1. The intersection of any basic
Special cases of linear programming Infeasible solution Multiple solution (infinitely many solution) Unbounded solution Degenerated solution Notes on the Simplex tableau 1. The intersection of any basic
Optimisation. 3/10/2010 Tibor Illés Optimisation
 Optimisation Lectures 3 & 4: Linear Programming Problem Formulation Different forms of problems, elements of the simplex algorithm and sensitivity analysis Lecturer: Tibor Illés tibor.illes@strath.ac.uk
Optimisation Lectures 3 & 4: Linear Programming Problem Formulation Different forms of problems, elements of the simplex algorithm and sensitivity analysis Lecturer: Tibor Illés tibor.illes@strath.ac.uk
Linear Programming: Computer Solution and Sensitivity Analysis
 Linear Programming: Computer Solution and Sensitivity Analysis Chapter 3 3-1 Chapter Topics Computer Solution Sensitivity Analysis 3-2 Computer Solution Early linear programming used lengthy manual mathematical
Linear Programming: Computer Solution and Sensitivity Analysis Chapter 3 3-1 Chapter Topics Computer Solution Sensitivity Analysis 3-2 Computer Solution Early linear programming used lengthy manual mathematical
MATH2070 Optimisation
 MATH2070 Optimisation Linear Programming Semester 2, 2012 Lecturer: I.W. Guo Lecture slides courtesy of J.R. Wishart Review The standard Linear Programming (LP) Problem Graphical method of solving LP problem
MATH2070 Optimisation Linear Programming Semester 2, 2012 Lecturer: I.W. Guo Lecture slides courtesy of J.R. Wishart Review The standard Linear Programming (LP) Problem Graphical method of solving LP problem
Sensitivity Analysis and Duality
 Sensitivity Analysis and Duality Part II Duality Based on Chapter 6 Introduction to Mathematical Programming: Operations Research, Volume 1 4th edition, by Wayne L. Winston and Munirpallam Venkataramanan
Sensitivity Analysis and Duality Part II Duality Based on Chapter 6 Introduction to Mathematical Programming: Operations Research, Volume 1 4th edition, by Wayne L. Winston and Munirpallam Venkataramanan
LP Definition and Introduction to Graphical Solution Active Learning Module 2
 LP Definition and Introduction to Graphical Solution Active Learning Module 2 J. René Villalobos and Gary L. Hogg Arizona State University Paul M. Griffin Georgia Institute of Technology Background Material
LP Definition and Introduction to Graphical Solution Active Learning Module 2 J. René Villalobos and Gary L. Hogg Arizona State University Paul M. Griffin Georgia Institute of Technology Background Material
Worked Examples for Chapter 5
 Worked Examples for Chapter 5 Example for Section 5.2 Construct the primal-dual table and the dual problem for the following linear programming model fitting our standard form. Maximize Z = 5 x 1 + 4 x
Worked Examples for Chapter 5 Example for Section 5.2 Construct the primal-dual table and the dual problem for the following linear programming model fitting our standard form. Maximize Z = 5 x 1 + 4 x
Linear and Combinatorial Optimization
 Linear and Combinatorial Optimization The dual of an LP-problem. Connections between primal and dual. Duality theorems and complementary slack. Philipp Birken (Ctr. for the Math. Sc.) Lecture 3: Duality
Linear and Combinatorial Optimization The dual of an LP-problem. Connections between primal and dual. Duality theorems and complementary slack. Philipp Birken (Ctr. for the Math. Sc.) Lecture 3: Duality
Water Resources Systems: Modeling Techniques and Analysis
 INDIAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE Water Resources Systems: Modeling Techniques and Analysis Lecture - 20 Course Instructor : Prof. P. P. MUJUMDAR Department of Civil Engg., IISc. 1 Summary of the previous lecture
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE Water Resources Systems: Modeling Techniques and Analysis Lecture - 20 Course Instructor : Prof. P. P. MUJUMDAR Department of Civil Engg., IISc. 1 Summary of the previous lecture
Deterministic Operations Research, ME 366Q and ORI 391 Chapter 2: Homework #2 Solutions
 Deterministic Operations Research, ME 366Q and ORI 391 Chapter 2: Homework #2 Solutions 11. Consider the following linear program. Maximize z = 6x 1 + 3x 2 subject to x 1 + 2x 2 2x 1 + x 2 20 x 1 x 2 x
Deterministic Operations Research, ME 366Q and ORI 391 Chapter 2: Homework #2 Solutions 11. Consider the following linear program. Maximize z = 6x 1 + 3x 2 subject to x 1 + 2x 2 2x 1 + x 2 20 x 1 x 2 x
R O B U S T E N E R G Y M AN AG E M E N T S Y S T E M F O R I S O L AT E D M I C R O G R I D S
 ROBUST ENERGY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM FOR ISOLATED MICROGRIDS Jose Daniel La r a Claudio Cañizares Ka nka r Bhattacharya D e p a r t m e n t o f E l e c t r i c a l a n d C o m p u t e r E n g i n e e r i n
ROBUST ENERGY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM FOR ISOLATED MICROGRIDS Jose Daniel La r a Claudio Cañizares Ka nka r Bhattacharya D e p a r t m e n t o f E l e c t r i c a l a n d C o m p u t e r E n g i n e e r i n
END3033 Operations Research I Sensitivity Analysis & Duality. to accompany Operations Research: Applications and Algorithms Fatih Cavdur
 END3033 Operations Research I Sensitivity Analysis & Duality to accompany Operations Research: Applications and Algorithms Fatih Cavdur Introduction Consider the following problem where x 1 and x 2 corresponds
END3033 Operations Research I Sensitivity Analysis & Duality to accompany Operations Research: Applications and Algorithms Fatih Cavdur Introduction Consider the following problem where x 1 and x 2 corresponds
Brief summary of linear programming and duality: Consider the linear program in standard form. (P ) min z = cx. x 0. (D) max yb. z = c B x B + c N x N
 Brief summary of linear programming and duality: Consider the linear program in standard form (P ) min z = cx s.t. Ax = b x 0 where A R m n, c R 1 n, x R n 1, b R m 1,and its dual (D) max yb s.t. ya c.
Brief summary of linear programming and duality: Consider the linear program in standard form (P ) min z = cx s.t. Ax = b x 0 where A R m n, c R 1 n, x R n 1, b R m 1,and its dual (D) max yb s.t. ya c.
Business Statistics. Lecture 10: Correlation and Linear Regression
 Business Statistics Lecture 10: Correlation and Linear Regression Scatterplot A scatterplot shows the relationship between two quantitative variables measured on the same individuals. It displays the Form
Business Statistics Lecture 10: Correlation and Linear Regression Scatterplot A scatterplot shows the relationship between two quantitative variables measured on the same individuals. It displays the Form
Liang Li, PhD. MD Anderson
 Liang Li, PhD Biostatistics @ MD Anderson Behavioral Science Workshop, October 13, 2014 The Multiphase Optimization Strategy (MOST) An increasingly popular research strategy to develop behavioral interventions
Liang Li, PhD Biostatistics @ MD Anderson Behavioral Science Workshop, October 13, 2014 The Multiphase Optimization Strategy (MOST) An increasingly popular research strategy to develop behavioral interventions
Graphical and Computer Methods
 Chapter 7 Linear Programming Models: Graphical and Computer Methods Quantitative Analysis for Management, Tenth Edition, by Render, Stair, and Hanna 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Introduction Many management
Chapter 7 Linear Programming Models: Graphical and Computer Methods Quantitative Analysis for Management, Tenth Edition, by Render, Stair, and Hanna 2008 Prentice-Hall, Inc. Introduction Many management
MS-E2140. Lecture 1. (course book chapters )
 Linear Programming MS-E2140 Motivations and background Lecture 1 (course book chapters 1.1-1.4) Linear programming problems and examples Problem manipulations and standard form Graphical representation
Linear Programming MS-E2140 Motivations and background Lecture 1 (course book chapters 1.1-1.4) Linear programming problems and examples Problem manipulations and standard form Graphical representation
ENM 202 OPERATIONS RESEARCH (I) OR (I) 2 LECTURE NOTES. Solution Cases:
 ENM 202 OPERATIONS RESEARCH (I) OR (I) 2 LECTURE NOTES Solution Cases: 1. Unique Optimal Solution Case 2. Alternative Optimal Solution Case 3. Infeasible Solution Case 4. Unbounded Solution Case 5. Degenerate
ENM 202 OPERATIONS RESEARCH (I) OR (I) 2 LECTURE NOTES Solution Cases: 1. Unique Optimal Solution Case 2. Alternative Optimal Solution Case 3. Infeasible Solution Case 4. Unbounded Solution Case 5. Degenerate
3E4: Modelling Choice. Introduction to nonlinear programming. Announcements
 3E4: Modelling Choice Lecture 7 Introduction to nonlinear programming 1 Announcements Solutions to Lecture 4-6 Homework will be available from http://www.eng.cam.ac.uk/~dr241/3e4 Looking ahead to Lecture
3E4: Modelling Choice Lecture 7 Introduction to nonlinear programming 1 Announcements Solutions to Lecture 4-6 Homework will be available from http://www.eng.cam.ac.uk/~dr241/3e4 Looking ahead to Lecture
Introduction. Very efficient solution procedure: simplex method.
 LINEAR PROGRAMMING Introduction Development of linear programming was among the most important scientific advances of mid 20th cent. Most common type of applications: allocate limited resources to competing
LINEAR PROGRAMMING Introduction Development of linear programming was among the most important scientific advances of mid 20th cent. Most common type of applications: allocate limited resources to competing
MAT016: Optimization
 MAT016: Optimization M.El Ghami e-mail: melghami@ii.uib.no URL: http://www.ii.uib.no/ melghami/ March 29, 2011 Outline for today The Simplex method in matrix notation Managing a production facility The
MAT016: Optimization M.El Ghami e-mail: melghami@ii.uib.no URL: http://www.ii.uib.no/ melghami/ March 29, 2011 Outline for today The Simplex method in matrix notation Managing a production facility The
Dr. S. Bourazza Math-473 Jazan University Department of Mathematics
 Dr. Said Bourazza Department of Mathematics Jazan University 1 P a g e Contents: Chapter 0: Modelization 3 Chapter1: Graphical Methods 7 Chapter2: Simplex method 13 Chapter3: Duality 36 Chapter4: Transportation
Dr. Said Bourazza Department of Mathematics Jazan University 1 P a g e Contents: Chapter 0: Modelization 3 Chapter1: Graphical Methods 7 Chapter2: Simplex method 13 Chapter3: Duality 36 Chapter4: Transportation
ECE 307- Techniques for Engineering Decisions
 ECE 307- Techniques for Engineering Decisions Lecture 4. Dualit Concepts in Linear Programming George Gross Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Universit of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign DUALITY
ECE 307- Techniques for Engineering Decisions Lecture 4. Dualit Concepts in Linear Programming George Gross Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Universit of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign DUALITY
The Uncertainty Threshold Principle: Some Fundamental Limitations of Optimal Decision Making under Dynamic Uncertainty
 The Uncertainty Threshold Principle: Some Fundamental Limitations of Optimal Decision Making under Dynamic Uncertainty Michael Athans, Richard Ku, Stanley Gershwin (Nicholas Ballard 538477) Introduction
The Uncertainty Threshold Principle: Some Fundamental Limitations of Optimal Decision Making under Dynamic Uncertainty Michael Athans, Richard Ku, Stanley Gershwin (Nicholas Ballard 538477) Introduction
Lec12p1, ORF363/COS323. The idea behind duality. This lecture
 Lec12 Page 1 Lec12p1, ORF363/COS323 This lecture Linear programming duality + robust linear programming Intuition behind the derivation of the dual Weak and strong duality theorems Max-flow=Min-cut Primal/dual
Lec12 Page 1 Lec12p1, ORF363/COS323 This lecture Linear programming duality + robust linear programming Intuition behind the derivation of the dual Weak and strong duality theorems Max-flow=Min-cut Primal/dual
Theory of constraints and linear programming: a reexamination
 Theory of constraints and linear programming: a reexamination Jaydeep Balakrishnan Operations Management Area Faculty of Management University of Calgary Calgary Alberta T2N 1N4 Canada Ph: (403) 220 7844
Theory of constraints and linear programming: a reexamination Jaydeep Balakrishnan Operations Management Area Faculty of Management University of Calgary Calgary Alberta T2N 1N4 Canada Ph: (403) 220 7844
CS 543 Page 1 John E. Boon, Jr.
 CS 543 Machine Learning Spring 2010 Lecture 05 Evaluating Hypotheses I. Overview A. Given observed accuracy of a hypothesis over a limited sample of data, how well does this estimate its accuracy over
CS 543 Machine Learning Spring 2010 Lecture 05 Evaluating Hypotheses I. Overview A. Given observed accuracy of a hypothesis over a limited sample of data, how well does this estimate its accuracy over
1 Review Session. 1.1 Lecture 2
 1 Review Session Note: The following lists give an overview of the material that was covered in the lectures and sections. Your TF will go through these lists. If anything is unclear or you have questions
1 Review Session Note: The following lists give an overview of the material that was covered in the lectures and sections. Your TF will go through these lists. If anything is unclear or you have questions
Slack Variable. Max Z= 3x 1 + 4x 2 + 5X 3. Subject to: X 1 + X 2 + X x 1 + 4x 2 + X X 1 + X 2 + 4X 3 10 X 1 0, X 2 0, X 3 0
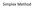 Simplex Method Slack Variable Max Z= 3x 1 + 4x 2 + 5X 3 Subject to: X 1 + X 2 + X 3 20 3x 1 + 4x 2 + X 3 15 2X 1 + X 2 + 4X 3 10 X 1 0, X 2 0, X 3 0 Standard Form Max Z= 3x 1 +4x 2 +5X 3 + 0S 1 + 0S 2
Simplex Method Slack Variable Max Z= 3x 1 + 4x 2 + 5X 3 Subject to: X 1 + X 2 + X 3 20 3x 1 + 4x 2 + X 3 15 2X 1 + X 2 + 4X 3 10 X 1 0, X 2 0, X 3 0 Standard Form Max Z= 3x 1 +4x 2 +5X 3 + 0S 1 + 0S 2
Yinyu Ye, MS&E, Stanford MS&E310 Lecture Note #06. The Simplex Method
 The Simplex Method Yinyu Ye Department of Management Science and Engineering Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305, U.S.A. http://www.stanford.edu/ yyye (LY, Chapters 2.3-2.5, 3.1-3.4) 1 Geometry of Linear
The Simplex Method Yinyu Ye Department of Management Science and Engineering Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305, U.S.A. http://www.stanford.edu/ yyye (LY, Chapters 2.3-2.5, 3.1-3.4) 1 Geometry of Linear
Asymptotic relations in Cournot s game
 MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Asymptotic relations in Cournot s game Marco Guerrazzi Departmento of Economics, University of Genoa November 0 Online at http://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/476/ MPRA Paper
MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Asymptotic relations in Cournot s game Marco Guerrazzi Departmento of Economics, University of Genoa November 0 Online at http://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/476/ MPRA Paper
Class 19. Daniel B. Rowe, Ph.D. Department of Mathematics, Statistics, and Computer Science. Marquette University MATH 1700
 Class 19 Daniel B. Rowe, Ph.D. Department of Mathematics, Statistics, and Computer Science Copyright 2017 by D.B. Rowe 1 Agenda: Recap Chapter 8.3-8.4 Lecture Chapter 8.5 Go over Exam. Problem Solving
Class 19 Daniel B. Rowe, Ph.D. Department of Mathematics, Statistics, and Computer Science Copyright 2017 by D.B. Rowe 1 Agenda: Recap Chapter 8.3-8.4 Lecture Chapter 8.5 Go over Exam. Problem Solving
Branch-and-Price-and-Cut for the Split Delivery Vehicle Routing Problem with Time Windows
 Branch-and-Price-and-Cut for the Split Delivery Vehicle Routing Problem with Time Windows Guy Desaulniers École Polytechnique de Montréal and GERAD Column Generation 2008 Aussois, France Outline Introduction
Branch-and-Price-and-Cut for the Split Delivery Vehicle Routing Problem with Time Windows Guy Desaulniers École Polytechnique de Montréal and GERAD Column Generation 2008 Aussois, France Outline Introduction
The use of shadow price is an example of sensitivity analysis. Duality theory can be applied to do other kind of sensitivity analysis:
 Sensitivity analysis The use of shadow price is an example of sensitivity analysis. Duality theory can be applied to do other kind of sensitivity analysis: Changing the coefficient of a nonbasic variable
Sensitivity analysis The use of shadow price is an example of sensitivity analysis. Duality theory can be applied to do other kind of sensitivity analysis: Changing the coefficient of a nonbasic variable
Solution Cases: 1. Unique Optimal Solution Reddy Mikks Example Diet Problem
 Solution Cases: 1. Unique Optimal Solution 2. Alternative Optimal Solutions 3. Infeasible solution Case 4. Unbounded Solution Case 5. Degenerate Optimal Solution Case 1. Unique Optimal Solution Reddy Mikks
Solution Cases: 1. Unique Optimal Solution 2. Alternative Optimal Solutions 3. Infeasible solution Case 4. Unbounded Solution Case 5. Degenerate Optimal Solution Case 1. Unique Optimal Solution Reddy Mikks
MS-E2140. Lecture 1. (course book chapters )
 Linear Programming MS-E2140 Motivations and background Lecture 1 (course book chapters 1.1-1.4) Linear programming problems and examples Problem manipulations and standard form problems Graphical representation
Linear Programming MS-E2140 Motivations and background Lecture 1 (course book chapters 1.1-1.4) Linear programming problems and examples Problem manipulations and standard form problems Graphical representation
ENGI 1313 Mechanics I
 ENGI 1313 Mechanics I Lectue 04: oce Vectos and System of Coplana oces Shawn Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. Assistant Pofesso aculty of Engineeing and Applied Science Memoial Univesity of Newfoundland spkenny@eng.mun.ca
ENGI 1313 Mechanics I Lectue 04: oce Vectos and System of Coplana oces Shawn Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. Assistant Pofesso aculty of Engineeing and Applied Science Memoial Univesity of Newfoundland spkenny@eng.mun.ca
ENGI 1313 Mechanics I
 ENGI 1313 Mechanics I Lecture 11: 2D and 3D Particle Equilibrium Shawn Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. Assistant Prfessr aculty f Engineering and Applied Science Memrial University f Newfundland spkenny@engr.mun.ca
ENGI 1313 Mechanics I Lecture 11: 2D and 3D Particle Equilibrium Shawn Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. Assistant Prfessr aculty f Engineering and Applied Science Memrial University f Newfundland spkenny@engr.mun.ca
Chapter 4 The Simplex Algorithm Part I
 Chapter 4 The Simplex Algorithm Part I Based on Introduction to Mathematical Programming: Operations Research, Volume 1 4th edition, by Wayne L. Winston and Munirpallam Venkataramanan Lewis Ntaimo 1 Modeling
Chapter 4 The Simplex Algorithm Part I Based on Introduction to Mathematical Programming: Operations Research, Volume 1 4th edition, by Wayne L. Winston and Munirpallam Venkataramanan Lewis Ntaimo 1 Modeling
System Planning Lecture 7, F7: Optimization
 System Planning 04 Lecture 7, F7: Optimization System Planning 04 Lecture 7, F7: Optimization Course goals Appendi A Content: Generally about optimization Formulate optimization problems Linear Programming
System Planning 04 Lecture 7, F7: Optimization System Planning 04 Lecture 7, F7: Optimization Course goals Appendi A Content: Generally about optimization Formulate optimization problems Linear Programming
Linear Programming. H. R. Alvarez A., Ph. D. 1
 Linear Programming H. R. Alvarez A., Ph. D. 1 Introduction It is a mathematical technique that allows the selection of the best course of action defining a program of feasible actions. The objective of
Linear Programming H. R. Alvarez A., Ph. D. 1 Introduction It is a mathematical technique that allows the selection of the best course of action defining a program of feasible actions. The objective of
MATH2070/2970 Optimisation
 MATH2070/2970 Optimisation Introduction Semester 2, 2012 Lecturer: I.W. Guo Lecture slides courtesy of J.R. Wishart Course Information Lecture Information Optimisation: Weeks 1 7 Contact Information Email:
MATH2070/2970 Optimisation Introduction Semester 2, 2012 Lecturer: I.W. Guo Lecture slides courtesy of J.R. Wishart Course Information Lecture Information Optimisation: Weeks 1 7 Contact Information Email:
(b) For the change in c 1, use the row corresponding to x 1. The new Row 0 is therefore: 5 + 6
 Chapter Review Solutions. Write the LP in normal form, and the optimal tableau is given in the text (to the right): x x x rhs y y 8 y 5 x x x s s s rhs / 5/ 7/ 9 / / 5/ / / / (a) For the dual, just go
Chapter Review Solutions. Write the LP in normal form, and the optimal tableau is given in the text (to the right): x x x rhs y y 8 y 5 x x x s s s rhs / 5/ 7/ 9 / / 5/ / / / (a) For the dual, just go
+ 5x 2. = x x. + x 2. Transform the original system into a system x 2 = x x 1. = x 1
 University of California, Davis Department of Agricultural and Resource Economics ARE 5 Optimization with Economic Applications Lecture Notes Quirino Paris The Pivot Method for Solving Systems of Equations...................................
University of California, Davis Department of Agricultural and Resource Economics ARE 5 Optimization with Economic Applications Lecture Notes Quirino Paris The Pivot Method for Solving Systems of Equations...................................
Formulating and Solving a Linear Programming Model for Product- Mix Linear Problems with n Products
 Formulating and Solving a Linear Programming Model for Product- Mix Linear Problems with n Products Berhe Zewde Aregawi Head, Quality Assurance of College of Natural and Computational Sciences Department
Formulating and Solving a Linear Programming Model for Product- Mix Linear Problems with n Products Berhe Zewde Aregawi Head, Quality Assurance of College of Natural and Computational Sciences Department
Standard Error of Technical Cost Incorporating Parameter Uncertainty
 Standard Error of Technical Cost Incorporating Parameter Uncertainty Christopher Morton Insurance Australia Group This presentation has been prepared for the Actuaries Institute 2012 General Insurance
Standard Error of Technical Cost Incorporating Parameter Uncertainty Christopher Morton Insurance Australia Group This presentation has been prepared for the Actuaries Institute 2012 General Insurance
Simplex tableau CE 377K. April 2, 2015
 CE 377K April 2, 2015 Review Reduced costs Basic and nonbasic variables OUTLINE Review by example: simplex method demonstration Outline Example You own a small firm producing construction materials for
CE 377K April 2, 2015 Review Reduced costs Basic and nonbasic variables OUTLINE Review by example: simplex method demonstration Outline Example You own a small firm producing construction materials for
Introduction to Operations Research
 Introduction to Operations Research (Week 4: Linear Programming: More on Simplex and Post-Optimality) José Rui Figueira Instituto Superior Técnico Universidade de Lisboa (figueira@tecnico.ulisboa.pt) March
Introduction to Operations Research (Week 4: Linear Programming: More on Simplex and Post-Optimality) José Rui Figueira Instituto Superior Técnico Universidade de Lisboa (figueira@tecnico.ulisboa.pt) March
Capacity Planning with uncertainty in Industrial Gas Markets
 Capacity Planning with uncertainty in Industrial Gas Markets A. Kandiraju, P. Garcia Herreros, E. Arslan, P. Misra, S. Mehta & I.E. Grossmann EWO meeting September, 2015 1 Motivation Industrial gas markets
Capacity Planning with uncertainty in Industrial Gas Markets A. Kandiraju, P. Garcia Herreros, E. Arslan, P. Misra, S. Mehta & I.E. Grossmann EWO meeting September, 2015 1 Motivation Industrial gas markets
Cournot and Bertrand Competition in a Differentiated Duopoly with Endogenous Technology Adoption *
 ANNALS OF ECONOMICS AND FINANCE 16-1, 231 253 (2015) Cournot and Bertrand Competition in a Differentiated Duopoly with Endogenous Technology Adoption * Hongkun Ma School of Economics, Shandong University,
ANNALS OF ECONOMICS AND FINANCE 16-1, 231 253 (2015) Cournot and Bertrand Competition in a Differentiated Duopoly with Endogenous Technology Adoption * Hongkun Ma School of Economics, Shandong University,
Near Optimal Solution for the Step Fixed Charge Transportation Problem
 Appl. Math. Inf. Sci. 7, No. 2L, 661-669 (2013) 661 Applied Mathematics & Information Sciences An International Journal http://dx.doi.org/10.12785/amis/072l41 Near Optimal Solution for the Step Fixed Charge
Appl. Math. Inf. Sci. 7, No. 2L, 661-669 (2013) 661 Applied Mathematics & Information Sciences An International Journal http://dx.doi.org/10.12785/amis/072l41 Near Optimal Solution for the Step Fixed Charge
4.6 Linear Programming duality
 4.6 Linear Programming duality To any minimization (maximization) LP we can associate a closely related maximization (minimization) LP Different spaces and objective functions but in general same optimal
4.6 Linear Programming duality To any minimization (maximization) LP we can associate a closely related maximization (minimization) LP Different spaces and objective functions but in general same optimal
Midterm Review. Yinyu Ye Department of Management Science and Engineering Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305, U.S.A.
 Midterm Review Yinyu Ye Department of Management Science and Engineering Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305, U.S.A. http://www.stanford.edu/ yyye (LY, Chapter 1-4, Appendices) 1 Separating hyperplane
Midterm Review Yinyu Ye Department of Management Science and Engineering Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305, U.S.A. http://www.stanford.edu/ yyye (LY, Chapter 1-4, Appendices) 1 Separating hyperplane
AAEC 6524: Environmental Theory and Policy Analysis. Outline. Theory of Externalities and Public Goods. Klaus Moeltner Spring 2019.
 AAEC 6524: Theory and Policy Analysis Theory of Externalities and Public Goods Klaus Moeltner Spring 2019 January 21, 2019 Outline Overarching and Related Fields and Microeconomics (consumer, firm, s)
AAEC 6524: Theory and Policy Analysis Theory of Externalities and Public Goods Klaus Moeltner Spring 2019 January 21, 2019 Outline Overarching and Related Fields and Microeconomics (consumer, firm, s)
Risk Analysis Framework for Severe Accident Mitigation Strategy in Nordic BWR: An Approach to Communication and Decision Making
 International Topical Meeting on Probabilistic Safety Assessment And Analysis, PSA 2017, September 24-28, 2017. Pittsburgh, PA. Risk Analysis Framework for Severe Accident Mitigation Strategy in Nordic
International Topical Meeting on Probabilistic Safety Assessment And Analysis, PSA 2017, September 24-28, 2017. Pittsburgh, PA. Risk Analysis Framework for Severe Accident Mitigation Strategy in Nordic
Lecture 14 Transportation Algorithm. October 9, 2009
 Transportation Algorithm October 9, 2009 Outline Lecture 14 Revisit the transportation problem Simplex algorithm for the balanced problem Basic feasible solutions Selection of the initial basic feasible
Transportation Algorithm October 9, 2009 Outline Lecture 14 Revisit the transportation problem Simplex algorithm for the balanced problem Basic feasible solutions Selection of the initial basic feasible
Prepared by: Assoc. Prof. Dr Bahaman Abu Samah Department of Professional Development and Continuing Education Faculty of Educational Studies
 Prepared by: Assoc. Prof. Dr Bahaman Abu Samah Department of Professional Development and Continuing Education Faculty of Educational Studies Universiti Putra Malaysia Serdang Participants to be able to:
Prepared by: Assoc. Prof. Dr Bahaman Abu Samah Department of Professional Development and Continuing Education Faculty of Educational Studies Universiti Putra Malaysia Serdang Participants to be able to:
ENGI 1313 Mechanics I
 ENGI 11 Mechancs I Lecture 40: Center of Gravty, Center of Mass and Geometrc Centrod Shan Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. ssstant Professor Faculty of Engneerng and ppled Scence Memoral Unversty of Nefoundland spkenny@engr.mun.ca
ENGI 11 Mechancs I Lecture 40: Center of Gravty, Center of Mass and Geometrc Centrod Shan Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. ssstant Professor Faculty of Engneerng and ppled Scence Memoral Unversty of Nefoundland spkenny@engr.mun.ca
Linear Programming and the Simplex method
 Linear Programming and the Simplex method Harald Enzinger, Michael Rath Signal Processing and Speech Communication Laboratory Jan 9, 2012 Harald Enzinger, Michael Rath Jan 9, 2012 page 1/37 Outline Introduction
Linear Programming and the Simplex method Harald Enzinger, Michael Rath Signal Processing and Speech Communication Laboratory Jan 9, 2012 Harald Enzinger, Michael Rath Jan 9, 2012 page 1/37 Outline Introduction
Tutorial 2: Modelling Transmission
 Tutorial 2: Modelling Transmission In our previous example the load and generation were at the same bus. In this tutorial we will see how to model the transmission of power from one bus to another. The
Tutorial 2: Modelling Transmission In our previous example the load and generation were at the same bus. In this tutorial we will see how to model the transmission of power from one bus to another. The
USAEE/IAEE. Diagnostic metrics for the adequate development of efficient-market baseload natural gas storage capacity.
 USAEE/IAEE Diagnostic metrics for the adequate development of efficient-market baseload natural gas storage capacity Colorado School of Mines November 13, 2017 Contact: eguzman.phd@gmail.com 1 / 28 Introduction
USAEE/IAEE Diagnostic metrics for the adequate development of efficient-market baseload natural gas storage capacity Colorado School of Mines November 13, 2017 Contact: eguzman.phd@gmail.com 1 / 28 Introduction
Mathematical Methods and Economic Theory
 Mathematical Methods and Economic Theory Anjan Mukherji Subrata Guha C 263944 OXTORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface SECTION I 1 Introduction 3 1.1 The Objective 3 1.2 The Tools for Section I 4 2 Basic
Mathematical Methods and Economic Theory Anjan Mukherji Subrata Guha C 263944 OXTORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface SECTION I 1 Introduction 3 1.1 The Objective 3 1.2 The Tools for Section I 4 2 Basic
CO350 Linear Programming Chapter 5: Basic Solutions
 CO350 Linear Programming Chapter 5: Basic Solutions 1st June 2005 Chapter 5: Basic Solutions 1 On Monday, we learned Recap Theorem 5.3 Consider an LP in SEF with rank(a) = # rows. Then x is bfs x is extreme
CO350 Linear Programming Chapter 5: Basic Solutions 1st June 2005 Chapter 5: Basic Solutions 1 On Monday, we learned Recap Theorem 5.3 Consider an LP in SEF with rank(a) = # rows. Then x is bfs x is extreme
End-User Gains from Input Characteristics Improvement
 End-User Gains from Input Characteristics Improvement David K. Lambert William W. Wilson* Paper presented at the Western Agricultural Economics Association Annual Meetings, Vancouver, British Columbia,
End-User Gains from Input Characteristics Improvement David K. Lambert William W. Wilson* Paper presented at the Western Agricultural Economics Association Annual Meetings, Vancouver, British Columbia,
CEE Computer Applications. Mathematical Programming (LP) and Excel Solver
 CEE 3804 - Computer Applications Mathematical Programming (LP) and Excel Solver Dr. Antonio A. Trani Professor of Civil and Environmental Engineering Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University
CEE 3804 - Computer Applications Mathematical Programming (LP) and Excel Solver Dr. Antonio A. Trani Professor of Civil and Environmental Engineering Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University
Algebraic Simplex Active Learning Module 4
 Algebraic Simplex Active Learning Module 4 J. René Villalobos and Gary L. Hogg Arizona State University Paul M. Griffin Georgia Institute of Technology Time required for the module: 50 Min. Reading Most
Algebraic Simplex Active Learning Module 4 J. René Villalobos and Gary L. Hogg Arizona State University Paul M. Griffin Georgia Institute of Technology Time required for the module: 50 Min. Reading Most
Answer the following questions: Q1: Choose the correct answer ( 20 Points ):
 Benha University Final Exam. (ختلفات) Class: 2 rd Year Students Subject: Operations Research Faculty of Computers & Informatics Date: - / 5 / 2017 Time: 3 hours Examiner: Dr. El-Sayed Badr Answer the following
Benha University Final Exam. (ختلفات) Class: 2 rd Year Students Subject: Operations Research Faculty of Computers & Informatics Date: - / 5 / 2017 Time: 3 hours Examiner: Dr. El-Sayed Badr Answer the following
CHAPTER-3 MULTI-OBJECTIVE SUPPLY CHAIN NETWORK PROBLEM
 CHAPTER-3 MULTI-OBJECTIVE SUPPLY CHAIN NETWORK PROBLEM 3.1 Introduction A supply chain consists of parties involved, directly or indirectly, in fulfilling customer s request. The supply chain includes
CHAPTER-3 MULTI-OBJECTIVE SUPPLY CHAIN NETWORK PROBLEM 3.1 Introduction A supply chain consists of parties involved, directly or indirectly, in fulfilling customer s request. The supply chain includes
Duality Theory, Optimality Conditions
 5.1 Duality Theory, Optimality Conditions Katta G. Murty, IOE 510, LP, U. Of Michigan, Ann Arbor We only consider single objective LPs here. Concept of duality not defined for multiobjective LPs. Every
5.1 Duality Theory, Optimality Conditions Katta G. Murty, IOE 510, LP, U. Of Michigan, Ann Arbor We only consider single objective LPs here. Concept of duality not defined for multiobjective LPs. Every
Mathematical Foundations -1- Constrained Optimization. Constrained Optimization. An intuitive approach 2. First Order Conditions (FOC) 7
 Mathematical Foundations -- Constrained Optimization Constrained Optimization An intuitive approach First Order Conditions (FOC) 7 Constraint qualifications 9 Formal statement of the FOC for a maximum
Mathematical Foundations -- Constrained Optimization Constrained Optimization An intuitive approach First Order Conditions (FOC) 7 Constraint qualifications 9 Formal statement of the FOC for a maximum
Welcome! Webinar Biostatistics: sample size & power. Thursday, April 26, 12:30 1:30 pm (NDT)
 . Welcome! Webinar Biostatistics: sample size & power Thursday, April 26, 12:30 1:30 pm (NDT) Get started now: Please check if your speakers are working and mute your audio. Please use the chat box to
. Welcome! Webinar Biostatistics: sample size & power Thursday, April 26, 12:30 1:30 pm (NDT) Get started now: Please check if your speakers are working and mute your audio. Please use the chat box to
Optimization Methods in Management Science
 Problem Set Rules: Optimization Methods in Management Science MIT 15.053, Spring 2013 Problem Set 1 (First Group of Students) Students with first letter of surnames A F Due: February 12, 2013 1. Each student
Problem Set Rules: Optimization Methods in Management Science MIT 15.053, Spring 2013 Problem Set 1 (First Group of Students) Students with first letter of surnames A F Due: February 12, 2013 1. Each student
ENGI 1313 Mechanics I
 ENGI 1313 Mechanics I Lectue 03: Foce Vectos and Paallelogam Law Shawn Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. Assistant Pofesso Faculty of Engineeing and Applied Science Memoial Univesity of Newfoundland spkenny@eng.mun.ca
ENGI 1313 Mechanics I Lectue 03: Foce Vectos and Paallelogam Law Shawn Kenny, Ph.D., P.Eng. Assistant Pofesso Faculty of Engineeing and Applied Science Memoial Univesity of Newfoundland spkenny@eng.mun.ca
A Grey-Based Approach to Suppliers Selection Problem
 A Grey-Based Approach to Suppliers Selection Problem Guo-Dong Li Graduate School of Science and Engineer Teikyo University Utsunomiya City, JAPAN Masatake Nagai Faculty of Engineering Kanagawa University
A Grey-Based Approach to Suppliers Selection Problem Guo-Dong Li Graduate School of Science and Engineer Teikyo University Utsunomiya City, JAPAN Masatake Nagai Faculty of Engineering Kanagawa University
ISE 330 Introduction to Operations Research: Deterministic Models. What is Linear Programming? www-scf.usc.edu/~ise330/2007. August 29, 2007 Lecture 2
 ISE 330 Introduction to Operations Research: Deterministic Models www-scf.usc.edu/~ise330/007 August 9, 007 Lecture What is Linear Programming? Linear Programming provides methods for allocating limited
ISE 330 Introduction to Operations Research: Deterministic Models www-scf.usc.edu/~ise330/007 August 9, 007 Lecture What is Linear Programming? Linear Programming provides methods for allocating limited
Data Privacy in Biomedicine. Lecture 11b: Performance Measures for System Evaluation
 Data Privacy in Biomedicine Lecture 11b: Performance Measures for System Evaluation Bradley Malin, PhD (b.malin@vanderbilt.edu) Professor of Biomedical Informatics, Biostatistics, & Computer Science Vanderbilt
Data Privacy in Biomedicine Lecture 11b: Performance Measures for System Evaluation Bradley Malin, PhD (b.malin@vanderbilt.edu) Professor of Biomedical Informatics, Biostatistics, & Computer Science Vanderbilt
Contents. Interactive Mapping as a Decision Support Tool. Map use: From communication to visualization. The role of maps in GIS
 Contents Interactive Mapping as a Decision Support Tool Claus Rinner Assistant Professor Department of Geography University of Toronto otru gis workshop rinner(a)geog.utoronto.ca 1 The role of maps in
Contents Interactive Mapping as a Decision Support Tool Claus Rinner Assistant Professor Department of Geography University of Toronto otru gis workshop rinner(a)geog.utoronto.ca 1 The role of maps in
Storing energy or Storing Consumption?
 Storing energy or Storing Consumption? It is not the same! Joachim Geske, Richard Green, Qixin Chen, Yi Wang 40th IAEE International Conference 18-21 June 2017, Singapore Motivation Electricity systems
Storing energy or Storing Consumption? It is not the same! Joachim Geske, Richard Green, Qixin Chen, Yi Wang 40th IAEE International Conference 18-21 June 2017, Singapore Motivation Electricity systems
x 4 = 40 +2x 5 +6x x 6 x 1 = 10 2x x 6 x 3 = 20 +x 5 x x 6 z = 540 3x 5 x 2 3x 6 x 4 x 5 x 6 x x
 MATH 4 A Sensitivity Analysis Example from lectures The following examples have been sometimes given in lectures and so the fractions are rather unpleasant for testing purposes. Note that each question
MATH 4 A Sensitivity Analysis Example from lectures The following examples have been sometimes given in lectures and so the fractions are rather unpleasant for testing purposes. Note that each question
CS261: A Second Course in Algorithms Lecture #9: Linear Programming Duality (Part 2)
 CS261: A Second Course in Algorithms Lecture #9: Linear Programming Duality (Part 2) Tim Roughgarden February 2, 2016 1 Recap This is our third lecture on linear programming, and the second on linear programming
CS261: A Second Course in Algorithms Lecture #9: Linear Programming Duality (Part 2) Tim Roughgarden February 2, 2016 1 Recap This is our third lecture on linear programming, and the second on linear programming
56:171 Operations Research Midterm Exam - October 26, 1989 Instructor: D.L. Bricker
 56:171 Operations Research Midterm Exam - October 26, 1989 Instructor: D.L. Bricker Answer all of Part One and two (of the four) problems of Part Two Problem: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 TOTAL Possible: 16 12 20 10
56:171 Operations Research Midterm Exam - October 26, 1989 Instructor: D.L. Bricker Answer all of Part One and two (of the four) problems of Part Two Problem: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 TOTAL Possible: 16 12 20 10
LINEAR PROGRAMMING. Introduction
 LINEAR PROGRAMMING Introduction Development of linear programming was among the most important scientific advances of mid-20th cent. Most common type of applications: allocate limited resources to competing
LINEAR PROGRAMMING Introduction Development of linear programming was among the most important scientific advances of mid-20th cent. Most common type of applications: allocate limited resources to competing
Assistant Prof. Abed Schokry. Operations and Productions Management. First Semester
 Chapter 3 Forecasting Assistant Prof. Abed Schokry Operations and Productions Management First Semester 2010 2011 Chapter 3: Learning Outcomes You should be able to: List the elements of a good forecast
Chapter 3 Forecasting Assistant Prof. Abed Schokry Operations and Productions Management First Semester 2010 2011 Chapter 3: Learning Outcomes You should be able to: List the elements of a good forecast
CS 275 Automata and Formal Language Theory
 CS 275 Automata and Formal Language Theory Course Notes Part III: Limits of Computation Chapter III.1: Introduction Anton Setzer http://www.cs.swan.ac.uk/ csetzer/lectures/ automataformallanguage/current/index.html
CS 275 Automata and Formal Language Theory Course Notes Part III: Limits of Computation Chapter III.1: Introduction Anton Setzer http://www.cs.swan.ac.uk/ csetzer/lectures/ automataformallanguage/current/index.html
Monopoly Regulation in the Presence of Consumer Demand-Reduction
 Monopoly Regulation in the Presence of Consumer Demand-Reduction Susumu Sato July 9, 2018 I study a monopoly regulation in the setting where consumers can engage in demand-reducing investments. I first
Monopoly Regulation in the Presence of Consumer Demand-Reduction Susumu Sato July 9, 2018 I study a monopoly regulation in the setting where consumers can engage in demand-reducing investments. I first
