Latent Dirichlet Alloca/on
|
|
|
- Shannon Carr
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Latent Dirichlet Alloca/on Blei, Ng and Jordan ( 2002 ) Presented by Deepak Santhanam
2 What is Latent Dirichlet Alloca/on? Genera/ve Model for collec/ons of discrete data Data generated by parameters which can be learned and used to do inference. LDA is a hierarchical Bayesian Model
3 LDA and Document Modeling A Document of a collec/on is modeled as a finite mixture over underlying topics. Topics in turn are modeled as an infinite mixture over an underlying set of topic probabili/es. Topic probabili/es are explicit representa/ons of a document. Find short descrip/ons of members while preserving sta/s/cal rela/ons. Document classifica/on is easier with LDA
4 Previous Schemes for Document Modeling! idf scheme where counts are taken for each word and document is modeled. Latent Seman.c Indexing which uses SVD to capture P idf features which capture most of the variance. plsi Each word in a document is a sample from a mixture model and generated from a single topic. (Each document is represented as a mixing propor/ons of topics and there is not probabilis/c model for these propor/ons)
5 An Early Example.. α θ β Z N w
6 An Early Example.. α θ β Z Words N w
7 An Early Example.. α Topics θ β Z Words N w
8 An Early Example.. α Topics θ β Z Words N w
9 Mixture of Topics α An Early Example.. Topics θ β Z Words N w Document
10 Mixture of Topics α An Early Example.. Topics θ β Z Words N w Document
11 Exchangeability and Bag of Words Assump/on that the order of words in the document can be neglected A finite set of Random Variables {x 1,..x N } is exchangeable if σ the joint distribu/on is invariant to any permuta/on of these RVs. i.e. if is a permuta/on of 1 to N: σ P(x 1,..., x N ) = P(x σ (1),..., x σ (N ) ) e.g : Any weighted average of i.i.d sequences of random variables is exchangeable.
12 De Fine\ s Theorem Can Rewrite the Joint of an infinitely exchangeable sequence of RVs by drawing a random parameter from some distribu/on and trea/ng the RVs as i.i.d condi/oned on that random parameter. θ Z n N
13 De Fine\ s Theorem Can Rewrite the Joint of an infinitely exchangeable sequence of RVs by drawing a random parameter from some distribu/on and trea/ng the RVs as i.i.d condi/oned on that random parameter. θ Random Parameter of a Mul/nomial over topics Z n N
14 De Fine\ s Theorem Can Rewrite the Joint of an infinitely exchangeable sequence of RVs by drawing a random parameter from some distribu/on and trea/ng the RVs as i.i.d condi/oned on that random parameter. θ Random Parameter of a Mul/nomial over topics Z n N Topics are now i.i.d condi/oned on theta.
15 LDA and Exchangeability Words are generated by topics with a fixed condi/onal distribu/on Topics are infinitely exchangeable within a document. For a document W= (w 1,w 2,..w N ) of N words and a corpus of M documents C = { W 1, W 2, W M } for k topics denoted by z, N p(w,z) = p(θ) p(z n θ) p(w n z n ) d(θ) n=1 What type of distribu/on can be used to make it easy for inference?
16 The Dirichlet Distribu/on A K Dimensional Dirichlet RV can take values in the (k 1) θ simplex and has the following density on that simplex Where is a k vector with components greater than 0. α Dirichlet makes it easy for inference as it has finite dimensional sufficient sta/s/cs and is a conjugate to the Mul/nomial distribu/on.
17 Genera/ve Process of LDA Choose N ~ Poisson(ξ) Choose θ ~ Dir(α) For each word w n : choose a topic z n ~ Mul6nomial ( ) Choose a word w n from a mul6nomial p(w n z n,β) probability condi6oned on the topic z n Beta is a k x v Matrix and β ij = p(w j =1 z i =1) θ
18 Graphical Model of LDA The joint over the topics and words is given by, Sampled once per corpus Sampled once every document Sampled once every word
19 The Marginal of a Document and The Probability of the Corpus. Integra/ng over the topic mixtures and summing over the words gives the Marginal of a document. Product of the Marginals of all documents gives the probability of the corpus Corpus level Document Level Word Level
20 Geometric Representa/on
21 Inference Problem We have to find the Posterior of the latent variables of a document. Intractable cause we need to marginalize over hidden variables. Tight Coupling between two parameters Use approximate inference like MCMC or varia.onal methods.
22 Varia/onal Inference Drop edges which cause the coupling in graphical model. Simplified graphical model with free varia/onal parameters Problema/c coupling not present in the simpler graphical model.
23 Problema/c edge Varia/onal Inference Drop edges which cause the coupling in graphcial model. Simplified graphical model with free varia/onal parameters Problema/c coupling not present in the simpler graphical model.
24 Varia/onal Inference Results in the following distribu/on : Minimize the Kullback Leibler divergence. Equa/ng deriva/ves of KL to zero, we get the update equa/ons,
25 Varia/onal Inference Results in the following distribu/on : Dirichlet Parameter Mul/nomial Parameter Minimize the Kullback Leibler divergence. Equa/ng deriva/ves of KL to zero, we get the update equa/ons,
26 Parameter Es/ma/on Using empirical Bayes Find the parameters which maximize the log likelihood of data. Intractable for same reasons. Varia/onal inference provided a /ght lower bound. Alterna/ng Varia/onal Expecta/on Maximiza/on: E Step : for each document find op/mizing values of varia/onal parameters. (γ,φ) M Step: Maximize the lower bound on the likelihood with respect to the model parameters. (α,β)
27 Smoothing Likelihood of previously unseen documents is always zero. Smooth matrix by considering its elements as RVs with a β posterior condi/oned on data. Do the whole inference procedure again for new model to get new update equa/ons. Another Dirichlet Prior Treat Elements of Beta as RVs endowed with a posterior
28 Smoothing Likelihood of previously unseen documents is always zero. Smooth matrix by considering its elements as RVs with a β posterior condi/oned on data. Do the whole inference procedure again for new model to get new update equa/ons. Final Hyper parameters
29 Extending LDA Make a con/nuous variant using gaussians instead of mul/nomials. Par/cular form of clustering by having a mixture of Dirichlet distribu/ons instead of one. What must be done to extend LDA to a more useful model? Can we use this LDA model in Computer Vision?
30 Applica/on in Computer Vision One of the methods extended in Describing visual scenes (Sudderth et al 2005) Topics in a scene Llama Sky Tree Grass Llama Llama Sky Tree Grass
31 Applica/on in Computer Vision One of the methods extended in Describing visual scenes (Sudderth et al 2005) Topics in a scene Spa/al rela/onships? Llama Sky Tree Grass Llama Llama Sky Tree Grass
32 Applica/on in Computer Vision One of the methods extended in Describing visual scenes (Sudderth et al 2005) Topics in a scene More Hierarchies.. Cooler Models.. Llama Sky Tree Grass Llama Llama Sky Tree Grass
33 Even cooler models..!
34 Take home message. LDA illustrates how Probabilis/c models can be scaled up. With good inference techniques, we can solve hard problems in mul/ple domains which have a mul/ple hierarchies. Genera/ve models are modular and extensible easily.
35 Thank You!
CS 6140: Machine Learning Spring 2017
 CS 6140: Machine Learning Spring 2017 Instructor: Lu Wang College of Computer and Informa@on Science Northeastern University Webpage: www.ccs.neu.edu/home/luwang Email: luwang@ccs.neu.edu Logis@cs Assignment
CS 6140: Machine Learning Spring 2017 Instructor: Lu Wang College of Computer and Informa@on Science Northeastern University Webpage: www.ccs.neu.edu/home/luwang Email: luwang@ccs.neu.edu Logis@cs Assignment
Document and Topic Models: plsa and LDA
 Document and Topic Models: plsa and LDA Andrew Levandoski and Jonathan Lobo CS 3750 Advanced Topics in Machine Learning 2 October 2018 Outline Topic Models plsa LSA Model Fitting via EM phits: link analysis
Document and Topic Models: plsa and LDA Andrew Levandoski and Jonathan Lobo CS 3750 Advanced Topics in Machine Learning 2 October 2018 Outline Topic Models plsa LSA Model Fitting via EM phits: link analysis
Non-Parametric Bayes
 Non-Parametric Bayes Mark Schmidt UBC Machine Learning Reading Group January 2016 Current Hot Topics in Machine Learning Bayesian learning includes: Gaussian processes. Approximate inference. Bayesian
Non-Parametric Bayes Mark Schmidt UBC Machine Learning Reading Group January 2016 Current Hot Topics in Machine Learning Bayesian learning includes: Gaussian processes. Approximate inference. Bayesian
Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA)
 Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) D. Blei, A. Ng, and M. Jordan. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 3:993-1022, January 2003. Following slides borrowed ant then heavily modified from: Jonathan Huang
Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) D. Blei, A. Ng, and M. Jordan. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 3:993-1022, January 2003. Following slides borrowed ant then heavily modified from: Jonathan Huang
13: Variational inference II
 10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models, Spring 2015 13: Variational inference II Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Ronghuo Zheng, Zhiting Hu, Yuntian Deng 1 Introduction We started to talk about variational
10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models, Spring 2015 13: Variational inference II Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Ronghuo Zheng, Zhiting Hu, Yuntian Deng 1 Introduction We started to talk about variational
CS 6140: Machine Learning Spring What We Learned Last Week. Survey 2/26/16. VS. Model
 Logis@cs CS 6140: Machine Learning Spring 2016 Instructor: Lu Wang College of Computer and Informa@on Science Northeastern University Webpage: www.ccs.neu.edu/home/luwang Email: luwang@ccs.neu.edu Assignment
Logis@cs CS 6140: Machine Learning Spring 2016 Instructor: Lu Wang College of Computer and Informa@on Science Northeastern University Webpage: www.ccs.neu.edu/home/luwang Email: luwang@ccs.neu.edu Assignment
CS 6140: Machine Learning Spring 2016
 CS 6140: Machine Learning Spring 2016 Instructor: Lu Wang College of Computer and Informa?on Science Northeastern University Webpage: www.ccs.neu.edu/home/luwang Email: luwang@ccs.neu.edu Logis?cs Assignment
CS 6140: Machine Learning Spring 2016 Instructor: Lu Wang College of Computer and Informa?on Science Northeastern University Webpage: www.ccs.neu.edu/home/luwang Email: luwang@ccs.neu.edu Logis?cs Assignment
Information retrieval LSI, plsi and LDA. Jian-Yun Nie
 Information retrieval LSI, plsi and LDA Jian-Yun Nie Basics: Eigenvector, Eigenvalue Ref: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/eigenvector For a square matrix A: Ax = λx where x is a vector (eigenvector), and
Information retrieval LSI, plsi and LDA Jian-Yun Nie Basics: Eigenvector, Eigenvalue Ref: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/eigenvector For a square matrix A: Ax = λx where x is a vector (eigenvector), and
Study Notes on the Latent Dirichlet Allocation
 Study Notes on the Latent Dirichlet Allocation Xugang Ye 1. Model Framework A word is an element of dictionary {1,,}. A document is represented by a sequence of words: =(,, ), {1,,}. A corpus is a collection
Study Notes on the Latent Dirichlet Allocation Xugang Ye 1. Model Framework A word is an element of dictionary {1,,}. A document is represented by a sequence of words: =(,, ), {1,,}. A corpus is a collection
Latent Dirichlet Allocation
 Outlines Advanced Artificial Intelligence October 1, 2009 Outlines Part I: Theoretical Background Part II: Application and Results 1 Motive Previous Research Exchangeability 2 Notation and Terminology
Outlines Advanced Artificial Intelligence October 1, 2009 Outlines Part I: Theoretical Background Part II: Application and Results 1 Motive Previous Research Exchangeability 2 Notation and Terminology
Lecture 13 : Variational Inference: Mean Field Approximation
 10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2017 Lecture 13 : Variational Inference: Mean Field Approximation Lecturer: Willie Neiswanger Scribes: Xupeng Tong, Minxing Liu 1 Problem Setup 1.1
10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2017 Lecture 13 : Variational Inference: Mean Field Approximation Lecturer: Willie Neiswanger Scribes: Xupeng Tong, Minxing Liu 1 Problem Setup 1.1
CS Lecture 18. Topic Models and LDA
 CS 6347 Lecture 18 Topic Models and LDA (some slides by David Blei) Generative vs. Discriminative Models Recall that, in Bayesian networks, there could be many different, but equivalent models of the same
CS 6347 Lecture 18 Topic Models and LDA (some slides by David Blei) Generative vs. Discriminative Models Recall that, in Bayesian networks, there could be many different, but equivalent models of the same
Introduction to Bayesian inference
 Introduction to Bayesian inference Thomas Alexander Brouwer University of Cambridge tab43@cam.ac.uk 17 November 2015 Probabilistic models Describe how data was generated using probability distributions
Introduction to Bayesian inference Thomas Alexander Brouwer University of Cambridge tab43@cam.ac.uk 17 November 2015 Probabilistic models Describe how data was generated using probability distributions
Bayesian Learning. HT2015: SC4 Statistical Data Mining and Machine Learning. Maximum Likelihood Principle. The Bayesian Learning Framework
 HT5: SC4 Statistical Data Mining and Machine Learning Dino Sejdinovic Department of Statistics Oxford http://www.stats.ox.ac.uk/~sejdinov/sdmml.html Maximum Likelihood Principle A generative model for
HT5: SC4 Statistical Data Mining and Machine Learning Dino Sejdinovic Department of Statistics Oxford http://www.stats.ox.ac.uk/~sejdinov/sdmml.html Maximum Likelihood Principle A generative model for
Non-parametric Clustering with Dirichlet Processes
 Non-parametric Clustering with Dirichlet Processes Timothy Burns SUNY at Buffalo Mar. 31 2009 T. Burns (SUNY at Buffalo) Non-parametric Clustering with Dirichlet Processes Mar. 31 2009 1 / 24 Introduction
Non-parametric Clustering with Dirichlet Processes Timothy Burns SUNY at Buffalo Mar. 31 2009 T. Burns (SUNY at Buffalo) Non-parametric Clustering with Dirichlet Processes Mar. 31 2009 1 / 24 Introduction
Bayesian networks Lecture 18. David Sontag New York University
 Bayesian networks Lecture 18 David Sontag New York University Outline for today Modeling sequen&al data (e.g., =me series, speech processing) using hidden Markov models (HMMs) Bayesian networks Independence
Bayesian networks Lecture 18 David Sontag New York University Outline for today Modeling sequen&al data (e.g., =me series, speech processing) using hidden Markov models (HMMs) Bayesian networks Independence
Modeling Environment
 Topic Model Modeling Environment What does it mean to understand/ your environment? Ability to predict Two approaches to ing environment of words and text Latent Semantic Analysis (LSA) Topic Model LSA
Topic Model Modeling Environment What does it mean to understand/ your environment? Ability to predict Two approaches to ing environment of words and text Latent Semantic Analysis (LSA) Topic Model LSA
Lecture 7: Con3nuous Latent Variable Models
 CSC2515 Fall 2015 Introduc3on to Machine Learning Lecture 7: Con3nuous Latent Variable Models All lecture slides will be available as.pdf on the course website: http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~urtasun/courses/csc2515/
CSC2515 Fall 2015 Introduc3on to Machine Learning Lecture 7: Con3nuous Latent Variable Models All lecture slides will be available as.pdf on the course website: http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~urtasun/courses/csc2515/
Recent Advances in Bayesian Inference Techniques
 Recent Advances in Bayesian Inference Techniques Christopher M. Bishop Microsoft Research, Cambridge, U.K. research.microsoft.com/~cmbishop SIAM Conference on Data Mining, April 2004 Abstract Bayesian
Recent Advances in Bayesian Inference Techniques Christopher M. Bishop Microsoft Research, Cambridge, U.K. research.microsoft.com/~cmbishop SIAM Conference on Data Mining, April 2004 Abstract Bayesian
Introduction to Probabilistic Machine Learning
 Introduction to Probabilistic Machine Learning Piyush Rai Dept. of CSE, IIT Kanpur (Mini-course 1) Nov 03, 2015 Piyush Rai (IIT Kanpur) Introduction to Probabilistic Machine Learning 1 Machine Learning
Introduction to Probabilistic Machine Learning Piyush Rai Dept. of CSE, IIT Kanpur (Mini-course 1) Nov 03, 2015 Piyush Rai (IIT Kanpur) Introduction to Probabilistic Machine Learning 1 Machine Learning
Density Estimation. Seungjin Choi
 Density Estimation Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr http://mlg.postech.ac.kr/
Density Estimation Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr http://mlg.postech.ac.kr/
Bayesian Nonparametric Models
 Bayesian Nonparametric Models David M. Blei Columbia University December 15, 2015 Introduction We have been looking at models that posit latent structure in high dimensional data. We use the posterior
Bayesian Nonparametric Models David M. Blei Columbia University December 15, 2015 Introduction We have been looking at models that posit latent structure in high dimensional data. We use the posterior
Latent Dirichlet Allocation Introduction/Overview
 Latent Dirichlet Allocation Introduction/Overview David Meyer 03.10.2016 David Meyer http://www.1-4-5.net/~dmm/ml/lda_intro.pdf 03.10.2016 Agenda What is Topic Modeling? Parametric vs. Non-Parametric Models
Latent Dirichlet Allocation Introduction/Overview David Meyer 03.10.2016 David Meyer http://www.1-4-5.net/~dmm/ml/lda_intro.pdf 03.10.2016 Agenda What is Topic Modeling? Parametric vs. Non-Parametric Models
13 : Variational Inference: Loopy Belief Propagation and Mean Field
 10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2012 13 : Variational Inference: Loopy Belief Propagation and Mean Field Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Peter Schulam and William Wang 1 Introduction
10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2012 13 : Variational Inference: Loopy Belief Propagation and Mean Field Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Peter Schulam and William Wang 1 Introduction
LDA with Amortized Inference
 LDA with Amortied Inference Nanbo Sun Abstract This report describes how to frame Latent Dirichlet Allocation LDA as a Variational Auto- Encoder VAE and use the Amortied Variational Inference AVI to optimie
LDA with Amortied Inference Nanbo Sun Abstract This report describes how to frame Latent Dirichlet Allocation LDA as a Variational Auto- Encoder VAE and use the Amortied Variational Inference AVI to optimie
Dirichlet Enhanced Latent Semantic Analysis
 Dirichlet Enhanced Latent Semantic Analysis Kai Yu Siemens Corporate Technology D-81730 Munich, Germany Kai.Yu@siemens.com Shipeng Yu Institute for Computer Science University of Munich D-80538 Munich,
Dirichlet Enhanced Latent Semantic Analysis Kai Yu Siemens Corporate Technology D-81730 Munich, Germany Kai.Yu@siemens.com Shipeng Yu Institute for Computer Science University of Munich D-80538 Munich,
Machine Learning Techniques for Computer Vision
 Machine Learning Techniques for Computer Vision Part 2: Unsupervised Learning Microsoft Research Cambridge x 3 1 0.5 0.2 0 0.5 0.3 0 0.5 1 ECCV 2004, Prague x 2 x 1 Overview of Part 2 Mixture models EM
Machine Learning Techniques for Computer Vision Part 2: Unsupervised Learning Microsoft Research Cambridge x 3 1 0.5 0.2 0 0.5 0.3 0 0.5 1 ECCV 2004, Prague x 2 x 1 Overview of Part 2 Mixture models EM
Lecture 3a: Dirichlet processes
 Lecture 3a: Dirichlet processes Cédric Archambeau Centre for Computational Statistics and Machine Learning Department of Computer Science University College London c.archambeau@cs.ucl.ac.uk Advanced Topics
Lecture 3a: Dirichlet processes Cédric Archambeau Centre for Computational Statistics and Machine Learning Department of Computer Science University College London c.archambeau@cs.ucl.ac.uk Advanced Topics
Computer Vision. Pa0ern Recogni4on Concepts Part I. Luis F. Teixeira MAP- i 2012/13
 Computer Vision Pa0ern Recogni4on Concepts Part I Luis F. Teixeira MAP- i 2012/13 What is it? Pa0ern Recogni4on Many defini4ons in the literature The assignment of a physical object or event to one of
Computer Vision Pa0ern Recogni4on Concepts Part I Luis F. Teixeira MAP- i 2012/13 What is it? Pa0ern Recogni4on Many defini4ons in the literature The assignment of a physical object or event to one of
COS513 LECTURE 8 STATISTICAL CONCEPTS
 COS513 LECTURE 8 STATISTICAL CONCEPTS NIKOLAI SLAVOV AND ANKUR PARIKH 1. MAKING MEANINGFUL STATEMENTS FROM JOINT PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS. A graphical model (GM) represents a family of probability distributions
COS513 LECTURE 8 STATISTICAL CONCEPTS NIKOLAI SLAVOV AND ANKUR PARIKH 1. MAKING MEANINGFUL STATEMENTS FROM JOINT PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS. A graphical model (GM) represents a family of probability distributions
Gibbs Sampling. Héctor Corrada Bravo. University of Maryland, College Park, USA CMSC 644:
 Gibbs Sampling Héctor Corrada Bravo University of Maryland, College Park, USA CMSC 644: 2019 03 27 Latent semantic analysis Documents as mixtures of topics (Hoffman 1999) 1 / 60 Latent semantic analysis
Gibbs Sampling Héctor Corrada Bravo University of Maryland, College Park, USA CMSC 644: 2019 03 27 Latent semantic analysis Documents as mixtures of topics (Hoffman 1999) 1 / 60 Latent semantic analysis
An Introduction to Expectation-Maximization
 An Introduction to Expectation-Maximization Dahua Lin Abstract This notes reviews the basics about the Expectation-Maximization EM) algorithm, a popular approach to perform model estimation of the generative
An Introduction to Expectation-Maximization Dahua Lin Abstract This notes reviews the basics about the Expectation-Maximization EM) algorithm, a popular approach to perform model estimation of the generative
Generative Clustering, Topic Modeling, & Bayesian Inference
 Generative Clustering, Topic Modeling, & Bayesian Inference INFO-4604, Applied Machine Learning University of Colorado Boulder December 12-14, 2017 Prof. Michael Paul Unsupervised Naïve Bayes Last week
Generative Clustering, Topic Modeling, & Bayesian Inference INFO-4604, Applied Machine Learning University of Colorado Boulder December 12-14, 2017 Prof. Michael Paul Unsupervised Naïve Bayes Last week
Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA)
 Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) A review of topic modeling and customer interactions application 3/11/2015 1 Agenda Agenda Items 1 What is topic modeling? Intro Text Mining & Pre-Processing Natural Language
Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) A review of topic modeling and customer interactions application 3/11/2015 1 Agenda Agenda Items 1 What is topic modeling? Intro Text Mining & Pre-Processing Natural Language
Clustering problems, mixture models and Bayesian nonparametrics
 Clustering problems, mixture models and Bayesian nonparametrics Nguyễn Xuân Long Department of Statistics Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Michigan Vietnam Institute
Clustering problems, mixture models and Bayesian nonparametrics Nguyễn Xuân Long Department of Statistics Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Michigan Vietnam Institute
A graph contains a set of nodes (vertices) connected by links (edges or arcs)
 BOLTZMANN MACHINES Generative Models Graphical Models A graph contains a set of nodes (vertices) connected by links (edges or arcs) In a probabilistic graphical model, each node represents a random variable,
BOLTZMANN MACHINES Generative Models Graphical Models A graph contains a set of nodes (vertices) connected by links (edges or arcs) In a probabilistic graphical model, each node represents a random variable,
Dirichlet Processes: Tutorial and Practical Course
 Dirichlet Processes: Tutorial and Practical Course (updated) Yee Whye Teh Gatsby Computational Neuroscience Unit University College London August 2007 / MLSS Yee Whye Teh (Gatsby) DP August 2007 / MLSS
Dirichlet Processes: Tutorial and Practical Course (updated) Yee Whye Teh Gatsby Computational Neuroscience Unit University College London August 2007 / MLSS Yee Whye Teh (Gatsby) DP August 2007 / MLSS
Graphical Models. Lecture 1: Mo4va4on and Founda4ons. Andrew McCallum
 Graphical Models Lecture 1: Mo4va4on and Founda4ons Andrew McCallum mccallum@cs.umass.edu Thanks to Noah Smith and Carlos Guestrin for some slide materials. Board work Expert systems the desire for probability
Graphical Models Lecture 1: Mo4va4on and Founda4ons Andrew McCallum mccallum@cs.umass.edu Thanks to Noah Smith and Carlos Guestrin for some slide materials. Board work Expert systems the desire for probability
Lecture 8: Graphical models for Text
 Lecture 8: Graphical models for Text 4F13: Machine Learning Joaquin Quiñonero-Candela and Carl Edward Rasmussen Department of Engineering University of Cambridge http://mlg.eng.cam.ac.uk/teaching/4f13/
Lecture 8: Graphical models for Text 4F13: Machine Learning Joaquin Quiñonero-Candela and Carl Edward Rasmussen Department of Engineering University of Cambridge http://mlg.eng.cam.ac.uk/teaching/4f13/
Latent Dirichlet Allocation
 Latent Dirichlet Allocation 1 Directed Graphical Models William W. Cohen Machine Learning 10-601 2 DGMs: The Burglar Alarm example Node ~ random variable Burglar Earthquake Arcs define form of probability
Latent Dirichlet Allocation 1 Directed Graphical Models William W. Cohen Machine Learning 10-601 2 DGMs: The Burglar Alarm example Node ~ random variable Burglar Earthquake Arcs define form of probability
Sta$s$cal sequence recogni$on
 Sta$s$cal sequence recogni$on Determinis$c sequence recogni$on Last $me, temporal integra$on of local distances via DP Integrates local matches over $me Normalizes $me varia$ons For cts speech, segments
Sta$s$cal sequence recogni$on Determinis$c sequence recogni$on Last $me, temporal integra$on of local distances via DP Integrates local matches over $me Normalizes $me varia$ons For cts speech, segments
CSE 473: Ar+ficial Intelligence. Hidden Markov Models. Bayes Nets. Two random variable at each +me step Hidden state, X i Observa+on, E i
 CSE 473: Ar+ficial Intelligence Bayes Nets Daniel Weld [Most slides were created by Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley. All CS188 materials are available at hnp://ai.berkeley.edu.]
CSE 473: Ar+ficial Intelligence Bayes Nets Daniel Weld [Most slides were created by Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley. All CS188 materials are available at hnp://ai.berkeley.edu.]
How to generate large-scale data from small-scale realworld
 How to generate large-scale data from small-scale realworld data sets? Gang Lu Institute of Computing Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences BigDataBench Tutorial MICRO 2014 Cambridge, UK INSTITUTE OF
How to generate large-scale data from small-scale realworld data sets? Gang Lu Institute of Computing Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences BigDataBench Tutorial MICRO 2014 Cambridge, UK INSTITUTE OF
Parametric Models. Dr. Shuang LIANG. School of Software Engineering TongJi University Fall, 2012
 Parametric Models Dr. Shuang LIANG School of Software Engineering TongJi University Fall, 2012 Today s Topics Maximum Likelihood Estimation Bayesian Density Estimation Today s Topics Maximum Likelihood
Parametric Models Dr. Shuang LIANG School of Software Engineering TongJi University Fall, 2012 Today s Topics Maximum Likelihood Estimation Bayesian Density Estimation Today s Topics Maximum Likelihood
Kernel Density Topic Models: Visual Topics Without Visual Words
 Kernel Density Topic Models: Visual Topics Without Visual Words Konstantinos Rematas K.U. Leuven ESAT-iMinds krematas@esat.kuleuven.be Mario Fritz Max Planck Institute for Informatics mfrtiz@mpi-inf.mpg.de
Kernel Density Topic Models: Visual Topics Without Visual Words Konstantinos Rematas K.U. Leuven ESAT-iMinds krematas@esat.kuleuven.be Mario Fritz Max Planck Institute for Informatics mfrtiz@mpi-inf.mpg.de
Introduction to Machine Learning
 Introduction to Machine Learning Brown University CSCI 1950-F, Spring 2012 Prof. Erik Sudderth Lecture 25: Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) Course Review and Advanced Topics Many figures courtesy Kevin
Introduction to Machine Learning Brown University CSCI 1950-F, Spring 2012 Prof. Erik Sudderth Lecture 25: Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) Course Review and Advanced Topics Many figures courtesy Kevin
Graphical Models. Lecture 5: Template- Based Representa:ons. Andrew McCallum
 Graphical Models Lecture 5: Template- Based Representa:ons Andrew McCallum mccallum@cs.umass.edu Thanks to Noah Smith and Carlos Guestrin for some slide materials. 1 Administra:on Homework #3 won t go
Graphical Models Lecture 5: Template- Based Representa:ons Andrew McCallum mccallum@cs.umass.edu Thanks to Noah Smith and Carlos Guestrin for some slide materials. 1 Administra:on Homework #3 won t go
Another Walkthrough of Variational Bayes. Bevan Jones Machine Learning Reading Group Macquarie University
 Another Walkthrough of Variational Bayes Bevan Jones Machine Learning Reading Group Macquarie University 2 Variational Bayes? Bayes Bayes Theorem But the integral is intractable! Sampling Gibbs, Metropolis
Another Walkthrough of Variational Bayes Bevan Jones Machine Learning Reading Group Macquarie University 2 Variational Bayes? Bayes Bayes Theorem But the integral is intractable! Sampling Gibbs, Metropolis
Mixed-membership Models (and an introduction to variational inference)
 Mixed-membership Models (and an introduction to variational inference) David M. Blei Columbia University November 24, 2015 Introduction We studied mixture models in detail, models that partition data into
Mixed-membership Models (and an introduction to variational inference) David M. Blei Columbia University November 24, 2015 Introduction We studied mixture models in detail, models that partition data into
Slides modified from: PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING CHRISTOPHER M. BISHOP
 Slides modified from: PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING CHRISTOPHER M. BISHOP Predic?ve Distribu?on (1) Predict t for new values of x by integra?ng over w: where The Evidence Approxima?on (1) The
Slides modified from: PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING CHRISTOPHER M. BISHOP Predic?ve Distribu?on (1) Predict t for new values of x by integra?ng over w: where The Evidence Approxima?on (1) The
Introduction to Particle Filters for Data Assimilation
 Introduction to Particle Filters for Data Assimilation Mike Dowd Dept of Mathematics & Statistics (and Dept of Oceanography Dalhousie University, Halifax, Canada STATMOS Summer School in Data Assimila5on,
Introduction to Particle Filters for Data Assimilation Mike Dowd Dept of Mathematics & Statistics (and Dept of Oceanography Dalhousie University, Halifax, Canada STATMOS Summer School in Data Assimila5on,
Topic Modelling and Latent Dirichlet Allocation
 Topic Modelling and Latent Dirichlet Allocation Stephen Clark (with thanks to Mark Gales for some of the slides) Lent 2013 Machine Learning for Language Processing: Lecture 7 MPhil in Advanced Computer
Topic Modelling and Latent Dirichlet Allocation Stephen Clark (with thanks to Mark Gales for some of the slides) Lent 2013 Machine Learning for Language Processing: Lecture 7 MPhil in Advanced Computer
Introduc)on to Ar)ficial Intelligence
 Introduc)on to Ar)ficial Intelligence Lecture 10 Probability CS/CNS/EE 154 Andreas Krause Announcements! Milestone due Nov 3. Please submit code to TAs! Grading: PacMan! Compiles?! Correct? (Will clear
Introduc)on to Ar)ficial Intelligence Lecture 10 Probability CS/CNS/EE 154 Andreas Krause Announcements! Milestone due Nov 3. Please submit code to TAs! Grading: PacMan! Compiles?! Correct? (Will clear
Bayesian Machine Learning
 Bayesian Machine Learning Andrew Gordon Wilson ORIE 6741 Lecture 2: Bayesian Basics https://people.orie.cornell.edu/andrew/orie6741 Cornell University August 25, 2016 1 / 17 Canonical Machine Learning
Bayesian Machine Learning Andrew Gordon Wilson ORIE 6741 Lecture 2: Bayesian Basics https://people.orie.cornell.edu/andrew/orie6741 Cornell University August 25, 2016 1 / 17 Canonical Machine Learning
Clustering with k-means and Gaussian mixture distributions
 Clustering with k-means and Gaussian mixture distributions Machine Learning and Object Recognition 2017-2018 Jakob Verbeek Clustering Finding a group structure in the data Data in one cluster similar to
Clustering with k-means and Gaussian mixture distributions Machine Learning and Object Recognition 2017-2018 Jakob Verbeek Clustering Finding a group structure in the data Data in one cluster similar to
Variational Inference (11/04/13)
 STA561: Probabilistic machine learning Variational Inference (11/04/13) Lecturer: Barbara Engelhardt Scribes: Matt Dickenson, Alireza Samany, Tracy Schifeling 1 Introduction In this lecture we will further
STA561: Probabilistic machine learning Variational Inference (11/04/13) Lecturer: Barbara Engelhardt Scribes: Matt Dickenson, Alireza Samany, Tracy Schifeling 1 Introduction In this lecture we will further
Graphical Models for Collaborative Filtering
 Graphical Models for Collaborative Filtering Le Song Machine Learning II: Advanced Topics CSE 8803ML, Spring 2012 Sequence modeling HMM, Kalman Filter, etc.: Similarity: the same graphical model topology,
Graphical Models for Collaborative Filtering Le Song Machine Learning II: Advanced Topics CSE 8803ML, Spring 2012 Sequence modeling HMM, Kalman Filter, etc.: Similarity: the same graphical model topology,
Mixtures of Gaussians. Sargur Srihari
 Mixtures of Gaussians Sargur srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu 1 9. Mixture Models and EM 0. Mixture Models Overview 1. K-Means Clustering 2. Mixtures of Gaussians 3. An Alternative View of EM 4. The EM Algorithm
Mixtures of Gaussians Sargur srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu 1 9. Mixture Models and EM 0. Mixture Models Overview 1. K-Means Clustering 2. Mixtures of Gaussians 3. An Alternative View of EM 4. The EM Algorithm
Bayesian Nonparametrics for Speech and Signal Processing
 Bayesian Nonparametrics for Speech and Signal Processing Michael I. Jordan University of California, Berkeley June 28, 2011 Acknowledgments: Emily Fox, Erik Sudderth, Yee Whye Teh, and Romain Thibaux Computer
Bayesian Nonparametrics for Speech and Signal Processing Michael I. Jordan University of California, Berkeley June 28, 2011 Acknowledgments: Emily Fox, Erik Sudderth, Yee Whye Teh, and Romain Thibaux Computer
CS145: INTRODUCTION TO DATA MINING
 CS145: INTRODUCTION TO DATA MINING Text Data: Topic Model Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@cs.ucla.edu December 4, 2017 Methods to be Learnt Vector Data Set Data Sequence Data Text Data Classification Clustering
CS145: INTRODUCTION TO DATA MINING Text Data: Topic Model Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@cs.ucla.edu December 4, 2017 Methods to be Learnt Vector Data Set Data Sequence Data Text Data Classification Clustering
CS 6140: Machine Learning Spring What We Learned Last Week 2/26/16
 Logis@cs CS 6140: Machine Learning Spring 2016 Instructor: Lu Wang College of Computer and Informa@on Science Northeastern University Webpage: www.ccs.neu.edu/home/luwang Email: luwang@ccs.neu.edu Sign
Logis@cs CS 6140: Machine Learning Spring 2016 Instructor: Lu Wang College of Computer and Informa@on Science Northeastern University Webpage: www.ccs.neu.edu/home/luwang Email: luwang@ccs.neu.edu Sign
Linear Dynamical Systems
 Linear Dynamical Systems Sargur N. srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu Machine Learning Course: http://www.cedar.buffalo.edu/~srihari/cse574/index.html Two Models Described by Same Graph Latent variables Observations
Linear Dynamical Systems Sargur N. srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu Machine Learning Course: http://www.cedar.buffalo.edu/~srihari/cse574/index.html Two Models Described by Same Graph Latent variables Observations
STAD68: Machine Learning
 STAD68: Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@utstat.toronto.edu! h0p://www.cs.toronto.edu/~rsalakhu/ Lecture 1 Evalua;on 3 Assignments worth 40%. Midterm worth 20%. Final
STAD68: Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@utstat.toronto.edu! h0p://www.cs.toronto.edu/~rsalakhu/ Lecture 1 Evalua;on 3 Assignments worth 40%. Midterm worth 20%. Final
Advanced Machine Learning
 Advanced Machine Learning Nonparametric Bayesian Models --Learning/Reasoning in Open Possible Worlds Eric Xing Lecture 7, August 4, 2009 Reading: Eric Xing Eric Xing @ CMU, 2006-2009 Clustering Eric Xing
Advanced Machine Learning Nonparametric Bayesian Models --Learning/Reasoning in Open Possible Worlds Eric Xing Lecture 7, August 4, 2009 Reading: Eric Xing Eric Xing @ CMU, 2006-2009 Clustering Eric Xing
ECE521 Tutorial 11. Topic Review. ECE521 Winter Credits to Alireza Makhzani, Alex Schwing, Rich Zemel and TAs for slides. ECE521 Tutorial 11 / 4
 ECE52 Tutorial Topic Review ECE52 Winter 206 Credits to Alireza Makhzani, Alex Schwing, Rich Zemel and TAs for slides ECE52 Tutorial ECE52 Winter 206 Credits to Alireza / 4 Outline K-means, PCA 2 Bayesian
ECE52 Tutorial Topic Review ECE52 Winter 206 Credits to Alireza Makhzani, Alex Schwing, Rich Zemel and TAs for slides ECE52 Tutorial ECE52 Winter 206 Credits to Alireza / 4 Outline K-means, PCA 2 Bayesian
Outline. Binomial, Multinomial, Normal, Beta, Dirichlet. Posterior mean, MAP, credible interval, posterior distribution
 Outline A short review on Bayesian analysis. Binomial, Multinomial, Normal, Beta, Dirichlet Posterior mean, MAP, credible interval, posterior distribution Gibbs sampling Revisit the Gaussian mixture model
Outline A short review on Bayesian analysis. Binomial, Multinomial, Normal, Beta, Dirichlet Posterior mean, MAP, credible interval, posterior distribution Gibbs sampling Revisit the Gaussian mixture model
Lecture 19, November 19, 2012
 Machine Learning 0-70/5-78, Fall 0 Latent Space Analysis SVD and Topic Models Eric Xing Lecture 9, November 9, 0 Reading: Tutorial on Topic Model @ ACL Eric Xing @ CMU, 006-0 We are inundated with data
Machine Learning 0-70/5-78, Fall 0 Latent Space Analysis SVD and Topic Models Eric Xing Lecture 9, November 9, 0 Reading: Tutorial on Topic Model @ ACL Eric Xing @ CMU, 006-0 We are inundated with data
IEOR E4570: Machine Learning for OR&FE Spring 2015 c 2015 by Martin Haugh. The EM Algorithm
 IEOR E4570: Machine Learning for OR&FE Spring 205 c 205 by Martin Haugh The EM Algorithm The EM algorithm is used for obtaining maximum likelihood estimates of parameters when some of the data is missing.
IEOR E4570: Machine Learning for OR&FE Spring 205 c 205 by Martin Haugh The EM Algorithm The EM algorithm is used for obtaining maximum likelihood estimates of parameters when some of the data is missing.
STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning
 STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@utstat.toronto.edu! http://www.utstat.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Sidney Smith Hall, Room 6002 Lecture 7 Approximate
STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@utstat.toronto.edu! http://www.utstat.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Sidney Smith Hall, Room 6002 Lecture 7 Approximate
Two Useful Bounds for Variational Inference
 Two Useful Bounds for Variational Inference John Paisley Department of Computer Science Princeton University, Princeton, NJ jpaisley@princeton.edu Abstract We review and derive two lower bounds on the
Two Useful Bounds for Variational Inference John Paisley Department of Computer Science Princeton University, Princeton, NJ jpaisley@princeton.edu Abstract We review and derive two lower bounds on the
Curve Fitting Re-visited, Bishop1.2.5
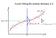 Curve Fitting Re-visited, Bishop1.2.5 Maximum Likelihood Bishop 1.2.5 Model Likelihood differentiation p(t x, w, β) = Maximum Likelihood N N ( t n y(x n, w), β 1). (1.61) n=1 As we did in the case of the
Curve Fitting Re-visited, Bishop1.2.5 Maximum Likelihood Bishop 1.2.5 Model Likelihood differentiation p(t x, w, β) = Maximum Likelihood N N ( t n y(x n, w), β 1). (1.61) n=1 As we did in the case of the
Bayesian Nonparametrics: Models Based on the Dirichlet Process
 Bayesian Nonparametrics: Models Based on the Dirichlet Process Alessandro Panella Department of Computer Science University of Illinois at Chicago Machine Learning Seminar Series February 18, 2013 Alessandro
Bayesian Nonparametrics: Models Based on the Dirichlet Process Alessandro Panella Department of Computer Science University of Illinois at Chicago Machine Learning Seminar Series February 18, 2013 Alessandro
Topic Models. Brandon Malone. February 20, Latent Dirichlet Allocation Success Stories Wrap-up
 Much of this material is adapted from Blei 2003. Many of the images were taken from the Internet February 20, 2014 Suppose we have a large number of books. Each is about several unknown topics. How can
Much of this material is adapted from Blei 2003. Many of the images were taken from the Internet February 20, 2014 Suppose we have a large number of books. Each is about several unknown topics. How can
Statistical learning. Chapter 20, Sections 1 3 1
 Statistical learning Chapter 20, Sections 1 3 Chapter 20, Sections 1 3 1 Outline Bayesian learning Maximum a posteriori and maximum likelihood learning Bayes net learning ML parameter learning with complete
Statistical learning Chapter 20, Sections 1 3 Chapter 20, Sections 1 3 1 Outline Bayesian learning Maximum a posteriori and maximum likelihood learning Bayes net learning ML parameter learning with complete
Applying LDA topic model to a corpus of Italian Supreme Court decisions
 Applying LDA topic model to a corpus of Italian Supreme Court decisions Paolo Fantini Statistical Service of the Ministry of Justice - Italy CESS Conference - Rome - November 25, 2014 Our goal finding
Applying LDA topic model to a corpus of Italian Supreme Court decisions Paolo Fantini Statistical Service of the Ministry of Justice - Italy CESS Conference - Rome - November 25, 2014 Our goal finding
Lecture 6: Graphical Models: Learning
 Lecture 6: Graphical Models: Learning 4F13: Machine Learning Zoubin Ghahramani and Carl Edward Rasmussen Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge February 3rd, 2010 Ghahramani & Rasmussen (CUED)
Lecture 6: Graphical Models: Learning 4F13: Machine Learning Zoubin Ghahramani and Carl Edward Rasmussen Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge February 3rd, 2010 Ghahramani & Rasmussen (CUED)
PMR Learning as Inference
 Outline PMR Learning as Inference Probabilistic Modelling and Reasoning Amos Storkey Modelling 2 The Exponential Family 3 Bayesian Sets School of Informatics, University of Edinburgh Amos Storkey PMR Learning
Outline PMR Learning as Inference Probabilistic Modelling and Reasoning Amos Storkey Modelling 2 The Exponential Family 3 Bayesian Sets School of Informatics, University of Edinburgh Amos Storkey PMR Learning
Introduc)on to Ar)ficial Intelligence
 Introduc)on to Ar)ficial Intelligence Lecture 13 Approximate Inference CS/CNS/EE 154 Andreas Krause Bayesian networks! Compact representa)on of distribu)ons over large number of variables! (OQen) allows
Introduc)on to Ar)ficial Intelligence Lecture 13 Approximate Inference CS/CNS/EE 154 Andreas Krause Bayesian networks! Compact representa)on of distribu)ons over large number of variables! (OQen) allows
Foundations of Nonparametric Bayesian Methods
 1 / 27 Foundations of Nonparametric Bayesian Methods Part II: Models on the Simplex Peter Orbanz http://mlg.eng.cam.ac.uk/porbanz/npb-tutorial.html 2 / 27 Tutorial Overview Part I: Basics Part II: Models
1 / 27 Foundations of Nonparametric Bayesian Methods Part II: Models on the Simplex Peter Orbanz http://mlg.eng.cam.ac.uk/porbanz/npb-tutorial.html 2 / 27 Tutorial Overview Part I: Basics Part II: Models
Learning Bayesian network : Given structure and completely observed data
 Learning Bayesian network : Given structure and completely observed data Probabilistic Graphical Models Sharif University of Technology Spring 2017 Soleymani Learning problem Target: true distribution
Learning Bayesian network : Given structure and completely observed data Probabilistic Graphical Models Sharif University of Technology Spring 2017 Soleymani Learning problem Target: true distribution
Expectation Propagation for Approximate Bayesian Inference
 Expectation Propagation for Approximate Bayesian Inference José Miguel Hernández Lobato Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Computer Science Department February 5, 2007 1/ 24 Bayesian Inference Inference Given
Expectation Propagation for Approximate Bayesian Inference José Miguel Hernández Lobato Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Computer Science Department February 5, 2007 1/ 24 Bayesian Inference Inference Given
Lecture 4: Probabilistic Learning. Estimation Theory. Classification with Probability Distributions
 DD2431 Autumn, 2014 1 2 3 Classification with Probability Distributions Estimation Theory Classification in the last lecture we assumed we new: P(y) Prior P(x y) Lielihood x2 x features y {ω 1,..., ω K
DD2431 Autumn, 2014 1 2 3 Classification with Probability Distributions Estimation Theory Classification in the last lecture we assumed we new: P(y) Prior P(x y) Lielihood x2 x features y {ω 1,..., ω K
Machine Learning. Gaussian Mixture Models. Zhiyao Duan & Bryan Pardo, Machine Learning: EECS 349 Fall
 Machine Learning Gaussian Mixture Models Zhiyao Duan & Bryan Pardo, Machine Learning: EECS 349 Fall 2012 1 The Generative Model POV We think of the data as being generated from some process. We assume
Machine Learning Gaussian Mixture Models Zhiyao Duan & Bryan Pardo, Machine Learning: EECS 349 Fall 2012 1 The Generative Model POV We think of the data as being generated from some process. We assume
Evaluation Methods for Topic Models
 University of Massachusetts Amherst wallach@cs.umass.edu April 13, 2009 Joint work with Iain Murray, Ruslan Salakhutdinov and David Mimno Statistical Topic Models Useful for analyzing large, unstructured
University of Massachusetts Amherst wallach@cs.umass.edu April 13, 2009 Joint work with Iain Murray, Ruslan Salakhutdinov and David Mimno Statistical Topic Models Useful for analyzing large, unstructured
EM & Variational Bayes
 EM & Variational Bayes Hanxiao Liu September 9, 2014 1 / 19 Outline 1. EM Algorithm 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Example: Mixture of vmfs 2. Variational Bayes 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Example: Bayesian Mixture of
EM & Variational Bayes Hanxiao Liu September 9, 2014 1 / 19 Outline 1. EM Algorithm 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Example: Mixture of vmfs 2. Variational Bayes 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Example: Bayesian Mixture of
Learning Deep Genera,ve Models
 Learning Deep Genera,ve Models Ruslan Salakhutdinov BCS, MIT and! Department of Statistics, University of Toronto Machine Learning s Successes Computer Vision: - Image inpain,ng/denoising, segmenta,on
Learning Deep Genera,ve Models Ruslan Salakhutdinov BCS, MIT and! Department of Statistics, University of Toronto Machine Learning s Successes Computer Vision: - Image inpain,ng/denoising, segmenta,on
Bayesian Methods: Naïve Bayes
 Bayesian Methods: aïve Bayes icholas Ruozzi University of Texas at Dallas based on the slides of Vibhav Gogate Last Time Parameter learning Learning the parameter of a simple coin flipping model Prior
Bayesian Methods: aïve Bayes icholas Ruozzi University of Texas at Dallas based on the slides of Vibhav Gogate Last Time Parameter learning Learning the parameter of a simple coin flipping model Prior
Image segmentation combining Markov Random Fields and Dirichlet Processes
 Image segmentation combining Markov Random Fields and Dirichlet Processes Jessica SODJO IMS, Groupe Signal Image, Talence Encadrants : A. Giremus, J.-F. Giovannelli, F. Caron, N. Dobigeon Jessica SODJO
Image segmentation combining Markov Random Fields and Dirichlet Processes Jessica SODJO IMS, Groupe Signal Image, Talence Encadrants : A. Giremus, J.-F. Giovannelli, F. Caron, N. Dobigeon Jessica SODJO
Chapter 8 PROBABILISTIC MODELS FOR TEXT MINING. Yizhou Sun Department of Computer Science University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
 Chapter 8 PROBABILISTIC MODELS FOR TEXT MINING Yizhou Sun Department of Computer Science University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign sun22@illinois.edu Hongbo Deng Department of Computer Science University
Chapter 8 PROBABILISTIC MODELS FOR TEXT MINING Yizhou Sun Department of Computer Science University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign sun22@illinois.edu Hongbo Deng Department of Computer Science University
Machine Learning Summer School
 Machine Learning Summer School Lecture 3: Learning parameters and structure Zoubin Ghahramani zoubin@eng.cam.ac.uk http://learning.eng.cam.ac.uk/zoubin/ Department of Engineering University of Cambridge,
Machine Learning Summer School Lecture 3: Learning parameters and structure Zoubin Ghahramani zoubin@eng.cam.ac.uk http://learning.eng.cam.ac.uk/zoubin/ Department of Engineering University of Cambridge,
Probabilistic Graphical Models
 Probabilistic Graphical Models Brown University CSCI 295-P, Spring 213 Prof. Erik Sudderth Lecture 11: Inference & Learning Overview, Gaussian Graphical Models Some figures courtesy Michael Jordan s draft
Probabilistic Graphical Models Brown University CSCI 295-P, Spring 213 Prof. Erik Sudderth Lecture 11: Inference & Learning Overview, Gaussian Graphical Models Some figures courtesy Michael Jordan s draft
Variational Methods in Bayesian Deconvolution
 PHYSTAT, SLAC, Stanford, California, September 8-, Variational Methods in Bayesian Deconvolution K. Zarb Adami Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge, UK This paper gives an introduction to the
PHYSTAT, SLAC, Stanford, California, September 8-, Variational Methods in Bayesian Deconvolution K. Zarb Adami Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge, UK This paper gives an introduction to the
Note 1: Varitional Methods for Latent Dirichlet Allocation
 Technical Note Series Spring 2013 Note 1: Varitional Methods for Latent Dirichlet Allocation Version 1.0 Wayne Xin Zhao batmanfly@gmail.com Disclaimer: The focus of this note was to reorganie the content
Technical Note Series Spring 2013 Note 1: Varitional Methods for Latent Dirichlet Allocation Version 1.0 Wayne Xin Zhao batmanfly@gmail.com Disclaimer: The focus of this note was to reorganie the content
AN INTRODUCTION TO TOPIC MODELS
 AN INTRODUCTION TO TOPIC MODELS Michael Paul December 4, 2013 600.465 Natural Language Processing Johns Hopkins University Prof. Jason Eisner Making sense of text Suppose you want to learn something about
AN INTRODUCTION TO TOPIC MODELS Michael Paul December 4, 2013 600.465 Natural Language Processing Johns Hopkins University Prof. Jason Eisner Making sense of text Suppose you want to learn something about
Probabilistic Time Series Classification
 Probabilistic Time Series Classification Y. Cem Sübakan Boğaziçi University 25.06.2013 Y. Cem Sübakan (Boğaziçi University) M.Sc. Thesis Defense 25.06.2013 1 / 54 Problem Statement The goal is to assign
Probabilistic Time Series Classification Y. Cem Sübakan Boğaziçi University 25.06.2013 Y. Cem Sübakan (Boğaziçi University) M.Sc. Thesis Defense 25.06.2013 1 / 54 Problem Statement The goal is to assign
PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING CHAPTER 2: PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS
 PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING CHAPTER 2: PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS Parametric Distributions Basic building blocks: Need to determine given Representation: or? Recall Curve Fitting Binary Variables
PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING CHAPTER 2: PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS Parametric Distributions Basic building blocks: Need to determine given Representation: or? Recall Curve Fitting Binary Variables
Deep Variational Inference. FLARE Reading Group Presentation Wesley Tansey 9/28/2016
 Deep Variational Inference FLARE Reading Group Presentation Wesley Tansey 9/28/2016 What is Variational Inference? What is Variational Inference? Want to estimate some distribution, p*(x) p*(x) What is
Deep Variational Inference FLARE Reading Group Presentation Wesley Tansey 9/28/2016 What is Variational Inference? What is Variational Inference? Want to estimate some distribution, p*(x) p*(x) What is
Computer Vision Group Prof. Daniel Cremers. 6. Mixture Models and Expectation-Maximization
 Prof. Daniel Cremers 6. Mixture Models and Expectation-Maximization Motivation Often the introduction of latent (unobserved) random variables into a model can help to express complex (marginal) distributions
Prof. Daniel Cremers 6. Mixture Models and Expectation-Maximization Motivation Often the introduction of latent (unobserved) random variables into a model can help to express complex (marginal) distributions
Collapsed Variational Bayesian Inference for Hidden Markov Models
 Collapsed Variational Bayesian Inference for Hidden Markov Models Pengyu Wang, Phil Blunsom Department of Computer Science, University of Oxford International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and
Collapsed Variational Bayesian Inference for Hidden Markov Models Pengyu Wang, Phil Blunsom Department of Computer Science, University of Oxford International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and

 Mixture Models Michael Kuhn 2017-8-26 Objec
Mixture Models Michael Kuhn 2017-8-26 Objec