Math 304 Answers to Selected Problems
|
|
|
- Gwendolyn Beasley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Math Answers to Selected Problems Section 6.. Find the general solution to each of the following systems. a y y + y y y + y e y y y y y + y f y y + y y y + 6y y y + y Answer: a This is a system of the form Y AY where A The eigenvalues of this matrix are λ and λ with corresponding eigenvectors v and v. Thus, e t and e t are both solutions to the system. The general solution is all linear combinations of these two solutions. y y c e t + c e t c e t + c e t c e t + c e t e This is a system of the form Y AY where A
2 The eigenvalues of this matrix are λ ± i. The eigenvector i corresponding to the eigenvalue λ + i is. Using this eigenvalue and eigenvector, we get the solution i e λt v e +it i e t cost + i sint i cost sint e t cost + i sint Separating into real and imaginary parts, we have i e Re e +it t sint e t cost i e Im e +it t cost e t sint Any linear combination of these is a solution, so the general solution is y y e c t sint e e t + c t cost cost e t sint c e t sint + c e t cost c e t cost + c e t sint f This is a system of the form Y AY where A 6 The eigenvalues of this matrix areλ, λ 5, λ with corresponding eigenvectors v, v 8, and
3 v. Thus, e t, e 5t 8, and e t are all solutions to the system. The general solution is all linear combinations of these three solutions. y y y c + c e 5t c + c e 5t + c e t c + 8c e 5t c + c e 5t 8. Solve each of the following initial value problems. + c e t a y y + y y y y y, y b y y y y y + y y, y c y y 6y y y y y y y y y y Answer: a This is a system of the form Y AY where A The eigenvalues of this matrix are λ and λ with corresponding eigenvectors v and v.
4 Thus, e t and e t are both solutions to the system. The general solution is all linear combinations of these two solutions. y y c e t + c e t c e t + c e t c e t + c e t The initial conditions tell us that c + c c + c Solving, we get c and c. Thus, the solution to the initial value problem is y e t + e t y e t + e t b This is a system of the form Y AY where A The eigenvalues of this matrix are λ ± i. The eigenvector i corresponding to the eigenvalue λ + i is v. Using this eigenvalue and eigenvector, we get the solution i e λt v e +it i e t cost + i sint i cost sint e t cost + i sint
5 Separating into real and imaginary parts, we have i Re e +it i Im e +it e t sint e t cost e t cost e t sint Any linear combination of these is a solution, so the general solution is y y e c t sint e e t + c t cost cost e t sint c e t sint + c e t cost c e t cost + c e t sint The initial conditions tell us that c c Thus, c and c. Thus, the solution to the initial value problem is y e t sint + e t cost y e t cost + e t sint c This is a system of the form Y AY where A 6 5
6 The eigenvalues of this matrix are λ, λ, and λ 6 with corresponding eigenvectors v, v, v. Thus, e t 6, e t and e t are all solutions to the system. The general solution is all linear combinations of these three solutions. y y y c e t 6 + c 6c e t + c + c e t c e t + c + c e t c e t + c + c e t The initial conditions tell us that + c e t 6c + c + c c + c + c c + c + c Solving, we get c, c, and c. Thus, the solution to the initial value problem is y 6e t e t y e t + + e t y e t + + e t 6
7 6. Solve the initial value problem y y + y + y y y + y y y, y,, y, y Answer: First, we set y y and y y, and we rewrite the equations as a system of linear differential equations: y y y y y y + y + y y y + y y This is a system of the form Y AY where A The eigenvalues of this matrix are λ, λ, λ, and λ with corresponding eigenvectors v, v, v, and v Thus, the general solution is y y y y c e t. +c e t 7 +c e t +c e t
8 The initial conditions tell us that c c + c + c c + c + c + c c + c + c + c c c + c + c Solving, we get that c, c, c, and c. Thus, the solution to the initial value problem is y e t e t + e t y e t e t + e t. Three masses are connected by a series of springs between two fixed points as shown in the figure. Assume that the springs all have the same spring constant, and let x t, x t, and x t represent the displacement of the respective masses at time t. a Derive a system of second-order differential equations that describes the motion of this system. b Solve the system if m m, m, k, and Answer: a x x x x x x m x t kx + kx x m x t kx x + kx x m x t kx x kx 8
9 b This is a system of the form X AX where A The eigenvalues of this matrix are λ, λ 6, and λ, with corresponding eigenvectors v, v, and v. For each of these e λt v and e λt v are solutions to the system. For λ, we have the solution e λ t v e it cos t + i sin t Separating into real and imaginary parts, we have Ree λ t v Ime λ t v For λ 6, we have the solution cos t cos t cos t sin t sin t sin t 9
10 e λ t v e 6it cos 6t + i sin 6t Separating into real and imaginary parts, we have Ree λ t v Ime λ t v For λ, we have the solution e λ t v e it cos 6t cos 6t sin 6t sin 6t cos t + i sin t Separating into real and imaginary parts, we have Ree λ t v Ime λ t v cos t cos t cos t sin t sin t sin t
11 The general solution is all linear combinations of the above solutions: X c cos t cos t cos t +c sin 6t sin 6t + c + c 5 sin t sin t sin t cos t cos t cos t + c + c 6 cos 6t cos 6t sin t sin t sin t From the initial condition x x x, we get the equations c + c + c 5 c + c 5 c c + c 5 Solving, we get c., c, c 5.. By inspection, we can see that c, c, and c 6 satisfies the initial condition x x x note that when you take the derivative of the above equation, the terms involving c, c, and c 5 all equal when t. Thus, the solution to the initial value problem is X. cos t +.9 cos t. cos t +. cos t. cos t +.9 cos t
Math 322. Spring 2015 Review Problems for Midterm 2
 Linear Algebra: Topic: Linear Independence of vectors. Question. Math 3. Spring Review Problems for Midterm Explain why if A is not square, then either the row vectors or the column vectors of A are linearly
Linear Algebra: Topic: Linear Independence of vectors. Question. Math 3. Spring Review Problems for Midterm Explain why if A is not square, then either the row vectors or the column vectors of A are linearly
+ i. cos(t) + 2 sin(t) + c 2.
 MATH HOMEWORK #7 PART A SOLUTIONS Problem 7.6.. Consider the system x = 5 x. a Express the general solution of the given system of equations in terms of realvalued functions. b Draw a direction field,
MATH HOMEWORK #7 PART A SOLUTIONS Problem 7.6.. Consider the system x = 5 x. a Express the general solution of the given system of equations in terms of realvalued functions. b Draw a direction field,
Even-Numbered Homework Solutions
 -6 Even-Numbered Homework Solutions Suppose that the matric B has λ = + 5i as an eigenvalue with eigenvector Y 0 = solution to dy = BY Using Euler s formula, we can write the complex-valued solution Y
-6 Even-Numbered Homework Solutions Suppose that the matric B has λ = + 5i as an eigenvalue with eigenvector Y 0 = solution to dy = BY Using Euler s formula, we can write the complex-valued solution Y
TheHarmonicOscillator
 TheHarmonicOscillator S F Ellermeyer October 9, The differential equation describing the motion of a bob on a spring (a harmonic oscillator) is m d y dt + bdy + ky () dt In this equation, y denotes the
TheHarmonicOscillator S F Ellermeyer October 9, The differential equation describing the motion of a bob on a spring (a harmonic oscillator) is m d y dt + bdy + ky () dt In this equation, y denotes the
Math 334 Midterm III KEY Fall 2006 sections 001 and 004 Instructor: Scott Glasgow
 Math 334 Midterm III KEY Fall 6 sections 1 and 4 Instructor: Scott Glasgow Please do NO write on this exam No credit will be given for such work Rather write in a blue book, or on your own paper, preferably
Math 334 Midterm III KEY Fall 6 sections 1 and 4 Instructor: Scott Glasgow Please do NO write on this exam No credit will be given for such work Rather write in a blue book, or on your own paper, preferably
1 Some general theory for 2nd order linear nonhomogeneous
 Math 175 Honors ODE I Spring, 013 Notes 5 1 Some general theory for nd order linear nonhomogeneous equations 1.1 General form of the solution Suppose that p; q; and g are continuous on an interval I; and
Math 175 Honors ODE I Spring, 013 Notes 5 1 Some general theory for nd order linear nonhomogeneous equations 1.1 General form of the solution Suppose that p; q; and g are continuous on an interval I; and
FINAL EXAM MATH303 Theory of Ordinary Differential Equations. Spring dx dt = x + 3y dy dt = x y.
 FINAL EXAM MATH0 Theory of Ordinary Differential Equations There are 5 problems on 2 pages. Spring 2009. 25 points Consider the linear plane autonomous system x + y x y. Find a fundamental matrix of the
FINAL EXAM MATH0 Theory of Ordinary Differential Equations There are 5 problems on 2 pages. Spring 2009. 25 points Consider the linear plane autonomous system x + y x y. Find a fundamental matrix of the
MathQuest: Differential Equations
 MathQuest: Differential Equations Solutions to Linear Systems. Consider the linear system given by dy dt = 4 True or False: Y e t t = is a solution. c False, but I am not very confident Y.. Consider the
MathQuest: Differential Equations Solutions to Linear Systems. Consider the linear system given by dy dt = 4 True or False: Y e t t = is a solution. c False, but I am not very confident Y.. Consider the
Math 216 Second Midterm 16 November, 2017
 Math 216 Second Midterm 16 November, 2017 This sample exam is provided to serve as one component of your studying for this exam in this course. Please note that it is not guaranteed to cover the material
Math 216 Second Midterm 16 November, 2017 This sample exam is provided to serve as one component of your studying for this exam in this course. Please note that it is not guaranteed to cover the material
Polytechnic Institute of NYU MA 2132 Final Practice Answers Fall 2012
 Polytechnic Institute of NYU MA Final Practice Answers Fall Studying from past or sample exams is NOT recommended. If you do, it should be only AFTER you know how to do all of the homework and worksheet
Polytechnic Institute of NYU MA Final Practice Answers Fall Studying from past or sample exams is NOT recommended. If you do, it should be only AFTER you know how to do all of the homework and worksheet
/ / MET Day 000 NC1^ INRTL MNVR I E E PRE SLEEP K PRE SLEEP R E
 05//0 5:26:04 09/6/0 (259) 6 7 8 9 20 2 22 2 09/7 0 02 0 000/00 0 02 0 04 05 06 07 08 09 0 2 ay 000 ^ 0 X Y / / / / ( %/ ) 2 /0 2 ( ) ^ 4 / Y/ 2 4 5 6 7 8 9 2 X ^ X % 2 // 09/7/0 (260) ay 000 02 05//0
05//0 5:26:04 09/6/0 (259) 6 7 8 9 20 2 22 2 09/7 0 02 0 000/00 0 02 0 04 05 06 07 08 09 0 2 ay 000 ^ 0 X Y / / / / ( %/ ) 2 /0 2 ( ) ^ 4 / Y/ 2 4 5 6 7 8 9 2 X ^ X % 2 // 09/7/0 (260) ay 000 02 05//0
Constant coefficients systems
 5.3. 2 2 Constant coefficients systems Section Objective(s): Diagonalizable systems. Real Distinct Eigenvalues. Complex Eigenvalues. Non-Diagonalizable systems. 5.3.. Diagonalizable Systems. Remark: We
5.3. 2 2 Constant coefficients systems Section Objective(s): Diagonalizable systems. Real Distinct Eigenvalues. Complex Eigenvalues. Non-Diagonalizable systems. 5.3.. Diagonalizable Systems. Remark: We
Solutions to Math 53 Math 53 Practice Final
 Solutions to Math 5 Math 5 Practice Final 20 points Consider the initial value problem y t 4yt = te t with y 0 = and y0 = 0 a 8 points Find the Laplace transform of the solution of this IVP b 8 points
Solutions to Math 5 Math 5 Practice Final 20 points Consider the initial value problem y t 4yt = te t with y 0 = and y0 = 0 a 8 points Find the Laplace transform of the solution of this IVP b 8 points
20D - Homework Assignment 5
 Brian Bowers TA for Hui Sun MATH D Homework Assignment 5 November 8, 3 D - Homework Assignment 5 First, I present the list of all matrix row operations. We use combinations of these steps to row reduce
Brian Bowers TA for Hui Sun MATH D Homework Assignment 5 November 8, 3 D - Homework Assignment 5 First, I present the list of all matrix row operations. We use combinations of these steps to row reduce
MATH 251 Examination II July 28, Name: Student Number: Section:
 MATH 251 Examination II July 28, 2008 Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 9 questions for a total of 100 points. In order to obtain full credit for partial credit problems, all work must be shown.
MATH 251 Examination II July 28, 2008 Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 9 questions for a total of 100 points. In order to obtain full credit for partial credit problems, all work must be shown.
MATH 251 Examination II April 7, 2014 FORM A. Name: Student Number: Section:
 MATH 251 Examination II April 7, 2014 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 12 questions for a total of 100 points. In order to obtain full credit for partial credit problems, all work must
MATH 251 Examination II April 7, 2014 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 12 questions for a total of 100 points. In order to obtain full credit for partial credit problems, all work must
Homogeneous Linear Systems of Differential Equations with Constant Coefficients
 Objective: Solve Homogeneous Linear Systems of Differential Equations with Constant Coefficients dx a x + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n, dx 2 a 2x + a 22 x 2 + + a 2n x n,. dx n = a n x + a n2 x 2 + + a nn x n.
Objective: Solve Homogeneous Linear Systems of Differential Equations with Constant Coefficients dx a x + a 2 x 2 + + a n x n, dx 2 a 2x + a 22 x 2 + + a 2n x n,. dx n = a n x + a n2 x 2 + + a nn x n.
Properties of Linear Transformations from R n to R m
 Properties of Linear Transformations from R n to R m MATH 322, Linear Algebra I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2015 Topic Overview Relationship between the properties of a matrix transformation
Properties of Linear Transformations from R n to R m MATH 322, Linear Algebra I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2015 Topic Overview Relationship between the properties of a matrix transformation
Math 216 Final Exam 24 April, 2017
 Math 216 Final Exam 24 April, 2017 This sample exam is provided to serve as one component of your studying for this exam in this course. Please note that it is not guaranteed to cover the material that
Math 216 Final Exam 24 April, 2017 This sample exam is provided to serve as one component of your studying for this exam in this course. Please note that it is not guaranteed to cover the material that
MATH 2250 Final Exam Solutions
 MATH 225 Final Exam Solutions Tuesday, April 29, 28, 6: 8:PM Write your name and ID number at the top of this page. Show all your work. You may refer to one double-sided sheet of notes during the exam
MATH 225 Final Exam Solutions Tuesday, April 29, 28, 6: 8:PM Write your name and ID number at the top of this page. Show all your work. You may refer to one double-sided sheet of notes during the exam
4.3 Linear, Homogeneous Equations with Constant Coefficients. Jiwen He
 4.3 Exercises Math 3331 Differential Equations 4.3 Linear, Homogeneous Equations with Constant Coefficients Jiwen He Department of Mathematics, University of Houston jiwenhe@math.uh.edu math.uh.edu/ jiwenhe/math3331
4.3 Exercises Math 3331 Differential Equations 4.3 Linear, Homogeneous Equations with Constant Coefficients Jiwen He Department of Mathematics, University of Houston jiwenhe@math.uh.edu math.uh.edu/ jiwenhe/math3331
3.3. SYSTEMS OF ODES 1. y 0 " 2y" y 0 + 2y = x1. x2 x3. x = y(t) = c 1 e t + c 2 e t + c 3 e 2t. _x = A x + f; x(0) = x 0.
 .. SYSTEMS OF ODES. Systems of ODEs MATH 94 FALL 98 PRELIM # 94FA8PQ.tex.. a) Convert the third order dierential equation into a rst oder system _x = A x, with y " y" y + y = x = @ x x x b) The equation
.. SYSTEMS OF ODES. Systems of ODEs MATH 94 FALL 98 PRELIM # 94FA8PQ.tex.. a) Convert the third order dierential equation into a rst oder system _x = A x, with y " y" y + y = x = @ x x x b) The equation
Eigenpairs and Diagonalizability Math 401, Spring 2010, Professor David Levermore
 Eigenpairs and Diagonalizability Math 40, Spring 200, Professor David Levermore Eigenpairs Let A be an n n matrix A number λ possibly complex even when A is real is an eigenvalue of A if there exists a
Eigenpairs and Diagonalizability Math 40, Spring 200, Professor David Levermore Eigenpairs Let A be an n n matrix A number λ possibly complex even when A is real is an eigenvalue of A if there exists a
Ex. 1. Find the general solution for each of the following differential equations:
 MATH 261.007 Instr. K. Ciesielski Spring 2010 NAME (print): SAMPLE TEST # 2 Solve the following exercises. Show your work. (No credit will be given for an answer with no supporting work shown.) Ex. 1.
MATH 261.007 Instr. K. Ciesielski Spring 2010 NAME (print): SAMPLE TEST # 2 Solve the following exercises. Show your work. (No credit will be given for an answer with no supporting work shown.) Ex. 1.
Math 216 Second Midterm 28 March, 2013
 Math 26 Second Midterm 28 March, 23 This sample exam is provided to serve as one component of your studying for this exam in this course. Please note that it is not guaranteed to cover the material that
Math 26 Second Midterm 28 March, 23 This sample exam is provided to serve as one component of your studying for this exam in this course. Please note that it is not guaranteed to cover the material that
Solution: In standard form (i.e. y + P (t)y = Q(t)) we have y t y = cos(t)
 Math 380 Practice Final Solutions This is longer than the actual exam, which will be 8 to 0 questions (some might be multiple choice). You are allowed up to two sheets of notes (both sides) and a calculator,
Math 380 Practice Final Solutions This is longer than the actual exam, which will be 8 to 0 questions (some might be multiple choice). You are allowed up to two sheets of notes (both sides) and a calculator,
Homework 1 Elena Davidson (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) (G) (H) (I)
 CS 106 Spring 2004 Homework 1 Elena Davidson 8 April 2004 Problem 1.1 Let B be a 4 4 matrix to which we apply the following operations: 1. double column 1, 2. halve row 3, 3. add row 3 to row 1, 4. interchange
CS 106 Spring 2004 Homework 1 Elena Davidson 8 April 2004 Problem 1.1 Let B be a 4 4 matrix to which we apply the following operations: 1. double column 1, 2. halve row 3, 3. add row 3 to row 1, 4. interchange
Exam in TMA4110 Calculus 3, June 2013 Solution
 Norwegian University of Science and Technology Department of Mathematical Sciences Page of 8 Exam in TMA4 Calculus 3, June 3 Solution Problem Let T : R 3 R 3 be a linear transformation such that T = 4,
Norwegian University of Science and Technology Department of Mathematical Sciences Page of 8 Exam in TMA4 Calculus 3, June 3 Solution Problem Let T : R 3 R 3 be a linear transformation such that T = 4,
General Response of Second Order System
 General Response of Second Order System Slide 1 Learning Objectives Learn to analyze a general second order system and to obtain the general solution Identify the over-damped, under-damped, and critically
General Response of Second Order System Slide 1 Learning Objectives Learn to analyze a general second order system and to obtain the general solution Identify the over-damped, under-damped, and critically
You may use a calculator, but you must show all your work in order to receive credit.
 Math 2410-010/015 Exam II April 7 th, 2017 Name: Instructions: Key Answer each question to the best of your ability. All answers must be written clearly. Be sure to erase or cross out any work that you
Math 2410-010/015 Exam II April 7 th, 2017 Name: Instructions: Key Answer each question to the best of your ability. All answers must be written clearly. Be sure to erase or cross out any work that you
2t t dt.. So the distance is (t2 +6) 3/2
 Math 8, Solutions to Review for the Final Exam Question : The distance is 5 t t + dt To work that out, integrate by parts with u t +, so that t dt du The integral is t t + dt u du u 3/ (t +) 3/ So the
Math 8, Solutions to Review for the Final Exam Question : The distance is 5 t t + dt To work that out, integrate by parts with u t +, so that t dt du The integral is t t + dt u du u 3/ (t +) 3/ So the
Math 216 Final Exam 14 December, 2012
 Math 216 Final Exam 14 December, 2012 This sample exam is provided to serve as one component of your studying for this exam in this course. Please note that it is not guaranteed to cover the material that
Math 216 Final Exam 14 December, 2012 This sample exam is provided to serve as one component of your studying for this exam in this course. Please note that it is not guaranteed to cover the material that
MATH 24 EXAM 3 SOLUTIONS
 MATH 4 EXAM 3 S Consider the equation y + ω y = cosω t (a) Find the general solution of the homogeneous equation (b) Find the particular solution of the non-homogeneous equation using the method of Undetermined
MATH 4 EXAM 3 S Consider the equation y + ω y = cosω t (a) Find the general solution of the homogeneous equation (b) Find the particular solution of the non-homogeneous equation using the method of Undetermined
systems of linear di erential If the homogeneous linear di erential system is diagonalizable,
 G. NAGY ODE October, 8.. Homogeneous Linear Differential Systems Section Objective(s): Linear Di erential Systems. Diagonalizable Systems. Real Distinct Eigenvalues. Complex Eigenvalues. Repeated Eigenvalues.
G. NAGY ODE October, 8.. Homogeneous Linear Differential Systems Section Objective(s): Linear Di erential Systems. Diagonalizable Systems. Real Distinct Eigenvalues. Complex Eigenvalues. Repeated Eigenvalues.
Problem 1: Solving a linear equation
 Math 38 Practice Final Exam ANSWERS Page Problem : Solving a linear equation Given matrix A = 2 2 3 7 4 and vector y = 5 8 9. (a) Solve Ax = y (if the equation is consistent) and write the general solution
Math 38 Practice Final Exam ANSWERS Page Problem : Solving a linear equation Given matrix A = 2 2 3 7 4 and vector y = 5 8 9. (a) Solve Ax = y (if the equation is consistent) and write the general solution
MATH 251 Examination II April 3, 2017 FORM A. Name: Student Number: Section:
 MATH 251 Examination II April 3, 2017 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 12 questions for a total of 100 points. In order to obtain full credit for partial credit problems, all work must
MATH 251 Examination II April 3, 2017 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 12 questions for a total of 100 points. In order to obtain full credit for partial credit problems, all work must
Math 115 HW #10 Solutions
 Math 11 HW #10 Solutions 1. Suppose y 1 (t and y 2 (t are both solutions of the differential equation P (ty + Q(ty + R(ty = 0. Show that, for any constants C 1 and C 2, the function C 1 y 1 (t + C 2 y
Math 11 HW #10 Solutions 1. Suppose y 1 (t and y 2 (t are both solutions of the differential equation P (ty + Q(ty + R(ty = 0. Show that, for any constants C 1 and C 2, the function C 1 y 1 (t + C 2 y
MATH 251 Examination II November 5, 2018 FORM A. Name: Student Number: Section:
 MATH 251 Examination II November 5, 2018 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 14 questions for a total of 100 points. In order to obtain full credit for partial credit problems, all work
MATH 251 Examination II November 5, 2018 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 14 questions for a total of 100 points. In order to obtain full credit for partial credit problems, all work
Differential equations
 Differential equations Math 7 Spring Practice problems for April Exam Problem Use the method of elimination to find the x-component of the general solution of x y = 6x 9x + y = x 6y 9y Soln: The system
Differential equations Math 7 Spring Practice problems for April Exam Problem Use the method of elimination to find the x-component of the general solution of x y = 6x 9x + y = x 6y 9y Soln: The system
MATH 320 INHOMOGENEOUS LINEAR SYSTEMS OF DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 MATH 2 INHOMOGENEOUS LINEAR SYSTEMS OF DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS W To find a particular solution for a linear inhomogeneous system of differential equations x Ax = ft) or of a mechanical system with external
MATH 2 INHOMOGENEOUS LINEAR SYSTEMS OF DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS W To find a particular solution for a linear inhomogeneous system of differential equations x Ax = ft) or of a mechanical system with external
Section 9.3 Phase Plane Portraits (for Planar Systems)
 Section 9.3 Phase Plane Portraits (for Planar Systems) Key Terms: Equilibrium point of planer system yꞌ = Ay o Equilibrium solution Exponential solutions o Half-line solutions Unstable solution Stable
Section 9.3 Phase Plane Portraits (for Planar Systems) Key Terms: Equilibrium point of planer system yꞌ = Ay o Equilibrium solution Exponential solutions o Half-line solutions Unstable solution Stable
π 1 = tr(a), π n = ( 1) n det(a). In particular, when n = 2 one has
 Eigen Methods Math 246, Spring 2009, Professor David Levermore Eigenpairs Let A be a real n n matrix A number λ possibly complex is an eigenvalue of A if there exists a nonzero vector v possibly complex
Eigen Methods Math 246, Spring 2009, Professor David Levermore Eigenpairs Let A be a real n n matrix A number λ possibly complex is an eigenvalue of A if there exists a nonzero vector v possibly complex
Midterm 1 NAME: QUESTION 1 / 10 QUESTION 2 / 10 QUESTION 3 / 10 QUESTION 4 / 10 QUESTION 5 / 10 QUESTION 6 / 10 QUESTION 7 / 10 QUESTION 8 / 10
 Midterm 1 NAME: RULES: You will be given the entire period (1PM-3:10PM) to complete the test. You can use one 3x5 notecard for formulas. There are no calculators nor those fancy cellular phones nor groupwork
Midterm 1 NAME: RULES: You will be given the entire period (1PM-3:10PM) to complete the test. You can use one 3x5 notecard for formulas. There are no calculators nor those fancy cellular phones nor groupwork
1 Planar rotations. Math Abstract Linear Algebra Fall 2011, section E1 Orthogonal matrices and rotations
 Math 46 - Abstract Linear Algebra Fall, section E Orthogonal matrices and rotations Planar rotations Definition: A planar rotation in R n is a linear map R: R n R n such that there is a plane P R n (through
Math 46 - Abstract Linear Algebra Fall, section E Orthogonal matrices and rotations Planar rotations Definition: A planar rotation in R n is a linear map R: R n R n such that there is a plane P R n (through
MATH 251 Final Examination August 10, 2011 FORM A. Name: Student Number: Section:
 MATH 251 Final Examination August 10, 2011 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 10 questions for a total of 150 points. In order to obtain full credit for partial credit problems, all work
MATH 251 Final Examination August 10, 2011 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 10 questions for a total of 150 points. In order to obtain full credit for partial credit problems, all work
Linear Differential Equations. Problems
 Chapter 1 Linear Differential Equations. Problems 1.1 Introduction 1.1.1 Show that the function ϕ : R R, given by the expression ϕ(t) = 2e 3t for all t R, is a solution of the Initial Value Problem x =
Chapter 1 Linear Differential Equations. Problems 1.1 Introduction 1.1.1 Show that the function ϕ : R R, given by the expression ϕ(t) = 2e 3t for all t R, is a solution of the Initial Value Problem x =
Math 331 Homework Assignment Chapter 7 Page 1 of 9
 Math Homework Assignment Chapter 7 Page of 9 Instructions: Please make sure to demonstrate every step in your calculations. Return your answers including this homework sheet back to the instructor as a
Math Homework Assignment Chapter 7 Page of 9 Instructions: Please make sure to demonstrate every step in your calculations. Return your answers including this homework sheet back to the instructor as a
Linear Systems. Class 27. c 2008 Ron Buckmire. TITLE Projection Matrices and Orthogonal Diagonalization CURRENT READING Poole 5.4
 Linear Systems Math Spring 8 c 8 Ron Buckmire Fowler 9 MWF 9: am - :5 am http://faculty.oxy.edu/ron/math//8/ Class 7 TITLE Projection Matrices and Orthogonal Diagonalization CURRENT READING Poole 5. Summary
Linear Systems Math Spring 8 c 8 Ron Buckmire Fowler 9 MWF 9: am - :5 am http://faculty.oxy.edu/ron/math//8/ Class 7 TITLE Projection Matrices and Orthogonal Diagonalization CURRENT READING Poole 5. Summary
Math 4B Notes. Written by Victoria Kala SH 6432u Office Hours: T 12:45 1:45pm Last updated 7/24/2016
 Math 4B Notes Written by Victoria Kala vtkala@math.ucsb.edu SH 6432u Office Hours: T 2:45 :45pm Last updated 7/24/206 Classification of Differential Equations The order of a differential equation is the
Math 4B Notes Written by Victoria Kala vtkala@math.ucsb.edu SH 6432u Office Hours: T 2:45 :45pm Last updated 7/24/206 Classification of Differential Equations The order of a differential equation is the
Systems of differential equations Handout
 Systems of differential equations Handout Peyam Tabrizian Friday, November 8th, This handout is meant to give you a couple more example of all the techniques discussed in chapter 9, to counterbalance all
Systems of differential equations Handout Peyam Tabrizian Friday, November 8th, This handout is meant to give you a couple more example of all the techniques discussed in chapter 9, to counterbalance all
The Exponential of a Matrix
 The Exponential of a Matrix 5-8- The solution to the exponential growth equation dx dt kx is given by x c e kt It is natural to ask whether you can solve a constant coefficient linear system x A x in a
The Exponential of a Matrix 5-8- The solution to the exponential growth equation dx dt kx is given by x c e kt It is natural to ask whether you can solve a constant coefficient linear system x A x in a
MATH 3321 Sample Questions for Exam 3. 3y y, C = Perform the indicated operations, if possible: (a) AC (b) AB (c) B + AC (d) CBA
 MATH 33 Sample Questions for Exam 3. Find x and y so that x 4 3 5x 3y + y = 5 5. x = 3/7, y = 49/7. Let A = 3 4, B = 3 5, C = 3 Perform the indicated operations, if possible: a AC b AB c B + AC d CBA AB
MATH 33 Sample Questions for Exam 3. Find x and y so that x 4 3 5x 3y + y = 5 5. x = 3/7, y = 49/7. Let A = 3 4, B = 3 5, C = 3 Perform the indicated operations, if possible: a AC b AB c B + AC d CBA AB
A = 3 B = A 1 1 matrix is the same as a number or scalar, 3 = [3].
![A = 3 B = A 1 1 matrix is the same as a number or scalar, 3 = [3]. A = 3 B = A 1 1 matrix is the same as a number or scalar, 3 = [3].](/thumbs/78/77913594.jpg) Appendix : A Very Brief Linear ALgebra Review Introduction Linear Algebra, also known as matrix theory, is an important element of all branches of mathematics Very often in this course we study the shapes
Appendix : A Very Brief Linear ALgebra Review Introduction Linear Algebra, also known as matrix theory, is an important element of all branches of mathematics Very often in this course we study the shapes
MTH 464: Computational Linear Algebra
 MTH 464: Computational Linear Algebra Lecture Outlines Exam 4 Material Prof. M. Beauregard Department of Mathematics & Statistics Stephen F. Austin State University April 15, 2018 Linear Algebra (MTH 464)
MTH 464: Computational Linear Algebra Lecture Outlines Exam 4 Material Prof. M. Beauregard Department of Mathematics & Statistics Stephen F. Austin State University April 15, 2018 Linear Algebra (MTH 464)
A VERY BRIEF LINEAR ALGEBRA REVIEW for MAP 5485 Introduction to Mathematical Biophysics Fall 2010
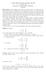 A VERY BRIEF LINEAR ALGEBRA REVIEW for MAP 5485 Introduction to Mathematical Biophysics Fall 00 Introduction Linear Algebra, also known as matrix theory, is an important element of all branches of mathematics
A VERY BRIEF LINEAR ALGEBRA REVIEW for MAP 5485 Introduction to Mathematical Biophysics Fall 00 Introduction Linear Algebra, also known as matrix theory, is an important element of all branches of mathematics
Math 20D Final Exam 8 December has eigenvalues 3, 3, 0 and find the eigenvectors associated with 3. ( 2) det
 Math D Final Exam 8 December 9. ( points) Show that the matrix 4 has eigenvalues 3, 3, and find the eigenvectors associated with 3. 4 λ det λ λ λ = (4 λ) det λ ( ) det + det λ = (4 λ)(( λ) 4) + ( λ + )
Math D Final Exam 8 December 9. ( points) Show that the matrix 4 has eigenvalues 3, 3, and find the eigenvectors associated with 3. 4 λ det λ λ λ = (4 λ) det λ ( ) det + det λ = (4 λ)(( λ) 4) + ( λ + )
Math 308 Practice Final Exam Page and vector y =
 Math 308 Practice Final Exam Page Problem : Solving a linear equation 2 0 2 5 Given matrix A = 3 7 0 0 and vector y = 8. 4 0 0 9 (a) Solve Ax = y (if the equation is consistent) and write the general solution
Math 308 Practice Final Exam Page Problem : Solving a linear equation 2 0 2 5 Given matrix A = 3 7 0 0 and vector y = 8. 4 0 0 9 (a) Solve Ax = y (if the equation is consistent) and write the general solution
Math 216 Final Exam 24 April, 2017
 Math 216 Final Exam 24 April, 2017 This sample exam is provided to serve as one component of your studying for this exam in this course. Please note that it is not guaranteed to cover the material that
Math 216 Final Exam 24 April, 2017 This sample exam is provided to serve as one component of your studying for this exam in this course. Please note that it is not guaranteed to cover the material that
Chapters 5 & 6: Theory Review: Solutions Math 308 F Spring 2015
 Chapters 5 & 6: Theory Review: Solutions Math 308 F Spring 205. If A is a 3 3 triangular matrix, explain why det(a) is equal to the product of entries on the diagonal. If A is a lower triangular or diagonal
Chapters 5 & 6: Theory Review: Solutions Math 308 F Spring 205. If A is a 3 3 triangular matrix, explain why det(a) is equal to the product of entries on the diagonal. If A is a lower triangular or diagonal
Week Quadratic forms. Principal axes theorem. Text reference: this material corresponds to parts of sections 5.5, 8.2,
 Math 051 W008 Margo Kondratieva Week 10-11 Quadratic forms Principal axes theorem Text reference: this material corresponds to parts of sections 55, 8, 83 89 Section 41 Motivation and introduction Consider
Math 051 W008 Margo Kondratieva Week 10-11 Quadratic forms Principal axes theorem Text reference: this material corresponds to parts of sections 55, 8, 83 89 Section 41 Motivation and introduction Consider
Math Ordinary Differential Equations Sample Test 3 Solutions
 Solve the following Math - Ordinary Differential Equations Sample Test Solutions (i x 2 y xy + 8y y(2 2 y (2 (ii x 2 y + xy + 4y y( 2 y ( (iii x 2 y xy + y y( 2 y ( (i The characteristic equation is m(m
Solve the following Math - Ordinary Differential Equations Sample Test Solutions (i x 2 y xy + 8y y(2 2 y (2 (ii x 2 y + xy + 4y y( 2 y ( (iii x 2 y xy + y y( 2 y ( (i The characteristic equation is m(m
Math 1302, Week 8: Oscillations
 Math 302, Week 8: Oscillations T y eq Y y = y eq + Y mg Figure : Simple harmonic motion. At equilibrium the string is of total length y eq. During the motion we let Y be the extension beyond equilibrium,
Math 302, Week 8: Oscillations T y eq Y y = y eq + Y mg Figure : Simple harmonic motion. At equilibrium the string is of total length y eq. During the motion we let Y be the extension beyond equilibrium,
Spring 2019 Exam 2 3/27/19 Time Limit: / Problem Points Score. Total: 280
 Math 307 Spring 2019 Exam 2 3/27/19 Time Limit: / Name (Print): Problem Points Score 1 15 2 20 3 35 4 30 5 10 6 20 7 20 8 20 9 20 10 20 11 10 12 10 13 10 14 10 15 10 16 10 17 10 Total: 280 Math 307 Exam
Math 307 Spring 2019 Exam 2 3/27/19 Time Limit: / Name (Print): Problem Points Score 1 15 2 20 3 35 4 30 5 10 6 20 7 20 8 20 9 20 10 20 11 10 12 10 13 10 14 10 15 10 16 10 17 10 Total: 280 Math 307 Exam
Def. (a, b) is a critical point of the autonomous system. 1 Proper node (stable or unstable) 2 Improper node (stable or unstable)
 Types of critical points Def. (a, b) is a critical point of the autonomous system Math 216 Differential Equations Kenneth Harris kaharri@umich.edu Department of Mathematics University of Michigan November
Types of critical points Def. (a, b) is a critical point of the autonomous system Math 216 Differential Equations Kenneth Harris kaharri@umich.edu Department of Mathematics University of Michigan November
MATH 312 Section 4.3: Homogeneous Linear Equations with Constant Coefficients
 MATH 312 Section 4.3: Homogeneous Linear Equations with Constant Coefficients Prof. Jonathan Duncan Walla Walla College Spring Quarter, 2007 Outline 1 Getting Started 2 Second Order Equations Two Real
MATH 312 Section 4.3: Homogeneous Linear Equations with Constant Coefficients Prof. Jonathan Duncan Walla Walla College Spring Quarter, 2007 Outline 1 Getting Started 2 Second Order Equations Two Real
Lecture Notes for Math 251: ODE and PDE. Lecture 30: 10.1 Two-Point Boundary Value Problems
 Lecture Notes for Math 251: ODE and PDE. Lecture 30: 10.1 Two-Point Boundary Value Problems Shawn D. Ryan Spring 2012 Last Time: We finished Chapter 9: Nonlinear Differential Equations and Stability. Now
Lecture Notes for Math 251: ODE and PDE. Lecture 30: 10.1 Two-Point Boundary Value Problems Shawn D. Ryan Spring 2012 Last Time: We finished Chapter 9: Nonlinear Differential Equations and Stability. Now
Math 310 Final Exam Solutions
 Math 3 Final Exam Solutions. ( pts) Consider the system of equations Ax = b where: A, b (a) Compute deta. Is A singular or nonsingular? (b) Compute A, if possible. (c) Write the row reduced echelon form
Math 3 Final Exam Solutions. ( pts) Consider the system of equations Ax = b where: A, b (a) Compute deta. Is A singular or nonsingular? (b) Compute A, if possible. (c) Write the row reduced echelon form
Math 333 Qualitative Results: Forced Harmonic Oscillators
 Math 333 Qualitative Results: Forced Harmonic Oscillators Forced Harmonic Oscillators. Recall our derivation of the second-order linear homogeneous differential equation with constant coefficients: my
Math 333 Qualitative Results: Forced Harmonic Oscillators Forced Harmonic Oscillators. Recall our derivation of the second-order linear homogeneous differential equation with constant coefficients: my
Do not write below here. Question Score Question Score Question Score
 MATH-2240 Friday, May 4, 2012, FINAL EXAMINATION 8:00AM-12:00NOON Your Instructor: Your Name: 1. Do not open this exam until you are told to do so. 2. This exam has 30 problems and 18 pages including this
MATH-2240 Friday, May 4, 2012, FINAL EXAMINATION 8:00AM-12:00NOON Your Instructor: Your Name: 1. Do not open this exam until you are told to do so. 2. This exam has 30 problems and 18 pages including this
Math 312 Lecture Notes Linear Two-dimensional Systems of Differential Equations
 Math 2 Lecture Notes Linear Two-dimensional Systems of Differential Equations Warren Weckesser Department of Mathematics Colgate University February 2005 In these notes, we consider the linear system of
Math 2 Lecture Notes Linear Two-dimensional Systems of Differential Equations Warren Weckesser Department of Mathematics Colgate University February 2005 In these notes, we consider the linear system of
spring mass equilibrium position +v max
 Lecture 20 Oscillations (Chapter 11) Review of Simple Harmonic Motion Parameters Graphical Representation of SHM Review of mass-spring pendulum periods Let s review Simple Harmonic Motion. Recall we used
Lecture 20 Oscillations (Chapter 11) Review of Simple Harmonic Motion Parameters Graphical Representation of SHM Review of mass-spring pendulum periods Let s review Simple Harmonic Motion. Recall we used
Exam 2 Study Guide: MATH 2080: Summer I 2016
 Exam Study Guide: MATH 080: Summer I 016 Dr. Peterson June 7 016 First Order Problems Solve the following IVP s by inspection (i.e. guessing). Sketch a careful graph of each solution. (a) u u; u(0) 0.
Exam Study Guide: MATH 080: Summer I 016 Dr. Peterson June 7 016 First Order Problems Solve the following IVP s by inspection (i.e. guessing). Sketch a careful graph of each solution. (a) u u; u(0) 0.
Linear algebra and differential equations (Math 54): Lecture 20
 Linear algebra and differential equations (Math 54): Lecture 20 Vivek Shende April 7, 2016 Hello and welcome to class! Last time We started discussing differential equations. We found a complete set of
Linear algebra and differential equations (Math 54): Lecture 20 Vivek Shende April 7, 2016 Hello and welcome to class! Last time We started discussing differential equations. We found a complete set of
MATH 251 Final Examination December 16, 2014 FORM A. Name: Student Number: Section:
 MATH 2 Final Examination December 6, 204 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 7 questions for a total of 0 points. In order to obtain full credit for partial credit problems, all work must
MATH 2 Final Examination December 6, 204 FORM A Name: Student Number: Section: This exam has 7 questions for a total of 0 points. In order to obtain full credit for partial credit problems, all work must
INHOMOGENEOUS LINEAR SYSTEMS OF DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 INHOMOGENEOUS LINEAR SYSTEMS OF DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Definitions and a general fact If A is an n n matrix and f(t) is some given vector function, then the system of differential equations () x (t) Ax(t)
INHOMOGENEOUS LINEAR SYSTEMS OF DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Definitions and a general fact If A is an n n matrix and f(t) is some given vector function, then the system of differential equations () x (t) Ax(t)
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 9.9. MATRICES 9 (Modal & spectral matrices) A.J.Hobson
 JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 9.9 MATRICES 9 (Modal & spectral matrices) by A.J.Hobson 9.9. Assumptions and definitions 9.9.2 Diagonalisation of a matrix 9.9.3 Exercises 9.9.4 Answers to exercises UNIT 9.9
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 9.9 MATRICES 9 (Modal & spectral matrices) by A.J.Hobson 9.9. Assumptions and definitions 9.9.2 Diagonalisation of a matrix 9.9.3 Exercises 9.9.4 Answers to exercises UNIT 9.9
1. Select the unique answer (choice) for each problem. Write only the answer.
 MATH 5 Practice Problem Set Spring 7. Select the unique answer (choice) for each problem. Write only the answer. () Determine all the values of a for which the system has infinitely many solutions: x +
MATH 5 Practice Problem Set Spring 7. Select the unique answer (choice) for each problem. Write only the answer. () Determine all the values of a for which the system has infinitely many solutions: x +
Second Order Systems
 Second Order Systems independent energy storage elements => Resonance: inertance & capacitance trade energy, kinetic to potential Example: Automobile Suspension x z vertical motions suspension spring shock
Second Order Systems independent energy storage elements => Resonance: inertance & capacitance trade energy, kinetic to potential Example: Automobile Suspension x z vertical motions suspension spring shock
Work sheet / Things to know. Chapter 3
 MATH 251 Work sheet / Things to know 1. Second order linear differential equation Standard form: Chapter 3 What makes it homogeneous? We will, for the most part, work with equations with constant coefficients
MATH 251 Work sheet / Things to know 1. Second order linear differential equation Standard form: Chapter 3 What makes it homogeneous? We will, for the most part, work with equations with constant coefficients
1 otherwise. Note that the area of the pulse is one. The Dirac delta function (a.k.a. the impulse) can be defined using the pulse as follows:
 The Dirac delta function There is a function called the pulse: { if t > Π(t) = 2 otherwise. Note that the area of the pulse is one. The Dirac delta function (a.k.a. the impulse) can be defined using the
The Dirac delta function There is a function called the pulse: { if t > Π(t) = 2 otherwise. Note that the area of the pulse is one. The Dirac delta function (a.k.a. the impulse) can be defined using the
Systems of Linear ODEs
 P a g e 1 Systems of Linear ODEs Systems of ordinary differential equations can be solved in much the same way as discrete dynamical systems if the differential equations are linear. We will focus here
P a g e 1 Systems of Linear ODEs Systems of ordinary differential equations can be solved in much the same way as discrete dynamical systems if the differential equations are linear. We will focus here
Perturbation Theory 1
 Perturbation Theory 1 1 Expansion of Complete System Let s take a look of an expansion for the function in terms of the complete system : (1) In general, this expansion is possible for any complete set.
Perturbation Theory 1 1 Expansion of Complete System Let s take a look of an expansion for the function in terms of the complete system : (1) In general, this expansion is possible for any complete set.
Math 215/255: Elementary Differential Equations I Harish N Dixit, Department of Mathematics, UBC
 Math 215/255: Elementary Differential Equations I Harish N Dixit, Department of Mathematics, UBC First Order Equations Linear Equations y + p(x)y = q(x) Write the equation in the standard form, Calculate
Math 215/255: Elementary Differential Equations I Harish N Dixit, Department of Mathematics, UBC First Order Equations Linear Equations y + p(x)y = q(x) Write the equation in the standard form, Calculate
Math 2142 Homework 5 Part 1 Solutions
 Math 2142 Homework 5 Part 1 Solutions Problem 1. For the following homogeneous second order differential equations, give the general solution and the particular solution satisfying the given initial conditions.
Math 2142 Homework 5 Part 1 Solutions Problem 1. For the following homogeneous second order differential equations, give the general solution and the particular solution satisfying the given initial conditions.
Find the general solution of the system y = Ay, where
 Math Homework # March, 9..3. Find the general solution of the system y = Ay, where 5 Answer: The matrix A has characteristic polynomial p(λ = λ + 7λ + = λ + 3(λ +. Hence the eigenvalues are λ = 3and λ
Math Homework # March, 9..3. Find the general solution of the system y = Ay, where 5 Answer: The matrix A has characteristic polynomial p(λ = λ + 7λ + = λ + 3(λ +. Hence the eigenvalues are λ = 3and λ
Old Math 330 Exams. David M. McClendon. Department of Mathematics Ferris State University
 Old Math 330 Exams David M. McClendon Department of Mathematics Ferris State University Last updated to include exams from Fall 07 Contents Contents General information about these exams 3 Exams from Fall
Old Math 330 Exams David M. McClendon Department of Mathematics Ferris State University Last updated to include exams from Fall 07 Contents Contents General information about these exams 3 Exams from Fall
Math 21b. Review for Final Exam
 Math 21b. Review for Final Exam Thomas W. Judson Spring 2003 General Information The exam is on Thursday, May 15 from 2:15 am to 5:15 pm in Jefferson 250. Please check with the registrar if you have a
Math 21b. Review for Final Exam Thomas W. Judson Spring 2003 General Information The exam is on Thursday, May 15 from 2:15 am to 5:15 pm in Jefferson 250. Please check with the registrar if you have a
Lecture Notes for Math 251: ODE and PDE. Lecture 12: 3.3 Complex Roots of the Characteristic Equation
 Lecture Notes for Math 21: ODE and PDE. Lecture 12: 3.3 Complex Roots of the Characteristic Equation Shawn D. Ryan Spring 2012 1 Complex Roots of the Characteristic Equation Last Time: We considered the
Lecture Notes for Math 21: ODE and PDE. Lecture 12: 3.3 Complex Roots of the Characteristic Equation Shawn D. Ryan Spring 2012 1 Complex Roots of the Characteristic Equation Last Time: We considered the
MATH 423 Linear Algebra II Lecture 33: Diagonalization of normal operators.
 MATH 423 Linear Algebra II Lecture 33: Diagonalization of normal operators. Adjoint operator and adjoint matrix Given a linear operator L on an inner product space V, the adjoint of L is a transformation
MATH 423 Linear Algebra II Lecture 33: Diagonalization of normal operators. Adjoint operator and adjoint matrix Given a linear operator L on an inner product space V, the adjoint of L is a transformation
Answers and Hints to Review Questions for Test (a) Find the general solution to the linear system of differential equations Y = 2 ± 3i.
 Answers and Hints to Review Questions for Test 3 (a) Find the general solution to the linear system of differential equations [ dy 3 Y 3 [ (b) Find the specific solution that satisfies Y (0) = (c) What
Answers and Hints to Review Questions for Test 3 (a) Find the general solution to the linear system of differential equations [ dy 3 Y 3 [ (b) Find the specific solution that satisfies Y (0) = (c) What
MAT187H1F Lec0101 Burbulla
 Spring 2017 Second Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equation DE: A(x) d 2 y dx 2 + B(x)dy dx + C(x)y = 0 This equation is called second order because it includes the second derivative of y; it is
Spring 2017 Second Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equation DE: A(x) d 2 y dx 2 + B(x)dy dx + C(x)y = 0 This equation is called second order because it includes the second derivative of y; it is
Autonomous Systems and Stability
 LECTURE 8 Autonomous Systems and Stability An autonomous system is a system of ordinary differential equations of the form 1 1 ( 1 ) 2 2 ( 1 ). ( 1 ) or, in vector notation, x 0 F (x) That is to say, an
LECTURE 8 Autonomous Systems and Stability An autonomous system is a system of ordinary differential equations of the form 1 1 ( 1 ) 2 2 ( 1 ). ( 1 ) or, in vector notation, x 0 F (x) That is to say, an
QUANTUM MECHANICS I PHYS 516. Solutions to Problem Set # 5
 QUANTUM MECHANICS I PHYS 56 Solutions to Problem Set # 5. Crossed E and B fields: A hydrogen atom in the N 2 level is subject to crossed electric and magnetic fields. Choose your coordinate axes to make
QUANTUM MECHANICS I PHYS 56 Solutions to Problem Set # 5. Crossed E and B fields: A hydrogen atom in the N 2 level is subject to crossed electric and magnetic fields. Choose your coordinate axes to make
Math 5BI: Problem Set 6 Gradient dynamical systems
 Math 5BI: Problem Set 6 Gradient dynamical systems April 25, 2007 Recall that if f(x) = f(x 1, x 2,..., x n ) is a smooth function of n variables, the gradient of f is the vector field f(x) = ( f)(x 1,
Math 5BI: Problem Set 6 Gradient dynamical systems April 25, 2007 Recall that if f(x) = f(x 1, x 2,..., x n ) is a smooth function of n variables, the gradient of f is the vector field f(x) = ( f)(x 1,
21.55 Worksheet 7 - preparation problems - question 1:
 Dynamics 76. Worksheet 7 - preparation problems - question : A coupled oscillator with two masses m and positions x (t) and x (t) is described by the following equations of motion: ẍ x + 8x ẍ x +x A. Write
Dynamics 76. Worksheet 7 - preparation problems - question : A coupled oscillator with two masses m and positions x (t) and x (t) is described by the following equations of motion: ẍ x + 8x ẍ x +x A. Write
Modal Decomposition and the Time-Domain Response of Linear Systems 1
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING.151 Advanced System Dynamics and Control Modal Decomposition and the Time-Domain Response of Linear Systems 1 In a previous handout
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING.151 Advanced System Dynamics and Control Modal Decomposition and the Time-Domain Response of Linear Systems 1 In a previous handout
Designing Information Devices and Systems II Spring 2018 J. Roychowdhury and M. Maharbiz Discussion 2A
 EECS 6B Designing Information Devices an Systems II Spring 208 J. Roychowhury an M. Maharbiz Discussion 2A Secon-Orer Differential Equations Secon-orer ifferential equations are ifferential equations of
EECS 6B Designing Information Devices an Systems II Spring 208 J. Roychowhury an M. Maharbiz Discussion 2A Secon-Orer Differential Equations Secon-orer ifferential equations are ifferential equations of
Notes on singular value decomposition for Math 54. Recall that if A is a symmetric n n matrix, then A has real eigenvalues A = P DP 1 A = P DP T.
 Notes on singular value decomposition for Math 54 Recall that if A is a symmetric n n matrix, then A has real eigenvalues λ 1,, λ n (possibly repeated), and R n has an orthonormal basis v 1,, v n, where
Notes on singular value decomposition for Math 54 Recall that if A is a symmetric n n matrix, then A has real eigenvalues λ 1,, λ n (possibly repeated), and R n has an orthonormal basis v 1,, v n, where
Pre-Calculus Exam 2009 University of Houston Math Contest. Name: School: There is no penalty for guessing.
 Pre-Calculus Exam 009 University of Houston Math Contest Name: School: Please read the questions carefully and give a clear indication of your answer on each question. There is no penalty for guessing.
Pre-Calculus Exam 009 University of Houston Math Contest Name: School: Please read the questions carefully and give a clear indication of your answer on each question. There is no penalty for guessing.
APPPHYS 217 Tuesday 6 April 2010
 APPPHYS 7 Tuesday 6 April Stability and input-output performance: second-order systems Here we present a detailed example to draw connections between today s topics and our prior review of linear algebra
APPPHYS 7 Tuesday 6 April Stability and input-output performance: second-order systems Here we present a detailed example to draw connections between today s topics and our prior review of linear algebra
