Bayesian Prediction of Code Output. ASA Albuquerque Chapter Short Course October 2014
|
|
|
- Christopher Hicks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bayesian Prediction of Code Output ASA Albuquerque Chapter Short Course October 2014
2 Abstract This presentation summarizes Bayesian prediction methodology for the Gaussian process (GP) surrogate representation of computer model output. The conditional predictive distribution for predicting unsampled code output is derived, followed by posterior distributions for GP regression and precision parameters based on two common prior distribution assumptions. These results lead to a description of the predictive distribution itself when the GP correlation parameters are assumed known. In the case of unknown correlation parameters, their posterior distribution is provided. Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) techniques are introduced as a means of sampling this posterior, and this results in a Monte Carlo method of sampling the predictive distribution when the GP correlation parameters are unknown. Two examples of Bayesian prediction of unsampled code output are provided to illustrate the methods discussed. 2
3 Bayesian Prediction: Framework Inference based on predictive distribution ytr s =(x tr 1,y s (x tr 1 )),...,(x tr n,y s (x tr n )) yte s =(x te 1,y s (x te 1 )),...,(x te n p,y s (x te n p )) training data test data Predictive distribution Z p( yte s ytr s )= Z = All uncertain model parameters p( y s te, y s tr ) d p( y s te y s tr, ) ( y s tr ) d Derived from process modeling assumptions, e.g. Gaussian process Derived analytically (conjugate prior) or sampled via MCMC 3
4 Bayesian Prediction: Sampling Distribution Joint Sampling Distribution (test and training data) (Yte s, Ytr) s Y s x te 1,...,Y s x te n p,y s x tr 1,...,Y s x tr n F = Fte N np +n F, F tr (n p+n) k regression matrix R = 1 R (given (β, λ, R)) Rte R te,tr R T te,tr R tr correlation (n p+n) (n p+n) Conditional Distribution (test data given training data) matrix p ( y s te y s tr,, ) is N np (m (y s te y s tr,, ),V (y s te y s tr,, )) m (y s te y s tr,, )=F te + R te,tr R 1 tr (y s tr F tr ) V (y s te y s tr,, )= 1 R te R te,tr R 1 tr R T te,tr 4
5 Prior Distributions: Case I (Informative) ( )isn k Bayesian Prediction: Priors and Posteriors I 0, ( ) is Gamma(a, b) 1 1 Posterior Distributions ( ytr) s is Gamma(a 1,b 1 ) a 1 =(2a + n)/2 b 1 = 2b + y s tr F tr b T R 1 tr ytr s F tr b T + b 0 1 b 0 /2 b = F T tr Rtr 1 1 F tr F T tr Rtr 1 ytr s and = 1 + F T trrtr 1 1 F tr ( ytr s )ist k 2a 1, bµ, b 1 /a1 b b 1 = + F T trr 1 tr F tr and bµ = b h F T trr 1 tr F tr b + 0 i 5
6 Prior Distributions: Case II (Noninformative) Posterior Distributions ( ytr) s is Gamma(a 1,b 1 ) Bayesian Prediction: Priors and Posteriors II ( ) / 1 independent of ( ) is Gamma(a, b) a 1 =(2a + n b 1 = 2b + k)/2 ytr s F tr b T R 1 tr y s tr F tr b /2 b = F T tr Rtr 1 1 F tr F T tr Rtr 1 ytr s ( ytr s )ist k 2a 1, b,b 1 F T trrtr 1 F tr Results for Jeffreys Prior Distribution (, ) / (1/ ): Set a = b =0 1 /a1 6
7 Predictive Distribution Bayesian Prediction: Predictive Distribution p( y s te y s tr )ist np (2a 1,µ te,b 1 te /a 1 ) µ te = F te bµ + R te,tr R 1 tr (y s tr F tr bµ) te = R te R te,tr R 1 tr R T te,tr + H te b H T te! Here, H te = F te R te,tr R 1 tr F tr! For Case I priors, bµ and b given on slide 54 For Case II priors, bµ = b and b = F T trrtr 1 1! F tr! For Je reys prior, µ te is the BLUP and te the associated prediction uncertainty 7
8 Bayesian Prediction: Uncertain Correlation Parameters Parametric Correlation Functions φ: Denotes uncertain correlation function parameters For example, consider the Gaussian correlation function parameterized by correlation length 0 < ρ < 1:# R ( u, v )=exp " 4 # kx log ( i )(u i v i ) 2 ; u, v 2 [0, 1] k i=1 =( 1,..., k ) Obtained from results on next slide Predictive Distribution Z p ( yte s ytr s )= p ( yte s ytr, s ) ( ytr s ) d Obtained from results on slide 7 8
9 Bayesian Prediction: Correlation Posterior Correlation Parameter Posterior Distribution ( ytr s ( ) ) / b a 1 1 R tr 1/2 F T trrtr 1 1/2 F tr 1/2 For ( ) / 1, use =1 Example: Gaussian Correlation ( 1,..., k ) independent i Beta ( a,b ) a =1, b =0.1 =) e ect sparsity ( 1,..., M ) sampled from ( y s tr ) via MCMC 9
10 Objective: Generate a sample from the target π(x) Algorithm: Repeat for j = 1, 2,, M proposal density Generate y from q(x j,!) and u from Uniform(0, 1) If ( h i min (y)q(y,x) u apple (x j, y) for (x, y) = (x)q(x,y), 1, if (x)q(x, y) > 0 1, otherwise set x j+1 = y Else, set x j+1 = x j Return values x 1,, x M Implementation: Discard initial m 0 samples as ``burn-in (x, y) =min MCMC: Metropolis-Hastings apple (y) (x), 1 Metropolis: symmetric proposal distribution q(y,x) = q(x,y) Challenge is choosing q(x,!) for effective mixing 23.4% multi-parameter, 44% single parameter, 57.4% Langevin diffusion 10
11 Bayesian Prediction: Estimation of Predictive Distribution Predictive Distribution Z p ( yte s ytr s )= p ( yte s ytr s, ) ( ytr s ) d Predictive Distribution Estimation Given ( 1,..., M ) ( ytr s ) sampled via MCMC, p ( y s te y s tr ) 1 M µ s te = 1 M s te = 1 M MX p ( yte s ytr, s i ) i=1 MX i=1 MX i=1 µ i te In previous example with uncertain correlation parameters (ξ = φ), estimated predictive distribution is a mixture of t-distributions h i te + µ i te µ s te µ i te µ s te T i 11
12 p ( y s te y s tr )= Z Bayesian Prediction: Damped Sine Example p ( y s te y s tr, ) ( y s tr ) d Realizations Priors: β = 0; λ ~ Gamma(5,5);# φ ~ Beta(1,0.1) y predictive standard error MAP Bayes Data x Small variation in conditional means compared with average conditional variances s te = v u t 1 M x MX h i=1 i te 2 + µ i te µ s te 2 i 12
13 Observed Failure Depth RMSPE = 17.3 r = 0.98 RMSPE = 17.9 r = 0.98 Bayesian Prediction of 174 Failure Depths Bayesian Prediction of y(x) Bayesian Prediction: Sheet Metal Pockets Example 6 code inputs 60 training runs 174 test runs Bayesian Prediction Standard Error REML EBLUP Standard Deviation Bayesian prediction standard errors tend to be larger than REML-EBLUP standard errors Prior Distributions: β = 0 λ ~ Gamma(5,5) ρ ~ Beta(5,1) Frequentist coverage: Nominal: 95% REML-EBLUP: 61% Bayes: 71% Estimated Bayesian Standard Deviation REML-EBLUP Prediction Standard Error 13
14 Bayesian prediction based on the predictive distribution: π( y new y current ) Derive analytically when possible Bayesian Prediction: Summary Realizations generated from parameter posterior (MCMC) and conditional predictive samples Many MCMC algorithms implemented in software MCMCpack, mcmc, adaptmcmc, AMCMC in R OpenBUGS, WinBUGS Delayed Rejection Adaptive Metropolis R package coda provides a suite of MCMC diagnostic tools 14
15 Andrieu, C. and Thoms, J. (2008). A tutorial on adaptive MCMC, Statistics and Computing, 18, Casella, G. and George, E. (1992). Explaining the Gibbs sampler, The American Statistician, 46, Chib, S. and Greenberg, E. (1995). Understanding the Metropolis-Hastings algorithm, The American Statistician, 49, Currin, C., Mitchell, T.J., Morris, M.D., and Ylvisaker, D. (1991). Bayesian prediction of deterministic functions, with applications to the design and analysis of computer experiments. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 86, Haario, H., Laine, M., and Mira, A. (2006). DRAM: Efficient adaptive MCMC, Statistics and Computing, 16, O Hagan, A. (1994). Kendall s Advanced Theory of Statistics, 2B, Bayesian Inference. London: Edward Arnold. Robert, C. and Casella, G. (2004). Monte Carlo Statistical Methods. New York: Springer. References Santner, T.J., Williams, B.J., and Notz, W.I. (2003). The Design and Analysis of Computer Experiments. New York: Springer. 15
Computer Practical: Metropolis-Hastings-based MCMC
 Computer Practical: Metropolis-Hastings-based MCMC Andrea Arnold and Franz Hamilton North Carolina State University July 30, 2016 A. Arnold / F. Hamilton (NCSU) MH-based MCMC July 30, 2016 1 / 19 Markov
Computer Practical: Metropolis-Hastings-based MCMC Andrea Arnold and Franz Hamilton North Carolina State University July 30, 2016 A. Arnold / F. Hamilton (NCSU) MH-based MCMC July 30, 2016 1 / 19 Markov
eqr094: Hierarchical MCMC for Bayesian System Reliability
 eqr094: Hierarchical MCMC for Bayesian System Reliability Alyson G. Wilson Statistical Sciences Group, Los Alamos National Laboratory P.O. Box 1663, MS F600 Los Alamos, NM 87545 USA Phone: 505-667-9167
eqr094: Hierarchical MCMC for Bayesian System Reliability Alyson G. Wilson Statistical Sciences Group, Los Alamos National Laboratory P.O. Box 1663, MS F600 Los Alamos, NM 87545 USA Phone: 505-667-9167
(5) Multi-parameter models - Gibbs sampling. ST440/540: Applied Bayesian Analysis
 Summarizing a posterior Given the data and prior the posterior is determined Summarizing the posterior gives parameter estimates, intervals, and hypothesis tests Most of these computations are integrals
Summarizing a posterior Given the data and prior the posterior is determined Summarizing the posterior gives parameter estimates, intervals, and hypothesis tests Most of these computations are integrals
Advanced Statistical Modelling
 Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) Methods and Their Applications in Bayesian Statistics School of Technology and Business Studies/Statistics Dalarna University Borlänge, Sweden. Feb. 05, 2014. Outlines 1
Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) Methods and Their Applications in Bayesian Statistics School of Technology and Business Studies/Statistics Dalarna University Borlänge, Sweden. Feb. 05, 2014. Outlines 1
Hastings-within-Gibbs Algorithm: Introduction and Application on Hierarchical Model
 UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS AT SAN ANTONIO Hastings-within-Gibbs Algorithm: Introduction and Application on Hierarchical Model Liang Jing April 2010 1 1 ABSTRACT In this paper, common MCMC algorithms are introduced
UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS AT SAN ANTONIO Hastings-within-Gibbs Algorithm: Introduction and Application on Hierarchical Model Liang Jing April 2010 1 1 ABSTRACT In this paper, common MCMC algorithms are introduced
Markov Chain Monte Carlo methods
 Markov Chain Monte Carlo methods Tomas McKelvey and Lennart Svensson Signal Processing Group Department of Signals and Systems Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden November 26, 2012 Today s learning
Markov Chain Monte Carlo methods Tomas McKelvey and Lennart Svensson Signal Processing Group Department of Signals and Systems Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden November 26, 2012 Today s learning
I. Bayesian econometrics
 I. Bayesian econometrics A. Introduction B. Bayesian inference in the univariate regression model C. Statistical decision theory D. Large sample results E. Diffuse priors F. Numerical Bayesian methods
I. Bayesian econometrics A. Introduction B. Bayesian inference in the univariate regression model C. Statistical decision theory D. Large sample results E. Diffuse priors F. Numerical Bayesian methods
CPSC 540: Machine Learning
 CPSC 540: Machine Learning MCMC and Non-Parametric Bayes Mark Schmidt University of British Columbia Winter 2016 Admin I went through project proposals: Some of you got a message on Piazza. No news is
CPSC 540: Machine Learning MCMC and Non-Parametric Bayes Mark Schmidt University of British Columbia Winter 2016 Admin I went through project proposals: Some of you got a message on Piazza. No news is
Ronald Christensen. University of New Mexico. Albuquerque, New Mexico. Wesley Johnson. University of California, Irvine. Irvine, California
 Texts in Statistical Science Bayesian Ideas and Data Analysis An Introduction for Scientists and Statisticians Ronald Christensen University of New Mexico Albuquerque, New Mexico Wesley Johnson University
Texts in Statistical Science Bayesian Ideas and Data Analysis An Introduction for Scientists and Statisticians Ronald Christensen University of New Mexico Albuquerque, New Mexico Wesley Johnson University
Kobe University Repository : Kernel
 Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI URL Note on the Sampling Distribution for the Metropolis-
Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI URL Note on the Sampling Distribution for the Metropolis-
Monte Carlo in Bayesian Statistics
 Monte Carlo in Bayesian Statistics Matthew Thomas SAMBa - University of Bath m.l.thomas@bath.ac.uk December 4, 2014 Matthew Thomas (SAMBa) Monte Carlo in Bayesian Statistics December 4, 2014 1 / 16 Overview
Monte Carlo in Bayesian Statistics Matthew Thomas SAMBa - University of Bath m.l.thomas@bath.ac.uk December 4, 2014 Matthew Thomas (SAMBa) Monte Carlo in Bayesian Statistics December 4, 2014 1 / 16 Overview
Hierarchical models. Dr. Jarad Niemi. August 31, Iowa State University. Jarad Niemi (Iowa State) Hierarchical models August 31, / 31
 Hierarchical models Dr. Jarad Niemi Iowa State University August 31, 2017 Jarad Niemi (Iowa State) Hierarchical models August 31, 2017 1 / 31 Normal hierarchical model Let Y ig N(θ g, σ 2 ) for i = 1,...,
Hierarchical models Dr. Jarad Niemi Iowa State University August 31, 2017 Jarad Niemi (Iowa State) Hierarchical models August 31, 2017 1 / 31 Normal hierarchical model Let Y ig N(θ g, σ 2 ) for i = 1,...,
CSC 2541: Bayesian Methods for Machine Learning
 CSC 2541: Bayesian Methods for Machine Learning Radford M. Neal, University of Toronto, 2011 Lecture 3 More Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods The Metropolis algorithm isn t the only way to do MCMC. We ll
CSC 2541: Bayesian Methods for Machine Learning Radford M. Neal, University of Toronto, 2011 Lecture 3 More Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods The Metropolis algorithm isn t the only way to do MCMC. We ll
Sampling Methods (11/30/04)
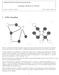 CS281A/Stat241A: Statistical Learning Theory Sampling Methods (11/30/04) Lecturer: Michael I. Jordan Scribe: Jaspal S. Sandhu 1 Gibbs Sampling Figure 1: Undirected and directed graphs, respectively, with
CS281A/Stat241A: Statistical Learning Theory Sampling Methods (11/30/04) Lecturer: Michael I. Jordan Scribe: Jaspal S. Sandhu 1 Gibbs Sampling Figure 1: Undirected and directed graphs, respectively, with
Bayesian Inference in GLMs. Frequentists typically base inferences on MLEs, asymptotic confidence
 Bayesian Inference in GLMs Frequentists typically base inferences on MLEs, asymptotic confidence limits, and log-likelihood ratio tests Bayesians base inferences on the posterior distribution of the unknowns
Bayesian Inference in GLMs Frequentists typically base inferences on MLEs, asymptotic confidence limits, and log-likelihood ratio tests Bayesians base inferences on the posterior distribution of the unknowns
Bayesian Inference and MCMC
 Bayesian Inference and MCMC Aryan Arbabi Partly based on MCMC slides from CSC412 Fall 2018 1 / 18 Bayesian Inference - Motivation Consider we have a data set D = {x 1,..., x n }. E.g each x i can be the
Bayesian Inference and MCMC Aryan Arbabi Partly based on MCMC slides from CSC412 Fall 2018 1 / 18 Bayesian Inference - Motivation Consider we have a data set D = {x 1,..., x n }. E.g each x i can be the
Bayesian Methods for Machine Learning
 Bayesian Methods for Machine Learning CS 584: Big Data Analytics Material adapted from Radford Neal s tutorial (http://ftp.cs.utoronto.ca/pub/radford/bayes-tut.pdf), Zoubin Ghahramni (http://hunch.net/~coms-4771/zoubin_ghahramani_bayesian_learning.pdf),
Bayesian Methods for Machine Learning CS 584: Big Data Analytics Material adapted from Radford Neal s tutorial (http://ftp.cs.utoronto.ca/pub/radford/bayes-tut.pdf), Zoubin Ghahramni (http://hunch.net/~coms-4771/zoubin_ghahramani_bayesian_learning.pdf),
Bayesian philosophy Bayesian computation Bayesian software. Bayesian Statistics. Petter Mostad. Chalmers. April 6, 2017
 Chalmers April 6, 2017 Bayesian philosophy Bayesian philosophy Bayesian statistics versus classical statistics: War or co-existence? Classical statistics: Models have variables and parameters; these are
Chalmers April 6, 2017 Bayesian philosophy Bayesian philosophy Bayesian statistics versus classical statistics: War or co-existence? Classical statistics: Models have variables and parameters; these are
Markov Chain Monte Carlo
 Markov Chain Monte Carlo Recall: To compute the expectation E ( h(y ) ) we use the approximation E(h(Y )) 1 n n h(y ) t=1 with Y (1),..., Y (n) h(y). Thus our aim is to sample Y (1),..., Y (n) from f(y).
Markov Chain Monte Carlo Recall: To compute the expectation E ( h(y ) ) we use the approximation E(h(Y )) 1 n n h(y ) t=1 with Y (1),..., Y (n) h(y). Thus our aim is to sample Y (1),..., Y (n) from f(y).
The Bayesian Choice. Christian P. Robert. From Decision-Theoretic Foundations to Computational Implementation. Second Edition.
 Christian P. Robert The Bayesian Choice From Decision-Theoretic Foundations to Computational Implementation Second Edition With 23 Illustrations ^Springer" Contents Preface to the Second Edition Preface
Christian P. Robert The Bayesian Choice From Decision-Theoretic Foundations to Computational Implementation Second Edition With 23 Illustrations ^Springer" Contents Preface to the Second Edition Preface
Modelling Operational Risk Using Bayesian Inference
 Pavel V. Shevchenko Modelling Operational Risk Using Bayesian Inference 4y Springer 1 Operational Risk and Basel II 1 1.1 Introduction to Operational Risk 1 1.2 Defining Operational Risk 4 1.3 Basel II
Pavel V. Shevchenko Modelling Operational Risk Using Bayesian Inference 4y Springer 1 Operational Risk and Basel II 1 1.1 Introduction to Operational Risk 1 1.2 Defining Operational Risk 4 1.3 Basel II
F denotes cumulative density. denotes probability density function; (.)
 BAYESIAN ANALYSIS: FOREWORDS Notation. System means the real thing and a model is an assumed mathematical form for the system.. he probability model class M contains the set of the all admissible models
BAYESIAN ANALYSIS: FOREWORDS Notation. System means the real thing and a model is an assumed mathematical form for the system.. he probability model class M contains the set of the all admissible models
Probabilistic Machine Learning
 Probabilistic Machine Learning Bayesian Nets, MCMC, and more Marek Petrik 4/18/2017 Based on: P. Murphy, K. (2012). Machine Learning: A Probabilistic Perspective. Chapter 10. Conditional Independence Independent
Probabilistic Machine Learning Bayesian Nets, MCMC, and more Marek Petrik 4/18/2017 Based on: P. Murphy, K. (2012). Machine Learning: A Probabilistic Perspective. Chapter 10. Conditional Independence Independent
Probabilistic Graphical Models Lecture 17: Markov chain Monte Carlo
 Probabilistic Graphical Models Lecture 17: Markov chain Monte Carlo Andrew Gordon Wilson www.cs.cmu.edu/~andrewgw Carnegie Mellon University March 18, 2015 1 / 45 Resources and Attribution Image credits,
Probabilistic Graphical Models Lecture 17: Markov chain Monte Carlo Andrew Gordon Wilson www.cs.cmu.edu/~andrewgw Carnegie Mellon University March 18, 2015 1 / 45 Resources and Attribution Image credits,
Advances and Applications in Perfect Sampling
 and Applications in Perfect Sampling Ph.D. Dissertation Defense Ulrike Schneider advisor: Jem Corcoran May 8, 2003 Department of Applied Mathematics University of Colorado Outline Introduction (1) MCMC
and Applications in Perfect Sampling Ph.D. Dissertation Defense Ulrike Schneider advisor: Jem Corcoran May 8, 2003 Department of Applied Mathematics University of Colorado Outline Introduction (1) MCMC
Introduction to Markov Chain Monte Carlo & Gibbs Sampling
 Introduction to Markov Chain Monte Carlo & Gibbs Sampling Prof. Nicholas Zabaras Sibley School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering 101 Frank H. T. Rhodes Hall Ithaca, NY 14853-3801 Email: zabaras@cornell.edu
Introduction to Markov Chain Monte Carlo & Gibbs Sampling Prof. Nicholas Zabaras Sibley School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering 101 Frank H. T. Rhodes Hall Ithaca, NY 14853-3801 Email: zabaras@cornell.edu
Stat 451 Lecture Notes Markov Chain Monte Carlo. Ryan Martin UIC
 Stat 451 Lecture Notes 07 12 Markov Chain Monte Carlo Ryan Martin UIC www.math.uic.edu/~rgmartin 1 Based on Chapters 8 9 in Givens & Hoeting, Chapters 25 27 in Lange 2 Updated: April 4, 2016 1 / 42 Outline
Stat 451 Lecture Notes 07 12 Markov Chain Monte Carlo Ryan Martin UIC www.math.uic.edu/~rgmartin 1 Based on Chapters 8 9 in Givens & Hoeting, Chapters 25 27 in Lange 2 Updated: April 4, 2016 1 / 42 Outline
Statistical Methods in Particle Physics Lecture 1: Bayesian methods
 Statistical Methods in Particle Physics Lecture 1: Bayesian methods SUSSP65 St Andrews 16 29 August 2009 Glen Cowan Physics Department Royal Holloway, University of London g.cowan@rhul.ac.uk www.pp.rhul.ac.uk/~cowan
Statistical Methods in Particle Physics Lecture 1: Bayesian methods SUSSP65 St Andrews 16 29 August 2009 Glen Cowan Physics Department Royal Holloway, University of London g.cowan@rhul.ac.uk www.pp.rhul.ac.uk/~cowan
Contents. Part I: Fundamentals of Bayesian Inference 1
 Contents Preface xiii Part I: Fundamentals of Bayesian Inference 1 1 Probability and inference 3 1.1 The three steps of Bayesian data analysis 3 1.2 General notation for statistical inference 4 1.3 Bayesian
Contents Preface xiii Part I: Fundamentals of Bayesian Inference 1 1 Probability and inference 3 1.1 The three steps of Bayesian data analysis 3 1.2 General notation for statistical inference 4 1.3 Bayesian
Lecture: Gaussian Process Regression. STAT 6474 Instructor: Hongxiao Zhu
 Lecture: Gaussian Process Regression STAT 6474 Instructor: Hongxiao Zhu Motivation Reference: Marc Deisenroth s tutorial on Robot Learning. 2 Fast Learning for Autonomous Robots with Gaussian Processes
Lecture: Gaussian Process Regression STAT 6474 Instructor: Hongxiao Zhu Motivation Reference: Marc Deisenroth s tutorial on Robot Learning. 2 Fast Learning for Autonomous Robots with Gaussian Processes
Kernel adaptive Sequential Monte Carlo
 Kernel adaptive Sequential Monte Carlo Ingmar Schuster (Paris Dauphine) Heiko Strathmann (University College London) Brooks Paige (Oxford) Dino Sejdinovic (Oxford) December 7, 2015 1 / 36 Section 1 Outline
Kernel adaptive Sequential Monte Carlo Ingmar Schuster (Paris Dauphine) Heiko Strathmann (University College London) Brooks Paige (Oxford) Dino Sejdinovic (Oxford) December 7, 2015 1 / 36 Section 1 Outline
Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC)
 Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC Dependent Sampling Suppose we wish to sample from a density π, and we can evaluate π as a function but have no means to directly generate a sample. Rejection sampling can
Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC Dependent Sampling Suppose we wish to sample from a density π, and we can evaluate π as a function but have no means to directly generate a sample. Rejection sampling can
Computer Vision Group Prof. Daniel Cremers. 11. Sampling Methods
 Prof. Daniel Cremers 11. Sampling Methods Sampling Methods Sampling Methods are widely used in Computer Science as an approximation of a deterministic algorithm to represent uncertainty without a parametric
Prof. Daniel Cremers 11. Sampling Methods Sampling Methods Sampling Methods are widely used in Computer Science as an approximation of a deterministic algorithm to represent uncertainty without a parametric
Computer Vision Group Prof. Daniel Cremers. 10a. Markov Chain Monte Carlo
 Group Prof. Daniel Cremers 10a. Markov Chain Monte Carlo Markov Chain Monte Carlo In high-dimensional spaces, rejection sampling and importance sampling are very inefficient An alternative is Markov Chain
Group Prof. Daniel Cremers 10a. Markov Chain Monte Carlo Markov Chain Monte Carlo In high-dimensional spaces, rejection sampling and importance sampling are very inefficient An alternative is Markov Chain
Principles of Bayesian Inference
 Principles of Bayesian Inference Sudipto Banerjee University of Minnesota July 20th, 2008 1 Bayesian Principles Classical statistics: model parameters are fixed and unknown. A Bayesian thinks of parameters
Principles of Bayesian Inference Sudipto Banerjee University of Minnesota July 20th, 2008 1 Bayesian Principles Classical statistics: model parameters are fixed and unknown. A Bayesian thinks of parameters
Learning the hyper-parameters. Luca Martino
 Learning the hyper-parameters Luca Martino 2017 2017 1 / 28 Parameters and hyper-parameters 1. All the described methods depend on some choice of hyper-parameters... 2. For instance, do you recall λ (bandwidth
Learning the hyper-parameters Luca Martino 2017 2017 1 / 28 Parameters and hyper-parameters 1. All the described methods depend on some choice of hyper-parameters... 2. For instance, do you recall λ (bandwidth
Gaussian Processes for Computer Experiments
 Gaussian Processes for Computer Experiments Jeremy Oakley School of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Sheffield www.jeremy-oakley.staff.shef.ac.uk 1 / 43 Computer models Computer model represented
Gaussian Processes for Computer Experiments Jeremy Oakley School of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Sheffield www.jeremy-oakley.staff.shef.ac.uk 1 / 43 Computer models Computer model represented
An introduction to Bayesian statistics and model calibration and a host of related topics
 An introduction to Bayesian statistics and model calibration and a host of related topics Derek Bingham Statistics and Actuarial Science Simon Fraser University Cast of thousands have participated in the
An introduction to Bayesian statistics and model calibration and a host of related topics Derek Bingham Statistics and Actuarial Science Simon Fraser University Cast of thousands have participated in the
STAT 518 Intro Student Presentation
 STAT 518 Intro Student Presentation Wen Wei Loh April 11, 2013 Title of paper Radford M. Neal [1999] Bayesian Statistics, 6: 475-501, 1999 What the paper is about Regression and Classification Flexible
STAT 518 Intro Student Presentation Wen Wei Loh April 11, 2013 Title of paper Radford M. Neal [1999] Bayesian Statistics, 6: 475-501, 1999 What the paper is about Regression and Classification Flexible
Online appendix to On the stability of the excess sensitivity of aggregate consumption growth in the US
 Online appendix to On the stability of the excess sensitivity of aggregate consumption growth in the US Gerdie Everaert 1, Lorenzo Pozzi 2, and Ruben Schoonackers 3 1 Ghent University & SHERPPA 2 Erasmus
Online appendix to On the stability of the excess sensitivity of aggregate consumption growth in the US Gerdie Everaert 1, Lorenzo Pozzi 2, and Ruben Schoonackers 3 1 Ghent University & SHERPPA 2 Erasmus
Computer Vision Group Prof. Daniel Cremers. 14. Sampling Methods
 Prof. Daniel Cremers 14. Sampling Methods Sampling Methods Sampling Methods are widely used in Computer Science as an approximation of a deterministic algorithm to represent uncertainty without a parametric
Prof. Daniel Cremers 14. Sampling Methods Sampling Methods Sampling Methods are widely used in Computer Science as an approximation of a deterministic algorithm to represent uncertainty without a parametric
Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) and Model Evaluation. August 15, 2017
 Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) and Model Evaluation August 15, 2017 Frequentist Linking Frequentist and Bayesian Statistics How can we estimate model parameters and what does it imply? Want to find the
Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) and Model Evaluation August 15, 2017 Frequentist Linking Frequentist and Bayesian Statistics How can we estimate model parameters and what does it imply? Want to find the
Bayesian Nonparametric Regression for Diabetes Deaths
 Bayesian Nonparametric Regression for Diabetes Deaths Brian M. Hartman PhD Student, 2010 Texas A&M University College Station, TX, USA David B. Dahl Assistant Professor Texas A&M University College Station,
Bayesian Nonparametric Regression for Diabetes Deaths Brian M. Hartman PhD Student, 2010 Texas A&M University College Station, TX, USA David B. Dahl Assistant Professor Texas A&M University College Station,
36-463/663: Hierarchical Linear Models
 36-463/663: Hierarchical Linear Models Taste of MCMC / Bayes for 3 or more levels Brian Junker 132E Baker Hall brian@stat.cmu.edu 1 Outline Practical Bayes Mastery Learning Example A brief taste of JAGS
36-463/663: Hierarchical Linear Models Taste of MCMC / Bayes for 3 or more levels Brian Junker 132E Baker Hall brian@stat.cmu.edu 1 Outline Practical Bayes Mastery Learning Example A brief taste of JAGS
ComputationalToolsforComparing AsymmetricGARCHModelsviaBayes Factors. RicardoS.Ehlers
 ComputationalToolsforComparing AsymmetricGARCHModelsviaBayes Factors RicardoS.Ehlers Laboratório de Estatística e Geoinformação- UFPR http://leg.ufpr.br/ ehlers ehlers@leg.ufpr.br II Workshop on Statistical
ComputationalToolsforComparing AsymmetricGARCHModelsviaBayes Factors RicardoS.Ehlers Laboratório de Estatística e Geoinformação- UFPR http://leg.ufpr.br/ ehlers ehlers@leg.ufpr.br II Workshop on Statistical
Bayesian Methods and Uncertainty Quantification for Nonlinear Inverse Problems
 Bayesian Methods and Uncertainty Quantification for Nonlinear Inverse Problems John Bardsley, University of Montana Collaborators: H. Haario, J. Kaipio, M. Laine, Y. Marzouk, A. Seppänen, A. Solonen, Z.
Bayesian Methods and Uncertainty Quantification for Nonlinear Inverse Problems John Bardsley, University of Montana Collaborators: H. Haario, J. Kaipio, M. Laine, Y. Marzouk, A. Seppänen, A. Solonen, Z.
Comparison of Three Calculation Methods for a Bayesian Inference of Two Poisson Parameters
 Journal of Modern Applied Statistical Methods Volume 13 Issue 1 Article 26 5-1-2014 Comparison of Three Calculation Methods for a Bayesian Inference of Two Poisson Parameters Yohei Kawasaki Tokyo University
Journal of Modern Applied Statistical Methods Volume 13 Issue 1 Article 26 5-1-2014 Comparison of Three Calculation Methods for a Bayesian Inference of Two Poisson Parameters Yohei Kawasaki Tokyo University
What is the most likely year in which the change occurred? Did the rate of disasters increase or decrease after the change-point?
 Chapter 11 Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods 11.1 Introduction In many applications of statistical modeling, the data analyst would like to use a more complex model for a data set, but is forced to resort
Chapter 11 Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods 11.1 Introduction In many applications of statistical modeling, the data analyst would like to use a more complex model for a data set, but is forced to resort
A note on Reversible Jump Markov Chain Monte Carlo
 A note on Reversible Jump Markov Chain Monte Carlo Hedibert Freitas Lopes Graduate School of Business The University of Chicago 5807 South Woodlawn Avenue Chicago, Illinois 60637 February, 1st 2006 1 Introduction
A note on Reversible Jump Markov Chain Monte Carlo Hedibert Freitas Lopes Graduate School of Business The University of Chicago 5807 South Woodlawn Avenue Chicago, Illinois 60637 February, 1st 2006 1 Introduction
An introduction to Sequential Monte Carlo
 An introduction to Sequential Monte Carlo Thang Bui Jes Frellsen Department of Engineering University of Cambridge Research and Communication Club 6 February 2014 1 Sequential Monte Carlo (SMC) methods
An introduction to Sequential Monte Carlo Thang Bui Jes Frellsen Department of Engineering University of Cambridge Research and Communication Club 6 February 2014 1 Sequential Monte Carlo (SMC) methods
ST 740: Markov Chain Monte Carlo
 ST 740: Markov Chain Monte Carlo Alyson Wilson Department of Statistics North Carolina State University October 14, 2012 A. Wilson (NCSU Stsatistics) MCMC October 14, 2012 1 / 20 Convergence Diagnostics:
ST 740: Markov Chain Monte Carlo Alyson Wilson Department of Statistics North Carolina State University October 14, 2012 A. Wilson (NCSU Stsatistics) MCMC October 14, 2012 1 / 20 Convergence Diagnostics:
Bayesian Methods in Multilevel Regression
 Bayesian Methods in Multilevel Regression Joop Hox MuLOG, 15 september 2000 mcmc What is Statistics?! Statistics is about uncertainty To err is human, to forgive divine, but to include errors in your design
Bayesian Methods in Multilevel Regression Joop Hox MuLOG, 15 september 2000 mcmc What is Statistics?! Statistics is about uncertainty To err is human, to forgive divine, but to include errors in your design
Bayesian Gaussian Process Regression
 Bayesian Gaussian Process Regression STAT8810, Fall 2017 M.T. Pratola October 7, 2017 Today Bayesian Gaussian Process Regression Bayesian GP Regression Recall we had observations from our expensive simulator,
Bayesian Gaussian Process Regression STAT8810, Fall 2017 M.T. Pratola October 7, 2017 Today Bayesian Gaussian Process Regression Bayesian GP Regression Recall we had observations from our expensive simulator,
Machine Learning using Bayesian Approaches
 Machine Learning using Bayesian Approaches Sargur N. Srihari University at Buffalo, State University of New York 1 Outline 1. Progress in ML and PR 2. Fully Bayesian Approach 1. Probability theory Bayes
Machine Learning using Bayesian Approaches Sargur N. Srihari University at Buffalo, State University of New York 1 Outline 1. Progress in ML and PR 2. Fully Bayesian Approach 1. Probability theory Bayes
Inferring biomarkers for Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis infection and disease progression in cattle using experimental data
 Inferring biomarkers for Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis infection and disease progression in cattle using experimental data 1,2,4, Gesham Magombedze, Tinevimbo Shiri, Shigetoshi Eda 4, 5,
Inferring biomarkers for Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis infection and disease progression in cattle using experimental data 1,2,4, Gesham Magombedze, Tinevimbo Shiri, Shigetoshi Eda 4, 5,
Report and Opinion 2016;8(6) Analysis of bivariate correlated data under the Poisson-gamma model
 Analysis of bivariate correlated data under the Poisson-gamma model Narges Ramooz, Farzad Eskandari 2. MSc of Statistics, Allameh Tabatabai University, Tehran, Iran 2. Associate professor of Statistics,
Analysis of bivariate correlated data under the Poisson-gamma model Narges Ramooz, Farzad Eskandari 2. MSc of Statistics, Allameh Tabatabai University, Tehran, Iran 2. Associate professor of Statistics,
MCMC Methods: Gibbs and Metropolis
 MCMC Methods: Gibbs and Metropolis Patrick Breheny February 28 Patrick Breheny BST 701: Bayesian Modeling in Biostatistics 1/30 Introduction As we have seen, the ability to sample from the posterior distribution
MCMC Methods: Gibbs and Metropolis Patrick Breheny February 28 Patrick Breheny BST 701: Bayesian Modeling in Biostatistics 1/30 Introduction As we have seen, the ability to sample from the posterior distribution
Bagging During Markov Chain Monte Carlo for Smoother Predictions
 Bagging During Markov Chain Monte Carlo for Smoother Predictions Herbert K. H. Lee University of California, Santa Cruz Abstract: Making good predictions from noisy data is a challenging problem. Methods
Bagging During Markov Chain Monte Carlo for Smoother Predictions Herbert K. H. Lee University of California, Santa Cruz Abstract: Making good predictions from noisy data is a challenging problem. Methods
Supplement to A Hierarchical Approach for Fitting Curves to Response Time Measurements
 Supplement to A Hierarchical Approach for Fitting Curves to Response Time Measurements Jeffrey N. Rouder Francis Tuerlinckx Paul L. Speckman Jun Lu & Pablo Gomez May 4 008 1 The Weibull regression model
Supplement to A Hierarchical Approach for Fitting Curves to Response Time Measurements Jeffrey N. Rouder Francis Tuerlinckx Paul L. Speckman Jun Lu & Pablo Gomez May 4 008 1 The Weibull regression model
Bayesian Analysis. Bayesian Analysis: Bayesian methods concern one s belief about θ. [Current Belief (Posterior)] (Prior Belief) x (Data) Outline
![Bayesian Analysis. Bayesian Analysis: Bayesian methods concern one s belief about θ. [Current Belief (Posterior)] (Prior Belief) x (Data) Outline Bayesian Analysis. Bayesian Analysis: Bayesian methods concern one s belief about θ. [Current Belief (Posterior)] (Prior Belief) x (Data) Outline](/thumbs/87/97378301.jpg) Bayesian Analysis DuBois Bowman, Ph.D. Gordana Derado, M. S. Shuo Chen, M. S. Department of Biostatistics and Bioinformatics Center for Biomedical Imaging Statistics Emory University Outline I. Introduction
Bayesian Analysis DuBois Bowman, Ph.D. Gordana Derado, M. S. Shuo Chen, M. S. Department of Biostatistics and Bioinformatics Center for Biomedical Imaging Statistics Emory University Outline I. Introduction
Spring 2006: Introduction to Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC)
 36-724 Spring 2006: Introduction to Marov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) Brian Juner February 16, 2006 Hierarchical Normal Model Direct Simulation An Alternative Approach: MCMC Complete Conditionals for Hierarchical
36-724 Spring 2006: Introduction to Marov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) Brian Juner February 16, 2006 Hierarchical Normal Model Direct Simulation An Alternative Approach: MCMC Complete Conditionals for Hierarchical
Density Estimation. Seungjin Choi
 Density Estimation Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr http://mlg.postech.ac.kr/
Density Estimation Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr http://mlg.postech.ac.kr/
Introduction to Machine Learning CMU-10701
 Introduction to Machine Learning CMU-10701 Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods Barnabás Póczos & Aarti Singh Contents Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods Goal & Motivation Sampling Rejection Importance Markov
Introduction to Machine Learning CMU-10701 Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods Barnabás Póczos & Aarti Singh Contents Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods Goal & Motivation Sampling Rejection Importance Markov
Computational statistics
 Computational statistics Markov Chain Monte Carlo methods Thierry Denœux March 2017 Thierry Denœux Computational statistics March 2017 1 / 71 Contents of this chapter When a target density f can be evaluated
Computational statistics Markov Chain Monte Carlo methods Thierry Denœux March 2017 Thierry Denœux Computational statistics March 2017 1 / 71 Contents of this chapter When a target density f can be evaluated
BAYESIAN METHODS FOR VARIABLE SELECTION WITH APPLICATIONS TO HIGH-DIMENSIONAL DATA
 BAYESIAN METHODS FOR VARIABLE SELECTION WITH APPLICATIONS TO HIGH-DIMENSIONAL DATA Intro: Course Outline and Brief Intro to Marina Vannucci Rice University, USA PASI-CIMAT 04/28-30/2010 Marina Vannucci
BAYESIAN METHODS FOR VARIABLE SELECTION WITH APPLICATIONS TO HIGH-DIMENSIONAL DATA Intro: Course Outline and Brief Intro to Marina Vannucci Rice University, USA PASI-CIMAT 04/28-30/2010 Marina Vannucci
MCMC algorithms for fitting Bayesian models
 MCMC algorithms for fitting Bayesian models p. 1/1 MCMC algorithms for fitting Bayesian models Sudipto Banerjee sudiptob@biostat.umn.edu University of Minnesota MCMC algorithms for fitting Bayesian models
MCMC algorithms for fitting Bayesian models p. 1/1 MCMC algorithms for fitting Bayesian models Sudipto Banerjee sudiptob@biostat.umn.edu University of Minnesota MCMC algorithms for fitting Bayesian models
Making rating curves - the Bayesian approach
 Making rating curves - the Bayesian approach Rating curves what is wanted? A best estimate of the relationship between stage and discharge at a given place in a river. The relationship should be on the
Making rating curves - the Bayesian approach Rating curves what is wanted? A best estimate of the relationship between stage and discharge at a given place in a river. The relationship should be on the
Markov chain Monte Carlo
 Markov chain Monte Carlo Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) Gibbs and Metropolis Hastings Slice sampling Practical details Iain Murray http://iainmurray.net/ Reminder Need to sample large, non-standard distributions:
Markov chain Monte Carlo Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) Gibbs and Metropolis Hastings Slice sampling Practical details Iain Murray http://iainmurray.net/ Reminder Need to sample large, non-standard distributions:
Computer Vision Group Prof. Daniel Cremers. 11. Sampling Methods: Markov Chain Monte Carlo
 Group Prof. Daniel Cremers 11. Sampling Methods: Markov Chain Monte Carlo Markov Chain Monte Carlo In high-dimensional spaces, rejection sampling and importance sampling are very inefficient An alternative
Group Prof. Daniel Cremers 11. Sampling Methods: Markov Chain Monte Carlo Markov Chain Monte Carlo In high-dimensional spaces, rejection sampling and importance sampling are very inefficient An alternative
Markov Chain Monte Carlo A Contribution to the Encyclopedia of Environmetrics
 Markov Chain Monte Carlo A Contribution to the Encyclopedia of Environmetrics Galin L. Jones and James P. Hobert Department of Statistics University of Florida May 2000 1 Introduction Realistic statistical
Markov Chain Monte Carlo A Contribution to the Encyclopedia of Environmetrics Galin L. Jones and James P. Hobert Department of Statistics University of Florida May 2000 1 Introduction Realistic statistical
Bayesian Computation
 Bayesian Computation CAS Centennial Celebration and Annual Meeting New York, NY November 10, 2014 Brian M. Hartman, PhD ASA Assistant Professor of Actuarial Science University of Connecticut CAS Antitrust
Bayesian Computation CAS Centennial Celebration and Annual Meeting New York, NY November 10, 2014 Brian M. Hartman, PhD ASA Assistant Professor of Actuarial Science University of Connecticut CAS Antitrust
ELEC633: Graphical Models
 ELEC633: Graphical Models Tahira isa Saleem Scribe from 7 October 2008 References: Casella and George Exploring the Gibbs sampler (1992) Chib and Greenberg Understanding the Metropolis-Hastings algorithm
ELEC633: Graphical Models Tahira isa Saleem Scribe from 7 October 2008 References: Casella and George Exploring the Gibbs sampler (1992) Chib and Greenberg Understanding the Metropolis-Hastings algorithm
17 : Markov Chain Monte Carlo
 10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models, Spring 2015 17 : Markov Chain Monte Carlo Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Heran Lin, Bin Deng, Yun Huang 1 Review of Monte Carlo Methods 1.1 Overview Monte Carlo
10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models, Spring 2015 17 : Markov Chain Monte Carlo Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Heran Lin, Bin Deng, Yun Huang 1 Review of Monte Carlo Methods 1.1 Overview Monte Carlo
Bayesian model selection in graphs by using BDgraph package
 Bayesian model selection in graphs by using BDgraph package A. Mohammadi and E. Wit March 26, 2013 MOTIVATION Flow cytometry data with 11 proteins from Sachs et al. (2005) RESULT FOR CELL SIGNALING DATA
Bayesian model selection in graphs by using BDgraph package A. Mohammadi and E. Wit March 26, 2013 MOTIVATION Flow cytometry data with 11 proteins from Sachs et al. (2005) RESULT FOR CELL SIGNALING DATA
Confidence Intervals. CAS Antitrust Notice. Bayesian Computation. General differences between Bayesian and Frequntist statistics 10/16/2014
 CAS Antitrust Notice Bayesian Computation CAS Centennial Celebration and Annual Meeting New York, NY November 10, 2014 Brian M. Hartman, PhD ASA Assistant Professor of Actuarial Science University of Connecticut
CAS Antitrust Notice Bayesian Computation CAS Centennial Celebration and Annual Meeting New York, NY November 10, 2014 Brian M. Hartman, PhD ASA Assistant Professor of Actuarial Science University of Connecticut
The Particle Filter. PD Dr. Rudolph Triebel Computer Vision Group. Machine Learning for Computer Vision
 The Particle Filter Non-parametric implementation of Bayes filter Represents the belief (posterior) random state samples. by a set of This representation is approximate. Can represent distributions that
The Particle Filter Non-parametric implementation of Bayes filter Represents the belief (posterior) random state samples. by a set of This representation is approximate. Can represent distributions that
Multivariate Normal & Wishart
 Multivariate Normal & Wishart Hoff Chapter 7 October 21, 2010 Reading Comprehesion Example Twenty-two children are given a reading comprehsion test before and after receiving a particular instruction method.
Multivariate Normal & Wishart Hoff Chapter 7 October 21, 2010 Reading Comprehesion Example Twenty-two children are given a reading comprehsion test before and after receiving a particular instruction method.
Calibration of Stochastic Volatility Models using Particle Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods
 Calibration of Stochastic Volatility Models using Particle Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods Jonas Hallgren 1 1 Department of Mathematics KTH Royal Institute of Technology Stockholm, Sweden BFS 2012 June
Calibration of Stochastic Volatility Models using Particle Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods Jonas Hallgren 1 1 Department of Mathematics KTH Royal Institute of Technology Stockholm, Sweden BFS 2012 June
Bayesian Estimation of Input Output Tables for Russia
 Bayesian Estimation of Input Output Tables for Russia Oleg Lugovoy (EDF, RANE) Andrey Polbin (RANE) Vladimir Potashnikov (RANE) WIOD Conference April 24, 2012 Groningen Outline Motivation Objectives Bayesian
Bayesian Estimation of Input Output Tables for Russia Oleg Lugovoy (EDF, RANE) Andrey Polbin (RANE) Vladimir Potashnikov (RANE) WIOD Conference April 24, 2012 Groningen Outline Motivation Objectives Bayesian
Bayesian Phylogenetics:
 Bayesian Phylogenetics: an introduction Marc A. Suchard msuchard@ucla.edu UCLA Who is this man? How sure are you? The one true tree? Methods we ve learned so far try to find a single tree that best describes
Bayesian Phylogenetics: an introduction Marc A. Suchard msuchard@ucla.edu UCLA Who is this man? How sure are you? The one true tree? Methods we ve learned so far try to find a single tree that best describes
TUNING OF MARKOV CHAIN MONTE CARLO ALGORITHMS USING COPULAS
 U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series A, Vol. 73, Iss. 1, 2011 ISSN 1223-7027 TUNING OF MARKOV CHAIN MONTE CARLO ALGORITHMS USING COPULAS Radu V. Craiu 1 Algoritmii de tipul Metropolis-Hastings se constituie într-una
U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series A, Vol. 73, Iss. 1, 2011 ISSN 1223-7027 TUNING OF MARKOV CHAIN MONTE CARLO ALGORITHMS USING COPULAS Radu V. Craiu 1 Algoritmii de tipul Metropolis-Hastings se constituie într-una
On Bayesian Computation
 On Bayesian Computation Michael I. Jordan with Elaine Angelino, Maxim Rabinovich, Martin Wainwright and Yun Yang Previous Work: Information Constraints on Inference Minimize the minimax risk under constraints
On Bayesian Computation Michael I. Jordan with Elaine Angelino, Maxim Rabinovich, Martin Wainwright and Yun Yang Previous Work: Information Constraints on Inference Minimize the minimax risk under constraints
Bayesian Inference and Decision Theory
 Bayesian Inference and Decision Theory Instructor: Kathryn Blackmond Laskey Room 2214 ENGR (703) 993-1644 Office Hours: Tuesday and Thursday 4:30-5:30 PM, or by appointment Spring 2018 Unit 6: Gibbs Sampling
Bayesian Inference and Decision Theory Instructor: Kathryn Blackmond Laskey Room 2214 ENGR (703) 993-1644 Office Hours: Tuesday and Thursday 4:30-5:30 PM, or by appointment Spring 2018 Unit 6: Gibbs Sampling
Bayes: All uncertainty is described using probability.
 Bayes: All uncertainty is described using probability. Let w be the data and θ be any unknown quantities. Likelihood. The probability model π(w θ) has θ fixed and w varying. The likelihood L(θ; w) is π(w
Bayes: All uncertainty is described using probability. Let w be the data and θ be any unknown quantities. Likelihood. The probability model π(w θ) has θ fixed and w varying. The likelihood L(θ; w) is π(w
Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods
 Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods John Geweke University of Iowa, USA 2005 Institute on Computational Economics University of Chicago - Argonne National Laboaratories July 22, 2005 The problem p (θ, ω I)
Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods John Geweke University of Iowa, USA 2005 Institute on Computational Economics University of Chicago - Argonne National Laboaratories July 22, 2005 The problem p (θ, ω I)
Theory and Methods of Statistical Inference
 PhD School in Statistics cycle XXIX, 2014 Theory and Methods of Statistical Inference Instructors: B. Liseo, L. Pace, A. Salvan (course coordinator), N. Sartori, A. Tancredi, L. Ventura Syllabus Some prerequisites:
PhD School in Statistics cycle XXIX, 2014 Theory and Methods of Statistical Inference Instructors: B. Liseo, L. Pace, A. Salvan (course coordinator), N. Sartori, A. Tancredi, L. Ventura Syllabus Some prerequisites:
Lecture Notes based on Koop (2003) Bayesian Econometrics
 Lecture Notes based on Koop (2003) Bayesian Econometrics A.Colin Cameron University of California - Davis November 15, 2005 1. CH.1: Introduction The concepts below are the essential concepts used throughout
Lecture Notes based on Koop (2003) Bayesian Econometrics A.Colin Cameron University of California - Davis November 15, 2005 1. CH.1: Introduction The concepts below are the essential concepts used throughout
Introduction to Bayesian Statistics and Markov Chain Monte Carlo Estimation. EPSY 905: Multivariate Analysis Spring 2016 Lecture #10: April 6, 2016
 Introduction to Bayesian Statistics and Markov Chain Monte Carlo Estimation EPSY 905: Multivariate Analysis Spring 2016 Lecture #10: April 6, 2016 EPSY 905: Intro to Bayesian and MCMC Today s Class An
Introduction to Bayesian Statistics and Markov Chain Monte Carlo Estimation EPSY 905: Multivariate Analysis Spring 2016 Lecture #10: April 6, 2016 EPSY 905: Intro to Bayesian and MCMC Today s Class An
Statistical Machine Learning Lecture 8: Markov Chain Monte Carlo Sampling
 1 / 27 Statistical Machine Learning Lecture 8: Markov Chain Monte Carlo Sampling Melih Kandemir Özyeğin University, İstanbul, Turkey 2 / 27 Monte Carlo Integration The big question : Evaluate E p(z) [f(z)]
1 / 27 Statistical Machine Learning Lecture 8: Markov Chain Monte Carlo Sampling Melih Kandemir Özyeğin University, İstanbul, Turkey 2 / 27 Monte Carlo Integration The big question : Evaluate E p(z) [f(z)]
MCMC and Gibbs Sampling. Kayhan Batmanghelich
 MCMC and Gibbs Sampling Kayhan Batmanghelich 1 Approaches to inference l Exact inference algorithms l l l The elimination algorithm Message-passing algorithm (sum-product, belief propagation) The junction
MCMC and Gibbs Sampling Kayhan Batmanghelich 1 Approaches to inference l Exact inference algorithms l l l The elimination algorithm Message-passing algorithm (sum-product, belief propagation) The junction
APM 541: Stochastic Modelling in Biology Bayesian Inference. Jay Taylor Fall Jay Taylor (ASU) APM 541 Fall / 53
 APM 541: Stochastic Modelling in Biology Bayesian Inference Jay Taylor Fall 2013 Jay Taylor (ASU) APM 541 Fall 2013 1 / 53 Outline Outline 1 Introduction 2 Conjugate Distributions 3 Noninformative priors
APM 541: Stochastic Modelling in Biology Bayesian Inference Jay Taylor Fall 2013 Jay Taylor (ASU) APM 541 Fall 2013 1 / 53 Outline Outline 1 Introduction 2 Conjugate Distributions 3 Noninformative priors
Monte Carlo integration
 Monte Carlo integration Eample of a Monte Carlo sampler in D: imagine a circle radius L/ within a square of LL. If points are randoml generated over the square, what s the probabilit to hit within circle?
Monte Carlo integration Eample of a Monte Carlo sampler in D: imagine a circle radius L/ within a square of LL. If points are randoml generated over the square, what s the probabilit to hit within circle?
Probabilistic Graphical Networks: Definitions and Basic Results
 This document gives a cursory overview of Probabilistic Graphical Networks. The material has been gleaned from different sources. I make no claim to original authorship of this material. Bayesian Graphical
This document gives a cursory overview of Probabilistic Graphical Networks. The material has been gleaned from different sources. I make no claim to original authorship of this material. Bayesian Graphical
STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning
 STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Computer Science! Department of Statistical Sciences! rsalakhu@cs.toronto.edu! h0p://www.cs.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Lecture 7 Approximate
STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Computer Science! Department of Statistical Sciences! rsalakhu@cs.toronto.edu! h0p://www.cs.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Lecture 7 Approximate
The Bayesian Approach to Multi-equation Econometric Model Estimation
 Journal of Statistical and Econometric Methods, vol.3, no.1, 2014, 85-96 ISSN: 2241-0384 (print), 2241-0376 (online) Scienpress Ltd, 2014 The Bayesian Approach to Multi-equation Econometric Model Estimation
Journal of Statistical and Econometric Methods, vol.3, no.1, 2014, 85-96 ISSN: 2241-0384 (print), 2241-0376 (online) Scienpress Ltd, 2014 The Bayesian Approach to Multi-equation Econometric Model Estimation
Applicability of subsampling bootstrap methods in Markov chain Monte Carlo
 Applicability of subsampling bootstrap methods in Markov chain Monte Carlo James M. Flegal Abstract Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) methods allow exploration of intractable probability distributions by
Applicability of subsampling bootstrap methods in Markov chain Monte Carlo James M. Flegal Abstract Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) methods allow exploration of intractable probability distributions by
Markov Chain Monte Carlo methods
 Markov Chain Monte Carlo methods By Oleg Makhnin 1 Introduction a b c M = d e f g h i 0 f(x)dx 1.1 Motivation 1.1.1 Just here Supresses numbering 1.1.2 After this 1.2 Literature 2 Method 2.1 New math As
Markov Chain Monte Carlo methods By Oleg Makhnin 1 Introduction a b c M = d e f g h i 0 f(x)dx 1.1 Motivation 1.1.1 Just here Supresses numbering 1.1.2 After this 1.2 Literature 2 Method 2.1 New math As
Tutorial on Probabilistic Programming with PyMC3
 185.A83 Machine Learning for Health Informatics 2017S, VU, 2.0 h, 3.0 ECTS Tutorial 02-04.04.2017 Tutorial on Probabilistic Programming with PyMC3 florian.endel@tuwien.ac.at http://hci-kdd.org/machine-learning-for-health-informatics-course
185.A83 Machine Learning for Health Informatics 2017S, VU, 2.0 h, 3.0 ECTS Tutorial 02-04.04.2017 Tutorial on Probabilistic Programming with PyMC3 florian.endel@tuwien.ac.at http://hci-kdd.org/machine-learning-for-health-informatics-course
Monte Carlo Methods. Leon Gu CSD, CMU
 Monte Carlo Methods Leon Gu CSD, CMU Approximate Inference EM: y-observed variables; x-hidden variables; θ-parameters; E-step: q(x) = p(x y, θ t 1 ) M-step: θ t = arg max E q(x) [log p(y, x θ)] θ Monte
Monte Carlo Methods Leon Gu CSD, CMU Approximate Inference EM: y-observed variables; x-hidden variables; θ-parameters; E-step: q(x) = p(x y, θ t 1 ) M-step: θ t = arg max E q(x) [log p(y, x θ)] θ Monte
Introduction to Bayesian Analysis Procedures (Chapter)
 SAS/STAT 9.3 User s Guide Introduction to Bayesian Analysis Procedures (Chapter) SAS Documentation This document is an individual chapter from SAS/STAT 9.3 User s Guide. The correct bibliographic citation
SAS/STAT 9.3 User s Guide Introduction to Bayesian Analysis Procedures (Chapter) SAS Documentation This document is an individual chapter from SAS/STAT 9.3 User s Guide. The correct bibliographic citation
