The Escape Model. Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim. with G.Giacinti, O.Kalashev, A.Nernov, V.Savchenko, D.Semikoz
|
|
|
- Stuart Logan Martin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Escape Model Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] with G.Giacinti, O.Kalashev, A.Nernov, V.Savchenko, D.Semikoz
2 Introduction Outline Outline of the talk 1 Introduction Results on Composition 2 Escape model Fluxes of groups of CR nuclei & knee Transition to extragalactic CRs Exgal. protons, γ s and ν s as CR secondaries 3 A recent nearby SN? Anisotropy Antimatter fluxes 4 Conclusions Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
3 Introduction Outline Outline of the talk 1 Introduction Results on Composition 2 Escape model Fluxes of groups of CR nuclei & knee Transition to extragalactic CRs Exgal. protons, γ s and ν s as CR secondaries 3 A recent nearby SN? Anisotropy Antimatter fluxes 4 Conclusions Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
4 Introduction Outline Outline of the talk 1 Introduction Results on Composition 2 Escape model Fluxes of groups of CR nuclei & knee Transition to extragalactic CRs Exgal. protons, γ s and ν s as CR secondaries 3 A recent nearby SN? Anisotropy Antimatter fluxes 4 Conclusions Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
5 Introduction Composition Composition of Galactic CRs: traditional view [Gaisser, Stanev, Tilav 13 ] sr -1 s -1 ] 4 3 Proton_total He_total C_total O_total Fe_total Z=53 group Z=80 group dn/de [GeV 2.6 E 1.6 m Pamela Proton Pamela He CreamII Proton CreamII He CreamII C CreamII O CreamII Mg CreamII Si CreamII Fe Primary Energy, E [GeV] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
6 Introduction Composition Composition of Galactic CRs: KASCADE-Grande 2013 ) 1.5 sr -1 s -1 ev -2 / (m 2.5 E EAS-TOP (Astrop.Phys.(1999)1) Tibet-III, QGSJET 01 (ApJ678(2008)1165) GAMMA (ICRC 2011) IceTop (arxiv: v1) TUNKA-133 (ICRC 2011) Yakutsk (NewJ.Phys11(2008)065008) KASCADE-Grande, QGSJET II (Astrop.Phys.36(2012)183) Akeno (J.Phys.G18(1992)423) AGASA (ICRC 2003) HiResI (PRL0(2008)11) HiResII (PRL0(2008)11) AUGER (arxiv:17:4809) AUGER AMIGA infill (ICRC 2011) diff. flux dj/de 15 KASCADE, all-part., QGSJET II (see Appendix A) KASCADE, light (p), QGSJET II (see Appendix A) KASCADE, medium (He+C+Si), QGSJET II (see Appendix A) KASCADE, heavy (Fe), QGSJET II (see Appendix A) KASCADE-Grande, all-part., QGSJET II (this work) KASCADE-Grande, light (p), QGSJET II (this work) KASCADE-Grande, medium (He+C+Si), QGSJET II (this work) KASCADE-Grande, heavy (Fe), QGSJET II (this work) primary energy E/eV 18 Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
7 Introduction Composition Composition of Galactic CRs: Auger [arxiv: ] 600 Sibyll 2.1 Sibyll 2.1 Sibyll 2.1 Fe N 500 He p Auger 400 log(e/ev) = log(e/ev) = log(e/ev) = N p < -4 p = p = QGSJET II-04 QGSJET II-04 QGSJET II log(e/ev) = log(e/ev) = log(e/ev) = N p < -4 p < -3 p = EPOS-LHC EPOS-LHC EPOS-LHC log(e/ev) = log(e/ev) = log(e/ev) = N p < -4 p = p = X max [g/cm 2 ] X max [g/cm 2 ] X max [g/cm 2 ] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
8 Introduction Composition Composition of Galactic CRs: Auger [arxiv: ] 600 Sibyll 2.1 Sibyll 2.1 Sibyll 2.1 Fe N 500 He p Auger 400 log(e/ev) = log(e/ev) = log(e/ev) = N p < -4 p = p = QGSJET II-04 QGSJET II-04 QGSJET II log(e/ev) = log(e/ev) = log(e/ev) = N p < -4 p < -3 p = EPOS-LHC EPOS-LHC EPOS-LHC log(e/ev) = log(e/ev) = log(e/ev) = composition ev consistent with N 200 p < -4 p = p = % 0 p, 50% He+N, < 20%Fe X max [g/cm 2 ] X max [g/cm 2 ] X max [g/cm 2 ] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
9 Introduction Composition Composition of Galactic CRs: 600 Sibyll 2.1 Sibyll 2.1 Sibyll 2.1 Fe N 500 He p Auger 400 log(e/ev) = log(e/ev) = log(e/ev) = N p < -4 p = p = QGSJET II-04 QGSJET II-04 QGSJET II log(e/ev) = log(e/ev) = log(e/ev) = N p < -4 p < -3 p = EPOS-LHC EPOS-LHC EPOS-LHC log(e/ev) = log(e/ev) = log(e/ev) = composition ev consistent with N p < -4 p = p = % 0 p, 50% He+N, < 20%Fe early transition X max [g/cm 2 ] from Galactic X max [g/cm to 2 ] extragalactic X max CRs [g/cm 2 ] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
10 Introduction Composition Transition to extragalactic CRs anisotropy limits dipole quadrupole Upper Limit - Dipole Amplitude Z=1 Z=26 1 E [EeV] Upper Limit - Amplitude λ Z=1 Z=26 1 E [EeV] dominant light Galactic composition around E = 18 ev excluded [Giacinti, MK, Semikoz, Sigl 12, PAO 13 ] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
11 Knee explanations Cosmic Ray Knee: steepening γ 0.4 at few 15 ev. ) 1.5 s -1 sr -1 ev -2 J(E) (m RHIC (p-p) HERA (γ-p) Equivalent c.m. energy 3 Tevatron (p-p) 4 7 TeV 14 TeV LHC (p-p) s pp (GeV) 5 HiRes-MIA HiRes I HiRes II Auger Scaled flux E ATIC PROTON RUNJOB KASCADE (QGSJET 01) KASCADE (SIBYLL 2.1) KASCADE-Grande 2009 Tibet ASg (SIBYLL 2.1) Energy 20 (ev/particle) 21 Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
12 Knee explanations Cosmic Ray Knee: 3 explanations. ) Equivalent c.m. energy 3 4 s pp (GeV) 5 6 s -1 sr -1 ev -2 J(E) (m RHIC (p-p) HERA (γ-p) Tevatron (p-p) 7 TeV 14 TeV LHC (p-p) HiRes-MIA HiRes I HiRes II Auger Scaled flux E ATIC KASCADE (QGSJET 01) 14 PROTON RUNJOB KASCADE (SIBYLL 2.1) KASCADE-Grande 2009 Tibet ASg (SIBYLL 2.1) Energy (ev/particle) change of interactions at multi-tev energies: excluded by LHC Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
13 Knee explanations Cosmic Ray Knee: 3 explanations. change of interactions at multi-tev energies: excluded by LHC change of propagation at R L l coh or E c ZeB l coh : change in diffusion from D(E) E 1/3 to Hall diffusion D(E) E small-angle scattering D(E) E 2 something intermediate? unavoidable effect, but for B few µg and l coh 30 pc at too high energy: E c /Z 15 B l c µg pc Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
14 Knee explanations Cosmic Ray Knee: 3 explanations maximal rigidity of dominant CR sources e.g. Hillas model E 2.6 I(E) [GeV 1.6 m -2 sr -1 s -1 ] p He C O Fe total E/eV Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
15 Knee explanations Cosmic Ray Knee: 3 explanations maximal rigidity of dominant CR sources e.g. Hillas model E 2.6 I(E) [GeV 1.6 m -2 sr -1 s -1 ] p He C O Fe total E/eV i = 1,...,3 types of CR sources, with slopes α A,i, rel. fractions f A,i Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
16 Knee explanations Cosmic Ray Knee: 3 explanations maximal rigidity of dominant CR sources e.g. Hillas model E 2.6 I(E) [GeV 1.6 m -2 sr -1 s -1 ] p He C O Fe total E/eV i = 1,...,3 types of CR sources, with slopes α A,i, rel. fractions f A,i no reliable estimate of E max,i, α A,i, and f A,i fit of many-parameter model to two observables: I tot and ln(a) Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
17 Knee explanations Cosmic Ray Knee: 3 explanations maximal energy: Gaisser, Stanev & Tilav version [ ] <lna> IC40/IT40 Kascade Tunka-133 HiResMia HiRes Auger TA H4a H3a Global Fit Global Fit with Population Primary Energy, E [GeV] 9 11 Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
18 Knee explanations Propagation in turbulent magnetic fields: Galactic magnetic field: regular + turbulent component turbulent: fluctuations on scales l min AU to l max ( 150) pc Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
19 Knee explanations Propagation in turbulent magnetic fields: Galactic magnetic field: regular + turbulent component turbulent: fluctuations on scales l min AU to l max ( 150) pc CRs scatter mainly on field fluctuations B(k) with kr L 1. Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
20 Knee explanations Propagation in turbulent magnetic fields: Galactic magnetic field: regular + turbulent component turbulent: fluctuations on scales l min AU to l max ( 150) pc CRs scatter mainly on field fluctuations B(k) with kr L 1. slope of power spectrum P(k) k α determines energy dependence of diffusion coefficient D(E) E β as β = 2 α: Kolmogorov α = 5/3 β = 1/3 Kraichnan α = 3/2 β = 1/2 Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
21 Knee explanations Propagation in turbulent magnetic fields: Galactic magnetic field: regular + turbulent component turbulent: fluctuations on scales l min AU to l max ( 150) pc CRs scatter mainly on field fluctuations B(k) with kr L 1. slope of power spectrum P(k) k α determines energy dependence of diffusion coefficient D(E) E β as β = 2 α: Kolmogorov α = 5/3 β = 1/3 Kraichnan α = 3/2 β = 1/2 observed energy spectrum of primaries: injection: dn/de E δ observed: dn/de E δ β δ and β are degenerated Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
22 Knee explanations Propagation in turbulent magnetic fields: Galactic magnetic field: regular + turbulent component turbulent: fluctuations on scales l min AU to l max ( 150) pc CRs scatter mainly on field fluctuations B(k) with kr L 1. slope of power spectrum P(k) k α determines energy dependence of diffusion coefficient D(E) E β as β = 2 α: Kolmogorov α = 5/3 β = 1/3 Kraichnan α = 3/2 β = 1/2 observed energy spectrum of primaries: injection: dn/de E δ observed: dn/de E δ β δ and β are degenerated anisotropy δ = 3D ij i ln(n) Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
23 Knee explanations Our approach: use model for Galactic magnetic field calculate trajectories x(t) via F L = qv B. Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
24 Knee explanations Our approach: use model for Galactic magnetic field calculate trajectories x(t) via F L = qv B. as preparation, let s calculate diffusion tensor in pure, isotropic turbulent magnetic field Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
25 Knee explanations Eigenvalues of D ij = x i x j /(2t) for E = 15 ev D(1PeV) (cm 2 /s) 1e+29 1e+28 d 3 d 2 d 1D Time (kyr) Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
26 Knee explanations Eigenvalues of D ij = x i x j /(2t) for E = 15 ev D(1PeV) (cm 2 /s) 1e+29 1e+28 d 3 d 2 d 1D Time (kyr) asymptotic value is smaller than extrapolated Galprop value [Giacinti, MK, Semikoz ( 12) ] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
27 Knee explanations Knee from Cosmic Ray Escape l coh and regular field B(x) fixed from observations LOFAR: lcoh < pc in disc determine magnitude of random B rms (x) from grammage X(E) Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
28 Knee explanations Knee from Cosmic Ray Escape l coh and regular field B(x) fixed from observations LOFAR: lcoh < pc in disc determine magnitude of random B rms (x) from grammage X(E) X(E) in g/cm β=1, L=pc β=0.1, L=pc 0.01 β=1/8, L=25pc δ=1/3 AMS-02 (a) AMS-02 (b) Jones E/Z in ev Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
29 Knee explanations Knee from Cosmic Ray Escape l coh and regular field B(x) fixed from observations LOFAR: lcoh < pc in disc determine magnitude of random B rms (x) from grammage X(E) X(E) in g/cm β=1, L=pc β=0.1, L=pc 0.01 β=1/8, L=25pc δ=1/3 AMS-02 (a) AMS-02 (b) Jones E/Z in ev prefers weak random fields fluxes I A (E) of all isotopes fixed by low-energy data Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
30 Knee explanations Galactic CRs: KASCADE-Grande 2013 ) 1.5 sr -1 s -1 ev -2 / (m EAS-TOP (Astrop.Phys.(1999)1) Tibet-III, QGSJET 01 (ApJ678(2008)1165) GAMMA (ICRC 2011) IceTop (arxiv: v1) TUNKA-133 (ICRC 2011) Yakutsk (NewJ.Phys11(2008)065008) KASCADE-Grande, QGSJET II (Astrop.Phys.36(2012)183) Akeno (J.Phys.G18(1992)423) AGASA (ICRC 2003) HiResI (PRL0(2008)11) HiResII (PRL0(2008)11) AUGER (arxiv:17:4809) AUGER AMIGA infill (ICRC 2011) diff. flux dj/de E KASCADE, all-part., QGSJET II (see Appendix A) KASCADE, light (p), QGSJET II (see Appendix A) KASCADE, medium (He+C+Si), QGSJET II (see Appendix A) KASCADE, heavy (Fe), QGSJET II (see Appendix A) KASCADE-Grande, all-part., QGSJET II (this work) KASCADE-Grande, light (p), QGSJET II (this work) KASCADE-Grande, medium (He+C+Si), QGSJET II (this work) KASCADE-Grande, heavy (Fe), QGSJET II (this work) primary energy E/eV 18 Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
31 Knee explanations Knee from Cosmic Ray Escape: proton energy spectra 13 E 2.5 F(E) [ev 2.5 /cm 2 /s/sr] KASCADE 2013 KASCADE Grande CREAM-2011 PAMELA pc e+ 1e+11 1e+12 1e+13 1e+14 1e+15 1e+16 1e+17 E [ev] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
32 Knee explanations Knee from Cosmic Ray Escape: He energy spectra 13 E 2.5 F(E) [ev 2.5 /cm 2 /s/sr] PAMELA 2011 CREAM-2011 KASCADE Grande KASCADE 2013 He 5 pc e+ 1e+11 1e+12 1e+13 1e+14 1e+15 1e+16 1e+17 E [ev] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
33 Knee explanations Knee from Cosmic Ray Escape: CNO energy spectra 13 E 2.5 F(E) [ev 2.5 /cm 2 /s/sr] KASCADE Grande CNO KASCADE 2013 CREAM C+O 9 CNO 25 pc e+12 1e+13 1e+14 1e+15 1e+16 1e+17 1e+18 1e+19 E [ev] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
34 Knee explanations Knee from Cosmic Ray Escape: total energy spectra E 2.5 F(E) [ev 2.5 /cm 2 /s/sr] Tibet KASCADE Grande Auger 2013 P He CNO Si Fe total E [ev] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
35 Knee explanations Knee from Cosmic Ray Escape: ln(a) ln(a) KASCADE-Grande KASCADE IceCube TUNKA Auger 0% exgal p p/fe exgal. mix 0 1e+15 1e+16 1e+17 1e+18 1e+19 1e+20 E/eV Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
36 Knee explanations Knee from Cosmic Ray Escape: ln(a) ln(a) KASCADE-Grande KASCADE IceCube TUNKA Auger 0% exgal p p/fe exgal. mix 0 1e+15 1e+16 1e+17 1e+18 1e+19 1e+20 E/eV exgal. mix: 60% p, 25% He, 15% N Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
37 Knee explanations Knee from Cosmic Ray Escape: dipole anisotropy -2-3 δ -4 1 PeV all data IceCube 2013 fit 1 SN 0 TeV Galactic total -5 Galactic E [ev] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
38 Knee explanations Knee from Cosmic Ray Escape: dipole anisotropy Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
39 Escape model Exgal. protons, γ s and ν s Extragalactic proton flux in escape model: 6 E 2 F(E) [ev/cm 2 /s/sr] KASCADE KASCADE Grande KASCADE Grande EG P 25 pc with Auger limit -1 Auger 2013 Auger 2013 Protons -2??? E [ev] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
40 Escape model Exgal. protons, γ s and ν s Extragalactic proton flux in escape model: 6 E 2 F(E) [ev/cm 2 /s/sr] KASCADE KASCADE Grande KASCADE Grande EG P 25 pc with Auger limit -1 Auger 2013 Auger 2013 Protons??? what are the sources? E [ev] testable via γ-ray and neutrinos? Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
41 Escape model Exgal. protons, γ s and ν s Normal and starburst galaxies: assume E 2.2 source spectrum starburst: B 0B MW rescale grammage and E max fix Q CR via SN/star formation rate vary gas density Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
42 Escape model Exgal. protons, γ s and ν s Normal and starburst galaxies: 00 ν gal (98%) je 2, ev cm -2 s -1 sr -1 0 p γ 1 ν EG KASCADE 2013 KASCADE Grande EG Auger 2013 Protons E, ev Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
43 Escape model Exgal. protons, γ s and ν s Normal and starburst galaxies: 00 ν gal (98%) je 2, ev cm -2 s -1 sr -1 0 p γ 1 ν EG KASCADE 2013 KASCADE Grande EG Auger 2013 Protons E, ev can not explain exgal. protons sources are thick can not be dominant sources of both EGRB and neutrinos Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
44 Escape model Exgal. protons, γ s and ν s Extragalactic proton flux in escape model: α p = 2.2 requires late redshift evolution: 20 N c (z)/n c (0) BL Lacs ρ. SNII (z)/ρ. SNII (0) z Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
45 Escape model Exgal. protons, γ s and ν s Extragalactic proton flux in escape model: α p = 2.2 requires late redshift evolution: 20 N c (z)/n c (0) BL Lacs ρ. SNII (z)/ρ. SNII (0) z BL Lacs/FR-I are promising sources Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
46 Escape model Exgal. protons, γ s and ν s Extragalactic proton flux in escape model: α p = 2.2 requires late redshift evolution: BL Lacs/FR-I are promising sources E 2 F(E) [ev/cm 2 /s/sr] KASCADE KASCADE Grande KASCADE Grande EG P 25 pc with Auger limit -1 Auger 2013 Auger 2013 Protons BL Lacs E [ev] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
47 Escape model Exgal. protons, γ s and ν s Diffuse fluxes from BL Lacs α = 2.17 and E τ = 3 11 ev 00 ν gal (75%) je 2, ev cm -2 s -1 sr -1 0 p γ 1 ν EG KASCADE 2013 KASCADE Grande EG Auger 2013 Protons E, ev Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
48 Escape model Exgal. protons, γ s and ν s Diffuse fluxes from BL Lacs α = 2.1 and E τ = 3 11 ev je 2, ev cm -2 s -1 sr ν gal (37%) p γ 1 ν EG KASCADE 2013 KASCADE Grande EG Auger 2013 Protons E, ev Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
49 Escape model Exgal. protons, γ s and ν s Diffuse fluxes from BL Lacs α = 2.1 and E τ = 3 14 ev 00 ν gal (85%) je 2, ev cm -2 s -1 sr -1 0 p γ 1 ν EG KASCADE 2013 KASCADE Grande EG Auger 2013 Protons E, ev Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
50 Escape model Exgal. protons, γ s and ν s Diffuse fluxes from BL Lacs 00 ν gal (75%) je 2, ev cm -2 s -1 sr -1 0 p γ 1 ν EG KASCADE 2013 KASCADE Grande EG Auger 2013 Protons E, ev BL Lac s can explain CR proton flux EGRB and large fraction of IceCube ν from pp interactions Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
51 Local source Anisotropies Anisotropy of a single source if only turbulent field: diffusion = random walk = free quantum particle number density is Gaussian with σ 2 = 4DT δ = 3D n c n = 3R 2T what happens for general fields? Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
52 Local source Anisotropies Anisotropy of a single source if only turbulent field: diffusion = random walk = free quantum particle number density is Gaussian with σ 2 = 4DT δ = 3D n c n = 3R 2T what happens for general fields? Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
53 Local source Anisotropies Anisotropy of a single source if only turbulent field: diffusion = random walk = free quantum particle number density is Gaussian with σ 2 = 4DT δ = 3D n c n = 3R 2T what happens for general fields? Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
54 Local source Anisotropies Anisotropy of a single source: only turbulent field B 0 = 0 G 3/2 50 pc / ct 1 kpc 0.1 Anisotropy (R / 50 pc) kpc Years [Savchenko, MK, Semikoz 15 ] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
55 Local source Anisotropies Anisotropy of a single source: plus regular B 0 = 1 G 3/2 50 pc / ct 1 kpc 0.1 Anisotropy (R / 50 pc) kpc Years [Savchenko, MK, Semikoz 15 ] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
56 Local source Anisotropies Anisotropy of a single source: B 0 = 1 G 3/2 50 pc / ct 1 kpc 0.1 Anisotropy (R / 50 pc) kpc Years regular field changes n(x), but keeps it Gaussian no change in δ Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
57 Local source Anisotropies Anisotropy of a single source: -3 δ -4 1 PeV all data IceCube TeV fit 1 SN Galactic -5 total [Savchenko, MK, Semikoz 15 ] E [ev] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
58 Local source Antimatter fluxes Single source: other signatures 2 Myr SN explains anomalous 60 Fe sediments [Ellis+ 96 ] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
59 Local source Antimatter fluxes Single source: other signatures 2 Myr SN explains anomalous 60 Fe sediments [Ellis+ 96 ] secondaries: p diffuse as p leads to constant p/p ratio p/p ratio fixed by source age p flux is predicted e + flux is predicted relative ratio of p and e + depends only on their Z factors Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
60 Local source Antimatter fluxes Single source: other signatures 2 Myr SN explains anomalous 60 Fe sediments [Ellis+ 96 ] secondaries: p diffuse as p leads to constant p/p ratio p/p ratio fixed by source age p flux is predicted e + flux is predicted relative ratio of p and e + depends only on their Z factors may responsible for different slopes of local p and nuclei fluxes Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
61 Local source Antimatter fluxes Single source: proton flux [MK, Neronov, Semikoz 15 ] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
62 Local source Antimatter fluxes Single source: positrons [MK, Neronov, Semikoz 15 ] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
63 Local source Antimatter fluxes Single source: antiprotons [MK, Neronov, Semikoz 15 ] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
64 Conclusions Conclusions I Knee due to CR escape recovery of fluxes as suggested by KASCADE-Grande probes GMF: suggests small Brms and small l coh transition to light-medium extragalactic CRs completed at 18 ev propagation feature is unavoidable, only possible to shift to higher energies source effects may be on top, but seem not necessary Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
65 Conclusions Conclusions I Knee due to CR escape recovery of fluxes as suggested by KASCADE-Grande probes GMF: suggests small Brms and small l coh transition to light-medium extragalactic CRs completed at 18 ev propagation feature is unavoidable, only possible to shift to higher energies source effects may be on top, but seem not necessary Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
66 Conclusions Conclusions I Knee due to CR escape recovery of fluxes as suggested by KASCADE-Grande probes GMF: suggests small Brms and small l coh transition to light-medium extragalactic CRs completed at 18 ev propagation feature is unavoidable, only possible to shift to higher energies source effects may be on top, but seem not necessary Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
67 Conclusions Conclusions I Knee due to CR escape recovery of fluxes as suggested by KASCADE-Grande probes GMF: suggests small Brms and small l coh transition to light-medium extragalactic CRs completed at 18 ev propagation feature is unavoidable, only possible to shift to higher energies source effects may be on top, but seem not necessary Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
68 Conclusions Conclusions II 1 Single source: anisotropy dipole formula δ = 3R/2T holds universally in quasi-gaussian regime plateau of δ points to dominance of single source 2 Single source: antimatter consistent explanation of p, p and e + fluxes consistent with 60 Fe and δ 3 local geometry of GMF is important Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
69 Conclusions Conclusions II 1 Single source: anisotropy dipole formula δ = 3R/2T holds universally in quasi-gaussian regime plateau of δ points to dominance of single source 2 Single source: antimatter consistent explanation of p, p and e + fluxes consistent with 60 Fe and δ 3 local geometry of GMF is important Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
70 Conclusions Conclusions II 1 Single source: anisotropy dipole formula δ = 3R/2T holds universally in quasi-gaussian regime plateau of δ points to dominance of single source 2 Single source: antimatter consistent explanation of p, p and e + fluxes consistent with 60 Fe and δ 3 local geometry of GMF is important Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Escape Model DESY Zeuthen, / 30
News from High-Energy Cosmic Rays and Neutrinos. Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim
 News from High-Energy Cosmic Rays and Neutrinos Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Introduction Outline of the talk 1 Introduction Is progress slow? Results on Composition γ s and ν s as CR secondaries
News from High-Energy Cosmic Rays and Neutrinos Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Introduction Outline of the talk 1 Introduction Is progress slow? Results on Composition γ s and ν s as CR secondaries
Charged Cosmic Rays and Neutrinos
 Charged Cosmic Rays and Neutrinos Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Introduction Outline of the talk 1 Introduction talk by F. Halzen 2 SNRs as Galactic CR sources 3 Extragalactic CRs transition anisotropies
Charged Cosmic Rays and Neutrinos Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Introduction Outline of the talk 1 Introduction talk by F. Halzen 2 SNRs as Galactic CR sources 3 Extragalactic CRs transition anisotropies
Galactic Neutrinos. Michael Kachelrieß. NTNU, Trondheim
 Galactic Neutrinos Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Introduction Outline of the talk 1 Introduction Observations Cascade limit and implications 2 Neutrinos from the Galactic CR sea Galactic plane
Galactic Neutrinos Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Introduction Outline of the talk 1 Introduction Observations Cascade limit and implications 2 Neutrinos from the Galactic CR sea Galactic plane
The 2 Icecube PeV events [A. ] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23
![The 2 Icecube PeV events [A. ] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23 The 2 Icecube PeV events [A. ] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran / 23](/thumbs/92/110652138.jpg) The 2 Icecube PeV events [A. Schuhkraft@NOW2012 ] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran 2012 1 / 23 The 2 Icecube PeV events [A. Schuhkraft@NOW2012 ] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU
The 2 Icecube PeV events [A. Schuhkraft@NOW2012 ] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU Trondheim) Cosmic Rays IPM School, Tehran 2012 1 / 23 The 2 Icecube PeV events [A. Schuhkraft@NOW2012 ] Michael Kachelrieß (NTNU
Cosmic Rays, Photons and Neutrinos
 Cosmic Rays, Photons and Neutrinos Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Introduction Outline Plan of the lectures: Cosmic rays Galactic cosmic rays Basic observations Acceleration Supernova remnants Problems
Cosmic Rays, Photons and Neutrinos Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Introduction Outline Plan of the lectures: Cosmic rays Galactic cosmic rays Basic observations Acceleration Supernova remnants Problems
Multi-Messenger Astonomy with Cen A?
 Multi-Messenger Astonomy with Cen A? Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Outline of the talk 1 Introduction 2 Dawn of charged particle astronomy? Expectations vs. Auger data Effects of cluster fields
Multi-Messenger Astonomy with Cen A? Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Outline of the talk 1 Introduction 2 Dawn of charged particle astronomy? Expectations vs. Auger data Effects of cluster fields
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 5 Aug 2014
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 5 Aug 2014 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 5 Aug 2014](/thumbs/88/115022632.jpg) Explaining the Spectra of Cosmic Ray Groups above the Knee by Escape from the Galaxy G. Giacinti 1, M. Kachelrieß 2, and D. V. Semikoz 3 1 University of Oxford, Clarendon Laboratory, Oxford, United Kingdom
Explaining the Spectra of Cosmic Ray Groups above the Knee by Escape from the Galaxy G. Giacinti 1, M. Kachelrieß 2, and D. V. Semikoz 3 1 University of Oxford, Clarendon Laboratory, Oxford, United Kingdom
Extensive Air Shower and cosmic ray physics above ev. M. Bertaina Univ. Torino & INFN
 Extensive Air Shower and cosmic ray physics above 10 17 ev M. Bertaina Univ. Torino & INFN ISMD 2015, Wildbad Kreuth 5-9 October 2015 Outline:» Part I: A general overview of cosmic ray science.» Part II:
Extensive Air Shower and cosmic ray physics above 10 17 ev M. Bertaina Univ. Torino & INFN ISMD 2015, Wildbad Kreuth 5-9 October 2015 Outline:» Part I: A general overview of cosmic ray science.» Part II:
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 8 Apr 2015
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 8 Apr 2015 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 8 Apr 2015](/thumbs/94/118445418.jpg) Physics Procedia 00 (2015) 1 Physics Procedia www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia 13th International Conference on Topics in Astroparticle and Underground Physics Cosmic Rays from the Knee to the Ankle arxiv:1504.01859v1
Physics Procedia 00 (2015) 1 Physics Procedia www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia 13th International Conference on Topics in Astroparticle and Underground Physics Cosmic Rays from the Knee to the Ankle arxiv:1504.01859v1
Ultra-High Energy Cosmic Rays (III)
 Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe in der Helmholtz-Gemeinschaft Ultra-High Energy Cosmic Rays (III) Ralph Engel Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe & Karlsruhe Institute of Technology Outline Brief overview (experimental
Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe in der Helmholtz-Gemeinschaft Ultra-High Energy Cosmic Rays (III) Ralph Engel Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe & Karlsruhe Institute of Technology Outline Brief overview (experimental
Air Shower Measurements from PeV to EeV
 Air Shower Measurements from PeV to EeV Andreas Haungs haungs@ik.fzk.de James L. Pinfold August 2006 TeV workshop Madison, US Andreas Haungs 1 Cosmic Rays around the knee(s) EeV PeV Knee 2 nd Knee? Ralph
Air Shower Measurements from PeV to EeV Andreas Haungs haungs@ik.fzk.de James L. Pinfold August 2006 TeV workshop Madison, US Andreas Haungs 1 Cosmic Rays around the knee(s) EeV PeV Knee 2 nd Knee? Ralph
ULTRA-HIGH ENERGY COSMIC RAY COMPOSITION and MUON CONTENT vs. HADRONIC MODELS. Esteban Roulet Bariloche, Argentina
 ULTRA-HIGH ENERGY COSMIC RAY COMPOSITION and MUON CONTENT vs. HADRONIC MODELS Esteban Roulet Bariloche, Argentina Many observables are sensitive to CR composition Shower maximum TA APP 64 (2014) Auger
ULTRA-HIGH ENERGY COSMIC RAY COMPOSITION and MUON CONTENT vs. HADRONIC MODELS Esteban Roulet Bariloche, Argentina Many observables are sensitive to CR composition Shower maximum TA APP 64 (2014) Auger
TeV Cosmic Ray Anisotropies at Various Angular Scales
 TeV Cosmic Ray Anisotropies at Various Angular Scales Gwenael Giacinti University of Oxford, Clarendon Laboratory Based on : GG & G.Sigl GG, M.Kachelriess, D.Semikoz Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 071101(2012)
TeV Cosmic Ray Anisotropies at Various Angular Scales Gwenael Giacinti University of Oxford, Clarendon Laboratory Based on : GG & G.Sigl GG, M.Kachelriess, D.Semikoz Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 071101(2012)
High-energy cosmic rays
 High-energy cosmic rays And their acceleration Tom Gaisser 1 Outline Sources and acceleration mechanism End of the galactic cosmic-ray spectrum Transition to extra-galactic population Key questions Tom
High-energy cosmic rays And their acceleration Tom Gaisser 1 Outline Sources and acceleration mechanism End of the galactic cosmic-ray spectrum Transition to extra-galactic population Key questions Tom
Latest results and perspectives of the KASCADE-Grande EAS facility
 Latest results and perspectives of the KASCADE-Grande EAS facility 29/6-2/7/2010, Nantes, France Andreas Haungs 1 Motivation KASCADE-Grande Knee EeV PeV g-eg? Radio?! KASCADE 10 15-10 17 ev: Origin of
Latest results and perspectives of the KASCADE-Grande EAS facility 29/6-2/7/2010, Nantes, France Andreas Haungs 1 Motivation KASCADE-Grande Knee EeV PeV g-eg? Radio?! KASCADE 10 15-10 17 ev: Origin of
Seeing the moon shadow in CRs
 Seeing the moon shadow in CRs and using the Earth field as a spectrometer Tibet III Amenomori et al. arxiv:0810.3757 see also ARGO-YBJ results Bartoli et. al, arxiv:1107.4887 Milargo: 100% coverage r owe
Seeing the moon shadow in CRs and using the Earth field as a spectrometer Tibet III Amenomori et al. arxiv:0810.3757 see also ARGO-YBJ results Bartoli et. al, arxiv:1107.4887 Milargo: 100% coverage r owe
Measurement of the cosmic ray spectrum and chemical composition in the ev energy range
 Measurement of the cosmic ray spectrum and chemical composition in the - 18 ev energy range Andrea Chiavassa 1, 1 Dipartimento di Fisica dell Universitá degli Studi di Torino & INFN Via Pietro Giuria 1,
Measurement of the cosmic ray spectrum and chemical composition in the - 18 ev energy range Andrea Chiavassa 1, 1 Dipartimento di Fisica dell Universitá degli Studi di Torino & INFN Via Pietro Giuria 1,
Cosmic-ray energy spectrum around the knee
 Cosmic-ray energy spectrum around the knee M. SHIBATA Department of Physics, Yokohama National University, Yokohama, 240-8501, Japan Interesting global and fine structures of cosmic-ray energy spectrum
Cosmic-ray energy spectrum around the knee M. SHIBATA Department of Physics, Yokohama National University, Yokohama, 240-8501, Japan Interesting global and fine structures of cosmic-ray energy spectrum
Propagation of TeV PeV Cosmic Rays in the Galactic Magnetic Field
 Propagation of TeV PeV Cosmic Rays in the Galactic Magnetic Field Gwenael Giacinti Clarendon Laboratory, University of Oxford In collaboration with : GG & G.Sigl / Based on : Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 071101(2012)
Propagation of TeV PeV Cosmic Rays in the Galactic Magnetic Field Gwenael Giacinti Clarendon Laboratory, University of Oxford In collaboration with : GG & G.Sigl / Based on : Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 071101(2012)
Questions 1pc = 3 ly = km
 Cosmic Rays Historical hints Primary Cosmic Rays: - Cosmic Ray Energy Spectrum - Composition - Origin and Propagation - The knee region and the ankle Secondary CRs: -shower development - interactions Detection:
Cosmic Rays Historical hints Primary Cosmic Rays: - Cosmic Ray Energy Spectrum - Composition - Origin and Propagation - The knee region and the ankle Secondary CRs: -shower development - interactions Detection:
ON PROBABLE CONTRIBUTION OF NEARBY SOURCES TO ANISOTROPY AND SPECTRUM OF COSMIC RAYS AT TEV-PEV-ENERGIES
 ON PROBABLE CONTRIBUTION OF NEARBY SOURCES TO ANISOTROPY AND SPECTRUM OF COSMIC RAYS AT TEV-PEV-ENERGIES SVESHNIKOVA L.G. 1, STRELNIKOVA O.N. 1, PTUSKIN V.S. 3 1 Lomonosov Moscow State University, SINP,
ON PROBABLE CONTRIBUTION OF NEARBY SOURCES TO ANISOTROPY AND SPECTRUM OF COSMIC RAYS AT TEV-PEV-ENERGIES SVESHNIKOVA L.G. 1, STRELNIKOVA O.N. 1, PTUSKIN V.S. 3 1 Lomonosov Moscow State University, SINP,
Antimatter from Supernova Remnants
 Antimatter from Supernova Remnants Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim with S. Ostapchenko, R. Tomàs - PAMELA anomaly )) )+ φ(e + ) / (φ(e + 0.4 0.3 0.2 Positron fraction φ(e 0.1 0.02 Muller & Tang 1987
Antimatter from Supernova Remnants Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim with S. Ostapchenko, R. Tomàs - PAMELA anomaly )) )+ φ(e + ) / (φ(e + 0.4 0.3 0.2 Positron fraction φ(e 0.1 0.02 Muller & Tang 1987
Probing the extragalactic cosmic rays origin with gamma-ray and neutrino backgrounds
 Probing the extragalactic cosmic rays origin with gamma-ray and neutrino backgrounds Denis Allard laboratoire Astroparticule et Cosmologie (APC, CNRS/Paris 7) in collaboration with Noemie Globus, E. Parizot,
Probing the extragalactic cosmic rays origin with gamma-ray and neutrino backgrounds Denis Allard laboratoire Astroparticule et Cosmologie (APC, CNRS/Paris 7) in collaboration with Noemie Globus, E. Parizot,
PROPAGATION OF UHE HEAVY NUCLEI IN THE GALACTIC MAGNETIC FIELD
 PROPAGATION OF UHE HEAVY NUCLEI IN THE GALACTIC MAGNETIC FIELD G. GIACINTI (APC Paris, France), M. KACHELRIESS (NTNU, Norway), D. V. SEMIKOZ (APC Paris, France), G. SIGL (U. Hamburg, Germany) Goal of the
PROPAGATION OF UHE HEAVY NUCLEI IN THE GALACTIC MAGNETIC FIELD G. GIACINTI (APC Paris, France), M. KACHELRIESS (NTNU, Norway), D. V. SEMIKOZ (APC Paris, France), G. SIGL (U. Hamburg, Germany) Goal of the
From the Knee to the toes: The challenge of cosmic-ray composition
 New Views of the Universe December 8 th 13 th, 2005, Chicago From the Knee to the toes: The challenge of cosmic-ray composition Jörg R. Hörandel University of Karlsruhe www-ik.fzk.de/~joerg New Views of
New Views of the Universe December 8 th 13 th, 2005, Chicago From the Knee to the toes: The challenge of cosmic-ray composition Jörg R. Hörandel University of Karlsruhe www-ik.fzk.de/~joerg New Views of
Cosmic Rays in large air-shower detectors
 Cosmic Rays in large air-shower detectors 2. The cosmic-ray spectrum from Galactic to Extra-galactic Seattle, July 2, 2009 Tom Gaisser 1 Cascade equations For hadronic cascades in the atmosphere X = depth
Cosmic Rays in large air-shower detectors 2. The cosmic-ray spectrum from Galactic to Extra-galactic Seattle, July 2, 2009 Tom Gaisser 1 Cascade equations For hadronic cascades in the atmosphere X = depth
Recent Results from the KASCADE-Grande Data Analysis
 Recent Results from the KASCADE-Grande Data Analysis Donghwa Kang for the KASCADE-Grande Collaboration Karlsruhe Institute of Technology 20 th ISVHECRI 21 25 May 2018, Nagoya, Japan Status & Prospect KASCADE
Recent Results from the KASCADE-Grande Data Analysis Donghwa Kang for the KASCADE-Grande Collaboration Karlsruhe Institute of Technology 20 th ISVHECRI 21 25 May 2018, Nagoya, Japan Status & Prospect KASCADE
Cosmic rays in the knee energy range
 Astrophys. Space Sci. Trans., 7, 295 301, 2011 doi:.5194/astra-7-295-2011 Author(s) 2011. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Astrophysics and Space Sciences Transactions Cosmic rays in the knee energy range A.
Astrophys. Space Sci. Trans., 7, 295 301, 2011 doi:.5194/astra-7-295-2011 Author(s) 2011. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Astrophysics and Space Sciences Transactions Cosmic rays in the knee energy range A.
Astroparticle Physics. Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim
 Astroparticle Physics Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Plan of the lectures: Today: High energy astrophysics Cosmic rays Observations Acceleration, possible sources High energy photons and neutrinos
Astroparticle Physics Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Plan of the lectures: Today: High energy astrophysics Cosmic rays Observations Acceleration, possible sources High energy photons and neutrinos
UHECR: Acceleration and Propagation
 UHECR: Acceleration and Propagation V. Berezinsky INFN, Gran Sasso Science Institute and Laboratori Nazionali del Gran Sasso, Italy ACCELERATION UHE particles with energies observed up to E 3 20 ev can
UHECR: Acceleration and Propagation V. Berezinsky INFN, Gran Sasso Science Institute and Laboratori Nazionali del Gran Sasso, Italy ACCELERATION UHE particles with energies observed up to E 3 20 ev can
The air-shower experiment KASCADE-Grande
 The air-shower experiment KASCADE-Grande Andreas Haungs KASCADE-Grande 1 Cosmic Rays around the knee(s) galactic origin of CR EeV PeV Knee 2 nd Knee? Ralph Engel, 2004 KASCADE 1995-2009 -Grande 2003-2009
The air-shower experiment KASCADE-Grande Andreas Haungs KASCADE-Grande 1 Cosmic Rays around the knee(s) galactic origin of CR EeV PeV Knee 2 nd Knee? Ralph Engel, 2004 KASCADE 1995-2009 -Grande 2003-2009
A few grams of matter in a bright world
 A few grams of matter in a bright world Benjamin Rouillé d Orfeuil (LAL) Fellow Collaborators: D. Allard, C. Lachaud & E. Parizot (APC) A. V. Olinto (University of Chicago) February 12 th 2013 LAL All
A few grams of matter in a bright world Benjamin Rouillé d Orfeuil (LAL) Fellow Collaborators: D. Allard, C. Lachaud & E. Parizot (APC) A. V. Olinto (University of Chicago) February 12 th 2013 LAL All
On the GCR/EGCR transition and UHECR origin
 UHECR 2014 13 15 October 2014 / Springdale (Utah; USA) On the GCR/EGCR transition and UHECR origin Etienne Parizot 1, Noémie Globus 2 & Denis Allard 1 1. APC Université Paris Diderot France 2. Tel Aviv
UHECR 2014 13 15 October 2014 / Springdale (Utah; USA) On the GCR/EGCR transition and UHECR origin Etienne Parizot 1, Noémie Globus 2 & Denis Allard 1 1. APC Université Paris Diderot France 2. Tel Aviv
TeV gamma-rays from UHECR sources 22 radio log10(e /ev ) 16 photon horizon γγ e + e CMB 14 IR kpc 10kpc 100kpc M pc Virgo 10M pc 100M pc G
 Gamma-rays from CR sources Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] TeV gamma-rays from UHECR sources 22 radio 20 18 log10(e /ev ) 16 photon horizon γγ e + e CMB 14 IR 12 10 kpc 10kpc 100kpc M pc Virgo 10M
Gamma-rays from CR sources Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] TeV gamma-rays from UHECR sources 22 radio 20 18 log10(e /ev ) 16 photon horizon γγ e + e CMB 14 IR 12 10 kpc 10kpc 100kpc M pc Virgo 10M
Ultra-High Energy Cosmic Rays: Results, and Prospects
 26th Texas Symposium on Relativistic Astrophysics, São Paulo, Brazil, 15.-20., 2012 Ultra-High Energy Cosmic Rays: Results, and Prospects Karl-Heinz Kampert, University Wuppertal Area Grant Karl-Heinz
26th Texas Symposium on Relativistic Astrophysics, São Paulo, Brazil, 15.-20., 2012 Ultra-High Energy Cosmic Rays: Results, and Prospects Karl-Heinz Kampert, University Wuppertal Area Grant Karl-Heinz
Mass composition studies around the knee with the Tunka-133 array. Epimakhov Sergey for the Tunka-133 collaboration
 Mass composition studies around the knee with the Tunka-133 array Epimakhov Sergey for the Tunka-133 collaboration The Tunka-133 array non-imaging wide-angle Cherenkov array the knee energy range Tunka
Mass composition studies around the knee with the Tunka-133 array Epimakhov Sergey for the Tunka-133 collaboration The Tunka-133 array non-imaging wide-angle Cherenkov array the knee energy range Tunka
ULTRA HIGH ENERGY COSMIC RAYS WHERE DO WE STAND AFTER 10 YEARS AT THE PIERRE AUGER OBSERVATORY
 Antoine Letessier Selvon (CNRS/UPMC) FRIF days Dourdan January 2014!1 ULTRA HIGH ENERGY COSMIC RAYS WHERE DO WE STAND AFTER YEARS AT THE PIERRE AUGER OBSERVATORY Antoine Letessier Selvon (CNRS/UPMC) FRIF
Antoine Letessier Selvon (CNRS/UPMC) FRIF days Dourdan January 2014!1 ULTRA HIGH ENERGY COSMIC RAYS WHERE DO WE STAND AFTER YEARS AT THE PIERRE AUGER OBSERVATORY Antoine Letessier Selvon (CNRS/UPMC) FRIF
Cosmic Ray Astronomy. Qingling Ni
 Cosmic Ray Astronomy Qingling Ni What is Cosmic Ray? Mainly charged particles: protons (hydrogen nuclei)+helium nuclei+heavier nuclei What s the origin of them? What happened during their propagation?
Cosmic Ray Astronomy Qingling Ni What is Cosmic Ray? Mainly charged particles: protons (hydrogen nuclei)+helium nuclei+heavier nuclei What s the origin of them? What happened during their propagation?
PeV Neutrinos from Star-forming Regions. Hajime Takami KEK, JSPS Fellow
 PeV Neutrinos from Star-forming Regions Hajime Takami KEK, JSPS Fellow Outline 0. Basic requirements for PeV neutrinos. Review on cosmogenic neutrinos for the PeV neutrinos. PeV neutrinos from Star-forming
PeV Neutrinos from Star-forming Regions Hajime Takami KEK, JSPS Fellow Outline 0. Basic requirements for PeV neutrinos. Review on cosmogenic neutrinos for the PeV neutrinos. PeV neutrinos from Star-forming
Status KASCADE-Grande. April 2007 Aspen workshop on cosmic ray physics Andreas Haungs 1
 Status KASCADE-Grande April 2007 Aspen workshop on cosmic ray physics Andreas Haungs 1 Cosmic Rays around the knee(s) Astrophysical questions for this energy range: (1 st ) knee Knee position Composition
Status KASCADE-Grande April 2007 Aspen workshop on cosmic ray physics Andreas Haungs 1 Cosmic Rays around the knee(s) Astrophysical questions for this energy range: (1 st ) knee Knee position Composition
Measurement of the Cosmic Ray Energy Spectrum with ARGO-YBJ
 Measurement of the Cosmic Ray Energy Spectrum with ARGO-YBJ Ivan De Mitri ( on behalf of the ARGO-YBJ collaboration ) Dipartimento di Matematica e Fisica " E. De Giorgi", Universita del Salento, Lecce,
Measurement of the Cosmic Ray Energy Spectrum with ARGO-YBJ Ivan De Mitri ( on behalf of the ARGO-YBJ collaboration ) Dipartimento di Matematica e Fisica " E. De Giorgi", Universita del Salento, Lecce,
An Auger Observatory View of Centaurus A
 An Auger Observatory View of Centaurus A Roger Clay, University of Adelaide based on work particularly done with: Bruce Dawson, Adelaide Jose Bellido, Adelaide Ben Whelan, Adelaide and the Auger Collaboration
An Auger Observatory View of Centaurus A Roger Clay, University of Adelaide based on work particularly done with: Bruce Dawson, Adelaide Jose Bellido, Adelaide Ben Whelan, Adelaide and the Auger Collaboration
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 28 Jan 2013
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 28 Jan 2013 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 28 Jan 2013](/thumbs/89/99036295.jpg) Measurements of the cosmic ray spectrum and average mass with IceCube Shahid Hussain arxiv:1301.6619v1 [astro-ph.he] 28 Jan 2013 Abstract Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Delaware for
Measurements of the cosmic ray spectrum and average mass with IceCube Shahid Hussain arxiv:1301.6619v1 [astro-ph.he] 28 Jan 2013 Abstract Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Delaware for
High Energy Cosmic Ray Interactions
 Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe in der Helmholtz-Gemeinschaft High Energy Cosmic Ray Interactions (Lecture 1: Basics) Ralph Engel Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) Outline Lecture 1 Basics, low-energy
Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe in der Helmholtz-Gemeinschaft High Energy Cosmic Ray Interactions (Lecture 1: Basics) Ralph Engel Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) Outline Lecture 1 Basics, low-energy
Ultra- high energy cosmic rays
 Ultra- high energy cosmic rays Tiina Suomijärvi Institut de Physique Nucléaire Université Paris Sud, Orsay, IN2P3/CNRS, France Atélier CTA, IAP, Paris, 30-31 June 2014 Outline Pierre Auger Observatory:
Ultra- high energy cosmic rays Tiina Suomijärvi Institut de Physique Nucléaire Université Paris Sud, Orsay, IN2P3/CNRS, France Atélier CTA, IAP, Paris, 30-31 June 2014 Outline Pierre Auger Observatory:
Extensive Air Showers and Particle Physics Todor Stanev Bartol Research Institute Dept Physics and Astronomy University of Delaware
 Extensive Air Showers and Particle Physics Todor Stanev Bartol Research Institute Dept Physics and Astronomy University of Delaware Extensive air showers are the cascades that develop in the atmosphere
Extensive Air Showers and Particle Physics Todor Stanev Bartol Research Institute Dept Physics and Astronomy University of Delaware Extensive air showers are the cascades that develop in the atmosphere
STATUS OF ULTRA HIGH ENERGY COSMIC RAYS
 STATUS OF ULTRA HIGH ENERGY COSMIC RAYS Esteban Roulet (Bariloche) COSMO / CosPA 2010, Tokyo Power law flux stochastic (Fermi) acceleration in shocks cosmic ray flux Small fractional energy gain after
STATUS OF ULTRA HIGH ENERGY COSMIC RAYS Esteban Roulet (Bariloche) COSMO / CosPA 2010, Tokyo Power law flux stochastic (Fermi) acceleration in shocks cosmic ray flux Small fractional energy gain after
Mass Composition Study at the Pierre Auger Observatory
 OBSERVATORY Mass Composition Study at the Pierre Auger Observatory Laura Collica for the Auger Milano Group 4.04.2013, Astrosiesta INAF Milano 1 Outline The physics: The UHECR spectrum Extensive Air Showers
OBSERVATORY Mass Composition Study at the Pierre Auger Observatory Laura Collica for the Auger Milano Group 4.04.2013, Astrosiesta INAF Milano 1 Outline The physics: The UHECR spectrum Extensive Air Showers
Ultrahigh Energy cosmic rays II
 Ultrahigh Energy cosmic rays II Today we will discuss the new data on UHECR presented during the last couple of years by the Auger observatory in Argentina. These data do not match previous analyses and
Ultrahigh Energy cosmic rays II Today we will discuss the new data on UHECR presented during the last couple of years by the Auger observatory in Argentina. These data do not match previous analyses and
Interpretation of cosmic ray spectrum above the knee measured by the Tunka-133 experiment
 Interpretation of cosmic ray spectrum above the knee measured by the Tunka-133 experiment L.G. Sveshnikova, L.A. Kuzmichev, E.E. Korosteleva, V.A. Prosin, V.S. Ptuskin et al Moscow State University Skobeltsyn
Interpretation of cosmic ray spectrum above the knee measured by the Tunka-133 experiment L.G. Sveshnikova, L.A. Kuzmichev, E.E. Korosteleva, V.A. Prosin, V.S. Ptuskin et al Moscow State University Skobeltsyn
Evidence of Stochastic Acceleration of Secondary. Antiprotons by Supernova Remnants! Ilias Cholis, 08/09/2017
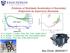 C [ ] -4 Evidence of Stochastic Acceleration of Secondary 2.2 1.0 2.0 1.8 1.6 1.4 1.2 C k p p Φ /Φ ratio fit Antiprotons by Supernova Remnants! 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0-6 - 1 k [ GV ] -1 AMS-02 PAMELA Fermi
C [ ] -4 Evidence of Stochastic Acceleration of Secondary 2.2 1.0 2.0 1.8 1.6 1.4 1.2 C k p p Φ /Φ ratio fit Antiprotons by Supernova Remnants! 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0-6 - 1 k [ GV ] -1 AMS-02 PAMELA Fermi
Gamma-ray and neutrino diffuse emissions of the Galaxy above the TeV
 Gamma-ray and neutrino diffuse emissions of the Galaxy above the TeV (with spatial dependent CR transport) D. Grasso (INFN, Pisa) with D. Gaggero, A. Marinelli, A. Urbano, M. Valli IceCube recent results
Gamma-ray and neutrino diffuse emissions of the Galaxy above the TeV (with spatial dependent CR transport) D. Grasso (INFN, Pisa) with D. Gaggero, A. Marinelli, A. Urbano, M. Valli IceCube recent results
Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays: Observations and Analysis
 Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays: Observations and Analysis NOT A NEW PROBLEM, STILL UNSOLVED John Linsley (PRL 10 (1963) 146) reports on the detection in Vulcano Ranch of an air shower of energy above 1020
Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays: Observations and Analysis NOT A NEW PROBLEM, STILL UNSOLVED John Linsley (PRL 10 (1963) 146) reports on the detection in Vulcano Ranch of an air shower of energy above 1020
Studies of Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays with the Pierre Auger Observatory
 Studies of Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays with the Pierre Auger Observatory Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, Brazil E-mail: haris@if.ufrj.br Aquiring data continuously from 004, the Pierre Auger
Studies of Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays with the Pierre Auger Observatory Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, Brazil E-mail: haris@if.ufrj.br Aquiring data continuously from 004, the Pierre Auger
Ultrahigh Energy Cosmic Rays propagation II
 Ultrahigh Energy Cosmic Rays propagation II The March 6th lecture discussed the energy loss processes of protons, nuclei and gamma rays in interactions with the microwave background. Today I will give
Ultrahigh Energy Cosmic Rays propagation II The March 6th lecture discussed the energy loss processes of protons, nuclei and gamma rays in interactions with the microwave background. Today I will give
Cosmic Rays: high/low energy connections
 Lorentz Center Workshop Cosmic Ray Interactions: Bridging High and Low Energy Astrophysics 1 Cosmic Rays: high/low energy connections Etienne Parizot APC University of Paris 7 2 Cosmic rays: messages and
Lorentz Center Workshop Cosmic Ray Interactions: Bridging High and Low Energy Astrophysics 1 Cosmic Rays: high/low energy connections Etienne Parizot APC University of Paris 7 2 Cosmic rays: messages and
Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays What we have learnt from. HiRes and Auger. Andreas Zech Observatoire de Paris (Meudon) / LUTh
 Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays What we have learnt from HiRes and Auger Andreas Zech Observatoire de Paris (Meudon) / LUTh École de Chalonge, Paris, Outline The physics of Ultra-High Energy Cosmic Rays
Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays What we have learnt from HiRes and Auger Andreas Zech Observatoire de Paris (Meudon) / LUTh École de Chalonge, Paris, Outline The physics of Ultra-High Energy Cosmic Rays
Measurement of the cosmic ray all-particle and light-component energy spectra with the ARGO- YBJ experiment
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Measurement of the cosmic ray all-particle and light-component energy spectra with the ARGO- YBJ experiment To cite this article: Ivan De Mitri and
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Measurement of the cosmic ray all-particle and light-component energy spectra with the ARGO- YBJ experiment To cite this article: Ivan De Mitri and
Air showers in IceCube. Cosmic rays Neutrinos Gamma rays
 Air showers in IceCube Cosmic rays Neutrinos Gamma rays Cosmic rays Cosmic accelerators produce rela9vis9c protons and nuclei (cosmic rays) CR sources (such as SNR, AGN, GRB) are likely neutrino sources
Air showers in IceCube Cosmic rays Neutrinos Gamma rays Cosmic rays Cosmic accelerators produce rela9vis9c protons and nuclei (cosmic rays) CR sources (such as SNR, AGN, GRB) are likely neutrino sources
Cosmic ray studies at the Yakutsk EAS array: energy spectrum and mass composition
 Cosmic ray studies at the Yakutsk EAS array: energy spectrum and mass composition S. P. Knurenko 1 and A. Sabourov 2 1 s.p.knurenko@ikfia.ysn.ru, 2 tema@ikfia.ysn.ru Yu. G. Shafer Institute of cosmophysical
Cosmic ray studies at the Yakutsk EAS array: energy spectrum and mass composition S. P. Knurenko 1 and A. Sabourov 2 1 s.p.knurenko@ikfia.ysn.ru, 2 tema@ikfia.ysn.ru Yu. G. Shafer Institute of cosmophysical
UHECR autocorrelation function after Auger
 UHECR autocorrelation function after Auger Pasquale D. Serpico based on work in collaboration with A. Cuoco, S. Hannestad,, T. Haugbølle,, M. Kachelrieß (arxiv:0709.2712; arxiv:0809.4003 :0809.4003) SOCoR
UHECR autocorrelation function after Auger Pasquale D. Serpico based on work in collaboration with A. Cuoco, S. Hannestad,, T. Haugbølle,, M. Kachelrieß (arxiv:0709.2712; arxiv:0809.4003 :0809.4003) SOCoR
Charged-particle and gamma-ray astronomy: deciphering charged messages from the world s most powerful
 Charged-particle and gamma-ray astronomy: deciphering charged messages from the world s most powerful Charged-particle astronomy coming of age How it is done The sources The signals What we have learned
Charged-particle and gamma-ray astronomy: deciphering charged messages from the world s most powerful Charged-particle astronomy coming of age How it is done The sources The signals What we have learned
Cosmic Ray Transport (in the Galaxy) Luke Drury. Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies Institiúid Ard-Léinn Bhaile Átha Cliath
 Cosmic Ray Transport (in the Galaxy) Luke Drury Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies Institiúid Ard-Léinn Bhaile Átha Cliath 1 A few disclaimers and preliminary remarks! Not my main field of research
Cosmic Ray Transport (in the Galaxy) Luke Drury Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies Institiúid Ard-Léinn Bhaile Átha Cliath 1 A few disclaimers and preliminary remarks! Not my main field of research
Possible Multi-Messenger Sources of Gravitational Waves and Particle Radiation
 Possible Multi-Messenger Sources of Gravitational Waves and Particle Radiation 1. High Energy Neutrinos 2. Gamma-Ray Bursts and Gravitational Waves 3. Pulsars and Magnetars 4. Diffuse GW Flux from Cosmological
Possible Multi-Messenger Sources of Gravitational Waves and Particle Radiation 1. High Energy Neutrinos 2. Gamma-Ray Bursts and Gravitational Waves 3. Pulsars and Magnetars 4. Diffuse GW Flux from Cosmological
Ultra-High Energy Cosmic Rays and the GeV-TeV Diffuse Gamma-Ray Flux
 The 4th International Workshop on The Highest Energy Cosmic Rays and Their Sources INR, Moscow May 20-22, 2008 Ultra-High Energy Cosmic Rays and the GeV-TeV Diffuse Gamma-Ray Flux Oleg Kalashev* (INR RAS)
The 4th International Workshop on The Highest Energy Cosmic Rays and Their Sources INR, Moscow May 20-22, 2008 Ultra-High Energy Cosmic Rays and the GeV-TeV Diffuse Gamma-Ray Flux Oleg Kalashev* (INR RAS)
Measurement of air shower maxima and p-air cross section with the Telescope Array
 Measurement of air shower maxima and p-air cross section with the Telescope Array Yoshiki Tsunesada Graduate School of Science, Osaka City University May 18 2016 QCD At Cosmic Energies VII, Χαλκίδα, Greece
Measurement of air shower maxima and p-air cross section with the Telescope Array Yoshiki Tsunesada Graduate School of Science, Osaka City University May 18 2016 QCD At Cosmic Energies VII, Χαλκίδα, Greece
Cosmic Rays in large air-shower detectors
 Cosmic Rays in large air-shower detectors The cosmic-ray spectrum from Galactic to extra-galactic Berlin, 2 Oct 2009 Tom Gaisser 1 Cascade equations For hadronic cascades in the atmosphere X = depth into
Cosmic Rays in large air-shower detectors The cosmic-ray spectrum from Galactic to extra-galactic Berlin, 2 Oct 2009 Tom Gaisser 1 Cascade equations For hadronic cascades in the atmosphere X = depth into
Intergalactic Magnetic Field and Arrival Direction of Ultra-High-Energy Protons
 Intergalactic Magnetic Field and Arrival Direction of Ultra-High-Energy Protons Dongsu Ryu (Chungnam National U, Korea) Hyesung Kang (Pusan National U, Korea) Santabrata Das (Indian Institute of Technology
Intergalactic Magnetic Field and Arrival Direction of Ultra-High-Energy Protons Dongsu Ryu (Chungnam National U, Korea) Hyesung Kang (Pusan National U, Korea) Santabrata Das (Indian Institute of Technology
OVERVIEW OF THE RESULTS
 VIIIth International Workshop on the Dark Side of the Universe, Buzios STUDY OF THE ULTRA HIGH ENERGY COSMIC RAYS WITH THE AUGER DATA OVERVIEW OF THE RESULTS H. Lyberis on behalf of the Pierre Auger Collaboration
VIIIth International Workshop on the Dark Side of the Universe, Buzios STUDY OF THE ULTRA HIGH ENERGY COSMIC RAYS WITH THE AUGER DATA OVERVIEW OF THE RESULTS H. Lyberis on behalf of the Pierre Auger Collaboration
Cosmic Rays in the Galaxy
 1, Over View Cosmic Rays in the Galaxy Discovery : Legendary baloon flight of Victor Hess Observation of Cosmic Rays : Satellite, Balloon (Direct), Air shower (Indirect) Energy Spectrum of Cosmic Rays
1, Over View Cosmic Rays in the Galaxy Discovery : Legendary baloon flight of Victor Hess Observation of Cosmic Rays : Satellite, Balloon (Direct), Air shower (Indirect) Energy Spectrum of Cosmic Rays
THE PIERRE AUGER OBSERVATORY: COSMIC ACCELERATORS AND THE MOST ENERGETIC PARTICLES IN THE UNIVERSE
 Proceedings of IPAC, Kyoto, Japan FRYMH3 THE PIERRE AUGER OBSERVATORY: COSMIC ACCELERATORS AND THE MOST ENERGETIC PARTICLES IN THE UNIVERSE J. Blümer, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Karlsruhe, Germany
Proceedings of IPAC, Kyoto, Japan FRYMH3 THE PIERRE AUGER OBSERVATORY: COSMIC ACCELERATORS AND THE MOST ENERGETIC PARTICLES IN THE UNIVERSE J. Blümer, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Karlsruhe, Germany
Cosmic rays in the local interstellar medium
 Cosmic rays in the local interstellar medium Igor V. Moskalenko Igor V. Moskalenko/NASA-GSFC 1 LMC (Magellanic Cloud Emission Nuclear Data-2004/09/28, Line Survey: Smith, Points) Santa Fe R - H G - [S
Cosmic rays in the local interstellar medium Igor V. Moskalenko Igor V. Moskalenko/NASA-GSFC 1 LMC (Magellanic Cloud Emission Nuclear Data-2004/09/28, Line Survey: Smith, Points) Santa Fe R - H G - [S
Cosmic Rays 1. Introduction
 Cosmic Rays 1. Introduction Lecture 1: Introduction to cosmic rays Lecture 2: Atmospheric µ and ν and ν telescopes Lecture 3: Giant air shower experiments Exercise: Expectations for γ-ray & ν-astronomy
Cosmic Rays 1. Introduction Lecture 1: Introduction to cosmic rays Lecture 2: Atmospheric µ and ν and ν telescopes Lecture 3: Giant air shower experiments Exercise: Expectations for γ-ray & ν-astronomy
UHECRs sources and the Auger data
 UHECRs sources and the Auger data M. Kachelrieß Institutt for fysikk, NTNU Trondheim, Norway I review the evidence for a correlation of the arrival directions of UHECRs observed by the Pierre Auger Observatory
UHECRs sources and the Auger data M. Kachelrieß Institutt for fysikk, NTNU Trondheim, Norway I review the evidence for a correlation of the arrival directions of UHECRs observed by the Pierre Auger Observatory
Primary Cosmic Rays : what are we learning from AMS
 Primary Cosmic Rays : what are we learning from AMS Roberto Battiston University and INFN-TIFPA of Trento HERD Workshop IHEP-Beijing December 2-3 2013 1 Agile Fermi PAMELA AMS Direct study of the HESS
Primary Cosmic Rays : what are we learning from AMS Roberto Battiston University and INFN-TIFPA of Trento HERD Workshop IHEP-Beijing December 2-3 2013 1 Agile Fermi PAMELA AMS Direct study of the HESS
KASCADE-Grande energy spectrum of cosmic rays interpreted with post-lhc hadronic interaction models
 of cosmic rays interpreted with post-lhc hadronic interaction models 3, W.D. Apel 1, J.C. Arteaga-Velázquez 2, K. Bekk 1, J. Blümer 1,4, H. Bozdog 1, I.M. Brancus 5, E. Cantoni 3,6, A. Chiavassa 3, F.
of cosmic rays interpreted with post-lhc hadronic interaction models 3, W.D. Apel 1, J.C. Arteaga-Velázquez 2, K. Bekk 1, J. Blümer 1,4, H. Bozdog 1, I.M. Brancus 5, E. Cantoni 3,6, A. Chiavassa 3, F.
Cosmogenic neutrinos II
 Cosmogenic neutrinos II Dependence of fluxes on the cosmic ray injection spectra and the cosmological evolution of the cosmic ray sources Expectations from the cosmic ray spectrum measured by the Auger
Cosmogenic neutrinos II Dependence of fluxes on the cosmic ray injection spectra and the cosmological evolution of the cosmic ray sources Expectations from the cosmic ray spectrum measured by the Auger
Looking Beyond the Standard Model with Energetic Cosmic Particles
 Looking Beyond the Standard Model with Energetic Cosmic Particles Andreas Ringwald http://www.desy.de/ ringwald DESY Seminar Universität Dortmund June 13, 2006, Dortmund, Germany 1. Introduction Looking
Looking Beyond the Standard Model with Energetic Cosmic Particles Andreas Ringwald http://www.desy.de/ ringwald DESY Seminar Universität Dortmund June 13, 2006, Dortmund, Germany 1. Introduction Looking
Cosmic Ray Physics with the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer
 Cosmic Ray Physics with the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer Università di Roma La Sapienza, INFN on behalf of AMS Collaboration Outline Introduction AMS02 Spectrometer Cosmic Rays: origin & propagations: Dominant
Cosmic Ray Physics with the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer Università di Roma La Sapienza, INFN on behalf of AMS Collaboration Outline Introduction AMS02 Spectrometer Cosmic Rays: origin & propagations: Dominant
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 2 Mar 2012
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 2 Mar 2012 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 2 Mar 2012](/thumbs/75/72219355.jpg) Spectrum of cosmic-ray nucleons, kaon production, and the atmospheric muon charge ratio arxiv:1111.6675v2 [astro-ph.he] 2 Mar 2012 Abstract Thomas K. Gaisser Bartol Research Institute and Dept. of Physics
Spectrum of cosmic-ray nucleons, kaon production, and the atmospheric muon charge ratio arxiv:1111.6675v2 [astro-ph.he] 2 Mar 2012 Abstract Thomas K. Gaisser Bartol Research Institute and Dept. of Physics
Lower bound on the extragalactic magnetic field
 Lower bound on the extragalactic magnetic field Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Dolag, MK, Ostapchenko, Tomàs 10 Neronov, Semikoz, MK, Ostapchenko, Elyiv 10 Introduction Mean free path of photons
Lower bound on the extragalactic magnetic field Michael Kachelrieß NTNU, Trondheim [] Dolag, MK, Ostapchenko, Tomàs 10 Neronov, Semikoz, MK, Ostapchenko, Elyiv 10 Introduction Mean free path of photons
The Most Energetic Particles in Nature
 ASIAA/CCMS/IAMS/LeCosPA/NTU-Phys Joint Colloquium, April 7, 2015 The Most Energetic Particles in Nature Karl-Heinz Kampert University of Wuppertal Area Grant Karl-Heinz Kampert Taipei Colloq, 7.04.2015
ASIAA/CCMS/IAMS/LeCosPA/NTU-Phys Joint Colloquium, April 7, 2015 The Most Energetic Particles in Nature Karl-Heinz Kampert University of Wuppertal Area Grant Karl-Heinz Kampert Taipei Colloq, 7.04.2015
The Galactic diffuse gamma ray emission in the energy range 30 TeV 3 PeV
 The Galactic diffuse gamma ray emission in the energy range 30 TeV 3 PeV Mount Rainier by Will Christiansen Silvia Vernetto & Paolo Lipari 35th ICRC 12-20 July 2017 - Busan - South Korea Gamma ray astronomy
The Galactic diffuse gamma ray emission in the energy range 30 TeV 3 PeV Mount Rainier by Will Christiansen Silvia Vernetto & Paolo Lipari 35th ICRC 12-20 July 2017 - Busan - South Korea Gamma ray astronomy
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 30 May 2014
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 30 May 2014 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 30 May 2014](/thumbs/95/124608543.jpg) PeV neutrinos from interactions of cosmic rays with the interstellar medium in the Galaxy A. Neronov 1, D.Semikoz 2, C.Tchernin 1 1 ISDC, Department of Astronomy, University of Geneva, Ch. d Ecogia 16,
PeV neutrinos from interactions of cosmic rays with the interstellar medium in the Galaxy A. Neronov 1, D.Semikoz 2, C.Tchernin 1 1 ISDC, Department of Astronomy, University of Geneva, Ch. d Ecogia 16,
Cosmic Ray Composition and Spectra : Progress since Aspen 05. Gaurang B. Yodh UC Irvine
 Cosmic Ray Composition and Spectra : Progress since Aspen 05 Gaurang B. Yodh UC Irvine In this talk I outline my take on the question of composition from about 1 TeV to the highest energies. Important
Cosmic Ray Composition and Spectra : Progress since Aspen 05 Gaurang B. Yodh UC Irvine In this talk I outline my take on the question of composition from about 1 TeV to the highest energies. Important
Review of direct measurements of cosmic rays. Sources of Galactic cosmic rays APC, Paris - December 7-9, 2016
 Review of direct measurements of cosmic rays Sources of Galactic cosmic rays APC, Paris - December 7-9, 2016 CR astrophуsics main problems Sources? - Accelerators? The basic paradigm of CR acceleration
Review of direct measurements of cosmic rays Sources of Galactic cosmic rays APC, Paris - December 7-9, 2016 CR astrophуsics main problems Sources? - Accelerators? The basic paradigm of CR acceleration
Neutrino Oscillations and Astroparticle Physics (5) John Carr Centre de Physique des Particules de Marseille (IN2P3/CNRS) Pisa, 10 May 2002
 Neutrino Oscillations and Astroparticle Physics (5) John Carr Centre de Physique des Particules de Marseille (IN2P3/CNRS) Pisa, 10 May 2002 n High Energy Astronomy Multi-Messanger Astronomy Cosmic Rays
Neutrino Oscillations and Astroparticle Physics (5) John Carr Centre de Physique des Particules de Marseille (IN2P3/CNRS) Pisa, 10 May 2002 n High Energy Astronomy Multi-Messanger Astronomy Cosmic Rays
Dark Matter in the Universe
 Dark Matter in the Universe NTNU Trondheim [] Experimental anomalies: WMAP haze: synchrotron radiation from the GC Experimental anomalies: WMAP haze: synchrotron radiation from the GC Integral: positron
Dark Matter in the Universe NTNU Trondheim [] Experimental anomalies: WMAP haze: synchrotron radiation from the GC Experimental anomalies: WMAP haze: synchrotron radiation from the GC Integral: positron
Overview: UHECR spectrum and composition Arrival directions and magnetic field Method for search for UHE nuclei sources Application to the Auger data
 Overview: UHECR spectrum and composition Arrival directions and magnetic field Method for search for UHE nuclei sources Application to the Auger data Acceleration of UHECR A.G.N. GRB Radio Galaxy Lobe
Overview: UHECR spectrum and composition Arrival directions and magnetic field Method for search for UHE nuclei sources Application to the Auger data Acceleration of UHECR A.G.N. GRB Radio Galaxy Lobe
Blazars as the Astrophysical Counterparts of the IceCube Neutrinos
 Blazars as the Astrophysical Counterparts of the IceCube Neutrinos Maria Petropoulou Department of Physics & Astronomy, Purdue University, West Lafayette, USA Einstein Fellows Symposium Harvard-Smithsonian
Blazars as the Astrophysical Counterparts of the IceCube Neutrinos Maria Petropoulou Department of Physics & Astronomy, Purdue University, West Lafayette, USA Einstein Fellows Symposium Harvard-Smithsonian
Extremely High Energy Neutrinos
 Extremely High Energy Neutrinos A. Ringwald http://www.desy.de/ ringwald DESY 6 th National Astroparticle Physics Symposium February 3, 2006, Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam, Netherlands Extremely high energy
Extremely High Energy Neutrinos A. Ringwald http://www.desy.de/ ringwald DESY 6 th National Astroparticle Physics Symposium February 3, 2006, Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam, Netherlands Extremely high energy
Lessons 19 and 20. Detection of C.R. with energy > TeV Study of the C.R. isotropy/anisotropy Ground based detectors:
 Lessons 19 and 20 Detection of C.R. with energy > TeV Study of the C.R. isotropy/anisotropy Ground based detectors: Detection at ground of extensive Air Showers: nature, direction and energy of the primary
Lessons 19 and 20 Detection of C.R. with energy > TeV Study of the C.R. isotropy/anisotropy Ground based detectors: Detection at ground of extensive Air Showers: nature, direction and energy of the primary
Investigation on mass composition of UHE cosmic rays using CRPropa 2.0
 Investigation on mass composition of UHE cosmic rays using CRPropa. G Rastegarzade B Parvizi,, Physics Department, Semnan University, Semnan, P.O. Box 596-599, Iran Email: G_ rastegar@alum.sharif.edu Abstract
Investigation on mass composition of UHE cosmic rays using CRPropa. G Rastegarzade B Parvizi,, Physics Department, Semnan University, Semnan, P.O. Box 596-599, Iran Email: G_ rastegar@alum.sharif.edu Abstract
The Pierre Auger Observatory Status - First Results - Plans
 The Pierre Auger Observatory Status - First Results - Plans Andreas Haungs for the Pierre Auger Collaboration Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe Germany haungs@ik.fzk.de Andreas Haungs Pierre Auger Observatory
The Pierre Auger Observatory Status - First Results - Plans Andreas Haungs for the Pierre Auger Collaboration Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe Germany haungs@ik.fzk.de Andreas Haungs Pierre Auger Observatory
The KASCADE-Grande Experiment
 The KASCADE-Grande Experiment O. Sima 1 for the KASCADE-Grande Collaboration 2 1 University of Bucharest, Romania 2 https://web.ikp.kit.edu/kascade/ CSSP14 Sinaia 2014 Overview 1. KASCADE-Grande experimental
The KASCADE-Grande Experiment O. Sima 1 for the KASCADE-Grande Collaboration 2 1 University of Bucharest, Romania 2 https://web.ikp.kit.edu/kascade/ CSSP14 Sinaia 2014 Overview 1. KASCADE-Grande experimental
P. Tinyakov 1 TELESCOPE ARRAY: LATEST RESULTS. P. Tinyakov. for the Telescope Array Collaboration. Telescope Array detector. Spectrum.
 1 1 Université Libre de Bruxelles, Bruxelles, Belgium Telescope Outline Telescope Global distributions Hot spot Correlation with LSS Other searches Telescope UHECR experiments Telescope ARRAY COLLABORATION
1 1 Université Libre de Bruxelles, Bruxelles, Belgium Telescope Outline Telescope Global distributions Hot spot Correlation with LSS Other searches Telescope UHECR experiments Telescope ARRAY COLLABORATION
ULTRA-HIGH ENERGY COSMIC RAYS
 ULTRA-HIGH ENERGY COSMIC RAYS P. Tinyakov Université Libre de Bruxelles (ULB), Brussels Odense Winter School, October 2012 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Extensive airshowers 3 Detection methods Surface Detectors
ULTRA-HIGH ENERGY COSMIC RAYS P. Tinyakov Université Libre de Bruxelles (ULB), Brussels Odense Winter School, October 2012 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Extensive airshowers 3 Detection methods Surface Detectors
Sep. 13, JPS meeting
 Recent Results on Cosmic-Rays by Fermi-LAT Sep. 13, 2010 @ JPS meeting Tsunefumi Mizuno (Hiroshima Univ.) On behalf of the Fermi-LAT collaboration 1 Outline Introduction Direct measurement of CRs CRs in
Recent Results on Cosmic-Rays by Fermi-LAT Sep. 13, 2010 @ JPS meeting Tsunefumi Mizuno (Hiroshima Univ.) On behalf of the Fermi-LAT collaboration 1 Outline Introduction Direct measurement of CRs CRs in
Parameters Sensitive to the Mass Composition of Cosmic Rays and Their Application at the Pierre Auger Observatory
 WDS'12 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part III, 137 141, 2012. ISBN 978-80-7378-226-9 MATFYZPRESS Parameters Sensitive to the Mass Composition of Cosmic Rays and Their Application at the Pierre Auger
WDS'12 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part III, 137 141, 2012. ISBN 978-80-7378-226-9 MATFYZPRESS Parameters Sensitive to the Mass Composition of Cosmic Rays and Their Application at the Pierre Auger
Physics and Astroparticle Physics A. A
 Physics and Astroparticle Physics A. A. 2018-2019 (6 c.f.u, 48 hours of lessons) Preliminary program Introduction to Cosmic rays Physics. Complementarity between the study of Cosmic Rays events/properties
Physics and Astroparticle Physics A. A. 2018-2019 (6 c.f.u, 48 hours of lessons) Preliminary program Introduction to Cosmic rays Physics. Complementarity between the study of Cosmic Rays events/properties
