Newton s First Law. ICP-Physics, Ave
|
|
|
- Doreen Fox
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Newton s First Law ICP-Physics, Ave
2 Newton s First Law of Motion An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. AKA: Law of Inertia
3 Two Clauses and a Condition There are two clauses (parts) to this statement one that predicts the behavior of stationary objects and the other that predicts the behavior of moving objects. See summary below
4 Two Clauses and a Condition The condition is described by the phrase, unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. As long as the forces on an object are balanced, the First Law of Motion applies.
5 Real World Application of Newton s First Law
6 Inertia and Mass Newton s First Law states that An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Objects tend to keep doing what they are doing. It is the natural tendency of objects to resist changes in their state of motion. This tendency to resist changes in their state of motion is described as inertia.
7 Galileo and the Concept of Inertia Galileo developed the concept of inertia in the 17 th century. Galileo reasoned that moving objects eventually stop because of a force call friction. In experiments using a pair of inclined planes facing each other, Galileo observed that a ball would roll down one plane and up the opposite plane to nearly but not quite, the same height. He postulated that if friction could be entirely eliminated, then the ball would reach exactly the same height. Newton built on Galileo s thoughts about motion.
8 Galileo and the Concept of Inertia
9 Mass as a Measure of the Amount of Inertia The tendency of an object to resist changes in its state of motion varies with mass. Mass is that quantity that is SOLELY dependent upon the inertia of an object. The more inertia an object has, the more mass that is has. A more massive object has a greater tendency to resist changes in its state of motion.
10 Mass as a Measure of the Amount of Inertia
11 Check Your Understanding Imagine a place in the cosmos far from all gravitational and frictional influences. Suppose that you visit that place (just suppose) and throw a rock. The rock will a) Gradually stop. b) Continue in motion in the same direction at constant speed.
12 Check Your Understanding Imagine a place in the cosmos far from all gravitational and frictional influences. Suppose that you visit that place (just suppose) and throw a rock. The rock will a) Gradually stop. b) Continue in motion in the same direction at constant speed.
13 Check Your Understanding A 2-kg object is moving horizontally with a speed of 4 m/s. How much net force is required to keep the object moving at this speed and in this direction?
14 Check Your Understanding A 2-kg object is moving horizontally with a speed of 4 m/s. How much net force is required to keep the object moving at this speed and in this direction? 0 N, An object in motion will maintain its state of motion. The presence of an unbalanced force changes the velocity.
15 Check Your Understanding Mac and Tosh are arguing in the cafeteria. Mac says that if he flings the Jell-O with a greater speed it will have a greater inertia. Tosh argues that inertia does not depend upon speed, but rather upon mass. Who do you agree with and why?
16 Check Your Understanding Mac and Tosh are arguing in the cafeteria. Mac says that if he flings the Jell- O with a greater speed it will have a greater inertia. Tosh argues that inertia does not depend upon speed, but rather upon mass. Who do you agree with and why? Tosh is correct. Inertia is that quantity which depends solely upon mass. The more mass, the more inertia.
17 Check Your Understanding Supposing you were in space in a weightless environment, would it require a force to set an object in motion? Absolutely YES!! Even in space, objects have mass. If they have mass, they have inertia. Newton s Laws rule EVERYWHERE!!
18 Check Your Understanding Fred spends most Sunday afternoons at rest on the sofa watching pro football games and consuming large quantities of food. What effect (if any) will this practice have on his inertia?
19 Check Your Understanding Fred spends most Sunday afternoons at rest on the sofa watching pro football games and consuming large quantities of food. What effect (if any) will this practice have on his inertia? Fred s inertia will increase. Fred will increase his mass if he makes this a habit. And, if his mass increases, then his inertia increases.
20 Check Your Understanding Two bricks are resting on the edge of the lab table. Shirley Sheshort stands on her toes and spots the two bricks. She acquires an intense desire to know which of the two bricks is most massive. Since Shirley is vertically challenged, she is unable to reach high enough to lift the bricks; she can however reach high enough to give the bricks a little push. Discuss how the process of pushing the bricks will allow Shirley to determine which of the two bricks is most massive. What difference will Shirley observe and how can this observation lead to the necessary conclusions?
21 Check Your Understanding Two bricks are resting on the edge of the lab table. Shirley Sheshort stands on her toes and spots the two bricks. She acquires an intense desire to know which of the two bricks is most massive. Since Shirley is vertically challenged, she is unable to reach high enough to lift the bricks; she can however reach high enough to give the bricks a little push. Discuss how the process of pushing the bricks will allow Shirley to determine which of the two bricks is most massive. What difference will Shirley observe and how can this observation lead to the necessary conclusions? The bricks, like any objects, possess inertia. That is, they resist changes in their state of motion. When Shirley pushes each of the bricks, the one that is heaviest will resist the most and vice versa.
22 State of Motion Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist changes in its state of motion. But, what is meant by state of motion? The state of motion of an object is defined by its velocity the speed and direction. So Inertia: Tendency of an object to resist changes in its velocity. An object at rest has zero velocity and, in the absence of an unbalanced force, will remain with zero velocity. An object in motion with a velocity of 2 m/s, East will (in the absence of an unbalanced force) remain in motion with a velocity of 2 m/s, East.
23 State of Motion Acceleration: the rate of change of velocity of an object EX: change in speed AND/OR direction of the object would result in a change in acceleration An object that does not change its velocity is said to have an acceleration of 0 m/s/s. So. Inertia: Tendency of an object to resist acceleration
24 An air track glider is shown moving across an air track. Air is blown through many small holes in the track in order to lift the glider off the track. The glider appears to move with constant speed/motion As they say, An object in motion.
25 Check Your Understanding A group of physics teachers is taking some time off for a little putt-putt golf. The 15 th hole at the Hole-In-One Putt-Putt Course has a large metal rim that putters must use to hide their ball toward the hole. Ms. Ave guides a golf ball around the metal rim. When the ball leaves the rim, which path (1,2, or 3) will the golf ball follow? Why?
26 Check Your Understanding A group of physics teachers is taking some time off for a little putt-putt golf. The 15 th hole at the Hole-In-One Putt-Putt Course has a large metal rim that putters must use to hide their ball toward the hole. Ms. Ave guides a golf ball around the metal rim. When the ball leaves the rim, which path (1, 2, or 3) will the golf ball follow? Why? Path 2. Once leaving the rim, the ball will follow an inertial path (straight line). The ball is moving to the right at the instant shown in the diagram. Once leaving the rim, there is no more unbalanced forces to change its state of motion.
27 Check Your Understanding A 4.0 kg object is moving across a friction-free surface with a constant velocity of 2 m/s. Which one of the following horizontal forces is necessary to maintain this state of motion? Why? a) 0 N b) 0.5 N c) 2.0 N d) 8.0 N e) Depends on the speed
28 Check Your Understanding A 4.0 kg object is moving across a friction-free surface with a constant velocity of 2 m/s. Which one of the following horizontal forces is necessary to maintain this state of motion? Why? O N. If an object is in motion, then it will stay in motion with those very same motion characteristics.
29 Balanced and Unbalanced Forces What is a balanced force? <-- This is a free body diagram There are two forces acting upon the book. One force gravity exerts a downward force. The other force push of the table on the book (AKA: normal force) pushes upward on the book. The two forces are of equal magnitude and in opposite direction they balance each other. The book is said to be in equilibrium (no unbalanced forces acting upon the object, so it maintains its state of motion.
30 Balanced and Unbalanced Forces What is an unbalanced force? The book in the visual above has been pushed to the left. It has balanced forces of gravity and normal force acting upon it. However, in addition, the book has a frictional force acting to the left that is unbalanced by a force to the right. As a result, the book changes it state of motion the book is not at equilibrium and is accelerating.
31 Check Your Understanding Which of the following dot diagrams best describes the motion of a falling box from the time that it is dropped to the time that it hits the bottom of a pool full of water? The arrows on the diagram represent the point at which the box hits the water. Support your answer with sound reasoning.
32 Check Your Understanding Tape A. The box first accelerates with a negative acceleration until it hits the water. Upon hitting the water, the box experiences a balance of forces (50 N down due to gravity and 50 N up due to water) Thus, the box will finish its motion moving with constant velocity even if that velocity is 0.
33 Check Your Understanding Several friends were watching the motion of the falling box. Being physics types, they began discussing the motion and made the following comments. Indicate whether each of the comments is correct or incorrect and support your answer. Comment 1: One the box hits the water, the forces are balanced and the box will stop. Comment 2: Upon hitting the water, the box will accelerate upwards because the water applies an upward force. Comment 3: Upon hitting the water, the box will bounce upwards due to the upward force.
34 Check Your Understanding Comment 1: One the box hits the water, the forces are balanced and the box will stop. Incorrect. Once the box hits the water, the forces are balanced which stops acceleration. However, the box does not stop moving.
35 Check Your Understanding Comment 2: Upon hitting the water, the box will accelerate upwards because the water applies an upward force and Comment 3: Upon hitting the water, the box will bounce upwards due to the upward force. Incorrect. Once the box hits the water, the forces are balanced. The box will continue in motion at a constant speed (0).
36 Check Your Understanding If the forces acting upon an object are balanced, then the object a. Must not be moving b. Must be moving with constant velocity c. Must not be accelerating d. None of these
37 Check Your Understanding If the forces acting upon an object are balanced, then the object a. Must not be moving b. Must be moving with constant velocity c. Must not be accelerating d. None of these
38 Title and Content Layout with Chart 6 Chart Title Category 1 Category 2 Category 3 Category 4 Series 1 Series 2 Series 3
39 Two Content Layout with Table First bullet point here Second bullet point here Third bullet point here Group 1 Group 2 Class Class Class
40 Title and Content Layout with SmartArt Step 1 Title Step 2 Title Step 3 Title Step 4 Title Task description Task description Task description Task description Task description Task description Task description Task description Task description Task description Task description
41
42
43
44
45
46
Vocabulary. The resistance of a body to changes to its state of motion. The sum of all forces acting on an object.
 Vocabulary Term A push or pull. Definition Inertia Newton The resistance of a body to changes to its state of motion. The metric unit of force. Net The sum of all forces acting on an object. Newton s 1
Vocabulary Term A push or pull. Definition Inertia Newton The resistance of a body to changes to its state of motion. The metric unit of force. Net The sum of all forces acting on an object. Newton s 1
FORCES AND THE LAWS OF MOTION
 FORCES AND THE LAWS OF MOTION FORCE A force is the cause of an acceleration, or the change in an object s velocity (speed or direction). Forces are usually thought of as a push or a pull. The SI unit of
FORCES AND THE LAWS OF MOTION FORCE A force is the cause of an acceleration, or the change in an object s velocity (speed or direction). Forces are usually thought of as a push or a pull. The SI unit of
Vocabulary. Force. Inertia. Newton. Net Force. Newton s 1 st Law. Newton s 2 nd Law. Newton s 3 rd Law. 1 Page
 Vocabulary Term Definition Force Inertia Newton Net Force Newton s 1 st Law Newton s 2 nd Law Newton s 3 rd Law 1 Page Newton s 1 st Law of Motion Every body persists in its state of rest or of uniform
Vocabulary Term Definition Force Inertia Newton Net Force Newton s 1 st Law Newton s 2 nd Law Newton s 3 rd Law 1 Page Newton s 1 st Law of Motion Every body persists in its state of rest or of uniform
Newton s First Law of Motion
 Newton s First Law of Motion First we need to define the word FORCE: The cause of motion (what causes objects to move) Two types of forces Pushes Pulls Slide from www.science-class.net Forces may be balanced
Newton s First Law of Motion First we need to define the word FORCE: The cause of motion (what causes objects to move) Two types of forces Pushes Pulls Slide from www.science-class.net Forces may be balanced
1) An object that isn't being pushed or pulled by an unbalance force stays still or keeps moving in a straight line at constant speed.
 Newton's Laws Newtons Three Laws (Remember a Law is the summary of the theory.) 1) An object that isn't being pushed or pulled by an unbalance force stays still or keeps moving in a straight line at constant
Newton's Laws Newtons Three Laws (Remember a Law is the summary of the theory.) 1) An object that isn't being pushed or pulled by an unbalance force stays still or keeps moving in a straight line at constant
Inertia and Mass. 7. Mass and velocity values for a variety of objects are listed below. Rank the objects from smallest to greatest inertia.
 Name: Inertia and Mass Read from Lesson 1 of the Newton's Laws chapter at The Physics Classroom: http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/newtlaws/u2l1a.html http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/newtlaws/u2l1b.html
Name: Inertia and Mass Read from Lesson 1 of the Newton's Laws chapter at The Physics Classroom: http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/newtlaws/u2l1a.html http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/newtlaws/u2l1b.html
First Things First. Newton s First Law
 First Things First Newton s First Law Quick Review In the last unit, we learned how motion can be described With words With graphs With diagrams With numbers and directions Intro In this unit, we ll learn
First Things First Newton s First Law Quick Review In the last unit, we learned how motion can be described With words With graphs With diagrams With numbers and directions Intro In this unit, we ll learn
Balanced forces do not cause an object to change its motion Moving objects will keep moving and stationary objects will stay stationary
 Newton s Laws Test 8.PS2.3) Create a demonstration of an object in motion and describe the position, force, and direction of the object. 8.PS2.4) Plan and conduct an investigation to provide evidence that
Newton s Laws Test 8.PS2.3) Create a demonstration of an object in motion and describe the position, force, and direction of the object. 8.PS2.4) Plan and conduct an investigation to provide evidence that
NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION
 Name Period Date NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION If I am anything, which I highly doubt, I have made myself so by hard work. Isaac Newton Goals: 1. Students will use conceptual and mathematical models to predict
Name Period Date NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION If I am anything, which I highly doubt, I have made myself so by hard work. Isaac Newton Goals: 1. Students will use conceptual and mathematical models to predict
Unit 1: Mechanical Equilibrium
 Unit 1: Mechanical Equilibrium Chapter: Two Mechanical Equilibrium Big Idea / Key Concepts Student Outcomes 2.1: Force 2.2: Mechanical Equilibrium 2.3: Support Force 2.4: Equilibrium for Moving Objects
Unit 1: Mechanical Equilibrium Chapter: Two Mechanical Equilibrium Big Idea / Key Concepts Student Outcomes 2.1: Force 2.2: Mechanical Equilibrium 2.3: Support Force 2.4: Equilibrium for Moving Objects
Name Class Date. height. Which ball would land first according to Aristotle? Explain.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Gravity and Motion 1. Suppose a baseball and a marble are dropped at the same time from the same height. Which ball would land first according to Aristotle?
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Gravity and Motion 1. Suppose a baseball and a marble are dropped at the same time from the same height. Which ball would land first according to Aristotle?
NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION. Review
 NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION Review BACKGROUND Sir Isaac Newton (1643-1727) an English scientist and mathematician famous for his discovery of the law of gravity also discovered the three laws of motion. He
NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION Review BACKGROUND Sir Isaac Newton (1643-1727) an English scientist and mathematician famous for his discovery of the law of gravity also discovered the three laws of motion. He
The Concept of Force. field forces d) The gravitational force of attraction between two objects. f) Force a bar magnet exerts on a piece of iron.
 Lecture 3 The Laws of Motion OUTLINE 5.1 The Concept of Force 5.2 Newton s First Law and Inertial Frames 5.3 Mass 5.4 Newton s Second Law 5.5 The Gravitational Force and Weight 5.6 Newton s Third Law 5.8
Lecture 3 The Laws of Motion OUTLINE 5.1 The Concept of Force 5.2 Newton s First Law and Inertial Frames 5.3 Mass 5.4 Newton s Second Law 5.5 The Gravitational Force and Weight 5.6 Newton s Third Law 5.8
Chapter 6. Preview. Section 1 Gravity and Motion. Section 2 Newton s Laws of Motion. Section 3 Momentum. Forces and Motion.
 Forces and Motion Preview Section 1 Gravity and Motion Section 2 Newton s Laws of Motion Section 3 Momentum Concept Mapping Section 1 Gravity and Motion Bellringer Answer the following question in your
Forces and Motion Preview Section 1 Gravity and Motion Section 2 Newton s Laws of Motion Section 3 Momentum Concept Mapping Section 1 Gravity and Motion Bellringer Answer the following question in your
What was Aristotle s view of motion? How did Galileo disagree with Aristotle? Which answers agrees with Aristotle s view? Eliminate the others.
 Quest Chapter 04 # Problem Hint 1 A ball rolls across the top of a billiard table and slowly comes to a stop. How would Aristotle interpret this observation? How would Galileo interpret it? 1. Galileo
Quest Chapter 04 # Problem Hint 1 A ball rolls across the top of a billiard table and slowly comes to a stop. How would Aristotle interpret this observation? How would Galileo interpret it? 1. Galileo
Forces. Brought to you by:
 Forces Brought to you by: Objects have force because of their mass and inertia Mass is a measure of the amount of matter/particles in a substance. Mass is traditionally measured with a balance. Inertia
Forces Brought to you by: Objects have force because of their mass and inertia Mass is a measure of the amount of matter/particles in a substance. Mass is traditionally measured with a balance. Inertia
Conceptual Physical Science
 Hewitt/Suchocki/Hewitt Conceptual Physical Science Fourth Edition Chapter 1: PATTERNS OF MOTION AND EQUILIBRIUM This lecture will help you understand: Aristotle on Motion Galileo s Concept of Inertia Mass
Hewitt/Suchocki/Hewitt Conceptual Physical Science Fourth Edition Chapter 1: PATTERNS OF MOTION AND EQUILIBRIUM This lecture will help you understand: Aristotle on Motion Galileo s Concept of Inertia Mass
January 5, SWBAT explain Newton s first law by describing it in a series of examples.
 January 5, 2017 Aims: SWBAT explain Newton s first law by describing it in a series of examples. Agenda 1. Do Now 2. Class Notes 3. Guided Practice 4. Independent Practice 5. Practicing our AIMS: Homework:
January 5, 2017 Aims: SWBAT explain Newton s first law by describing it in a series of examples. Agenda 1. Do Now 2. Class Notes 3. Guided Practice 4. Independent Practice 5. Practicing our AIMS: Homework:
Inertia and Mass. 7. Mass and velocity values for a variety of objects are listed below. Rank the objects from smallest to greatest inertia.
 Inertia and Mass Read from Lesson 1 of the Newton's Laws chapter at The Physics Classroom: http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/newtlaws/u2l1a.html http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/newtlaws/u2l1b.html
Inertia and Mass Read from Lesson 1 of the Newton's Laws chapter at The Physics Classroom: http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/newtlaws/u2l1a.html http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/newtlaws/u2l1b.html
Forces. A force is a push or a pull on an object
 Forces Forces A force is a push or a pull on an object Arrows are used to represent forces. The direction of the arrow represent the direction the force that exist or being applied. Forces A net force
Forces Forces A force is a push or a pull on an object Arrows are used to represent forces. The direction of the arrow represent the direction the force that exist or being applied. Forces A net force
SPS8. STUDENTS WILL DETERMINE RELATIONSHIPS AMONG FORCE, MASS, AND MOTION.
 MOTION & FORCES SPS8. STUDENTS WILL DETERMINE RELATIONSHIPS AMONG FORCE, MASS, AND MOTION. A. CALCULATE VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION. B. APPLY NEWTON S THREE LAWS TO EVERYDAY SITUATIONS BY EXPLAINING THE
MOTION & FORCES SPS8. STUDENTS WILL DETERMINE RELATIONSHIPS AMONG FORCE, MASS, AND MOTION. A. CALCULATE VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION. B. APPLY NEWTON S THREE LAWS TO EVERYDAY SITUATIONS BY EXPLAINING THE
MOTION & FORCES. Observing Motion. Speed and Velocity. Distance vs. Displacement CHAPTERS 11 & 12
 Observing Motion CHAPTERS 11 & 12 MOTION & FORCES Everything surrounding us is in motion, but it is relative to other object that remain in place. Motion is observed using a frame of reference. Motion
Observing Motion CHAPTERS 11 & 12 MOTION & FORCES Everything surrounding us is in motion, but it is relative to other object that remain in place. Motion is observed using a frame of reference. Motion
TEK 8.6C: Newton s Laws
 Name: Teacher: Pd. Date: TEK 8.6C: Newton s Laws TEK 8.6C: Investigate and describe applications of Newton's law of inertia, law of force and acceleration, and law of action-reaction such as in vehicle
Name: Teacher: Pd. Date: TEK 8.6C: Newton s Laws TEK 8.6C: Investigate and describe applications of Newton's law of inertia, law of force and acceleration, and law of action-reaction such as in vehicle
Newton s Laws of Motion
 Newton s Laws of Motion I. Law of Inertia II. F=ma III. Action Reaction Newton s Laws of Motion 1 st Law An object at rest will stay at rest, and an object in motion will stay in motion at constant velocity,
Newton s Laws of Motion I. Law of Inertia II. F=ma III. Action Reaction Newton s Laws of Motion 1 st Law An object at rest will stay at rest, and an object in motion will stay in motion at constant velocity,
Newton s Laws of Motion. Steve Case NMGK-8 University of Mississippi October 2005
 Newton s Laws of Motion Steve Case NMGK-8 University of Mississippi October 2005 Background Sir Isaac Newton (1643-1727) an English scientist and mathematician famous for his discovery of the law of gravity
Newton s Laws of Motion Steve Case NMGK-8 University of Mississippi October 2005 Background Sir Isaac Newton (1643-1727) an English scientist and mathematician famous for his discovery of the law of gravity
Forces and Newton s Laws Reading Notes. Give an example of a force you have experienced continuously all your life.
 Forces and Newton s Laws Reading Notes Name: Section 4-1: Force What is force? Give an example of a force you have experienced continuously all your life. Give an example of a situation where an object
Forces and Newton s Laws Reading Notes Name: Section 4-1: Force What is force? Give an example of a force you have experienced continuously all your life. Give an example of a situation where an object
Laws of Force and Motion
 Does anything happen without a cause? Many people would say yes, because that often seems to be our experience. A cup near the edge of a table suddenly crashes to the floor. An apple falls from a tree
Does anything happen without a cause? Many people would say yes, because that often seems to be our experience. A cup near the edge of a table suddenly crashes to the floor. An apple falls from a tree
Ch. 2 The Laws of Motion
 Ch. 2 The Laws of Motion Lesson 1 Gravity and Friction Force - A push or pull we pull on a locker handle push a soccer ball or on the computer keys Contact force - push or pull on one object by another
Ch. 2 The Laws of Motion Lesson 1 Gravity and Friction Force - A push or pull we pull on a locker handle push a soccer ball or on the computer keys Contact force - push or pull on one object by another
Redhound Day 2 Assignment (continued)
 Redhound Day 2 Assignment (continued) Directions: Watch the power point and answer the questions on the last slide Which Law is It? on your own paper. You will turn this in for a grade. Background Sir
Redhound Day 2 Assignment (continued) Directions: Watch the power point and answer the questions on the last slide Which Law is It? on your own paper. You will turn this in for a grade. Background Sir
Newton s Contributions. Calculus Light is composed of rainbow colors Reflecting Telescope Laws of Motion Theory of Gravitation
 Newton s Contributions Calculus Light is composed of rainbow colors Reflecting Telescope Laws of Motion Theory of Gravitation Newton s First Law (law of inertia) An object at rest tends to stay at rest
Newton s Contributions Calculus Light is composed of rainbow colors Reflecting Telescope Laws of Motion Theory of Gravitation Newton s First Law (law of inertia) An object at rest tends to stay at rest
What does the lab partner observe during the instant the student pushes off?
 Motion Unit Review State Test Questions 1. To create real-time graphs of an object s displacement versus time and velocity versus time, a student would need to use a A motion sensor.b low- g accelerometer.
Motion Unit Review State Test Questions 1. To create real-time graphs of an object s displacement versus time and velocity versus time, a student would need to use a A motion sensor.b low- g accelerometer.
What is a Force? Free-Body diagrams. Contact vs. At-a-Distance 11/28/2016. Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion
 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion What is a Force? In generic terms: a force is a push or a pull exerted on an object that could cause one of the following to occur: A linear acceleration of the object
Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion What is a Force? In generic terms: a force is a push or a pull exerted on an object that could cause one of the following to occur: A linear acceleration of the object
PS 300 extra credit for exam 1 (5% max) due 2/13/18
 PS 300 extra credit for exam 1 (5% max) due 2/13/18 Name: 1. Name three physical properties that describes an object: mass, temperature, density, volume. 2. What is the mass of gasoline (ρ = 0.680 g/cm
PS 300 extra credit for exam 1 (5% max) due 2/13/18 Name: 1. Name three physical properties that describes an object: mass, temperature, density, volume. 2. What is the mass of gasoline (ρ = 0.680 g/cm
Newton s Laws of Motion
 Newton s Laws of Motion 1 of 28 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Newton s Laws of Motion 2 of 28 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Introducing balanced forces 3 of 28 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What is Newton s first law? 4 of 28 Boardworks
Newton s Laws of Motion 1 of 28 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Newton s Laws of Motion 2 of 28 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Introducing balanced forces 3 of 28 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What is Newton s first law? 4 of 28 Boardworks
Forces. Dynamics FORCEMAN
 1 Forces Dynamics FORCEMAN 2 What causes things to move? Forces What is a force? A push or a pull that one body exerts on another. 3 Balanced No change in motion 4 5 Unbalanced If the forces acting on
1 Forces Dynamics FORCEMAN 2 What causes things to move? Forces What is a force? A push or a pull that one body exerts on another. 3 Balanced No change in motion 4 5 Unbalanced If the forces acting on
Yanbu University College. General Studies Department. Phsc001 Course (111) Chapter2 (forces) Worksheet Solutions
 1 Yanbu University College General Studies Department Phsc001 Course (111) Chapter2 (forces) Worksheet Solutions 2 Chapter 2 Worksheet Part 1 Matching: Match the definitions with the given concepts. 1.
1 Yanbu University College General Studies Department Phsc001 Course (111) Chapter2 (forces) Worksheet Solutions 2 Chapter 2 Worksheet Part 1 Matching: Match the definitions with the given concepts. 1.
Force Test Review. 1. Give two ways to increase acceleration. You can increase acceleration by decreasing mass or increasing force.
 Force Test Review 1. Give two ways to increase acceleration. You can increase acceleration by decreasing mass or increasing force. 2. Define weight. The force of gravity on an object at the surface of
Force Test Review 1. Give two ways to increase acceleration. You can increase acceleration by decreasing mass or increasing force. 2. Define weight. The force of gravity on an object at the surface of
Motion *All matter in the universe is constantly at motion Motion an object is in motion if its position is changing
 Aim: What is motion? Do Now: Have you ever seen a race? Describe what occurred during it. Homework: Vocabulary Define: Motion Point of reference distance displacement speed velocity force Textbook: Read
Aim: What is motion? Do Now: Have you ever seen a race? Describe what occurred during it. Homework: Vocabulary Define: Motion Point of reference distance displacement speed velocity force Textbook: Read
3. What type of force is the woman applying to cart in the illustration below?
 Name: Forces and Motion STUDY GUIDE Directions: Answer the following questions. 1. What is a force? a. A type of energy b. The rate at which an object performs work c. A push or a pull d. An object that
Name: Forces and Motion STUDY GUIDE Directions: Answer the following questions. 1. What is a force? a. A type of energy b. The rate at which an object performs work c. A push or a pull d. An object that
FORCES. Integrated Science Unit 8. I. Newton s Laws of Motion
 Integrated Science Unit 8 FORCES I. Newton s Laws of Motion A. Newton s First Law Sir Isaac Newton 1643 1727 Lincolnshire, England 1. An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion maintains
Integrated Science Unit 8 FORCES I. Newton s Laws of Motion A. Newton s First Law Sir Isaac Newton 1643 1727 Lincolnshire, England 1. An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion maintains
CHAPTER 2. FORCE and Motion. CHAPTER s Objectives
 19 CHAPTER 2 FORCE and Motion CHAPTER s Objectives To define a force To understand the relation between force and motion In chapter 1, we understood that the Greek philosopher Aristotle was the first who
19 CHAPTER 2 FORCE and Motion CHAPTER s Objectives To define a force To understand the relation between force and motion In chapter 1, we understood that the Greek philosopher Aristotle was the first who
Unit 4 Forces (Newton s Laws)
 Name: Pd: Date: Unit Forces (Newton s Laws) The Nature of Forces force A push or pull exerted on an object. newton A unit of measure that equals the force required to accelerate kilogram of mass at meter
Name: Pd: Date: Unit Forces (Newton s Laws) The Nature of Forces force A push or pull exerted on an object. newton A unit of measure that equals the force required to accelerate kilogram of mass at meter
Chapter 4 Force and Motion
 Chapter 4 Force and Motion Units of Chapter 4 The Concepts of Force and Net Force Inertia and Newton s First Law of Motion Newton s Second Law of Motion Newton s Third Law of Motion More on Newton s Laws:
Chapter 4 Force and Motion Units of Chapter 4 The Concepts of Force and Net Force Inertia and Newton s First Law of Motion Newton s Second Law of Motion Newton s Third Law of Motion More on Newton s Laws:
Isaac Newton was a British scientist whose accomplishments
 E8 Newton s Laws of Motion R EA D I N G Isaac Newton was a British scientist whose accomplishments included important discoveries about light, motion, and gravity. You may have heard the legend about how
E8 Newton s Laws of Motion R EA D I N G Isaac Newton was a British scientist whose accomplishments included important discoveries about light, motion, and gravity. You may have heard the legend about how
Chapter Test A. Teacher Notes and Answers Forces and the Laws of Motion. Assessment
 Assessment Chapter Test A Teacher Notes and Answers Forces and the Laws of Motion CHAPTER TEST A (GENERAL) 1. c 2. d 3. d 4. c 5. c 6. c 7. c 8. b 9. d 10. d 11. c 12. a 13. d 14. d 15. b 16. d 17. c 18.
Assessment Chapter Test A Teacher Notes and Answers Forces and the Laws of Motion CHAPTER TEST A (GENERAL) 1. c 2. d 3. d 4. c 5. c 6. c 7. c 8. b 9. d 10. d 11. c 12. a 13. d 14. d 15. b 16. d 17. c 18.
Conceptual Physics Fundamentals. Chapter 3: EQUILIBRIUM AND LINEAR MOTION
 Conceptual Physics Fundamentals Chapter 3: EQUILIBRIUM AND LINEAR MOTION This lecture will help you understand: Aristotle on Motion Galileo s Concept of Inertia Mass A Measure of Inertia Net Force The
Conceptual Physics Fundamentals Chapter 3: EQUILIBRIUM AND LINEAR MOTION This lecture will help you understand: Aristotle on Motion Galileo s Concept of Inertia Mass A Measure of Inertia Net Force The
A N D. c h a p t e r 1 2 M O T I O N F O R C E S
 F O R C E S A N D c h a p t e r 1 2 M O T I O N What is a FORCE? A FORCE is a push or pull that acts on an object. A force can cause a resting object to move OR Accelerate a moving object by: changing
F O R C E S A N D c h a p t e r 1 2 M O T I O N What is a FORCE? A FORCE is a push or pull that acts on an object. A force can cause a resting object to move OR Accelerate a moving object by: changing
The Laws of Motion. Newton s Second Law
 The Laws of Motion Newton s Second Law Key Concepts What is Newton s second law of motion? How does centripetal force affect circular motion? What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide
The Laws of Motion Newton s Second Law Key Concepts What is Newton s second law of motion? How does centripetal force affect circular motion? What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide
Newton s Laws of Motion
 Newton s Laws of Motion I. Law of Inertia II. F=ma III. Action-Reaction Newton s Laws of Motion 1 st Law An object at rest will stay at rest, and an object in motion will stay in motion at a constant velocity,
Newton s Laws of Motion I. Law of Inertia II. F=ma III. Action-Reaction Newton s Laws of Motion 1 st Law An object at rest will stay at rest, and an object in motion will stay in motion at a constant velocity,
Forces & Newton s Laws. Honors Physics
 Forces & Newton s Laws Honors Physics Newton s 1 st Law An object in motion stays in motion, and an object at rest stays at rest, unless an unbalanced force acts on it. An object will maintain a constant
Forces & Newton s Laws Honors Physics Newton s 1 st Law An object in motion stays in motion, and an object at rest stays at rest, unless an unbalanced force acts on it. An object will maintain a constant
Isaac Newton was a British scientist whose accomplishments
 E8 Newton s Laws of Motion R EA D I N G Isaac Newton was a British scientist whose accomplishments included important discoveries about light, motion, and gravity. You may have heard the legend about how
E8 Newton s Laws of Motion R EA D I N G Isaac Newton was a British scientist whose accomplishments included important discoveries about light, motion, and gravity. You may have heard the legend about how
Units. Example Problem 1. Time (s) Distance (m)
 Time (s) Distance (m) Units Speed: average speed and Instantaneous speed (m/s) Velocity (m/s) +direction Acceleration (m/s 2 ) Force (N) or lbs Inertia (Kg) Density (g/ml) Example Problem 1 Which of the
Time (s) Distance (m) Units Speed: average speed and Instantaneous speed (m/s) Velocity (m/s) +direction Acceleration (m/s 2 ) Force (N) or lbs Inertia (Kg) Density (g/ml) Example Problem 1 Which of the
PHYSICS. Chapter 5 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT Pearson Education, Inc.
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 5 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 5 Force and Motion IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about the connection between force and motion.
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 5 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 5 Force and Motion IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about the connection between force and motion.
2. SKIP THIS YEAR What event will produce the greatest increase in the gravitational force between the two masses?
 Forces Review: look over all labs and worksheets. Your answers should be in another color pen. This is not all inclusive of items on the test but a very close representation. 1. The table shows the results
Forces Review: look over all labs and worksheets. Your answers should be in another color pen. This is not all inclusive of items on the test but a very close representation. 1. The table shows the results
Four naturally occuring forces
 Forces System vs Environment: system the object the force is applied to environment the world around the object that exerts the force Type Forces: Contact is applied by touching Long range exerted without
Forces System vs Environment: system the object the force is applied to environment the world around the object that exerts the force Type Forces: Contact is applied by touching Long range exerted without
Newton s Laws of Motion
 Newton's Laws of Motion The British scientist Sir Isaac Newton (164 177) was able to state rules that describe the effects of forces on the motion of objects. These rules are known as Newton's law's of
Newton's Laws of Motion The British scientist Sir Isaac Newton (164 177) was able to state rules that describe the effects of forces on the motion of objects. These rules are known as Newton's law's of
Newton s first law. Objectives. Assessment. Assessment. Assessment. Assessment 5/20/14. State Newton s first law and explain its meaning.
 Newton s first law Objectives State Newton s first law and explain its meaning. Calculate the effect of forces on objects using the law of inertia. Explain conceptually why moving objects do not always
Newton s first law Objectives State Newton s first law and explain its meaning. Calculate the effect of forces on objects using the law of inertia. Explain conceptually why moving objects do not always
Laws of Motion. What is force? What happens when you push or pull objects? Some examples of pushing and pulling. Definition Force:
 1 Laws of Motion What is force? What happens when you push or pull objects? Some examples of pushing and pulling Kicking Pushing Lifting Squeezing Definition Force: Activity: Tug of war In a tug of war,
1 Laws of Motion What is force? What happens when you push or pull objects? Some examples of pushing and pulling Kicking Pushing Lifting Squeezing Definition Force: Activity: Tug of war In a tug of war,
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 3834-1 - Page 1 1) If a woman runs 100 meters north and then 70 meters south, her total displacement is A) 170 m south B) 170 m north C) 30 m south D) 30 m north 2) The graph below represents the
Name: 3834-1 - Page 1 1) If a woman runs 100 meters north and then 70 meters south, her total displacement is A) 170 m south B) 170 m north C) 30 m south D) 30 m north 2) The graph below represents the
A. true. 6. An object is in motion when
 1. The SI unit for speed is A. Miles per hour B. meters per second 5. Frictional forces are greatest when both surfaces are rough. A. true B. false 2. The combination of all of the forces acting on an
1. The SI unit for speed is A. Miles per hour B. meters per second 5. Frictional forces are greatest when both surfaces are rough. A. true B. false 2. The combination of all of the forces acting on an
Force. The cause of an acceleration or change in an object s motion. Any kind of a push or pull on an object.
 Force The cause of an acceleration or change in an object s motion. Any kind of a push or pull on an object. Forces do not always give rise to motion. Forces can be equal and opposite. Force is a vector
Force The cause of an acceleration or change in an object s motion. Any kind of a push or pull on an object. Forces do not always give rise to motion. Forces can be equal and opposite. Force is a vector
General Physics I Spring Applying Newton s Laws
 General Physics I Spring 2011 Applying Newton s Laws 1 Equilibrium An object is in equilibrium if the net force acting on it is zero. According to Newton s first law, such an object will remain at rest
General Physics I Spring 2011 Applying Newton s Laws 1 Equilibrium An object is in equilibrium if the net force acting on it is zero. According to Newton s first law, such an object will remain at rest
for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
 for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction Name Period Date Newton s Three Laws of Motion Study Guide 1. Gina is driving her car down the street. She has a teddy bear sitting on the back
for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction Name Period Date Newton s Three Laws of Motion Study Guide 1. Gina is driving her car down the street. She has a teddy bear sitting on the back
Where to aim in order to Hit the Falling object (ignore air friction)?
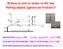 Where to aim in order to Hit the Falling object (ignore air friction)? y x Ignoring friction y = v 0y t 1/2gt 2 t = x/v 0x, v 0y /v 0x = h/x y = h 1/2gt 2 In the same time the monkey falls 1/2gt 2, i.e.
Where to aim in order to Hit the Falling object (ignore air friction)? y x Ignoring friction y = v 0y t 1/2gt 2 t = x/v 0x, v 0y /v 0x = h/x y = h 1/2gt 2 In the same time the monkey falls 1/2gt 2, i.e.
Make sure you know the three laws inside and out! You must know the vocabulary too!
 Newton's Laws Study Guide Test March 9 th The best plan is to study every night for 15 to 20 minutes. Make sure you know the three laws inside and out! You must know the vocabulary too! Newton s First
Newton's Laws Study Guide Test March 9 th The best plan is to study every night for 15 to 20 minutes. Make sure you know the three laws inside and out! You must know the vocabulary too! Newton s First
Newton s Laws of Motion. I. Law of Inertia II. F=ma III. Action-Reaction
 Newton s Laws of Motion I. Law of Inertia II. F=ma III. Action-Reaction While most people know what Newton's laws say, many people do not know what they mean (or simply do not believe what they mean).
Newton s Laws of Motion I. Law of Inertia II. F=ma III. Action-Reaction While most people know what Newton's laws say, many people do not know what they mean (or simply do not believe what they mean).
Do Now: Why are we required to obey the Seat- Belt law?
 Do Now: Why are we required to obey the Seat- Belt law? Newton s Laws of Motion Newton s First Law An object at rest remains at rest and an object in motion remains in motion with the same speed and direction.
Do Now: Why are we required to obey the Seat- Belt law? Newton s Laws of Motion Newton s First Law An object at rest remains at rest and an object in motion remains in motion with the same speed and direction.
Who was Isaac Newton?
 Forces & Motion Who was Isaac Newton? Born: December 25, 1643 in England (the same year Galileo died) knighted by Queen Anne in 1705 to become Sir Isaac Newton at age 64 The first person to describe universal
Forces & Motion Who was Isaac Newton? Born: December 25, 1643 in England (the same year Galileo died) knighted by Queen Anne in 1705 to become Sir Isaac Newton at age 64 The first person to describe universal
3/10/2019. What Is a Force? What Is a Force? Tactics: Drawing Force Vectors
 What Is a Force? A force acts on an object. A force requires an agent, something that acts on the object. If you throw a ball, your hand is the agent or cause of the force exerted on the ball. A force
What Is a Force? A force acts on an object. A force requires an agent, something that acts on the object. If you throw a ball, your hand is the agent or cause of the force exerted on the ball. A force
Force - a push or a pull A force described by its strength and by the direction in which it acts The SI unit for force is the newton (N)
 Forces Force - a push or a pull A force described by its strength and by the direction in which it acts The SI unit for force is the newton (N) The direction and strength of forces can be represented by
Forces Force - a push or a pull A force described by its strength and by the direction in which it acts The SI unit for force is the newton (N) The direction and strength of forces can be represented by
12.1 Forces and Motion Notes
 12.1 Forces and Motion Notes What Is a Force? A is a push or a pull that acts on an object. A force can cause a object to, or it can a object by changing the object s speed or direction. Force can be measured
12.1 Forces and Motion Notes What Is a Force? A is a push or a pull that acts on an object. A force can cause a object to, or it can a object by changing the object s speed or direction. Force can be measured
Chapter 6 Study Questions Name: Class:
 Chapter 6 Study Questions Name: Class: Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A feather and a rock dropped at the same time from
Chapter 6 Study Questions Name: Class: Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A feather and a rock dropped at the same time from
Introductory Physics, High School Learning Standards for a Full First-Year Course
 Introductory Physics, High School Learning Standards for a Full First-Year Course I. C O N T E N T S T A N D A R D S Central Concept: Newton s laws of motion and gravitation describe and predict the motion
Introductory Physics, High School Learning Standards for a Full First-Year Course I. C O N T E N T S T A N D A R D S Central Concept: Newton s laws of motion and gravitation describe and predict the motion
Engineering Systems & Investigation. Dynamic Systems Fundamentals
 Engineering Systems & Investigation Dynamic Systems Fundamentals Dynamics: Linear Motion Linear Motion Equations s.u.v.a.t s = Displacement. u = Initial Velocity. v = Final Velocity. a = Acceleration.
Engineering Systems & Investigation Dynamic Systems Fundamentals Dynamics: Linear Motion Linear Motion Equations s.u.v.a.t s = Displacement. u = Initial Velocity. v = Final Velocity. a = Acceleration.
Newton s Laws of Motion and Gravitation
 Newton s Laws of Motion and Gravitation Introduction: In Newton s first law we have discussed the equilibrium condition for a particle and seen that when the resultant force acting on the particle is zero,
Newton s Laws of Motion and Gravitation Introduction: In Newton s first law we have discussed the equilibrium condition for a particle and seen that when the resultant force acting on the particle is zero,
What Is a Force? Slide Pearson Education, Inc.
 What Is a Force? A force acts on an object. A force requires an agent, something that acts on the object. If you throw a ball, your hand is the agent or cause of the force exerted on the ball. A force
What Is a Force? A force acts on an object. A force requires an agent, something that acts on the object. If you throw a ball, your hand is the agent or cause of the force exerted on the ball. A force
Chapter 4 Newton s Laws
 Chapter 4 Newton s Laws Isaac Newton 1642-1727 Some inventions and discoveries: 3 laws of motion Universal law of gravity Calculus Ideas on: Sound Light Thermodynamics Reflecting telescope In this chapter,
Chapter 4 Newton s Laws Isaac Newton 1642-1727 Some inventions and discoveries: 3 laws of motion Universal law of gravity Calculus Ideas on: Sound Light Thermodynamics Reflecting telescope In this chapter,
Phys 111 Exam 1 September 22, 2015
 Phys 111 Exam 1 September 22, 2015 1. The time T required for one complete oscillation of a mass m on a spring of force constant k is T = 2π m k. Find the dimension of k to be dimensionally correct for
Phys 111 Exam 1 September 22, 2015 1. The time T required for one complete oscillation of a mass m on a spring of force constant k is T = 2π m k. Find the dimension of k to be dimensionally correct for
PYP 001 FIRST MAJOR EXAM CODE: TERM: 151 SATURDAY, OCTOBER 17, 2015 PAGE: 1
 TERM: 151 SATURDAY, OCTOBER 17, 2015 PAGE: 1 *Read the following (20) questions and choose the right answer: 1 The figure below represents the speed-time graph for the motion of a vehicle during a 7.0-minute
TERM: 151 SATURDAY, OCTOBER 17, 2015 PAGE: 1 *Read the following (20) questions and choose the right answer: 1 The figure below represents the speed-time graph for the motion of a vehicle during a 7.0-minute
Chapter 2. Forces & Newton s Laws
 Chapter 2 Forces & Newton s Laws 1st thing you need to know Everything from chapter 1 Speed formula Acceleration formula All their units There is only 1 main formula, but some equations will utilize previous
Chapter 2 Forces & Newton s Laws 1st thing you need to know Everything from chapter 1 Speed formula Acceleration formula All their units There is only 1 main formula, but some equations will utilize previous
A scalar quantity has just magnitude A vector quantity has both magnitude and direction
 Name Date Mods REVIEW FOR MIDYEAR ASSESSMENT 1. Physics is the most basic science because Physics supports chemistry, chemistry supports biology. The ideas of physics are fundamental to these more complicated
Name Date Mods REVIEW FOR MIDYEAR ASSESSMENT 1. Physics is the most basic science because Physics supports chemistry, chemistry supports biology. The ideas of physics are fundamental to these more complicated
Forces. Video Demos. Graphing HW: October 03, 2016
 Distance (m or km) : Create a story using the graph. Describe what will be happening at each point during the day (A-D). Example: Trump has a busy day. He is currently at Trump Tower in NY. A- Trump jumps
Distance (m or km) : Create a story using the graph. Describe what will be happening at each point during the day (A-D). Example: Trump has a busy day. He is currently at Trump Tower in NY. A- Trump jumps
Chapter 4. The Laws of Motion
 Chapter 4 The Laws of Motion Classical Mechanics Describes the relationship between the motion of objects in our everyday world and the forces acting on them Conditions when Classical Mechanics does not
Chapter 4 The Laws of Motion Classical Mechanics Describes the relationship between the motion of objects in our everyday world and the forces acting on them Conditions when Classical Mechanics does not
FORCE AND MOTION. Conceptual Questions F G as seen in the figure. n, and a kinetic frictional force due to the rough table surface f k
 FORCE AND MOTION 5 Conceptual Questions 5.1. Two forces are present, tension T in the cable and gravitational force 5.. F G as seen in the figure. Four forces act on the block: the push of the spring F
FORCE AND MOTION 5 Conceptual Questions 5.1. Two forces are present, tension T in the cable and gravitational force 5.. F G as seen in the figure. Four forces act on the block: the push of the spring F
If there is nothing pushing on an object, it will not move. If there is nothing pushing on an object, it will not stop. The List:
 If there is nothing pushing on an object, it will not move. If there is nothing pushing on an object, it will not stop. The List: No Push No Go No Push No Stop No Push No Speed Up No Push No Slow Down
If there is nothing pushing on an object, it will not move. If there is nothing pushing on an object, it will not stop. The List: No Push No Go No Push No Stop No Push No Speed Up No Push No Slow Down
BEFORE YOU READ. Forces and Motion Gravity and Motion STUDY TIP. After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
 CHAPTER 2 1 SECTION Forces and Motion Gravity and Motion BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How does gravity affect objects? How does air resistance
CHAPTER 2 1 SECTION Forces and Motion Gravity and Motion BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How does gravity affect objects? How does air resistance
UNIT XX: DYNAMICS AND NEWTON S LAWS. DYNAMICS is the branch of mechanics concerned with the forces that cause motions of bodies
 I. Definition of FORCE UNIT XX: DYNAMICS AND NEWTON S LAWS DYNAMICS is the branch of mechanics concerned with the forces that cause motions of bodies FORCE is a quantitative interaction between two (or
I. Definition of FORCE UNIT XX: DYNAMICS AND NEWTON S LAWS DYNAMICS is the branch of mechanics concerned with the forces that cause motions of bodies FORCE is a quantitative interaction between two (or
Science Teaching Junkie Science Teaching Junkie
 Science Teaching Junkie Thank you for your purchase. I hope you enjoy the Force and Motion for Interactive Science Notebooks! It includes 30 pages of foldables and flippables for student notebooks. Many
Science Teaching Junkie Thank you for your purchase. I hope you enjoy the Force and Motion for Interactive Science Notebooks! It includes 30 pages of foldables and flippables for student notebooks. Many
Newton s Laws of Motion
 DUY TAN UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL SCIENCE Newton s Laws of Motion Lecturer: HO VAN TUYEN Da Nang, 2017 Motions Newton s Contributions Sir Isaac Newton (1643-1727) an English scientist and mathematician.
DUY TAN UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL SCIENCE Newton s Laws of Motion Lecturer: HO VAN TUYEN Da Nang, 2017 Motions Newton s Contributions Sir Isaac Newton (1643-1727) an English scientist and mathematician.
KEY NNHS Introductory Physics: MCAS Review Packet #1 Introductory Physics, High School Learning Standards for a Full First-Year Course
 Introductory Physics, High School Learning Standards for a Full First-Year Course I. C ONTENT S TANDARDS Central Concept: Newton s laws of motion and gravitation describe and predict the motion of 1.1
Introductory Physics, High School Learning Standards for a Full First-Year Course I. C ONTENT S TANDARDS Central Concept: Newton s laws of motion and gravitation describe and predict the motion of 1.1
Newton s Laws Review
 Newton s Laws Review THE SCIENCES OF MOTION Prior to this unit, we had been studying, which is the science of describing motion with words, numbers, pictures, and symbols, and no attention was given to
Newton s Laws Review THE SCIENCES OF MOTION Prior to this unit, we had been studying, which is the science of describing motion with words, numbers, pictures, and symbols, and no attention was given to
Chapter: Newton s Laws of Motion
 Table of Contents Chapter: Newton s Laws of Motion Section 1: Motion Section 2: Newton s First Law Section 3: Newton s Second Law Section 4: Newton s Third Law 1 Motion What is motion? Distance and Displacement
Table of Contents Chapter: Newton s Laws of Motion Section 1: Motion Section 2: Newton s First Law Section 3: Newton s Second Law Section 4: Newton s Third Law 1 Motion What is motion? Distance and Displacement
Physics 12 Unit 2: Vector Dynamics
 1 Physics 12 Unit 2: Vector Dynamics In this unit you will extend your study of forces. In particular, we will examine force as a vector quantity; this will involve solving problems where forces must be
1 Physics 12 Unit 2: Vector Dynamics In this unit you will extend your study of forces. In particular, we will examine force as a vector quantity; this will involve solving problems where forces must be
Physics 10. Lecture 3A
 Physics 10 Lecture 3A "Your education is ultimately the flavor left over after the facts, formulas, and diagrams have been forgotten." --Paul G. Hewitt Support Forces If the Earth is pulling down on a
Physics 10 Lecture 3A "Your education is ultimately the flavor left over after the facts, formulas, and diagrams have been forgotten." --Paul G. Hewitt Support Forces If the Earth is pulling down on a
Sir Isaac Newton ( ) One of the world s greatest scientists Developed the 3 Laws of Motion
 Motion and Forces Sir Isaac Newton (1643 1727) One of the world s greatest scientists Developed the 3 Laws of Motion Newton s Laws of Motion 1 st Law Law of Inertia 2 nd Law Force = Mass x Acceleration
Motion and Forces Sir Isaac Newton (1643 1727) One of the world s greatest scientists Developed the 3 Laws of Motion Newton s Laws of Motion 1 st Law Law of Inertia 2 nd Law Force = Mass x Acceleration
*ANSWER KEY * ANSWER KEY* ANSWER KEY* Newton's First Law of Motion Study Guide
 *ANSWER KEY * ANSWER KEY* ANSWER KEY* Newton's First Law of Motion Study Guide Newton's First Law of Motion (Law of Inertia) An object at rest will remain at rest unless acted on by an unbalanced force.
*ANSWER KEY * ANSWER KEY* ANSWER KEY* Newton's First Law of Motion Study Guide Newton's First Law of Motion (Law of Inertia) An object at rest will remain at rest unless acted on by an unbalanced force.
Newton s Laws of Motion
 Newton s Laws of Motion While most people know what Newton's Laws are, many people do not understand what they mean. Newton s Laws of Motion 1 st Law An object at rest will stay at rest, and an object
Newton s Laws of Motion While most people know what Newton's Laws are, many people do not understand what they mean. Newton s Laws of Motion 1 st Law An object at rest will stay at rest, and an object
A force is could described by its magnitude and by the direction in which it acts.
 8.2.a Forces Students know a force has both direction and magnitude. P13 A force is could described by its magnitude and by the direction in which it acts. 1. Which of the following could describe the
8.2.a Forces Students know a force has both direction and magnitude. P13 A force is could described by its magnitude and by the direction in which it acts. 1. Which of the following could describe the
Physics Revision Guide Volume 1
 Physics Revision Guide Volume 1 "Many people do not plan to fail, they just fail to plan!" Develop a customized success plan Create necessity in you to take action now Boost your confidence in your revision
Physics Revision Guide Volume 1 "Many people do not plan to fail, they just fail to plan!" Develop a customized success plan Create necessity in you to take action now Boost your confidence in your revision
Test Wed, Feb 8 th 7pm, G20 MING HSIEH Bring your calculator and #2 pencil with a good eraser! 20 Multiple choice questions from:
 Test Wed, Feb 8 th 7pm, G20 MING HSIEH Bring your calculator and #2 pencil with a good eraser! 20 Multiple choice questions from: Chapter 1 (except section 1.2 and 1.7): Unit conversions, estimating, trigonometry,
Test Wed, Feb 8 th 7pm, G20 MING HSIEH Bring your calculator and #2 pencil with a good eraser! 20 Multiple choice questions from: Chapter 1 (except section 1.2 and 1.7): Unit conversions, estimating, trigonometry,
