Bayesian model selection in graphs by using BDgraph package
|
|
|
- Miranda Elinor Page
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bayesian model selection in graphs by using BDgraph package A. Mohammadi and E. Wit March 26, 2013
2 MOTIVATION Flow cytometry data with 11 proteins from Sachs et al. (2005)
3 RESULT FOR CELL SIGNALING DATA
4 Gaussian graphical model Respect to graph G = (V, E) as M G = { } N p (0, Σ) K = Σ 1 is positive definite based on G Pairwise Markov property X i X j X V\{i,j} k ij = 0,
5 BIRTH-DEATH PROCESS Spacial birth-death process: Preston (1976) Birth-death MCMC: Stephen (2000) in mixture models
6 BIRTH-DEATH MCMC DESIGN General birth-death process Continuous Markov process Birth and death events are independent Poisson processes Time of birth or death event is exponentially distributed Birth-death process in GGM Adding new edge in birth and deleting edge in death time
7 SIMPLE CASE
8 SIMPLE CASE
9 SIMPLE CASE
10 BALANCE CONDITION Preston (1976): Backward Kolmogorov Under Balance condition, process converges to unique stationary distribution. Mohammadi and Wit (2013): BDMCMC in GGM Stationary distribution = Posterior distribution of (G,K) So, relative sojourn time in graph G = posterior probability of G
11 PROPOSED BDMCMC ALGORITHM Step 1: (a). Calculate birth and death rates β ξ (K) = λ b, new link ξ = (i, j) δ ξ (K) = b ξ(k ξ )p(g ξ, K ξ x) λ b, existing link ξ = (i, j) p(g, K x) (b). Calculate waiting time, (c). Simulate type of jump, birth or death Step 2: Sampling new precision matrix: K + ξ or K ξ
12 PROPOSED PRIOR DISTRIBUTIONS Prior for graph Discrete Uniform Truncated Poisson according to number of links Prior for precision matrix G-Wishart: W G (b, D) p(k G) K (b 2)/2 exp { 1 } 2 tr(dk) I G (b, D) = K (b 2)/2 exp { 1 } P G 2 tr(dk) dk
13 SPECIFIC ELEMENT OF BDMCMC Sampling from G-Wishart distribution Block Gibbs sampler Edgewise block Gibbs sampler According to maximum cliques Metropolis-Hastings algorithm Computing death rates δ ξ (K) = p(g ξ, K ξ x) p(g, K x) γ bb ξ (k ξ ) = I G (b, D) ( K ξ (b, D) K I G ξ ) (b 2)/2 { exp 1 } 2 tr(d (K ξ K)) γ b
14 Ratio of normalizing constant I G (b, D) I G ξ(b, D) = 2 Γ πt ii t jj Γ ( ) b+νi 2 ( b+νi 1 2 ) E G [f T (ψ ν )] E G ξ [f T (ψ ν )] Plot for ratio of normalizing constants ratio of expectation number of nodes
15 Death rates for high-dimensional cases δ ξ (K) = 2 πt ii t jj Γ ( ) b+νi 2 ( ) b+νi 1 2 Γ { exp 1 2 tr(d (K ξ K)) ) (b 2)/2 ( K ξ K } γ b b ξ (k ξ ) BDgraph package bdmcmc.high : for high-dimensional graphs bdmcmc.low : for low-dimensional graphs
16 SIMULATION: 8 NODES } M G = {N 8 (0, Σ) K = Σ 1 P G K =
17 SOME RESULT Effect of Sample size Number of data p(true graph data) false positive false negative
18 SIMULATION: 120 NODES M G = {N 120 (0, Σ) K = Σ 1 P G }, n = Priors: K W G (3, I 120 ) and G TU(all possible graphs) iterations and 5000 iterations as burn-in Result Time 4 hours p(true graph data) = 0.09 which is most probable graph
19 SUMMARY
20 Thanks for your attention References MOHAMMADI, A. AND E. C. WIT (2013) Gaussian graphical model determination based on birth-death MCMC inference, arxiv preprint arxiv: v4 WANG, H. AND S. LI (2012) Efficient Gaussian graphical model determination under G-Wishart prior distributions. Electronic Journal of Statistics, 6: ATAY-KAYIS, A. AND H. MASSAM (2005) A Monte Carlo method for computing the marginal likelihood in nondecomposable Gaussian graphical models. Biometrika Trust, 92(2): PRESTON, C. J. (1976) Special birth-and-death processes. Bull. Inst. Internat. Statist., 34:
Gaussian graphical model determination based on birth-death MCMC inference
 Gaussian graphical model determination based on birth-death MCMC inference Abdolreza Mohammadi Johann Bernoulli Institute, University of Groningen, Netherlands a.mohammadi@rug.nl Ernst C. Wit Johann Bernoulli
Gaussian graphical model determination based on birth-death MCMC inference Abdolreza Mohammadi Johann Bernoulli Institute, University of Groningen, Netherlands a.mohammadi@rug.nl Ernst C. Wit Johann Bernoulli
Bayesian Model Determination in Complex Systems
 Bayesian Model Determination in Complex Systems PhD thesis to obtain the degree of PhD at the University of Groningen on the authority of the Rector Magnificus Prof. E. Sterken and in accordance with the
Bayesian Model Determination in Complex Systems PhD thesis to obtain the degree of PhD at the University of Groningen on the authority of the Rector Magnificus Prof. E. Sterken and in accordance with the
Package BDgraph. June 21, 2018
 Version 2.51 Date 2018-06-18 Package BDgraph June 21, 2018 Title Bayesian Structure Learning in Graphical Models using Birth-Death MCMC Author Reza Mohammadi [aut, cre] ,
Version 2.51 Date 2018-06-18 Package BDgraph June 21, 2018 Title Bayesian Structure Learning in Graphical Models using Birth-Death MCMC Author Reza Mohammadi [aut, cre] ,
Introduction to Machine Learning CMU-10701
 Introduction to Machine Learning CMU-10701 Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods Barnabás Póczos & Aarti Singh Contents Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods Goal & Motivation Sampling Rejection Importance Markov
Introduction to Machine Learning CMU-10701 Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods Barnabás Póczos & Aarti Singh Contents Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods Goal & Motivation Sampling Rejection Importance Markov
STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning
 STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Computer Science! Department of Statistical Sciences! rsalakhu@cs.toronto.edu! h0p://www.cs.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Lecture 7 Approximate
STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Computer Science! Department of Statistical Sciences! rsalakhu@cs.toronto.edu! h0p://www.cs.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Lecture 7 Approximate
Computer Vision Group Prof. Daniel Cremers. 10a. Markov Chain Monte Carlo
 Group Prof. Daniel Cremers 10a. Markov Chain Monte Carlo Markov Chain Monte Carlo In high-dimensional spaces, rejection sampling and importance sampling are very inefficient An alternative is Markov Chain
Group Prof. Daniel Cremers 10a. Markov Chain Monte Carlo Markov Chain Monte Carlo In high-dimensional spaces, rejection sampling and importance sampling are very inefficient An alternative is Markov Chain
Bayesian Inference of Multiple Gaussian Graphical Models
 Bayesian Inference of Multiple Gaussian Graphical Models Christine Peterson,, Francesco Stingo, and Marina Vannucci February 18, 2014 Abstract In this paper, we propose a Bayesian approach to inference
Bayesian Inference of Multiple Gaussian Graphical Models Christine Peterson,, Francesco Stingo, and Marina Vannucci February 18, 2014 Abstract In this paper, we propose a Bayesian approach to inference
Markov Chain Monte Carlo Inference. Siamak Ravanbakhsh Winter 2018
 Graphical Models Markov Chain Monte Carlo Inference Siamak Ravanbakhsh Winter 2018 Learning objectives Markov chains the idea behind Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) two important examples: Gibbs sampling
Graphical Models Markov Chain Monte Carlo Inference Siamak Ravanbakhsh Winter 2018 Learning objectives Markov chains the idea behind Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) two important examples: Gibbs sampling
CS242: Probabilistic Graphical Models Lecture 7B: Markov Chain Monte Carlo & Gibbs Sampling
 CS242: Probabilistic Graphical Models Lecture 7B: Markov Chain Monte Carlo & Gibbs Sampling Professor Erik Sudderth Brown University Computer Science October 27, 2016 Some figures and materials courtesy
CS242: Probabilistic Graphical Models Lecture 7B: Markov Chain Monte Carlo & Gibbs Sampling Professor Erik Sudderth Brown University Computer Science October 27, 2016 Some figures and materials courtesy
Hmms with variable dimension structures and extensions
 Hmm days/enst/january 21, 2002 1 Hmms with variable dimension structures and extensions Christian P. Robert Université Paris Dauphine www.ceremade.dauphine.fr/ xian Hmm days/enst/january 21, 2002 2 1 Estimating
Hmm days/enst/january 21, 2002 1 Hmms with variable dimension structures and extensions Christian P. Robert Université Paris Dauphine www.ceremade.dauphine.fr/ xian Hmm days/enst/january 21, 2002 2 1 Estimating
Markov Chain Monte Carlo
 1 Motivation 1.1 Bayesian Learning Markov Chain Monte Carlo Yale Chang In Bayesian learning, given data X, we make assumptions on the generative process of X by introducing hidden variables Z: p(z): prior
1 Motivation 1.1 Bayesian Learning Markov Chain Monte Carlo Yale Chang In Bayesian learning, given data X, we make assumptions on the generative process of X by introducing hidden variables Z: p(z): prior
Markov Chain Monte Carlo
 Markov Chain Monte Carlo Recall: To compute the expectation E ( h(y ) ) we use the approximation E(h(Y )) 1 n n h(y ) t=1 with Y (1),..., Y (n) h(y). Thus our aim is to sample Y (1),..., Y (n) from f(y).
Markov Chain Monte Carlo Recall: To compute the expectation E ( h(y ) ) we use the approximation E(h(Y )) 1 n n h(y ) t=1 with Y (1),..., Y (n) h(y). Thus our aim is to sample Y (1),..., Y (n) from f(y).
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture 24
 Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture 24 Graphical Models: Approximate Inference Course Webpage : http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs4786/2016sp/ BELIEF PROPAGATION OR MESSAGE PASSING Each
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture 24 Graphical Models: Approximate Inference Course Webpage : http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs4786/2016sp/ BELIEF PROPAGATION OR MESSAGE PASSING Each
(5) Multi-parameter models - Gibbs sampling. ST440/540: Applied Bayesian Analysis
 Summarizing a posterior Given the data and prior the posterior is determined Summarizing the posterior gives parameter estimates, intervals, and hypothesis tests Most of these computations are integrals
Summarizing a posterior Given the data and prior the posterior is determined Summarizing the posterior gives parameter estimates, intervals, and hypothesis tests Most of these computations are integrals
Likelihood-free MCMC
 Bayesian inference for stable distributions with applications in finance Department of Mathematics University of Leicester September 2, 2011 MSc project final presentation Outline 1 2 3 4 Classical Monte
Bayesian inference for stable distributions with applications in finance Department of Mathematics University of Leicester September 2, 2011 MSc project final presentation Outline 1 2 3 4 Classical Monte
Markov Networks.
 Markov Networks www.biostat.wisc.edu/~dpage/cs760/ Goals for the lecture you should understand the following concepts Markov network syntax Markov network semantics Potential functions Partition function
Markov Networks www.biostat.wisc.edu/~dpage/cs760/ Goals for the lecture you should understand the following concepts Markov network syntax Markov network semantics Potential functions Partition function
CPSC 540: Machine Learning
 CPSC 540: Machine Learning MCMC and Non-Parametric Bayes Mark Schmidt University of British Columbia Winter 2016 Admin I went through project proposals: Some of you got a message on Piazza. No news is
CPSC 540: Machine Learning MCMC and Non-Parametric Bayes Mark Schmidt University of British Columbia Winter 2016 Admin I went through project proposals: Some of you got a message on Piazza. No news is
April 20th, Advanced Topics in Machine Learning California Institute of Technology. Markov Chain Monte Carlo for Machine Learning
 for for Advanced Topics in California Institute of Technology April 20th, 2017 1 / 50 Table of Contents for 1 2 3 4 2 / 50 History of methods for Enrico Fermi used to calculate incredibly accurate predictions
for for Advanced Topics in California Institute of Technology April 20th, 2017 1 / 50 Table of Contents for 1 2 3 4 2 / 50 History of methods for Enrico Fermi used to calculate incredibly accurate predictions
Learning the hyper-parameters. Luca Martino
 Learning the hyper-parameters Luca Martino 2017 2017 1 / 28 Parameters and hyper-parameters 1. All the described methods depend on some choice of hyper-parameters... 2. For instance, do you recall λ (bandwidth
Learning the hyper-parameters Luca Martino 2017 2017 1 / 28 Parameters and hyper-parameters 1. All the described methods depend on some choice of hyper-parameters... 2. For instance, do you recall λ (bandwidth
The ratio of normalizing constants for Bayesian graphical Gaussian model selection Mohammadi, A.; Massam, Helene; Letac, Gerard
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository The ratio of normalizing constants for Bayesian graphical Gaussian model selection Mohammadi, A.; Massam, Helene; Letac, Gerard Published in: ArXiv e-prints Link to
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository The ratio of normalizing constants for Bayesian graphical Gaussian model selection Mohammadi, A.; Massam, Helene; Letac, Gerard Published in: ArXiv e-prints Link to
Supplement to A Hierarchical Approach for Fitting Curves to Response Time Measurements
 Supplement to A Hierarchical Approach for Fitting Curves to Response Time Measurements Jeffrey N. Rouder Francis Tuerlinckx Paul L. Speckman Jun Lu & Pablo Gomez May 4 008 1 The Weibull regression model
Supplement to A Hierarchical Approach for Fitting Curves to Response Time Measurements Jeffrey N. Rouder Francis Tuerlinckx Paul L. Speckman Jun Lu & Pablo Gomez May 4 008 1 The Weibull regression model
Monte Carlo in Bayesian Statistics
 Monte Carlo in Bayesian Statistics Matthew Thomas SAMBa - University of Bath m.l.thomas@bath.ac.uk December 4, 2014 Matthew Thomas (SAMBa) Monte Carlo in Bayesian Statistics December 4, 2014 1 / 16 Overview
Monte Carlo in Bayesian Statistics Matthew Thomas SAMBa - University of Bath m.l.thomas@bath.ac.uk December 4, 2014 Matthew Thomas (SAMBa) Monte Carlo in Bayesian Statistics December 4, 2014 1 / 16 Overview
Bayesian Methods for Machine Learning
 Bayesian Methods for Machine Learning CS 584: Big Data Analytics Material adapted from Radford Neal s tutorial (http://ftp.cs.utoronto.ca/pub/radford/bayes-tut.pdf), Zoubin Ghahramni (http://hunch.net/~coms-4771/zoubin_ghahramani_bayesian_learning.pdf),
Bayesian Methods for Machine Learning CS 584: Big Data Analytics Material adapted from Radford Neal s tutorial (http://ftp.cs.utoronto.ca/pub/radford/bayes-tut.pdf), Zoubin Ghahramni (http://hunch.net/~coms-4771/zoubin_ghahramani_bayesian_learning.pdf),
Markov Chain Monte Carlo methods
 Markov Chain Monte Carlo methods Tomas McKelvey and Lennart Svensson Signal Processing Group Department of Signals and Systems Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden November 26, 2012 Today s learning
Markov Chain Monte Carlo methods Tomas McKelvey and Lennart Svensson Signal Processing Group Department of Signals and Systems Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden November 26, 2012 Today s learning
Computer Vision Group Prof. Daniel Cremers. 11. Sampling Methods: Markov Chain Monte Carlo
 Group Prof. Daniel Cremers 11. Sampling Methods: Markov Chain Monte Carlo Markov Chain Monte Carlo In high-dimensional spaces, rejection sampling and importance sampling are very inefficient An alternative
Group Prof. Daniel Cremers 11. Sampling Methods: Markov Chain Monte Carlo Markov Chain Monte Carlo In high-dimensional spaces, rejection sampling and importance sampling are very inefficient An alternative
Computational statistics
 Computational statistics Markov Chain Monte Carlo methods Thierry Denœux March 2017 Thierry Denœux Computational statistics March 2017 1 / 71 Contents of this chapter When a target density f can be evaluated
Computational statistics Markov Chain Monte Carlo methods Thierry Denœux March 2017 Thierry Denœux Computational statistics March 2017 1 / 71 Contents of this chapter When a target density f can be evaluated
Bayesian Estimation with Sparse Grids
 Bayesian Estimation with Sparse Grids Kenneth L. Judd and Thomas M. Mertens Institute on Computational Economics August 7, 27 / 48 Outline Introduction 2 Sparse grids Construction Integration with sparse
Bayesian Estimation with Sparse Grids Kenneth L. Judd and Thomas M. Mertens Institute on Computational Economics August 7, 27 / 48 Outline Introduction 2 Sparse grids Construction Integration with sparse
MCMC and Gibbs Sampling. Kayhan Batmanghelich
 MCMC and Gibbs Sampling Kayhan Batmanghelich 1 Approaches to inference l Exact inference algorithms l l l The elimination algorithm Message-passing algorithm (sum-product, belief propagation) The junction
MCMC and Gibbs Sampling Kayhan Batmanghelich 1 Approaches to inference l Exact inference algorithms l l l The elimination algorithm Message-passing algorithm (sum-product, belief propagation) The junction
Stat 535 C - Statistical Computing & Monte Carlo Methods. Lecture 18-16th March Arnaud Doucet
 Stat 535 C - Statistical Computing & Monte Carlo Methods Lecture 18-16th March 2006 Arnaud Doucet Email: arnaud@cs.ubc.ca 1 1.1 Outline Trans-dimensional Markov chain Monte Carlo. Bayesian model for autoregressions.
Stat 535 C - Statistical Computing & Monte Carlo Methods Lecture 18-16th March 2006 Arnaud Doucet Email: arnaud@cs.ubc.ca 1 1.1 Outline Trans-dimensional Markov chain Monte Carlo. Bayesian model for autoregressions.
Efficient adaptive covariate modelling for extremes
 Efficient adaptive covariate modelling for extremes Slides at www.lancs.ac.uk/ jonathan Matthew Jones, David Randell, Emma Ross, Elena Zanini, Philip Jonathan Copyright of Shell December 218 1 / 23 Structural
Efficient adaptive covariate modelling for extremes Slides at www.lancs.ac.uk/ jonathan Matthew Jones, David Randell, Emma Ross, Elena Zanini, Philip Jonathan Copyright of Shell December 218 1 / 23 Structural
Bayesian spatial hierarchical modeling for temperature extremes
 Bayesian spatial hierarchical modeling for temperature extremes Indriati Bisono Dr. Andrew Robinson Dr. Aloke Phatak Mathematics and Statistics Department The University of Melbourne Maths, Informatics
Bayesian spatial hierarchical modeling for temperature extremes Indriati Bisono Dr. Andrew Robinson Dr. Aloke Phatak Mathematics and Statistics Department The University of Melbourne Maths, Informatics
27 : Distributed Monte Carlo Markov Chain. 1 Recap of MCMC and Naive Parallel Gibbs Sampling
 10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2014 27 : Distributed Monte Carlo Markov Chain Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Pengtao Xie, Khoa Luu In this scribe, we are going to review the Parallel
10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2014 27 : Distributed Monte Carlo Markov Chain Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Pengtao Xie, Khoa Luu In this scribe, we are going to review the Parallel
On Bayesian Computation
 On Bayesian Computation Michael I. Jordan with Elaine Angelino, Maxim Rabinovich, Martin Wainwright and Yun Yang Previous Work: Information Constraints on Inference Minimize the minimax risk under constraints
On Bayesian Computation Michael I. Jordan with Elaine Angelino, Maxim Rabinovich, Martin Wainwright and Yun Yang Previous Work: Information Constraints on Inference Minimize the minimax risk under constraints
The Ising model and Markov chain Monte Carlo
 The Ising model and Markov chain Monte Carlo Ramesh Sridharan These notes give a short description of the Ising model for images and an introduction to Metropolis-Hastings and Gibbs Markov Chain Monte
The Ising model and Markov chain Monte Carlo Ramesh Sridharan These notes give a short description of the Ising model for images and an introduction to Metropolis-Hastings and Gibbs Markov Chain Monte
An Introduction to Reversible Jump MCMC for Bayesian Networks, with Application
 An Introduction to Reversible Jump MCMC for Bayesian Networks, with Application, CleverSet, Inc. STARMAP/DAMARS Conference Page 1 The research described in this presentation has been funded by the U.S.
An Introduction to Reversible Jump MCMC for Bayesian Networks, with Application, CleverSet, Inc. STARMAP/DAMARS Conference Page 1 The research described in this presentation has been funded by the U.S.
Bayesian Nonparametric Regression for Diabetes Deaths
 Bayesian Nonparametric Regression for Diabetes Deaths Brian M. Hartman PhD Student, 2010 Texas A&M University College Station, TX, USA David B. Dahl Assistant Professor Texas A&M University College Station,
Bayesian Nonparametric Regression for Diabetes Deaths Brian M. Hartman PhD Student, 2010 Texas A&M University College Station, TX, USA David B. Dahl Assistant Professor Texas A&M University College Station,
Graphical Models and Kernel Methods
 Graphical Models and Kernel Methods Jerry Zhu Department of Computer Sciences University of Wisconsin Madison, USA MLSS June 17, 2014 1 / 123 Outline Graphical Models Probabilistic Inference Directed vs.
Graphical Models and Kernel Methods Jerry Zhu Department of Computer Sciences University of Wisconsin Madison, USA MLSS June 17, 2014 1 / 123 Outline Graphical Models Probabilistic Inference Directed vs.
MH I. Metropolis-Hastings (MH) algorithm is the most popular method of getting dependent samples from a probability distribution
 MH I Metropolis-Hastings (MH) algorithm is the most popular method of getting dependent samples from a probability distribution a lot of Bayesian mehods rely on the use of MH algorithm and it s famous
MH I Metropolis-Hastings (MH) algorithm is the most popular method of getting dependent samples from a probability distribution a lot of Bayesian mehods rely on the use of MH algorithm and it s famous
Control Variates for Markov Chain Monte Carlo
 Control Variates for Markov Chain Monte Carlo Dellaportas, P., Kontoyiannis, I., and Tsourti, Z. Dept of Statistics, AUEB Dept of Informatics, AUEB 1st Greek Stochastics Meeting Monte Carlo: Probability
Control Variates for Markov Chain Monte Carlo Dellaportas, P., Kontoyiannis, I., and Tsourti, Z. Dept of Statistics, AUEB Dept of Informatics, AUEB 1st Greek Stochastics Meeting Monte Carlo: Probability
The Origin of Deep Learning. Lili Mou Jan, 2015
 The Origin of Deep Learning Lili Mou Jan, 2015 Acknowledgment Most of the materials come from G. E. Hinton s online course. Outline Introduction Preliminary Boltzmann Machines and RBMs Deep Belief Nets
The Origin of Deep Learning Lili Mou Jan, 2015 Acknowledgment Most of the materials come from G. E. Hinton s online course. Outline Introduction Preliminary Boltzmann Machines and RBMs Deep Belief Nets
Stat 516, Homework 1
 Stat 516, Homework 1 Due date: October 7 1. Consider an urn with n distinct balls numbered 1,..., n. We sample balls from the urn with replacement. Let N be the number of draws until we encounter a ball
Stat 516, Homework 1 Due date: October 7 1. Consider an urn with n distinct balls numbered 1,..., n. We sample balls from the urn with replacement. Let N be the number of draws until we encounter a ball
Bayesian Inference for Gaussian Mixed Graph Models
 Bayesian Inference for Gaussian Mixed Graph Models Ricardo Silva Gatsby Computational Neuroscience Unit University College London rbas@gatsby.ucl.ac.uk Zoubin Ghahramani Department of Engineering University
Bayesian Inference for Gaussian Mixed Graph Models Ricardo Silva Gatsby Computational Neuroscience Unit University College London rbas@gatsby.ucl.ac.uk Zoubin Ghahramani Department of Engineering University
Inference in Bayesian Networks
 Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Inference in graphical models Description Assume we have evidence e on the state of a subset of variables E in the model (i.e. Bayesian Network)
Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Inference in graphical models Description Assume we have evidence e on the state of a subset of variables E in the model (i.e. Bayesian Network)
Bayesian Inference for Gaussian Mixed Graph Models
 Bayesian Inference for Gaussian Mixed Graph Models Ricardo Silva Gatsby Computational Neuroscience Unit University College London rbas@gatsby.ucl.ac.uk Zoubin Ghahramani Department of Engineering University
Bayesian Inference for Gaussian Mixed Graph Models Ricardo Silva Gatsby Computational Neuroscience Unit University College London rbas@gatsby.ucl.ac.uk Zoubin Ghahramani Department of Engineering University
Dynamic models. Dependent data The AR(p) model The MA(q) model Hidden Markov models. 6 Dynamic models
 6 Dependent data The AR(p) model The MA(q) model Hidden Markov models Dependent data Dependent data Huge portion of real-life data involving dependent datapoints Example (Capture-recapture) capture histories
6 Dependent data The AR(p) model The MA(q) model Hidden Markov models Dependent data Dependent data Huge portion of real-life data involving dependent datapoints Example (Capture-recapture) capture histories
Bayesian (conditionally) conjugate inference for discrete data models. Jon Forster (University of Southampton)
 Bayesian (conditionally) conjugate inference for discrete data models Jon Forster (University of Southampton) with Mark Grigsby (Procter and Gamble?) Emily Webb (Institute of Cancer Research) Table 1:
Bayesian (conditionally) conjugate inference for discrete data models Jon Forster (University of Southampton) with Mark Grigsby (Procter and Gamble?) Emily Webb (Institute of Cancer Research) Table 1:
The Particle Filter. PD Dr. Rudolph Triebel Computer Vision Group. Machine Learning for Computer Vision
 The Particle Filter Non-parametric implementation of Bayes filter Represents the belief (posterior) random state samples. by a set of This representation is approximate. Can represent distributions that
The Particle Filter Non-parametric implementation of Bayes filter Represents the belief (posterior) random state samples. by a set of This representation is approximate. Can represent distributions that
Advanced Statistical Modelling
 Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) Methods and Their Applications in Bayesian Statistics School of Technology and Business Studies/Statistics Dalarna University Borlänge, Sweden. Feb. 05, 2014. Outlines 1
Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) Methods and Their Applications in Bayesian Statistics School of Technology and Business Studies/Statistics Dalarna University Borlänge, Sweden. Feb. 05, 2014. Outlines 1
Advances and Applications in Perfect Sampling
 and Applications in Perfect Sampling Ph.D. Dissertation Defense Ulrike Schneider advisor: Jem Corcoran May 8, 2003 Department of Applied Mathematics University of Colorado Outline Introduction (1) MCMC
and Applications in Perfect Sampling Ph.D. Dissertation Defense Ulrike Schneider advisor: Jem Corcoran May 8, 2003 Department of Applied Mathematics University of Colorado Outline Introduction (1) MCMC
Convex Optimization CMU-10725
 Convex Optimization CMU-10725 Simulated Annealing Barnabás Póczos & Ryan Tibshirani Andrey Markov Markov Chains 2 Markov Chains Markov chain: Homogen Markov chain: 3 Markov Chains Assume that the state
Convex Optimization CMU-10725 Simulated Annealing Barnabás Póczos & Ryan Tibshirani Andrey Markov Markov Chains 2 Markov Chains Markov chain: Homogen Markov chain: 3 Markov Chains Assume that the state
Contents. Part I: Fundamentals of Bayesian Inference 1
 Contents Preface xiii Part I: Fundamentals of Bayesian Inference 1 1 Probability and inference 3 1.1 The three steps of Bayesian data analysis 3 1.2 General notation for statistical inference 4 1.3 Bayesian
Contents Preface xiii Part I: Fundamentals of Bayesian Inference 1 1 Probability and inference 3 1.1 The three steps of Bayesian data analysis 3 1.2 General notation for statistical inference 4 1.3 Bayesian
Markov-Chain Monte Carlo
 Markov-Chain Monte Carlo CSE586 Computer Vision II Spring 2010, Penn State Univ. References Recall: Sampling Motivation If we can generate random samples x i from a given distribution P(x), then we can
Markov-Chain Monte Carlo CSE586 Computer Vision II Spring 2010, Penn State Univ. References Recall: Sampling Motivation If we can generate random samples x i from a given distribution P(x), then we can
Session 5B: A worked example EGARCH model
 Session 5B: A worked example EGARCH model John Geweke Bayesian Econometrics and its Applications August 7, worked example EGARCH model August 7, / 6 EGARCH Exponential generalized autoregressive conditional
Session 5B: A worked example EGARCH model John Geweke Bayesian Econometrics and its Applications August 7, worked example EGARCH model August 7, / 6 EGARCH Exponential generalized autoregressive conditional
Theory of Stochastic Processes 8. Markov chain Monte Carlo
 Theory of Stochastic Processes 8. Markov chain Monte Carlo Tomonari Sei sei@mist.i.u-tokyo.ac.jp Department of Mathematical Informatics, University of Tokyo June 8, 2017 http://www.stat.t.u-tokyo.ac.jp/~sei/lec.html
Theory of Stochastic Processes 8. Markov chain Monte Carlo Tomonari Sei sei@mist.i.u-tokyo.ac.jp Department of Mathematical Informatics, University of Tokyo June 8, 2017 http://www.stat.t.u-tokyo.ac.jp/~sei/lec.html
Down by the Bayes, where the Watermelons Grow
 Down by the Bayes, where the Watermelons Grow A Bayesian example using SAS SUAVe: Victoria SAS User Group Meeting November 21, 2017 Peter K. Ott, M.Sc., P.Stat. Strategic Analysis 1 Outline 1. Motivating
Down by the Bayes, where the Watermelons Grow A Bayesian example using SAS SUAVe: Victoria SAS User Group Meeting November 21, 2017 Peter K. Ott, M.Sc., P.Stat. Strategic Analysis 1 Outline 1. Motivating
A Review of Pseudo-Marginal Markov Chain Monte Carlo
 A Review of Pseudo-Marginal Markov Chain Monte Carlo Discussed by: Yizhe Zhang October 21, 2016 Outline 1 Overview 2 Paper review 3 experiment 4 conclusion Motivation & overview Notation: θ denotes the
A Review of Pseudo-Marginal Markov Chain Monte Carlo Discussed by: Yizhe Zhang October 21, 2016 Outline 1 Overview 2 Paper review 3 experiment 4 conclusion Motivation & overview Notation: θ denotes the
VCMC: Variational Consensus Monte Carlo
 VCMC: Variational Consensus Monte Carlo Maxim Rabinovich, Elaine Angelino, Michael I. Jordan Berkeley Vision and Learning Center September 22, 2015 probabilistic models! sky fog bridge water grass object
VCMC: Variational Consensus Monte Carlo Maxim Rabinovich, Elaine Angelino, Michael I. Jordan Berkeley Vision and Learning Center September 22, 2015 probabilistic models! sky fog bridge water grass object
Monte Carlo Methods. Leon Gu CSD, CMU
 Monte Carlo Methods Leon Gu CSD, CMU Approximate Inference EM: y-observed variables; x-hidden variables; θ-parameters; E-step: q(x) = p(x y, θ t 1 ) M-step: θ t = arg max E q(x) [log p(y, x θ)] θ Monte
Monte Carlo Methods Leon Gu CSD, CMU Approximate Inference EM: y-observed variables; x-hidden variables; θ-parameters; E-step: q(x) = p(x y, θ t 1 ) M-step: θ t = arg max E q(x) [log p(y, x θ)] θ Monte
Bayesian Analysis of Mixture Models with an Unknown Number of Components an alternative to reversible jump methods
 Bayesian Analysis of Mixture Models with an Unknown Number of Components an alternative to reversible jump methods Matthew Stephens Λ Department of Statistics University of Oxford Submitted to Annals of
Bayesian Analysis of Mixture Models with an Unknown Number of Components an alternative to reversible jump methods Matthew Stephens Λ Department of Statistics University of Oxford Submitted to Annals of
MCMC: Markov Chain Monte Carlo
 I529: Machine Learning in Bioinformatics (Spring 2013) MCMC: Markov Chain Monte Carlo Yuzhen Ye School of Informatics and Computing Indiana University, Bloomington Spring 2013 Contents Review of Markov
I529: Machine Learning in Bioinformatics (Spring 2013) MCMC: Markov Chain Monte Carlo Yuzhen Ye School of Informatics and Computing Indiana University, Bloomington Spring 2013 Contents Review of Markov
Bayesian Image Segmentation Using MRF s Combined with Hierarchical Prior Models
 Bayesian Image Segmentation Using MRF s Combined with Hierarchical Prior Models Kohta Aoki 1 and Hiroshi Nagahashi 2 1 Interdisciplinary Graduate School of Science and Engineering, Tokyo Institute of Technology
Bayesian Image Segmentation Using MRF s Combined with Hierarchical Prior Models Kohta Aoki 1 and Hiroshi Nagahashi 2 1 Interdisciplinary Graduate School of Science and Engineering, Tokyo Institute of Technology
Results: MCMC Dancers, q=10, n=500
 Motivation Sampling Methods for Bayesian Inference How to track many INTERACTING targets? A Tutorial Frank Dellaert Results: MCMC Dancers, q=10, n=500 1 Probabilistic Topological Maps Results Real-Time
Motivation Sampling Methods for Bayesian Inference How to track many INTERACTING targets? A Tutorial Frank Dellaert Results: MCMC Dancers, q=10, n=500 1 Probabilistic Topological Maps Results Real-Time
Introduction to Bayesian methods in inverse problems
 Introduction to Bayesian methods in inverse problems Ville Kolehmainen 1 1 Department of Applied Physics, University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio, Finland March 4 2013 Manchester, UK. Contents Introduction
Introduction to Bayesian methods in inverse problems Ville Kolehmainen 1 1 Department of Applied Physics, University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio, Finland March 4 2013 Manchester, UK. Contents Introduction
Marginal Specifications and a Gaussian Copula Estimation
 Marginal Specifications and a Gaussian Copula Estimation Kazim Azam Abstract Multivariate analysis involving random variables of different type like count, continuous or mixture of both is frequently required
Marginal Specifications and a Gaussian Copula Estimation Kazim Azam Abstract Multivariate analysis involving random variables of different type like count, continuous or mixture of both is frequently required
Bayesian Model Comparison:
 Bayesian Model Comparison: Modeling Petrobrás log-returns Hedibert Freitas Lopes February 2014 Log price: y t = log p t Time span: 12/29/2000-12/31/2013 (n = 3268 days) LOG PRICE 1 2 3 4 0 500 1000 1500
Bayesian Model Comparison: Modeling Petrobrás log-returns Hedibert Freitas Lopes February 2014 Log price: y t = log p t Time span: 12/29/2000-12/31/2013 (n = 3268 days) LOG PRICE 1 2 3 4 0 500 1000 1500
Bayesian Graphical Models for Structural Vector AutoregressiveMarch Processes 21, / 1
 Bayesian Graphical Models for Structural Vector Autoregressive Processes Daniel Ahelegbey, Monica Billio, and Roberto Cassin (2014) March 21, 2015 Bayesian Graphical Models for Structural Vector AutoregressiveMarch
Bayesian Graphical Models for Structural Vector Autoregressive Processes Daniel Ahelegbey, Monica Billio, and Roberto Cassin (2014) March 21, 2015 Bayesian Graphical Models for Structural Vector AutoregressiveMarch
Sampling Methods (11/30/04)
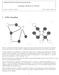 CS281A/Stat241A: Statistical Learning Theory Sampling Methods (11/30/04) Lecturer: Michael I. Jordan Scribe: Jaspal S. Sandhu 1 Gibbs Sampling Figure 1: Undirected and directed graphs, respectively, with
CS281A/Stat241A: Statistical Learning Theory Sampling Methods (11/30/04) Lecturer: Michael I. Jordan Scribe: Jaspal S. Sandhu 1 Gibbs Sampling Figure 1: Undirected and directed graphs, respectively, with
Sampling Algorithms for Probabilistic Graphical models
 Sampling Algorithms for Probabilistic Graphical models Vibhav Gogate University of Washington References: Chapter 12 of Probabilistic Graphical models: Principles and Techniques by Daphne Koller and Nir
Sampling Algorithms for Probabilistic Graphical models Vibhav Gogate University of Washington References: Chapter 12 of Probabilistic Graphical models: Principles and Techniques by Daphne Koller and Nir
Stochastic Proximal Gradient Algorithm
 Stochastic Institut Mines-Télécom / Telecom ParisTech / Laboratoire Traitement et Communication de l Information Joint work with: Y. Atchade, Ann Arbor, USA, G. Fort LTCI/Télécom Paristech and the kind
Stochastic Institut Mines-Télécom / Telecom ParisTech / Laboratoire Traitement et Communication de l Information Joint work with: Y. Atchade, Ann Arbor, USA, G. Fort LTCI/Télécom Paristech and the kind
Sampling Rejection Sampling Importance Sampling Markov Chain Monte Carlo. Sampling Methods. Oliver Schulte - CMPT 419/726. Bishop PRML Ch.
 Sampling Methods Oliver Schulte - CMP 419/726 Bishop PRML Ch. 11 Recall Inference or General Graphs Junction tree algorithm is an exact inference method for arbitrary graphs A particular tree structure
Sampling Methods Oliver Schulte - CMP 419/726 Bishop PRML Ch. 11 Recall Inference or General Graphs Junction tree algorithm is an exact inference method for arbitrary graphs A particular tree structure
The Bayesian Choice. Christian P. Robert. From Decision-Theoretic Foundations to Computational Implementation. Second Edition.
 Christian P. Robert The Bayesian Choice From Decision-Theoretic Foundations to Computational Implementation Second Edition With 23 Illustrations ^Springer" Contents Preface to the Second Edition Preface
Christian P. Robert The Bayesian Choice From Decision-Theoretic Foundations to Computational Implementation Second Edition With 23 Illustrations ^Springer" Contents Preface to the Second Edition Preface
Estimating the marginal likelihood with Integrated nested Laplace approximation (INLA)
 Estimating the marginal likelihood with Integrated nested Laplace approximation (INLA) arxiv:1611.01450v1 [stat.co] 4 Nov 2016 Aliaksandr Hubin Department of Mathematics, University of Oslo and Geir Storvik
Estimating the marginal likelihood with Integrated nested Laplace approximation (INLA) arxiv:1611.01450v1 [stat.co] 4 Nov 2016 Aliaksandr Hubin Department of Mathematics, University of Oslo and Geir Storvik
Bayesian Inference in GLMs. Frequentists typically base inferences on MLEs, asymptotic confidence
 Bayesian Inference in GLMs Frequentists typically base inferences on MLEs, asymptotic confidence limits, and log-likelihood ratio tests Bayesians base inferences on the posterior distribution of the unknowns
Bayesian Inference in GLMs Frequentists typically base inferences on MLEs, asymptotic confidence limits, and log-likelihood ratio tests Bayesians base inferences on the posterior distribution of the unknowns
Kernel adaptive Sequential Monte Carlo
 Kernel adaptive Sequential Monte Carlo Ingmar Schuster (Paris Dauphine) Heiko Strathmann (University College London) Brooks Paige (Oxford) Dino Sejdinovic (Oxford) December 7, 2015 1 / 36 Section 1 Outline
Kernel adaptive Sequential Monte Carlo Ingmar Schuster (Paris Dauphine) Heiko Strathmann (University College London) Brooks Paige (Oxford) Dino Sejdinovic (Oxford) December 7, 2015 1 / 36 Section 1 Outline
Calibration of Stochastic Volatility Models using Particle Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods
 Calibration of Stochastic Volatility Models using Particle Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods Jonas Hallgren 1 1 Department of Mathematics KTH Royal Institute of Technology Stockholm, Sweden BFS 2012 June
Calibration of Stochastic Volatility Models using Particle Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods Jonas Hallgren 1 1 Department of Mathematics KTH Royal Institute of Technology Stockholm, Sweden BFS 2012 June
ST 740: Markov Chain Monte Carlo
 ST 740: Markov Chain Monte Carlo Alyson Wilson Department of Statistics North Carolina State University October 14, 2012 A. Wilson (NCSU Stsatistics) MCMC October 14, 2012 1 / 20 Convergence Diagnostics:
ST 740: Markov Chain Monte Carlo Alyson Wilson Department of Statistics North Carolina State University October 14, 2012 A. Wilson (NCSU Stsatistics) MCMC October 14, 2012 1 / 20 Convergence Diagnostics:
18 : Advanced topics in MCMC. 1 Gibbs Sampling (Continued from the last lecture)
 10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2014 18 : Advanced topics in MCMC Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Jessica Chemali, Seungwhan Moon 1 Gibbs Sampling (Continued from the last lecture)
10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2014 18 : Advanced topics in MCMC Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Jessica Chemali, Seungwhan Moon 1 Gibbs Sampling (Continued from the last lecture)
Bayesian inference for multivariate extreme value distributions
 Bayesian inference for multivariate extreme value distributions Sebastian Engelke Clément Dombry, Marco Oesting Toronto, Fields Institute, May 4th, 2016 Main motivation For a parametric model Z F θ of
Bayesian inference for multivariate extreme value distributions Sebastian Engelke Clément Dombry, Marco Oesting Toronto, Fields Institute, May 4th, 2016 Main motivation For a parametric model Z F θ of
An ABC interpretation of the multiple auxiliary variable method
 School of Mathematical and Physical Sciences Department of Mathematics and Statistics Preprint MPS-2016-07 27 April 2016 An ABC interpretation of the multiple auxiliary variable method by Dennis Prangle
School of Mathematical and Physical Sciences Department of Mathematics and Statistics Preprint MPS-2016-07 27 April 2016 An ABC interpretation of the multiple auxiliary variable method by Dennis Prangle
LECTURE 15 Markov chain Monte Carlo
 LECTURE 15 Markov chain Monte Carlo There are many settings when posterior computation is a challenge in that one does not have a closed form expression for the posterior distribution. Markov chain Monte
LECTURE 15 Markov chain Monte Carlo There are many settings when posterior computation is a challenge in that one does not have a closed form expression for the posterior distribution. Markov chain Monte
Lecture 7 and 8: Markov Chain Monte Carlo
 Lecture 7 and 8: Markov Chain Monte Carlo 4F13: Machine Learning Zoubin Ghahramani and Carl Edward Rasmussen Department of Engineering University of Cambridge http://mlg.eng.cam.ac.uk/teaching/4f13/ Ghahramani
Lecture 7 and 8: Markov Chain Monte Carlo 4F13: Machine Learning Zoubin Ghahramani and Carl Edward Rasmussen Department of Engineering University of Cambridge http://mlg.eng.cam.ac.uk/teaching/4f13/ Ghahramani
17 : Markov Chain Monte Carlo
 10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models, Spring 2015 17 : Markov Chain Monte Carlo Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Heran Lin, Bin Deng, Yun Huang 1 Review of Monte Carlo Methods 1.1 Overview Monte Carlo
10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models, Spring 2015 17 : Markov Chain Monte Carlo Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Heran Lin, Bin Deng, Yun Huang 1 Review of Monte Carlo Methods 1.1 Overview Monte Carlo
Markov Chain Monte Carlo
 Markov Chain Monte Carlo (and Bayesian Mixture Models) David M. Blei Columbia University October 14, 2014 We have discussed probabilistic modeling, and have seen how the posterior distribution is the critical
Markov Chain Monte Carlo (and Bayesian Mixture Models) David M. Blei Columbia University October 14, 2014 We have discussed probabilistic modeling, and have seen how the posterior distribution is the critical
MCMC 2: Lecture 2 Coding and output. Phil O Neill Theo Kypraios School of Mathematical Sciences University of Nottingham
 MCMC 2: Lecture 2 Coding and output Phil O Neill Theo Kypraios School of Mathematical Sciences University of Nottingham Contents 1. General (Markov) epidemic model 2. Non-Markov epidemic model 3. Debugging
MCMC 2: Lecture 2 Coding and output Phil O Neill Theo Kypraios School of Mathematical Sciences University of Nottingham Contents 1. General (Markov) epidemic model 2. Non-Markov epidemic model 3. Debugging
Markov Chains and MCMC
 Markov Chains and MCMC Markov chains Let S = {1, 2,..., N} be a finite set consisting of N states. A Markov chain Y 0, Y 1, Y 2,... is a sequence of random variables, with Y t S for all points in time
Markov Chains and MCMC Markov chains Let S = {1, 2,..., N} be a finite set consisting of N states. A Markov chain Y 0, Y 1, Y 2,... is a sequence of random variables, with Y t S for all points in time
Modelling Operational Risk Using Bayesian Inference
 Pavel V. Shevchenko Modelling Operational Risk Using Bayesian Inference 4y Springer 1 Operational Risk and Basel II 1 1.1 Introduction to Operational Risk 1 1.2 Defining Operational Risk 4 1.3 Basel II
Pavel V. Shevchenko Modelling Operational Risk Using Bayesian Inference 4y Springer 1 Operational Risk and Basel II 1 1.1 Introduction to Operational Risk 1 1.2 Defining Operational Risk 4 1.3 Basel II
Bayesian inference for general Gaussian graphical models with application to multivariate lattice data
 Bayesian inference for general Gaussian graphical models with application to multivariate lattice data Adrian Dobra, Alex Lenkoski and Abel odriguez arxiv:1005.4094v1 [stat.me] 21 May 2010 Abstract We
Bayesian inference for general Gaussian graphical models with application to multivariate lattice data Adrian Dobra, Alex Lenkoski and Abel odriguez arxiv:1005.4094v1 [stat.me] 21 May 2010 Abstract We
Machine Learning. Probabilistic KNN.
 Machine Learning. Mark Girolami girolami@dcs.gla.ac.uk Department of Computing Science University of Glasgow June 21, 2007 p. 1/3 KNN is a remarkably simple algorithm with proven error-rates June 21, 2007
Machine Learning. Mark Girolami girolami@dcs.gla.ac.uk Department of Computing Science University of Glasgow June 21, 2007 p. 1/3 KNN is a remarkably simple algorithm with proven error-rates June 21, 2007
Markov Chain Monte Carlo methods
 Markov Chain Monte Carlo methods By Oleg Makhnin 1 Introduction a b c M = d e f g h i 0 f(x)dx 1.1 Motivation 1.1.1 Just here Supresses numbering 1.1.2 After this 1.2 Literature 2 Method 2.1 New math As
Markov Chain Monte Carlo methods By Oleg Makhnin 1 Introduction a b c M = d e f g h i 0 f(x)dx 1.1 Motivation 1.1.1 Just here Supresses numbering 1.1.2 After this 1.2 Literature 2 Method 2.1 New math As
eqr094: Hierarchical MCMC for Bayesian System Reliability
 eqr094: Hierarchical MCMC for Bayesian System Reliability Alyson G. Wilson Statistical Sciences Group, Los Alamos National Laboratory P.O. Box 1663, MS F600 Los Alamos, NM 87545 USA Phone: 505-667-9167
eqr094: Hierarchical MCMC for Bayesian System Reliability Alyson G. Wilson Statistical Sciences Group, Los Alamos National Laboratory P.O. Box 1663, MS F600 Los Alamos, NM 87545 USA Phone: 505-667-9167
Markov Chain Monte Carlo, Numerical Integration
 Markov Chain Monte Carlo, Numerical Integration (See Statistics) Trevor Gallen Fall 2015 1 / 1 Agenda Numerical Integration: MCMC methods Estimating Markov Chains Estimating latent variables 2 / 1 Numerical
Markov Chain Monte Carlo, Numerical Integration (See Statistics) Trevor Gallen Fall 2015 1 / 1 Agenda Numerical Integration: MCMC methods Estimating Markov Chains Estimating latent variables 2 / 1 Numerical
ABC methods for phase-type distributions with applications in insurance risk problems
 ABC methods for phase-type with applications problems Concepcion Ausin, Department of Statistics, Universidad Carlos III de Madrid Joint work with: Pedro Galeano, Universidad Carlos III de Madrid Simon
ABC methods for phase-type with applications problems Concepcion Ausin, Department of Statistics, Universidad Carlos III de Madrid Joint work with: Pedro Galeano, Universidad Carlos III de Madrid Simon
Hamiltonian Monte Carlo for Scalable Deep Learning
 Hamiltonian Monte Carlo for Scalable Deep Learning Isaac Robson Department of Statistics and Operations Research, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill isrobson@email.unc.edu BIOS 740 May 4, 2018
Hamiltonian Monte Carlo for Scalable Deep Learning Isaac Robson Department of Statistics and Operations Research, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill isrobson@email.unc.edu BIOS 740 May 4, 2018
Supplementary Notes: Segment Parameter Labelling in MCMC Change Detection
 Supplementary Notes: Segment Parameter Labelling in MCMC Change Detection Alireza Ahrabian 1 arxiv:1901.0545v1 [eess.sp] 16 Jan 019 Abstract This work addresses the problem of segmentation in time series
Supplementary Notes: Segment Parameter Labelling in MCMC Change Detection Alireza Ahrabian 1 arxiv:1901.0545v1 [eess.sp] 16 Jan 019 Abstract This work addresses the problem of segmentation in time series
arxiv: v1 [stat.co] 2 Nov 2017
![arxiv: v1 [stat.co] 2 Nov 2017 arxiv: v1 [stat.co] 2 Nov 2017](/thumbs/86/93943752.jpg) Binary Bouncy Particle Sampler arxiv:1711.922v1 [stat.co] 2 Nov 217 Ari Pakman Department of Statistics Center for Theoretical Neuroscience Grossman Center for the Statistics of Mind Columbia University
Binary Bouncy Particle Sampler arxiv:1711.922v1 [stat.co] 2 Nov 217 Ari Pakman Department of Statistics Center for Theoretical Neuroscience Grossman Center for the Statistics of Mind Columbia University
Markov Chain Monte Carlo Lecture 6
 Sequential parallel tempering With the development of science and technology, we more and more need to deal with high dimensional systems. For example, we need to align a group of protein or DNA sequences
Sequential parallel tempering With the development of science and technology, we more and more need to deal with high dimensional systems. For example, we need to align a group of protein or DNA sequences
Log Gaussian Cox Processes. Chi Group Meeting February 23, 2016
 Log Gaussian Cox Processes Chi Group Meeting February 23, 2016 Outline Typical motivating application Introduction to LGCP model Brief overview of inference Applications in my work just getting started
Log Gaussian Cox Processes Chi Group Meeting February 23, 2016 Outline Typical motivating application Introduction to LGCP model Brief overview of inference Applications in my work just getting started
16 : Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC)
 10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2014 16 : Markov Chain Monte Carlo MCMC Lecturer: Matthew Gormley Scribes: Yining Wang, Renato Negrinho 1 Sampling from low-dimensional distributions
10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2014 16 : Markov Chain Monte Carlo MCMC Lecturer: Matthew Gormley Scribes: Yining Wang, Renato Negrinho 1 Sampling from low-dimensional distributions
Perfect simulation of repulsive point processes
 Perfect simulation of repulsive point processes Mark Huber Department of Mathematical Sciences, Claremont McKenna College 29 November, 2011 Mark Huber, CMC Perfect simulation of repulsive point processes
Perfect simulation of repulsive point processes Mark Huber Department of Mathematical Sciences, Claremont McKenna College 29 November, 2011 Mark Huber, CMC Perfect simulation of repulsive point processes
A comparison of reversible jump MCMC algorithms for DNA sequence segmentation using hidden Markov models
 A comparison of reversible jump MCMC algorithms for DNA sequence segmentation using hidden Markov models Richard J. Boys Daniel A. Henderson Department of Statistics, University of Newcastle, U.K. Richard.Boys@ncl.ac.uk
A comparison of reversible jump MCMC algorithms for DNA sequence segmentation using hidden Markov models Richard J. Boys Daniel A. Henderson Department of Statistics, University of Newcastle, U.K. Richard.Boys@ncl.ac.uk
